Patents
Literature
687 results about "Global network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
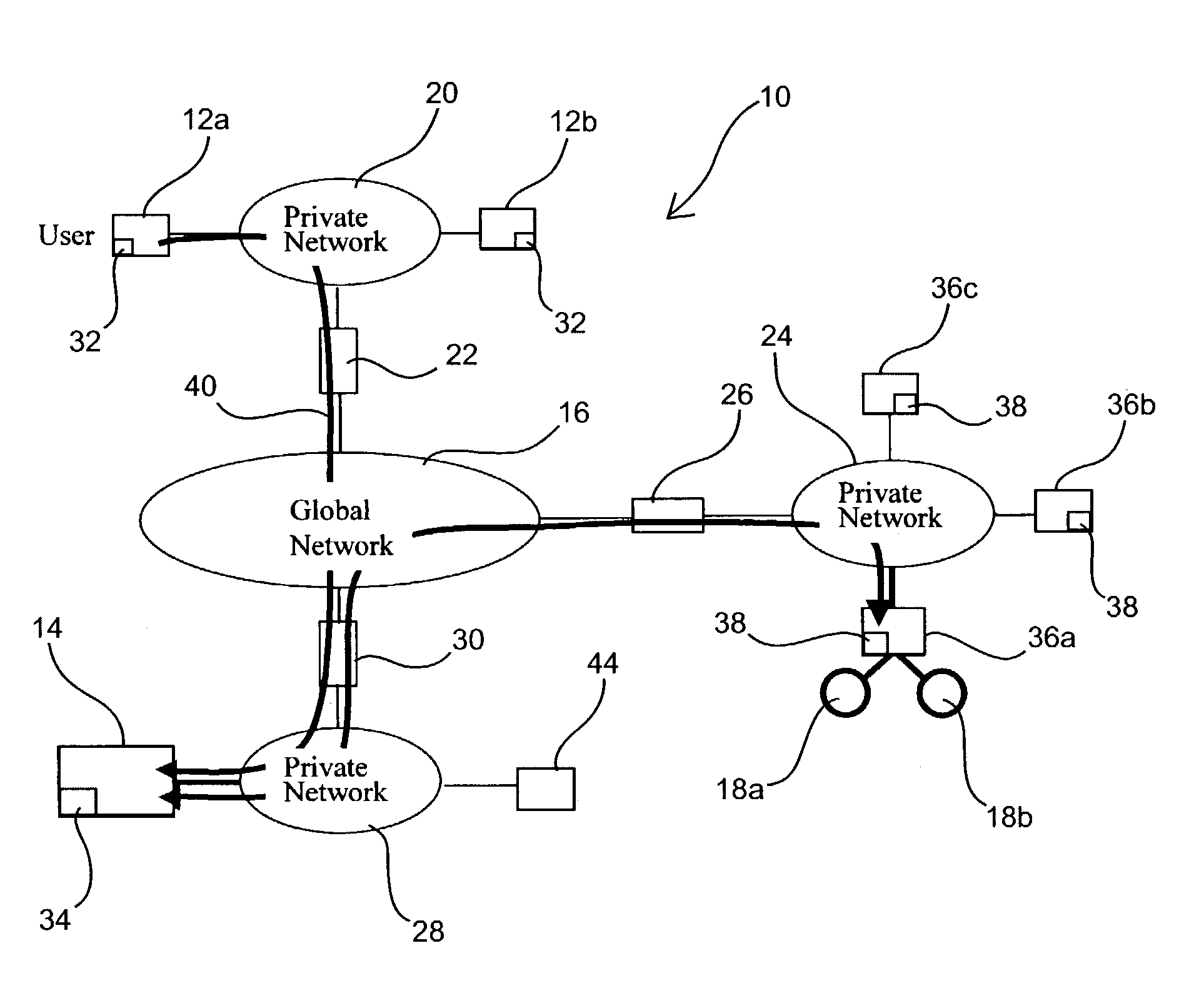
A global network is any communication network which spans the entire Earth. The term, as used in this article refers in a more restricted way to bidirectional communication networks, and to technology-based networks. Early networks such as international mail and unidirectional communication networks, such as radio and television, are described elsewhere.
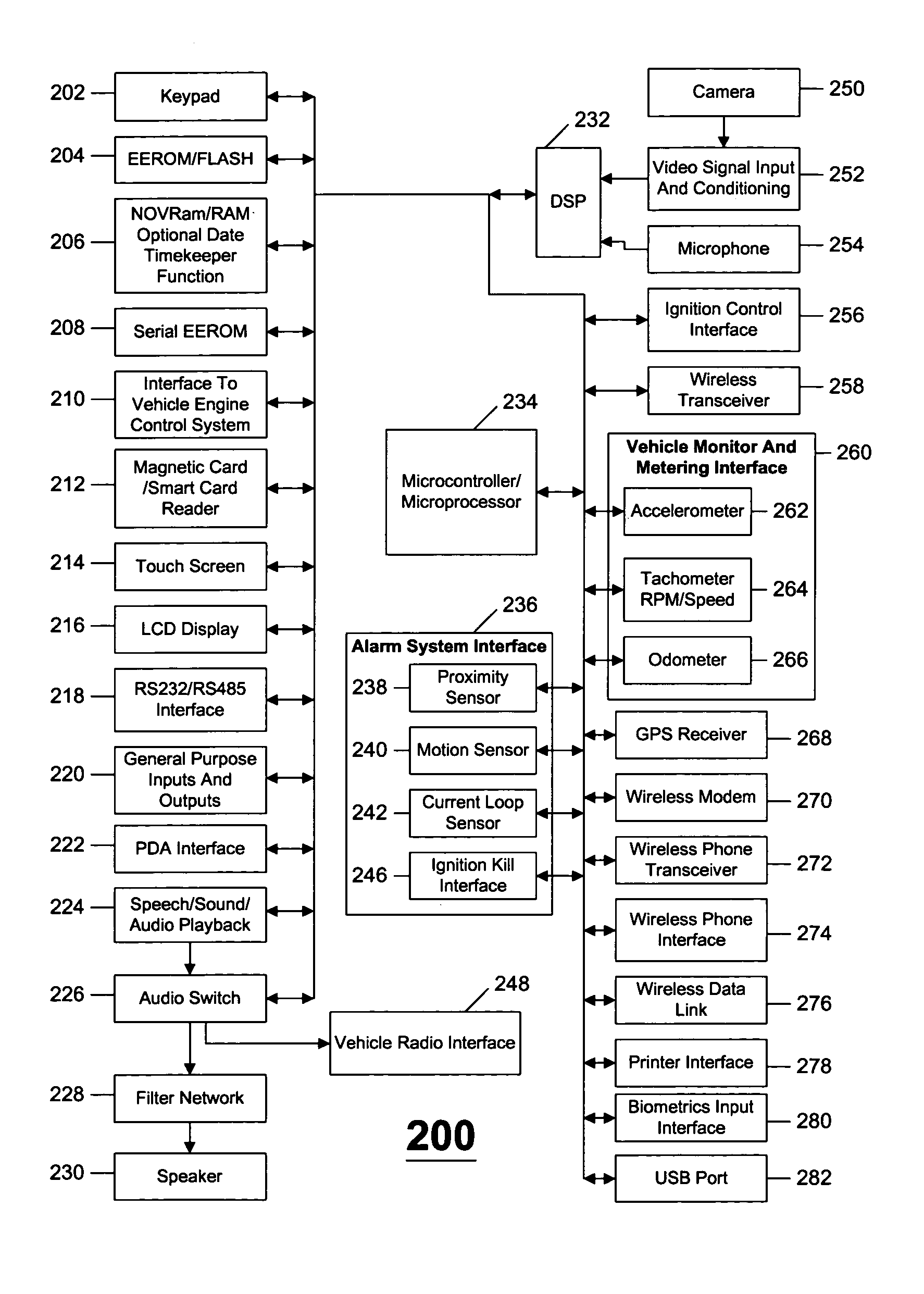
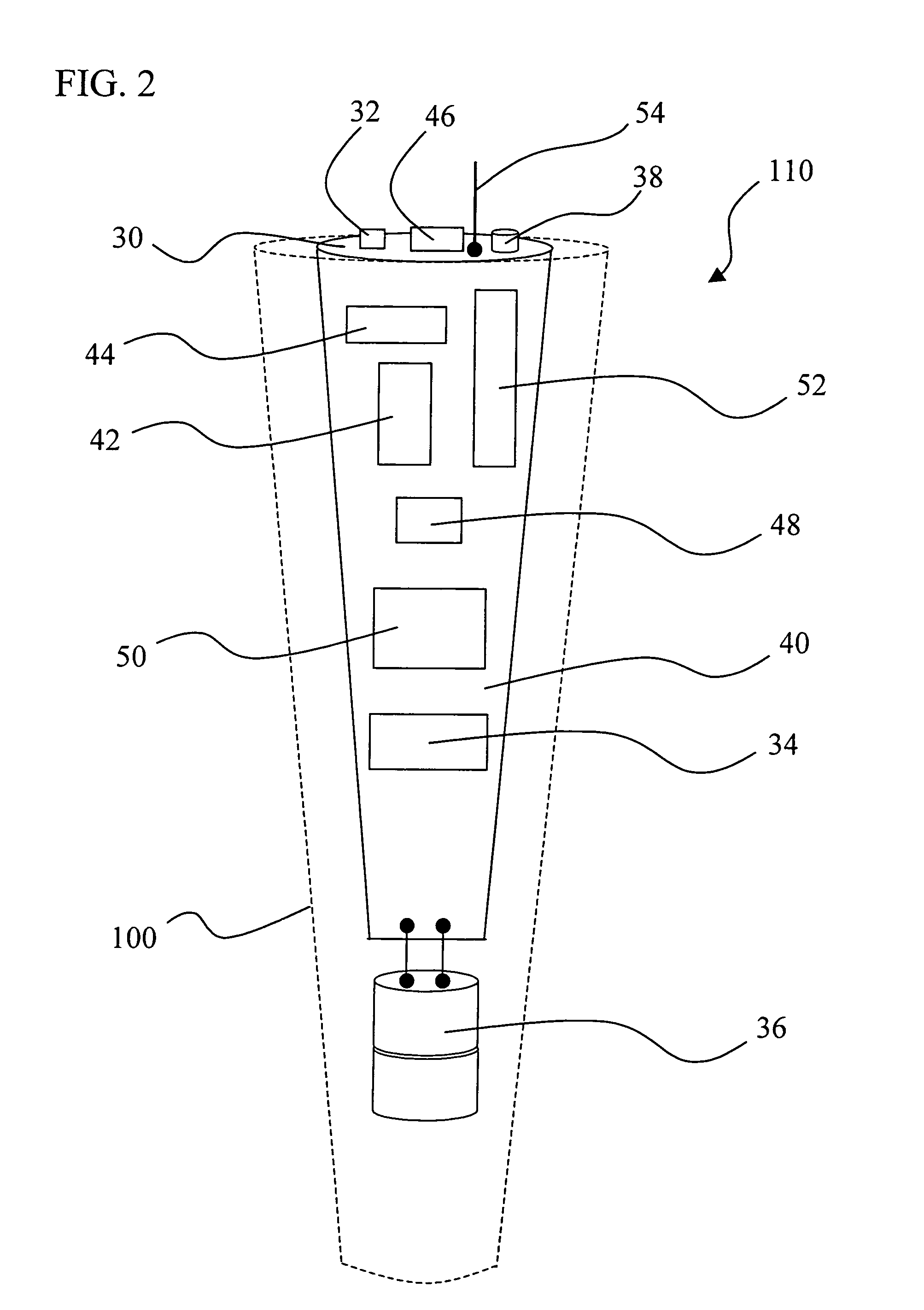
Wireless vehicle diagnostics device and method with service and part determination capabilities
InactiveUS7502672B1Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesMotor vehicle partBusiness transactions
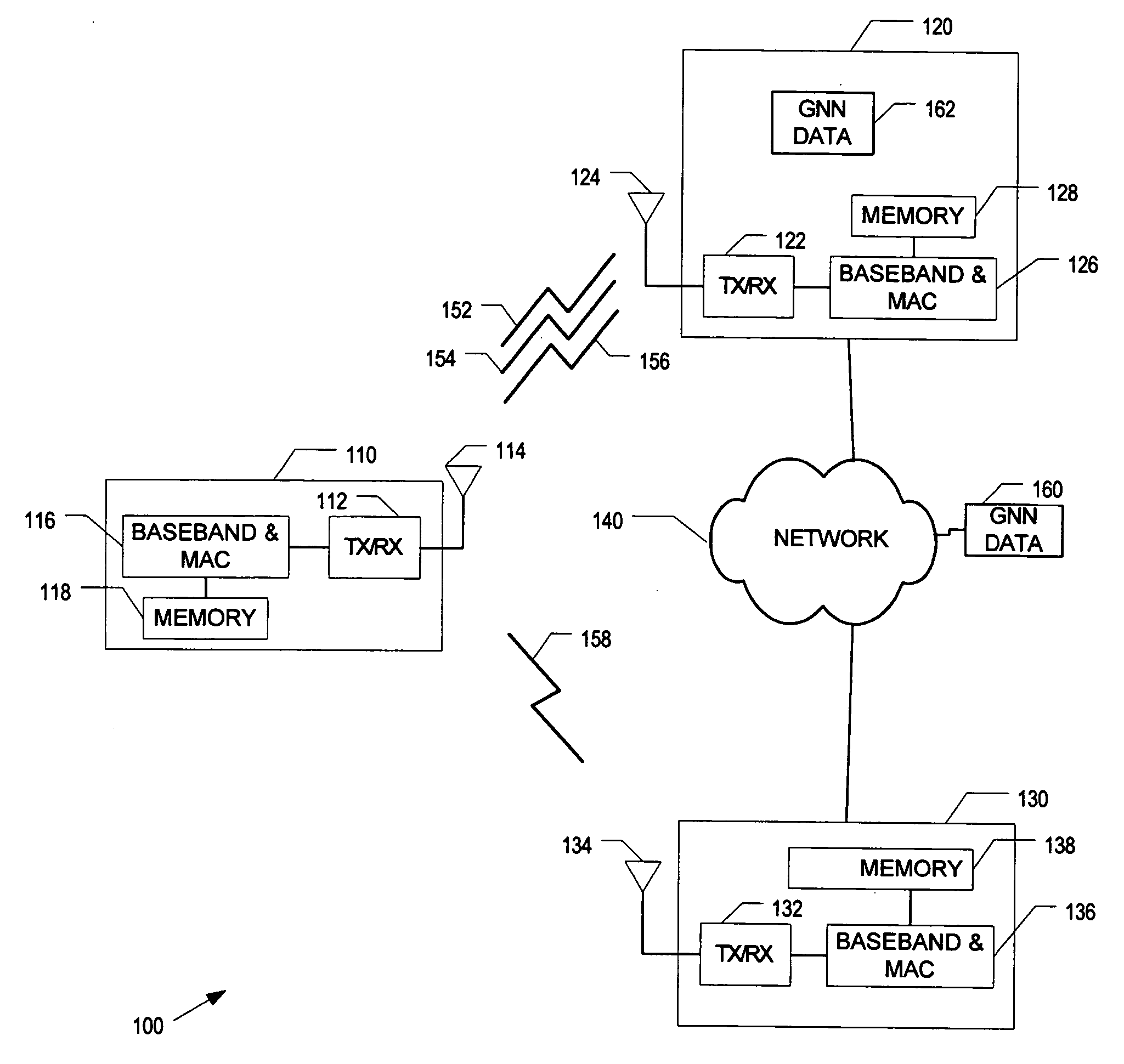
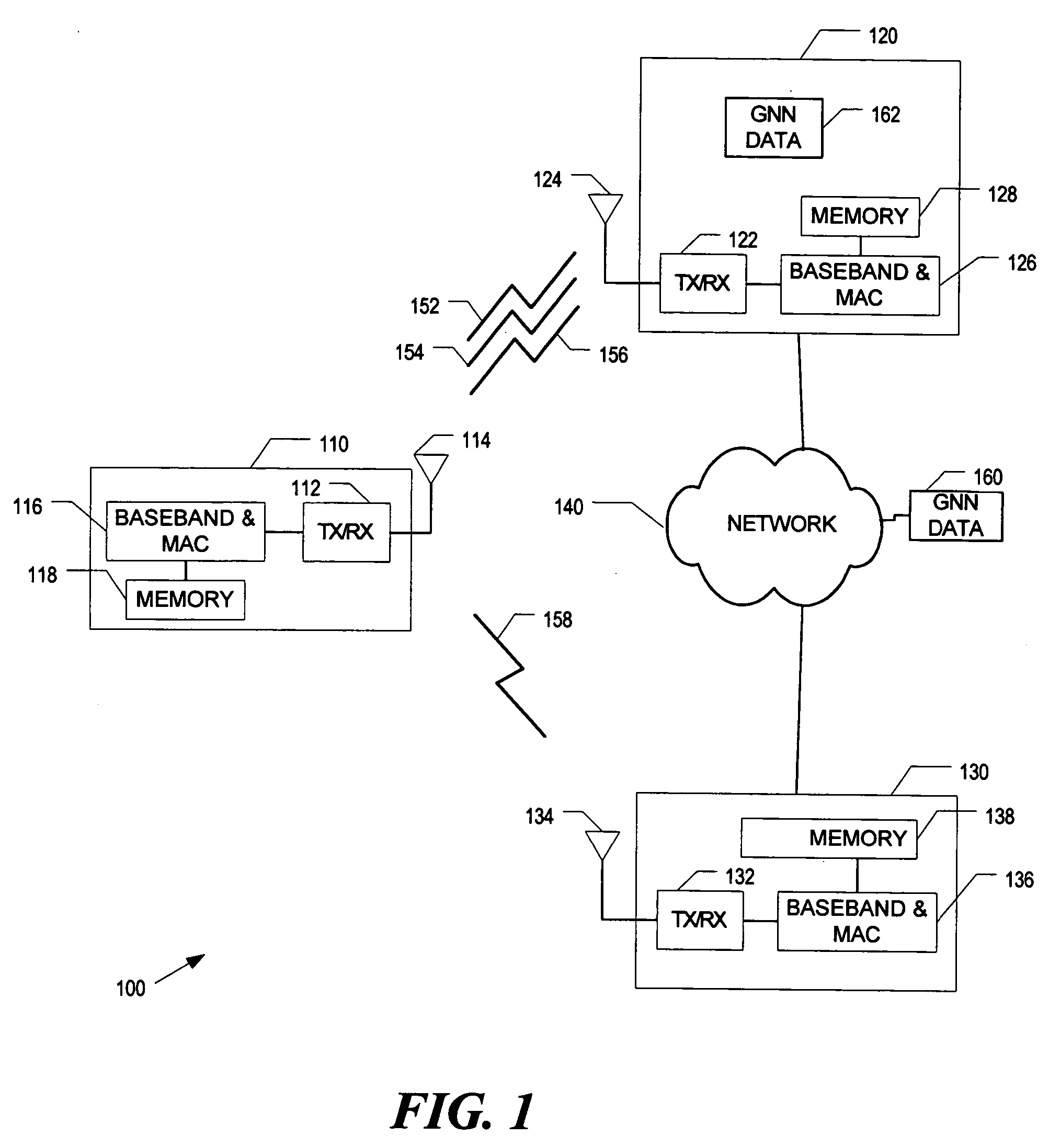
An in-vehicle device data communicates with global network based data processing resources for the purpose of transacting e-commerce and e-business. The in-vehicle device and the global network based data processing resources can effectuate a wide variety of e-commerce and e-business including accessing auto part databases, warranty, customer, and other remote databases. In addition, e-commerce and e-business transactions can include vehicle security and vehicle service management, data communicating Internet based radio, audio, MP3, MPEG, video, and other types of data. Furthermore, e-commerce and e-business transactions can include interactive advertising, promotional offers, coupons, and supporting other remote data communications.Furthermore, the in-vehicle device can also effectuate remote monitoring of vehicle performance, data communicating and accessing remote global network based content and data, and effectuating adjustments and control of vehicle operation. Remote monitoring and control of vehicle operation can be by way of a global network based data processing resources.
Owner:USA TECH INC
Motion tracking and analysis apparatus and method and system implementations thereof
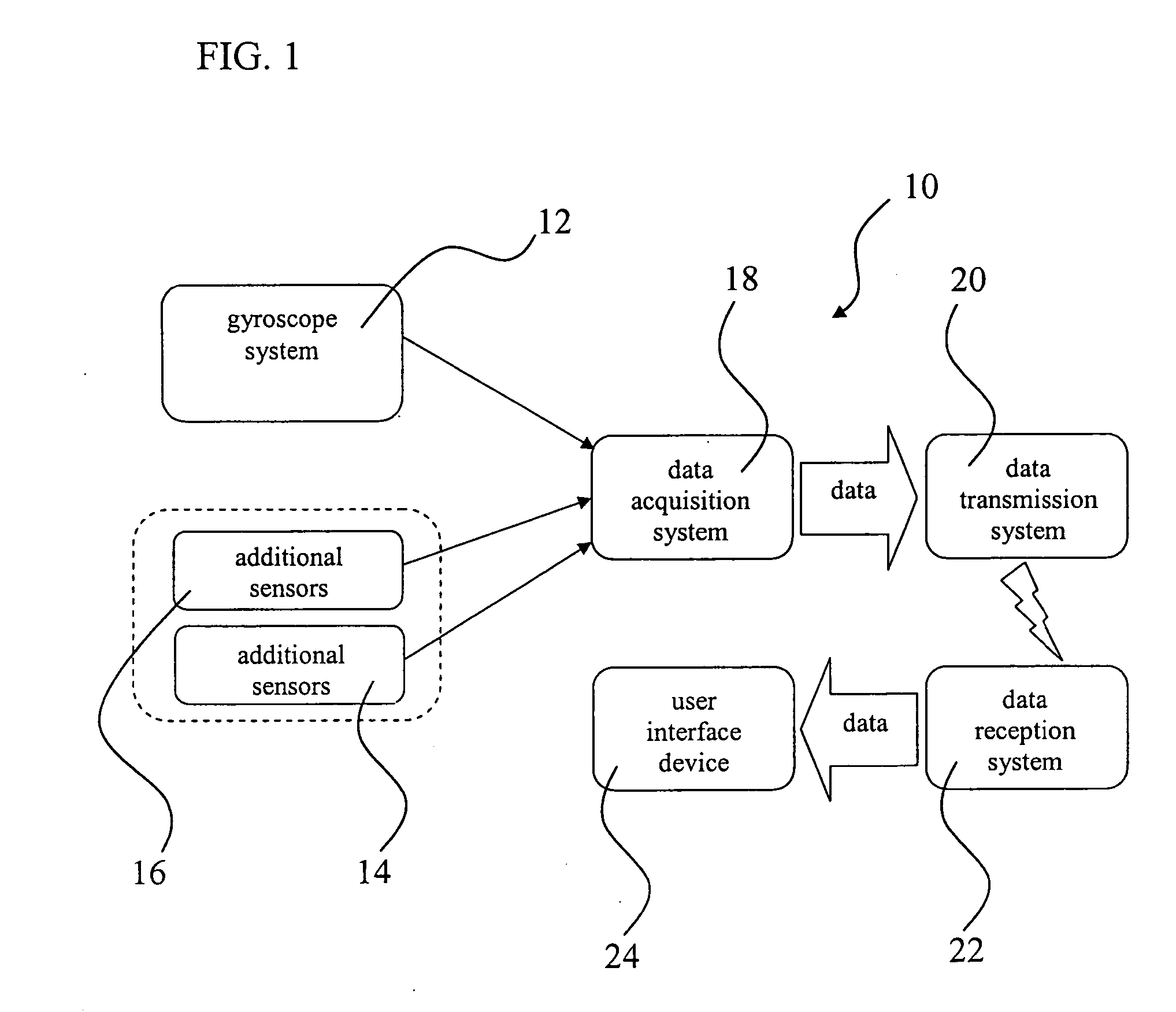
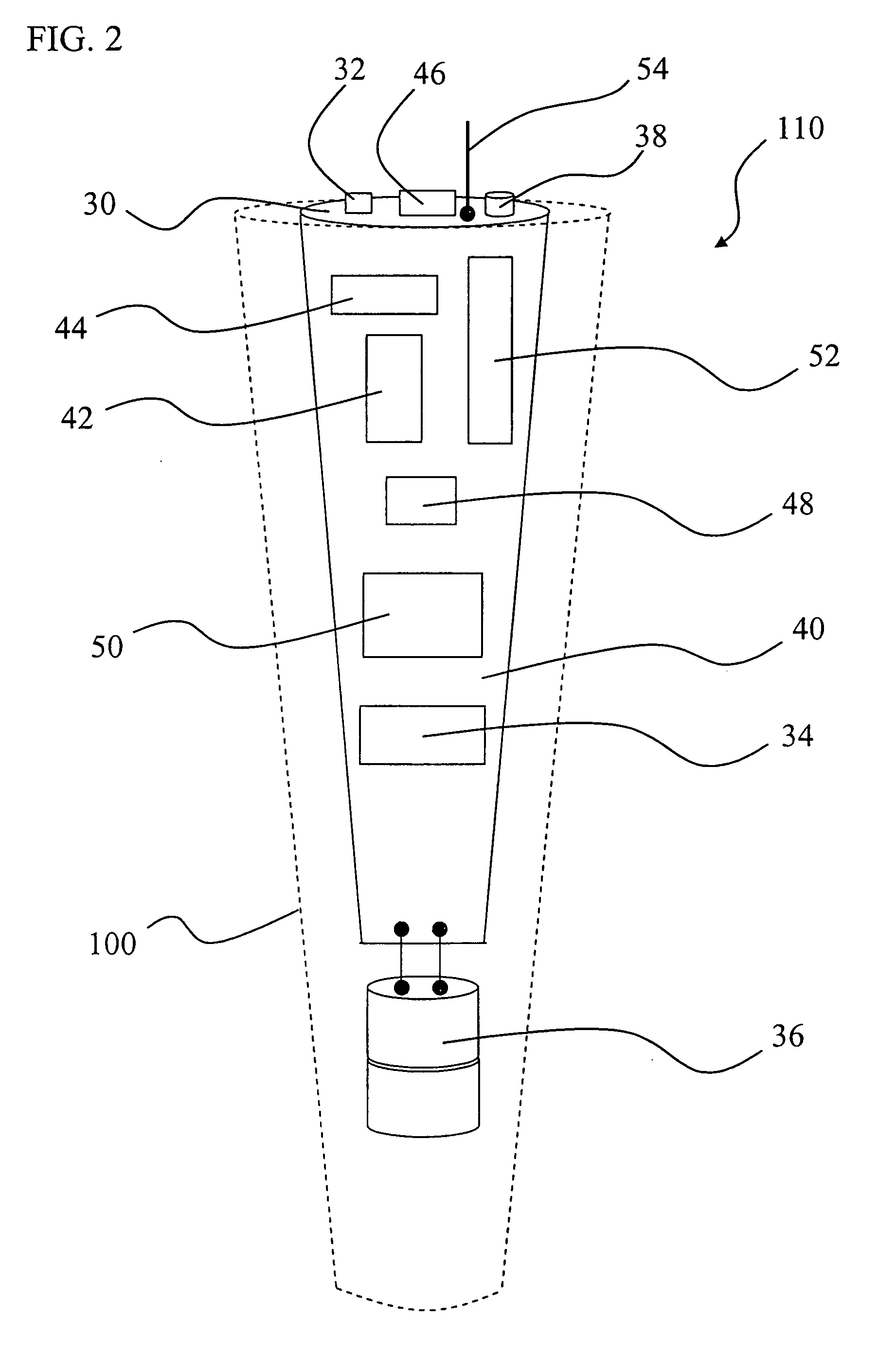
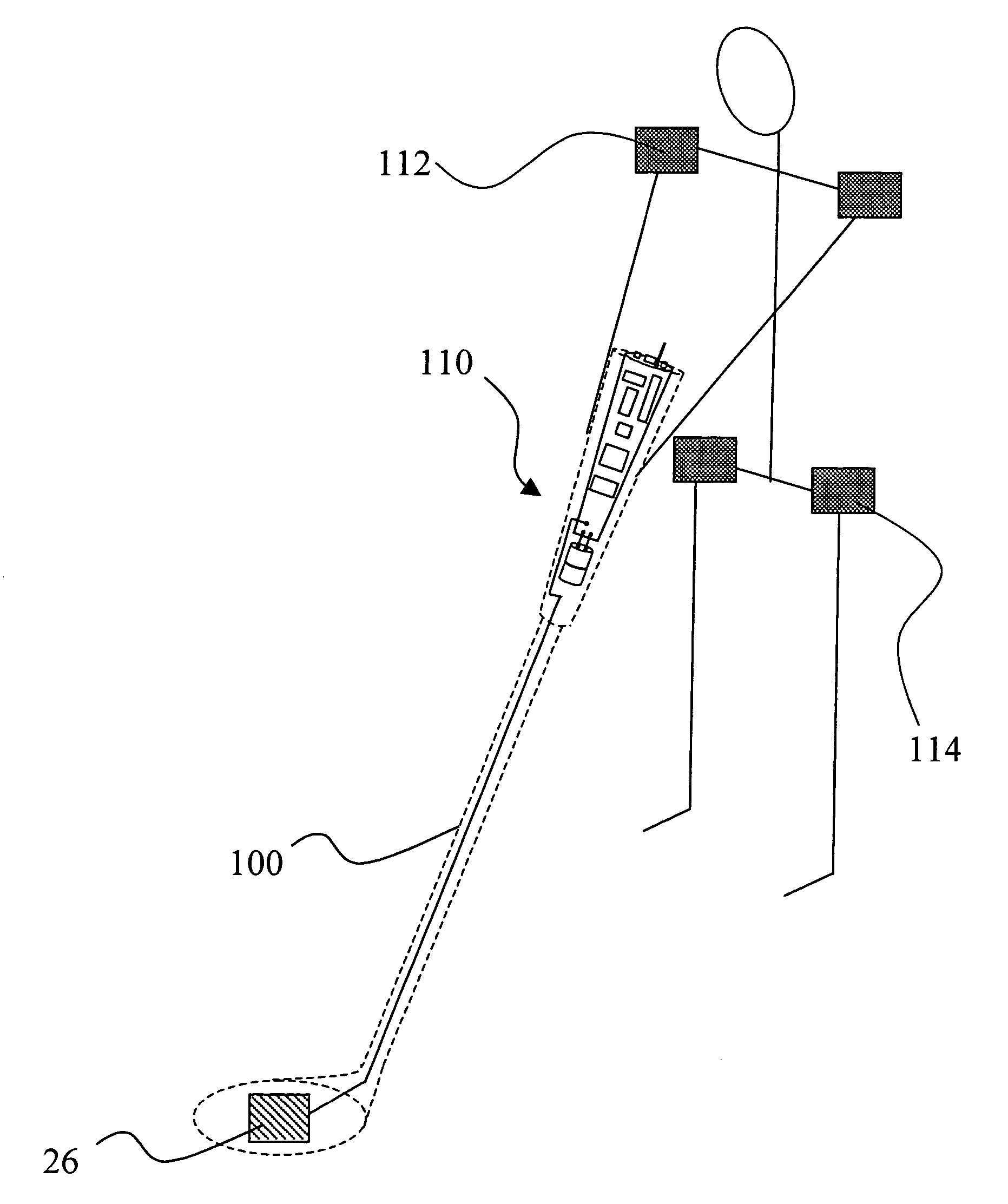
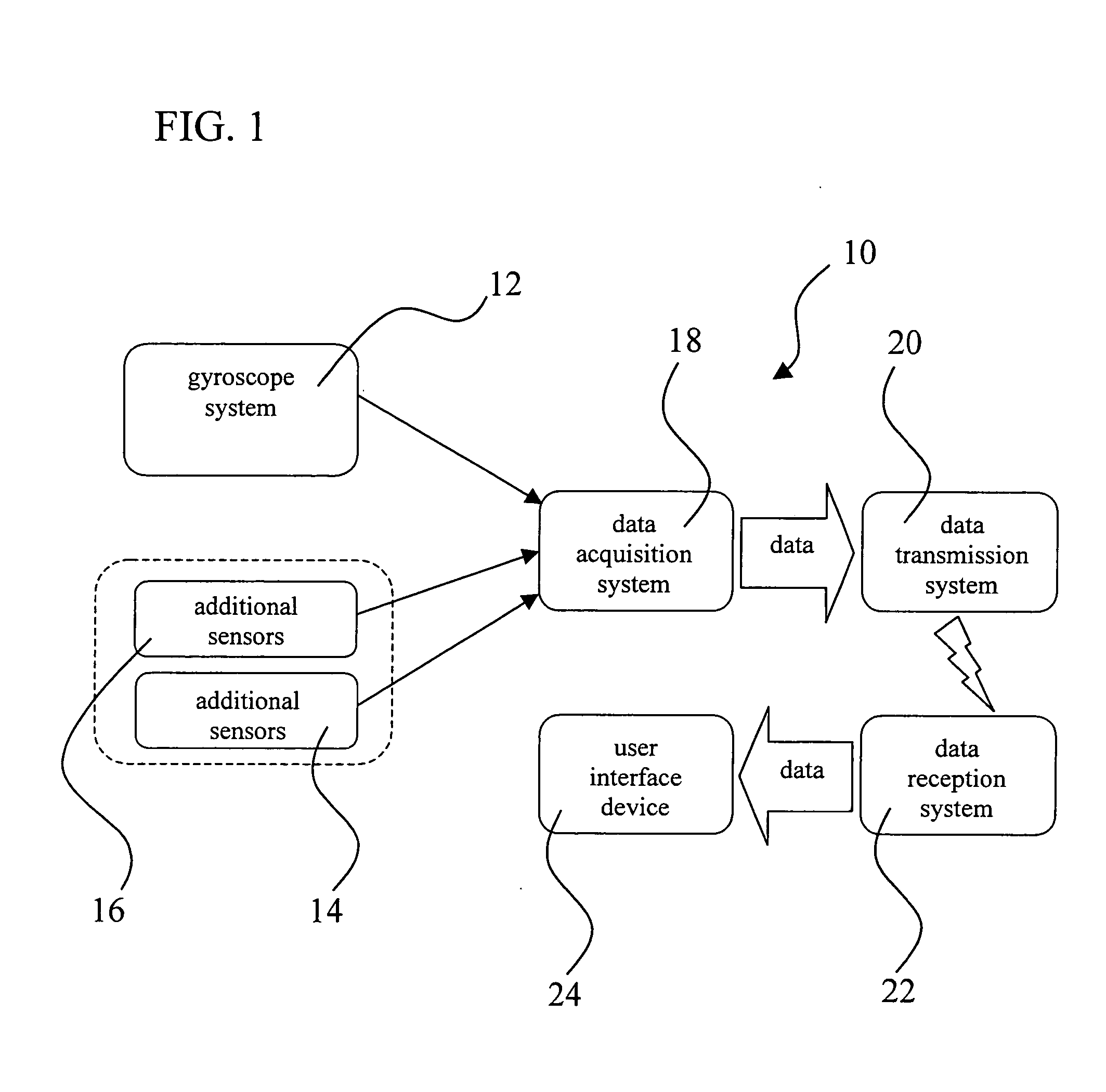
An orientation and position tracking system and method in three-dimensional space and over a period of time utilizing multiple inertial and other sensors for determining motion parameters to measure orientation and position of a moveable object. The sensors, for example vibrational and angular velocity sensors, generate signals characterizing the motion of the moveable object. The information is received by a data acquisition system and processed by a microcontroller. The data is then transmitted to an external data reception system (locally based or a global network), preferably via wireless communication. The information can then be displayed and presented to the user through a variety of means including audio, visual, and tactile. According to various embodiments, the present invention provides for a motion tracking apparatus and method for implementation in motion systems including systems to teach motion to a group and for body motion capture and analysis systems.
