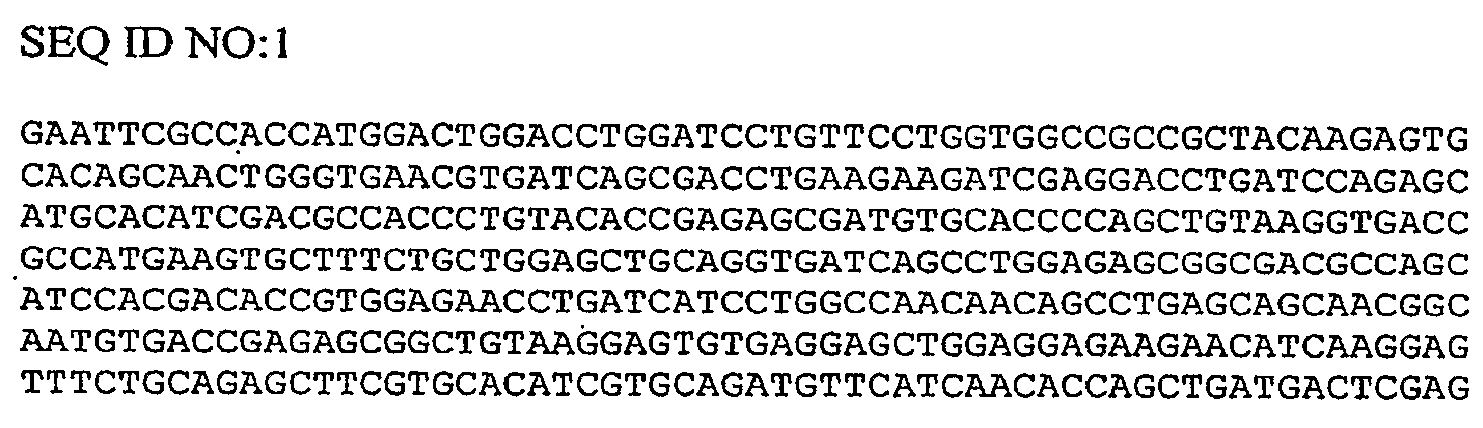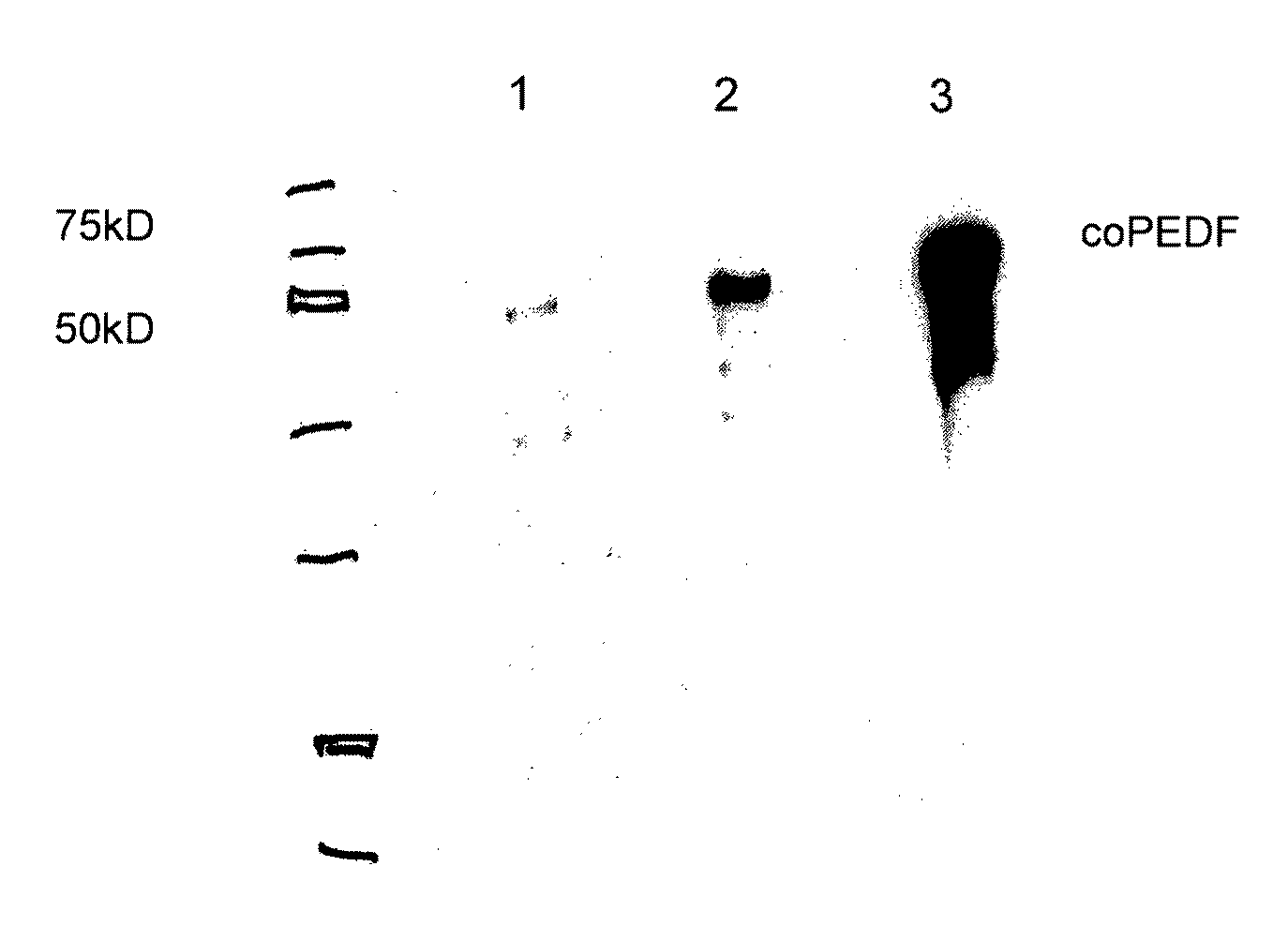Patents
Literature
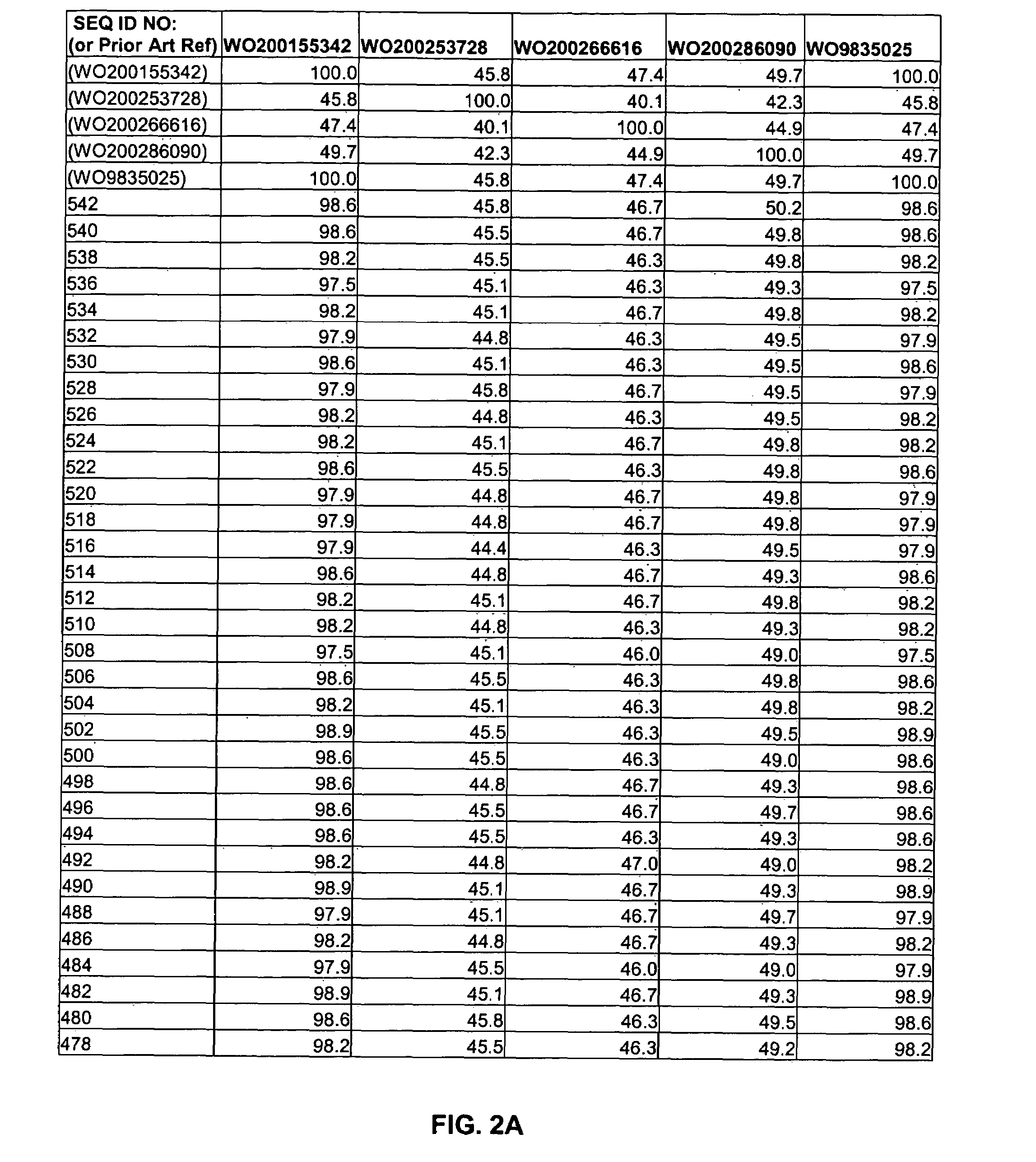
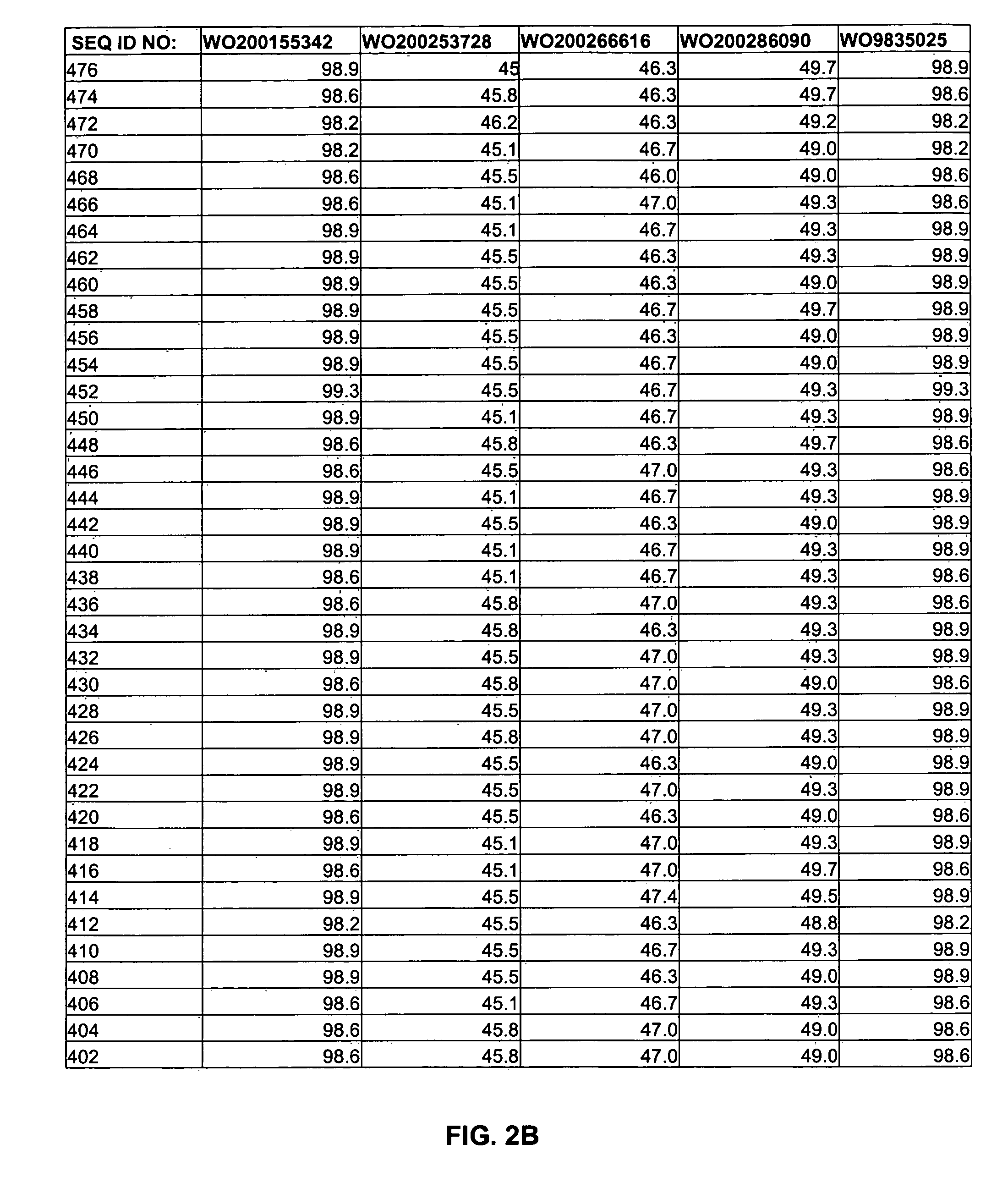
564 results about "Codon optimized" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
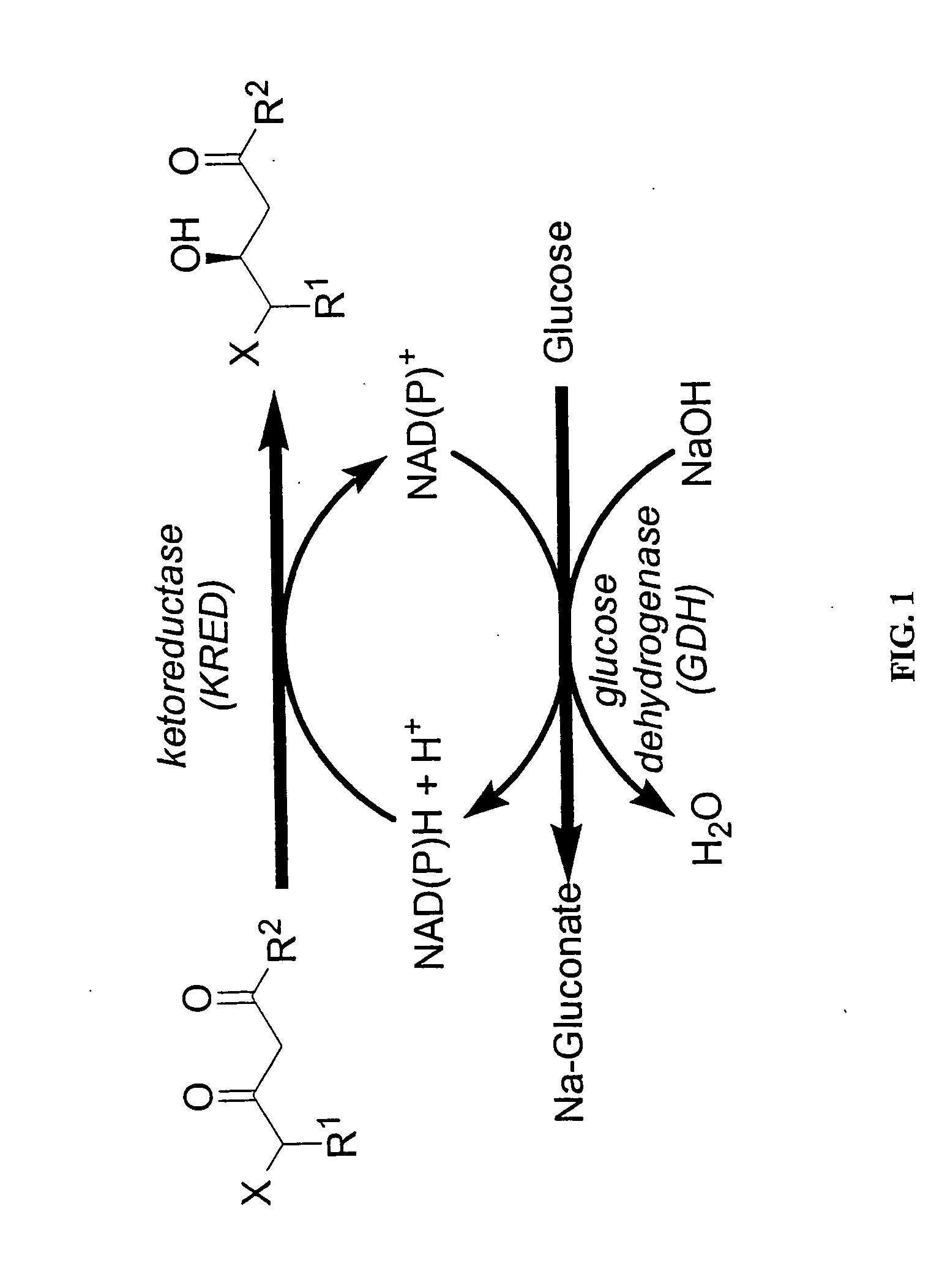
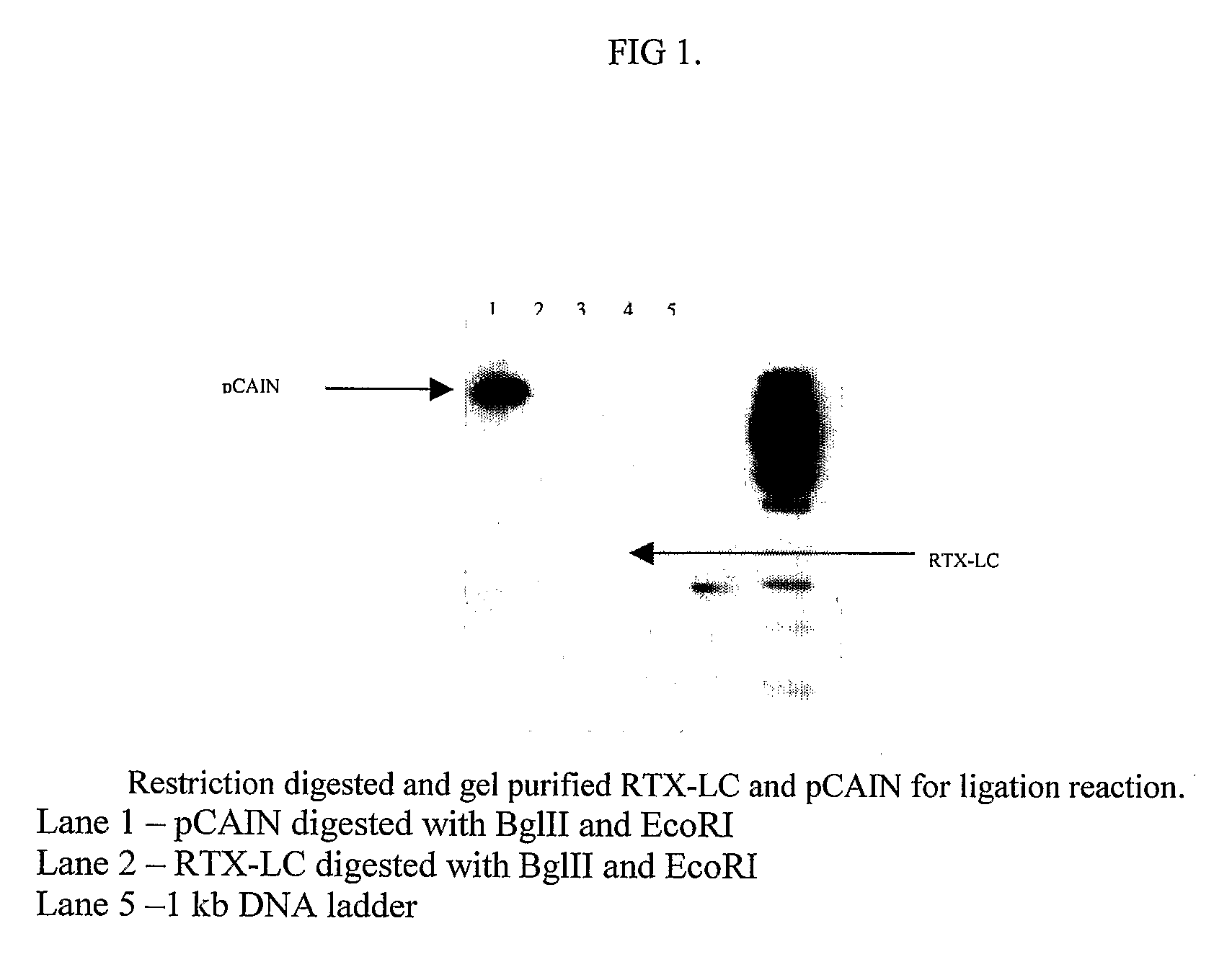
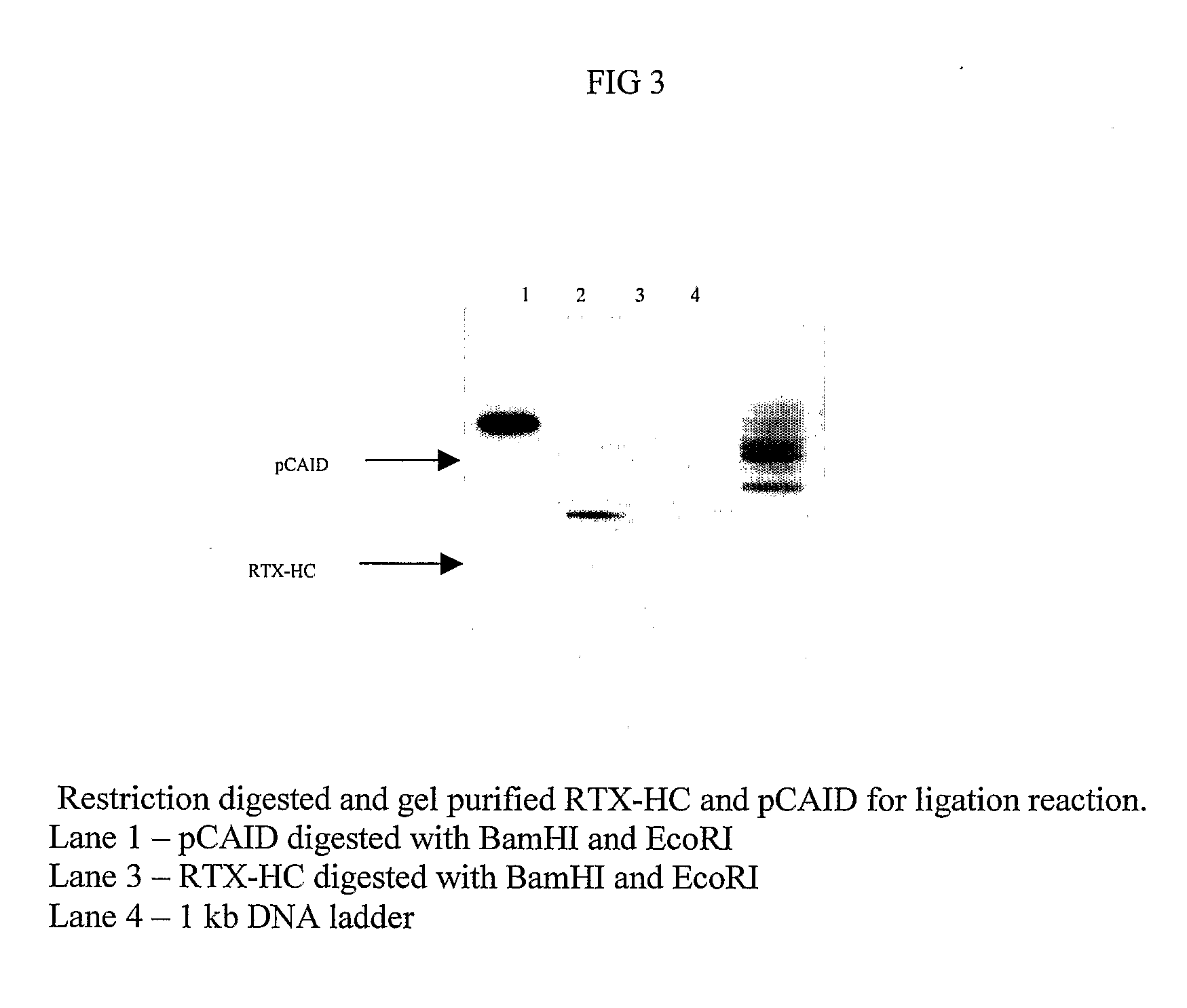
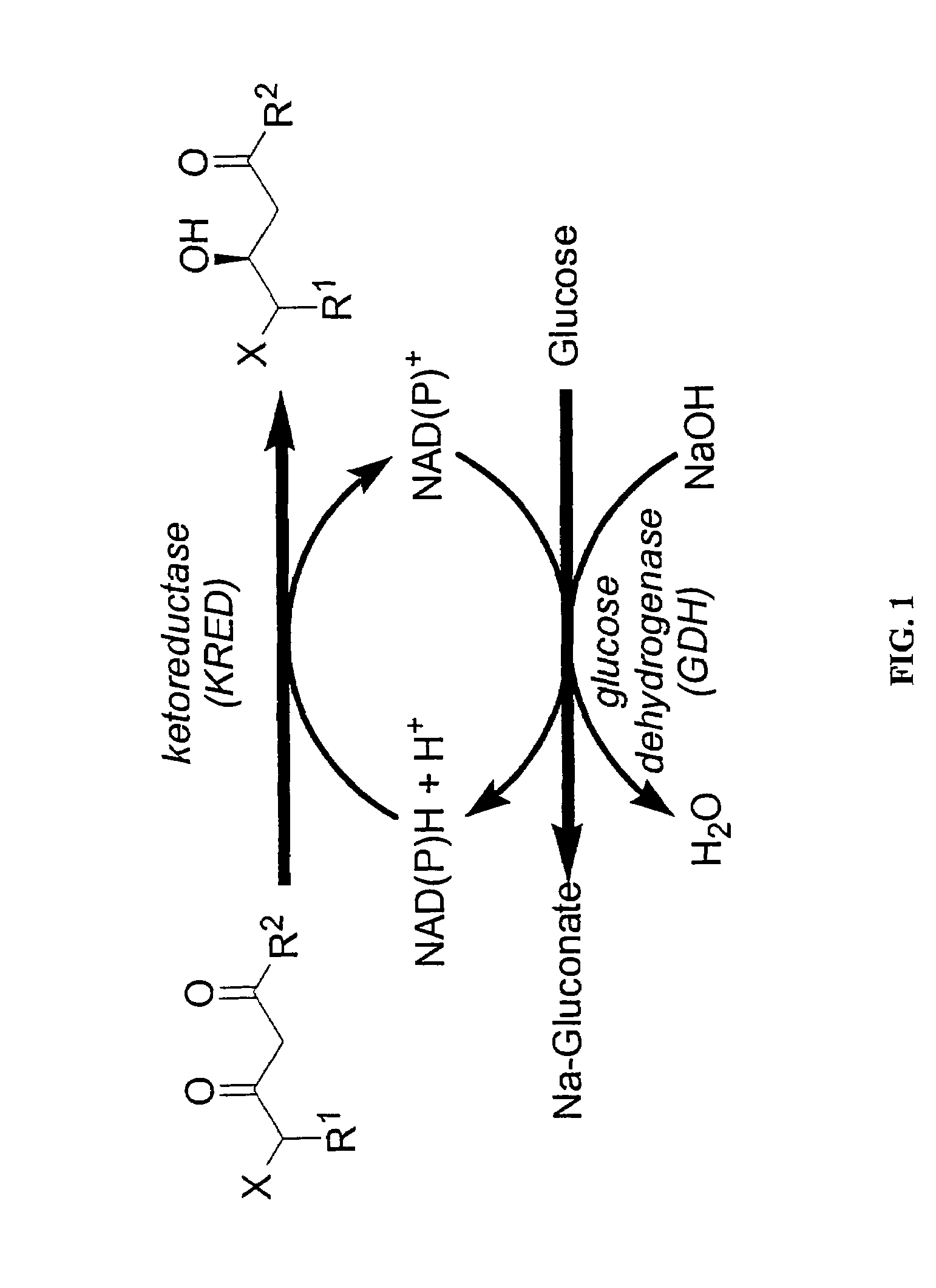
Ketoreductase polypeptides and related polynucleotides
ActiveUS20060195947A1High activityDecrease in absorbanceSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesNucleotidePolynucleotide
The present invention is directed to variant polypeptides having enhanced ketoreductase activity and / or thermostability for use in the stereospecific reduction of ketones. In addition, the present invention is directed to polynucleotides that encode the ketoreductase polypeptides, including codon optimized versions of the polynucleotides which provide for enhanced expression in host cells. In another aspect, the present invention is directed to nucleotide constructs, vectors and host cells that are transformed with polynucleotides of the present invention.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
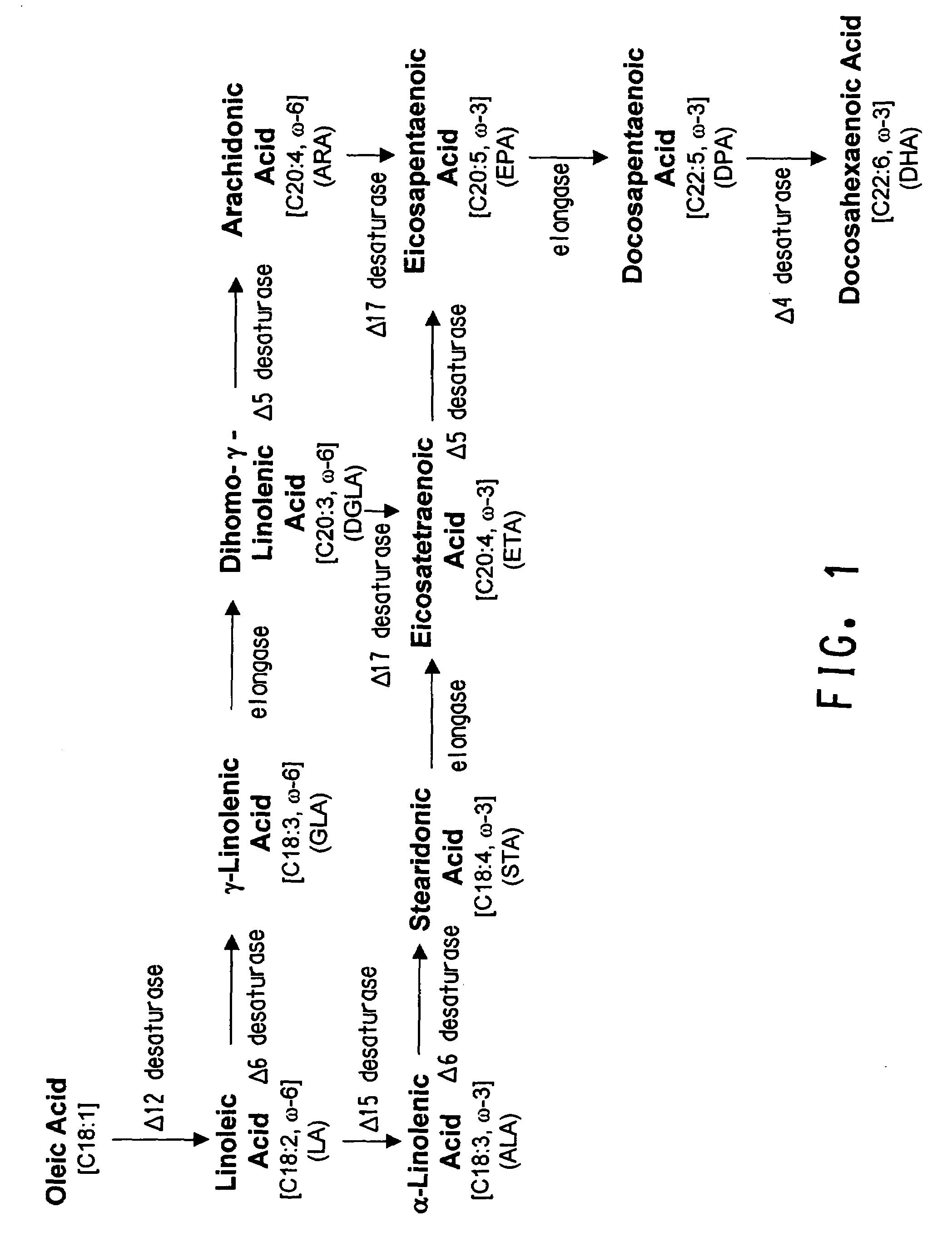
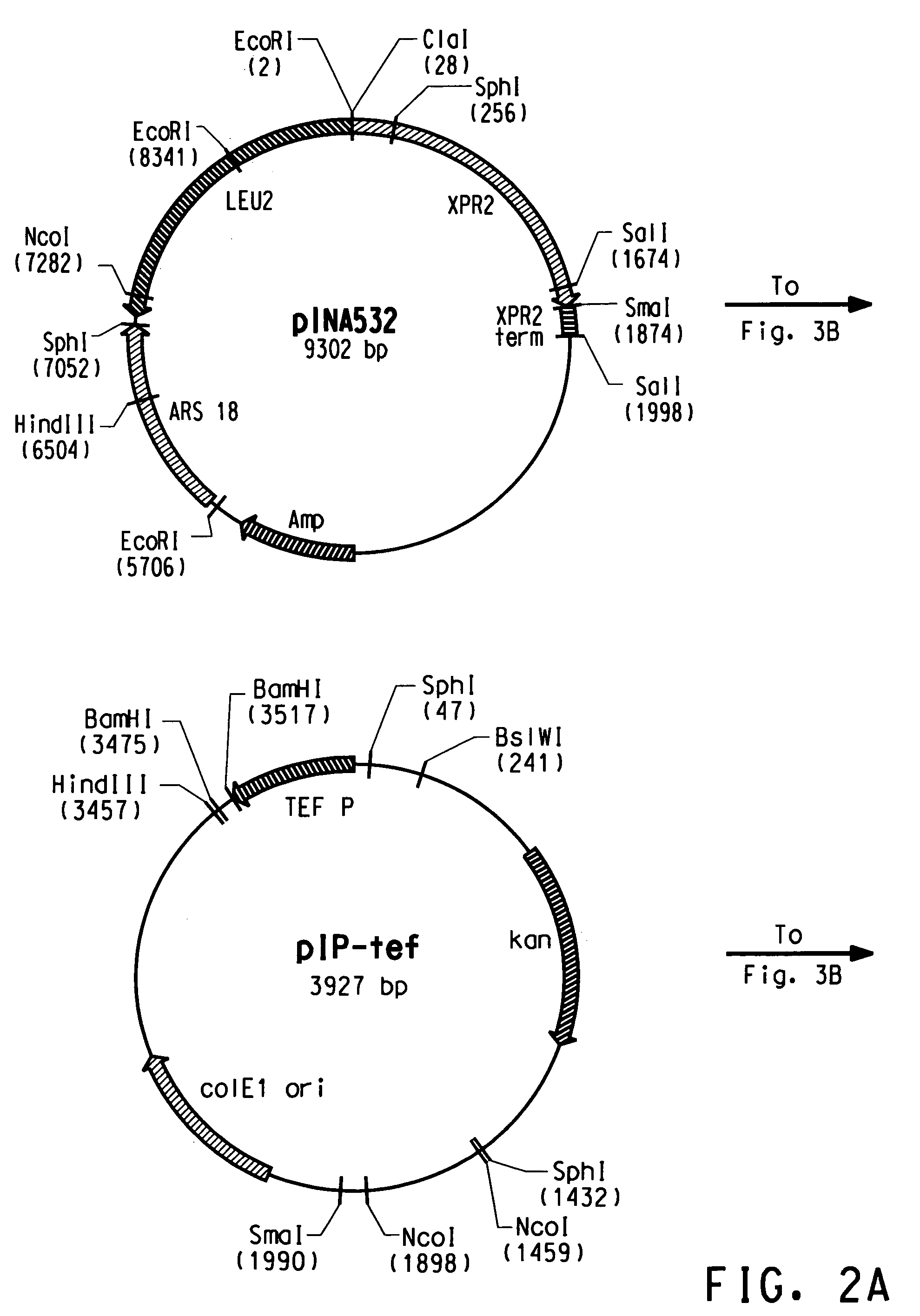
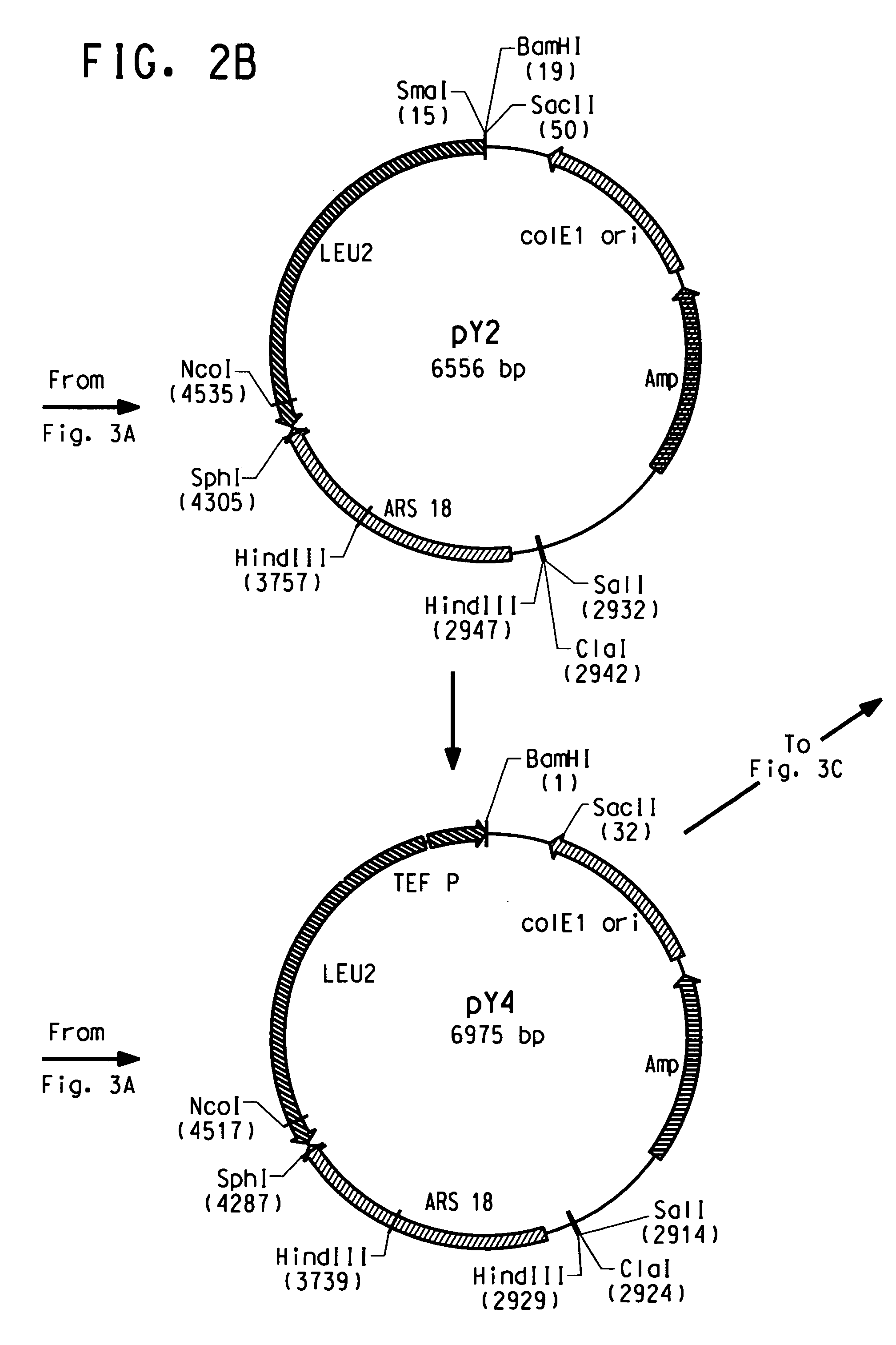
Codon-optimized genes for the production of polyunsaturated fatty acids in oleaginous yeasts
The present invention relates to fatty acid desaturases and elongases able to catalyze the conversion of linoleic acid (LA) to γ-linolenic acid (GLA); α-linoleic acid (ALA) to stearidonic acid (STA); GLA to dihomo-γ-linoleic acid (DGLA); STA to eicosatetraenoic acid (ETA); DGLA to ETA; eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) to docosapentaenoic acid (DPA); and arachidonic acid (ARA) to EPA. Nucleic acid sequences encoding codon-optimized desaturases and elongases, nucleic acid sequences which hybridize thereto, DNA constructs comprising the codon-optimized desaturase or elongases, and recombinant host microorganisms expressing increased levels of desaturase or elongase are described.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Codon-optimized polynucleotide-based vaccines against human cytomegalovirus infection
InactiveUS20080085870A1Reduce in quantityDecreased immunological responseOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenAdjuvant
The invention is related to polynucleotide-based cytomegalovirus vaccines. In particular, the invention is plasmids operably encoding HCMV antigens, in which the naturally-occurring coding regions for the HCMV antigens have been modified for improved translation in human or other mammalian cells through codon optimization. HCMV antigens which are useful in the invention include, but are not limited to pp65, glycoprotein B (gB), IE1, and fragments, variants or derivatives of either of these antigens. In certain embodiments, sequences have been deleted, e.g., the Arg435-Lys438 putative kinase in pp65 and the membrane anchor and endocellular domains in gB. The invention is further directed to methods to induce an immune response to HCMV in a mammal, for example, a human, comprising delivering a plasmid encoding a codon-optimized HCMV antigen as described above. The invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising plasmids encoding a codon-optimized HCMV antigen as described above, and further comprising adjuvants, excipients, or immune modulators.
