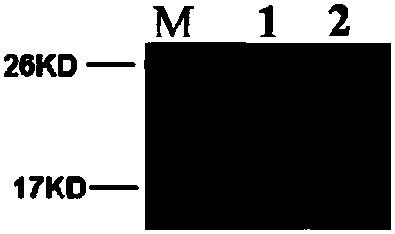Patents
Literature
65 results about "Comparative genomics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Comparative genomics is a field of biological research in which the genomic features of different organisms are compared. The genomic features may include the DNA sequence, genes, gene order, regulatory sequences, and other genomic structural landmarks. In this branch of genomics, whole or large parts of genomes resulting from genome projects are compared to study basic biological similarities and differences as well as evolutionary relationships between organisms. The major principle of comparative genomics is that common features of two organisms will often be encoded within the DNA that is evolutionarily conserved between them. Therefore, comparative genomic approaches start with making some form of alignment of genome sequences and looking for orthologous sequences (sequences that share a common ancestry) in the aligned genomes and checking to what extent those sequences are conserved. Based on these, genome and molecular evolution are inferred and this may in turn be put in the context of, for example, phenotypic evolution or population genetics.
Method for developing dendranthema SSR (Simple Sequence Repeat) primer based on transcriptome sequencing
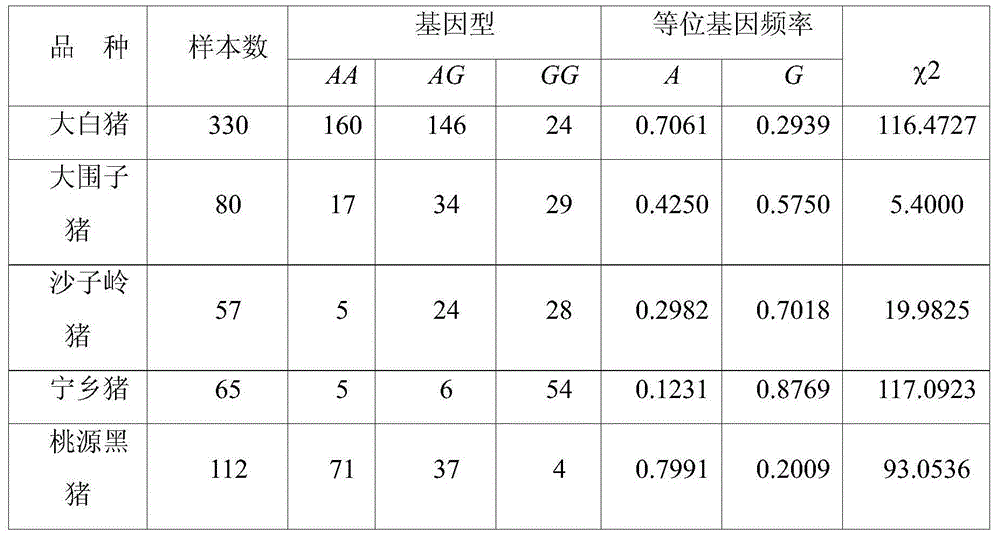
ActiveCN103233075AAdd raw dataOvercoming access difficultiesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceLymphatic Spread
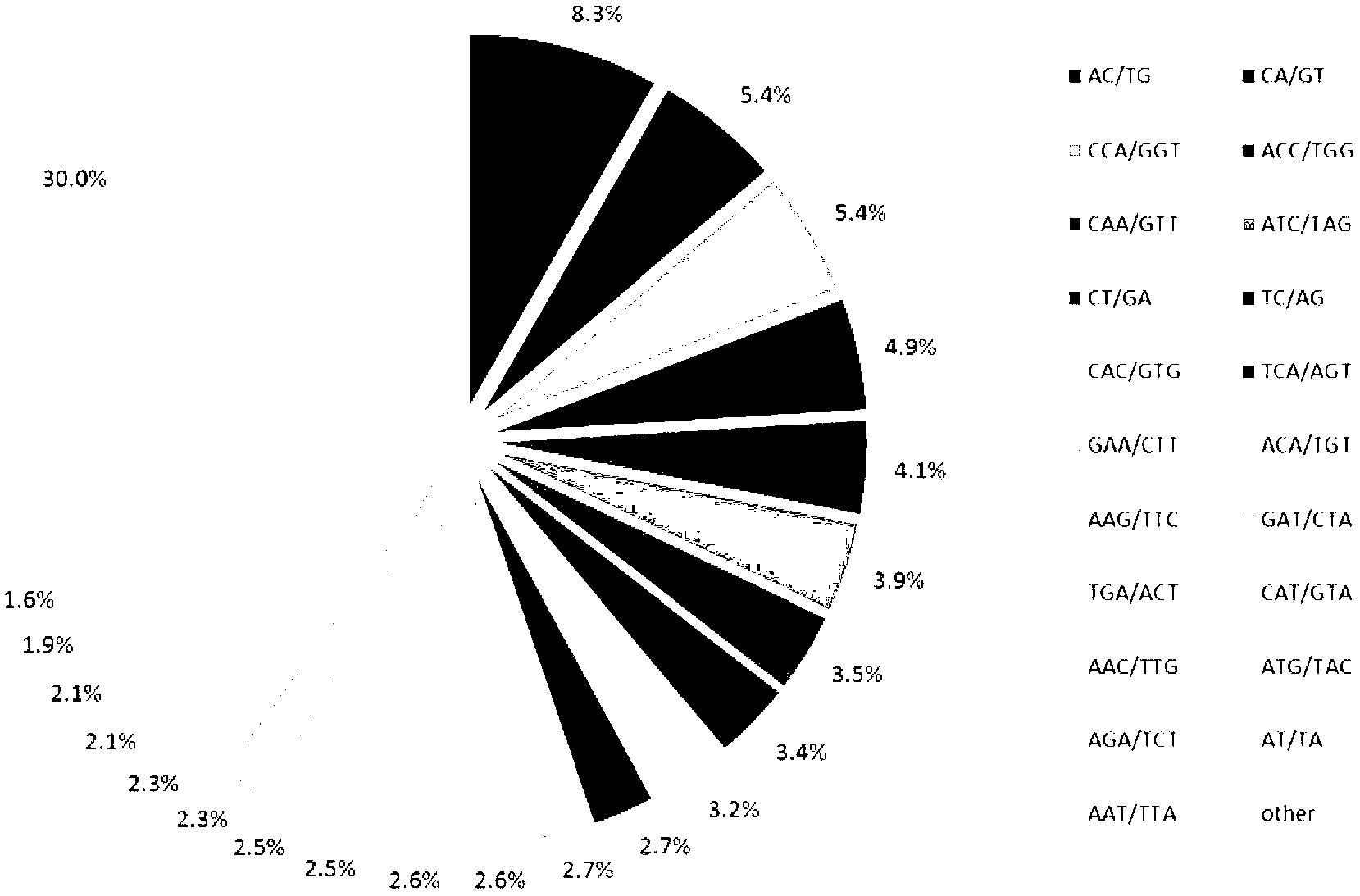
The invention belongs to biotechnology field, and relates to a method for developing a dendranthema SSR (Simple Sequence Repeat) primer based on transcriptome sequencing. A lot of sequence information is processed in batch for searching an SSR sequence and designing an SSR labeled primer based on the transcriptome sequencing by utilizing EST-SSR (Expressed Sequence Tags-Simple Sequence Repeat) interspecific metastasis and using a Perl (Practical Extraction and Reporting Language) programming language method in combination, so that the defects of low efficiency, long time consumption, high cost and the like of the SSR development are conquered. Different dendranthema materials are selected for verifying the designed SSR primer, and the primer is a successful SSR primer if detected out by any strip. By adopting the method, 1788 pairs of SSR primers are successively designed, so that a novel method and thinking are provided for the development of the dendranthema SSR primer to further achieve molecular marker assistant selection breeding and comparative genomics research.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
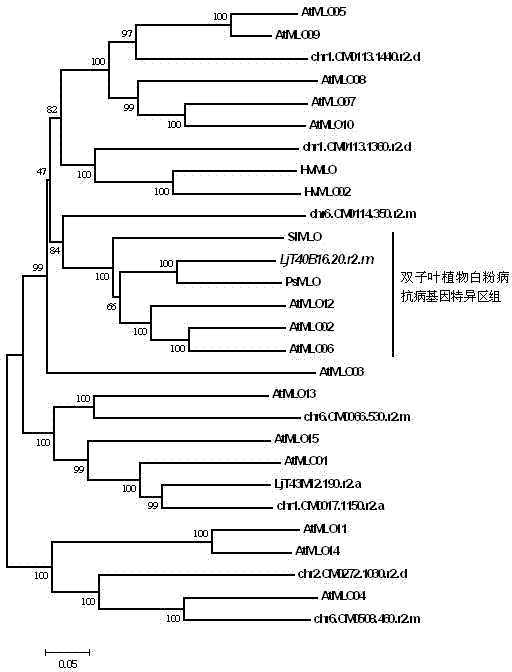
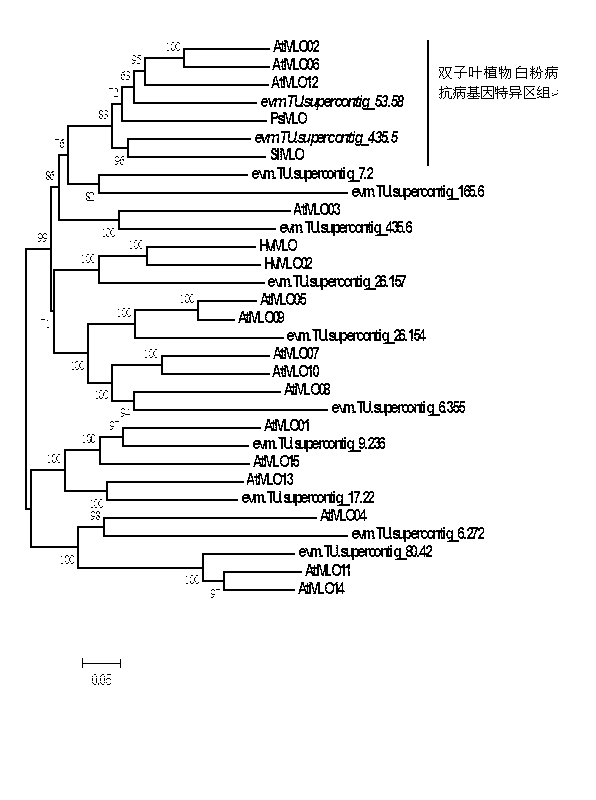
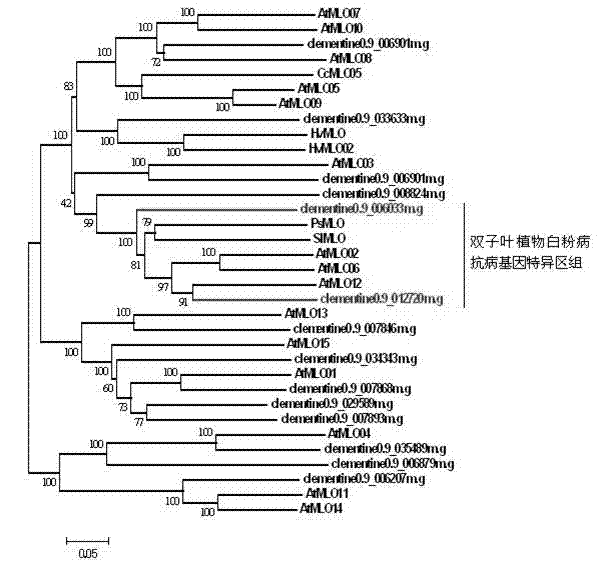
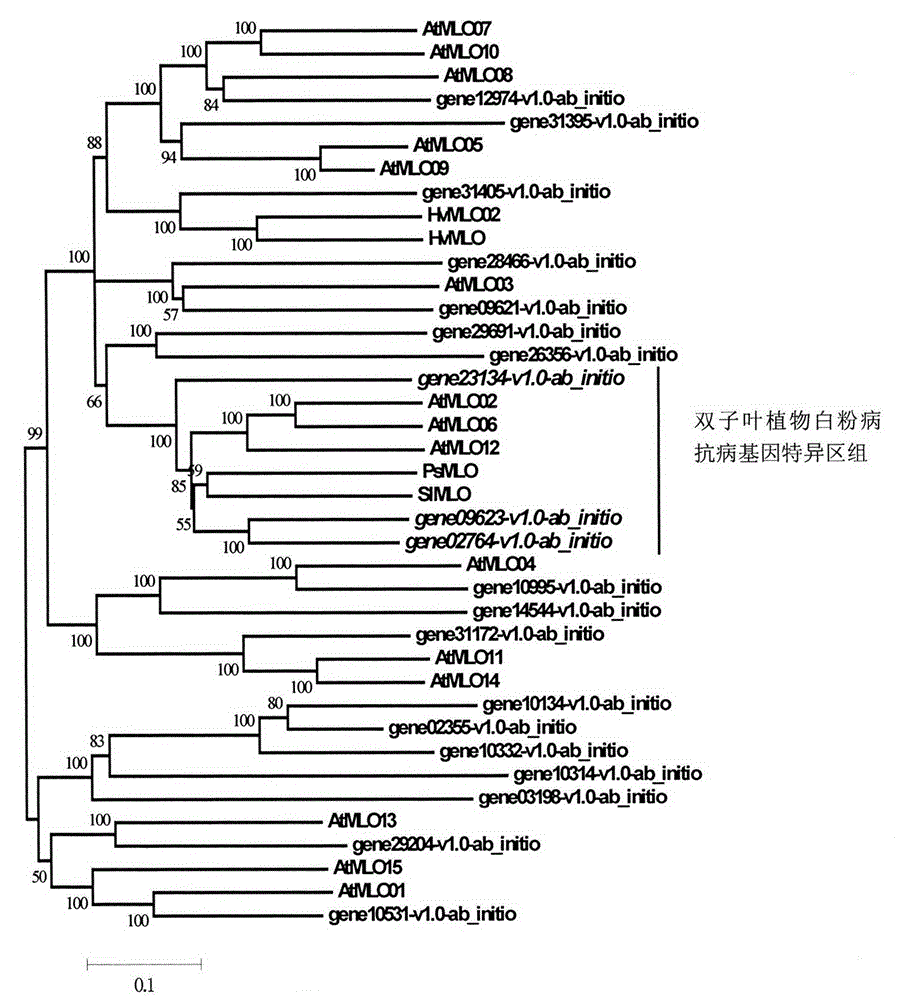
Rapid identification of powdery mildew resistance Lotus corniculatus genes utilizing comparative genomics
InactiveCN102703463AShorten digging cycleRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyGenetics genomics
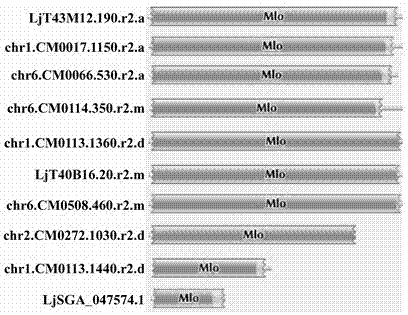
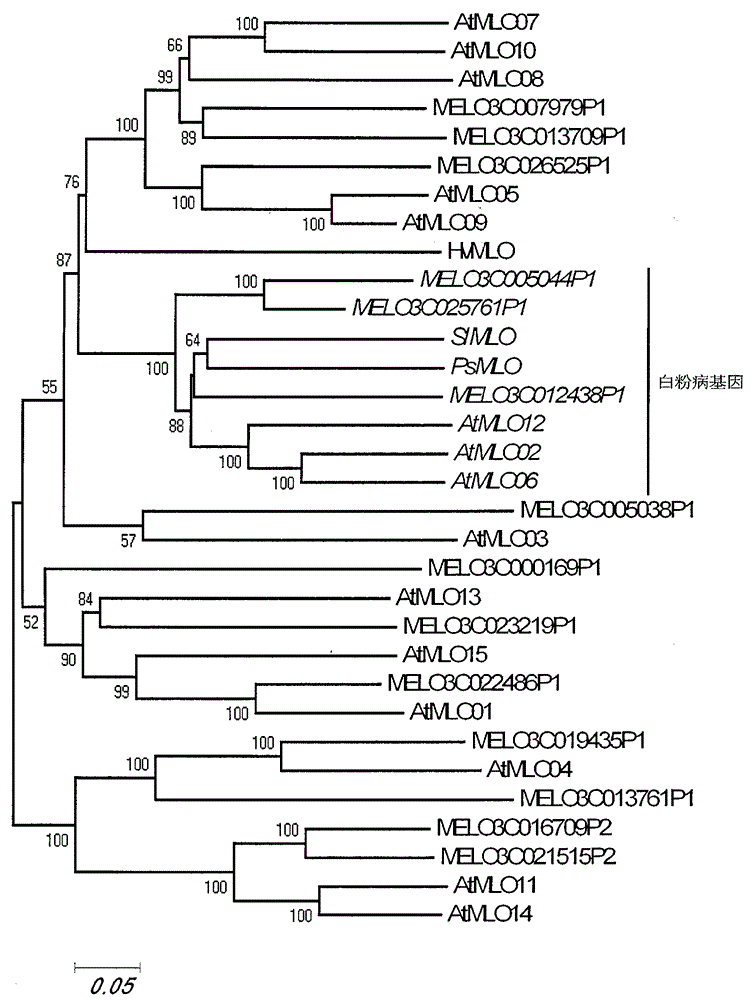
The invention relates to rapid identification of powdery mildew resistance Lotus corniculatus genes utilizing comparative genomics, relates to knowledge of subjects such as plant comparative genomics, genetics and bioinformatics, and belongs to the technical field of plant biotechnology. The rapid identification of powdery mildew resistance Lotus corniculatus genes utilizing the comparative genomics mainly includes the steps of firstly, downloading full genomic sequences of Lotus corniculatus and collecting MLO (mildew resistance locus o) genes; secondly, identifying the MLO genes; thirdly, identifying phylogenetic relationship of the MLO genes; and fourthly comparing the MLO powdery mildew resistance genes. By the rapid identification, mining cycle of the powdery mildew resistance genes is shortened, and the powdery mildew resistance genes can be identified quickly. Corresponding co-separation functional marks (SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism), Scar and the like) can be developed through candidate powdery mildew resistance genes identified, the rapid identification is also available for molecular marker-assisted selection of the powdery mildew resistance genes, and accuracy is high. The rapid identification can also be used with other molecular markers for resistance genes to create multiresistance breeding materials, and accordingly breeding period is shortened, breeding efficiency is improved, and basis for elaborating powdery mildew resistance Lotus corniculatus molecular mechanisms is laid.
