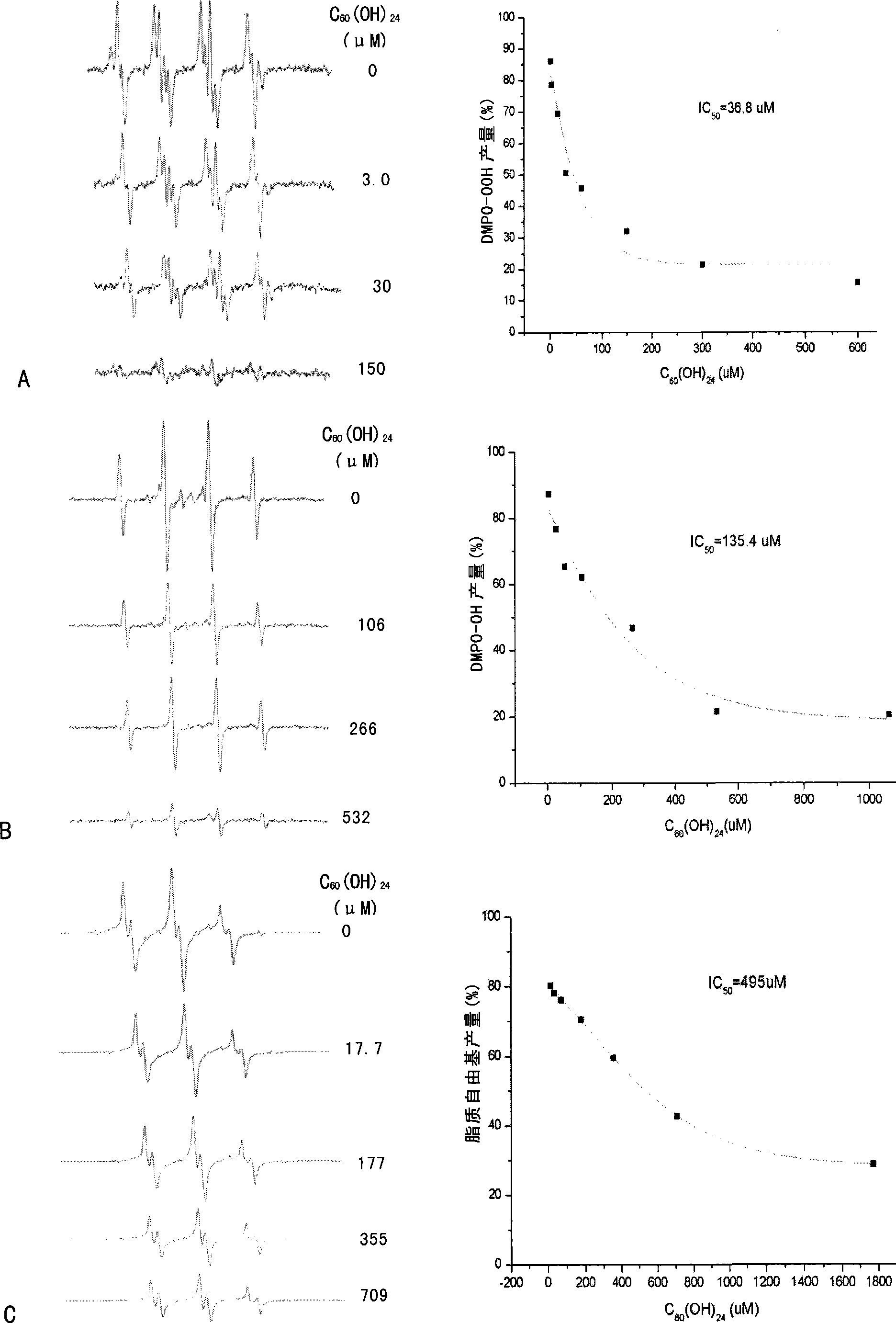Patents
Literature
36 results about "Cellular model" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
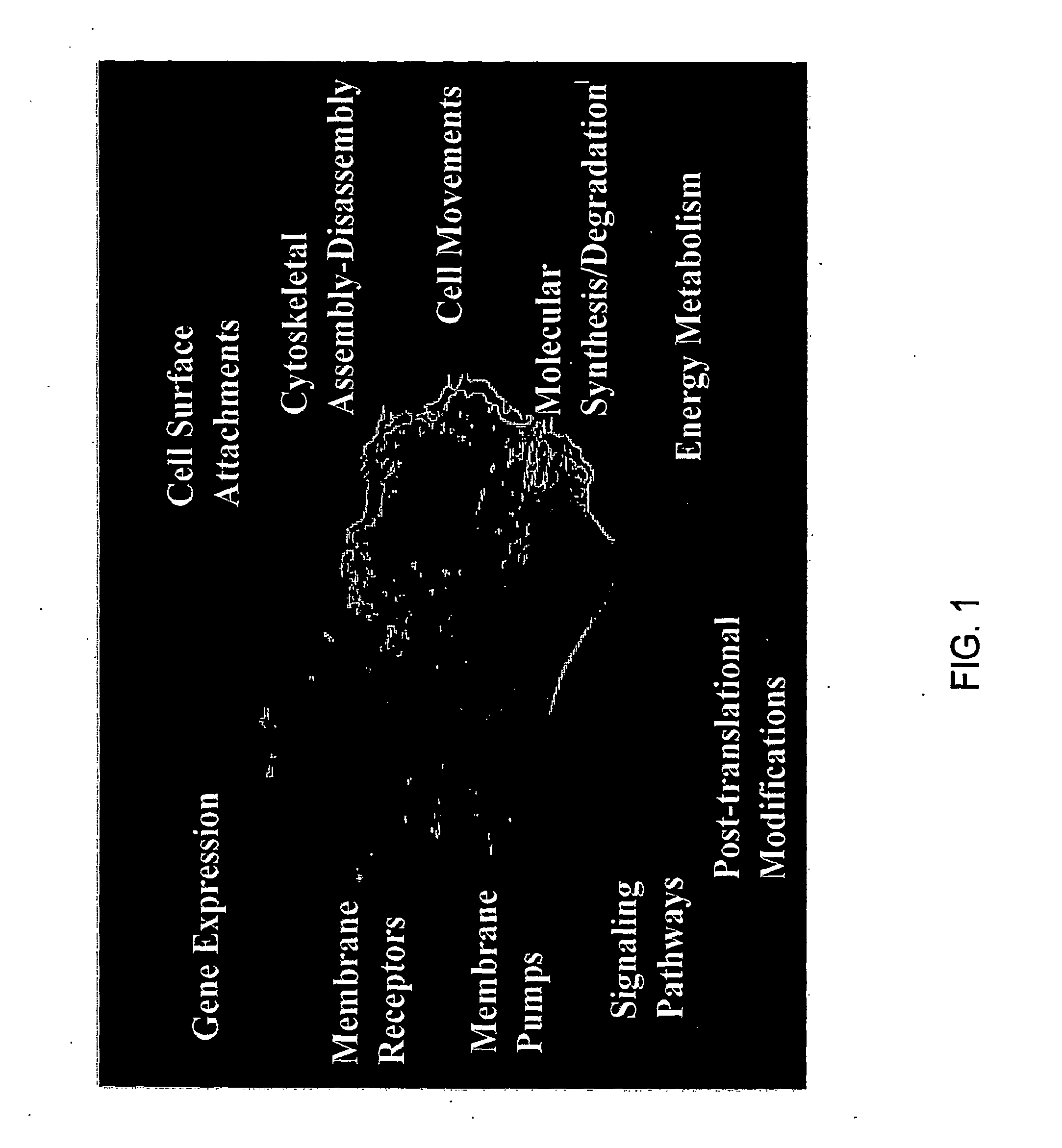
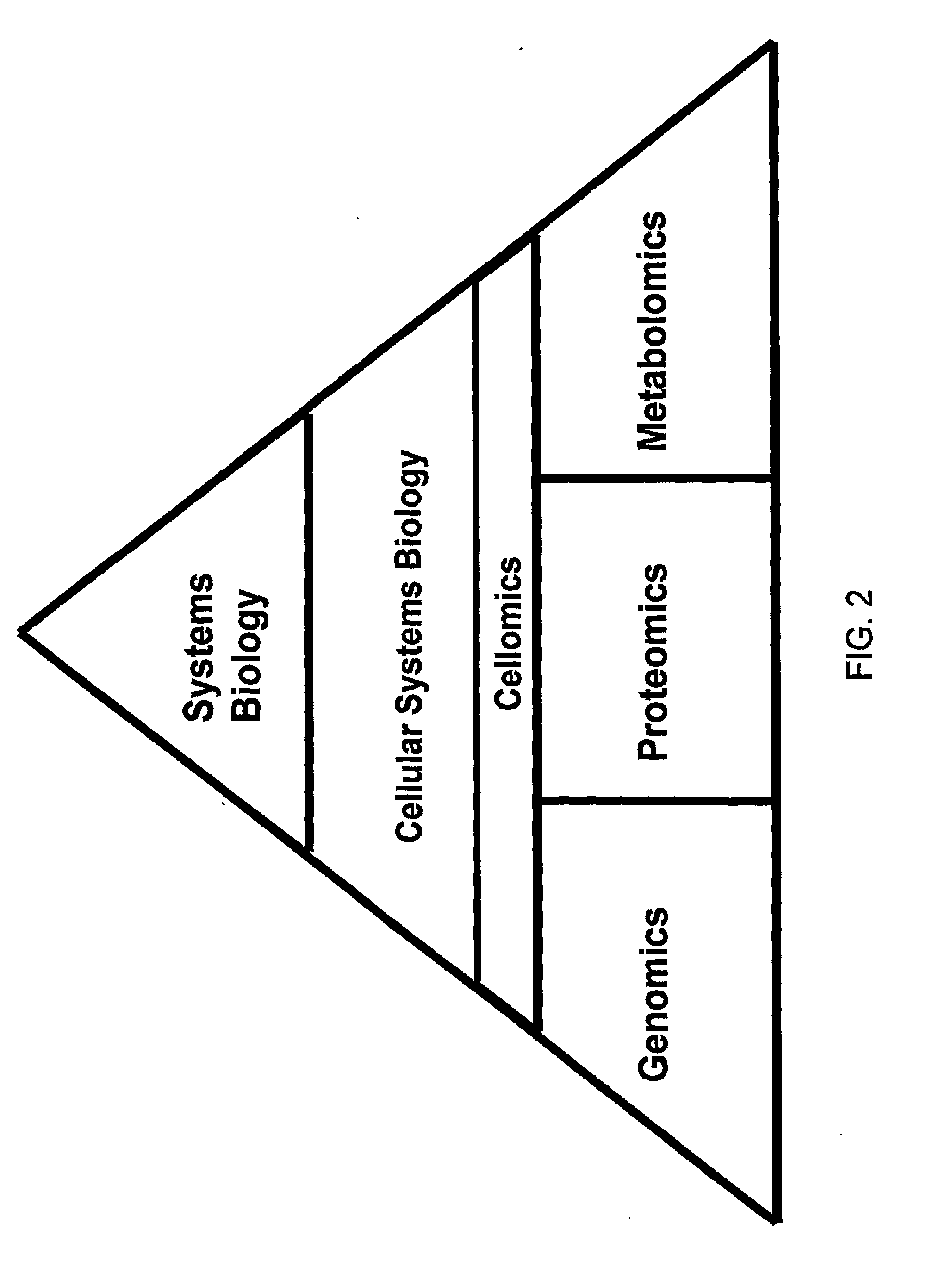
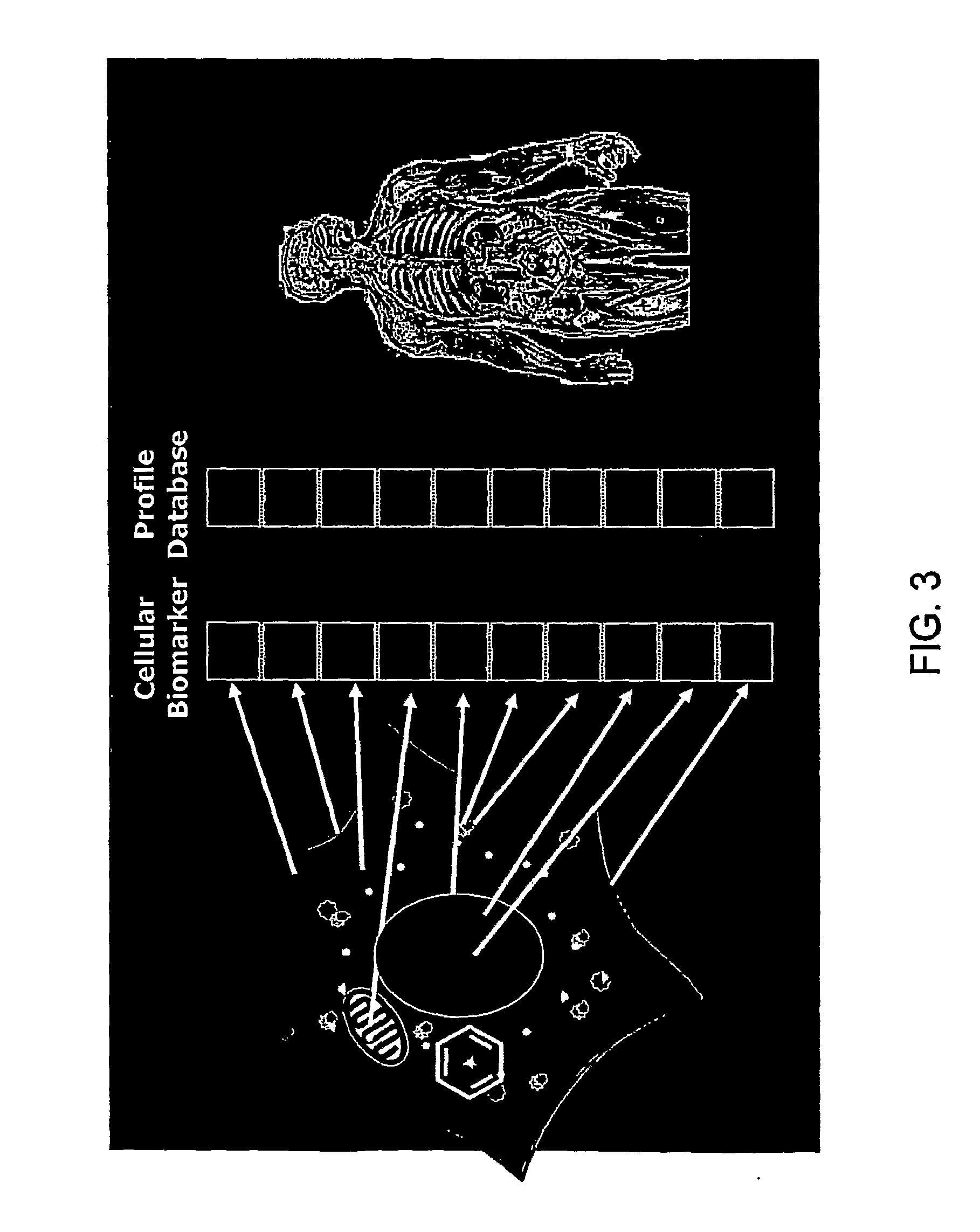
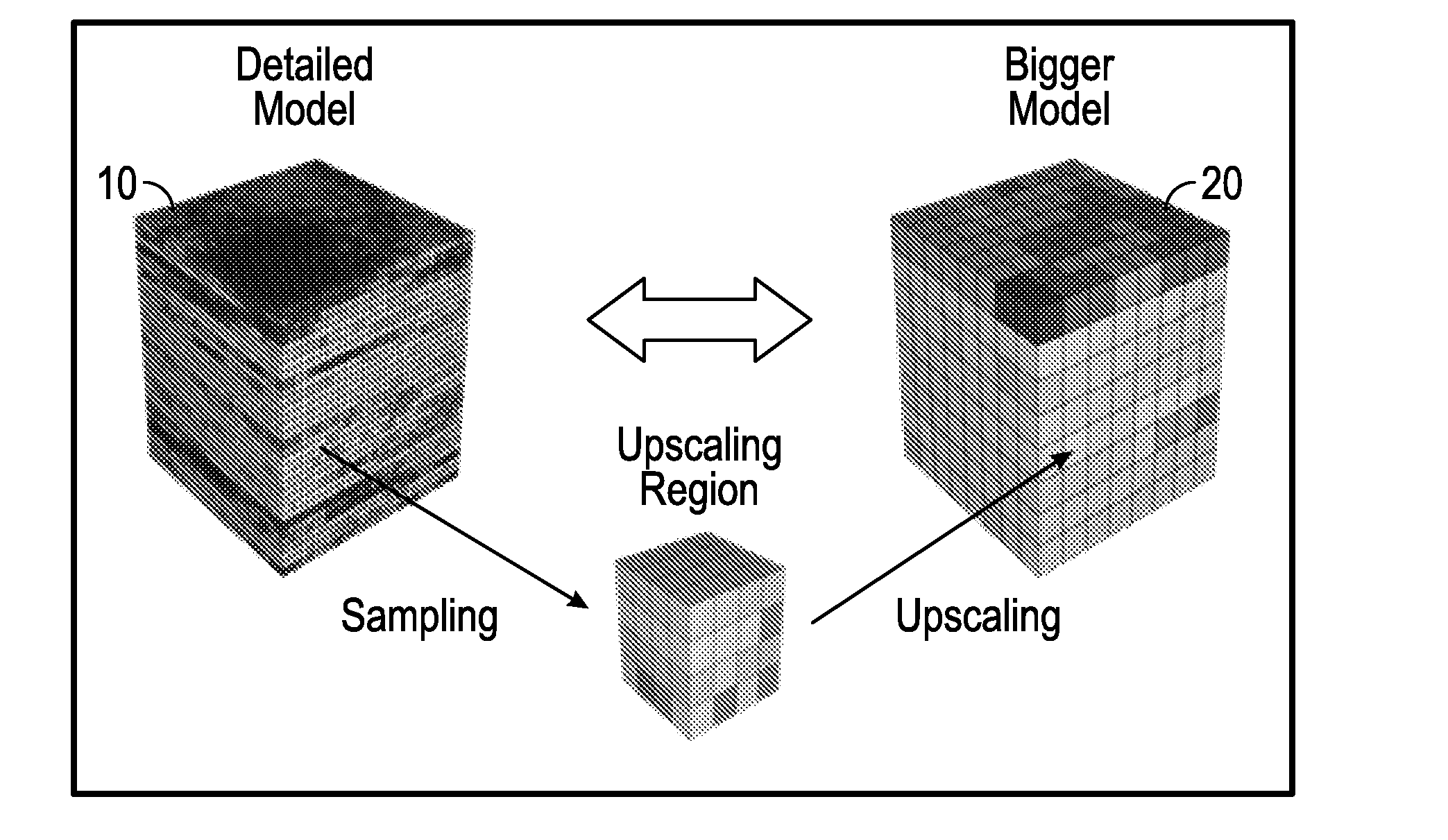
Creating a cellular model has been a particularly challenging task of systems biology and mathematical biology. It involves developing efficient algorithms, data structures, visualization and communication tools to orchestrate the integration of large quantities of biological data with the goal of computer modeling.
Method for Modeling a Disease
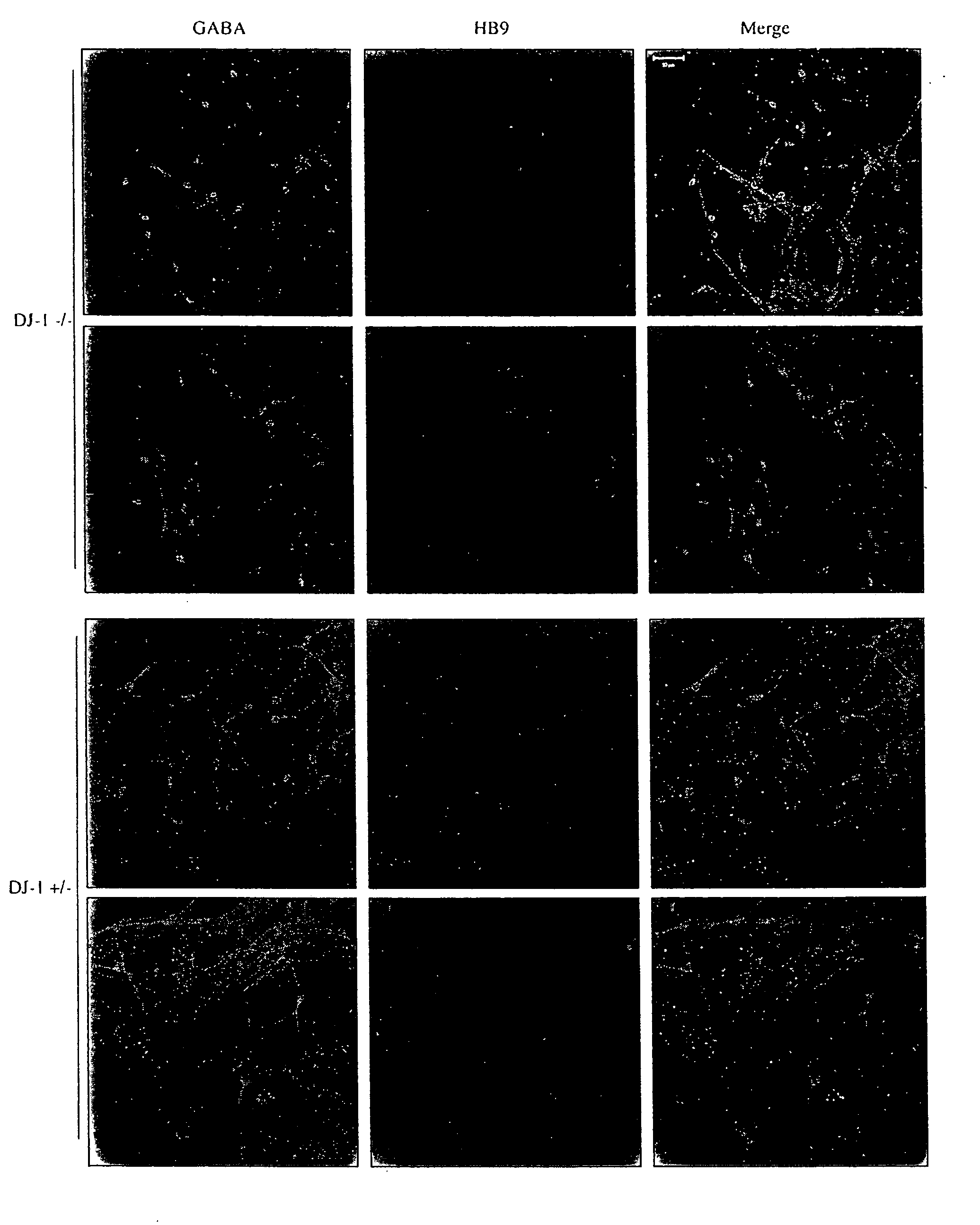
The invention described herein provides for methods of profiling cellular models of disease. Cellular systems biology is the investigation of the integrated and interacting networks of genes, proteins, and metabolites that are responsible for normal and abnormal cell functions. Methods and reagents for the profiling a disease state, the treatment of a disease state and assaying of treatments of a disease state are provided.
