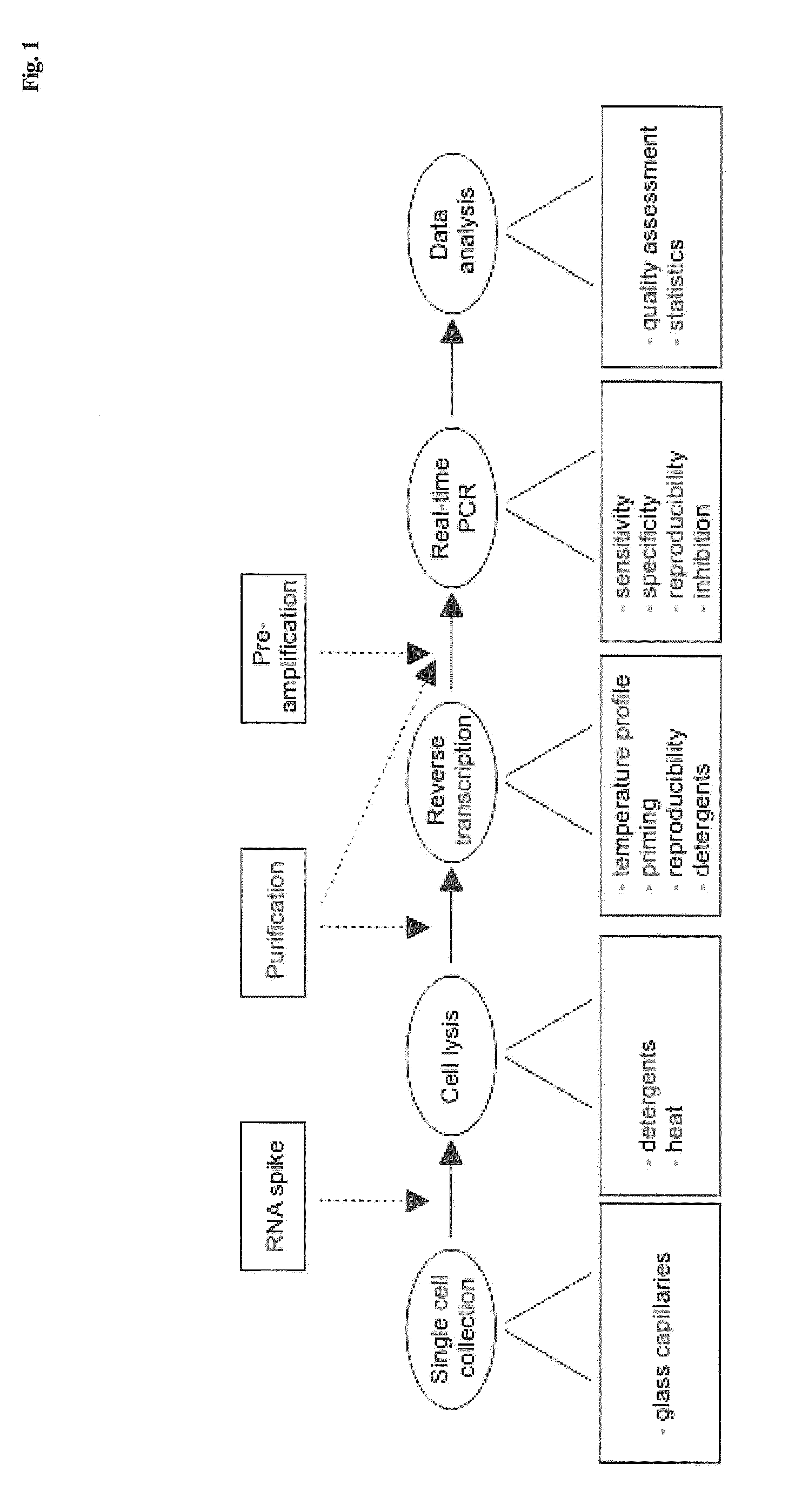
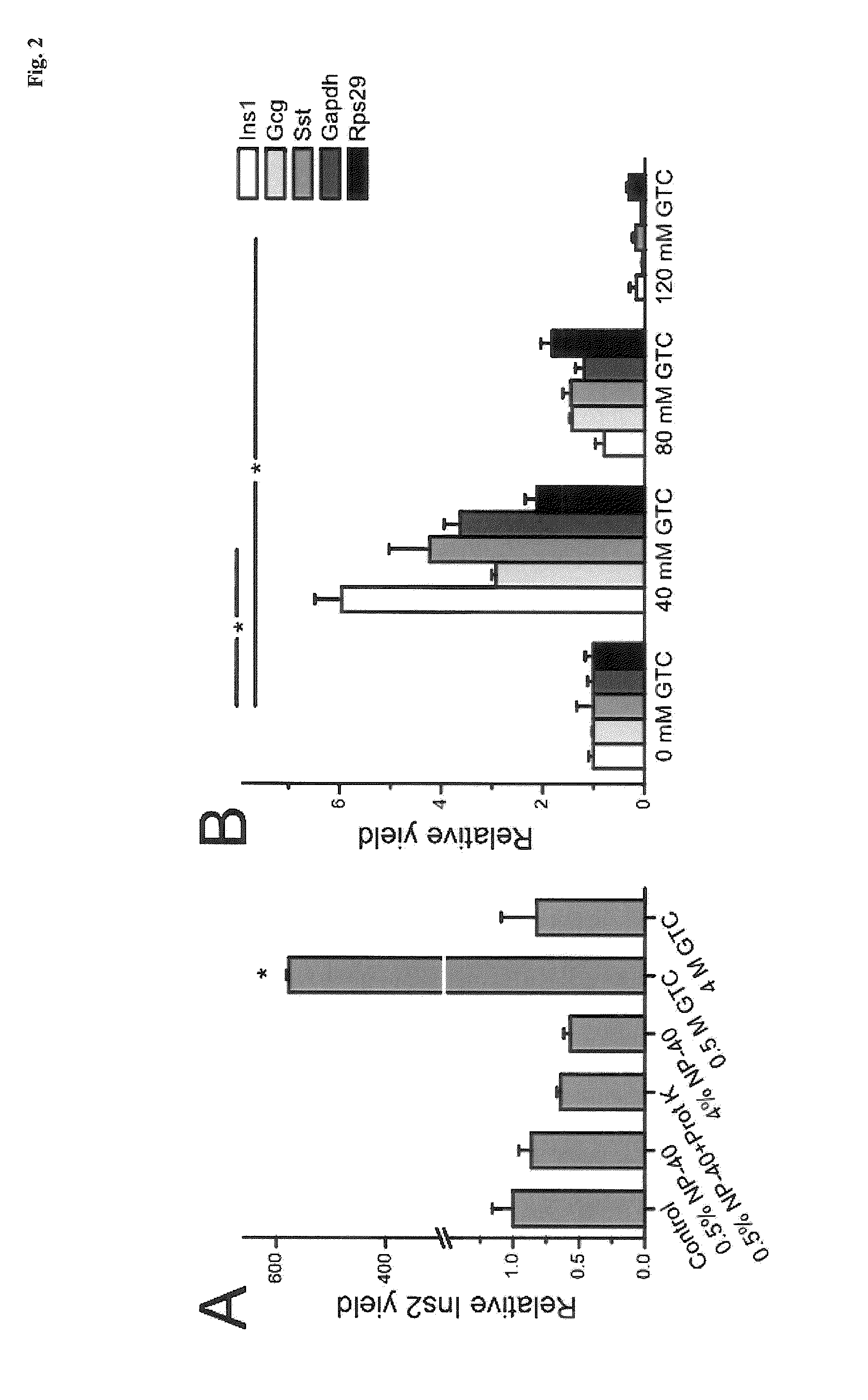
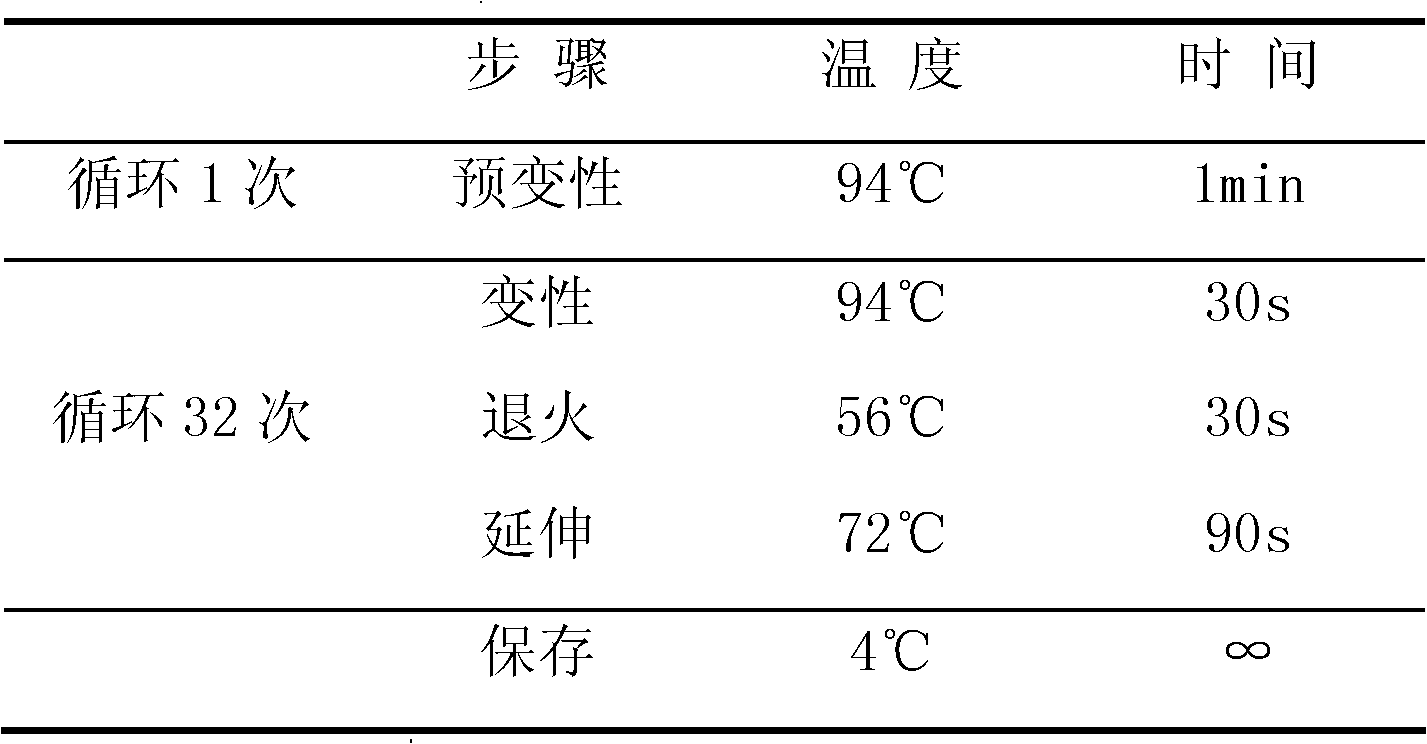
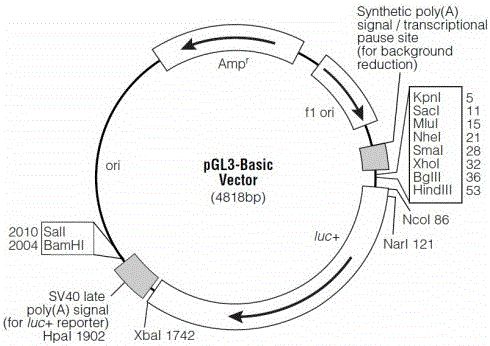
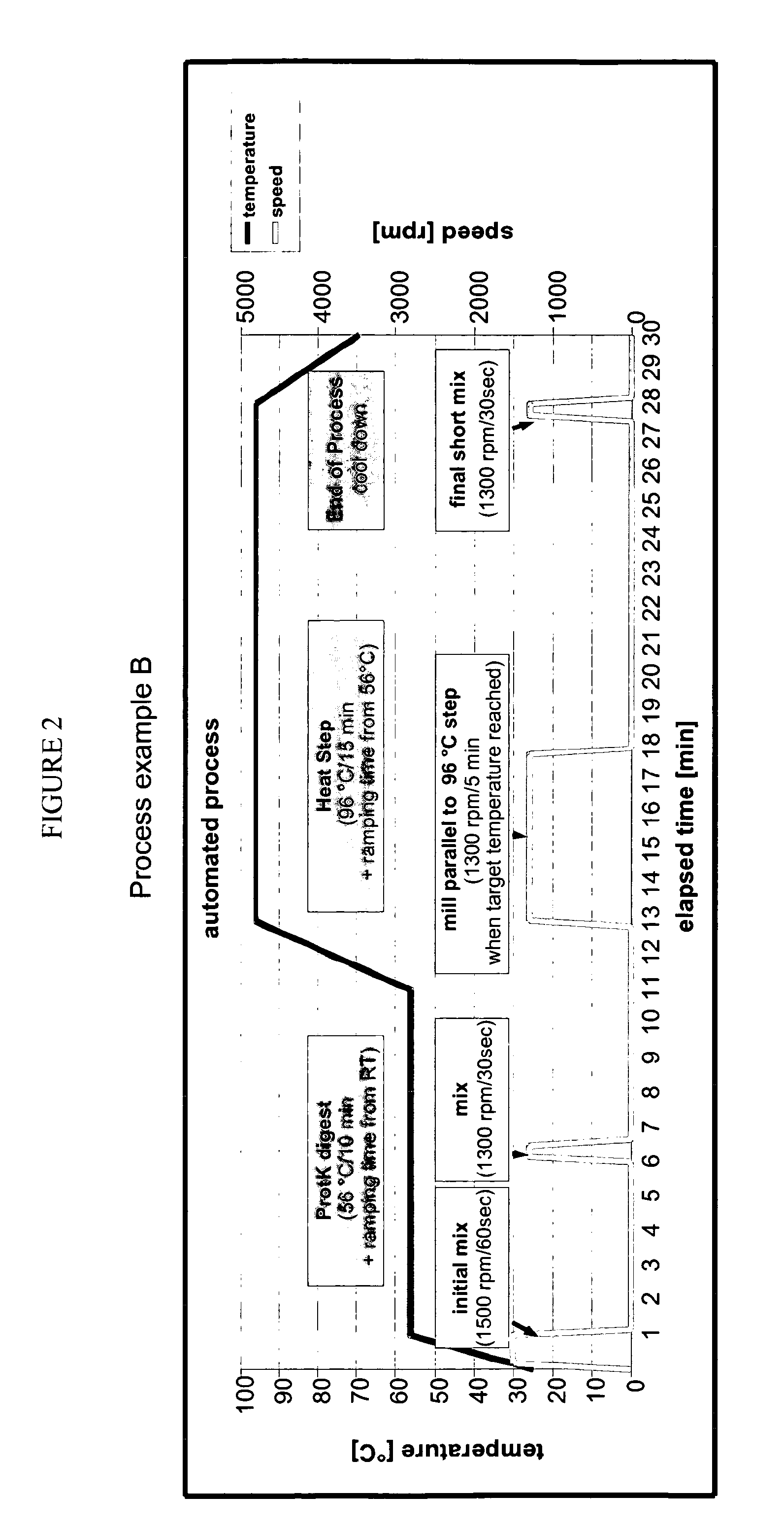
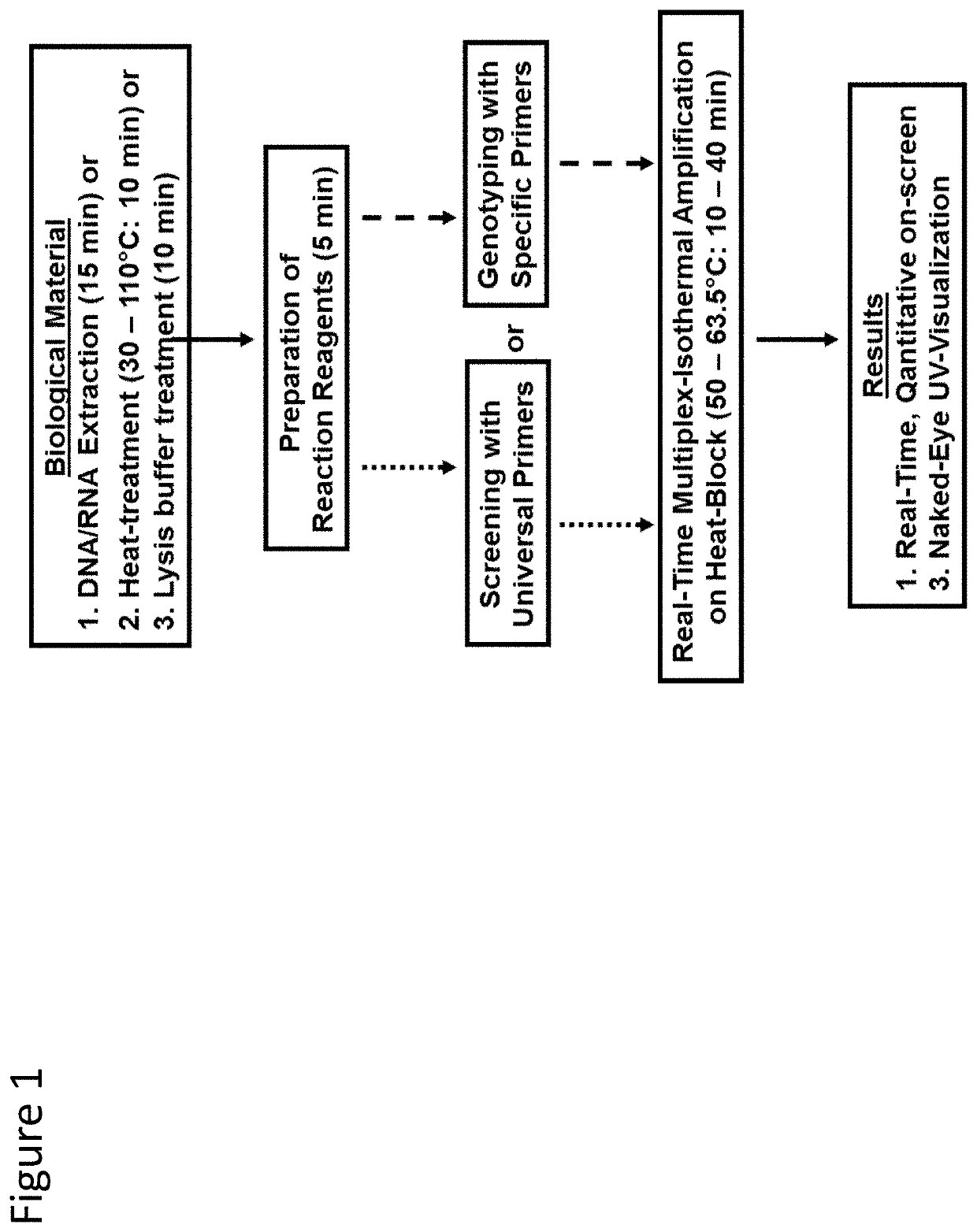
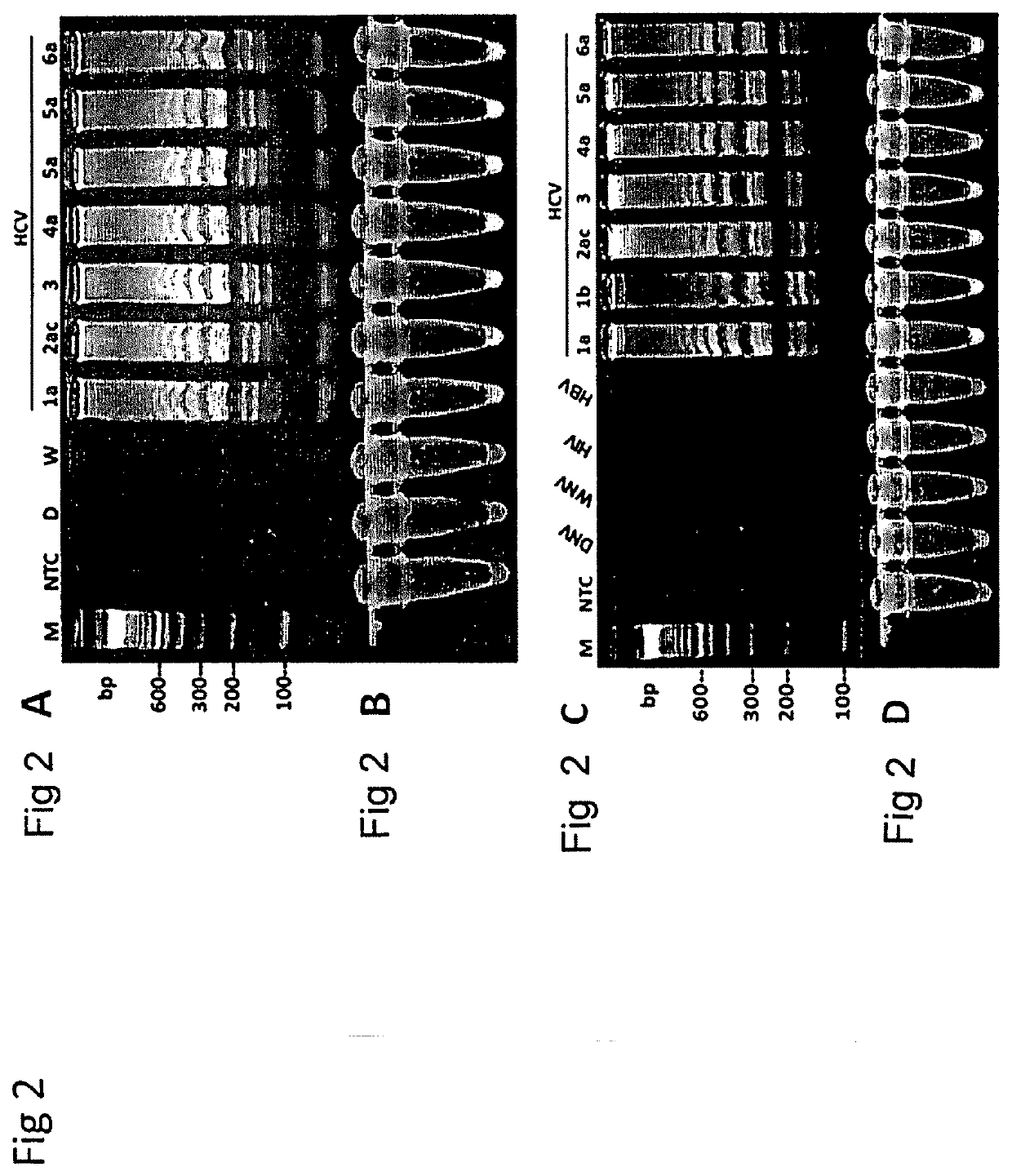
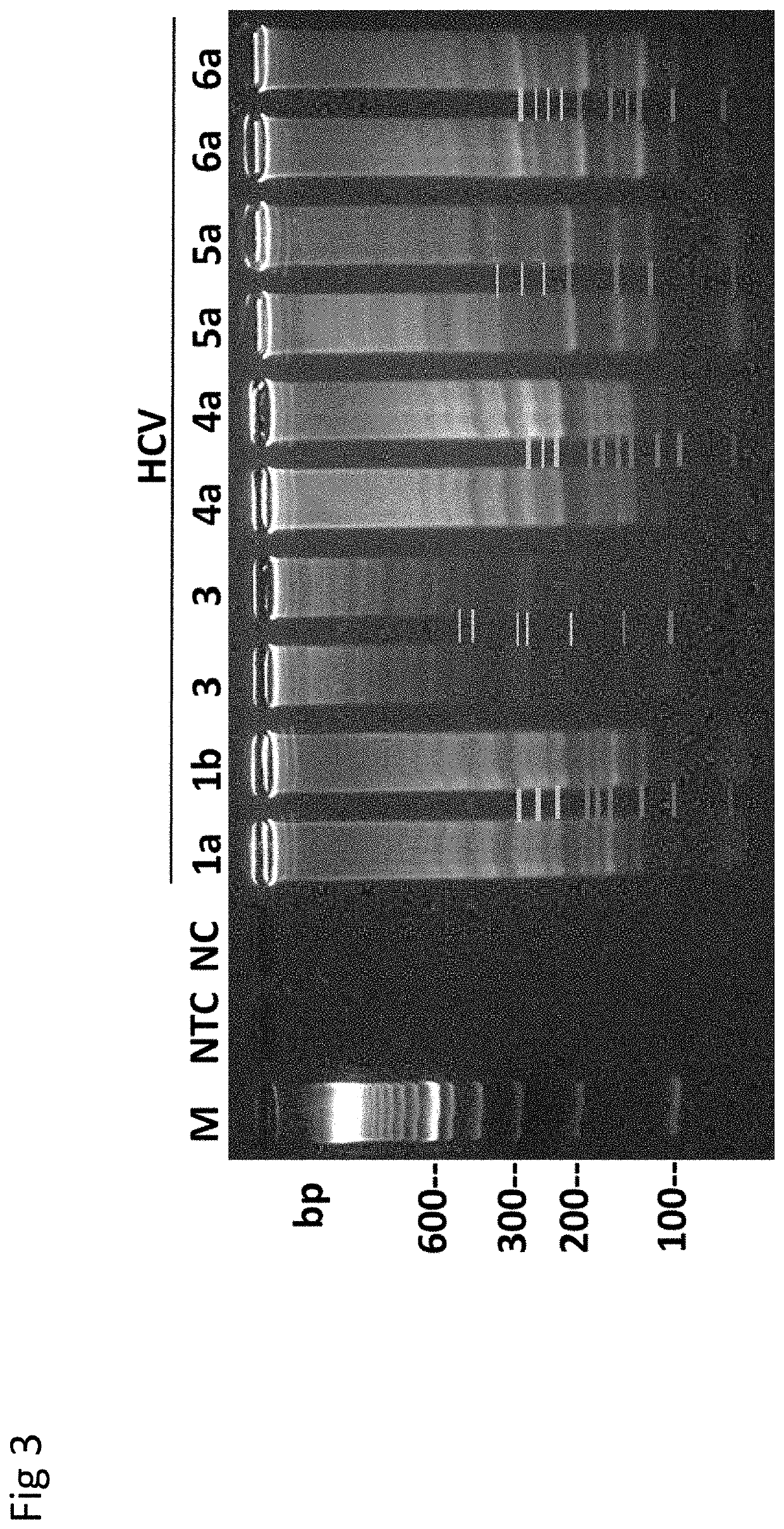
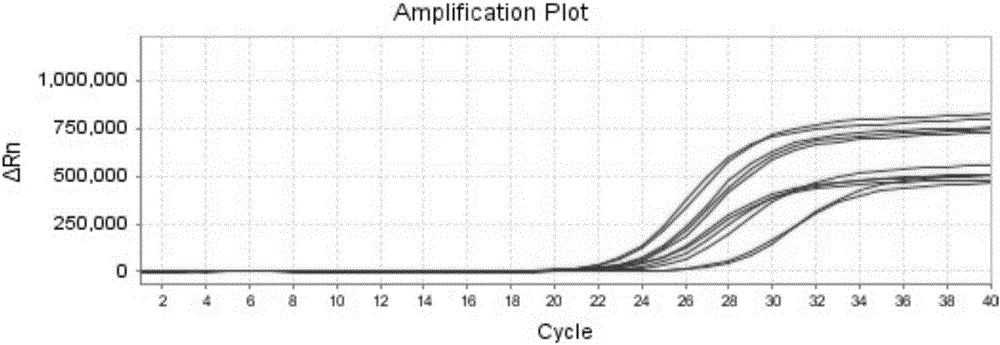
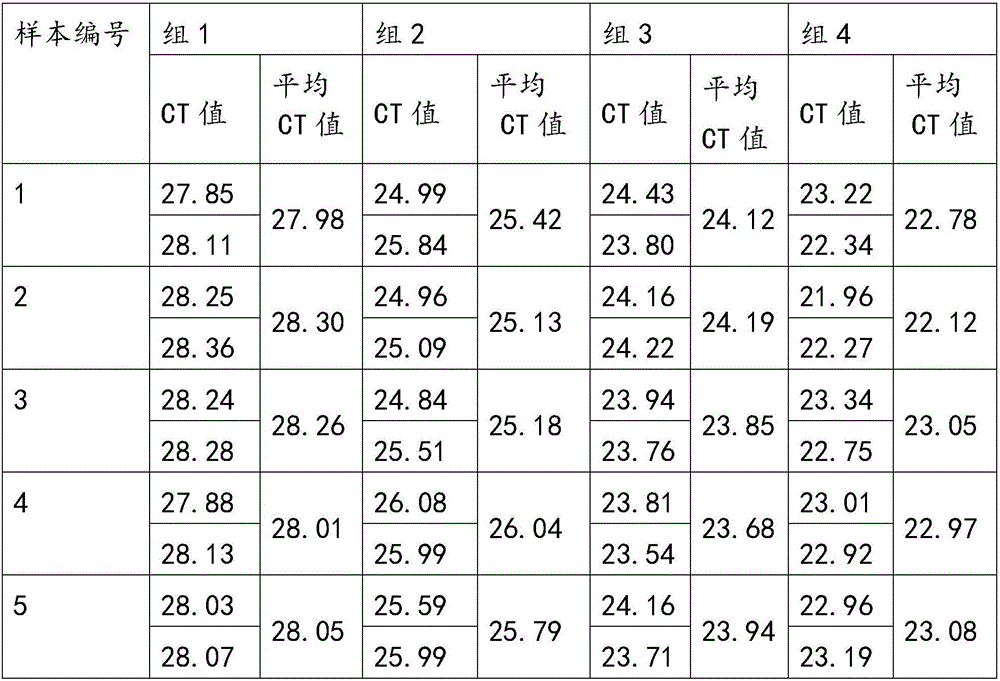
Patents
Literature
415 results about "Lysis buffer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
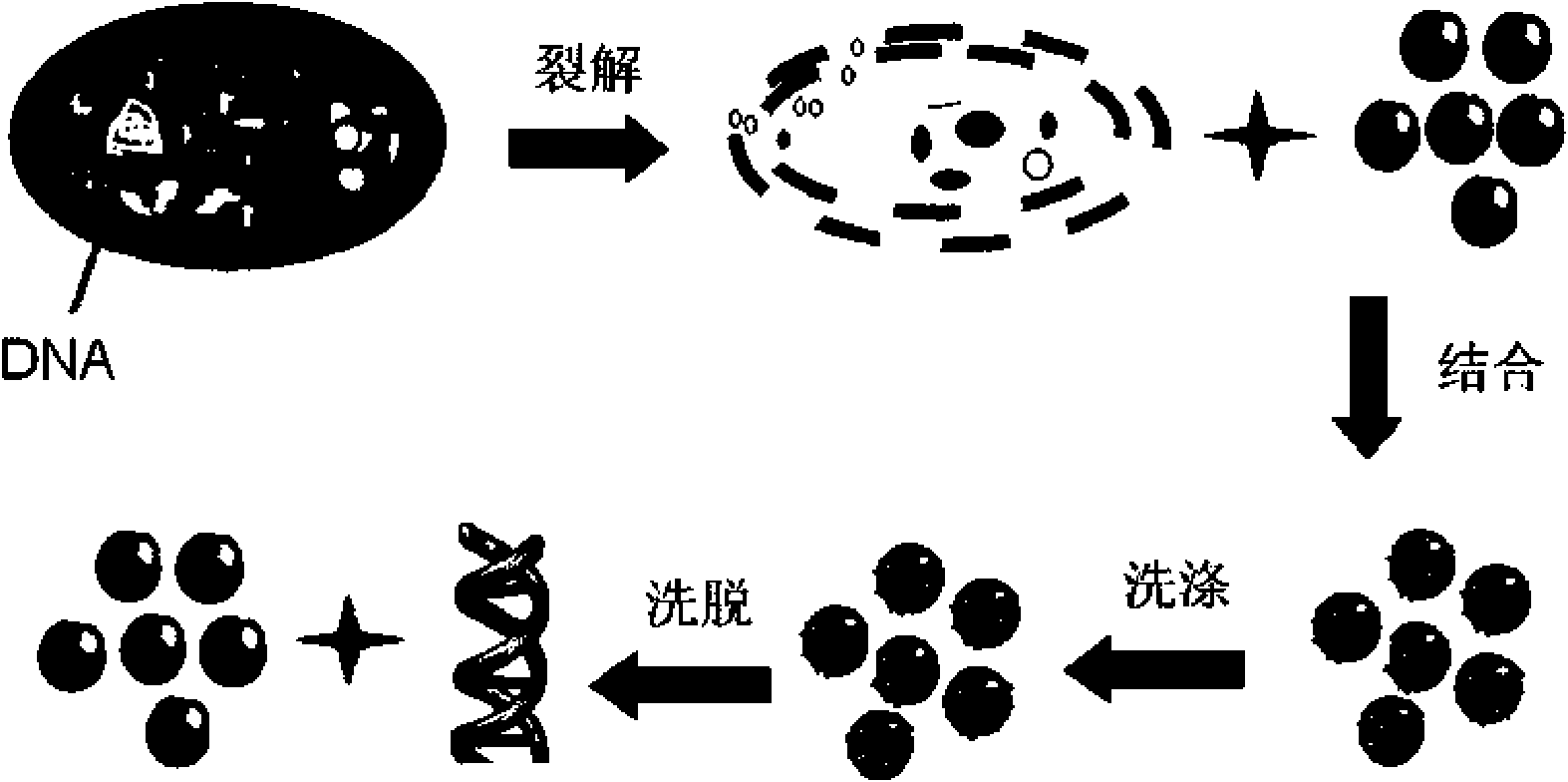
A lysis buffer is a buffer solution used for the purpose of breaking open cells for use in molecular biology experiments that analyze the labile macromolecules of the cells (e.g. western blot for protein, or for DNA extraction). Most lysis buffers contain buffering salts (e.g. Tris-HCl) and ionic salts (e.g. NaCl) to regulate the pH and osmolarity of the lysate. Sometimes detergents (such as Triton X-100 or SDS) are added to break up membrane structures. For lysis buffers targeted at protein extraction, protease inhibitors are often included, and in difficult cases may be almost required. Lysis buffers can be used on both animal and plant tissue cells.
