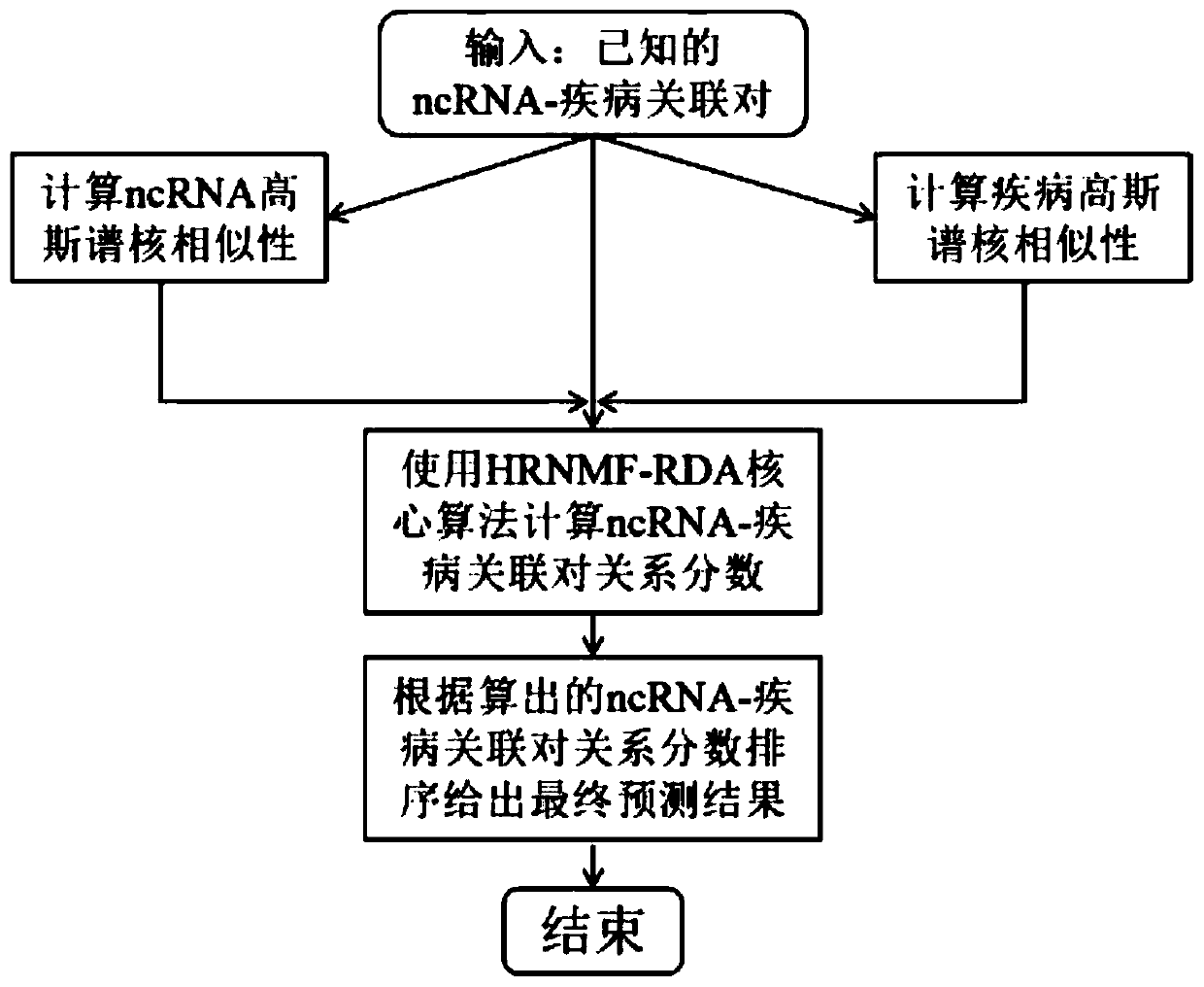
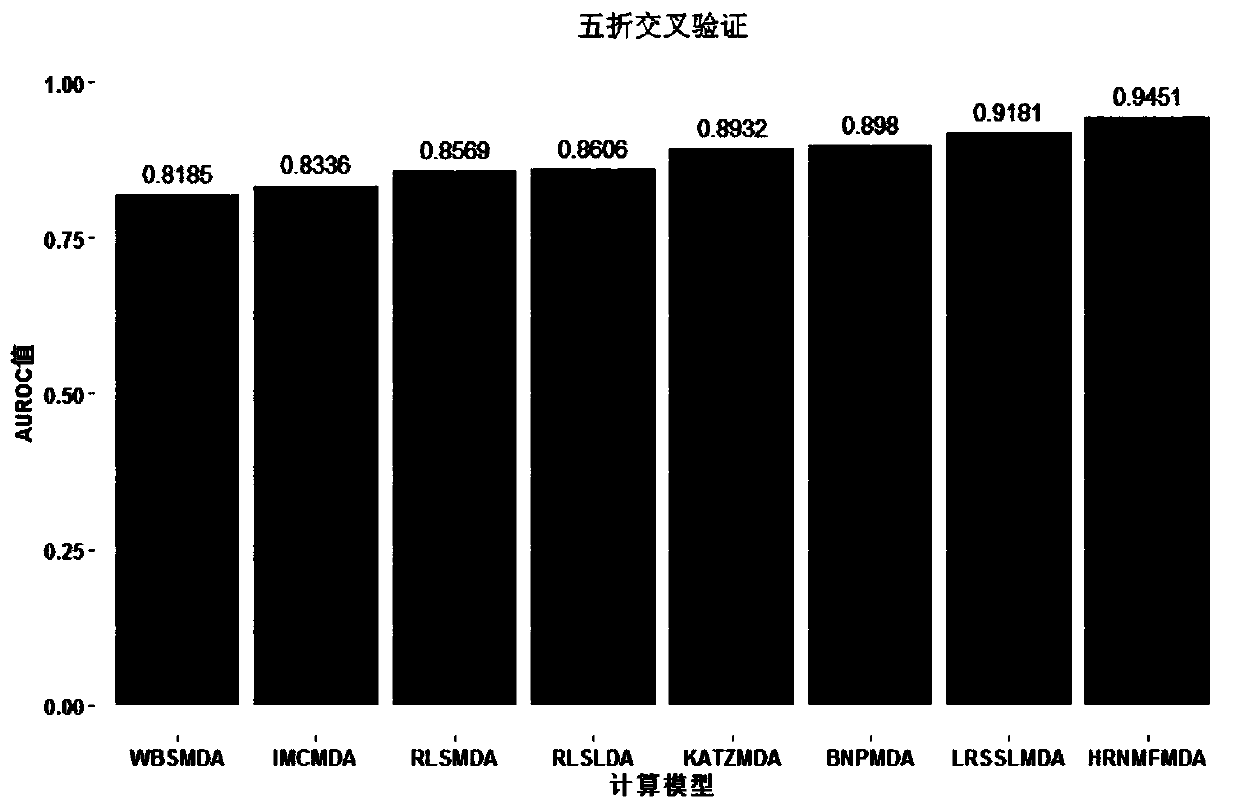
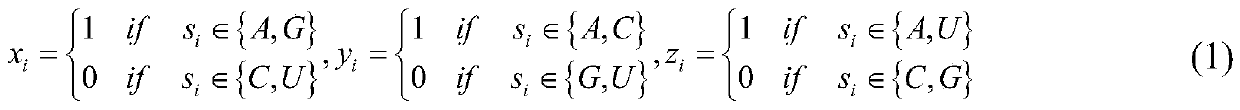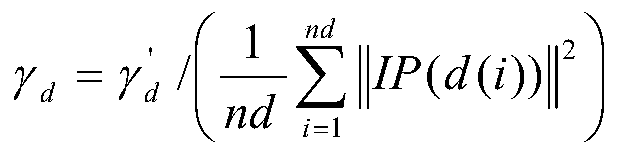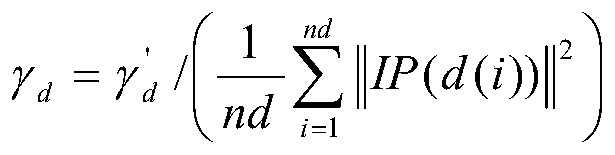Patents
Literature
82 results about "Systems biology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
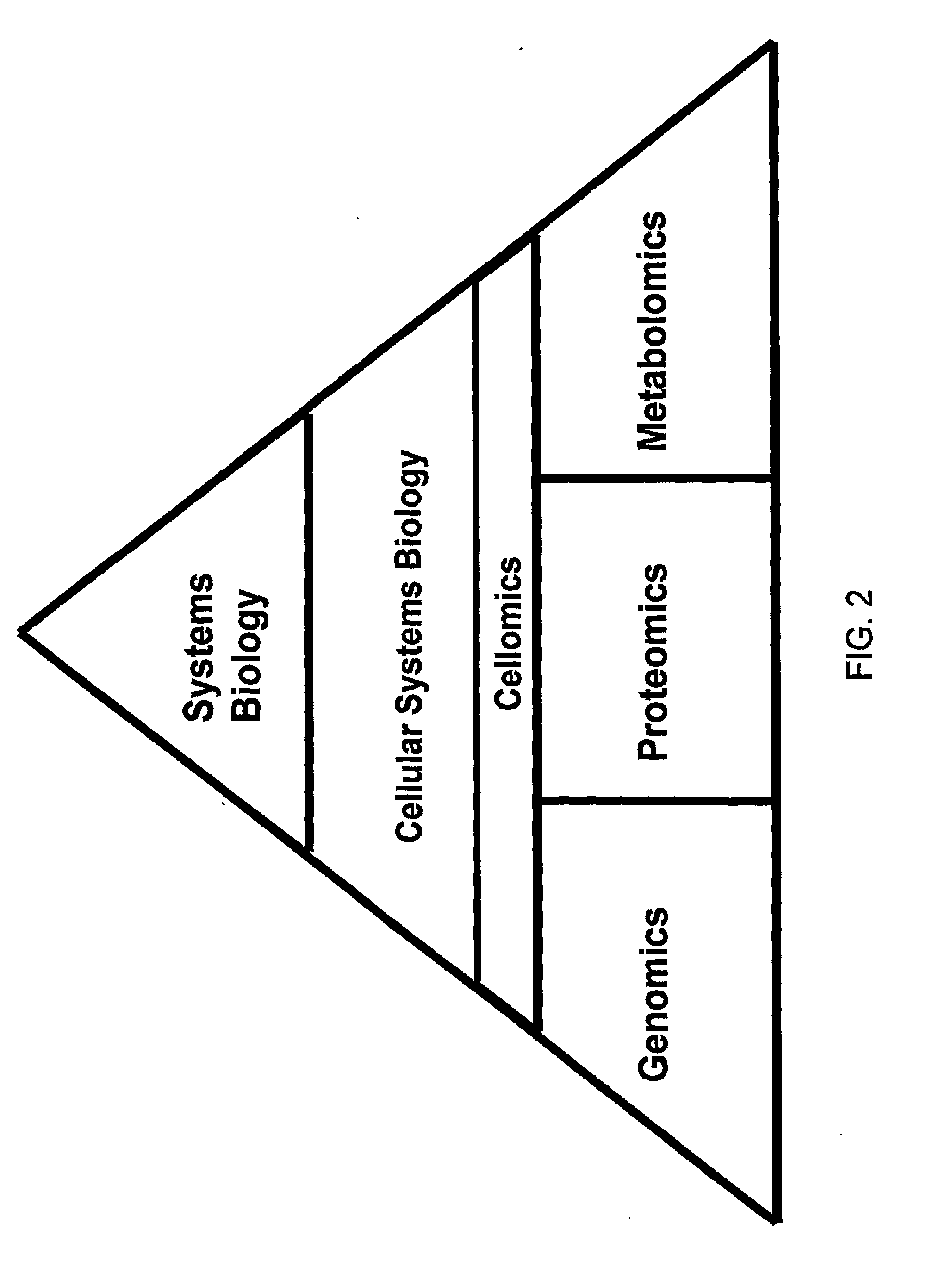
Systems biology is the computational and mathematical analysis and modeling of complex biological systems. It is a biology-based interdisciplinary field of study that focuses on complex interactions within biological systems, using a holistic approach (holism instead of the more traditional reductionism) to biological research.
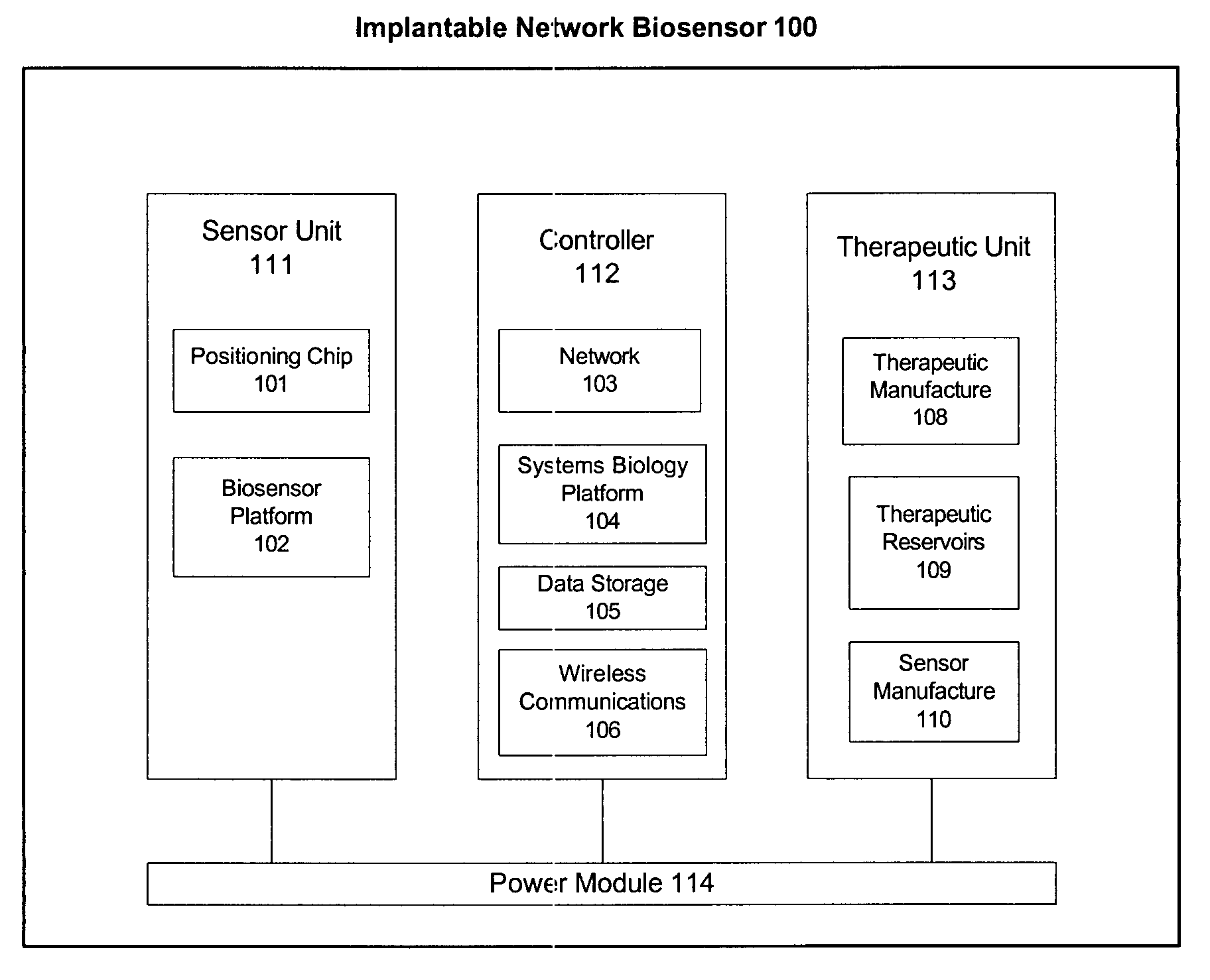
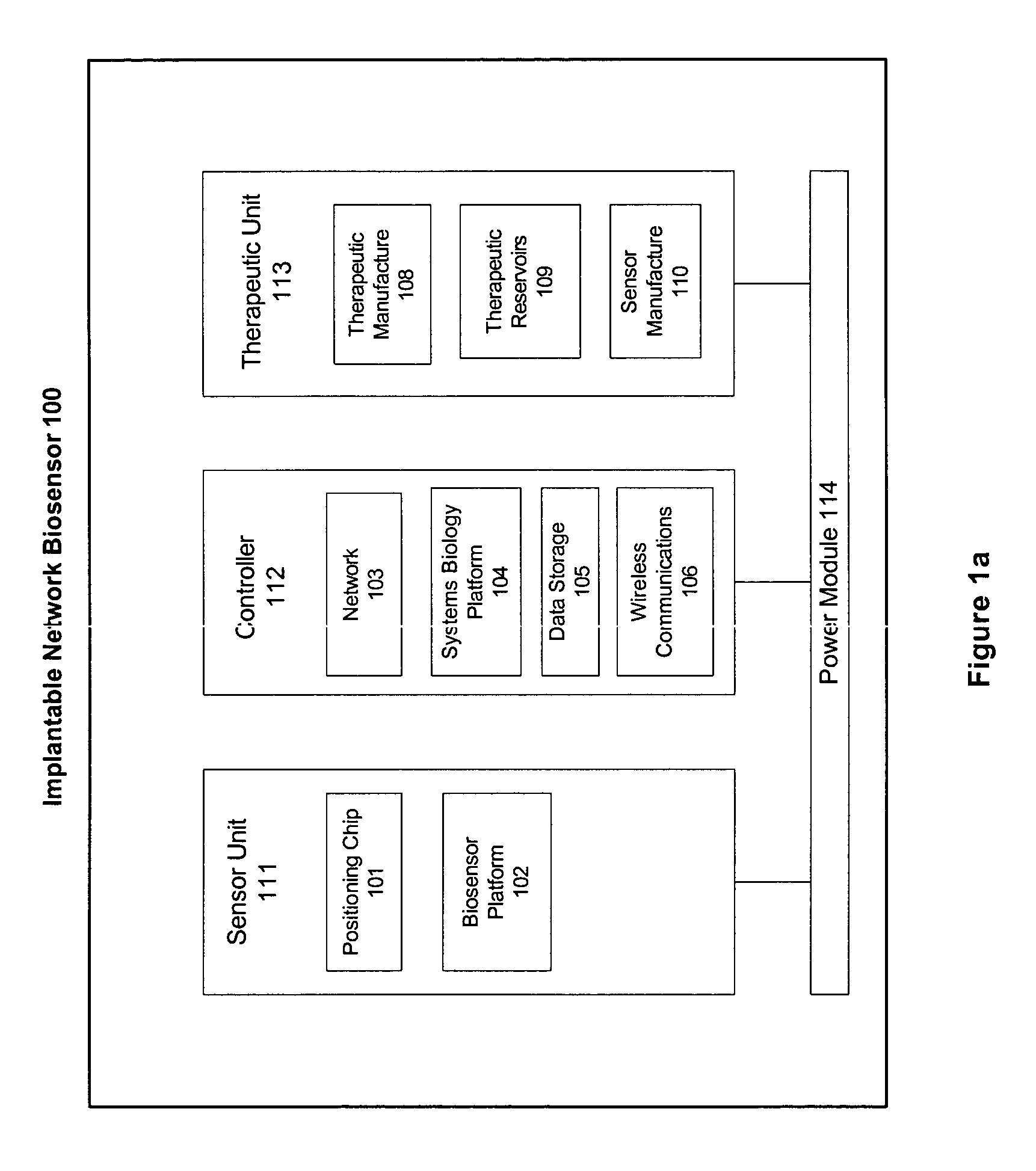
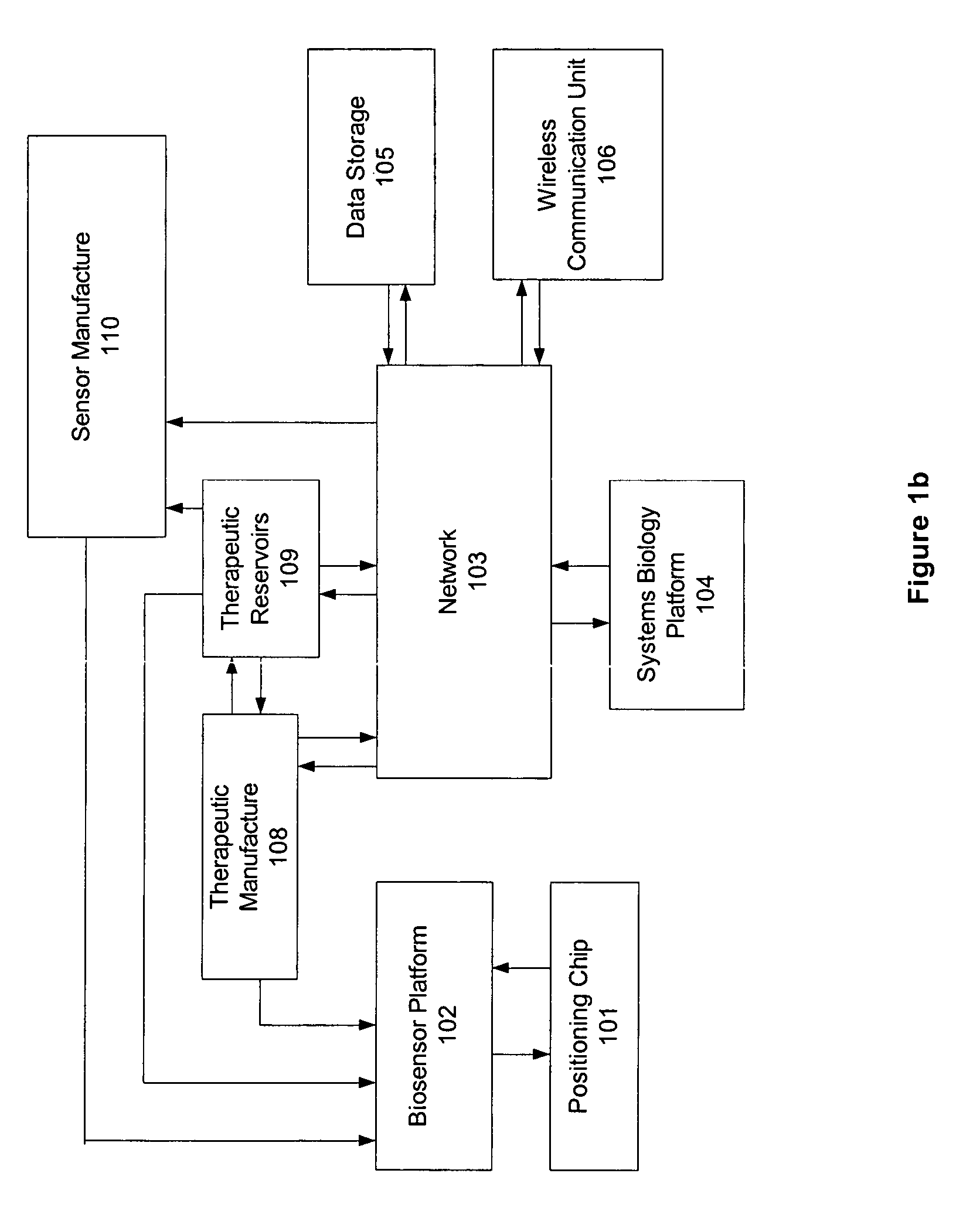
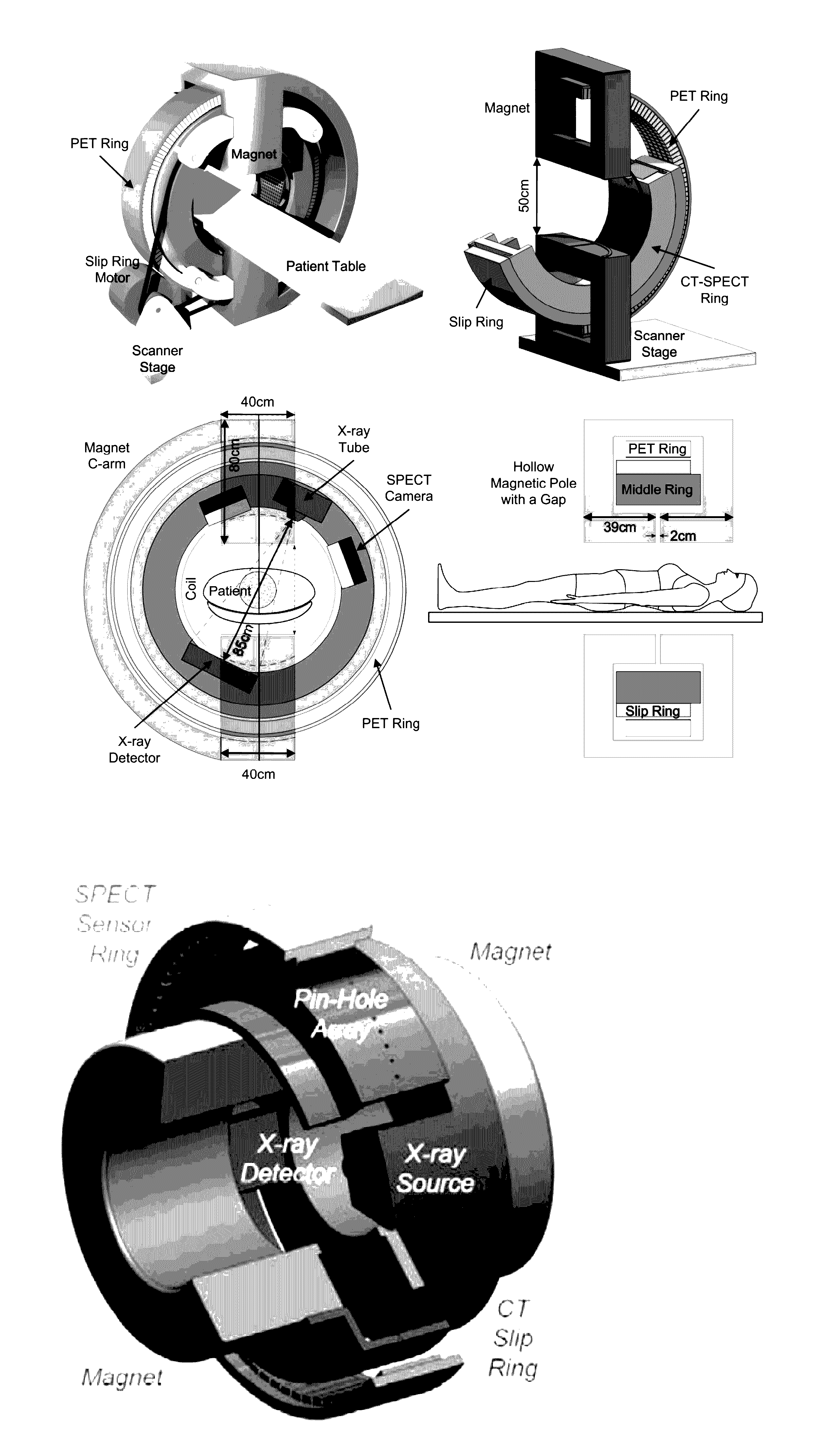
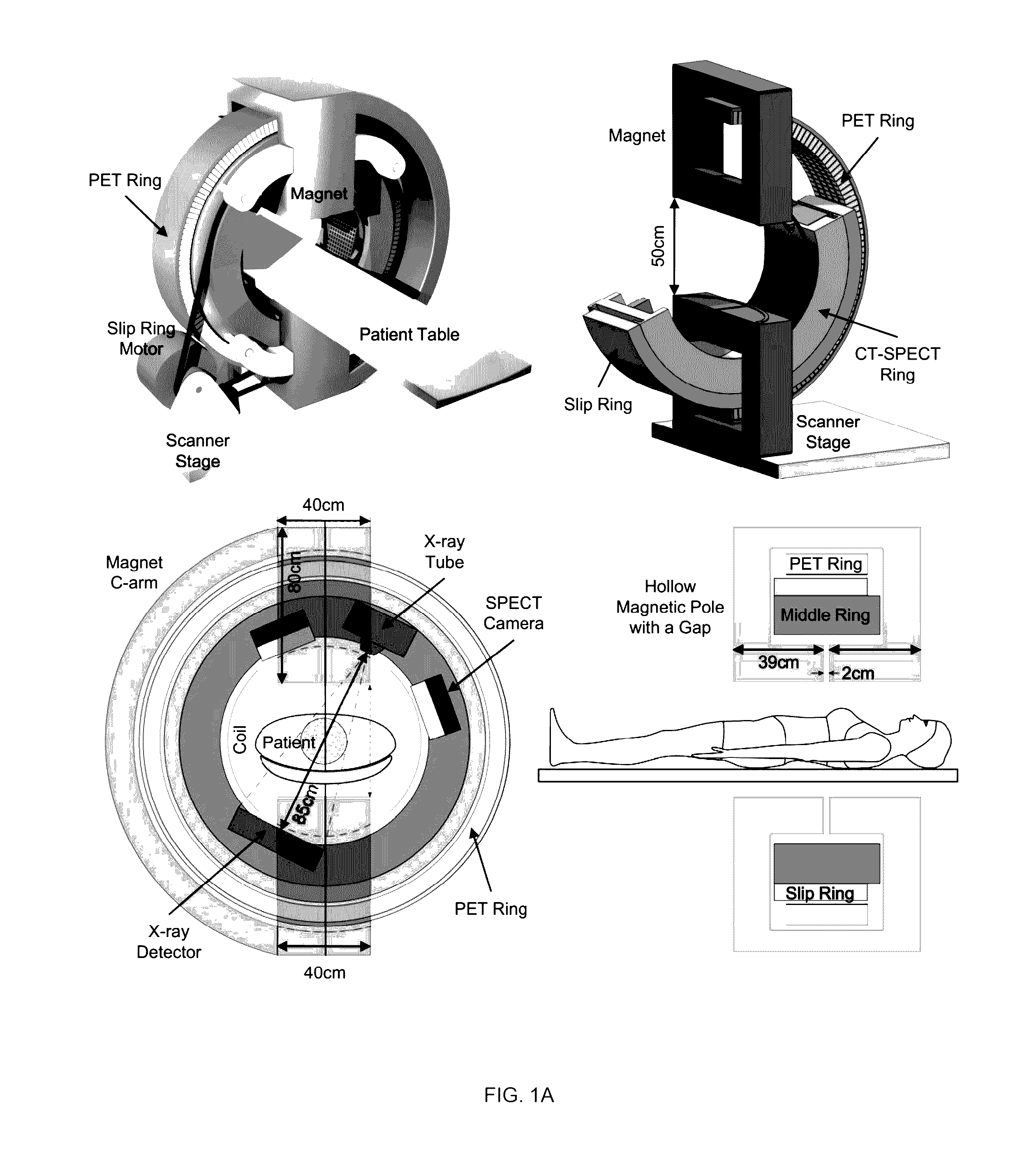
Omni-Tomographic Imaging for Interior Reconstruction using Simultaneous Data Acquisition from Multiple Imaging Modalities
InactiveUS20120265050A1Less importantLow costUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityModern medicine
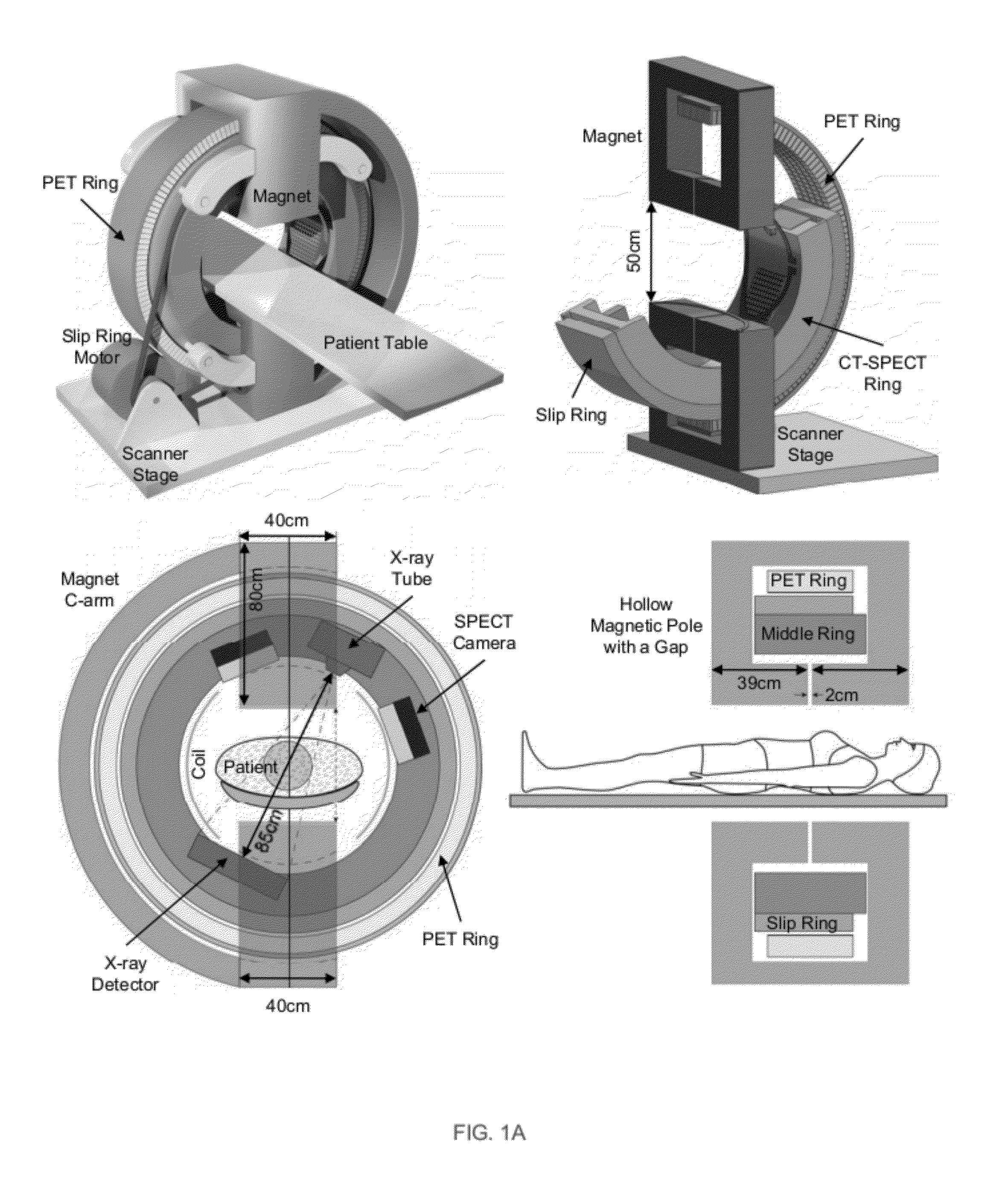
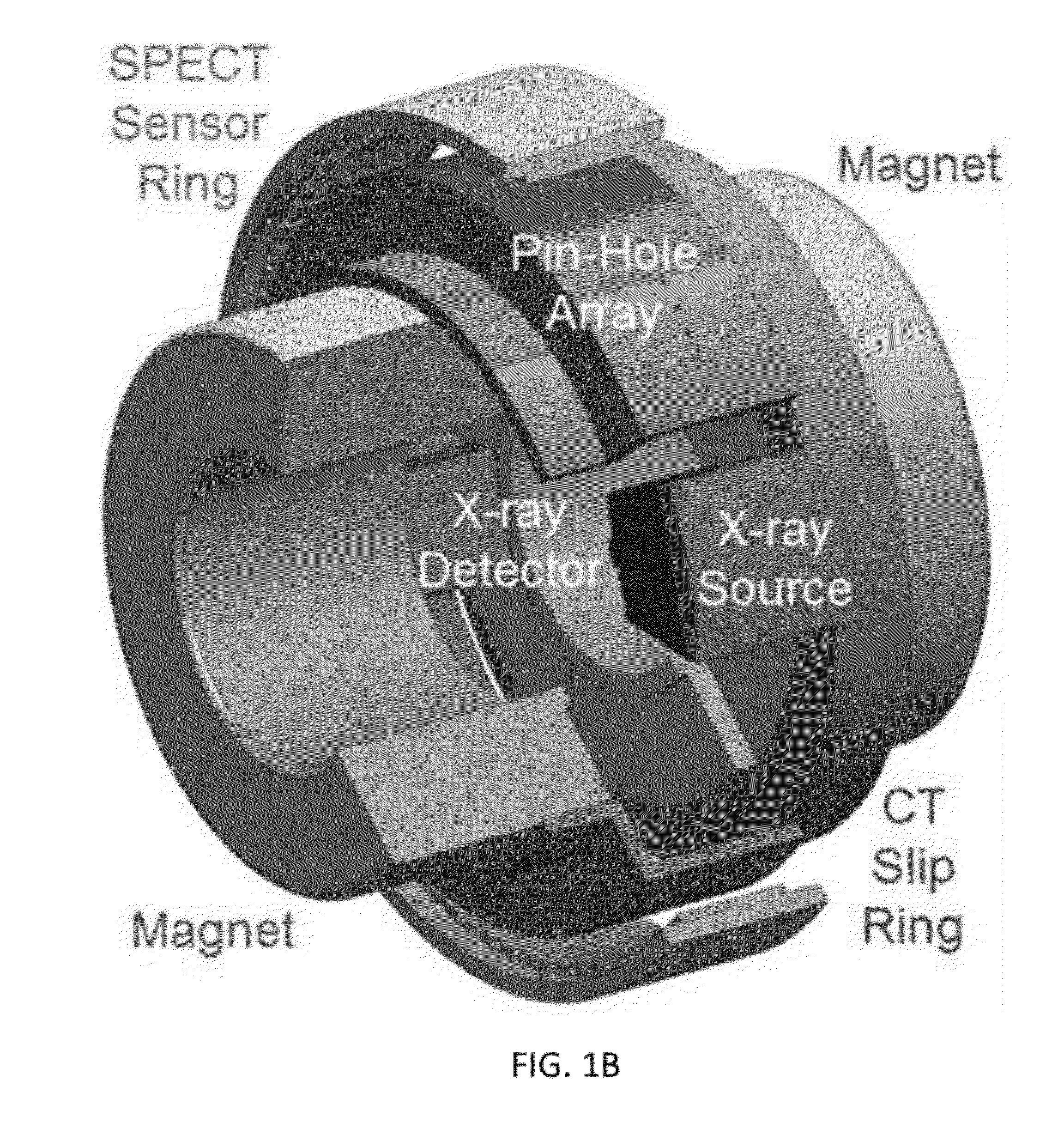
Embodiments of the invention relate to omni-tomographic imaging or grand fusion imaging, i.e., large scale fusion of simultaneous data acquisition from multiple imaging modalities such as CT, MRI, PET, SPECT, US, and optical imaging. A preferred omni-tomography system of the invention comprises two or more imaging modalities operably configured for concurrent signal acquisition for performing ROI-targeted reconstruction and contained in a single gantry with a first inner ring as a permanent magnet; a second middle ring containing an x-ray tube, detector array, and a pair of SPECT detectors; and a third outer ring for containing PET crystals and electronics. Omni-tomography offers great synergy in vivo for diagnosis, intervention, and drug development, and can be made versatile and cost-effective, and as such is expected to become an unprecedented imaging platform for development of systems biology and modern medicine.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
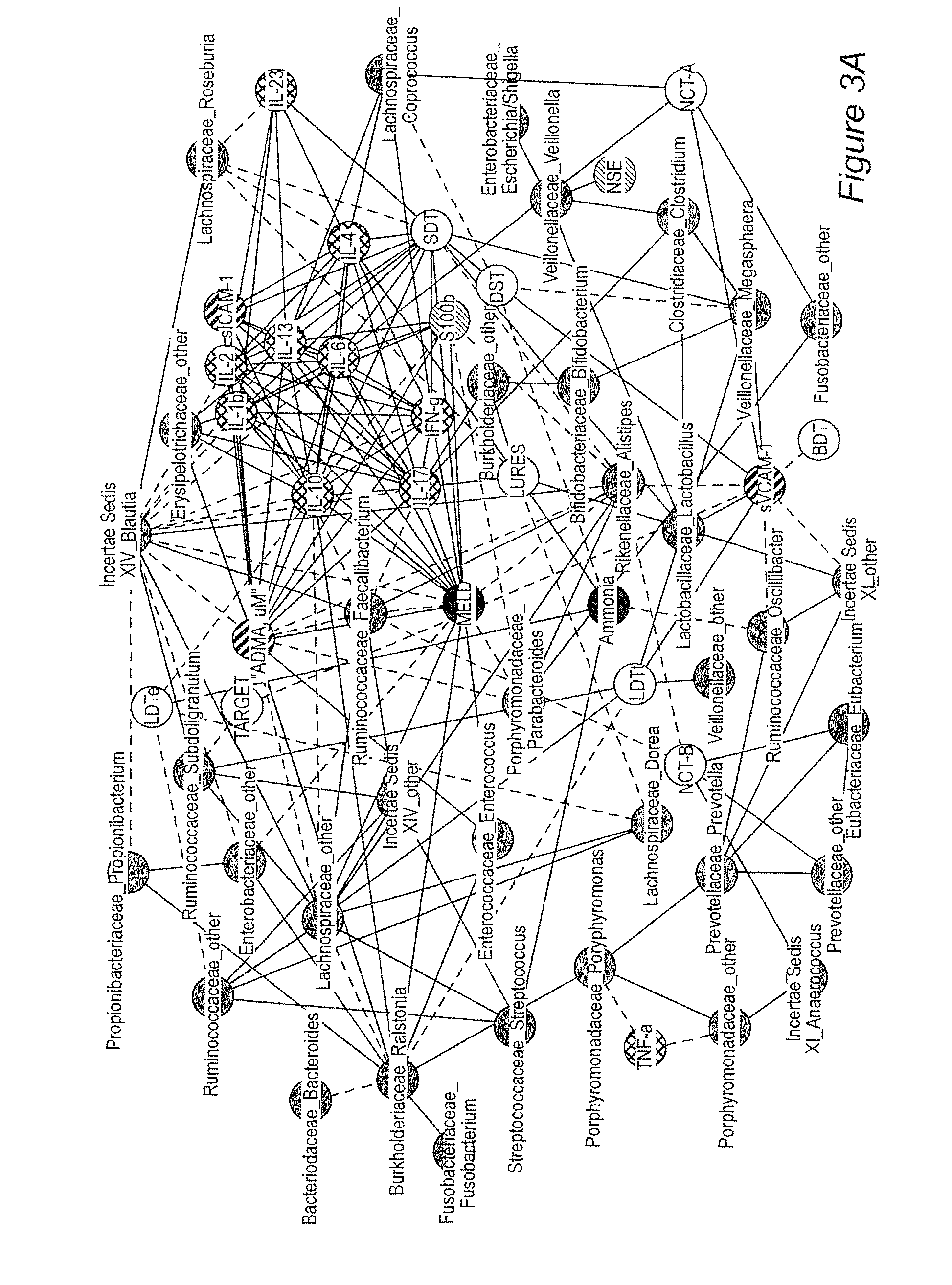
Gut microflora as biomarkers for the prognosis of cirrhosis and brain dysfunction
InactiveUS20140179726A1Efficacy of treatmentReduce the amount requiredBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseTreatment targets
