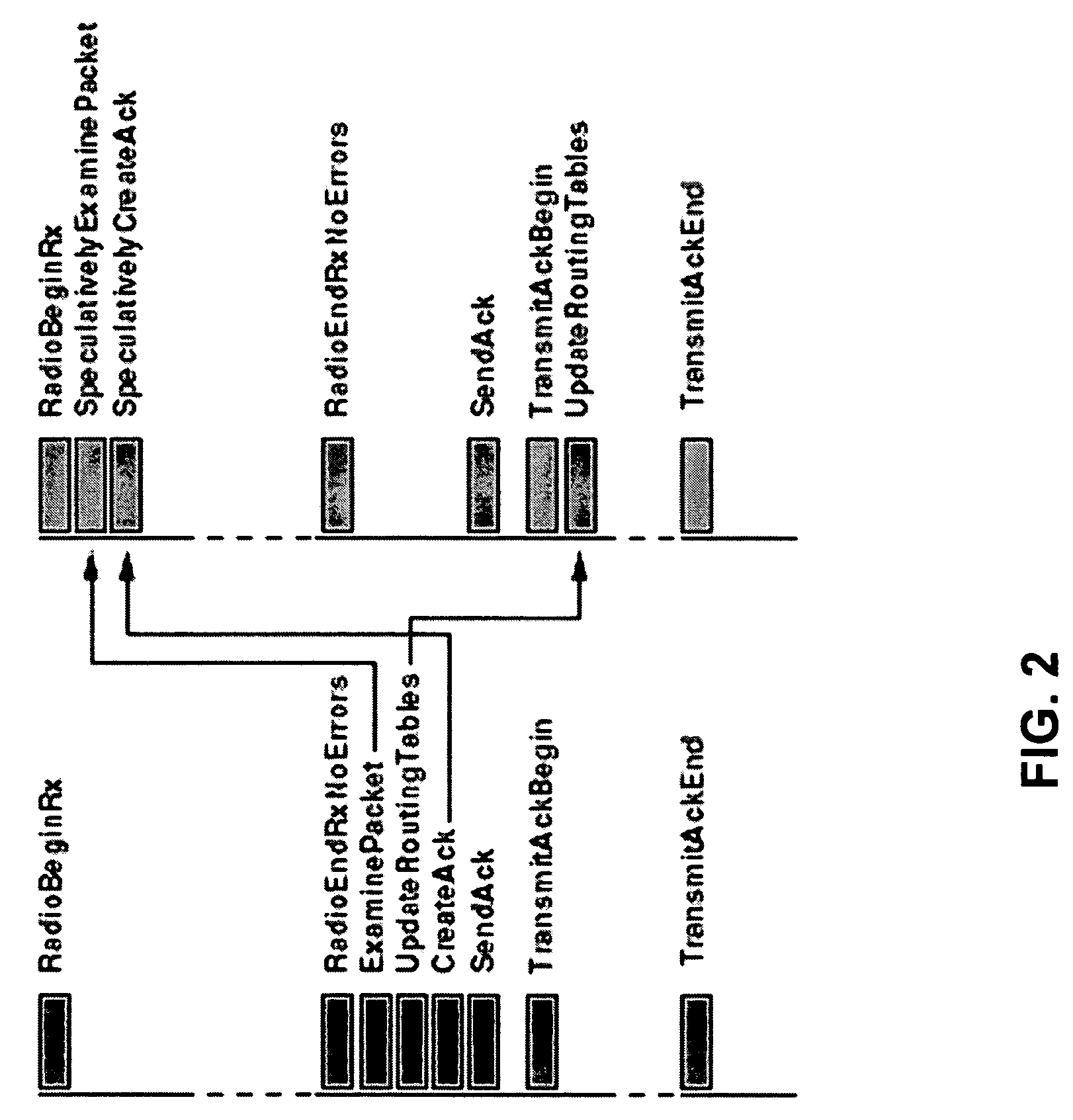
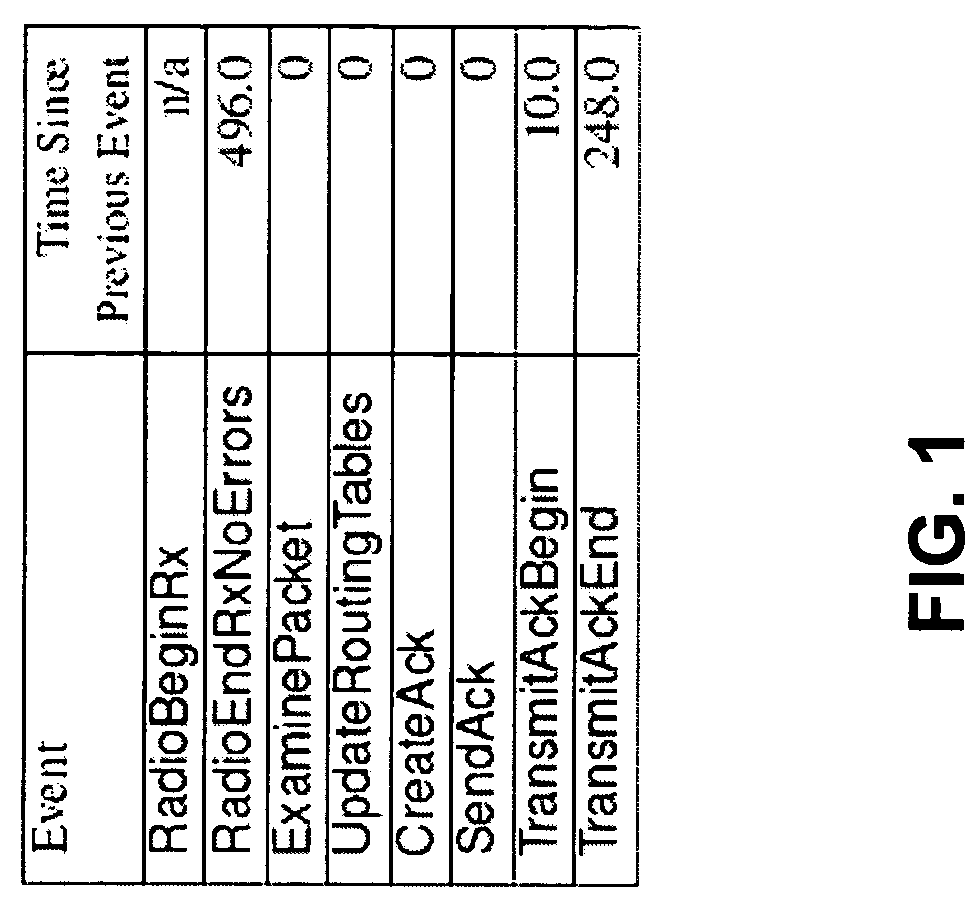
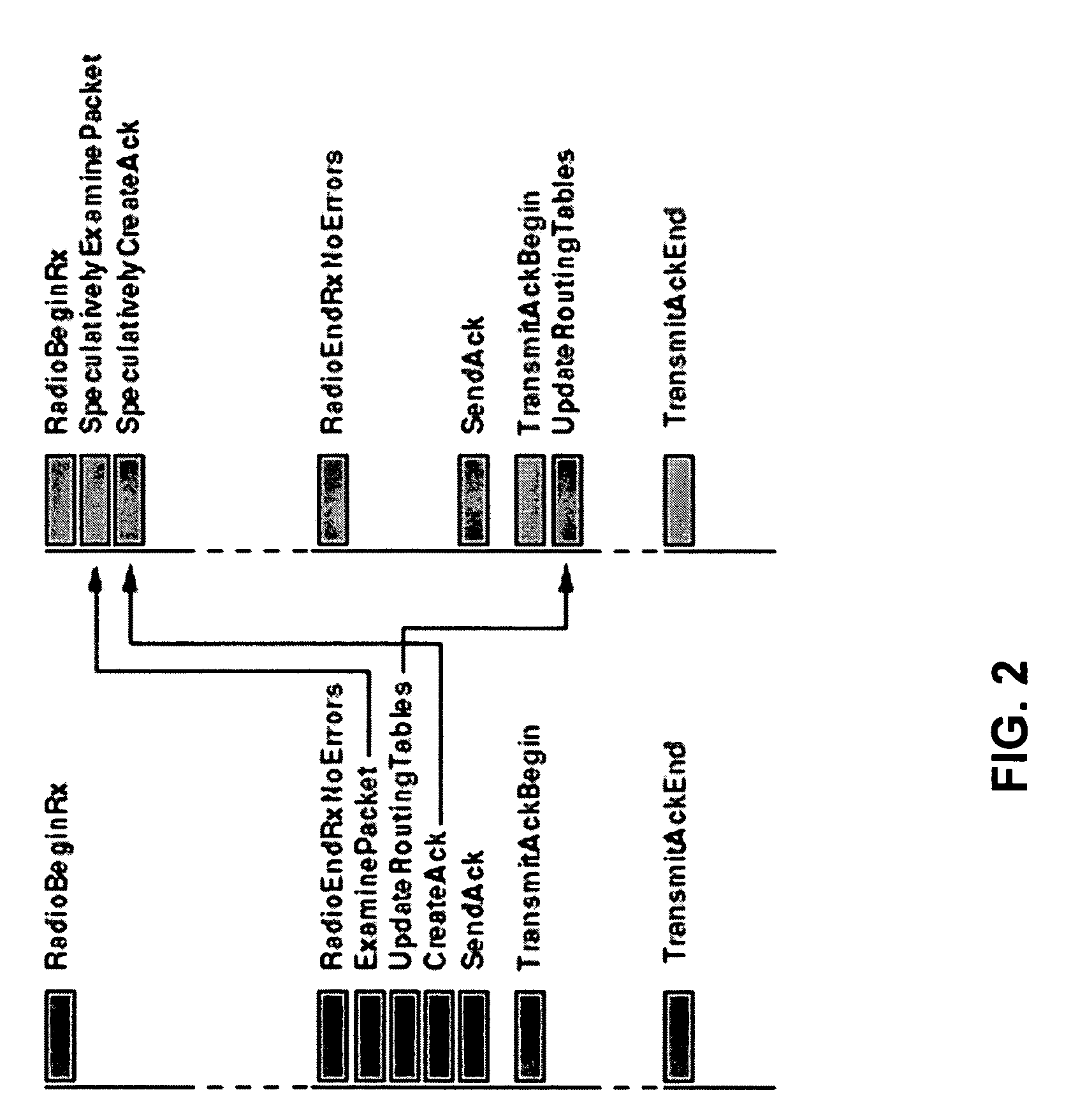
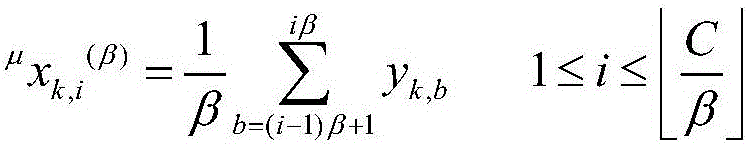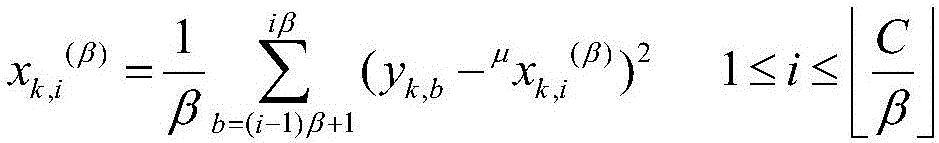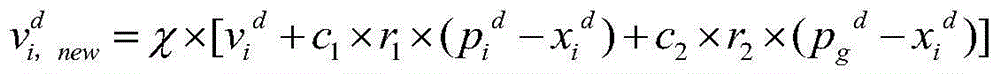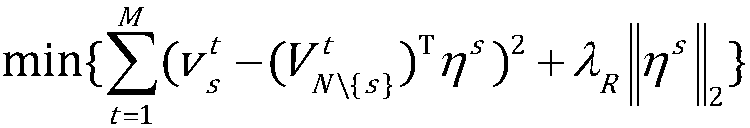Patents
Literature
123 results about "Scale-free network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
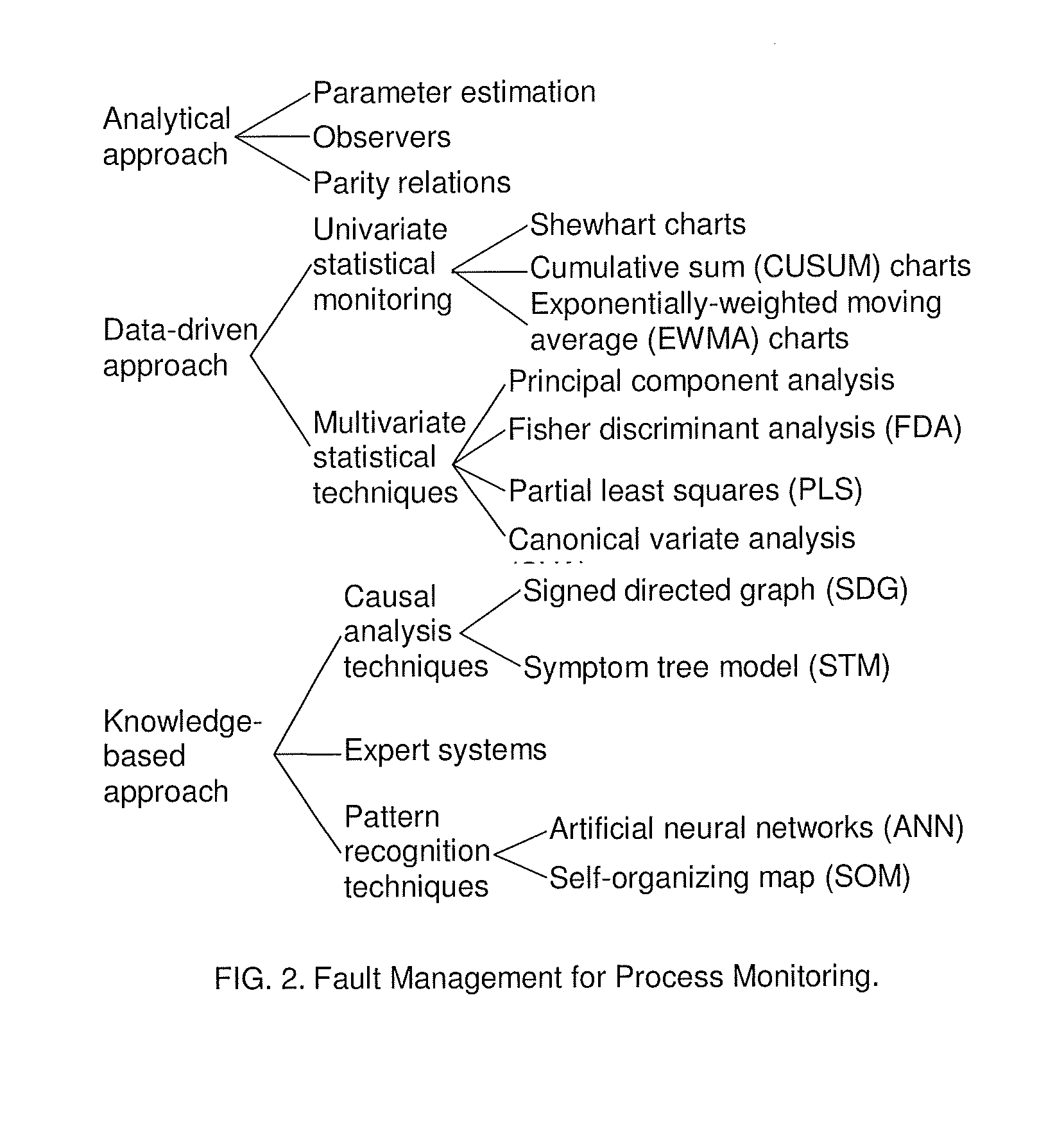
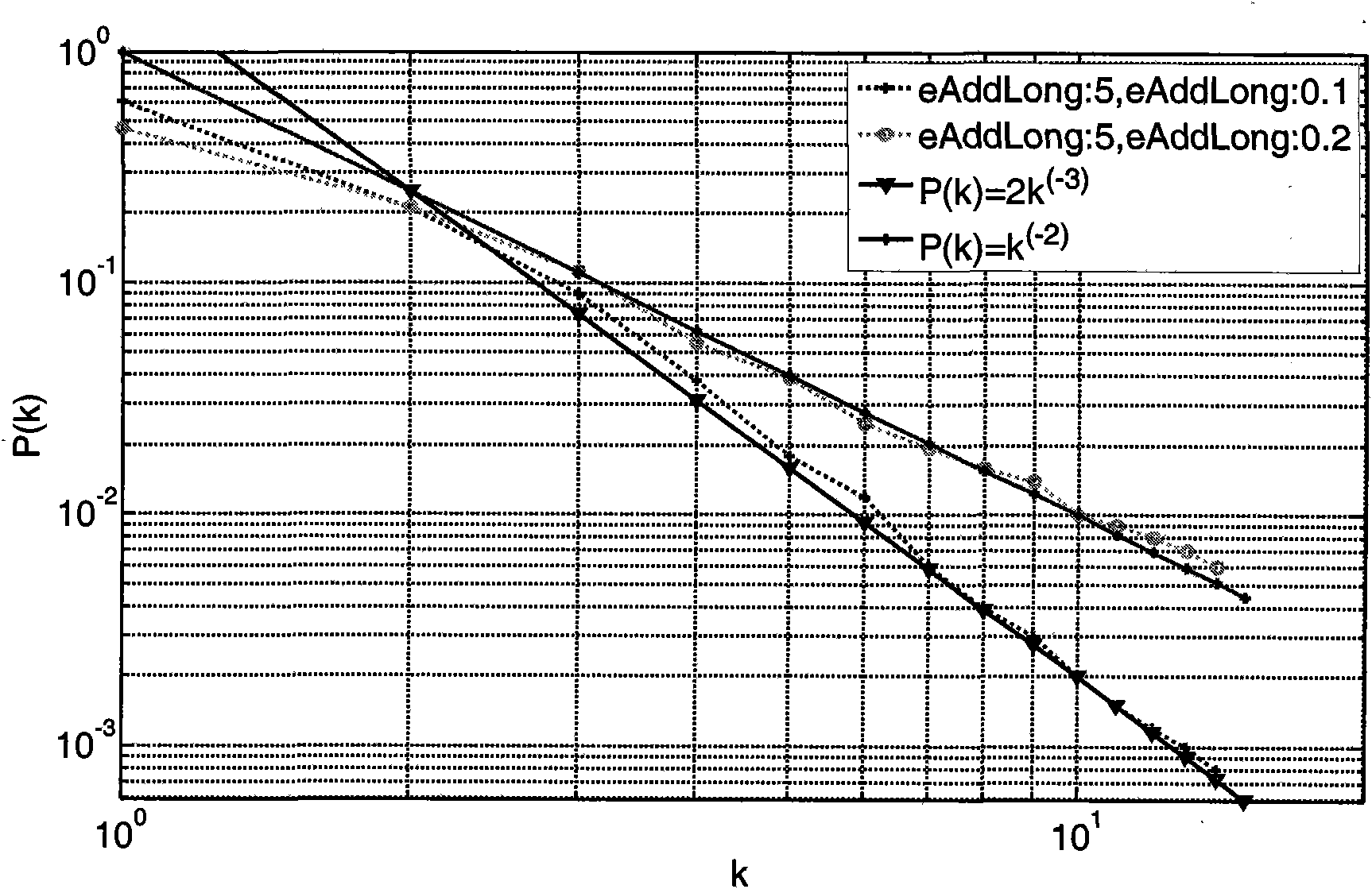
A scale-free network is a network whose degree distribution follows a power law, at least asymptotically. That is, the fraction P(k) of nodes in the network having k connections to other nodes goes for large values of k as P(k) ∼ k⁻γ where γ is a parameter whose value is typically in the range 2 < γ < 3 (wherein the second moment of k⁻γ is infinite but the first moment is finite), although occasionally it may lie outside these bounds.