Method of preparing cell lysate
InactiveUS7258976B2Simple preparation processStable outputSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementTransfer cellCell layer
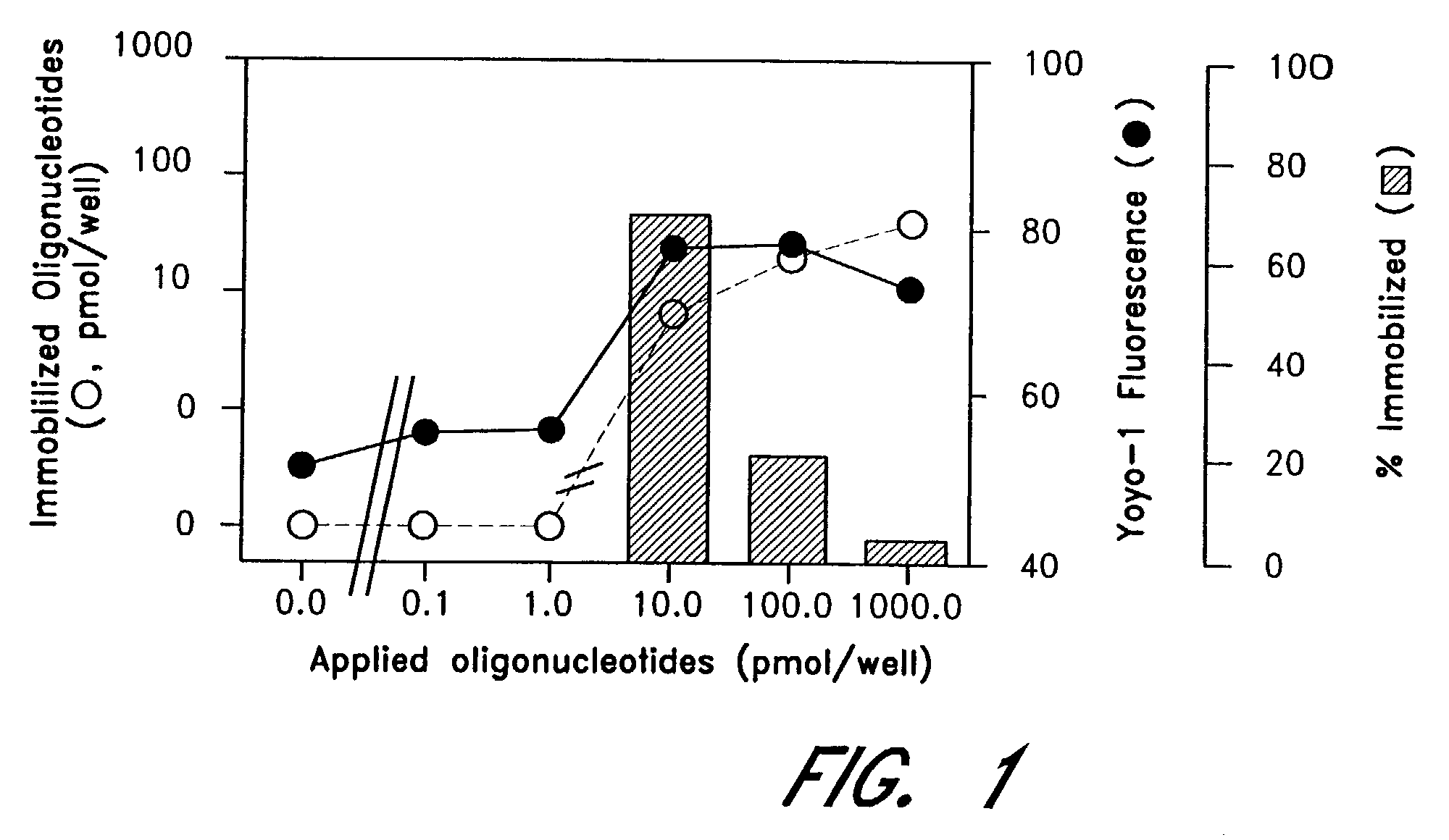
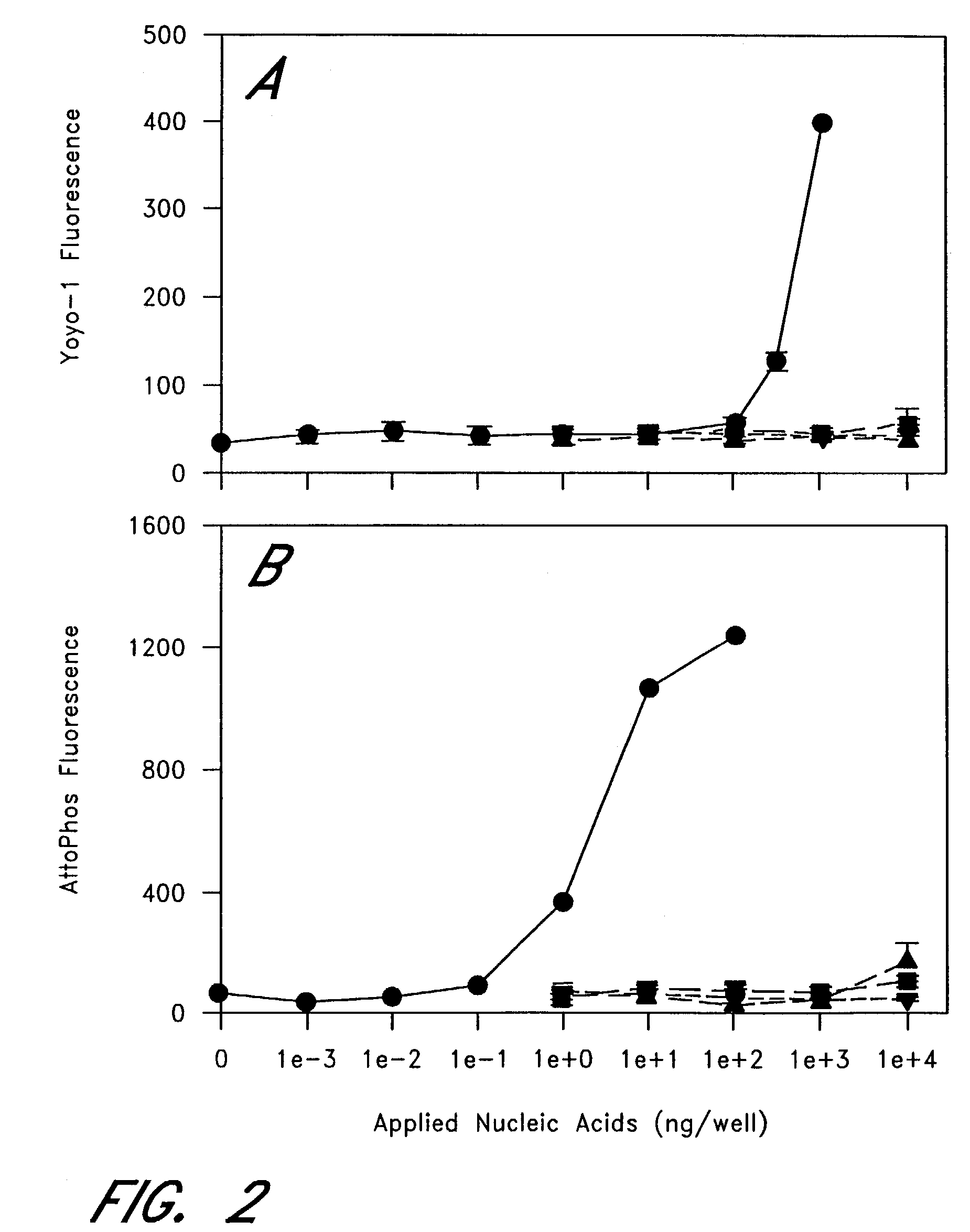
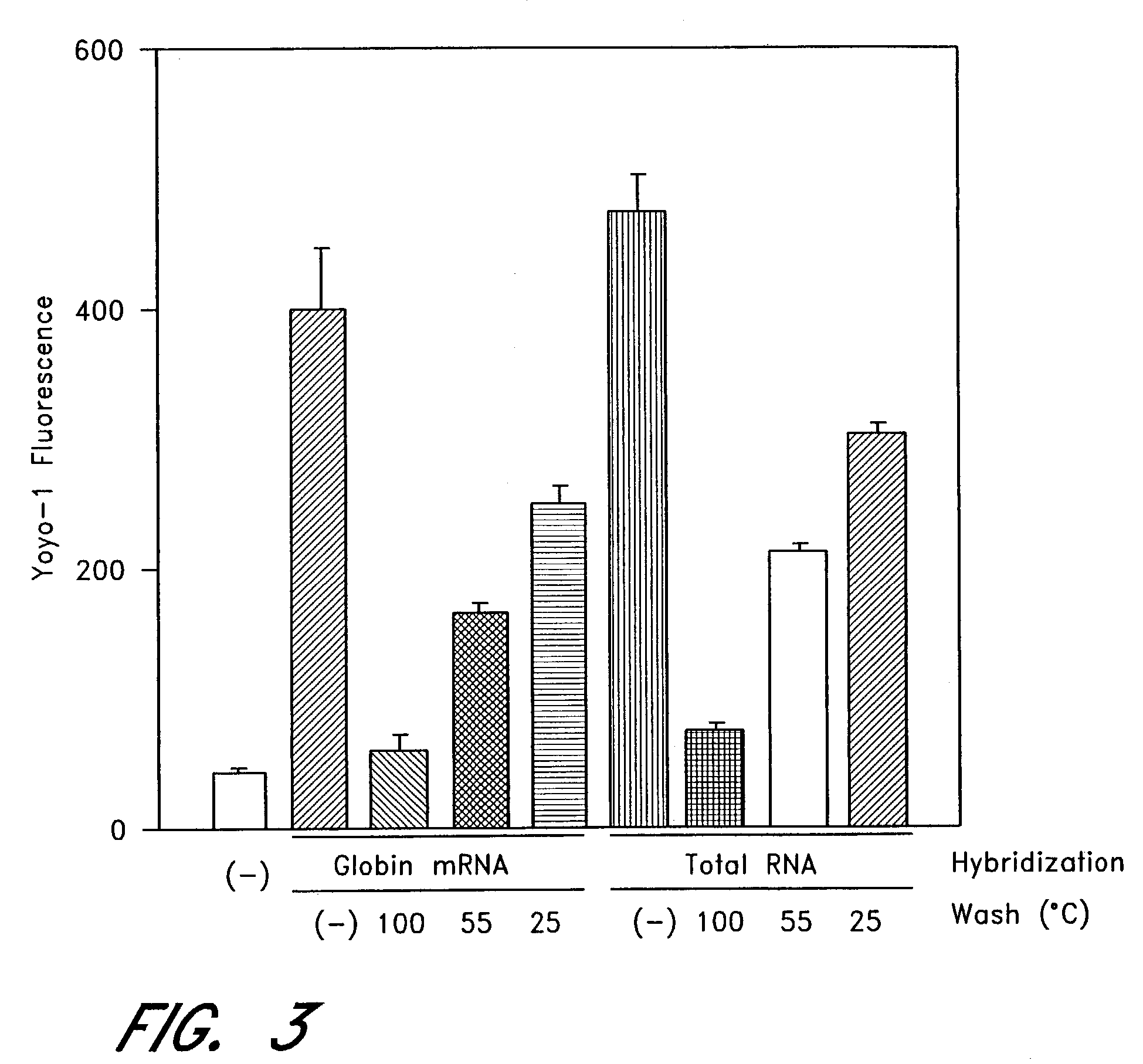
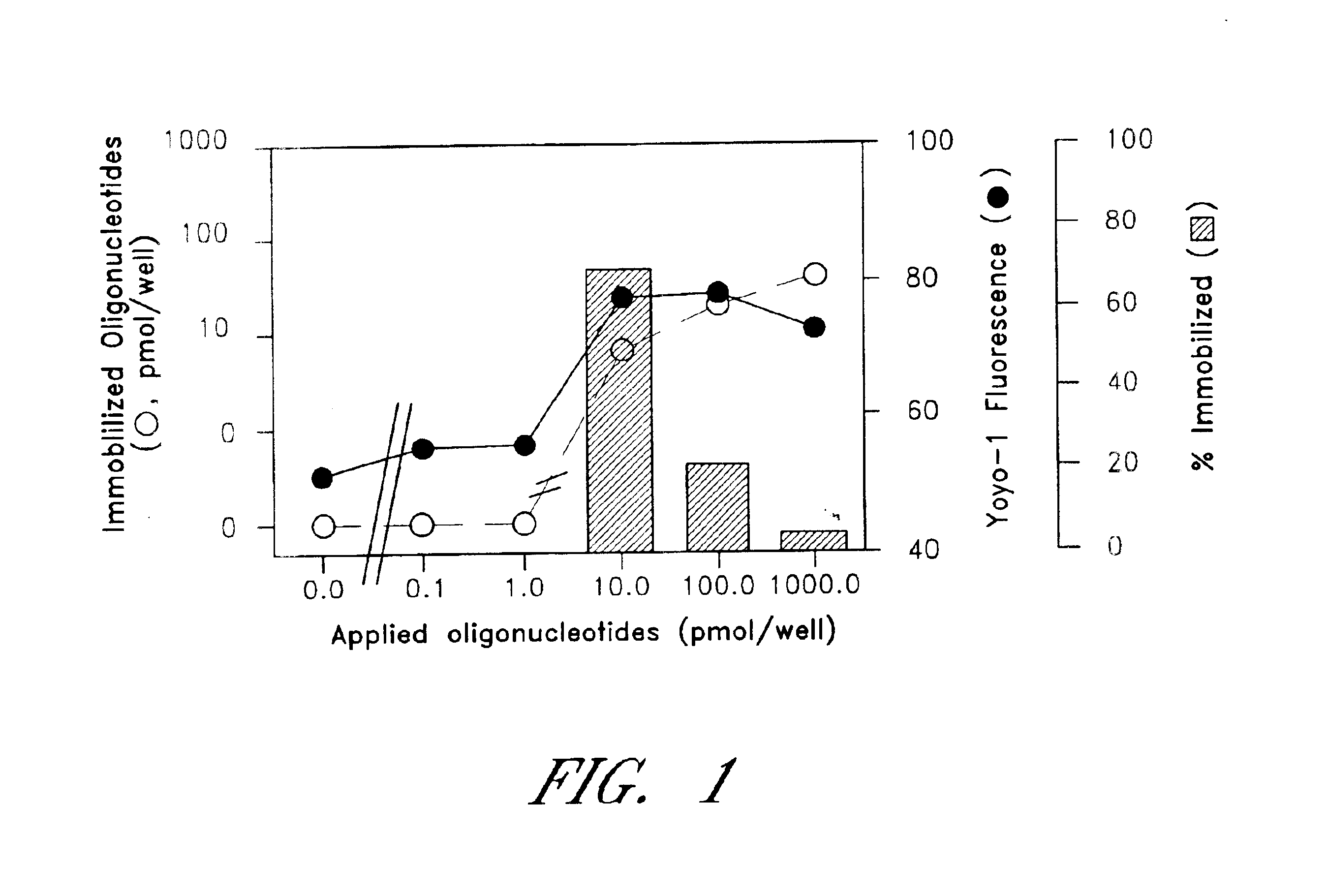
The entire process of reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is simplified by using oligonucleotide-immobilized microplates made of, e.g., polypropylene, to which oligonucleotides are securely immobilized and which can be subjected to thermal cycles of PCR. RT-PCR is preferably conducted in solid-phase. Capturing of mRNA and RT-PCR can be conducted in the same plates. The cDNA synthesized from the mRNA captured on the microplates can be used more than once. Further, in combination with the microplates, a filter plate is used for the preparation of cell lysates wherein target cells are placed on the filter plate, and a lysis buffer is passed through the cell layer on the filter to transfer cell lysate directly to the microplate via well-to-well communication.