Owner:常熟市支塘镇新盛技术咨询服务有限公司
Application of bioinformatics in fast identifying powdery mildew resistance gene of carica papaya l
InactiveCN102719448AShorten digging cycleRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyPapaya family
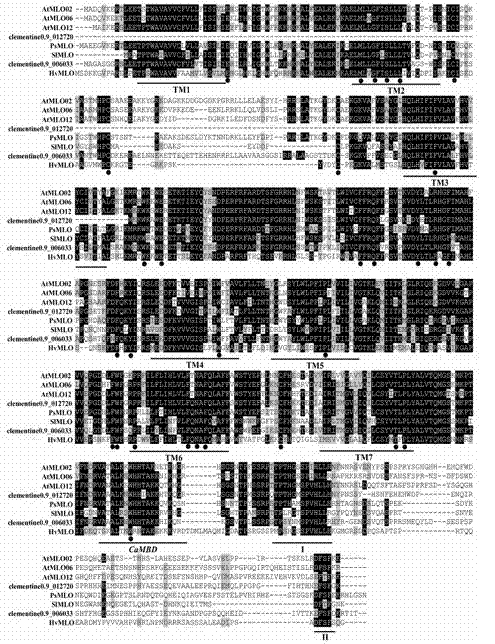
The invention relates to fast identification of a powdery mildew resistance gene of carica papaya l, relating to subject knowledge including plant comparative genomics, genetics, bioinformatics and the like, belonging to the field of plant biotechnology sciences. Application of the invention mainly comprises the steps: 1) downloading complete genome sequence of the carica papaya l and acquiring MLO-type genes; 2) identifying the MLO-type genes; 3) researching phylogenetic relationships of the MLO-type genes; and 4) comparing MLO-type powdery mildew resistance genes. The invention has the advantages that discovery period of the powdery mildew resistance gene of the carica papaya l is effectively shortened, which assists in fast identification of the powdery mildew resistance gene; that identified candidate powdery mildew resistance genes are developed with corresponding co-segregation functional markers (SNP, SCAR, etc.), which can be used in fast auxiliary selection of molecular markers of the powdery mildew resistance gene with high accuracy; that other molecular markers of resistance genes can be combined to formulate multi-resistance breeding materials, which shortens breeding years and improves breeding yields; and that a foundation is laid to illustrate the powdery mildew resistance gene of the carica papaya l.
Owner:常熟市支塘镇新盛技术咨询服务有限公司
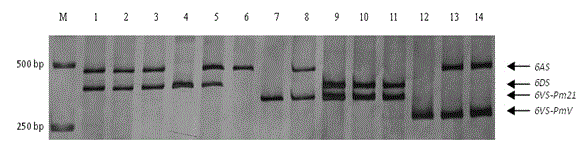
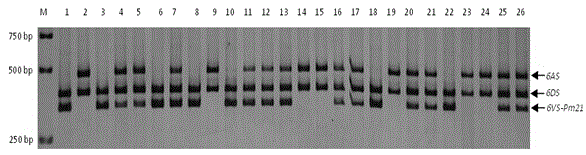
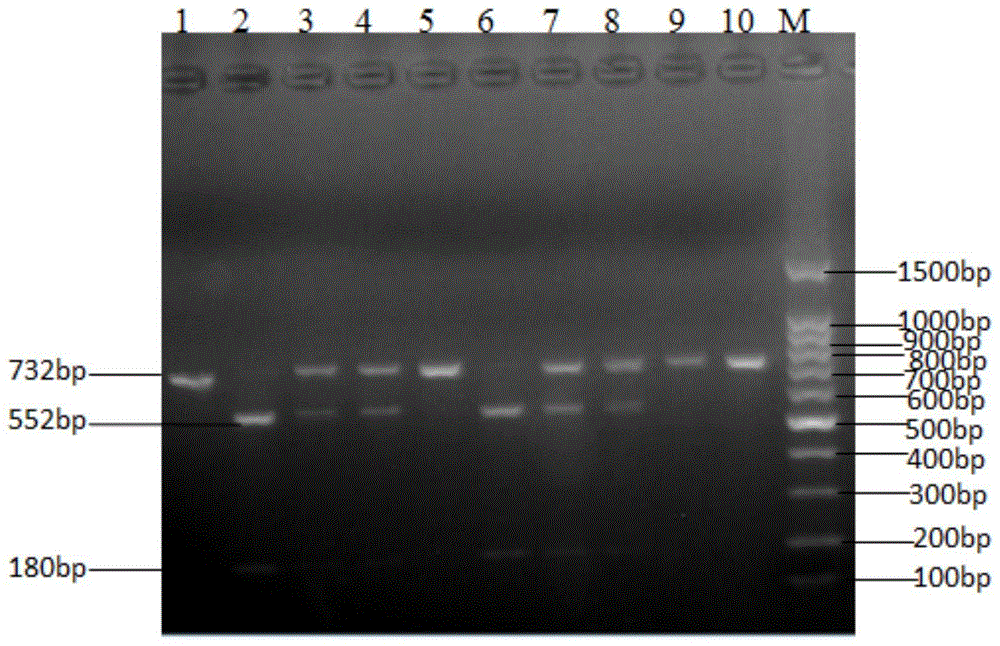
Haynaldia villosa's 6VS chromosome specific molecular marker 6VS-BH1 and application thereof
InactiveCN104877996AStrong brightnessWide range of annealing temperaturesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyMarker-assisted selection
The invention relates to a haynaldia villosa's 6VS chromosome specific molecular marker 6VS-BH1 and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical fields of molecular biology and genetic breeding science. The labeled primer 6VS-BH1 is developed on the basis of wheat-brachypodium distachyon comparative genomics means, and the specific sequence is 6VS-BH1F, as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and 6VS-BH1R, as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The molecular marker 6VS-BH1 has the advantages of wide annealing temperature range (60-66 DEG C), good stability, strong product brightness, high resolution and the like. The molecular marker 6VS-BH1, as a co-dominant marker, not only can be used for effectively tracing haynaldia villosa's 6VS chromosome in wheat background, but also can be used for distinguishing a homozygote and heterozygote and for distinguishing a Pm21 gene carried translocation line T6VS.6AL and a PmV gene carried translocation line T6VS.6DL. Therefore, the molecular marker 6VS-BH1 disclosed by the invention has an important practical value in the molecular marker-assisted selection breeding of wheat powdery mildew and the pyramiding breeding of Pm21 gene and PmV gene.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
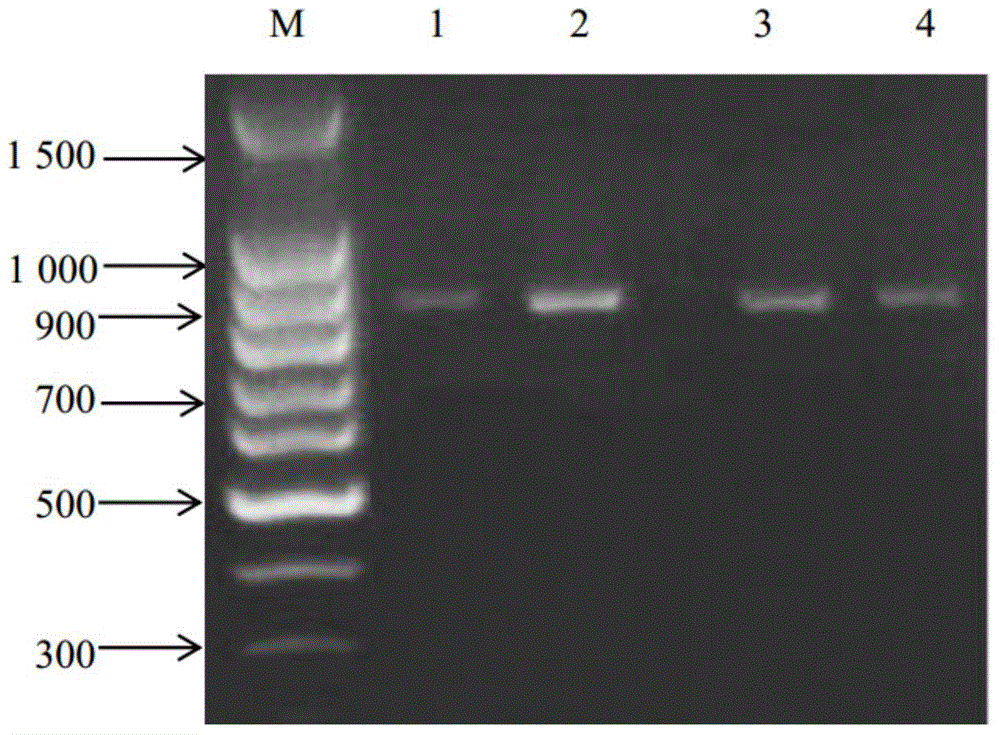
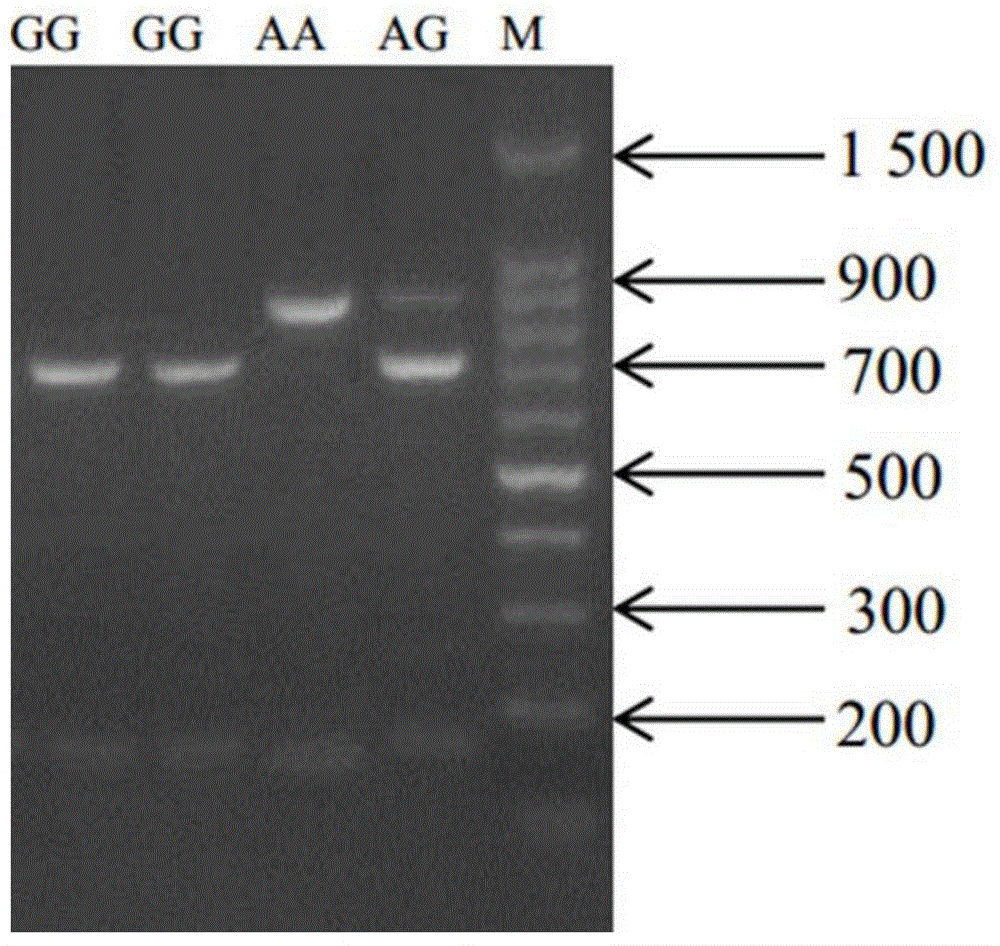
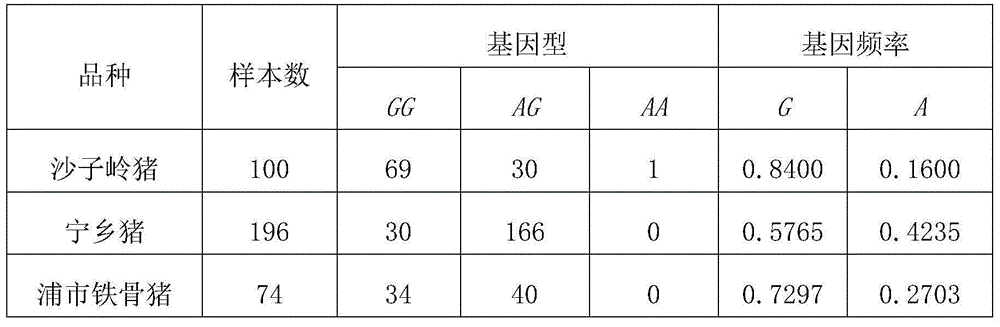
Clone and application of pig meat quality character relevance WNT10B gene molecular mark
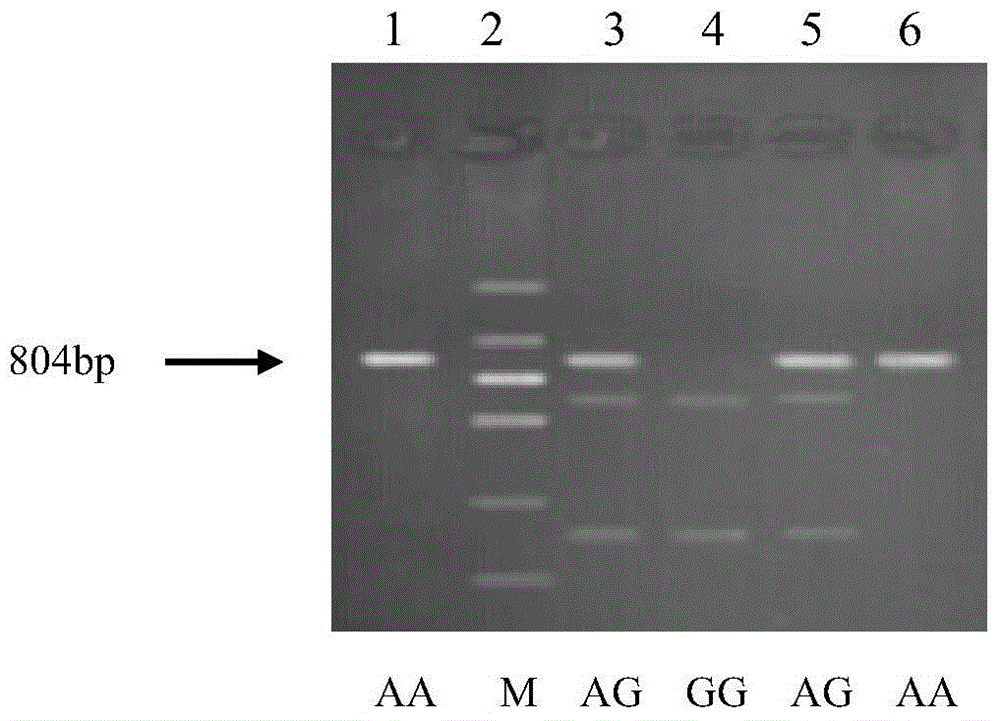
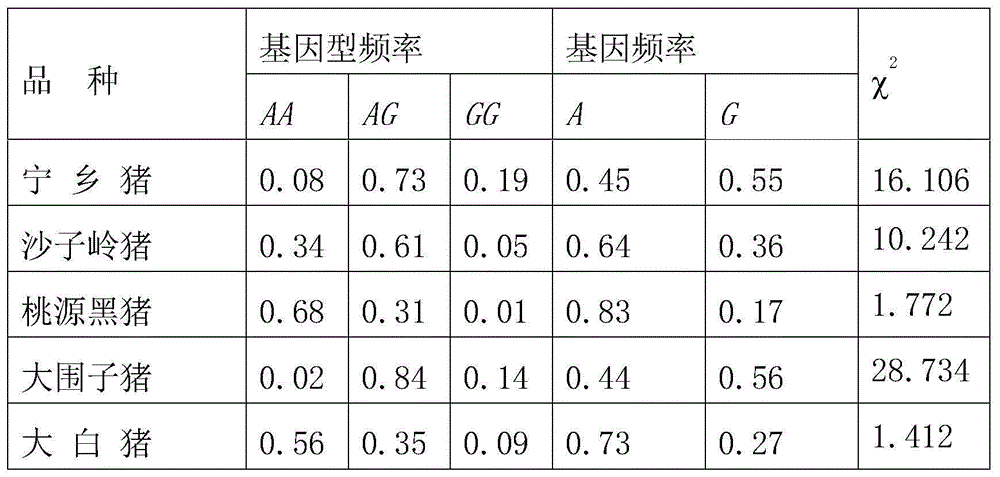
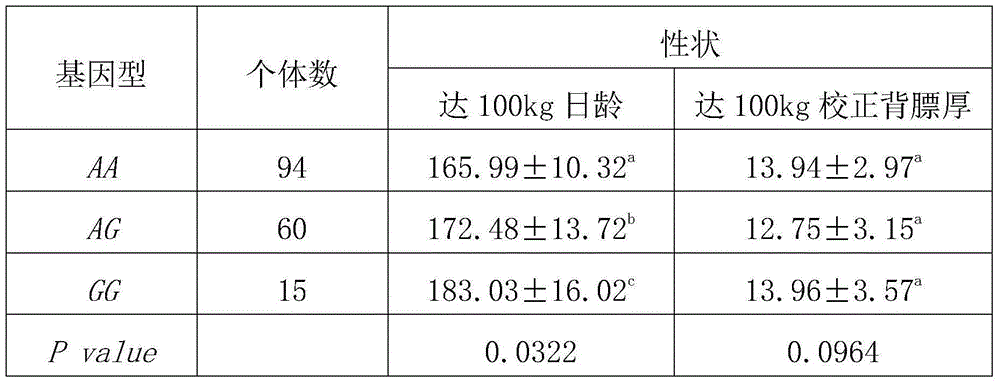
The invention belongs to the field of the livestock molecule molecular biological technique and particularly relates to a clone and the application of a pig meat quality character relevance WNT10B gene molecular mark. The molecular mark is obtained by cloning pig WNT10B genes, and the sequence of the WNT10B molecular mark of the WNT10B gene is shown in SEQ ID NO:1. According to the polymorphism of the WNT10B, a primer is designed according to the WNT10B gene sequence of people with a genomics method, the genomic DNA of pigs is used as the template for amplification, SNP is screened by amplified fragments through sequencing, PCR-RFLP is used for conducting gene typing, a basic group mutation is found at the 552 bp position, polymorphism of PCR-RFLP-Sal I is caused, a new molecular mark is provided for auxiliary selection of the pig meat quality character mark, and the mark can be used for detecting the conditions of domestic and foreign pig breeds.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Rapid identification of powdery mildew gene of Medicago truncatula by utilizing comparative genomics