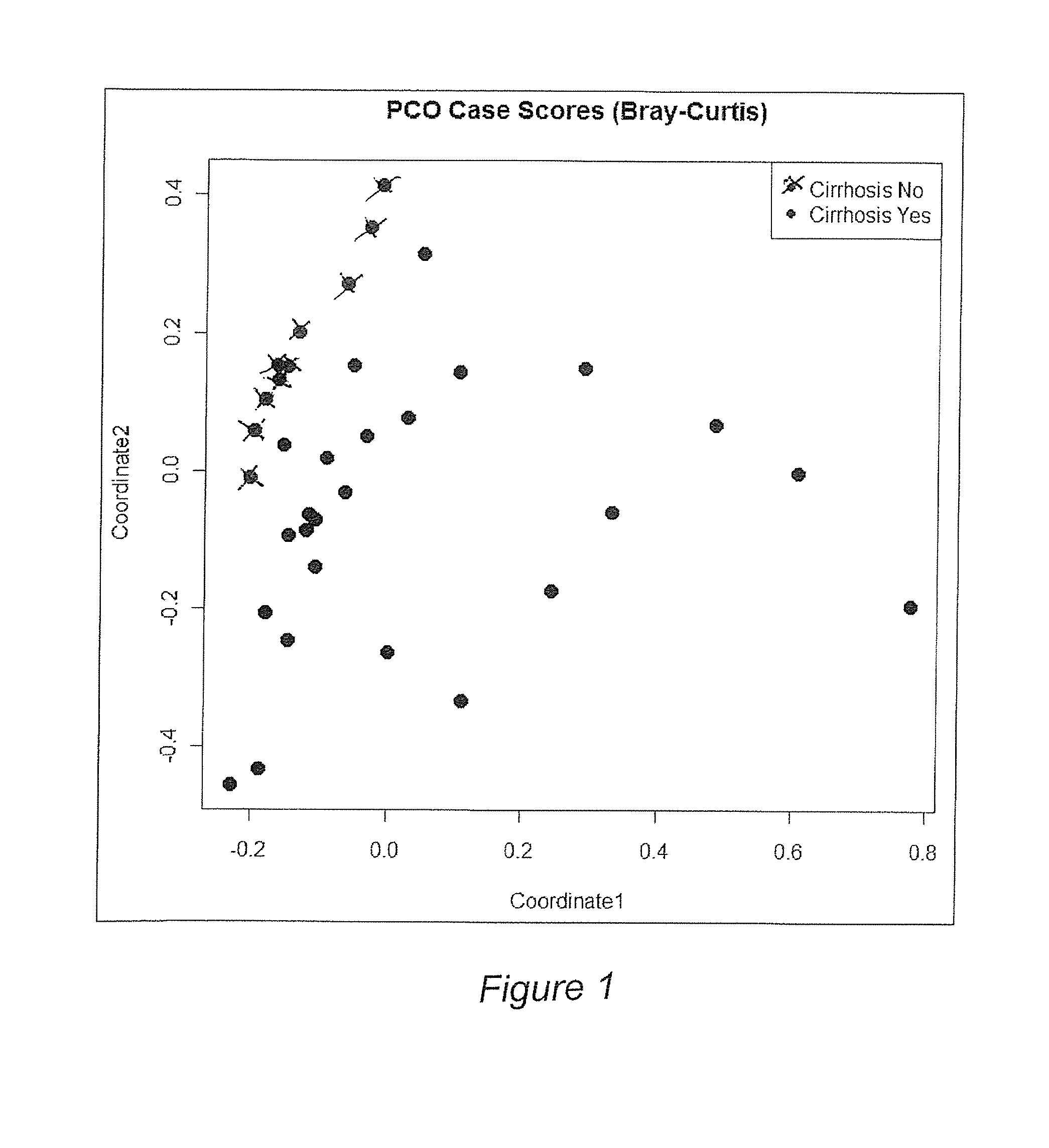
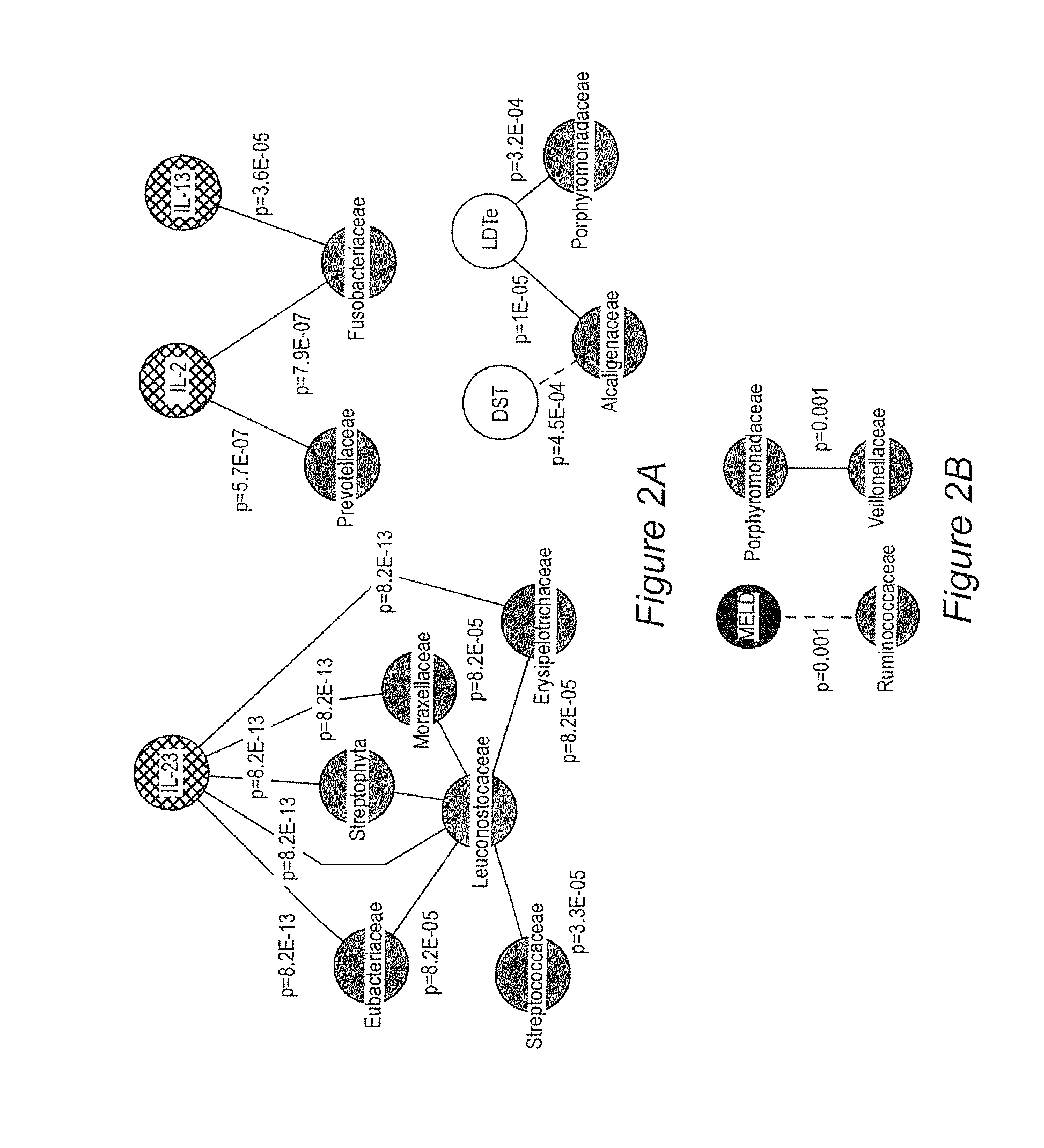
A systems biology approach is used to characterize and relate the intestinal (gut) microbiome of a host organism (e.g. a human) to physiological processes within the host. Information regarding the types and relative amounts of gut microflora is correlated with physiological processes indicative of e.g., a patient's risk of developing a disease or condition, likelihood of responding to a particular treatment, for adjusting treatment protocols, etc. The information is also used to identify novel suitable therapeutic targets and / or to develop and monitor the outcome of therapeutic treatments. An exemplary disease / condition is the development of hepatic encephalopathy (HE), particularly in patients with liver cirrhosis.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV +1
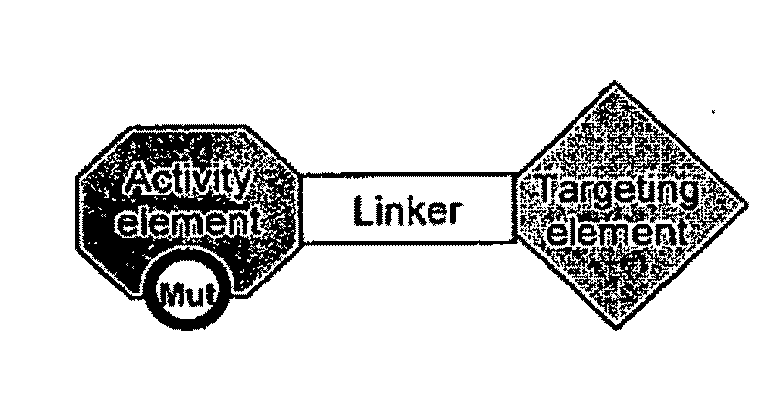
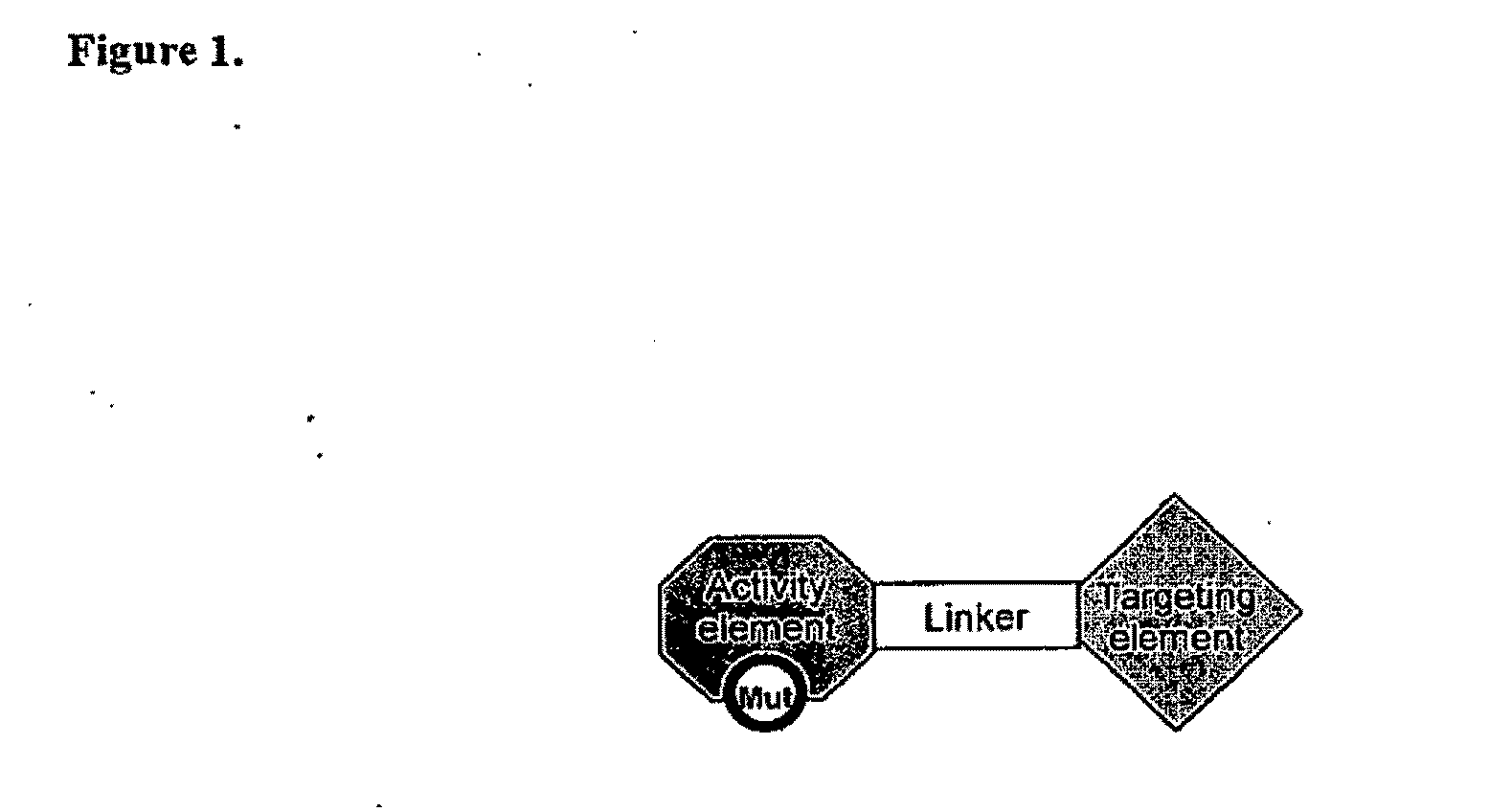
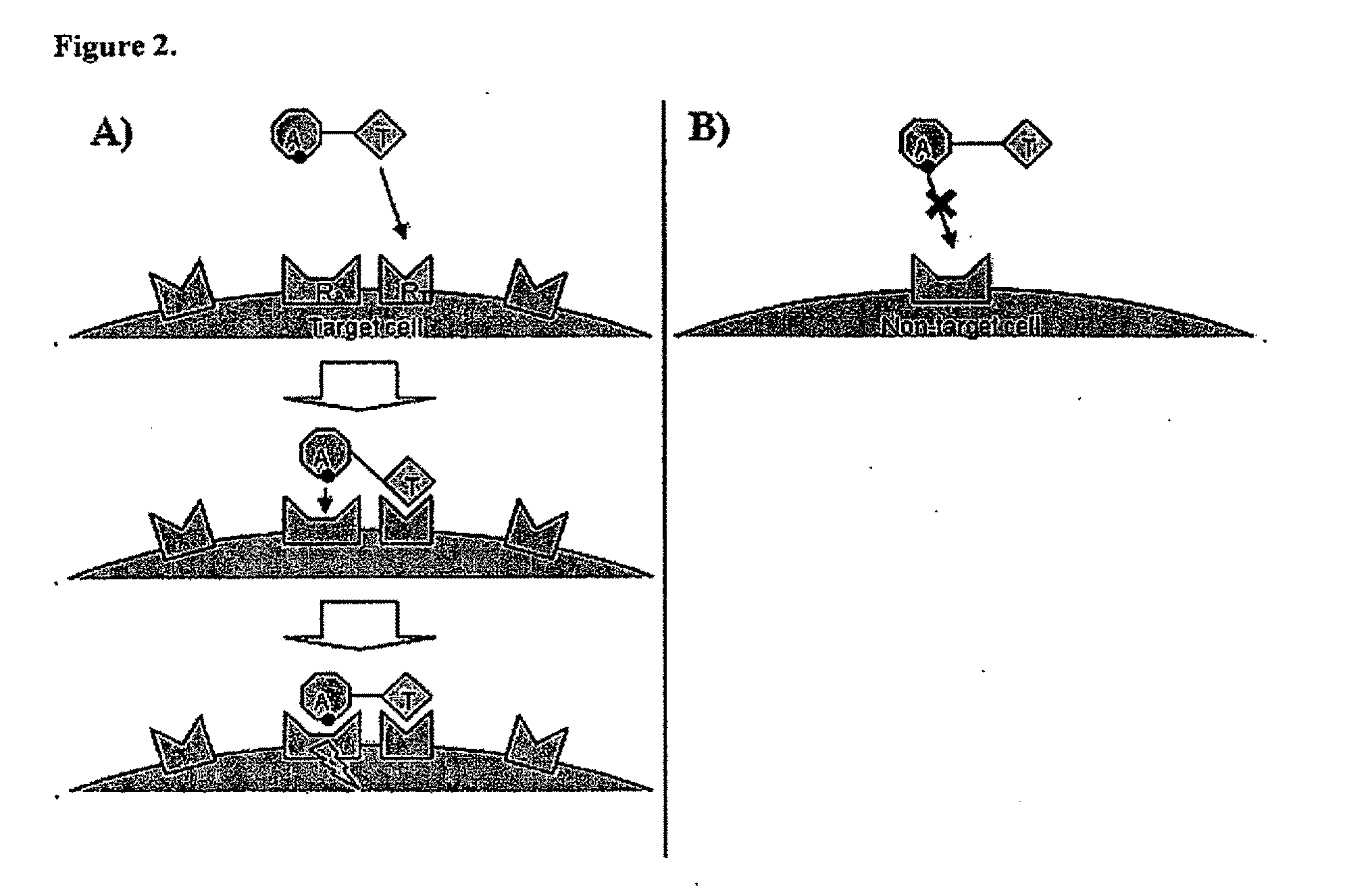
Chimeric activators: quantitatively designed protein therapeutics and uses thereof
ActiveUS20110274658A1Reduced cell-activating propertyAvoid and reduce unwanted side effectObesity gene productsPeptide/protein ingredientsChimerin ProteinsApoptosis
Aspects of the invention provide methods for harnessing the potential of proteins that occur naturally (e.g., in humans) and that have serious but finite toxicity. Aspects of the invention relate to a quantitative systems-biological and structural approach to design a class Mof chimeric proteins that avoid the toxicity of protein drugs while retaining their desired activities. In particular, chimeric proteins containing a variant form of a natural protein fused to a targeting moiety may be administered to a subject to target a signal (e.g., induction of apoptosis) to particular cells without having a generalized toxic effect
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Method for Modeling a Disease
The invention described herein provides for methods of profiling cellular models of disease. Cellular systems biology is the investigation of the integrated and interacting networks of genes, proteins, and metabolites that are responsible for normal and abnormal cell functions. Methods and reagents for the profiling a disease state, the treatment of a disease state and assaying of treatments of a disease state are provided.