Owner:RESONAC CORPORATION +1
Method for extracting and purifying nucleic acid from samples by magnetic beads
ActiveCN101665785AIncrease productionHigh puritySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMagnetic beadElution
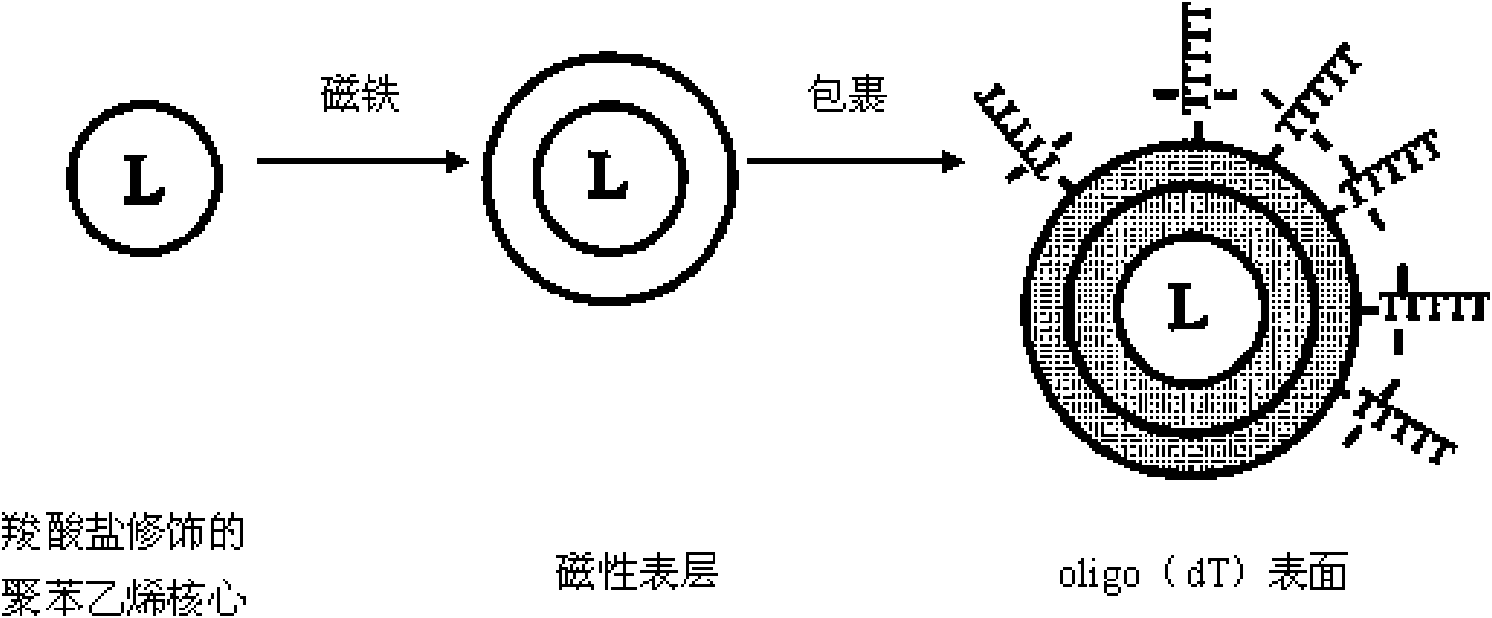
The invention relates to a method for extracting and purifying nucleic acid from samples by magnetic beads, which comprises the following steps: (1) magnetic bead treatment: modifying the magnetic beads by peptide-oligonucleotide; (2) cell lysis: adding the sample containing target nucleic acid and needing to be separated into a centrifuge tube, and then adding lysis buffer to lyse the cells; (3)nucleic acid adsorption: adding the magnetic beads modified by the peptide-oligonucleotide into the solution to lead the nucleic acid to be adsorbed on the surfaces of the magnetic beads; placing thecentrifuge tube into a magnetism separation machine to lead the magnetic beads to be adsorbed on the tube side; (4) impurities removal: adding aqueous phase buffer solution to wash the magnetic bead which are adsorbed with the nucleic acid on the surfaces and adsorbed on the tube side so as to separate other impurities on the magnetic bead; and (5) nucleic acid recovery: directly taking the nucleic acid adsorbed on the surfaces of the magnetic beads as the template for PCR amplification, or adding elution buffer to lead the nucleic acid molecules adsorbed on the surfaces of the magnetic beadsto be released into the buffer for downstream experiments. The magnetic beads used by the method can be reserved at the temperature of 4 DEG C or -20 DEG C, and have convenient transport, high adsorption efficient and lower cost. The nucleic acid extracted and purified by the method has wide application range.
Owner:SANSURE BIOTECH INC
Adsorption of nucleic acids to a solid phase
ActiveUS20050214926A1Eliminate needImprove propertiesSugar derivativesAxially engaging brakesLysis bufferLiquid phase
The present invention is directed to a method for adsorbing, i.e. non-covalently binding, nucleic acids to a solid phase using a two-step procedure. Furthermore, the present invention pertains to a method for isolating nucleic acids from a biological sample. In the first step of the procedure, lysis is effected by mixing the biological sample with an aequous lysis buffer containing a chaotropic agent and incubating the mixture; in the second step, the concentration of the chaotropic agent in the mixture is increased and the mixture is contacted with the solid phase, whereby the nucleic acids in the liquid phase is adsorbed to the solid phase.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Method and device for the handling of samples and reagents
InactiveUS20020182718A1Facilitated reaction kineticsHigh yieldBioreactor/fermenter combinationsShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersReagentClosed system
Nucleic acids are extracted rapidly, safely and directly from a sample without pipetting steps by using predispensed, interconnectable vessels. These vessels are used separately or interconnected according to the mictrotiter standard format. The sample is mixed with lysis buffer and the nucleic acids bound to a matrix in a closed system, comprising at least two interconnectable volumes. By forcing the sample and buffer mixture back and forth from one volume to another, passing a narrow passage, thorough mixing is ensured.
Owner:MALMOQVIST MATS +1
Technique for producing ultra-low molecular heparin sodium (calcium)
InactiveCN101519459AImprove securityGood and long-lasting antithrombotic effectPulmonary artery embolismDisease
Aiming at the conditions that heparin has severe bleeding side effects in clinical practice and clinical application thereof is restricted, the invention discloses a technique for producing ultra-low molecular heparin sodium (calcium). The technique comprises the following steps of: taking heparin sodium solution, adding sodium nitrite solution for cracking; adjusting the lysis buffer by using alkaline; absorbing impurities by using an anion-exchange column; washing for obtaining ultra-low molecular heparin calcium; carrying out filtration by using an ultrafiltration membrane and obtaining a precipitate by using alcohol; and after desalting, dehydration, re-precipitation, cooling and drying, obtaining a finished product of ultra-low molecular heparin calcium. The product has better and safer antithrombotic effect under low level of anticoagulation, and can be widely used for preventing and treating diseases such as deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and the like.
Owner:SUZHOU FAST BIOLOGICAL PHARMACY TECH
Nucleic acid extraction and purification method based on nanometer magnetic beads and kit
ActiveCN103820431AHigh purityLower performance requirementsDNA preparationPurification methodsRNA extraction
The invention discloses a nucleic acid extraction and purification method based on nanometer magnetic beads, comprising the following steps: mixing a biological sample and a lysis buffer to make nanometer magnetic beads in the lysis buffer and nucleic acid DNA / RNA which moves into the lysis buffer form a magnetic bead-nucleic acid compound; transferring the compound under the action of a magnetic field to a washing buffer to wash off impurities on the magnetic bead-nucleic acid compound; and transferring the washed magnetic bead- nucleic acid compound under the action of the magnetic field to an elution buffer so as to elute and recover nucleic acid. The nanometer magnetic beads used in the invention have advantages of uniform size, smooth surface, large surface area ratio, high adsorption capacity of nucleic acid, fast magnetic response speed and rapid separation, and can be stored together with the lysis buffer at room temperature for a long time. The extracted nucleic acid DNA / RNA has high purity, is complete and can be directly used for follow-up detection. The method provided by the invention has shorter nucleic acid extraction time than a general magnetic bead method by the use of a nucleic acid extraction reagent, is more suitable for automation and is adopted to realize high-flux nucleic acid DNA / RNA extraction.
Owner:苏州天隆生物科技有限公司
Direct RT-PCR on oligonucleotide-immobilized PCR microplates
InactiveUS6844158B1Simple preparation processStable outputSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementTransfer cellCell layer
The entire process of reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is simplified by using oligonucleotide-immobilized microplates made of, e.g., polypropylene, to which oligonucleotides are securely immobilized and which can be subjected to thermal cycles of PCR. RT-PCR is preferably conducted in solid-phase. Capturing of mRNA and RT-PCR can be conducted in the same plates. The cDNA synthesized from the mRNA captured on the microplates can be used more than once. Further, in combination with the microplates, a filter plate is used for the preparation of cell lysates wherein target cells are placed on the filter plate, and a lysis buffer is passed through the cell layer on the filter to transfer cell lysate directly to the microplate via well-to-well communication.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD +1
Adsorption of nucleic acids to a solid phase
ActiveUS7491495B2Improve propertiesReduce surface tensionSugar derivativesAxially engaging brakesLysis bufferLiquid phase
The present invention is directed to a method for adsorbing, i.e. non-covalently binding, nucleic acids to a solid phase using a two-step procedure. Furthermore, the present invention pertains to a method for isolating nucleic acids from a biological sample. In the first step of the procedure, lysis is effected by mixing the biological sample with an aqueous lysis buffer containing a chaotropic agent and incubating the mixture; in the second step, the concentration of the chaotropic agent in the mixture is increased and the mixture is contacted with the solid phase, whereby the nucleic acids in the liquid phase is adsorbed to the solid phase.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Protein synthesis system for increasing expression amount of foreign protein and application method of protein synthesis system
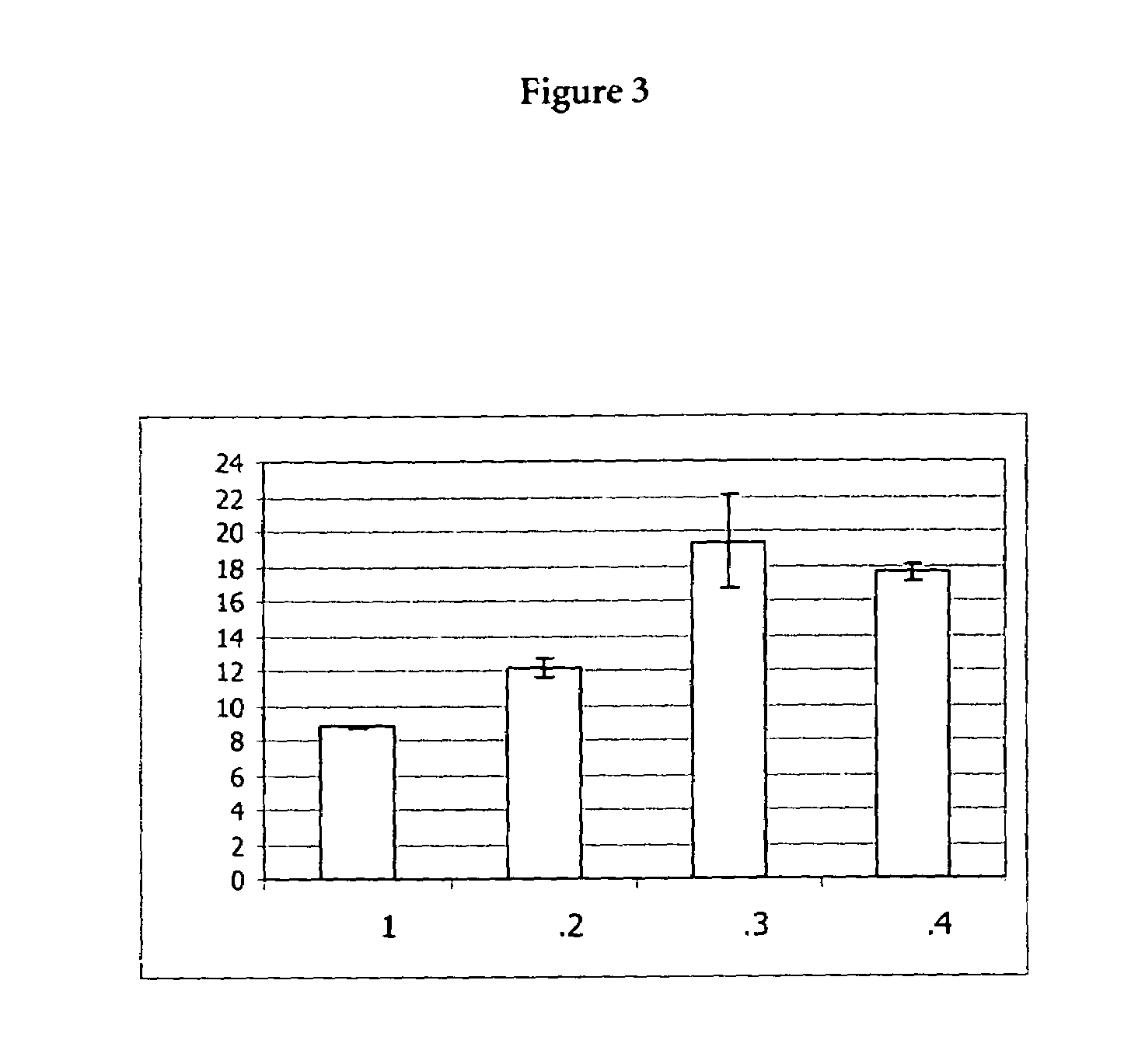
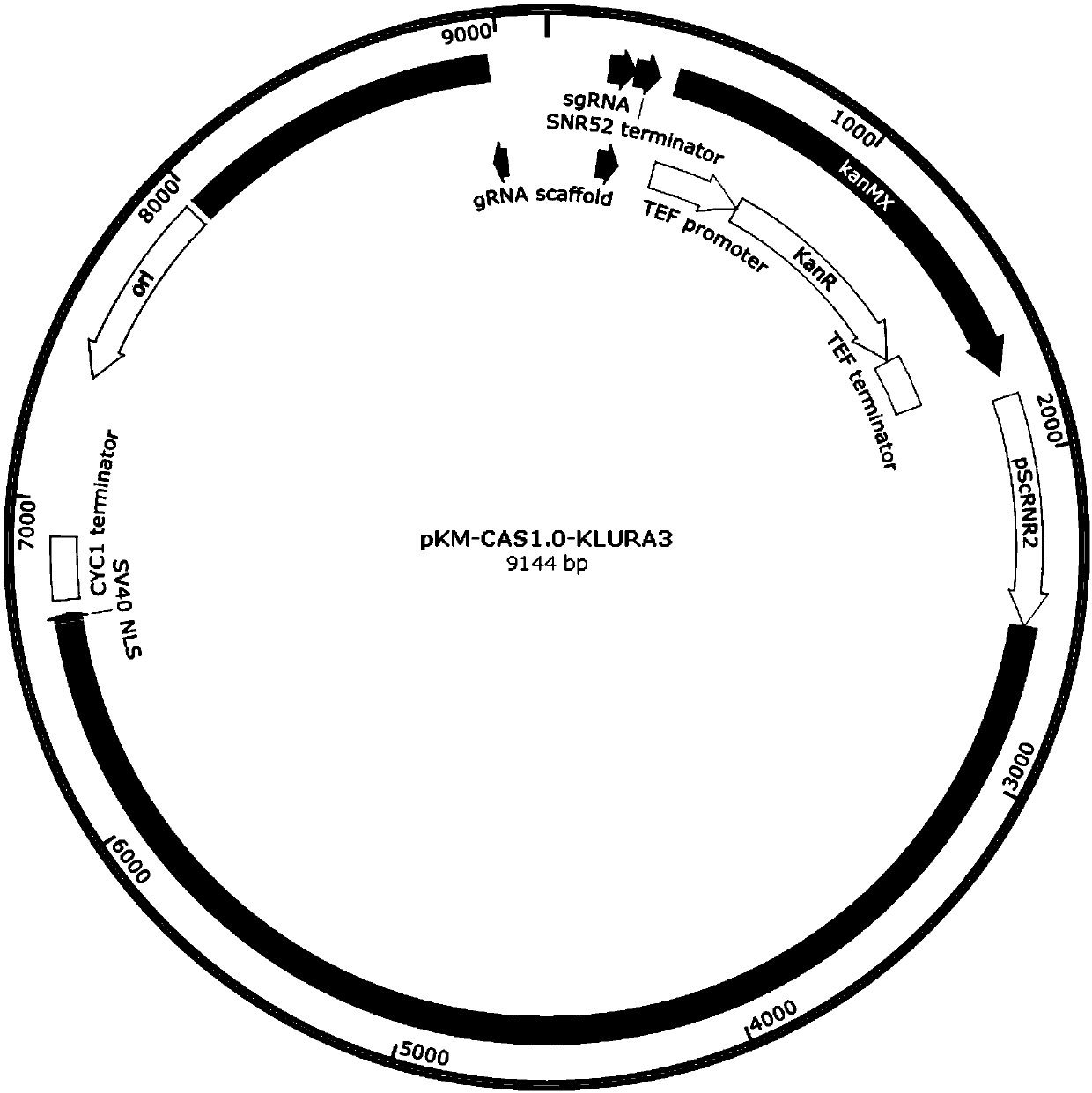
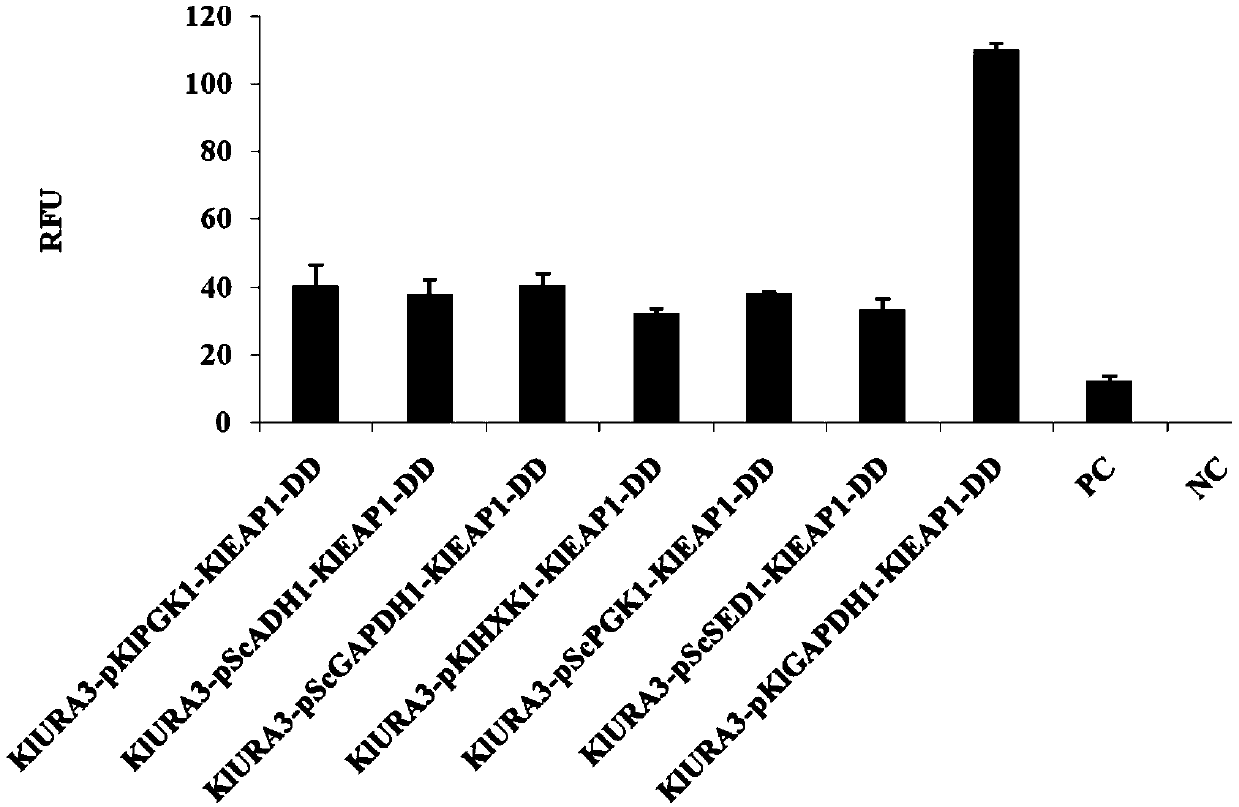
The invention provides a protein synthesis system for increasing the expression amount of a foreign protein and an application method of the protein synthesis system. Specifically, a poly-nucleotide sequence or vector constructed by a strong promoter sequence is inserted in front of a nucleotide sequence for encoding an eIF4E binding protein, over-expression of eIF4E binding proteins such as Eap1and p20 can be achieved, and foreign protein synthesis is implemented by using the improved cell lysis buffer. The invention provides the protein synthesis system for increasing the expression amountof the foreign protein, and by adopting the synthesis system provided by the invention, the efficiency of protein translation can be remarkably improved.