InactiveCN102719445AQuick assist selectionImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyRapid identification
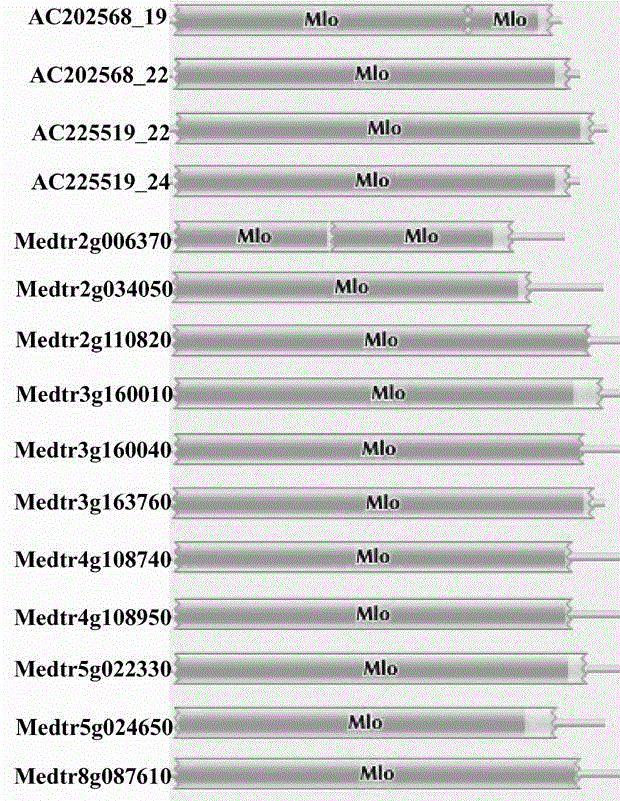
The present invention is rapid identification of a powdery mildew gene of Medicago truncatula, relates to discipline knowledge of plant comparative genomics, genetics and bioinformatics and belongs to the technical field of plant biotechnology. The invention mainly comprises the following steps: 1) download of Medicago truncatula genome sequence and collection of an MLO gene; 2) identification of MLO type gene; 3) MLO gene phylogenetic relationship; and 4) comparison of MLO type powdery mildew gene. The invention effectively shortens a mining cycle of the powdery mildew gene of Medicago truncatula and facilitates the rapid identification of the powdery mildew gene. The identified candidate powdery mildew genes can be used to develop corresponding coseparation functional markers (SNP and SCAR, etc.), and can also be used quickly for molecular marker assisted selection of powdery mildew resistant gene, and has high accuracy. Combined with other disease resistant gene molecular markers, the identified candidate powdery mildew genes can be used in development of multiresistance breeding material, so as to shorten the breeding period and improve breeding efficiency. The invention lays foundation to elaborate molecular mechanism of powdery mildew resistance of Medicago truncatula.
Owner:常熟市支塘镇新盛技术咨询服务有限公司
Method for rapidly identifying orange MLO powdery mildew resistance gene
InactiveCN102719446AShorten digging cycleRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyRapid identification
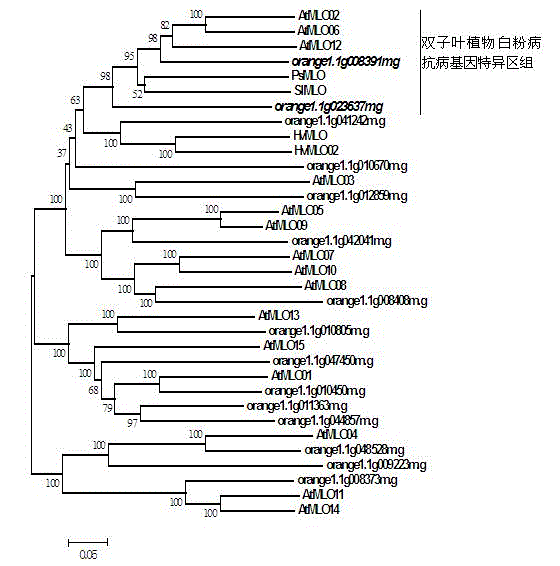
The present invention is a method for rapidly identifying an orange MLO powdery mildew resistance gene, relating to plant comparative genomics, genetics, bioinformatics and other disciplines of knowledge, and belonging to the field of plant biotechnology science. The method in the invention mainly comprises the following steps of: 1) download of an orange full genome sequence and collection of an MLO gene; 2) identification of the MLO gene; 3) identification of a candidate MLO powdery mildew gene through phylogenetic relationship of the MLO gene; and 4) comparison of the MLO powdery mildew gene. The method in the invention can effectively shorten a mining cycle of the orange powdery mildew gene, facilitating rapid identification of the powdery mildew gene; the method can develop corresponding cosegregation functional markers (SNP, SCAR and the like) through the identified candidate powdery mildew gene and can also be used in fast molecular marker-assisted selection of the powdery mildew resistance gene with high accuracy; the method can also create multiple breeding materials with resistance property through combination of other resistance gene molecular markers, shortening a breeding period and improving breeding efficiency; the method can further lays a foundation for describing an orange powdery mildew resistance molecular mechanism.
Owner:常熟市支塘镇新盛技术咨询服务有限公司
Method for quickly identifying manihot esculenta mildew-resistance locus (MLO) gene by applying comparative genomics
InactiveCN102796745AShorten digging cycleRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesDiseaseGenetics genomics
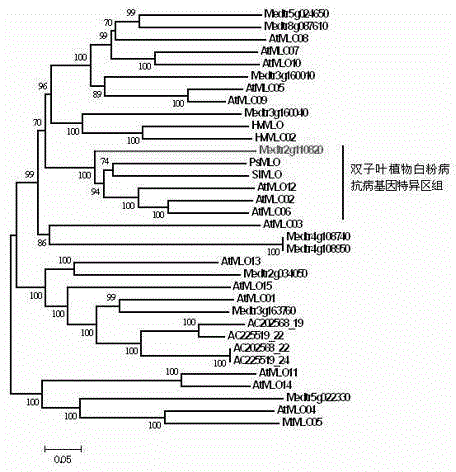
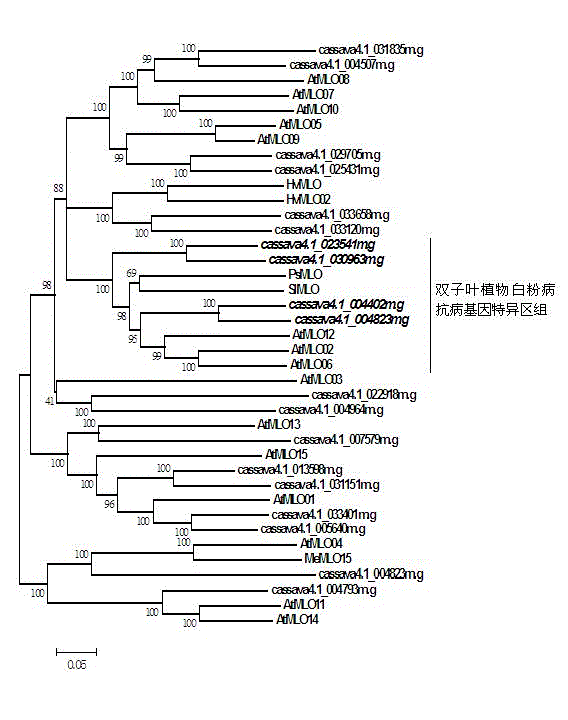
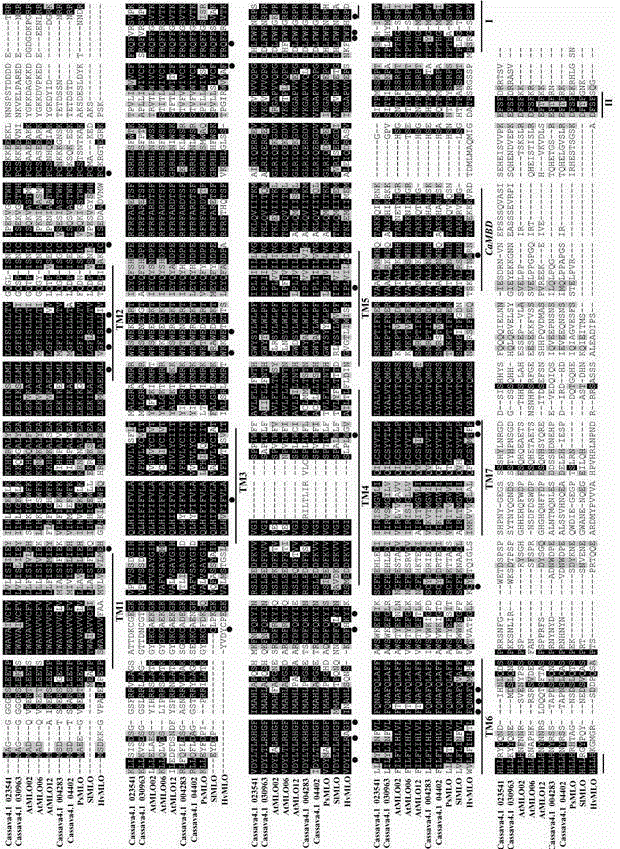
The invention discloses a method for quickly identifying a manihot esculenta mildew-resistance locus (MLO) gene, relates to knowledge of plant comparative genomics, genetics, bioinformatics and the like and belongs to the field of plant biotechnology science. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: 1) downloading a manihot esculenta whole genome sequence, and collecting the MLO gene; 2) identifying the MLO gene; 3) identifying the MLO gene according to the MLO gene phylogenetic relationship; and 4) comparing the MLO genes. By the method, the discovery cycle of the manihot esculenta MLO gene is shortened effectively, and the MLO gene can be quickly identified; corresponding coseparation functional markers (single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and specific combining ability (SCA)) can be developed by the identified candidate MLO gene, and the method can be quickly used for molecular marker auxiliary selection of the MLO gene, and is high in accuracy; by combining other disease-resistant gene molecular markers, multiresistance breeding materials can be prepared, the breeding cycle is shortened, and the breeding efficiency is improved; and the foundation is laid for elaborating a manihot esculenta MLO gene molecular mechanism.