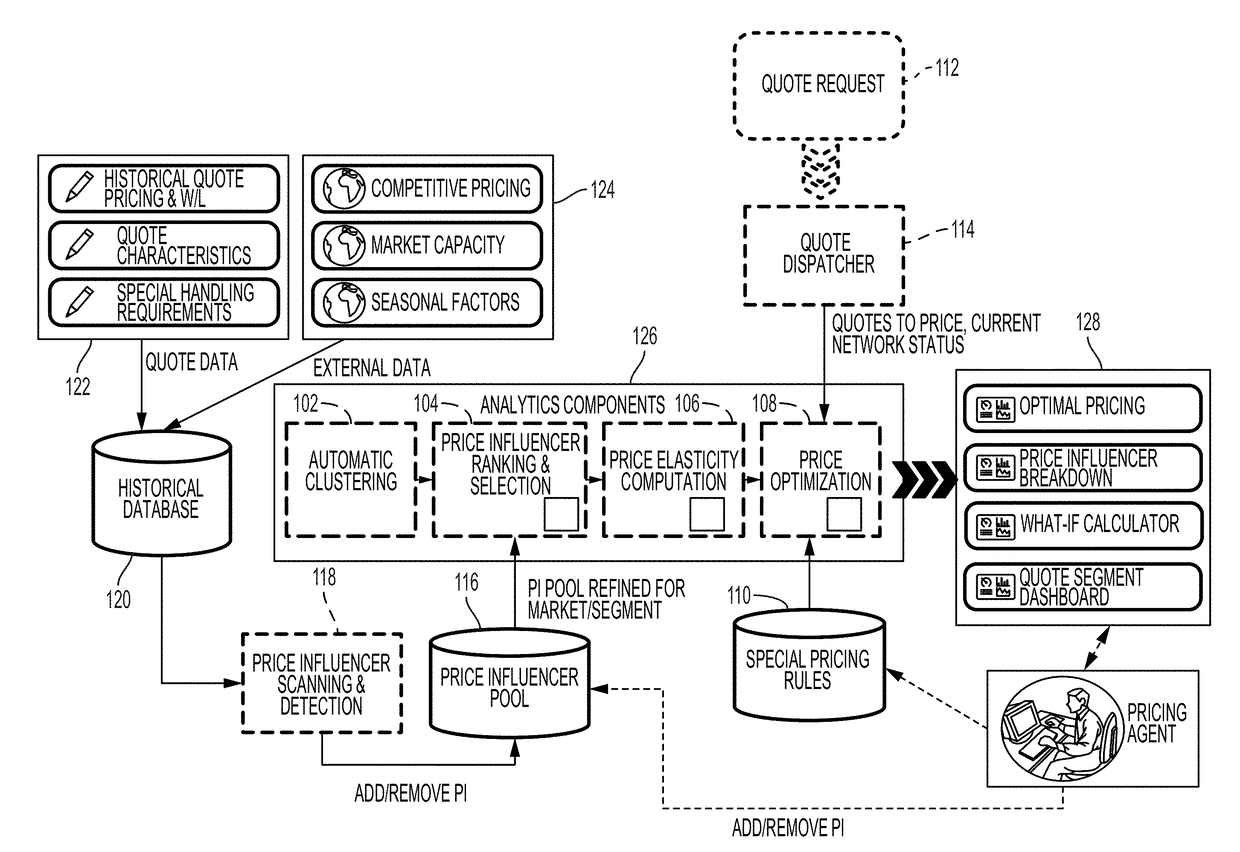
Training a machine to automate spot pricing of logistics services in a large-scale network
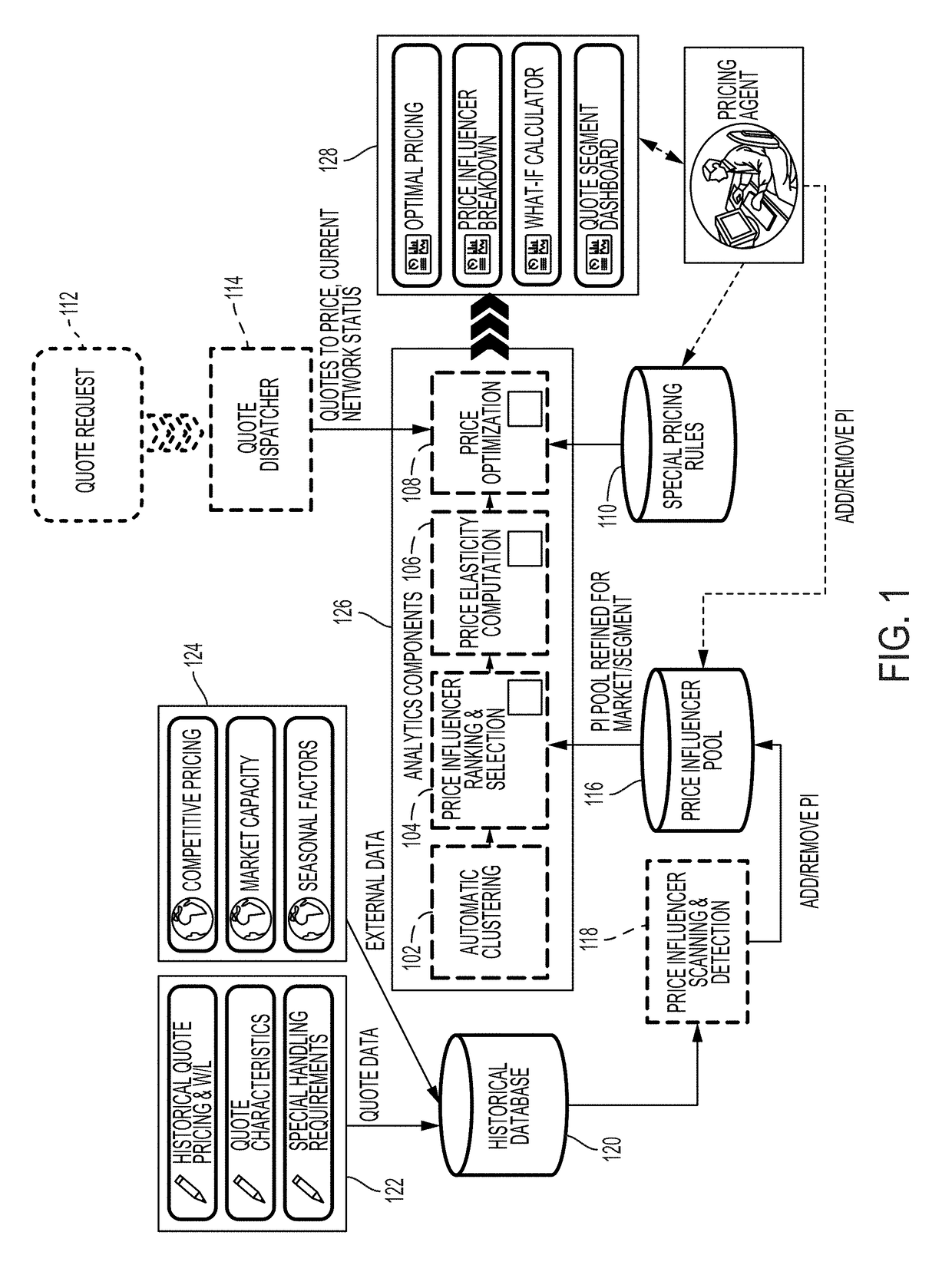
A machine learning algorithm is trained to learn to cluster a plurality of original-destination routes in a network for transporting cargo into a plurality of clusters based on similarities of the original-destination routes, and to learn to cluster the plurality of clusters into a plurality of subgroups based on customer behavior. Influencing criteria associated with each of the subgroups may be determined and based on the influencing criteria, a price elasticity curve for each of the subgroups may be generated. Based on the price elasticity curve and current network traffic, cargo transportation price associated with each of the subgroups may be determined.
Owner:IBM CORP
Community division method in complex network
InactiveCN101383748AEmbody the essential characteristicsReflect the interactionStar/tree networksSpecial data processing applicationsMacroscopic scaleGranularity
The invention provides a community classification method in complex network, a plurality of different nodes having partial influences are taken as the cores, the influences of the nodes are caused to evenly diffuse from the core outwards layer by layer, finally the node having the greatest influence becomes the core, the influences of the nodes in layer-by-layer expansion continuously attenuate, the interconnection of the nodes form a local region which expands until the method stops, the influences of the nodes are slight and can reach the edge of the network of the local region. For a large-scale unordered complex network, the positions of the nodes having different importance degrees can be rapidly located, a great deal of more fine-granularity information is dug out, simultaneously the original structural character of the network is kept unchanged, and the original large-scale complex network is simplified and downsized, so that not only the efficiency of search can be improved, but also the structure of the large-scale network from macroscopic view can be more clearly analyzed.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
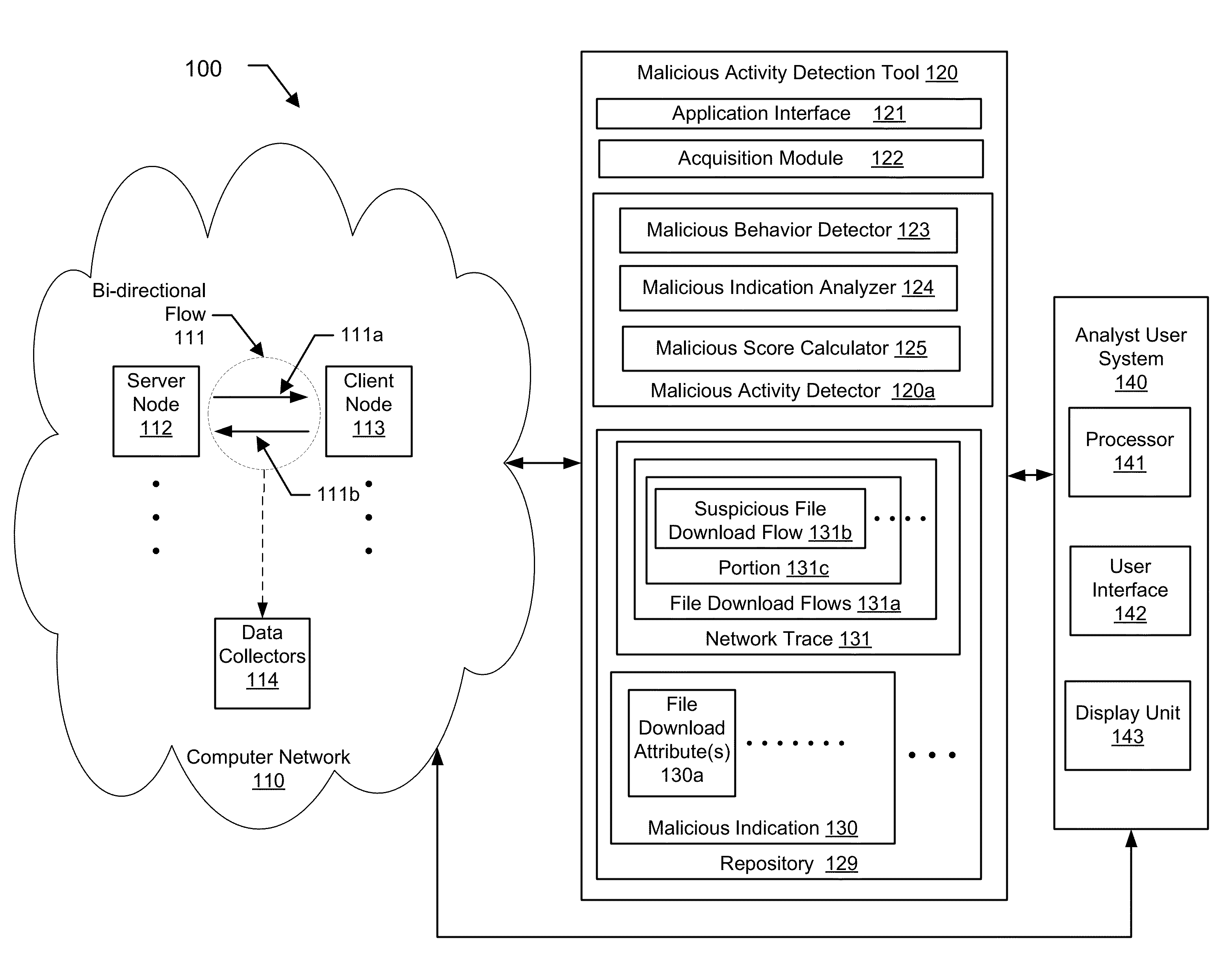
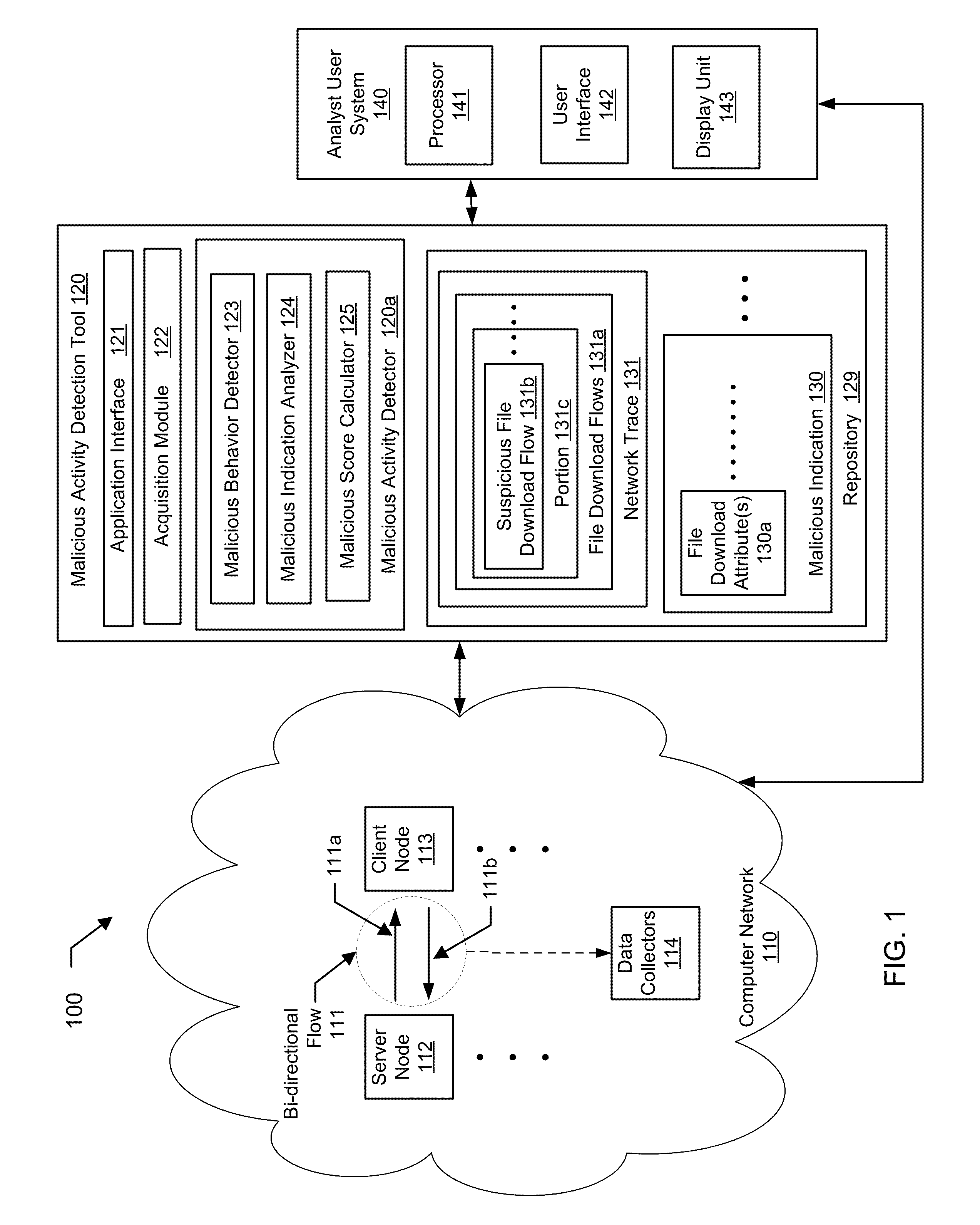
Detecting malware infestations in large-scale networks
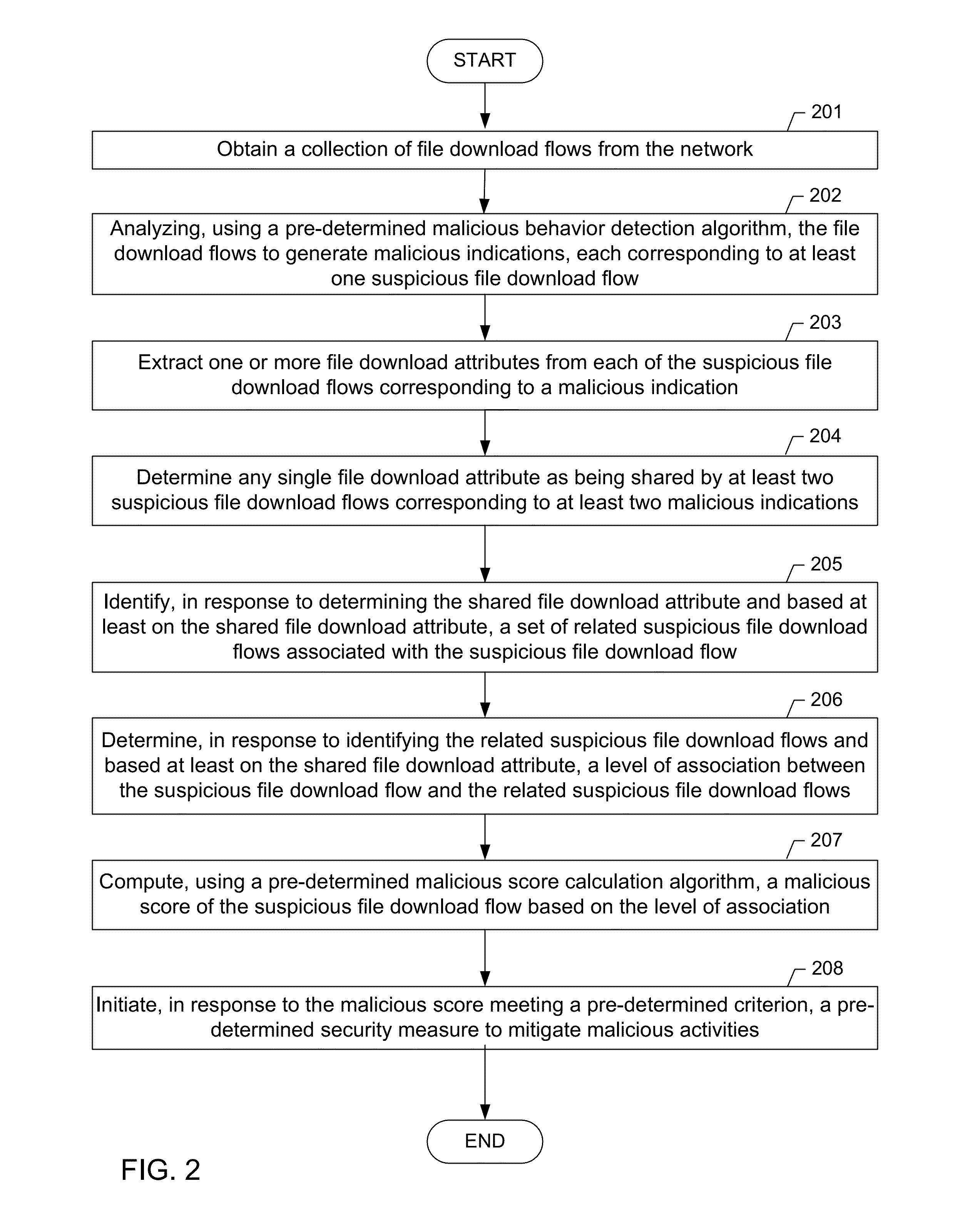
A method for detecting a malicious activity in a network. The method includes obtaining file download flows from the network, analyzing, the file download flows to generate malicious indications using a pre-determined malicious behavior detection algorithm, extracting a file download attribute from a suspicious file download flow of a malicious indication, wherein the file download attribute represents one or more of the URL, the FQDN, the top-level domain name, the URL path, the URL file name, and the payload of the suspicious file download flow, determining the file download attribute as being shared by at least two suspicious file download flows, identifying related suspicious file download flows and determining a level of association between based at least on the file download attribute, computing a malicious score of the suspicious file download flow based on the level of association, and presenting the malicious score to an analyst user of the network.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
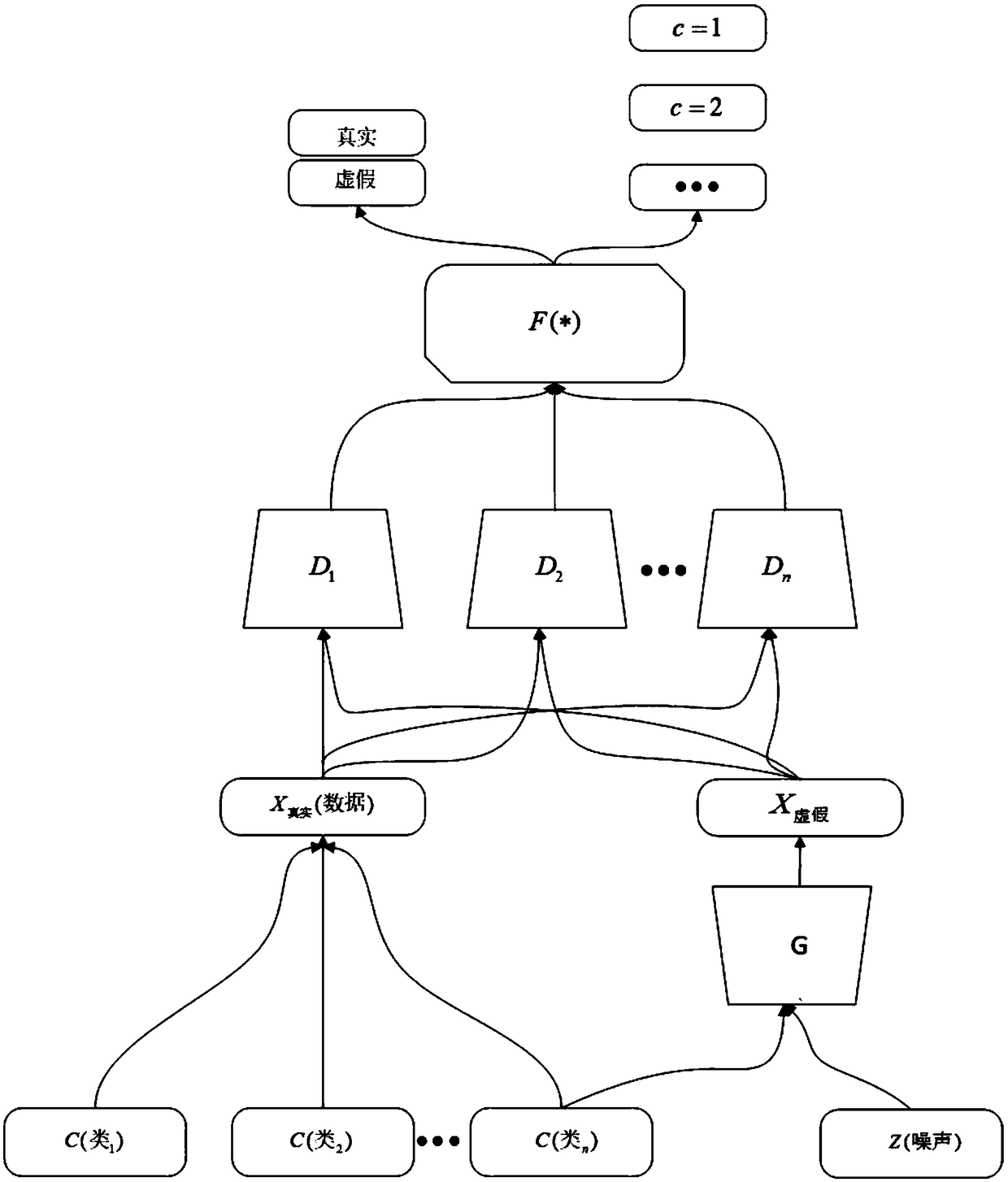
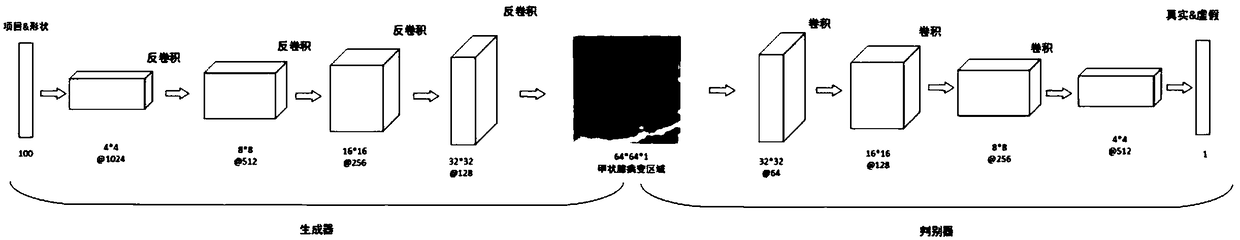
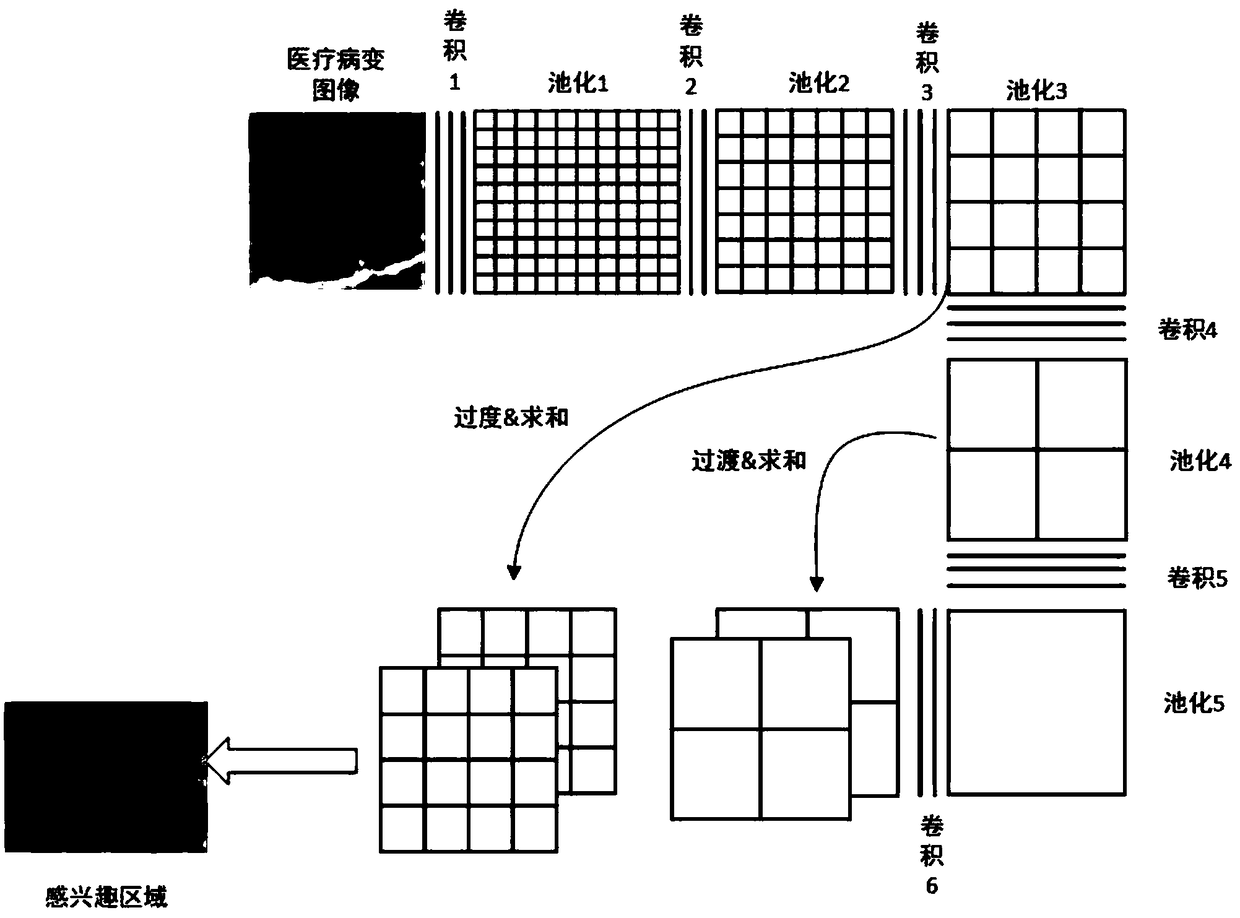
Medical image synthesis and classification method based on a conditional multi-judgment generative adversarial network
ActiveCN109493308AMultiple variabilityImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisData setClassification methods
The invention discloses a medical image synthesis and classification method based on a conditional multi-judgment generative adversarial network. The method comprises the following steps: 1, segmenting a lesion area in a computed tomography (CT) image, and extracting a lesion interested area (Region of Interest, ROIs for short); 2, performing data preprocessing on the lesion ROIs extracted in thestep 1; 3, designing a Conditional Multi-Discriminant Generative Adversarial Network (Conditional Multi-) based on multiple conditions The method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing aCMDGAN model architecture for short, and training the CMDGAN model architecture by using an image in the second step to obtain a generation model; 4, performing synthetic data enhancement on the extracted lesion ROIs by using the generation model obtained in the step 3; and 5, designing a multi-scale residual network (Multiscale ResNet Network for short), and training the multi-scale residual network. According to the method provided by the invention, the synthetic medical image data set with high quality can be generated, and the classification accuracy of the classification network on the test image is relatively high, so that auxiliary diagnosis can be better provided for medical workers.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
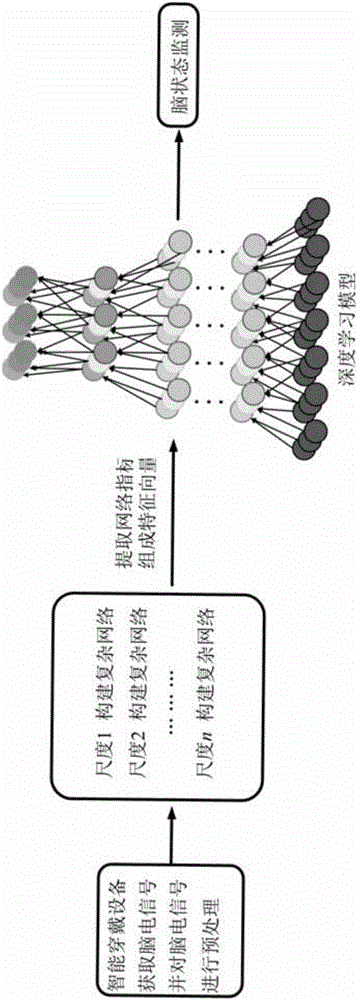
Deep learning model based on multi-scale network and application in brain state monitoring
A deep learning model based on a multi-scale network and application in brain state monitoring are provided. A model establishing method comprises steps of: preprocessing and multi-scale transforming a measured multichannel signal; obtaining a multi-scale weighted recursive network and a cross-recursive rate matrix corresponding to the multi-scale weighted recursive network of the multichannel signal in all scales; extracting the network indexes of the multi-scale weighted recursive network at different scales; at each scale, retaining relatively large elements in the cross recursive rate matrix and obtaining an unweighted adjacent matrix and a multi-scale unweighted recursive network corresponding thereto; for each value of a variable in the set range, obtaining the multi-scale unweighted recursive network and the adjacent matrix corresponding to the multi-scale unweighted recursive network, extracting the network indexes of the multi-scale unweighted recursive network at different scales, calculating the integral of the network indexes when the variable is changed in the set range, and the integral as the final network index of the multi-scale unweighted recursive network under each scale; and training the deep learning model and monitoring a brain state.