Owner:CELLUMEN INC
Data acquisition system for nuclein and fluorescent dual module integral small animal molecules imaging
InactiveCN101057788ASmall doseEasy to implementSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsQuantum yieldScintillation crystals
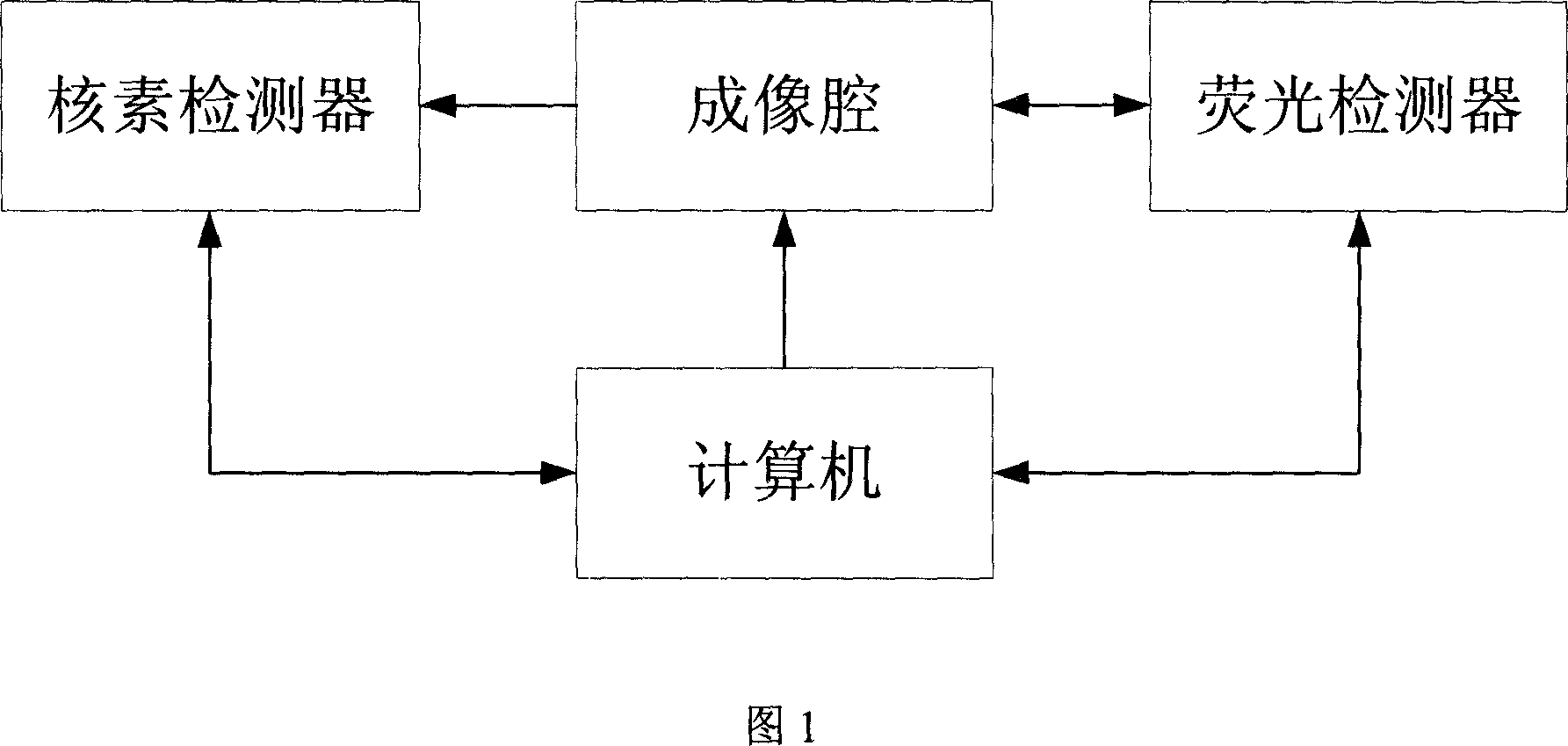
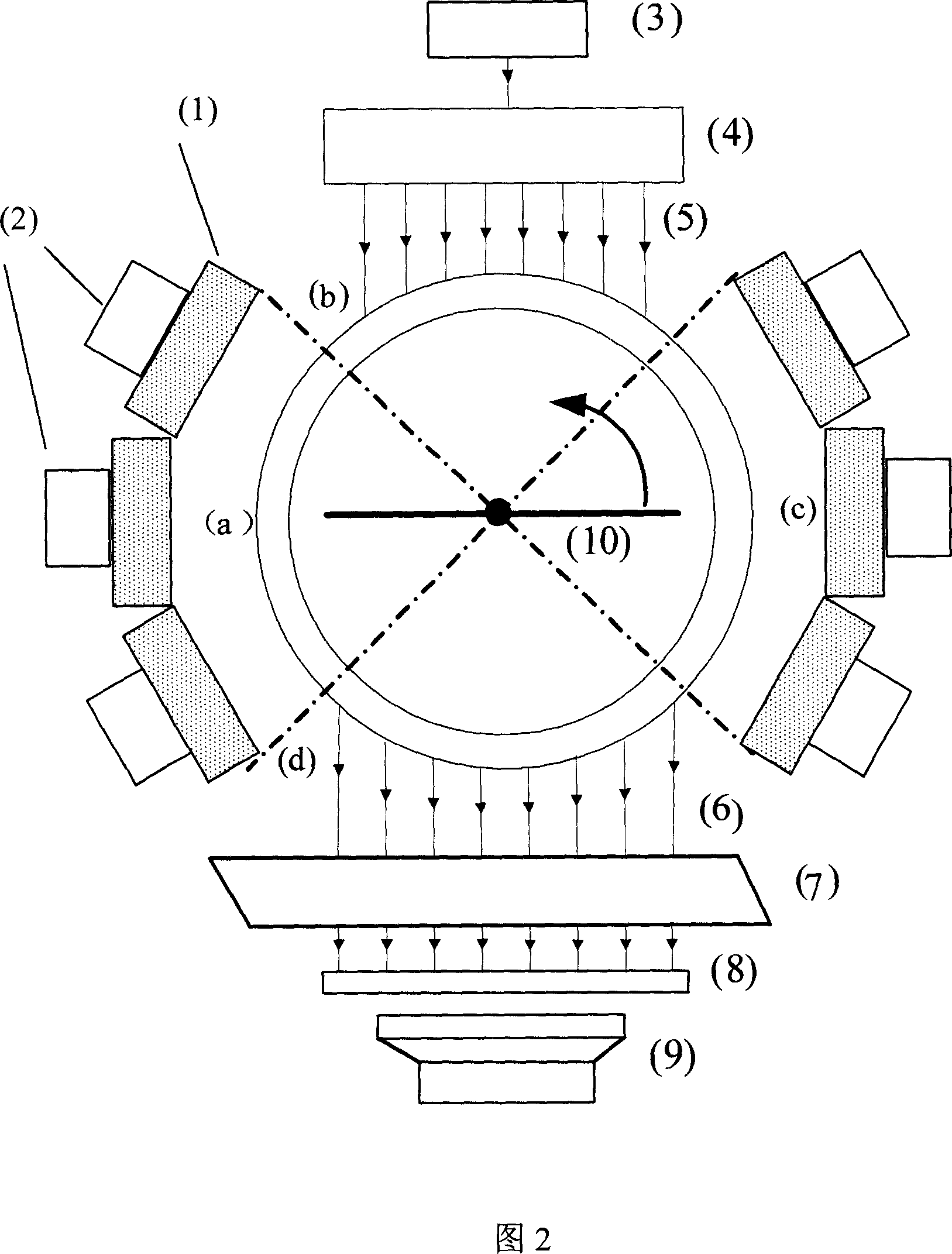
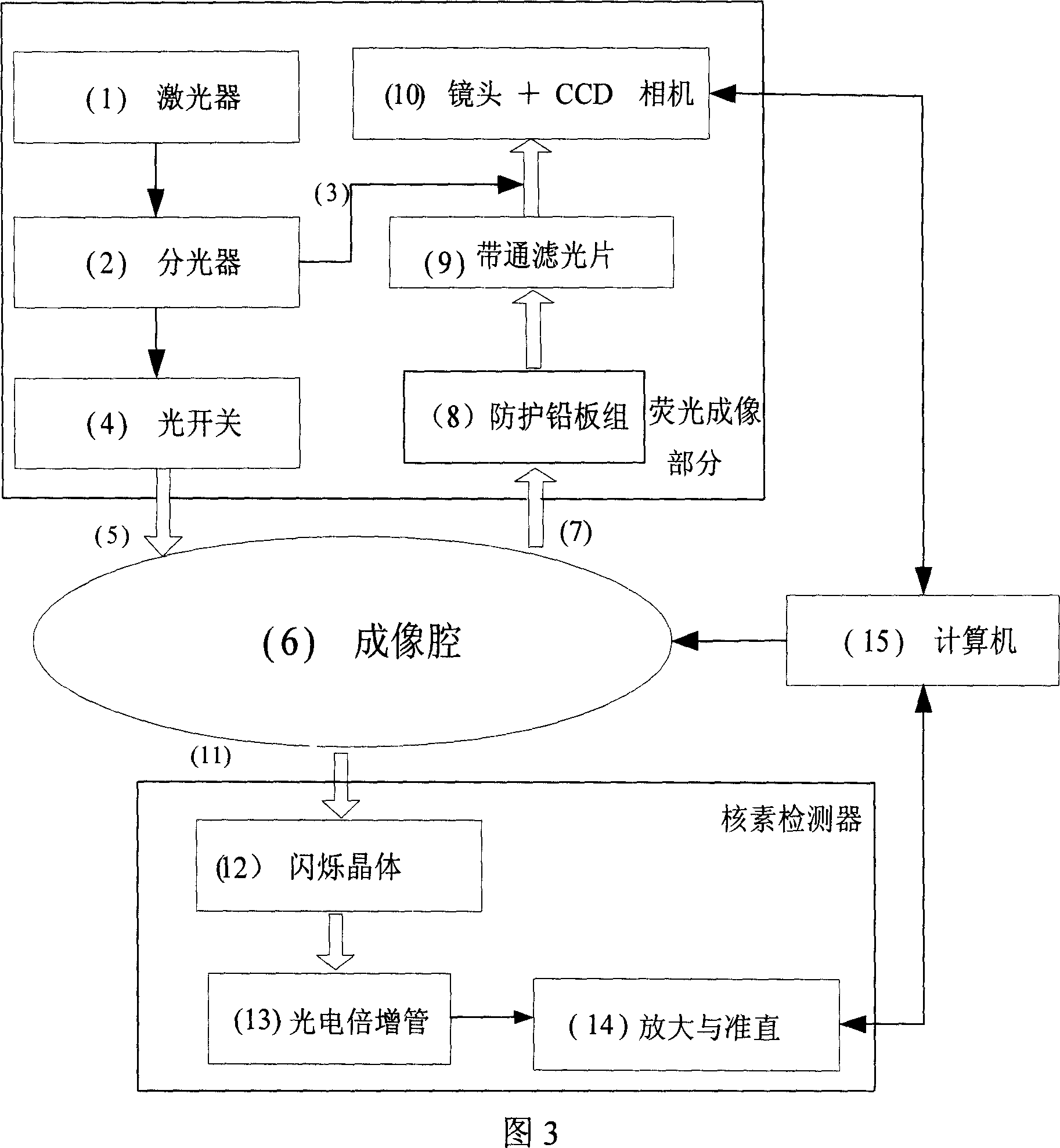
The invention belongs to the field of application of near-infrared laser, nuclear irradiation, electron and image rebuild in systematic biology and medicine. It is characterized in that high-specificity nuclear species and fluorescent probe are implanted in live animal to realize double mark of muscle deep layer or internal organ tumor cell. The emission signal of nuclear species is checked by sensitive electron-multiplier phototube in array copulation position of scintillation crystal; feeble fluorescent signal generated by visible light or infrared agitation is checked by high quantum yield CCD camera. The two checking systems are orthogonally arranged in the same surface, the live nuclear species and fluorescent signal can be checked simultaneously through rotary image cavity, and double module three dimensional tomography image of small animal can be rebuilt with software algorism. The invention is characterized by multi-image forming modules, abundant information and simple operation.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Pharmaceutical activity prediction and selection method based on genetic expressions and drug targets
InactiveCN106055921AEasy to useImprove efficiencyProteomicsGenomicsPersonalizationApplicability domain
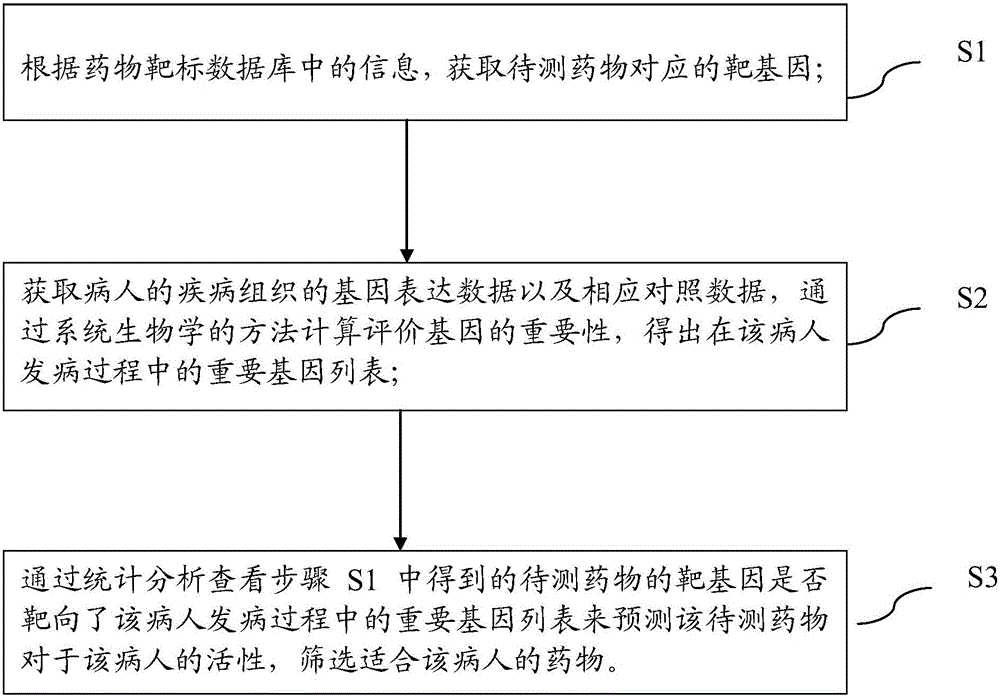
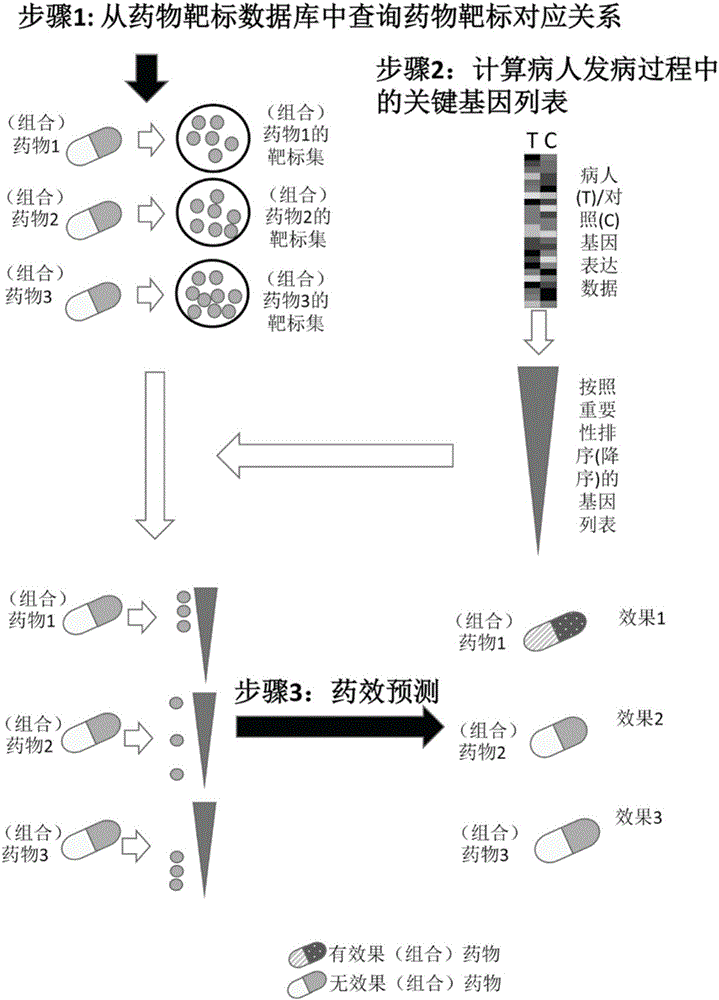
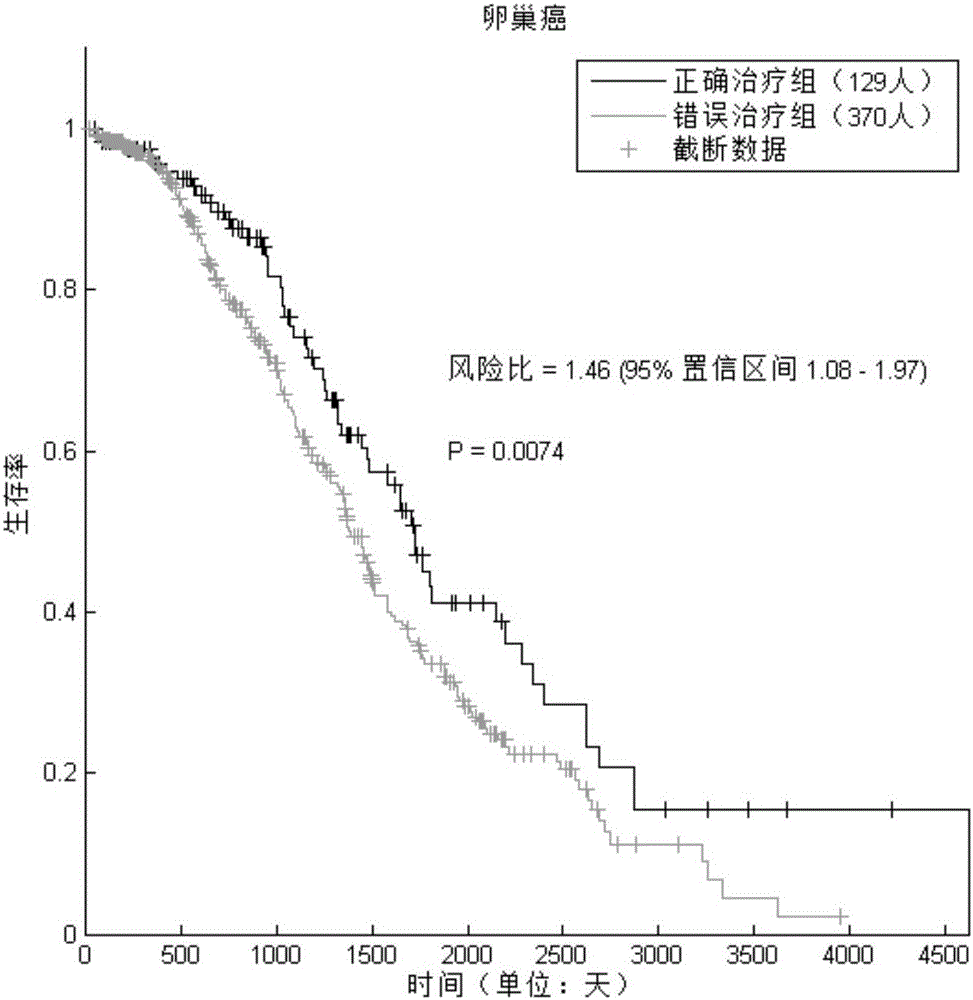
The invention discloses a pharmaceutical activity prediction and selection method based on genetic expressions and drug targets. The method comprises following steps: 1) obtaining target genes corresponding to drugs to be detected according to information in drug target database; obtaining genetic expression data of disease tissues of patients and corresponding compression data and obtaining important genetic lists of morbidity processes of patients by evaluating importance of genes through a systems biology method; 2) searching for whether the target genes obtained in the step 1) target the important gene lists during mobility of the patients or not through statistical analysis of in order to predict pharmaceutical activity of patients and select drugs suited to patients. The method is easily used with high efficiency and broad application scope. The prediction method can be used for selecting drugs suitable for individual patients such that a personalized treatment schme can be provided for patients.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Drug Repositioning Methods For Targeting Breast Tumor Initiating Cells
InactiveUS20120296090A1Quick translationInhibit breast TICsMedical simulationOrganic chemistryOncologyPharmacology
Disclosed are systems biology-based methods for repositioning known pharmaceutical compounds to new indications, through the identification of network-based signatures. In particular, the invention provides new and useful methods for selecting drugs or combinations of drugs (and preferably previously-approved drugs) for use in new therapeutic indications. Also disclosed are methods for identifying anti-breast tumor initiating cell (TIC)-based therapeutics from within populations of target compounds. In illustrative embodiments, the invention provides methods and computer programs for the repositioning of FDA-approved pharmaceutical compounds to new indications using network-based signature analysis coupled with conventional in vitro and in vivo testing of identified drug candidates. The invention also allows identification of drugs or drug combinations for treating unmet medical needs including, for example, “orphan” diseases.