Owner:KANGMA SHANGHAI BIOTECH LTD
Kit and method for fast separating virus nucleic acid from biological sample
The invention discloses a kit and a method for fast separating virus nucleic acid from a biological sample, in order to fast separate virus nucleic acid from a cell-free biological sample. The kit disclosed by the invention comprises a lysis buffer solution, a magnetic bead, a washing buffer solution and an elution buffer solution. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the steps of: disintegrating a biomaterial so that the magnetic bead and the nucleic acid form a complex, separating the complex under the action of an externally-applied magnetic field, removing impurities by washing, and then eluting and recovering the nucleic acid. The method for extracting the nucleic acid is simple, convenient and safe in operation, low in cost, intact in nucleic acid and high in purity, and the nucleic acid can be directly applied to subsequent experiments. The kit can be used for efficiently extracting the virus nucleic acid in combination with an automated nucleic acid extracting instrument and can also be used for extracting the nucleic acid by means of manual operation.
Owner:GENMAG BIOTECH
Extracting method of viral nucleic acid capable of being used for high flux full automation extraction by magnetic bead method
ActiveCN101851617ASimple and fast operationEasy to realize high-throughput automationDNA preparationHigh fluxMagnetic bead
The invention provides an extracting method of viral nucleic acid capable of being used for high flux full automation extraction by a magnetic bead method, which is characterized by comprising the steps of separating viruses via a magnetic bead I: absorbing the viruses to the magnetic bead I from a biological sample to obtain the magnetic bead I with the viruses which is called as a virus-magnetic bead I composite for short, additionally adding a magnetic field to separate the virus-magnetic bead I composite from the sample, suspending the virus-magnetic bead I composite in a lysis buffer I, dissociating the virus from the magnetic bead I in the lysis buffer, additionally adding a magnetic field to remove the magnetic bead I, and heating to crack the virus; and separating a viral nucleic acid via a magnetic bead II: absorbing the viral nucleic acid in a viral lysate via the magnetic bead II, additionally adding a magnetic field to separate the magnetic bead II with the viral nucleic acid from the viral lysate, washing the magnetic bead II with the viral nucleic acid by using a washing solution, and eluting the viral nucleic acid from the magnetic bead II by using a solution to obtain a purified viral nucleic acid. In the invention, cracking cells and separating viruses are completed at one step in one tube by using the magnetic beads; and extraction of the viruses and the viral nucleic acid can be achieved by using two magnetic beads so that the extraction process is simple and rapid without a complicated device, and high pass automatic operation is easy to be realized.
Owner:宁波市博坤生物科技有限公司
Pinewood nematoda detection reagent-box and detection method
InactiveCN1529164AImprove practicalityImprove detection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementWood testingNematodePinewood nematode
Two pairs of primer are designed: Pl / P3 is an idiocratic primer for pine wood nematode; P2 / P3 an idiocratic primer for quasi pine wood nematode. The kit includes 1.25ml solution I,1ml solution II, 100U tag enzyme, and 50ul for each contrapositive DNA of wireworm. The solution I is as following constitutes: Worm Lysis Buffer, 500mM KCl, 100mMTris-ClpH 8.0, 15mM MgCl2, 10mMDTT, 4.5% Tween20, 0.1%gelatin, 0.2ug / ul protease K. The solution II is as following constitutes: 2xPCR reaction Buffer, 4.0mM MgCl2, 0.2mM dNTP, 0.8 mu MP1, P2, P3. The invented kit possesses high specificity, sensitiveness and stability, providing fast, sensitive and specific technical method.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method and device for treating sample and reagent
InactiveCN1409761ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBuffer solutionBiomedical engineering
Nucleic acids are extracted rapidly, safely and directly from a sample without pipetting steps by using predispensed, interconnectable vessels. These vessels are used separately or interconnected according to the mictrotitre standard format. The sample is mixed with lysis buffer and the nucleic acids bound to a matrix in a closed system, comprising at least two interconnectable volumes. By forcing the sample and buffer mixture back and forth from one volume to another, passing a narrow passage, thorough mixing is ensured.
Owner:阿尔法赫里克斯有限公司
Method for extracting nucleic acid by using magnetic nanoparticles and application thereof
InactiveCN103834637AAchieve separationImplement extractionDNA preparationElutionMagnetite Nanoparticles
The invention provides a method for extracting nucleic acid by using magnetic nanoparticles and an application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: I, cracking a sample by using a cracking buffer liquid to obtain a sample cracking liquid; II, adding 5-100 microliters of liquid of magnetic nanoparticles into 20-100 microliters of the obtained sampling cracking liquid, adding 20-500 microliters of combined buffer liquid, uniformly mixing, transferring into a centrifugal tube, keeping on a magnetic frame for 10-50 seconds, and removing the liquid after nucleic acid is adsorbed and separated by the magnetic nanoparticles to obtain magnetic nanoparticles adsorbed with the nucleic acid; III, adding 50-200 microliters of washing buffer liquid into the magnetic nanoparticles adsorbed with the nucleic acid, uniformly mixing, keeping on the magnetic frame for 10-50 seconds, washing at least once, and removing the liquid; and IV, adding 20-50 microliters of elution buffer liquid into the washed magnetic nanoparticles adsorbed with the nucleic acid, uniformly mixing, keeping on the magnetic frame for 10-50 seconds, and collecting the eluent after fully eluting to obtain the nucleic acid is in the eluent. By adopting the method, the extraction of miRNA (micro Ribonucleic Acid) is realized for the first time, and high extraction efficiency is achieved.
Owner:陆欣华
Reagent box and method for genome extraction on automatic nucleic acid extraction workstation
ActiveCN101323852AWide applicabilityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationMagnetic beadGenotyping
The invention discloses a reagent kit for extracting genome on an automated nucleic acid extraction workstation, and a method thereof, wherein, the reagent kit contains a lysis buffer, a guanidinium buffer, a bead and an eluent; the method comprises the steps of: disintegrating biological tissues or cells by using the lysis buffer, adsorbing DNA by using the bead in the reagent kit, removing impurity by using a cleaning solution and finally recycling the DNA by using the eluent to finish the extraction of the DNA. A regular PCR, a fluorescent quantitation PCR, Genotyping, STR and other various follow-up processing operations can be carried to the extracted DNA. The reagent kit and the method of the invention have the advantages of having wide sample applicability of the reagent, being easy to be operated, and requiring no centrifugalization processing in the whole process, thus being beneficial to the advance of the follow-up operation; the invention can cooperate with the automated nucleic acid extraction workstation to carry out effective DNA extraction and can be used in gene extraction with manual operation.
Owner:BEIJING EASTWIN SCI
Novel CTC (circulating tumor cell) enrichment technology and preparation method of kit
InactiveCN103725648ARaise the ratioReceive treatment wellTumor/cancer cellsHigh concentrationVenous blood
The invention discloses a novel CTC (circulating tumor cell) enrichment technology and a preparation method of a kit. The technology comprises the steps as follows: through permutation and combination of all possible CD45 isomer protein sequence information, designing antigens, thereby producing multiple antibodies, screening out one antibody capable of recognizing all CD45 isomers, coupling the antibody onto a magnetic bead, and further capturing all leukocytes from blood; collecting 10 ml of peripheral venous blood; removing red blood cells through lysis by an osmosis lysis buffer; mixing a designed specific antibody, the magnetic bead and the rest cell sap containing no red blood cells to separate leukocytes; and obtaining a cell population containing CTCs with higher concentration. According to the technology, a negative collection technology is adopted, so that the proportion of the CTCs is increased substantially, and the rapid and accurate detection is facilitated; meanwhile, a negative screening means is adopted, so that the CTCs are reserved without loss, and the fact that tumor diseases cannot be detected and the treatment for patients is delayed due to the loss of certain CTCs is prevented.