Owner:钧晟(天津)科技发展有限公司
Bridging centrality: a concept and formula to identify bridging nodes in scale-free networks
InactiveUS20070286218A1Maintain structural integrityDisrupt flowData switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsScale-free networkTraffic flow
A method for identifying a bridge node in a network using a processor and memory unit in a specially programmed special purpose-purpose computer including the steps of, for each node in a plurality of nodes in the network: determining a global metric proportional to total traffic flow in the network and through the node; determining a local metric proportional to traffic flow between the node and each second node in the network connected to the node and traffic flow between each second node and each third node in the network connected to a second node; determining a second local metric proportional to the respective traffic flows between each node and each second node; and calculating a respective combination of the global metric and the first and second local metrics; and selecting, a bridge node from among the plurality of nodes based on the respective combinations.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Personal music recommendation mapping
InactiveUS20100328312A1Digital data information retrievalDrawing from basic elementsGraphicsData set
Scale free network datasets, such as music tracks, playlists and other media item recommendations are analyzed and presented in a graphic map display (FIG. 1) for visualization, preferably in an interactive environment (FIG. 2). A plotting and visualization system generally comprises a network extraction routine, coupled with a high performance eigendecomposition (map layout calculation) algorithm, and a novel visualization interaction methodology.
Owner:APPLE INC
Particle swarm optimization method based on complex network
ActiveCN103971160AImprove convenienceGuaranteed activityBiological modelsLocal optimumInformation transmission
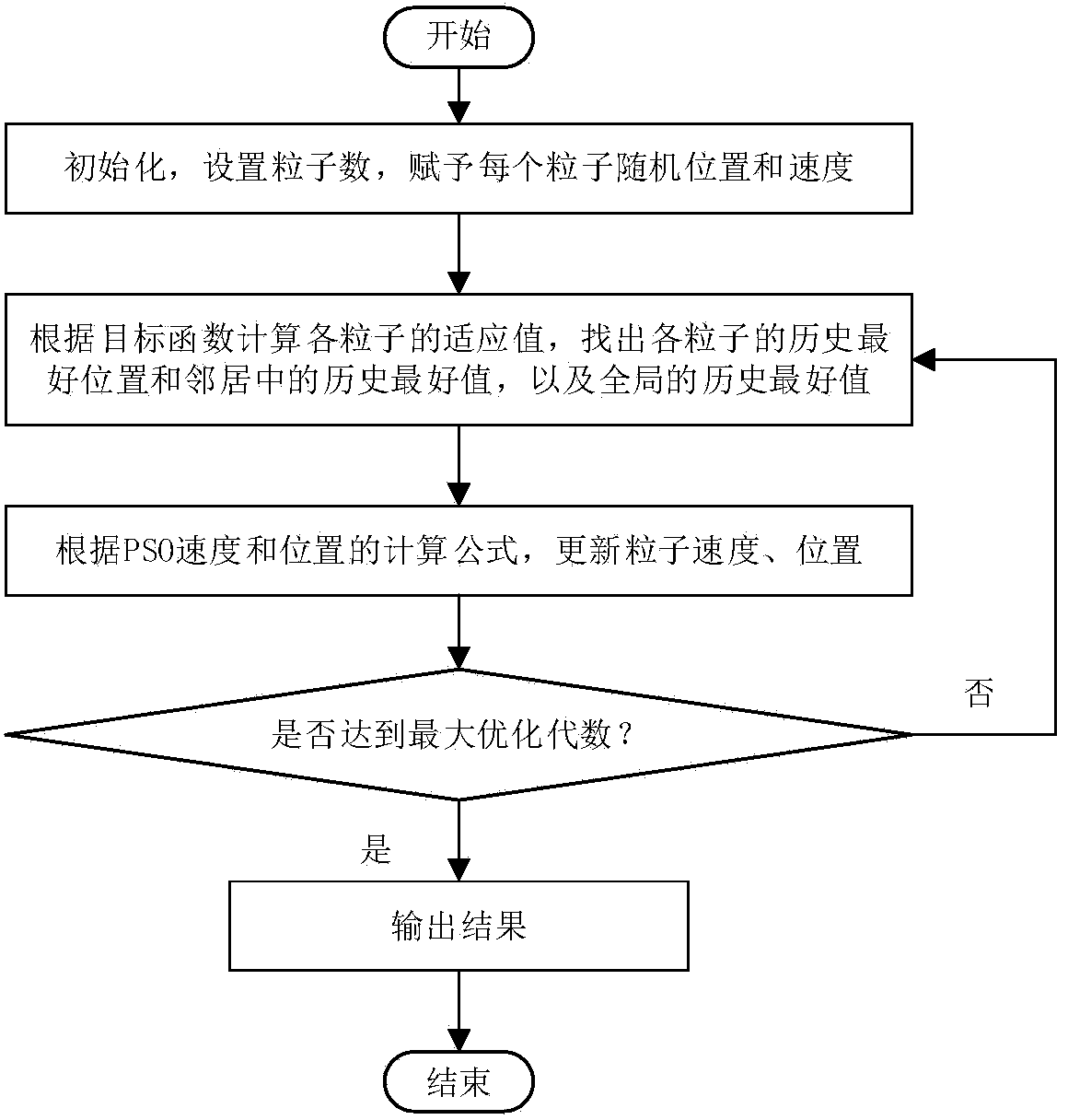
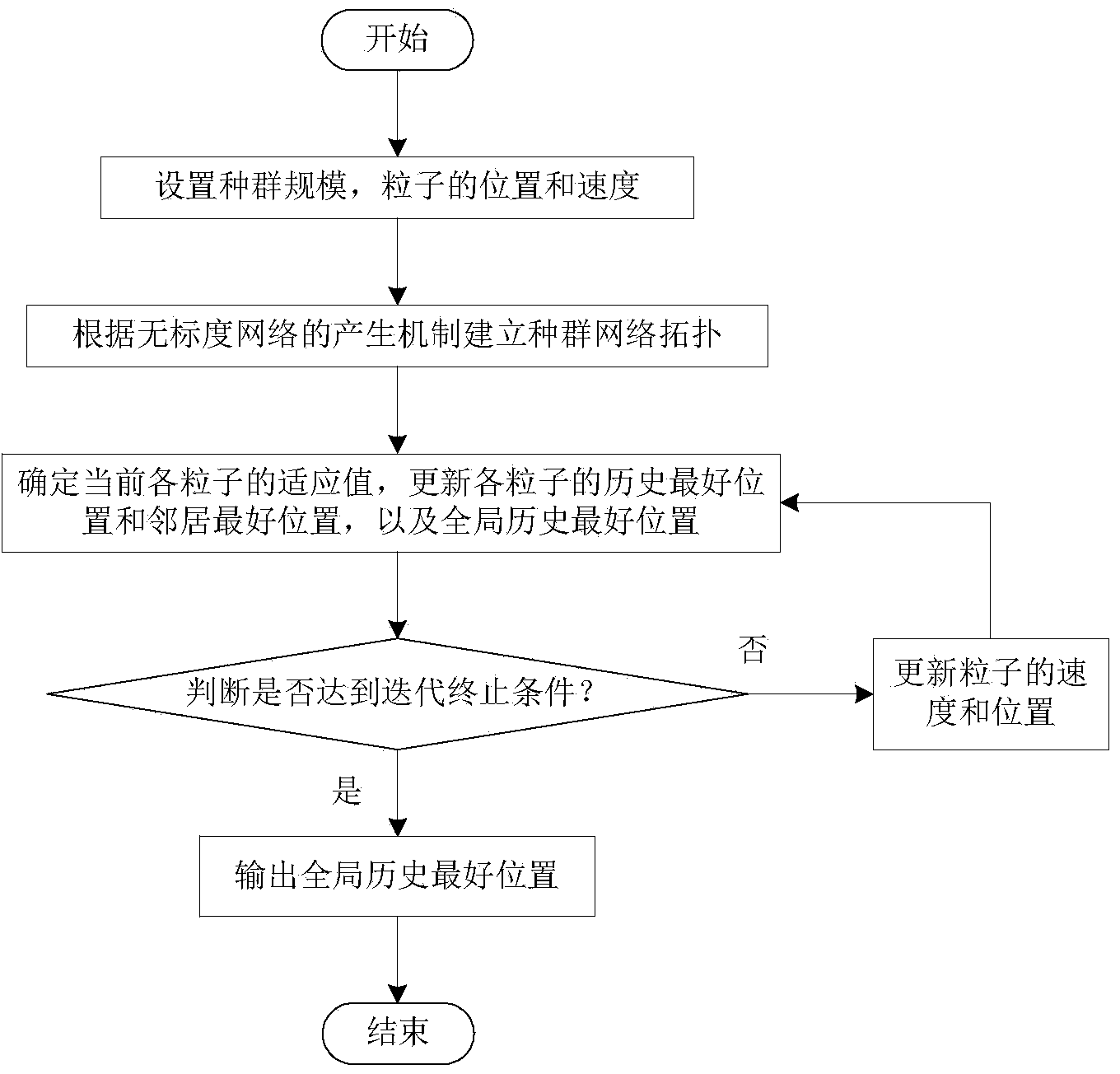
The invention relates to a particle swarm optimization method based on a complex network. The particle swarm optimization method is used for solving the multiobjective optimization problem in the real world. The particle swarm optimization method based on the complex network comprises the steps that the population network topology is established according to a scale-free network generation mechanism, the optimization space, the population size, the positions of particles and the speeds of the particles are determined, the adaptive value is calculated according to a fitness function, the historical best position of each particle, the historical best position of the corresponding neighbor particle and the global historical best position of the particles are recorded, the positions and the speeds of the particles are updated in an iteration mode every time, the adaptive value is calculated again until iteration is completed, and the global best position is output. The particle swarm optimization method based on the complex network further provides four indexes for evaluating the optimal performance of center particles and non-center particles, the influence in neighborhood, the information transmission capacity, the advantages and disadvantages of the adaptive value and the capacity for maintaining population activeness. By means of the particle swarm optimization method based on the complex network, the local optimum can be effectively avoided, and the convergence rate and the optimization effect for resolving targets are balanced through the application of the particle swarm optimization algorithm.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for establishing scale-free sensor having survivability
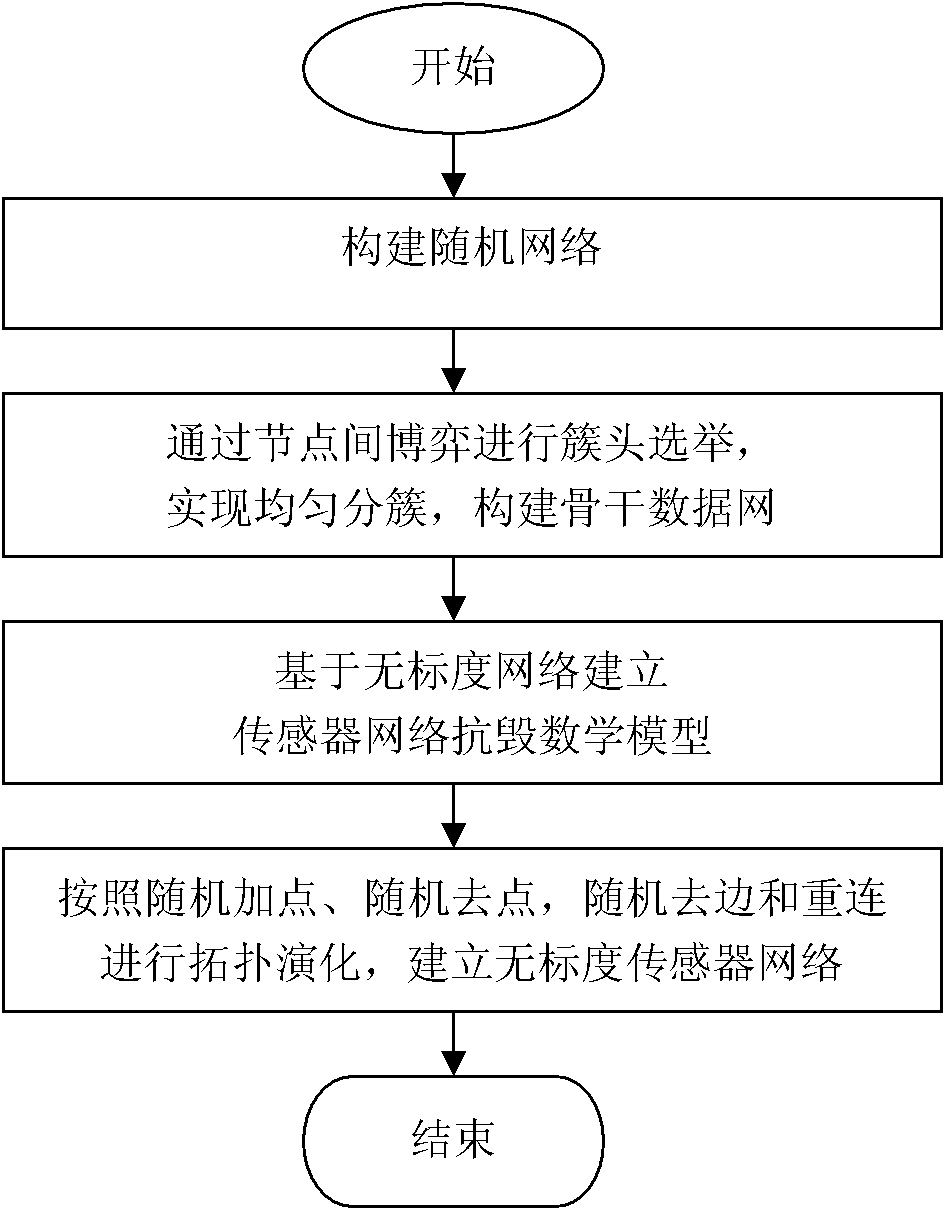
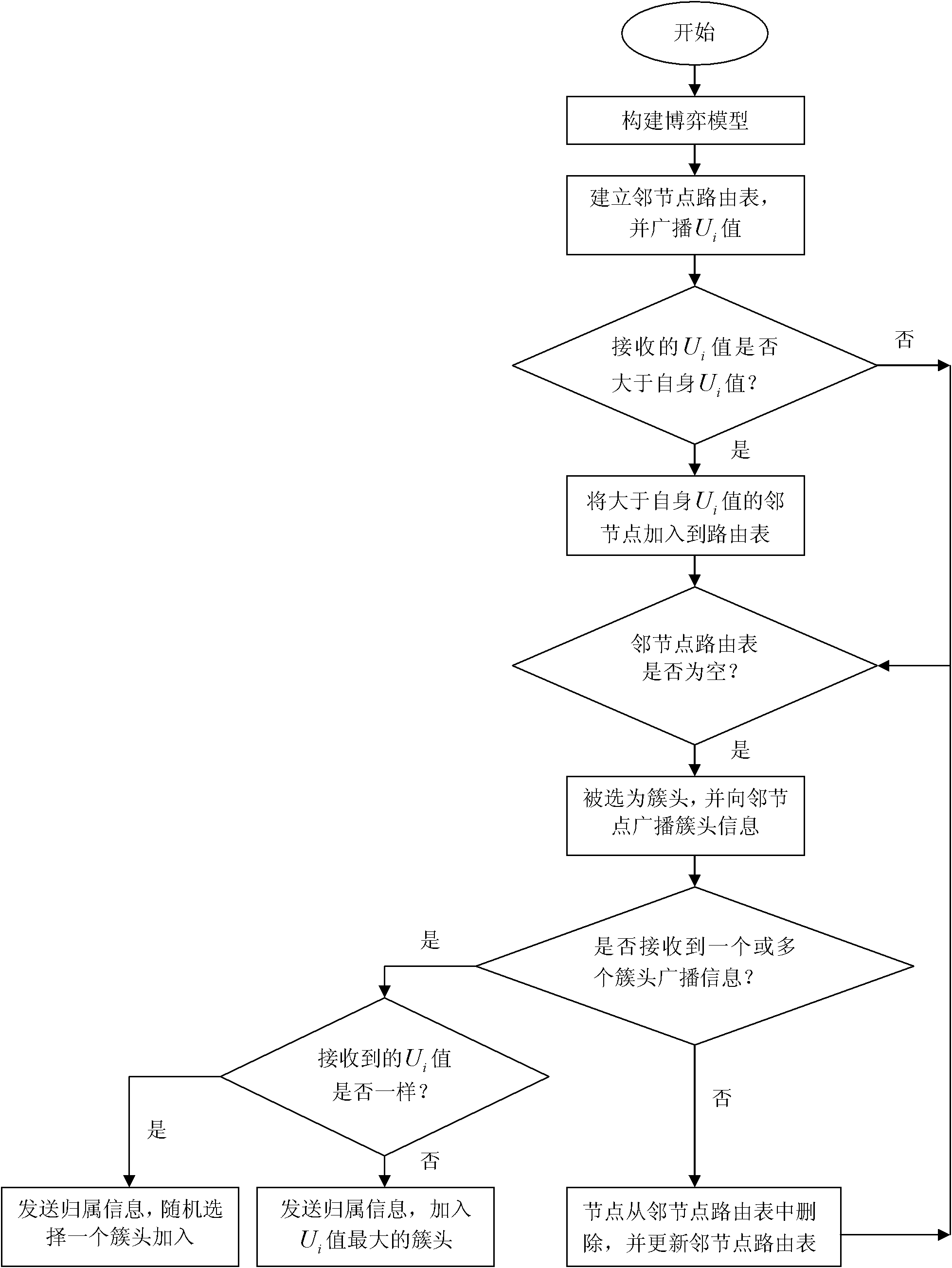
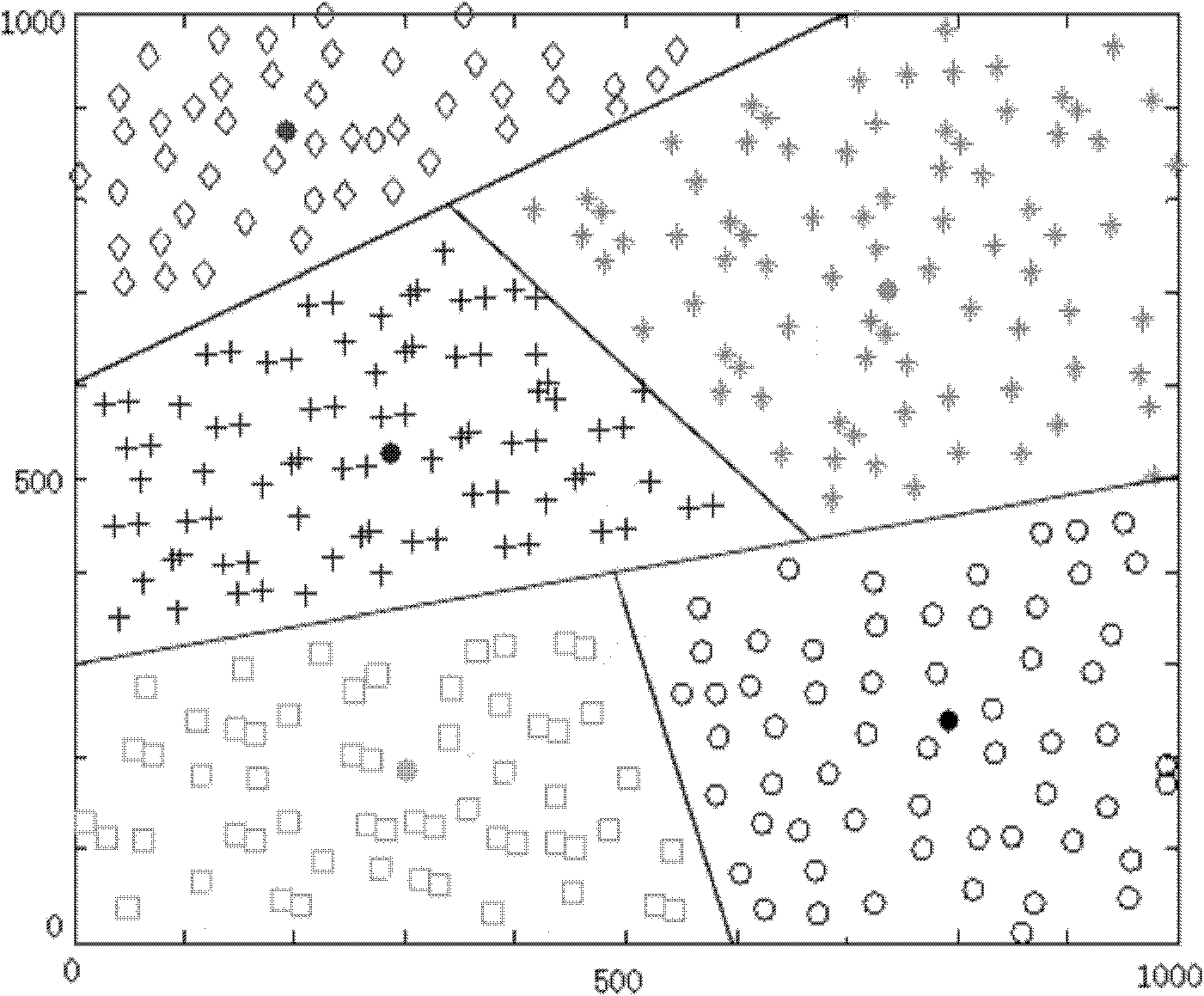
InactiveCN102098691AEvenly distributedImprove adjustabilityNetwork topologiesNetwork planningRobustificationNatural disaster
The invention discloses a method for establishing a scale-free sensor having survivability, mainly solving the problems of bad survivability, low adjustability and low universality in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps: selecting cluster heads according to games among nodes, and evenly distributing the cluster heads; then performing topology evolution on the cluster heads according to evolution means of a scale-free network to obtain survivable mathematical models of the scale-free sensor network; and finally constructing the sensor network by fully considering randomly adding points, randomly removing points, randomly trimming and reconnection according to actual application characteristics of the sensor network. The sensor network established by the method in the invention has the scale-free characteristic, excellent adjustability and universality, and the network has excellent survivability to random and deliberate attacks; the network can satisfy the requirements of severe environments such as natural disasters, military application and the like on robustness of the sensor network.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
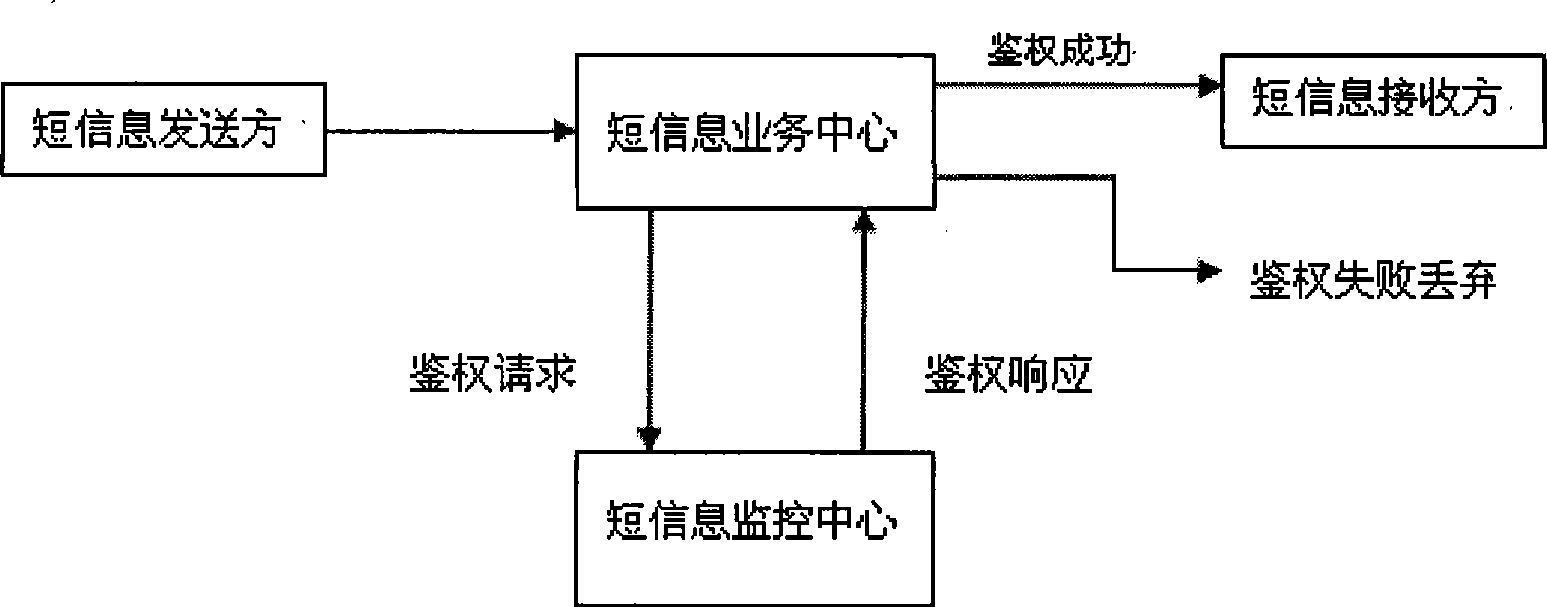
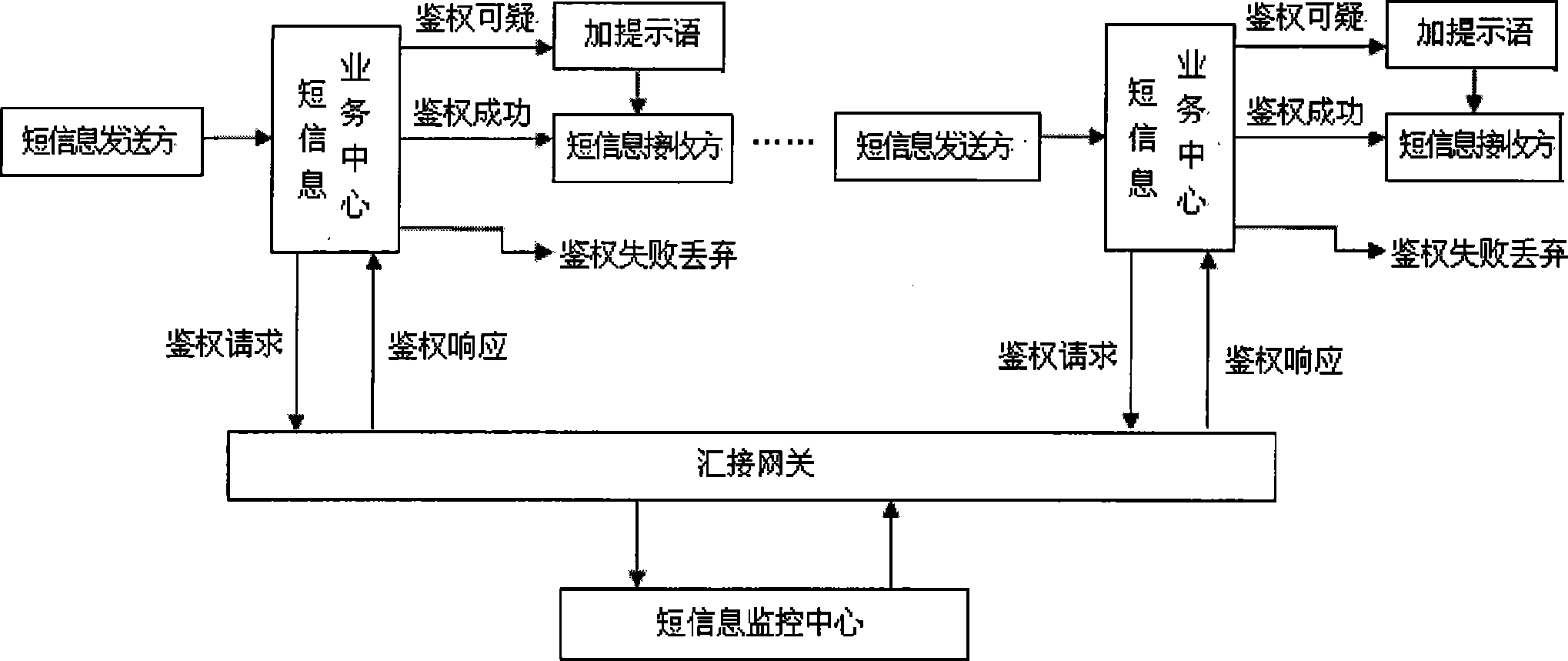
Short message monitoring method ensuring identity of sender based social network mechanism
InactiveCN101389074ASolid theoretical foundationAutomatic identity verificationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSecuring communicationShort Message ServiceThird generation