Owner:THE METHODIST HOSPITAL RES INST
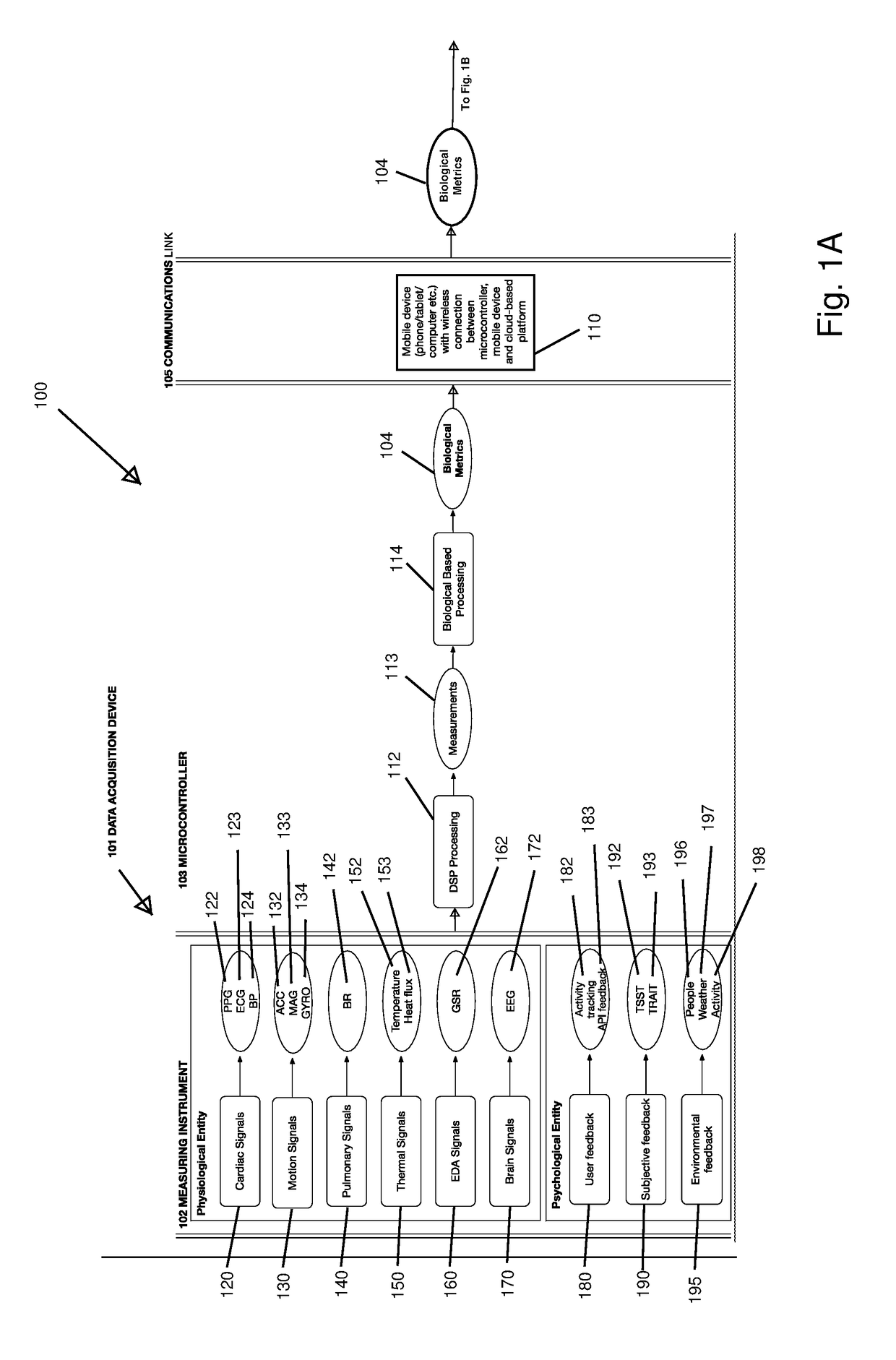
Non-Invasive Physiological Quantification of Stress Levels
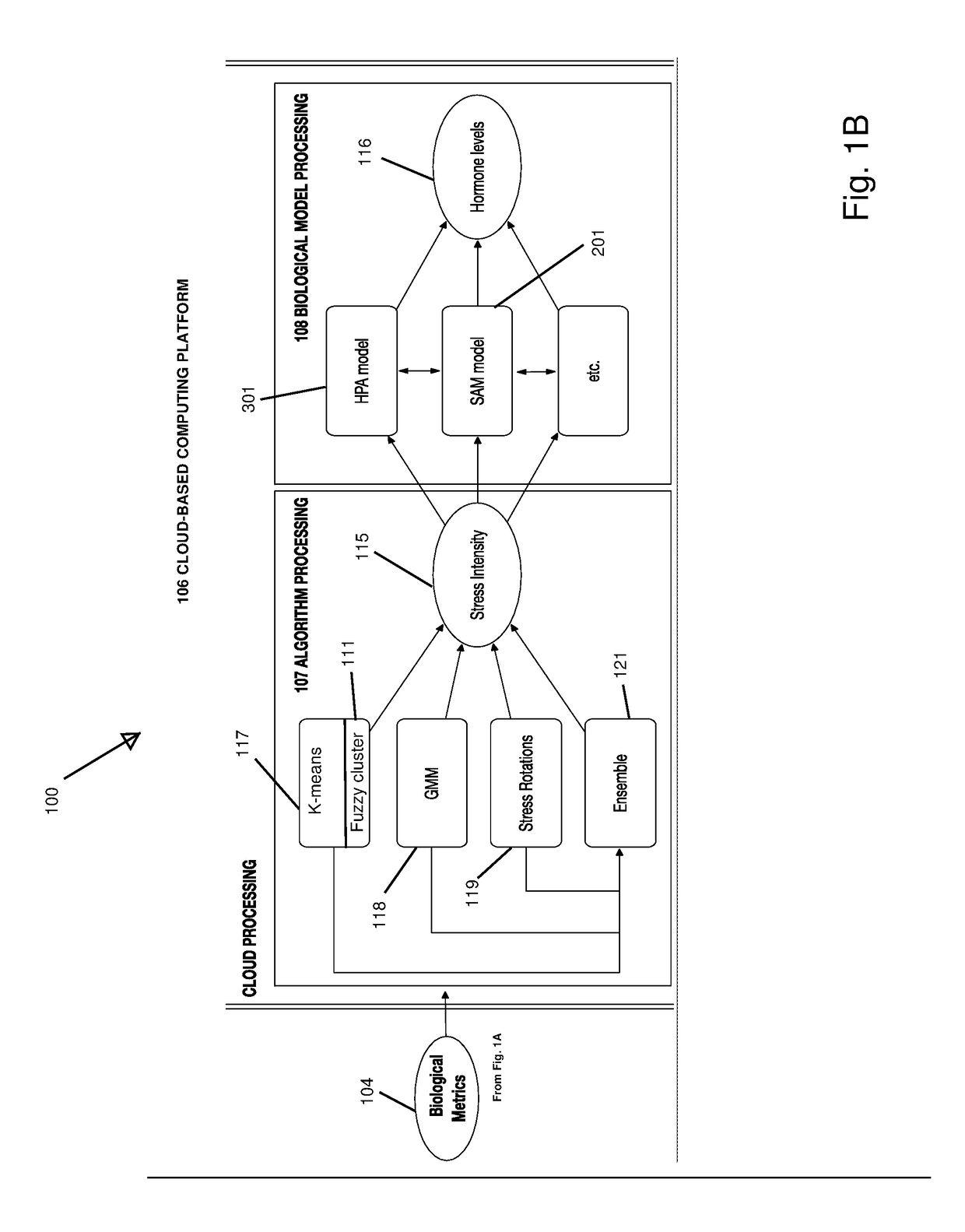
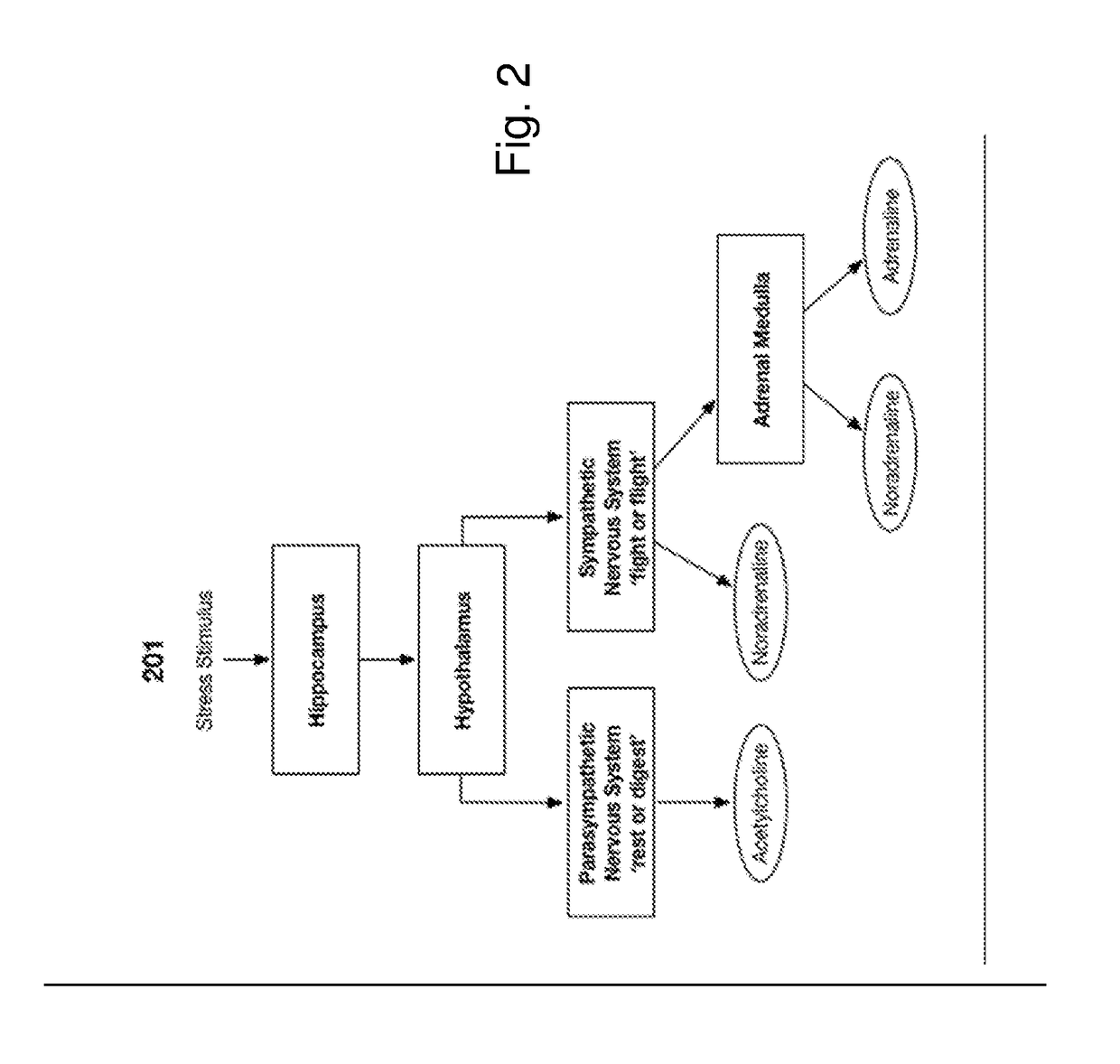
InactiveUS20170127993A1Inertial sensorsEvaluation of blood vesselsChronic stressMeasuring instrument
A data acquisition device includes measuring instruments to generate physiological and / or psychological data streams. Microprocessors within the acquisition device process the generated data streams into metrics, which feed into stress function algorithms. Algorithm processing may occur either on the device, or metrics may be communicated via wireless communication for external processing on mobile devices and / or cloud-based platforms. The calculated stress functions inform cloud-based computational systems biology-derived models describing the dynamics of hormones and neurotransmitters released in the body in response to stressful stimuli. Stress hormone levels are quantified using these models, and are used in combination to serve as biologically inspired metrics of acute and chronic stress an individual is experiencing.
Owner:LIFEQ GLOBAL LTD
Method for predicting N6-methyladenosine modification site in RNA based on stacking integration
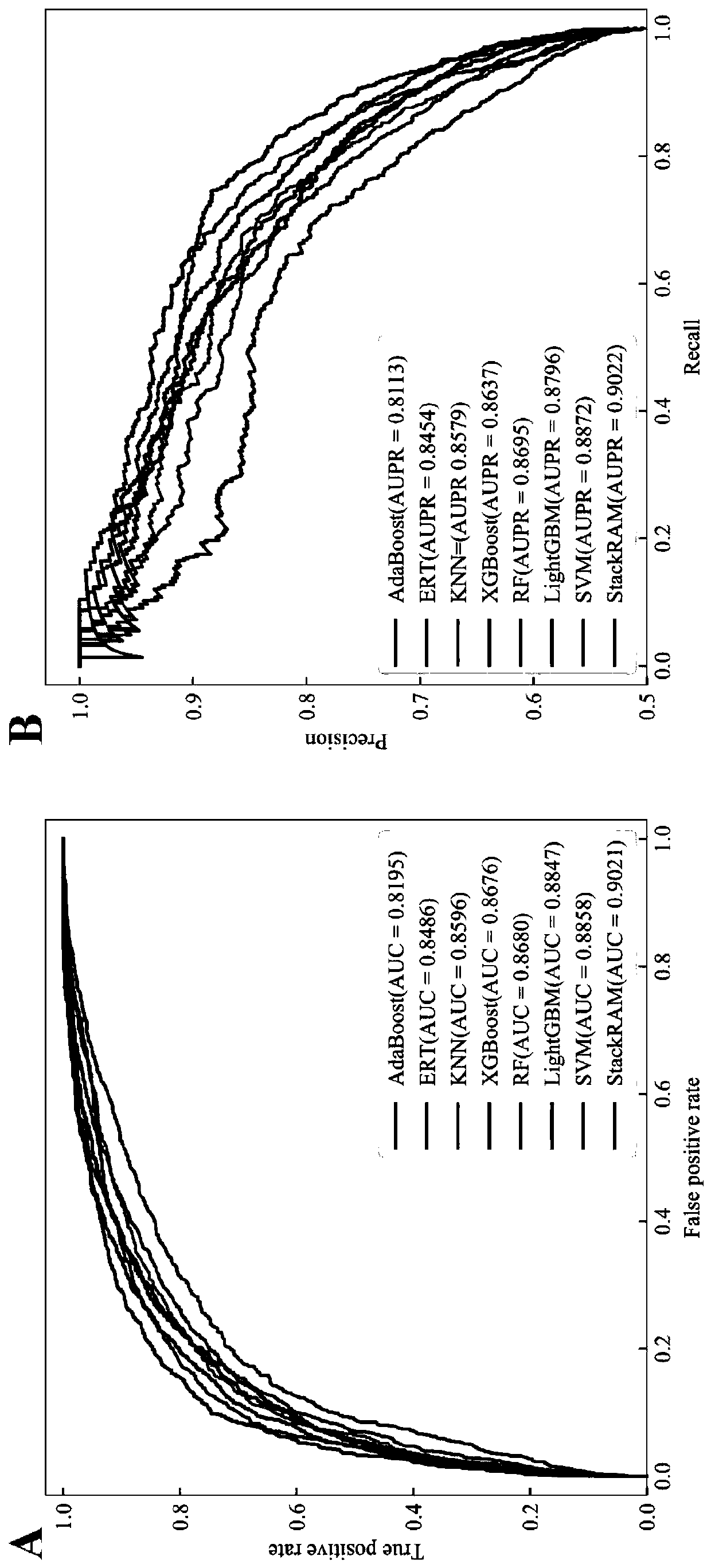
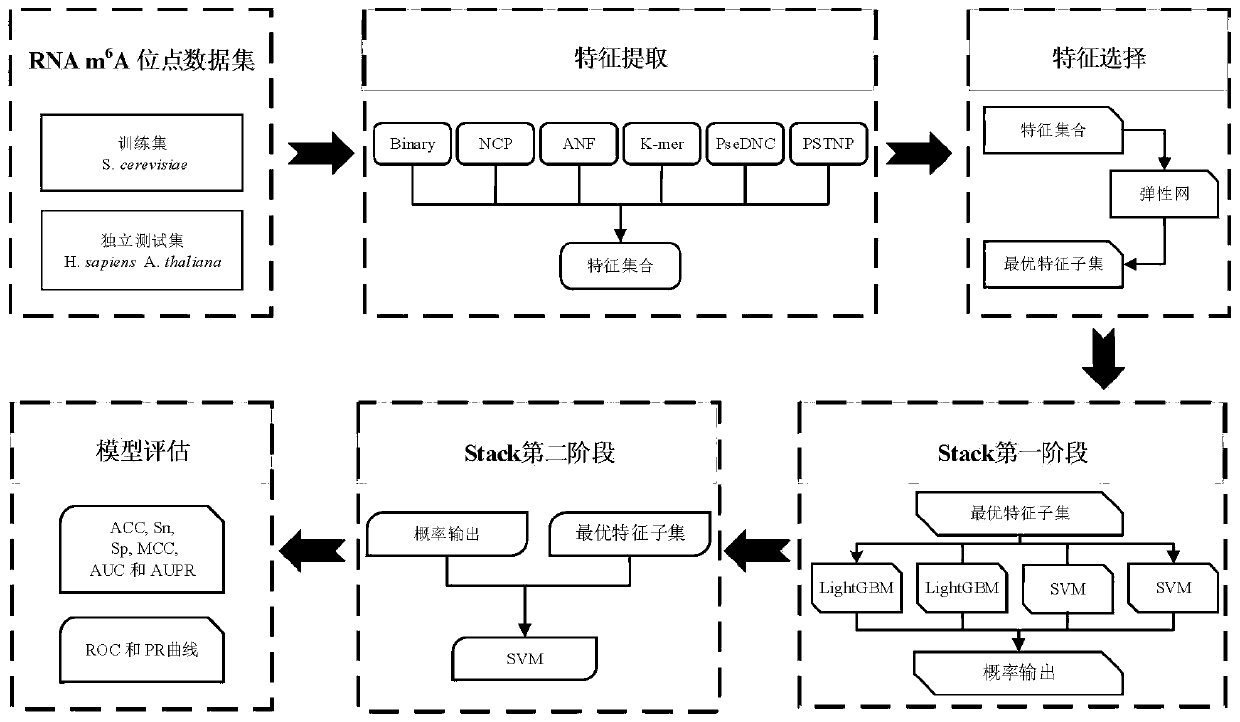
ActiveCN111161793APredictableIncrease computing speedBiostatisticsProteomicsDimensionality reductionRNA Sequence
The invention discloses a method for predicting an N6-methyladenosine modification site in RNA based on stacking integration, belonging to the field of systems biology. The method comprises the following steps: extracting RNA sequence features of three species, namely saccharomyces cerevisiae, homo sapiens and arabidopsis thaliana through six feature extraction methods, and conducting feature fusion to obtain an initial feature space of an original data set; performing dimensionality reduction on the initial feature space by using an elastic network, eliminating redundant and noise features, and reserving important features related to model classification so as to obtain an optimal feature set; inputting optimal feature subsets and corresponding category labels into stacking integration for model training, and evaluating the prediction performance of a model in combination with evaluation indexes to obtain a prediction model; and inputting a to-be-predicted RNA sequence in a test set into the prediction model, predicting the m6A site and outputting the m6A site. The prediction accuracy of the model on the test set reaches 92.30% and 87.06% respectively, and the model has good development potential in the aspect of cross-species prediction and is expected to become a useful tool for identifying the m6A site.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method For Predicting Biological Systems Responses
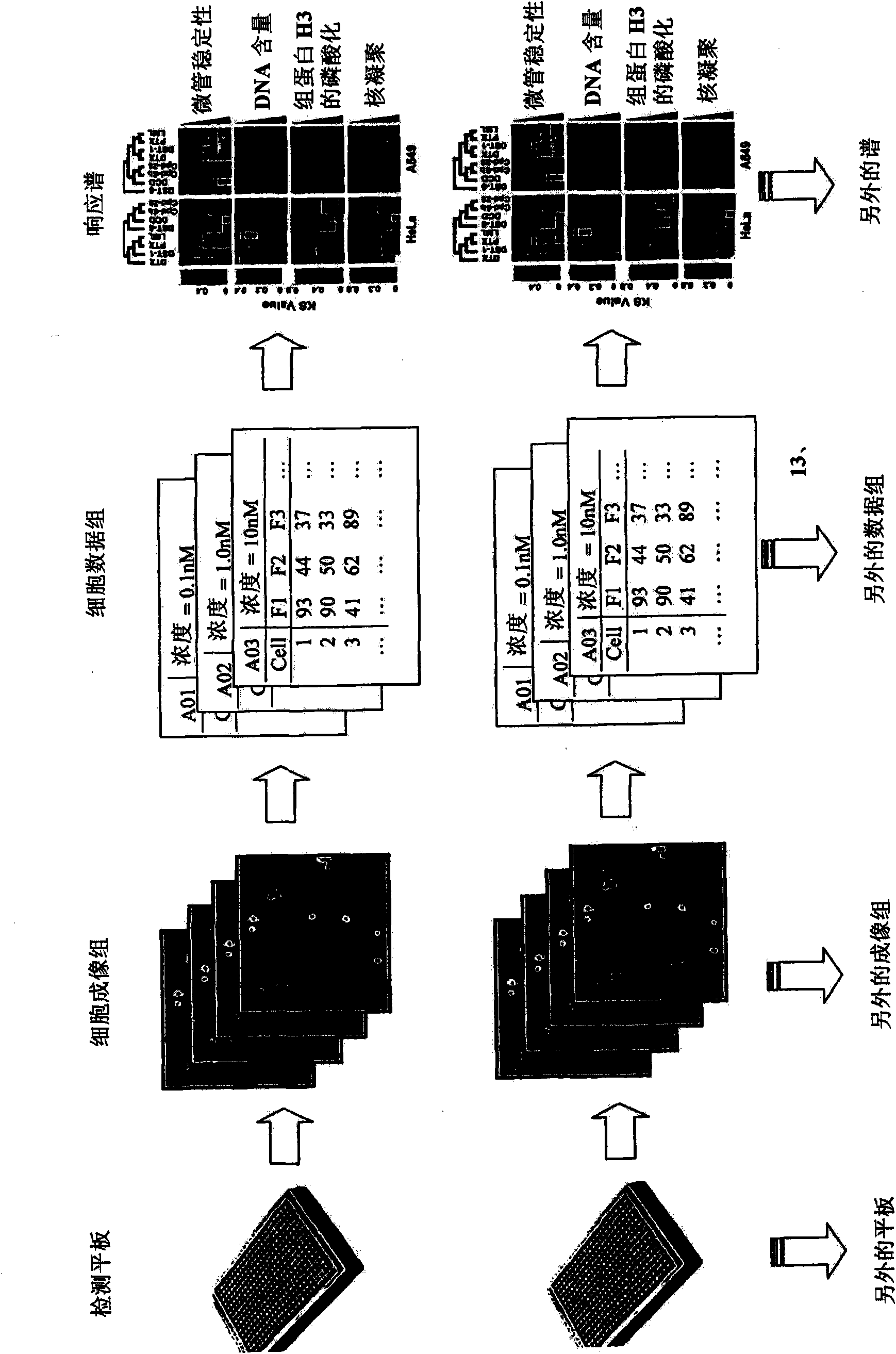
InactiveUS20090170091A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisInformaticsSystems biology
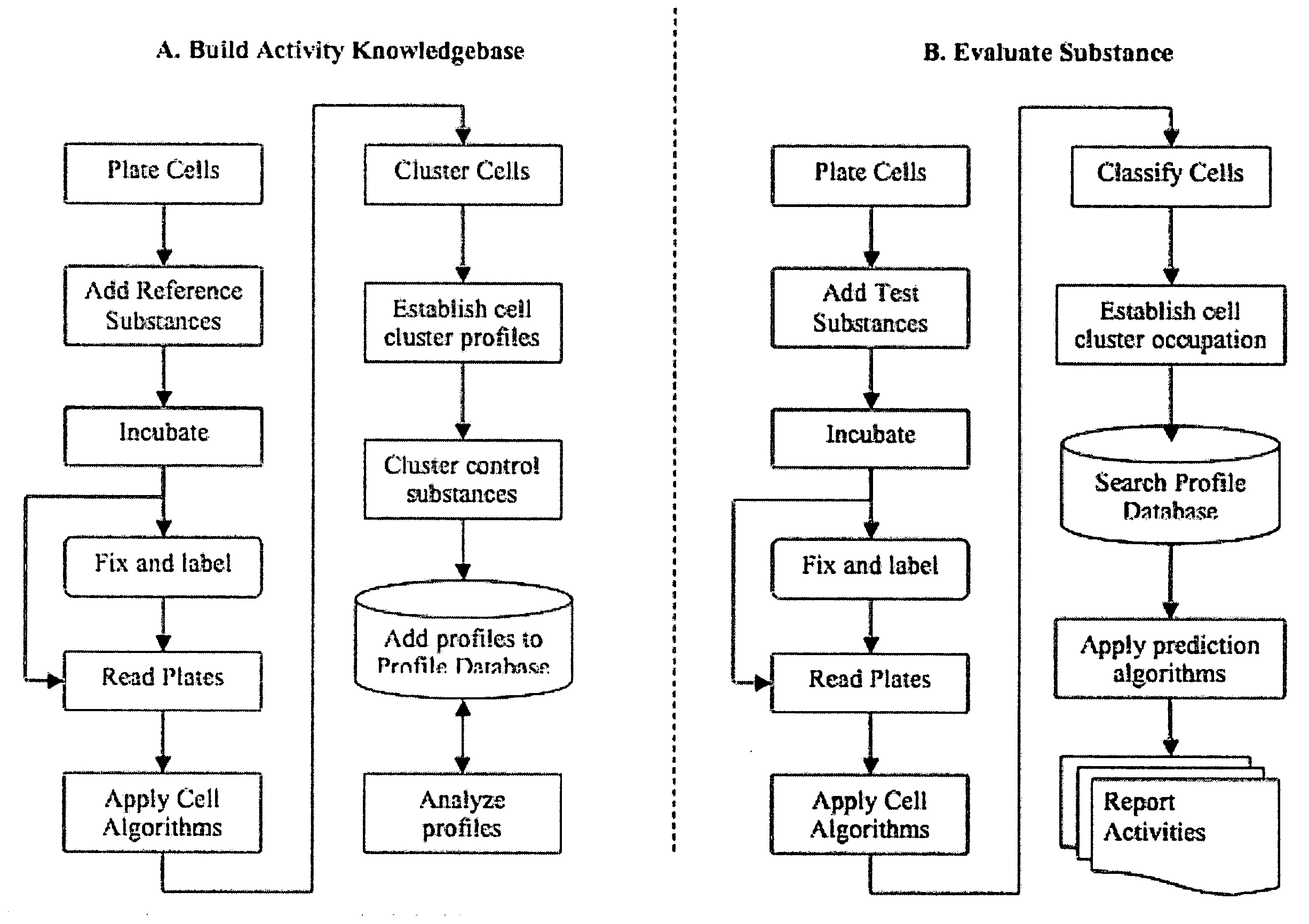
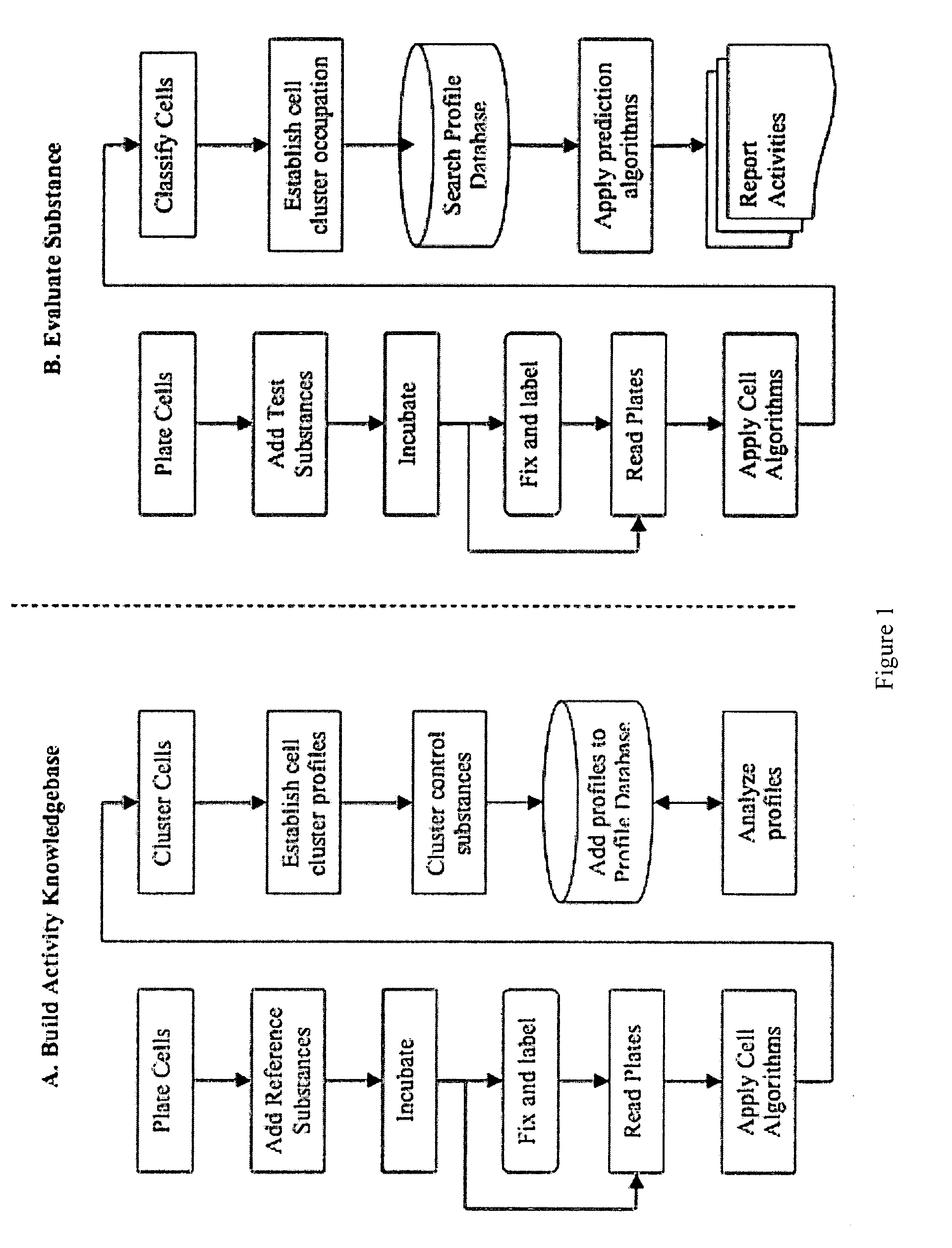
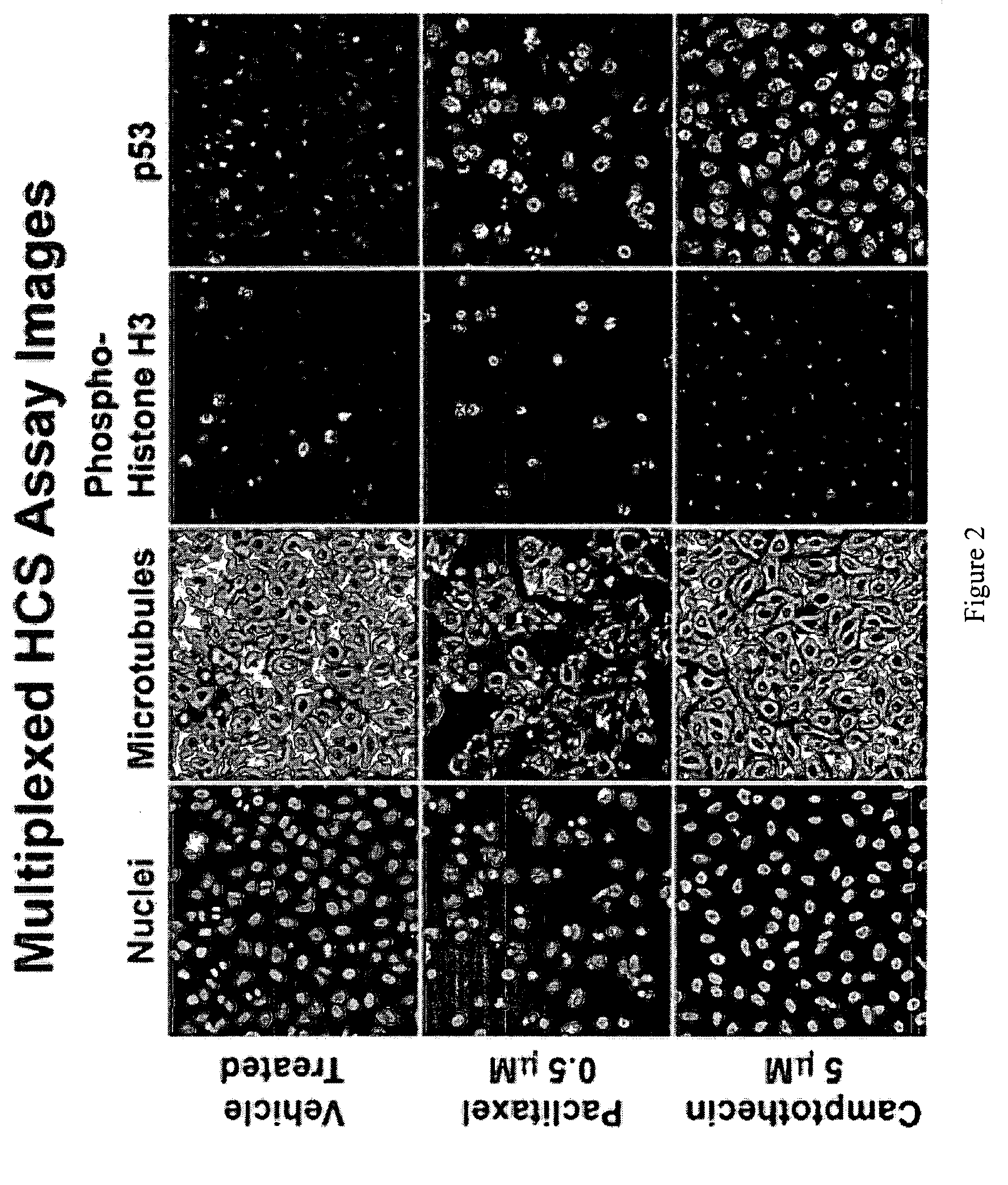
The inventive method employs a “systems biology” approach to predicting biological responses resulting from exposure to the test substance. In one embodiment, the invention provides an automated method for predicting the biological systems effects of a test substance. In another embodiment, the invention provides a method for constructing a knowledgebase (or database) of response profiles for reference substances with known biological systems effects. In another embodiment, the invention provides a set of protocols and software tools used to carry out the profiling. Another embodiment of the invention is a panel of reagents and protocols required for generating response profiles, either to create an knowledgebase, or to use with an existing knowledgebase and informatics software to profile substance physiological effects. Another embodiment of the invention is a database of physiological profiles.