Owner:VICAL INC
Microbially expressed xylanases and their use as feed additives and other uses
The present invention relates to codon-optimized xylanase coding sequences and the expression of xylanases in microbes and yeast. The invention further relates to using multiple copies of the xylanase expression construct for high levels of protein expression. The invention also relates to the use of xylanases as feed or food additives. The invention also relates to methods of expression of enzymes to increase thermotolerance by expressing them in organisms that glycosylate proteins compared to expression that the same enzyme without the glycosylation. Further, the invention relates to methods of preparing feed, enzyme feed additives, and methods of reducing the feed conversion ration or increasing weight gain of animals.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Vaccines and immunotherapeutics using codon optimized IL-15 and methods for using the same
InactiveUS8178660B2Sugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsImmunotherapeutic agentRecombinant vaccines
Nucleic acid molecules that encode IL-15 or fragments thereof, which express protein at a higher level than nucleic acid molecules with native coding sequences for IL-15 are disclosed. Nucleic acid molecules with additional modifications such as the absence of coding sequences for IL-15 signal sequences and / or the absence of IL-15 untranslated sequences and / or inclusion of non-IL-15 signal sequences are also disclosed. Vectors, including plasmids and viral vectors, comprising such nucleic acid molecules; and to host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules are disclosed as well as methods of using such nucleic acid molecules alone or in combination with nucleic acid sequences encoding immunogens which are part of the nucleic acid molecules and / or part of a different nucleic acid molecule. Recombinant vaccines and live attenuated pathogens encoding fusion proteins, and methods of using the same, are disclosed.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
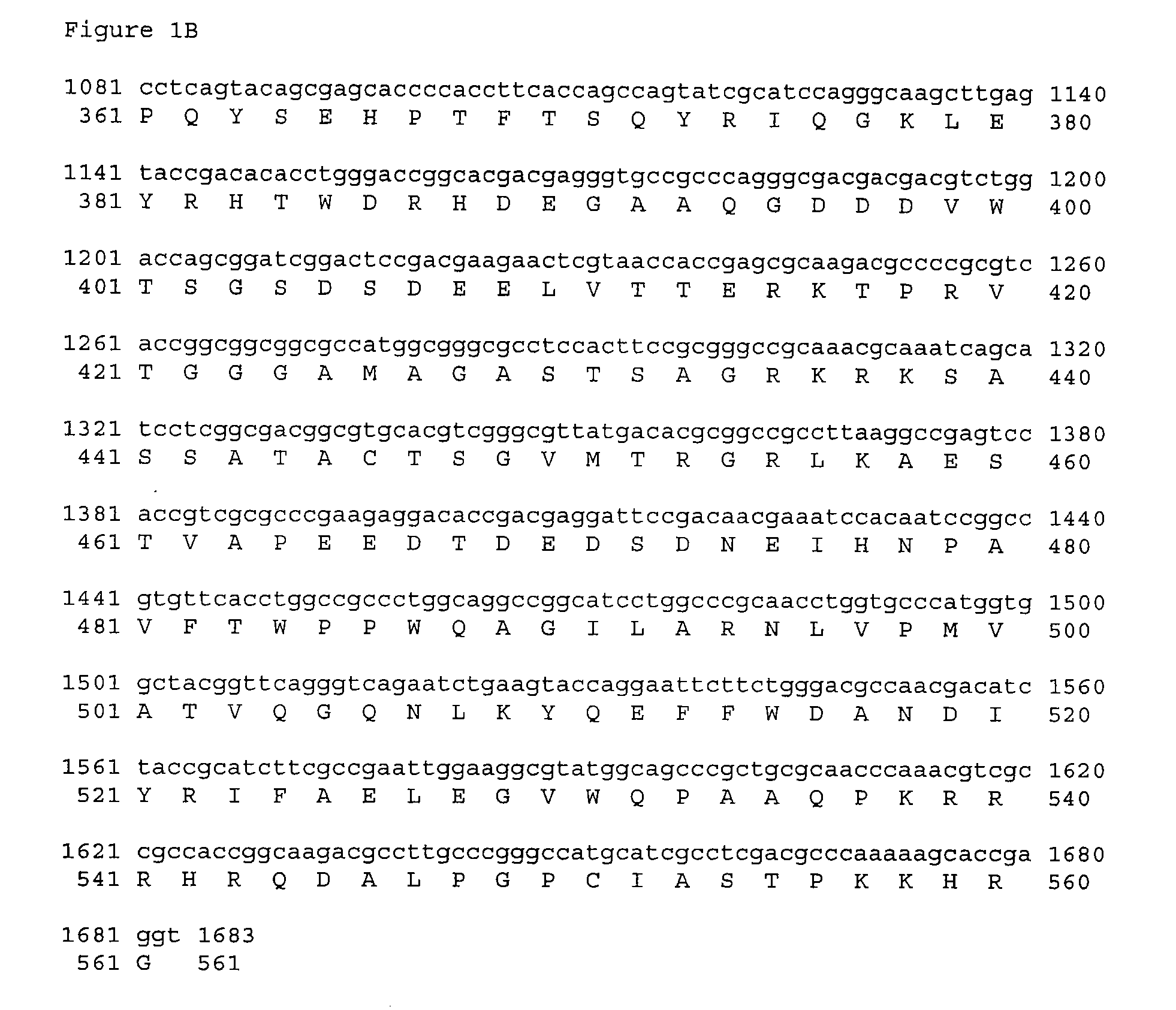
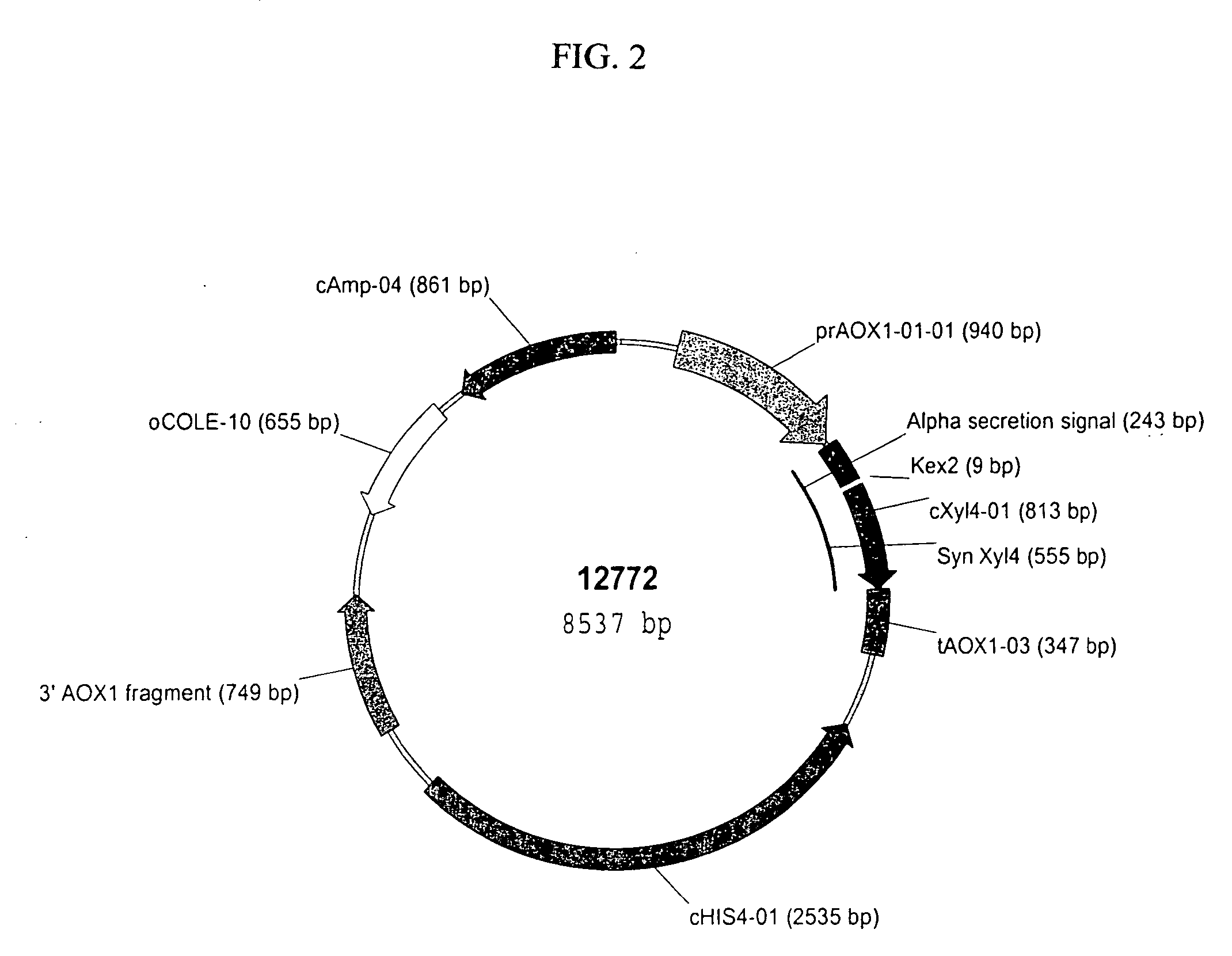
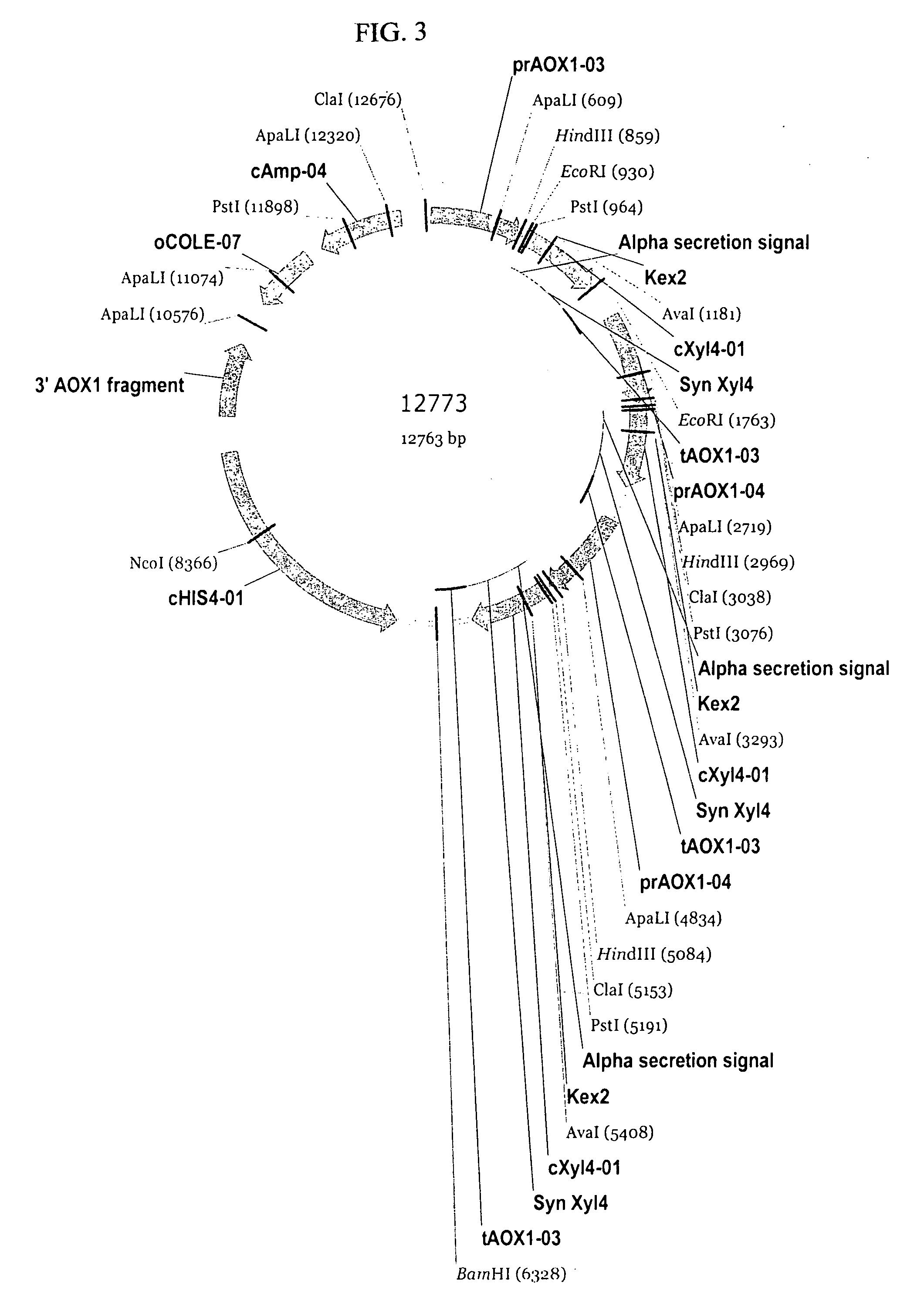
Compositions and Methods for Use of Pigment Epithelial Derived Factor (PEDF) Peptide Fragments
InactiveUS20090069241A1Organic active ingredientsNervous disorderPIGMENT EPITHELIUM-DERIVED FACTORPeptide fragment
The invention provides PEDF peptides which retain the biological activity of full-length PEDF. Fusion proteins comprising a PEDF peptide are also provided. The invention further provides a codon-optimized PEDF coding sequence and method of expressing it in bacteria. Compositions, methods of use and kits are also provided.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
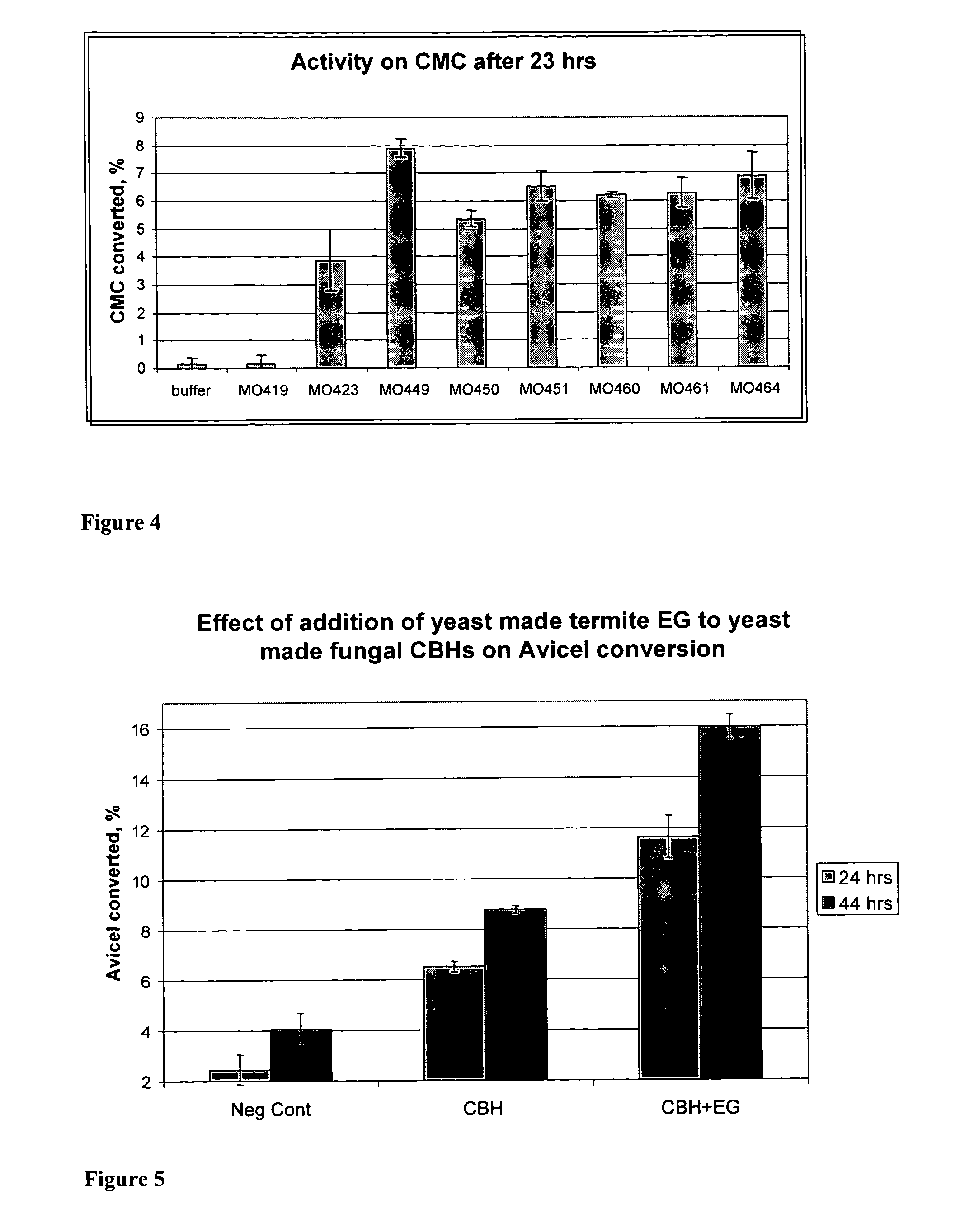
Heterologous Expression of Termite Cellulases Yeast
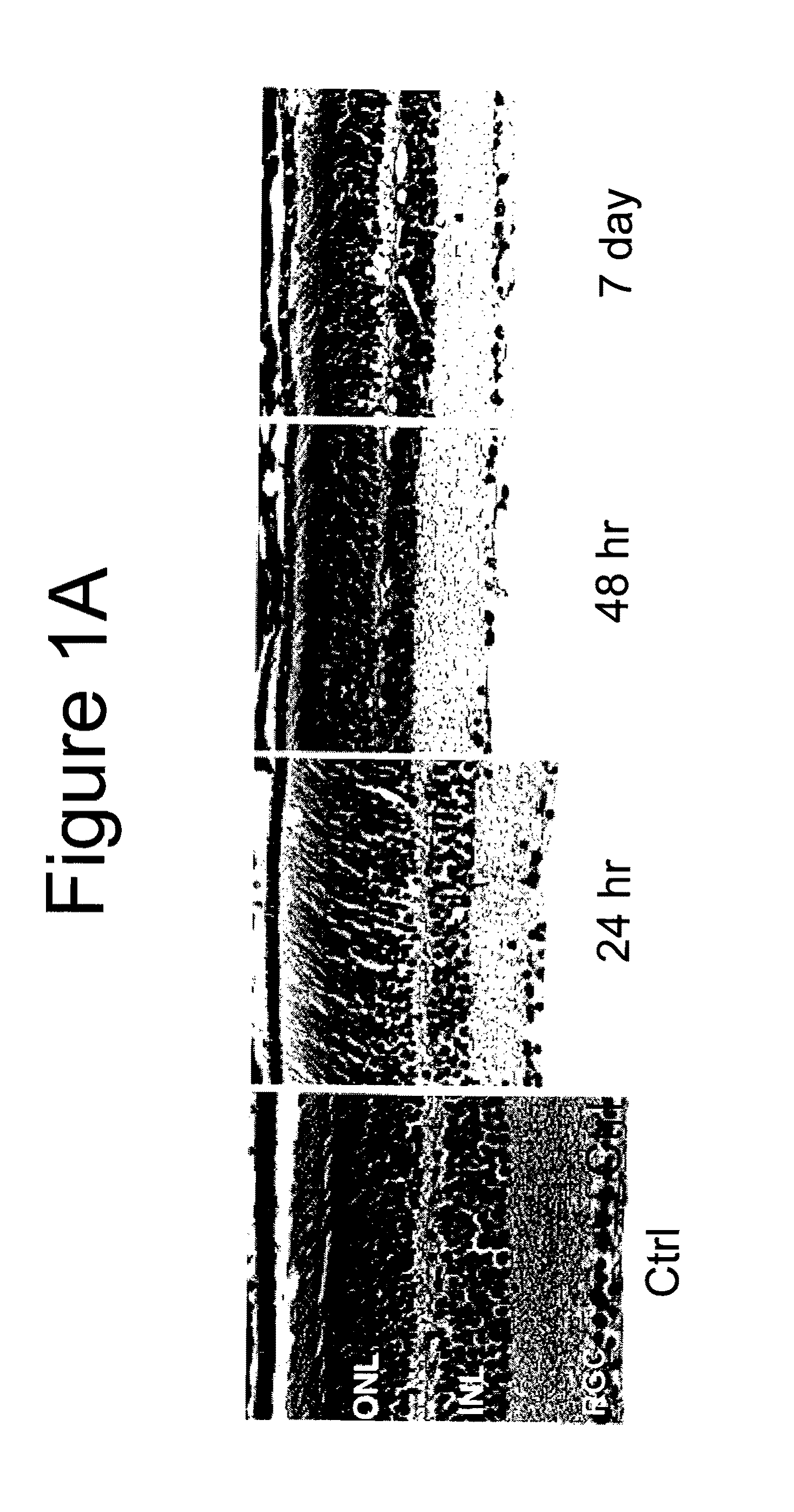
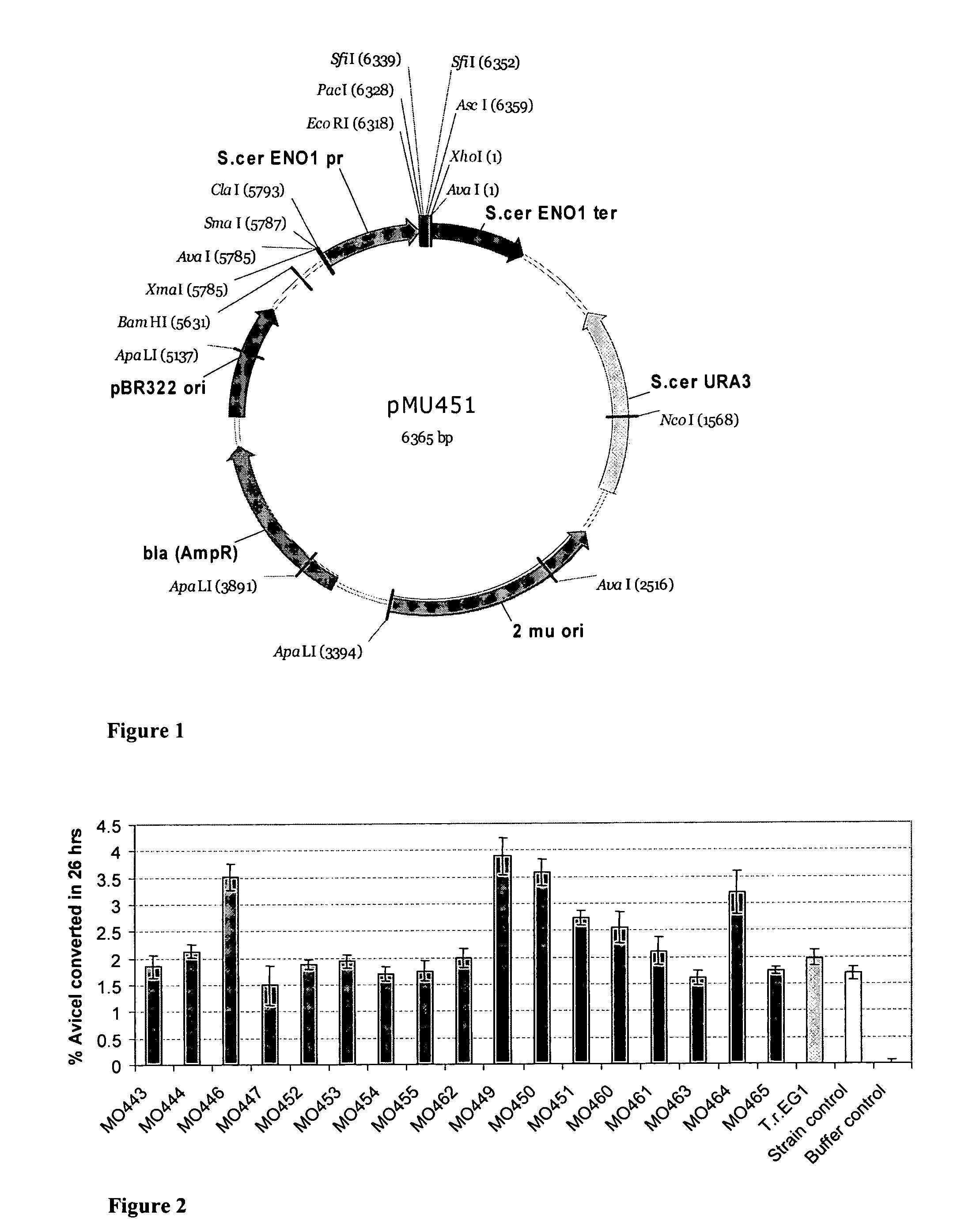
The present invention provides for heterologous expression of termite and termite-associated symbiont cellulases. The cellulases can, for example, be codon-optimized and expressed in yeast host cells, such as the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The cellulases can also be co-expressed in host cells with other cellulases. The expression in such host cells of the termite and termite-associated symbiont cellulases, and variants and combinations thereof, result in yeast with improved cellulosic activity. Thus, such genes and expression systems are useful for efficient and cost-effective consolidated bioprocessing systems.