Owner:FORTESCUE CORP
Method and apparatus for determining orientation and position of a moveable object
InactiveUS20050032582A1Gymnastic exercisingNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsMicrocontrollerObject motion
An orientation and position tracking system in three-dimensional space and over a period of time utilizing multiple inertial and other sensors for determining motion parameters to measure orientation and position of a moveable object. The sensors, for example vibrational and angular velocity sensors, generate signals characterizing the motion of the moveable object. The information is received by a data acquisition system and processed by a microcontroller. The data is then transmitted via wireless communication to an external data reception system (locally based or a global network). The information can then be displayed and presented to the user through a variety of means including audio, visual, and tactile.
Owner:FORTESCUE CORP
Global network based vehicle safety and security telematics
InactiveUS6853894B1Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesCommand and controlIn vehicle
The present invention relates to a global network based vehicle safety and security system and method. In this regard, a global network based data processing resource can wirelessly data communicate with an in-vehicle device to control and monitor vehicle safety and security. In addition, data communicated between the vehicle and global network based data processing resources can control, monitor, and track the vehicle as well as data communicate command and control functions, such as disabling vehicle operation. Furthermore, alarm and alerting functions can effectuate the notification of other data processing resources and or other agency or emergency resources.Vehicle and in-vehicle device data, including safety and security data gathered at data processing resources can be utilized to effectuate a wide variety of data dissemination. Such data dissemination can include warning, alarm, safety, or security determinations, and or other reporting or analysis related to vehicle safety and or security.
Owner:USA TECH INC
Access and control system for network-enabled devices
InactiveUS7120692B2Reduce computational overheadReduce communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlControl systemSecure transmission
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Transparent, look-up-free packet forwarding method for optimizing global network throughput based on real-time route status
ActiveUS20040032856A1Fast protection re-routingEfficient multicastingData switching by path configurationPrivate networkOSI model
A packet forwarding method for optimizing packet traffic flow across communications networks and simplifying network management. The invention provides look-up-free and packet-layer-protocol transparent forwarding of multi-protocol packet traffic among Layer-N (N=2 or upper in the ISO OSI model) nodes. The invention enables flexible and efficient packet multicast and anycast capabilities along with real-time dynamic load balancing and fast packet-level traffic protection rerouting. Applications include fast and efficient packet traffic forwarding across administrative domains of Internet, such as an ISP's backbone or an enterprise virtual private network, as well as passing packet traffic over a neutral Internet exchange facility between different administrative domains.
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
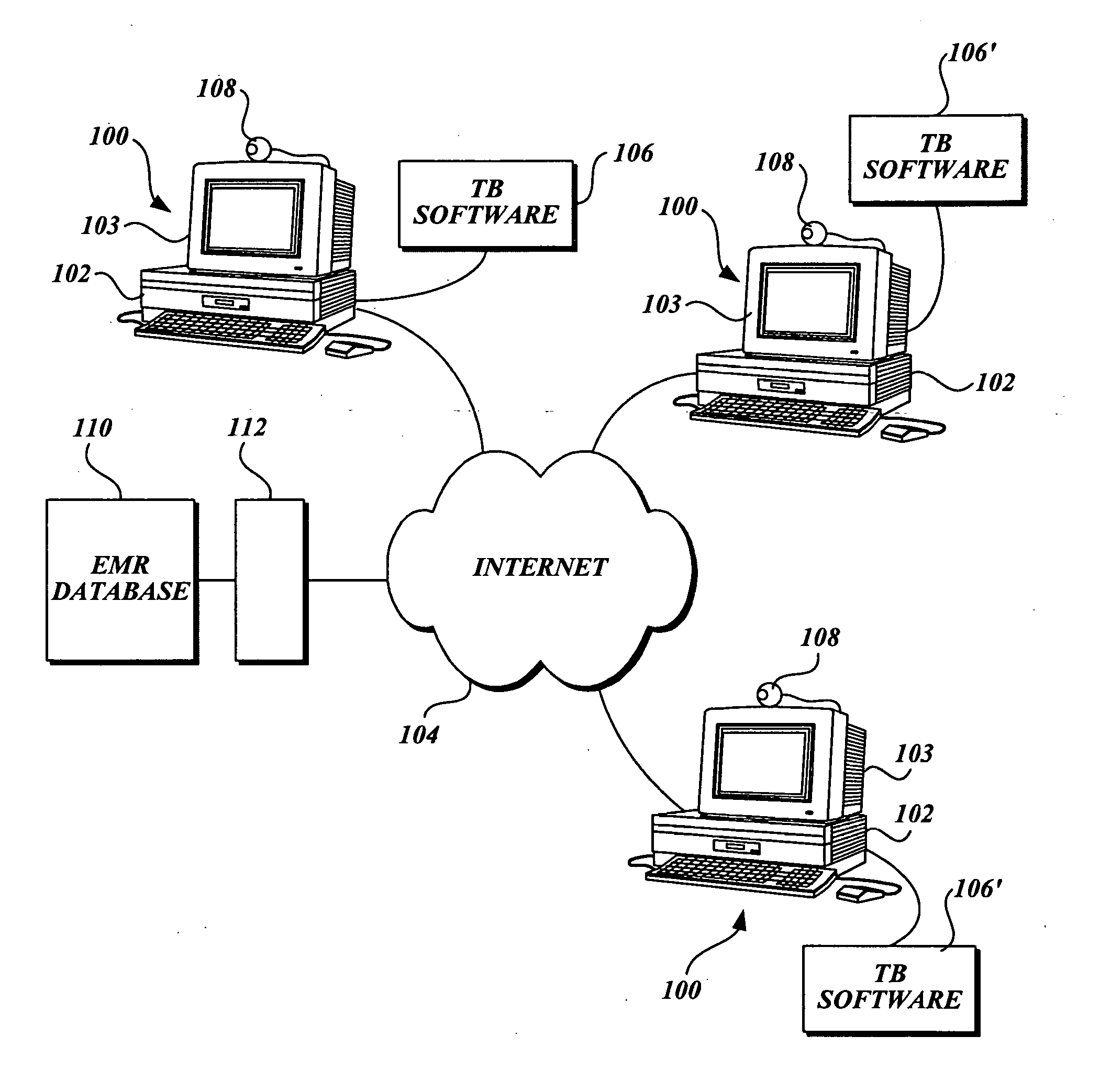
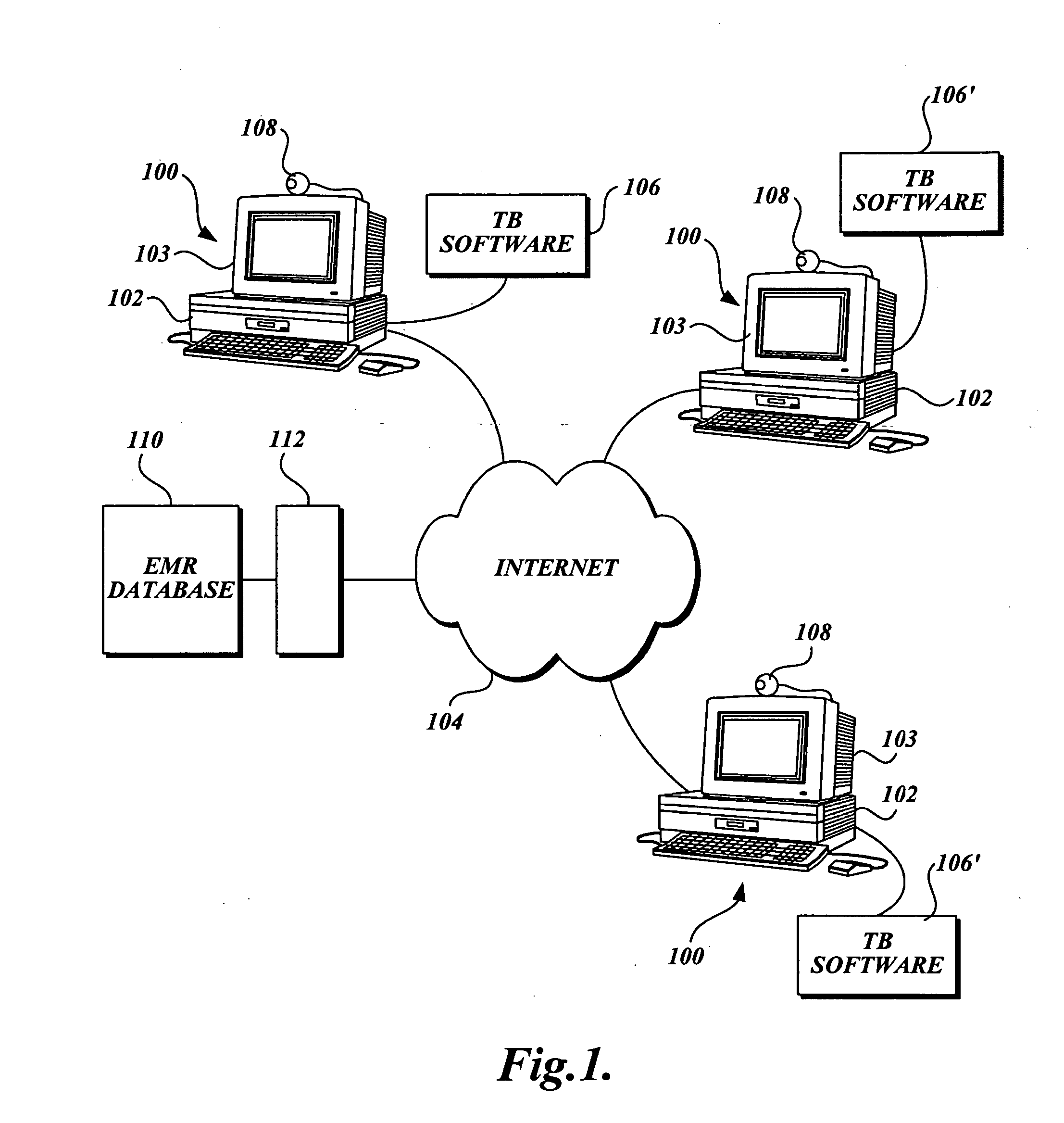
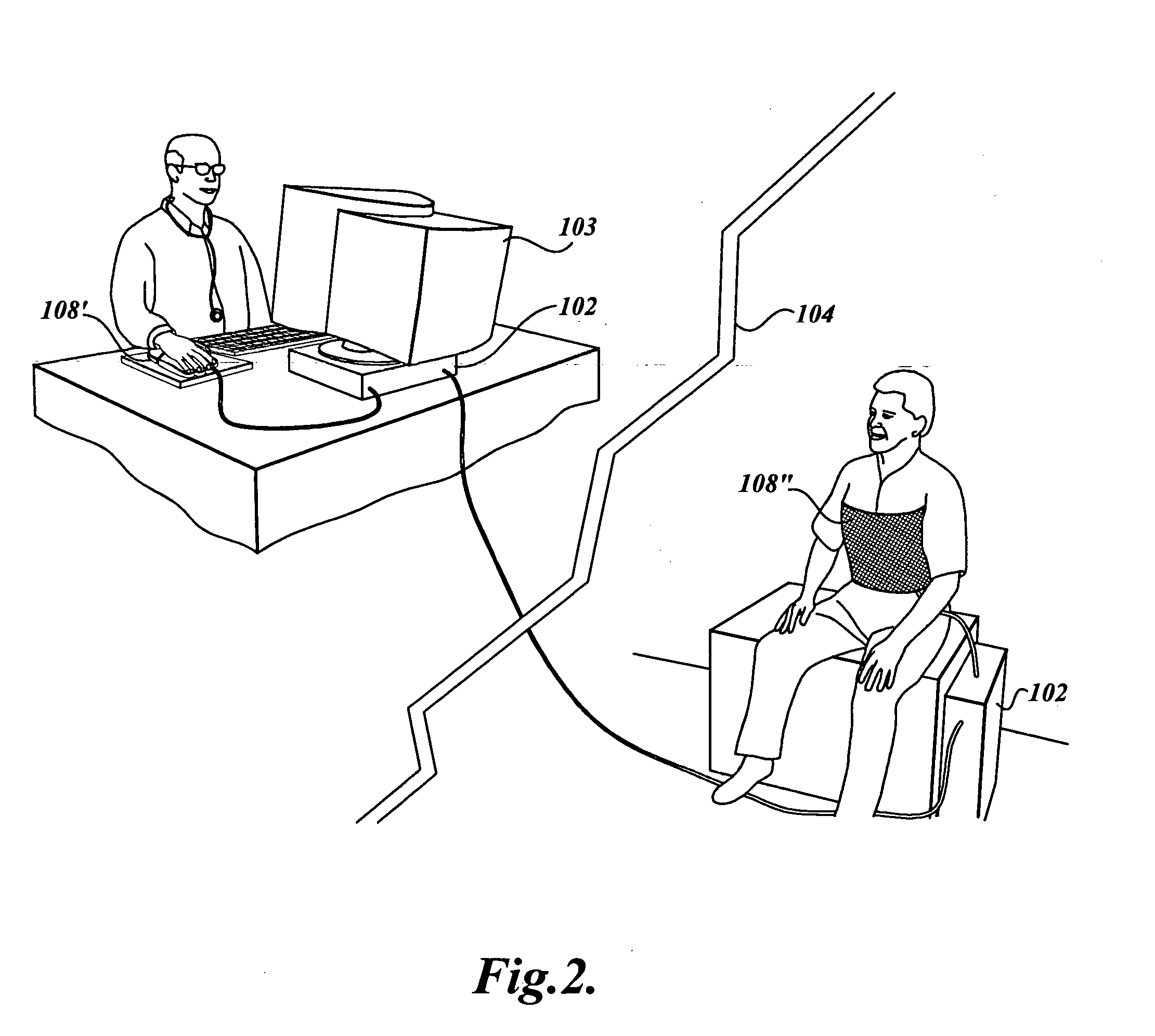