Owner:CHANGSHA YINGRUN BIOTECH
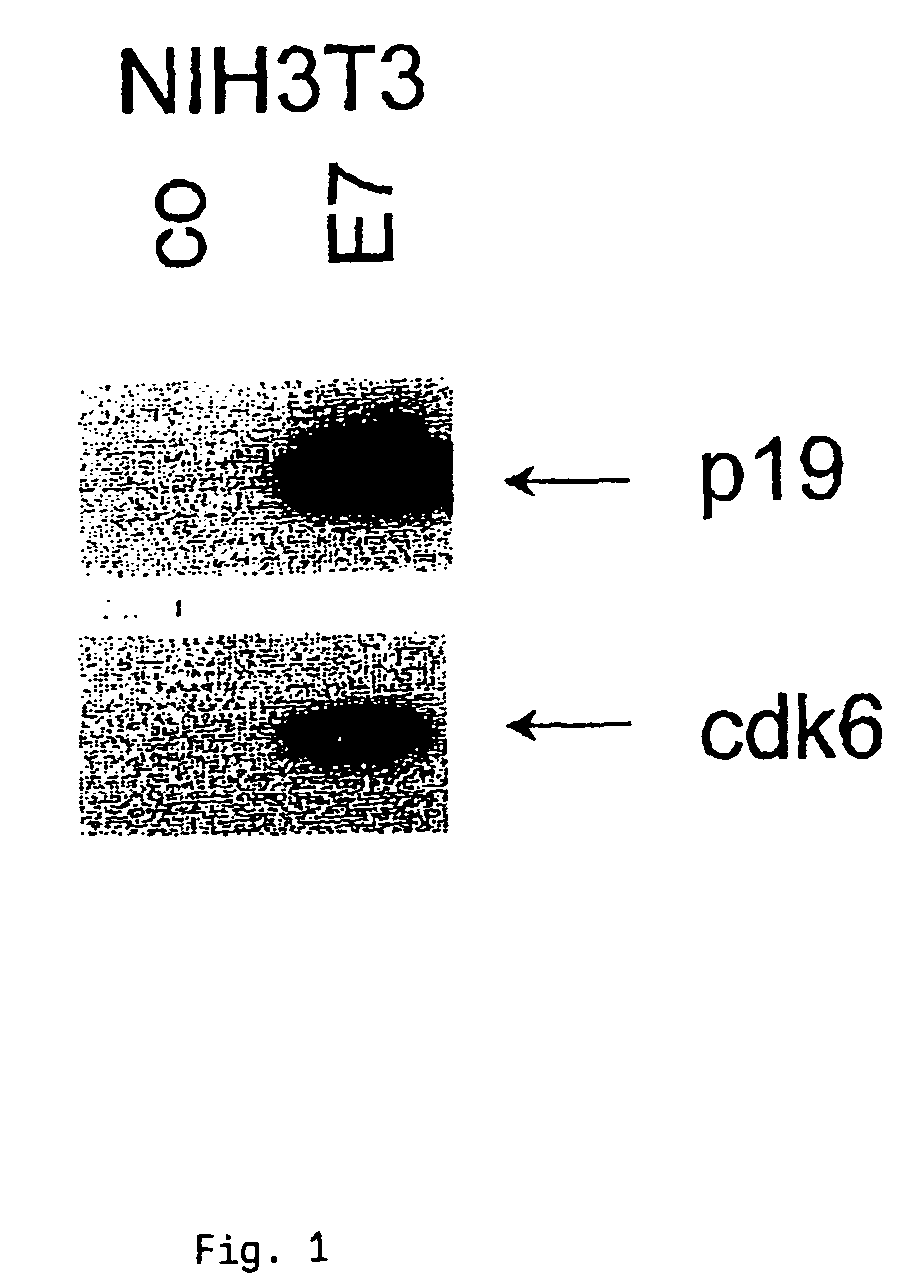
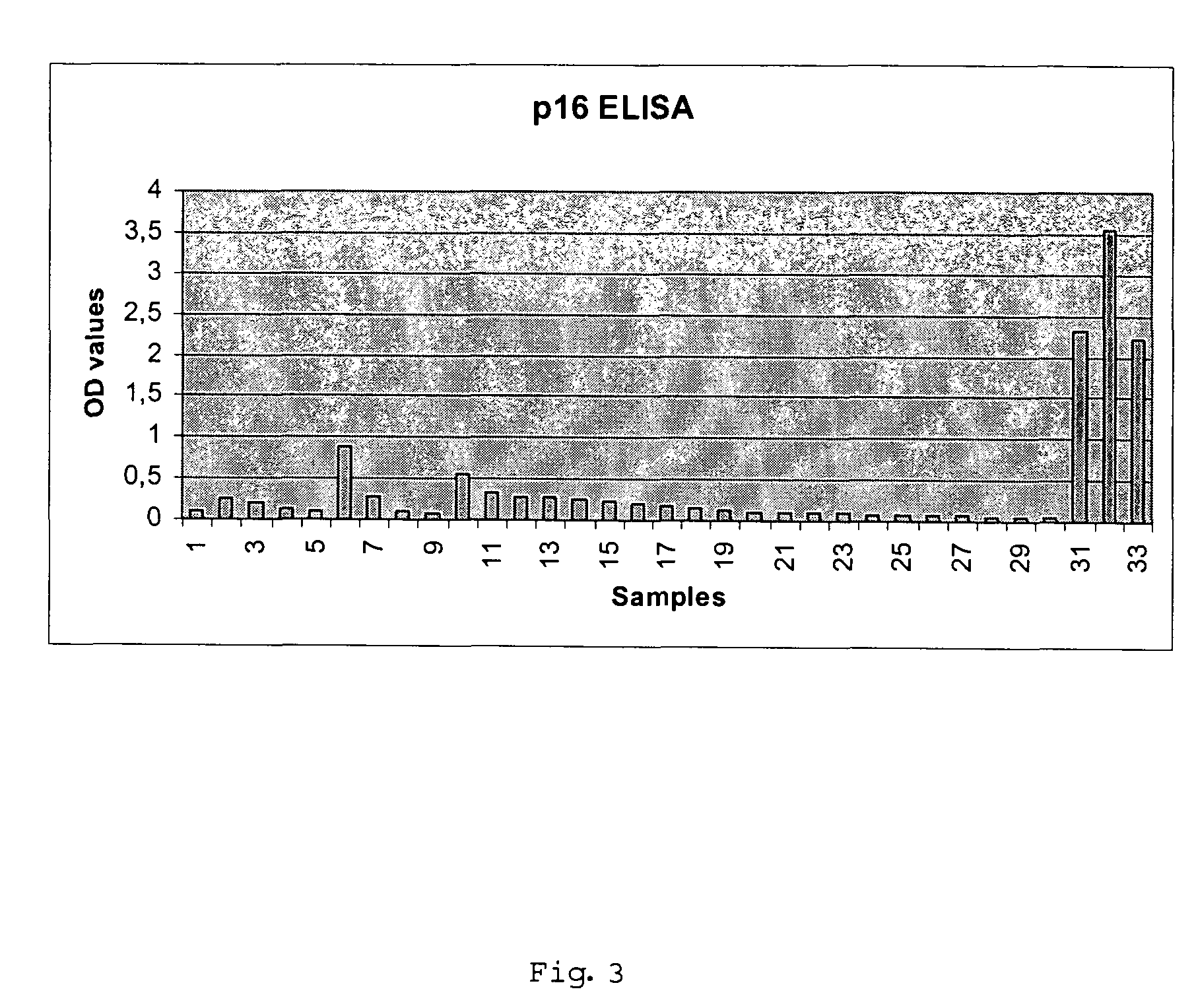
Method for detecting carcinomas in a solubilized cervical body sample
ActiveUS7306926B2Biological material analysisPeptide preparation methodsCervical intraepithelial neoplasiaMultiple Tumor Suppressor-1
The present invention relates to a method for the early diagnosis of carcinomas and their preliminary stages, which comprises determining the overexpression of a cell cycle regulatory protein in a solubilized body sample. The present invention is particularly directed to a method for detecting cervical carcinomas, cervical intraepithelial neoplasias, or cervical carcinomas in-situ from a solubilized cervical body sample of a human subject, by solubilizing the cervical body sample in a lysis buffer, and determining the overexpression of cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor p16 in the solubilized cervical sample. The invention also concerns a test kit usable for this purpose as well as an in-vitro diagnostic device.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
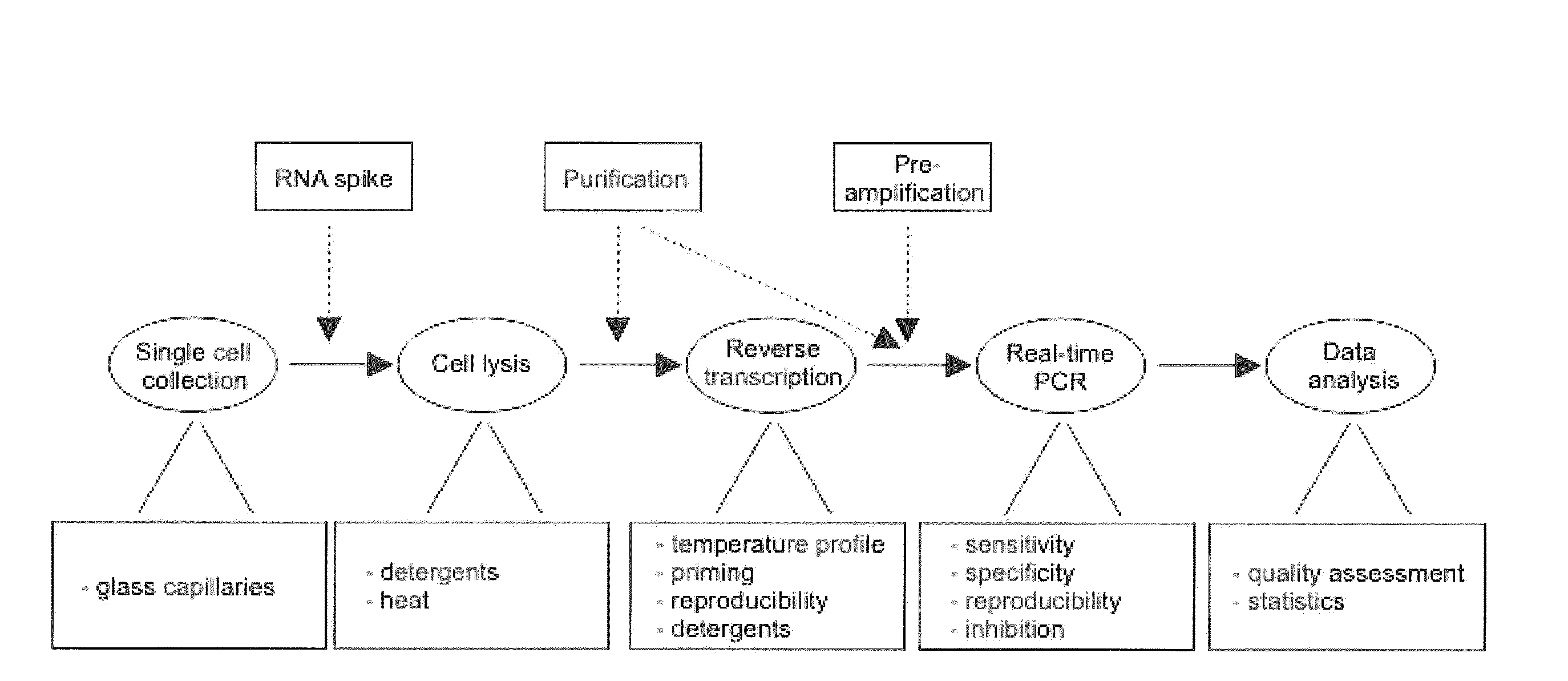
Lysis and reverse transcription for mRNA quantification
InactiveUS20110136180A1Prevent evaporationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationOligo dtBiology
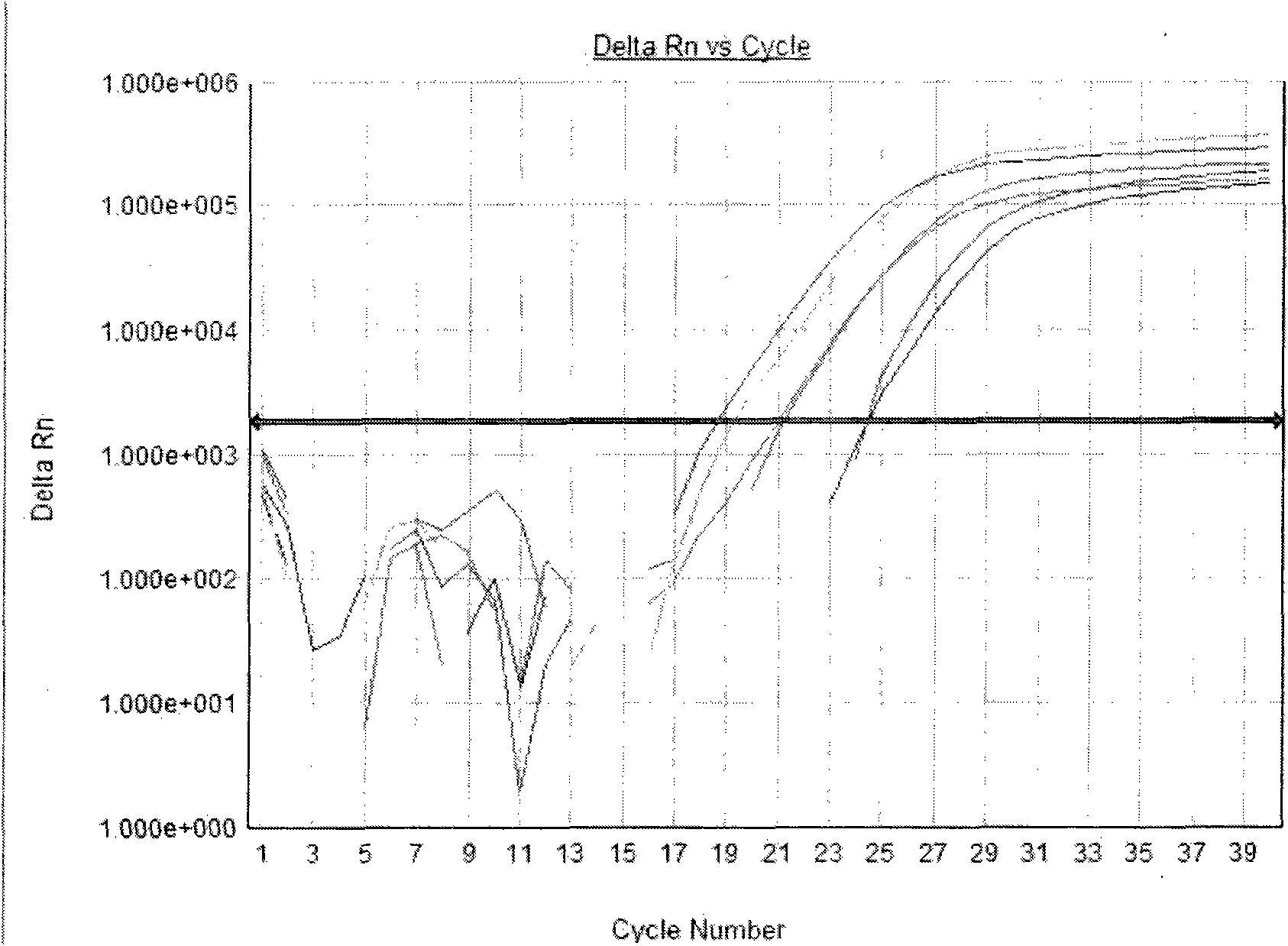
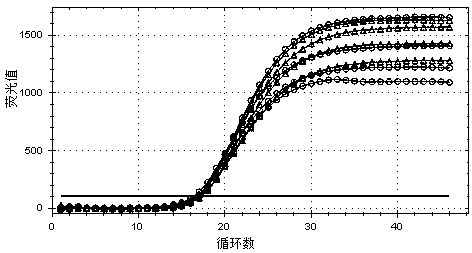
The present invention is directed to a method for performing an RT-PCR for amplifying a target RNA comprising the steps of a) lysis of a cellular sample which is supposed to contain the target RNA with a lysis buffer comprising between 0.2 M and 1 M Guanidine Thiocyanate, b) diluting the sample to an extend such that Guanidine Thiocyanate is present in a concentration of about 30 to 50 mM, c) reverse transcribing in the presence of a mixture of first strand cDNA synthesis primers, the mixture consisting of oligo dT primers and random primers, and d) subjecting the sample to multiple cycles of a thermocycling protocol and monitoring amplification of the first strand cDNA in real time, characterized in that steps a) to c) are done in the same vessel.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Kit for detecting aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 gene polymorphism and amplification method and detection method thereof
InactiveCN103184268AImprove detection efficiencyReduce testing costsMicrobiological testing/measurementGlycerolPolymerase L
The present invention discloses a kit for detecting aldehyde dehydrogenase 2(ALDH2) gene polymorphism by using the single-tube bidirectional allele-specific amplification technology combined with the SNP sensitivity molecular switch technology, and an amplification method and a detection method thereof. The kit genotypes the Glu487Lys(rs671) site on the aldehyde dehydrogenase 2. The kit includes amplification buffer, polymerase, cell lysis buffer and glycerol, and can complete the genotyping for the SNP site in one PCR reaction so as to understand the genotype of the aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 subject and the product activity thereof.
