Patents
Literature
66results about How to "Quick translation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
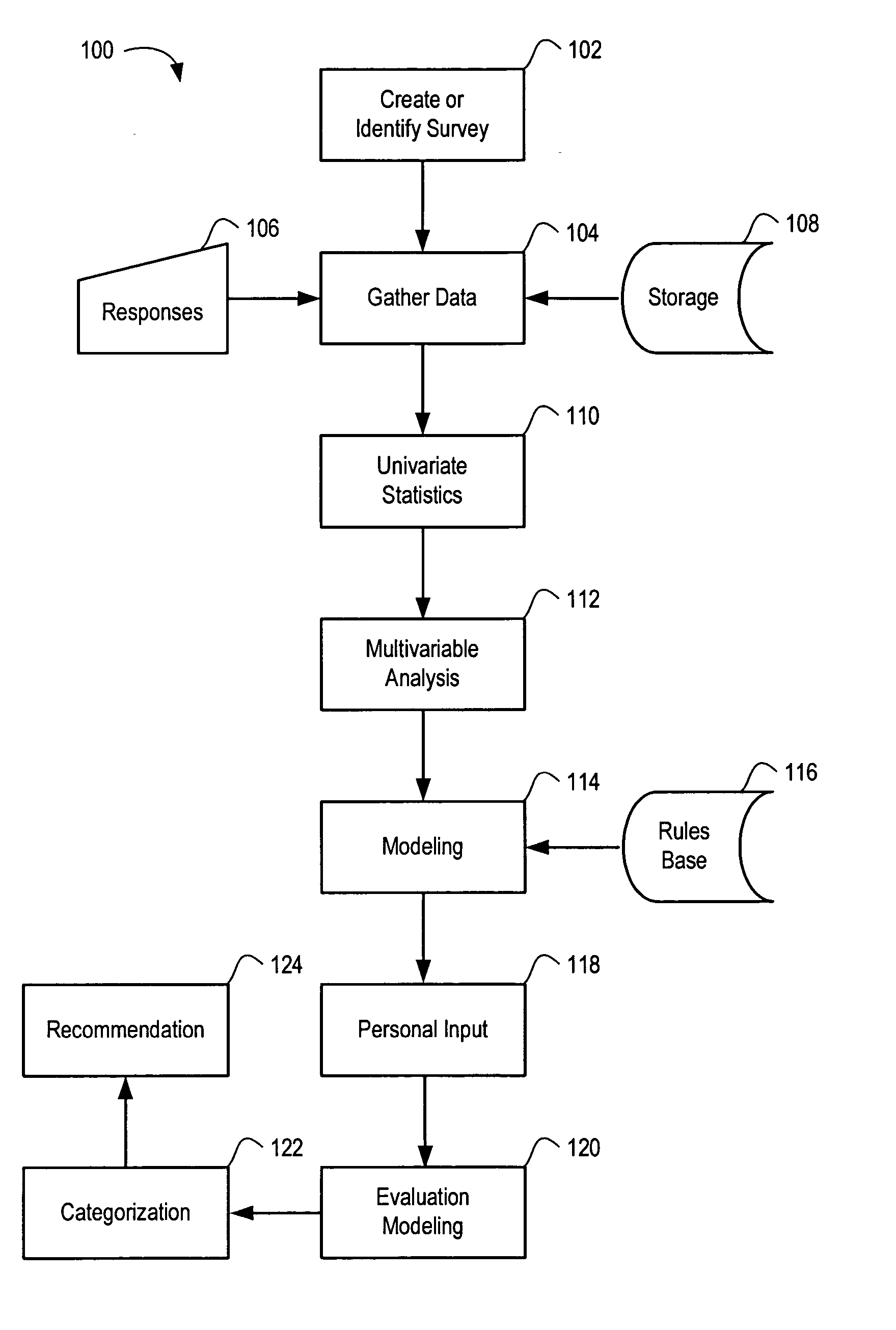
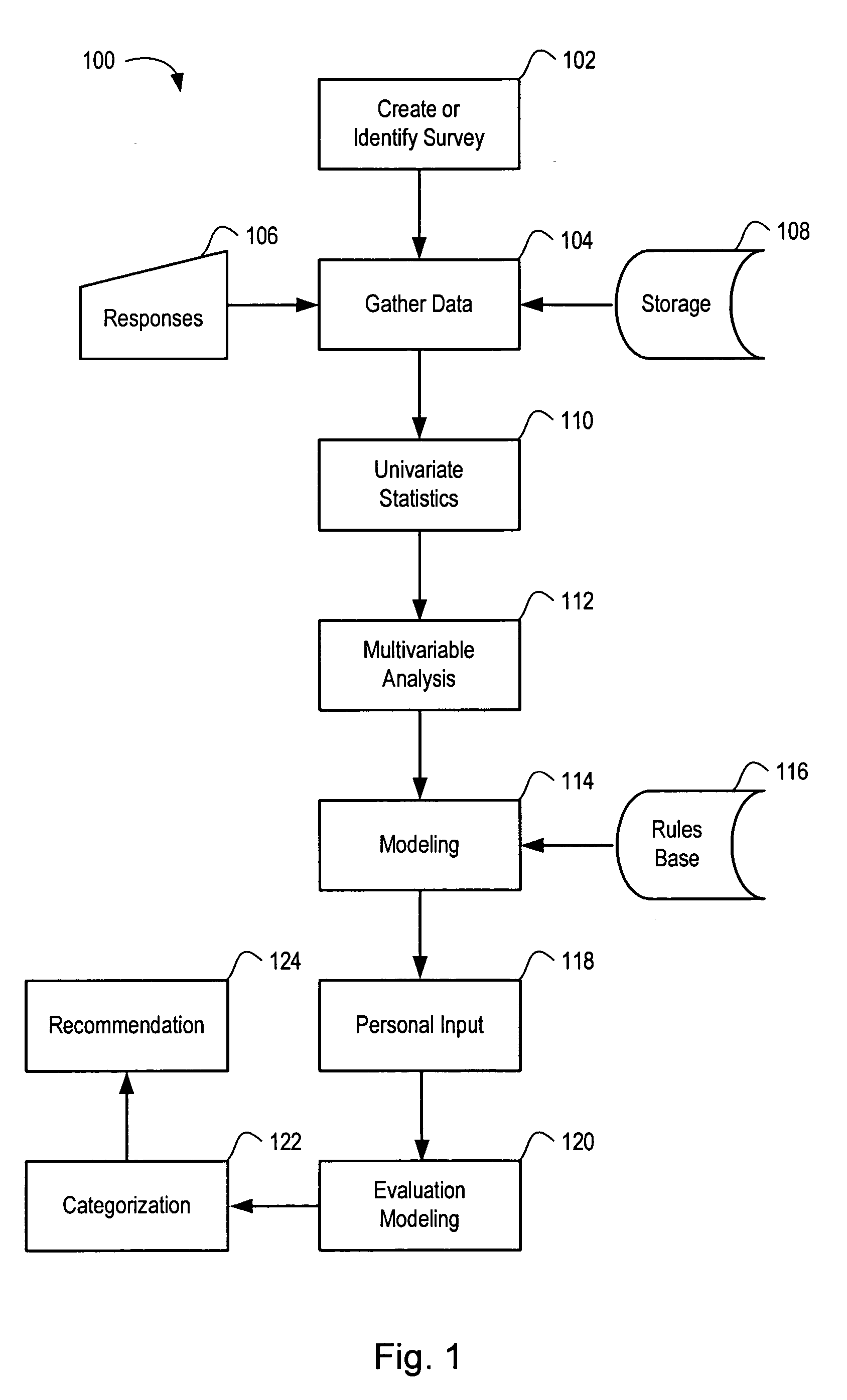
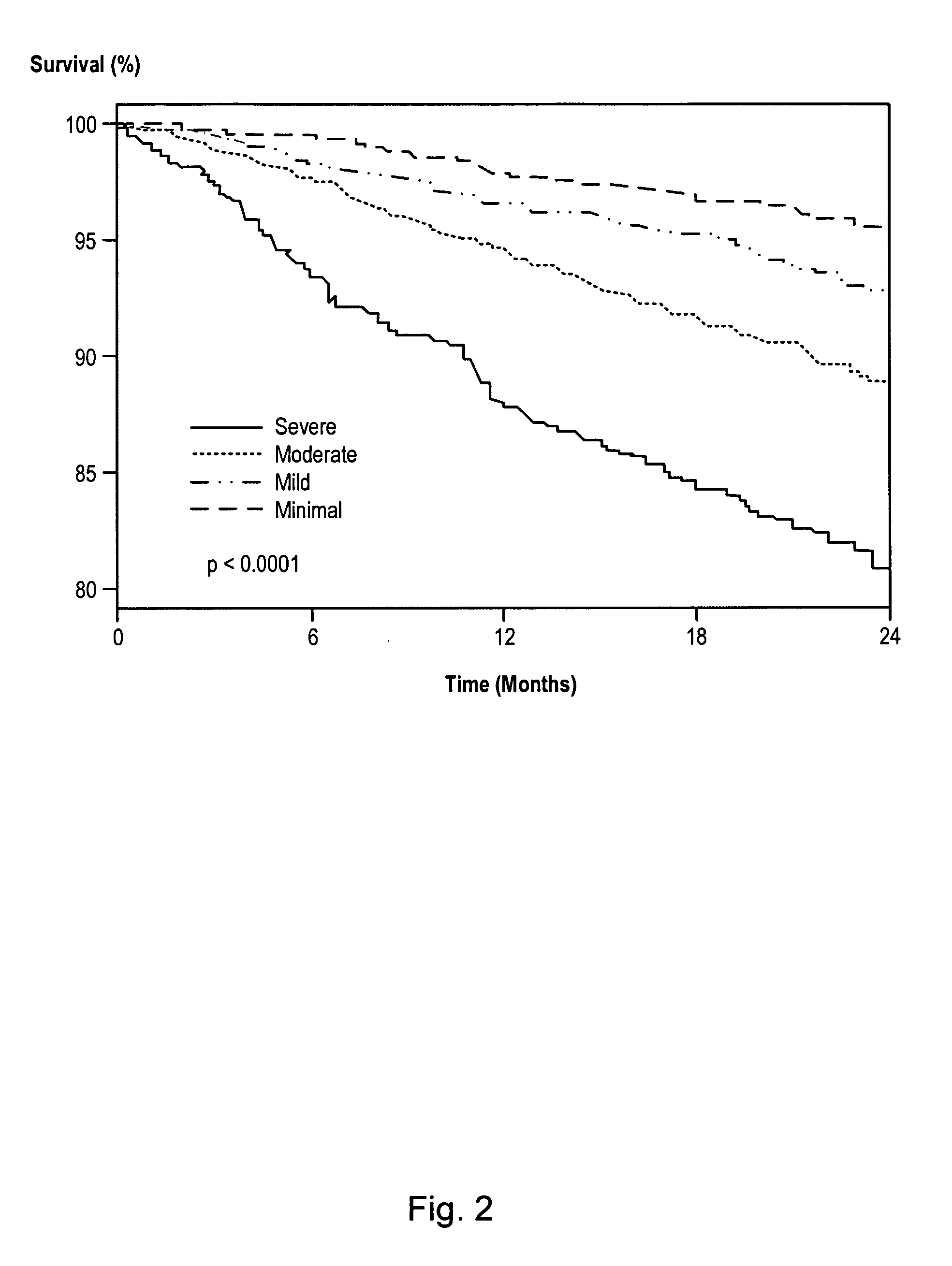
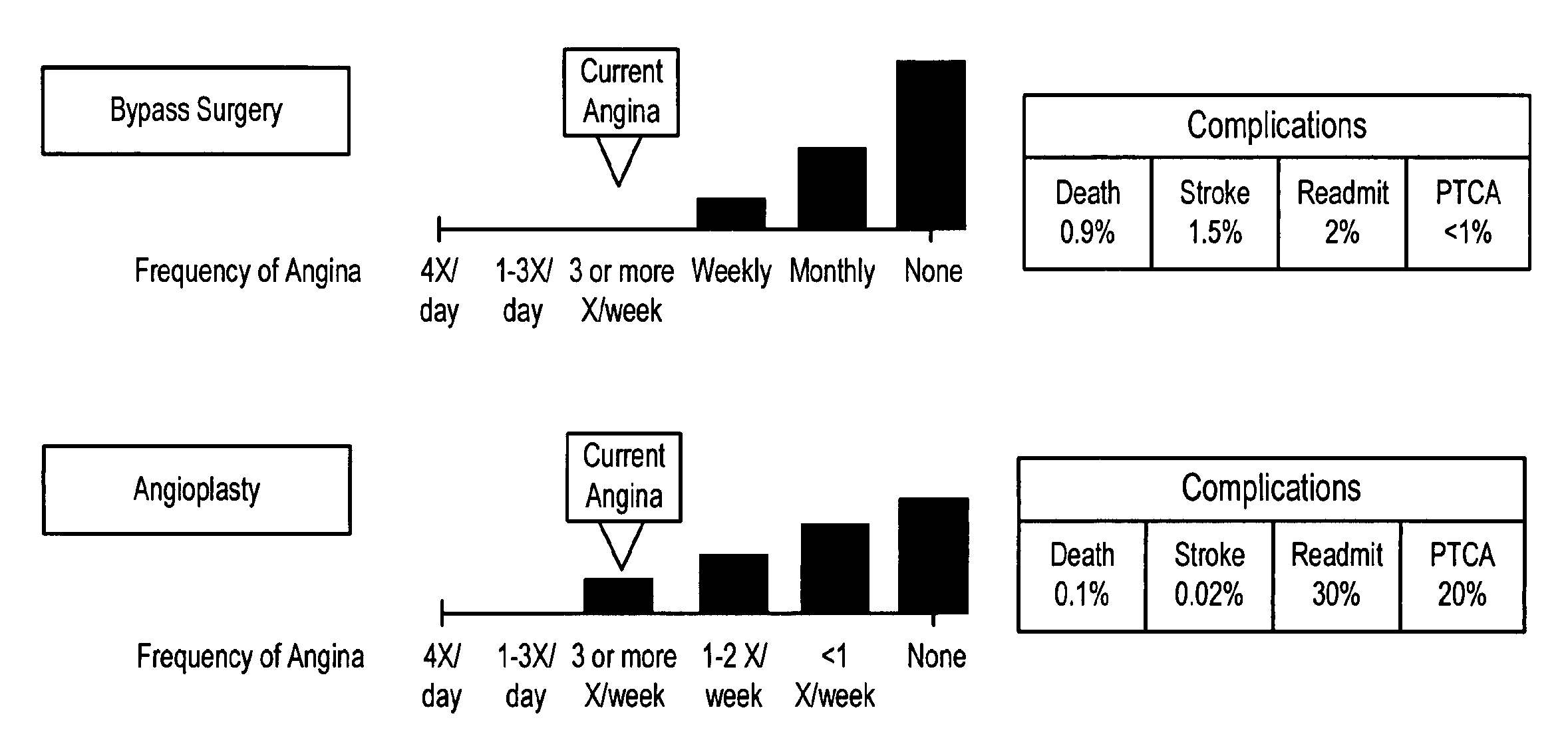
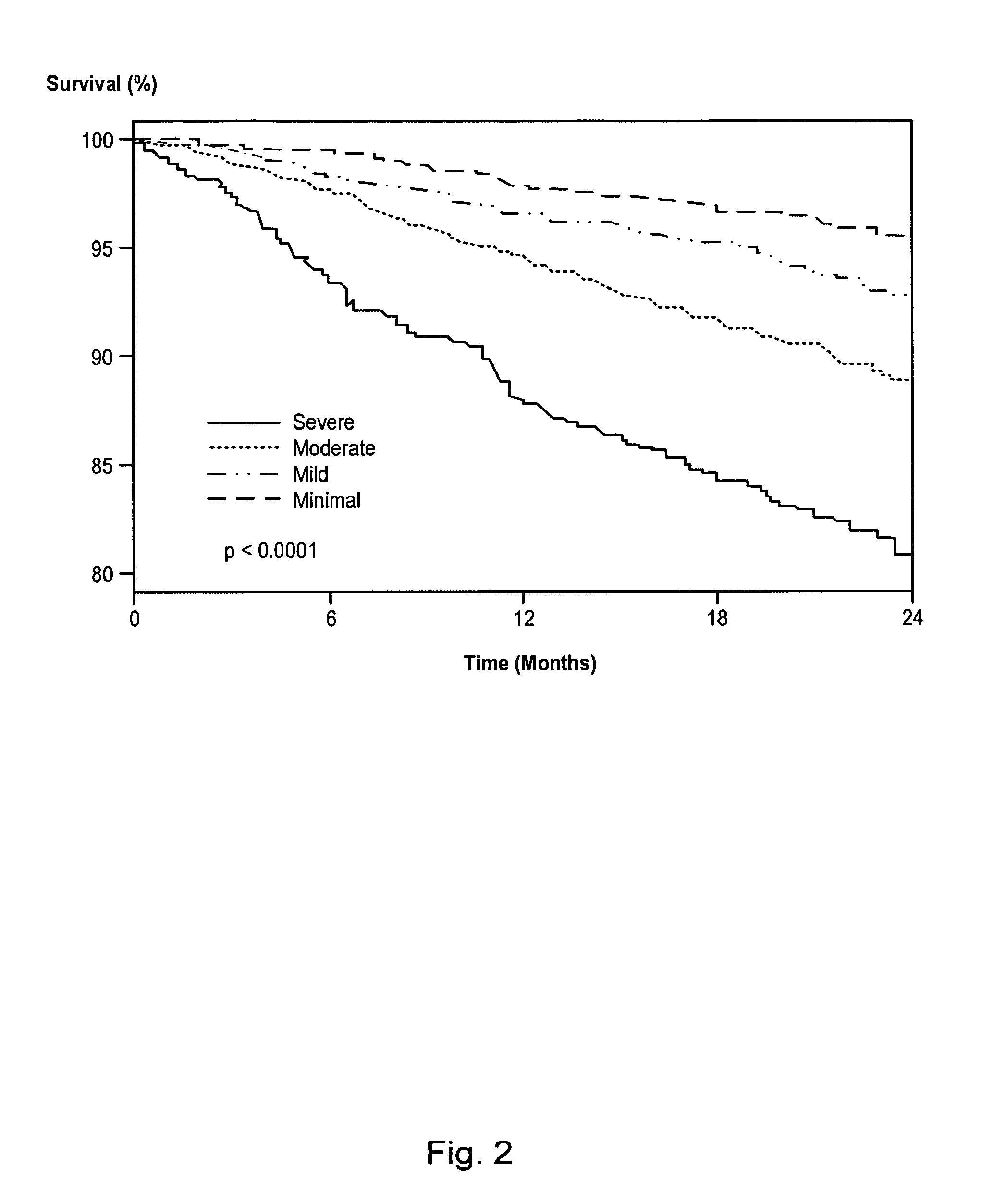
Systems and methods for risk stratification of patient populations
ActiveUS20050203773A1Disseminate reduced redundancy requestsReduce redundancyAnalogue computers for chemical processesComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionProgram instructionHealth risk
A statistical processing system includes a server operably configured with program instructions implementing a plurality of statistical models to at least one of (a) predict a health outcome based on questionnaire responses, (b) assist a patient's choice of therapeutic modality based on questionnaire responses, and (c) assess a health risk or status based on questionnaire responses. Also provided is a research agency communicating with the server and contracted to provide the statistical models using a visual interface communicated by the server. The server is configured to analyze requests received from users relating to a plurality of said statistical models to reduce redundancy in requests for patient data.