Multifunction telemedicine software with integrated electronic medical record
InactiveUS20050149364A1Input/output for user-computer interactionDiagnostic recording/measuringMedical recordElectronic medical record
A teleconferencing system is disclosed that enables patient and physician teleconferencing stations (100) to communicate over a global network (104), wherein the teleconferencing stations include access to a database of electronic medical records (110). The system includes means for instant text messaging (130), audio / video conferencing (142), and secure e-mail exchange (146). The patient and physician have differential access to the electronic medical records, such that the electronic medical records can be updated. The physician station includes means for capturing image data received from the patient station and storing the captured image data into a medical record. In the preferred embodiment the system is able to teleconference more than two stations at a time. In the preferred embodiment, the physician station includes means for entering a prescription (310) and for entering hospital orders (304).
Owner:CEL KOM LLC
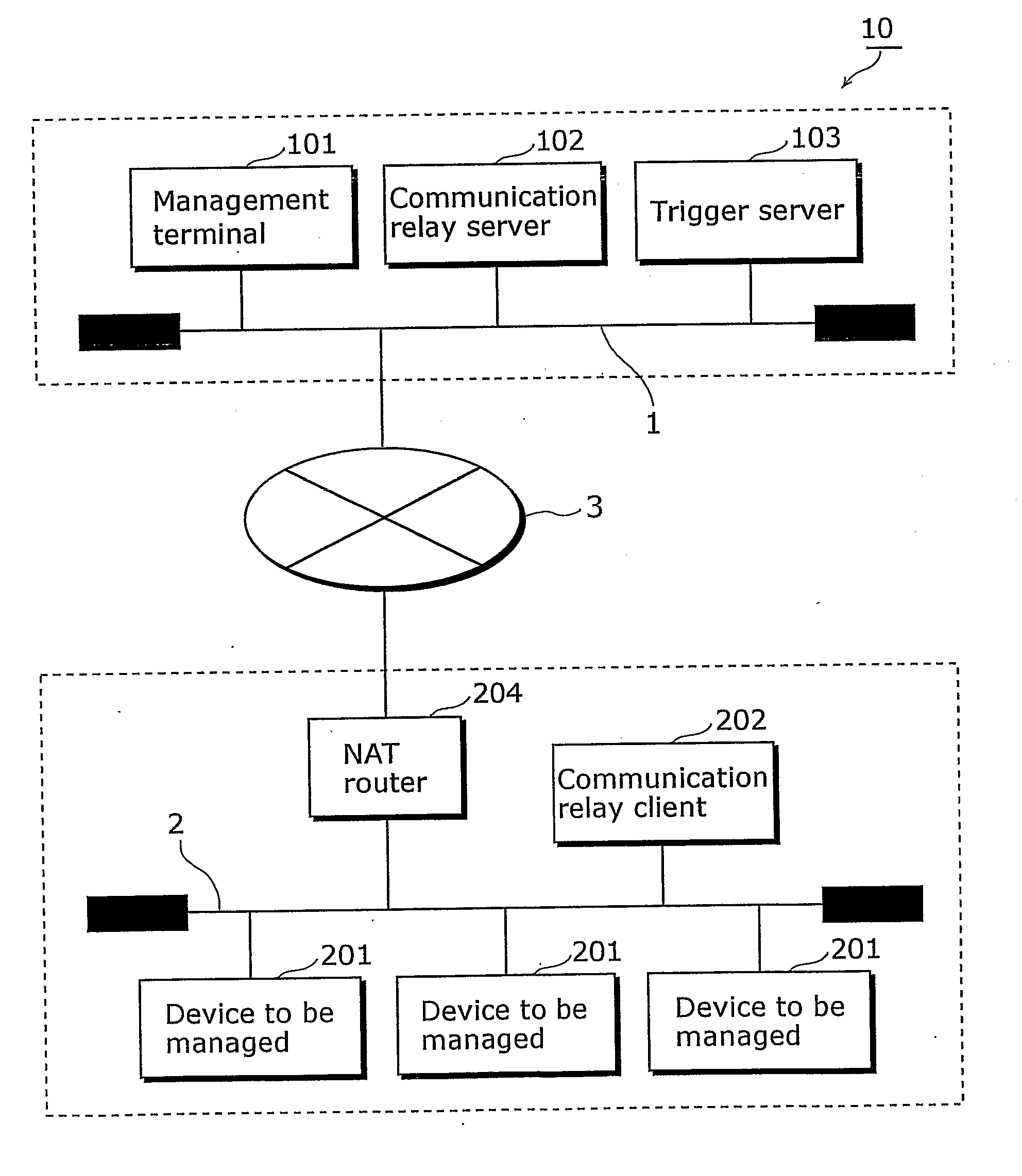
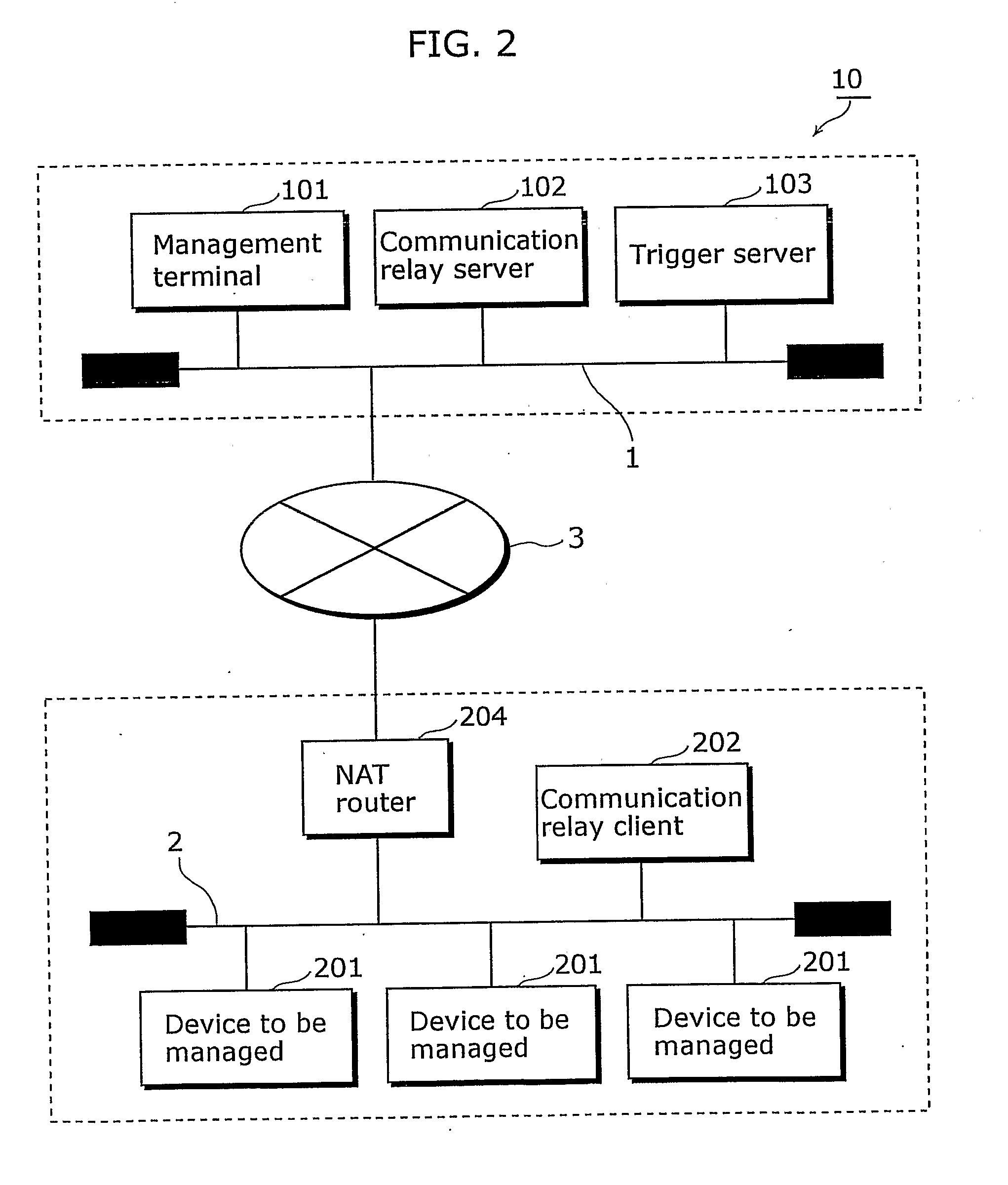
Communication network system and communication apparatus
InactiveUS20070147419A1Secure performanceSpecial service provision for substationTime-division multiplexNetwork onNetworked system
The present invention provides a communication network system in which communication can be securely performed via a global network from an existing terminal apparatus to an existing device connected to a local network without needing a special gateway function in a router and without performing a special setting in the router. In the communication network system (10), a communication relay client (202) performs polling on a management center network (1) via a NAT router (204); a communication relay server (102) converts a packet transmitted from a management terminal (101); and the communication relay client (202) receives the converted packet as a response to the polling via the NAT router (204) from the side of the management center network (1). The communication relay client (202) converts the converted packet to the original packet, and transmits the original packet to a device to be managed (201).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
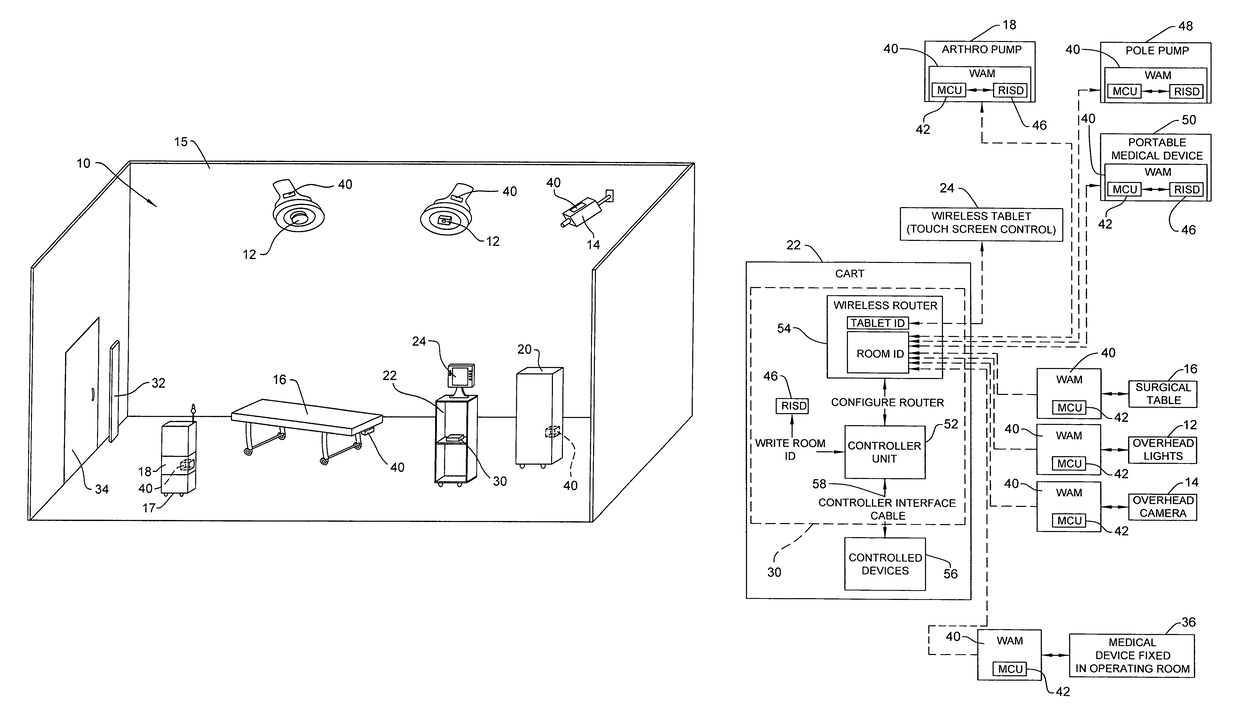
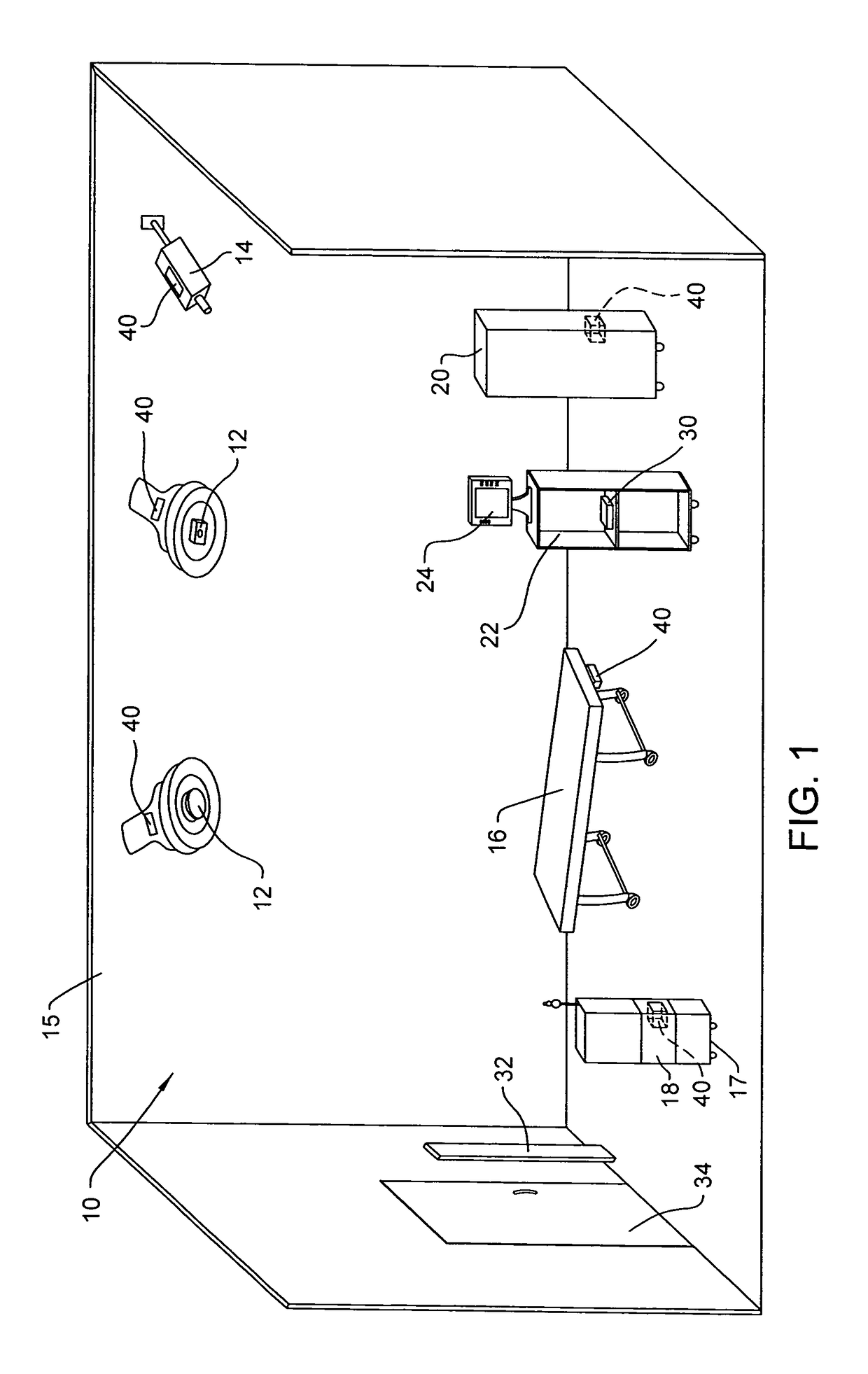
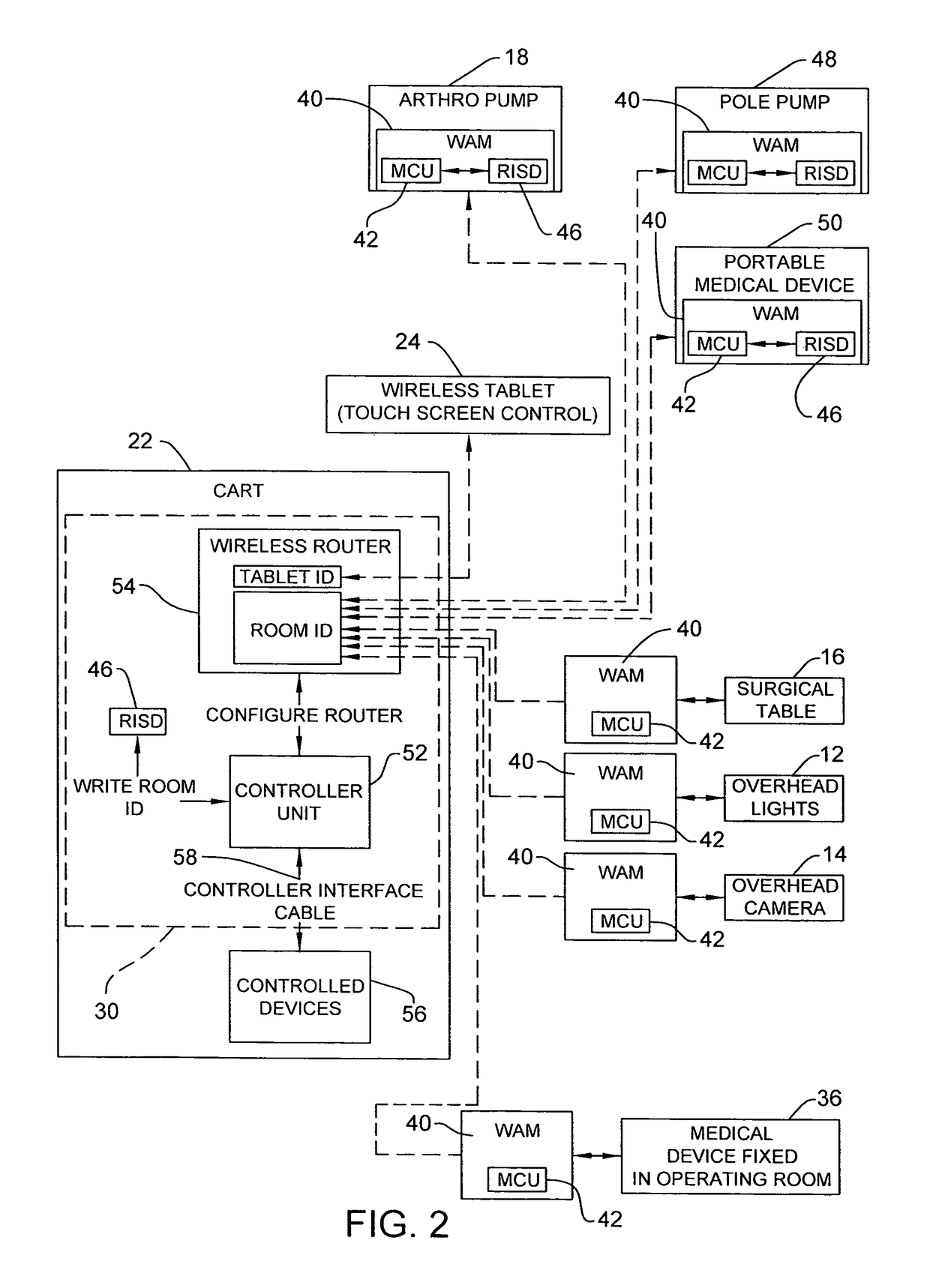
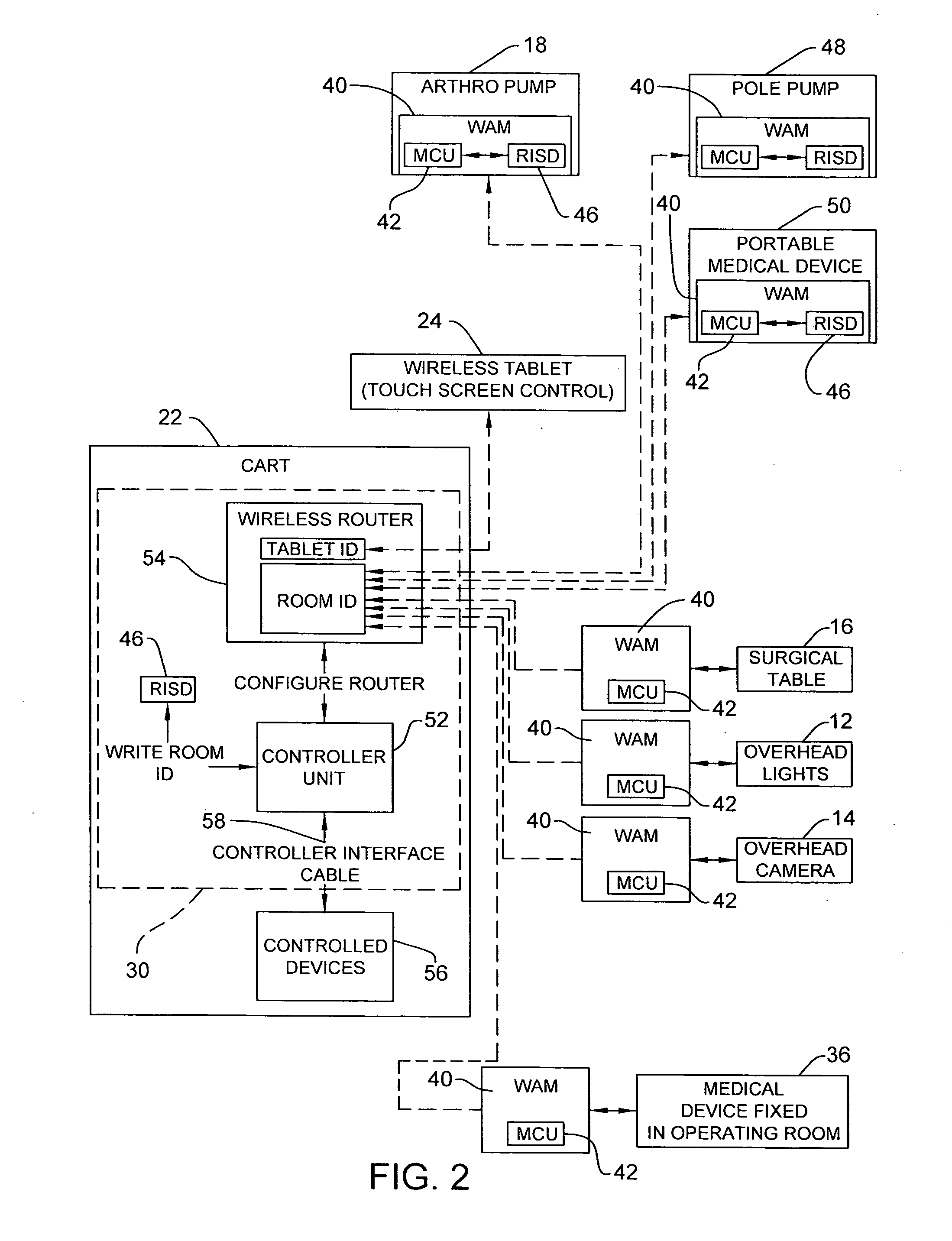
Wireless medical room control arrangement for control of a plurality of medical devices
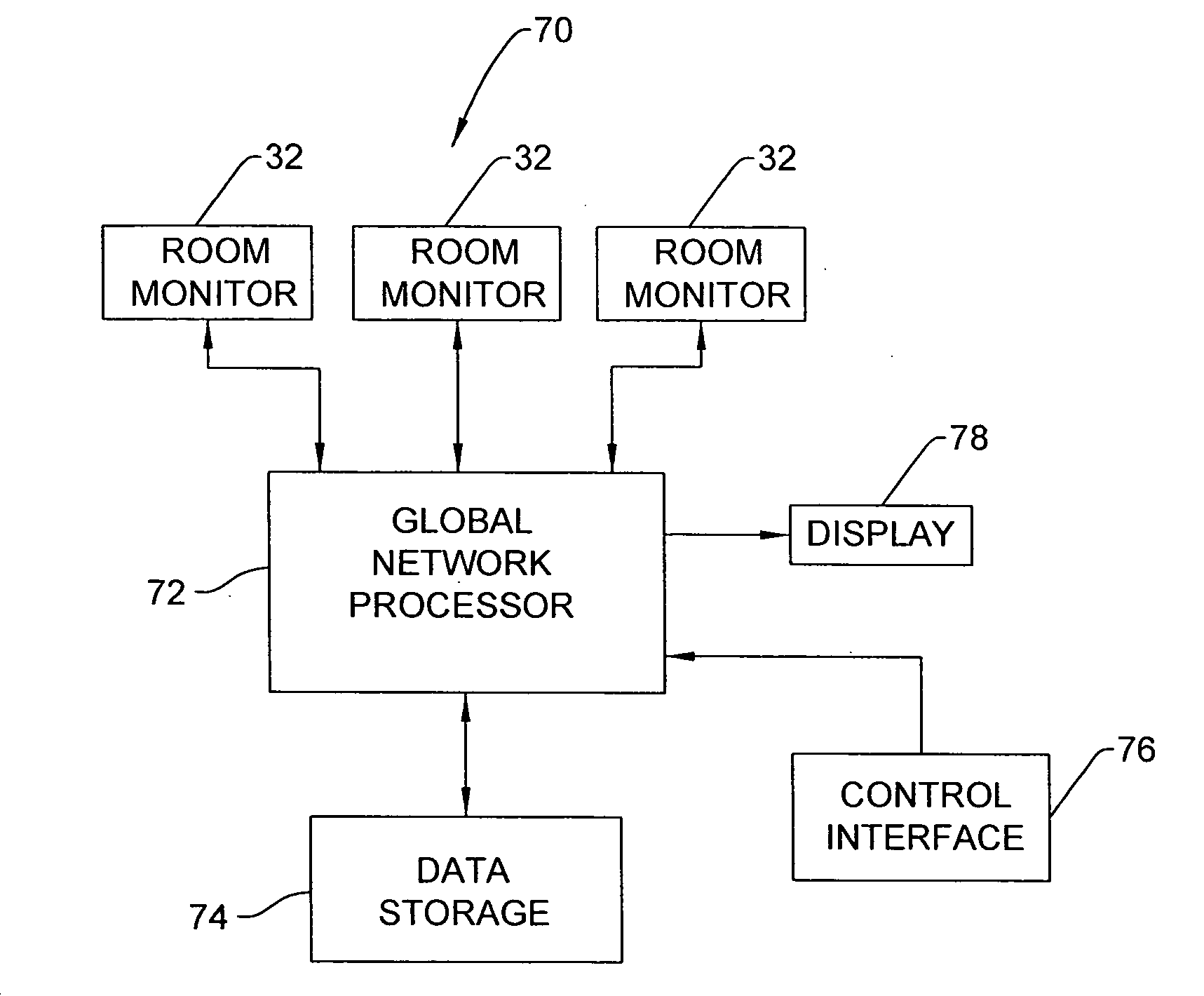
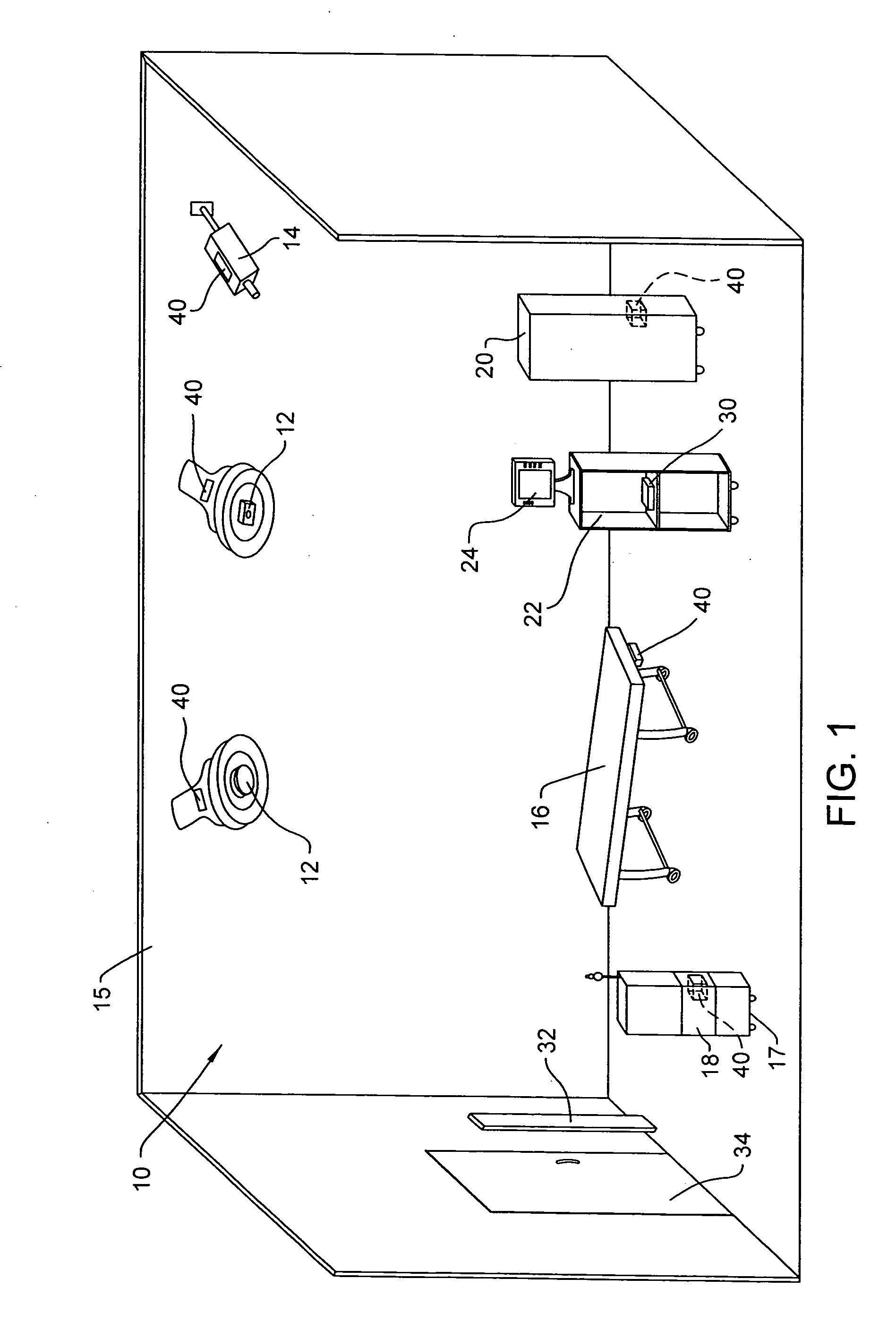
A wireless medical room control arrangement includes a wireless controller having a wireless router. A room identifier and a device identifier are stored in the controller. A communication interface sends commands to and receives commands from the wireless controller. In response to commands from the interface, the wireless controller sends wireless control signals to operate medical devices in the room. A room monitor adjacent a doorway provides room identifiers to medical devices and wireless controllers entering the room and provides dummy identifiers to medical devices and controllers exiting the room. The room monitors may connect to a global network processor that determines the location of the medical devices in a medical facility.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
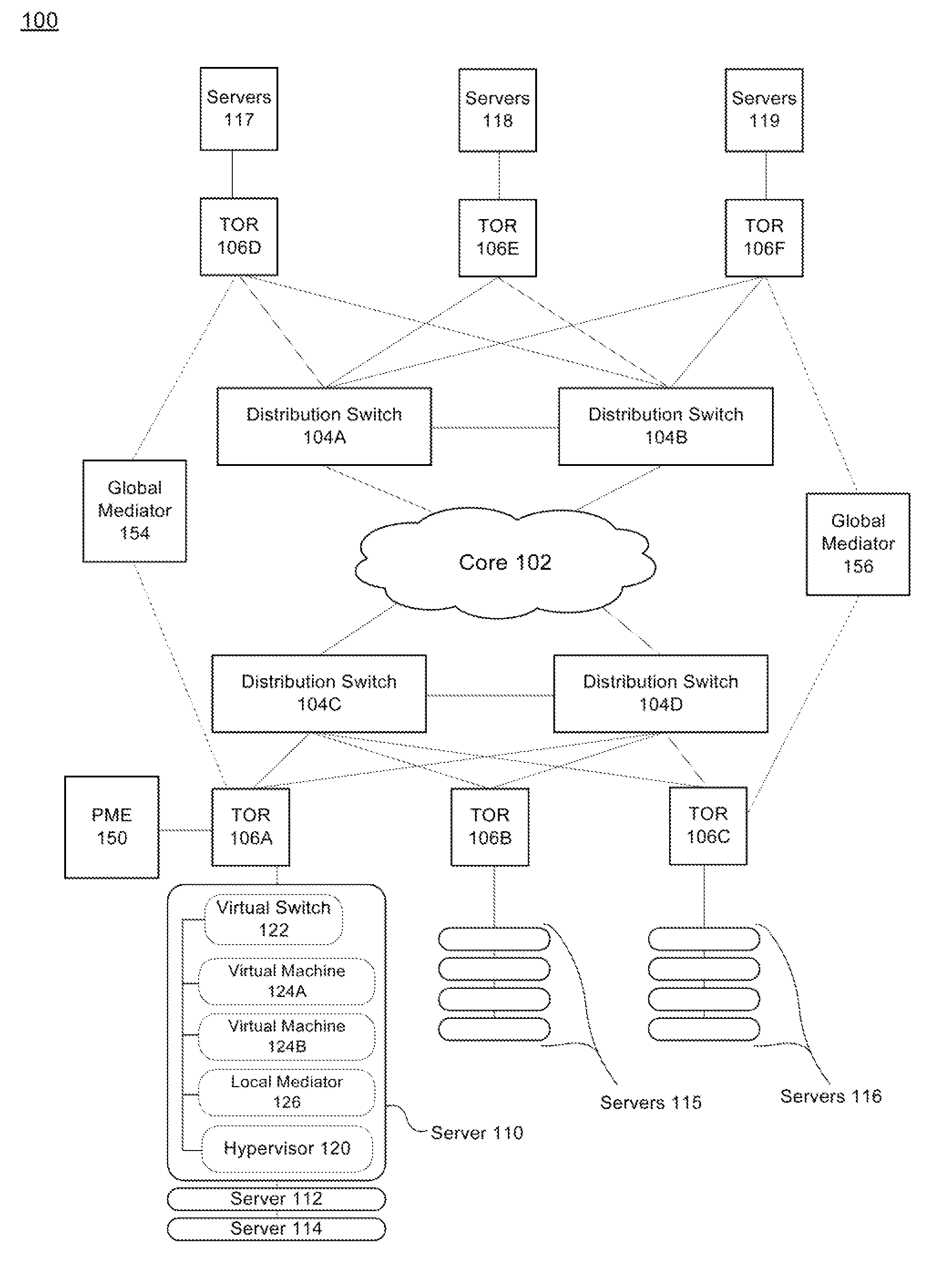
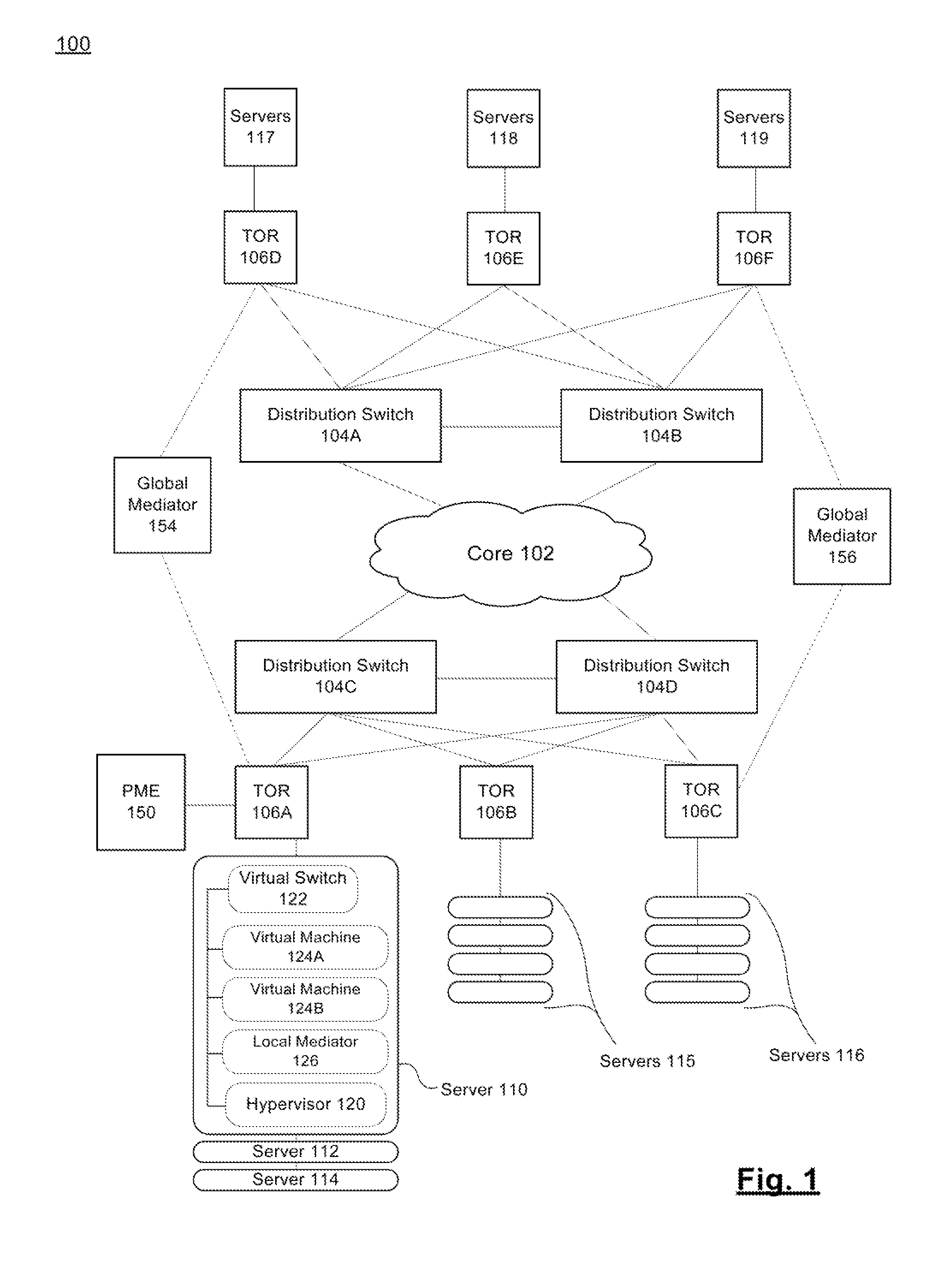