Owner:UNION STEMCELL & GENE ENG +1
Fast and efficient saliva DNA extraction kit and extraction method
InactiveCN106350509AEasy to operateThe operation process method is fastDNA preparationMagnetic beadA-DNA
The invention discloses a fast and efficient saliva DNA extraction kit and an extraction method. The fast and efficient saliva DNA extraction kit contains cell lysis buffer, DNA combined liquid, rinsing liquid and eluant. The extraction method of saliva DNA at least comprises the following three steps: (1) cell lysis: adding the cell lysis buffer into saliva, thereby obtaining the cell lysis buffer containing free DNA; (2) adding DNA combined liquid into the cell lysis buffer obtained in the step (1), thereby obtaining a DNA-magnetic bead absorbing compound; (3) utilizing rinsing liquid and eluant to elute the compound generated in the step (2), and removing RNA and other impurities, thereby obtaining high-purity DNA. The novel cell lysis buffer is adopted by the fast and efficient saliva DNA extraction kit; the cost is low; the extracted DNA purity is high; the completeness is excellent; no RNA is remained; the fast and efficient saliva DNA extraction kit can be applied to high-throughput sequencing, genetic typing and general molecular biological experiment operation.
Owner:哈尔滨博泰生物科技有限公司
Method of detection of transcription factor expression activity by luciferase reporter gene system
InactiveCN106399461ALow costGood price advantageMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisMarket potentialTime-Consuming
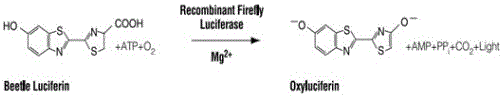
The invention provides a method of detection of transcription factor expression activity by a luciferase reporter gene system; the method comprises the steps: based on the luciferase characteristics of being lasting, stable and easy to detect, co-transfecting cells with a luciferase reporter gene vector containing a target gene promoter and a transcription factor expression plasmid; after the cells are cultured, carrying out lysis of a certain number of cells with a cell lysis buffer liquid, collecting a lysate containing luciferase, and centrifuging to take a supernatant; and then real-timely detecting luciferase expression intensity data in a luciferase activity detection buffer liquid, at the same time, detecting the luciferase concentration, correcting, and then calculating to obtain the transcription factor expression quantity, namely the transcription factor expression activity needing to detection. The method is simpler and more feasible in whole operation process, shorter in time consuming, higher in flux, relatively high in repeatability and accuracy, and lower in operating costs, thereby having broad application prospects, and having excellent market potential.
Owner:MIAOSHUN SHANGHAI BIOTECH CO LTD
Universally Applicable Lysis Buffer and Processing Methods for the Lysis of Bodily Samples
ActiveUS20130065223A1Universally applicableHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseRespiratory disease
The present invention provides a universally applicable lysis buffer comprising a chaotropic 5 agent, a reducing agent, and a proteolytic enzyme suitable for processing a wide variety o different sample types, such as different types of bodily samples relevant for the diagnosis o a respiratory disease. Furthermore, the present invention provides the use of a chaotropic agent, a reducing agent, and a proteolytic enzyme for the lysis of a broad spectrum of bodily samples. Moreover, the present invention provides a method for processing bodily samples which is universally applicable to the lysis of a variety of different types of bodily samples. Furthermore, the present invention provides methods for analyzing a bodily sample or for detecting the presence of a pathogen in a bodily sample, preferably, for diagnosing a respiratory disease, such as pneumonia or tuberculosis. Preferably, these methods are universally applicable to a variety of sample types, are applicable as one-tube-processes, are 15 suitable for performance in a high-throughput setting, and are automatable.
Owner:CURETIS GMBH
Method for separating free nucleic acid from blood serum or blood plasma sample by using magnetic bead
InactiveCN103952397AGuaranteed purityAvoid the inconvenience caused by high temperature incubationDNA preparationMagnetic beadBlood plasma
The invention relates to a method for separating free nucleic acid from a blood serum or blood plasma sample by using a magnetic bead, and belongs to the field of nucleic acid purification. The method comprises the following steps: firstly adding the blood serum / blood plasma sample, a lysis buffer, protease K and magnetic bead suspension liquid into a nuclease-free centrifugal tube, fully and uniformly mixing, then performing pyrolysis, adsorbing nucleic acid on the surface of the magnetic bead, performing purification under the effect of an external magnetic field, removing impurities such as protein, polysaccharide, salt and the like through a rinsing step, and finally eluting by adding nuclease-free water to obtain a free nucleic acid solution. The method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of simplicity, high speed, stability, high efficiency and cheap price; the purified free nucleic acid is complete and high in purity, and can be directly used for subsequent experiments.
Owner:TIANGEN BIOTECH BEIJING
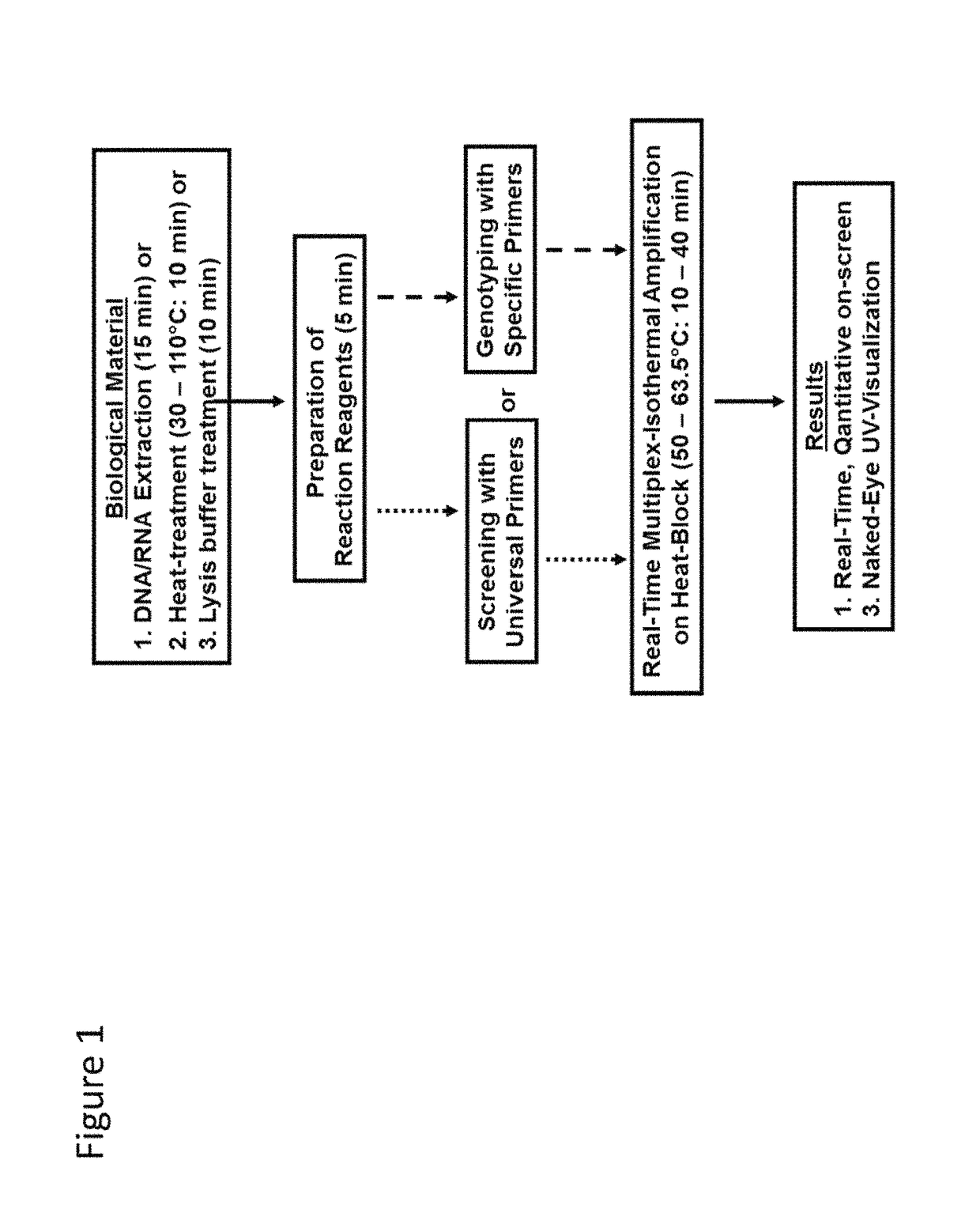
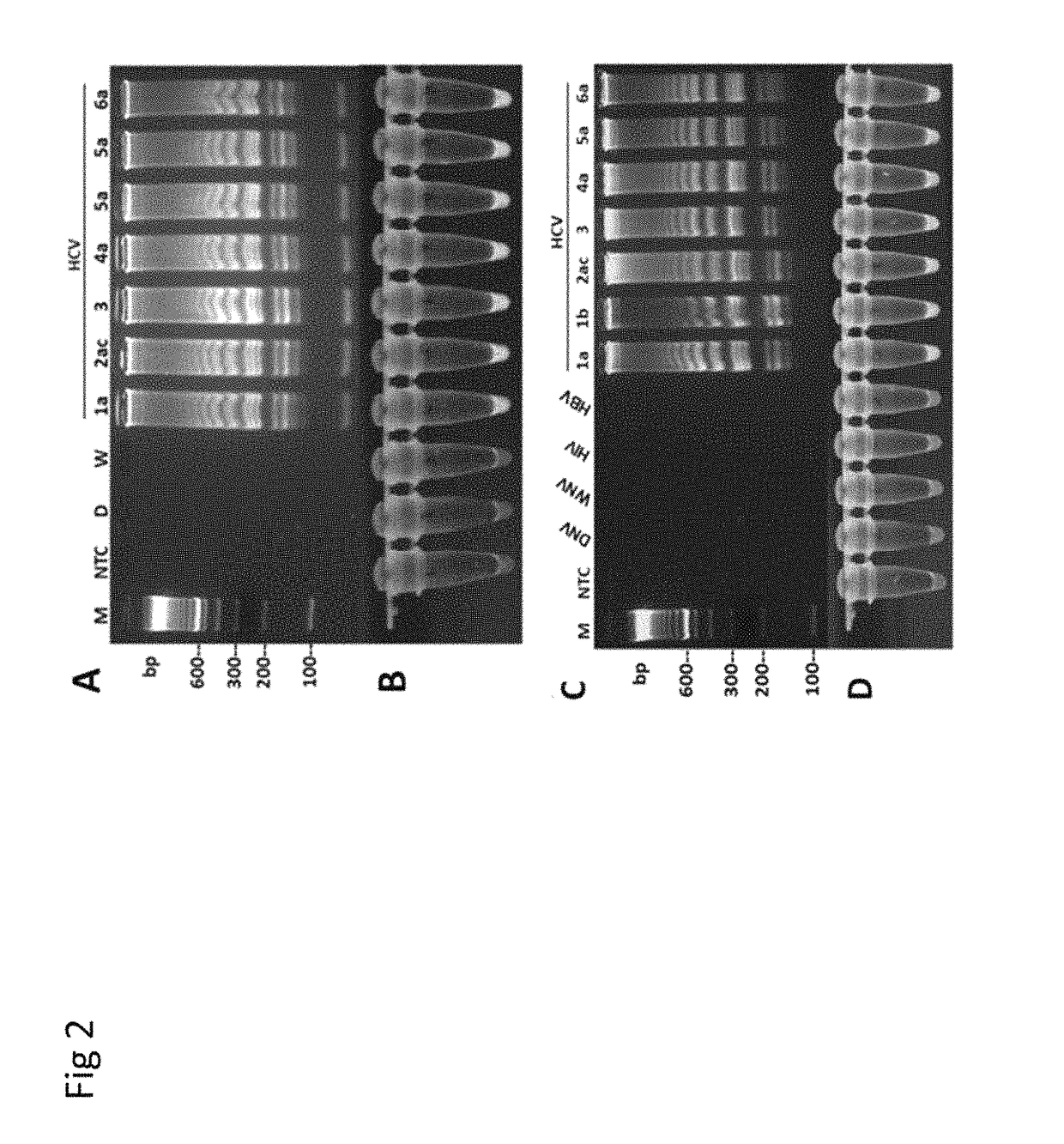
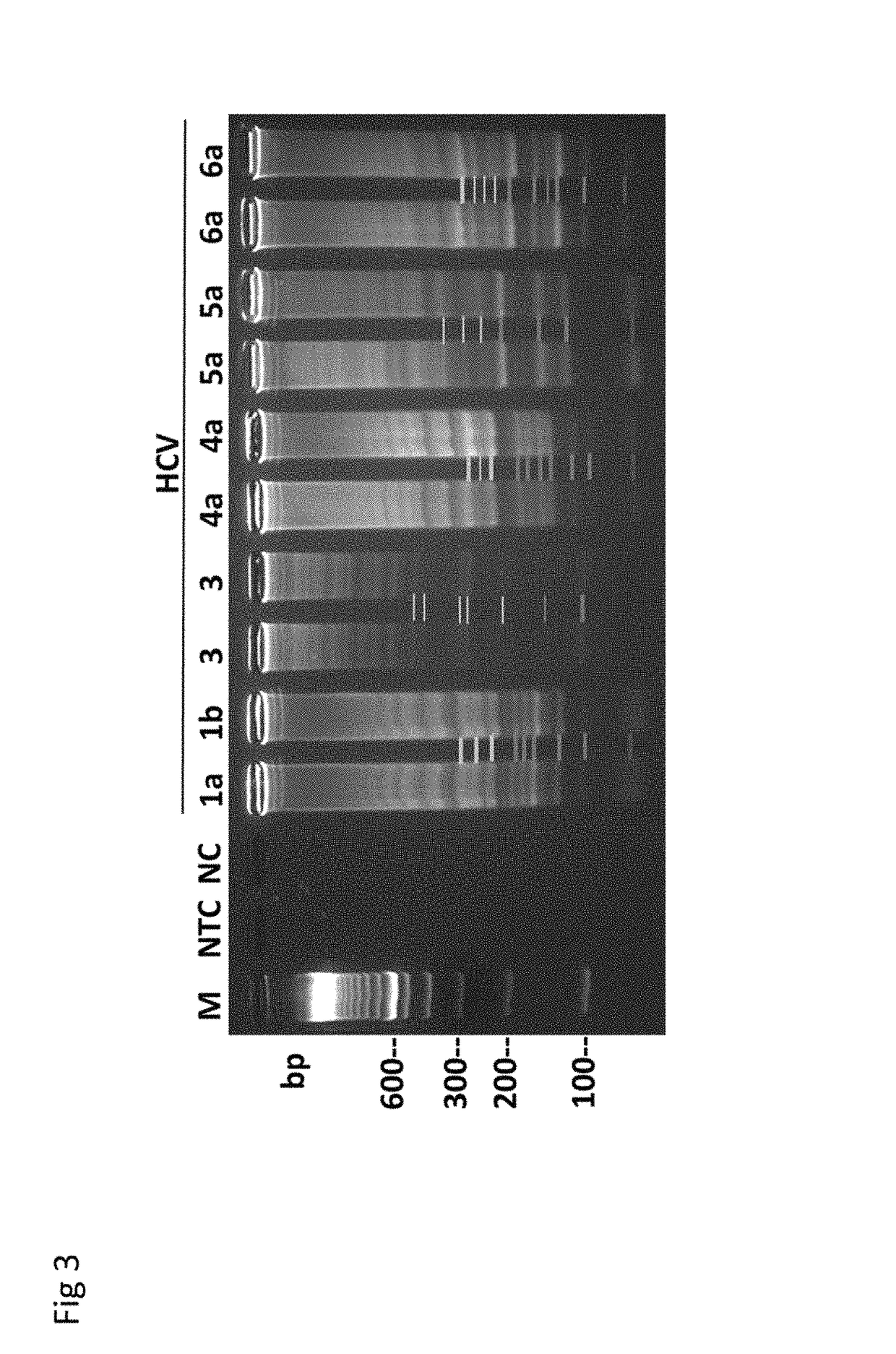
Methods for real-time multiplex isothermal detection and identification of bacterial, viral, and protozoan nucleic acids
ActiveUS20200048722A1Flexible processFacilitate strand displacementMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesProtozoaLoop-mediated isothermal amplification
Herein disclosed are rapid real-time isothermal multiplex methods of detecting, identifying and quantifying bacterial, viral, and protozoan nucleic acids in a sample. These include contacting the sample with two or more sets of pathogen-specific reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification primers and novel oligofluorophores specific for the target bacterial, viral, and parasitic nucleic acids of interest such as human immunodeficiency virus, Ebola virus, Marburg virus, Yellow fever virus, hepatitis-B virus, Lassa fever virus, Plasmodium, hepatitis-C virus, hepatitis-E virus, dengue virus, Chikungunya virus, Japanese Encephalitis virus, Middle Eastern Respiratory Syndrome Corona virus, Mycobacterium, West Nile virus, Cytomegalovirus, Parvovirus, Leishmania, Trypanosoma, and Zika virus nucleic acids, under conditions sufficient to produce detectable real-time amplification signals in about 10 to 40 minutes. The amplification signals are produced by pathogen-specific fluorogenic labels included in one or more of the primers. Also, novel reaction and sample lysis buffers, primers, and kits for rapid multiplex detection, quantification, and identification of bacterial, viral, and protozoan nucleic acids by real-time isothermal amplification are herein disclosed.