Owner:LALLEMAND HUNGARY LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT LLC
Method for the Production of a Monoclonal Antibody to CD20 for the Treatment of B-Cell Lymphoma
InactiveUS20090285795A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsDNA constructMammalian expression
The present invention relates to the recombinant method used for the production of soluble form of an antibody that binds to CD20 for treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory, low-grade or follicular, CD20-positive, B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL). The treatment will comprise the use of immunologically active anti-CD20 antibodies; or radiolabeled anti-CD20 antibodies and or cooperative strategies where both labeled and non-labeled antibodies will be used for treatment of NHL. The procedure describes the de novo synthesis of the nucleic acid sequence encoding anti-CD20, transformation of the constructed nucleic acid sequences into competent bacteria and the sub-cloning of the same into mammalian expression vectors for expression of the desired protein. DNA constructs comprising the control elements associated with the gene of interest has been disclosed. The nucleic acid sequence of interest has been codon optimized to permit expression in the suitable mammalian host cells.
Owner:AVESTHAGEN
Ketoreductase polypeptides and related polynucleotides
ActiveUS7629157B2Improve thermal stabilityHigh activitySugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesNucleotidePolynucleotide
The present invention is directed to variant polypeptides having enhanced ketoreductase activity and / or thermostability for use in the stereospecific reduction of ketones. In addition, the present invention is directed to polynucleotides that encode the ketoreductase polypeptides, including codon optimized versions of the polynucleotides which provide for enhanced expression in host cells. In another aspect, the present invention is directed to nucleotide constructs, vectors and host cells that are transformed with polynucleotides of the present invention.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
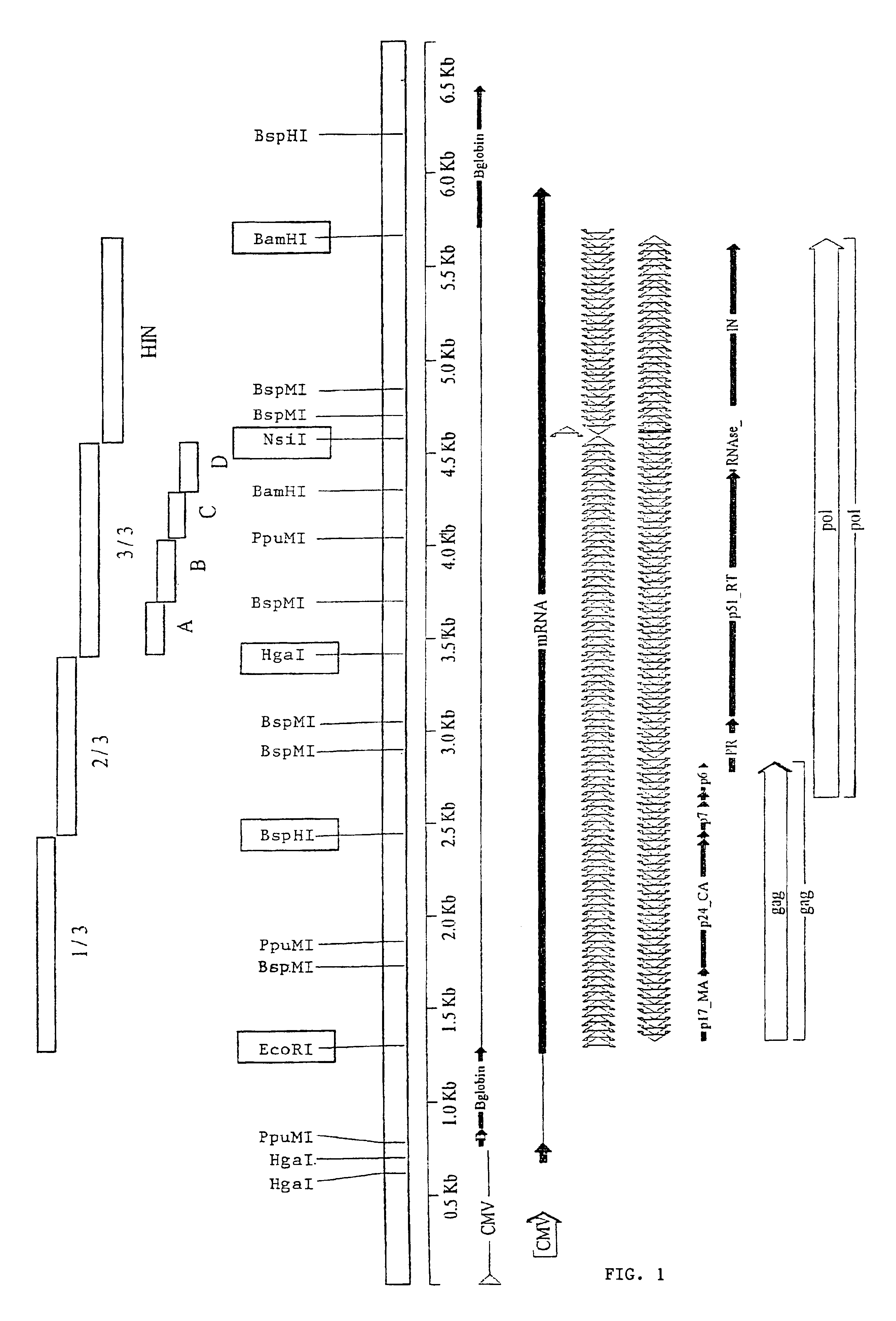
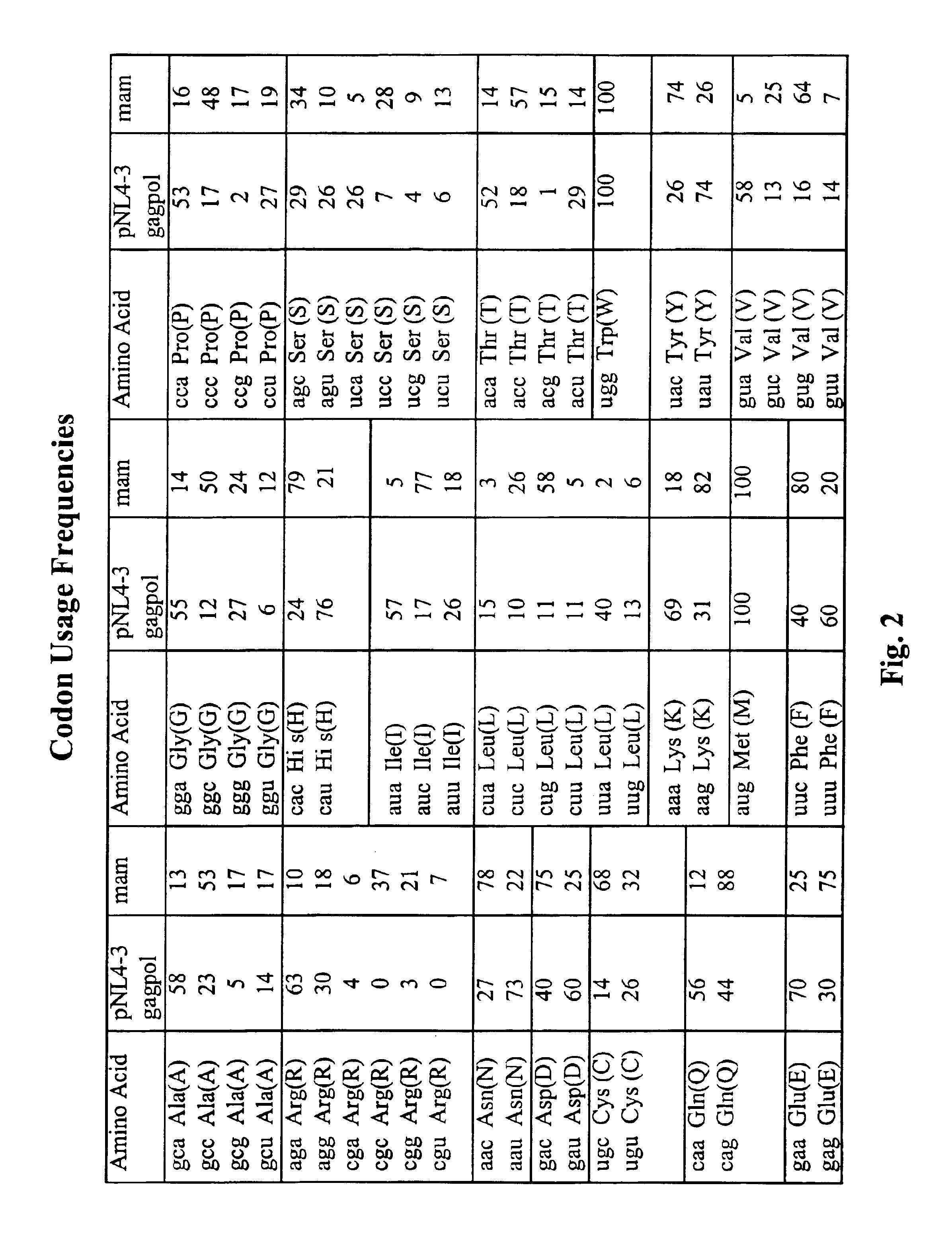
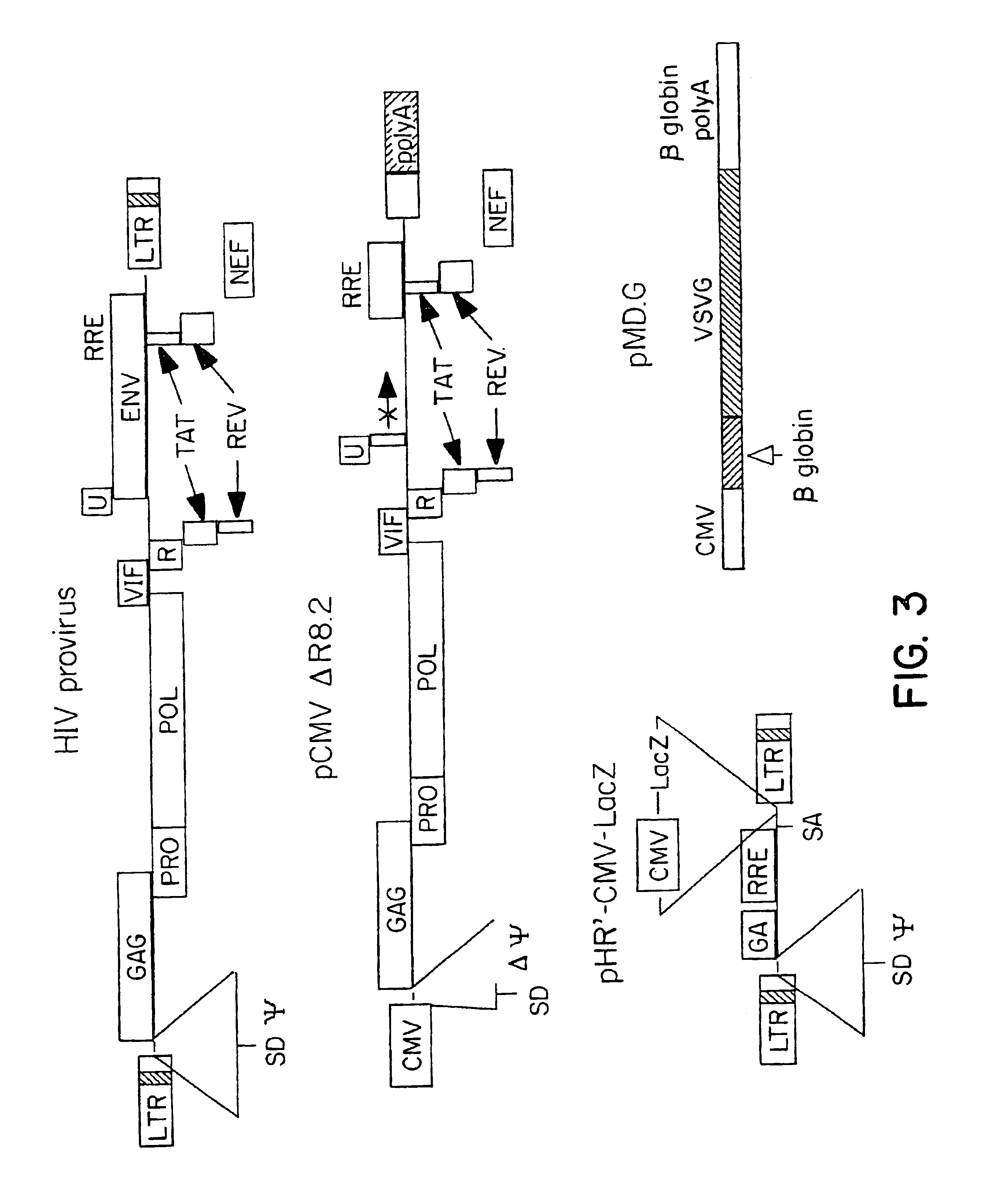
Packaging cells comprising codon-optimized gagpol sequences and lacking lentiviral accessory proteins
Owner:OXFORD BIOMEDICA (UK) LTD
Optimization of gene sequences of virus-like particles for expression in insect cells
InactiveUS20040121465A1Improve the level ofMinimize the numberAnimal cellsViral antigen ingredientsPolynucleotideTGE VACCINE
Codon optimized polynucleotides for optimal expression of recombinant proteins in eukaryotic cells are provided. The codon optimized polynucleotides encode a viral capsid protein that self assembles into a virus-like particle. The virus-like particle is expressed extracellularly and exhibits conformational antigenic epitopes capable of raising neutralizing antibodies. Pharmaceutical compositions, vaccines, and diagnostic test kits containing the gene products of the codon-optimized polynucleotides are also provided.