The invention discloses a short message monitoring method that determines identity of senders based on social network mechanism. Short message is a shortcut method that applies wireless communication technology, which is not different from face to face communication, letter communication, voice conversation and Email communication in essence. The social network belongs to scale-free networks in complex network category. Clustering is a basic characteristic of the social network. The invention starting from clustering of the social network to implement short message preprocess and re-real time filtering based on communication historical records between short message senders and receivers and between receivers determines identity of the senders to block spam short messages. A short message monitoring centre is used in a hardware platform using symmetrical multi-process SMP technology. The monitoring centre is characterized in free maintenance, high blocking rate, low mis-judgment, which is not applicable for text short message filtering, but also effective to voice short message, multi-media short message in 3G generation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
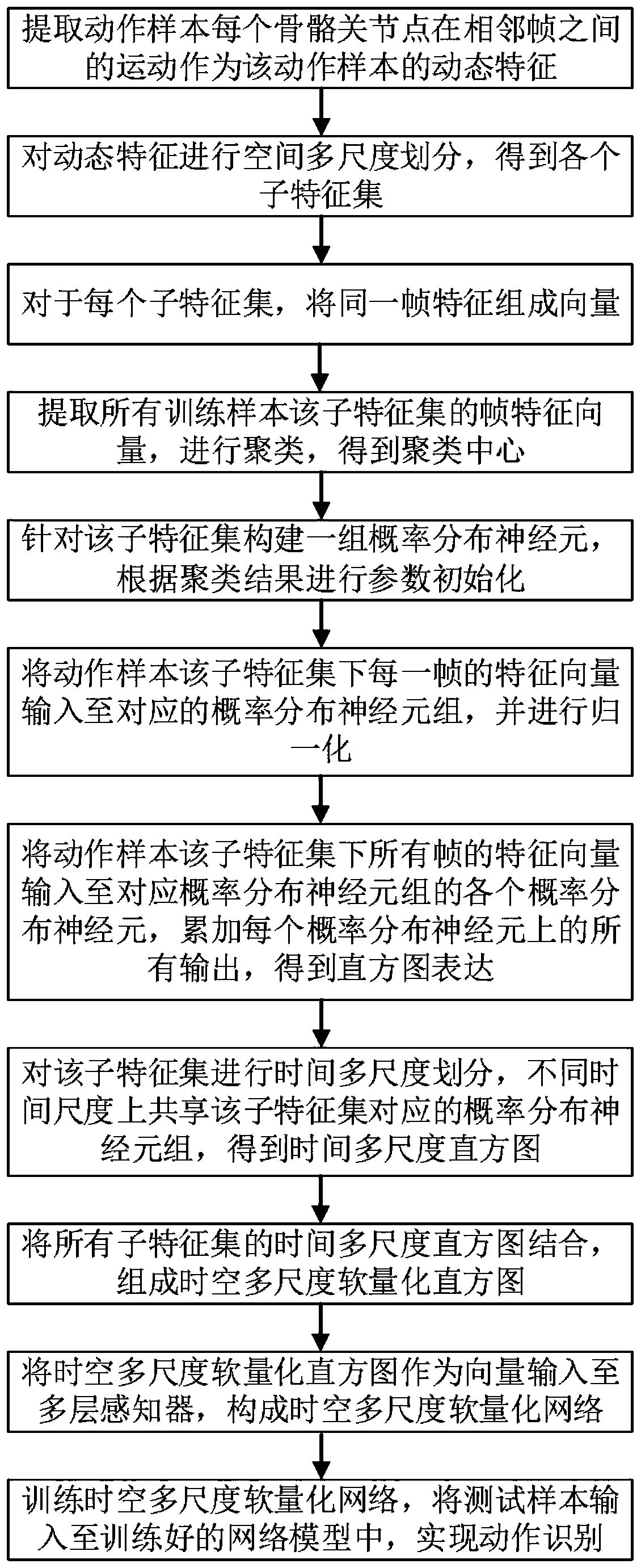
Human body action recognition method
ActiveCN110119707AImprove discriminationReduce in quantityCharacter and pattern recognitionHuman bodyFeature vector
The invention provides a human body action recognition method. The method comprises the following steps of extracting movement of each skeleton joint point of an action sample between adjacent framesto serve as dynamic characteristics of the action sample; performing spatial multi-scale division on the dynamic features to obtain each sub-feature set; for each sub-feature set, enabling motion features of all skeleton joint points in the same frame to form vectors; extracting frame feature vectors of the sub-feature sets of all training samples, and performing clustering to obtain a clusteringcenter; inputting the feature vectors of all frames of the action sample into probability distribution neurons constructed by each sub-feature set, and accumulating all outputs on each probability distribution neuron to obtain histogram expression; performing time multi-scale division on the sub-feature set to obtain a time multi-scale histogram; forming a space-time multi-scale soft quantizationhistogram; forming a space-time multi-scale soft quantization network; and training the space-time multi-scale soft network, and inputting the test sample into the trained network model to realize action recognition.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
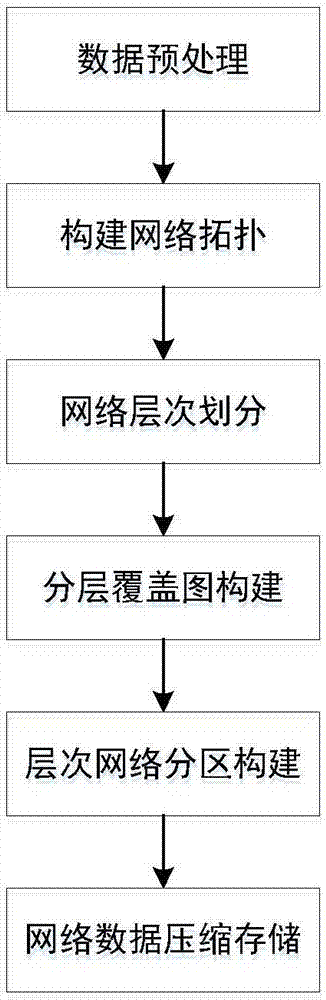
Hierarchical network construction method for data compression storage of massive road network
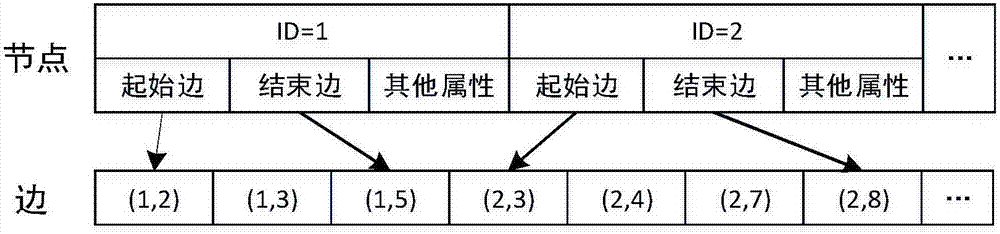
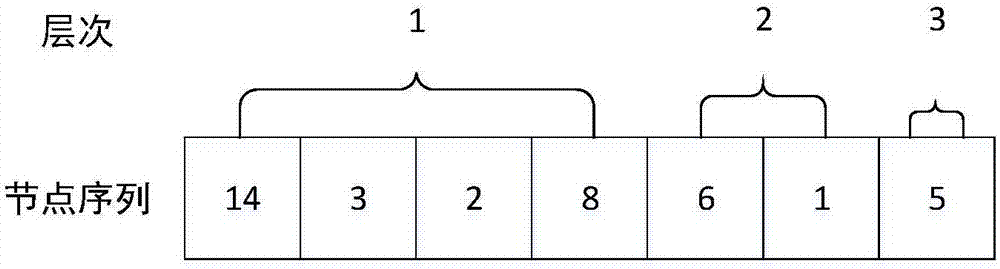
ActiveCN107330030AAvoid repeated searchesImprove compression efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsGeographical information databasesData compressionRelevant information
The invention discloses a hierarchical network construction method for the data compression storage of a massive road network. The method comprises the steps that hierarchy division is conducted on massive network data, the level of division can be set by parameters; based on the network layer division, a network overlay map is constructed, topology features of an upper layer network based on the shortest path are reconstructed, so that the upper layer network still has connectivity; the network is partitioned on the basis of hierarchical network overlay map; on the basis of the hierarchical network overlay map, partitioning is conducted on the network; on the basis of the hierarchical partition construction, the nodes in a region are compressed, and by calculating reachable nearest neighbor partition boundary nodes, a node is attached to the boundary nodes and relevant information is saved, so that the compression of the massive network data is achieved. The hierarchical network construction method is mainly used for the hierarchical construction and compression storage of a large-scale road network, the whole structure and topological features of the network can be kept well after the large-scale compression of the network, and the efficiency of the analysis algorithm for a sub network can be improved.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
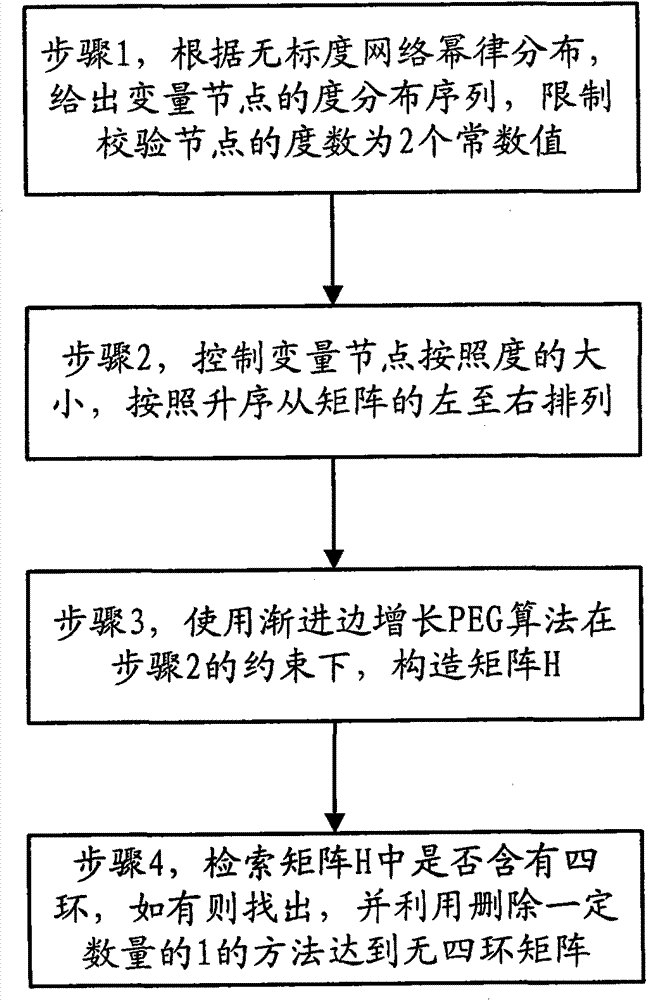
Construction method for low-density parity-check code
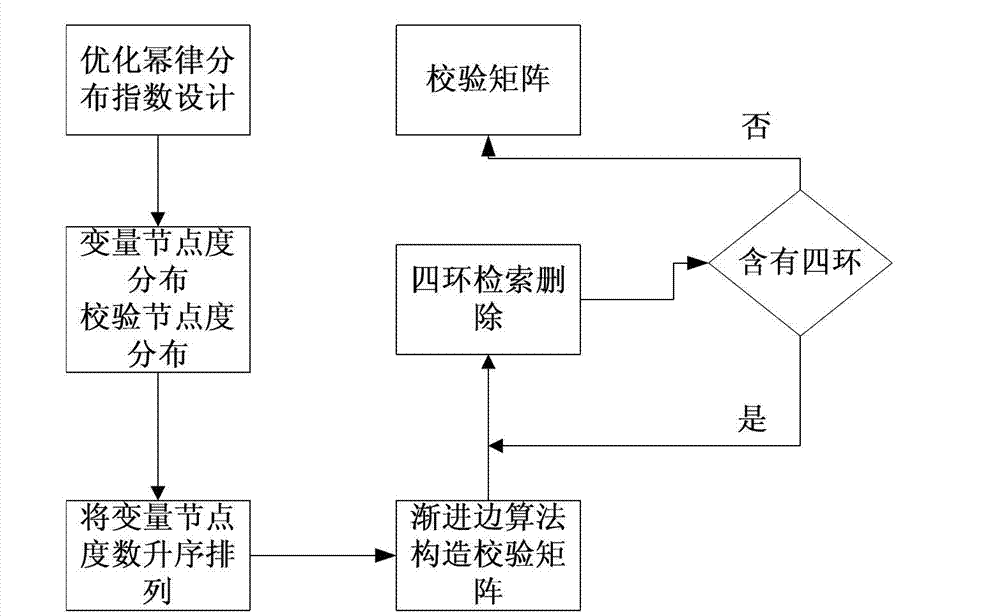
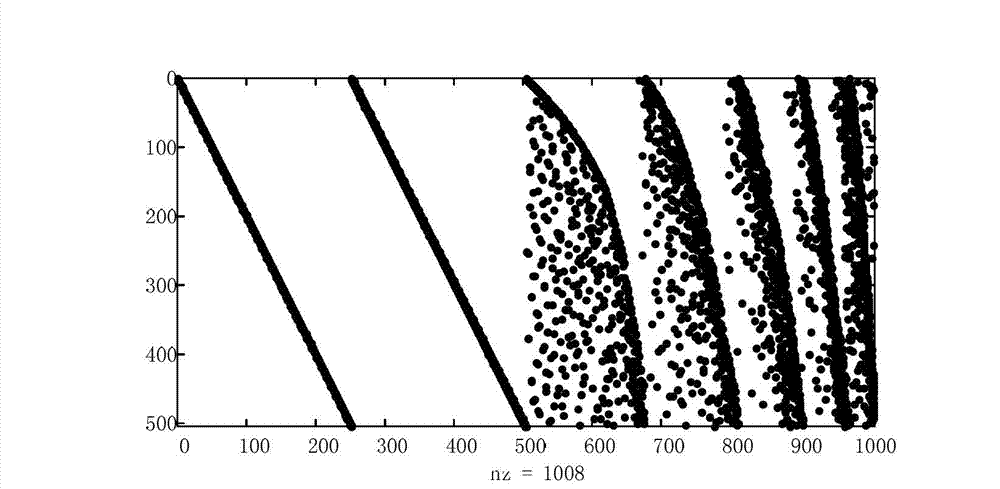
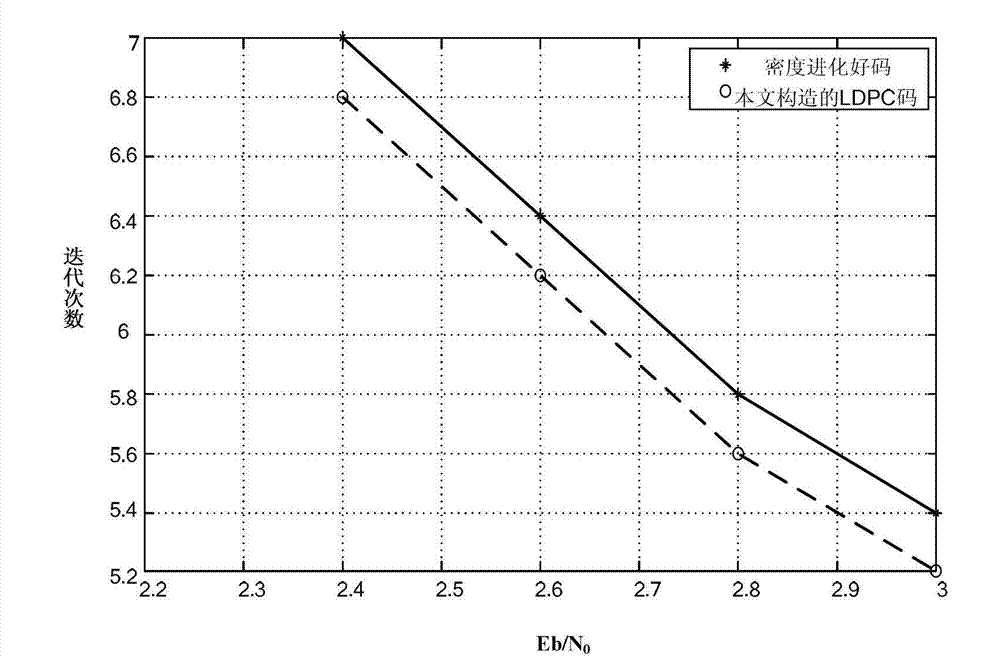
InactiveCN102811063AIterative decoding time reductionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsRound complexityLow-density parity-check code
The invention provides a construction method for a low-density parity-check code. A check matrix of the low-density parity-check code comprises variable nodes and check nodes. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: giving a degree distribution sequence of the variable nodes according to the power-law distribution of a scale-free network, and simultaneously limiting the degree of each check node to be two constant values; controlling the arrangement of the variable nodes from the left to right of the matrix according to an ascending sequence of degrees; constructing the check matrix under the constraint of the step 2 by using a progressive edge growth algorithm; and checking whether the check matrix obtained by the step 3 comprises four rings or not, and if the check matrix obtained by the step 3 comprises the four rings, finding the four rings, deleting a certain number l of rings by using a searing algorithm for the four rings to obtain a matrix without the four rings to obtain a final check matrix. The performance of the low-density parity-check code obtained by the method is not remarkably different from that of the conventional high-quality code, the complexity of the low-density parity-check code is remarkably lowered, and iterative decoding time is shortened.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