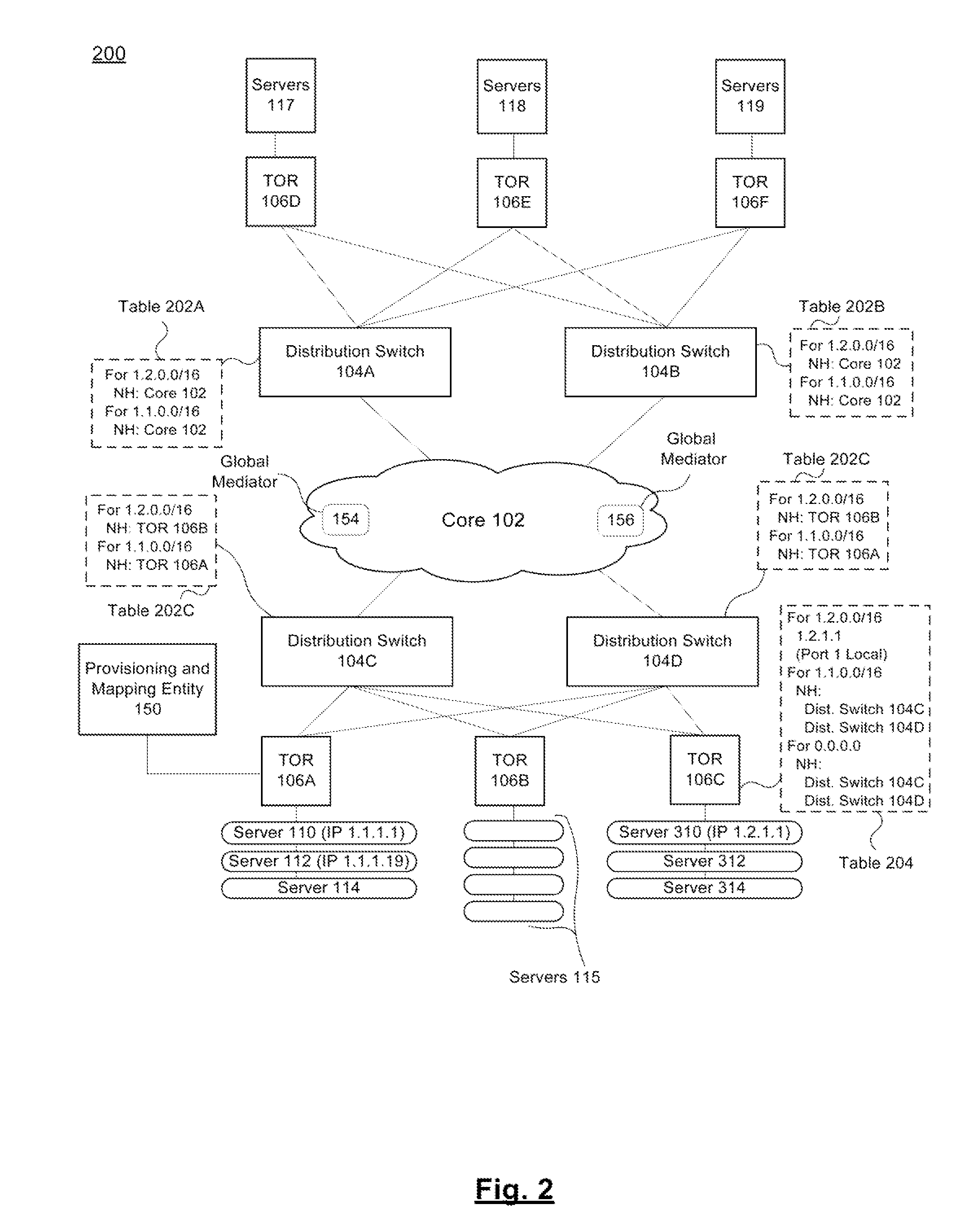
Systems and methods for a data center architecture facilitating layer 2 over layer 3 communication
ActiveUS20150030024A1Data switching by path configurationProgram controlNetwork addressGlobal network
An information handling system is provided. The information handling system includes a plurality of core devices coupled to each other and to a plurality of distribution devices and a plurality of top-of-rack devices coupled to a plurality of servers and to the distribution devices. The plurality of servers are running hypervisors thereon that each manage a virtual switch and a plurality of virtual machines (VMs). The information handling system further includes a plurality of local network address resolution mediators, with each local network address resolution mediator running on one of the plurality of servers and receiving packets from VMs running thereon, and a global network address resolution mediator running on one of the plurality of core devices. The global network address resolution mediator is in communication with each of the plurality of local network address resolution mediators to collect and distribute packets from the plurality of VMs.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
Transparent, look-up-free packet forwarding method for optimizing global network throughput based on real-time route status
ActiveUS7254138B2Improve performanceFast and efficient packet-level traffic protection re-routingError preventionTransmission systemsPrivate networkOSI model
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
Distributed network control method and device
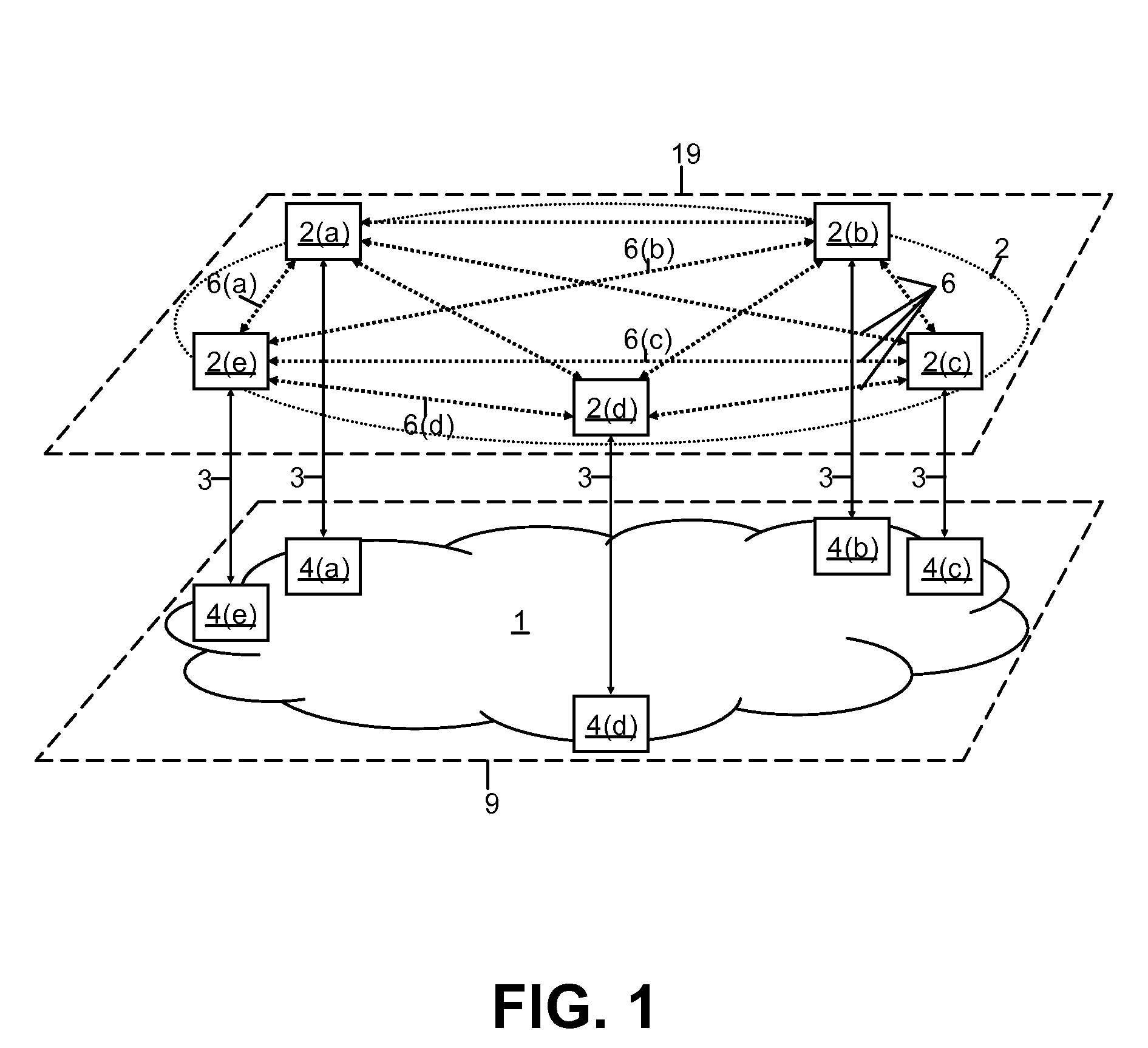
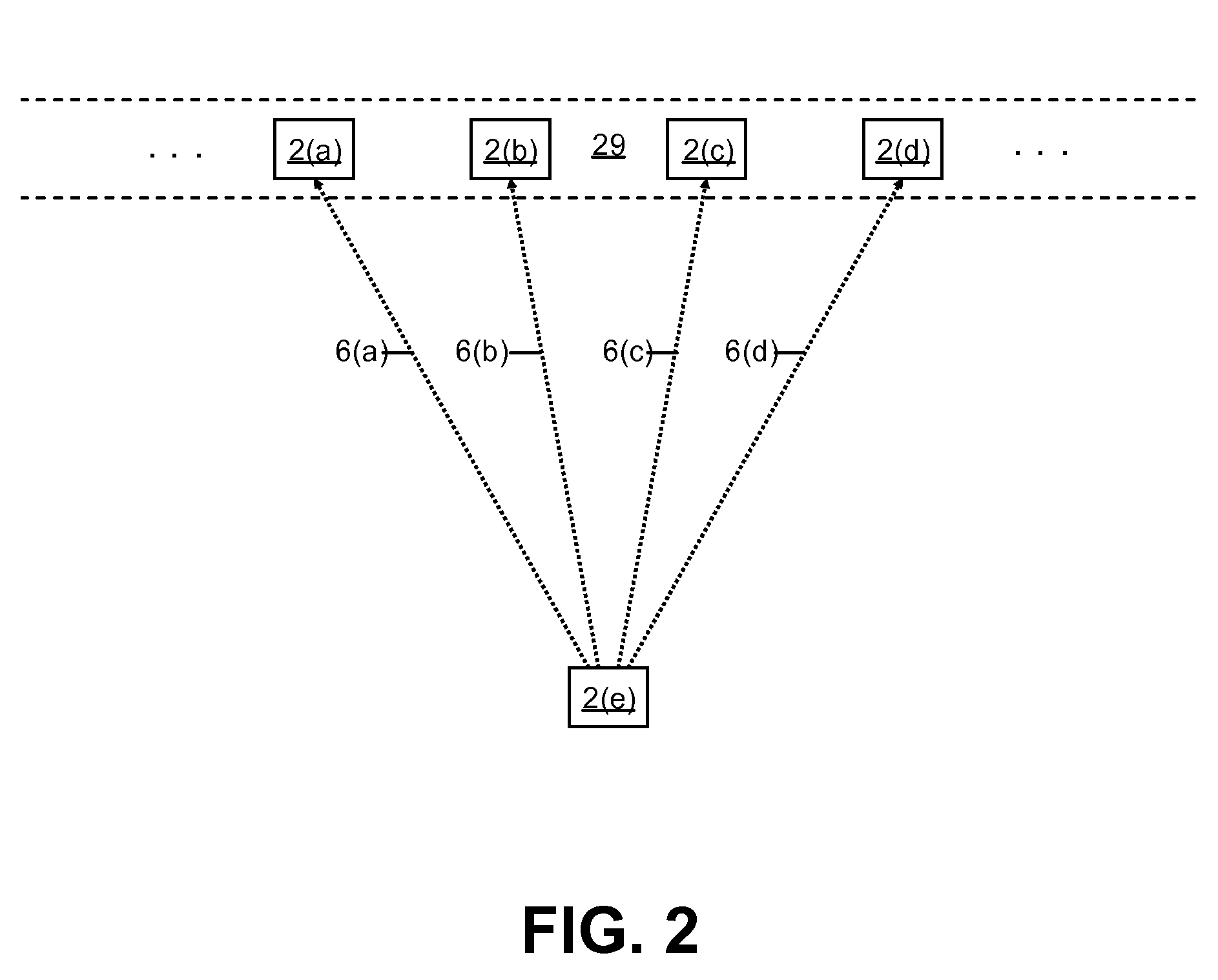
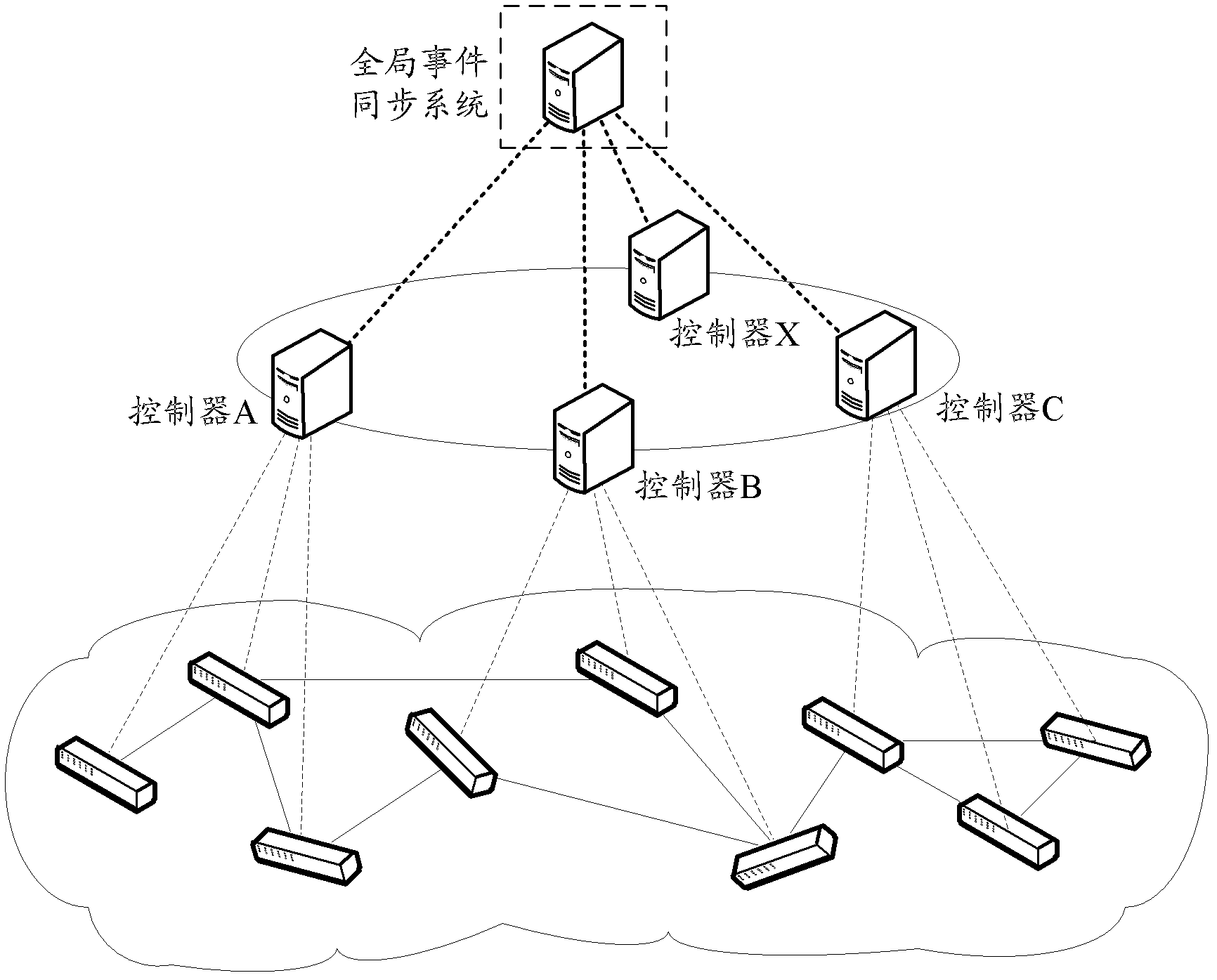
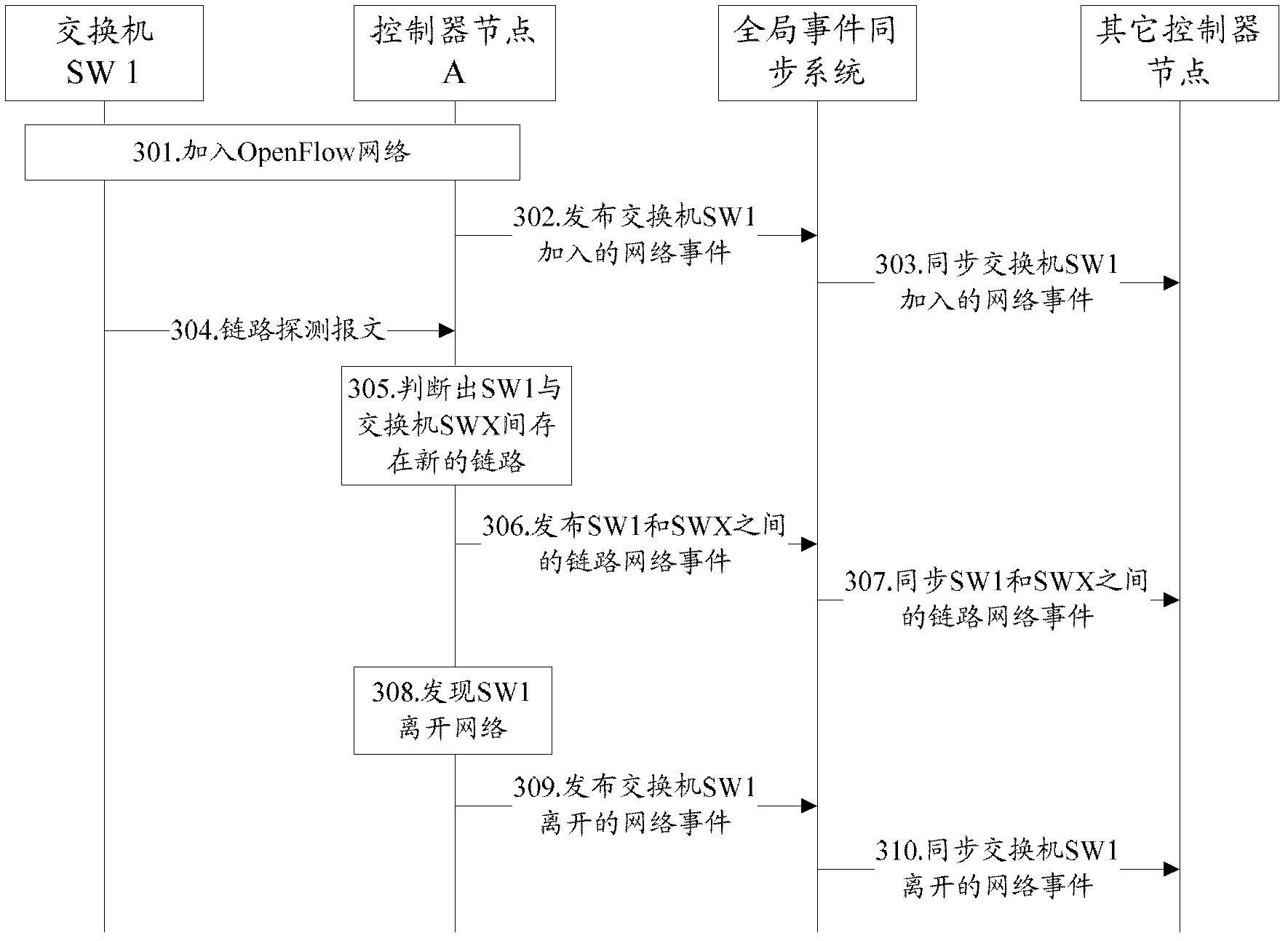
ActiveCN102594689AAvoid performance bottlenecksData switching networksTopology informationNetwork control
The invention discloses a distributed network control method. A plurality of controller nodes form a distributed controller network, and each controller node manages one or more pieces of switch equipment. The method comprises the following steps that: the controller node receives information reported by a switch, synchronizes network topology change information in the information among all the controller nodes, and stores host position information in the information into a distributed control network; and when receiving a data stream processing request, the controller node queries the destination address information of a data stream from the distributed controller network, and establishes a data exchange path for the data stream according to locally stored global network topology information. The invention also provides a distributed network control device. According to the technical scheme, the problem of performance bottleneck of a network controller can be solved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Global network neighborhood: scheme for providing information about available networks in a geographical location
InactiveUS20060092890A1Assess restrictionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsGeographic regionsDistributed computing
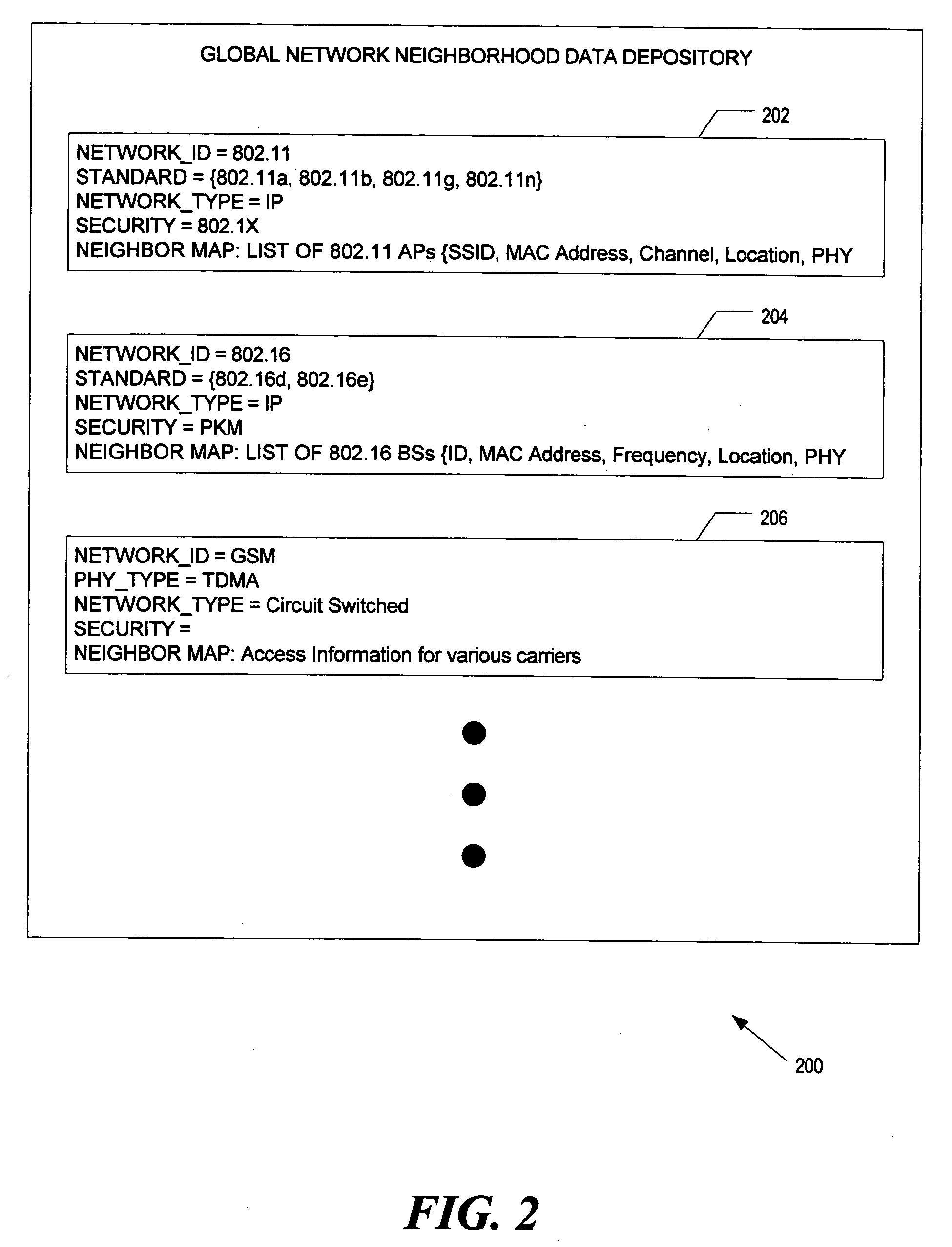
A method and apparatus supporting a discovery technique of multiple available networks is disclosed. A global network neighborhood data depository contains attributes of multiple networks that are available in a geographic region. The attributes aid in network discovery and selection of an optimum network for communication for devices capable of communicating via multiple networks.