Owner:TERUMO MEDICAL CORP
High-performance location management platform
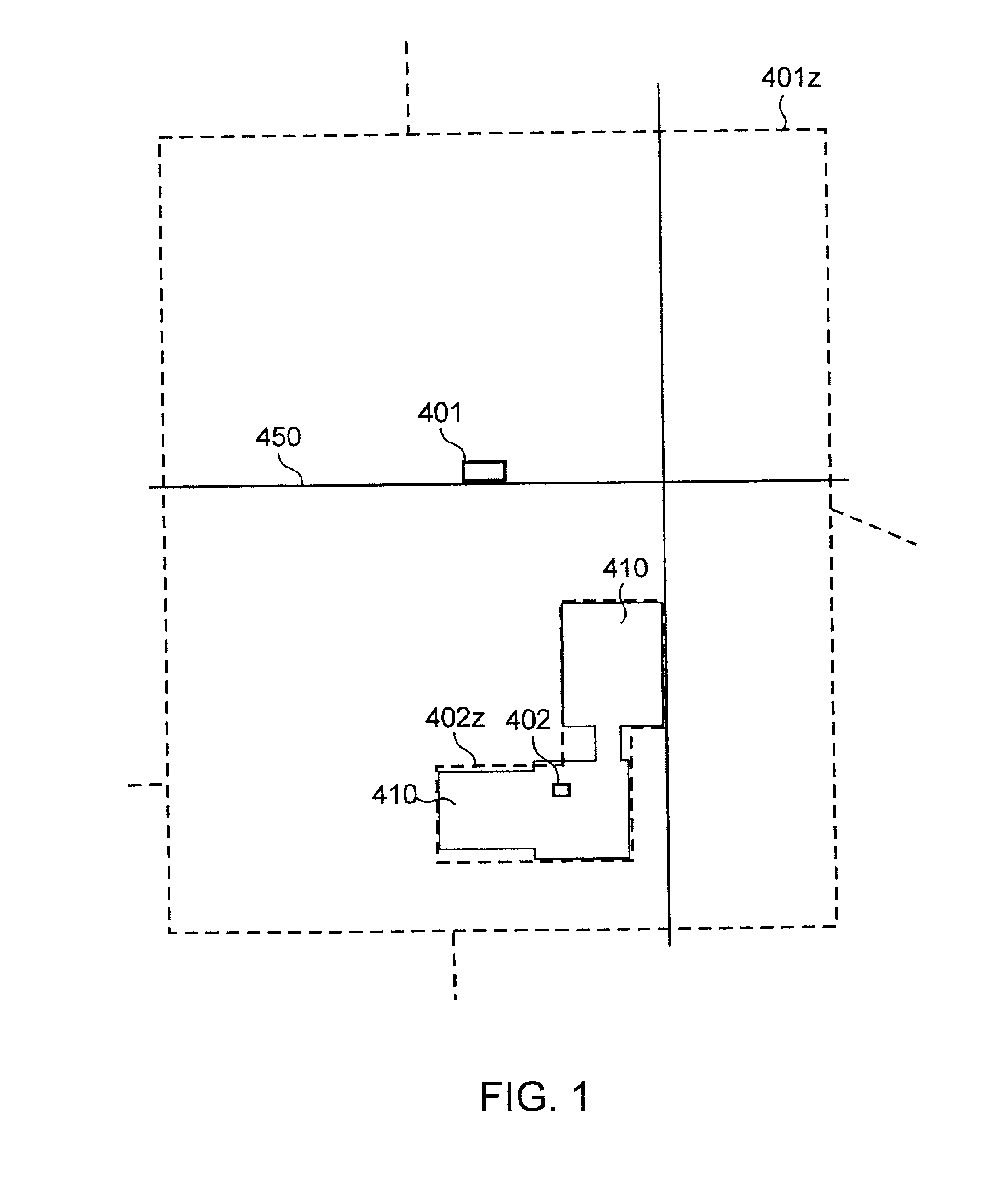
InactiveUS6868410B2Quick translationEliminate mass-storage accessesData processing applicationsDigital computer detailsMass storageLongitude
An apparatus and method for rapid translation of geographic latitude and longitude into any of a number of application-specific location designations or location classifications, including street address, nearest intersection, PSAP (Public Safety Answering Point) zone, telephone rate zone, franchise zone, or other geographic, administrative, governmental or commercial division of territory. The speed of translation meets call-setup requirements for call-processing applications such as PSAP determination, and meets caller response expectations for caller queries such as the location of the