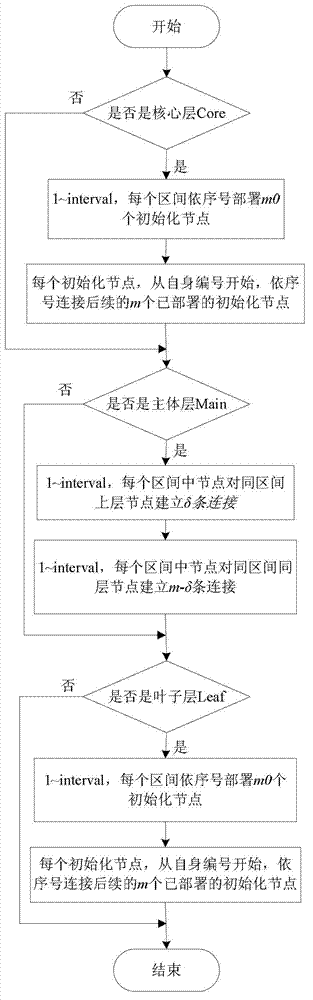
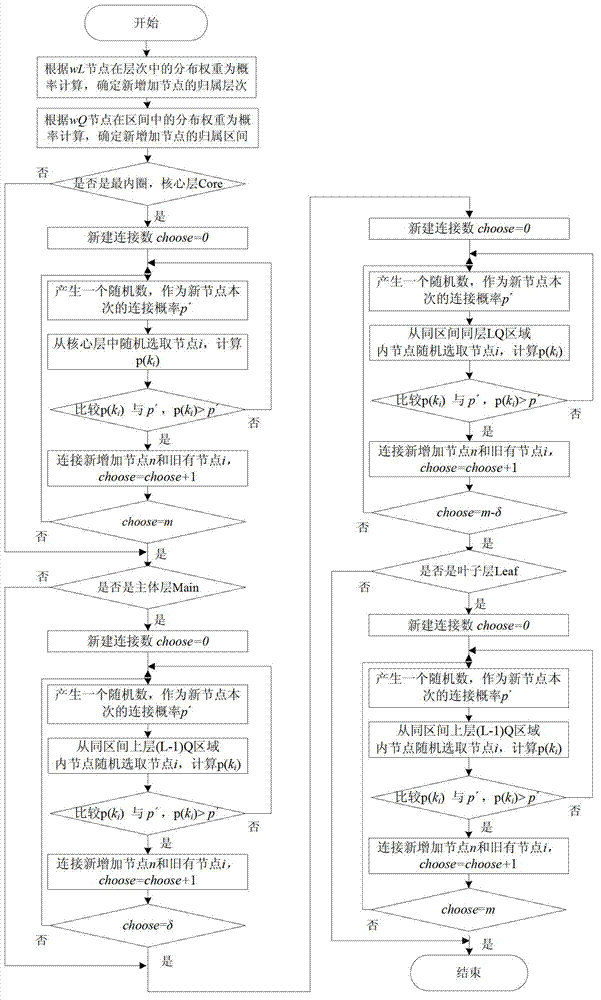
Scale-free network based router-level topology modeling method
The invention discloses a scale-free network based router-level topology modeling method. According to characteristics of increasing and preferential connection of a scale-free network, new added nodes are connected to old nodes, and many of the old nodes are connected so that nodes in a router-level topology are distributed in a power law mode; according to functions, organization relations and types of the nodes, the nodes in the router-level topology are divided into three layers of a core layer, a leaf layer and a main layer, and the layers are expandable; when the router-level topology is flattened to a plane, a radar chart is used for dividing connection quadrants, and the inside of the quadrants can be continuously refined and split; and as for the router-level topology, new nodes can be added to the layers / the quadrants according to ratios, and namely, probability calculation is performed according to weight to determine areas which the new added nodes belong to. By means of the mixing modeling method, degrees of coincidence with actual conditions are higher.
Owner:THE 28TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
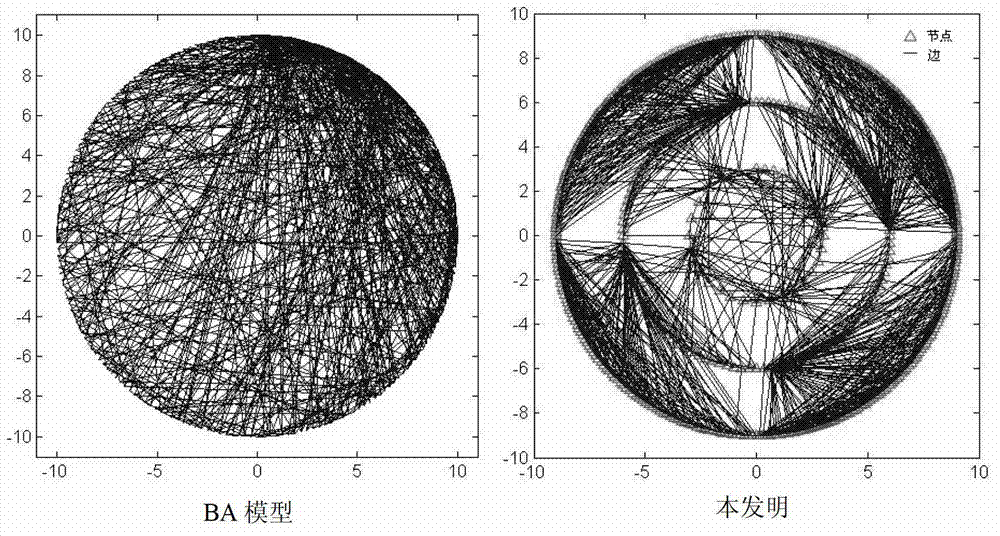
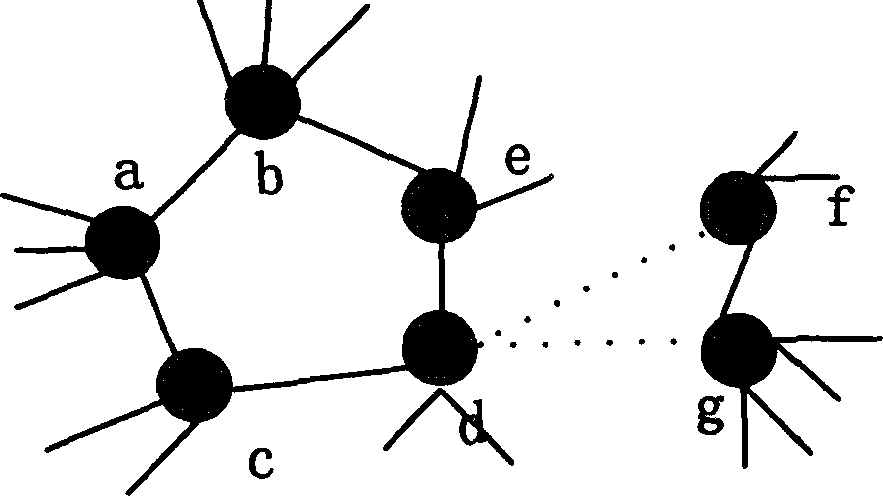
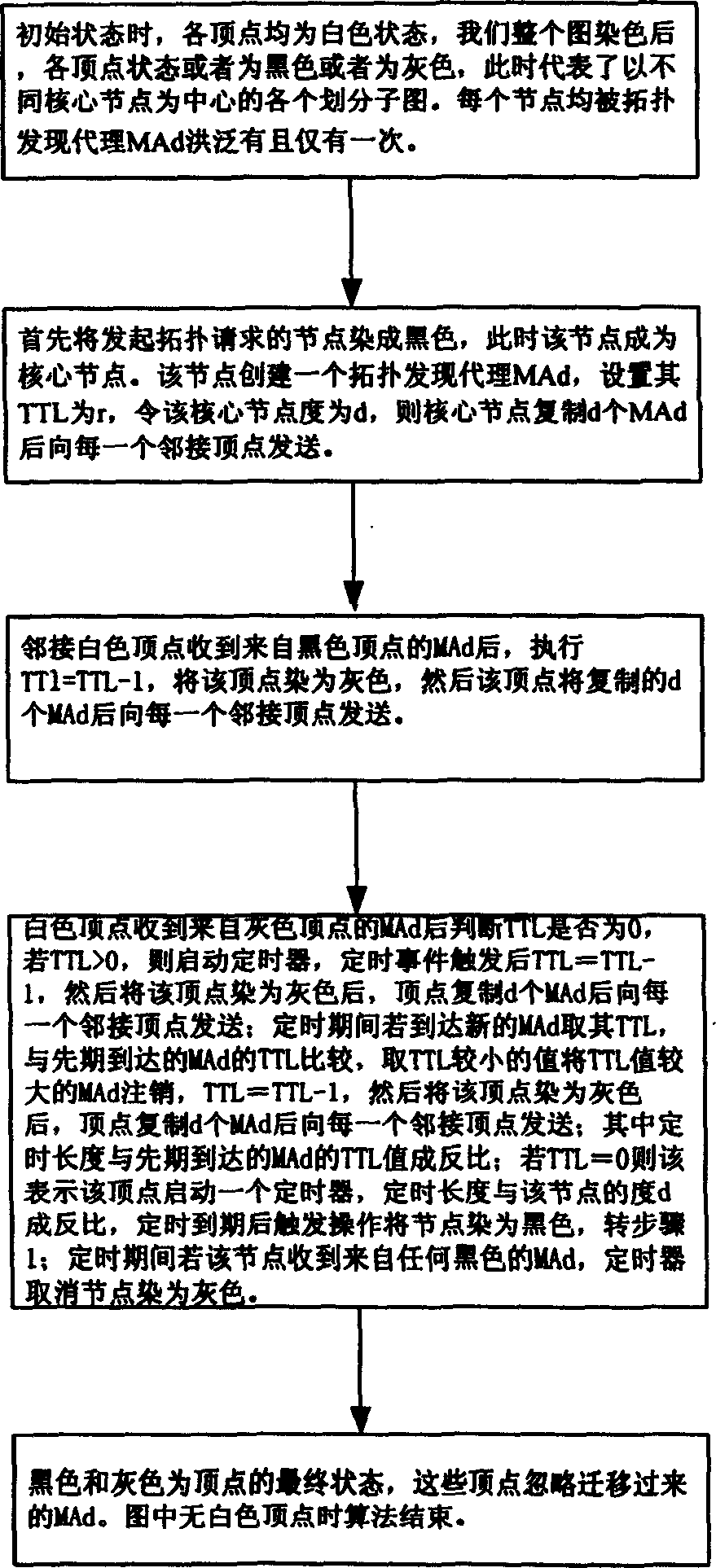
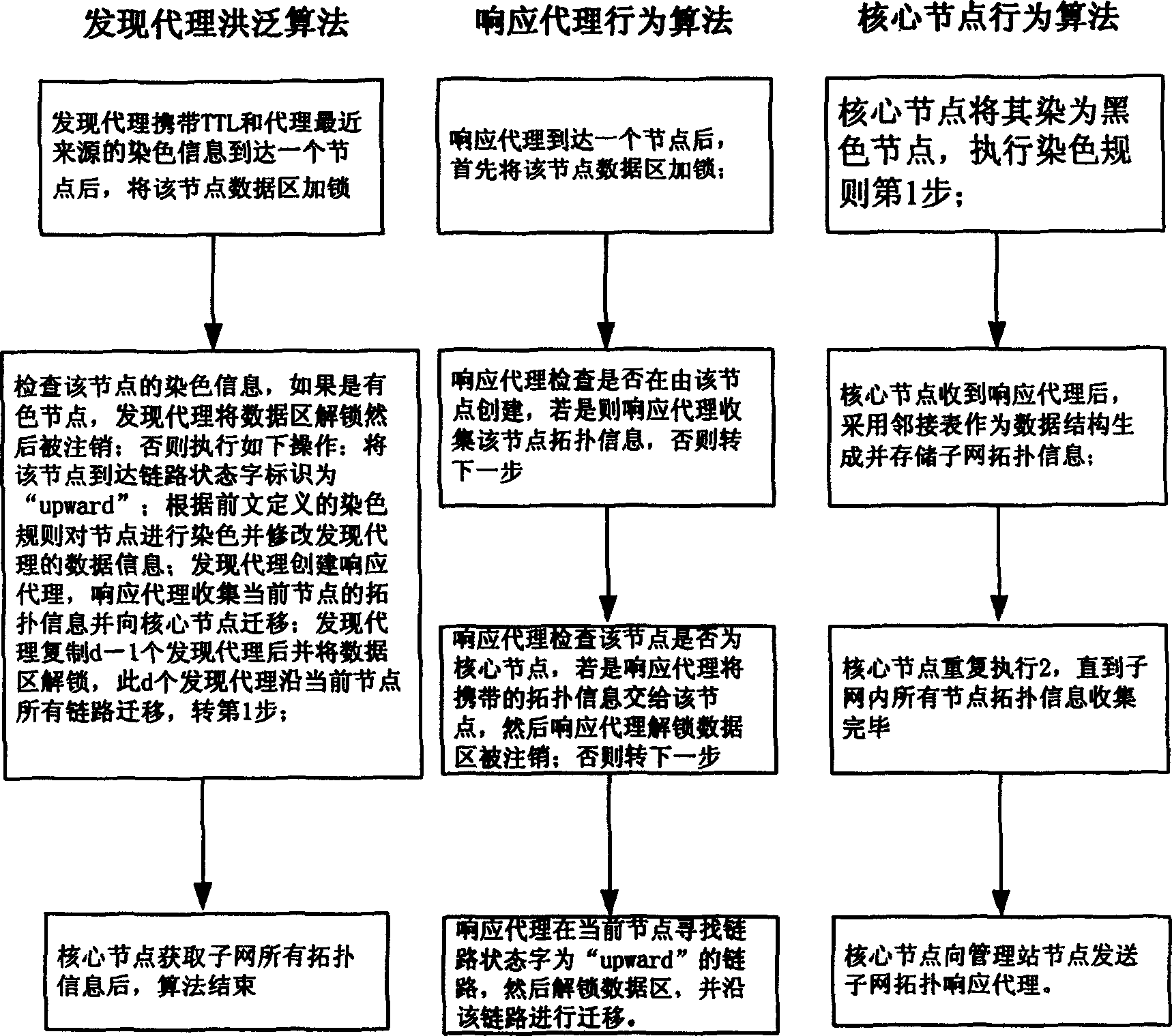
Topological project based on mobile agency in large scale network
InactiveCN1674546ARealize SegmentationReduce development difficultyData switching by path configurationNetwork managementScale-free network
The present invention relates to a topological scheme based on mobile commission in large-scale network. Said scheme includes two portion, namely, adopting vertex staining rule made by mobile commission and utilizing several mobile commissions to make cooperation and obtain subnet topological information, and further can obtain catanet topological information. Said scheme can solve the topological problem of large-scale network so as to provide effective and reliable assurance for further network management and network plan.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
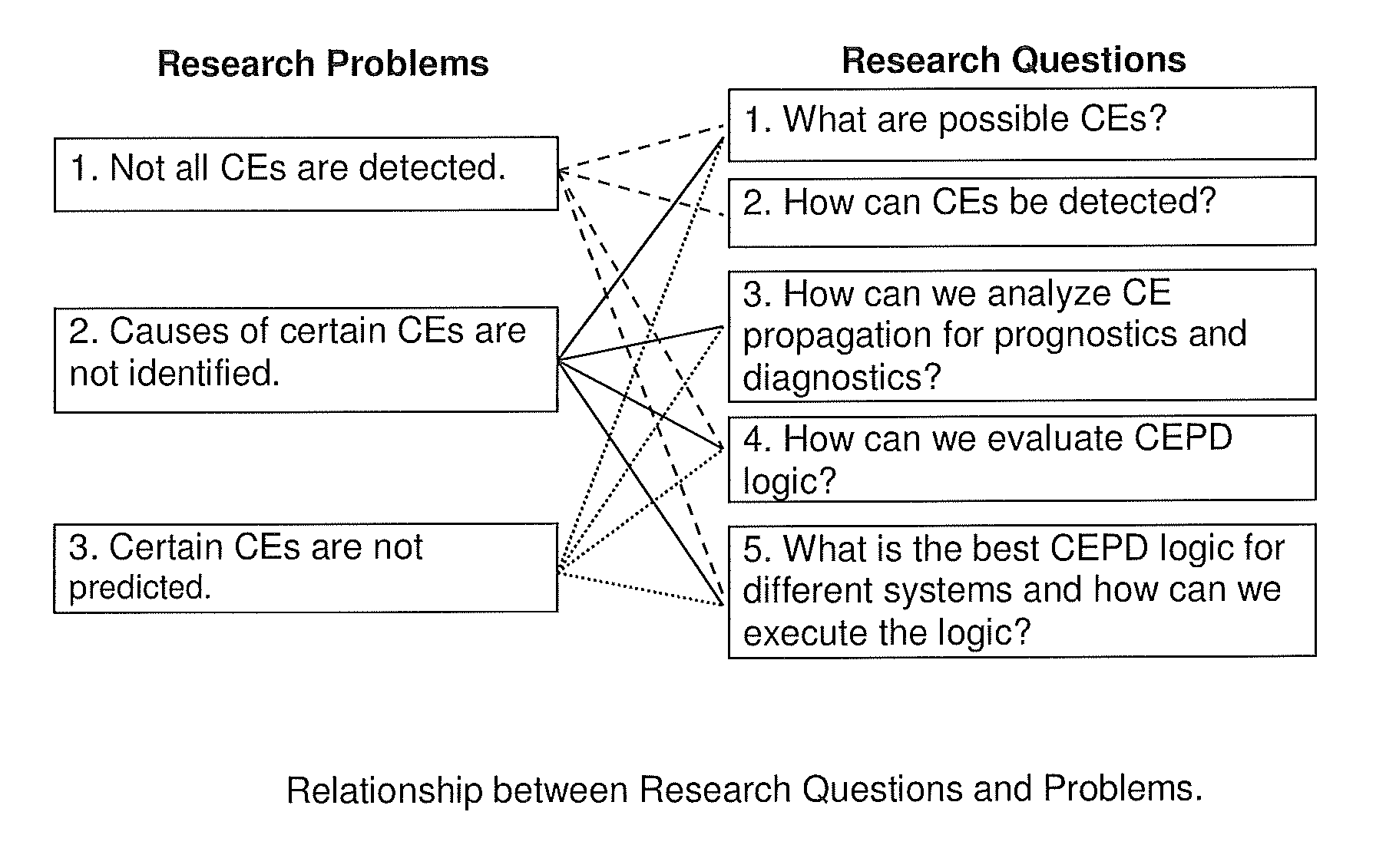
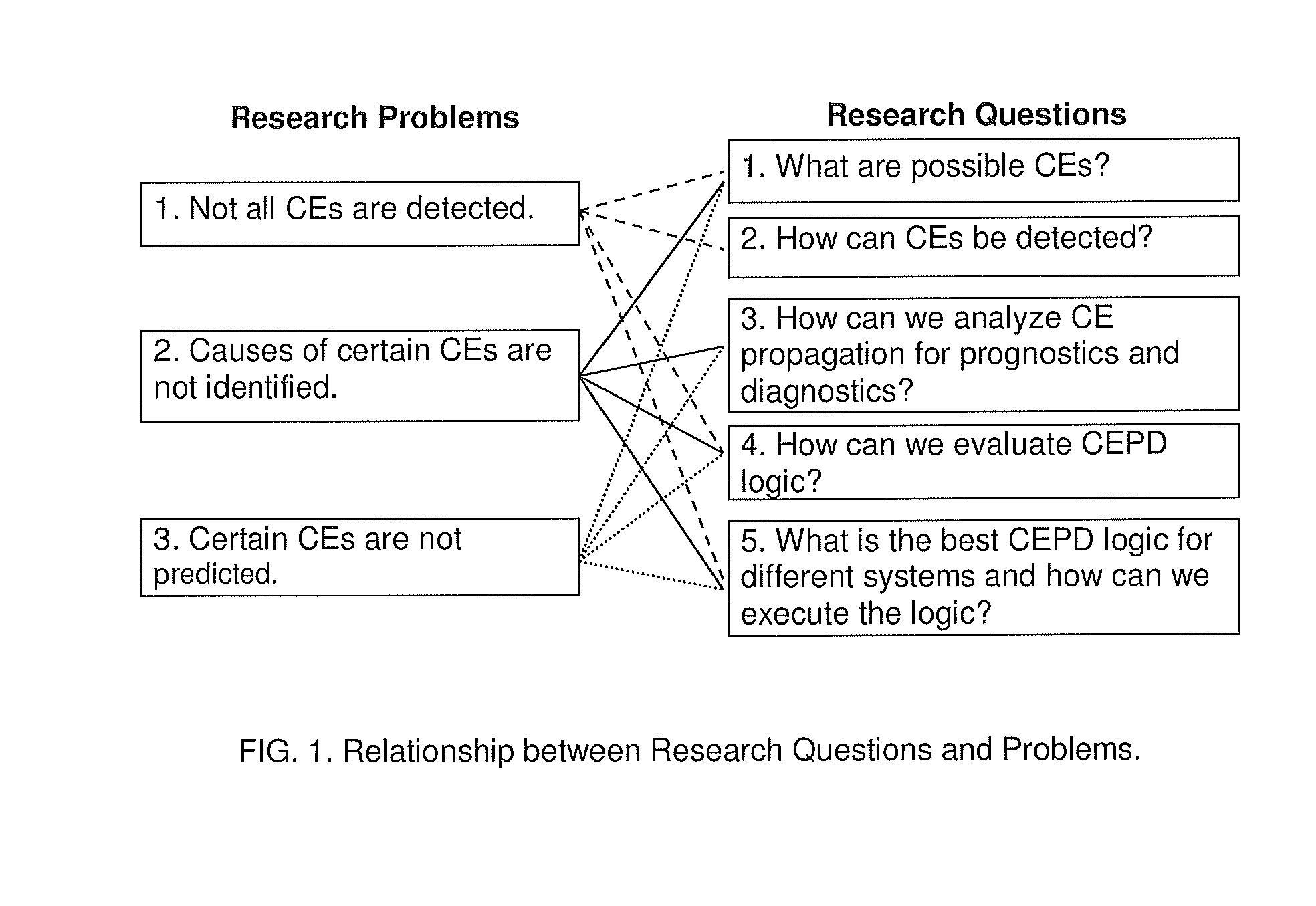
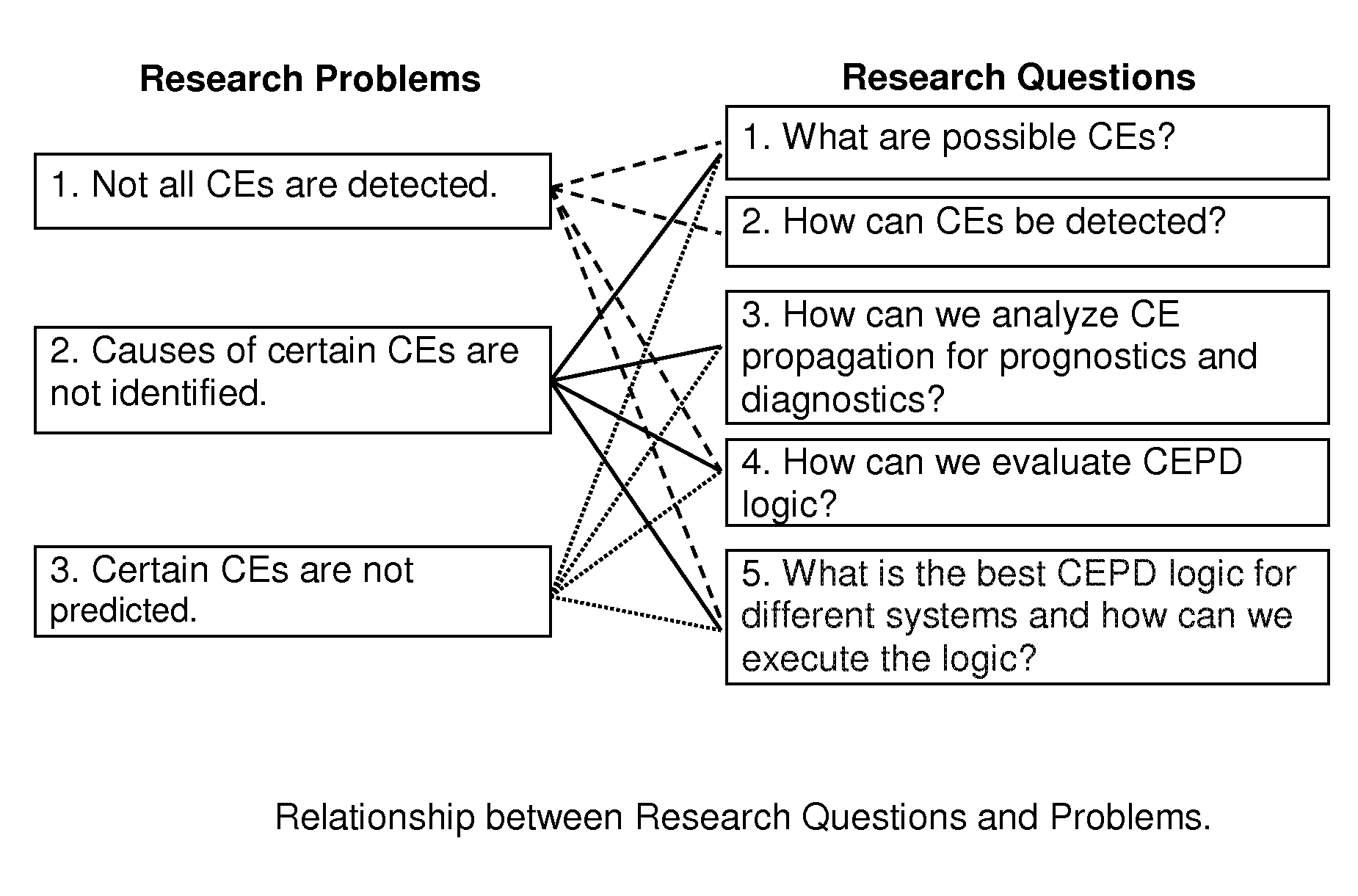
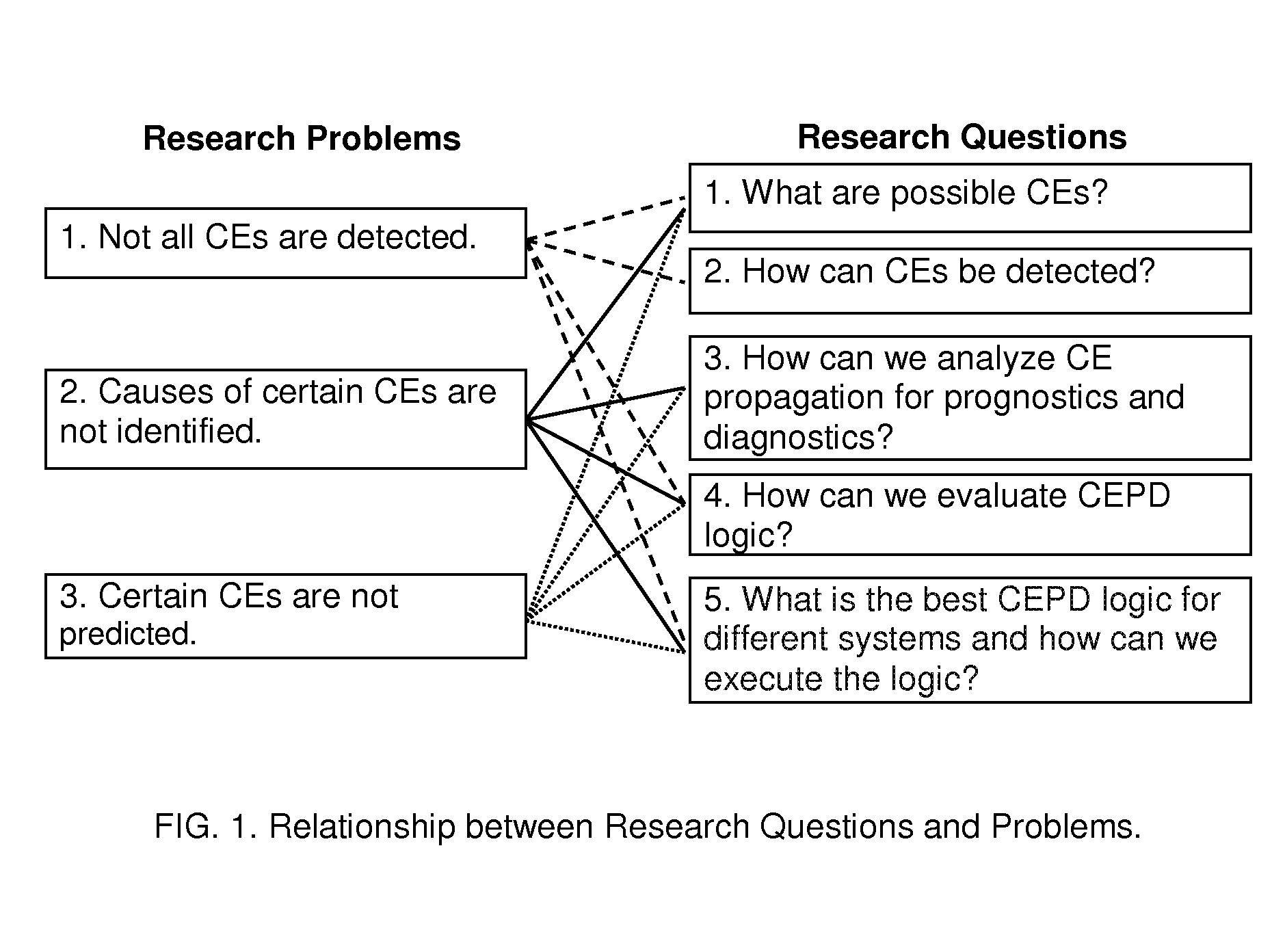
Interactive, Constraint-Network Prognostics and Diagnostics To Control Errors and Conflicts (IPDN)
ActiveUS20150301878A1Testing/monitoring control systemsNon-redundant fault processingError preventionScale-free network
Methods for interactively preventing and detecting conflicts and errors (CEs) through prognostics and diagnostics. Centralized and Decentralized Conflict and Error Prevention and Detection (CEPD) Logic is developed for prognostics and diagnostics over three types of real-world constraint networks: random networks (RN), scale-free networks (SFN), and Bose-Einstein condensation networks (BECN). A method is provided for selecting an appropriate CEPD algorithm from a plurality of algorithms having either centralized or decentralized CEPD logic, based on analysis of the characteristics of the CEPD algorithms and the characteristics of the constraint network.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
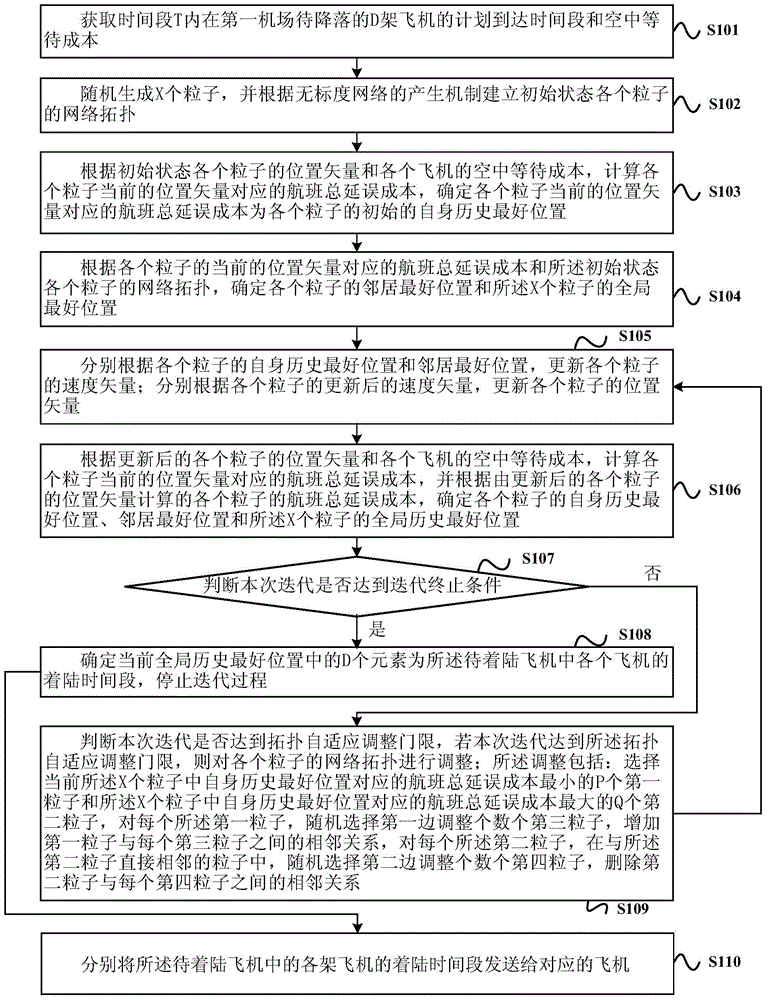
Flight scheduling method and flight scheduling device
ActiveCN104881720AFirmly connectedReduce connectionsForecastingBiological modelsLocal optimumArrival time
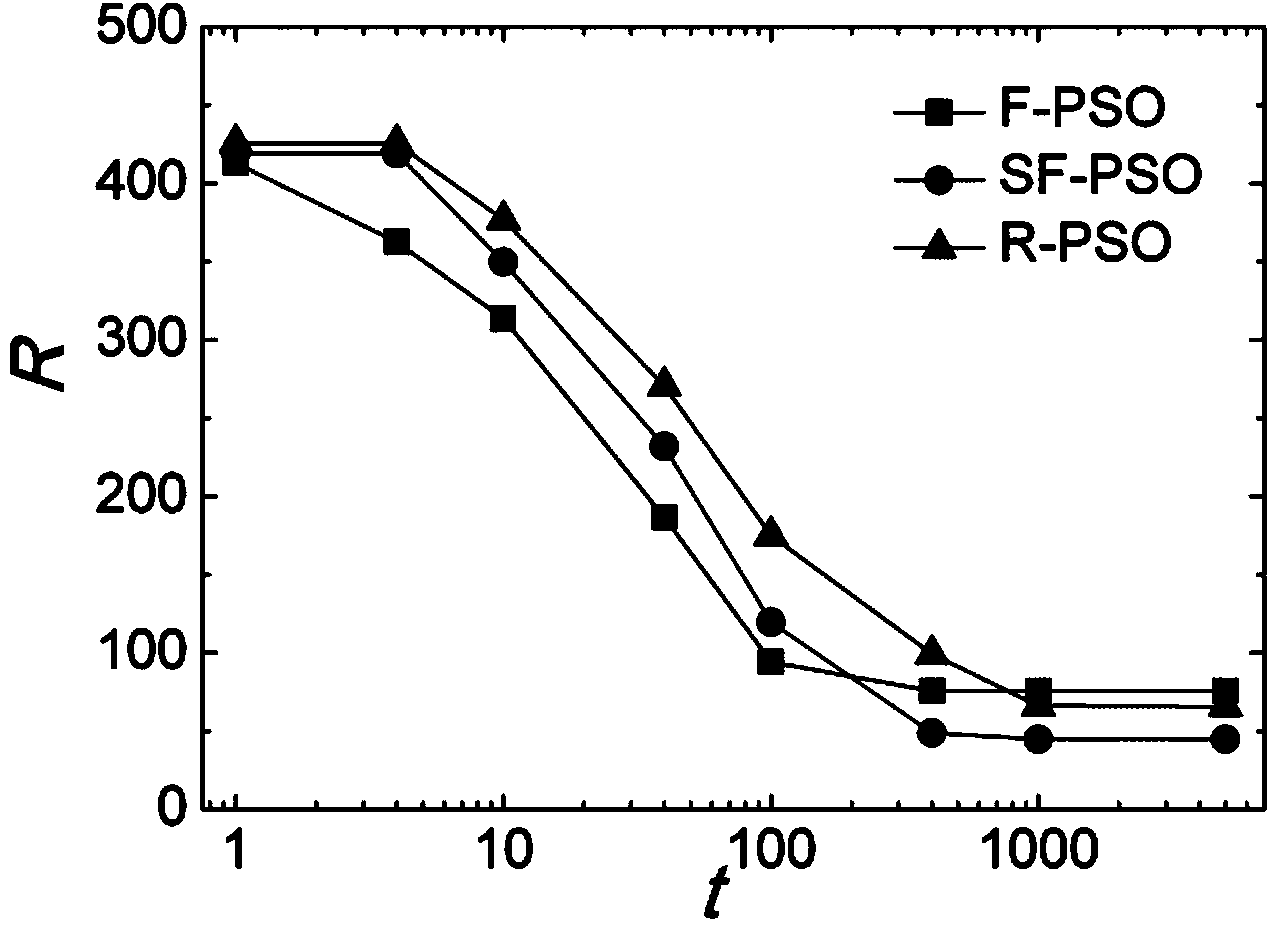
The invention provides a flight scheduling method and a flight scheduling device. According to the flight scheduling method, a generation mechanism of a scale-free network is adopted when the landing time of each flight is determined through the flight scheduling arrival time and the waiting cost in the air of each plane so as to generate a particle swarm network topology of the landing time of each flight, connection between P particles whose flight waiting cost is the minimum and other particles in the network topology are increased, and connection between Q particles whose flight waiting cost is the maximum and other particles in the network topology is reduced at the same time. According to the invention, a connection weight of the particles which are the closest to an optimal flight scheduling time result is increased, and a connection weight of the particles which are the furthest to the optimal flight scheduling time result is reduced, thereby enabling the convergence time of a finally acquired flight landing time result to be shortened, and improving the efficiency in determining the landing time of each flight. Due to a heterogeneity characteristic of the scale-free network, the diversity of the particle population network topology is ensured, and a result acquired by adopting a regular network is prevented from running into local optimum.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Event-synchronization protocol for parallel simulation of large-scale wireless networks
ActiveUS20090187395A1Easy to scaleAnalogue computers for electric apparatusRadio transmissionEvent synchronizationTimestamp
An event synchronization protocol called time-based synchronization (TBS) is employed to control operation of a network simulation. In TBS, processors in the simulated network execute events based on comparisons between timestamps for each event and a value generated by a time tracking device in the processor. In this manner, event execution is not dependent on other processes in the network and the simulation can actually be carried out at speeds faster than real time. A multiprocessor network is specially designed to execute TBS-based simulations.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Hybrid networks