Owner:常熟市支塘镇新盛技术咨询服务有限公司
Rapid identification of MLO (mildew resistance locus o) powdery mildew resistance Poncirus trifoliata genes
InactiveCN102703464AShorten digging cycleRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyRapid identification
The invention relates to rapid identification of powdery mildew resistance Poncirus trifoliata genes, relates to knowledge of subjects such as plant comparative genomics, genetics and bioinformatics, and belongs to the technical field of plant biotechnology. The rapid identification mainly includes the steps of firstly, downloading full genomic sequences of Poncirus trifoliate and collecting MLO genes; secondly, identifying the MLO genes; thirdly, identifying phylogenetic relationship of the MLO genes; and fourthly, comparing the MLO powdery mildew resistance genes. By the rapid identification, mining cycle of the powdery mildew resistance Poncirus trifoliata genes is shortened effectively, and the powdery mildew resistance genes can be identified quickly. Corresponding co-separation functional marks (SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism), Scar and the like) can be developed through candidate powdery mildew resistance genes identified, the rapid identification is also available for molecular marker-assisted selection of the powdery mildew resistance genes, and accuracy is high. The rapid identification can also be used with other resistance gene molecular markers to create multiresistance breeding materials, breeding period is shortened, breeding efficiency is improved, and basis for elaborating powdery mildew resistance Poncirus trifoliata molecular mechanisms is laid.
Owner:常熟市支塘镇新盛技术咨询服务有限公司
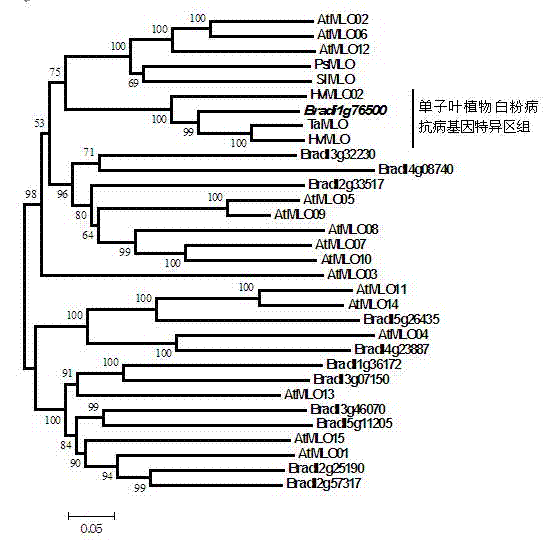
Rapid identification of anti-powdery-mildew gene of Brachypodium distachyon
InactiveCN102703462AShorten digging cycleRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyBrachypodium sylvaticum
The invention relates to rapid identification of anti-powdery-mildew gene of Brachypodium distachyon, relates to the knowledge of plant comparative genomics, genetics, biological information and other subjects, and belongs to the scientific field of plant biotechnology. The rapid identification of anti-powdery-mildew gene of Brachypodium distachyon comprises the main steps of: (1) downloading full genome sequences of Brachypodium distachyon and collecting MLO (mildew resistance locus o) type gene; (2) identifying the MLO type gene; (3) analyzing the MLO type gene historical development relation; and (4) comparing the MLO type powdery mildew gene. According to the rapid identification of anti-powdery-mildew gene of Brachypodium distachyon provided by the invention, the excavation period of the anti-powdery-mildew gene of Brachypodium distachyon is effectively shortened, and the rapid identification of the powdery mildew gene is facilitated; the identified powdery mildew gene can be used for developing corresponding coseparation functional markers (SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism), SCAR (sequence-characterized amplified region), and the like), and can also be rapidly used for assisted selection of molecule markers of anti-powdery-mildew gene, and the accuracy is high; development of multi-resistance breeding materials can be carried out by combining with other anti-disease gene molecule markers, the breeding time is shortened and the breeding efficiency is improved; and foundation is established for expounding the molecular mechanism of the anti-powdery-mildew gene of Brachypodium distachyon.
Owner:常熟市支塘镇新盛技术咨询服务有限公司
LAMP method for detecting enterobacteriaceae food-borne pathogenic bacteria, nucleic acid and primer pairs
ActiveCN105803064AThe detection process is fastReliable resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesFood bornePathogenic bacteria
The invention relates to an LAMP method for detecting enterobacteriaceae food-borne pathogenic bacteria, nucleic acid and primer pairs and belongs to the technical field of food safety detection.The LAMP method includes the following steps that a common gene sequence of the enterobacteriaceae pathogenic bacteria is screened out through bioinformatics and comparative genomics, and the specific amplification primer pairs are designed according to the sequence; an LAMP detection system is established by optimizing reaction conditions.The invention further relates to nucleic acid with the base sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1 and a group (three pairs) of primers.The base sequences of the primers are shown in SEQ ID NO:2, SEQ ID NO:3, SEQ ID NO:4, SEQ ID NO:5, SEQ ID NO:6 and SEQ ID NO:7.Compared with the prior art, the detection method is used for detecting enterobacteriaceae, detection time is short, cost is low, higher practicality is achieved, the detection result is specific, and result judgment is simple.
Owner:杭州海关技术中心
Method and system for comparative genomics
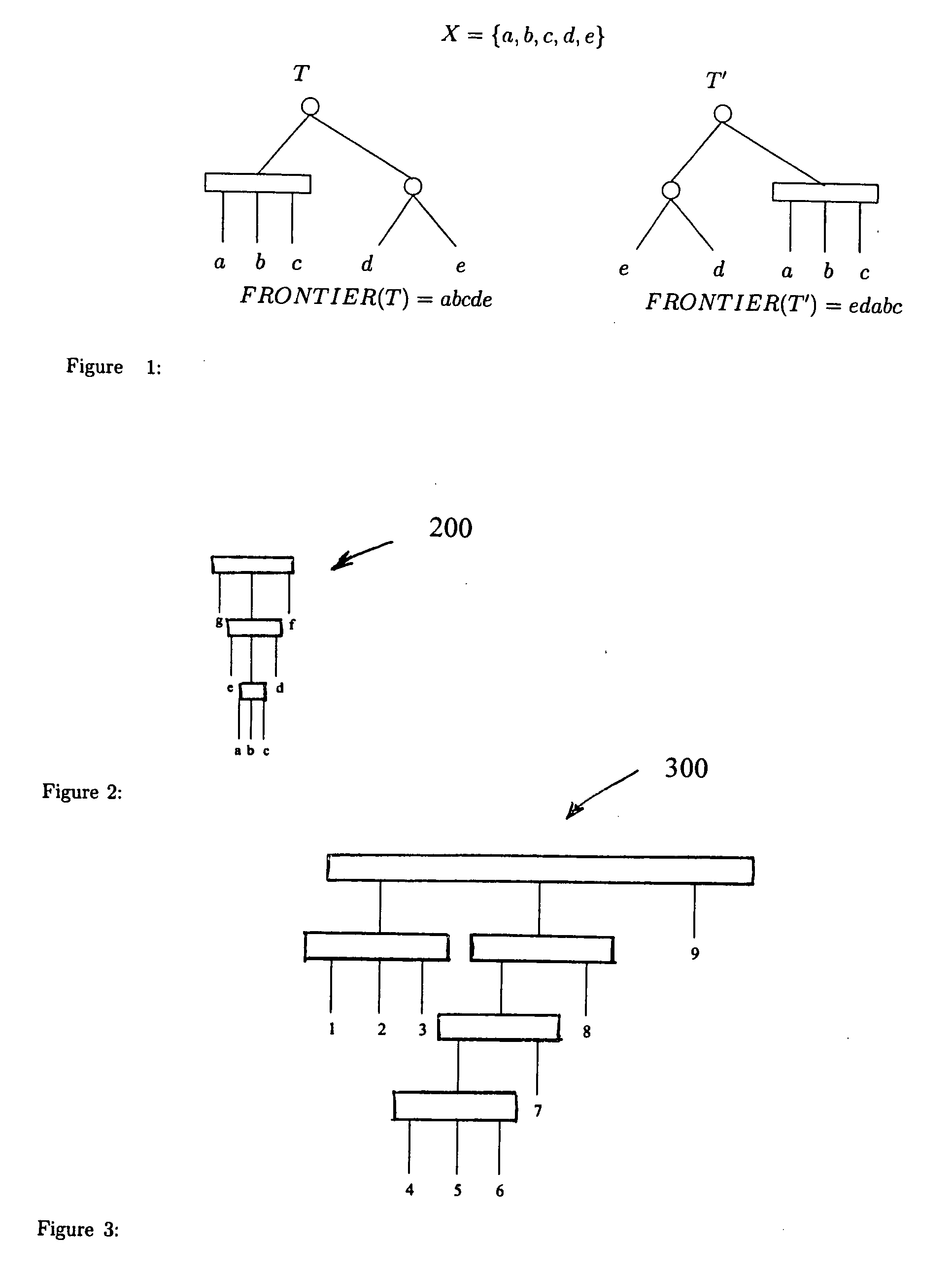
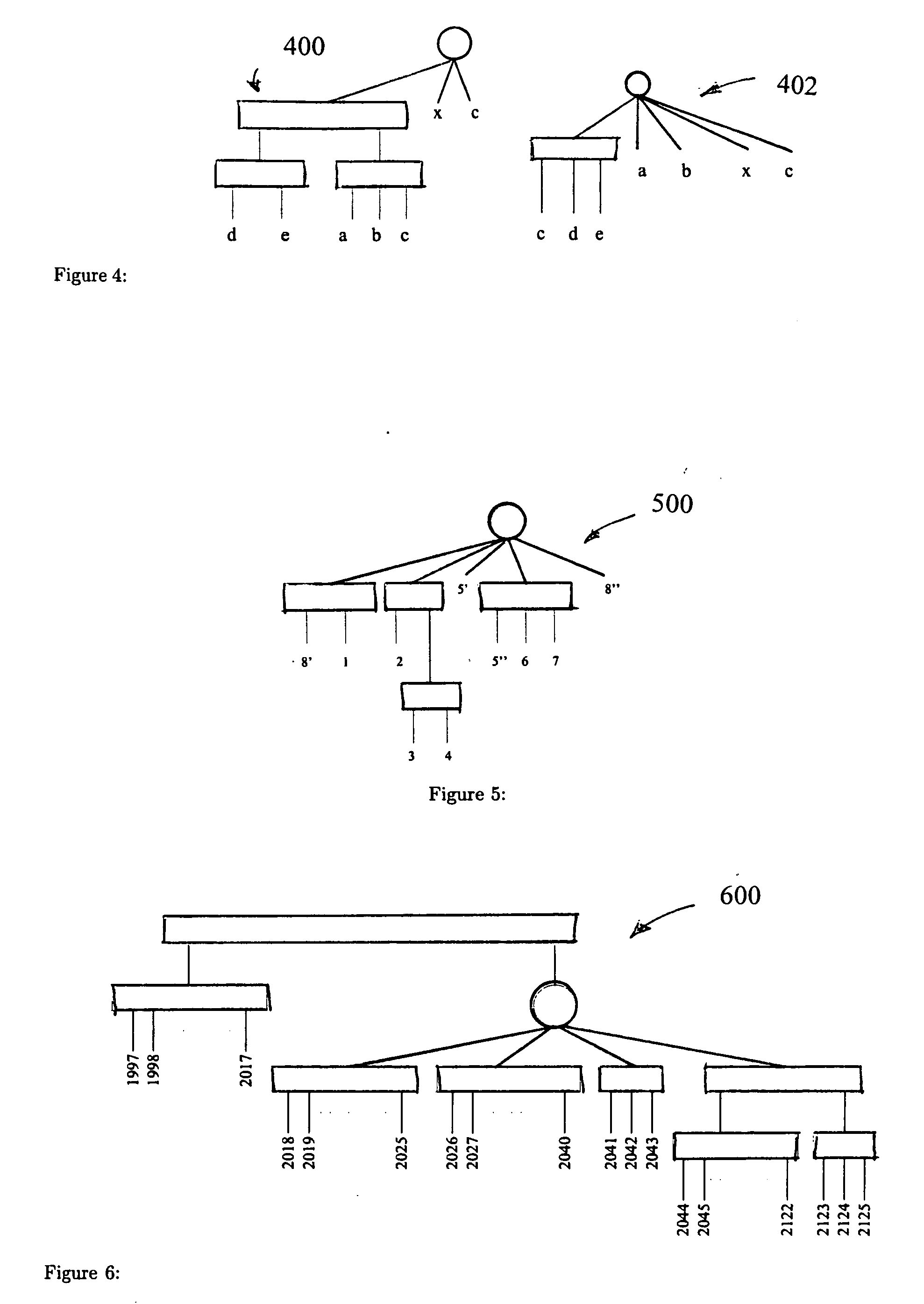
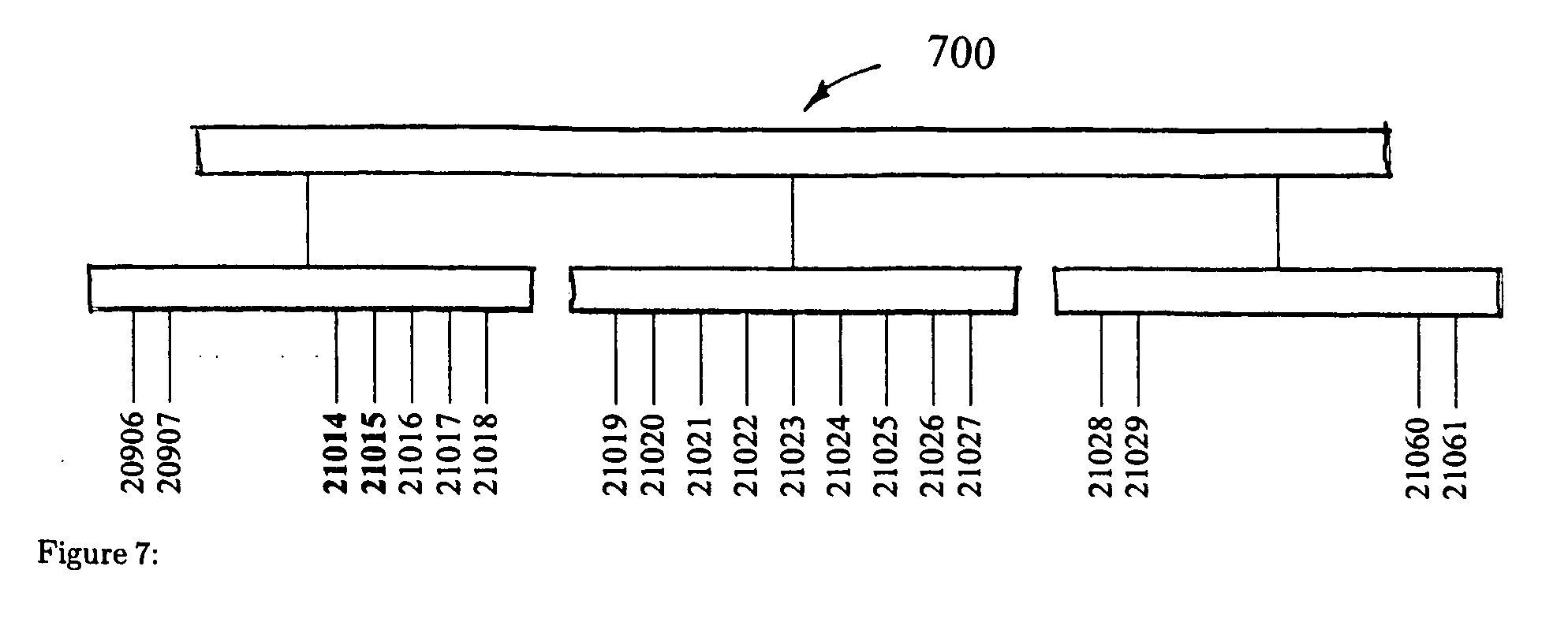
A method and system for representing a similarity between at least two genomes that includes detecting gene clusters which are common to the at least two genomes and representing the common gene clusters in a PQ tree. The PQ tree includes a first internal node (P node), that allows permutation of the children thereof, and a second internal node (Q node), that maintains unidirectional order of the children thereof.