Owner:CELLUMEN INC
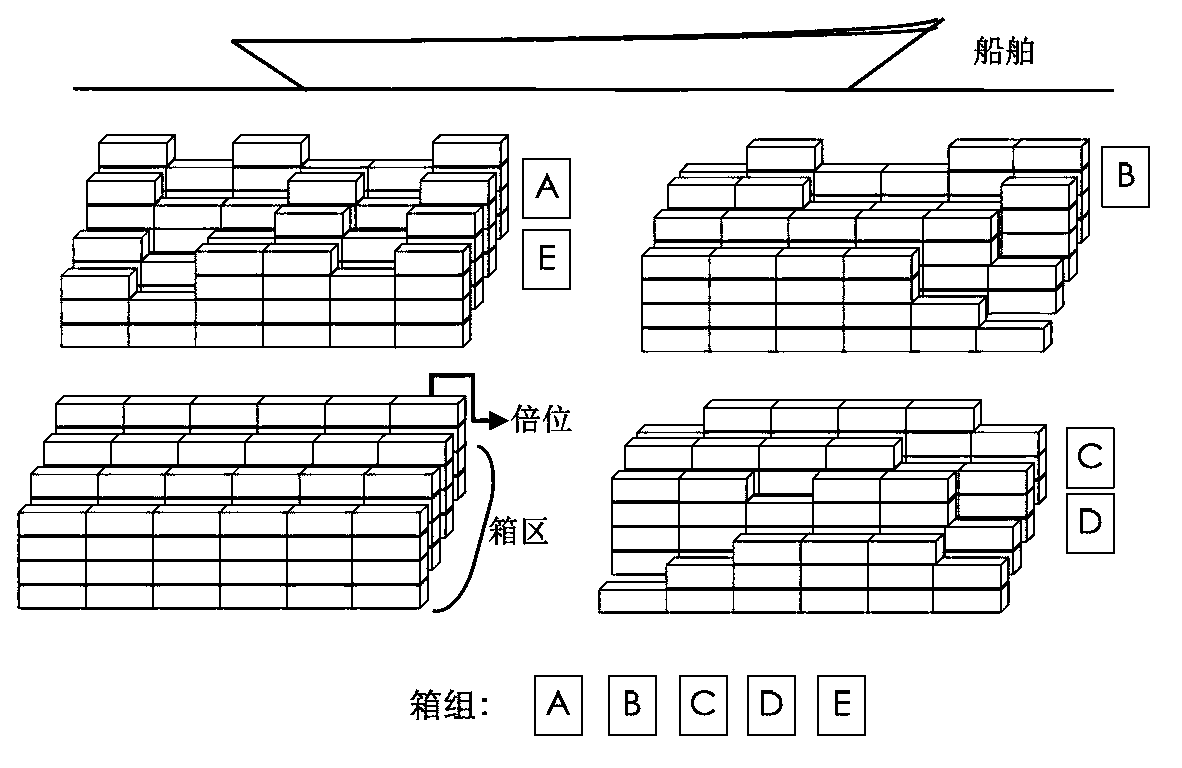
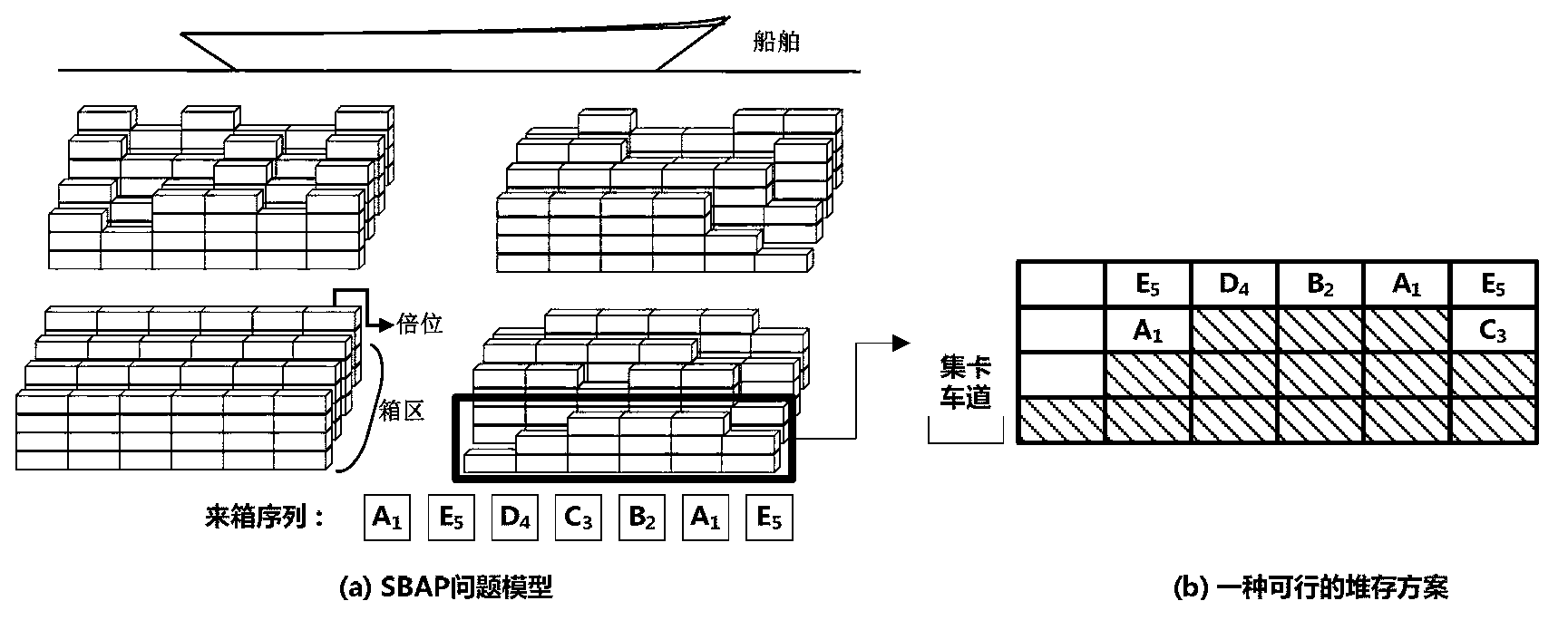
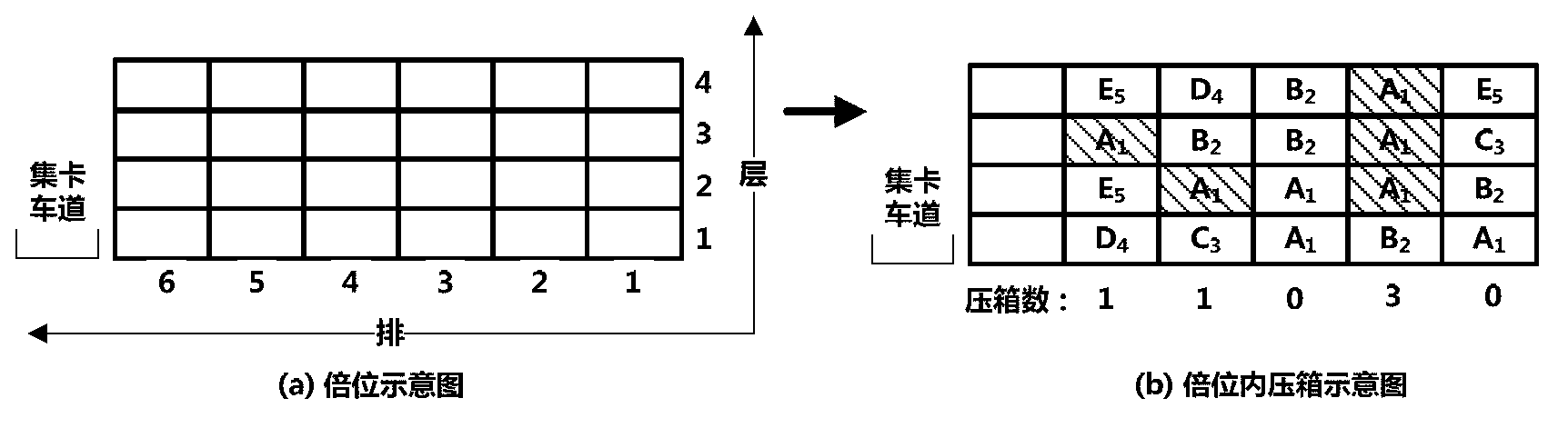
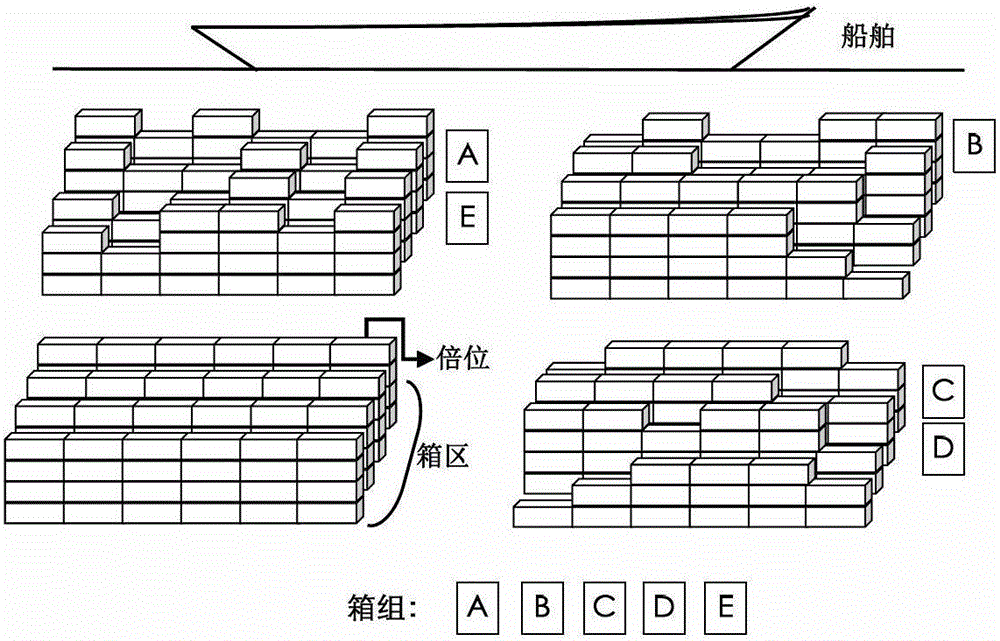
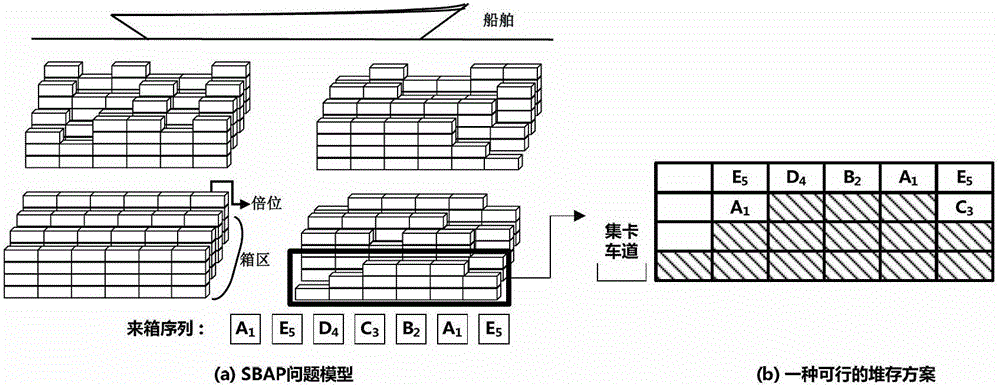
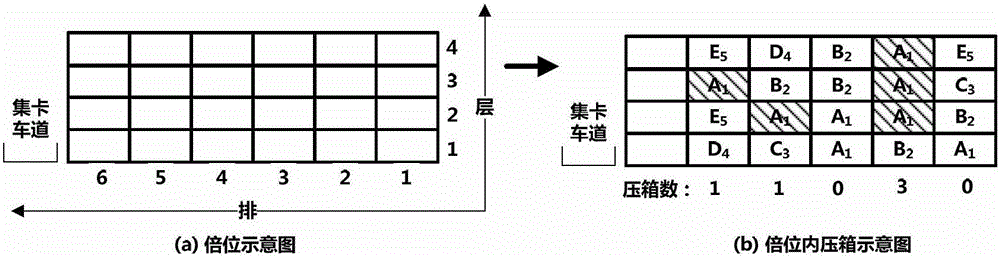
Scheduling method for export container wharf pile-up space
InactiveCN103246941AGood optimal solutionAvoid simultaneous shipmentsForecastingLogisticsTheory modelCellular automation
The invention discloses a scheduling method for an export container wharf pile-up space. Two-stage modeling is performed from plan allocation to dynamic allocation. At a pre-allocation stage, a block plan is researched, and the follow-up dynamic allocation is guided by the block plan. In the block plan, a block allocation model based on the ecological neutral theory is proposed. According to the block allocation model, container blocks are abstracted as islands, and container groups are abstracted as species, and thus, a process of allocating the container groups to the container blocks is escaped into a process that ecological selection is performed on the islands by a plurality of species. Based on the block allocation model, by aiming at the characteristic of the block plan problem, the block allocation model is optimized by the scheduling method for the export container wharf pile-up space, and an improved ecological neutral theory model is proposed. At a dynamic allocation stage, yard bay allocation and container space allocation are combined, solving is optimized by bi-objective combination, and a combination cellular automaton model is proposed. According to the combination cellular automaton model, the yard bay allocation is abstracted as an external cellular model, and the container space allocation is abstracted as an internal cellular model.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
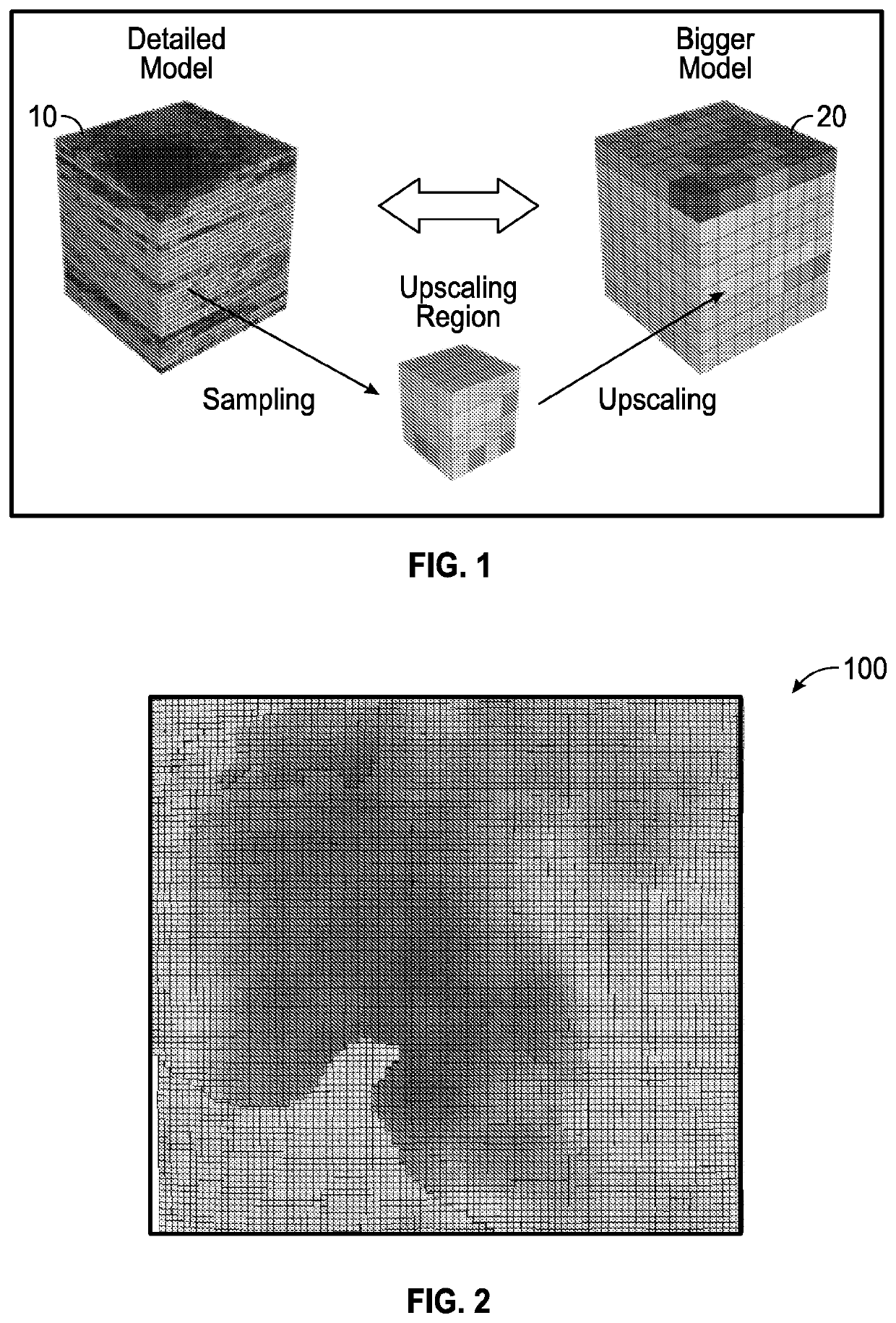
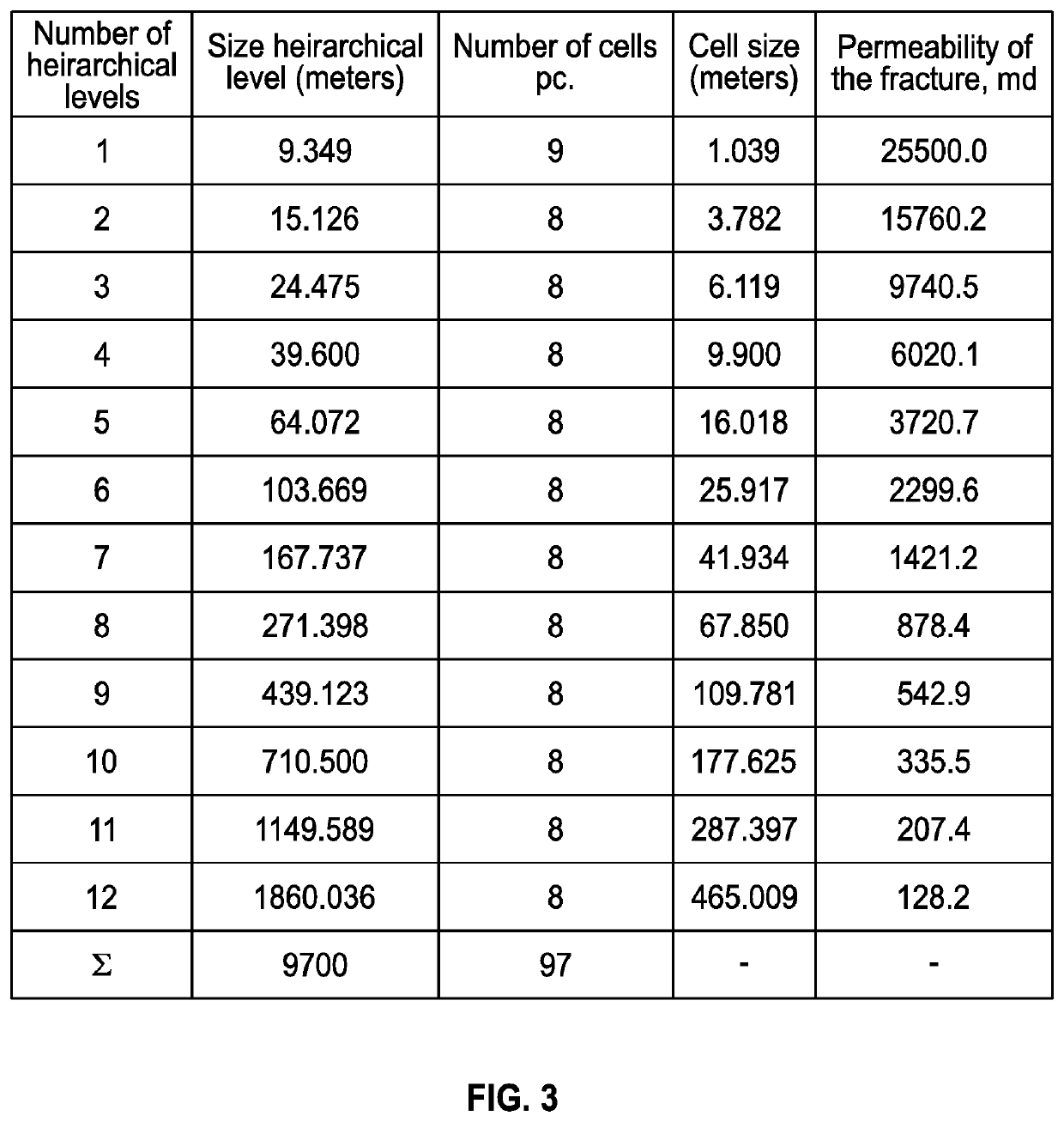
Discrete irregular cellular models for simulating the development of fractured reservoirs
ActiveUS20160196367A1Reduce in quantityFluid removalComputation using non-denominational number representationReservoir modelingCellular model
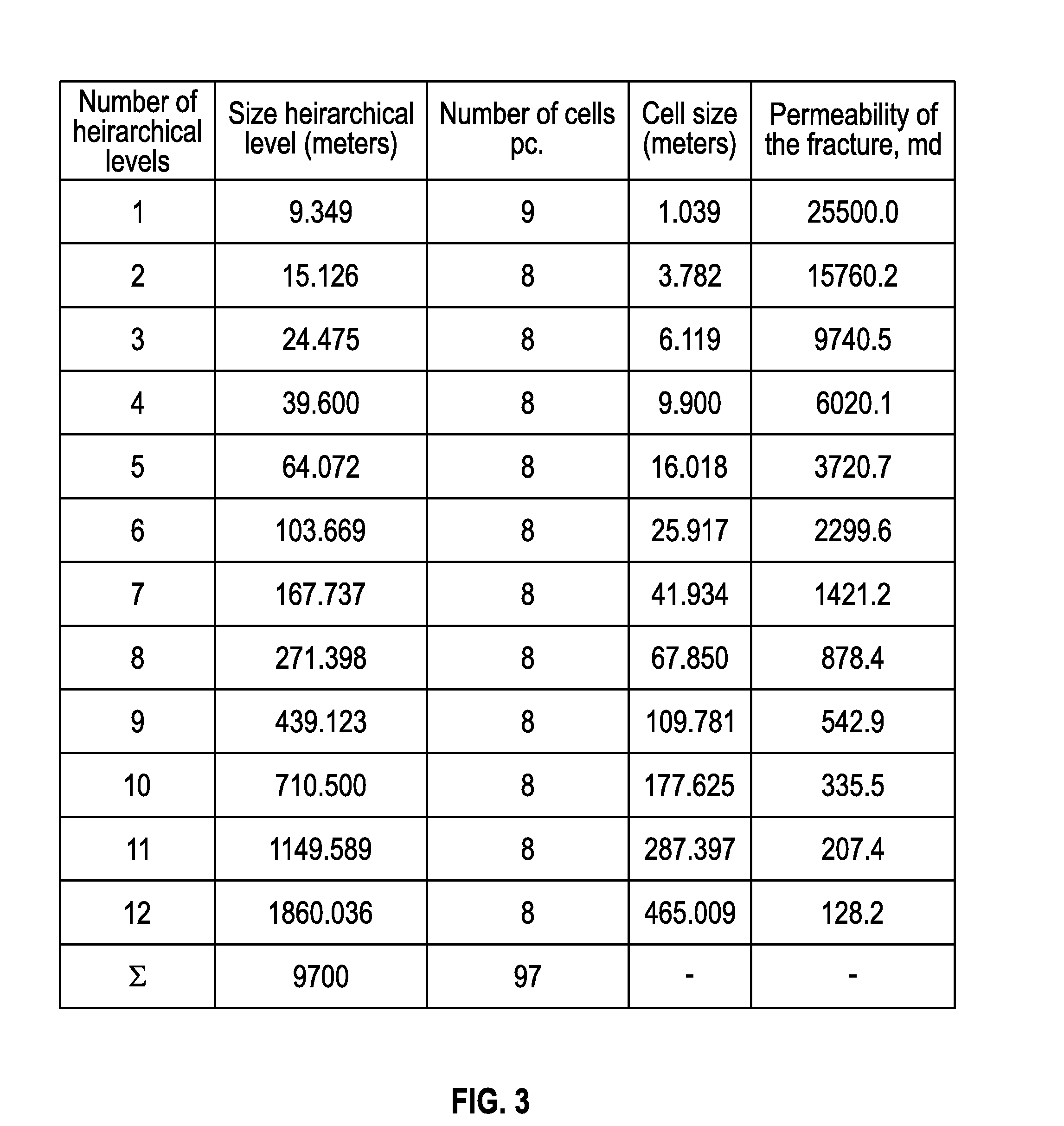
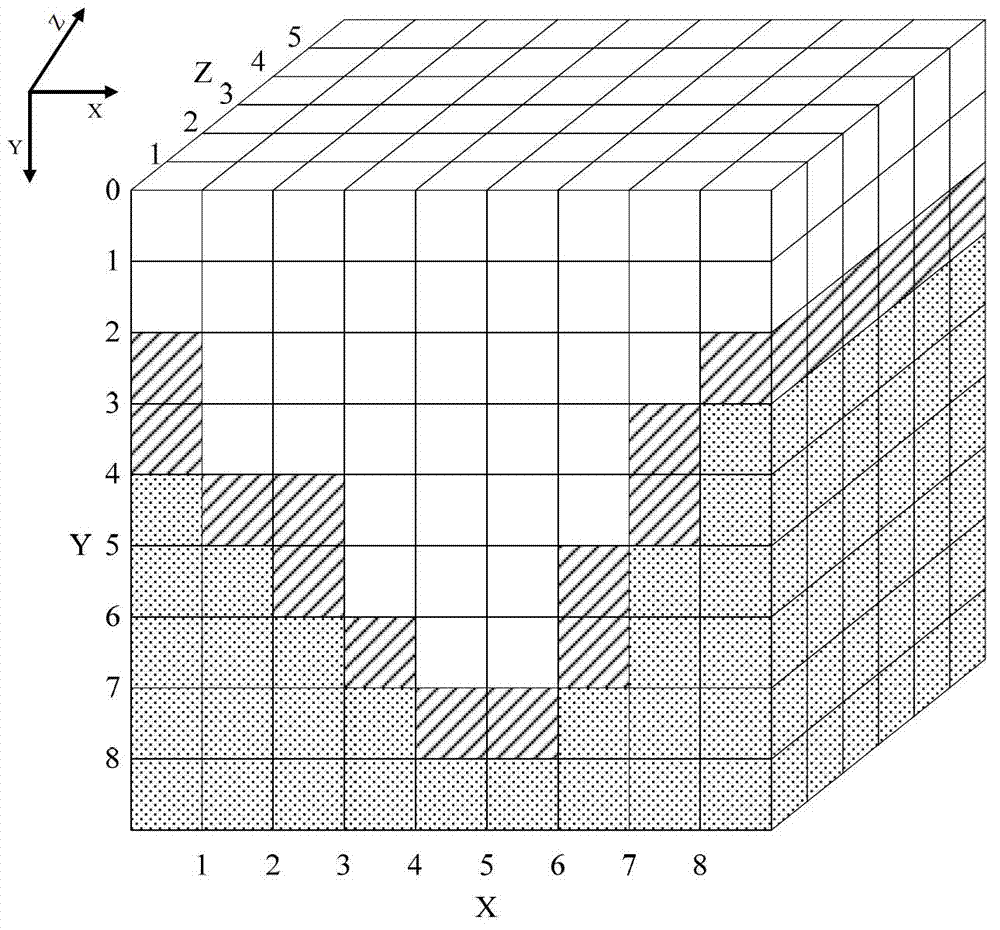
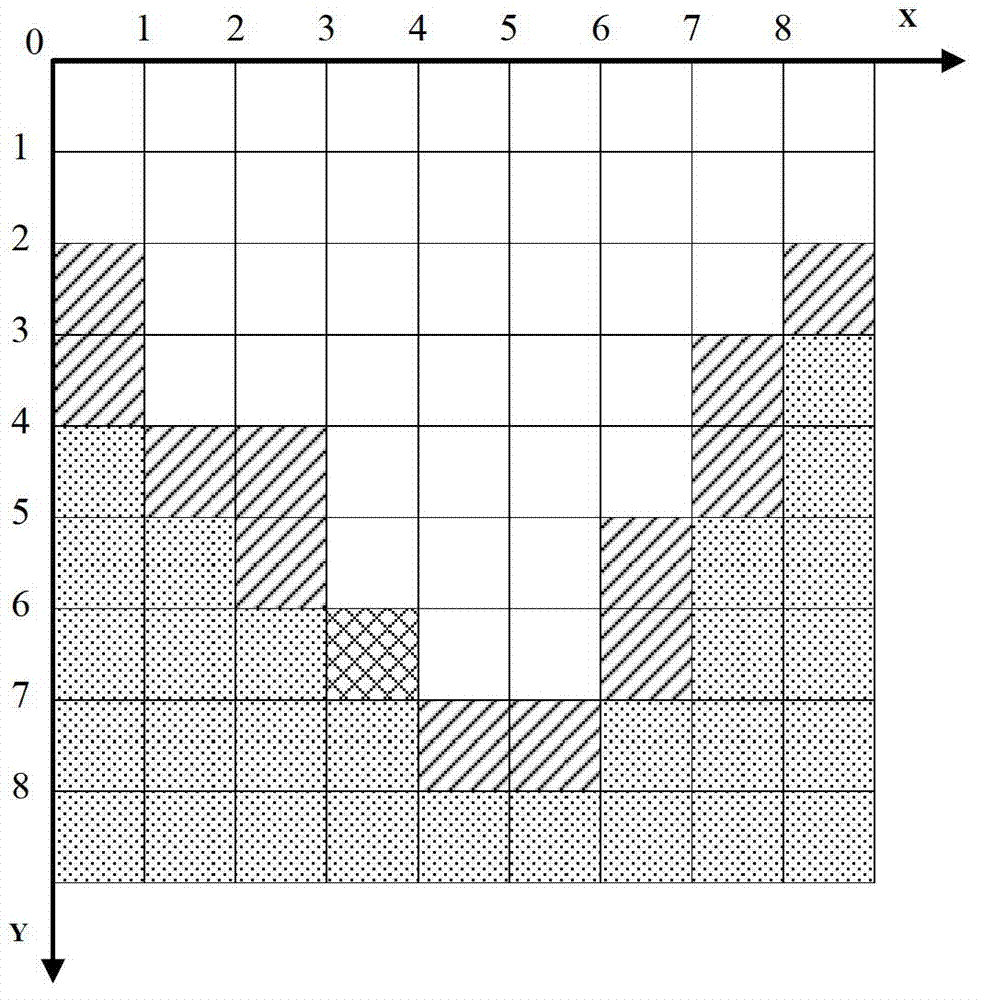
An electronically stored model for a reservoir can include a plurality of hierarchical levels and a plurality of cells representing corresponding portions of the reservoir. The model can include a dimension and a cell number corresponding to the reservoir. A dimension of a cell of an nth hierarchical level can be defined in terms of a dimension of a cell of a first hierarchical level and an array of vertex coordinates along one or more axes can be generated. The model can include a ratio of dimensions among hierarchical levels for improved reservoir modeling. The model can include a ratio of permeability among hierarchical levels for improved reservoir modeling.
Owner:PETROLEUM FRACTURED RESERVOIR SOLUTIONS
Method for determining incident angle of particles in three-dimensional cellular model etching process
InactiveCN102930143ASolve reductionReduce processingSpecial data processing applicationsComputation complexityCellular model
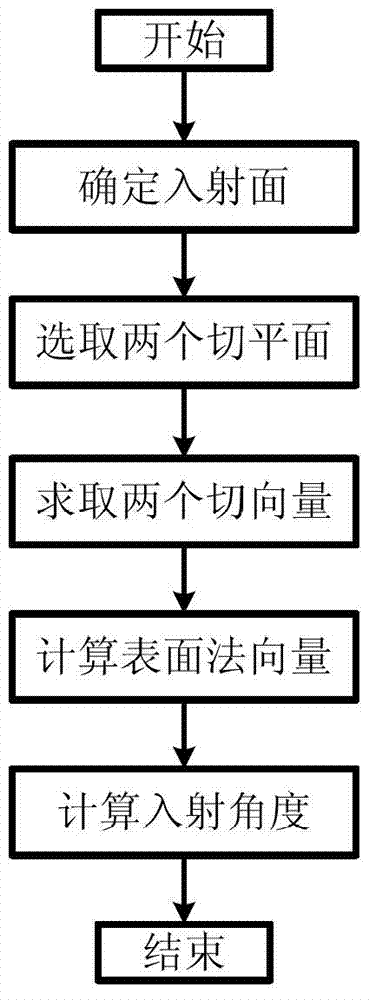
The invention relates to a method for determining an incident angle of particles in a three-dimensional cellular model etching process, which belongs to the field of the etching process in the micro-electron machining; and the method comprises the following steps of selecting two tangent planes which are vertical to an incident plane according to an incident direction of etching particles; respectively selecting surface cellular surrounding an incident point on the two tangent planes, adopting a position coordinate as a data sampling point, conducting fitting calculation by adopting a two-dimensional curve fitting method, and further solving a tangent vector of the incident point on the two coordinate axis directions; and finally conducting cross-product operation for the two tangent vectors to solve the normal surface vector of the incident point, and acquiring the incident angle of the etching particles. A three-dimensional curve fitting problem is converted to two two-dimensional curve fitting to be solved, so that the solution of multi-element equations can be reduced, the calculation complexity is reduced, and simultaneously the treatment of ill-conditioned system of equations in a polygonal curve fitting can be avoided; and the calculation accuracy and the operation speed can be greatly improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
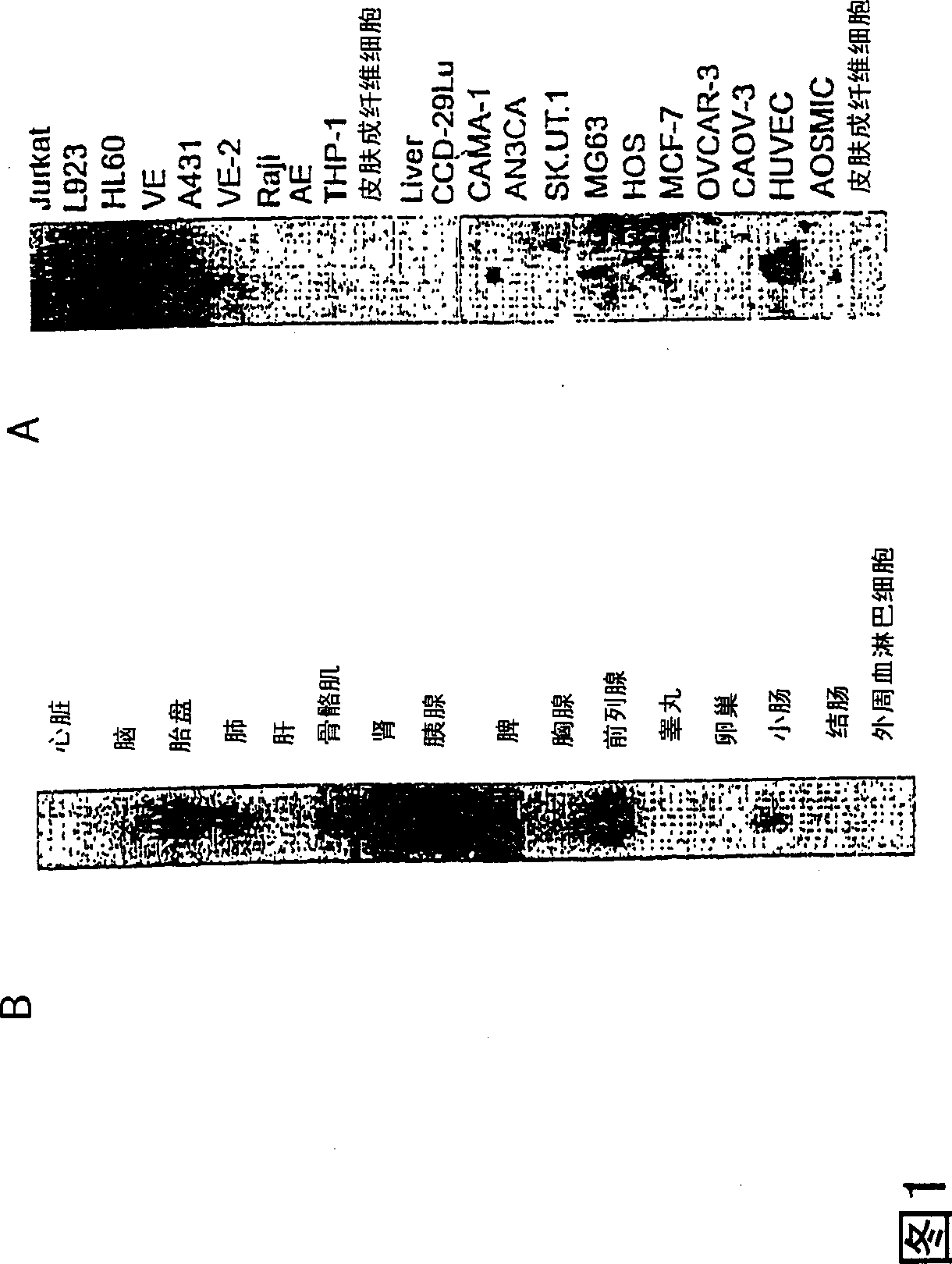
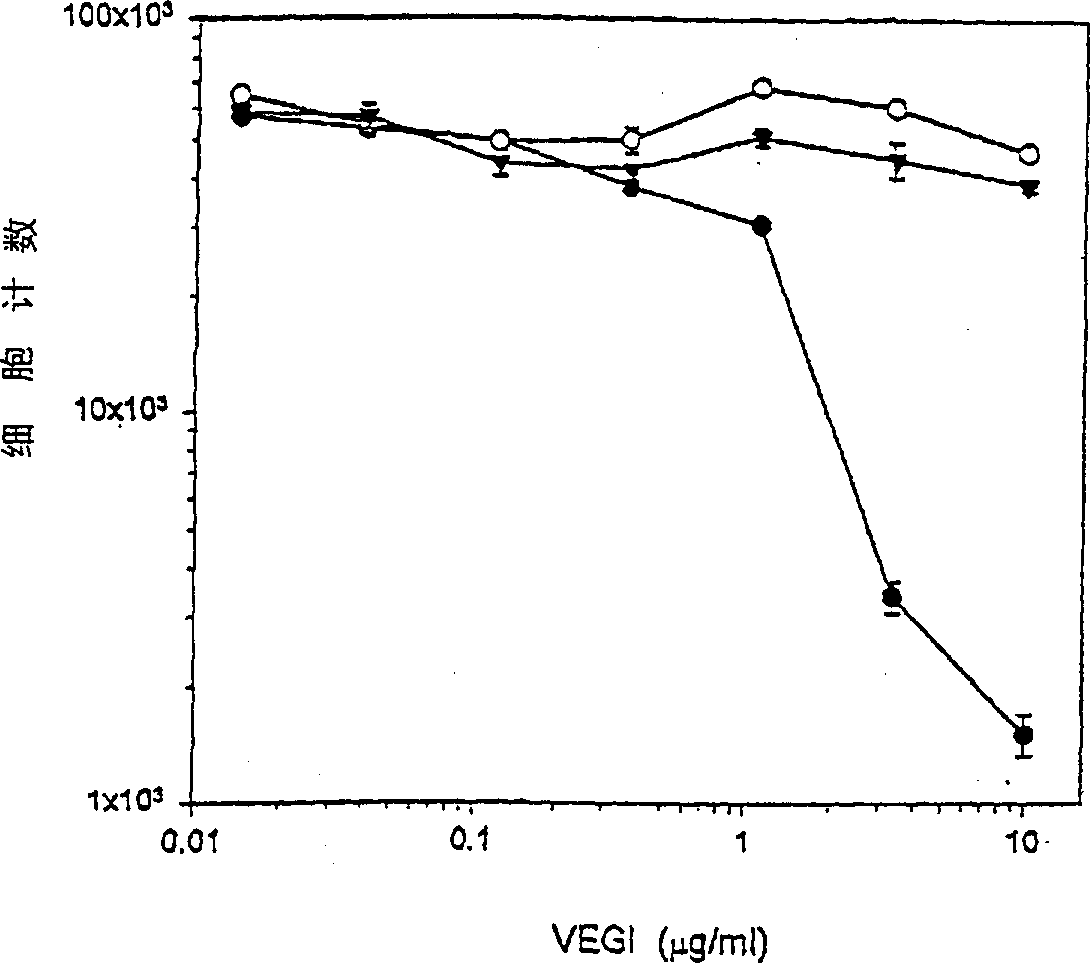