InactiveUS7962632B2Flexibility of serviceUser may experienceMultiple digital computer combinationsTwo-way working systemsThird generationThe Internet
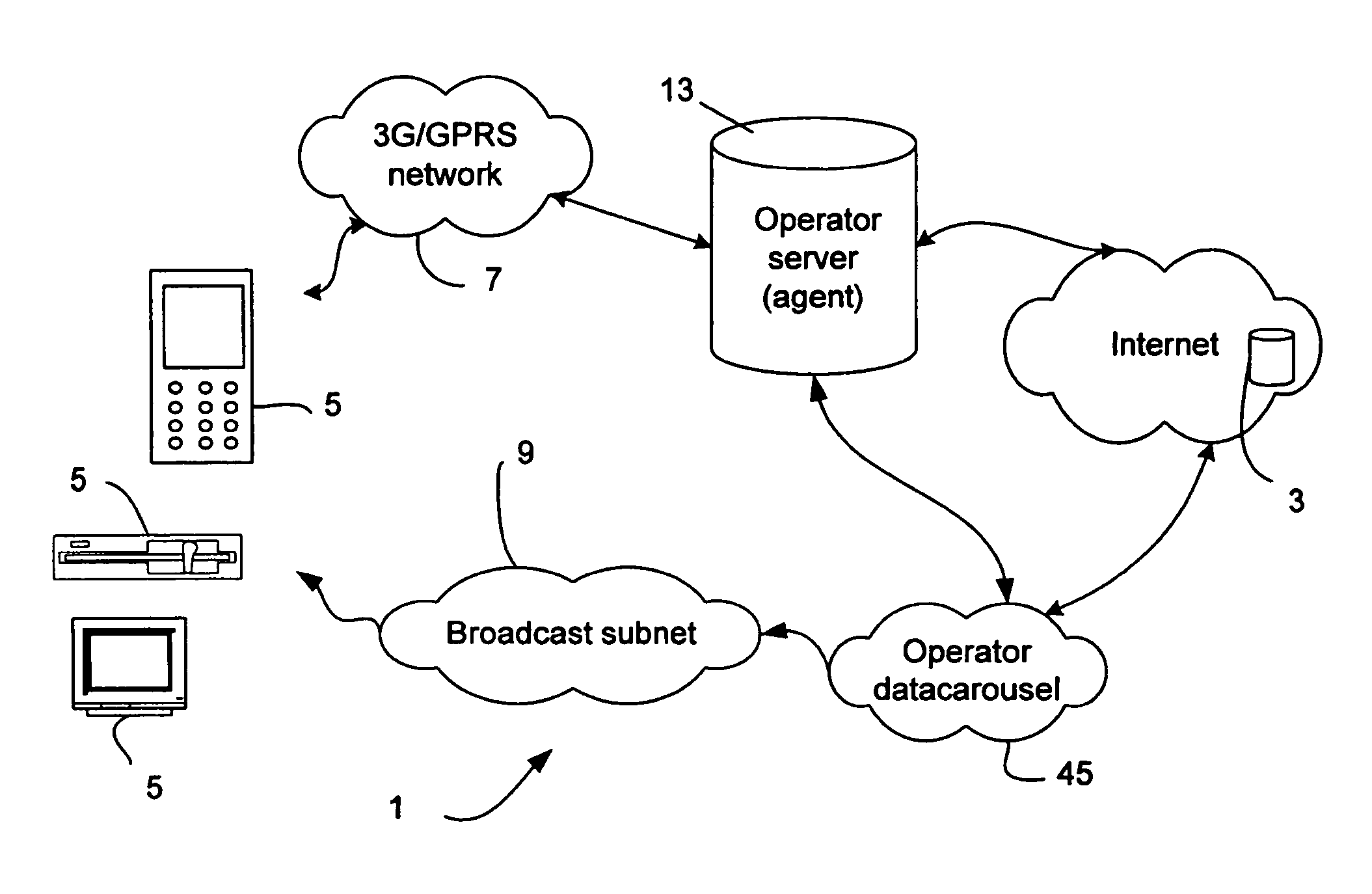
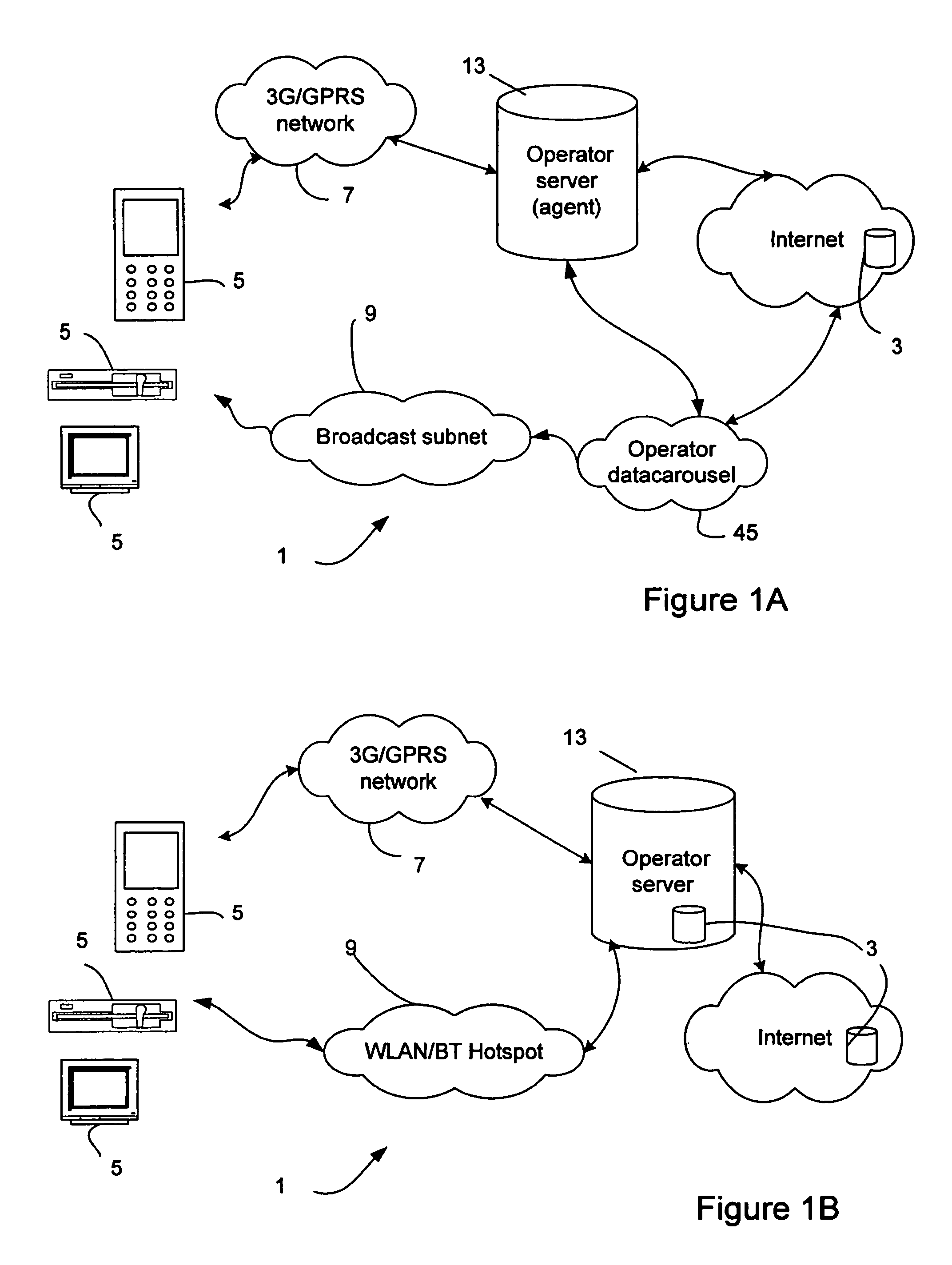
A user through a mobile or fixed terminal (5) informs an agent (33) hosted by an operator server (13) of subjects in respect of which content is requested. The agent (33) searches the internet for relevant content, and determines from a set of user preferences, relating to cost and timing of delivery preferences, a network for use in delivering the content to the terminal. Delivery may be made by a free network, e.g. a WLAN or Bluetooth network, if one is available, or over an expensive network such as a 3G, GSM or GPRS network if the content is requited quickly. If delivery is to be made over a broadcast network (11), such as a DVB-T network (11), a signal is sent to the terminal over a mobile telephone network (7) giving the time of broadcast, in response to which the terminal (5) enables its broadcast receiver at the appropriate time. Also, the agent (33) periodically reviews the content on a data carousel (45) which is awaiting broadcast, and informs the terminal (5) of any forthcoming content which is relevant to the user request.
Owner:RPX CORP
Interactive, constraint-network prognostics and diagnostics to control errors and conflicts (IPDN)
ActiveUS9009530B1Avoid detectionTesting/monitoring control systemsSoftware testing/debuggingError preventionScale-free network
Methods for interactively preventing and detecting conflicts and errors (CEs) through prognostics and diagnostics. Centralized and Decentralized Conflict and Error Prevention and Detection (CEPD) Logic is developed for prognostics and diagnostics over three types of real-world constraint networks: random networks (RN), scale-free networks (SFN), and Bose-Einstein condensation networks (BECN). A method is provided for selecting an appropriate CEPD algorithm from a plurality of algorithms having either centralized or decentralized CEPD logic, based on analysis of the characteristics of the CEPD algorithms and the characteristics of the constraint network.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Building method of complex network
InactiveCN103870691AEasy to buildReduce computational complexitySpecial data processing applicationsScale-free networkComputer science
The invention discloses a building method of a complex network. The building method comprises main steps of generated network determination, adjacent matrix calculation, degree distribution polynomial determination, complex network adjacent matrix calculation and the like. The complex network obtained by adopting the building method simultaneously has the self-similarity and worldlet characteristics, the self-similarity characteristic derives from the fractal matrix form adjacent matrix generated through Kronecker product iteration of the generated network adjacent matrix, and the worldlet characteristic derives from the network with the diameter not exceeding two times of the diameter of the generated network. In addition, the degree distribution of the complex network can be theoretically worked out through the number multiplication and coefficient multiplication operation of the degree distribution polynomial expression form. Studies show that the degree distribution of the complex network does not meet the power-law distribution, i.e., the complex network is not a scale-free network.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Calculation method for optimizing municipal drainage network plane layout design
InactiveCN104462714AHigh degree of fitEasy to planGenetic modelsSpecial data processing applicationsScale-free networkCalculation methods
The invention discloses a calculation method for optimizing a municipal drainage network plane layout design. The calculation method is characterized by mainly comprising three steps that firstly, a construction cost fitness function which has high matching degree with drainage network assessment is constructed; secondly, an initialized population is obtained from a tree structure genetic algorithm initializing scheme based on the divide-and-conquer method; thirdly, an expanded variable population is obtained by utilizing a line-adding and circle-breaking method. The calculation method for optimizing the municipal drainage network plane layout design has the advantages that the matching degree between the constructed construction cost fitness function and the drainage network assessment is high, so a drainage network can be well planned; the tree structure genetic algorithm initializing scheme based on the divide-and-conquer method enables an initialized scheme of a tree structure to be completed rapidly, and large-scale initialization of the large-scale pipe network can be achieved; a variation algorithm of the drainage network is simpler by utilizing the line-adding and circle-breaking method, a novel pipe network planning map can be generated after each line is cut out in a circle with added lines, and variation diversity is guaranteed.
Owner:HEBEI INSTITUTE OF ARCHITECTURE AND CIVIL ENGINEERING
Dynamic link predication method of network structure
InactiveCN105490858AApplicable AnalysisImprove forecast accuracyData switching networksCurrent meterComputation complexity