Owner:IBM CORP
Development method of chrysanthemum SSR (Simple Sequence Repeat) primer
InactiveCN103233074AOvercoming access difficultiesOvercoming the problem of no SSR primersMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMarker-assisted selectionComputer science
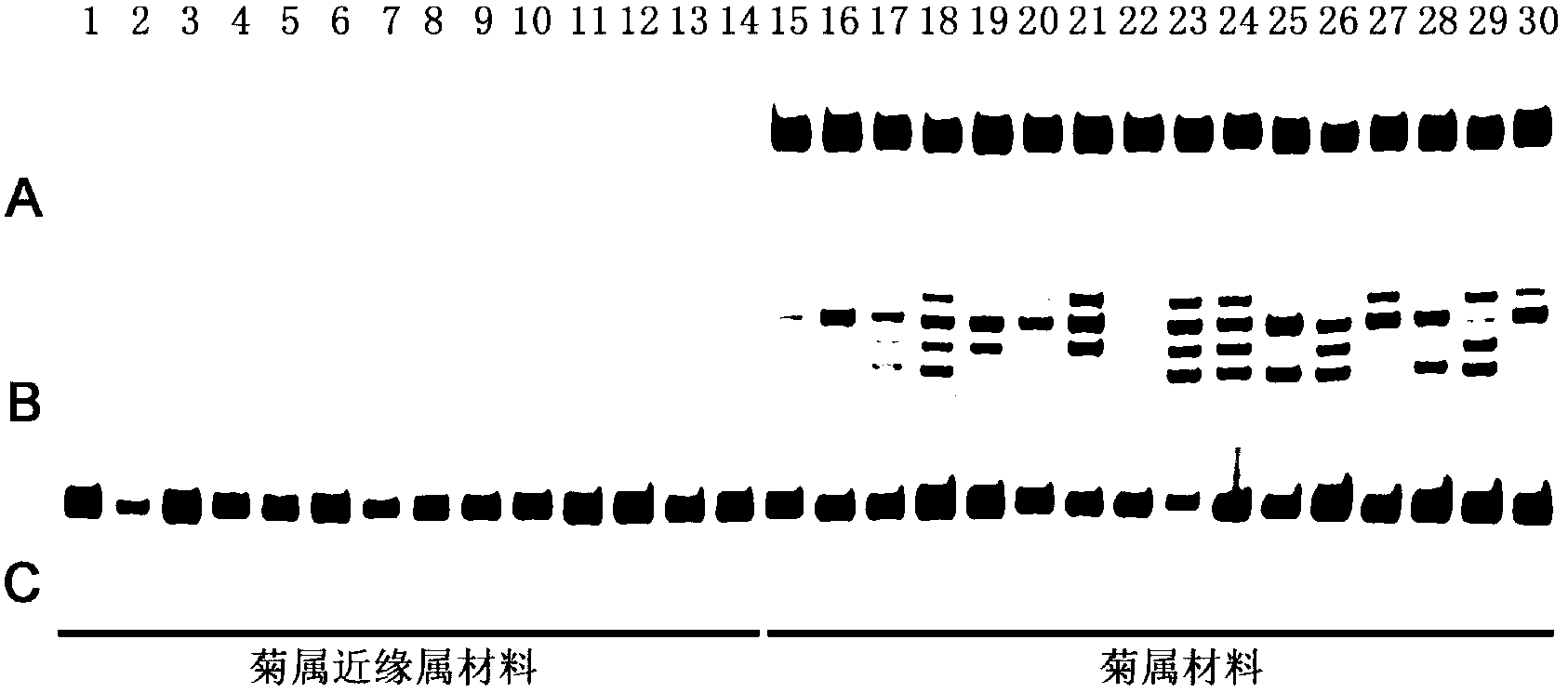
The invention belongs to biotechnology field, and relates to a development method of a chrysanthemum SSR (Simple Sequence Repeat) primer. A lot of sequence information is processed in batch for searching an SSR sequence and designing an SSR labeled primer by utilizing the existing sequence data in an NCBI (National Center of Biotechnology Information) database and using a Perl (Practical Extraction and Reporting Language) programming language method in combination, so that the defects of low efficiency, long time consumption, high cost and the like of the SSR development are conquered. Different cultivated chrysanthemum types are used as materials for verifying the designed SSR primer, and the primer is a successful SSR primer if detected out by any strip. By adopting the method, 363 pairs of SSR primers are successively designed, so that a novel method and thinking are provided for the development of the chrysanthemum SSR primer to further achieve molecular marker assistant selection breeding and comparative genomics research.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Rapid Identification of pear powdery mildew resistance gene
InactiveCN104561027AShorten digging cycleImprove identification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringAgricultural scienceRapid identification
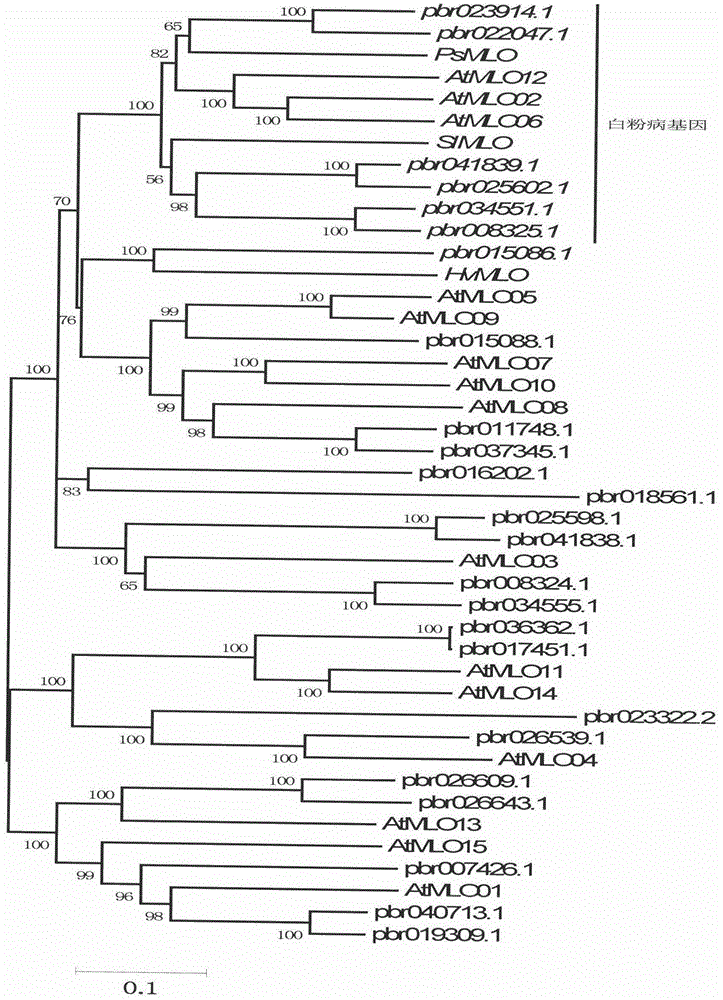
The invention relates to rapid identification of a pear powdery mildew resistance gene, and relates to the subject knowledge of plant comparative genomics, genetics and bioinformatics, belonging to the field of science of biotechnology. The rapid identification of the pear powdery mildew resistance gene comprises the following main steps of: 1) downloading of a complete genome sequence of a pear and collection of an MLO gene; 2) identification of the MLO gene; 3) MLO gene phylogenetic relationship; and 4) comparison of an MLO powdery mildew gene. The rapid identification of the pear powdery mildew resistance gene, provided by the invention, has the advantages of effectively shortening the pear powdery mildew gene mining period, and being favorable for the rapid identification of the powdery mildew gene; corresponding co-segregation functional markers (SNP, SCAR and the like) can be developed through the identification of candidate powdery mildew genes, and the co-segregation functional markers can be rapidly used for the molecular marker-assisted selection of the powdery mildew resistance gene, so that the accuracy is high; by combining other powdery mildew resistance gene molecular markers, a multi-resistance breeding material can be created, the breeding period can be shortened, and the breeding efficiency can be improved; a foundation is laid for explaining a pear powdery mildew resistance molecular mechanism.
Owner:CHANGSHU CITY DONGBANG DONGDUN VEGETABLE PROFESSION COOP
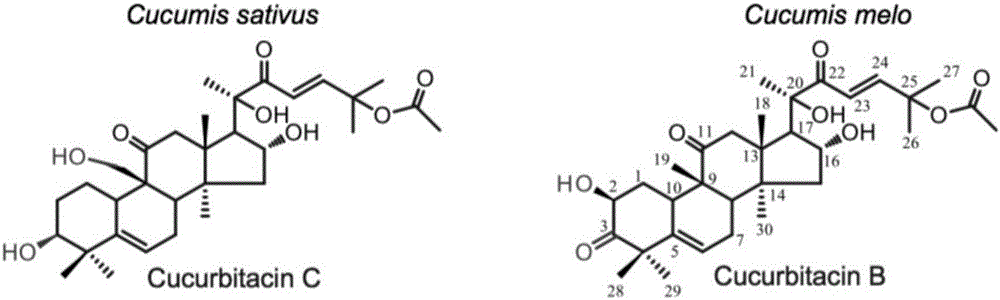
Transcription factors participating in regulating and controlling synthesis of bitter principles of cucumis melo and application of transcription factors
ActiveCN110317829ACo-domesticationPlant peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionNicotiana tabacumCotyledon plant
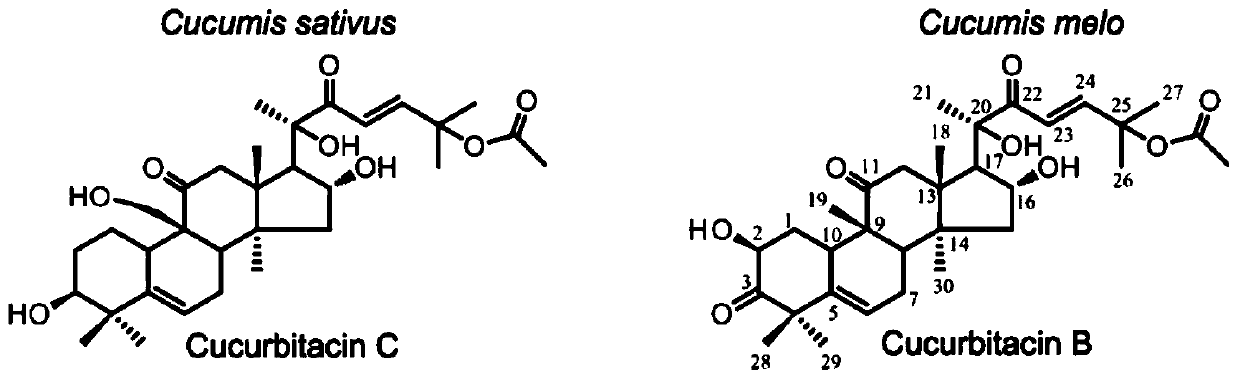
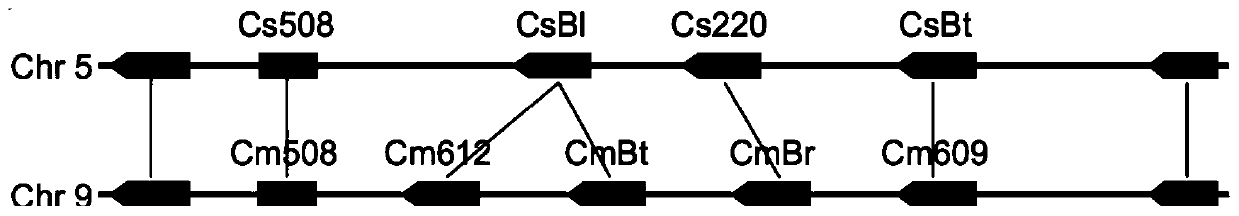
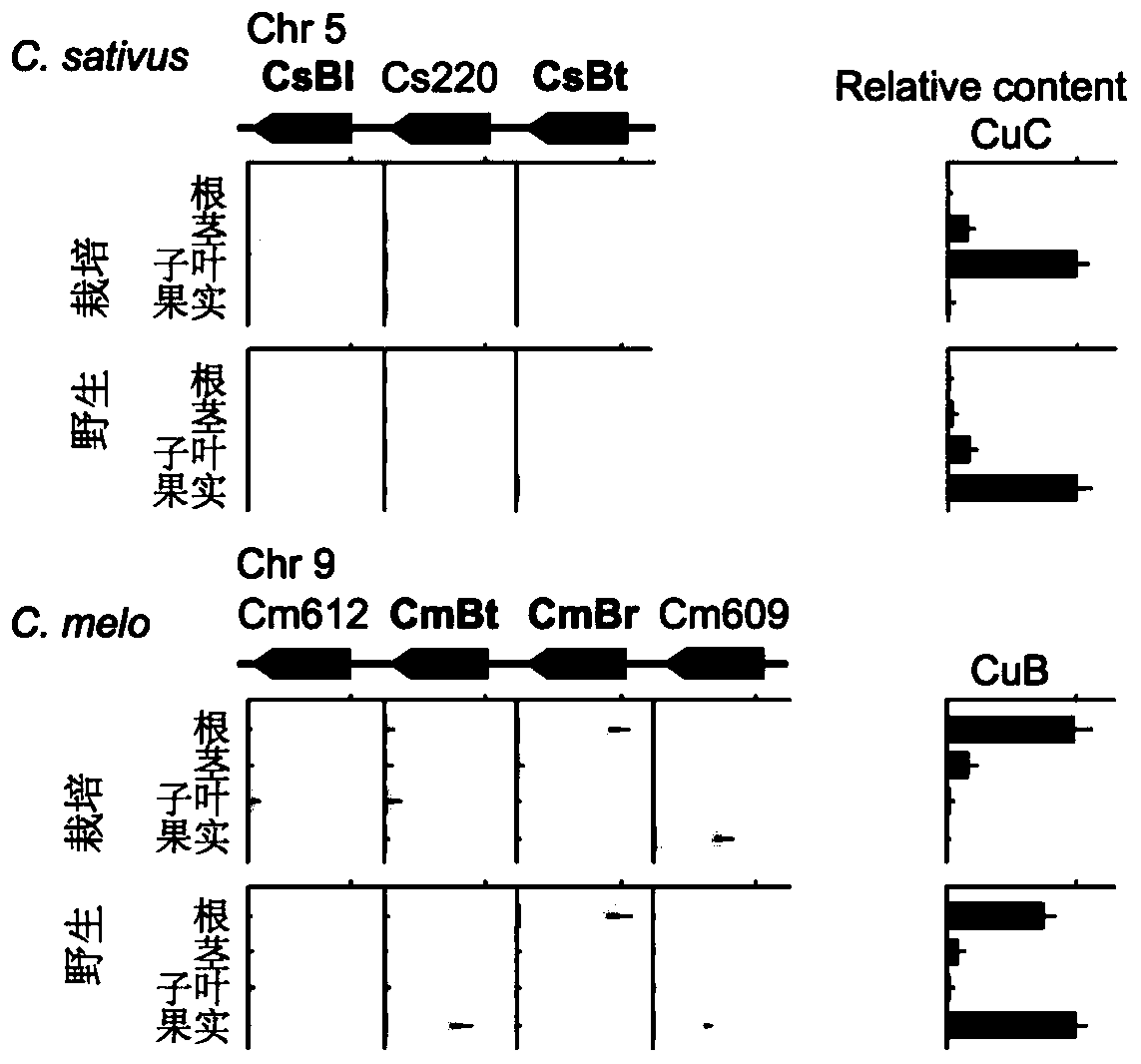
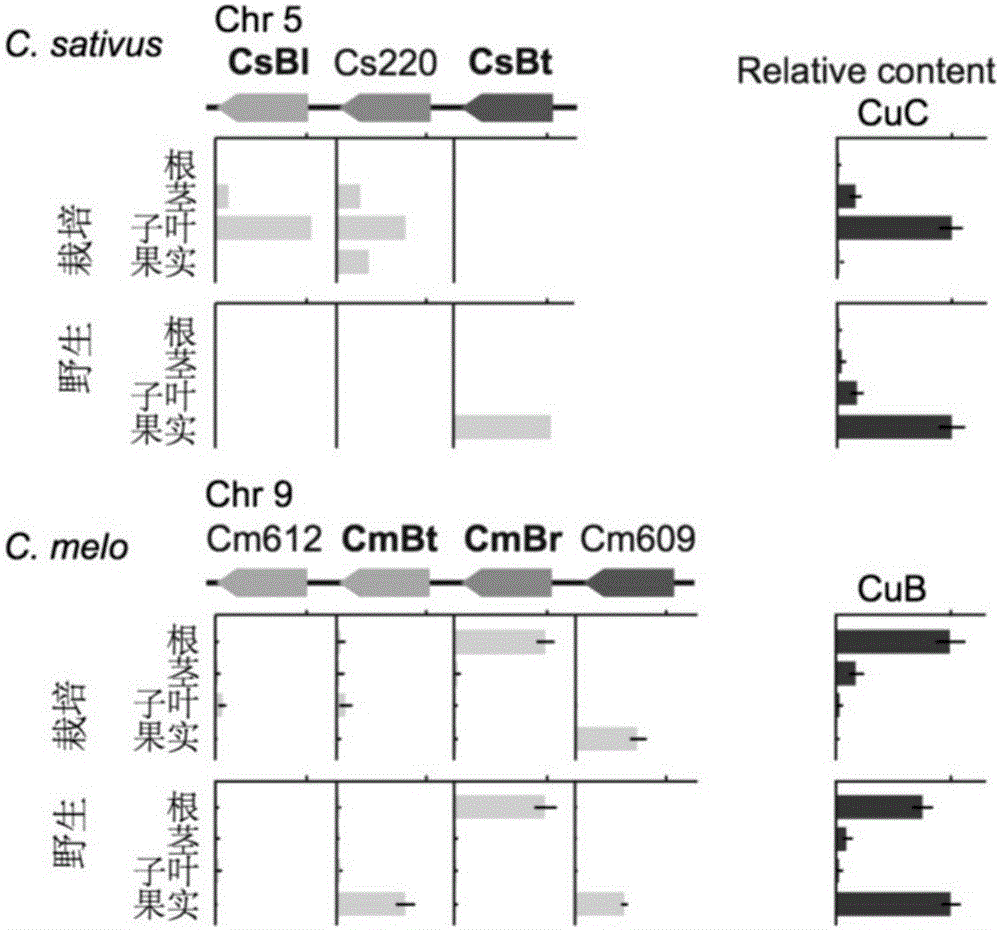
The invention provides transcription factors participating in regulating and controlling synthesis of bitter principles of cucumis melo and application of the transcription factors. A comparative genomics method is utilized for the first time, and the two bHLH transcription factors CmBr and CmBt for controlling synthesis of bitter taste are discovered in genomes of the cucumis melo, and separatelycontrol formation of the bitter taste in roots and wild fruits. Through a yeast one-hybrid technology, a gel retardation test and a tobacco transient expression system, it is proved that the two transcription factors can be directly combined with a promoter region of a bitter principle synthesis gene, and then the expression of the synthesis gene is activated; meanwhile, through transient expression of cotyledons of the cucumis melo, it is proved genetically that the overexpression of CmBr and CmBt can activate the expression of the bitter taste synthesis gene, so that the cotyledons withoutthe bitter taste obtain the phenotype of the bitter taste. The CmBt gene is located in a domestication region. The invention further discloses a molecular mechanism for formation of the bitter taste of the cucumis melo, and a theoretical basis is provided for breeding of the cucumis melo without the bitter taste.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Molecular cloning of GLP2R gene fragments associated with pork quality traits and application of GLP2R gene fragments
The invention belongs to the technical field of livestock molecular biology and particularly relates to a molecular cloning of GLP2R gene fragments associated with pork quality traits and application of GLP2R gene fragments. The human GLP2R gene sequence is taken as a seed sequence, specific primers are designed by BLASTN in GenBank and referring to swine EST of which the homology is above 80% and swine GLP2R gene cDNA full-length is cloned by RACE. DNA sequence of the swine GLP2R gene fragments is shown in SEQ ID NO:1. GLP2R gene polymorphism is determined by designing a primer based on human GLP2R gene via comparative genomics method, amplifying by swine genomic DNA as template, screening SNP from amplification fragment via sequencing, and genotyping by PCR-RFLP. A / G base mutation resulting in PCR-RFLP-BstEII polymorphism is found at 244bp, a new molecular marker is provided for swine marker-assisted selection and the situation of pig breeds at home and abroad can be detected by the marker.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