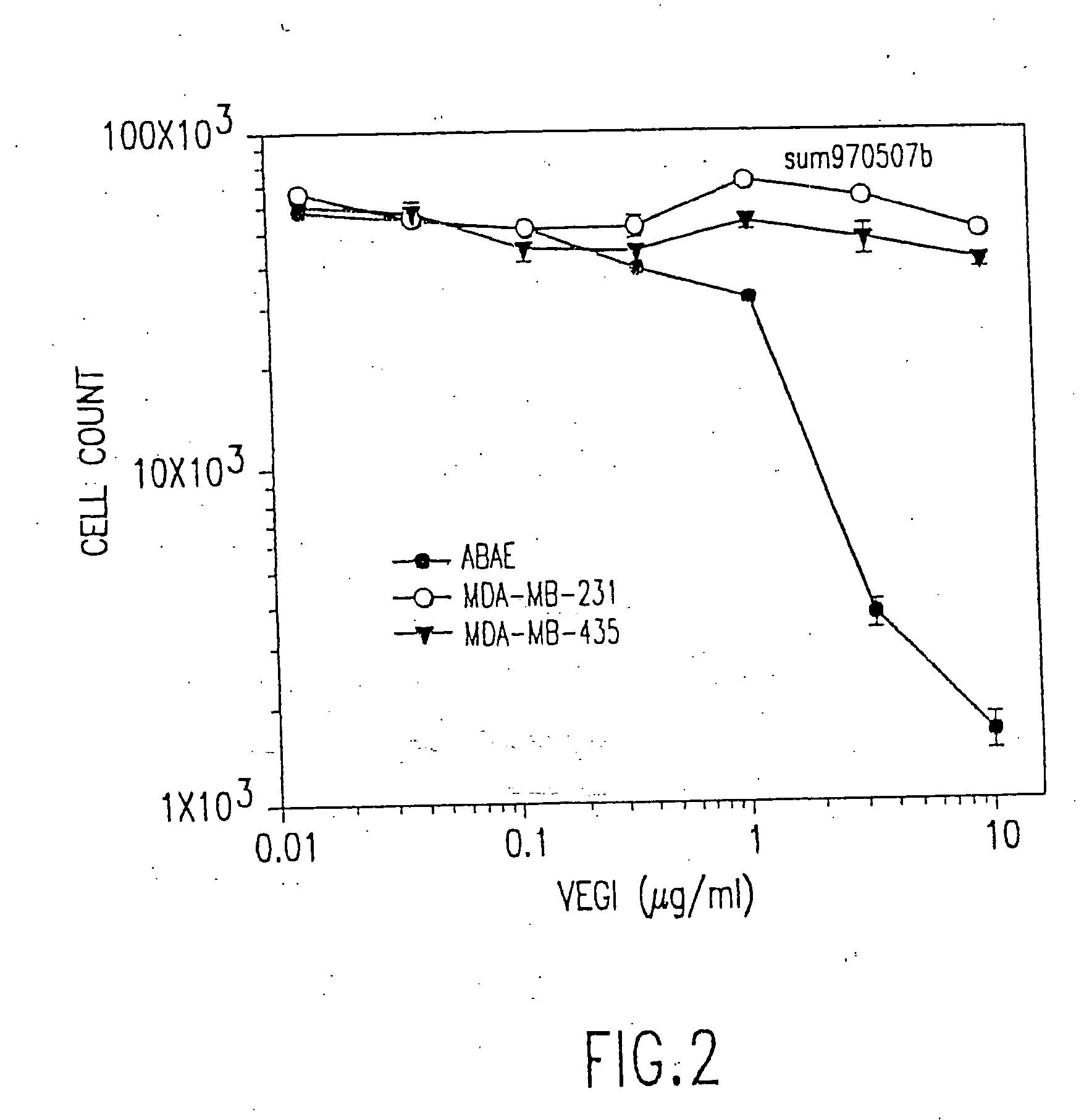
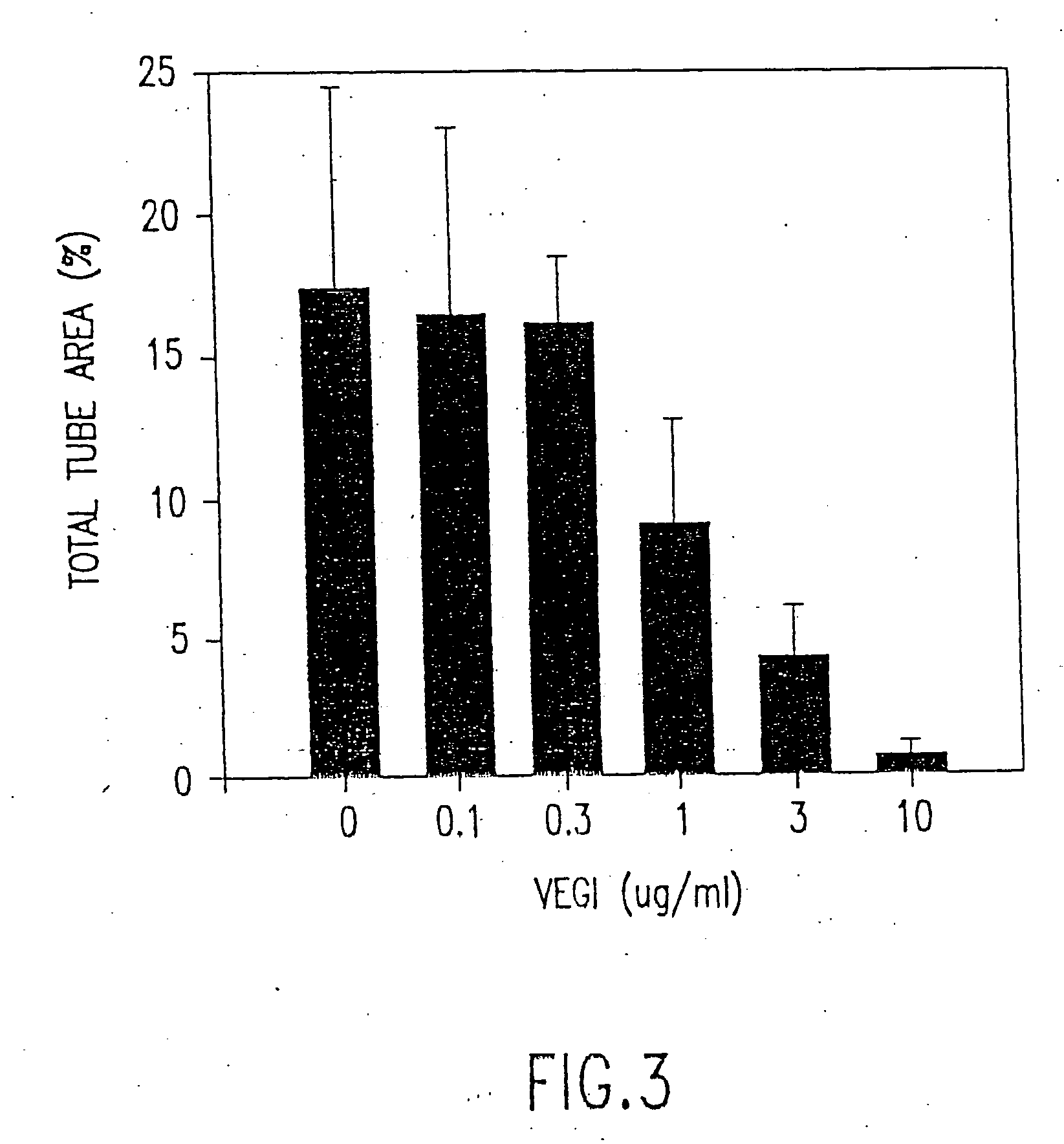
VEGI, an inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth
The present invention relates to a vascular endothelial cell inhibitor, VEGI, capable of inhibiting angiogenesis in cellular models and tumourigenesis in animal models, and methods of use.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC +1
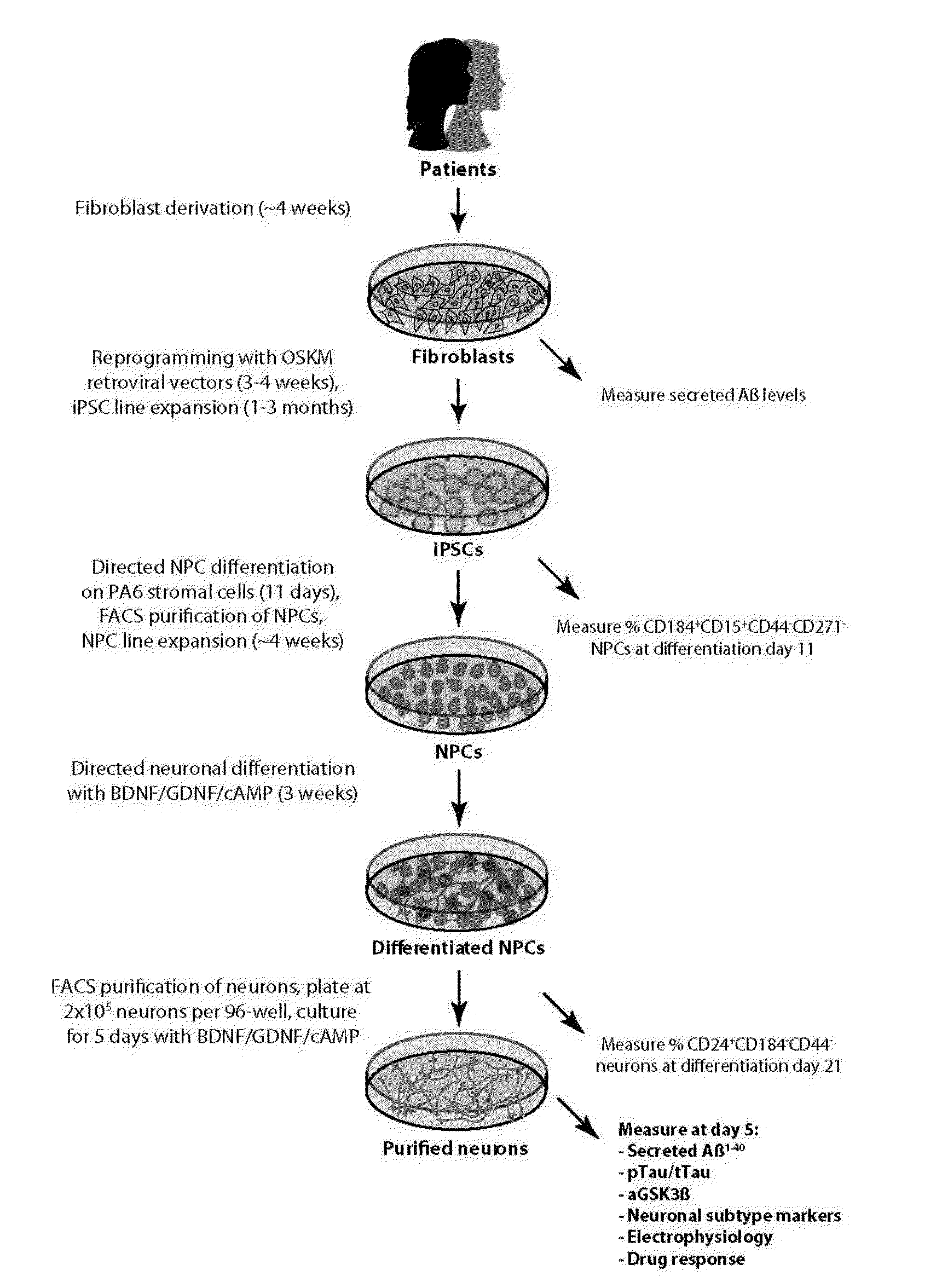
Alzheimer's Disease Cellular Model for Diagnostic and Therapeutic Development
InactiveUS20140011197A1Suitable for measuringGenetically modified cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementCellular modelDisease patient
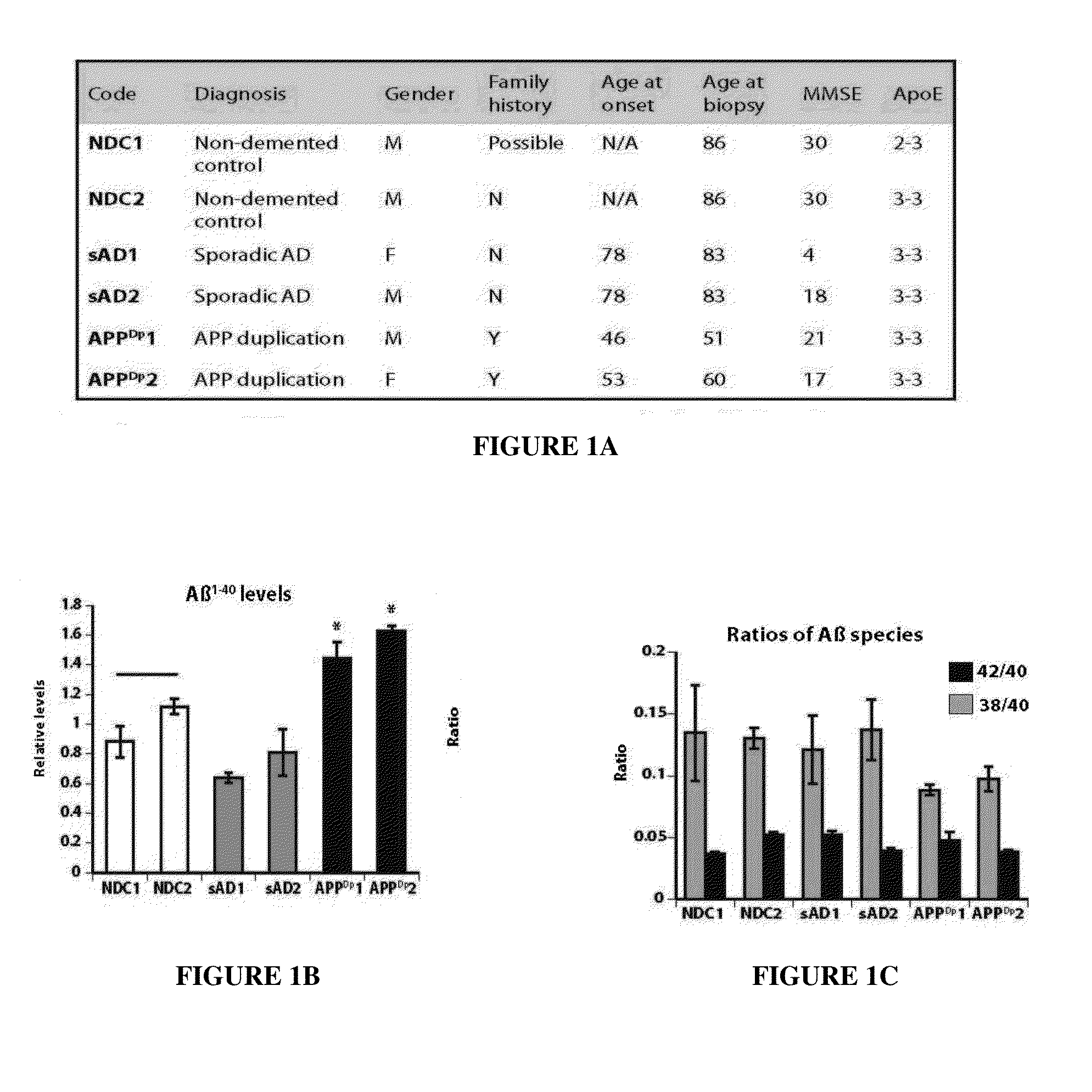
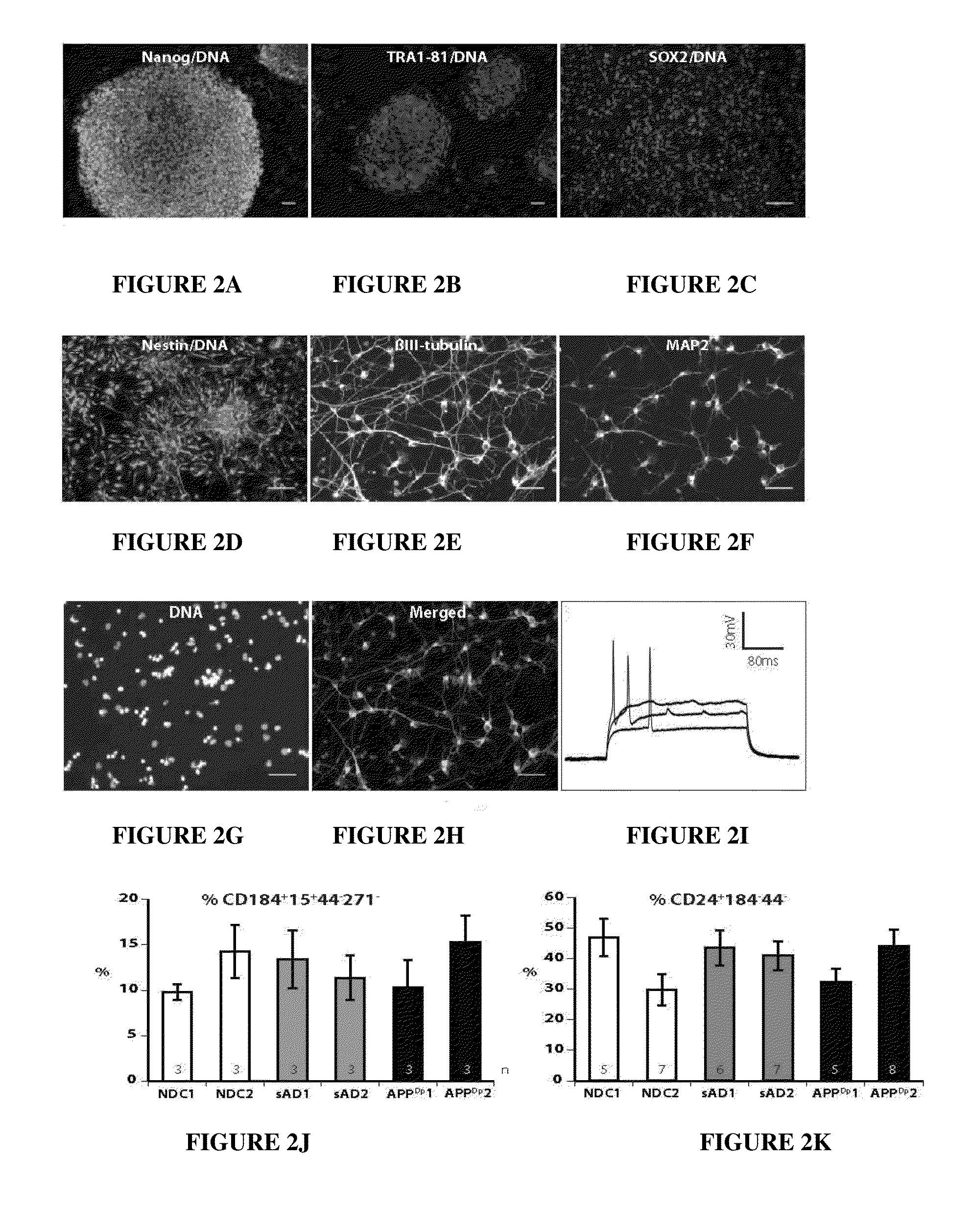
Stem-cell derived human neuronal models that mimic human Alzheimer's disease, including hereditary and sporadic Alzheimer's disease, comprising neural stem cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Also provided are purified human neurons developed from the neural stem cells that carry genomes from the Alzheimer's disease patients. The human neuronal models are neuronal models for hereditary and sporadic Alzheimer's disease, and are suitable for measurement of key behaviors of the Alzheimer's disease, providing further diagnostic tools for the development of sporadic Alzheimer's disease, and assisting in drug testing for the therapeutic treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
VEGI, an inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth
InactiveUS20050214305A1Promote angiogenesisUpregulating angiogenesisVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsCellular modelVascular endothelium
The present invention relates to a vascular endothelial cell inhibitor, VEGI, capable of inhibiting angiogenesis in cellular models and tumourigenesis in animal models, and methods of use.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC +1
Method for generating progressive solid models based on cellular topology
InactiveUS7197441B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsComputation using non-denominational number representationCellular topologyCellular model
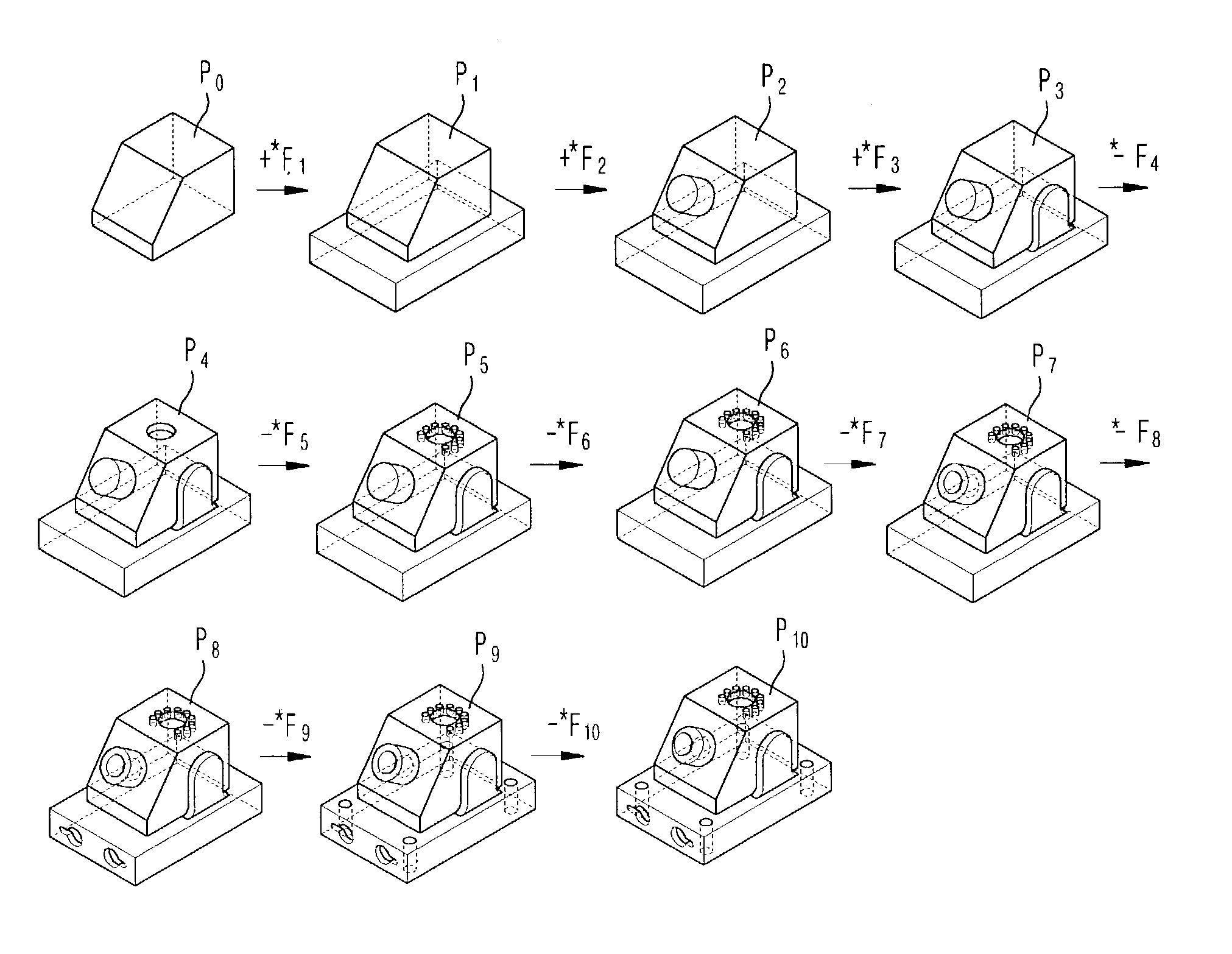
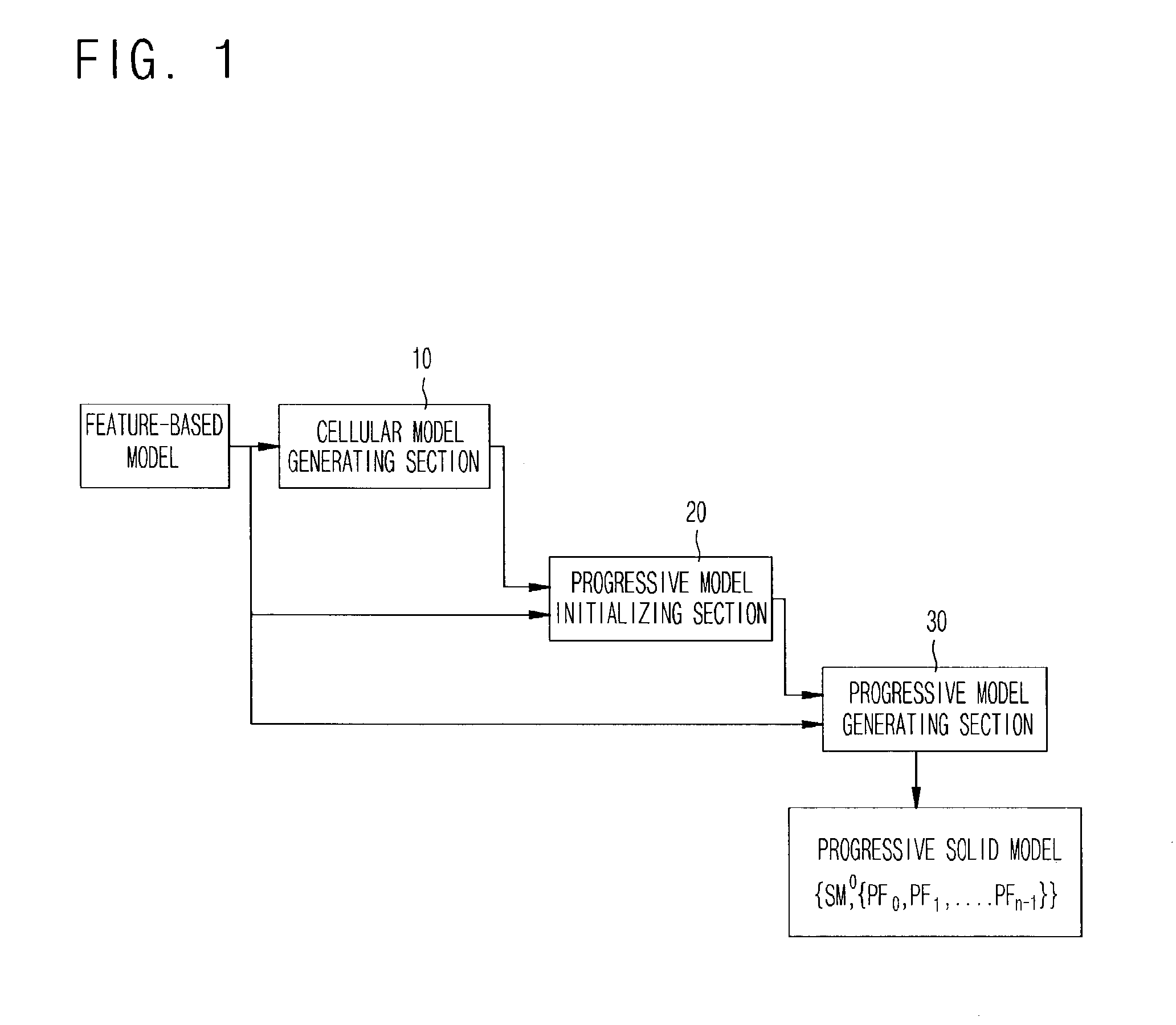
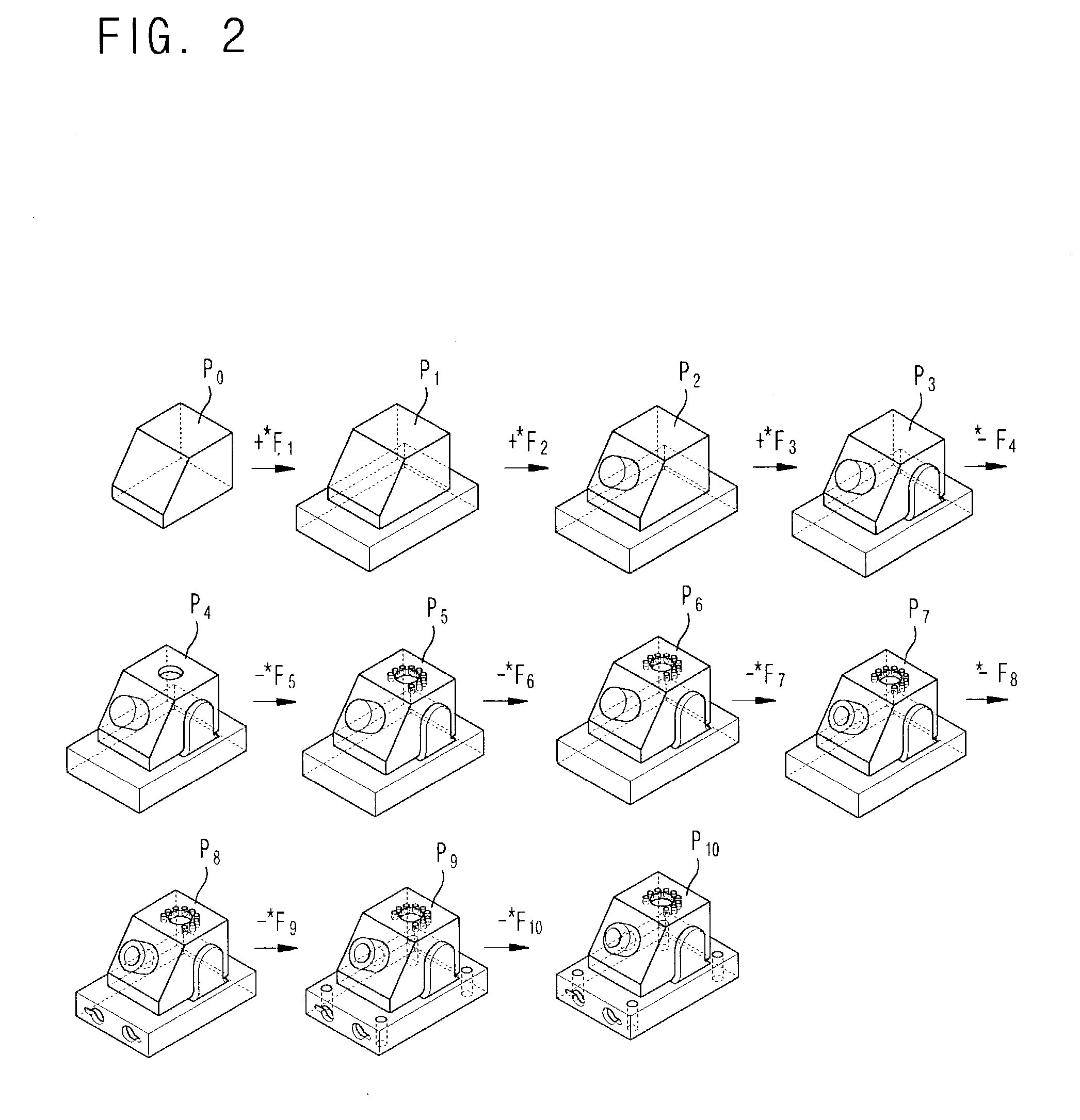
Disclosed is a method for generating progressive solid models based on a cellular topology. A cellular model generating section 10, if a specific feature-based model is inputted, performs a mapping operation on the input feature-based model with reference to an internal feature library, thereby generating cellular topology models based on feature models. A progressive model initializing section 20 composes cells by use of volume attributes of the cells according to a relationship between the input feature-based model and the cells obtained from the cellular topology model to generate an initial cellular model SM0 which is simplified to generate a progressive solid model, and then searches n delta volumes DVi transiting the initial cellular topology model SM0 by composing and decomposing the cells so as to progressively complement the difference between the initial cellular topology model SM0 and the input feature-based model. A progressive model generating section 30 generates n progressive features PFi defined as a face subset of the delta volume and corresponding attributes from the n delta volumes DVi, and outputs n progressive cellular models PFi and the initial cellular model SM0 as the progressive solid model in the form of {SM0, {PF0, PF1, . . . , PFn−1}}.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Instantaneous Isochron Attribute-based Geobody Identification for Reservoir Modeling
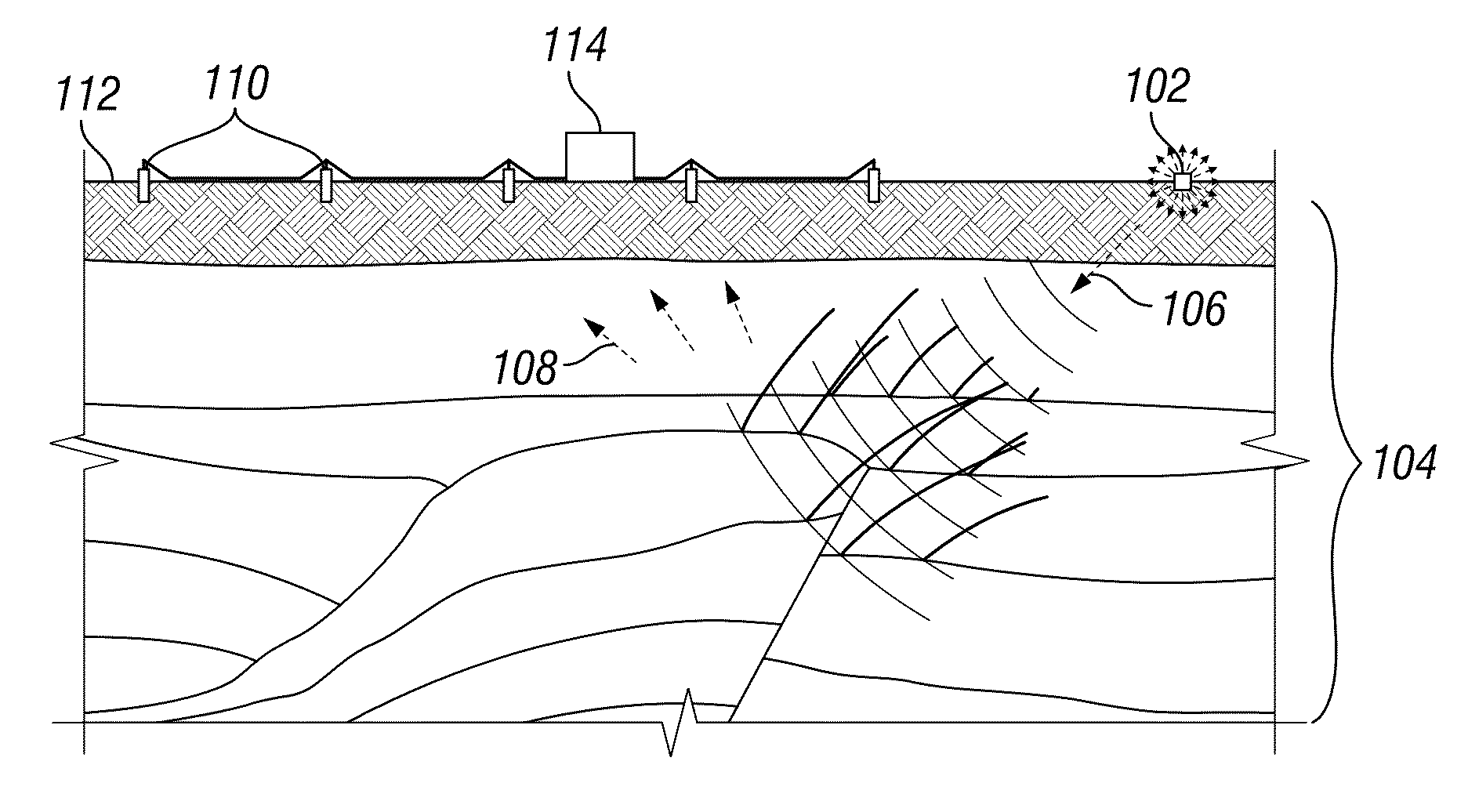
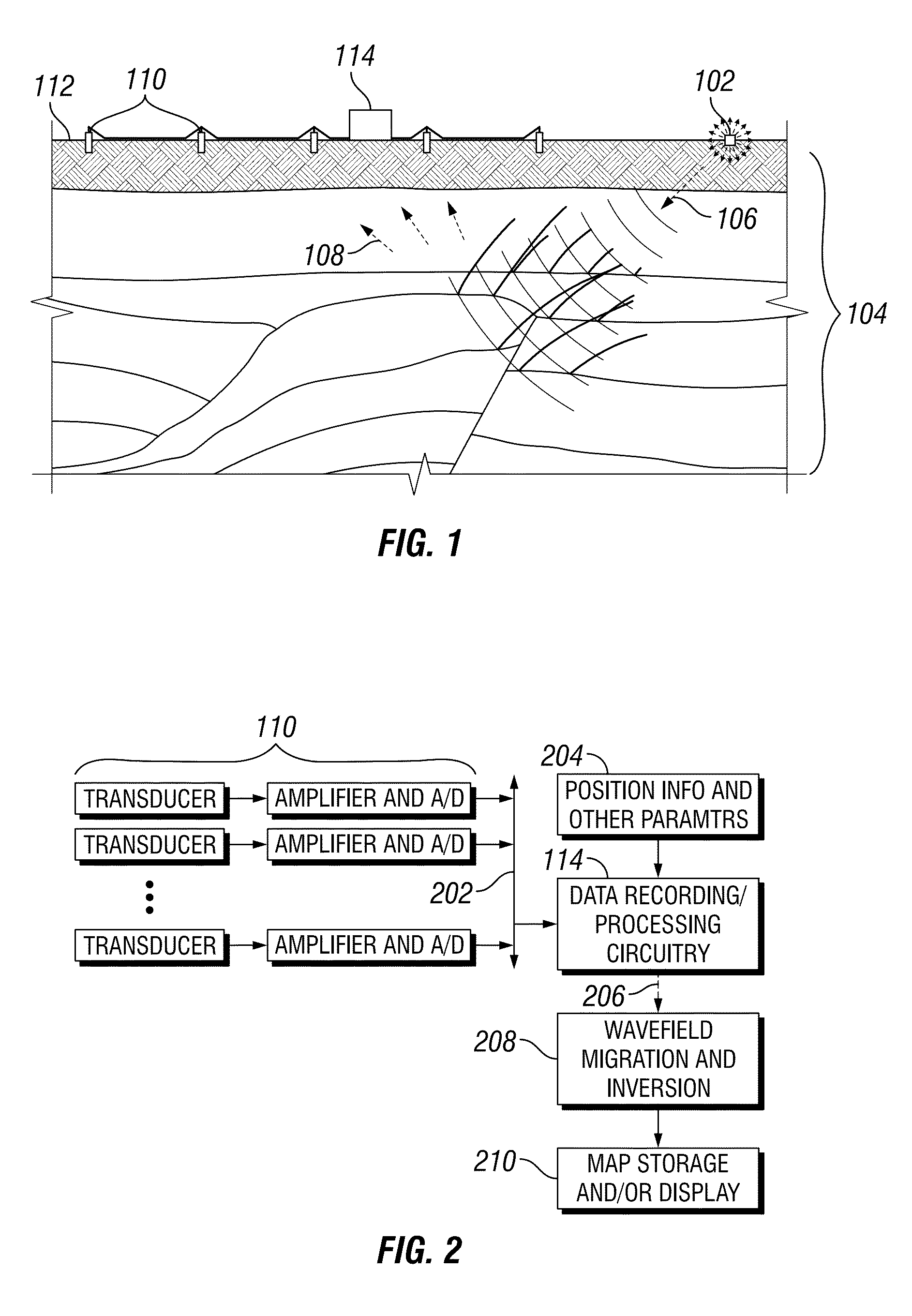
ActiveUS20150369935A1Robust identificationSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsHorizonCellular model
Automated systems and methods that provide robust identification of regions of interest for reservoir modeling are disclosed herein. One embodiment includes: obtaining a seismic image of a subsurface region; performing full-volume horizon picking and deriving an instantaneous isochron attribute (IIA) value for each point in the seismic image; identifying one or more geobodies within the seismic image based at least in part on the IIA values; and representing the one or more geobodies in a geocellular model. The identifying of geobodies may include: applying IIA value filtering to isolate intervals of rapid or slow deposition in the seismic image; determining a reservoir-non-reservoir indicator attribute value for each point in the seismic image; applying reservoir-non-reservoir indicator value filtering to isolate subintervals of presumed reservoirs or non-reservoirs in said isolated intervals; determining a pay indicator attribute value for each point in the seismic image; and applying pay indicator value filtering to isolate presumed pay zones in said isolated subintervals.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