Owner:INTEL CORP
System and method for integration of a universally publicly accessible global network
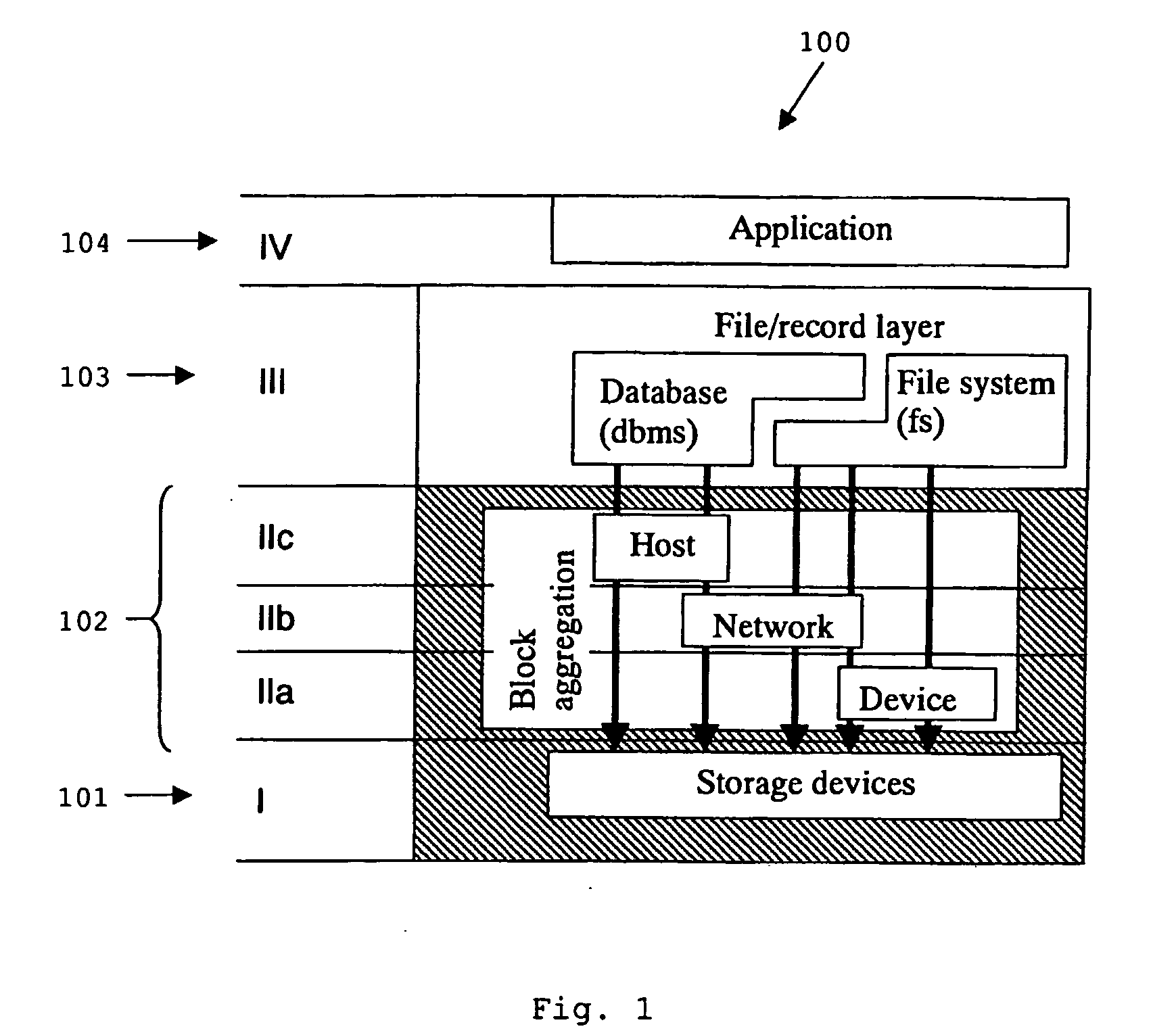
InactiveUS20050102374A1Improve efficiencySignificant financial magnitudeMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksIntegrated softwareApplication software
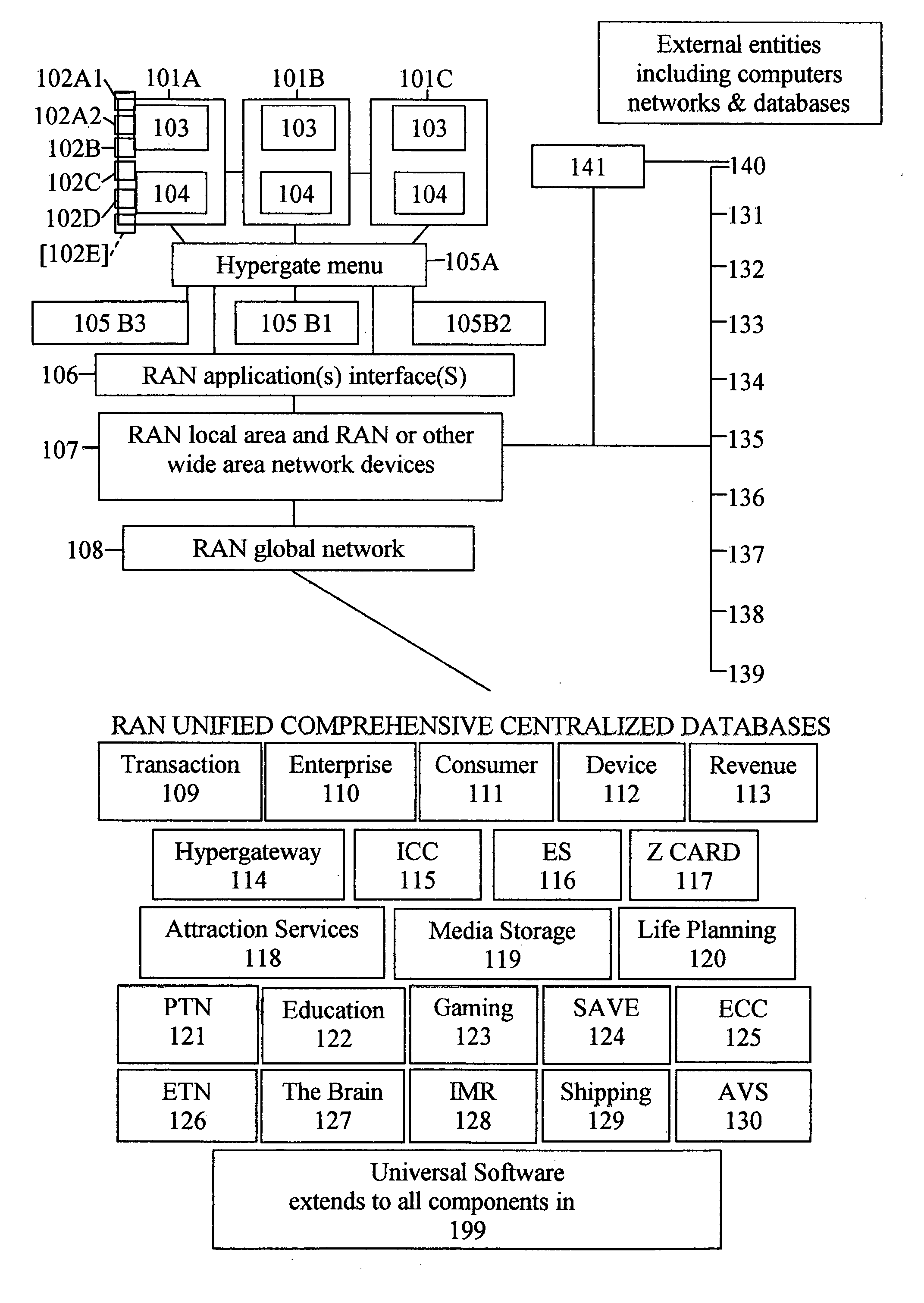
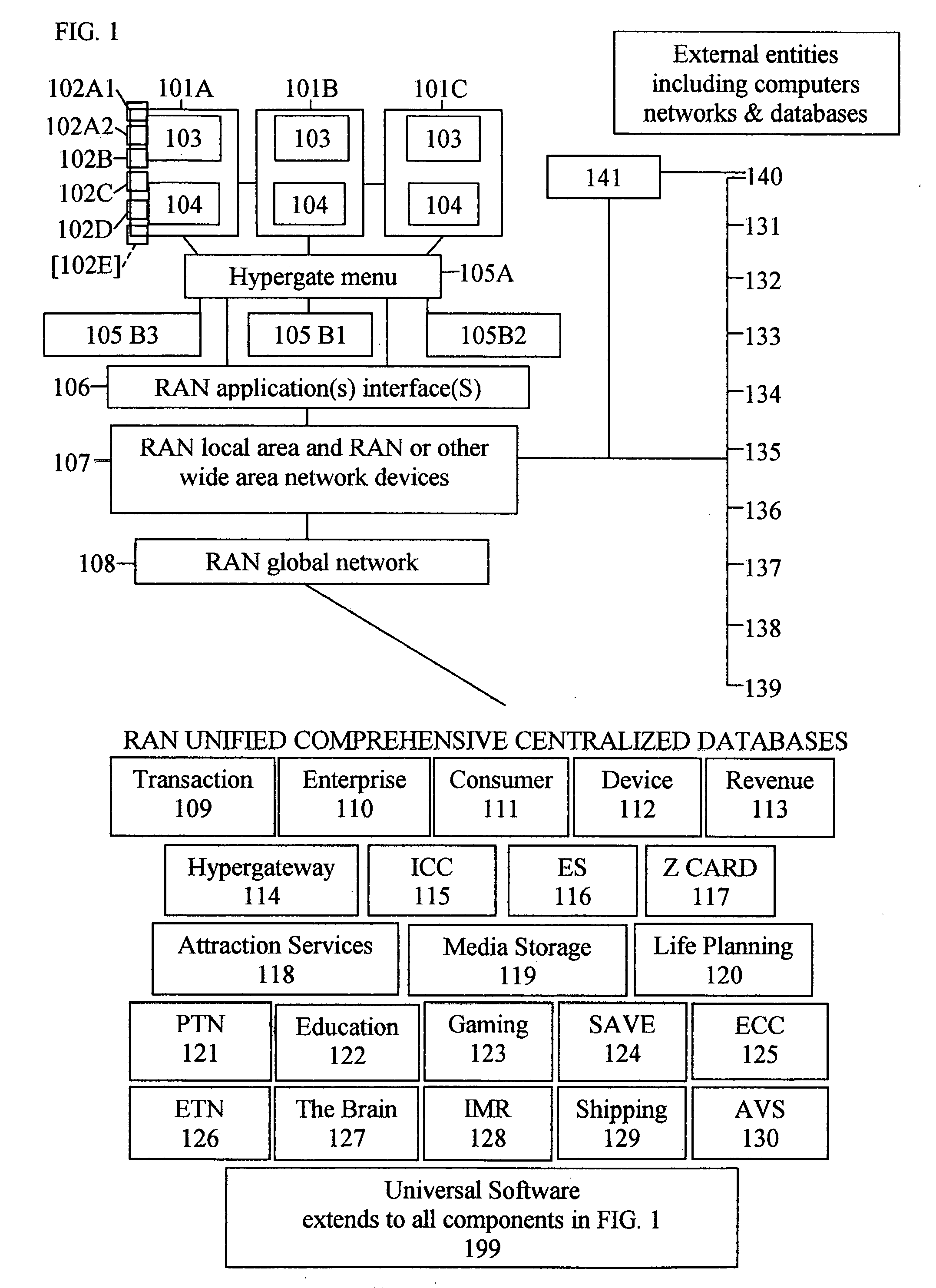
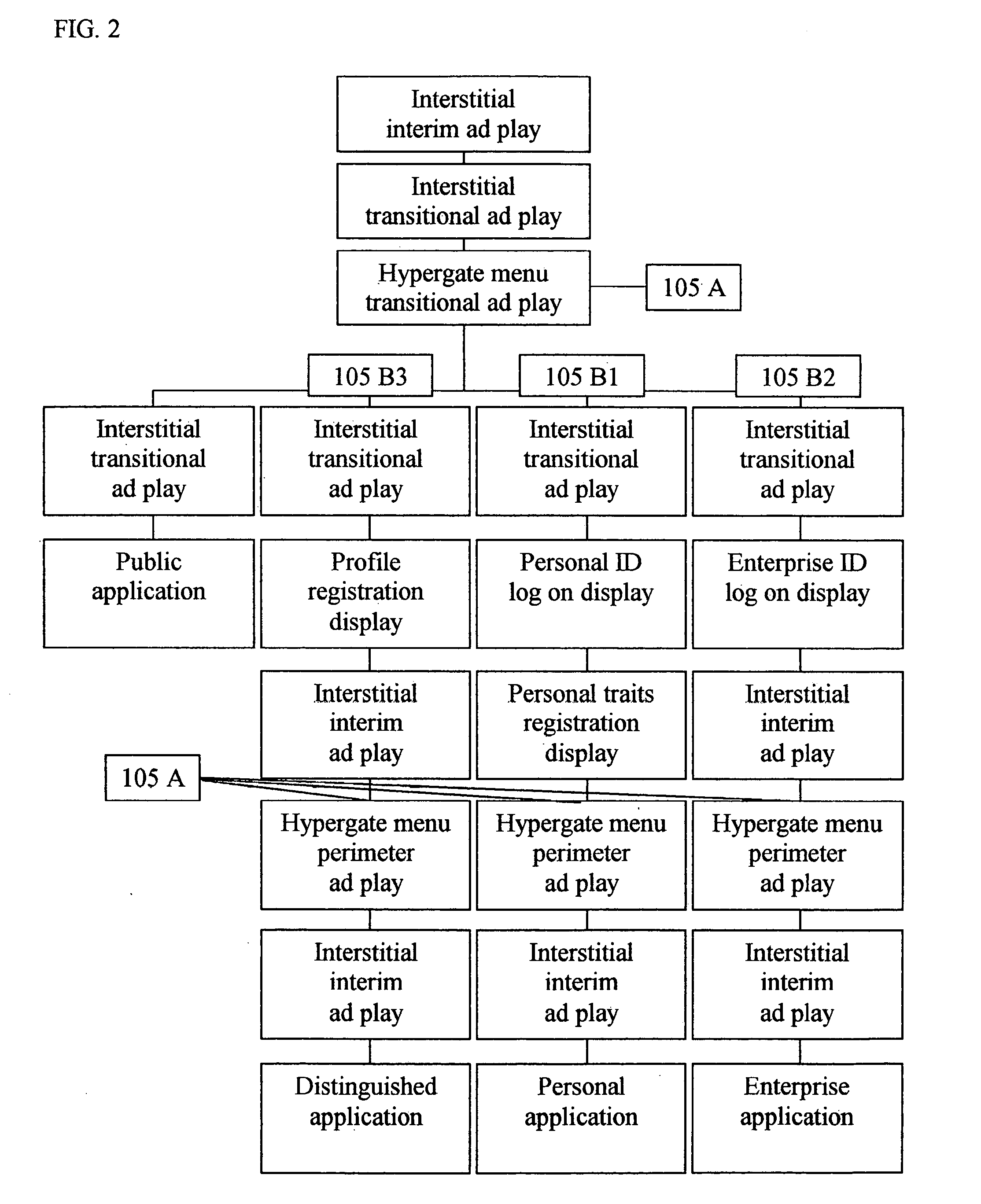
The present invention is a system and method for integrated operation, provision of user services, and management and control, for a publicly accessible global network. The global network has one or more horizontal levels for the provision of user services, network operation, overall management and control in a vertical hierarchy, and one or more horizontal levels of data management, including data capture, processing, analysis, reporting, etc. The system further includes Universal Software which integrates the functionalities of various software platforms into one unified integrated software. The system incorporates a plurality of components for connecting any user directly to applications, and enterprise sites and consumer sites for connecting users via the global network directly to other networks, data bases and computer devices, of emergency services personnel / agencies, for performing simultaneously mathematical formulae, algorithms or procedures, and for displaying and updating advertisements appearing at specific points in a software operation.
Owner:ZEPHYR MEDIA
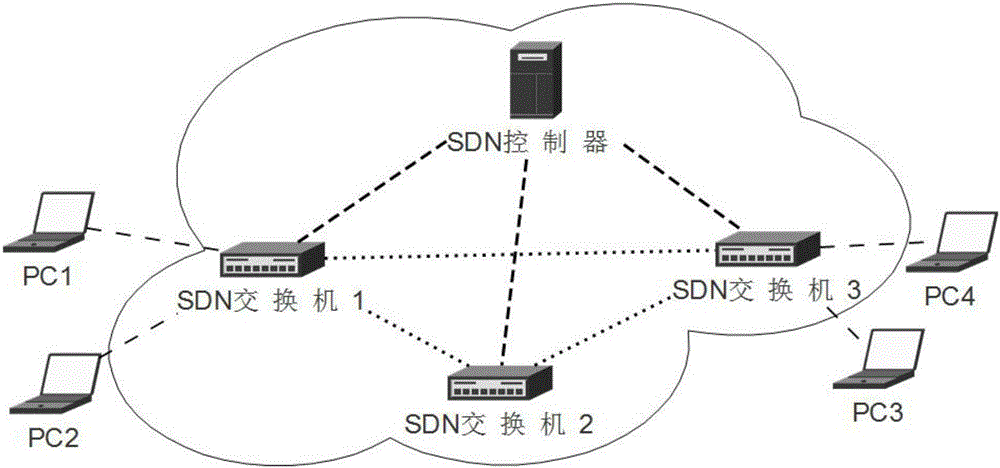
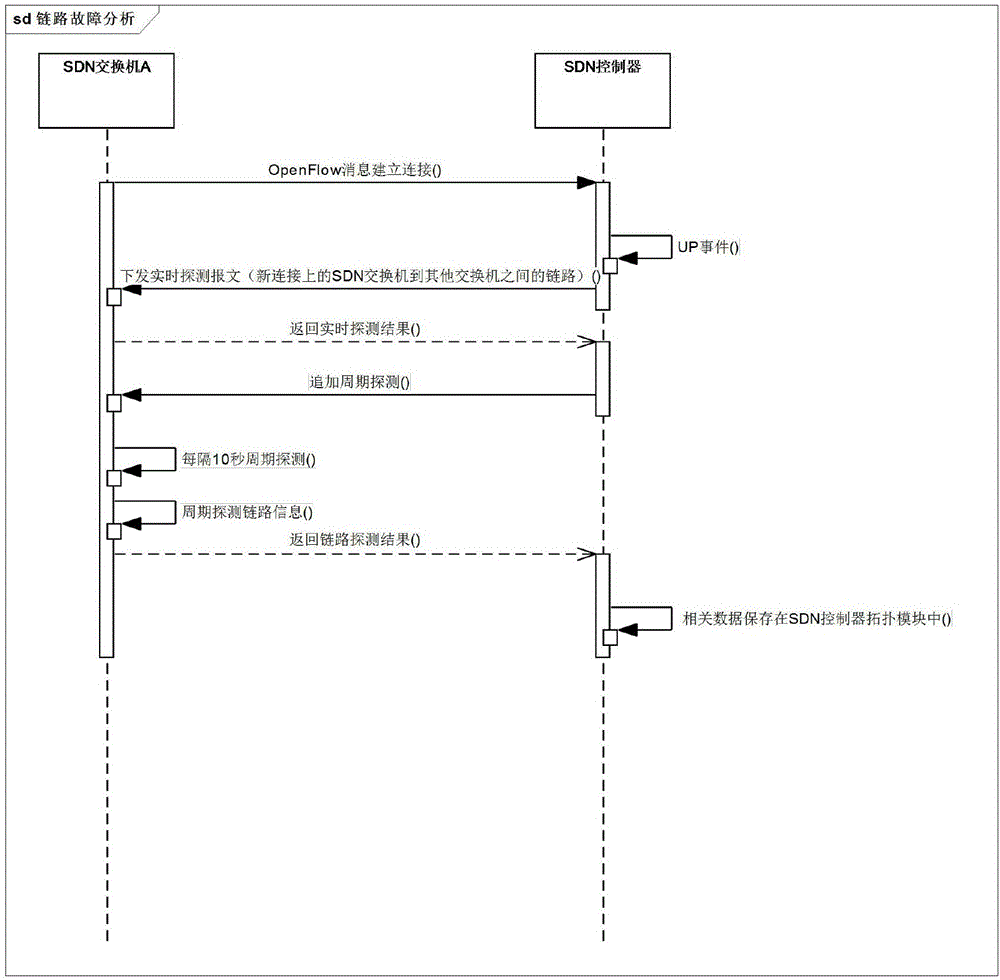
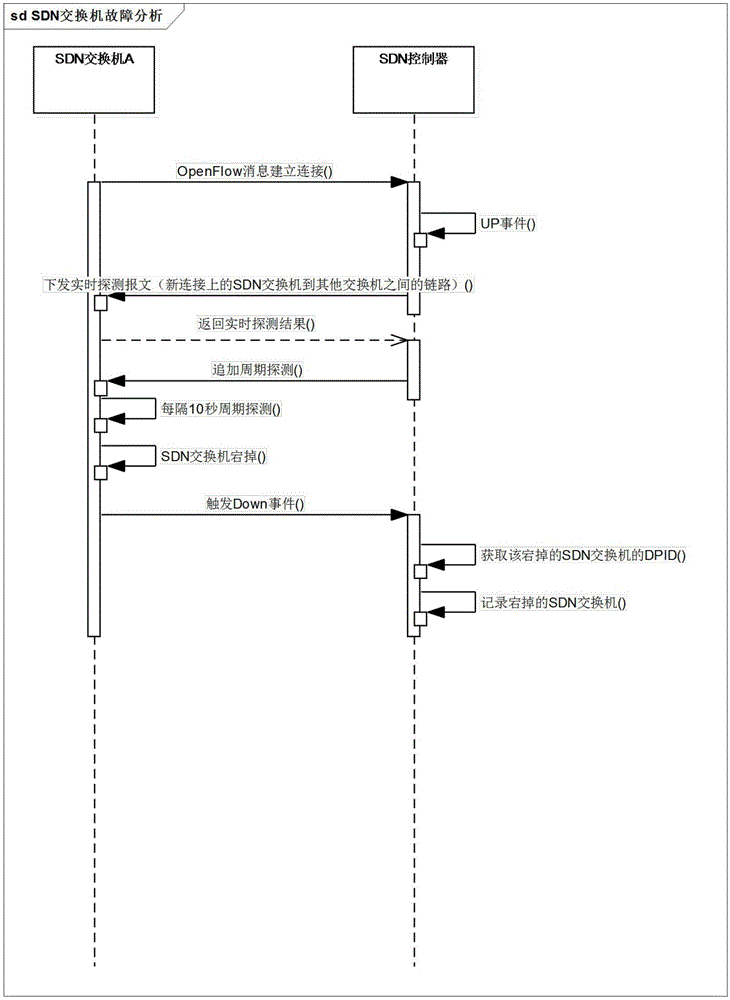
System and method for realizing automatic network failure analysis based on SDN technology
ActiveCN106130766AAdaptableStrong reliabilityData switching networksFailure analysisNetwork topology
The invention relates to a system and a method for realizing automatic network failure analysis based on SDN technology. The system comprises one SDN controller and multiple SDN switches. The SDN controller realizes real-time detection and cycle detection of each link in network topology, and monitors states of the SDN switches in real time and maintains the global network topology. The SDN controller comprises an OpenFlow module, an OpenFlow extension module, an event module, a topology module and a detection module. The detection module comprises a real-time detection module and a cycle detection module. With the system and the method, the whole network can be monitored, and network failure analysis is realized.
Owner:WUHAN GREENET INFORMATION SERVICE
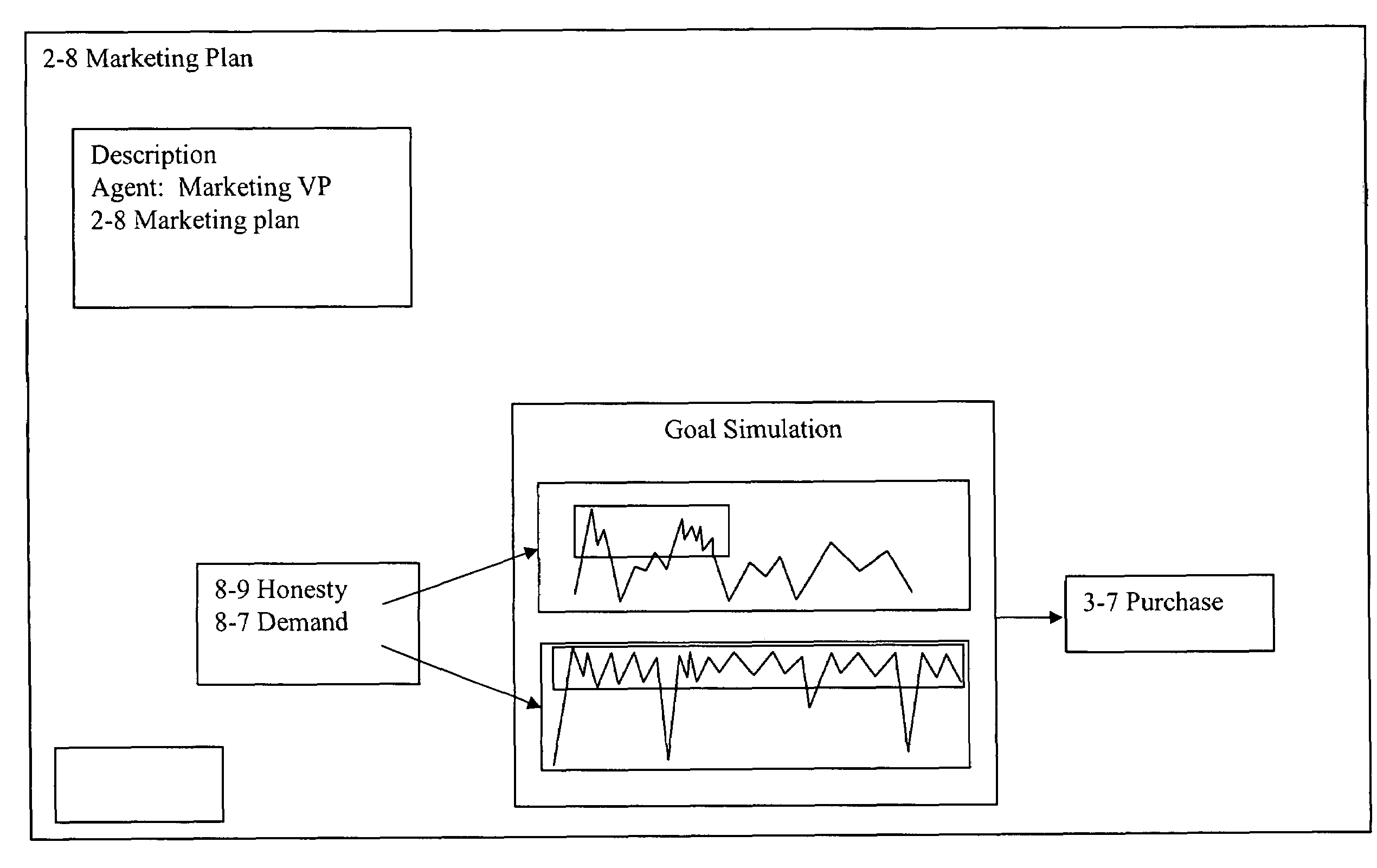
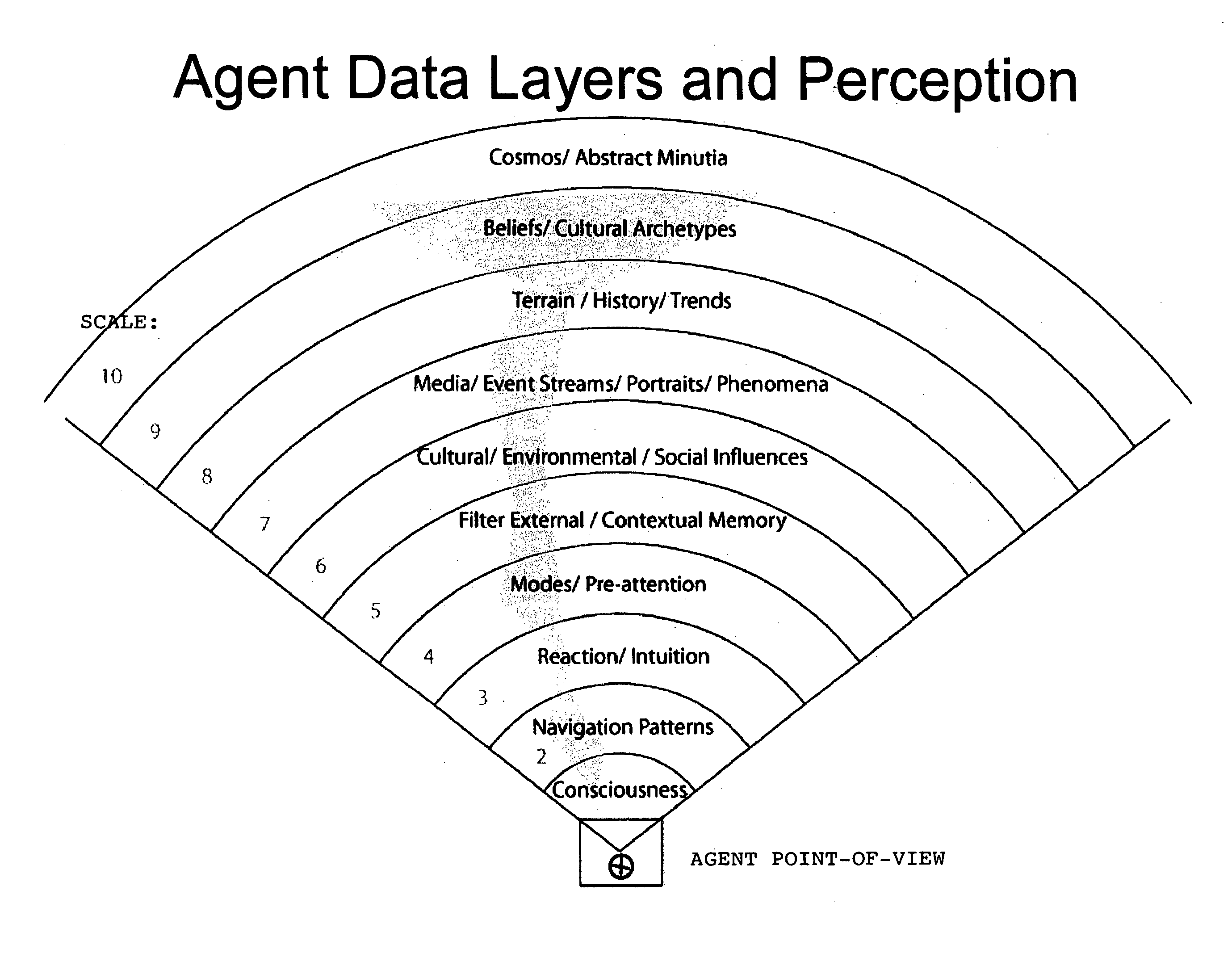
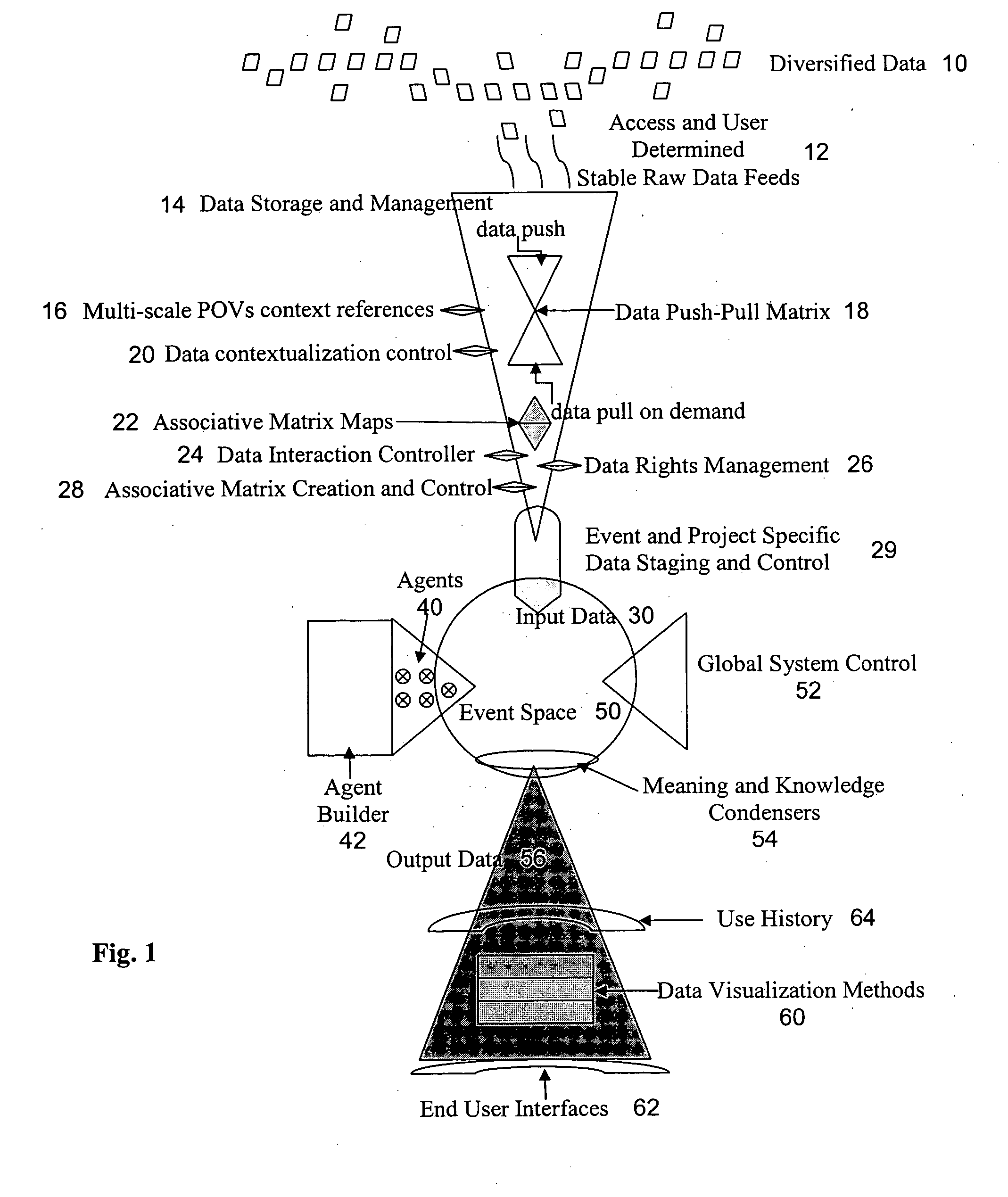
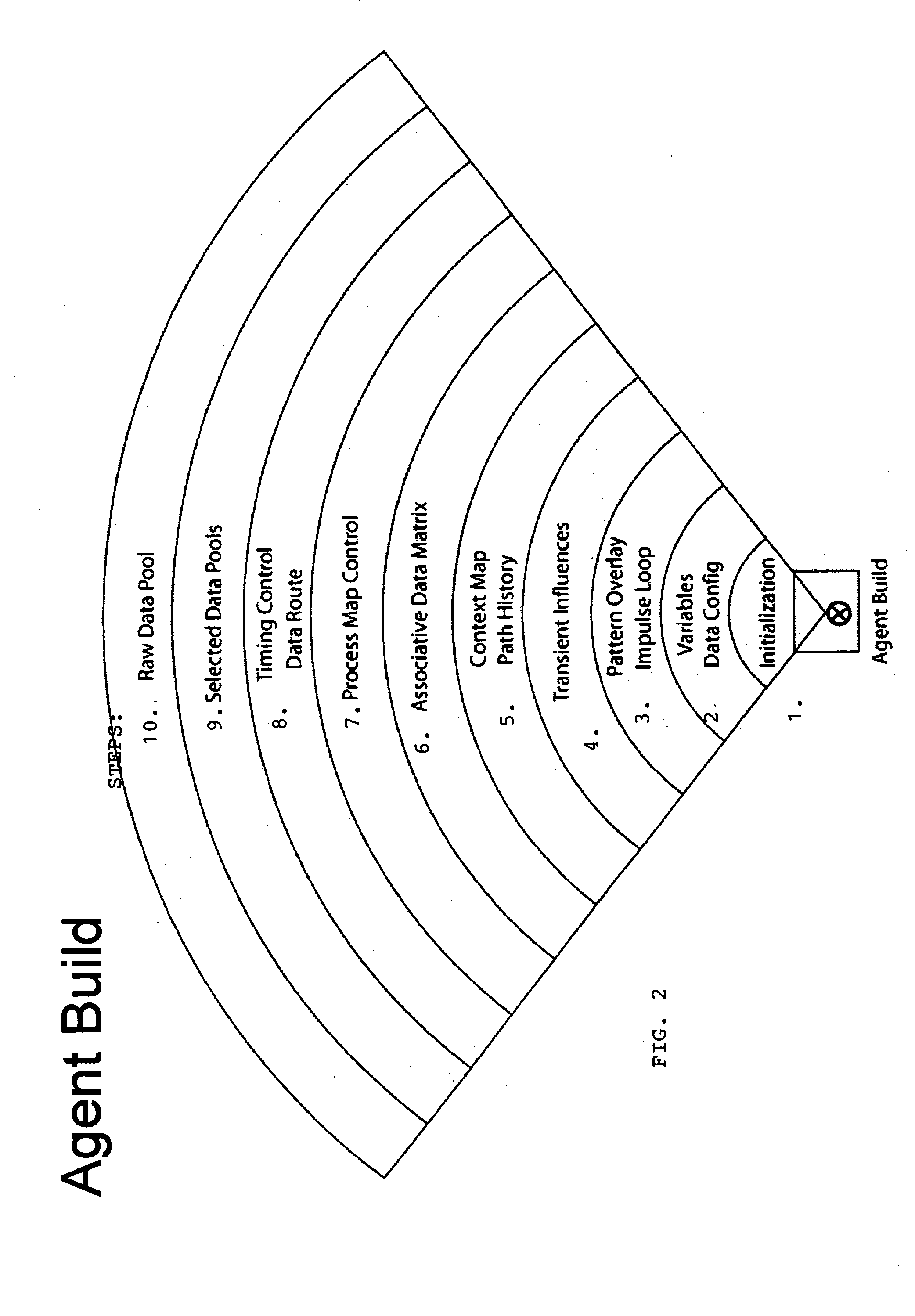
Cultural simulation model for modeling of agent behavioral expression and simulation data visualization methods
ActiveUS7263474B2Accurately indicatedDrawing from basic elementsSpeech analysisData sourceVisual tool
A computer simulation method is provided for modeling the behavioral expression of one or more computerized agents for running a simulation against real-world input data, and providing a visual display identifying elements in the input data corresponding to the modeled agent(s) response(s). Simulations can be run on sources of input data on global networks for agent types of different cultures, societies, and behaviors, such as news feeds, text communications, and reports, in order to identify keywords or phrases therein that correspond to agent behavioral expressions being monitored. Robust new visual tools are provided for discerning patterns and trends in the simulation data, including waveform charts, star charts, grid charts, and pole charts.