Owner:CELLUMEN INC
Polypeptide chip and application thereof in virus detection
The invention provides a polypeptide chip, which comprises a substrate and n polypeptides distributed on the substrate in an array, each polypeptide sequence has 10-20 amino acids, a group consistingof sequences of first to nth polypeptides covers at least 95% of a viral protein sequence, the adjacent polypeptides have an overlap of 3-8 amino acids, and n is 810-1370. According to the method, proteomics and system biology strategies are adopted, all coded protein sequences of COVID-19 are extracted from NCBI data, an SARS-CoV-2 virus proteome polypeptide chip is designed and prepared, and panoramic scanning of all SARS-CoV-2 virus antibodies in blood of a novel pneumonia virus infected patient is achieved.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
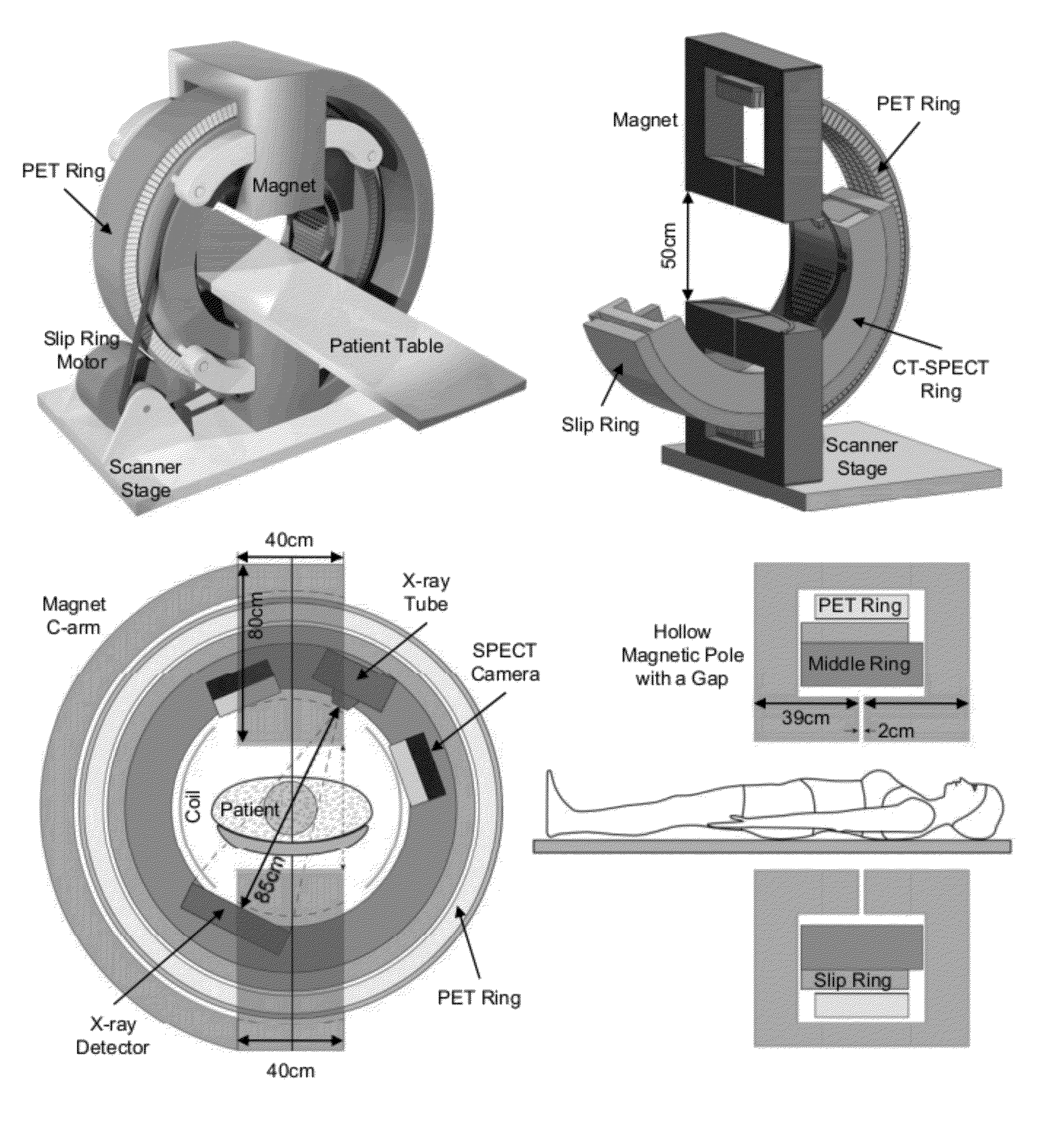
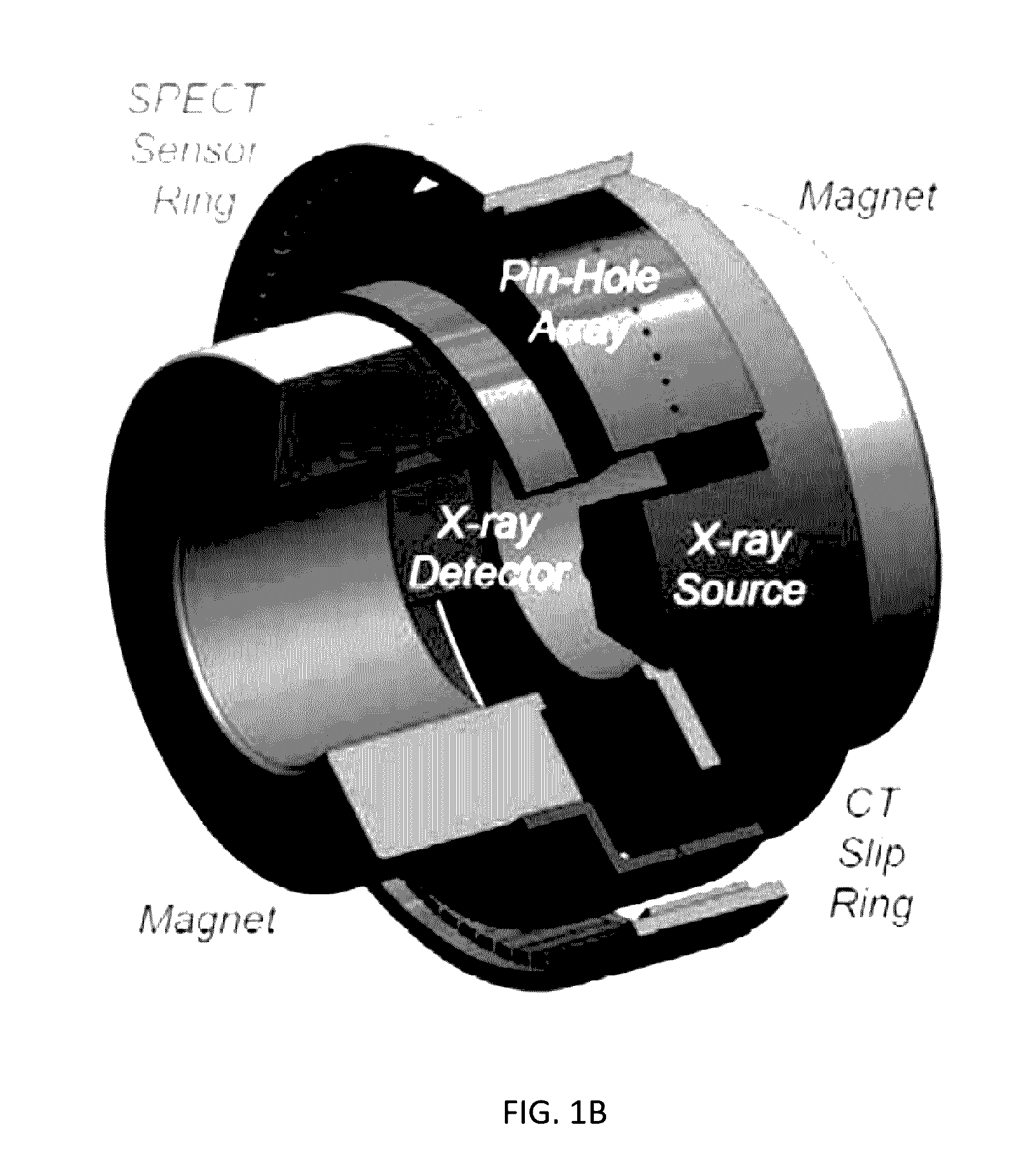
Omni-Tomographic Imaging for Interior Reconstruction using Simultaneous Data Acquisition from Multiple Imaging Modalities
InactiveUS20160282432A1Low costReduce electromagnetic interferenceDiagnostics using lightMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityModern medicine
Embodiments of the invention relate to omni-tomographic imaging or grand fusion imaging, i.e., large scale fusion of simultaneous data acquisition from multiple imaging modalities such as CT, MRI, PET, SPECT, US, and optical imaging. A preferred omni-tomography system of the invention comprises two or more imaging modalities operably configured for concurrent signal acquisition for performing ROI-targeted reconstruction and contained in a single gantry with a first inner ring as a permanent magnet; a second middle ring containing an x-ray tube, detector array, and a pair of SPECT detectors; and a third outer ring for containing PET crystals and electronics. Omni-tomography offers great synergy in vivo for diagnosis, intervention, and drug development, and can be made versatile and cost-effective, and as such is expected to become an unprecedented imaging platform for development of systems biology and modern medicine.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
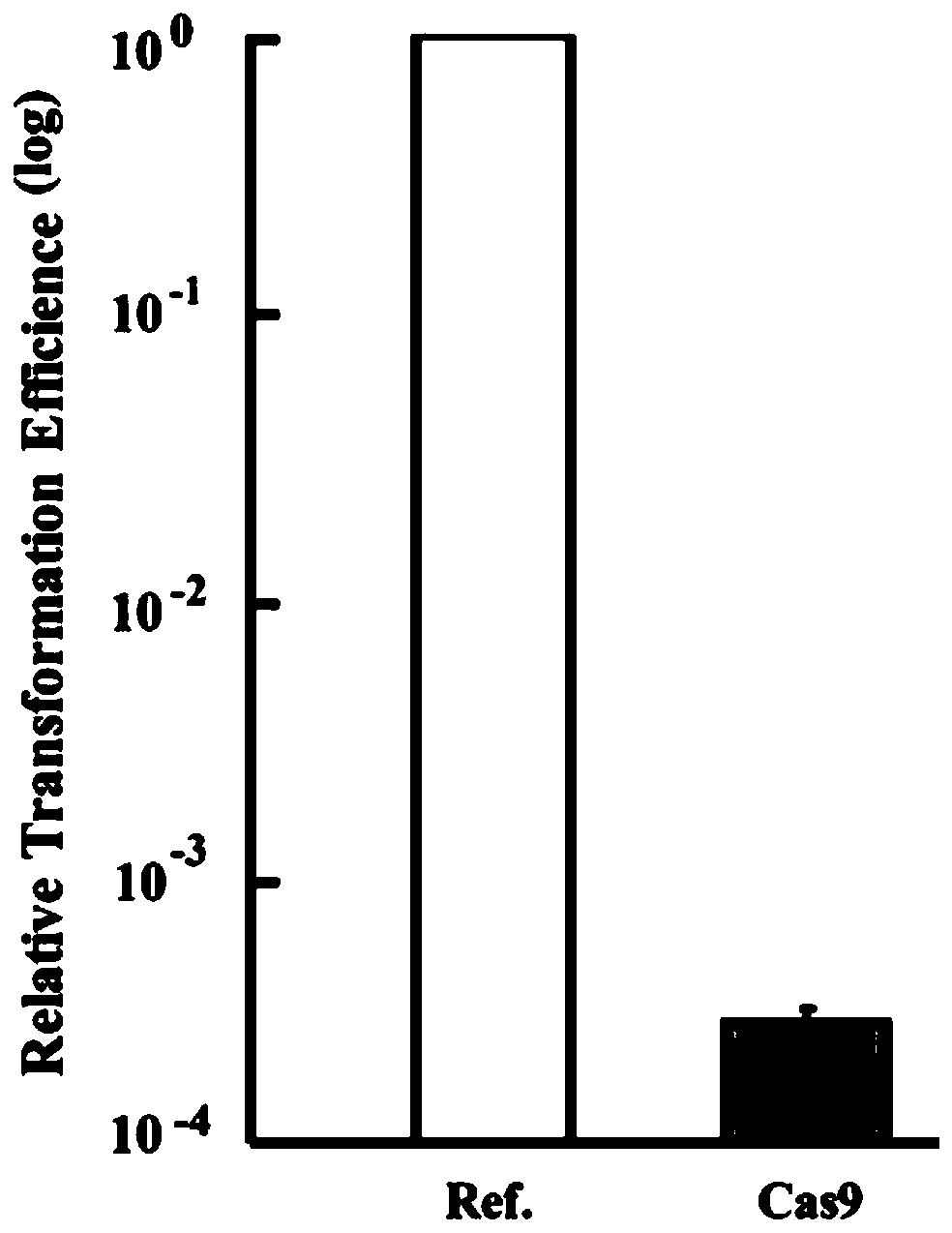
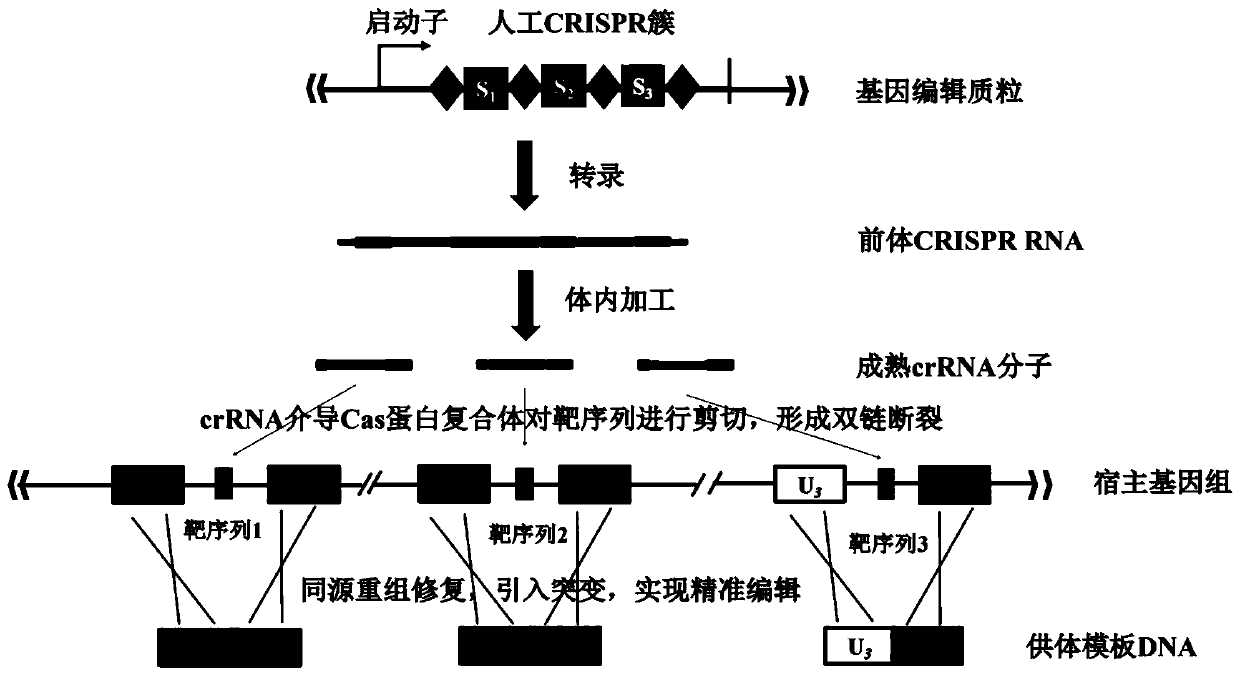
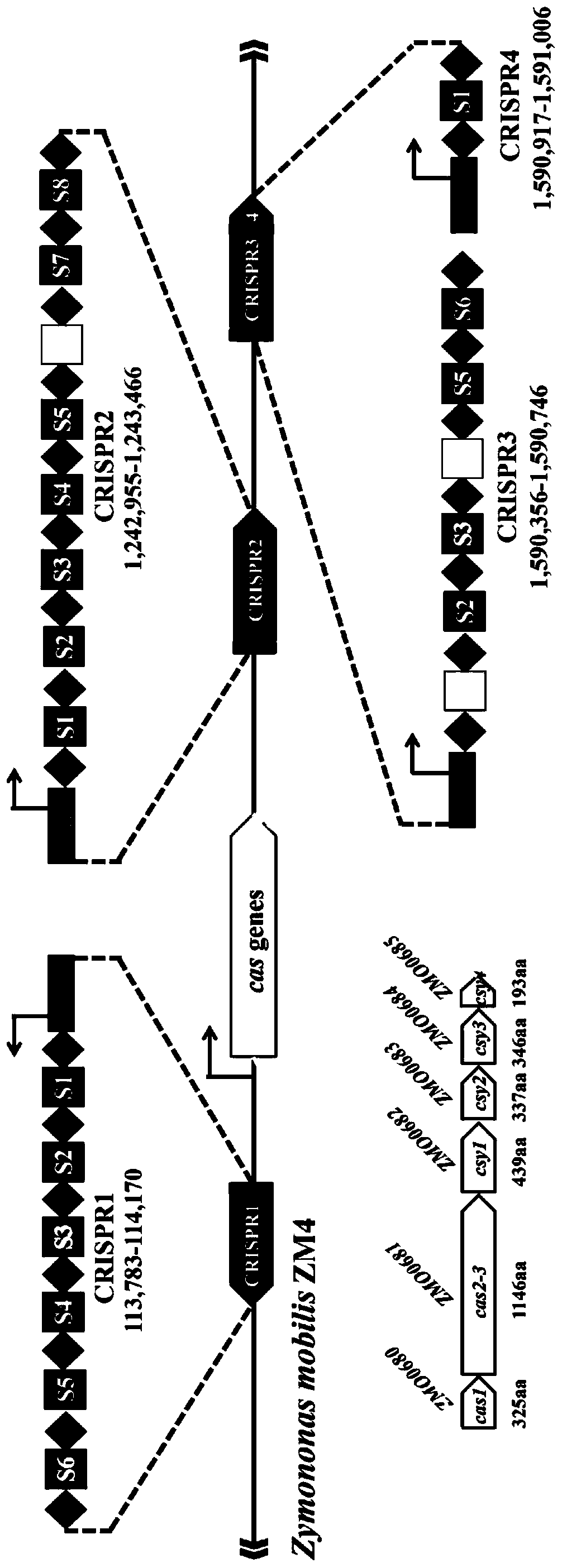
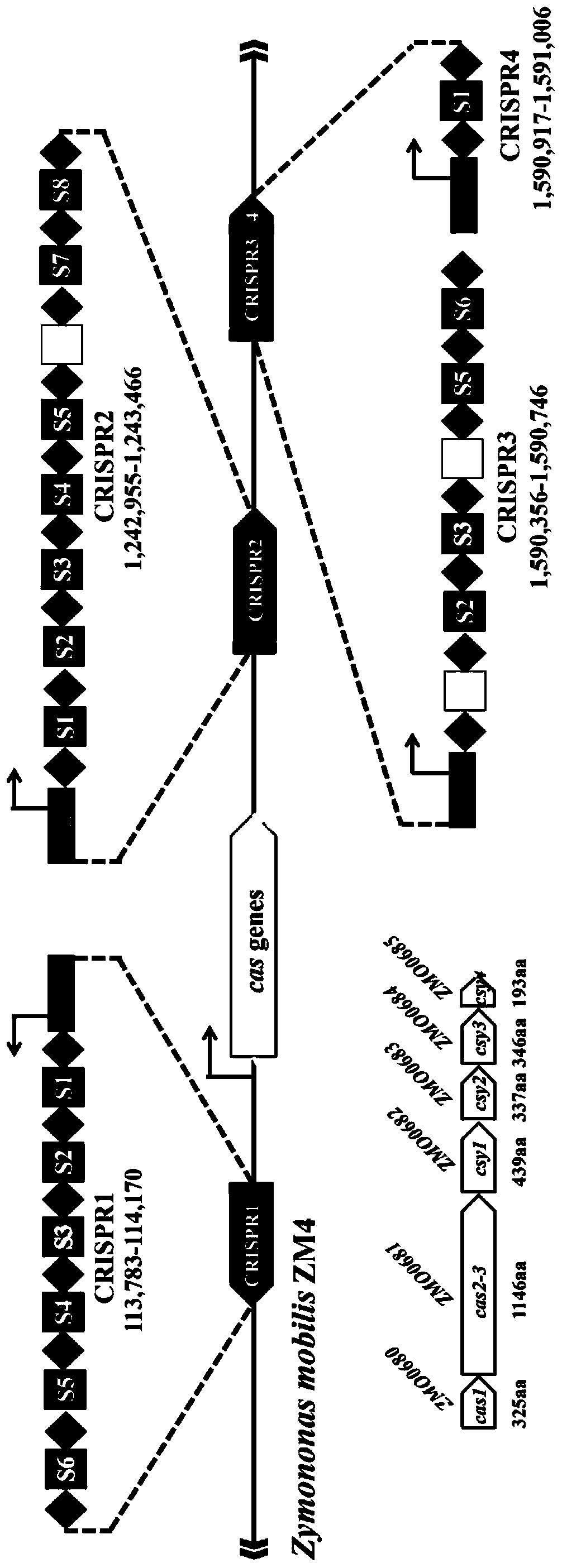
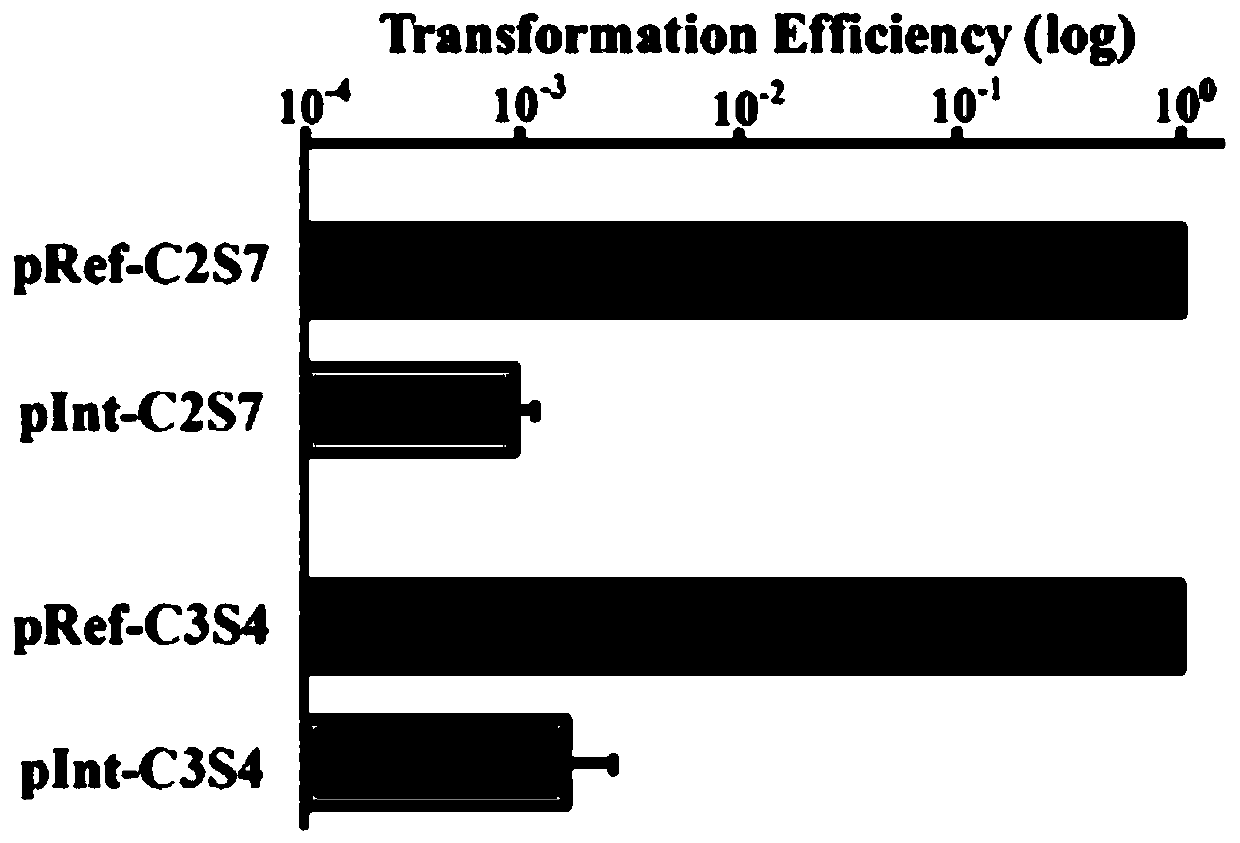
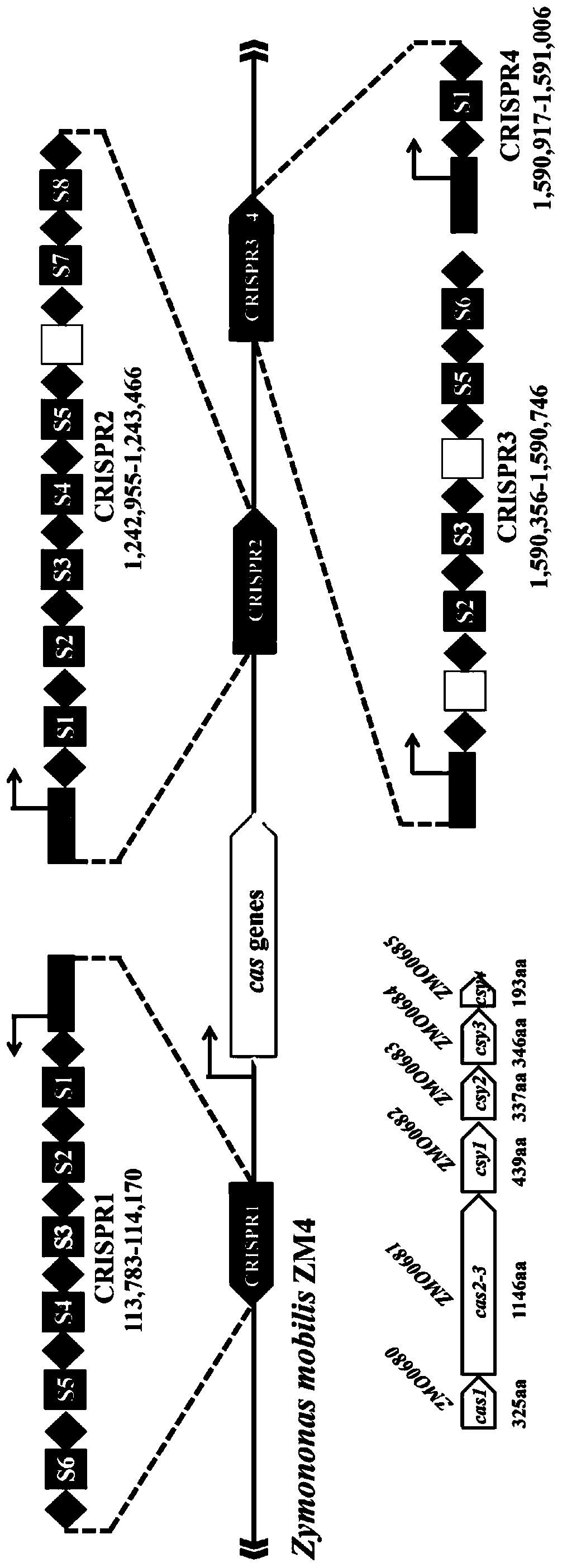
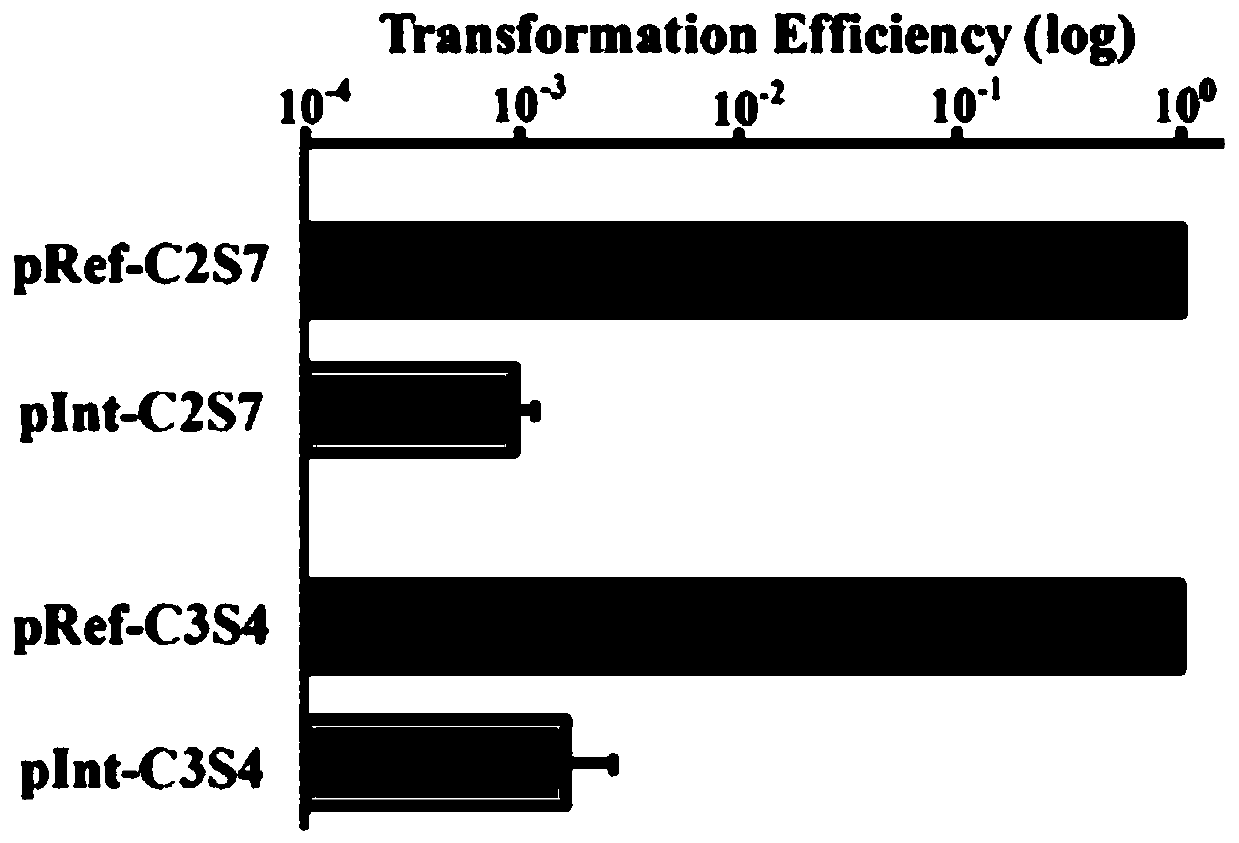
Multi-gene locus simultaneous editing method based on endogenous CRISPR-Cas system of zymomonas mobilis and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a multi-gene locus simultaneous editing method based on an endogenous CRISPR-Cas system of zymomonas mobilis and application thereof. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: constructing a plasmid containing an artificial CRISPR expression unit; selecting a plurality of target editing target loci, and designing a gRNA sequence; connecting a plurality of gRNA sequences in series, and constructing the gRNA sequences on the plasmid containing the artificial CRISPR expression unit; constructing a donor DNA sequence on a vector to obtain an edited plasmid; and transforming the edited plasmid into competent cells for editing. The method constructs a gene editing platform by utilizing theendogenous CRISPR-Cas system of zymomonas mobilis, breaks the limitation of low efficiency of exogenous CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing in the strain, realizes rapid and efficient knockout of multiple genes in the strain, and promotes the development of metabolic engineering, systemic biology and synthetic biology.
Owner:武汉睿嘉康生物科技有限公司
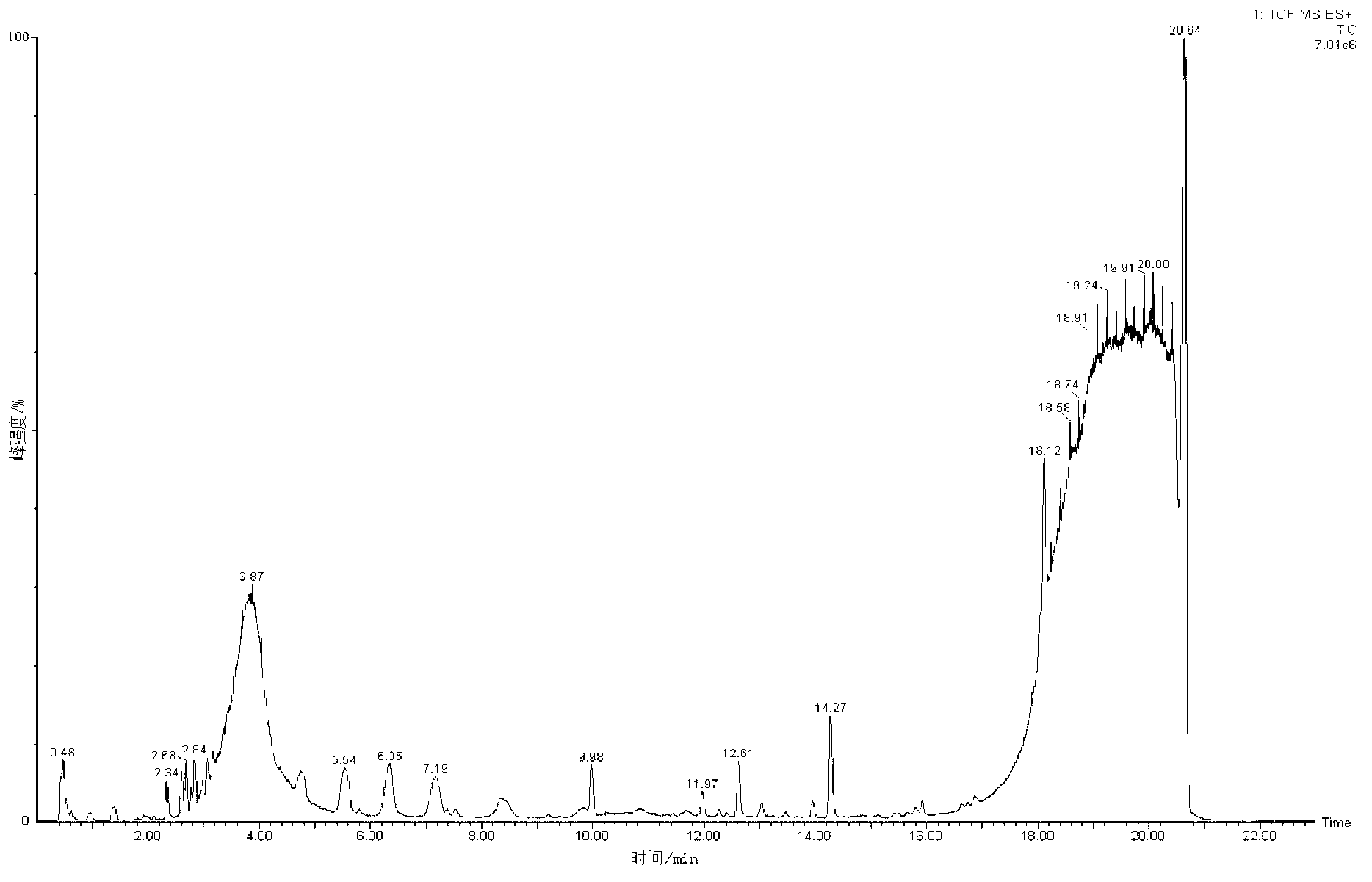
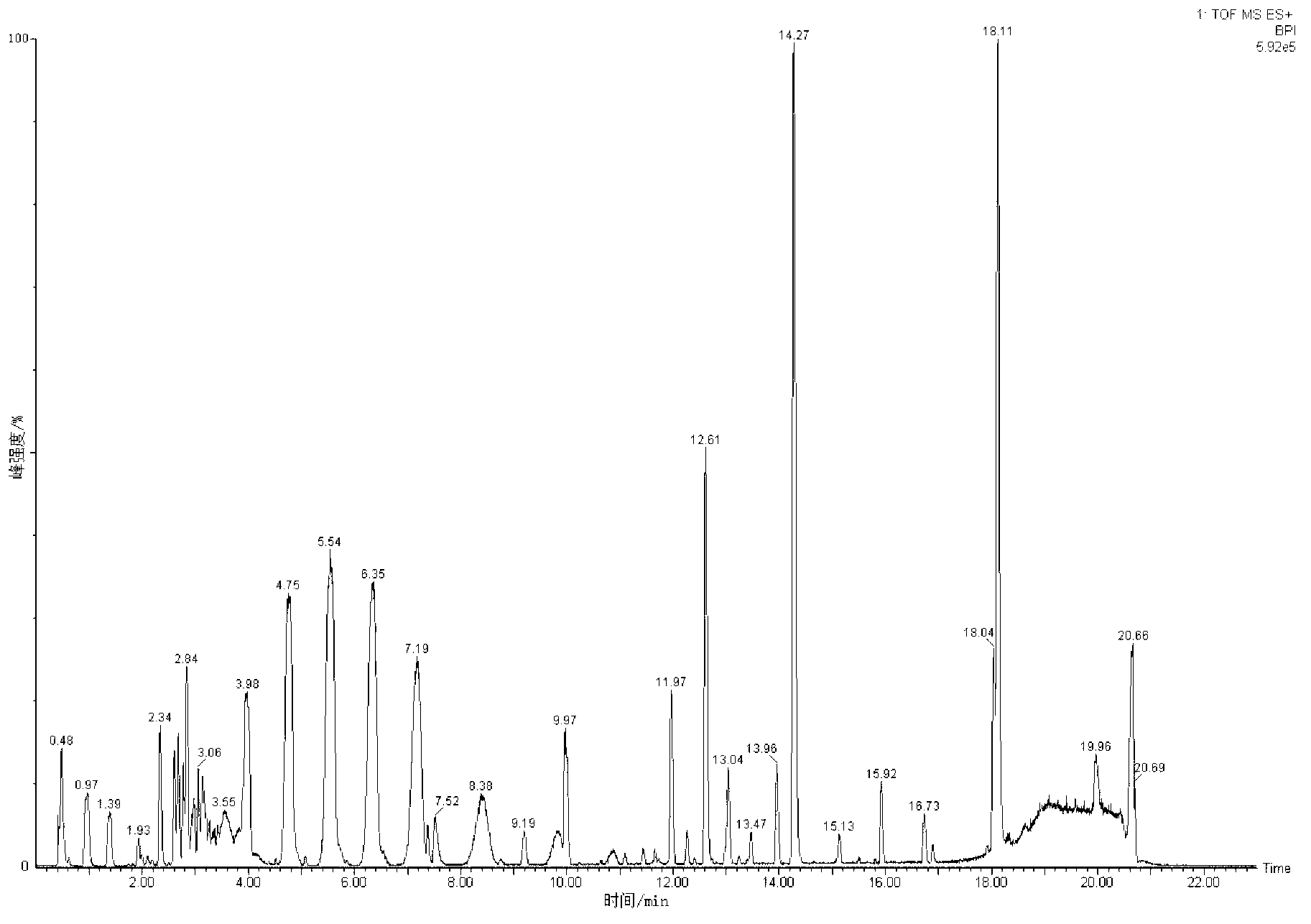
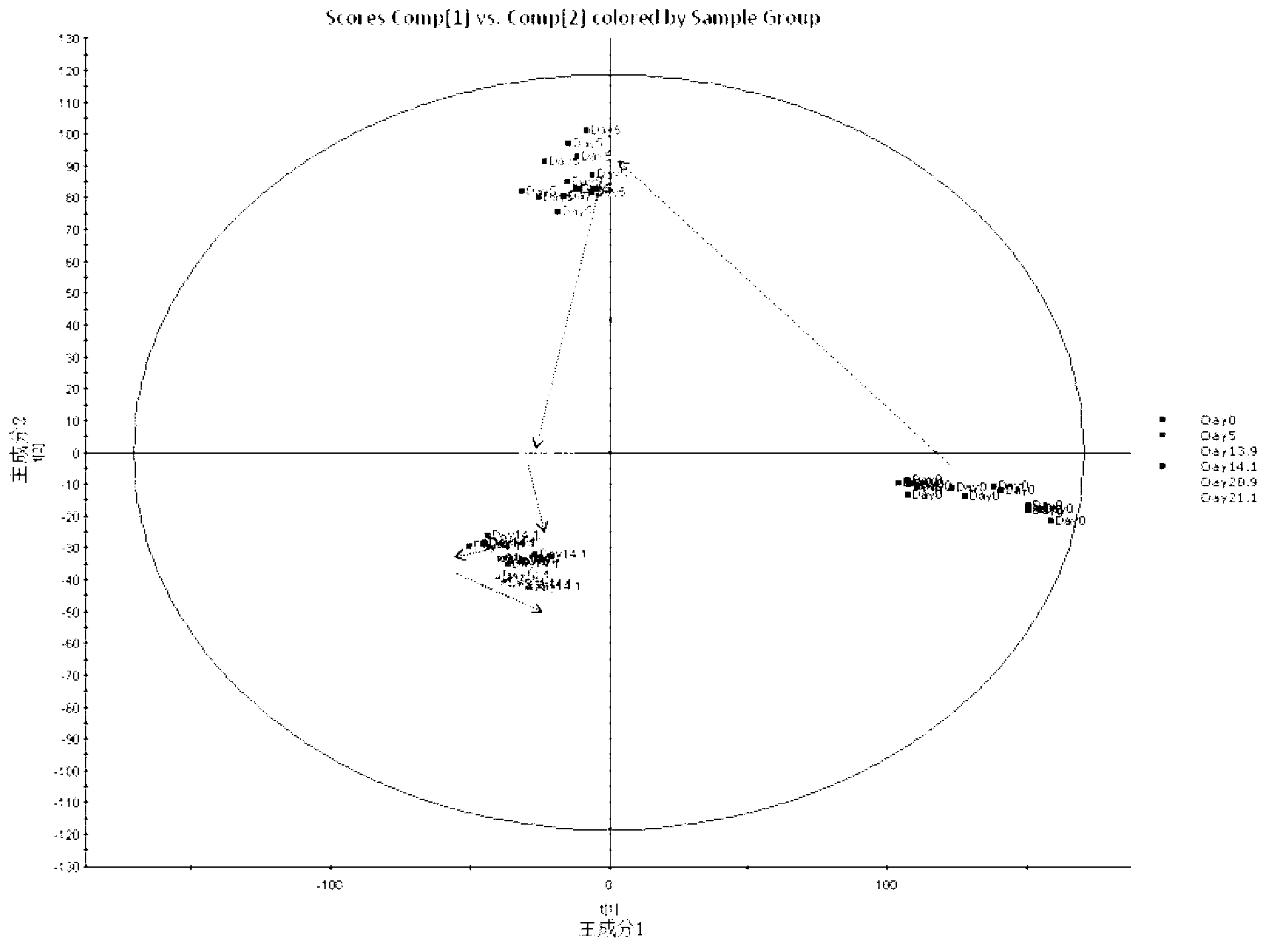
Metabonomics analysis method base on acute anaphylactic reaction
ActiveCN103235073AOvercome subjectivityOvercoming sensitivityComponent separationHypersensitive responseMetabolome