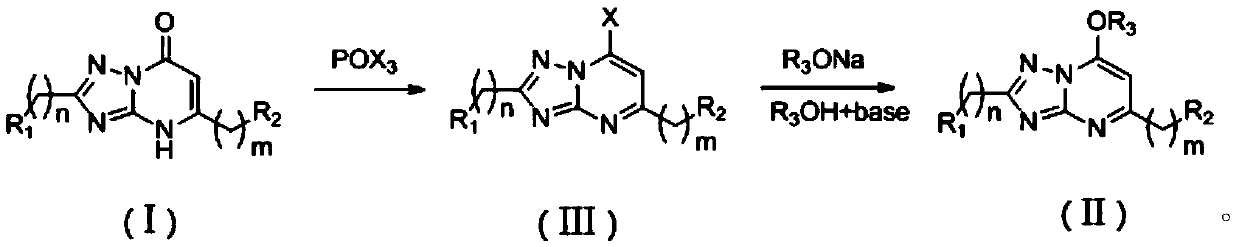
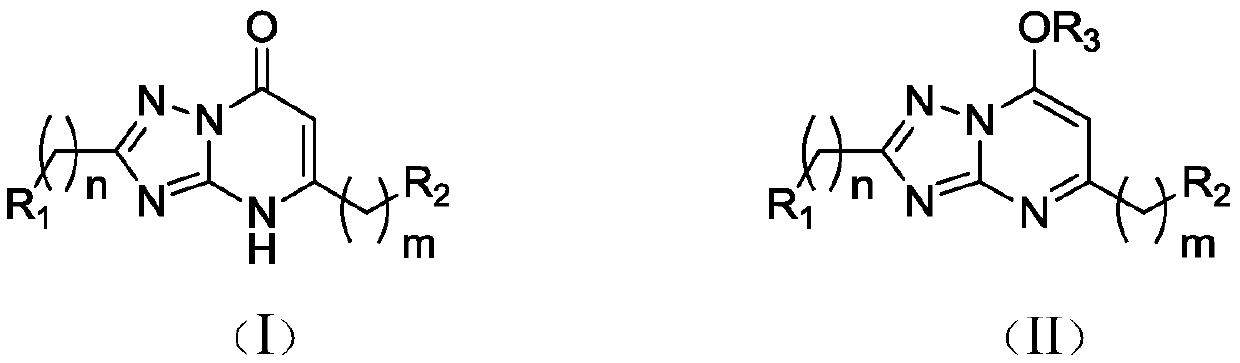
Application of 1,2,4-triazole heterocyclic compound in preparation of drugs to prevent or treat central system related diseases
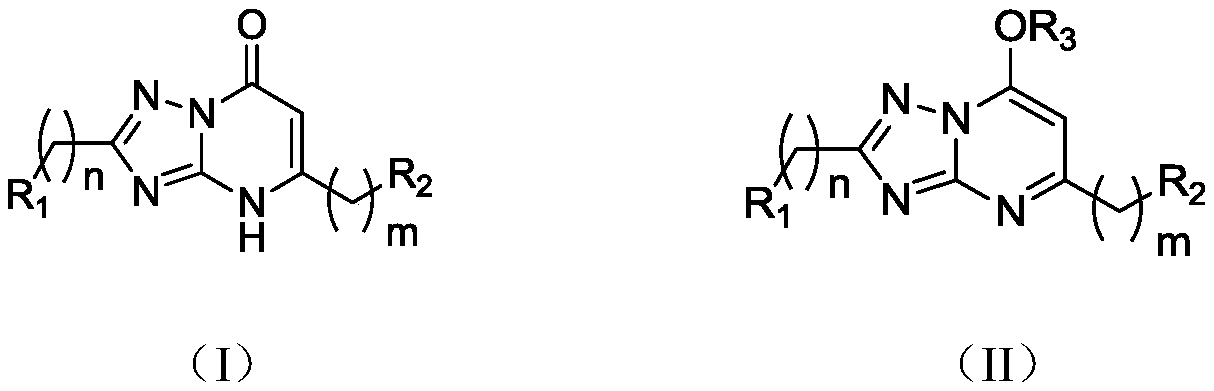
InactiveCN110251518AGood inhibitory effectWell sedatedOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseCellular model
The invention relates to the technical field of 1,2,4-triazole heterocyclic compounds and discloses application of a 1,2,4-triazole heterocyclic compound in the preparation of drugs to prevent or treat central system related diseases. The 1,2,4-triazole heterocyclic compound [1,2,4]-triazolo-[1,5-a]pyrimidone heterocyclic compound shown as the general formula (I) or 7-alkoxy-1,2,4-triazolo-[1,5-a]pyrimidine heterocyclic compound shown as the general formula (II). The 1,2,4-triazole heterocyclic compound disclosed herein can well inhibit, on cellular models, intracellular calcium ion oscillations and 4-AP induced epilepsy, and on animal models (mouse), has good anti-epilepsy activity and significant calming effect.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for constructing chicken-gene-EphA2-knocked-out cell line based on CRISPR-Cas9 editing technology
InactiveCN111304172AGreat Applied Research ValueGenetically modified cellsTransferasesCellular modelSubcloning
The invention relates to a method for constructing a chicken-gene-EphA2-knocked-out cell line based on a CRISPR-Cas9 editing technology. The method comprises the principle and most-core key technologyas follows: the chicken-EphA2-knocked-out cell line is obtained through scientifically and reasonably constructing chicken-gene-EphA2-targeted sgRNA, then, transfecting sgRNA and Cas9 gene carried lentiCRISPR v2 plasmids, achieving gene silencing by using a CRISPR-Cas9 system, killing negative cells through drug screening, and then, acquiring monoclonal cell strains through a subcloning method. Through the invention, a method for targeted knockout of a chicken gene EphA2 based on the CRISPR-Cas9 and the sgRNA targeting to the chicken gene EphA2 are constructed, so that a chicken-gene-EphA2-knocked-out cell model is expectedly obtained and is applied to researches on related diseases. The construction of the chicken-gene-EphA2-targeted-knocked-out cell line based on the CRISPR-Cas9 is notreported in related fields, and the method will fill up vacancies of related technologies at home and abroad and has a relatively high application research value.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
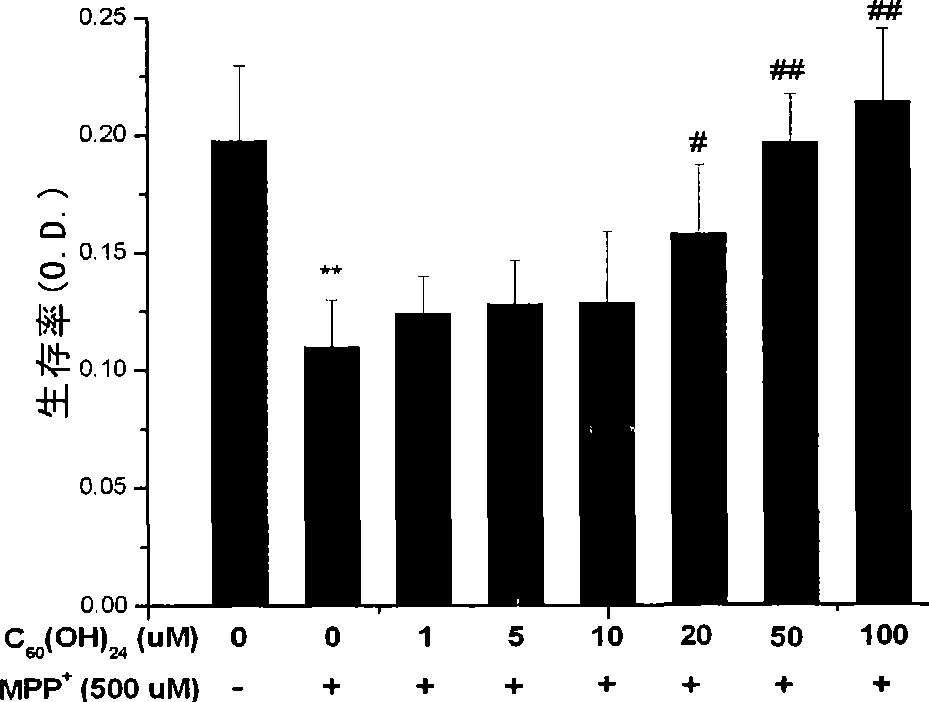
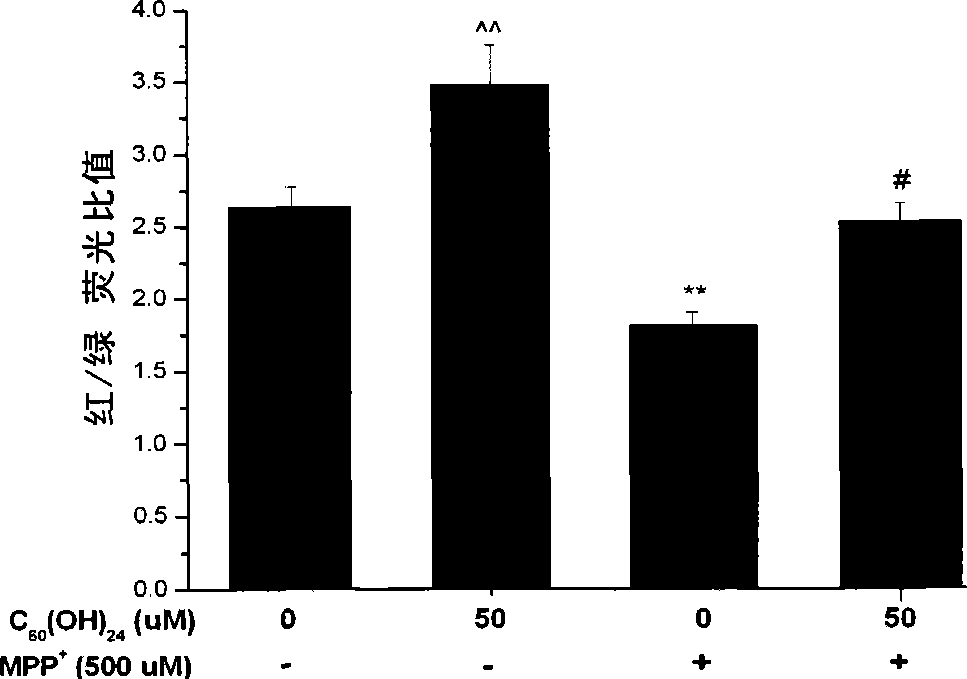
Use of C60 polyhydroxy derivates in preventing and treating related disease of mitochondria damage
InactiveCN101396372AGood effectEffective WaysNervous disorderMetabolism disorderDiseaseCellular model
The invention belongs to the biological and medical field and discloses an application of a C60 or C60 polyhydroxy derivative in preparing a combination for preventing and remedying the related diseases of mitochondrial injury (such as neurodegenerative disease or radiation sickness). The invention constructs a cellular model and an animal model with the related diseases of the mitochondrial injury, demonstrates the excellent efficacy of the C60 or C60 polyhydroxy derivative for preventing and remedying the related diseases of the mitochondrial injury and provides an effective approach for developing multifunctional drugs with mitochondria as a target point accordingly.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Human Cellular Models with Biosensors
This invention provides biosensors, cell models, and methods of their use for monitoring ionic or voltage responses to contact with bioactive agents. Biosensors can include targeting domains, sensing domains and reporting domains. Biosensors can be introduced into cells reprogrammed to represent experimental or pathologic cells of interest. Model cells expressing the biosensors can be contacted with putative bioactive agents to determine possible activities.
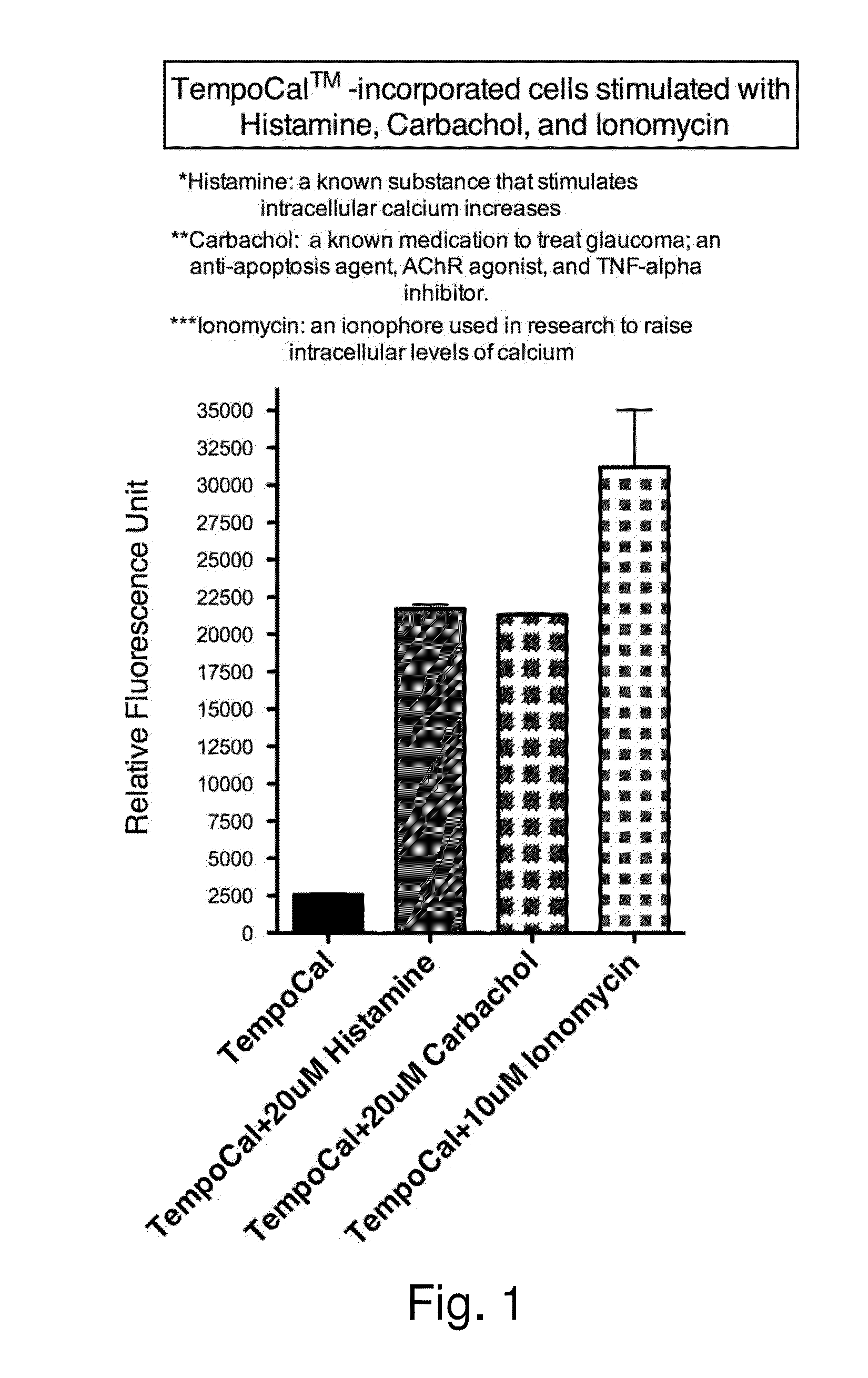
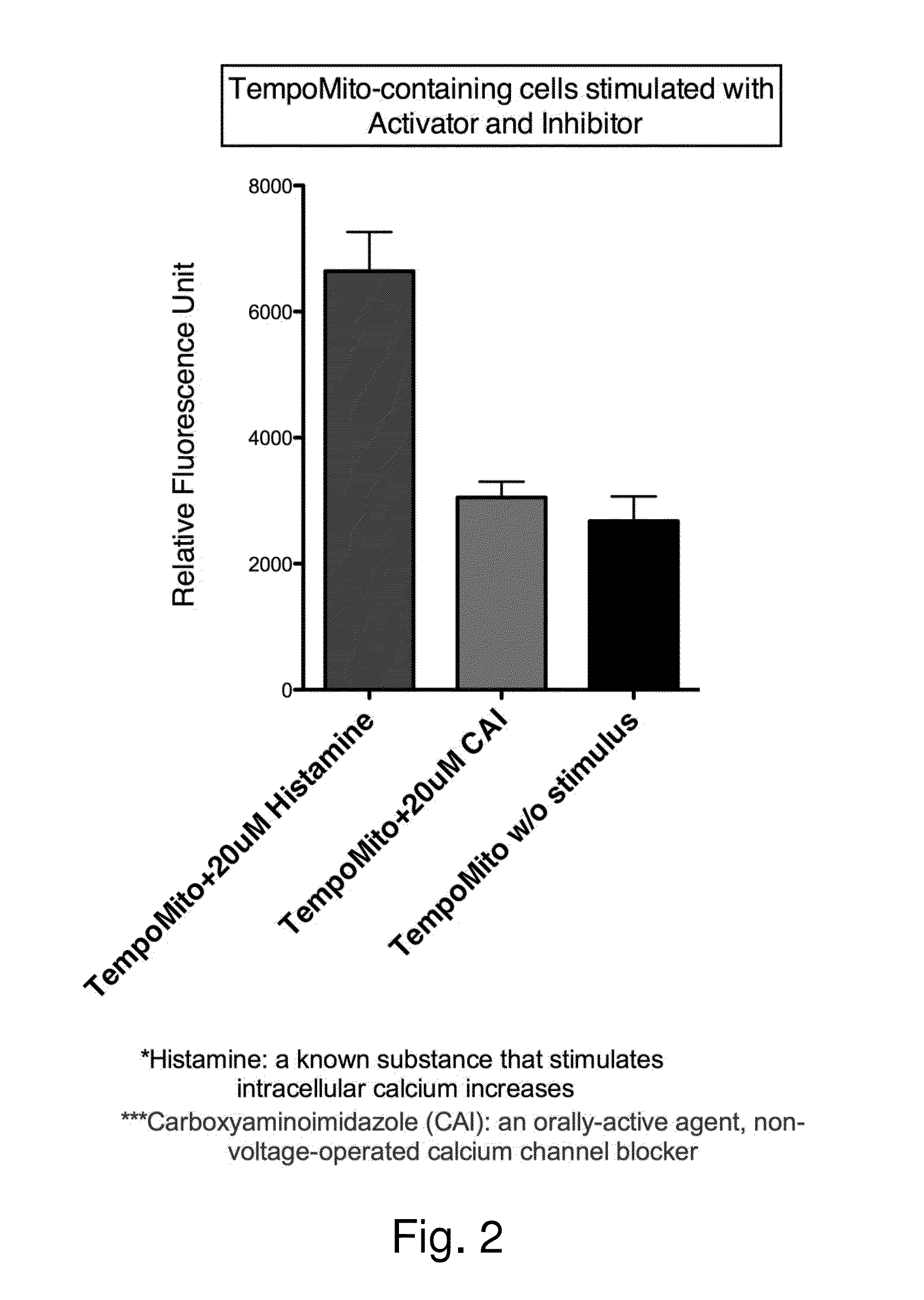
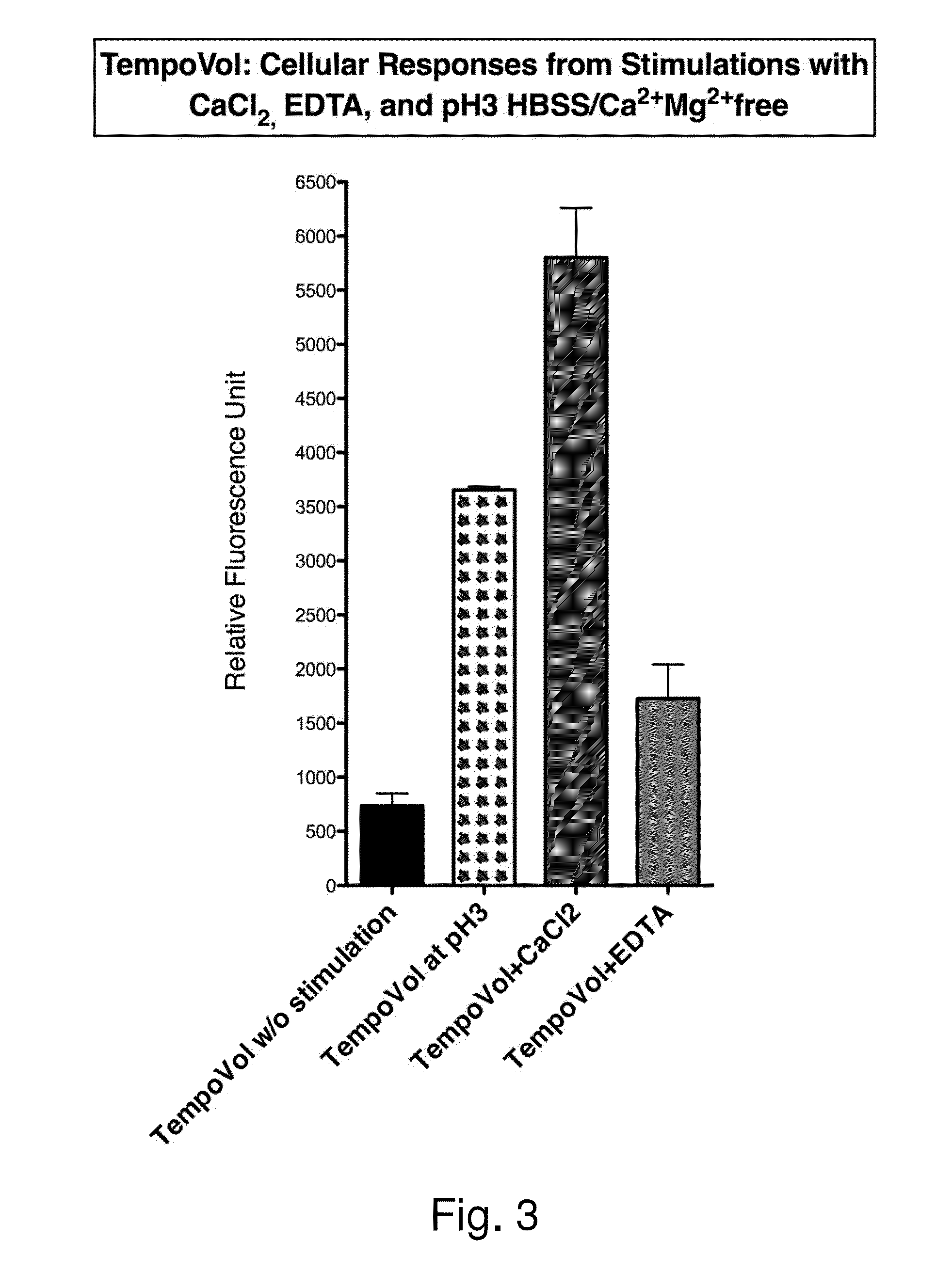
Owner:TEMPO BIOSCI
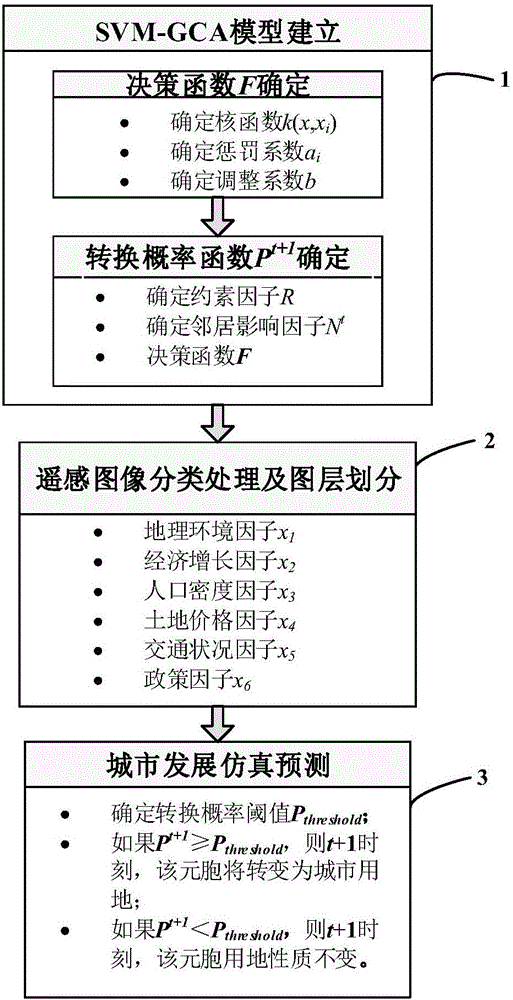
SVM-GCA (Support Vector Machine-based Geographical Cellular Automata)-based urban spatial development simulation and prediction method