Owner:NYAN DOUGBEH CHRIS
Magnetic bead nucleic acid extraction method
InactiveCN106591297AIncrease concentrationHigh purityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationFluorescenceMagnetic bead
The invention discloses a magnetic bead nucleic acid extraction method. The method includes: adding a cracking buffer solution into a biological sample, and conducting cracking separation of nucleic acid in the biological sample; combining nucleic acid with nano magnetic beads in the cracking buffer solution to form a magnetic bead-nucleic acid compound under the action of an external magnetic field; adding a washing buffer solution into the magnetic bead-nucleic acid compound to conduct centrifugal washing so as to remove impurities from the magnetic bead-nucleic acid compound, and collecting the washed magnetic bead-nucleic acid compound; adding an elution buffer solution into the washed magnetic bead-nucleic acid compound, and adding a disinhibition agent; directly subjecting a mixture of the magnetic bead-nucleic acid compound and the elution buffer solution to subsequent fluorescence quantitative PCR reaction. The method provided by the invention replaces a magnetic frame with centrifugation for adsorption of magnetic beads, and separates eluent and magnetic beads, can set different rotation speeds and time according to different types of nucleic acid so as to thoroughly separate the eluent and magnetic beads, thus improving the extraction concentration and purity.
Owner:解码(上海)生物医药科技有限公司
Methods for real-time multiplex isothermal detection and identification of bacterial, viral, and protozoan nucleic acids
ActiveUS10072309B1Flexible processFacilitate strand displacementMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesProtozoaFluorescence
Herein disclosed are rapid real-time isothermal multiplex methods of detecting, identifying and quantifying bacterial, viral, and protozoan nucleic acids in a sample. These include contacting the sample with two or more sets of pathogen-specific reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification primers and novel oligofluorophores specific for the target bacterial, viral, and parasitic nucleic acids of interest such as human immunodeficiency virus, Ebola virus, Marburg virus, Yellow fever virus, hepatitis-B virus, Lassa fever virus, Plasmodium, hepatitis-C virus, hepatitis-E virus, dengue virus, Chikungunya virus, Japanese Encephalitis virus, Middle Eastern Respiratory Syndrome Corona virus, Mycobacterium, West Nile virus, Cytomegalovirus, Parvovirus, Leishmania, Trypanosoma, and Zika virus nucleic acids, under conditions sufficient to produce detectable real-time amplification signals in about 10 to 40 minutes. The amplification signals are produced by pathogen-specific fluorogenic labels included in one or more of the primers. Also, novel reaction and sample lysis buffers, primers, and kits for rapid multiplex detection, quantification, and identification of bacterial, viral, and protozoan nucleic acids by real-time isothermal amplification are herein disclosed.
Owner:NYAN DOUGBEH CHRIS
Wild ginseng protein extracting method suitable for dielectrophoresis
InactiveCN101906130AImprove solubilityReduce Denaturing PrecipitationPeptide preparation methodsElectrophoresisCentrifugation
The invention discloses a wild ginseng protein extracting method suitable for dielectrophoresis. The method comprises the following steps of: taking wild ginseng as an experimental material, fully grinding the wild ginseng in liquid nitrogen and transferring the obtained product to a centrifuge tube; adding acetone solution precooled at the temperature of -20 DEG C into the centrifuge tube, washing sample powder for 3 times, collecting sediments by centrifugation and drying the obtained product at room temperature for 20min to obtain the crude extract of the wild ginseng protein; dissolving the crude extract of the wild ginseng protein into lysis buffer, and performing ultrasonic cell disintegration and extracting the supernate by centrifugation to obtain the high-quality solution of the wild ginseng protein. The wild ginseng protein extracting method for the dielectrophoresis is simple and fast, can obtain an electrophoresis pattern having a high repeatability and resolution, is favorable for subsequent protein identification by mass spectrographic analysis and provides a technical support for the proteomic research of the wild ginseng.
Owner:BEIHUA UNIV
Assay for transposase accessible chromatin using sequencing (ATAC-seq) method applied to zebrafish embryos
InactiveCN105463089AHigh degree of enrichmentSimple stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationWater bathsFluorescence
The invention relates to an assay for transposase accessible chromatin using sequencing (ATAC-seq) method applied to zebrafish embryos. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, performing zebrafish embryo sample pretreatment; adding lysis buffer into the embryos; cracking the embryos in a water bath by using a wild-neck spearhead; performing a transposition reaction immediately and purifying DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid); determining a cycle number for library establishment by using a real-time fluorescence quantification method; directly performing library establishment and sequencing by using a further PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) method. A regulatory sequence on genome chromatin can be located and decoded by the ATAC-seq method and a DNase-seq (DNase I hypersensitive sites sequencing) method, but the steps in ATAC-seq are simpler, a required cell quantity is smaller, the ATAC-seq is more helpful under the situation that a large quantity of cells cannot be obtained, and the data enriching degree of the ATAC-seq is higher according to an assay result. The ATAC-seq method is further applied to zebrafish embryo cells. Thus, an effective and simple method is provided for the researches of changes of chromatin structures in early developing processes of living organisms and corresponding gene expression regulation and control researches.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Extraction method of total genome DNA from microbes
The invention discloses an extraction method of total genome DNA from microbes, comprising the following steps of: adding a lysis buffer and lysozyme to a sample to be extracted to enable bacterial cells to fully rupture and release DNA; and extracting the obtained crude extract DNA by phenol / chloroform / isoamyl alcohol extracting solutions to obtain purified total genome DNA of microbes. The extraction method disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects of big DNA release amount, simple experiment conditions, low cost and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
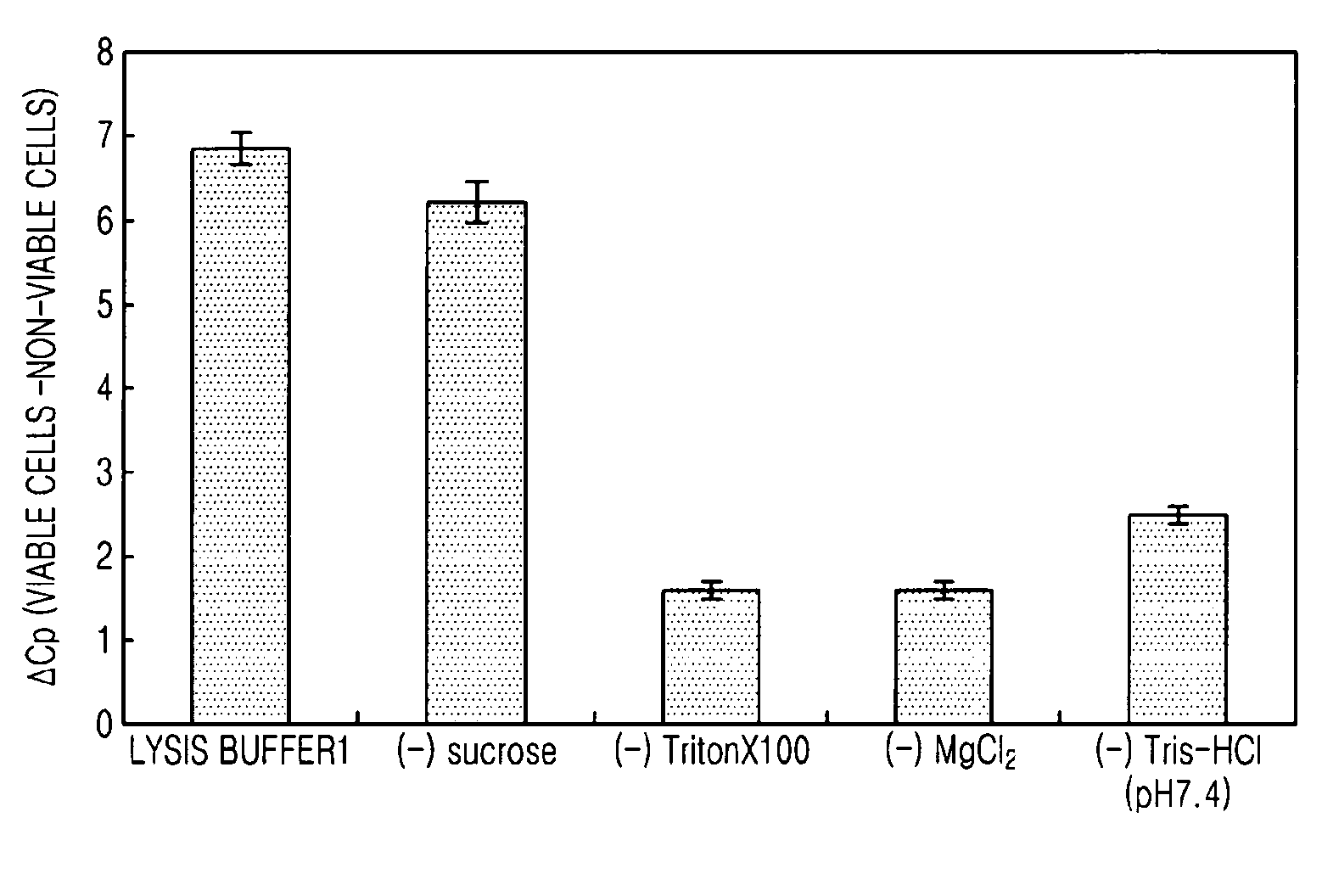
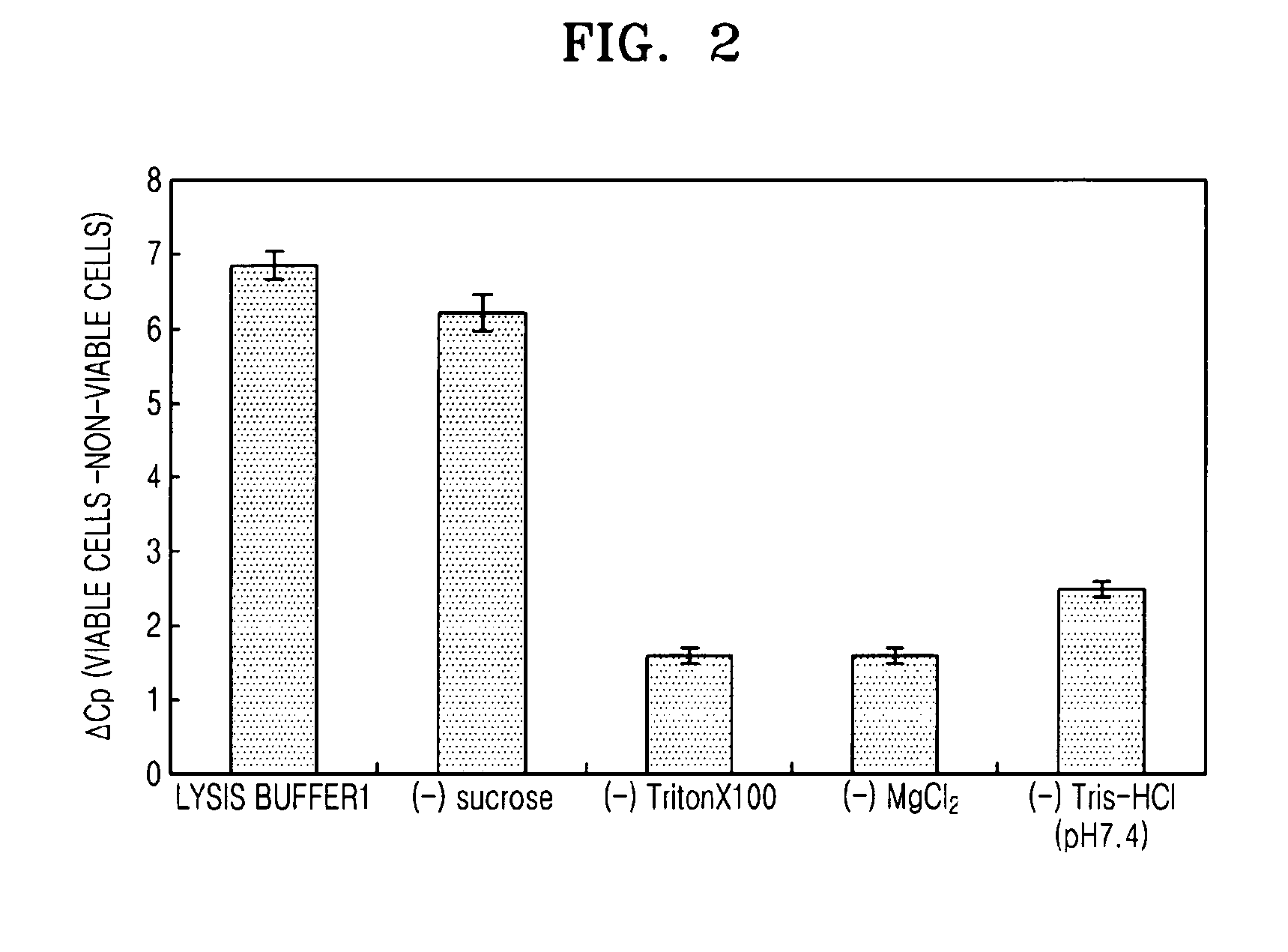
Method of selectively lysing non-viable cells in cell population in sample
InactiveUS20090142798A1Microbiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationViable cellSURFACTANT BLEND
The present invention provides a method of selectively lysing non-viable cells from a cell population within a sample, the method including selectively lysing non-viable cells by mixing a cell-containing sample with a lysis buffer including a non-ionic surfactant and a divalent cation salt.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com