The invention discloses a metabonomics analysis method base on acute anaphylactic reaction. The invention mainly starts from the systems biology, and applies a UPLC-QTof / MS technology platform for UPLC and SPE-RRLC-Q-TOF combination, and establishes an acute anaphylactic reaction guinea pig serum metabonomics evaluation model, and provides a basis for further research of medicament acute anaphylactic reaction. During analysis, the UPLC and SPE-RRLC-Q-TOF combination technology is used for detecting serum samples of normal guinea pig and experiment guinea pig with acute anaphylactic reaction generated by induction, and a metabolome spectrogram is obtained by an acquisition method after optimization, and a mode identification method suitable for evaluating animal acute anaphylactic reaction is established for analyzing the metabolome data, which establishes a base for subsequently and furtherly screening biological tag with characteristics and developing a new animal acute anaphylactic reaction detection method.
Owner:HUNAN INST FOR FOOD & DRUG CONTROL
Genome editing method based on zymomonas mobilis endogenous CRISPR-Cas system and application thereof
ActiveCN110358768AAvoid cytotoxicityRealize simultaneous editingBacteriaStable introduction of DNABasic researchZymomonas mobilis
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, particularly relates to a genome editing method based on a zymomonas mobilis endogenous CRISPR-Cas system and application thereof and aims at taking Z.mobilis 4 as a type strain and utilizing the I-F type CRISPR-Cas system coded by its genome to establish a genome editing platform. A powerful tool is provided for basic research and application research in the strain and similar cells, and the development of metabolic engineering, system biology and synthetic biology is promoted. According to the technical scheme, the genome editing method is characterized by comprising the steps of constructing a plasmid containing an artificial CRISPR expression unit; selecting a guide RNA sequence aiming at a target site; constructing aguide RNA primer sequence on the plasmid containing the artificial CRISPR expression unit; constructing a donor DNA sequence on a vector to obtain an editing plasmid; transforming the editing plasmidinto competent cells for editing.
Owner:武汉睿嘉康生物科技有限公司
New plasma membrane biomarkers preferentially expressed in pancreatic beta cells useful in imaging or targeting beta cells
ActiveUS20100322850A1Evaluate effectivenessEarly detectionDisease diagnosisDiagnostic recording/measuringDiseaseDendritic cell
The present invention is directed to the identification of a biomarker specifically located in the plasma membrane of pancreatic beta cells. It was selected by a Systems Biology approach on Massively Parallel Signal Sequencing datasets obtained in human islets and Affymetrix microarray datasets on human islets, purified rat primary beta and non beta cells and insulinoma cells. Based on a set of specific features the biomarker is a unique candidate for imaging and targeting strategies to study the pancreatic beta cell mass in health and disease (T1 D, T2D, pancreatic cancers, obesity, islet transplantation, beta cell regeneration). The five specific features of the selected biomarkers are: 1) Preferentially expressed in pancreatic islets as compared to surrounding tissues; 2) Higher expression in pancreatic beta cells than in pancreatic alpha cells or than in other islet non-beta cells; 3) Expression levels in pancreatic beta cells are higher or comparable to glucokinase which is an enzyme specifically expressed in the pancreatic beta cell; 4) Located in the membrane and as such targetable with antibodies, peptides or small molecules which allows imaging, targeting and immunohistochemistry; and 5) Expression is not induced during the process of inflammation of the beta cell mass and the protein is not enriched in T-cells and dendritic cells or in other cells participating in the inflammation process.