InactiveCN106251014ASolve the problem of excessive error in simulation prediction resultsAvoid askingForecastingCharacter and pattern recognitionState predictionCellular model
The invention belongs to the virtual geographic environment and simulation research field of geographic information systems, and relates to urban spatial development simulation and prediction technologies, in particular, an SVM-GCA (Support Vector Machine-based Geographical Cellular Automata)-based urban spatial development simulation and prediction method. According to the method of the invention, a support vector machine technology is adopted to design an urban cellular land use property change decision function; a support vector machine-based geographic cellular model is put forward based on the urban cellular land use property change decision function; and the urban spatial development simulation and prediction method is put forward based on the model. According to the method of the invention, the linear defect of an existing geographic cellular model is eliminated. The method has high simulation speed and high simulation precision. The support vector machine technology is adopted to build the urban cellular model, so that the typical nonlinear problem of geographic cellular state prediction is solved, and therefore, the problem of large error of a simulation prediction result caused by the linearity of a traditional geographic cellular model can be solved. Compared with an existing method, the method of the invention just requires a small number of samples, has higher computation efficiency and higher precision.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
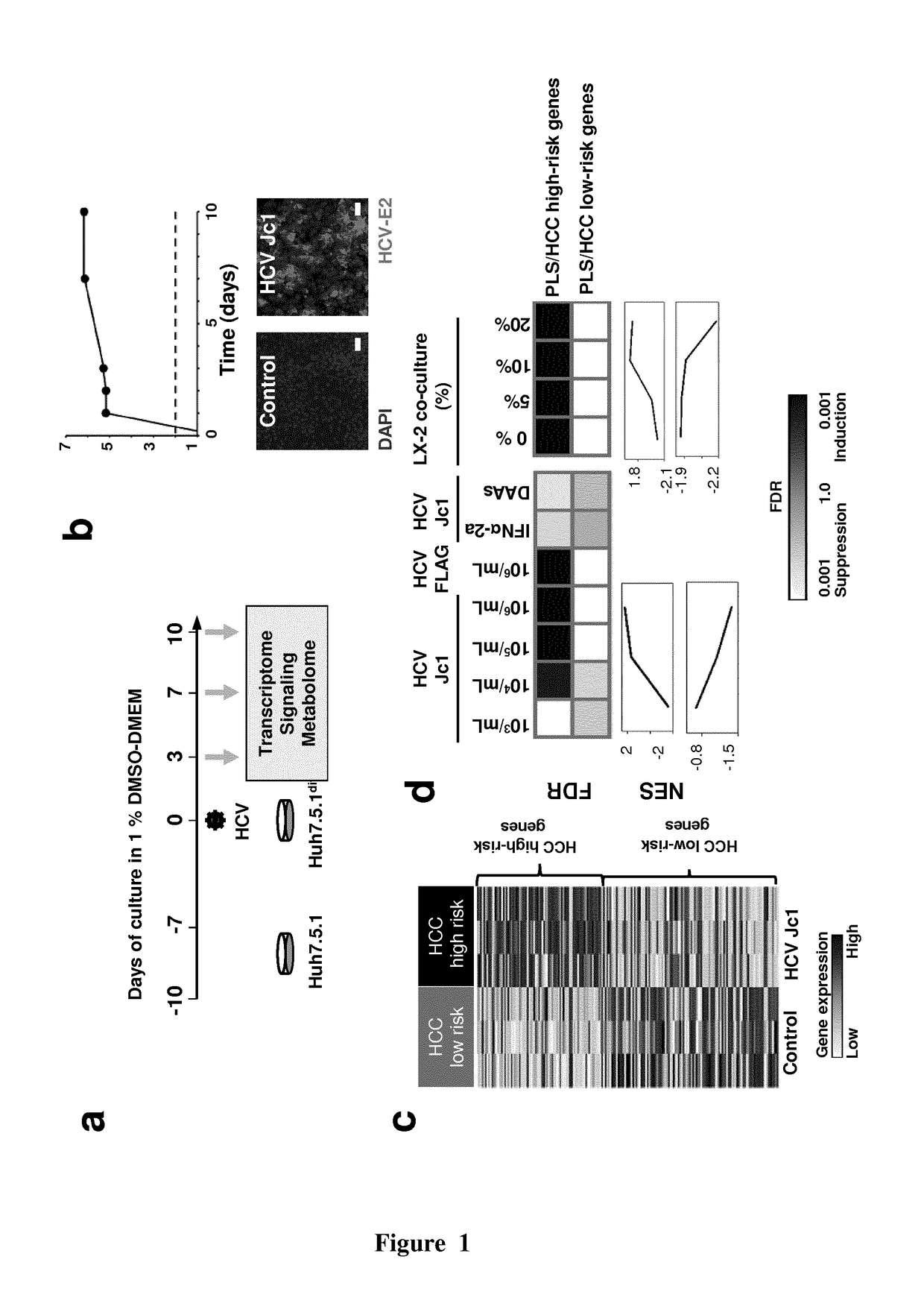
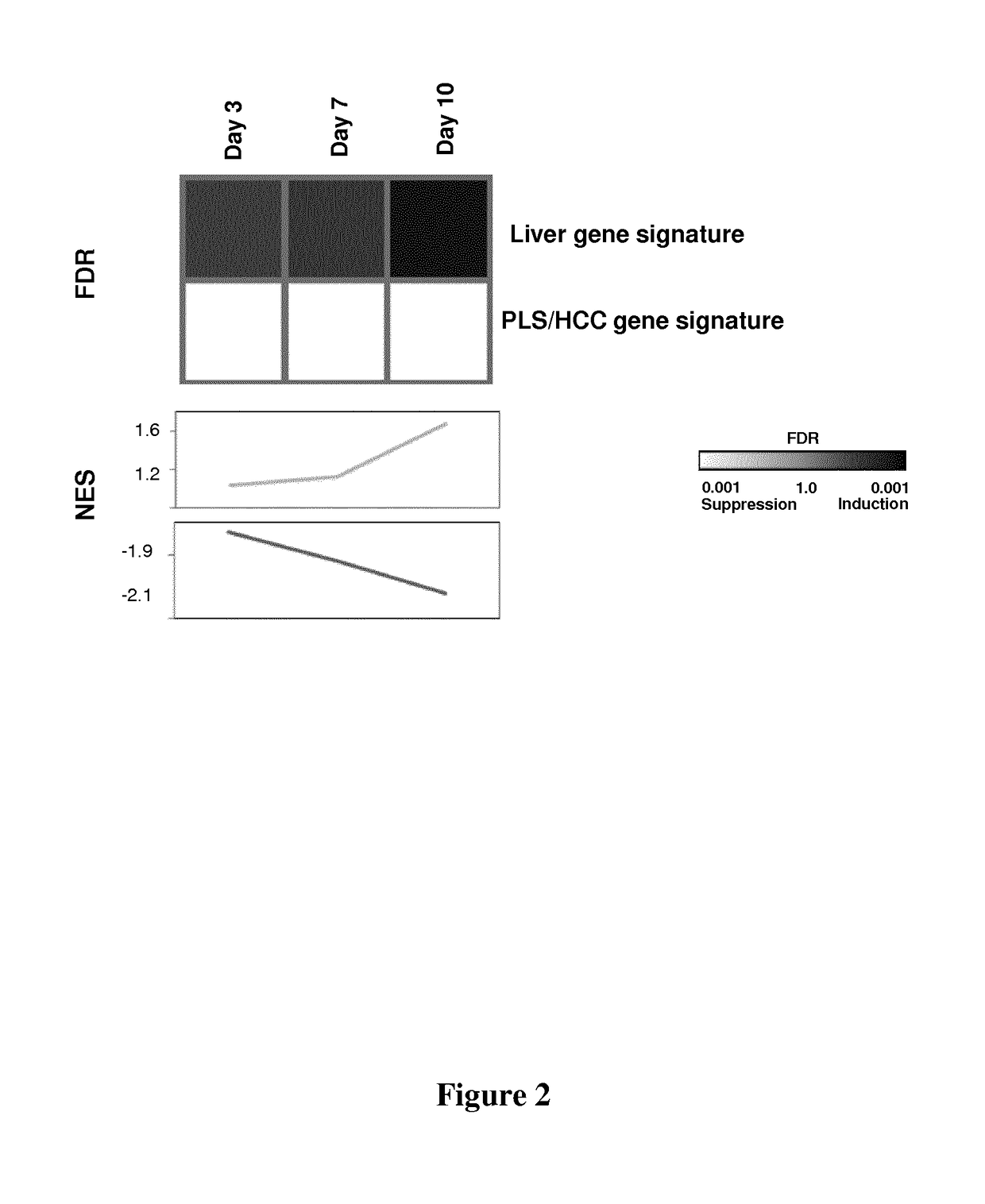
Clinical gene signature-based human cell culture model and uses thereof
ActiveUS20180119096A1Improved prognosisOrganic active ingredientsHepatocytesHepatocellular carcinomaCellular model
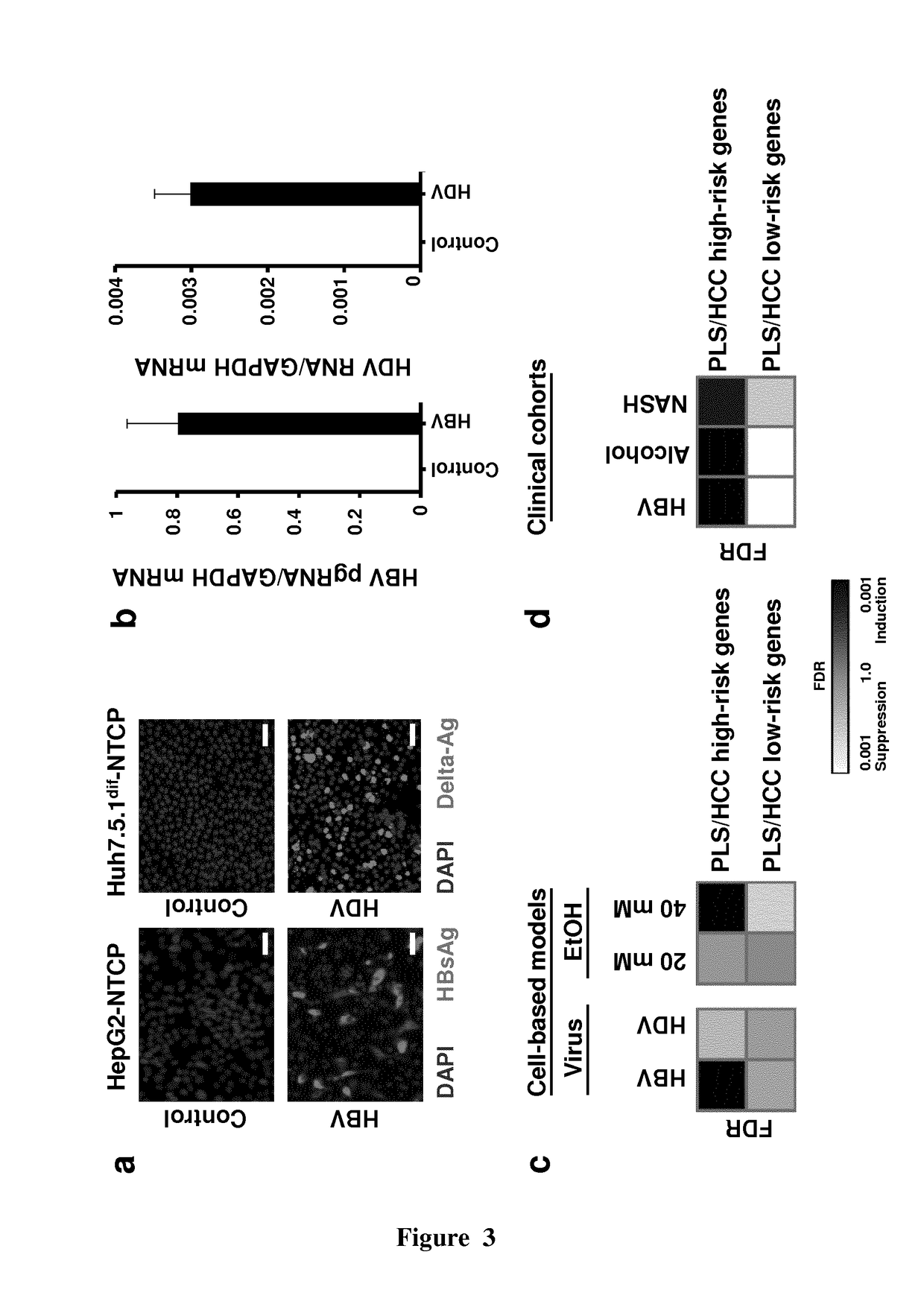
The present invention provides a simple and robust human liver cell-based system in which persistent hepatitis C infection, persistent hepatitis B infection or ethanol exposure induces a clinical Prognostic Liver Signature (PLS) high-risk gene signature. The cellular model system for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) / cirrhosis development and progression may be used in the screening of compounds useful in the treatment and / or prevention of cirrhosis and / or HCC as well as in the identification biomarkers for the prediction of liver disease (especially cirrhosis) progression and HCC. The present invention also relates to specific compounds that have been identified, using such screening methods, as useful in the treatment and / or the prevention of HCC / cirrhosis.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF STRASBOURG +2
Method for the isolation, purification and amplification of renal progenitors cd133+cd24+ from the urine of patients suffering from renal diseases
InactiveUS20160333318A1Fast and efficientEasy to purifyArtificial cell constructsDisease diagnosisZona glomerulosaIn vitro study
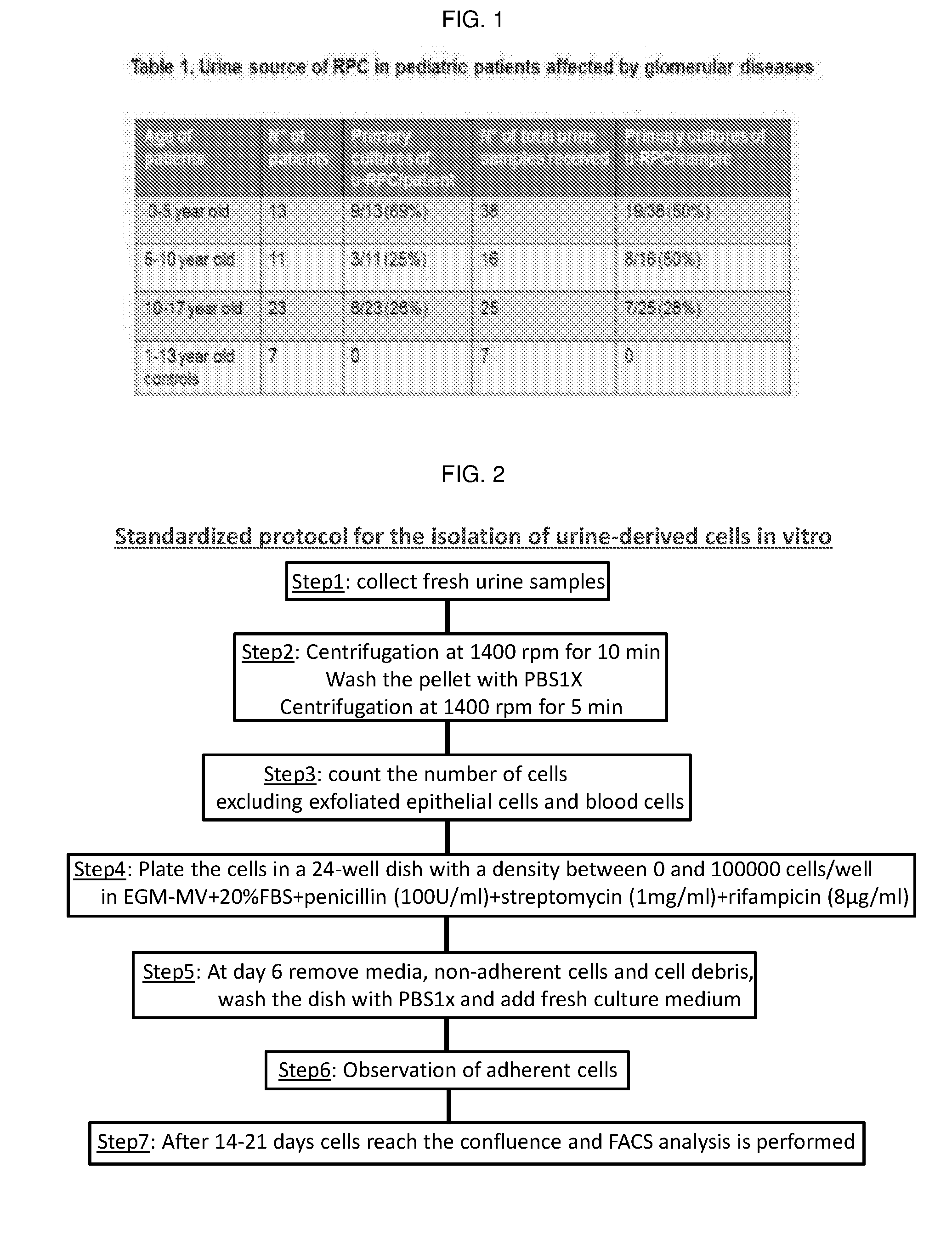
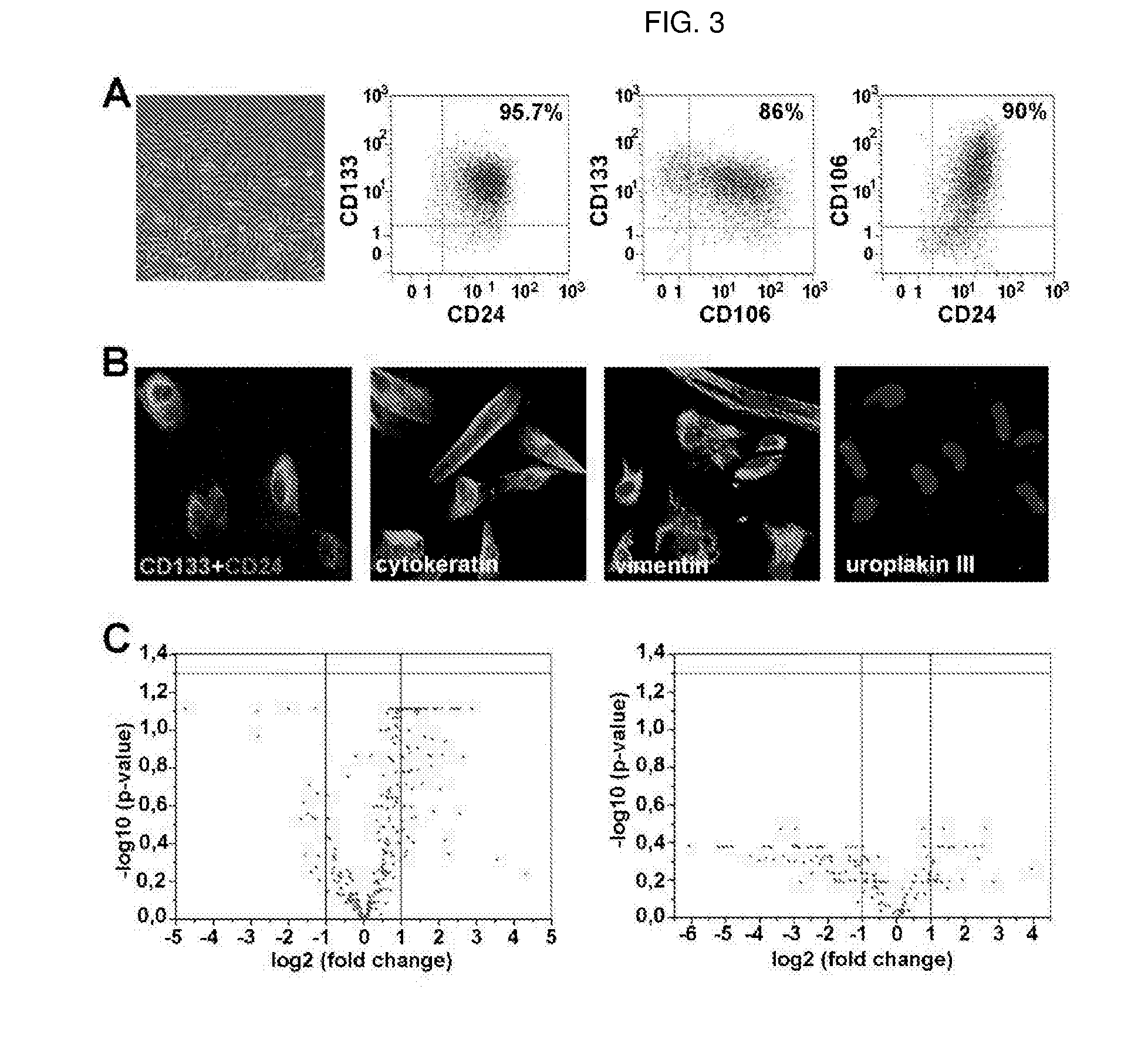
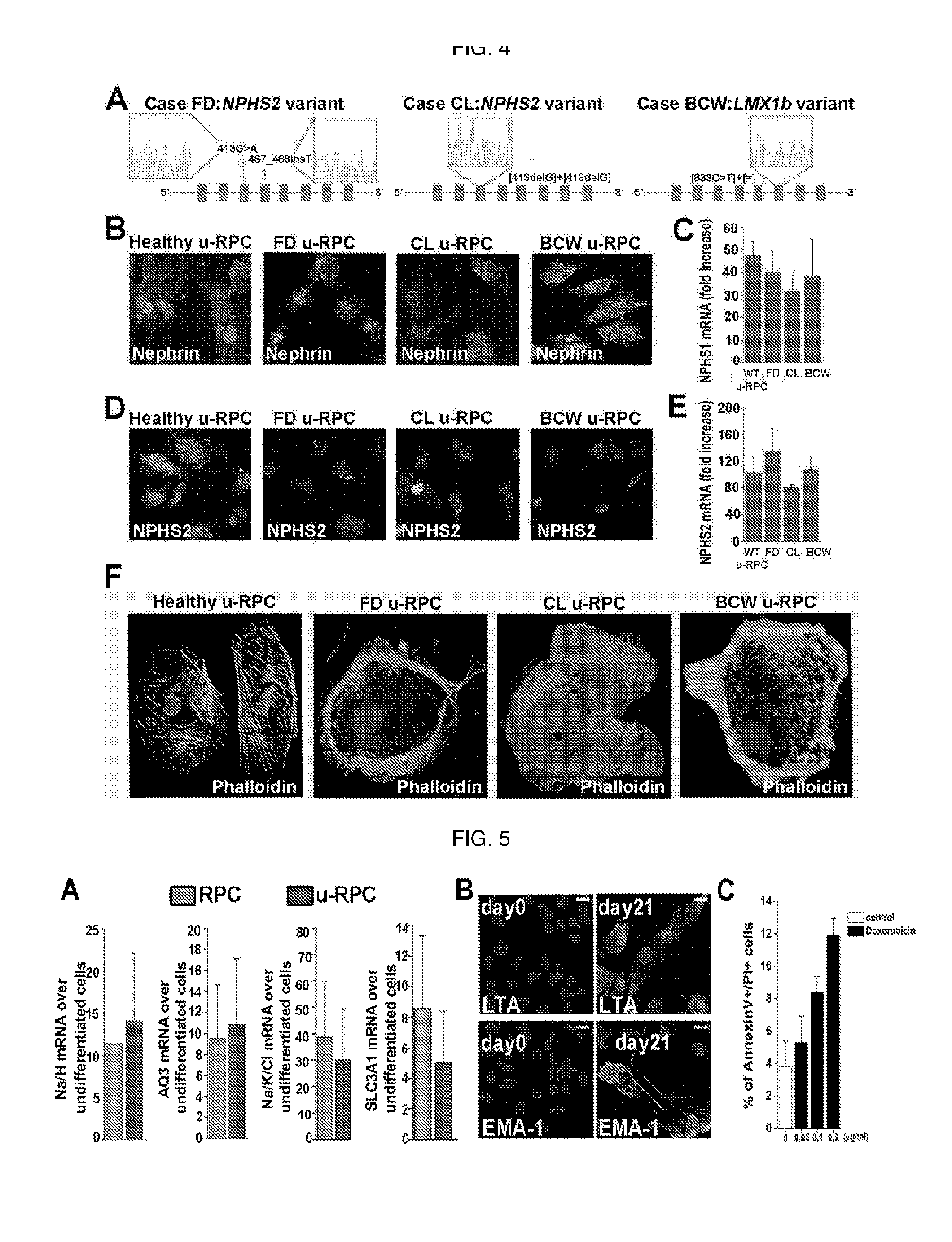
The present invention describes a non-invasive method to isolate with high efficiency, purity and reproducibility the population of renal progenitors CD133+CD24+, from urine samples of patients suffering from various glomerular diseases. Said renal progenitors can then easily be induced to differentiate into podocytes. The isolation of renal progenitors with the method of the invention allows the use of said cells as a cellular model of a disease for the in vitro study of genetic excluding exfoliated epithelial cells and blood cells mutations due to the podocyte or for the study of renal toxicity induced by potentially nephrotoxic drugs on the tubules.
Owner:AZIENDA OSPEDALIERO UNIVRIA MEYER
Method to identify ligands for sigma-1 receptors
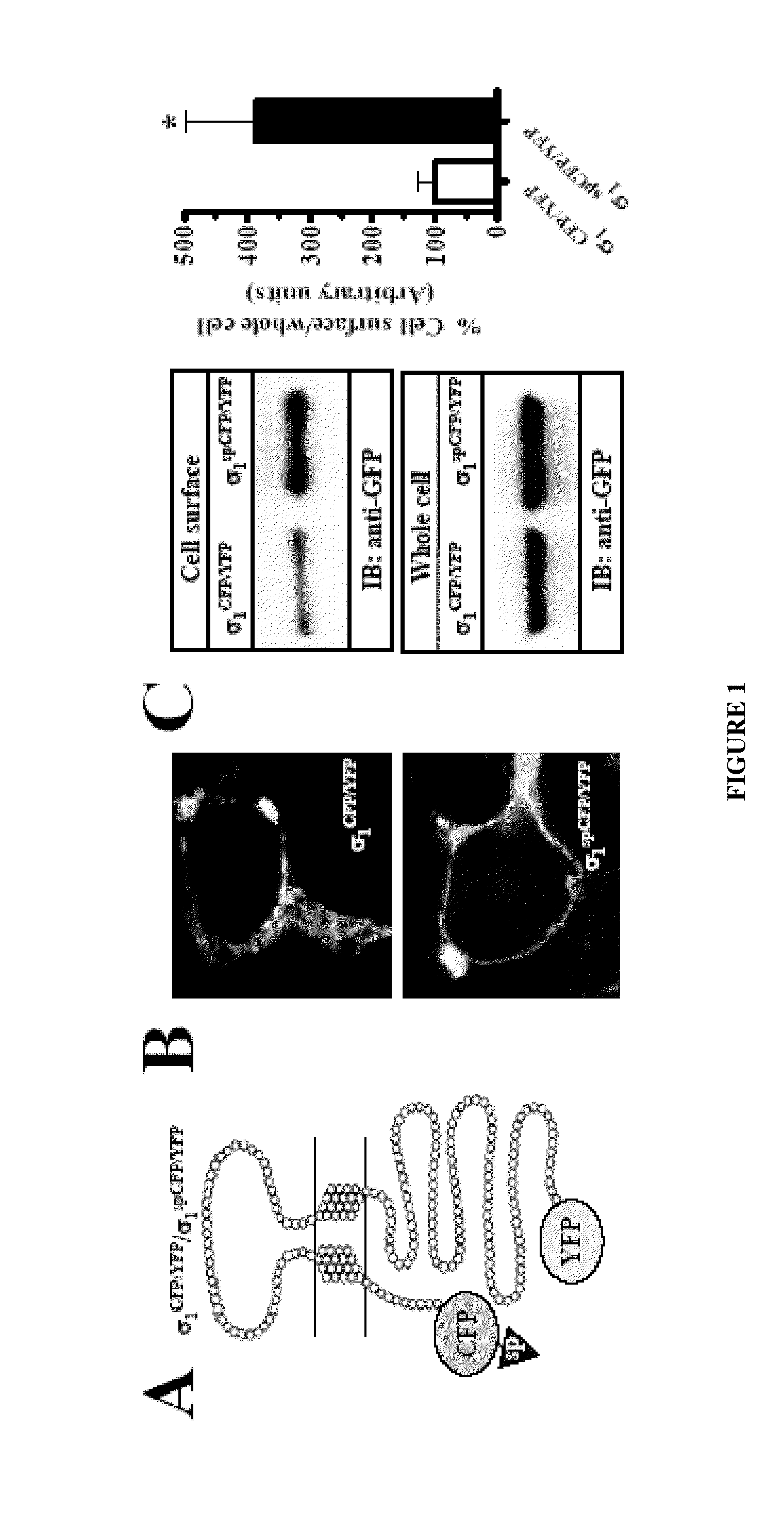
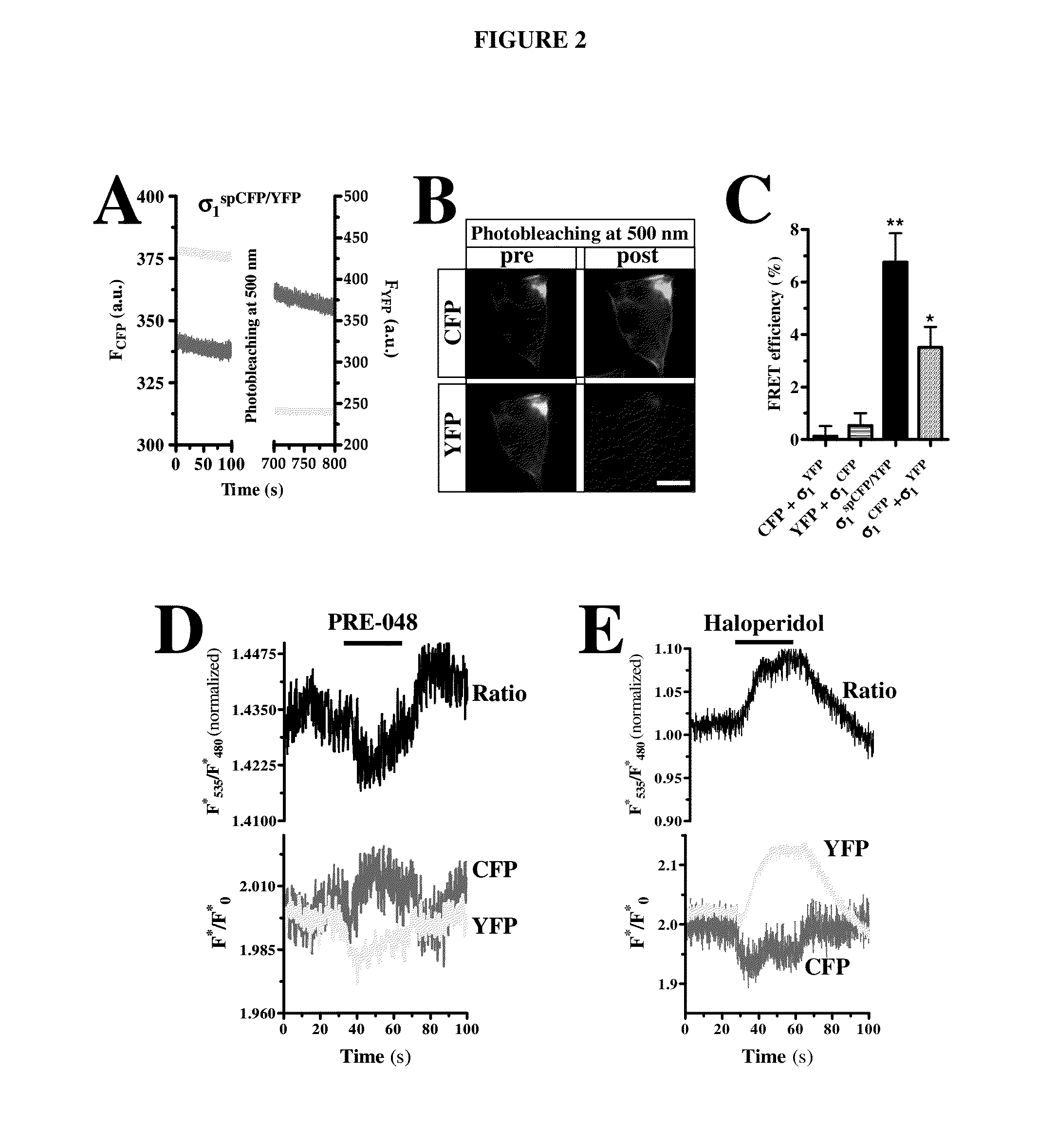
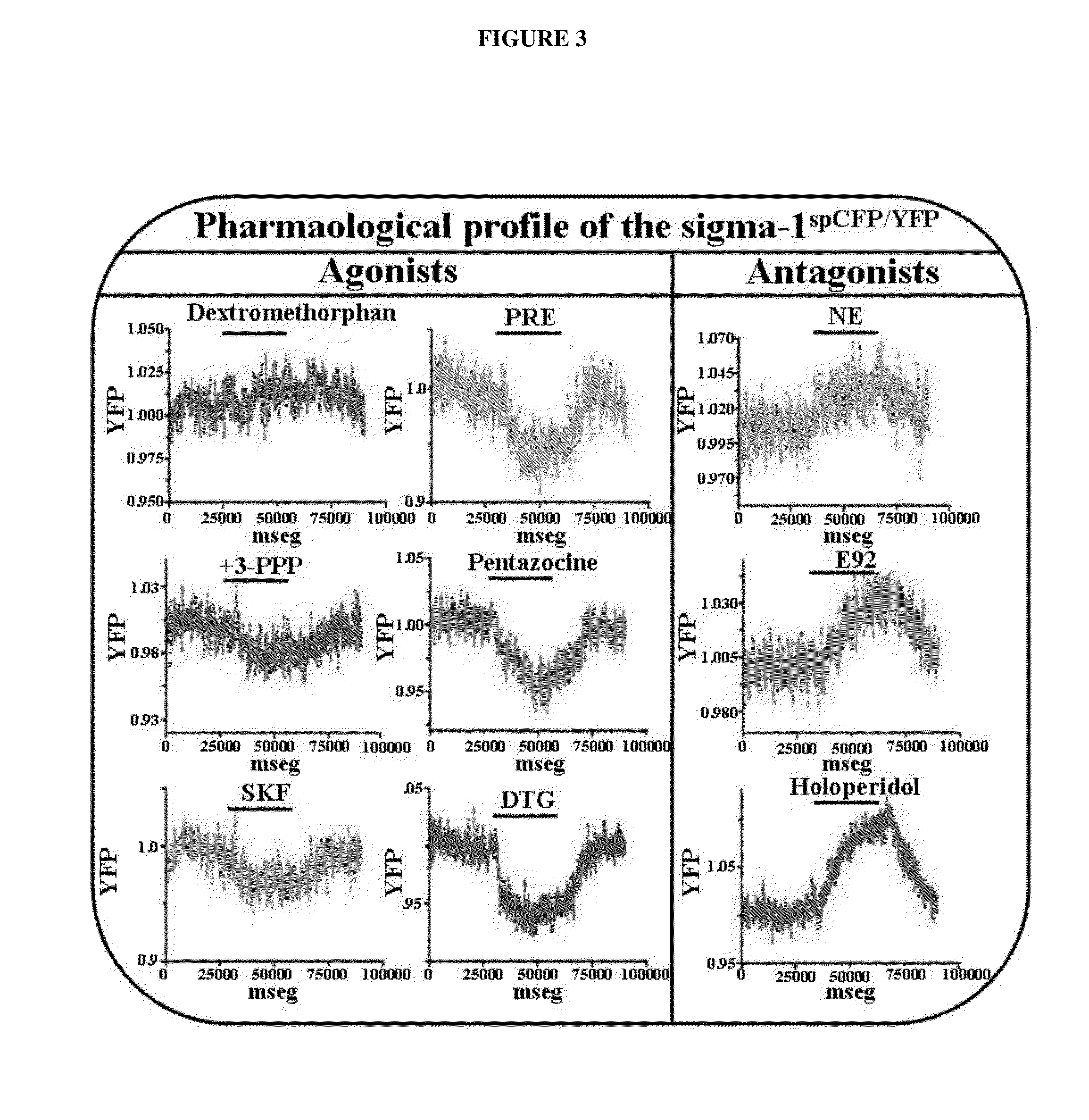
InactiveUS20150010917A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesCellular modelSigma-2 receptor
An assay for identifying ligands of the σ1 receptor based on a fusion protein comprising the σ1 receptor flanked by two fluorophores, so that said fluorophores are capable of producing constitutive FRET when no ligand is bound to the σ1 receptor. The fusion protein of the invention also allows the simultaneous determination whether the newly determined ligand is an agonist or an antagonist. Said fusion protein has been expressed in a cell, giving rise to a new cellular model useful for identifying σ1 receptor ligands, and additionally for discriminating between agonists and antagonists.