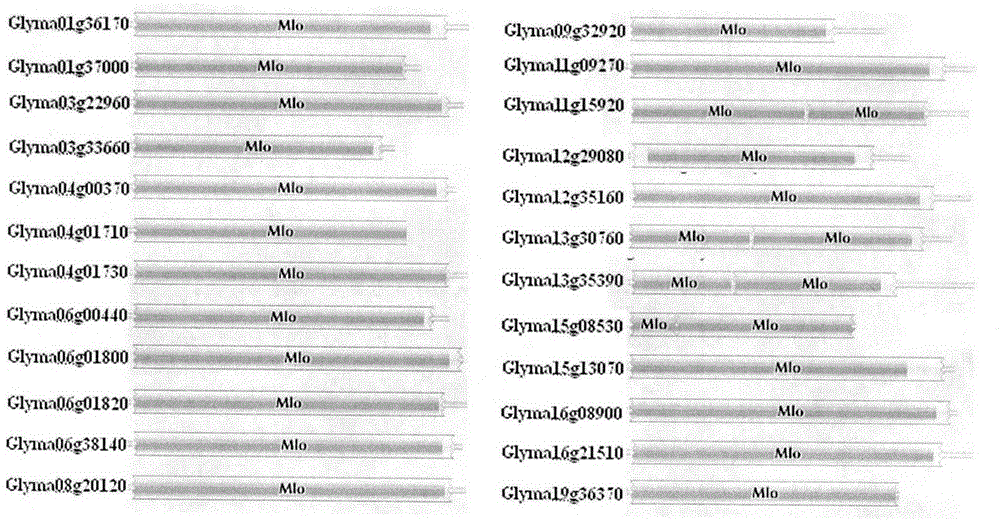
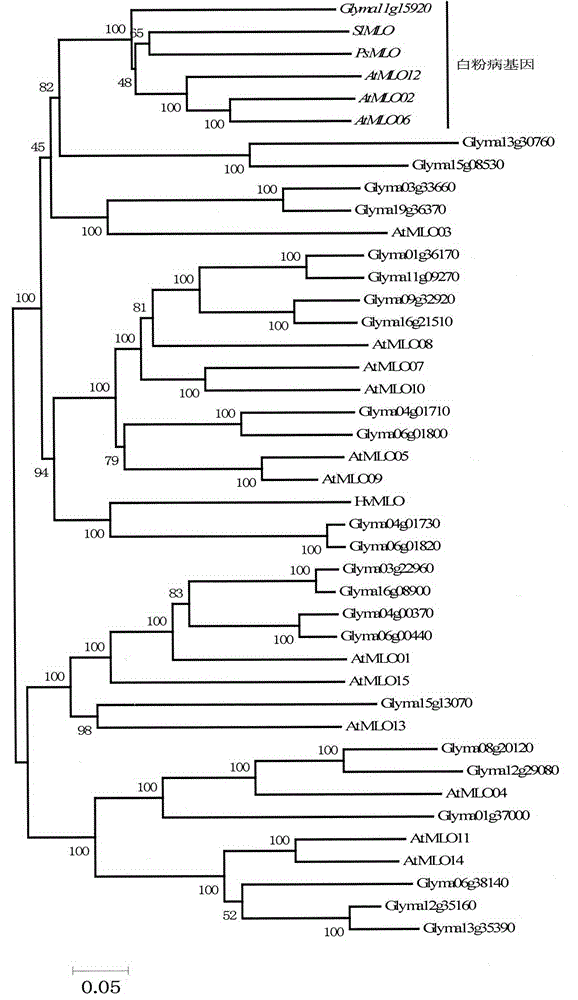
Rapid identification of soybean anti-powdery mildew gene by using candidate gene strategy
InactiveCN104593481AShorten digging cycleImprove identification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsCandidate Gene Association StudyRapid identification
The invention provides rapid identification of soybean anti-powdery mildew gene, relates to knowledge in the disciplines of plant comparative genomics, genetics and bioinformatics, and belongs to the scientific field of plant biotechnology. The invention includes the steps of: 1) downloading the soybean whole genome sequence and acquiring MLO type gene; 2) identifying the MLO genotype; 3) identifying MLO gene phylogenetic relationship; and 4) comparing MLO-type powdery mildew gene. The invention effectively shortens the gene mining cycle for soybean powdery mildew, and is conducive to the rapid identification of anti-powdery mildew gene; corresponding coseparation functional markers (SNP, scar, etc.) are developed through the identified candidate powdery mildew genes, and the identified candidate powdery mildew genes can also be used for fast molecular marker assisted selection of anti-powdery mildew genes and have high accuracy; and combined with other resistant gene molecular markers, multi-resistance breeding material can be created, so as to shorten the breeding period and improve breeding efficiency. Therefore, the invention lays foundation for the explanation of powdery mildew resistant molecular mechanism of soybean.
Owner:JIANGSU CHANGSHU MODERN AGRI IND PARK DEV
Transcription factor participating into regulation of muskmelon bitter principle synthesis and application of transcription factor
The invention provides a transcription factor participating into regulation of muskmelon bitter principle synthesis and application of the transcription factor. A comparative genomics method is firstly utilized for finding two bHLH transcription factors CmBr and CmBt which control bitter synthesis in a muskmelon genome, the two bHLH transcription factors are respectively used for controlling the bitter formation at the root part and in the wild fruit. A yeast one-hybrid technology, a gel retardant experiment and a tobacco transient expression system are used for proving that the two transcription factors can be directly combined to a promoter region of a bitter principle synthesis gene, and can activate the expression of the synthesis gene; the muskmelon cotyledon transient expression proves that the overexpression of each of the CmBr and the CmBt can activate the expression of the bitter synthesis gene from the genetics, so that the bitter-free cotyledon can acquire the bitter phenotype. The CmBt gene is located in a domestication region. The invention further discloses a molecule mechanism of the muskmelon bitter formation, and provides the theoretical basis for the breeding of the bitter-free muskmelon.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Cloning and application of pork quality character related GADD45G gene molecule marker
The invention belongs to the technical field of livestock molecular marker biology and particularly relates to cloning and application of a pork quality character related GADD45G gene molecule marker. The molecule marker provided by the invention is obtained by cloning a GADD45G gene and the sequence of the GADD45G molecule marker is shown in SEQ ID No.1. For polymorphism of the GADD45G gene, a primer is designed by using a comparative genomic method according to the GADD45G gene sequence of a human body, the genome DNA of a pig is used as a template for amplification, in an amplified fragment, sequencing is used for screening SNP, PCR-RFLP is used for genetic typing, that A / G base mutation exists at 640th bp in the SEQ ID No.1 is found, PCR-RFLP-PstI polymorphism is caused and the molecule marker can be used for association analysis of pork quality characters. According to the invention, the novel molecular marker is provided for pork quality character marker assistant selection.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Molecular cloning and application of pork quality character related gene Myo6 (Myosin 6)
The invention belongs to the technical field of livestock molecular biology, and particularly relates to molecular cloning and application of pork quality character related gene Myo6 (Myosin 6). The molecular marker disclosed by the invention is obtained through cloning the Myo6 gene, and the sequence of the Myo6 molecular marker is described as SEQ ID NO: 1. The polymorphism of the Myo6 gene is as follows: a primer is designed by using the comparative genomics method according to the My06 gene sequence of human, the genome DNA of pigs is adopted as a template for amplification, SNP is screened by sequencing the amplified fragments, genotyping is carried out by using PCR-RFLP, a G / A base mutation at 709bp is discovered, and PCR-RFLP-Xba I polymorphism is caused. The molecular cloning and application of pork quality character related gene Myo6 provide a novel molecular marker for the assistant selection of pig markers.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
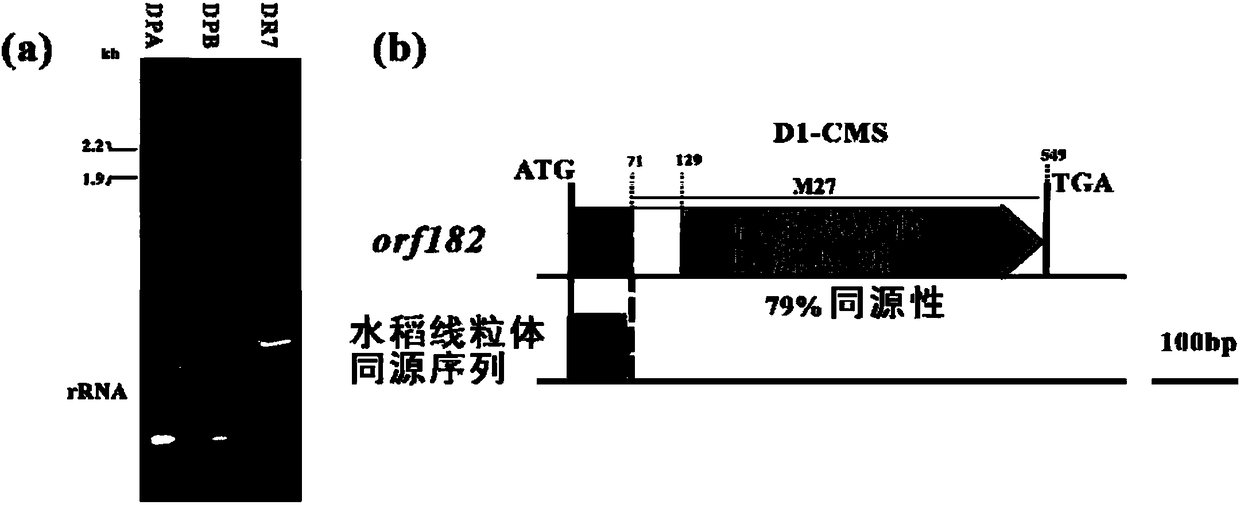
Rice mitochondria sterility gene and application thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of rice breeding, and specifically relates to a rice mitochondria sterility gene and the application thereof. The invention discloses a rice mitochondria sterility gene and a coding sequence thereof, and D1 type cytoplasm can be quickly and efficiently screened and authenticated from wild rice for cultivation of a D1 type cytoplasm sterile line by designing a specific molecular marker through the gene sequence. A mitochondrial genome specific sequence of the D1 type cytoplasm sterile is authenticated through comparative genomics, sterility related ORFs are authenticated through gene predication and differential expression analysis, and a plant transformation vecter is constructed for transforming maintenance line verification and sterility function.