Owner:SEASEER R&D
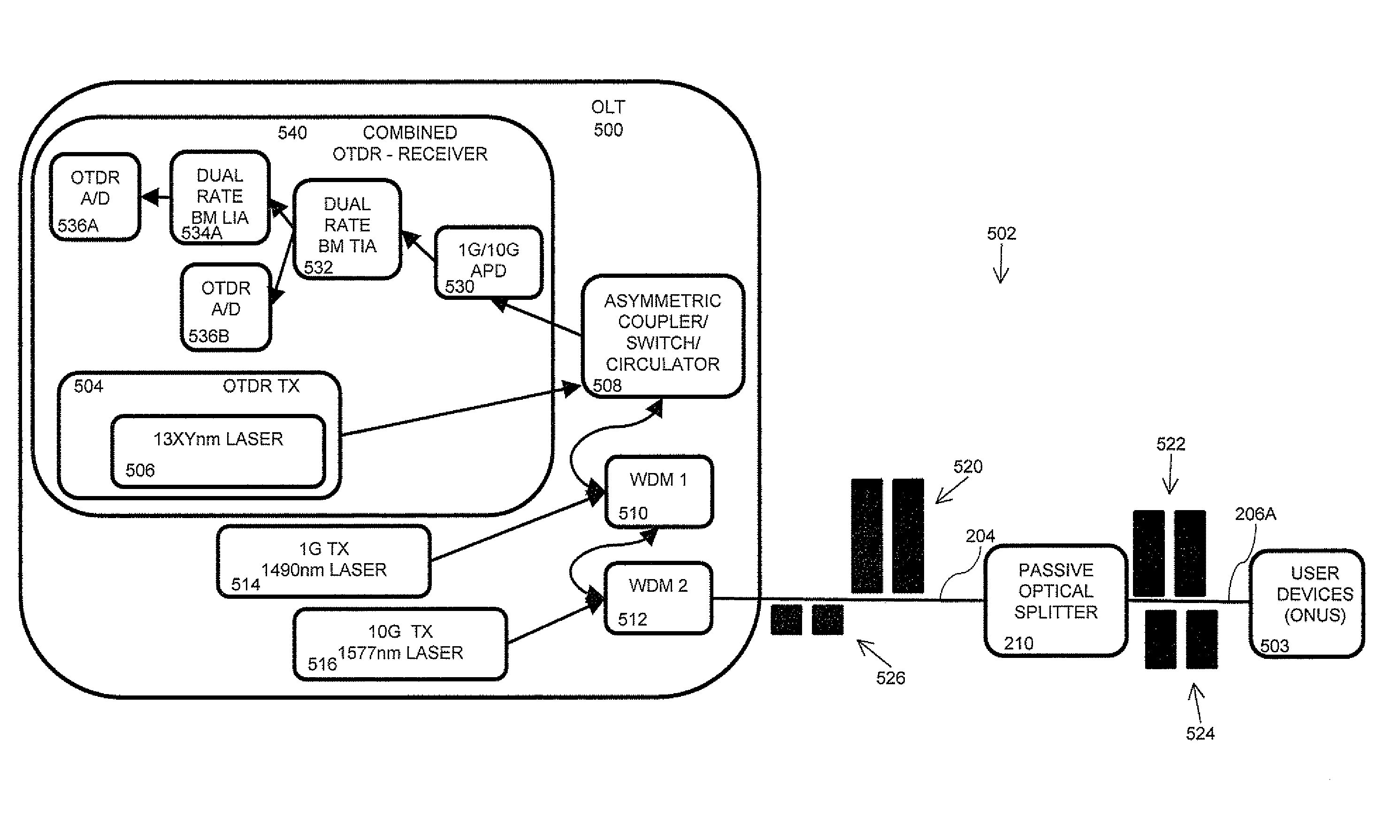
Passive optical network (PON) in-band optical time domain reflectometer (OTDR)
ActiveUS20110013904A1Material analysis by optical meansTransmission monitoringSignal onNetwork Communication Protocols
An in-band OTDR uses a network's communication protocols to perform OTDR testing on a link. Because the OTDR signal (probe pulse) is handled like a data signal, the time required for OTDR testing is typically about the same as the time required for other global network events, and is not considered an interruption of service to users. A network equipment includes an optical time domain reflectometry (OTDR) transmitter and receiver, each operationally connected to a link to transmit and receive, respectively, an OTDR signal. When an OTDR is to be performed, a network device operationally connected to the link actuates the OTDR transmitter to transmit the OTDR signal on the link during a determined test time based on a communications protocol of the link, during which data signals are not transmitted to the network equipment. A processing system processes the OTDR signal to provide OTDR test results.
Owner:MICROSEMI ISRAEL STORAGE SOLUTIONS LTD
Systems, methods and programming for routing and indexing globally addressable objects and associated business models
InactiveUS7054867B2Load balancingEfficient algorithmDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsGlobal networkMetadata
Methods, apparatus, and programming recorded in machine readable memory are provided for the index, search and retrieval of objects on a global network. This inventive system embeds a distributed index in a routing layer to enable fast search. The method provides dynamic insertion, lookup, retrieval, and deletion of participating nodes, objects and associated metadata in a completely decentralized fashion. Nodes can dynamically join and leave the network. This infrastructure can be applied to content networks for publishing, searching, downloading, and streaming.
Owner:SKYRIS NETWORKS +1
System and method for monitoring global network performance
ActiveUS7478151B1Scalable and cost-effectiveDigital computer detailsTransmissionPrivate networkThe Internet
The present invention provides a system and method for monitoring global network performance across a public Wide Area Network (WAN), and / or private networking through a secure IPSec gateway, and providing a user interface for performance metrics through a secure Internet browser.
Owner:DYNATRACE
Global network computers
InactiveUS20060177226A1High potential economic savingOptimize networkMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlBroadband transmissionThe Internet
This invention generally relates to one or more computer networks having computers like personal computers or network servers with microprocessors linked by broadband transmission means and having hardware, software, firmware, and other means such that at least one parallel processing operation occurs that involve at least two computers in the network. More particularly, this invention relates to one or more large networks composed of smaller networks and large numbers of computers connected, like the Internet, wherein more than one separate parallel processing operation involving more than one different set of computers occurs simultaneously and wherein ongoing processing linkages can be established between virtually any microprocessors of separate computers connected to the network. Still more particularly, this invention relates to business arrangements enabling the shared used of network microprocessors for parallel and other processing, wherein personal computer owners provide microprocessor processing power to a network, preferably for parallel processing, in exchange for network linkage to other personal and other computers supplied by network providers, including linkage to other microprocessors for parallel or other processing; the basis of the exchange between owners and providers being whatever terms to which the parties agree, subject to governing laws, regulations, or rules, including payment from either party to the other based on periodic measurement of net use or provision of processing power.
Owner:ELLIS III FRAMPTON E
Securing of software defined network controllers
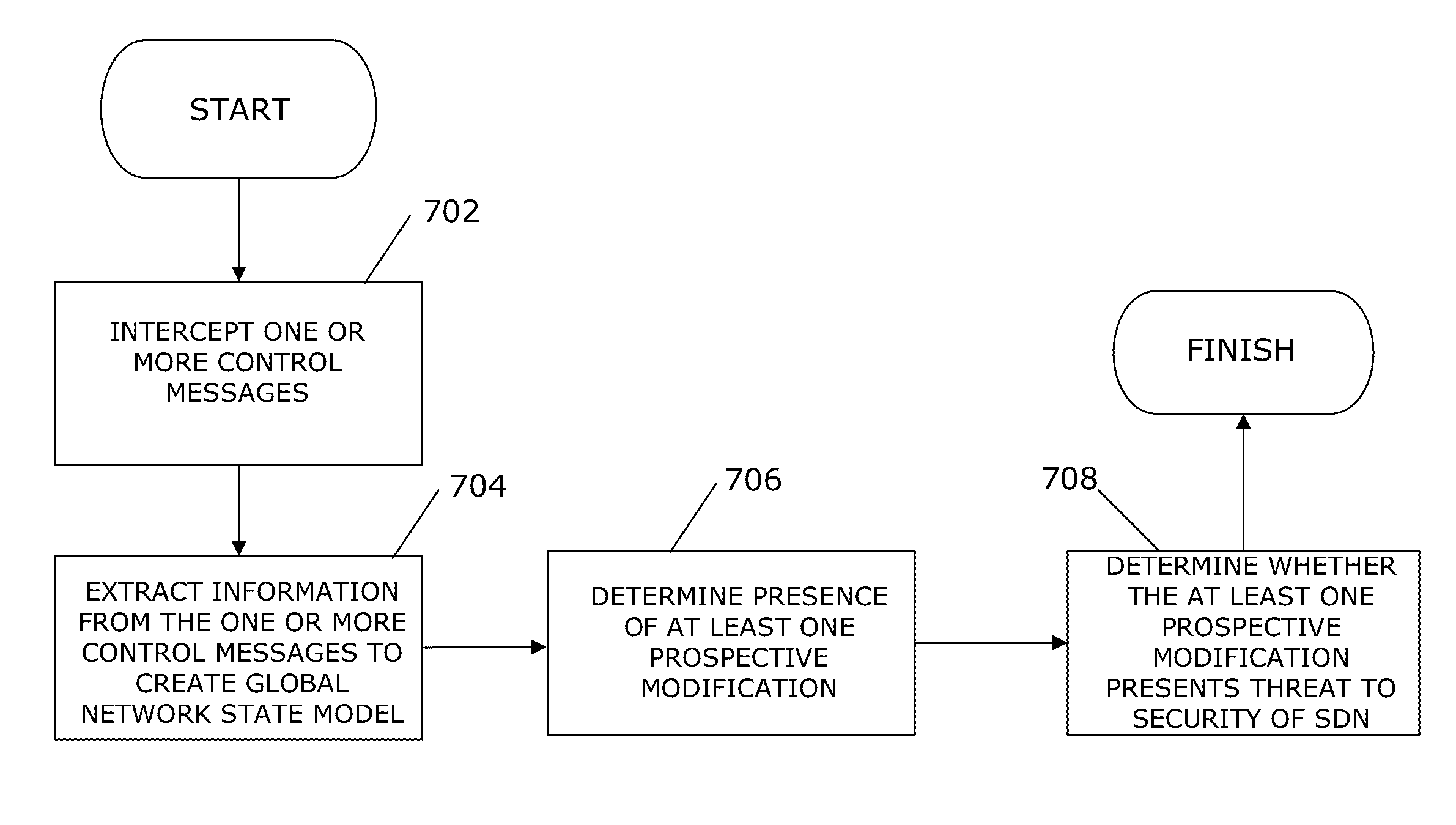
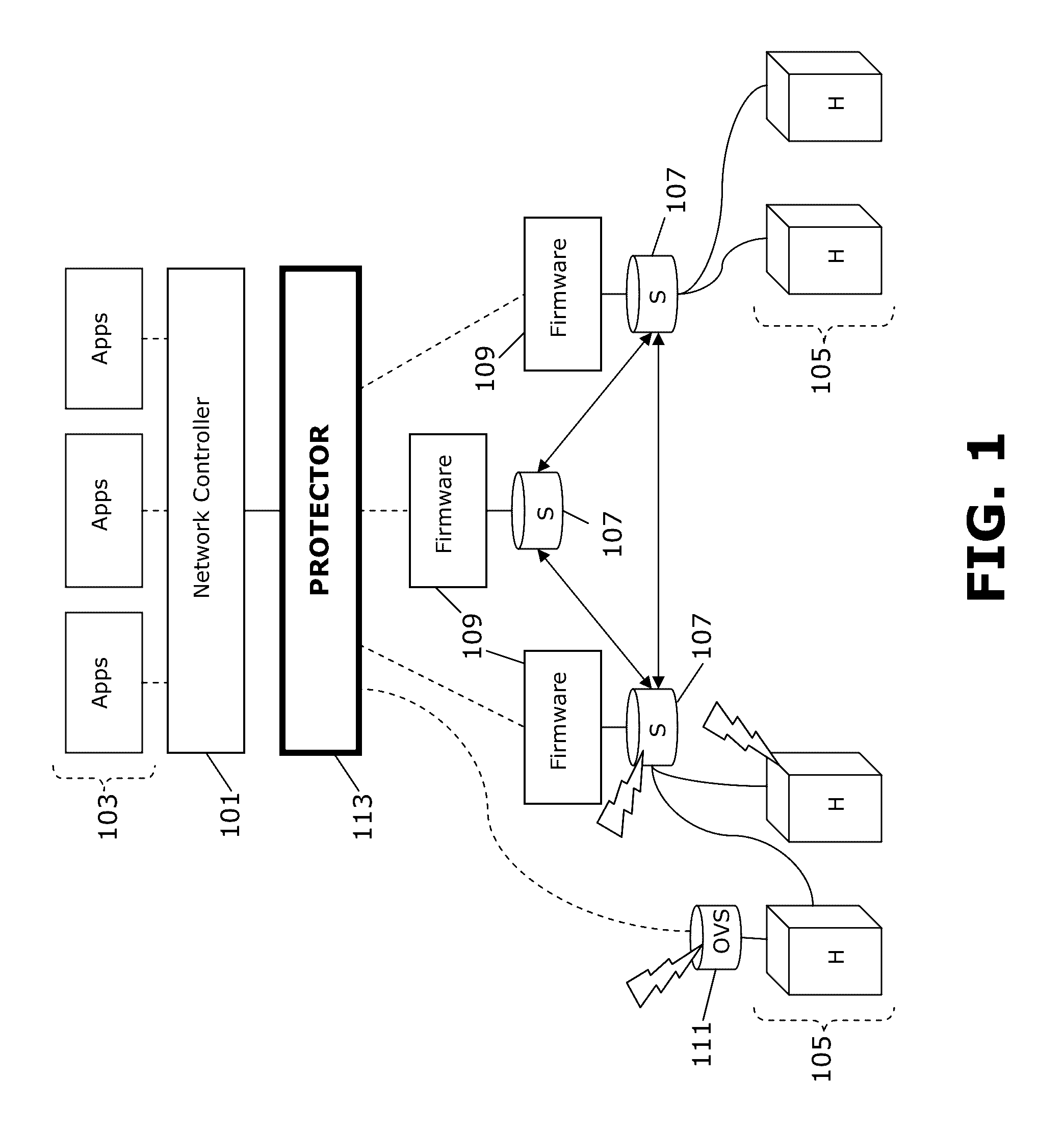
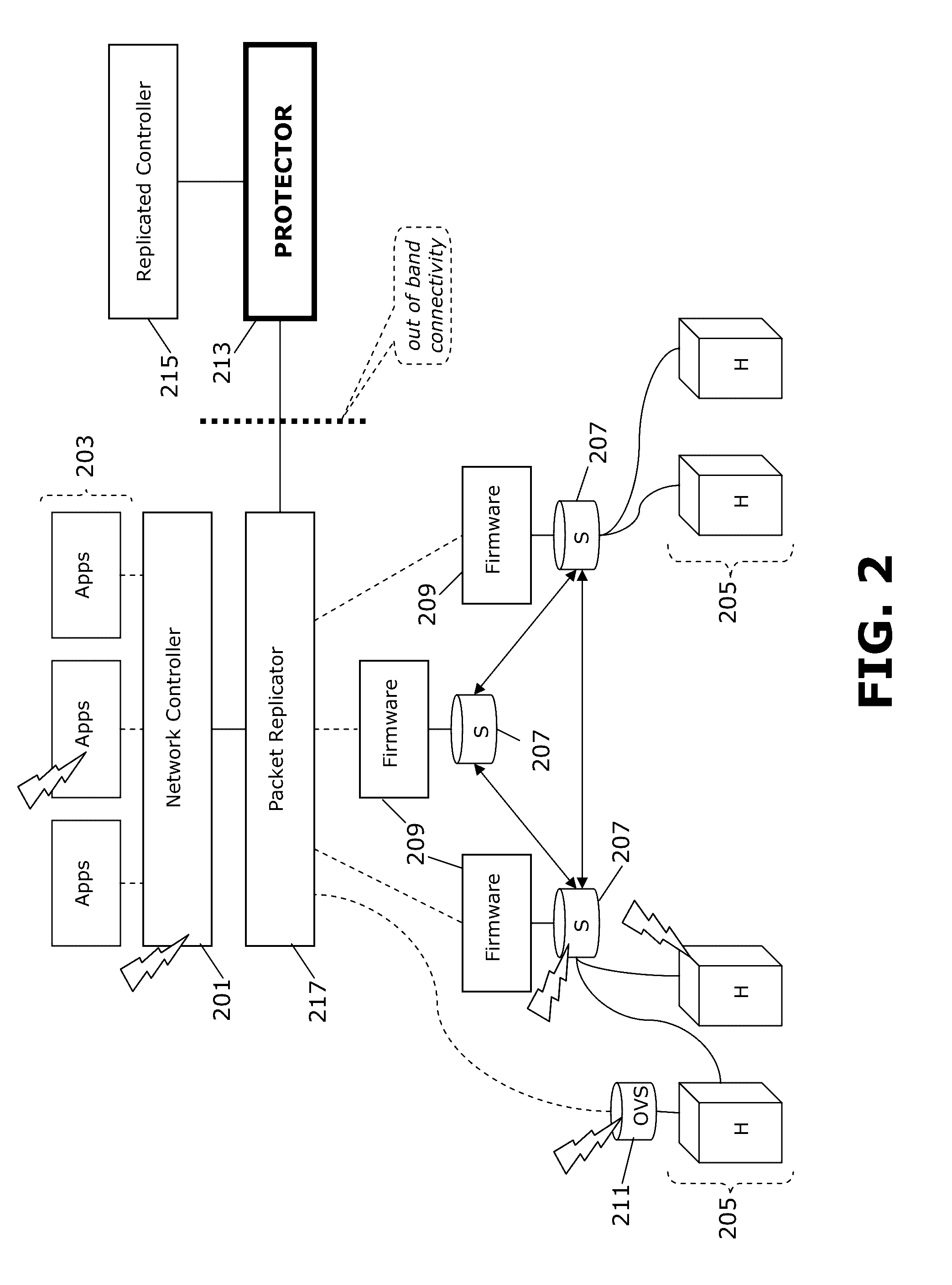
Methods and arrangements for securing a software defined network. One or more control messages are intercepted. Information is extracted from the one or more control messages to create a global network state model, and there is determined, from the extracted information, presence of at least one prospective modification to the global network state model. Thereupon, a determination is made as to whether the at least one prospective modification presents a threat to security of the software defined network. Other variants and embodiments are broadly contemplated herein.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method of controlling the communication between a machine using private addresses and a communication device connected to a global network
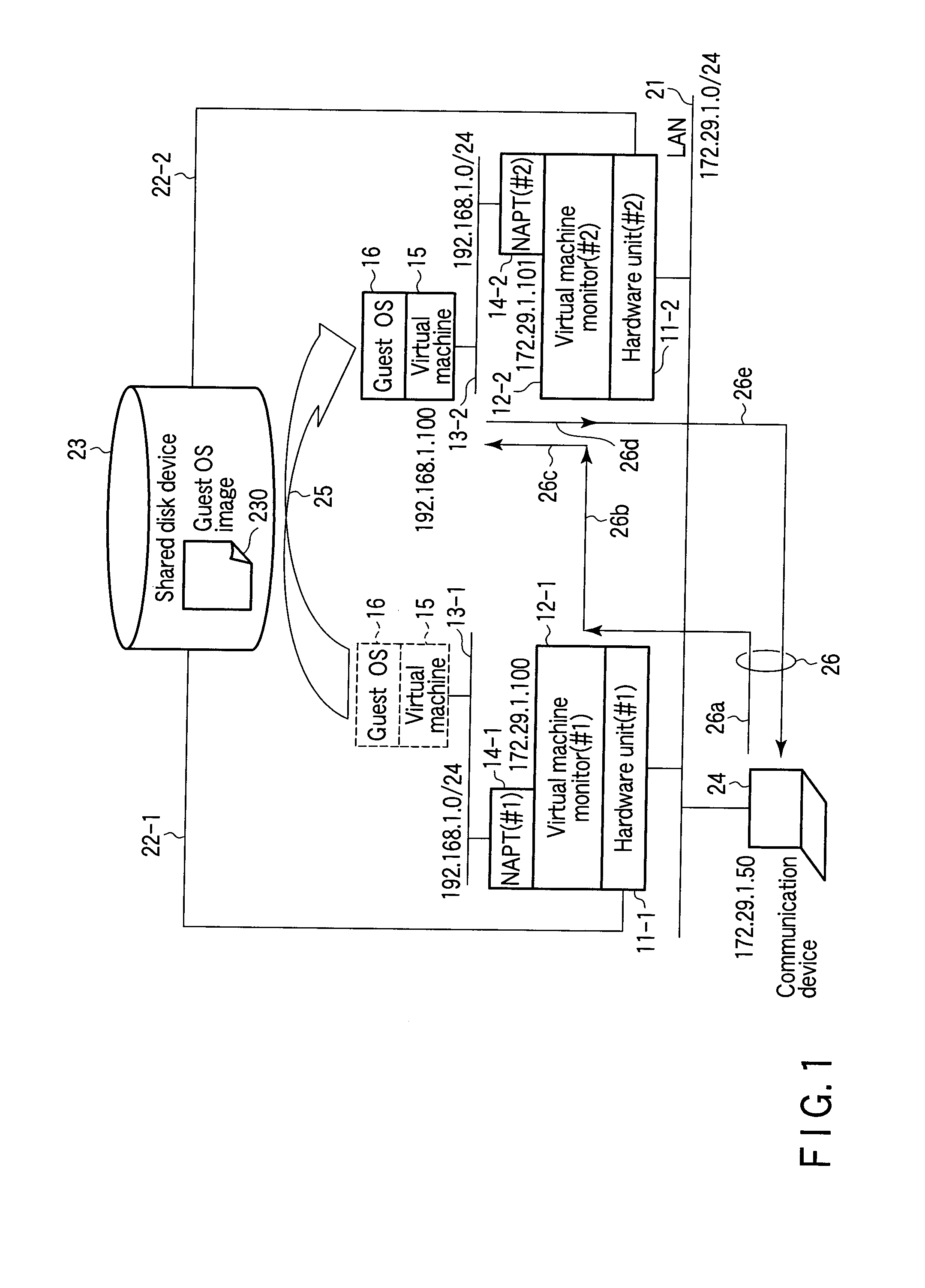
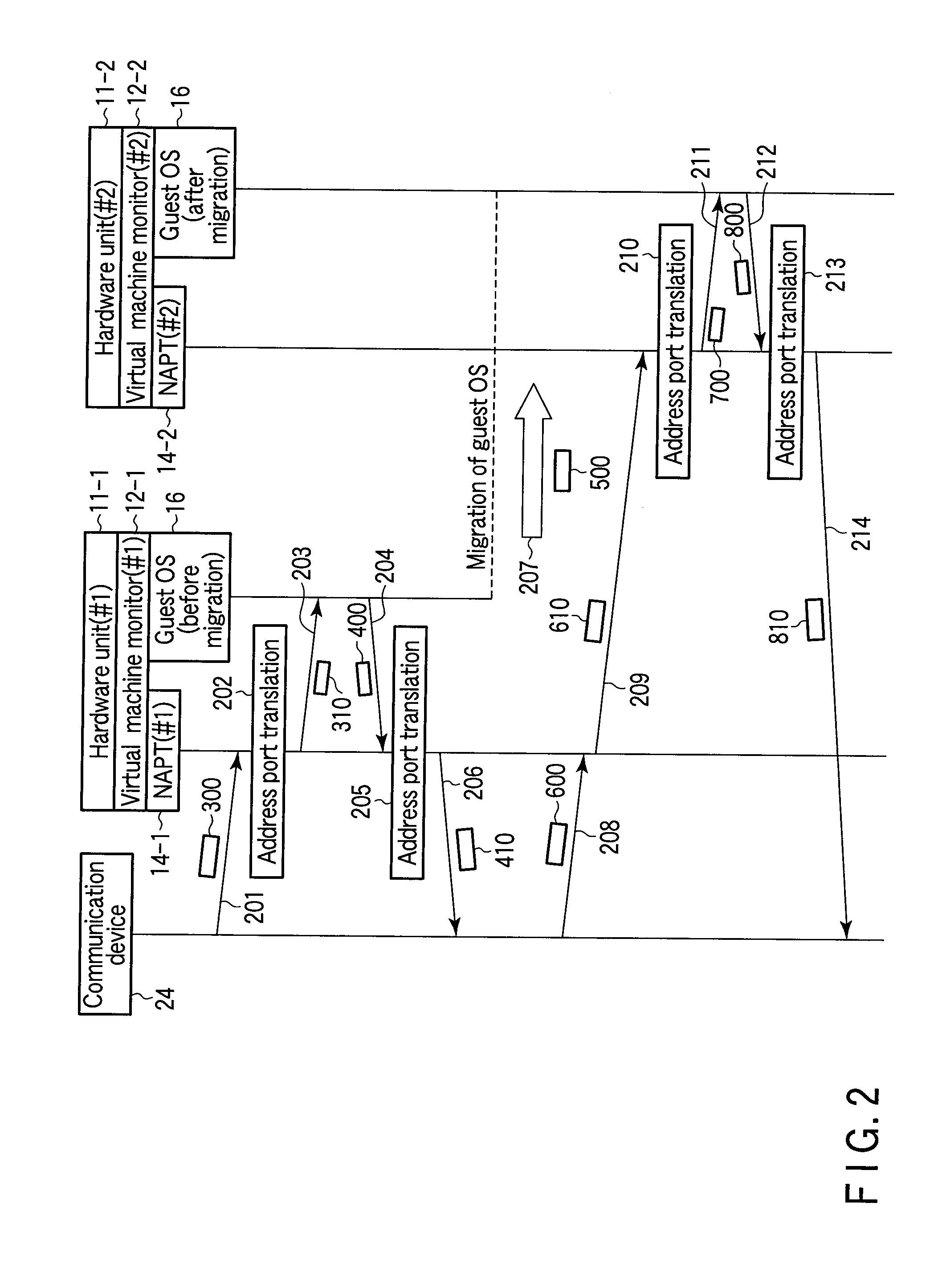
InactiveUS20100115080A1Computer security arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsNetwork address port translationPrivate address
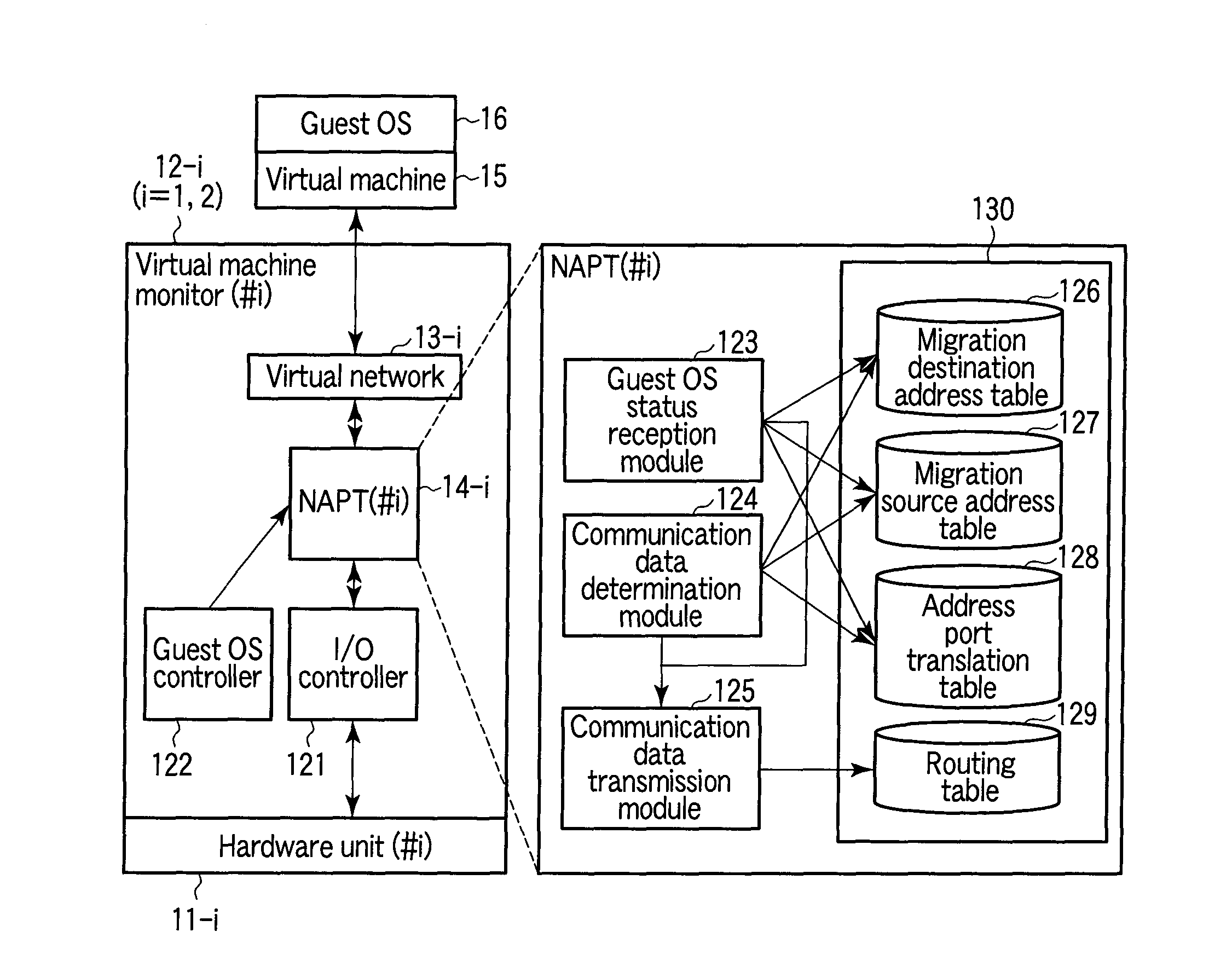