Owner:NOVAVAX
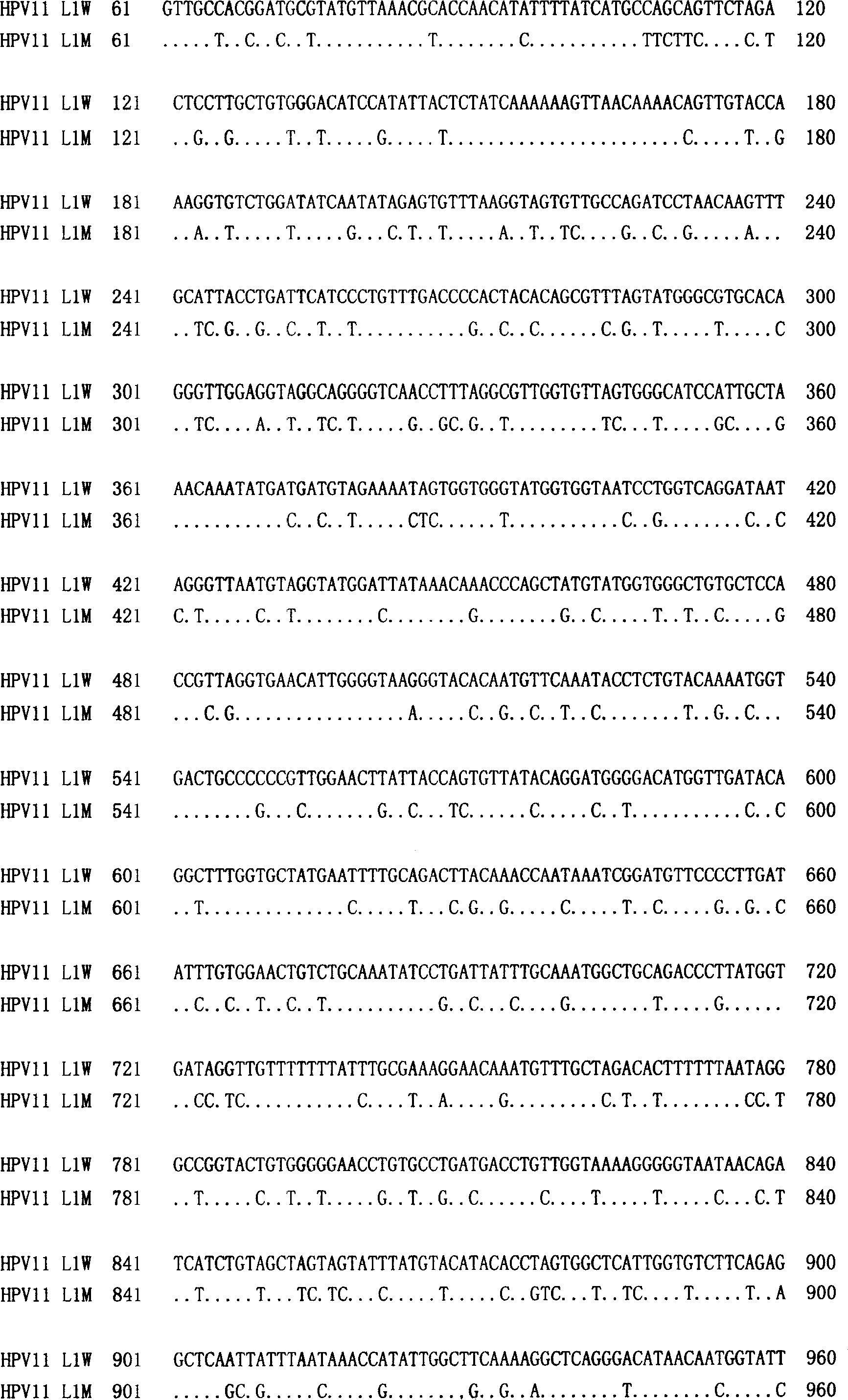
Method of increasing yield of human papilloma virus L1 albumen pronucleus expression
ActiveCN101016542ALow costHigh expressionViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsTGE VACCINENucleic acid sequence
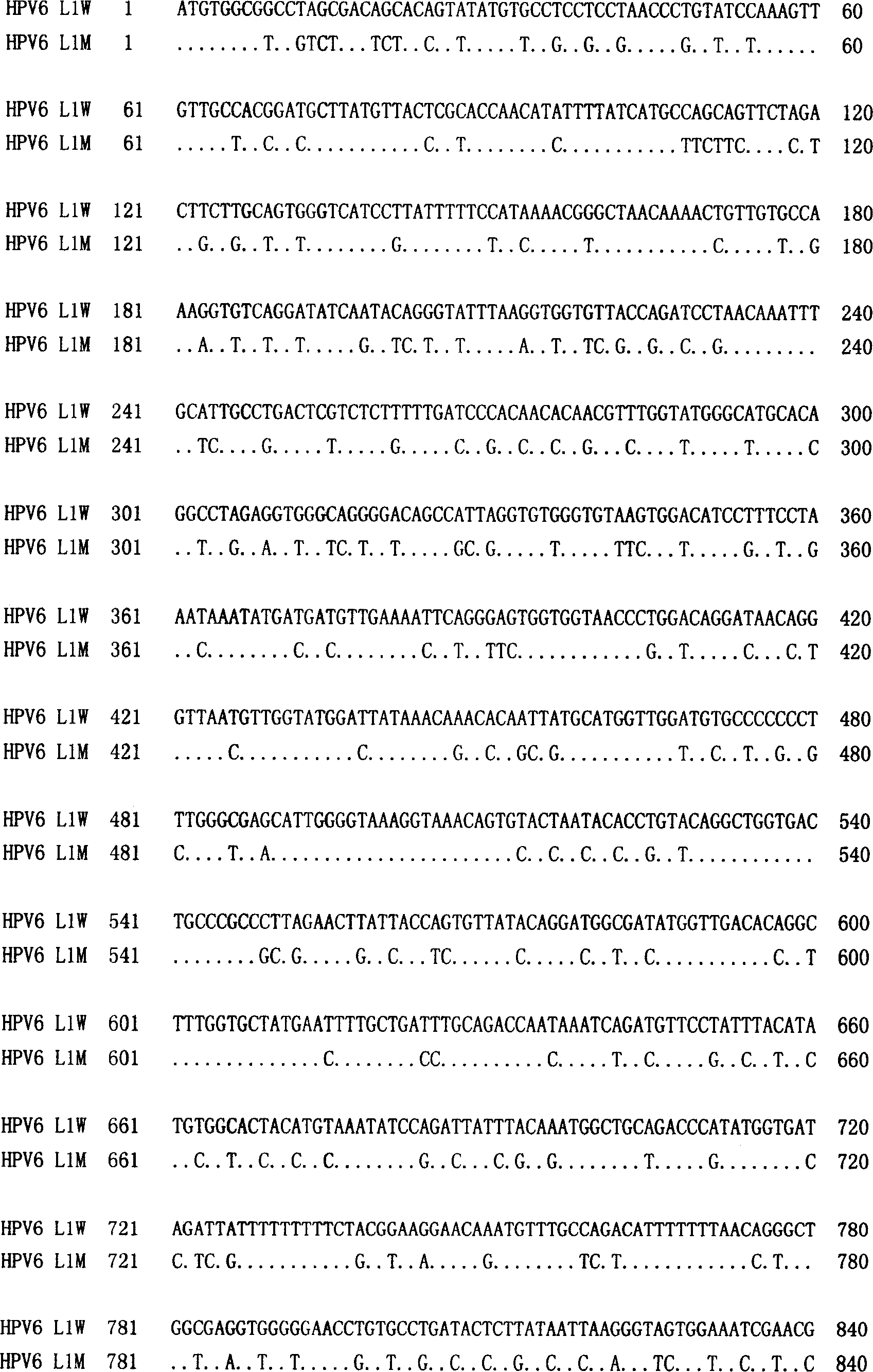
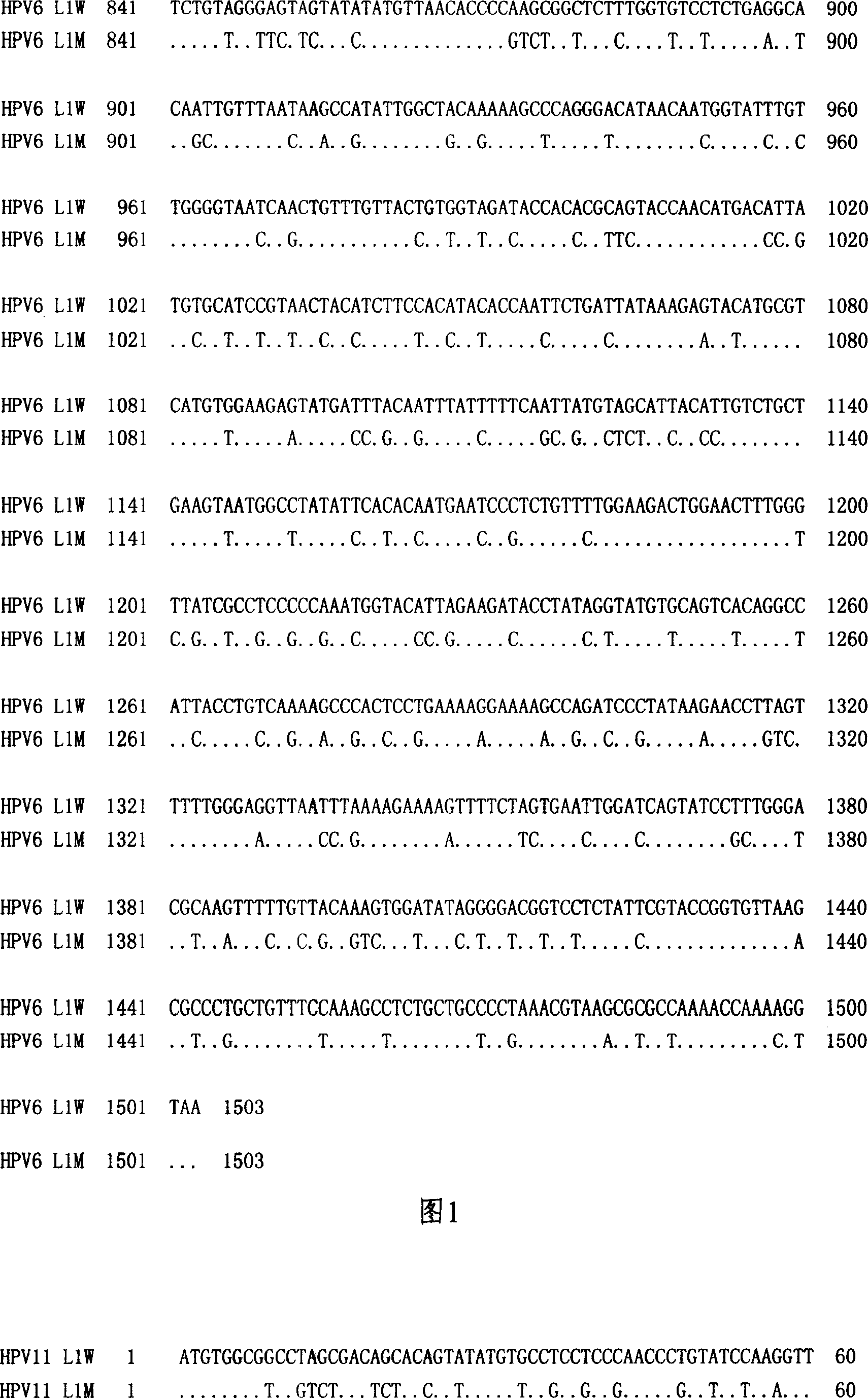
The invention discloses a method to increase human papilloma virus L1 protein pronucleus expression productivity and also discloses a encode HPV L1 protein codon majorizing nucleic acid sequence from this method, which is characterized by the following: supplying expression carrier and host cell and HPVL1 protein poly body of nucleic acid sequence; disclosing appliance in preparing vaccine, drug compound and immunodiagnosis or antibody. The nucleic acid sequence expressing quantity possesses distinctive improvement, which decreases the preparing cost effectively.
Owner:BEIJING HEALTH GUARD BIOTECH
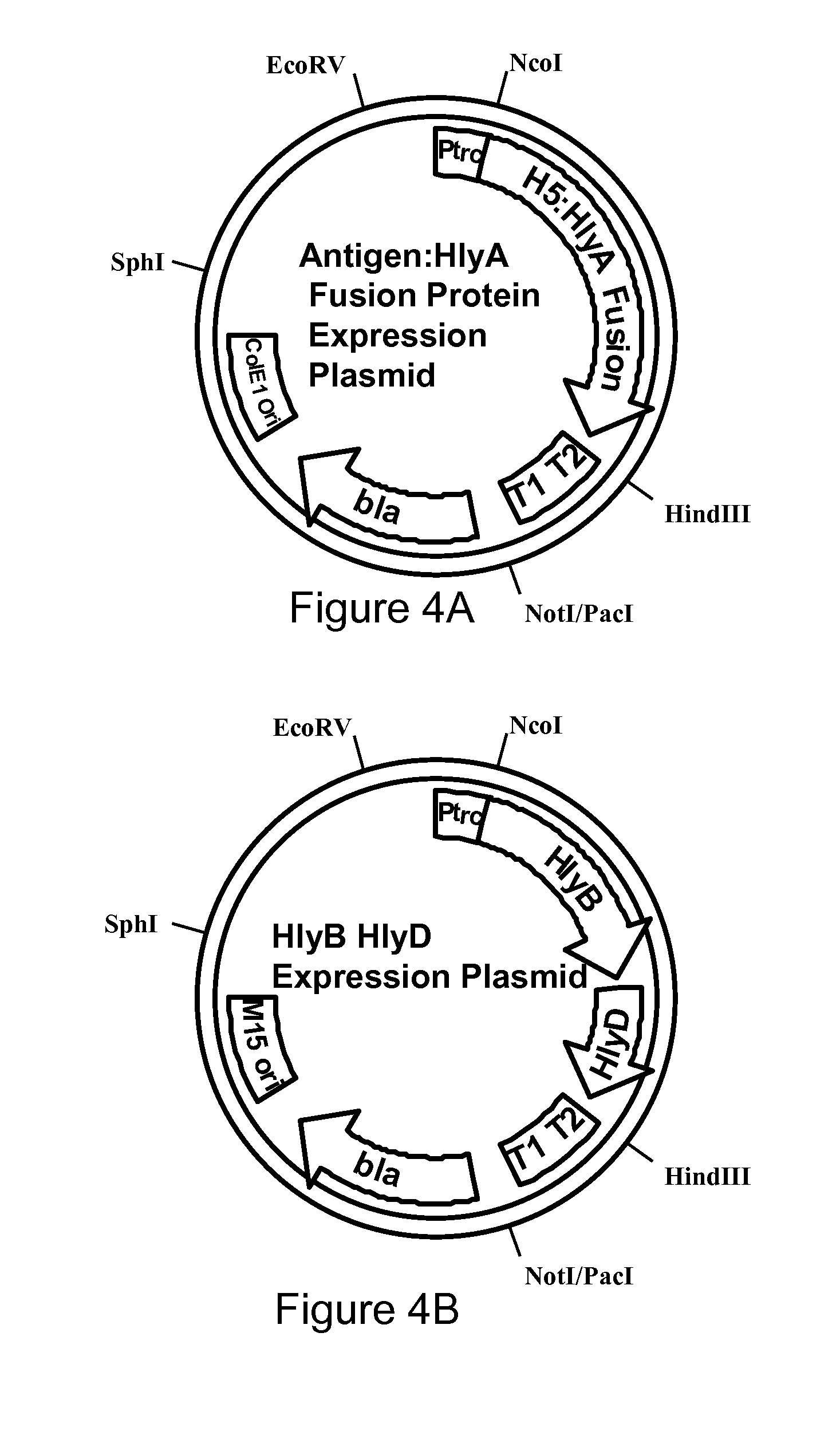
Live bacterial vaccines for viral infection prophylaxis or treatment
ActiveUS20120142080A1Enhance immune responseAntibacterial agentsSsRNA viruses negative-senseBacteroidesDNA construct
A live bacterium, having a DNA construct stabilized against transduction of other bacteria, having a promoter sequence and encoding a fusion peptide, comprising a bacterial secretion peptide portion and a non-bacterial immunogenic polypeptide portion, having a nucleotide sequence coding for the non-bacterial immunogenic polypeptide portion which has at least one codon optimized for bacterial expression. The bacterium has a secretion mechanism which interacts with at least the bacterial secretion peptide portion to cause a secretion of the fusion peptide from the bacterium, and a genetic virulence attenuating mutation. The bacterium is adapted to act as an animal vaccine, to transiently infect a tissue of the animal, and cause an immunity response to the non-bacterial immunogenic polypeptide portion in the animal to a non-bacterial organism associated with the non-bacterial immunogenic polypeptide portion.