Owner:LAB DEL DR ESTEVE SA
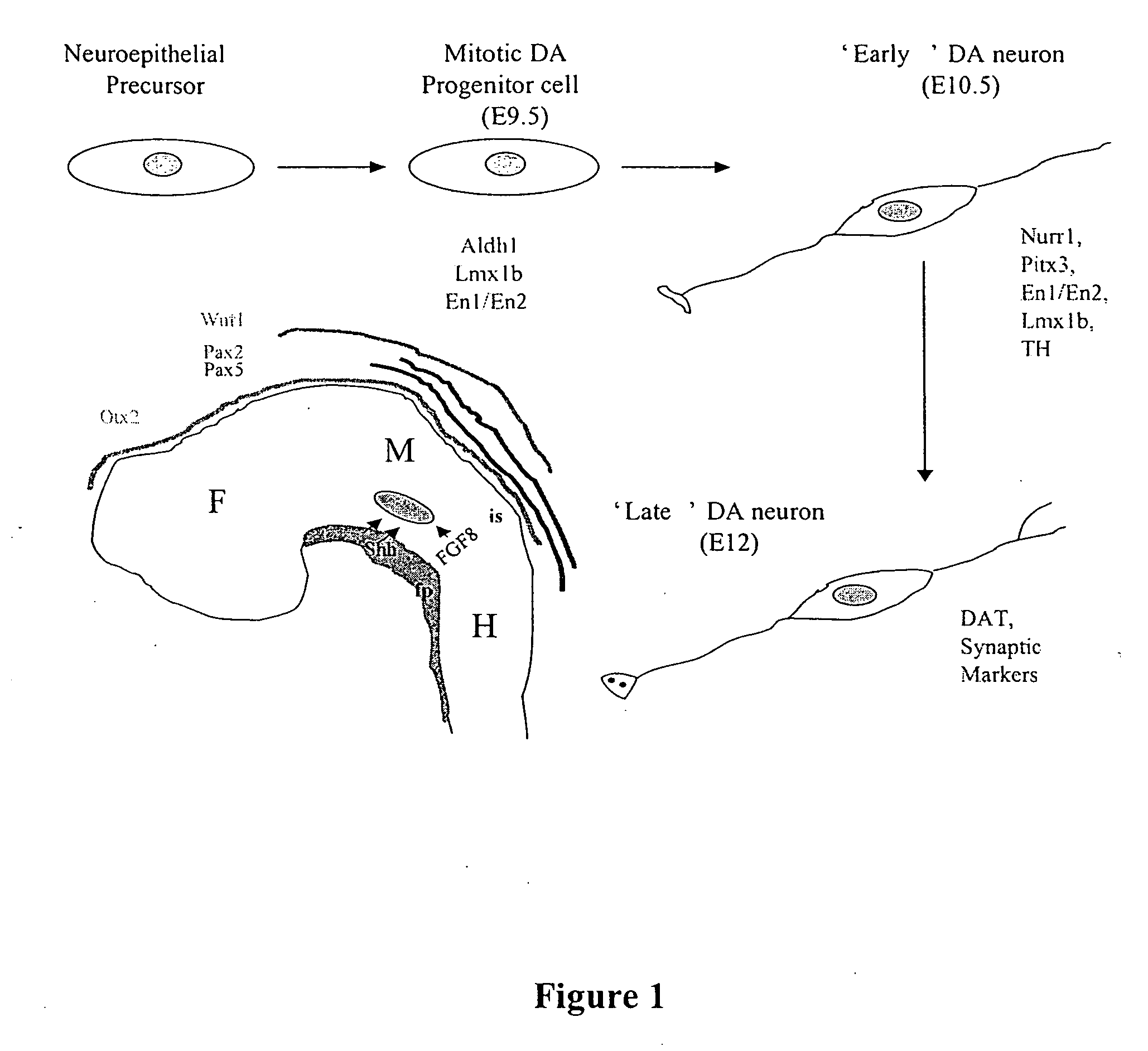
Cellular models of neuron-associated disorders and uses thereof
The present invention describes two new cell lines derived from embryonic stem cells and useful for analyzing and studying neuron-associated disorders. The present invention further relates to methods of analyzing stem cell differentiation, and methods of identifying new therapies for neuron-associated diseases
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Method and for wide track erasure in a hard disk drive
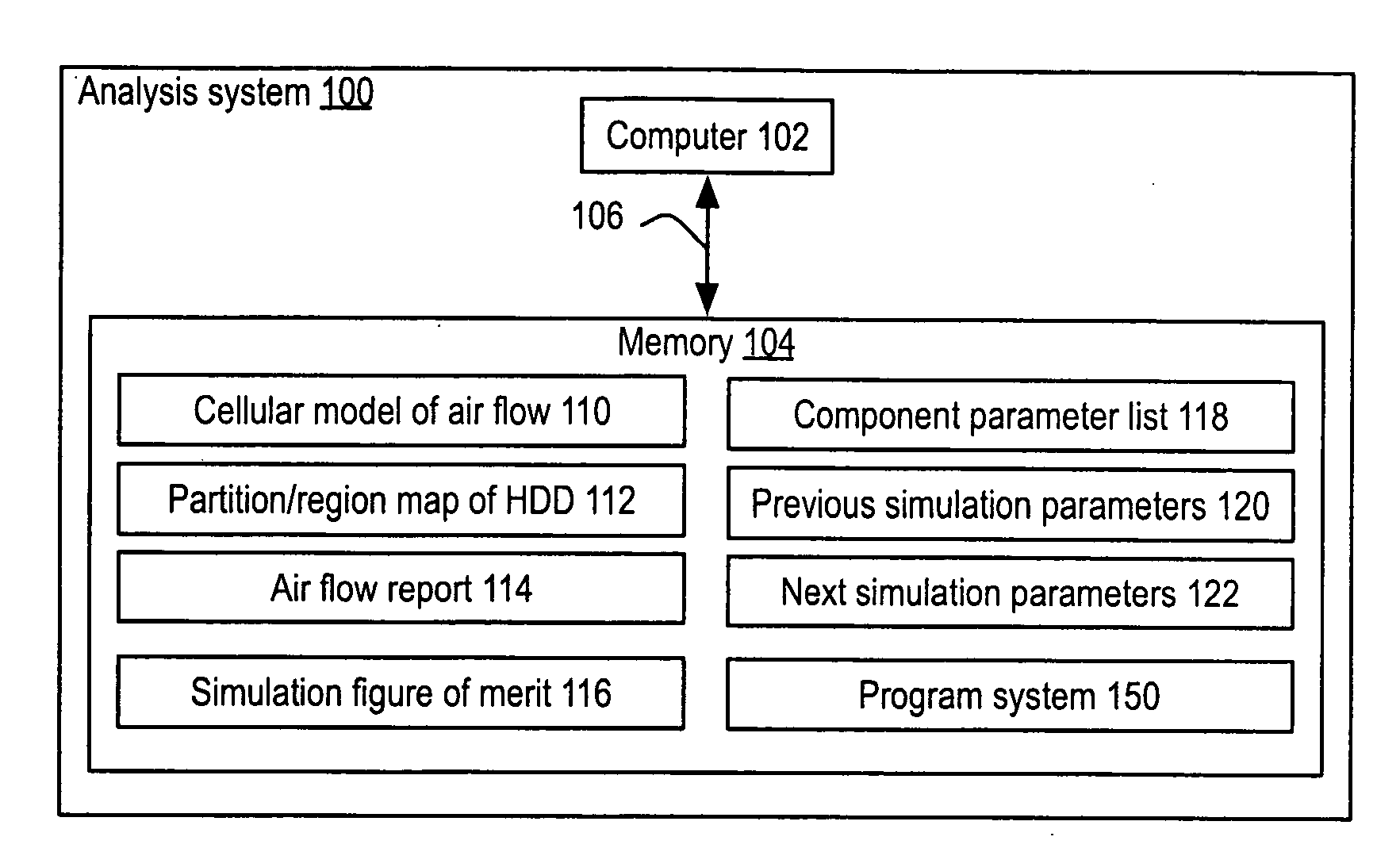
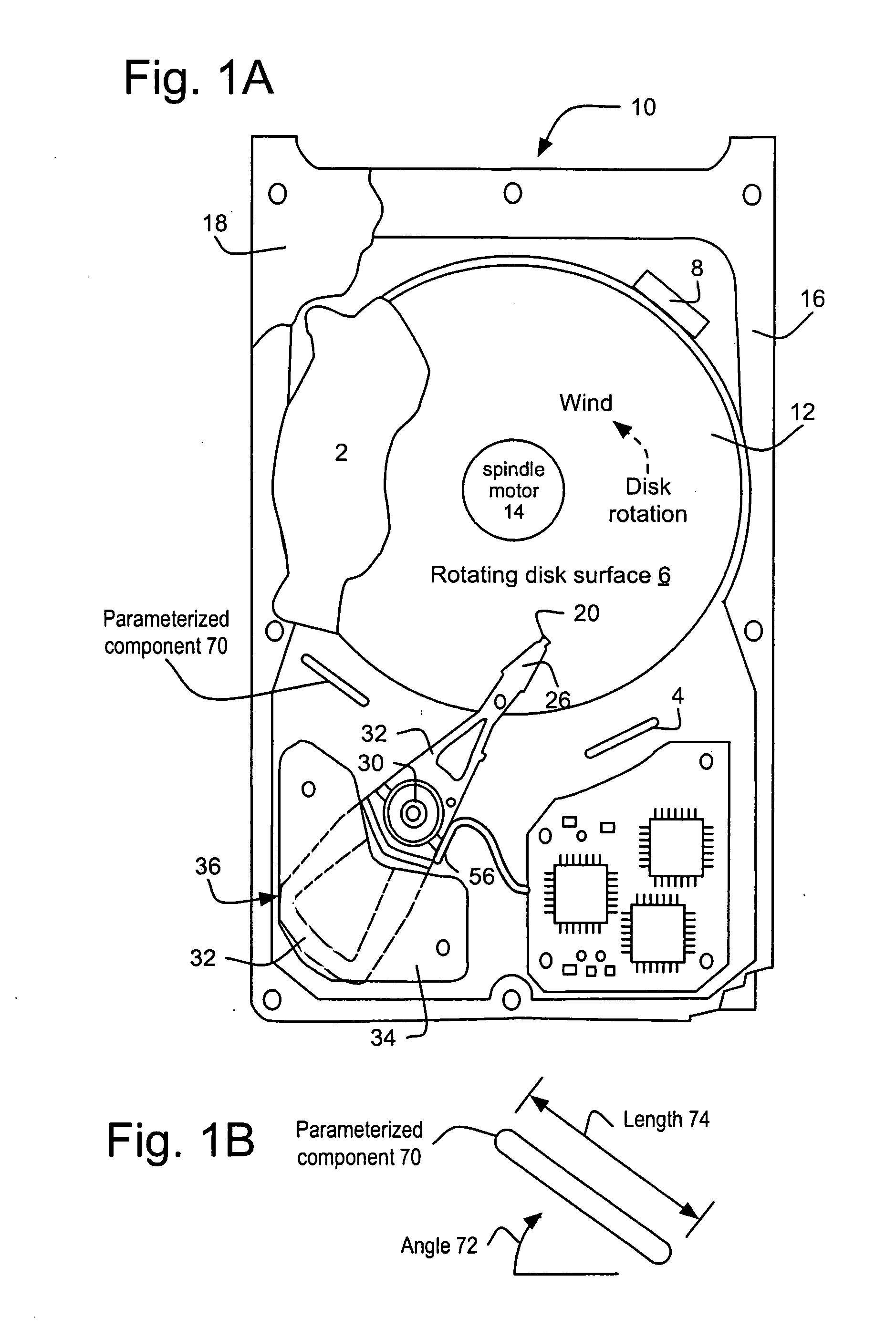
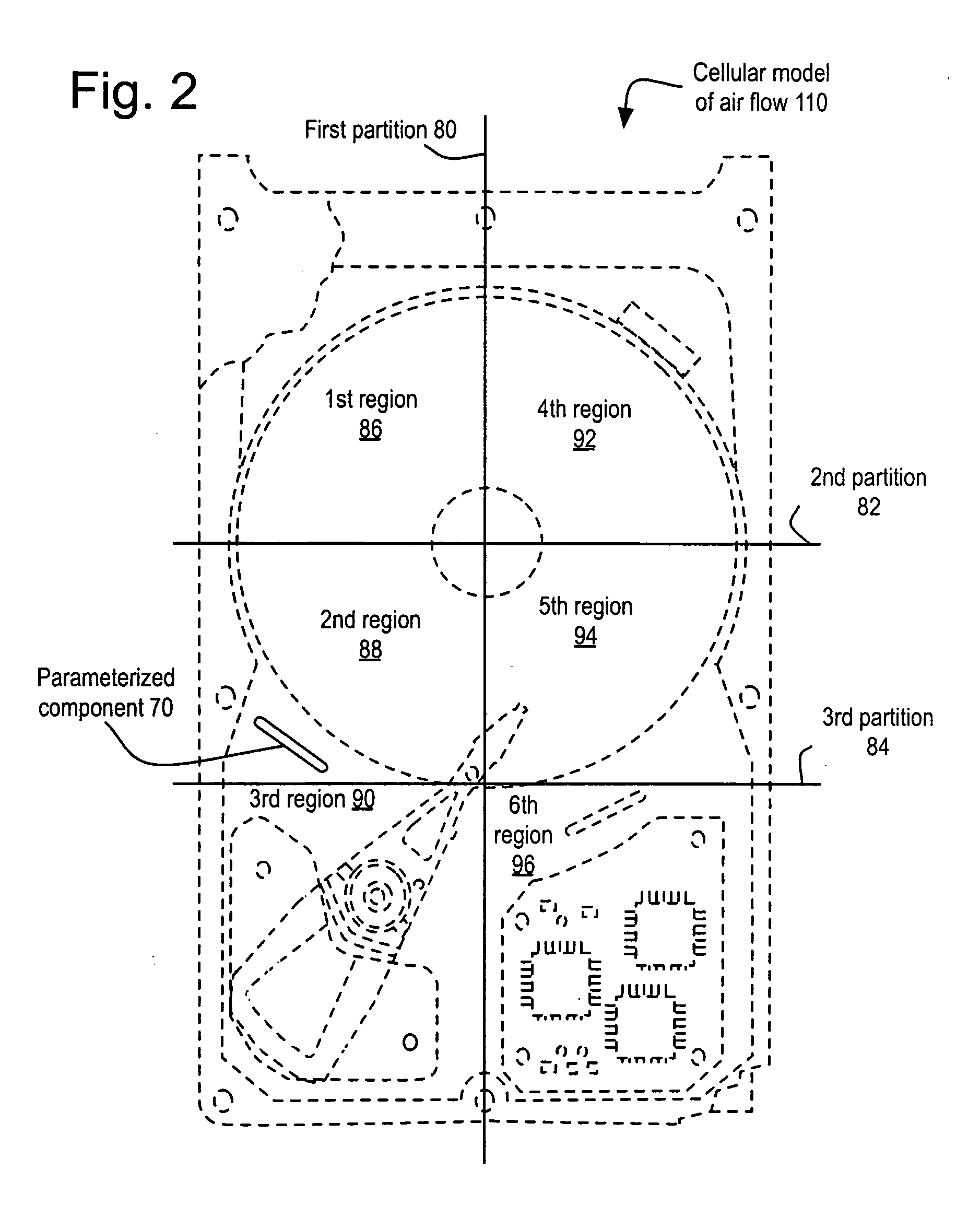
InactiveUS20090210206A1Cancel noiseImprove accuracyAnalogue computers for electric apparatusDesign optimisation/simulationHard disc driveCellular model
A method and its implementation as a program system are disclosed herein for generating an air flow report based upon a cellular model of the air flow of a hard disk drive including a parameterized component approximated by a component parameter list and a map of the partitioned regions of the hard disk drive. The air flow report is generated based upon the cellular model and a partition / region map. The partition / region map lumps the simulation domain into a small number of regions and then calculates the fluxes across boundaries of the regions. These fluxes accumulate the results of many individual cells, averaging out small variations caused by rounding and / or the convergence properties of the specific cellular approach used. A simulation figure of merit is calculated from the air flow report that further refines the accuracy, effectively removing even more noise.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
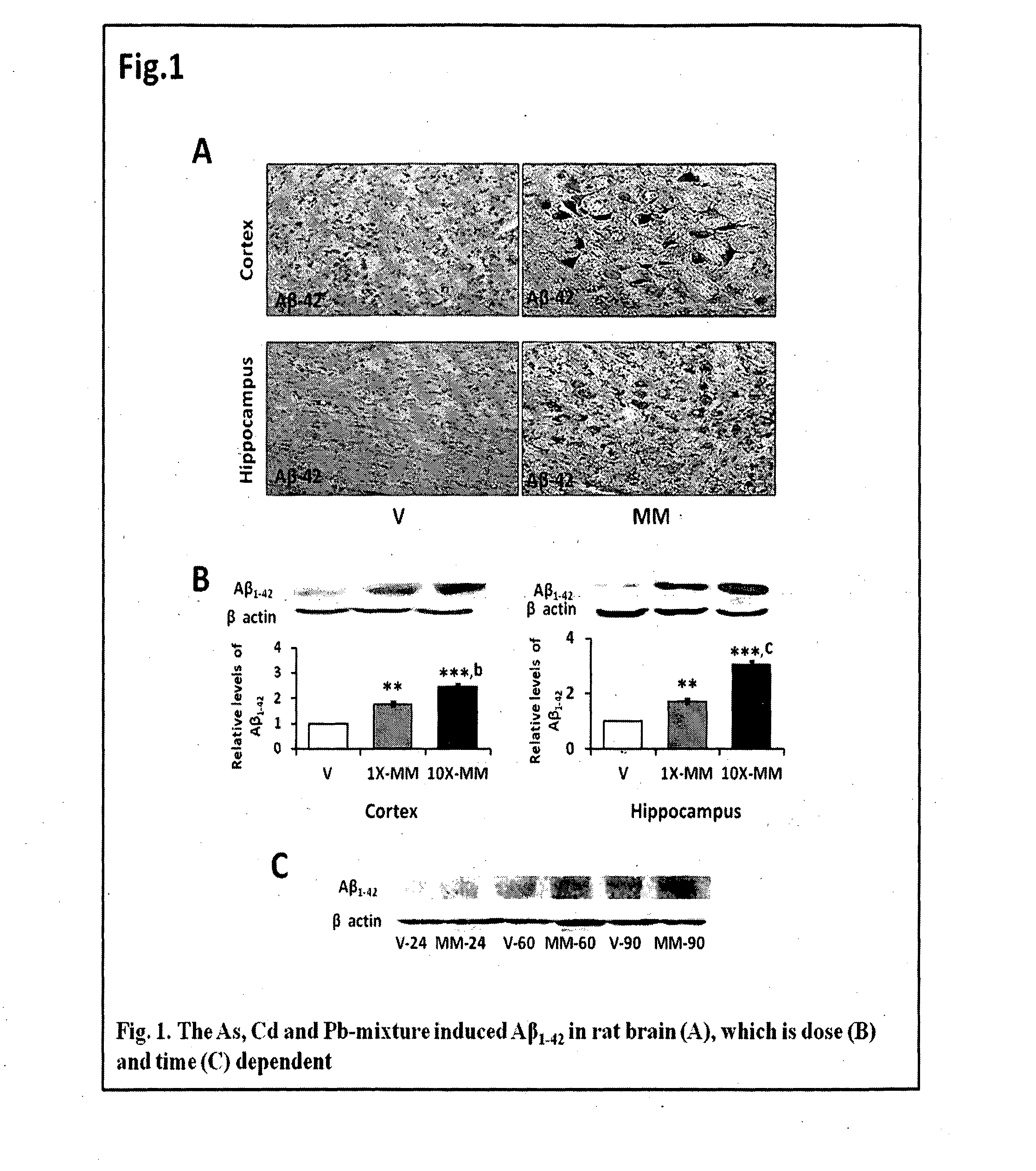
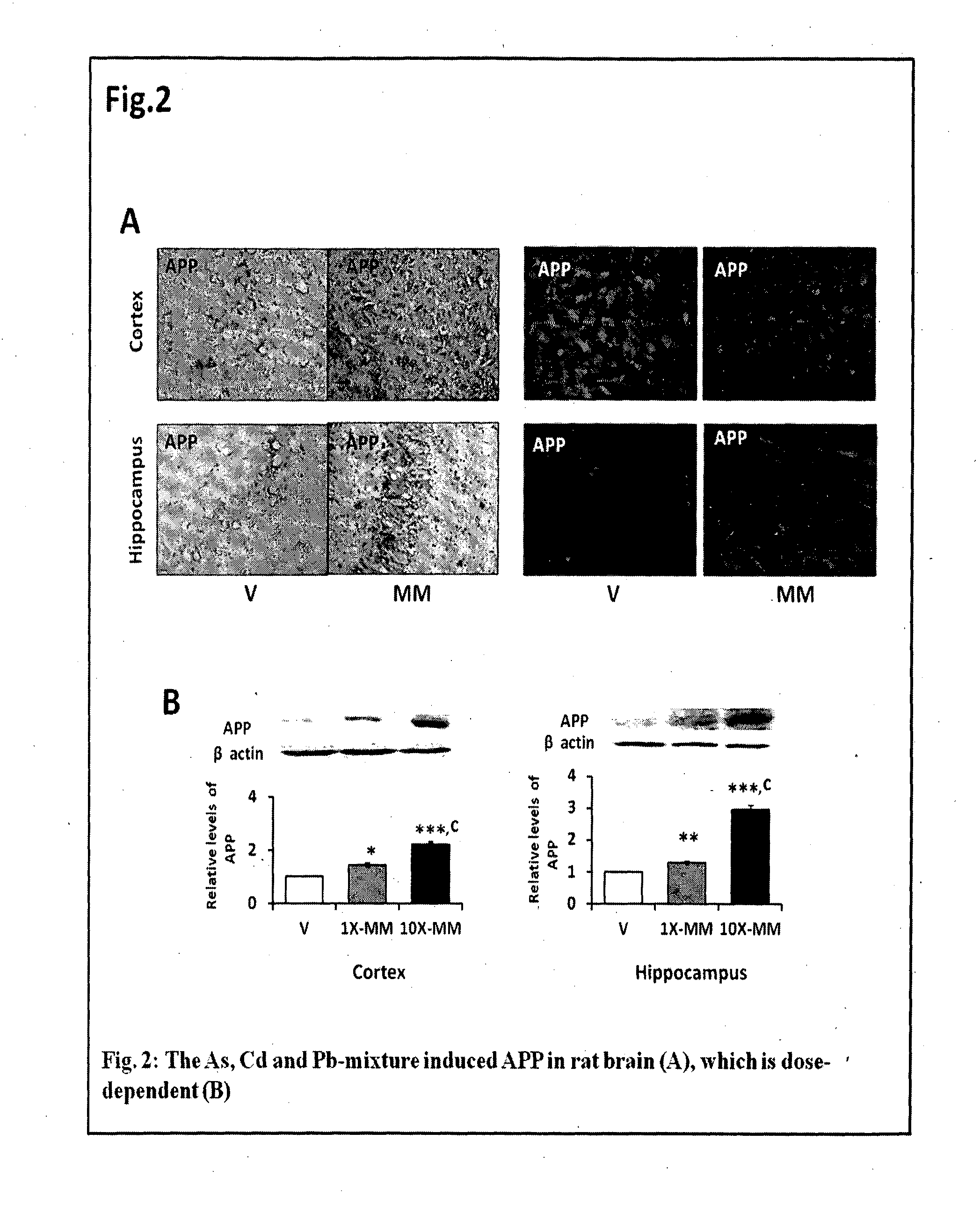
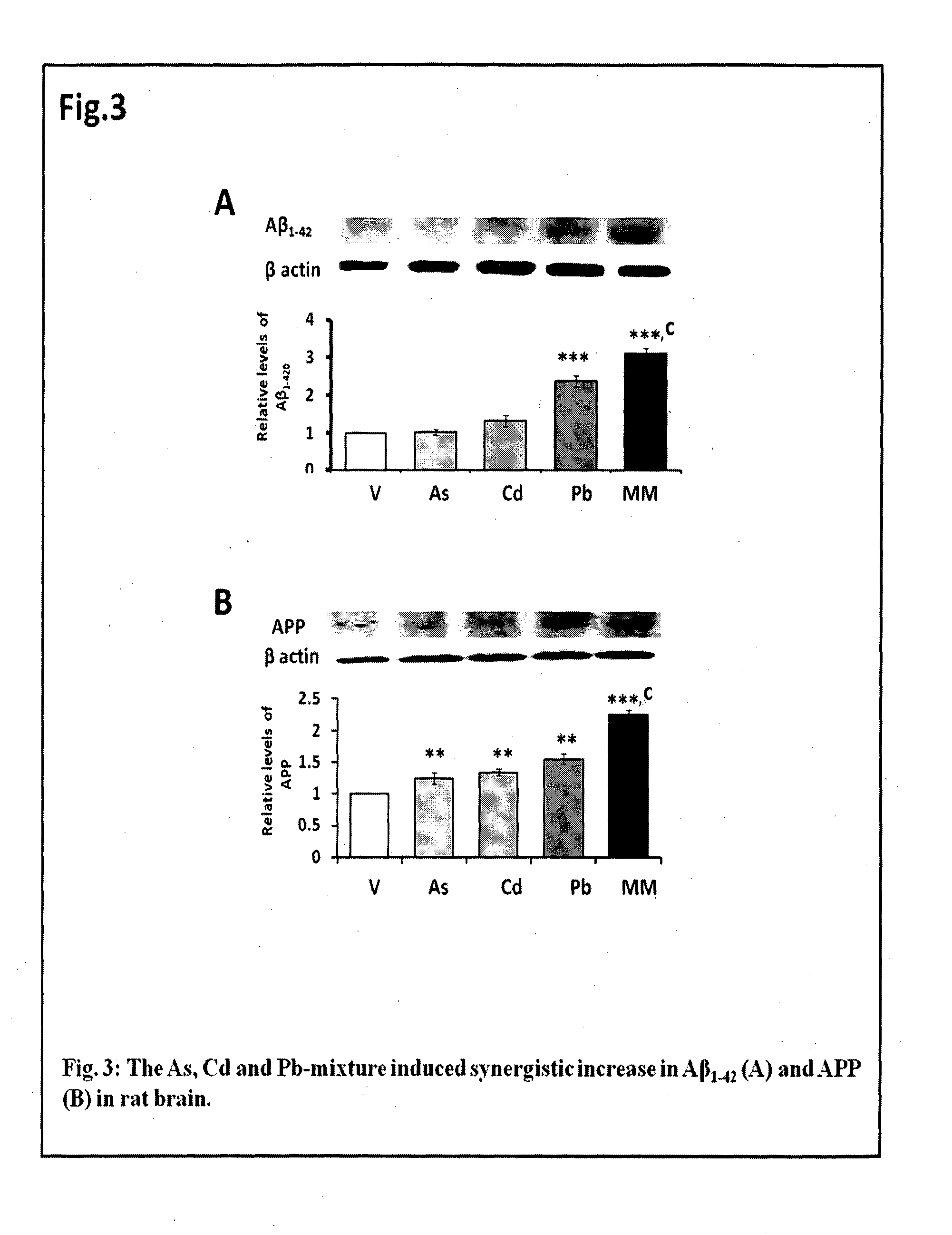
Model of alzheimer's disease
InactiveUS20160081312A1Synergistic effectReduce riskCompounds screening/testingHeavy metal active ingredientsCellular modelApoptosis
The invention features a non-transgenic rat model for early AD, using a metal mixture of As, Cd and Pb, characterized by enhanced synergistic amyloidogenicity in rat cortex and hippocampus. This model can serve as a tool for (a) AD-directed drug screening, and (b) determining mechanism of AD pathogenicity. It features induction of the A?-mediated apoptosis and induction of inflammation in rodent brain. The invention features novel astrocyte and neuronal cellular models for AD, using a metal mixture of As, Cd and Pb, characterized by enhanced synergistic amyloidogenicity. This model can serve as a tool for (a) AD-directed drug screening in astrocytes and neurons, and (b) determining mechanism of AD pathogenicity in cells. It features induction of the A?-mediated apoptosis and induction of inflammation in astrocytes and neurons.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
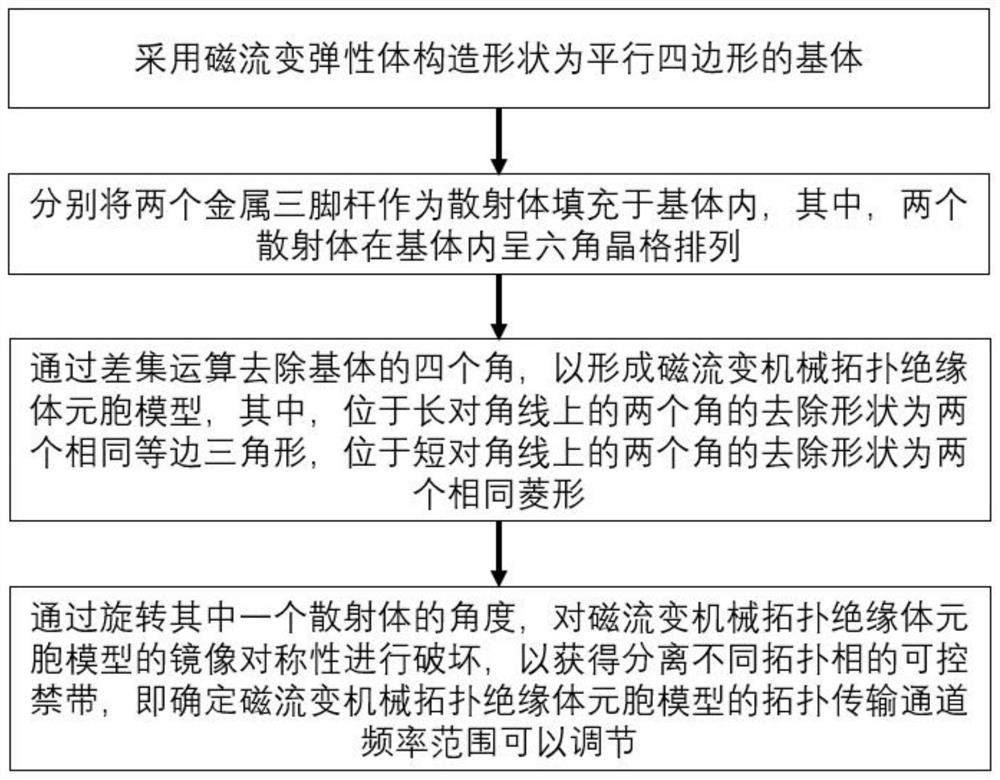
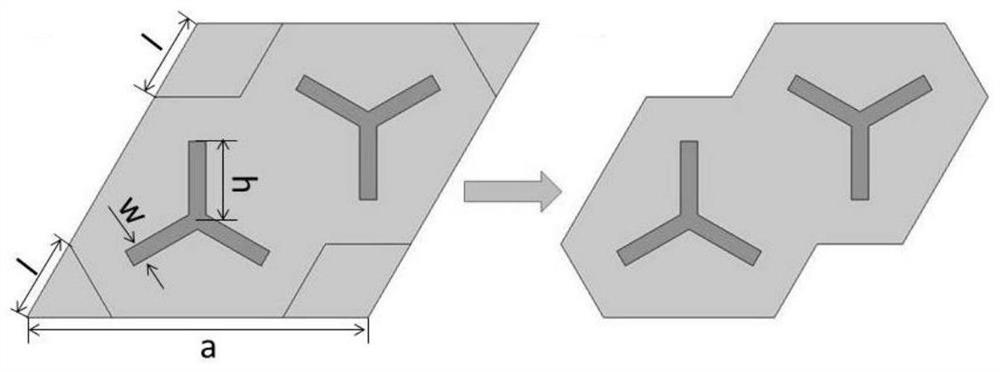
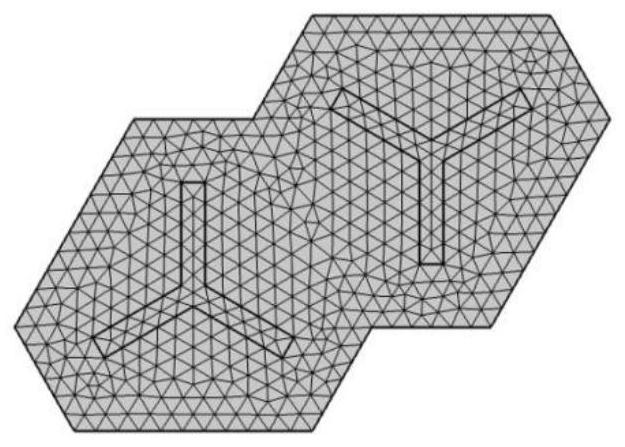
Design method of topological insulator cellular model of magneto-rheological machine
The invention discloses a design method of a topological insulator cellular model of magnetorheological machinery. The design method comprises the following steps: constructing a parallelogram-shaped matrix by adopting a magnetorheological elastomer; using the two metal three-legged rods as scatterers to be filled in the base body; removing four corners of the matrix through difference set operation to form a topological insulator cellular model of the magneto-rheological machine; and destroying the mirror symmetry of the magnetorheological mechanical topological insulator cellular model by rotating the angle of one scatterer, so that a controllable forbidden band for separating different topological phases is obtained, that is, the frequency range of a topological transmission channel of the magnetorheological mechanical topological insulator cellular model is determined to be adjustable. According to the invention, the magneto-rheological mechanical topological insulator cellular model with an adjustable topological transmission channel frequency range is constructed by using the magneto-rheological elastomer as a matrix and the metal tripod as a scatterer in the matrix, so that the model is suitable for complex and changeable actual conditions.