Owner:UNIV LIBRE DE BRUXELIES +2
Network modeling for drug toxicity prediction
InactiveUS20160306948A1Chemical property predictionDrug and medicationsNetwork modelDrug side effect
A computational systems pharmacology framework consisting of statistical modeling and machine learning based on comprehensive integration of systems biology data, including drug target data, protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks, and gene ontology (GO) annotations, and reported drug side effects, can predict drug toxicity or drug adverse reactions (ADRs). Biomolecular network and gene annotation information can significantly improve the predictive accuracy of ADR of drugs under development. The use of PPI networks can increase prediction specificity, and the use of GO annotations can increase prediction sensitivity.
Owner:MEDEOLINX
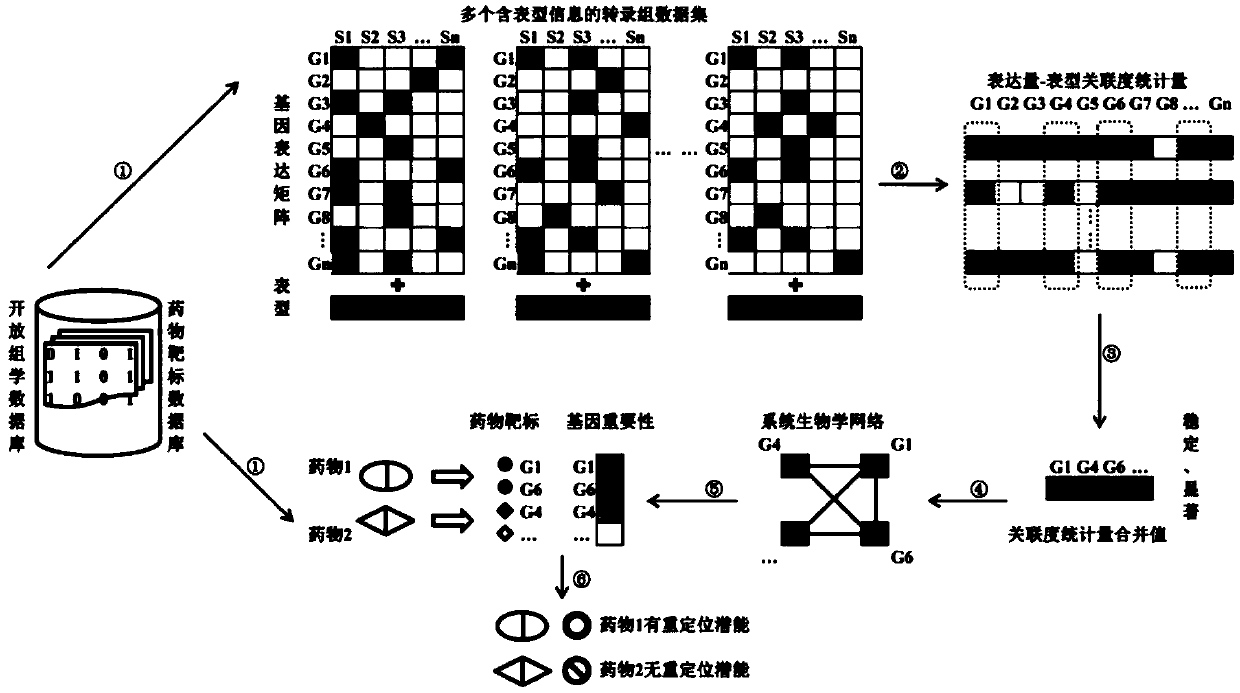
Repositioning drug discovery method based on integration of a plurality of transcriptome data sets and drug target information
ActiveCN108694991AAuthoritative and extensive data sourcesClear principleDrug and medicationsHybridisationDiseaseNODAL
The invention relates to a repositioning drug discovery method based on integration of a plurality of transcriptome data sets and drug target information. The method comprises: step one, for any disease, a plurality of transcriptome data sets containing phenotype information are obtained from an openomics database; step two, correlation statistic values of all genes and phenotypes in all transcriptome data sets are calculated based on a statistical analysis method and quantitative combination is carried out on the correlation statistic values to obtain a combination value; step three, a systembiology network is constructed; step four, an importance score of each gene is calculated based on a node sorting algorithm; step five, a target gene list of a to-be-tested drug is obtained; and stepsix, the importance of the gene of the to-be-tested drug is detected and analyzed by statistics and whether the to-be-tested drug is a repositioning drug is predicted. The method having advantages ofclear principle, high efficiency, low cost and wide application range can be applied to screening and research and development of repositioning drugs for various diseases, especially the malignant tumor.
Owner:ZHONGNAN HOSPITAL OF WUHAN UNIV
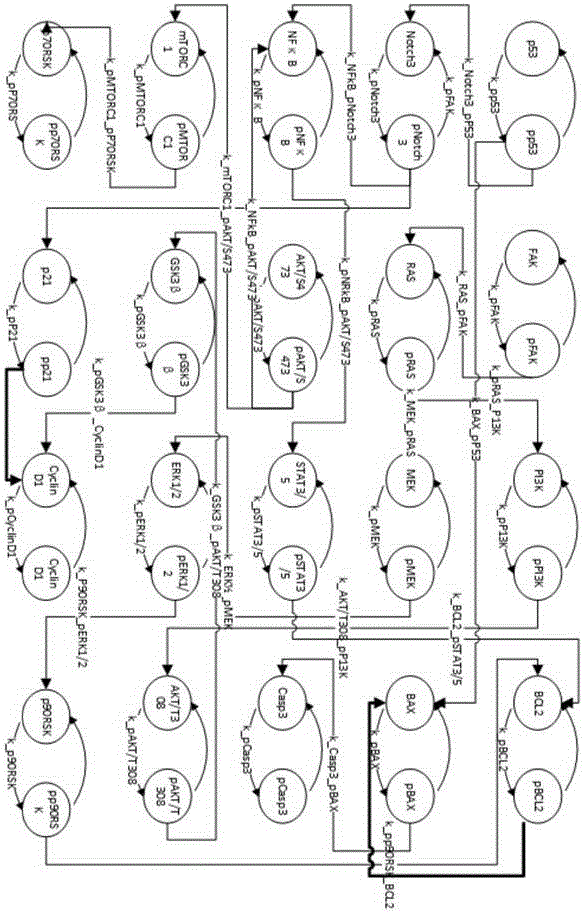
Myeloma signal path mechanism confirming method based on modular factor graph
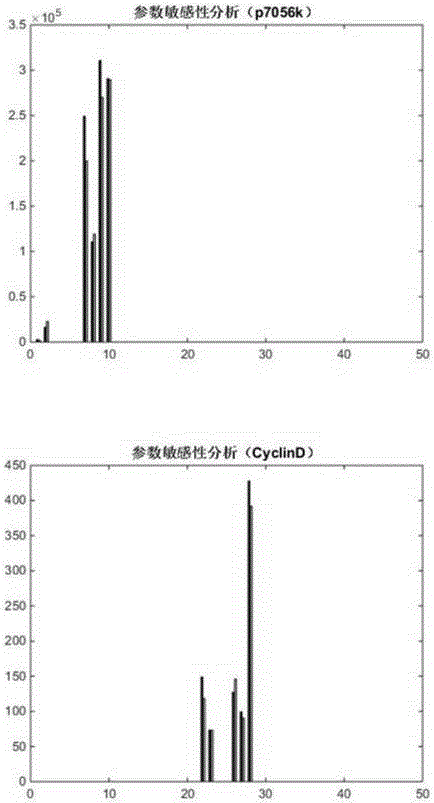
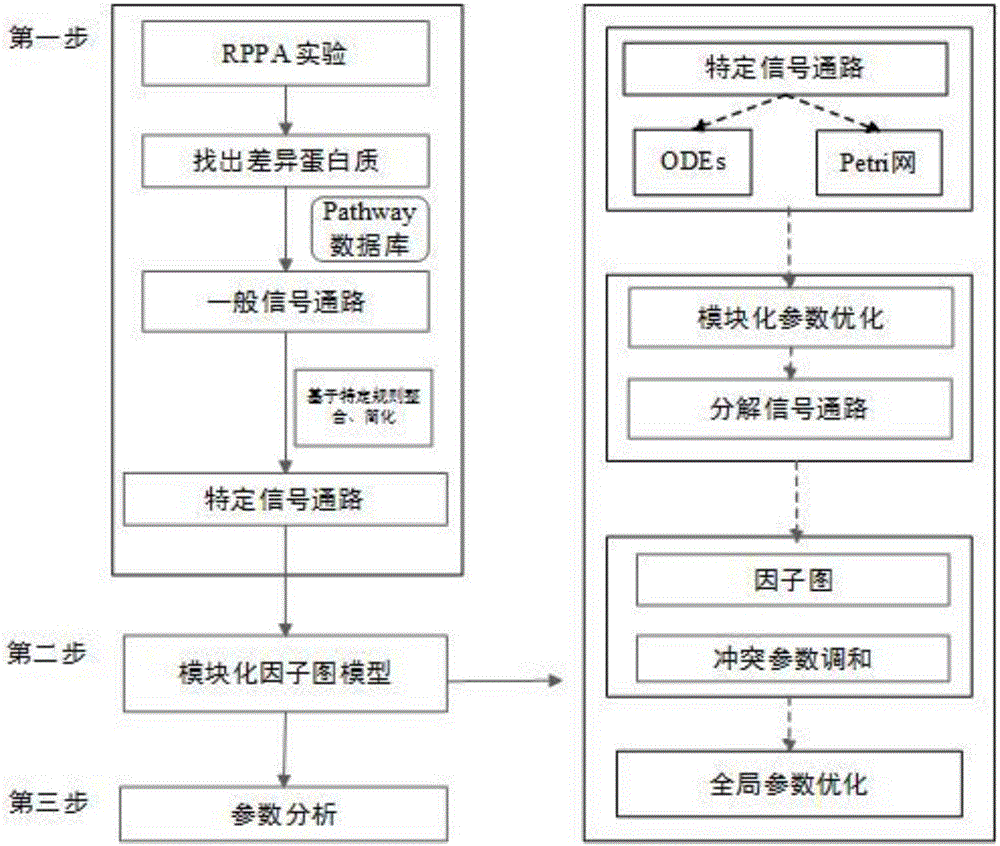
ActiveCN106503483AAchieve associativityAutomatic conversionSystems biologySpecial data processing applicationsSlope stability analysisSystems biology
The invention provides a myeloma signal path mechanism confirming method based on a modular factor graph. The method comprises the steps that 1, RPPA data is obtained; 2, the RPPA data is preprocessed, and key proteins are screened in a coarse-grained mode; 3, based on the key proteins screened in the coarse-grained mode, mutual effect channels of proteins in cells in a rigid cell environment are established to form signal channels; 4, an ordinary differential equation is adopted to describe the signal channels, the signal channels are decomposed into multiple small modules, and parameter optimization is conducted on the small modules to establish a system biology model; 5, parameter analysis is conducted on the system biology model, wherein the parameter analysis includes stability analysis and sensitivity analysis. By the adoption of the method, the calculation cost of the system model in signal channel detection is effectively reduced, and the calculation efficiency is improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Antivirals
InactiveUS20100272706A1Inhibit and decrease viral infectionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSelect agentGene silencing
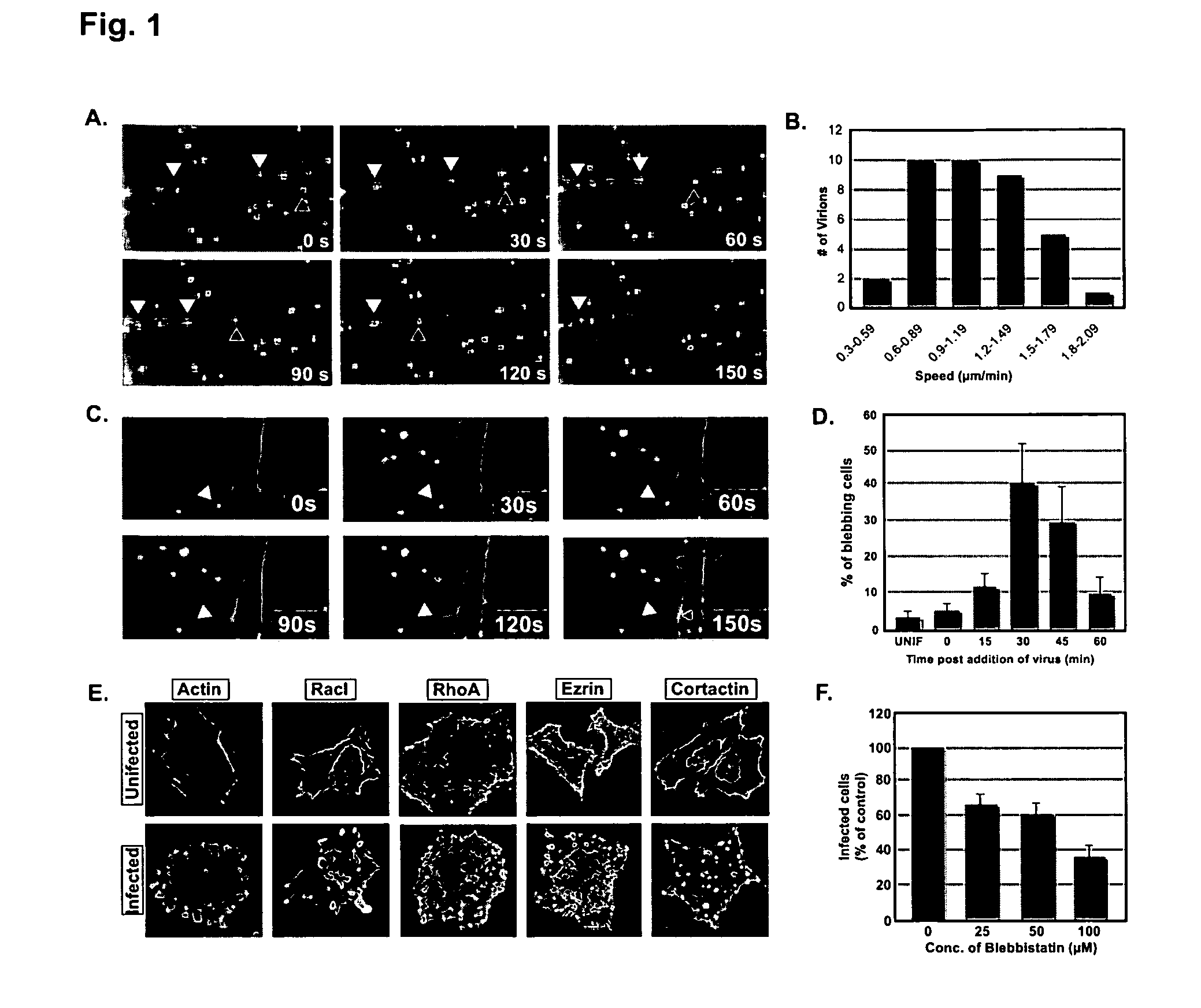
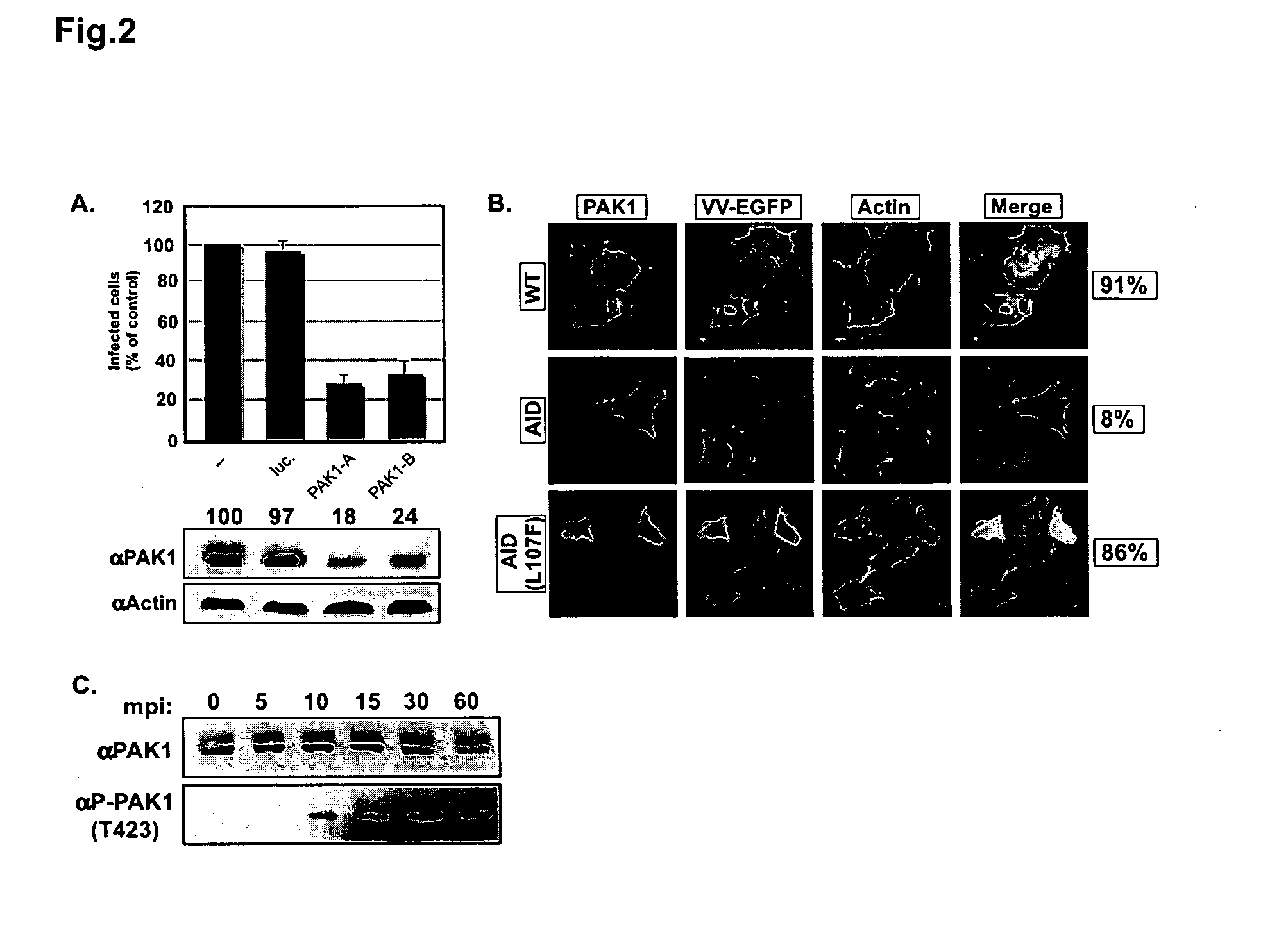
This invention provides methods for inhibiting or treating infection by viruses, in particular pox viruses by modulating a kinase, in particular by inhibiting a host cell kinase, involved in mediating viral infection. Methods to identify, validate, and classify the cellular proteins required by viruses during infection of host cells in order to select agents which can inhibit viral infection are described herein. Using a systems biology approach the virus / host cell interaction is studied from initial attachment of the incoming virus to the cell surface, to entry, transcription, replication, biosynthesis, and assembly of progeny particles. The method employs a siRNA screening platform and uses gene silencing to map the ‘viral infectome’—a compilation of cellular proteins that the virus needs to establish infection and drive the infectious cycle. Charting the infectome provides information on the viral biology by the identification of host cell proteins involved in viral infection and allows the development of novel anti-viral drugs that prevent the viruses from establishing productive infection in cells.
Owner:MERCER JASON +4
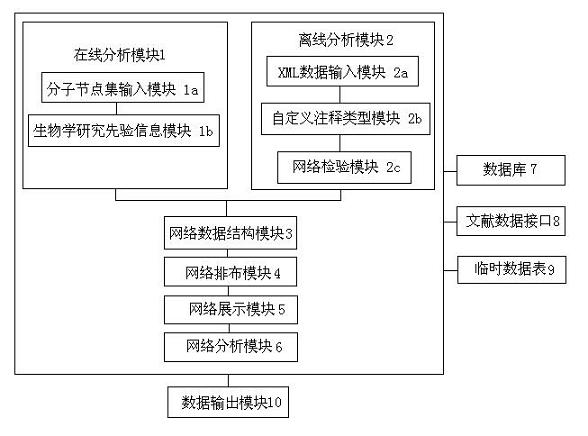
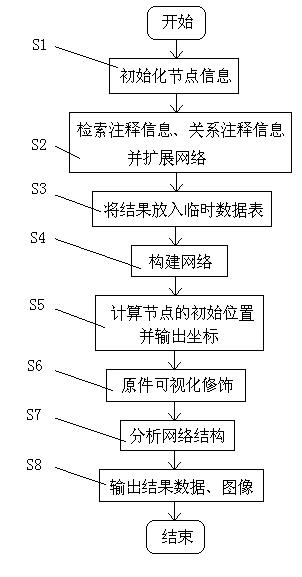
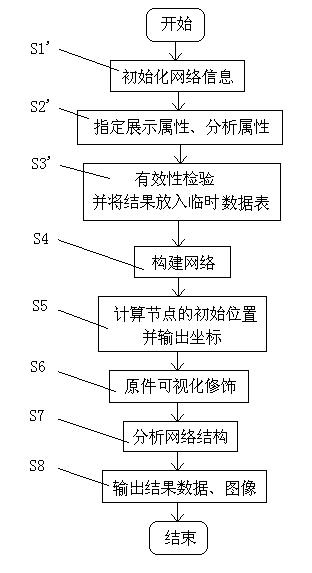
Biomolecular network exhibition analysis system and analysis method thereof
The invention provides a biomolecular network exhibition analysis system which comprises an online analysis module, an offline analysis module, a network data structure module, a network assignment module, a network exhibition module, a network analysis module, a database, a document data interface, a temporary data table and a data output module. The invention can automatically establish and annotate the relevant biomolecular network based on internet resource connection through a biomolecular database based on attention protein and gene sets. The invention also provides an analysis method of the biomolecular network exhibition analysis system, which integrates the existing research annotation information in system biology and bioinformatics based on the biomolecular network characteristics, uses a free network as a base model, combines the biomolecular network characteristics and refines node and relation types.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Method for establishing and analyzing scale metabolism network model of actinoplanetes genomes
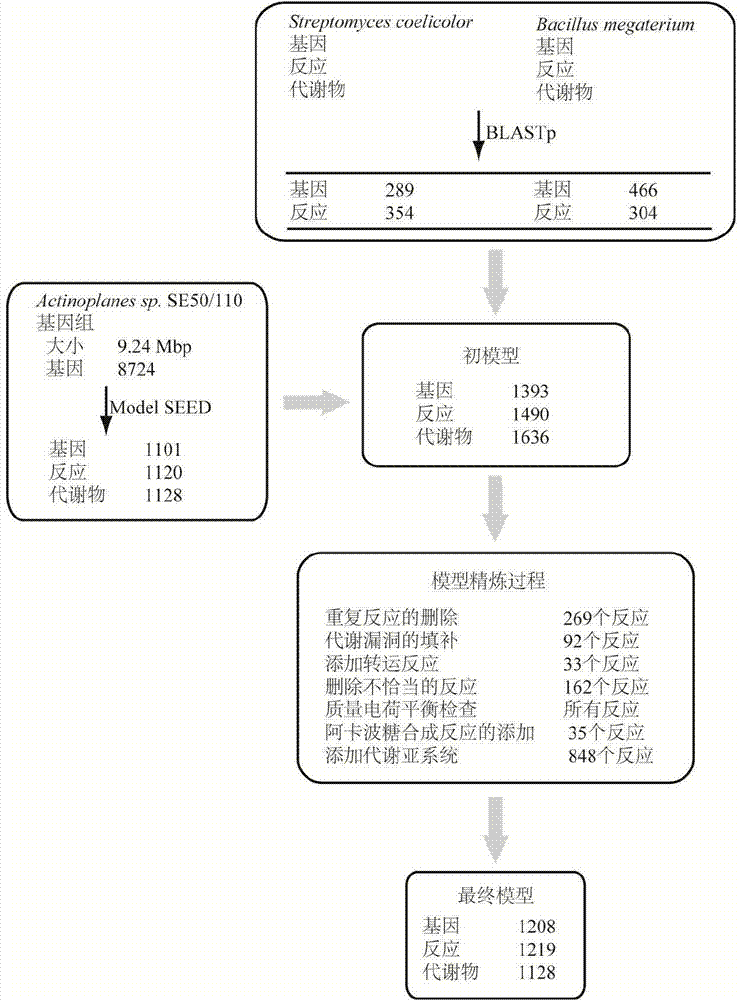
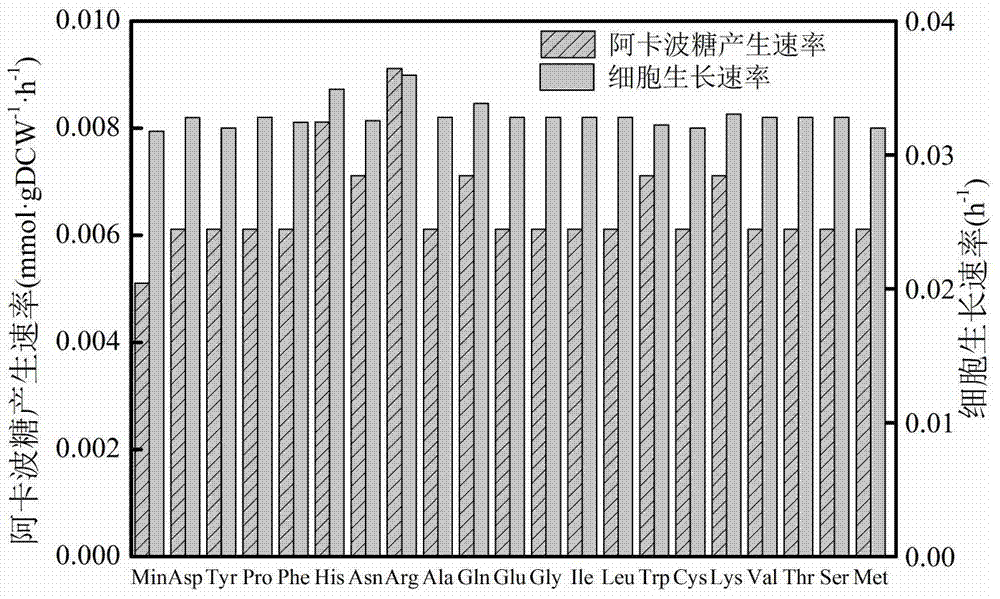
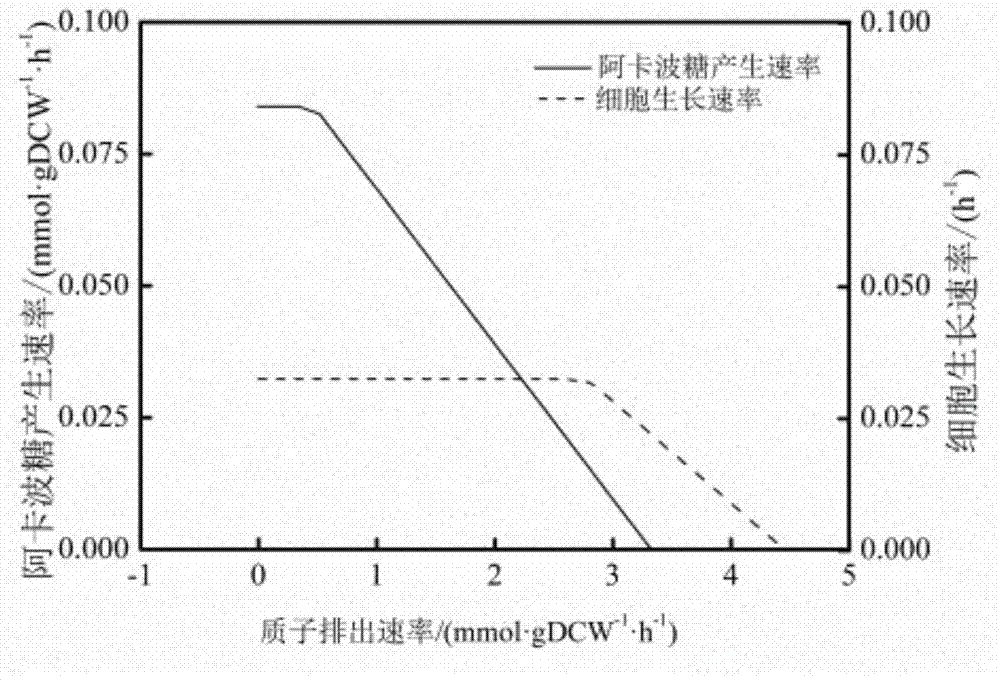
InactiveCN104745661AImprove accuracyStrong reliabilityOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderNetwork modelMetabolic network model
The invention discloses a method for establishing and analyzing a scale metabolism network model of actinoplanetes genomes, and belongs to the field of systems biology. Cell growth simulation, essential growth essential genes and reaction verification are carried on the scale metabolism network model of actinoplanetes genomes established based on the method on a system level, a strategy is provided for simulating and improving acarbose yield, and an important platform is provided for comprehensively understanding the metabolic characteristics of actinoplanetes and improving the acarbose fermentation level. The invention provides multiple methods for improving the acarbose yield, the acarbose yield can be increased by 53.5% by adding nicotinic acid, and the acarbose yield is respectively increased by 29.6%, 26.5%, 26.3%, 11.8% and 9.2% by adding glutamic acid, cysteine, lysine, glutamine and asparagines.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for predicting biological systems responses in hepatocytes
The inventive method employs a ''systems biology'' approach to predicting hepatotoxicity and other biological hepatocyte responses resulting from exposure to the test substance. In one embodiment, the invention provides an automated method for predicting the hepatocyte biological systems effect of a test substance. In another embodiment, the invention provides a method for constructing a knowledgebase (or database) of cellular systems biology response profiles for reference substances with known biological systems effects. In another embodiment, the invention provides a set of protocols and software tools used to carry out the profiling. Another embodiment of the invention is a panel of reagents. In another embodiment, the invention provides a set of protocols and software tools used to carry out the profiling. Another embodiment of the invention is a panel of reagents and protocols required for generating cellular systems biology response profiles, either to create a knowledgebase, or to use with an existing knowledgebase and informatics software to profile substance physiological effects. Another embodiment of the invention is a database of physiological profiles.