Owner:AVIEX TECH
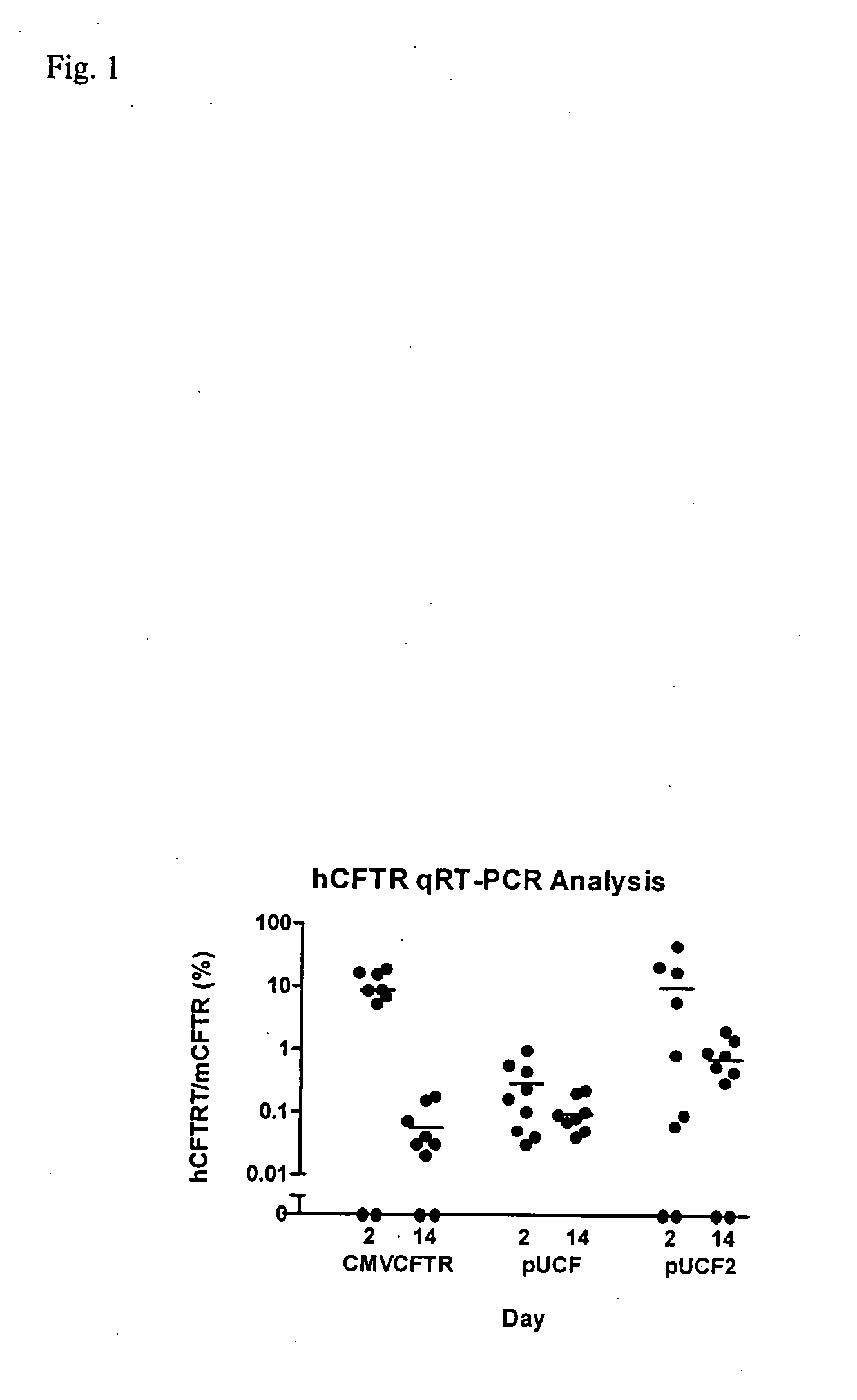
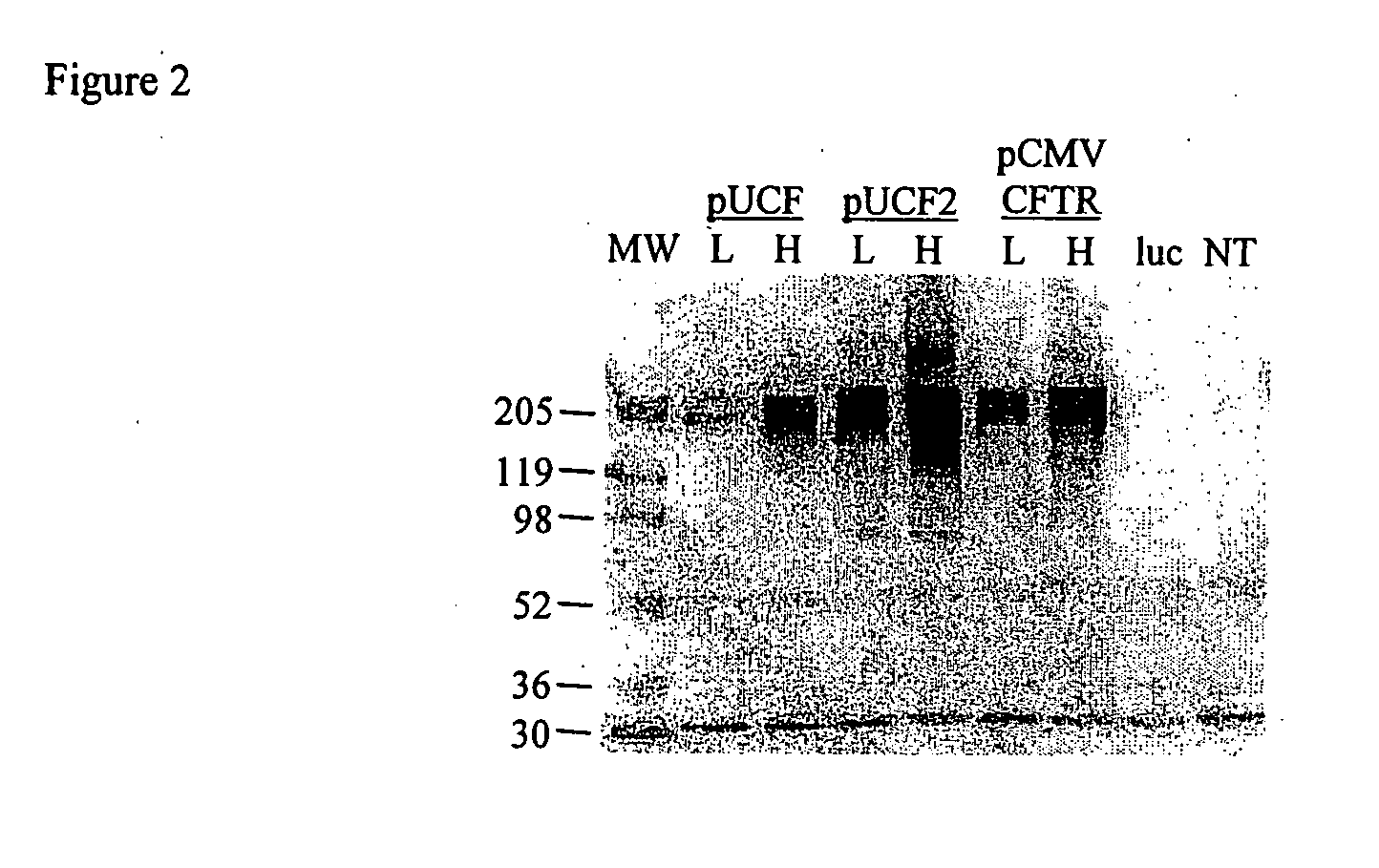
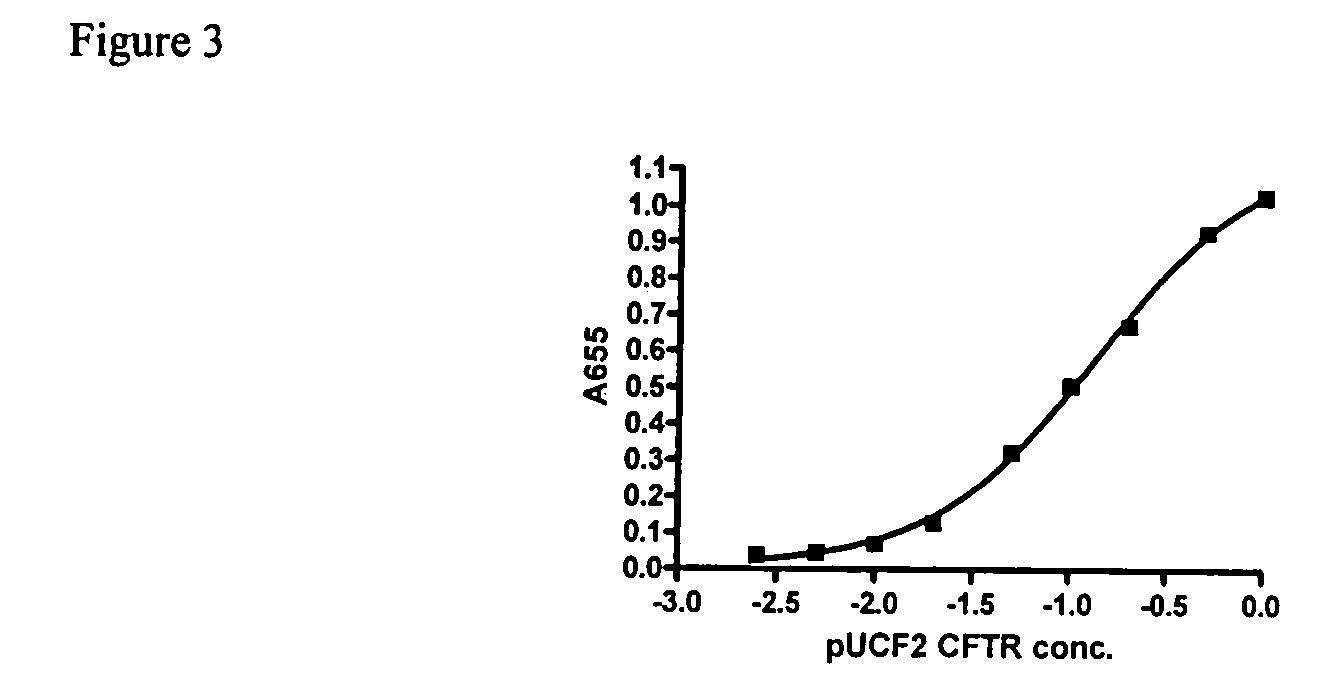
Codon optimized cftr
A synthetic hCFTR DNA sequence has been developed that produces remarkably high levels of hCFTR mRNA and protein in dosed murine lungs and human cells in culture compared to the natural hCFTR cDNA. This synthetic DNA addresses problems inherent in some natural cDNAs, such as premature transcriptional truncation sites introduced during cDNA synthesis. Introns are initially present in mRNA until the mRNA is processed. cDNA made from processed mRNA is devoid of introns. Thus DNA sequences (exon junctions) are present in a cDNA molecule which are not present in cells in nature. These exon junctions may affect transcription. Methods for improving expression of CFTR are based on sequence changes in cDNA molecules. The improvement methods may be applied to other cDNA molecules which are refractory to in vivo expression efforts. Compositions embodying the sequence changes increase the production of both transgenic mRNA and protein from cDNA molecules.
Owner:COPERNICUS THERAPEUTICS
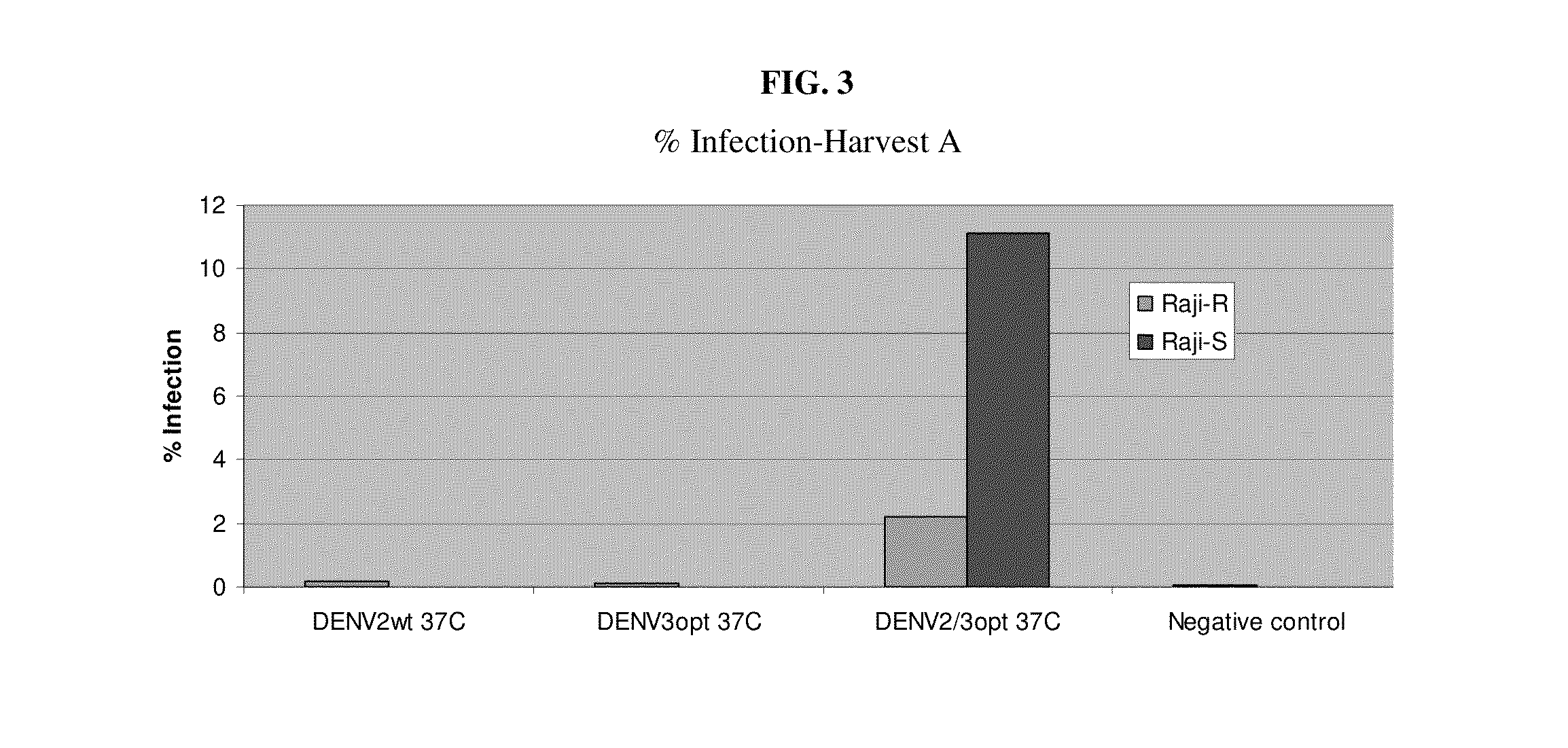
Flavivirus reporter virus and methods of making and using the same
The present invention relates to the production and uses of flavivirus replicons and flavivirus particles and reporter virus particles. The present invention relates to the production and uses of chimeric and codon-optimized flavivirus virus replicons and flavivirus virus particles and reporter virus particles.
Owner:INTEGRAL MOLECULAR
Preparation of PCV2 ORF2 capsid protein virus-like particles derived from escherichia coli
InactiveCN103173470AKeep natural activityHigh activityBacteriaViral antigen ingredientsEscherichia coliOrf2 gene
The invention relates to porcine circovirus PCV2 ORF2 gene optimized by using escherichia coli expression codon and a preparation method of PCV2 ORF2 capsid protein virus-like particles derived from the escherichia coli.
Owner:SA BIOTECH (SUZHOU) PTE LTD
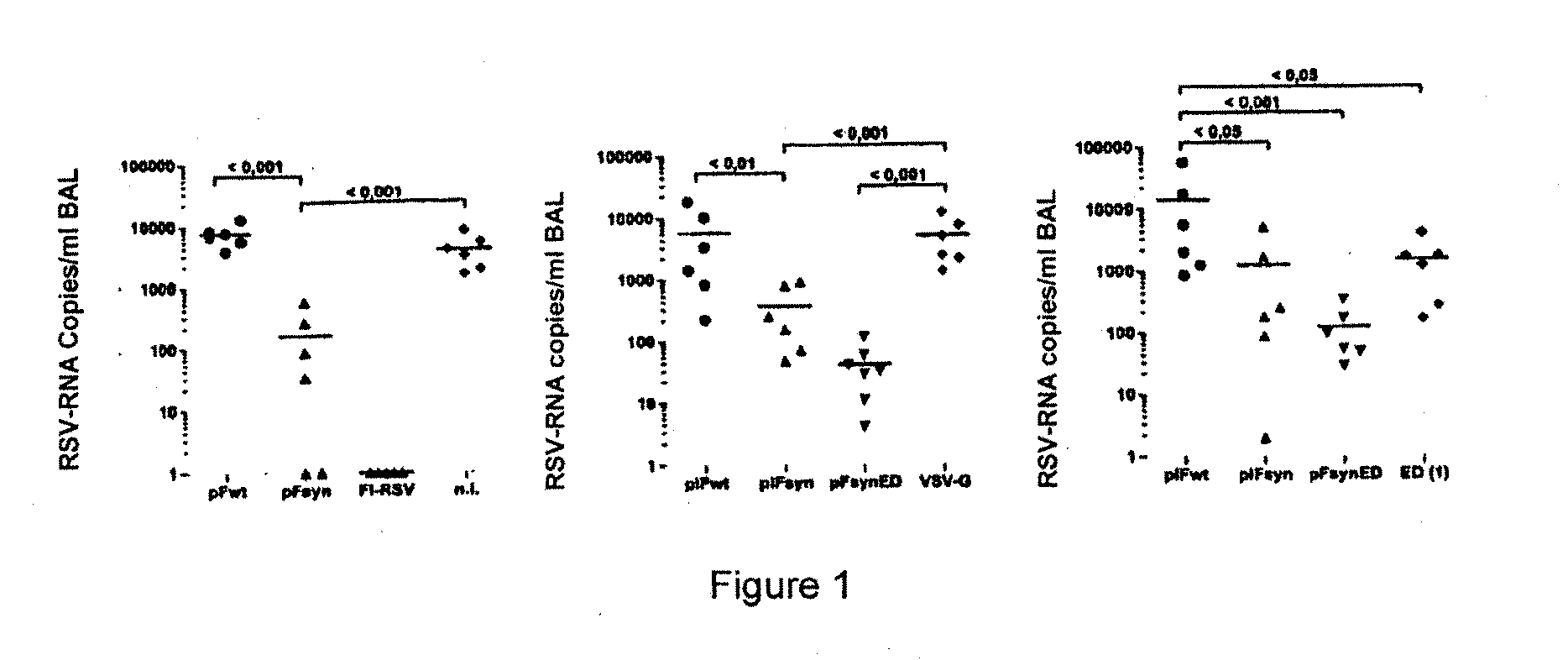
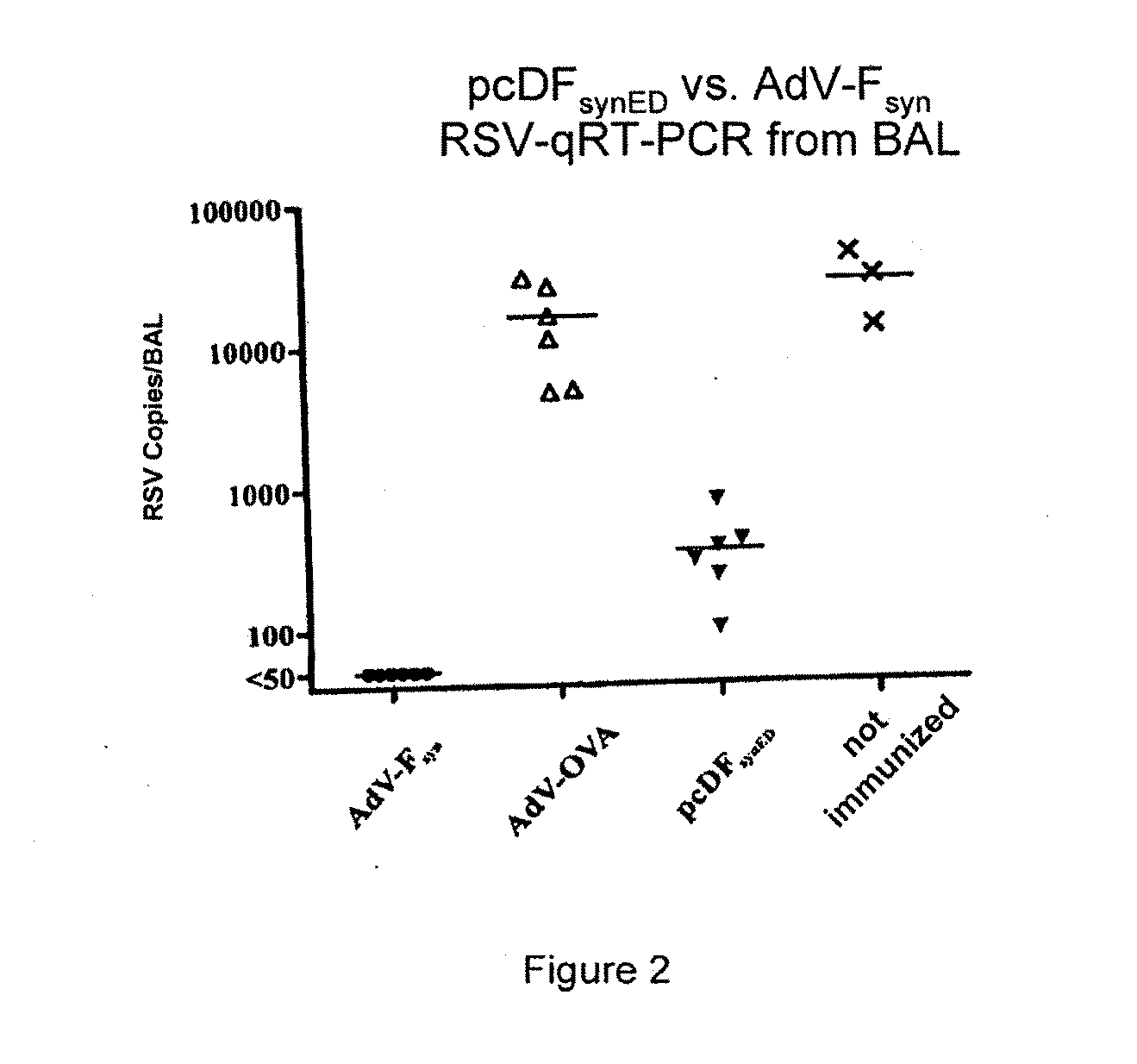
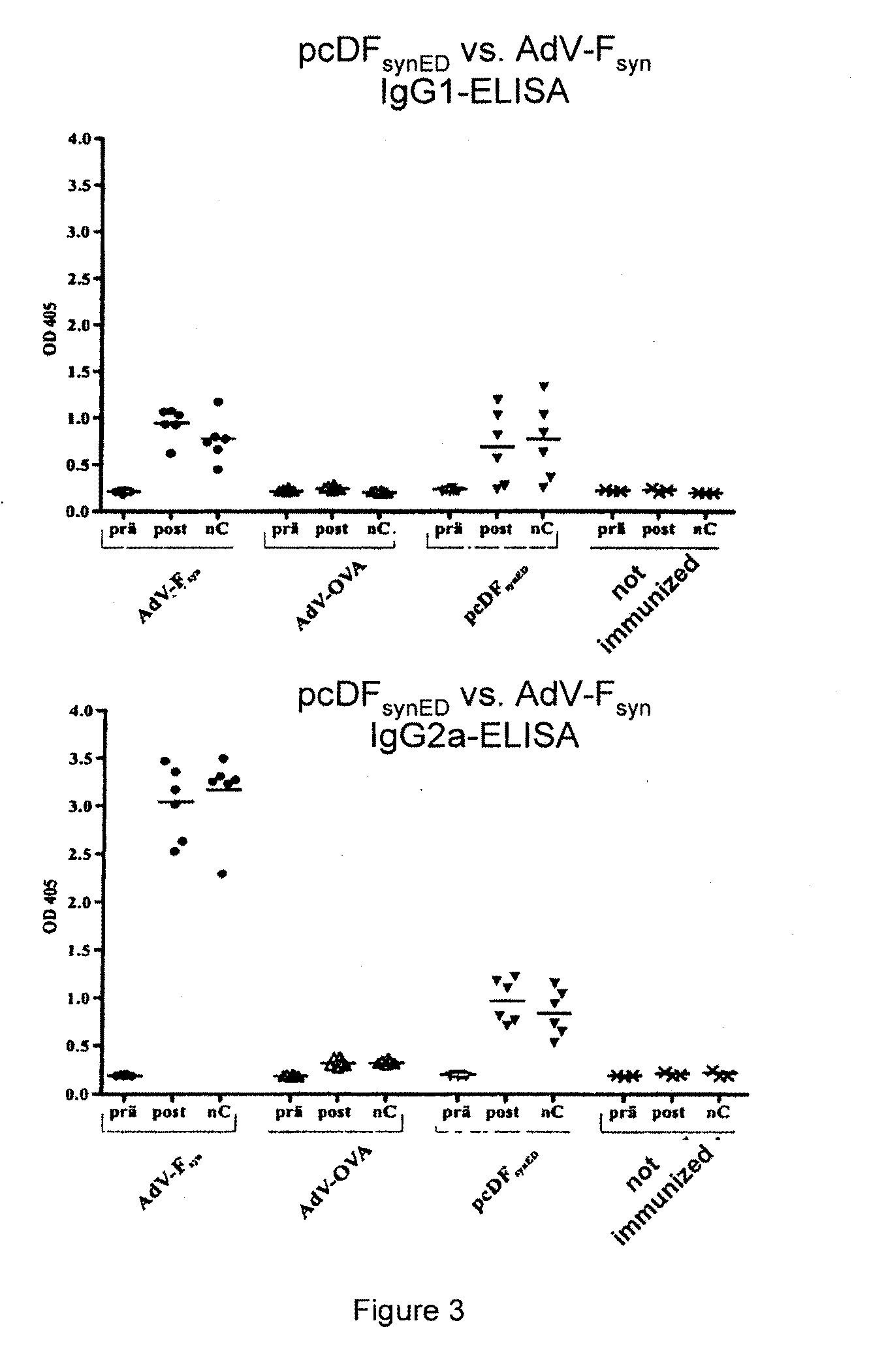
Rsv f-protein and its use
InactiveUS20100111989A1Inhibit expressionSsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesF proteinHuman cell
The present invention relates to a nucleic acid molecule, which codes for the F-protein of the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) or a fragment thereof, for the expression in a human cell environment of codon optimized variants of said nucleic acid molecule, vectors and compositions comprising said nucleic acid molecules and the use thereof as vaccines and polypeptides coded by the nucleic acid molecules and method for the production thereof.