Owner:ZAOZHUANG UNIV
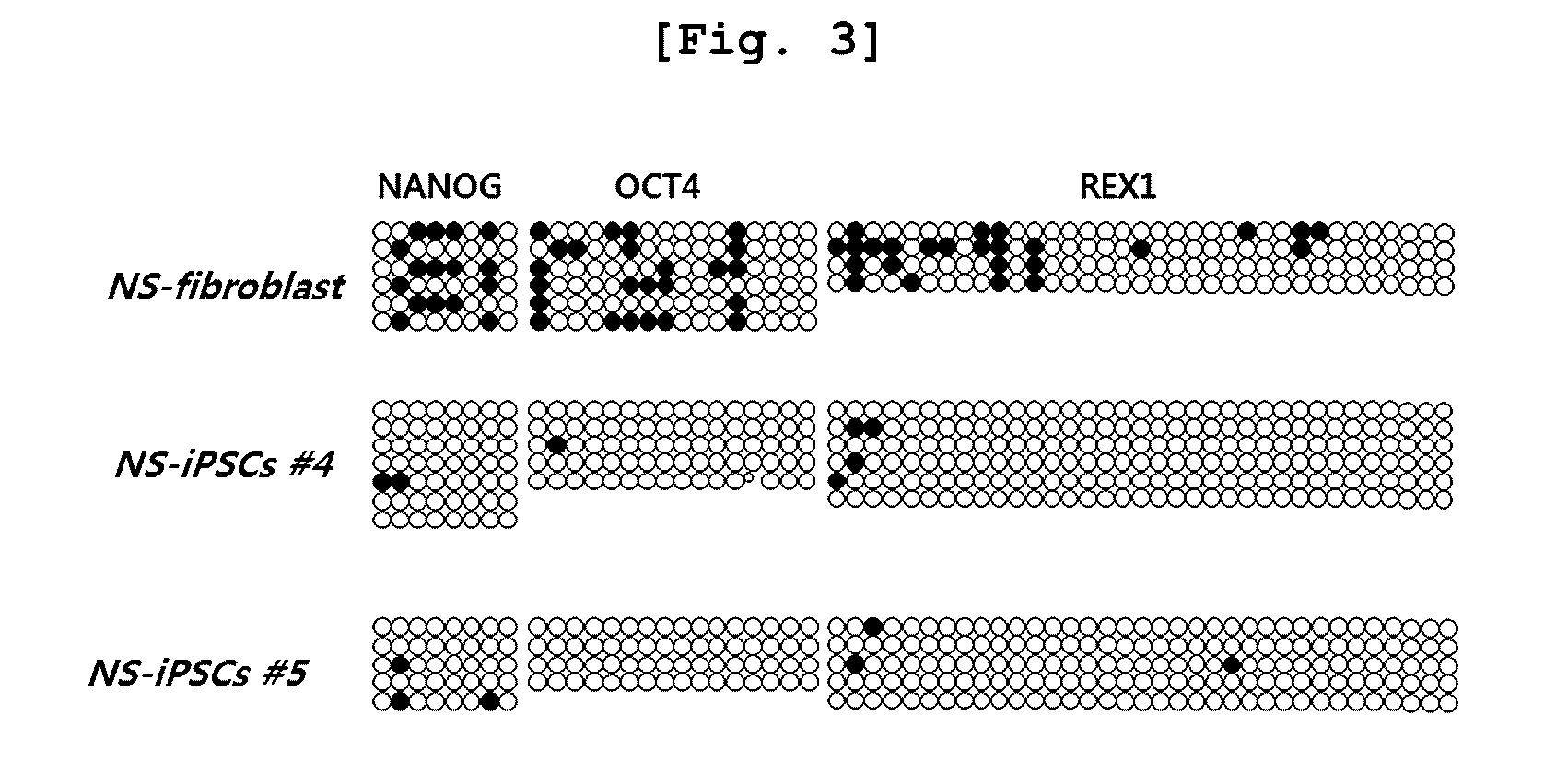
Induced pluripotent stem cell model of noonan syndrome and use thereof
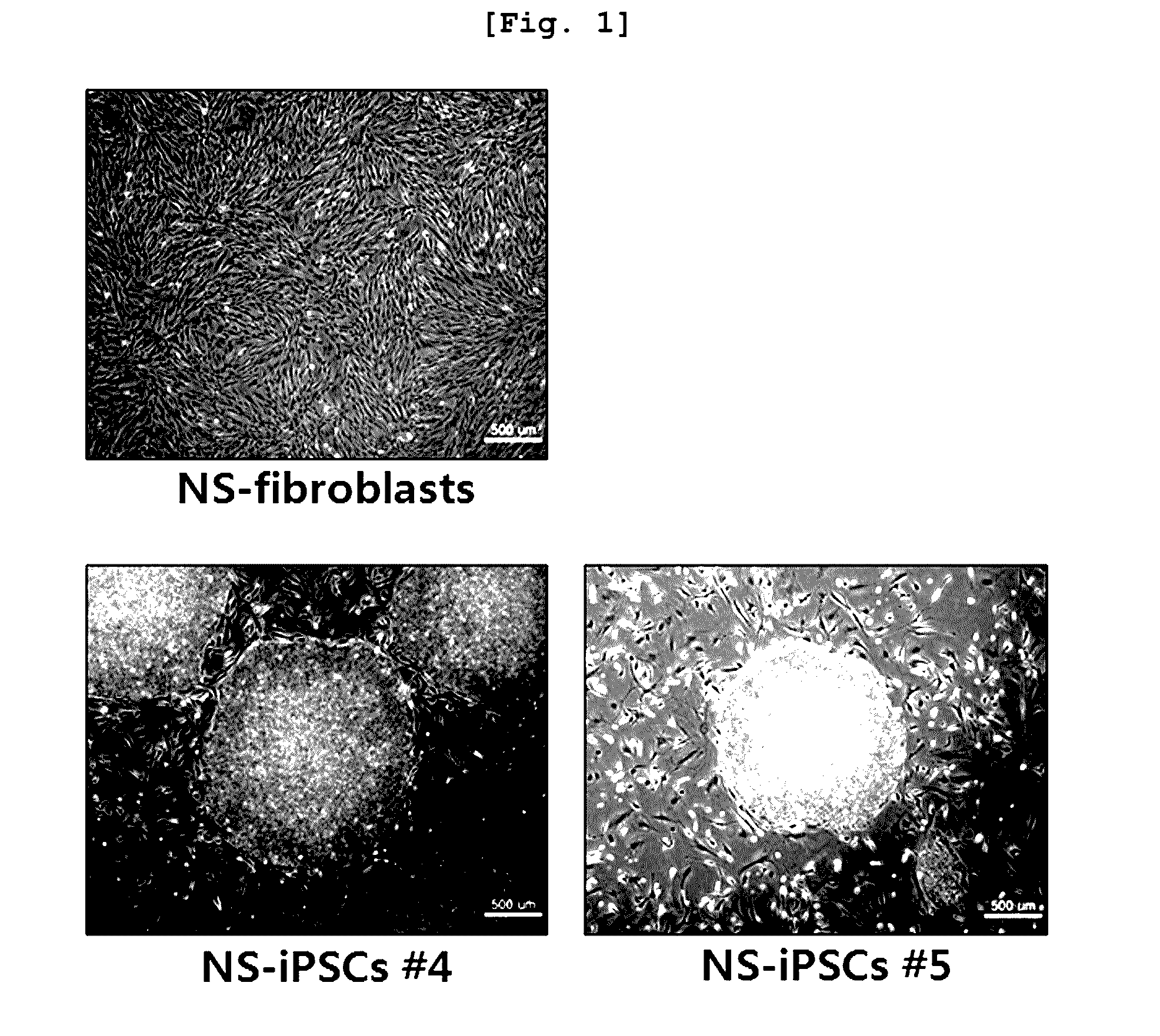
InactiveUS20170016886A1Reduce expressionEasy to useNervous system cellsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsGerm layerNeural cell
The present invention relates to an induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) model of Noonan syndrome, a preparation method thereof, and uses to study of the pathogenesis of Noonan syndrome and a therapeutic agent screening method. Particularly, induced pluripotent stem cells from dermal fibroblasts of a Noonan syndrome-patient (NS-iPSCs) were generated, and differentiated into embryoid bodies (EBs), neural rosettes and neural cells. These iPSCs exhibited the normal morphology while showed reduced differentiation potency compare to control cell lines. NS-iPSCs were developed into embryoid bodies and neural rosettes by naturally and chemically directed differentiation. Interestingly, embryoid bodies and neural rosettes induced via chemically directed differentiation exhibited normal morphology and expressed ectoderm, neural rosettes and neural marker genes similar to normal cells. Thus, the cellular model can be useful in analytical research to understand pathogenesis of Noonan syndrome and establish screening method of the therapeutic agent.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
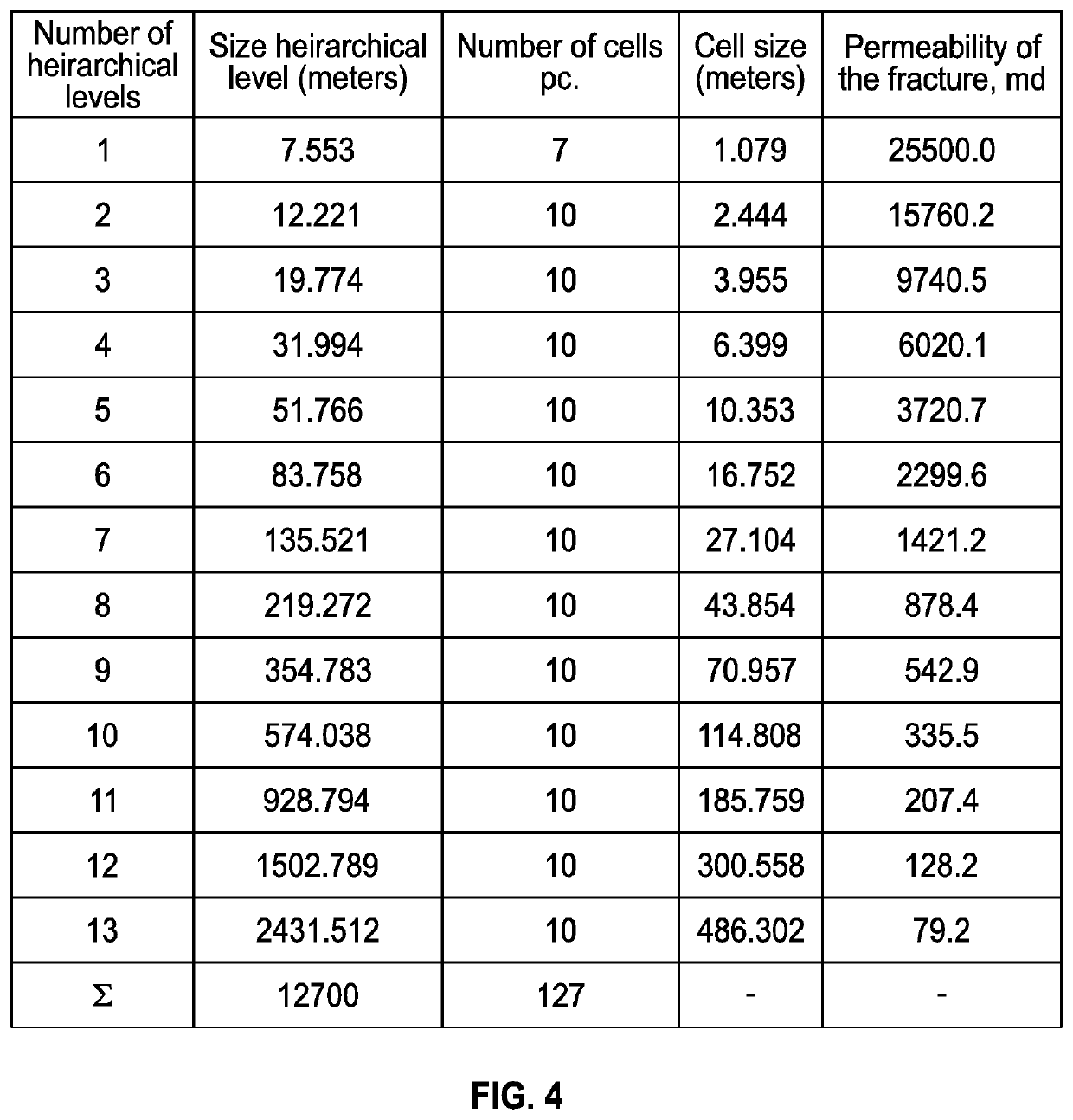
Discrete irregular cellular models for simulating the development of fractured reservoirs
ActiveUS10846443B2Reduce in quantityFluid removalDesign optimisation/simulationCellular modelReservoir modeling
An electronically stored model for a reservoir can include a plurality of hierarchical levels and a plurality of cells representing corresponding portions of the reservoir. The model can include a dimension and a cell number corresponding to the reservoir. A dimension of a cell of an nth hierarchical level can be defined in terms of a dimension of a cell of a first hierarchical level and an array of vertex coordinates along one or more axes can be generated. The model can include a ratio of dimensions among hierarchical levels for improved reservoir modeling. The model can include a ratio of permeability among hierarchical levels for improved reservoir modeling.
Owner:PETROLEUM FRACTURED RESERVOIR SOLUTIONS
Cell BHK/slam/v based on a small ruminant pestilence virus receptor
PendingCN109266615AImprove cloning efficiencyEfficient removalImmunoglobulin superfamilyGenetically modified cellsTiterCellular model
The invention provides a cell BHK / slam / v based on a small ruminant pestilence virus receptor, the accession number of which is CCTCC NO:C201739, and a small ruminant pestilence virus receptor-goat lymphocyte signaling activation factor V (GLSAF-V) expressed by the cell can enhance the small ruminant pestilence virus replication function, overexpressing of specific cell receptors of the small ruminant pestilence virus by the cell shortens the time of virus collection (from 4-7 days to 3-4 days), the viral titer of small ruminant pestilence virus was increased (ct value increased from 20.19 to 17.01), the copy number of the same volume virus was also increased (copy number increased from 5.6*10<6> to 4.9*10<8>), and the cost was saved. It provides a good tool for isolation of small ruminantpestilence virus and production of vaccine virus, and also provides a cellular model for the study of pathogenesis of small ruminant pestilence virus. The invention also provides the preparation and application of the cell.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
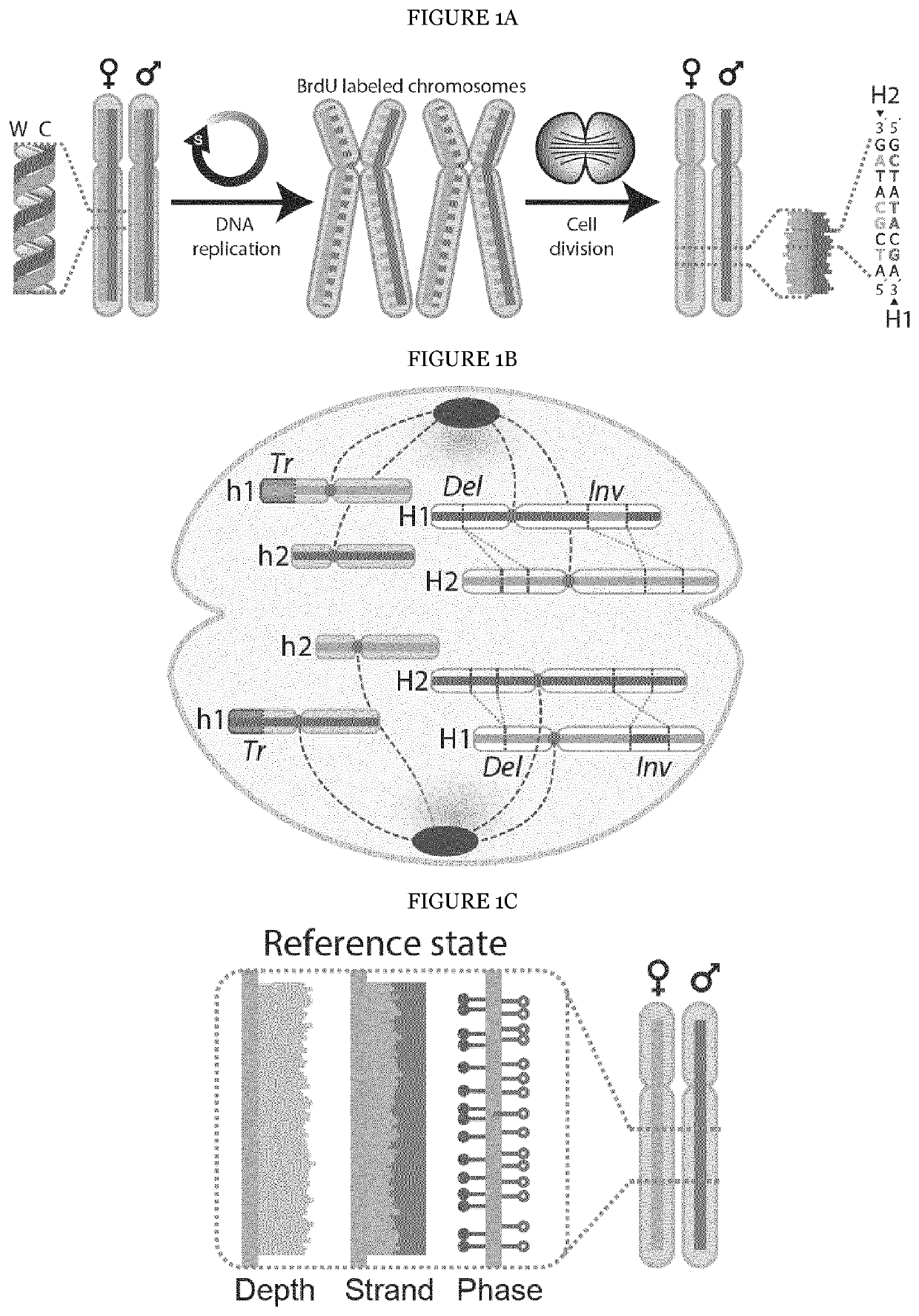
Comprehensive detection of single cell genetic structural variations
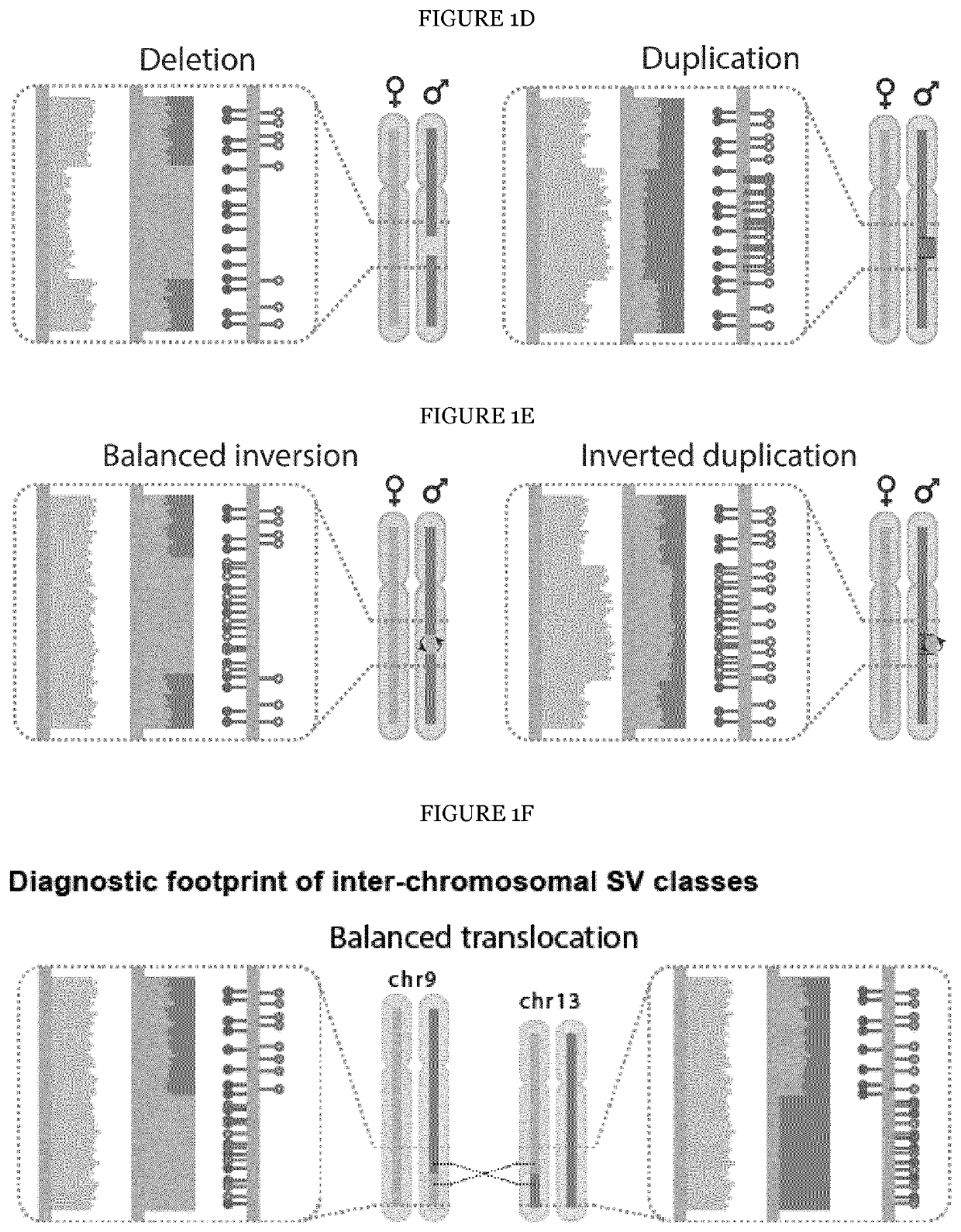
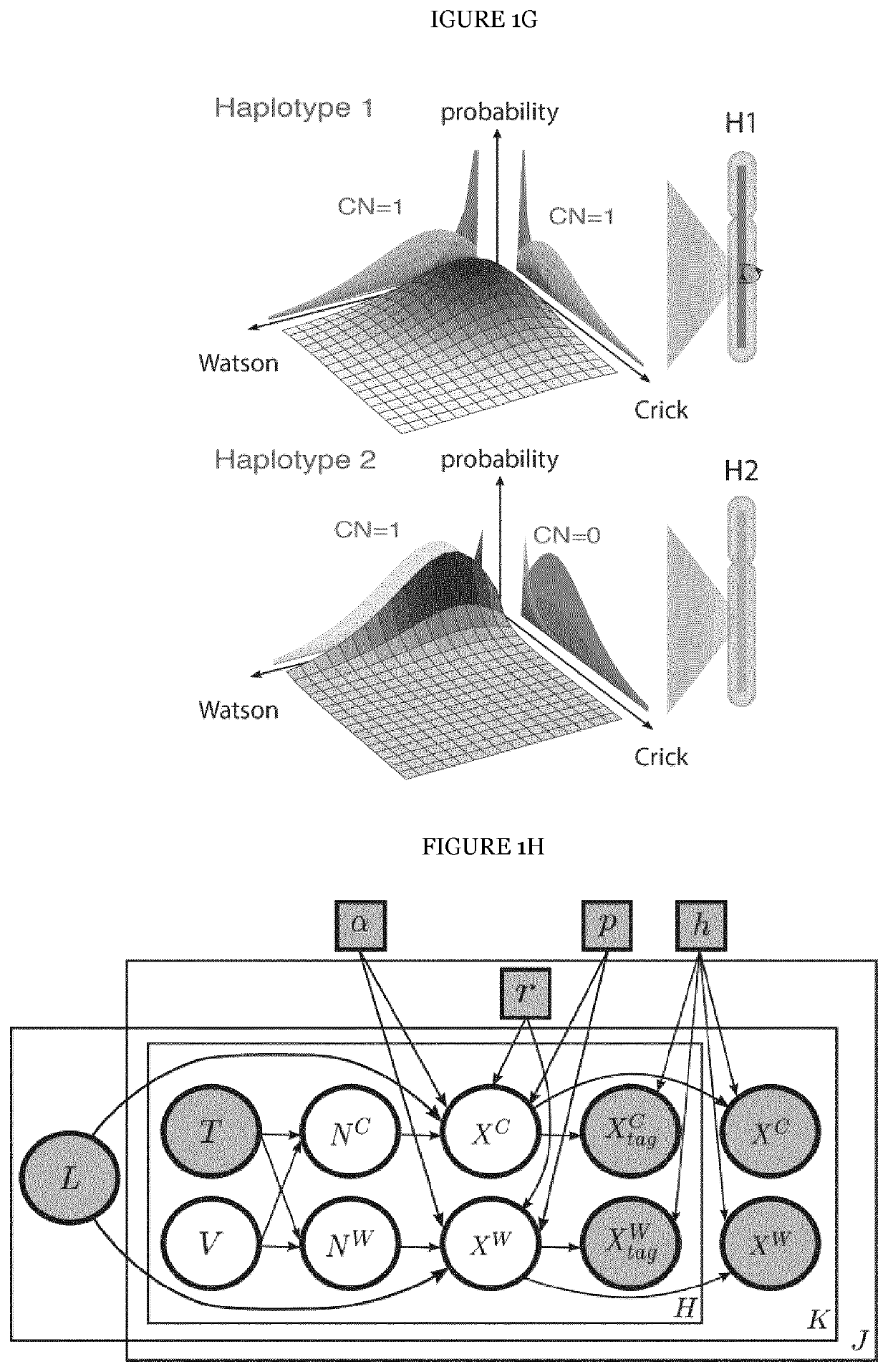
The present invention provides a method for detecting structural variations (SV) within genomes of single cells or population of single cells by integrating a three-layered information of sequencing read depth, read strand orientation and haplotype phase. The method of the invention can detect deletions, duplications, polyploidies, translocations, inversions, and copy number neutral loss of heterozygosity (CNN-LOH), and more. The method of the invention can fully karyotype a genome comprehensively, and may be applied in research and clinical approaches. For example, the methods of the invention are useful for analysing cellular samples of patients for diagnosing or aiding a diagnosis, in reproductive medicine to detect embryonic abnormalities, or during therapeutic approaches based on cellular therapies to quality control genetically engineered cells, such as in adoptive T cell therapy and others. The method of the invention may further be applied in research to decipher the karyotypes of cellular models (cell lines), patient samples, or to further unravel genetic and mechanistic pathways leading to the generation of any SV within genomes.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV +2
Cell BHK/slam based on small ruminant animal disease virus receptor
PendingCN109266614AImprove cloning efficiencyEfficient removalGenetically modified cellsPeptidesCellular modelVaccine virus
The invention provides a cell BHK / slam based on a small ruminant animal disease virus receptor, which is deposited under the accession number of CCTCC NO:C201895, and the small ruminant pestilence virus receptor-intact goat lymphocyte signal activation factor ORF expressed by the cell Is complete and has a function of significantly enhancing the replication of small ruminant animal disease virus,the cell shortens the time of virus collection after cytopathic lesions(from 4-7 days to 3-4 days) through overexpressing of specific cell receptors of the small ruminant animal disease virus, the viral titer of small ruminant animal disease virus (ct value increased from 20.66 to 16.91) is improved, the copy number of the same volume virus (copy number increased from 4.1*10<7> to 5.3*10<8>) wereincreased significantly, and the cost was saved. It provides a good tool for isolation of small ruminant animal disease virus and production of vaccine virus, and also provides a cellular model for the study of pathogenesis of small ruminant animal disease virus. The invention also provides the preparation and application of the cell.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