Owner:JIANGXI SUPER RICE RES & DEV CENT (HAINAN RICE BREEDING CENT OF JIANGXI ACAD OF AGRI SCI) +1
Rapid identification of MLO (Mycoplasma Like Organism) powdery mildew resistant genes of melon
InactiveCN104561024AShorten digging cycleImprove identification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationRapid identificationOrganism
The invention relates to rapid identification of MLO (Mycoplasma Like Organism) powdery mildew resistant genes of a melon, relates to comparative genomics of plants, genetics, bioinformatics and other disciplinary knowledge, and belongs to the field of biotechnology science of plants. The rapid identification is mainly carried by the following steps: 1) downloading the whole genome sequence of the melon, and acquiring MLO genes; 2) identifying the MLO genes; 3) obtaining the phylogenetic relationship of MLO genes; 4) comparing MLO powdery mildew resistant genes. By virtue of adopting the rapid identification, the powdery mildew resistant genes mining cycle of the melon can be effectively reduced, which is beneficial to the rapid identification of powdery mildew resistant genes; the identified candidate powdery mildew resistant genes are utilized to develop corresponding coseparation functional markers (such as SNR and SCAR) and can also be quickly used for assistant selection of molecular markers resistant to powdery mildew resistant genes, and the accuracy is high; in combination with other anti-disease gene molecular markers, a plurality of resistive breeding materials can be created, the breeding periods can be reduced, and the breeding efficiency can be increased; the foundation is provided for describing a powdery mildew resistant molecular mechanisms of the melon.
Owner:南农大(常熟)新农村发展研究院有限公司
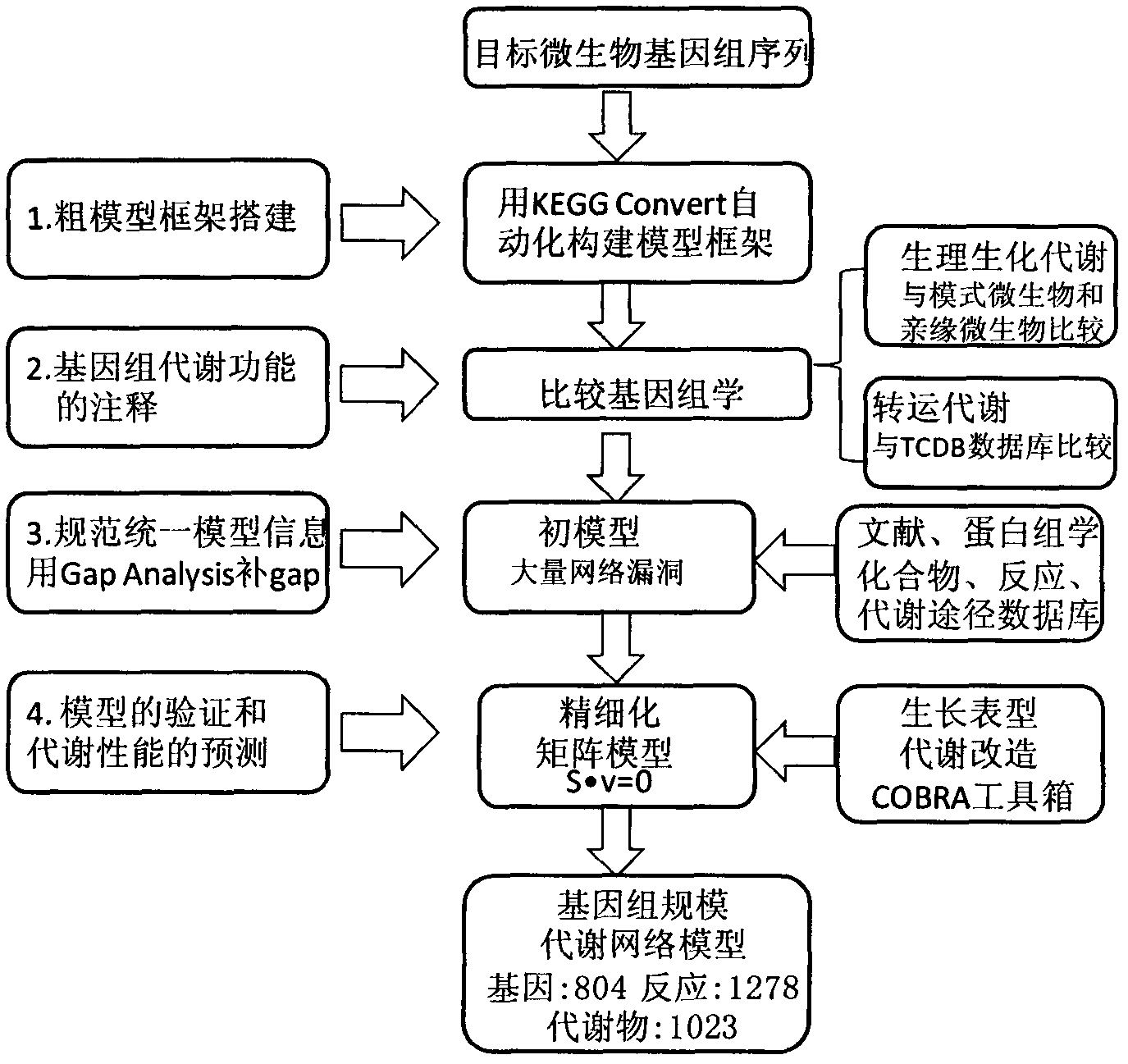
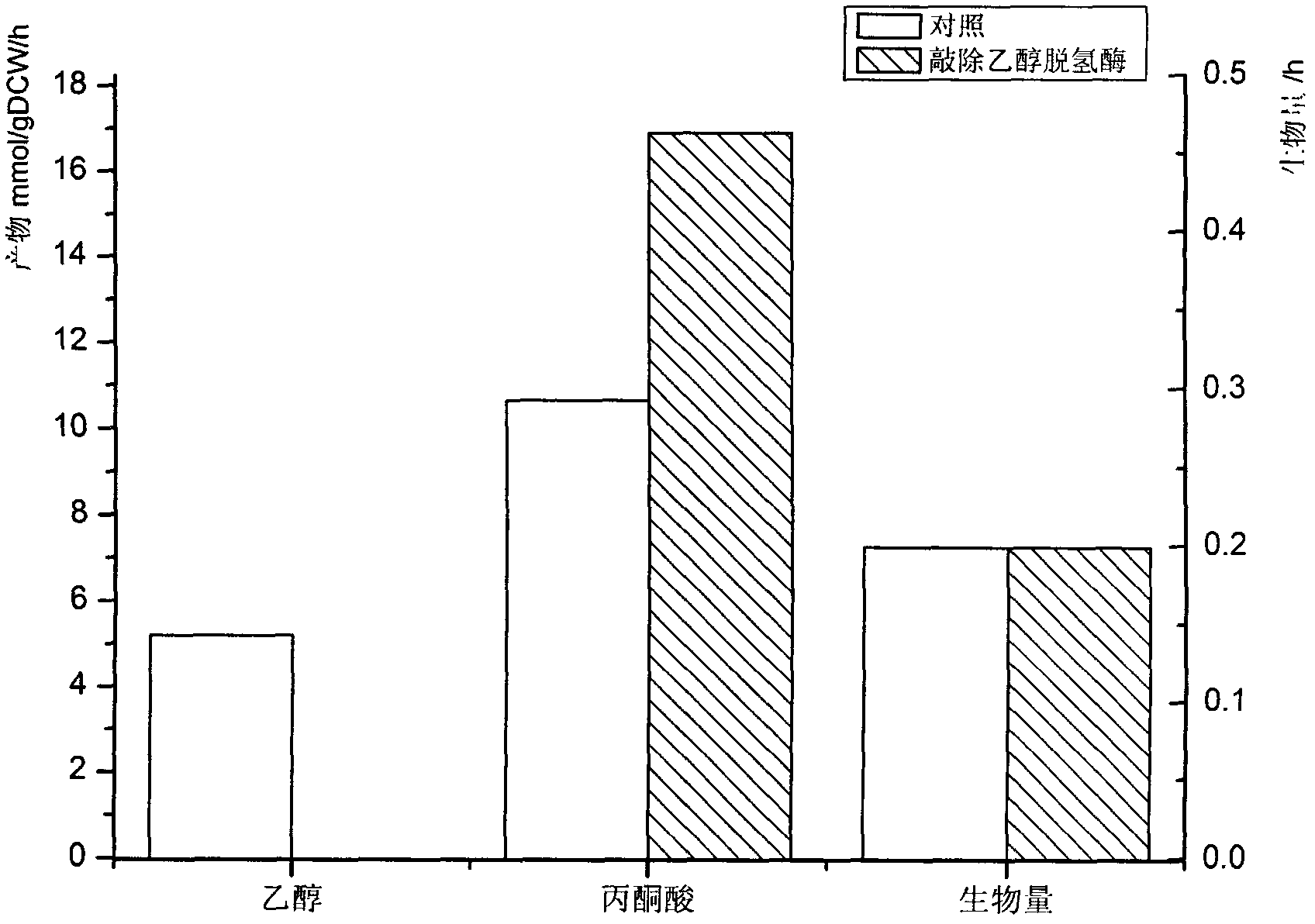
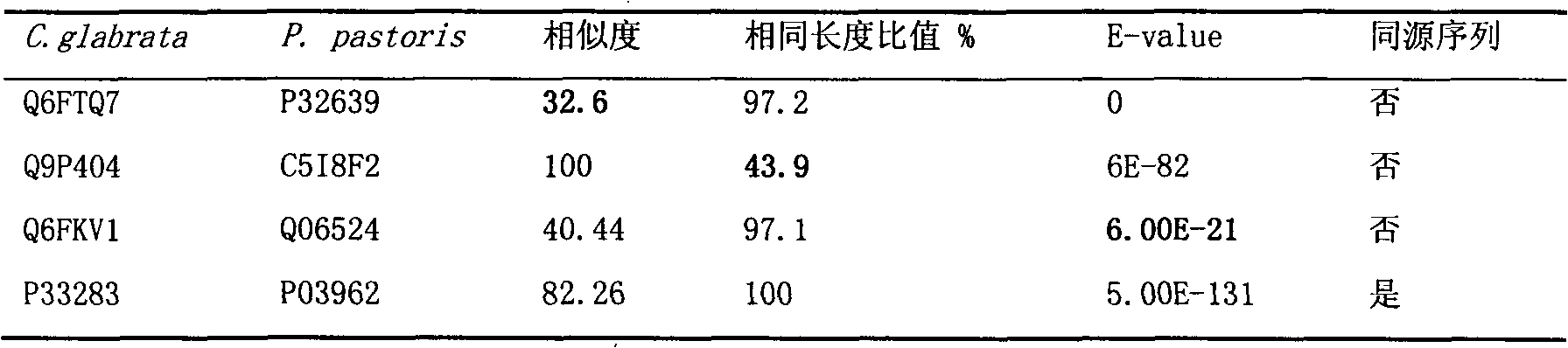
Construction and application technology of Torulopsis glabrata genome metabolism model
InactiveCN102622533AIncrease productionSpecial data processing applicationsTorulopsis glabrataEthanol dehydrogenase
The invention discloses a construction method and an application technology of a Torulopsis glabrata genome-scale metabolism network model, belonging to the field of systems biology. The construction method of the model is an all-round semi-automatic construction method of combining comparative genomics annotation and bacteria-specific information of Torulopsis glabrata protein homology based on an automatic model. The invention provides a method for characterizing auxotroph characteristics in a Torulopsis glabrata metabolism network by adding necessary nutrient substances, lacked in bacteria, to a biomass equation. Alcohol dehydrogenase is knocked out by using single genes in the Torulopsis glabrata metabolism network model, and flow equilibrium analysis is applied, so that the output of pyruvic acid is increased. The construction method and the application technology of the Torulopsis glabrata genome-scale metabolism network model provide a high-efficient platform for fully understanding and reforming physiological and biochemical metabolisms of the Torulopsis glabrata.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Rapid identification of strawberry powdery mildew gene by using comparative genomics
InactiveCN104611407AShorten digging cycleImprove identification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesFragariaAgricultural science
Owner:CHANGSHU CITY BEIBANG TOWN BEIGANG VEGETABLE SPECIALIZED COOP
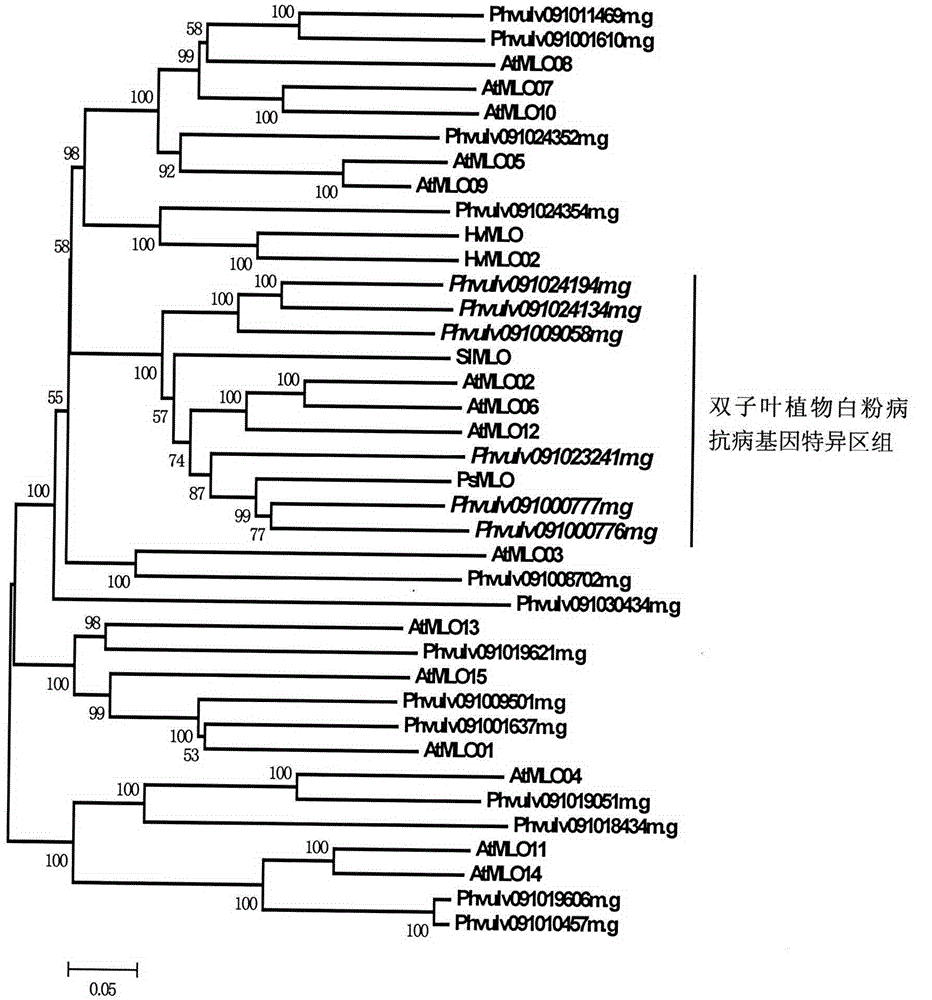
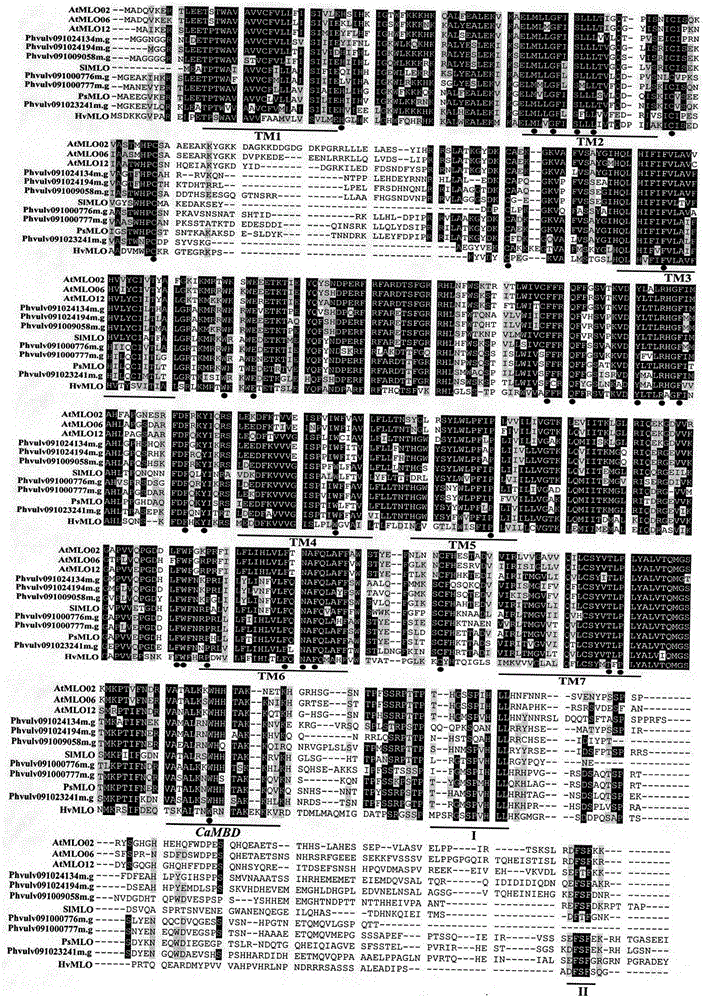
Application of comparative genomics to rapid identification of phaseolus vulgaris mildew resistance locus o gene
InactiveCN104593480AShorten digging cycleImprove identification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsRapid identificationOrganism
Relating to plant comparative genomics, genetics, bioinformatics and other disciplinary knowledge, the invention belongs to the scientific field of plant biotechnology, and discloses rapid identification of phaseolus vulgaris mildew resistance locus o gene. The main steps include: 1) download of phaseolus vulgaris whole genome sequence and acquisition of MLO type gene; 2) identification of MLO type gene; 3) MLO type gene phylogenetic relationship; and 4) comparison of MLO type powdery mildew. The invention effectively shortens the mining cycle of phaseolus vulgaris powdery mildew gene, and is conducive to rapid identification of powdery mildew gene. Corresponding coseparation functional markers (SNP, SCAR and the like) are developed through identified candidate powdery mildew genes, which also can be used for molecular marker-assisted selection of mildew resistance locus o gene and have high accuracy. Multi-resistance breeding materials can be created by combining other resistant gene molecular markers, the breeding period can be shortened, and the breeding efficiency is improved, thus laying the foundation for elaborating the phaseolus vulgaris mildew resistance molecular mechanism.
Owner:JIANGSU CHANGSHU MODERN AGRI IND PARK DEV
Rapid identification of powdery mildew resistant gene of Chinese cabbage by using comparative genomics
InactiveCN104593379AShorten digging cycleRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationRapid identificationGenotype