Owner:PEVION BIOTECH +1
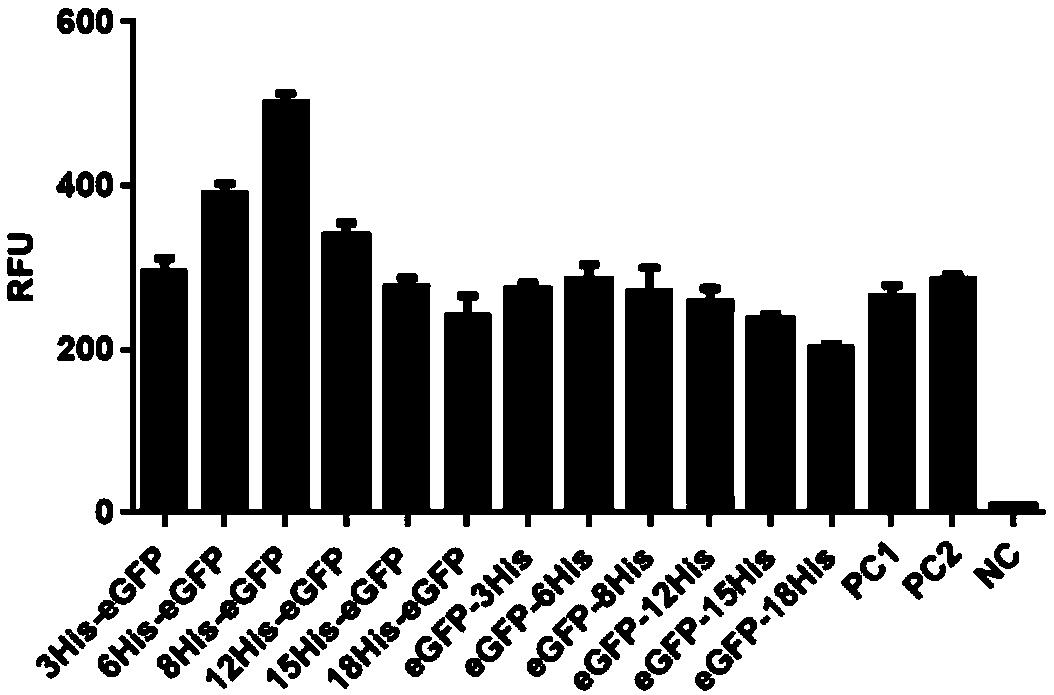
Multiple His sequence tag and application of multiple His sequence tag to protein expression and purification
The invention provides a multiple His sequence tag and application of the multiple His sequence tag to protein expression and purification. Specifically, a nucleic acid builder is composed of coding sequences of nHis, catenation sequences (including the codon optimized catenation sequence and the un-optimized catenation sequence) and coding sequences of foreign proteins. By applying the nucleic acid builder to a protein synthesis system, the translation efficiency of target proteins can be improved, and the foreign proteins can be expressed and purified.
Owner:KANGMA SHANGHAI BIOTECH LTD
Vaccines and immunotherapeutics using codon optimized il-15 and methods for using the same
InactiveUS20100003277A1Sugar derivativesViral antigen ingredientsImmunotherapeutic agentRecombinant vaccines
Nucleic acid molecules that encode IL-15 or fragments thereof, which express protein at a higher level than nucleic acid molecules with native coding sequences for IL-15 are disclosed. Nucleic acid molecules with additional modifications such as the absence of coding sequences for IL-15 signal sequences and / or the absence of IL-15 untranslated sequences and / or inclusion of non-IL-15 signal sequences are also disclosed. Vectors, including plasmids and viral vectors, comprising such nucleic acid molecules; and to host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules are disclosed as well as methods of using such nucleic acid molecules alone or in combination with nucleic acid sequences encoding immunogens which are part of the nucleic acid molecules and / or part of a different nucleic acid molecule. Recombinant vaccines and live attenuated pathogens encoding fusion proteins, and methods of using the same, are disclosed.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
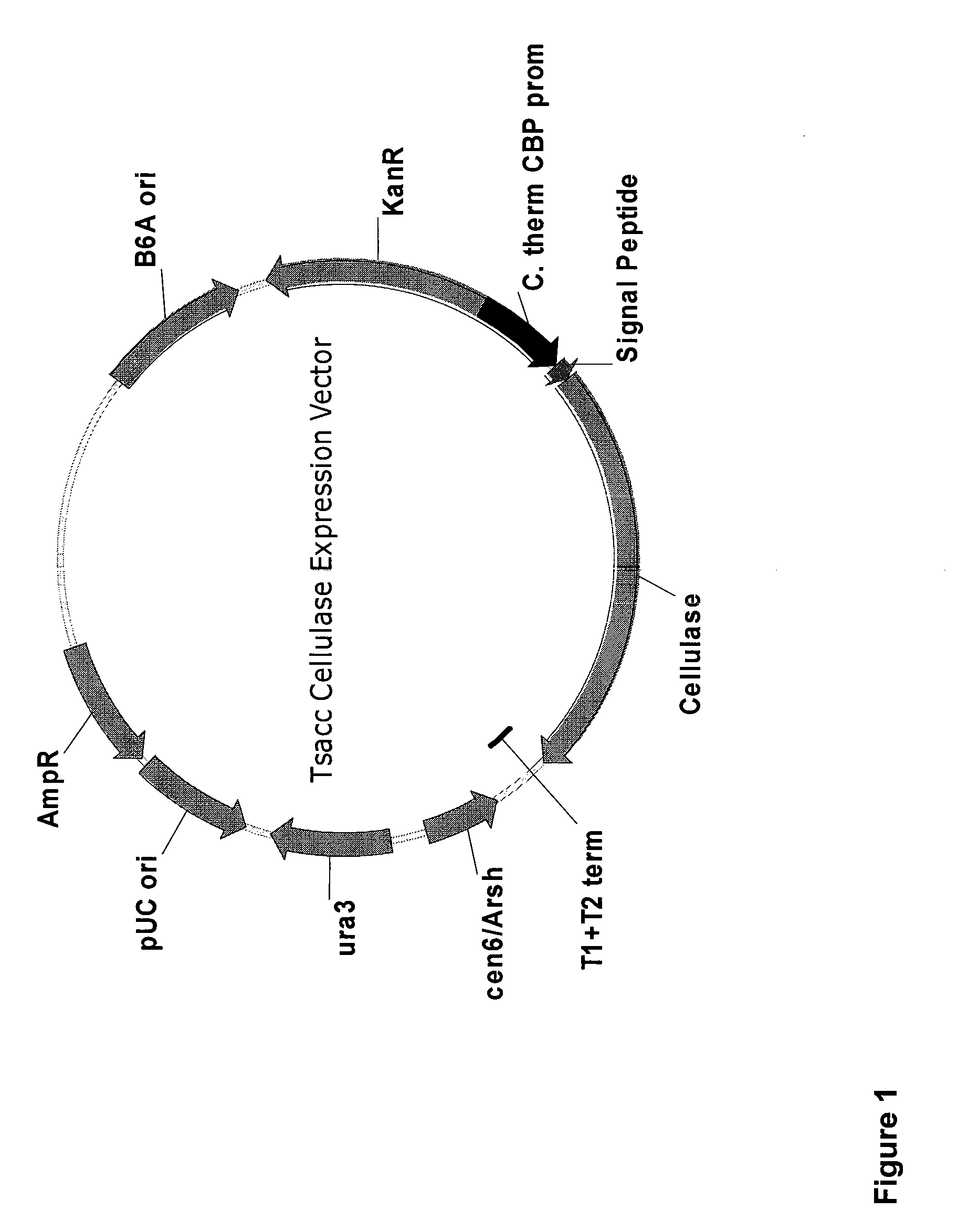
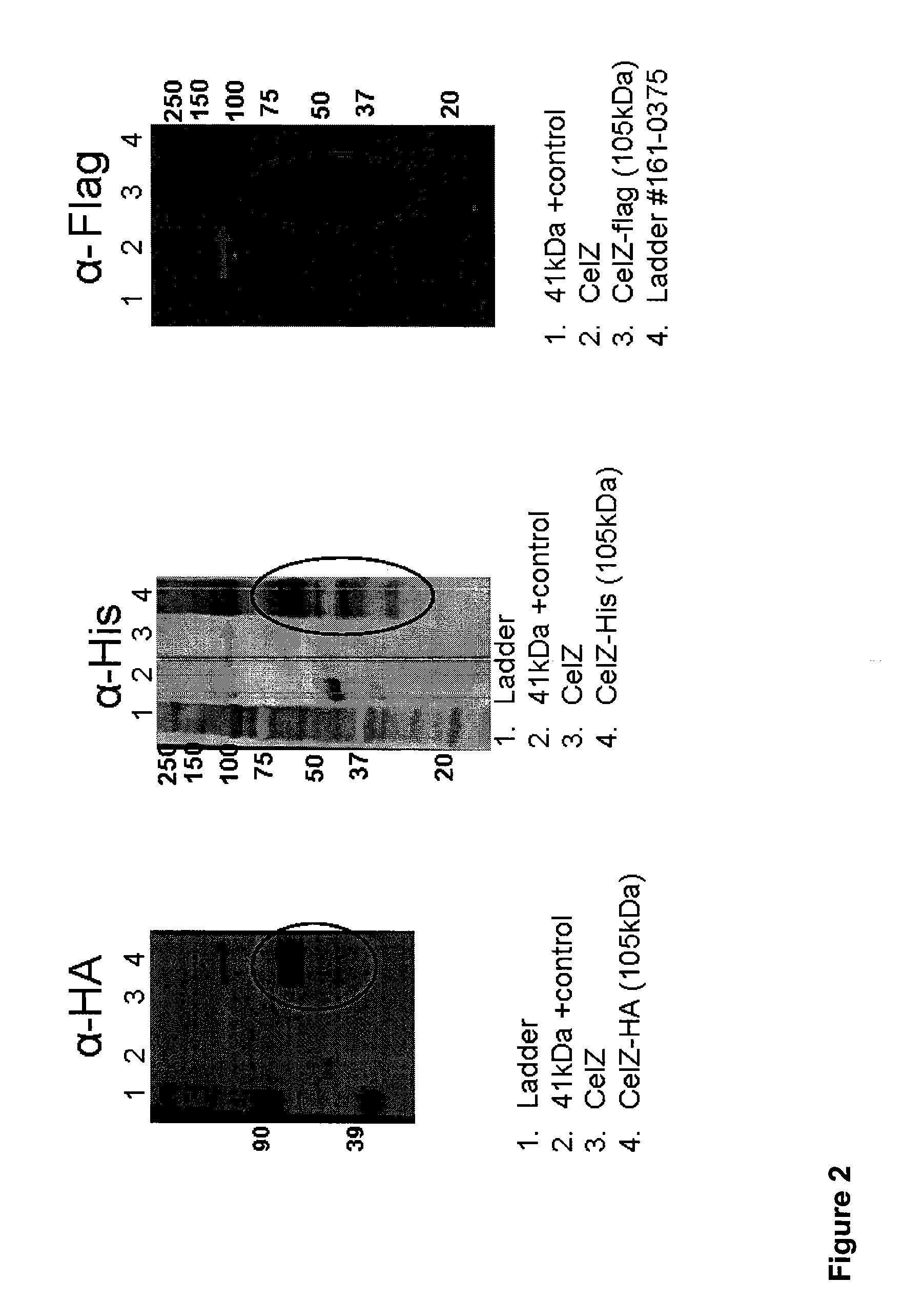
Heterologous Biomass Degrading Enzyme Expression in Thermoanaerobacterium Saccharolyticum
InactiveUS20120040409A1Increased chaperone activityDecrease protease activityBacteriaSugar derivativesThermoanaerobacterium saccharolyticumNucleotide
Thermophilic gram-positive anaerobic host cells, for example Thermoanaerobacterium saccharolyticum (“T sacch”), express heterologous biomass degrading enzymes, such as cellulases, and are able to produce useful fermentation products from cellulose. Useful fermentation products include, for example, ethanol, acetic acid, lactic acid or CO2. In order to provide maximum expression and activity levels, biomass degrading enzymes can be expressed from codon-optimized nucleotide sequences, can be expressed under the control of a high-efficiency promoter, and / or can be fused to a signal peptide. In addition, the host cell, for example, a T sacch host cell, can be genetically altered to further improve ethanol production, for example by disrupting the production of organic products other than ethanol.
Owner:ENCHI
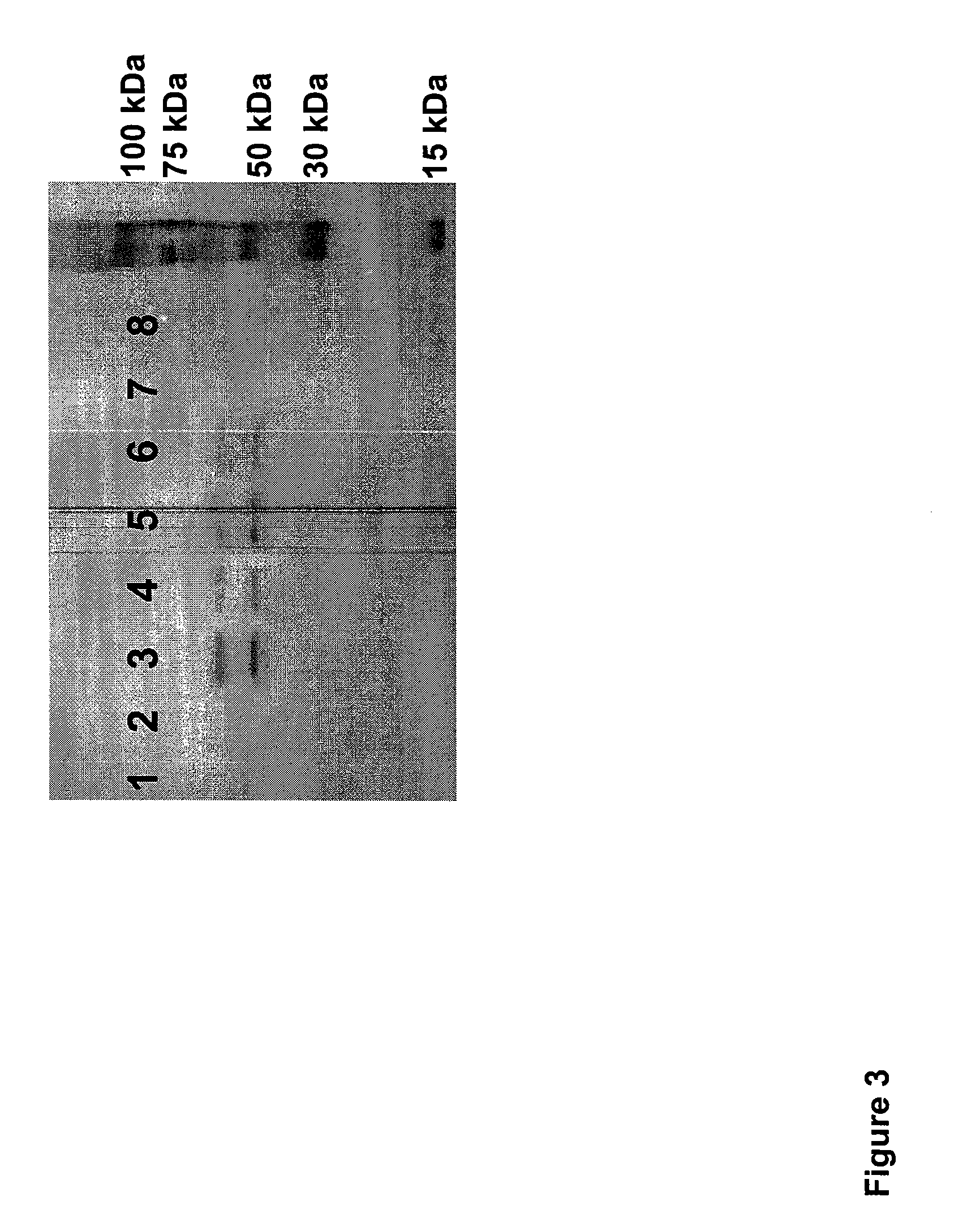
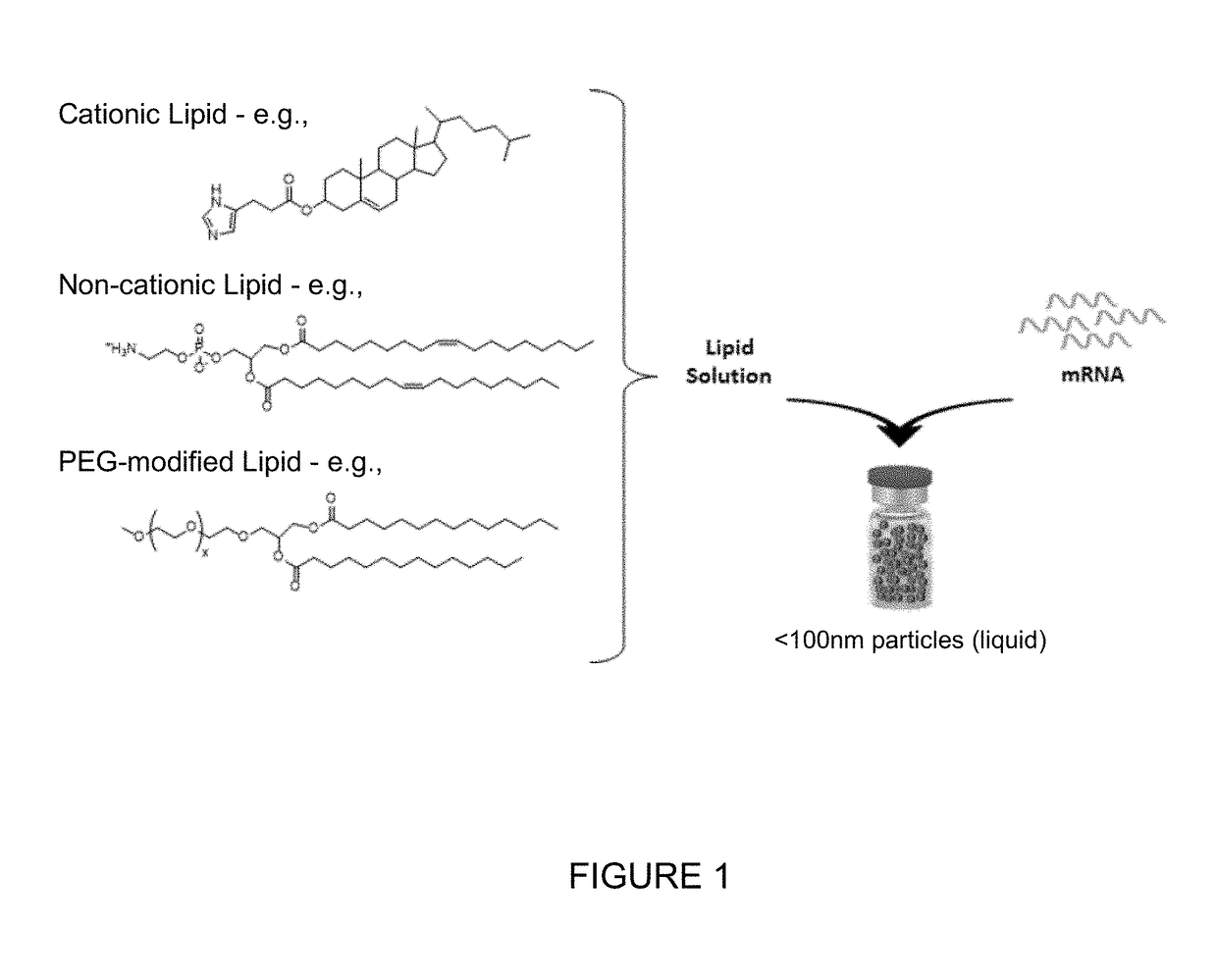
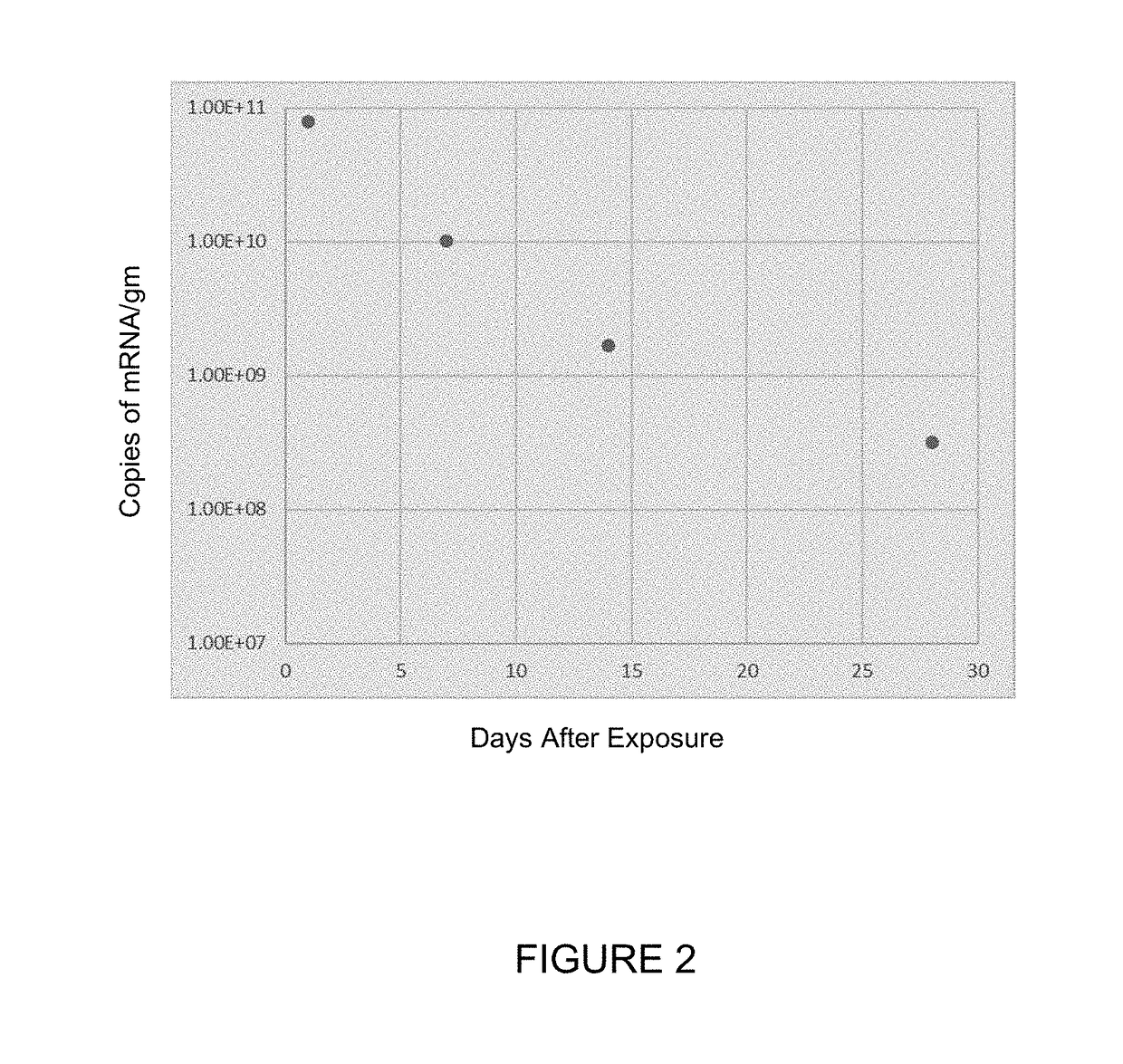
TREATMENT OF CYSTIC FIBROSIS BY DELIVERY OF CODON-OPTIMIZED mRNA ENCODING CFTR
The present invention provides, among other things, methods of treating cystic fibrosis, comprising a step of administering to a subject in need of treatment a composition comprising an mRNA encoding a Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) protein, wherein the mRNA encoding the CFTR protein comprises a polynucleotide sequence at least 80% identical to SEQ ID NO: 1, wherein the mRNA is at a concentration of at least 0.4 mg / mL, and wherein the step of administering comprises inhalation.
Owner:TRANSLATE BIO INC
Codon-optimized polynucleotide-based vaccines against Bacillus anthracis infection
The invention is related to polynucleotide-based anthrax vaccines. In particular, the invention is plasmids operably encoding Bacillus anthracis antigens, in which the naturally-occurring coding regions for the B. anthracis antigens have been modified for improved translation in human or other mammalian cells through codon optimization. In certain embodiments, the coding regions are also modified so as to remove potential N-linked glycosylation sites. B. anthracis antigens which are useful in the invention include, but are not limited to protective antigen (PA), lethal factor (LF), and fragments, variants or derivatives of either of these antigens. The invention is further directed to methods to induce an immune response to B. anthracis in a mammal, for example, a human, comprising delivering a plasmid encoding a codon-optimized B. anthracis antigen as described above. The invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising plasmids encoding a codon-optimized B. anthracis antigen as described above, and further comprising adjuvants, excipients, or immune modulators.