The invention provides a dynamic link predication method of a network structure. The method comprises the following steps: step one, inputting a network structure corresponding to a service object; step two, performing Jaccard distance conversion on the input network structure to obtain a processed network structure; step three, calculating the distance between every two nodes in the network structure; step four, obtaining a network structure with a marked priority at current time; step five, repeatedly executing the step one to the step four at next time to obtain a network structure with a marked priority at the next time, wherein the priority of each link at the next time is postponed to the priority at the current time, and the priorities of the links are successively marked from high to low according to time; and step fix, taking a network structure with a marked priority at each time as a predication result of one network structure for a user to perform analysis processing on the service object. According to the invention, based on a dynamic network topology structure, a dynamic evolution mechanism of a complex network is taken into consideration, the calculation complexity is quite low, and the method provided by the invention is applied to link prediction of a large-scale network.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
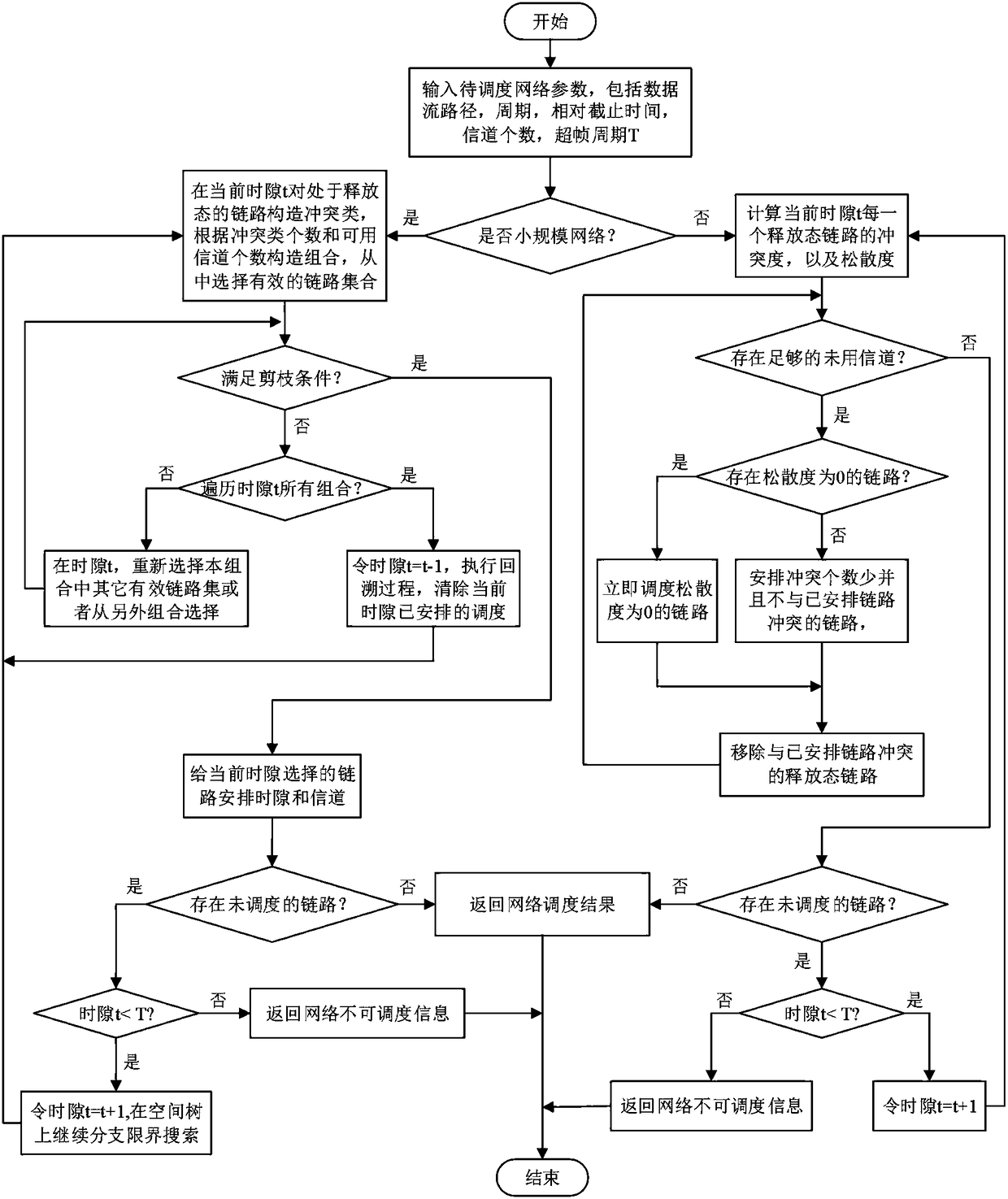
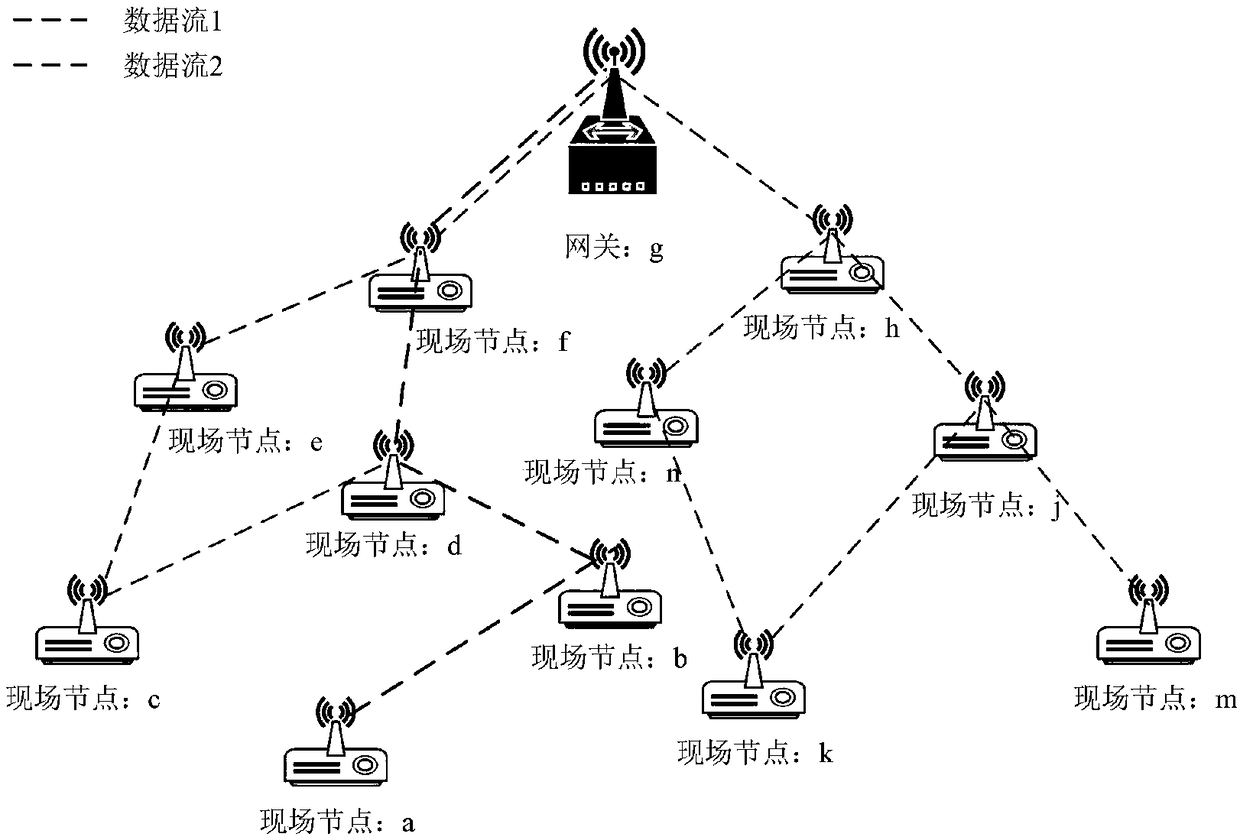
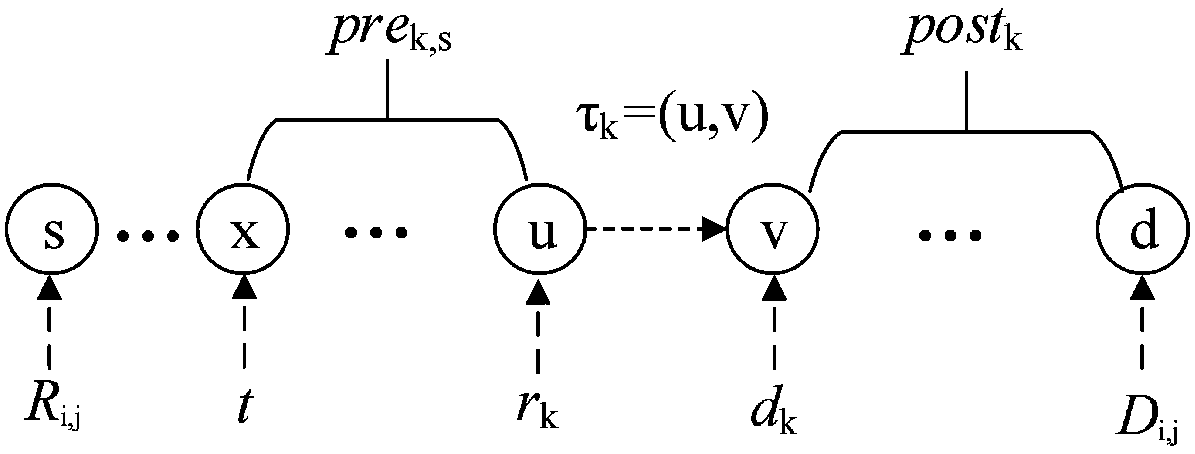
Industrial wireless network deterministic scheduling method supporting transmission delay optimization
ActiveCN108184244AOptimal Scheduling Success RateExtension of timeWireless communicationScale-free networkComputer science
The invention relates to an industrial wireless network deterministic scheduling method supporting transmission delay optimization, and belongs to the technical field of industrial wireless networks.For a small-scale network, a branch and bound method based on link conflict classification is adopted; the method is an optimal algorithm; due to release-state link classification, pruning condition judgment on an effective link subset is carried out; continuous searching is carried out in a solution space tree; when the network has a feasible solution, a scheduling solution satisfying deterministic demands can be searched through the algorithm; for a large-scale network, a heuristic scheduling algorithm based on maximum parallel transmission is adopted; and, due to combined scheduling on thelink conflict degree and the loose degree, the scheduling solution can be obtained in a relatively short time. According to the scheduling method provided in the invention, on the premise that the deterministic transmission demands of a data flow are satisfied, the network average transmission delay also can be reduced; and the overall communication performance of the network is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
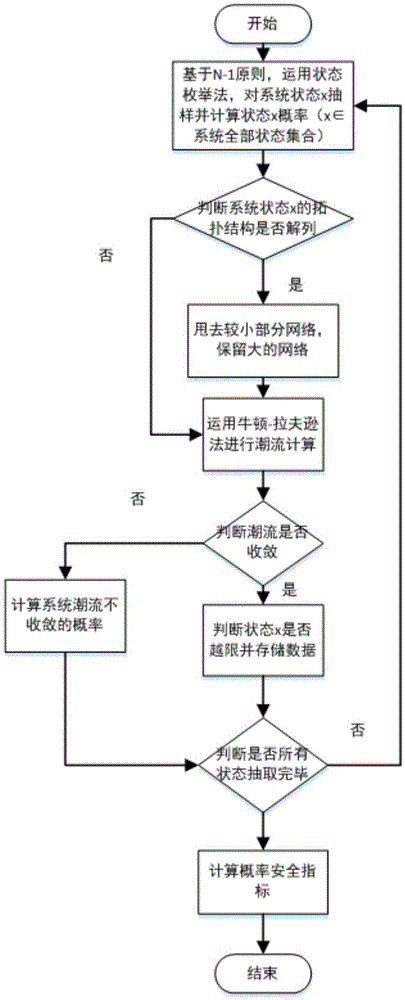
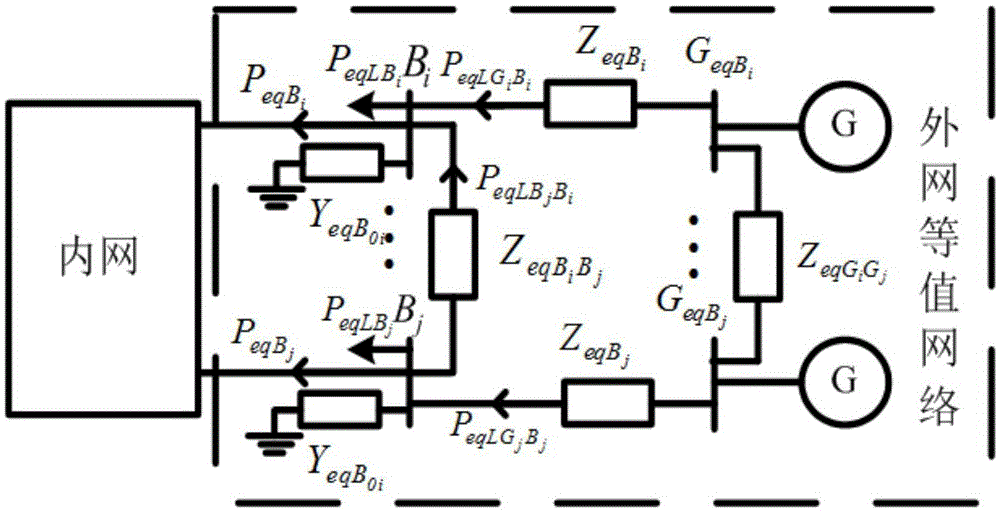
Probability static safety analysis method considering flow-and-sensitivity consistency equivalence
InactiveCN105656036ACalculation speedEnsure comprehensivenessData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmSecurity analysis
The invention discloses a probability static safety analysis method considering the flow-and-sensitivity consistency equivalence. The probability static safety analysis method includes the steps that basic data of a whole network is input, wherein the basic data comprises parameters and connected relations of system elements, the dividing condition of an internal network and an external network and the available rate of all the elements; equivalent networks are built according to a static equivalent method considering the sensitivity consistency and the element-type comprehensiveness, and the parameters of all the equivalent networks are calculated; according to the N-1 principle, the internal-network system states are sampled with the state enumeration method, whether the network topology is split or not is analyzed, and whether branch circuits or nodes exceed the limit or not is calculated and judged in a flow mode; the probability safety index of a system and the elements is synthetically calculated and compared with the result obtained based on the conventional on-hook equivalence theory. By means of the probability static safety analysis method, the comprehensiveness of equivalent elements can be described, the operating condition of the practical external network can be well simulated, the suitable power and voltage support can be provided for the internal network, the original large-scale external network is replaced with a small-scale network, and the calculation efficiency of probability static safety analysis is improved.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
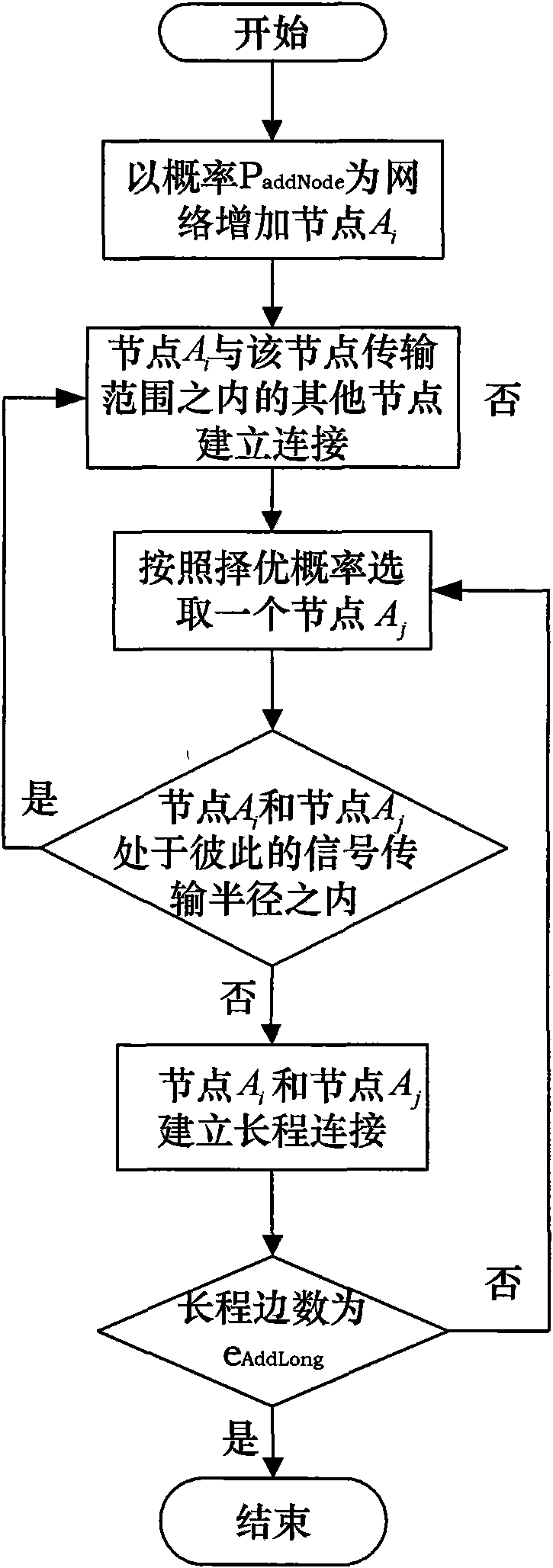
Mobile scale-free self-organizing network model building method
InactiveCN101572961AHas scale-free propertiesImprove connectivityEnergy efficient ICTNetwork topologiesNormal densityWireless sensor networking
The invention discloses a mobile scale-free self-organizing network model building method. Firstly the whole simulation zone of the whole network is supposed to be [X, Y]; signal transmission radius of a node is r0; space distribution probability density function of the node is pdfUnifonn, and border effect of the node is neglected; the network is supposed to be not provided with a node or a border; the node number of the whole network is N; then the network is added with nodes under the condition that probability PAddNode is equal to 1; a connection of the node Ai in local world is built; finally the node Ai is added with eAddLong long range connections in probability PAddLong. The scale-free network topology provided by the invention is more close to the real world. The scale-free network has high robustness on random node failure, therefore the scale-free network can optimize network connectivity, prolong life period of the network, save energy, improve throughput rate and capacity of the network and make the network to be more robust and scalability and can improve network search protocol efficiency.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
