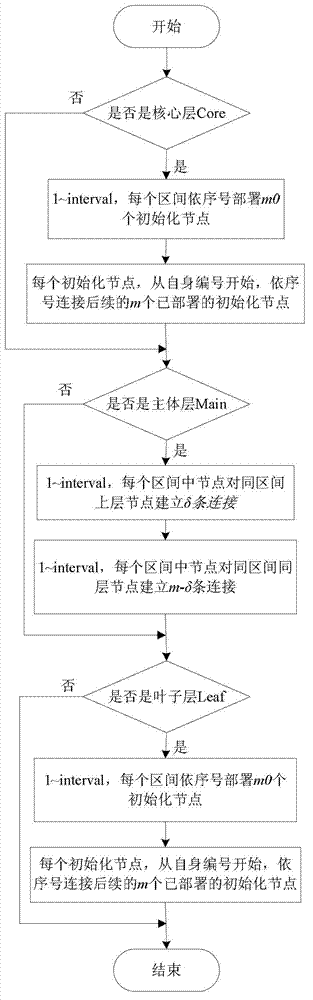
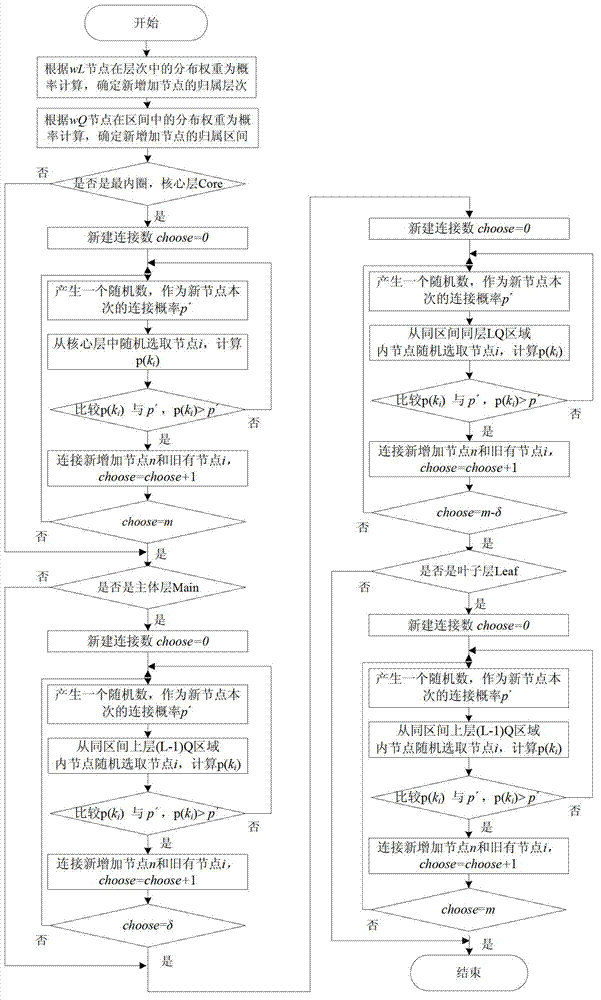
Scale-free network based router-level topology modeling method
A modeling method and routing-level technology, applied in the direction of data exchange network, digital transmission system, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as inaccuracy and achieve a high degree of compliance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0068] (1) Traditional BA model L=1, Q=1;
[0069] (2) In the present invention, L=3, Q=4, wL=1:5:15, wQ=1:1:1:1, 3 layers and 4 quadrants, the nodes are distributed in each layer according to the wL ratio, and each layer of nodes Evenly distributed in each quadrant.
[0070] The general variable values are shown in Table 2.
[0071] Table 2 Value table of common variables in DHQW model
[0072]
[0073]
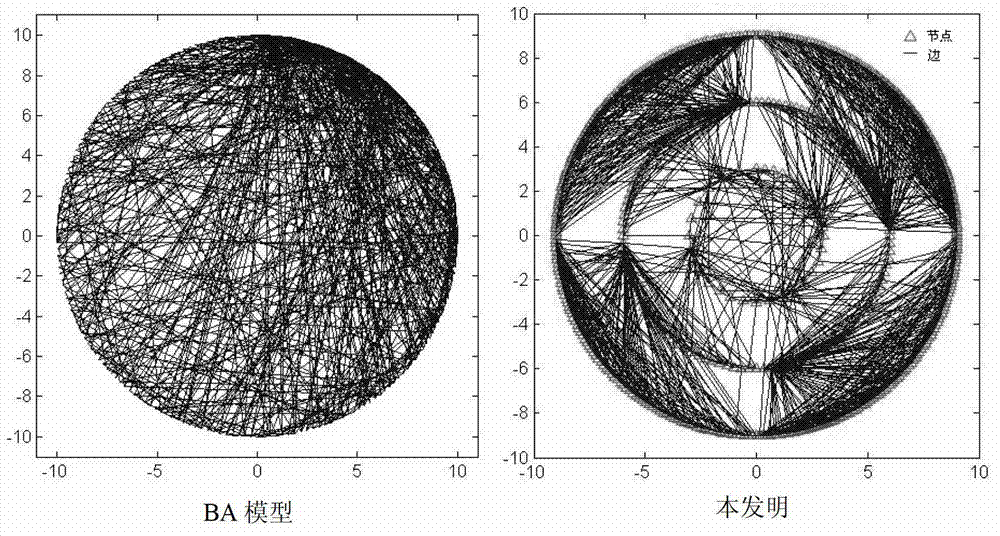
[0074] Traditional BA model compares with the topological graph of the present invention as image 3 As shown, it can be seen that the topology structures of the two are completely different, and the present invention has a higher degree of conformity to the actual topology. The effectiveness of the present invention is tested by comparing the network statistical characteristic values of the two implementation examples: node degree distribution, average path length, and network efficiency.
[0075] The node degree distribution is one of the most basic geometric...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com