Owner:VICAL INC
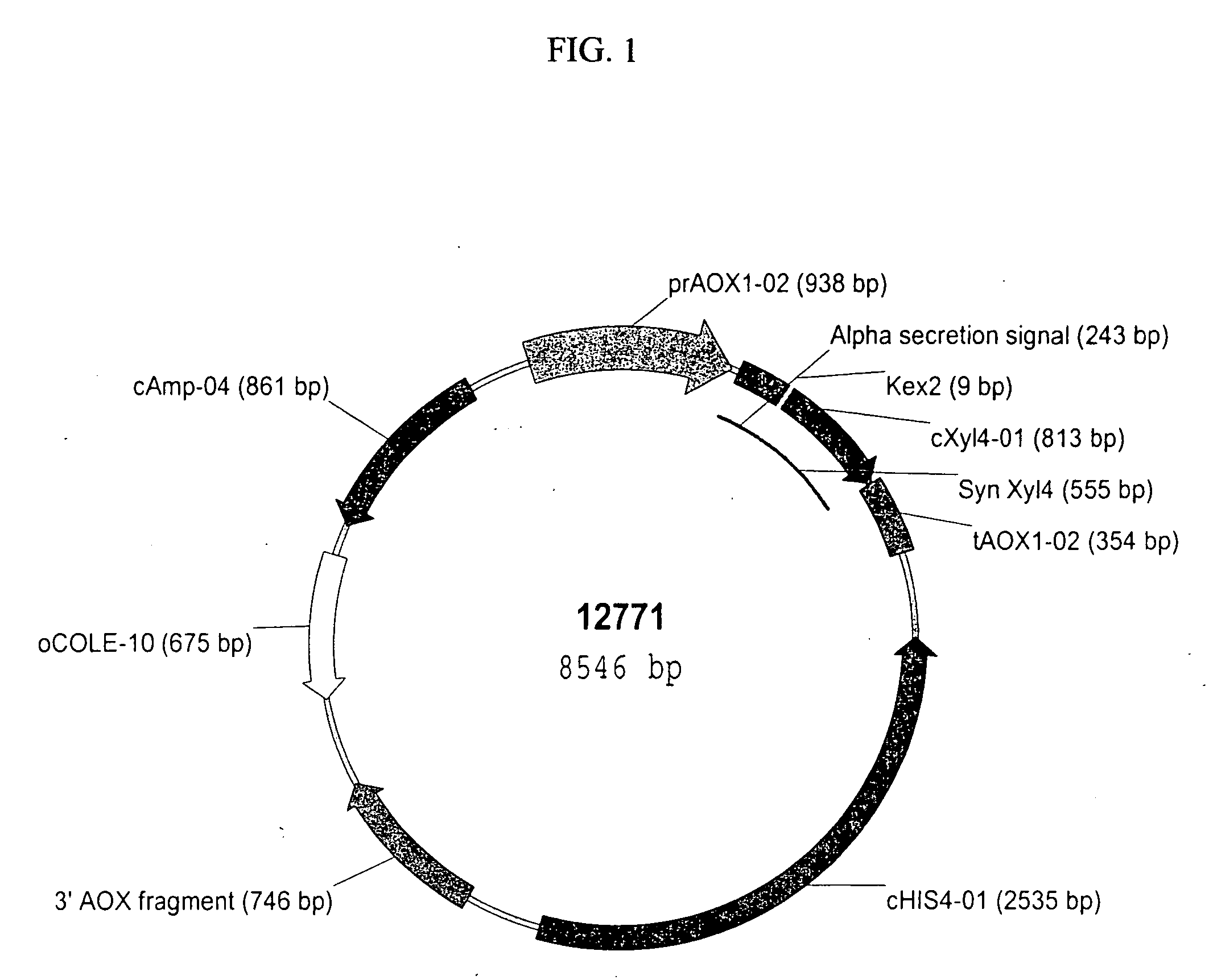
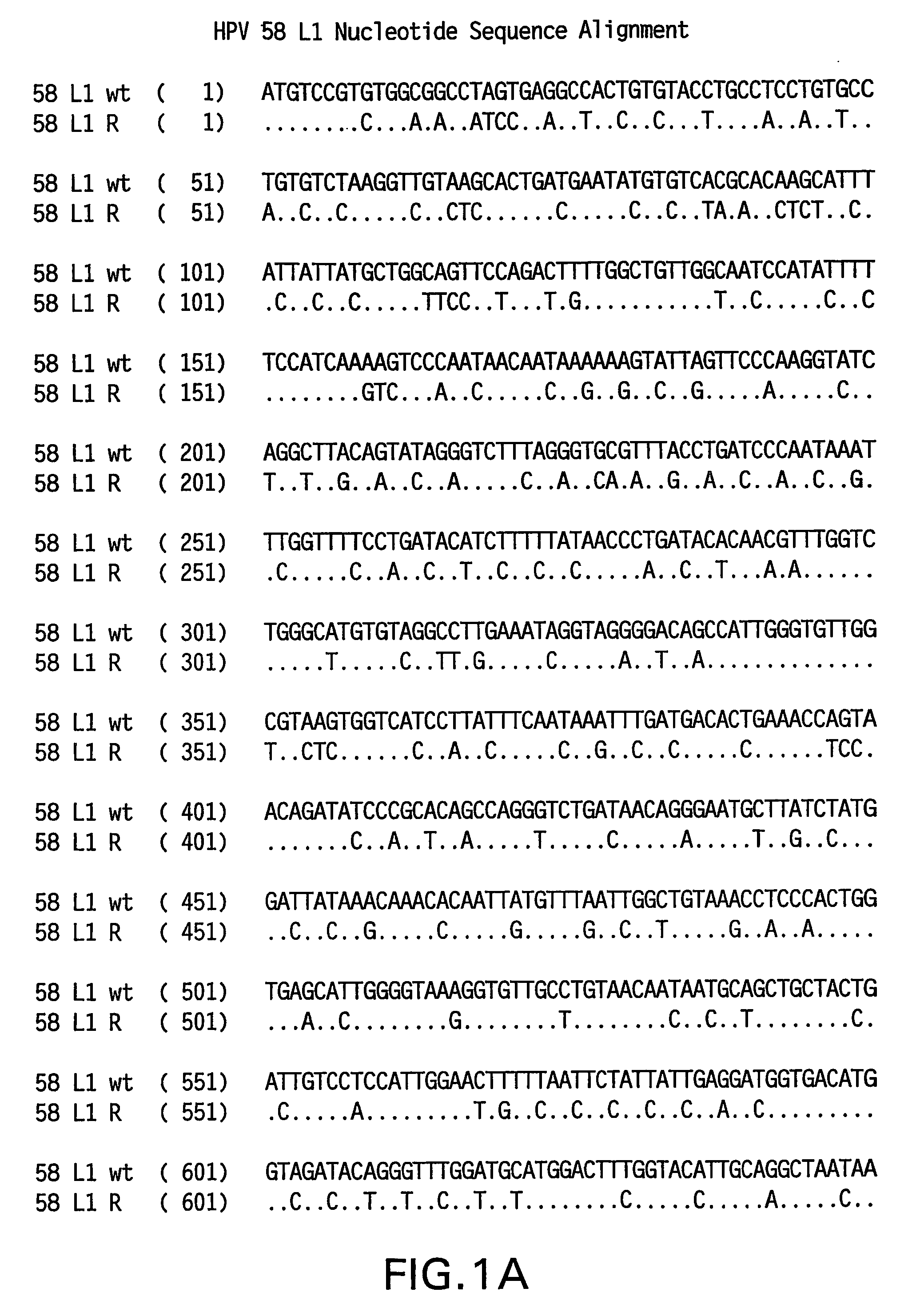
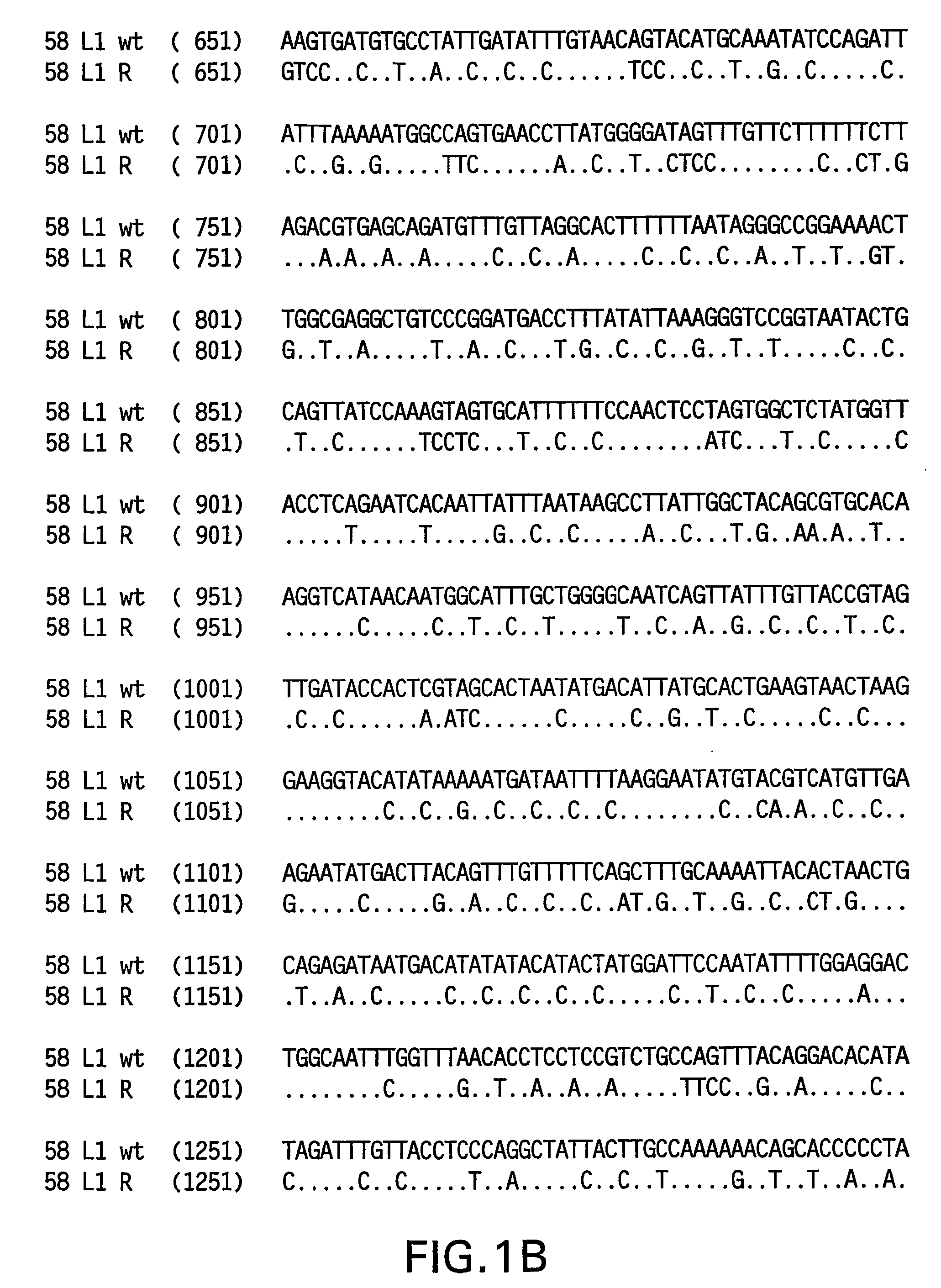
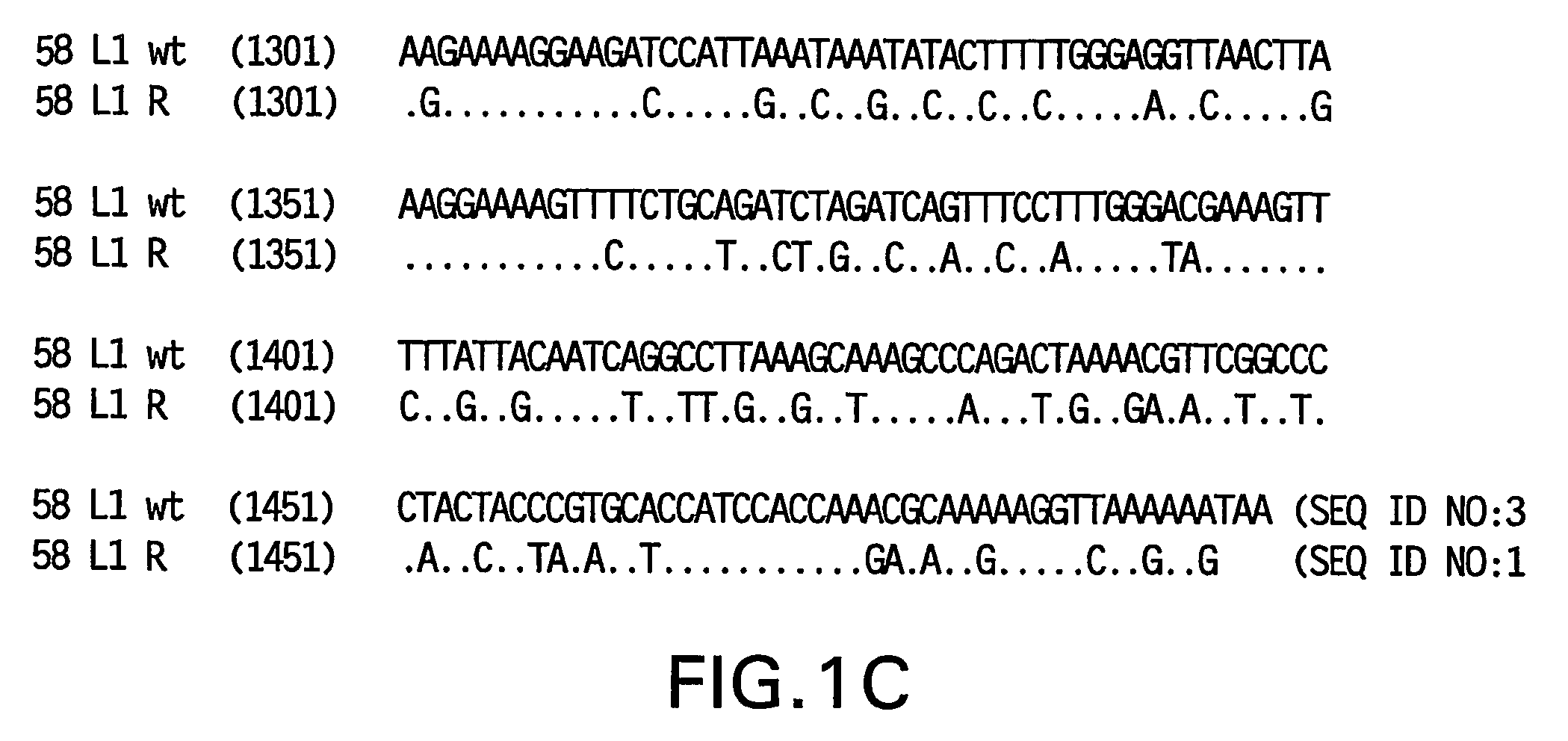
Optimized expression of HPV 58 L1 in yeast
Synthetic DNA molecules encoding the HPV58 L1 protein are provided. Specifically, the present invention provides polynucleotides encoding HPV58 L1 protein, wherein said polynucleotides are codon-optimized for high level expression in a yeast cell. The synthetic molecules may be used to produce HPV58 virus-like particles (VLPs), and to produce vaccines and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the HPV58 VLPs. The vaccines of the present invention provide effective imnunoprophylaxis against papillomavirus infection through neutralizing antibody and cell-mediated immunity and are also useful for treatment of existing HPV infections.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Recombinant viral-based malaria vaccines
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
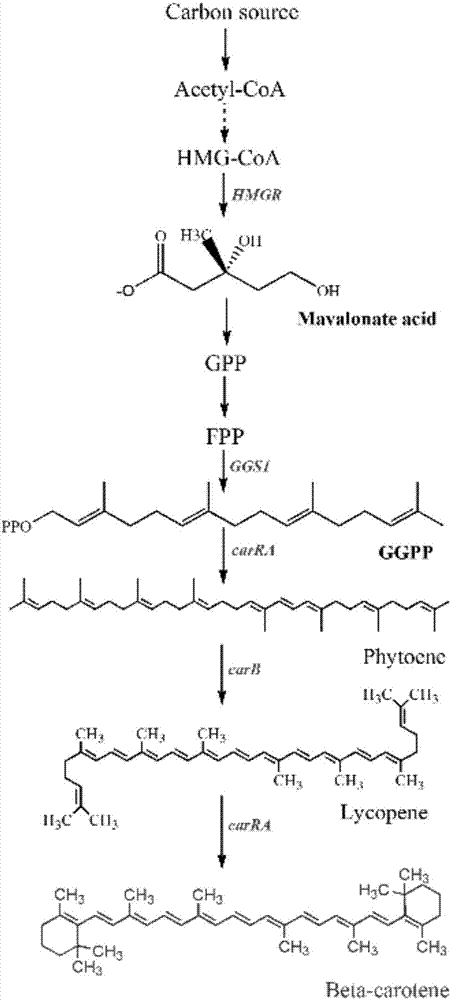
Recombinant bacterium for producing beta-carotene as well as construction method and application of recombinant bacterium
The invention discloses a recombinant bacterium for producing beta-carotene as well as a construction method and application of the recombinant bacterium. The construction method comprises the following steps: respectively constructing superstrong gene expression modules of protein phytoene synthetase / lycopene cyclase coded by beta-carotene synthetic genes optimized by codons, phytoene dehydrogenase, protein geranyl diphosphate synthase coded by MAV (micro aerial vehicle) pathway genes and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase; assembling the gene expression modules in vitro, so as to obtain four plasmids of the gene expression modules, integrating the plasmids into a host bacteria genome which does not produce beta-carotene and screening orange single colonies, so as to obtain the recombinant bacterium for producing beta-carotene. The recombinant bacterium disclosed by the invention is adopted for producing beta-carotene by fermental cultivation, and the yield of beta-carotene can reach 26.03mg / g DCW. Therefore, the recombinant bacterium has high performance of producing beta-carotene.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
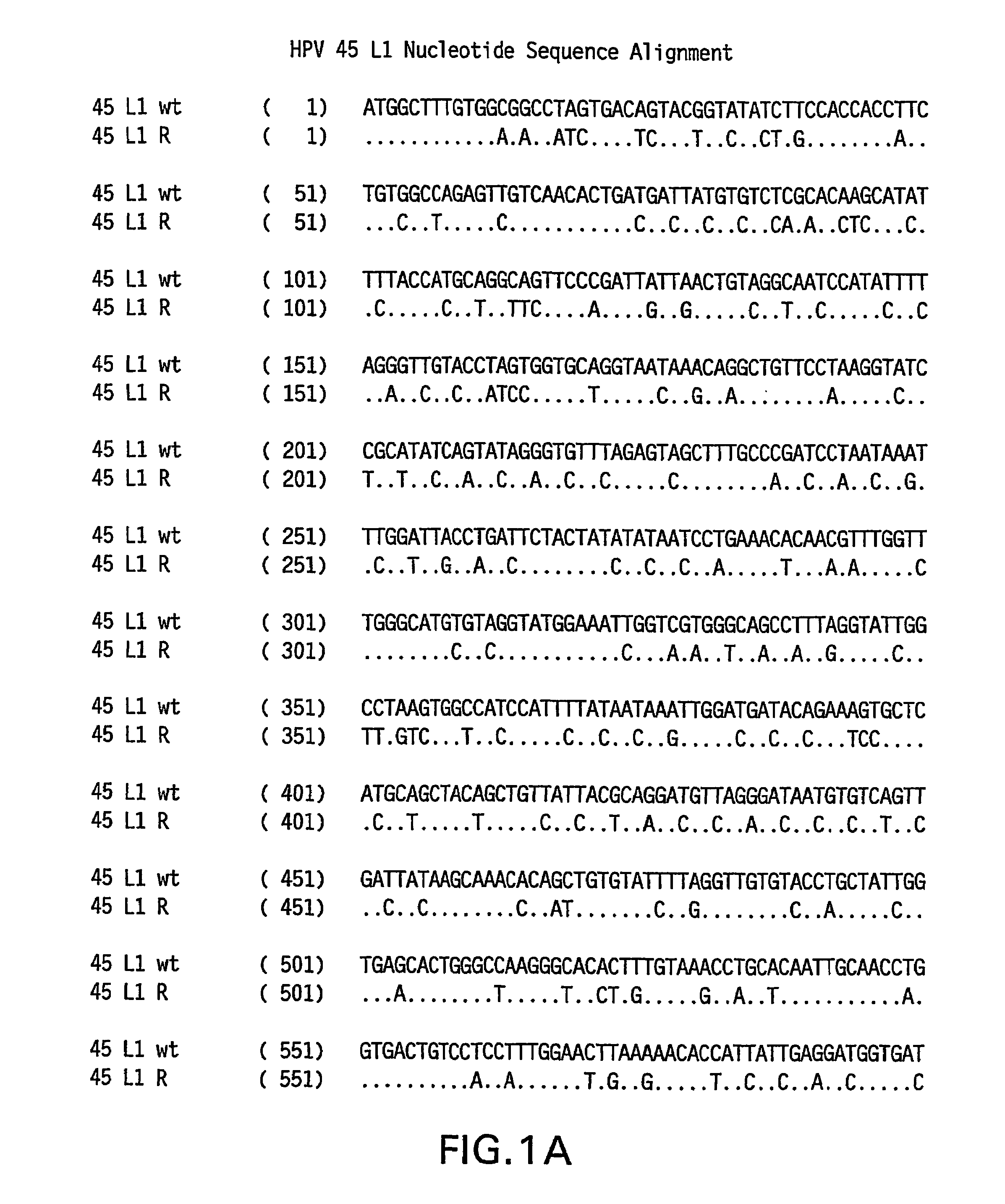
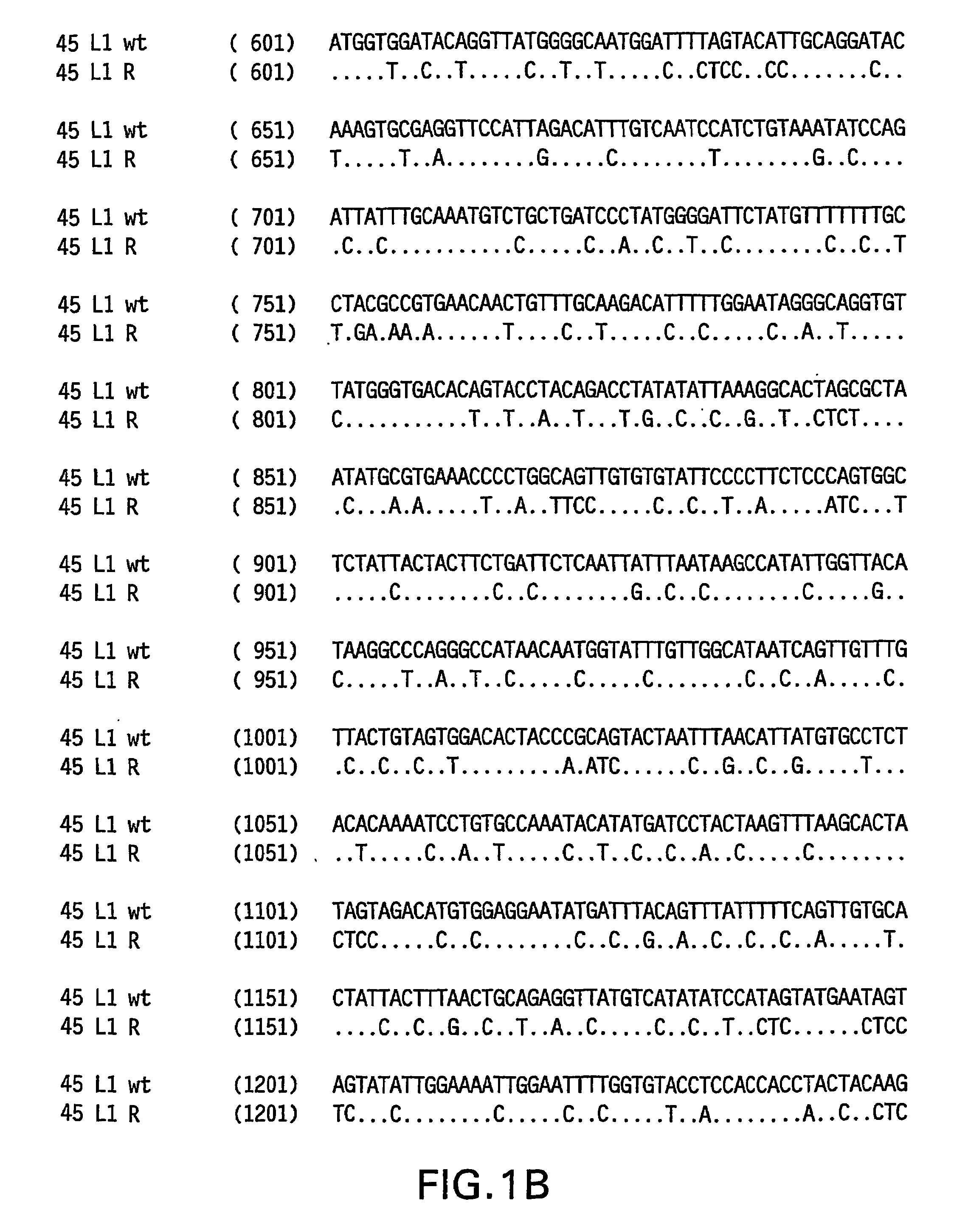
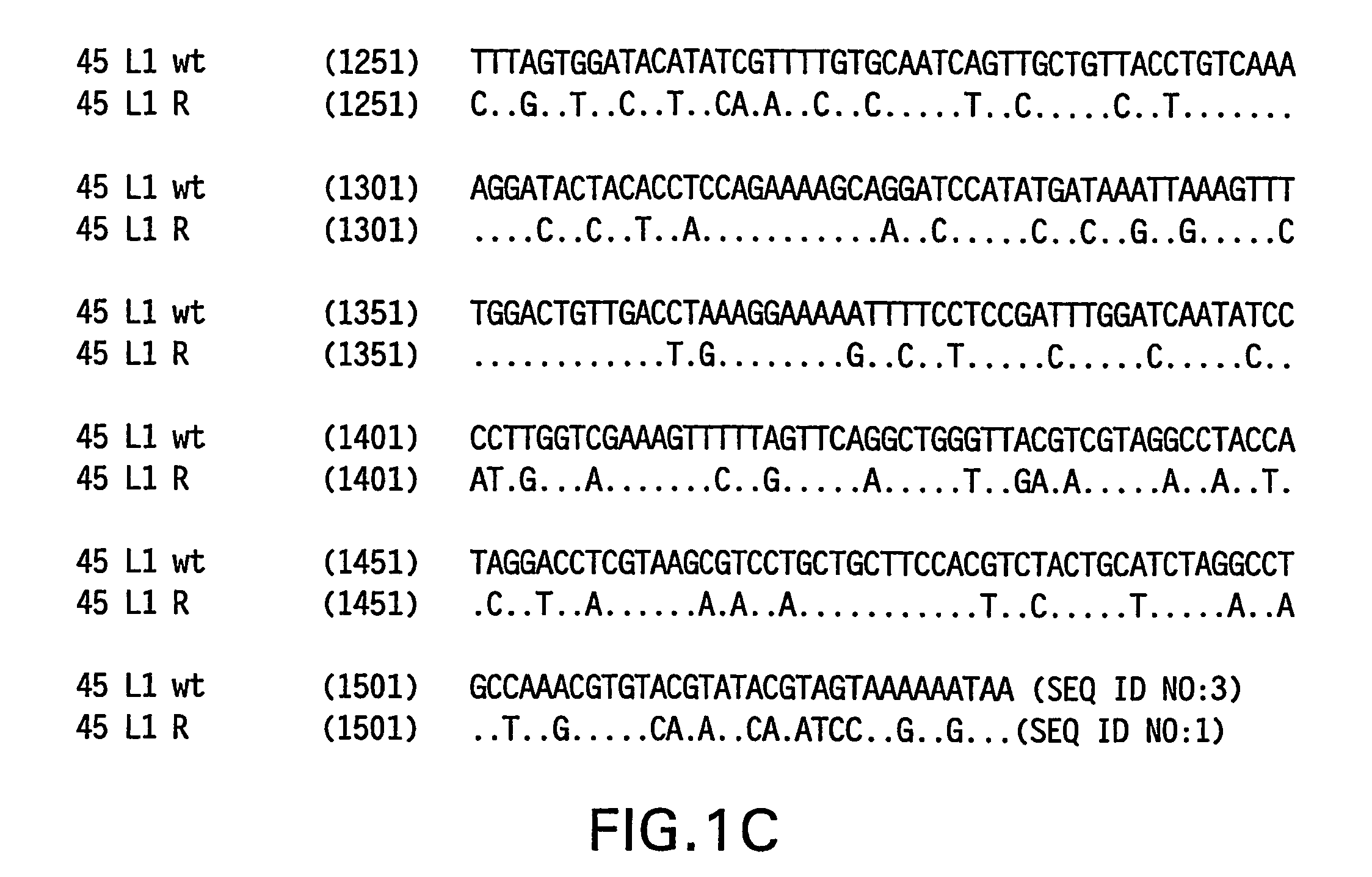
Optimized expression of HPV 45 L1 in yeast
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
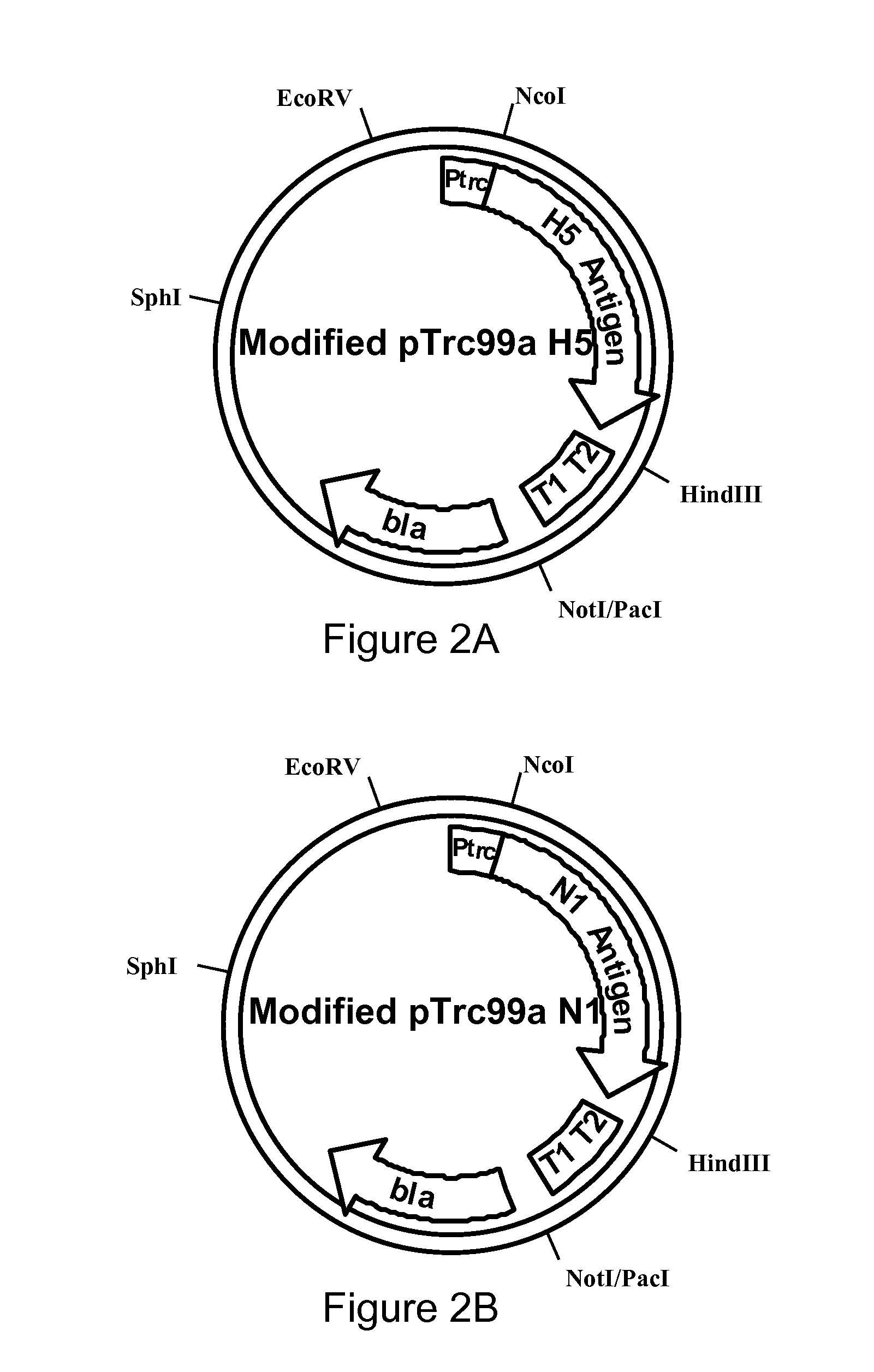
Antiviral agents and vaccines against influenza
InactiveUS20090208531A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseOrganic active ingredientsHemagglutininPrime boost
These vaccines target H5N1, H1, H3 and other subtypes of influenza and are designed to elicit neutralizing antibodies, as well as cellular immunity. The DNA vaccines express hemagglutinin (HA) or nucleoprotein (NP) proteins from influenza which are codon optimized and / or contain modifications to protease cleavage sites of HA which affect the normal function of the protein. Adenoviral constructs expressing the same inserts have been engineered for prime boost strategies. Protein-based vaccines based on protein production from insect or mammalian cells using foldon trimerization stabilization domains with or without cleavage sites to assist in purification of such proteins have been developed. Another embodiment of this invention is the work with HA pseudotyped lentiviral vectors which would be used to screen for neutralizing antibodies in patients and to screen for diagnostic and therapeutic antivirals such as monoclonal antibodies.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Modified Luciola cruciata luciferase gene and protein