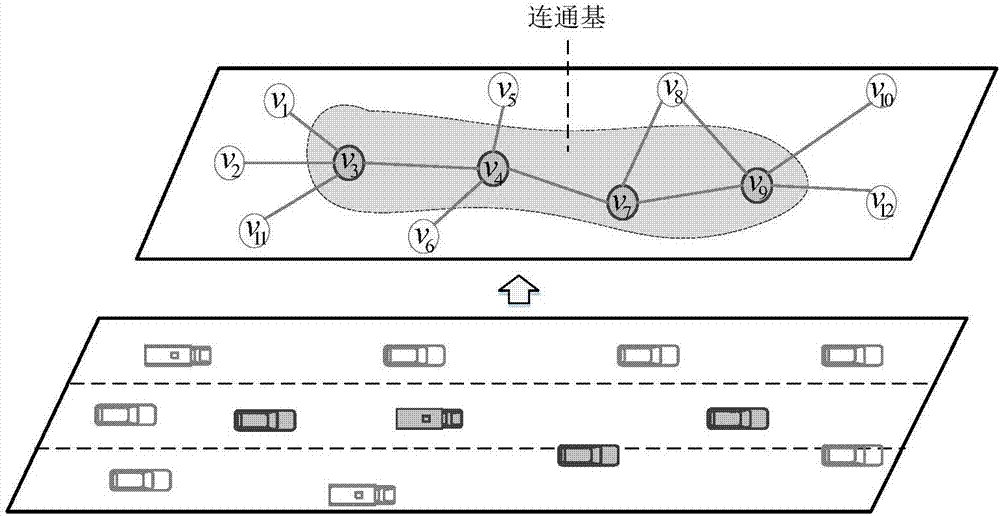
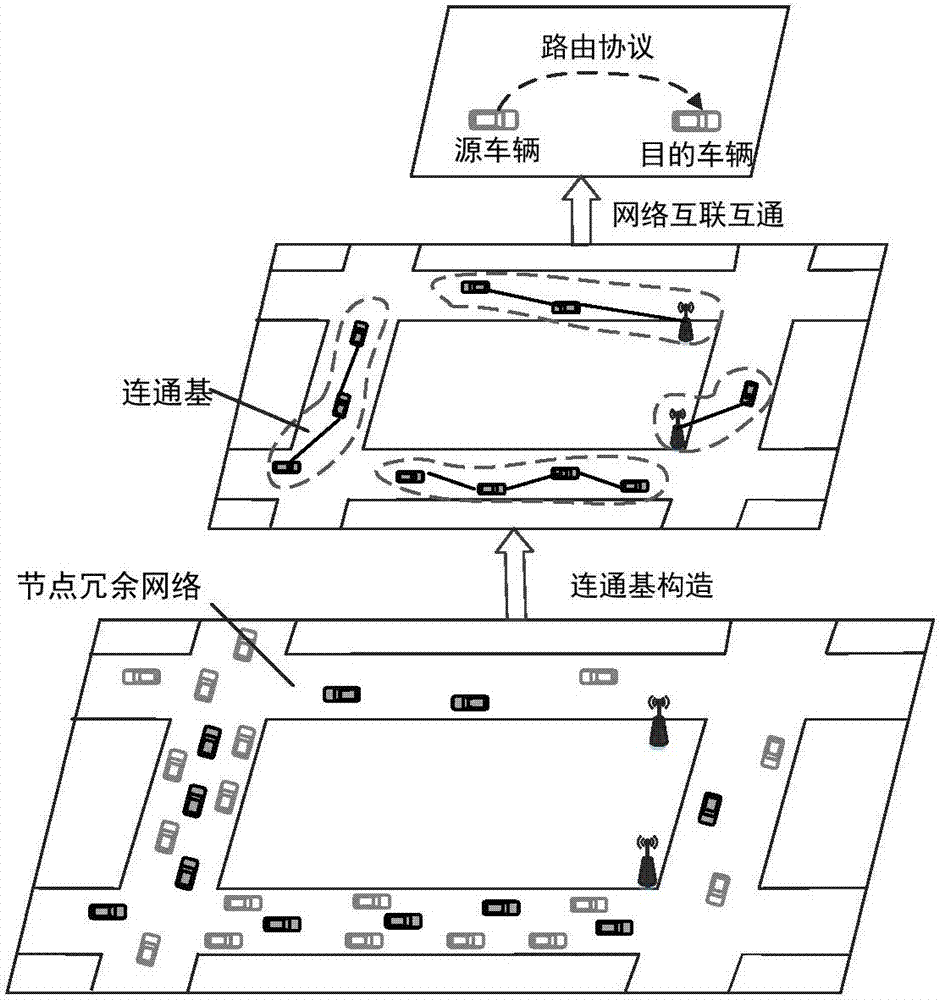
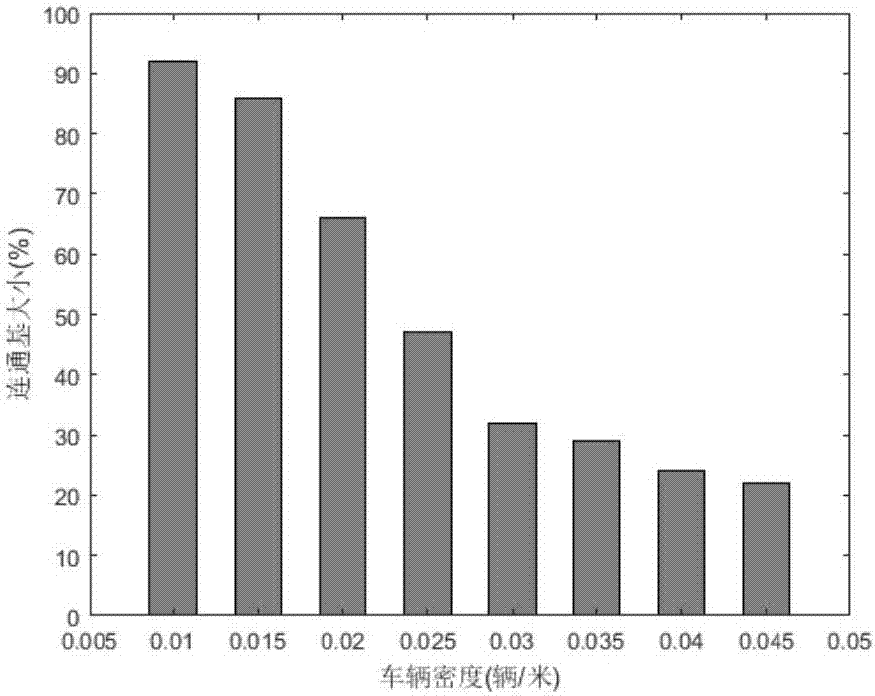
IOV large-scale network interconnected and intercommunicated communication base component construction method
ActiveCN107196835ASolve the problem of low communication efficiencyWireless commuication servicesNetworks interconnectionCouplingInterconnection
An IOV large-scale network objectively has low interconnection and intercommunication coupling degree due to the characteristics of enormous IOV large-scale network nodes in city scenes, frequent topological change, crisscrossed roads and the like. For the above problem, by considering the IOV network node redundancy characteristics, an IOV network topological structure, namely an IOV communication base, is provided; and furthermore, a communication base construction method is provided by utilization of a heuristic algorithm. By means of the IOV large-scale network interconnected and intercommunicated communication base component construction method in the invention, the problems of signal interference, network congestion and low communication efficiency due to the fact that IOV large-scale network redundant nodes substantially participate in communication in a city scene can be effectively solved; the IOV large-scale network interconnected and intercommunicated real-time performance and stability can be improved easily; and simultaneously, relatively high transmission efficiency can be provided for design and operation of IOV application services.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Event-synchronization protocol for parallel simulation of large-scale wireless networks
ActiveUS7564809B1Easy to scaleAnalogue computers for electric apparatusRadio transmissionTimestampEvent synchronization
An event synchronization protocol called time-based synchronization (TBS) is employed to control operation of a network simulation. In TBS, processors in the simulated network execute events based on comparisons between timestamps for each event and a value generated by a time tracking device in the processor. In this manner, event execution is not dependent on other processes in the network and the simulation can actually be carried out at speeds faster than real time. A multiprocessor network is specially designed to execute TBS-based simulations.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
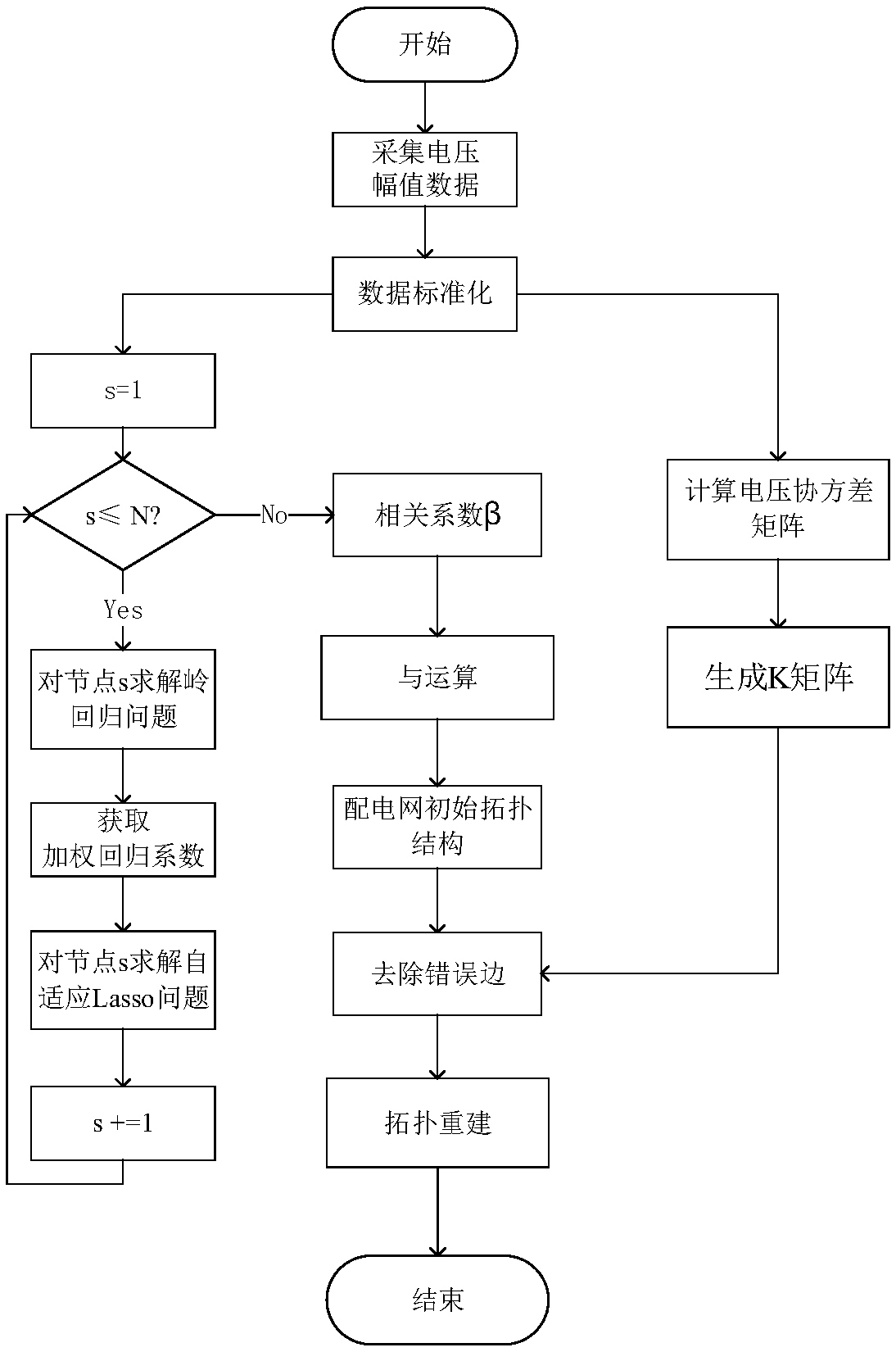
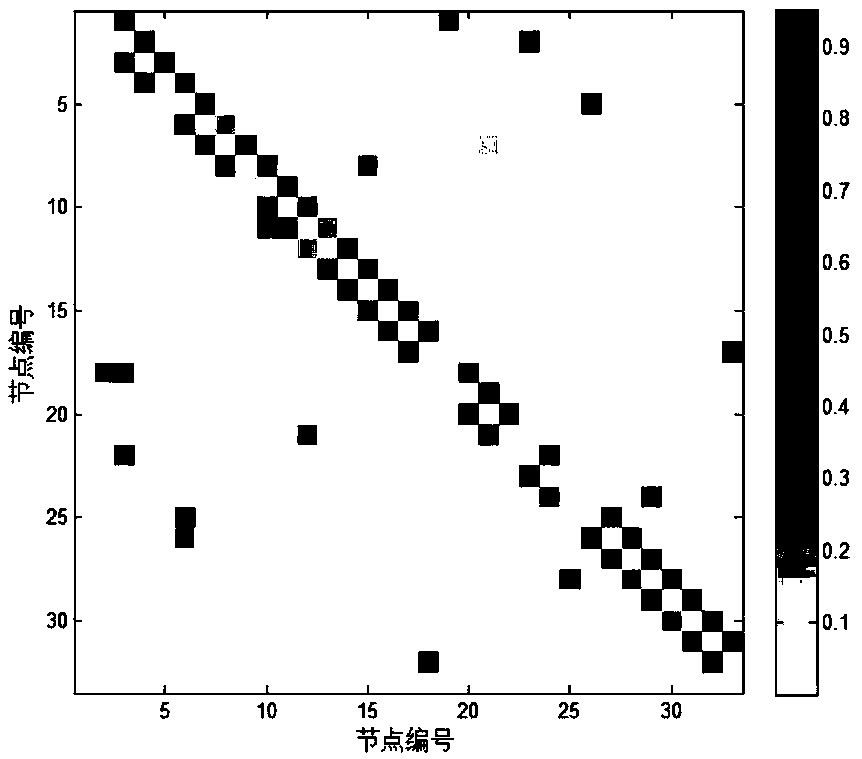
A distribution network topology reconstruction method based on adaptive sparse regression method
InactiveCN109193635ASimple methodMiscalculationAc network circuit arrangementsReconstruction methodScale-free network
The invention relates to a distribution network topology reconstruction method based on an adaptive sparse regression method, belonging to the technical field of distribution network topology analysis. The distribution network topological structure reconstruction method of the invention designs an algorithm which does not need prior knowledge of the distribution network and branch measurement dataaccording to the characteristic that branch measurement equipment is difficult to install in the distribution network, and can complete the topological reconstruction of the distribution network onlythrough the sequential voltage data of the distribution network bus bar, and the method is simple and easy to operate. The invention solves the problem of biased estimation by using the adaptive Lasso algorithm on the original Lasso algorithm. At the same time, a supplementary criterion is added to correct the wrong estimation when the algorithm does not meet the feasible conditions, which improves the accuracy of the algorithm. The method can be used in loop-free network or loop-network, and the topology reconstruction of distribution network can be carried out in a short time.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Compressive sensing method based on scale-free complex network LDPC code
InactiveCN103248371AImprove performanceReduce complexityError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsImaging processingRadar imaging
The invention provides a compressive sensing method based on a scale-free complex network LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) code, which comprises two processes of the sensing matrix construction and the signal reconstruction arithmetic. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: sparsely representing a signal x by adopting appropriate basis function, constructing a check matrix H of an irregular low complexity and scale-free network LDPC code, taking the check matrix H of the scale-free network LDPC code as the sensing matrix phi of the compressive sensing arithmetic, calculating the measured value y which equals to phi x, and reconstructing an original signal from the measured value by utilizing a belief propagation (BP) decoding algorithm. The method has the advantages that the constructed scale-free network LDPC code with good performance is applied to the compressive sensing; compressive sensing signal reconstruction is realized by utilizing the decoding method; the method can be applied to the fields such as signal processing, image processing, error correction coding and radar imaging; and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com