According to one embodiment, when having received first communication data addressed to a machine migrated to a second network address port translation module, a first network address port translation module translates a destination network address in the first communication data into a global address of the second network address port translation module. The first network address port translation module transfers the translated first communication data as second communication data to the second network address port translation module. When having received the second communication data transferred by the first network address port translation module, the second network address port translation module transmits third communication data addressed to the machine corresponding to the second communication data to the machine.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
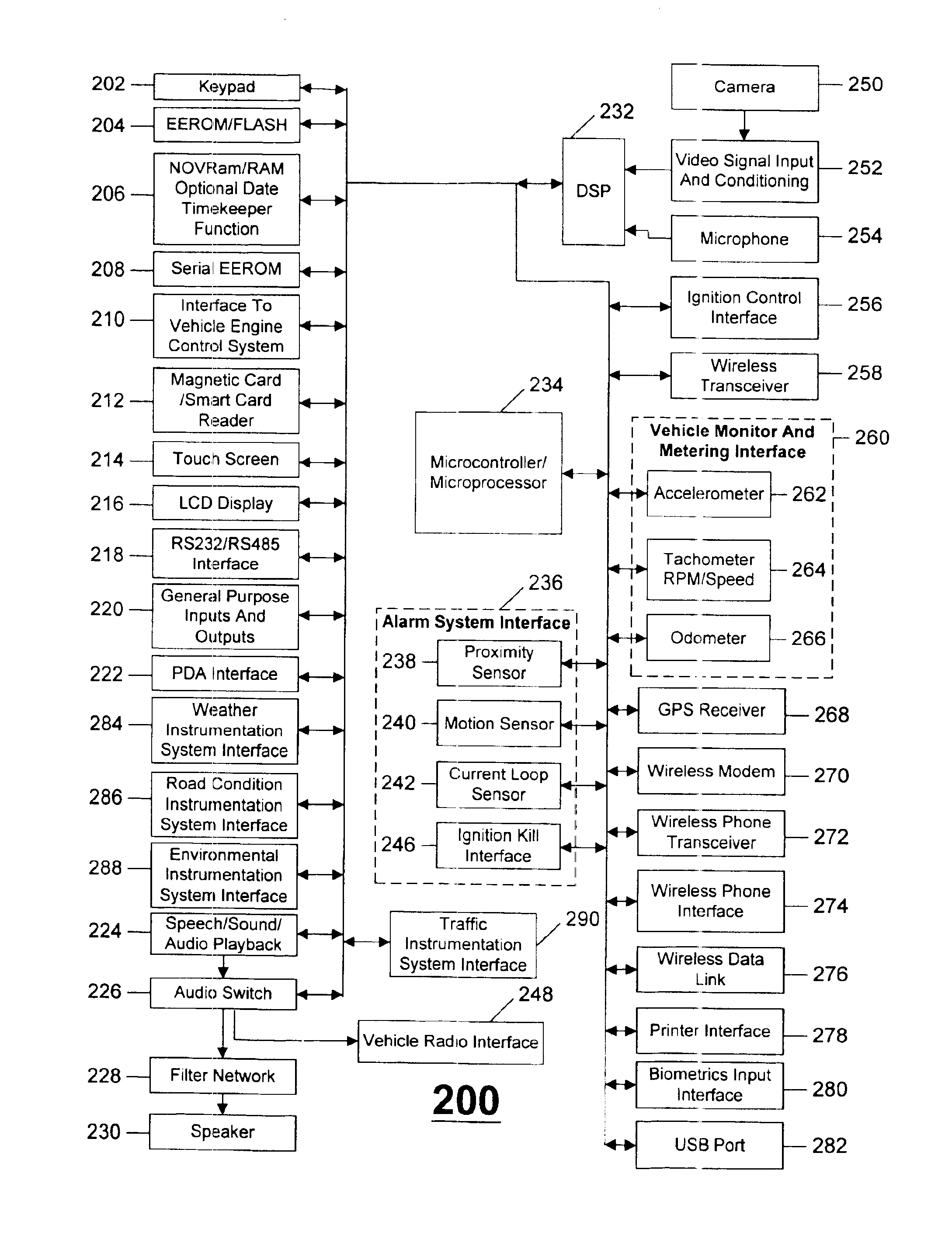
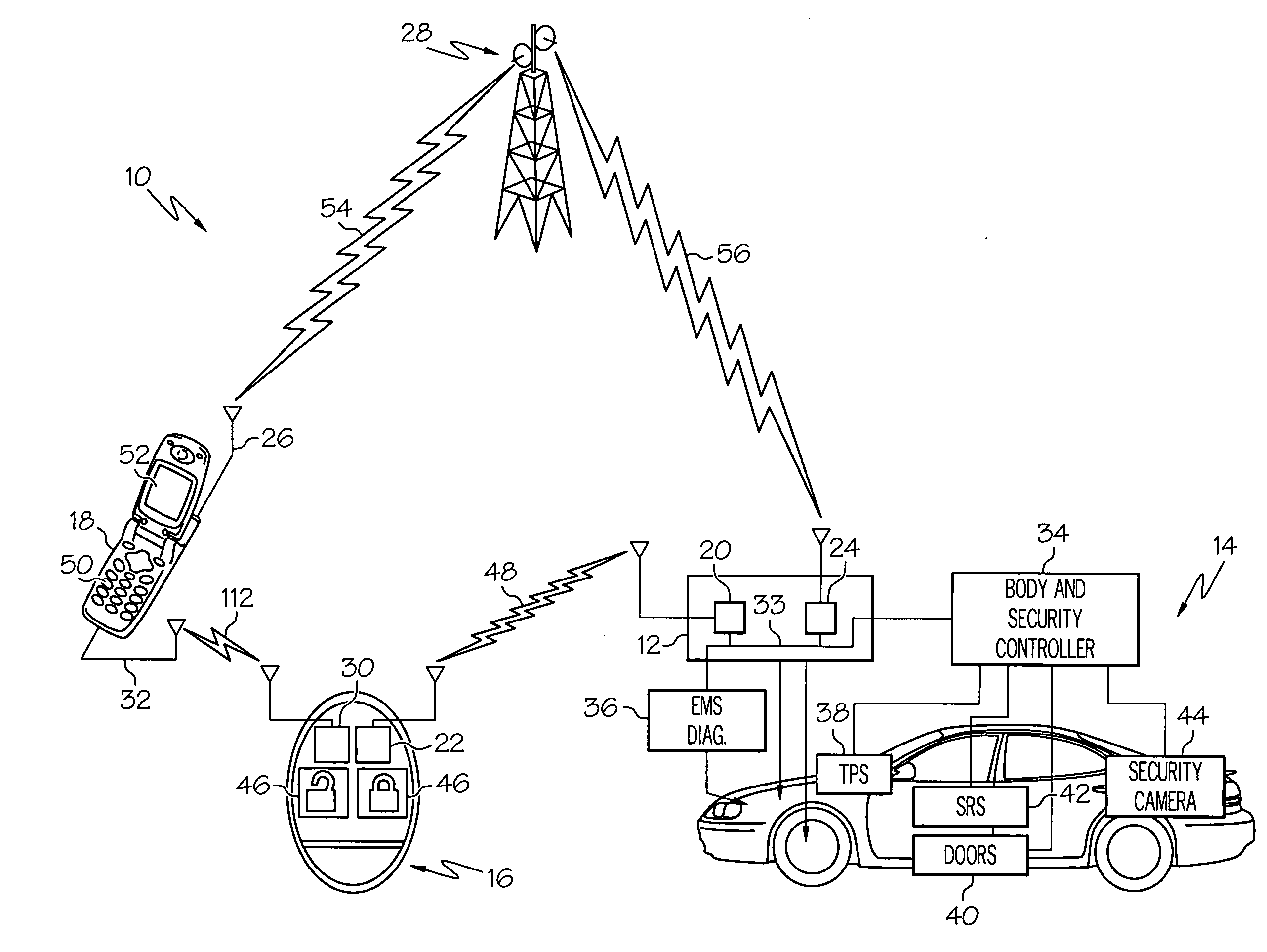
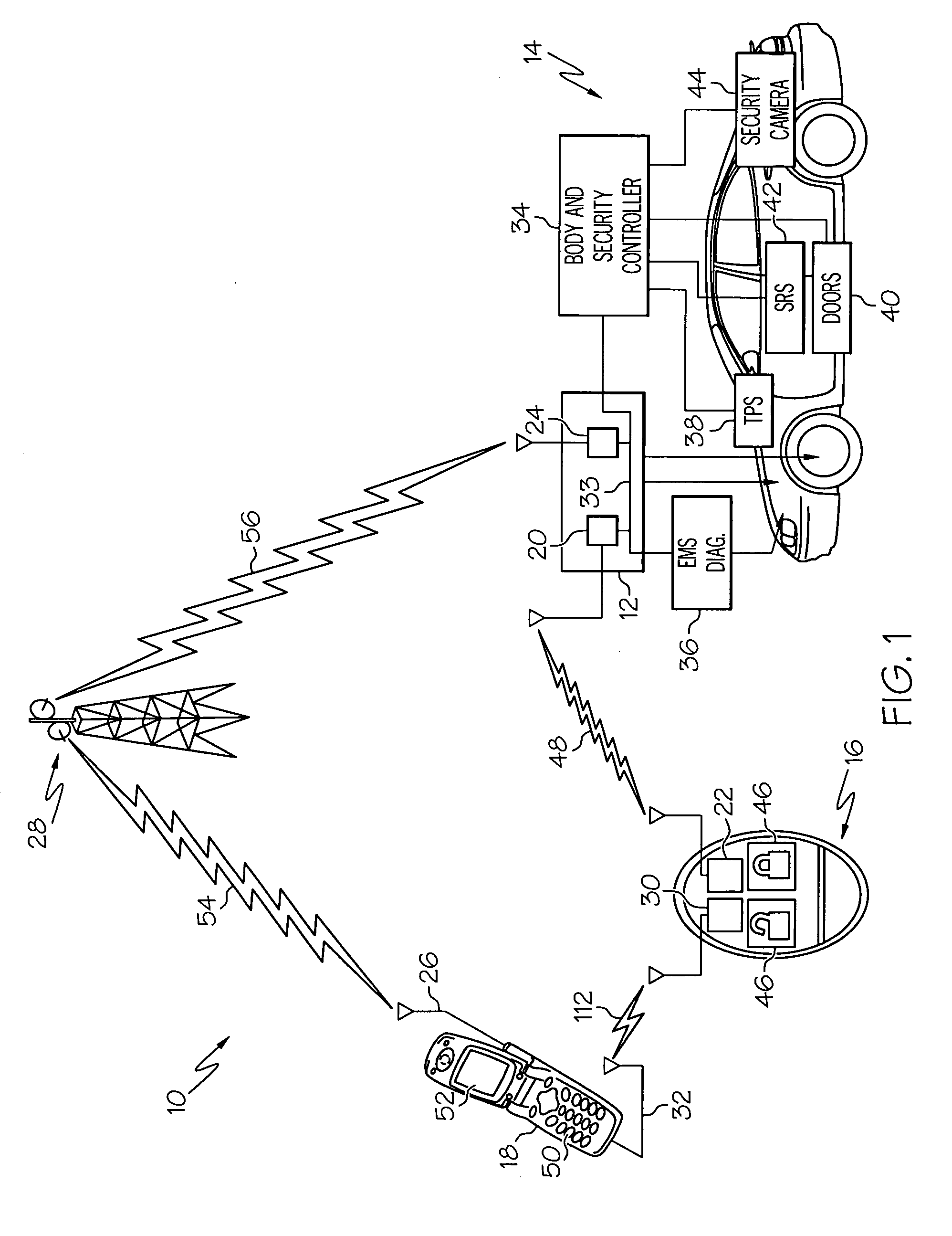
Fault tolerant vehicle communication and control apparatus
ActiveUS20090096576A1Registering/indicating working of vehiclesDigital data processing detailsTransceiverEngineering
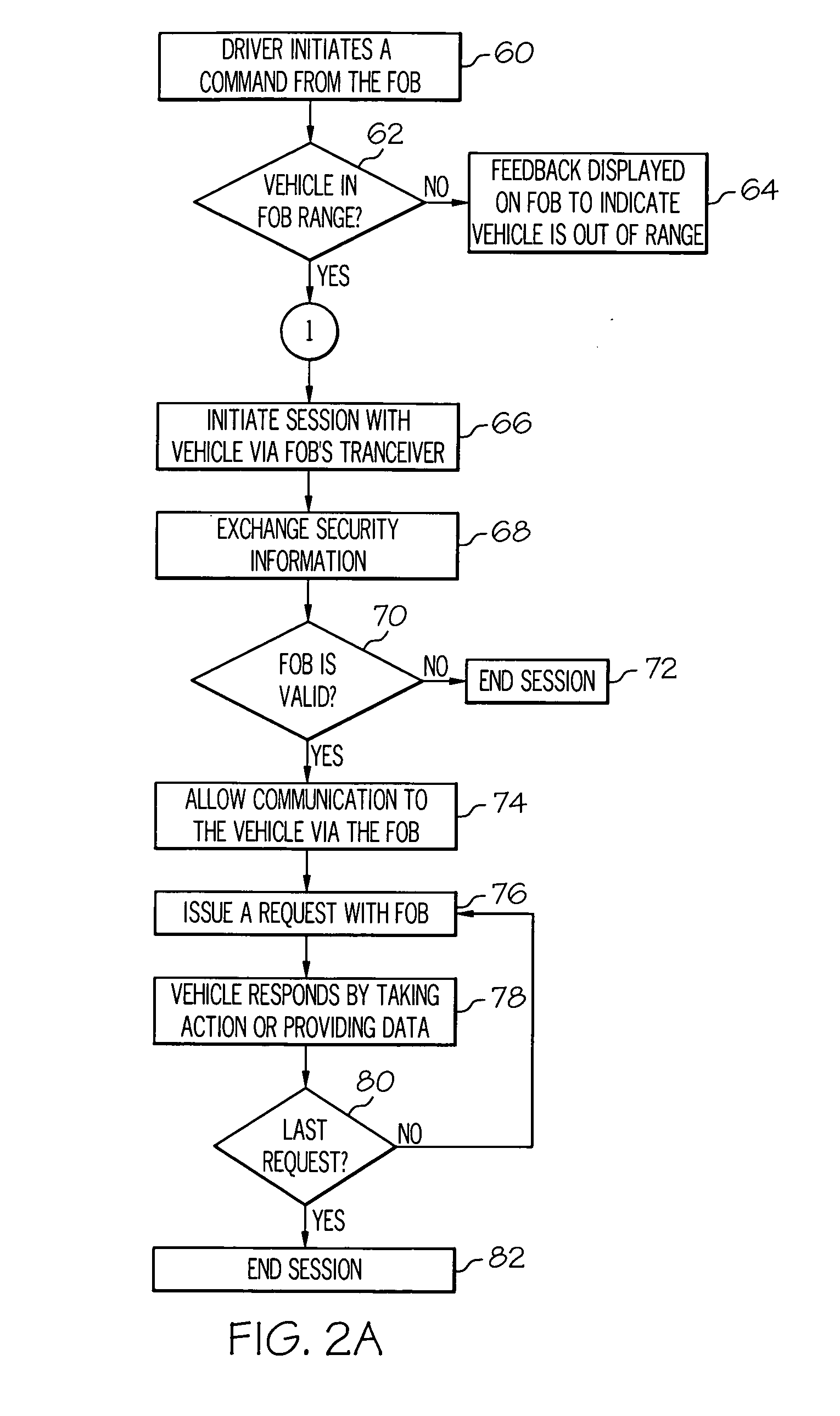
Medium-range and global network information and control for a vehicle is achieved with a portable wireless key fob, a user-provided nomadic device, and a vehicle-installed telematics unit including a medium-range RF transceiver and a wireless network transceiver. The fob includes a medium-range RF transceiver for bi-directional communication with the telematics unit, and a short-range wireless transceiver for bi-directional communication with the nomadic device. The fob communicates with the telematics unit in a conventional manner, and also relays information between the telematics unit and the nomadic device. If a communication initiated via the fob cannot be completed because the fob is out of range, the communication is sent to the nomadic device for network transmission to the telematics unit. If a communication initiated via the nomadic device cannot be completed due to inadequate signal reception, the communication is sent to the fob for RF transmission to the telematics unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Resolving multiple master node conflict in a DDB
ActiveUS7269648B1Simple technologyDigital computer detailsDatabase distribution/replicationSingle point of failureUser interface
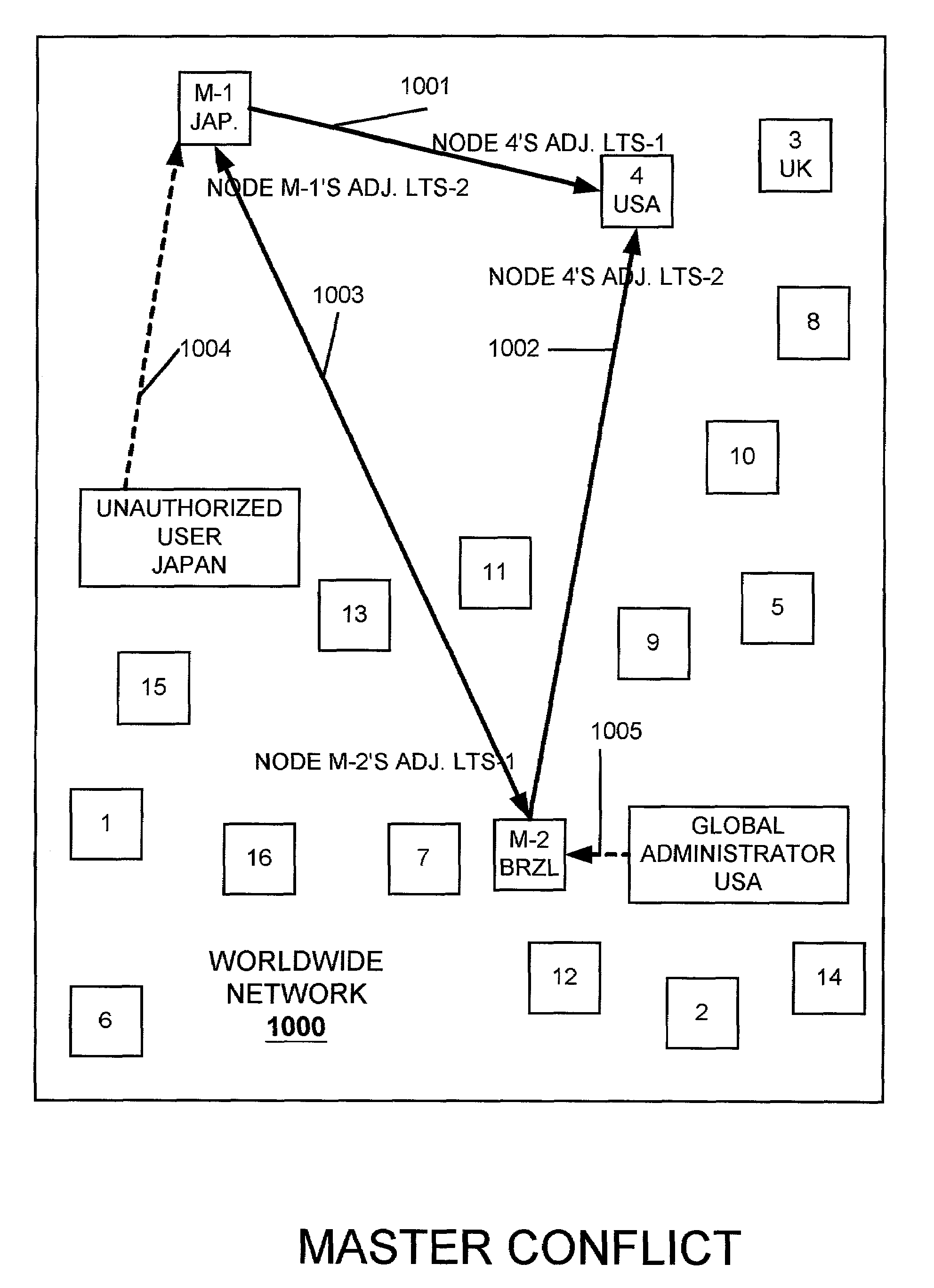
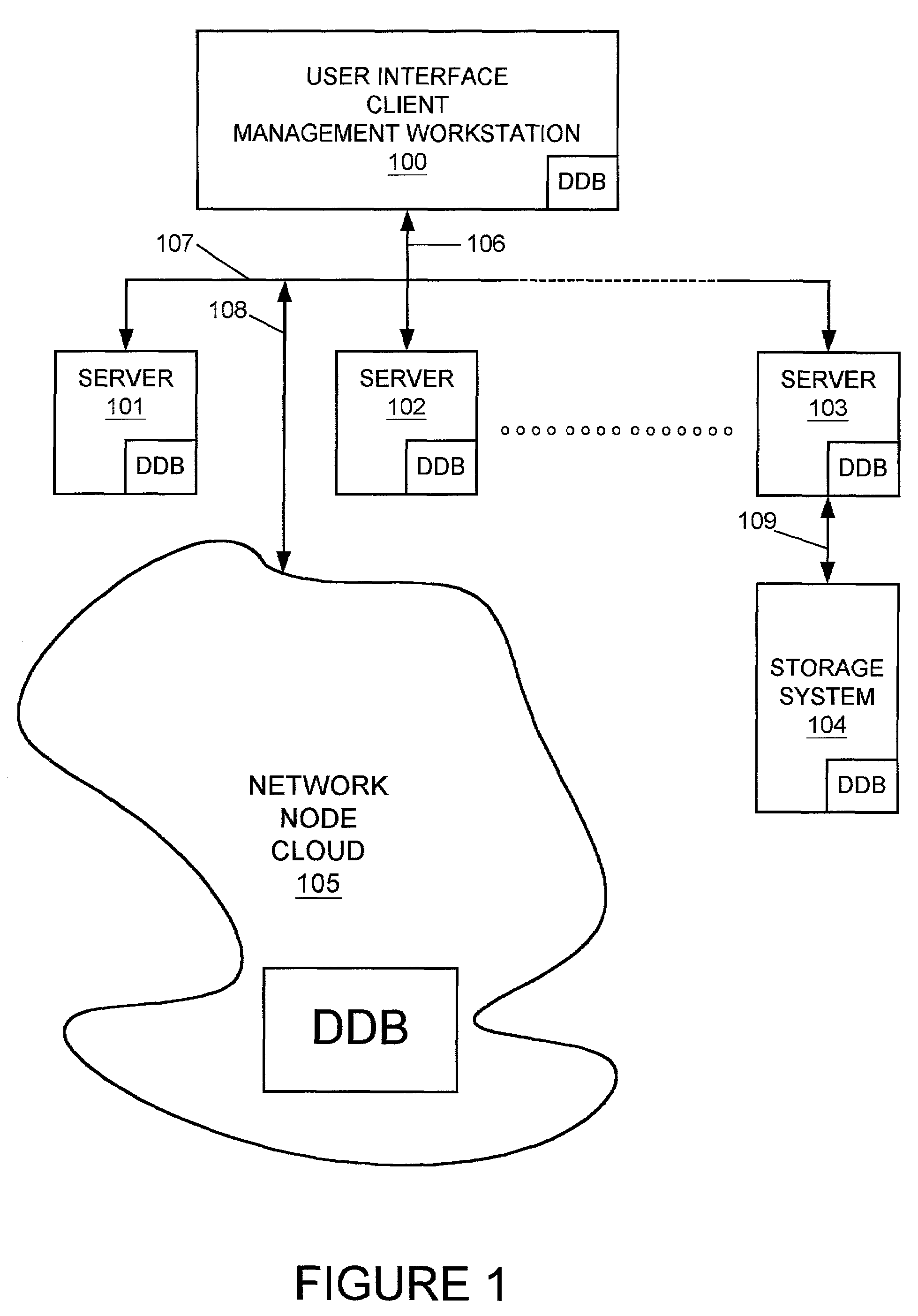
In a computer network having a plurality of computer nodes, a directory database (DDB) distributed throughout the network in each of the nodes, the contents of the DDB being maintained consistent or replicated throughout the network through the use of one of its nodes having been appointed as master node. The master node has a privileged status as compared to the other nodes. The master node updates each DDB in each node in its network or domain configuration when the configuration changes. A global administrator is a privileged user compared to other computer network users who has authority to replace or select a master node and to configure a domain, and who performs these and other functions by way of computer terminal screen dialogs offered by a graphical user interface (GUI) associated with the computer network. Only one master node per domain is permitted and if the password-protected global administrator's security is breached, other users may select other master nodes for the same network resulting in master to master conflict. In the case of multiple master nodes attempting to be master for the same nodes in the same network at the same time, this conflict is resolved in one embodiment of the present invention by allowing the most recently selected purported master node to be the actual master node. This resolution is obtained in a manner that avoids a single point of failure. After resolution of this conflict the result is communicated by the prevailing master node to all nodes in the network. This resolution takes into account a global network with varying time zones, and further takes into account the remote possibility of a simultaneous appointment of two masters.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Cultural simulation model for modeling of agent behavioral expression and simulation data visualization methods
ActiveUS20040181376A1Accurately indicatedDrawing from basic elementsSpeech analysisVisual toolData visualization
A computer simulation method is provided for modeling the behavioral expression of one or more agents in an environment to be simulated, then running a simulation of the modeled agent(s) against real-world information as input data reflecting changing conditions of the environment being simulated, and obtaining an output based on the modeled agent(s) response(s). The simulation method models the underlying cultural, social, and behavioral characteristics on which agent behaviors and actions are based, rather than modeling fixed rules for the agent's actions. The input data driving the simulation are constituted by real-world information reflecting the changing conditions of the environment being simulated, rather than an artificial set of predefined initial conditions which do not change over time. As a result, the simulation output of the modeled agent's responses to the input information can indicate more accurately how that type of participant in the simulated environment might respond under real-world conditions. Simulations can be run on global networks for agent types of different cultures, societies, and behaviors, with global sources of information. Simulation environments can include problems and situations in a wide range of human activity. Robust new visual tools are provided for discerning patterns and trends in the simulation data, including waveform charts, star charts, grid charts, and pole chart series.