InactiveUS7723502B2Improved luciferase proteinImprove thermal stabilitySugar derivativesPeptide preparation methodsLuciola cruciataADAMTS Proteins
A codon optimized and stabilized luciferase gene based upon the sequence of the natural luciferase gene isolated from Luciola cruciata (Japanese firefly) and a novel recombinant DNA characterized by incorporating this new gene coding for a novel luciferase into a vector DNA for improved activities in mammalian cells, are disclosed. This new luciferase exhibits long-wavelength light emission, as well as improved thermostability and higher expression levels in mammalian cell systems, compared to native luciferase.
Owner:MARKER GENE TECH
Method for efficiently expressing antibacterial peptide NZ2114 in recombinant pichia pastoris
ActiveCN103045636ARealize large-scale productionFungiMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisChemical synthesis
The invention provides a method for efficiently expressing an antibacterial peptide NZ2114 in recombinant pichia pastoris. An expression vector comprising a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) sequence of the antibacterial peptide NZ2114 which is subjected to optimization coding by yeast preferred codons is constructed, pichia pastoris is transformed, the obtained recombinant pichia pastoris secretes to generate the antibacterial peptide NZ2114 by fermentation cultivation. According to the invention, by optimizing the genic sequence of the antibacterial peptide NZ2114 and constructing the special expression vector, efficient expression of the antibacterial peptide NZ2114 in the pichia pastoris is realized for the first time; yield breaks through the gram-grade level; the problem of excessively low yield or excessively high chemical synthesis cost in the large-scale production is solved; a perfect purification system is established; scale production can be realized; the method can be applied to the fields of development of antibacterial agents, development of feed additives and the like and has high application values and broad market prospects.
Owner:FEED RESEARCH INSTITUTE CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Compositions for the inactivation of virus replication and methods of making and using the same
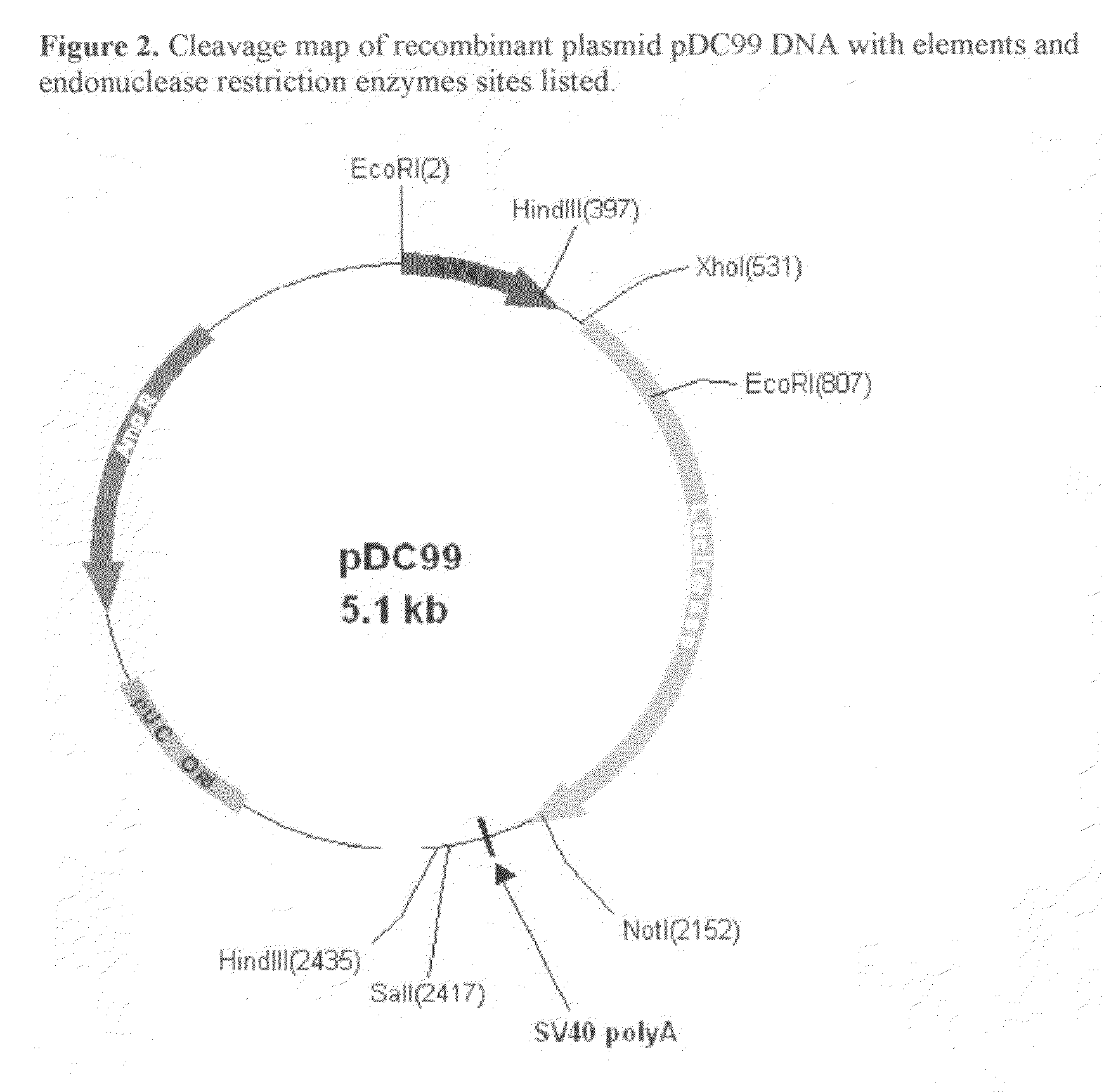
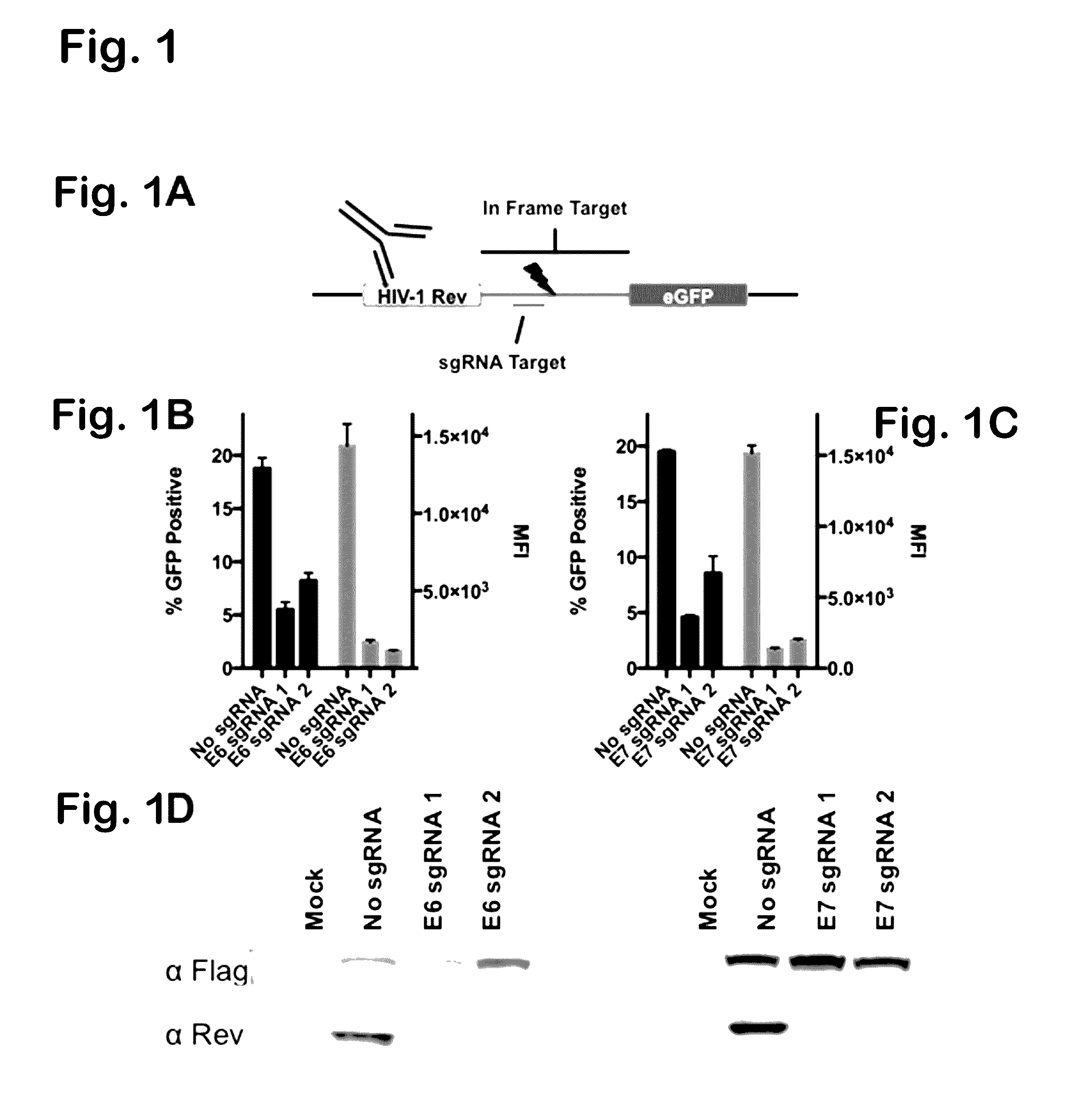
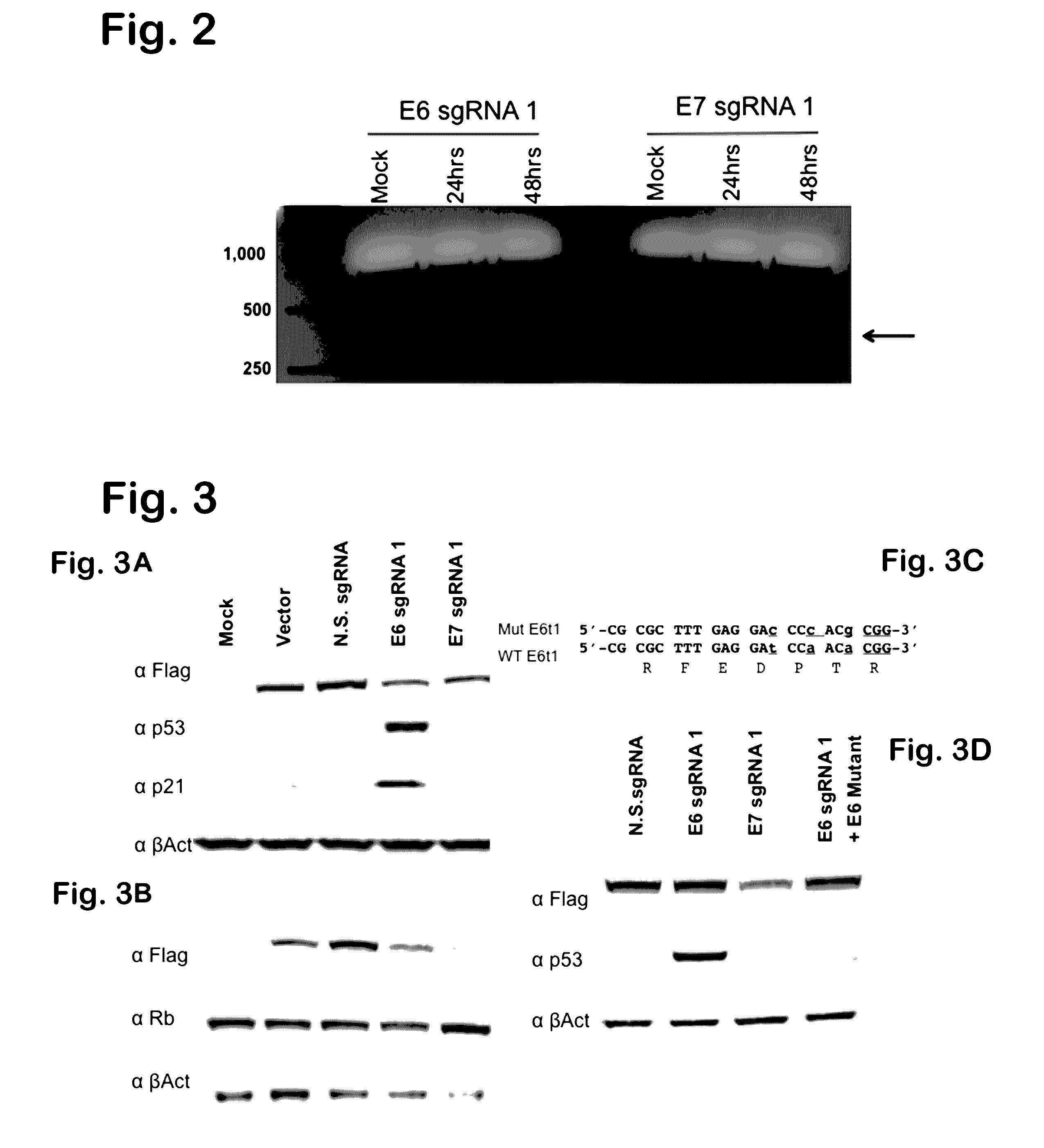
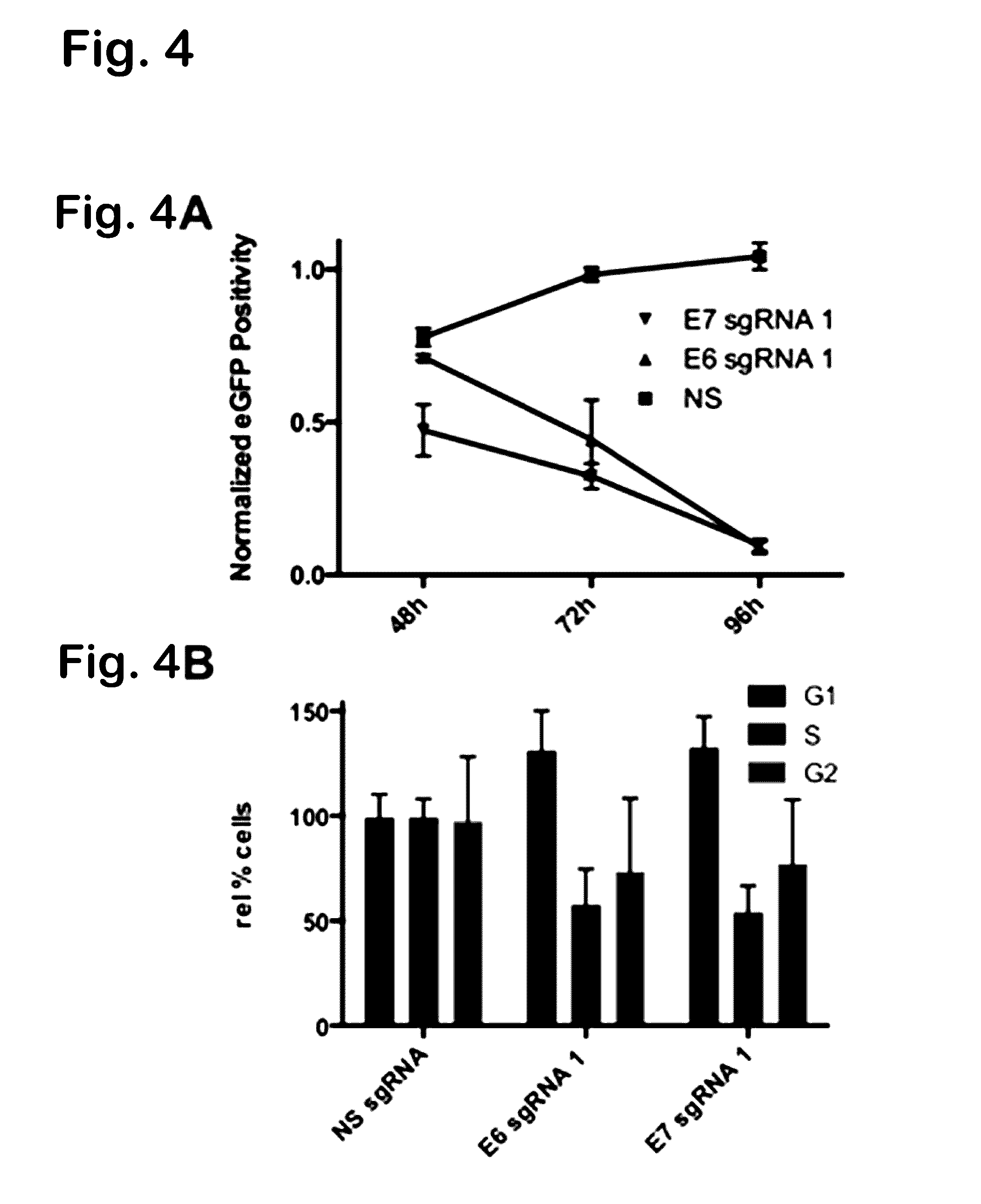
ActiveUS20170049909A1Improve the level ofAccurate separationPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifHydrolasesEpitopeNucleotide
Provided herein are recombinant constructs, vectors and expression cassettes including a first promoter which is suitably a tRNA promoter operably connected to a first polynucleotide encoding a first single guide RNA and a second promoter operably connected to a second polynucleotide encoding a Cas9 polypeptide. The first single guide RNA includes a first portion complementary to a strand of a target sequence of a DNA virus and a second portion capable of interacting with the Cas9 polypeptide. Also provided are codon optimized Staphylococcus aureus derived Cas9 polynucleotides and polypeptides with nuclear localization signals and optionally an epitope tag. Also provided are constructs for production of sgRNAs including a tRNA. Methods of inhibiting viral replication, inhibiting expression of a target sequence from a virus or treating a viral infection or viral induced cancer using the compositions are also provided.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com