Method for rapidly analyzing eukaryotic protein genomic data
A protein genome and eukaryotic technology, applied in the field of protein genome data analysis, can solve the problems of limited application scope, only support data statistics, and high limitations, and achieve the effects of improving reliability, rapid identification and analysis, and improving coverage.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
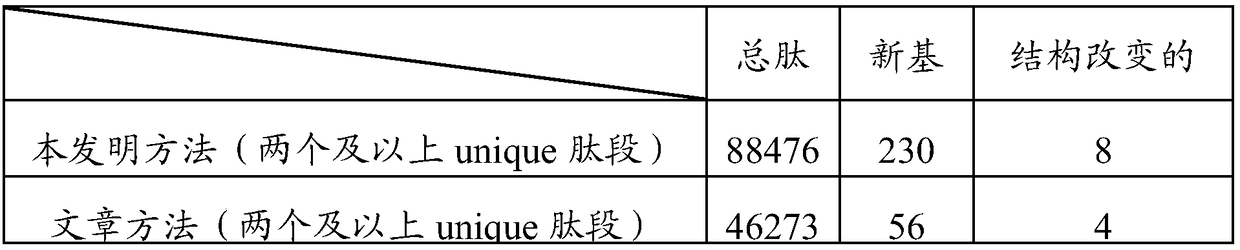
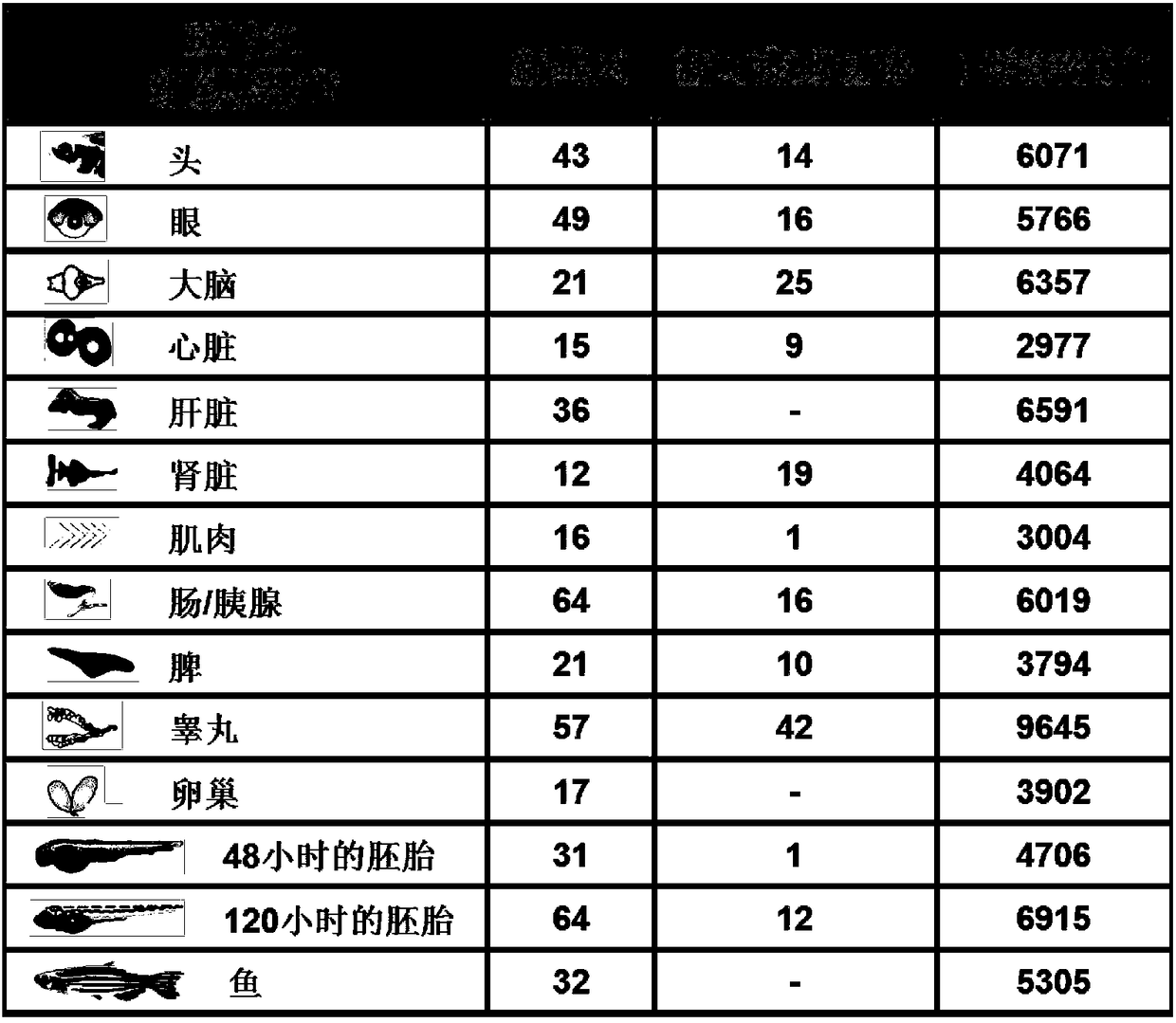
[0068]The mass spectrum data in Example 1 are from published articles [KelkarDS, Provost E, Chaerkady R, Muthusamy B, Manda SS, Subbannayya T, Selvan LDN, Wang CH, Datta KK, Woo S, DwivediSB, Renuse S, Getnet D, Huang TC , Kim MS, Pinto SM, Mitchell CJ, Madgundu AK, Kumar P, Sharma J, Advani J, Dey G, Balakrishnan L, Syed N, Nanjappa V, Subbannayya Y, Goel R, Prasad TSK, Bafna V, Sirdeshmukh R, Gowda H, Wang C, Leach SD, Pandey A, "Annotation of the Zebrafish Genome through an Integrated Transcriptomic and Proteomic Analysis", Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 2014, 13:3184-3198]
[0069] Example 1
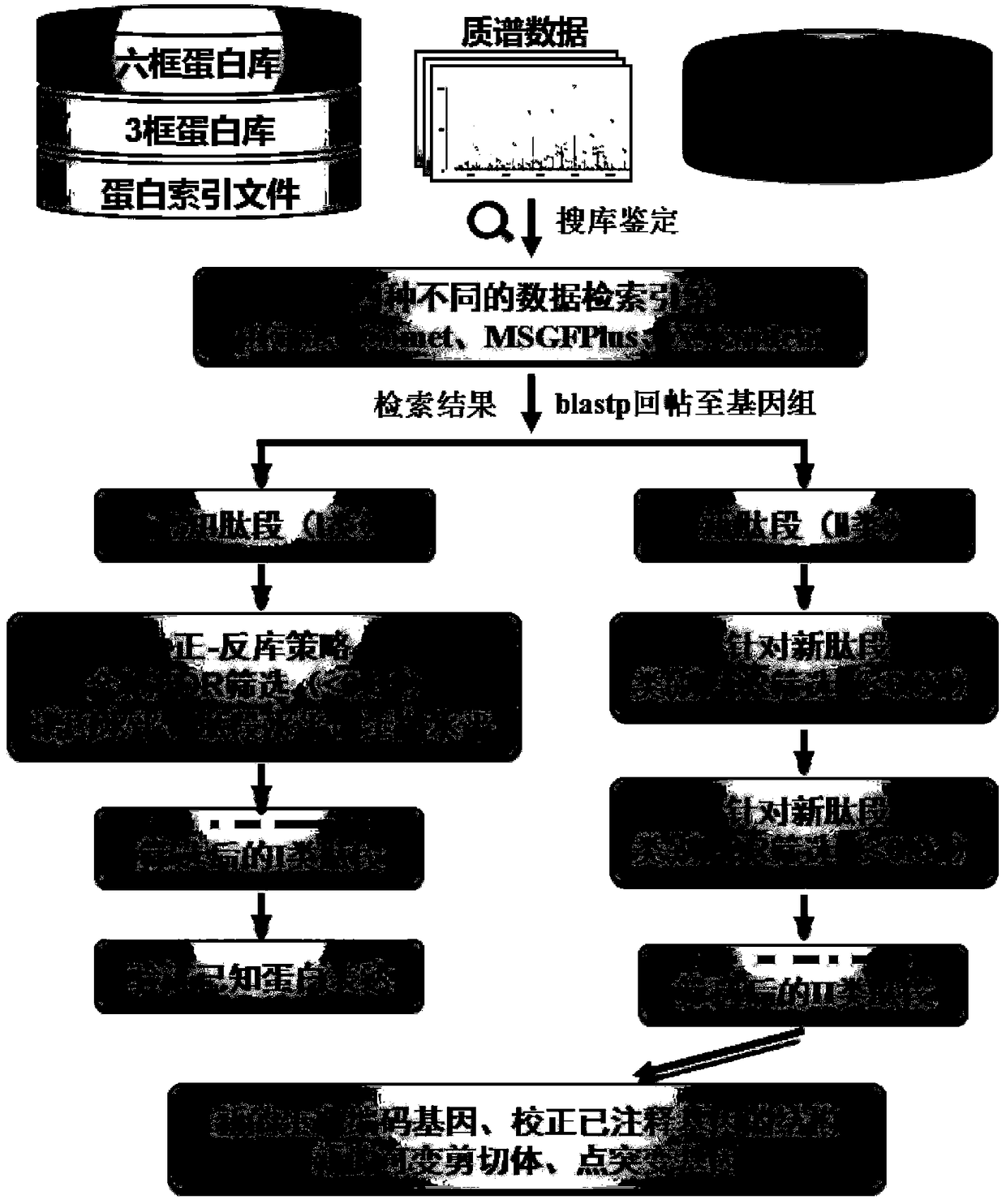
[0070] Zebrafish genome re-annotation, the steps are as follows:
[0071] Download the whole genome sequence of zebrafish from the Ensembl website, the GFF format file, the protein library sequence of the proteome (46260 known protein sequences are predicted), and the zebrafish transcriptome sequence from NCBI.
[0072] Merge the assembled transcriptome data, EST sequences and no...
Embodiment 2
[0092] Phaeodactylum tricornutum genome re-annotation, the steps are as follows:
[0093] 1) According to the experimental method in the literature [Yang MK, YangYH, ChenZ, Zhang J, LinY, Wang Y, XiongQ, Li T, Ge F, Bryant DA, Zhao JD, "Proteogenomic analysis and global discovery of posttranslational modifications in prokaryotes", 2014 , 111(52):E5633-E5642], extract Phaeodactylum tricornutum protein, and digest the total protein with enzymatic digestion to obtain a peptide mixture solution, use Thermo LTQExactive mass spectrometer to detect the obtained peptide solution, collect mass spectrometry data, a total of Collect 1555391 mass spectra.
[0094] 2) Using the same method as in Example 1, download the complete genome sequence of Phaeodactylum tricornutum from the JGI Genome Portal website, the transcriptome sequence, the GFF format file, the protein library sequence of the proteome (10567 known protein sequences), and Use ProteoWizard to convert the original data into a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com