Owner:SEASEER R&D
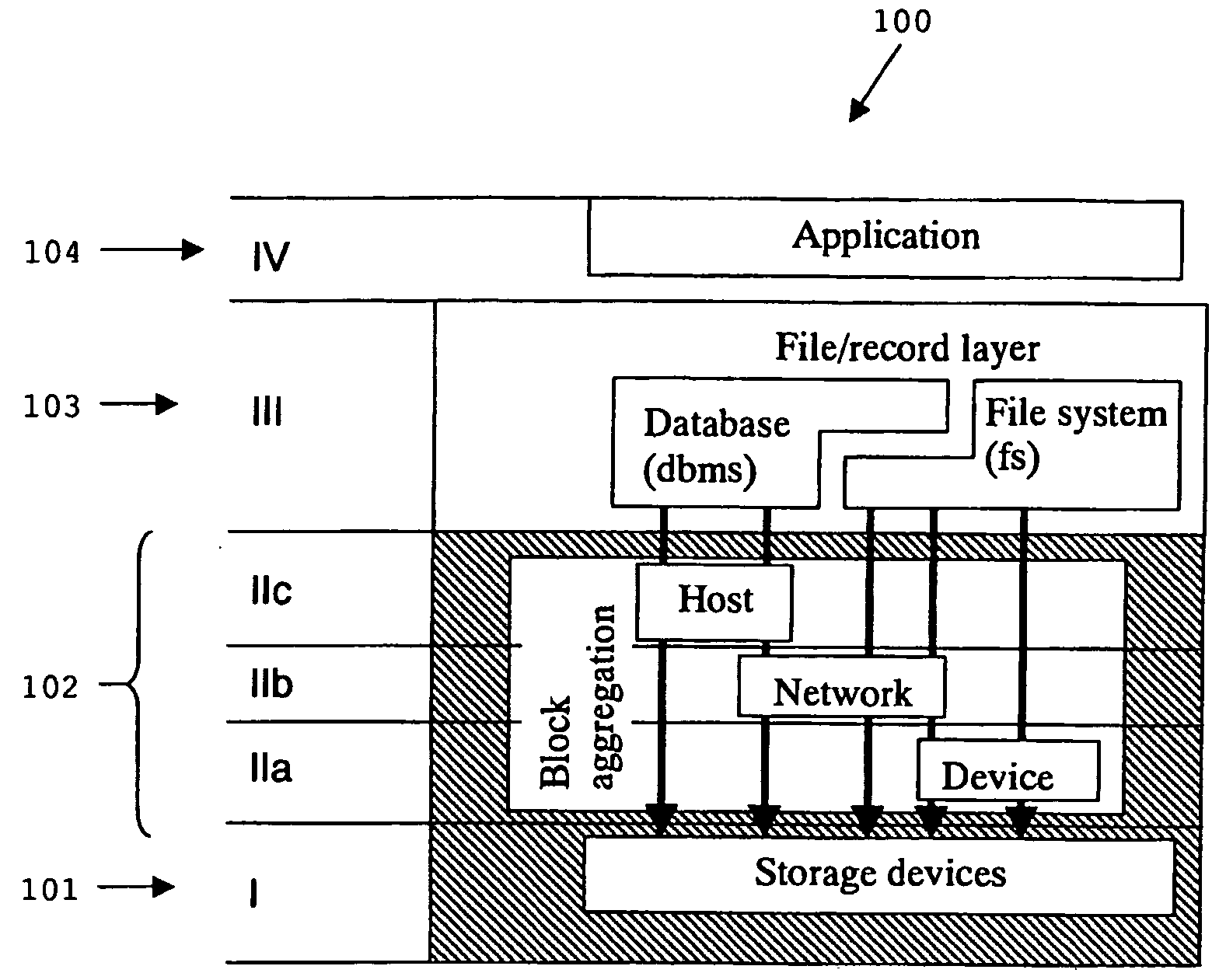
Shared storage network system and a method for operating a shared storage network system
InactiveUS20090094380A1Improve efficiencyImprove performanceDigital computer detailsInternal/peripheral component protectionBurst transmissionNetworked system
A shared storage network system comprises at least one storage client and a plurality of storage servers, each providing a storage portion of the shared storage network system, each storage portion being divided into a plurality of sectors, each sector being divided into a plurality of blocks, a virtual block identifier being associated to each of the blocks such that the entirety of all of the virtual block identifiers of the blocks form a global block address space in which each of the virtual block identifiers is unique. The plurality of storage servers and the at least one storage client are grouped into a plurality of local area networks interconnected with preferred optical channels to form a global network. The at least one storage client is adapted to have read and / or write access to at least one block of at least one of the storage portions associated to one of the local area networks which differs from the local area network of the storage client. The plurality of local area networks are interconnected such that in case of a read or a write access of one of the at least one storage client to at least one of the blocks, the virtual block address of a block to which access is desired is translated into a physical block address to identify the physical block associated with the virtual block. The shared storage network system is further adapted to implement a storage data transmission scheme comprising an optical burst mode flow control and an optical stop-over burst transmission method.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Wireless medical room control arrangement for control of a plurality of medical devices
ActiveUS20090300507A1Local control/monitoringElectric testing/monitoringCommunication interfaceWireless router
A wireless medical room control arrangement includes a wireless controller having a wireless router. A room identifier and a device identifier are stored in the controller. A communication interface sends commands to and receives commands from the wireless controller. In response to commands from the interface, the wireless controller sends wireless control signals to operate medical devices in the room. A room monitor adjacent a doorway provides room identifiers to medical devices and wireless controllers entering the room and provides dummy identifiers to medical devices and controllers exiting the room. The room monitors may connect to a global network processor that determines the location of the medical devices in a medical facility.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
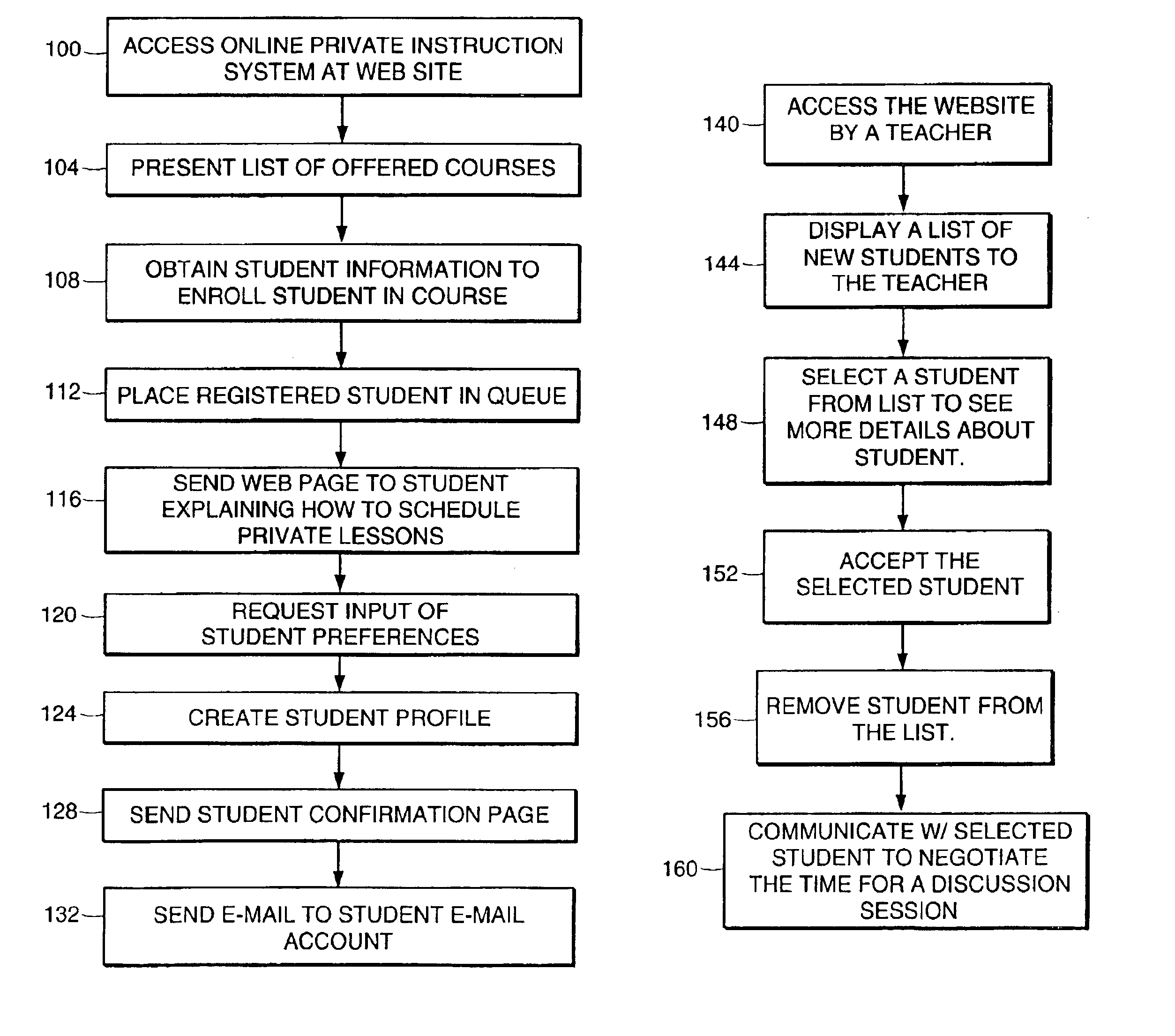
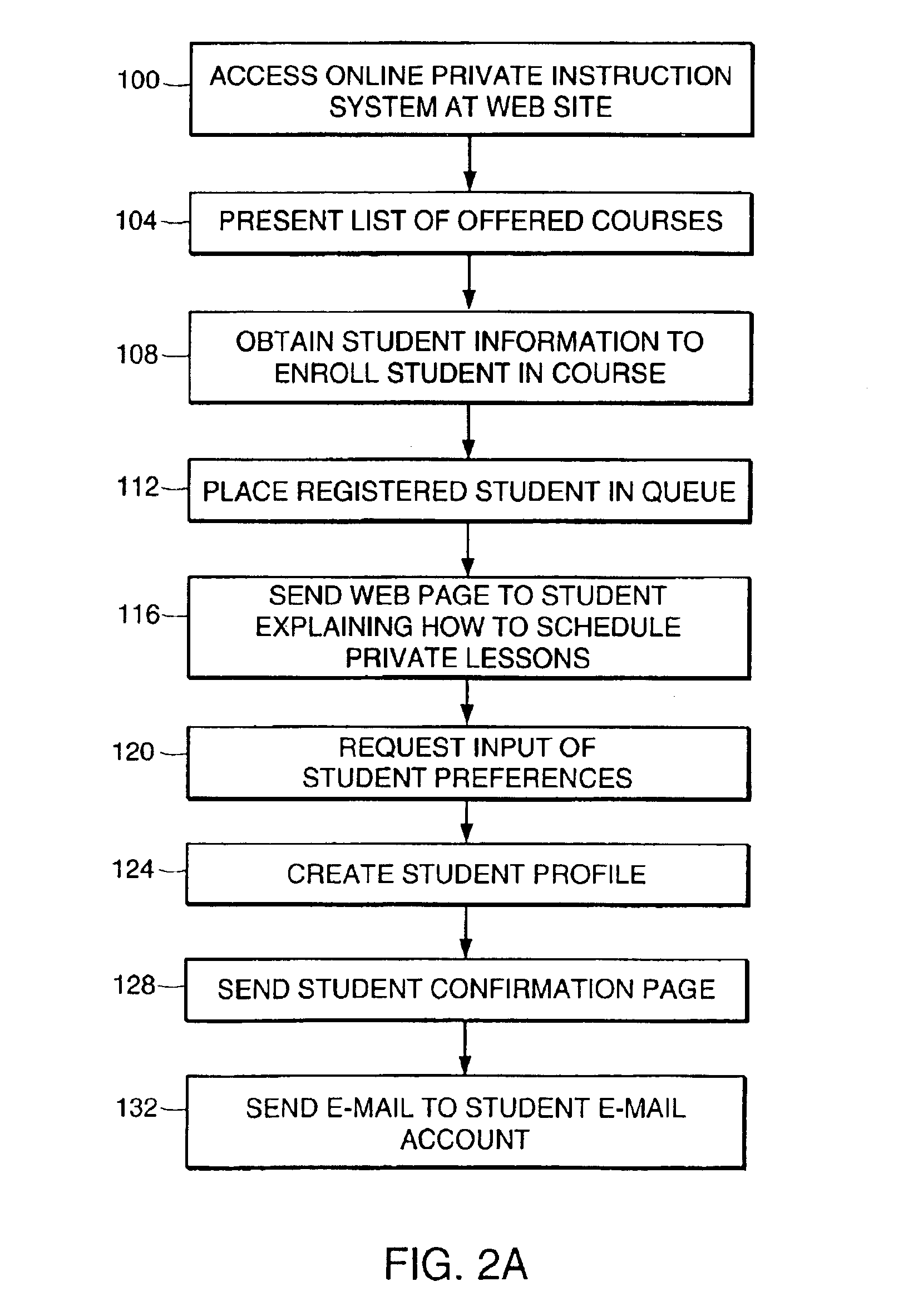
System and method of matching teachers with students to facilitate conducting online private instruction over a global network
Described are a system and method for facilitating private instruction over a network between a teacher and a student. Profile information is received from each student who registers for a private course. Each student who registers for a private course is included in a list of students who are unassigned to a teacher. Each teacher who is able to teach a private course has access over the network to the list of students and the profile information of the students. One of the teachers who is able to teach a given private course is assigned to one of the students in the list of students enrolled in that given private course based upon the profile information of that student.
Owner:SIGNUM INT AG
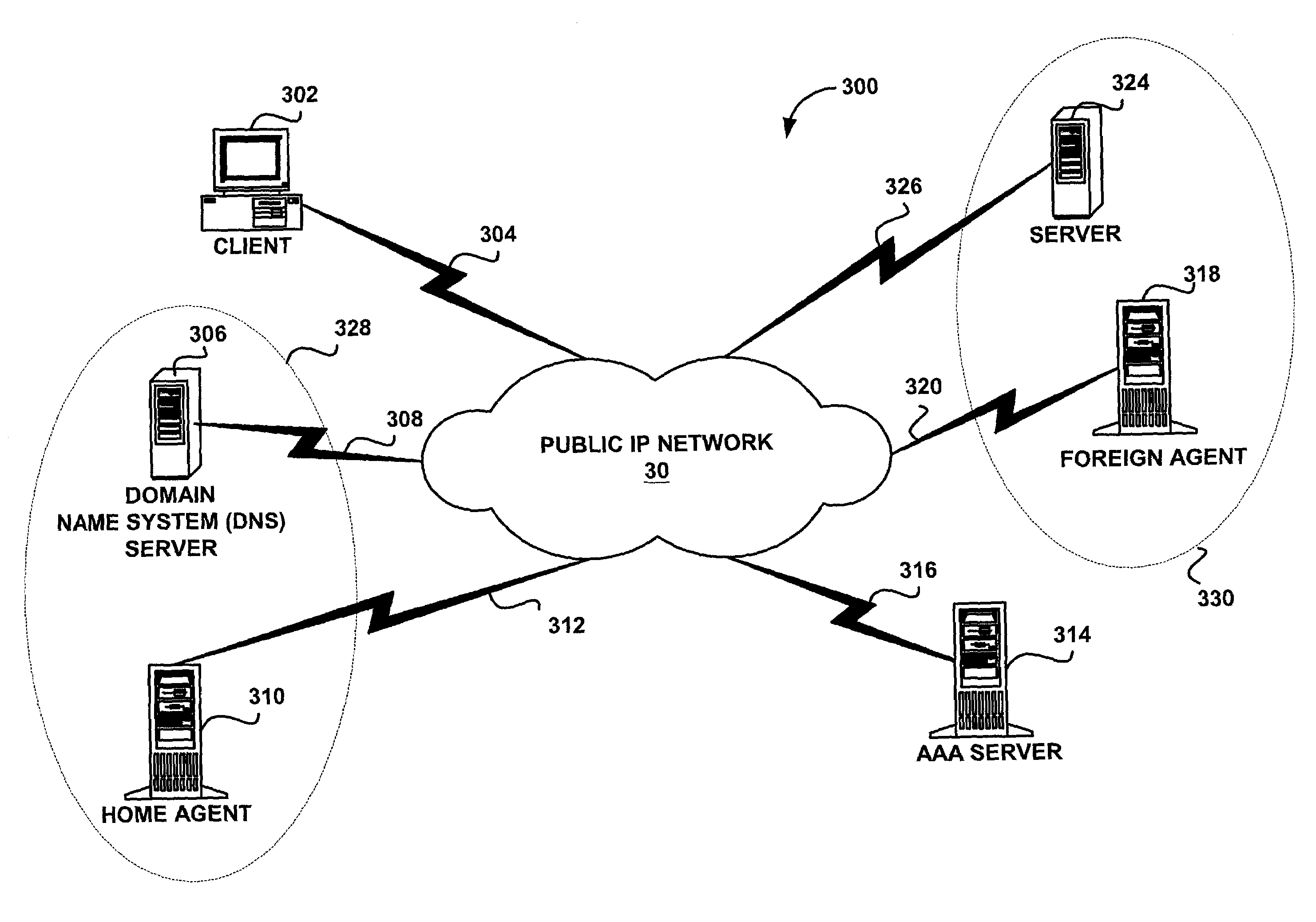
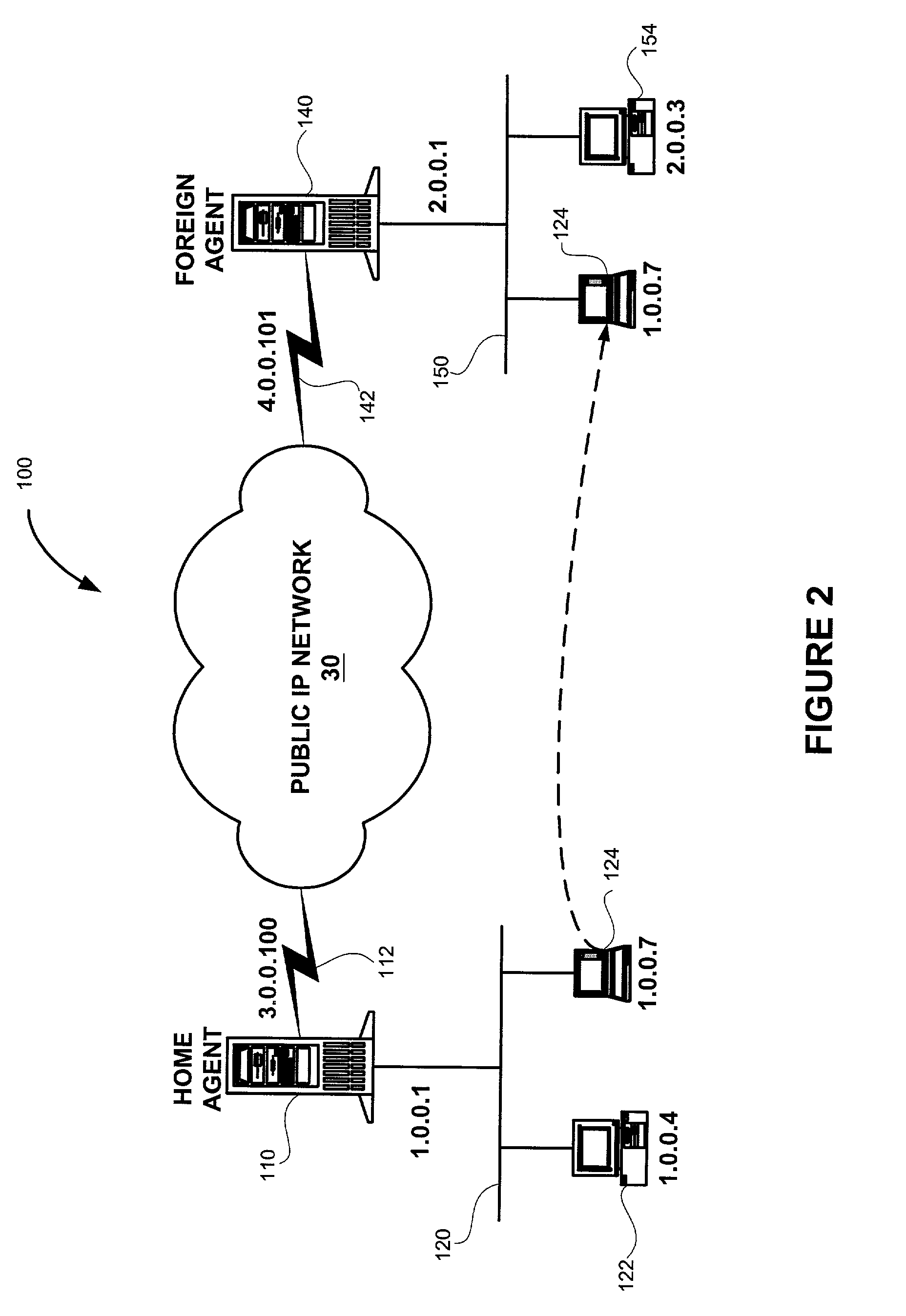
Method and apparatus for global server load balancing
InactiveUS7305429B2Readily apparentMultiple digital computer combinationsWireless network protocolsIp addressData center
A system and method are shown for load balancing across global network resources using an existing network protocol, such as Mobile IP, having a redirect feature. According to one method, each of a plurality of servers at a data center uses Mobile IP to obtain an IP address that is also provided to a content server site. Further, a content server site includes a plurality of IP addresses assigned to the plurality of servers and creates a load database including load data for each server. When a client request is received at the content server site from a client device, the content server site determines a network address of a server to process the client request based on the load data, and provides the network address of the server to the client device. When the client device receives the network address of the server, the client device sends an application request to the selected server, and the selected server sends an application response to the client device.
Owner:UTSTARCOM INC
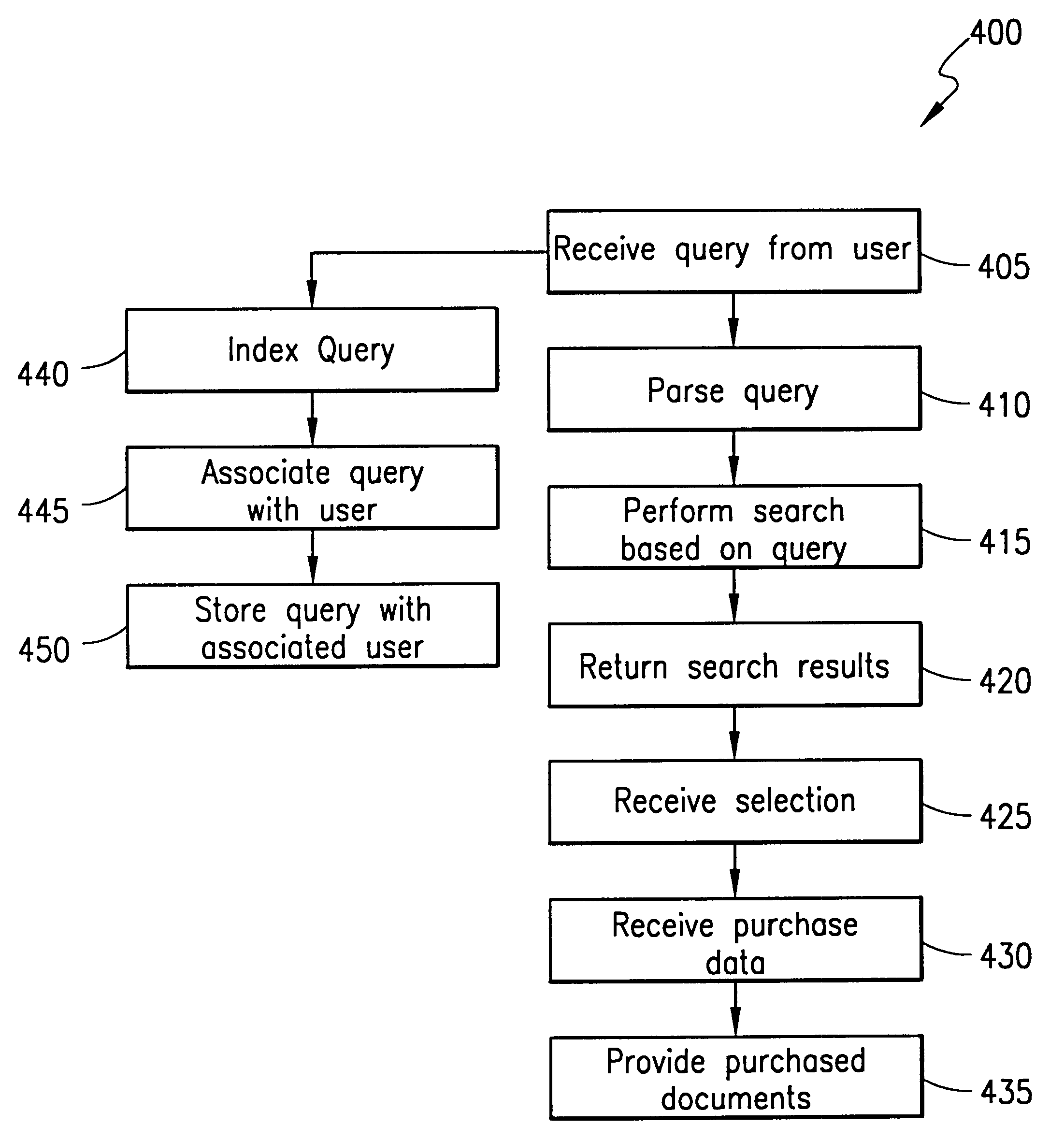
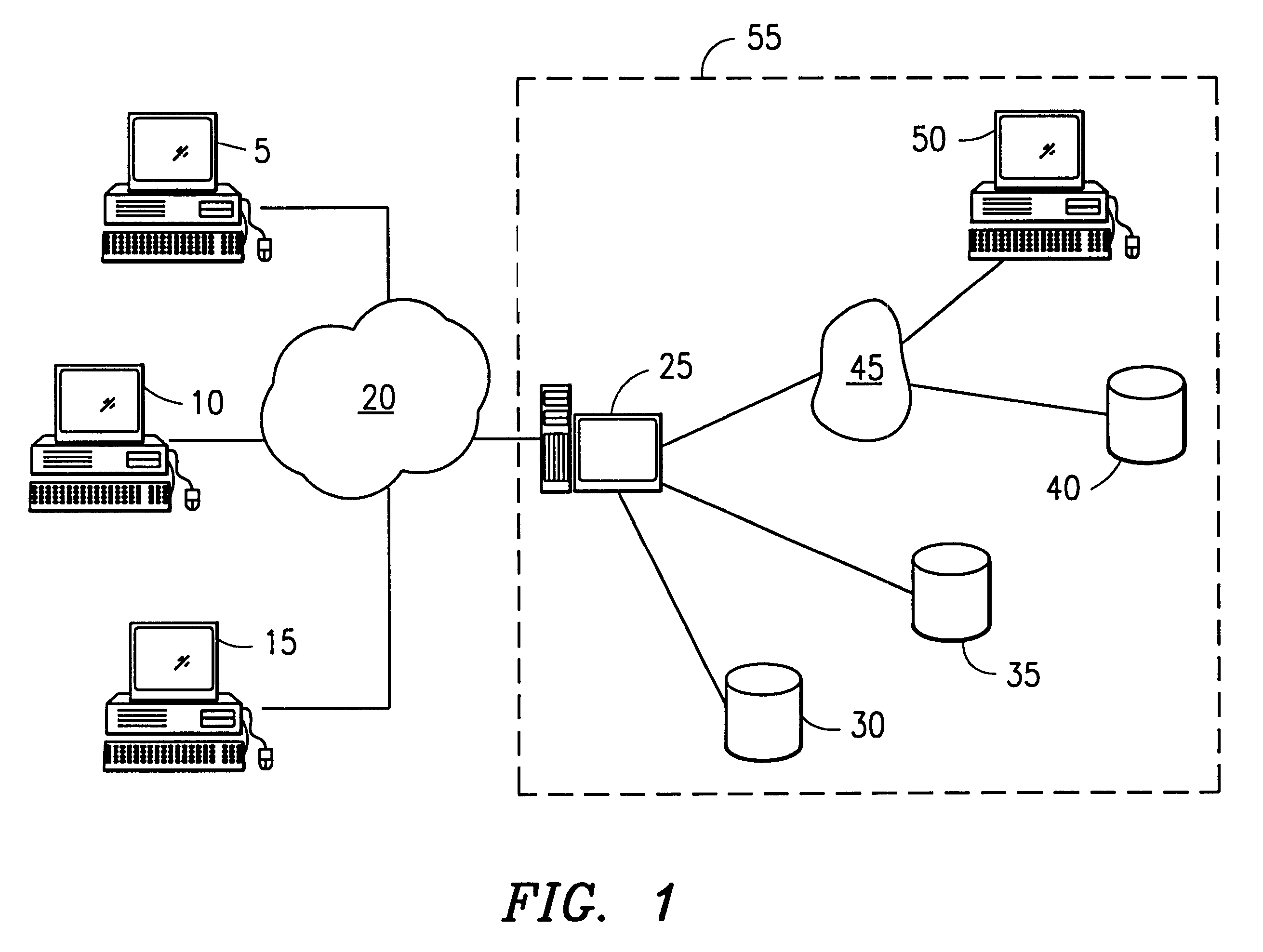
Information storage, retrieval and delivery system and method operable with a computer network
A system and method for collecting, indexing, searching, accessing and downloading of data over local and global computer networks. The data is reposed in a central database, where it is indexed and interrelated documents by attributes characteristic of the data type. The data is typically objects such as documents, queries, attribute lists and the like. The data is indexed and managed using a relational database management system (RDBMS). The central database and the RDBMS reside in a server that can be coupled to the global network through a network / user interface, queries received by a user based on known network protocols are converted to a format such as SQL understood by the RDBMS. Objects can be returned as an image file for viewing by the user, and can be purchased for downloading to the user's computer through some security mechanism, such as membership in a group having access to the database. Content to the database may be provided by individuals or proprietors of other databases, either run the network or through direct input to the server. Content to the database can also be self-generated by the RDBMS.
Owner:TRIALSMITH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com