Owner:CELLUMEN INC
Method for highly efficiently deleting large fragments of genome based on endogenous CRISPR-Cas system of zymomonas mobilis and application thereof
ActiveCN110408642ADelete efficientAvoid cytotoxicityHydrolasesStable introduction of DNACompetent cellSynthetic biology
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and in particular, relates to a method for highly efficiently deleting large fragments of a genome based on an endogenous CRISPR-Cas system of zymomonas mobilis and an application thereof. The method includes the steps: constructing a plasmid containing an artificial CRISPR expression unit; determining a large-fragment editing target site, selecting a guideRNA sequence for the editing target site and designing a primer; constructing the guideRNA primer sequence to the plasmid containing the artificial CRISPR expression unit,and constructing a vector; constructing a donor DNA sequence to the vector, to obtain an editing plasmid; and transforming the editing plasmid into a receptive cell, and editing. With a high-throughput gene editing platform based on the endogenous CRISPR-Cas system of zymomonas mobilis, the editing purpose of deleting the large fragments of the genome of the strain is achieved, and the developmentof metabolic engineering, system biology and synthetic biology is promoted.
Owner:武汉睿嘉康生物科技有限公司
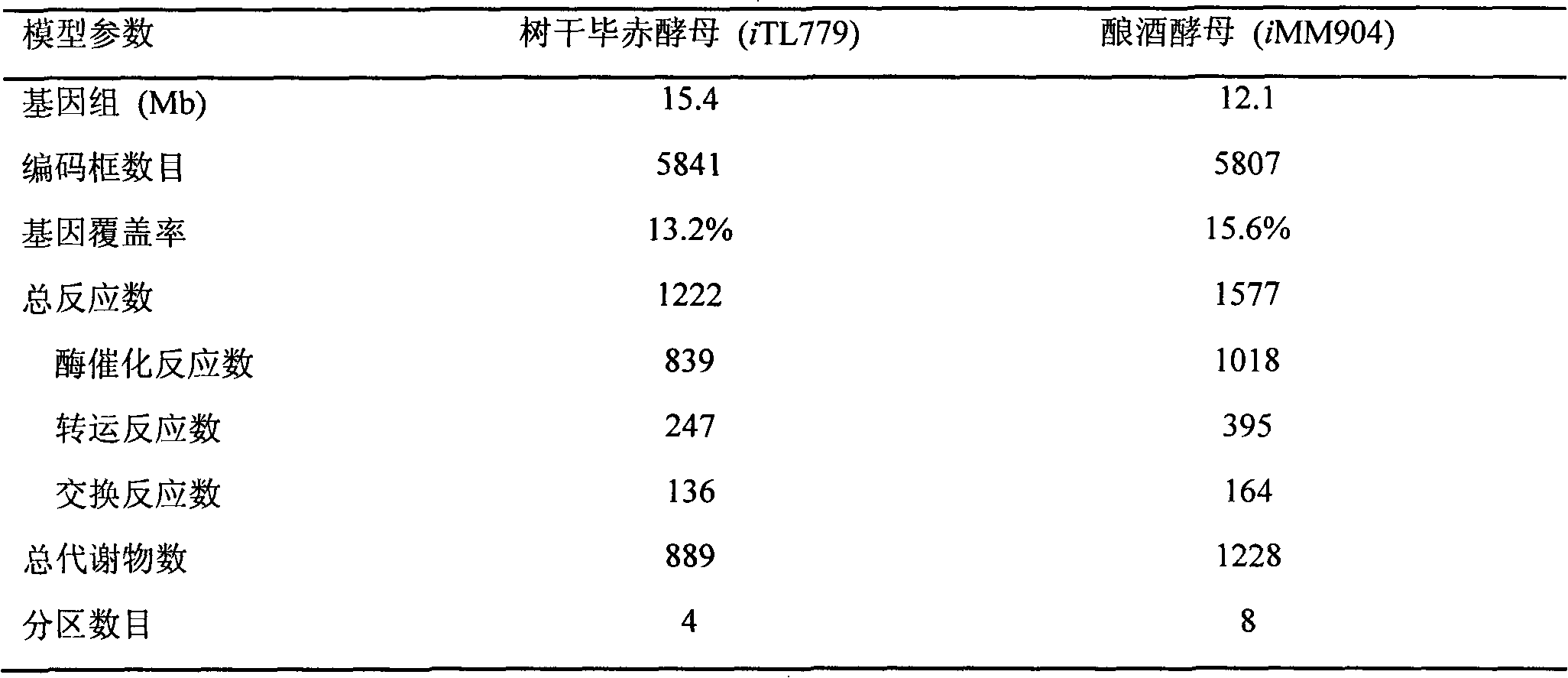
Pichia stipitis genome-scale metabolic network model construction and analysis method
The present invention describes an integrated genome-scale metabolic network model construction and analysis method with Pichia stipitis as an example, belonging to the system biology field. Based on the method, a constructed and obtained Pichia stipitis genome-scale metabolic network model is subjected to cell growth simulation of a system level and identification of a minimal gene and reaction set, and an important platform is provided for comprehensive understanding of metabolic characteristics and mechanism of the Pichia stipitis is provided.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
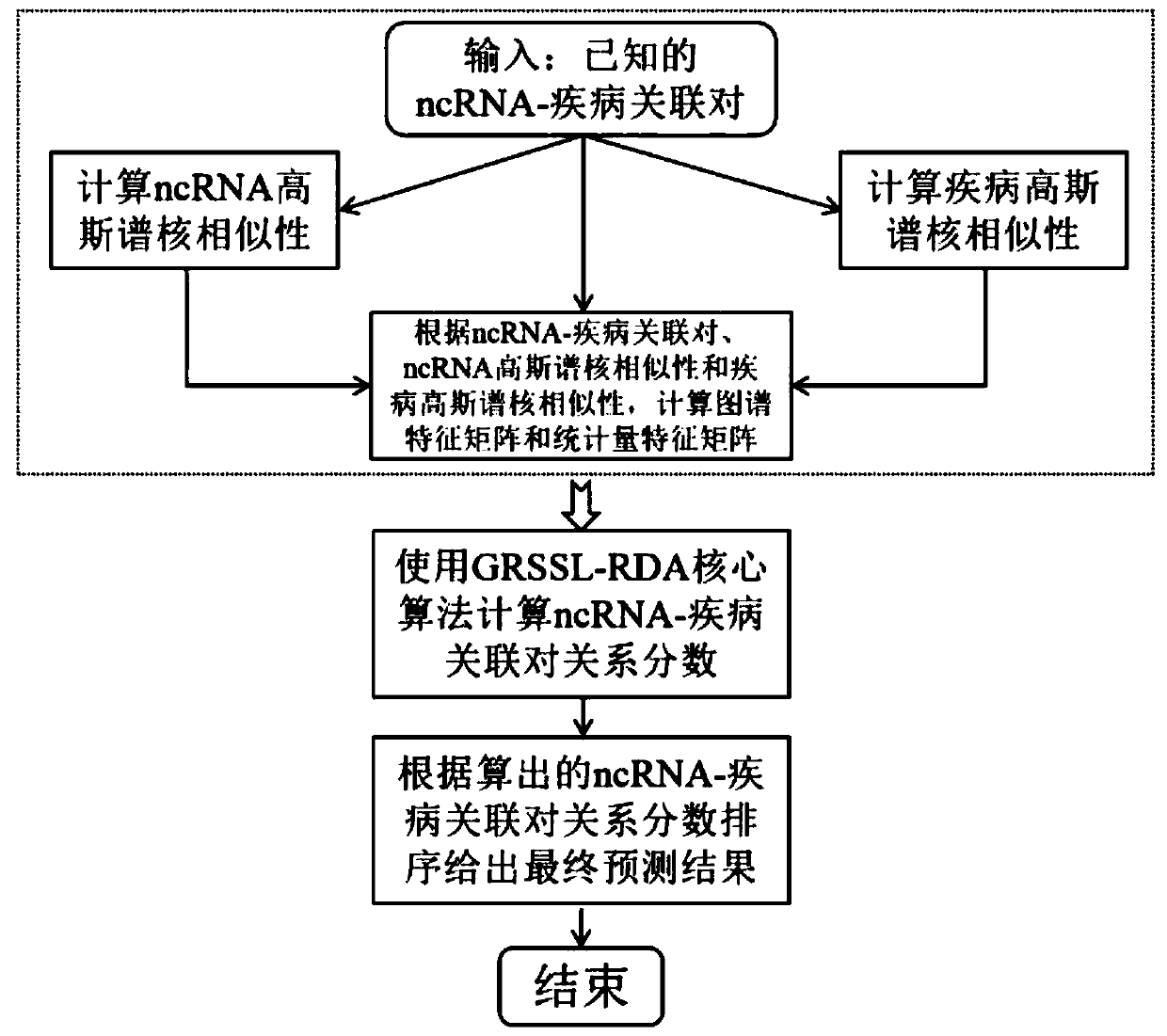
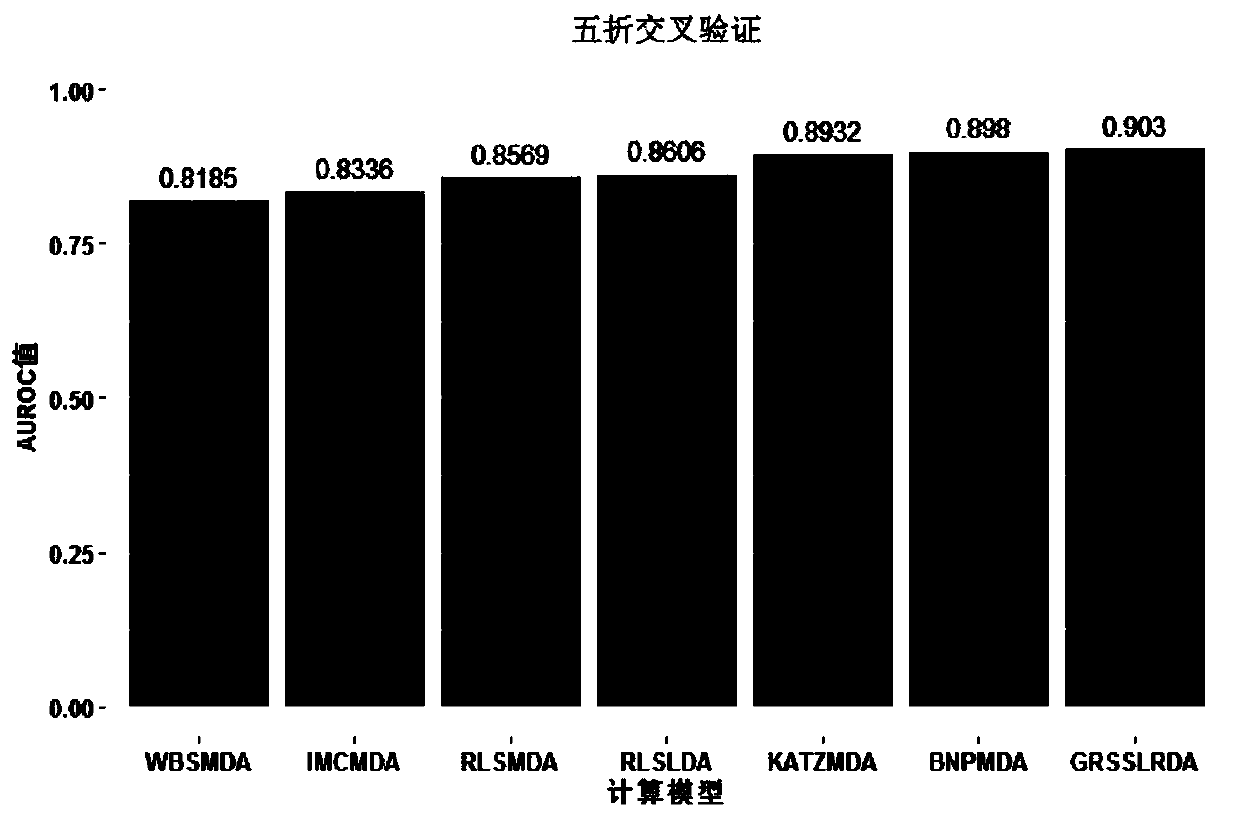
Non-coded RNA and disease association prediction method based on sparse subspace learning
ActiveCN110767263AReduce difficultyImprove predictive performanceMedical simulationBiostatisticsAlgorithmGraph theoretic
The invention discloses a non-coded RNA and disease association prediction method based on sparse subspace learning and belongs to the field of system biology. The method comprises steps of 1, constructing an adjacency matrix associated with non-coded RNA-diseases, and then respectively calculating Gaussian spectrum kernel similarity of the non-coded RNA and Gaussian spectrum kernel similarity ofthe diseases; 2, calculating a graph theory characteristic matrix and a statistic characteristic matrix according to two similarity matrixes and an adjacent matrix, further constructing a target function and solving a mapping matrix G; and 3, solving non-coded RNA-disease association pair relationship score prediction matrixes, and performing sorting to give the final prediction result. The methodis advantaged in that a graph theory, a statistical method and a machine learning method are fused, the information of a negative sample in the non-coded RNA-disease associated data can be effectively utilized, the non-coded RNA with significant correlation to disease occurrence and development can be efficiently, accurately and quickly predicted, and problems of long time consumption and high cost of a biological experiment method are effectively solved.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Non-coding RNA and disease relation prediction method based on Hessian regular non-negative matrix factorization
ActiveCN110556184AAccurate predictionReduce the consumption of manpower and material resourcesMedical simulationProteomicsAlgorithmNon-coding RNA
The invention discloses a non-coding RNA and disease relationship prediction method based on Hessian regular non-negative matrix factorization, and belongs to the field of system biology. The method mainly comprises the following three steps: 1, respectively calculating Gaussian spectrum kernel similarity of non-coding RNA and Gaussian spectrum kernel similarity of diseases; 2, calculating a prediction score of the non-coding RNA-disease association pair by using an iterative solution algorithm; 3, sorting the scores according to the calculated non-coding RNA-disease association, and giving afinal prediction result. According to the method, the internal manifold structure of the data is described meticulously through Hessian regularization, so that the information of a negative sample iseffectively utilized; the l2, 1 norm constraint and the approximate orthogonal constraint ensure the group sparsity of the coding matrix, and the influence of noise data can be weakened. According tothe method, a relatively reliable prediction result can be obtained, and the problems of long consumed time and high cost of a biological experiment method are effectively solved.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
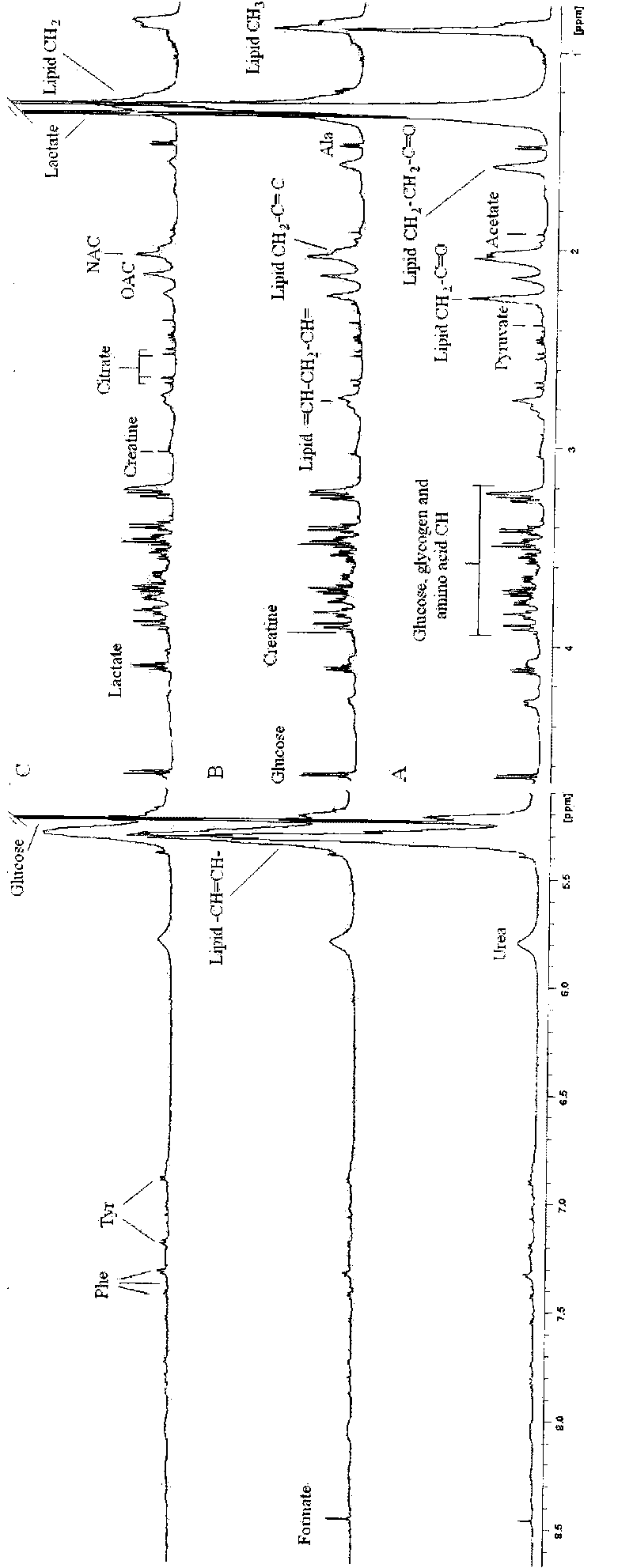
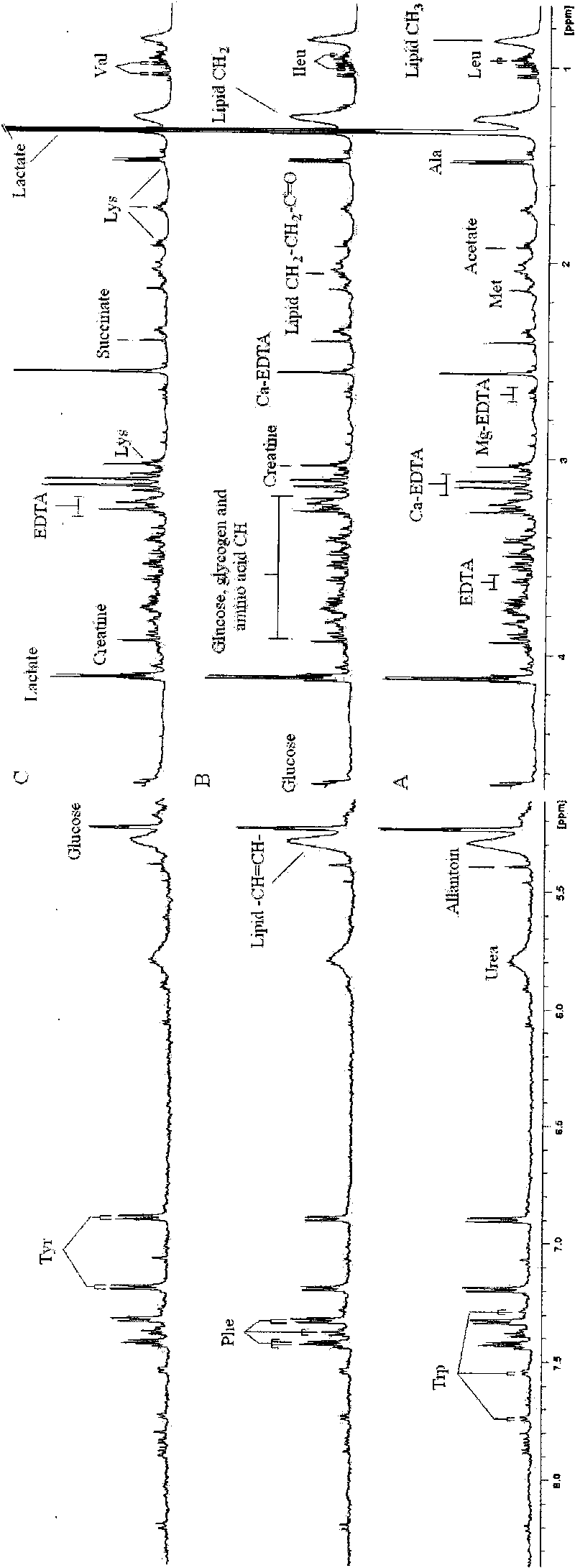
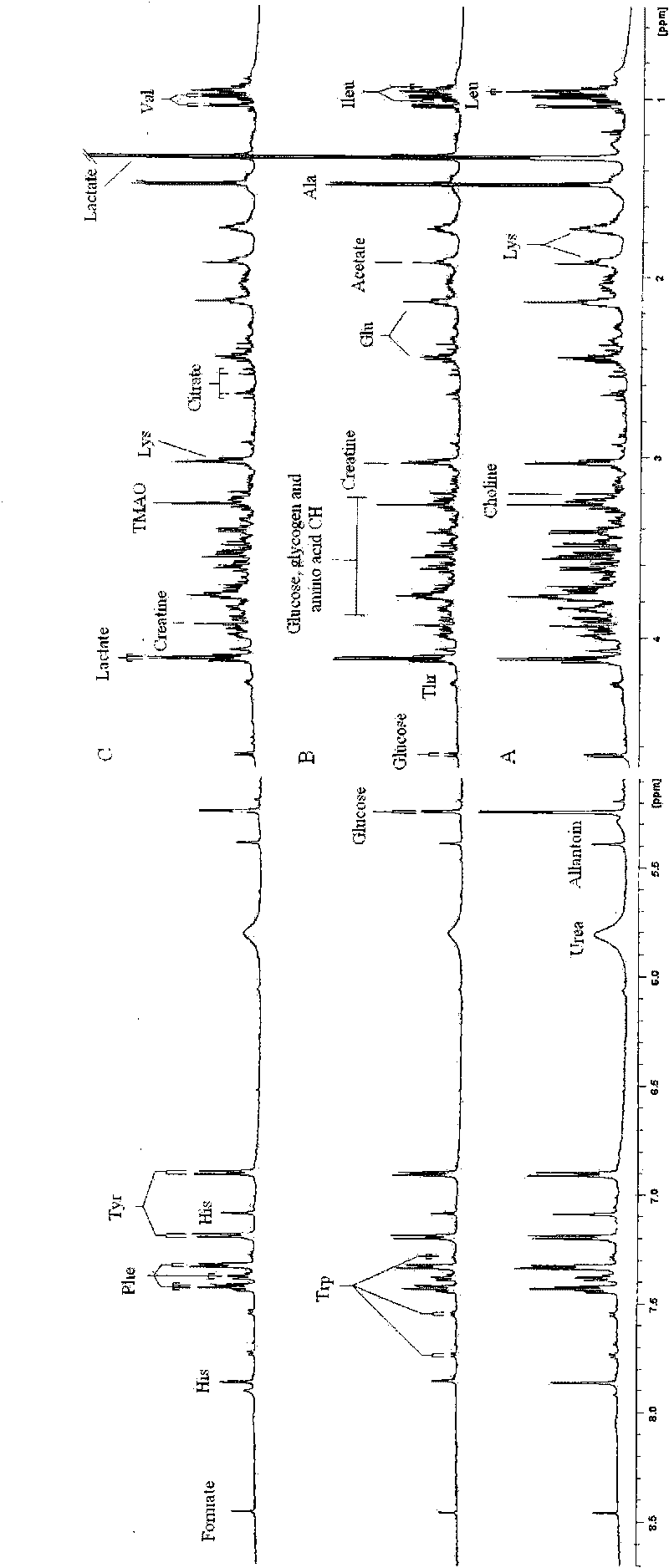
Application of metabonomic technology in intrauterine growth retardation
InactiveCN101713753AIncreased sensitivityAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceBiological testingGenomicsAmniotic fluid
The invention relates to application of metabonomic technology in intrauterine growth retardation, which is mainly characterized by starting from the view of system biology (Cowley AW Jr.The elusive field of systems biology. Physiol Genomics.2004;16(3):285-286), and applying a magnetic resonance spectroscopy technology based metabonomic method to seek a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrogram capable of specifically reflecting the intrauterine growth retardation in the peripheral blood of an experimental pregnant animal or a pregnant woman so as to provide proofs for further diagnosing the intrauterine growth retardation. The application comprises the following steps: during analysis, detecting a biological sample (comprising parent blood, embryo blood and amniotic fluid) of the pregnant animal or the pregnant woman in normal pregnancy and intrauterine growth retardation experiment by using nuclear magnetic resonance technology, acquiring a metabonomic spectrogram, analyzing the metabonomic spectrogram by using a pattern identification method, determining the metabonomic change of the intrauterine growth retardation through analysis and comparison, and acquiring one or more (groups of) nuclear magnetic resonance spectrograms for reflecting the intrauterine growth retardation from the metabonomic change so as to provide theoretical and experimental proofs for the subsequent further determination of a biomarker and the application of the metabonomic technology in the intrauterine growth retardation. The application has the advantages of high sensitivity, good specificity, early stage, non-invasion or micro-invasion and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com