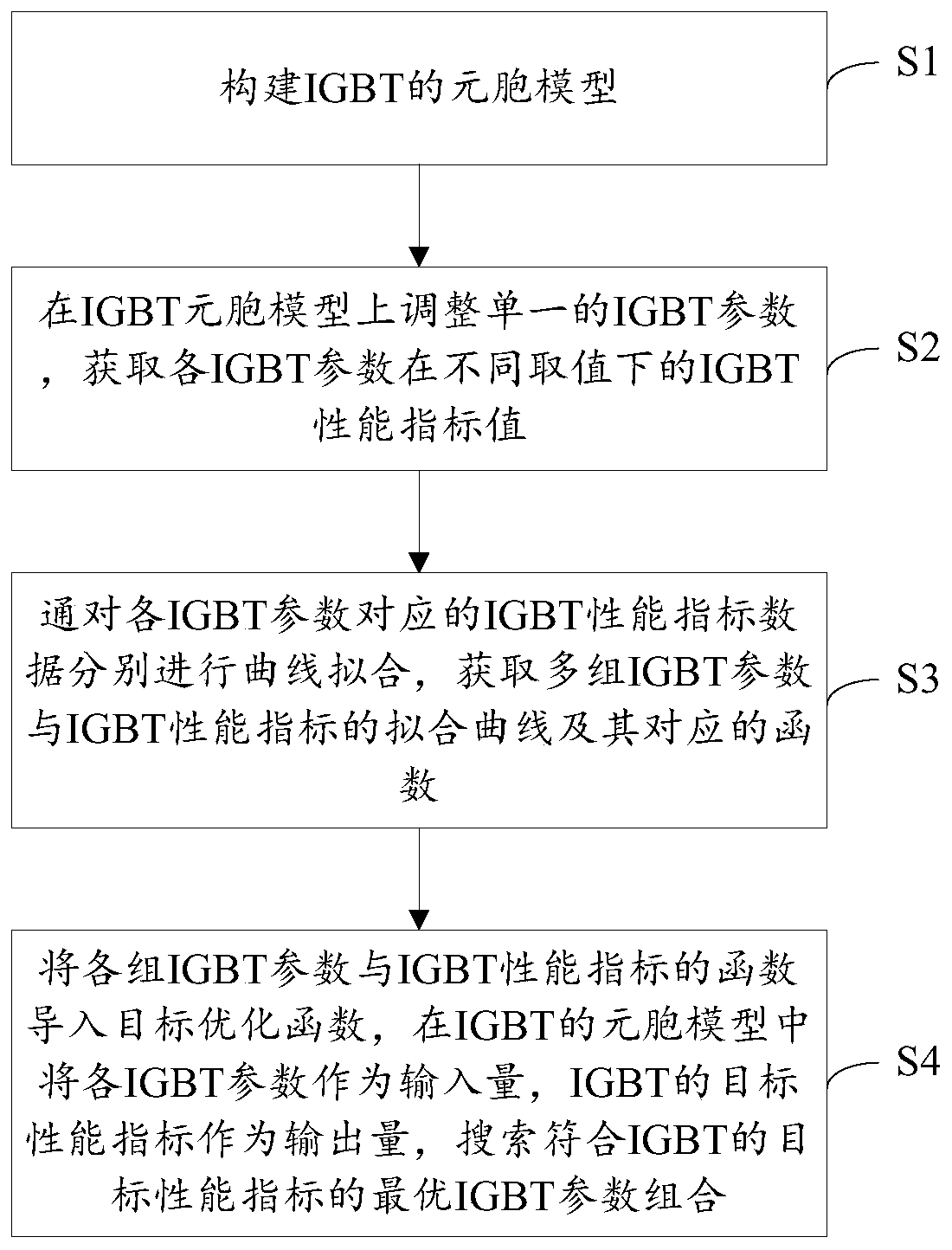
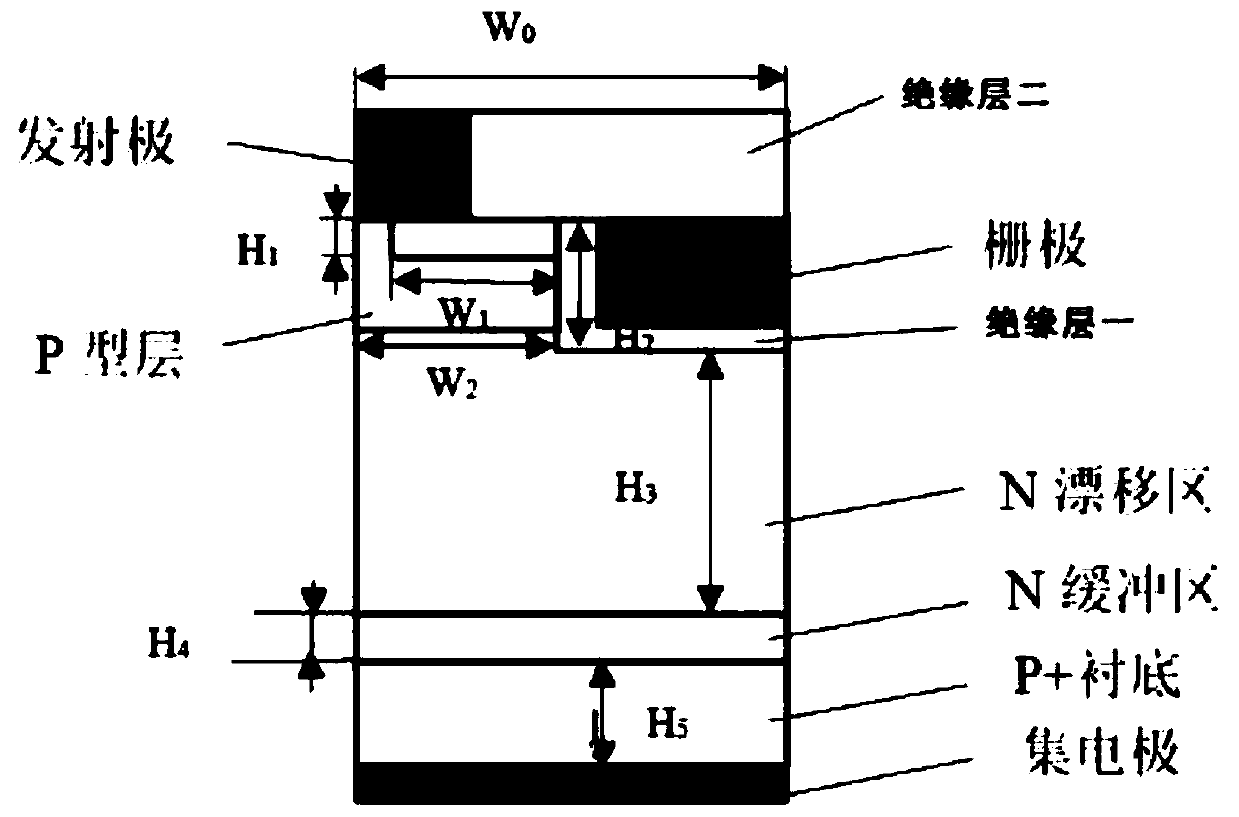
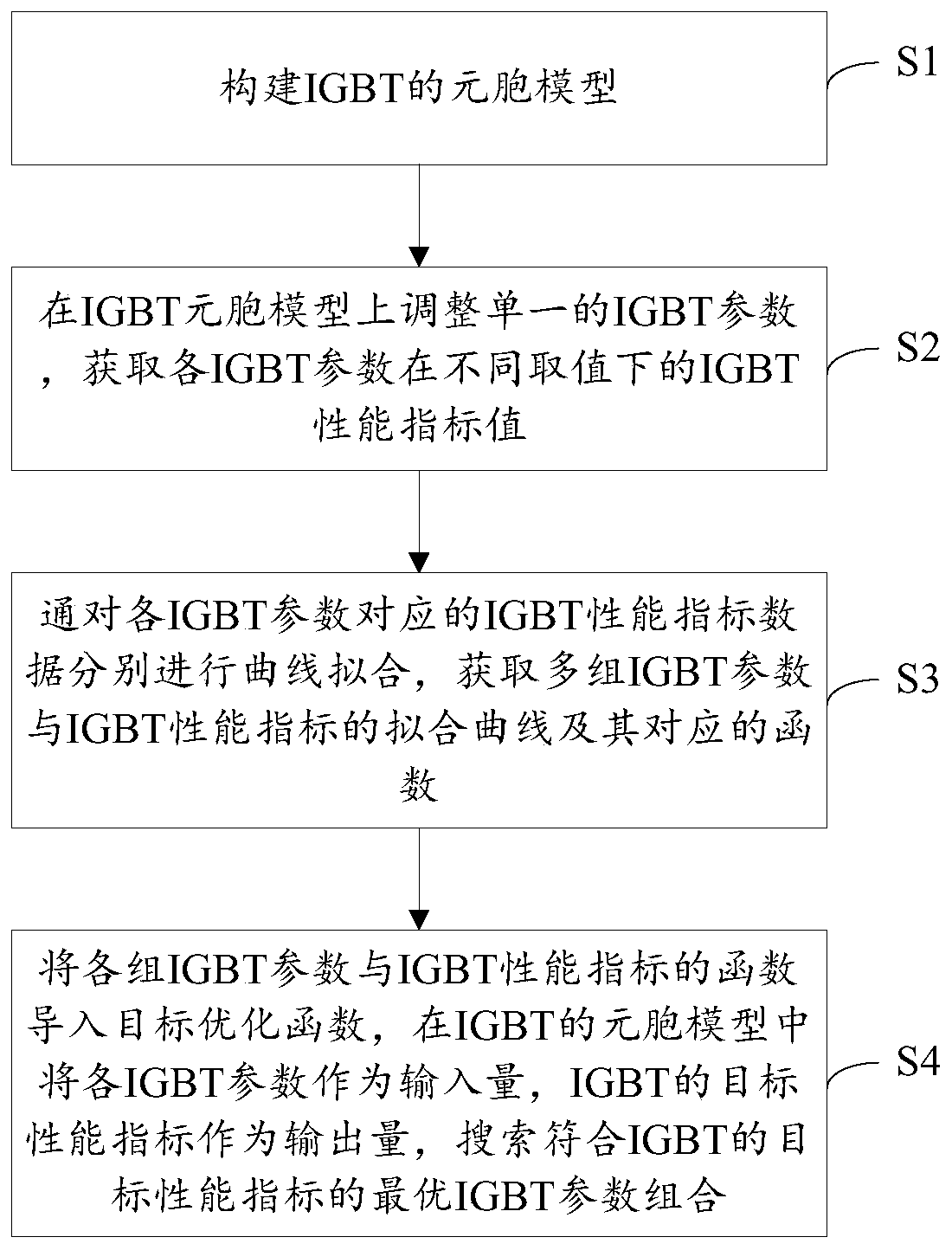
IGBT design method
ActiveCN111159921AShorten the design cycleReduce design costDesign optimisation/simulationSemiconductor devicesCellular modelPerformance index
The invention is applicable to the technical field of IGBT design, and provides an IGBT design method, which comprises the following steps: S1, constructing a cellular model of an IGBT; s2, adjustinga single IGBT parameter on the IGBT cellular model, wherein the IGBT parameter comprises a cellular structure parameter and a process parameter; and obtaining IGBT performance index values of the IGBTparameters under different values; s3, respectively carrying out curve fitting on the IGBT performance index data corresponding to each IGBT parameter to obtain a fitting curve of a plurality of groups of IGBT parameters and IGBT performance indexes and corresponding functions; and S4, importing the function of each group of IGBT parameters and the IGBT performance index into a target optimization function, taking each IGBT parameter as an input quantity and the target performance index of the IGBT as an output quantity in a cellular model of the IGBT, and searching an optimal IGBT parametercombination conforming to the target performance index of the IGBT. The required IGBT structure can be quickly positioned through simulation software, and the structure process parameters of the IGBTstructure can be determined, so that the design period and the design cost of the IGBT are greatly shortened and reduced.
Owner:安徽瑞迪微电子有限公司
A storage space scheduling method for export container terminals
InactiveCN103246941BGood optimal solutionAvoid simultaneous shipmentsForecastingLogisticsContainerizationCellular automation
An export container terminal storage space scheduling method and two-stage modeling from planned allocation to dynamic allocation. Study the location plan in the pre-allocation stage, and use the location plan to guide subsequent dynamic allocation. The location plan proposes a location allocation model based on ecological neutrality theory. The model abstracts box areas as islands and box groups as species. The process of allocating box groups to box areas is transformed into ecological selection of islands by several species; Based on this model, the present invention optimizes the model according to the characteristics of the location planning problem and proposes an improved ecologically neutral theoretical model. In the dynamic allocation stage, double position allocation and container entry position selection are combined, dual-objective combination optimization is solved, and a combined cellular automaton model is proposed; the model abstracts the double position allocation as an outer cellular model, and the approach position selection is abstracted as Intracellular model.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Dipeptide mimetics of ngf and bdnf neurotrophins
ActiveUS20150111828A1Increased phosphorylationNervous disorderDipeptide ingredientsDipeptidePhosphorylation
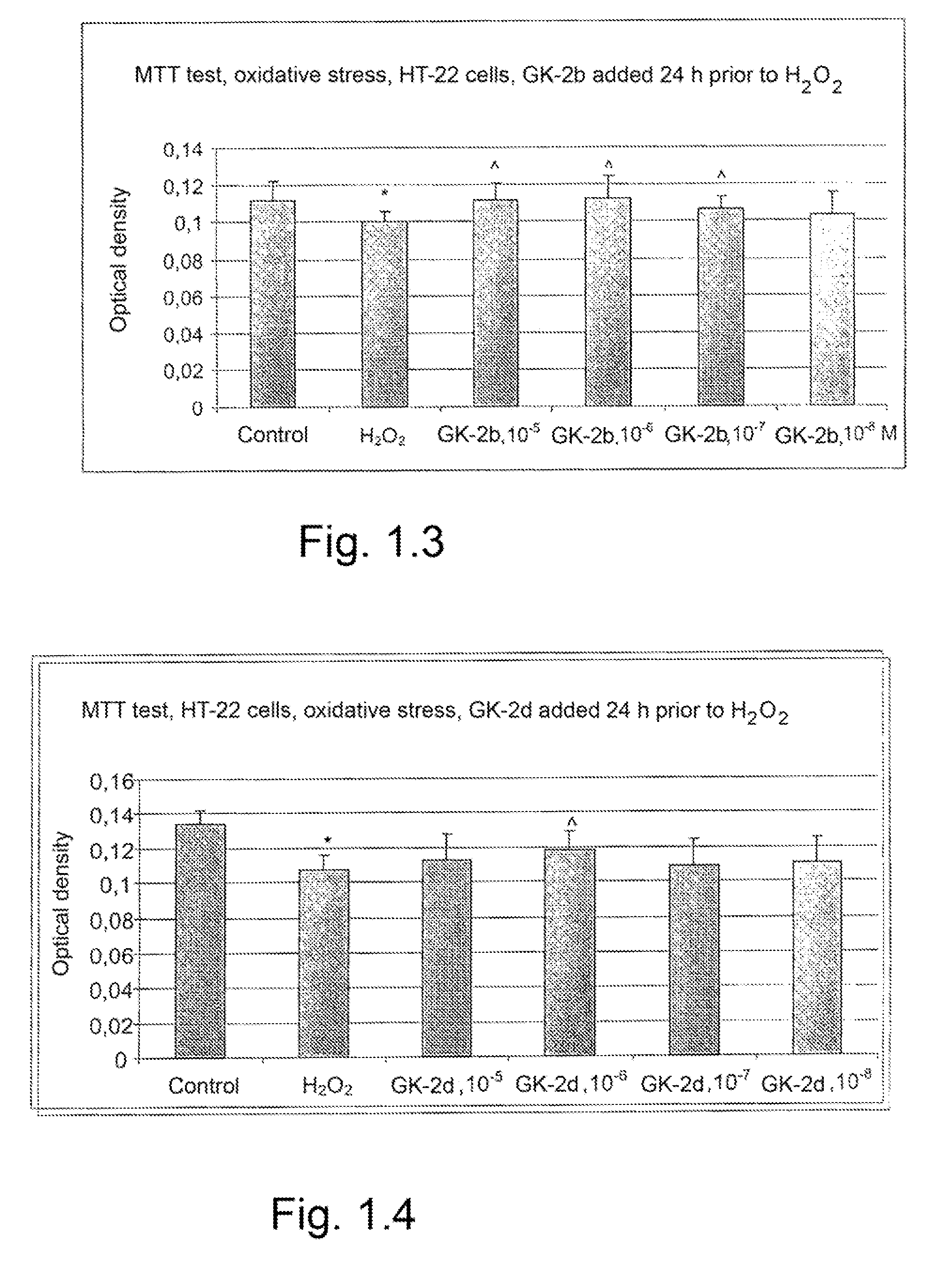
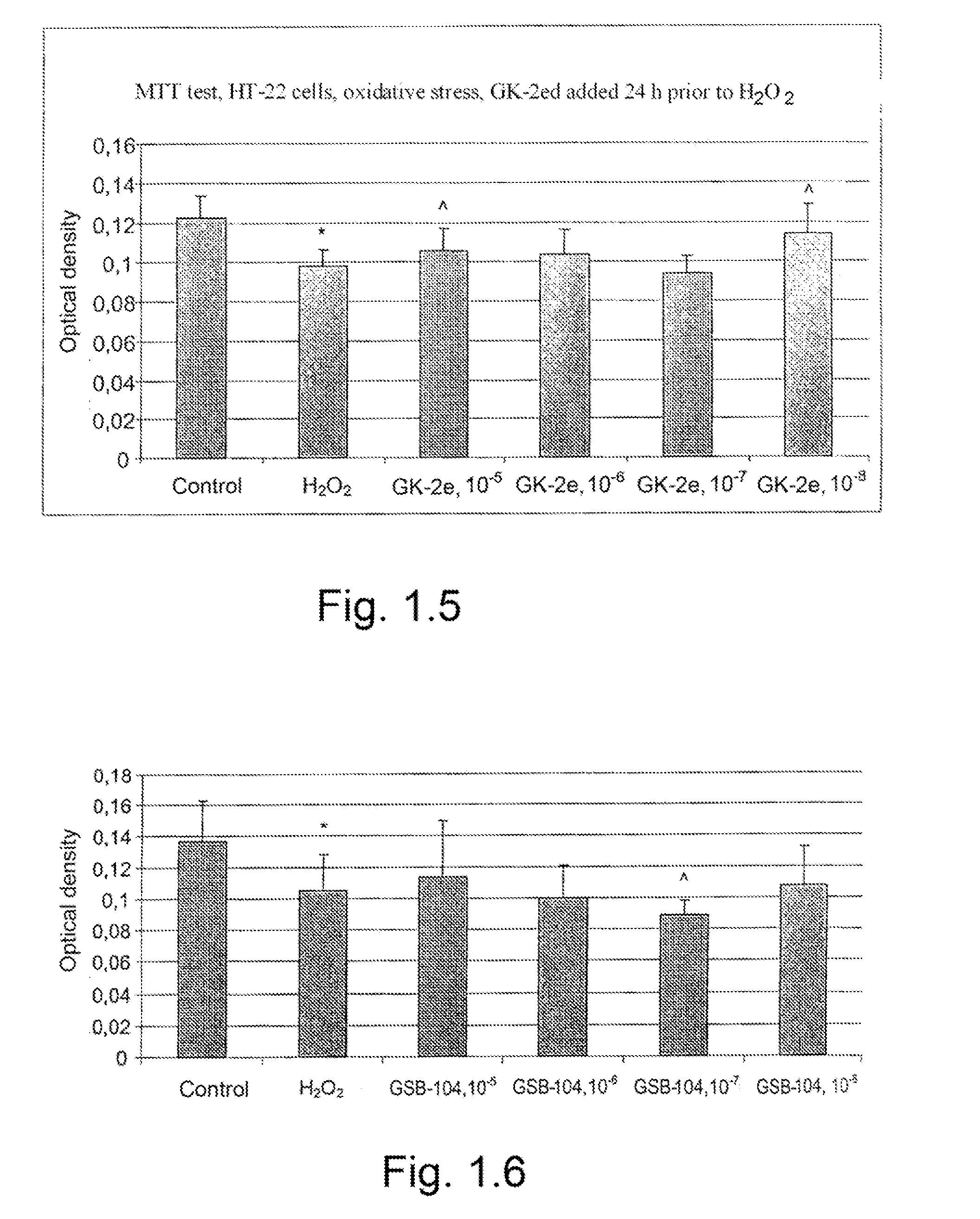
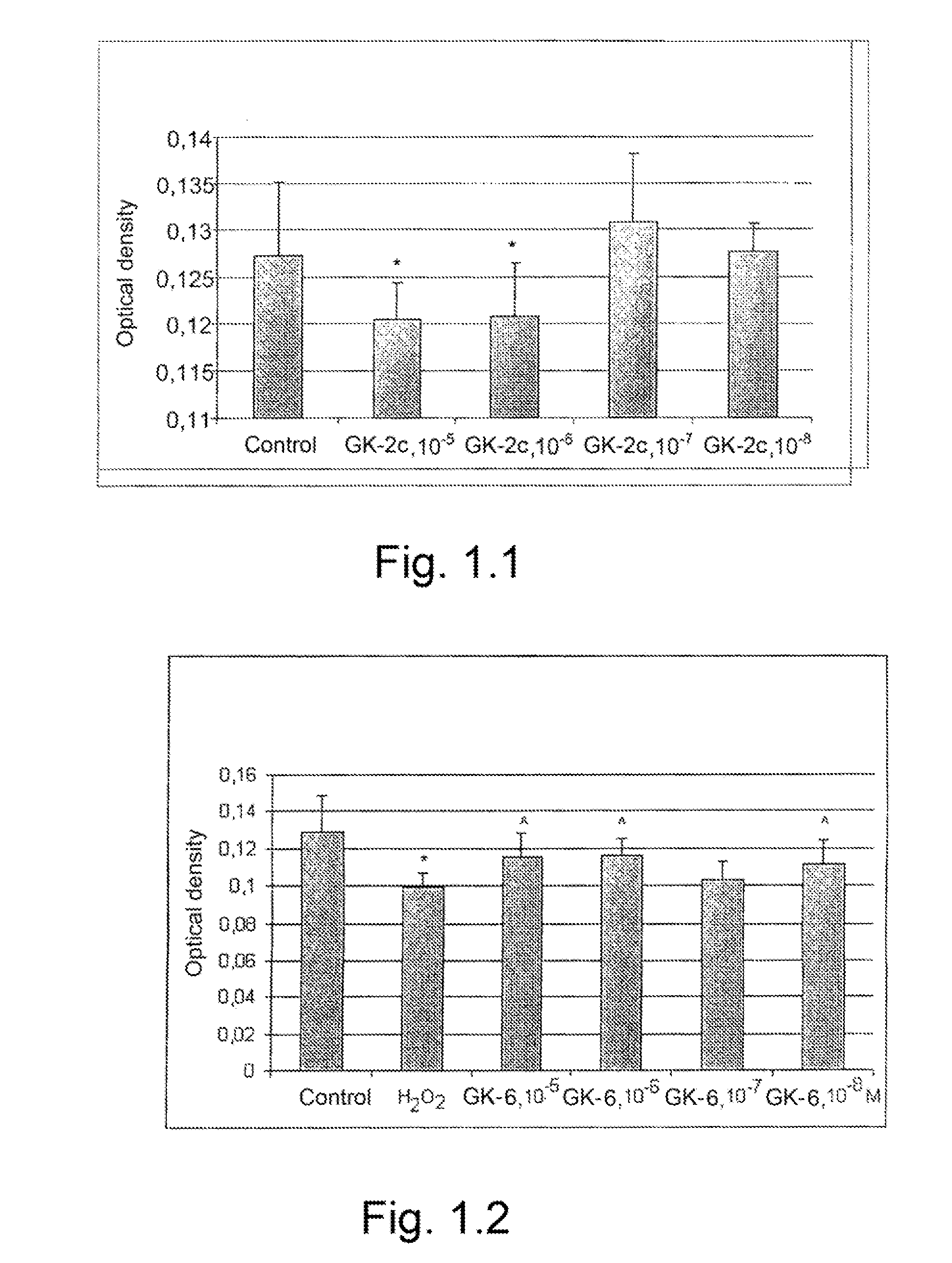
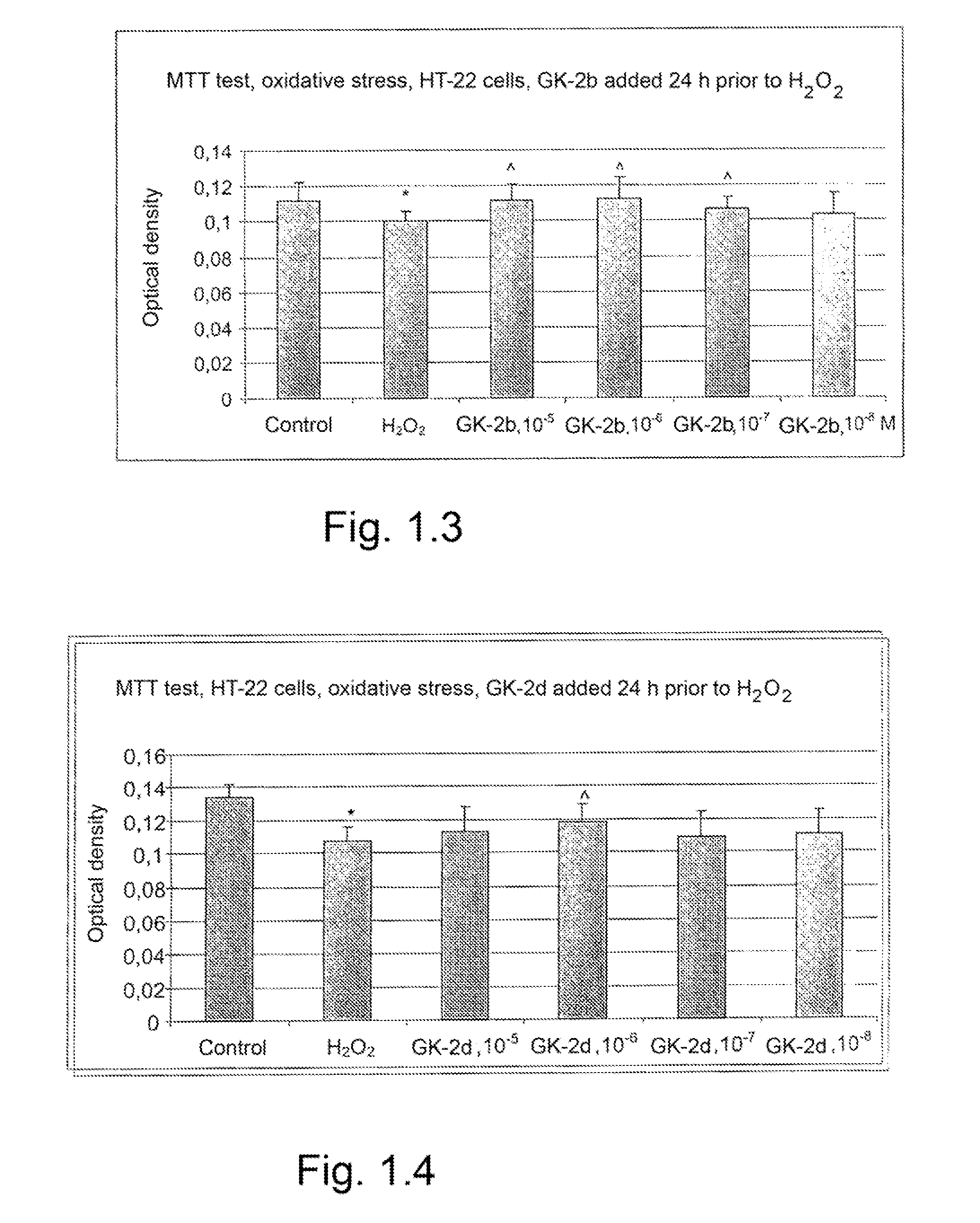
The invention relates to compounds having either agonist or antagonist activities for the neurotrophins NGF and BDNF and represented by monomeric or dimeric substituted dipeptides that are analogs of the exposed portions of loop 1 or loop 4 regions of these neurotrophins near or at a beta-turn of the respective loop. N-acylated substituents of these dipeptides are biostereoisomers of the amino acid residues preceding these dipeptide sequences in the neurotrophin primary structure. The dimeric structure is produced advantageously by using hexamethylenediamine to which dipeptides are attached via their carboxyl groups. The claimed compounds displayed neuroprotective and differentiation-inducing activities in cellular models and enhanced the amount of phosphorylated tyrosine kinase A and the heat shock proteins Hsp32 and Hsp70 in the concentration range of 10−9 to 10−5 M. They also displayed neuroprotective, anti-parkinsonian, anti-stroke, anti-ischemic, anti-depressant and anti-amnestic activities in animal models and were active in experimental models of Alzheimer's disease. These in vivo effects of the claimed compounds are displayed in the dose range of 0.01 to 10 mg / kg when administered intraperitoneally.
Owner:UCHREZHDENIE ROSSIJSKOJ AKADI MEDITSINSKIKH NAUK NAUCHNO ISSLEDOVATELSKIJ INST FARMAKOLOGII IMENI V V ZAKUSOVA RAMN
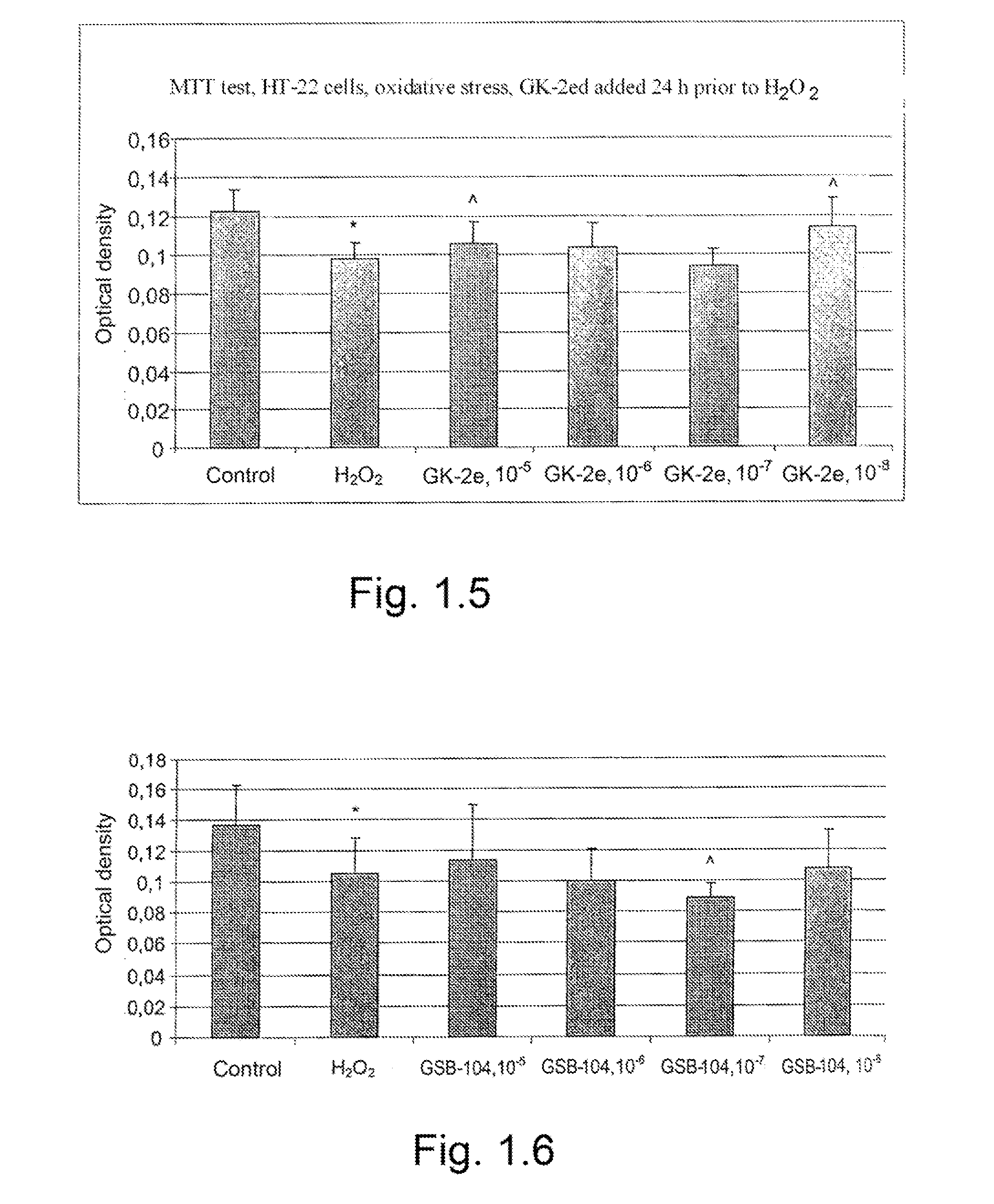
Dipeptide mimetics of ngf and bdnf neurotrophins
The invention relates to compounds having either agonist or antagonist activities for the neurotrophins NGF and BDNF and represented by monomeric or dimeric substituted dipeptides that are analogs of the exposed portions of loop 1 or loop 4 regions of these neurotrophins near or at a beta-turn of the respective loop. N-acylated substituents of these dipeptides are biostereoisomers of the amino acid residues preceding these dipeptide sequences in the neurotrophin primary structure. The dimeric structure is produced advantageously by using hexamethylenediamine to which dipeptides are attached via their carboxyl groups. The claimed compounds displayed neuroprotective and differentiation-inducing activities in cellular models and enhanced the amount of phosphorylated tyrosine kinase A and the heat shock proteins Hsp32 and Hsp70 in the concentration range of 10−9 to 10−5 M. They also displayed neuroprotective, anti-parkinsonian, anti-stroke, anti-ischemic, anti-depressant and anti-amnestic activities in animal models and were active in experimental models of Alzheimer's disease. These in vivo effects of the claimed compounds are displayed in the dose range of 0.01 to 10 mg / kg when administered intraperitoneally.
Owner:UCHREZHDENIE ROSSIJSKOJ AKADI MEDITSINSKIKH NAUK NAUCHNO ISSLEDOVATELSKIJ INST FARMAKOLOGII IMENI V V ZAKUSOVA RAMN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com