The invention provides rapid identification of powdery mildew resistant gene of Chinese cabbage, relates to knowledge in the disciplines of plant comparative genomics, genetics and bioinformatics, and belongs to the scientific field of plant biotechnology. The invention includes the steps of: 1) downloading the whole genome sequence of Chinese cabbage and acquiring MLO type gene; 2) identifying the MLO genotype; 3) identifying MLO gene phylogenetic relationship; and 4) comparing MLO-type powdery mildew gene. The invention effectively shortens the gene mining cycle for Chinese cabbage powdery mildew, and is conducive to the rapid identification of powdery mildew resistant gene; corresponding coseparation functional markers (SNP, SCAR, etc.) are developed through the identified candidate powdery mildew genes, and the identified candidate powdery mildew genes can also be used for fast molecular marker assisted selection of powdery mildew resistant genes and have high accuracy; combined with other resistant gene molecular markers, multi-resistance breeding material can be created, so as to shorten the breeding period and improve breeding efficiency. Therefore, the invention lays foundation for the explanation of powdery mildew resistant molecular mechanism of Chinese cabbage.
Owner:JIANGSU CHANGSHU MODERN AGRI IND PARK DEV
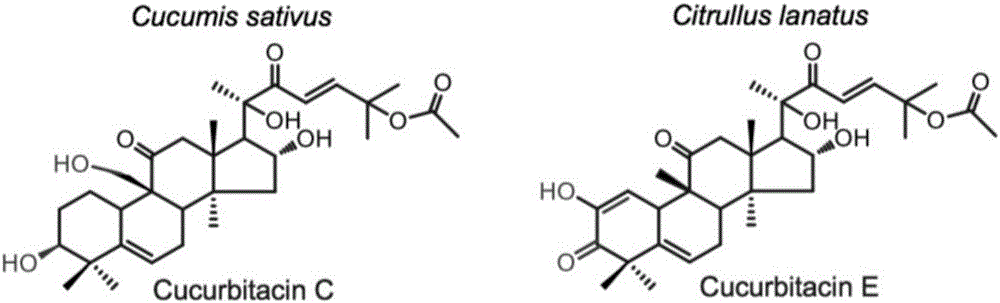
Transcription factor participating in regulating watermelon bitter principle and application thereof
ActiveCN106518994ATranslation terminated earlyMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesYeastGene Position
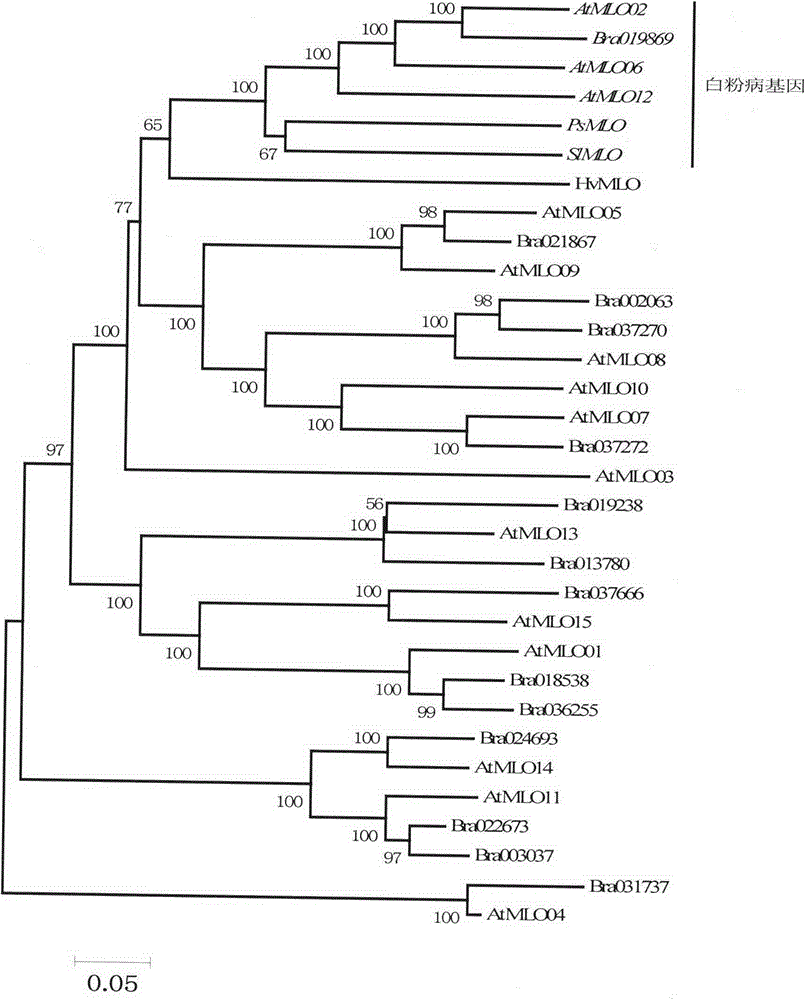
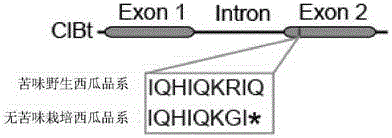
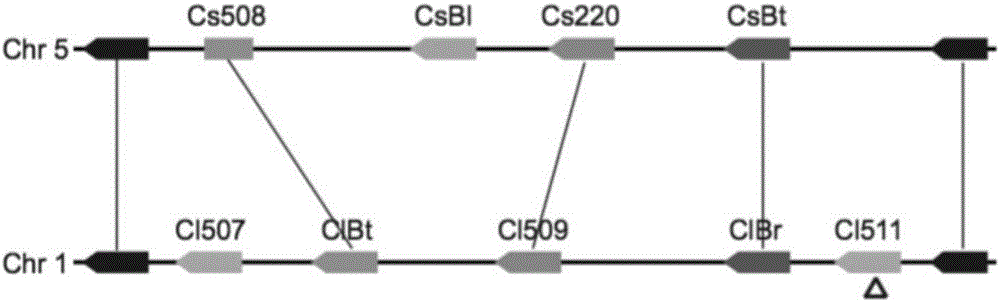
The invention provides a transcription factor participating in regulating watermelon bitter principle and an application thereof. Two bHLH transcription factors ClBr and ClBt controlling bitterness synthesis are discovered in watermelon genome for the first time by use of comparative genomics, wherein the two bHLH transcription factors control the formation of bitterness in the root and wild fruits respectively. The yeast one-hybrid technology, gel retardation experiment and tobacco transient expression system prove that the two transcription factors can be directly combined to the promoter area of the bitter principle synthesis gene and activate the expression of the synthesis gene; and meanwhile, through the transient expression of watermelon cotyledon, the overexpression of ClBr and ClBt is genetically proven to activate the expression of the bitterness synthesis gene so that the bitterless cotyledon obtains a bitterness phenotype. The ClBt gene encodes the mutation of an SNP so that the bitter fruit loses bitterness; and moreover, the gene positioned in an acclimation area is an acclimation gene. The invention further discloses a molecular mechanism forming watermelon bitterness and provides a theoretical basis for bitterless watermelon breeding.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Soybean vernalization gene GmVRN1 and colonizing method and application thereof
The invention discloses a soybean vernalization gene GmVRN1 and a colonizing method and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of resources and environment. Related genes of vernalization approaches in a soybean genome is explored through comparative genomics, real-time PCR technology is applied to screening of vernalization approach gene difference expression of AtDREB1A genetically-modified soybean, the soybean vernalization gene GmVRN1 is colonized, and application authentication is performed on a flowering phase regulating and controlling function of the soybean vernalization gene GmVRN1 by converting arabidopsis.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Molecular cloning and application of pig backfat thickness related SLC13A5 gene
The invention belongs to the technical field of livestock molecular biology, and particularly relates to molecular cloning and application of a pig backfat thickness related SLC13A5 gene. A molecular marker disclosed by the invention is obtained by SLC13A5 gene cloning, and a sequence marked by an SLC13A5 molecule is shown in SEQ ID NO:1. According to the polymorphism of the SLC13A5 gene, a primer is designed according to SLC13A5 gene sequence of human by using a comparative genomic method and amplified by taking pig genome DNA as a template; SNP of the amplified fragment is screened in a sequencing manner; PCR-RFLP is utilized to implement genetic typing; base mutation of one T / C at the 251bp is found, which causes PCR-RFLP-Bsu36I polymorphism; moreover, the marker is used for detecting the conditions of Chinese and foreign pig breeds. The invention provides new molecular marking for pig marker assisted selection.
Owner:HUNAN CHUWEIXIANG AGRICUTLTURE CO LTD
Fluorescent quantitative PCR method for detecting fish parvalbumin and primer pair
ActiveCN105349540AQuick checkEnsure safetyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAdditive ingredientPcr method
The invention relates to a fluorescent quantitative PCR method for detecting fish parvalbumin and a primer pair and belongs to the technical field of food safety detection. The PCR method comprises the following steps: I, designing a specific amplification primer pair; II, extracting DNA of a sample; III, judging whether the sample contains a parvalbumin gene or not through an amplification curve and a dissolution curve; the invention further relates to the primer pair. To be specific, the primer pair is as follows: base sequences of the fish parvalbumin are shown as SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2. Compared with the prior art, the fluorescent quantitative PCR method and the primer pair have the advantages as follows: by using bioinformatics and comparative genomics, the shared gene sequences of fish parvalbumin are selected, the specific amplification primer pair is designed according to the sequences, the primer pair provided by the invention can be used for carrying out fluorescent quantitative PCR detection on samples to detected and can rapidly, sensitively and specifically detect the allergen ingredient namely parvalbumin in different kinds of fishes and fish products in food.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACAD OF SCI & TECH FOR INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com