nearest commercial establishment of a given type. To complete its translation process in a timely manner, a memory-stored spatial database is used to eliminate mass-storage accesses during operation, a spatial indexing scheme such as an R-tree over the spatial database is used to locate a caller within a specific rectangular area, and an optimized set of point-in-polygon algorithms is used to narrow the caller's location to a specific zone identified in the database. Additional validation processing is supplied to verify intersections or street addresses returned for a given latitude and longitude. Automatic conversion of latitude-longitude into coordinates in different map projection systems is provided.The memory-stored database is built in a compact and optimized form from a relational spatial database as required. The R-tree spatial indexing of the memory-stored database allows for substantially unlimited scalability of database size without degradation of response time. Maximum performance for database retrievals is assured by isolating the retrieval process from all updating and maintenance processes. Hot update of the in-memory database is provided without degradation of response time.
Owner:PRECISELY SOFTWARE INC +1
Systems and methods for risk stratification of patient populations
ActiveUS7853456B2Disseminate reduced redundancy requestsReduce redundancyAnalogue computers for chemical processesComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionHealth riskProgram instruction
A statistical processing system includes a server operably configured with program instructions implementing a plurality of statistical models to at least one of (a) predict a health outcome based on questionnaire responses, (b) assist a patient's choice of therapeutic modality based on questionnaire responses, and (c) assess a health risk or status based on questionnaire responses. Also provided is a research agency communicating with the server and contracted to provide the statistical models using a visual interface communicated by the server. The server is configured to analyze requests received from users relating to a plurality of said statistical models to reduce redundancy in requests for patient data.
Owner:TERUMO MEDICAL CORP
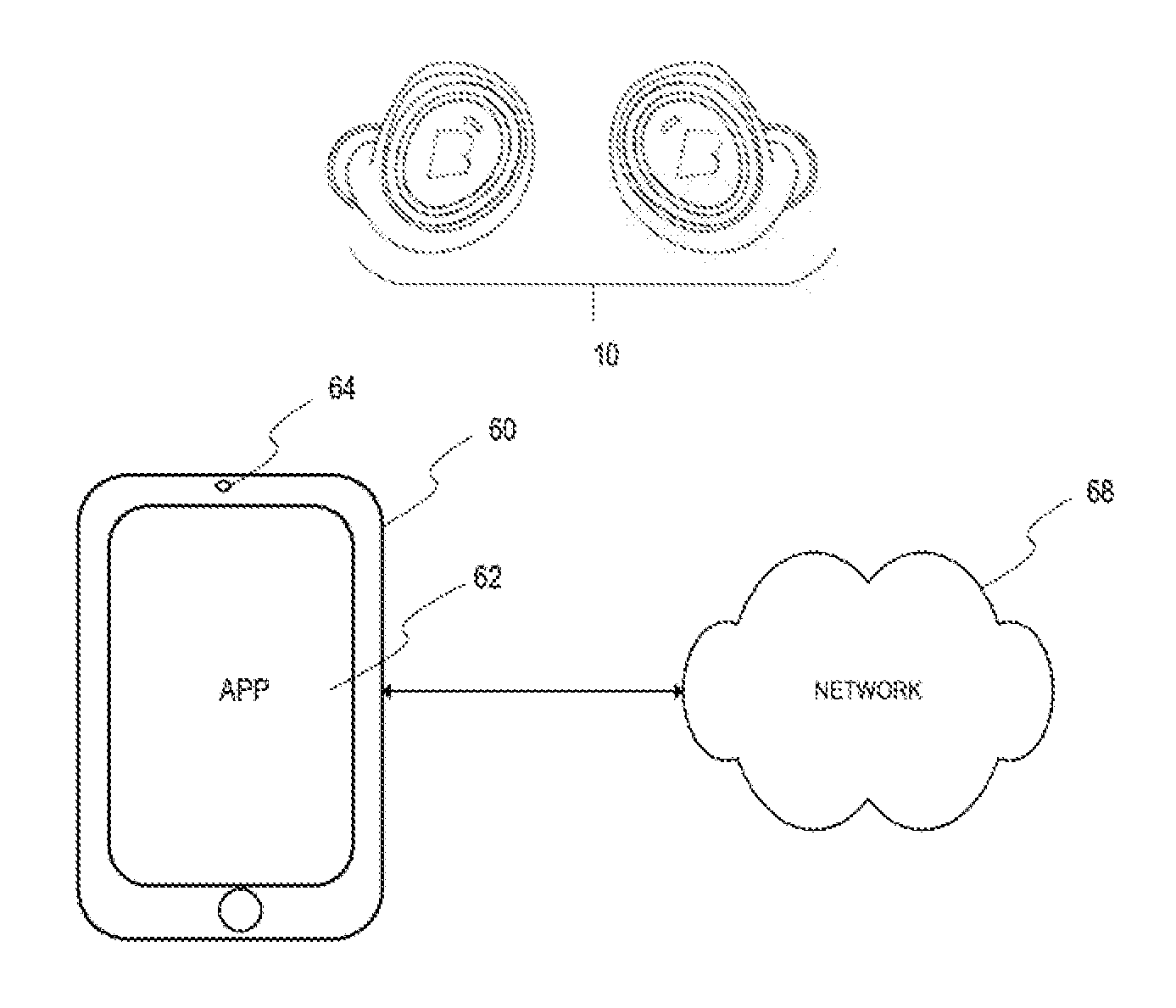
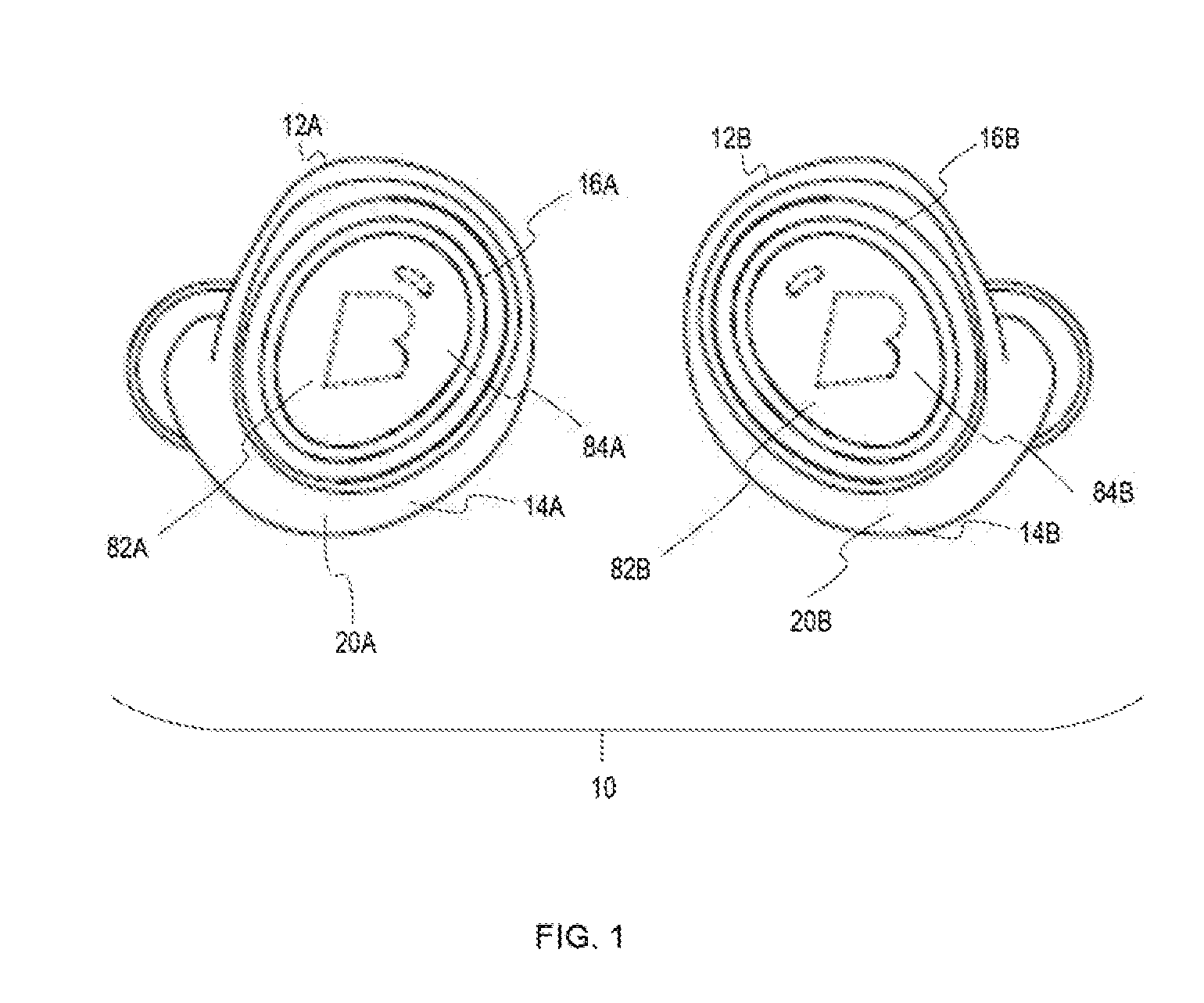
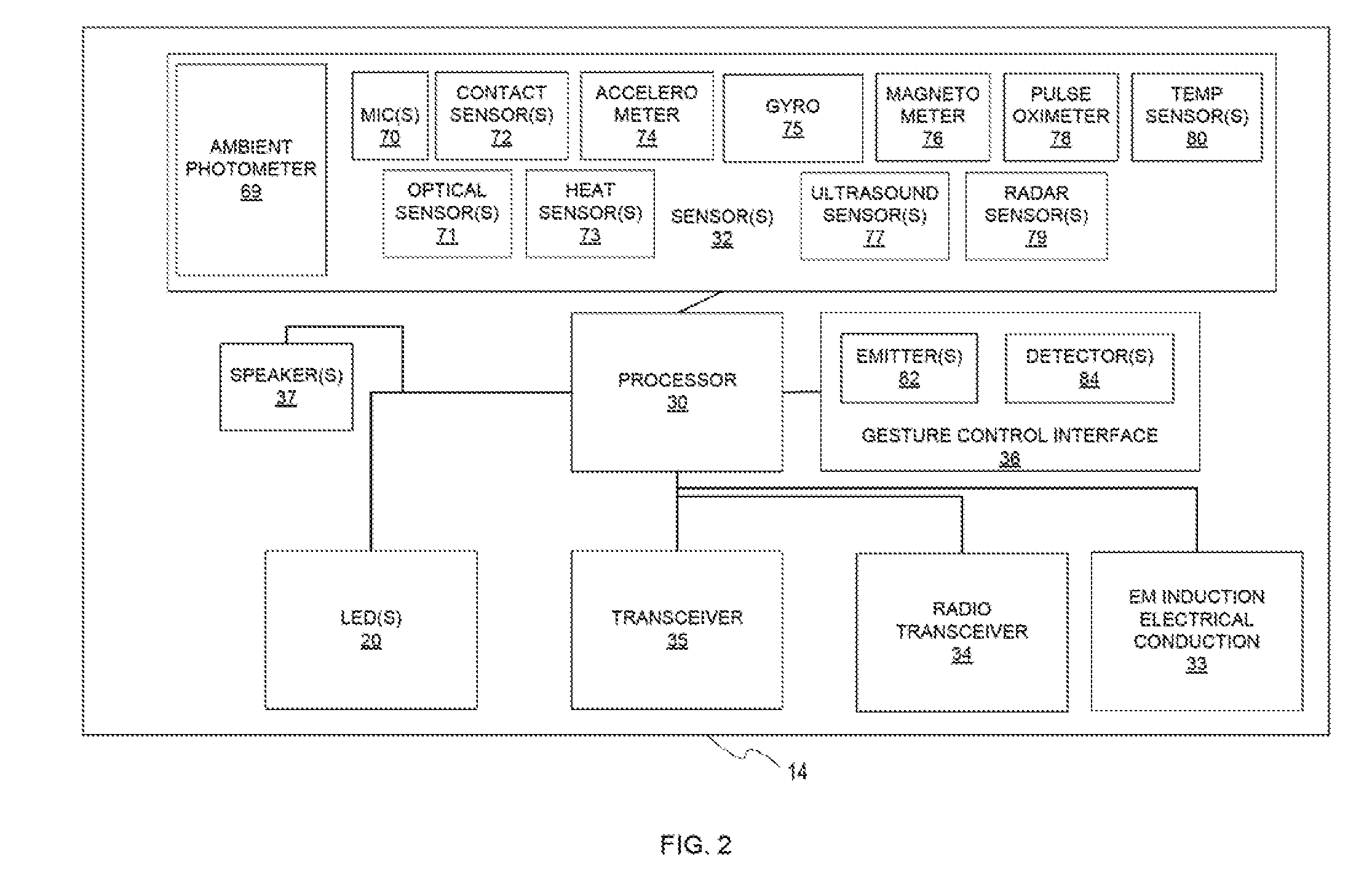
Gesture Based Control System Based Upon Device Orientation System and Method
ActiveUS20170060269A1Rapidly interpretRapid responseDetails for portable computersSatellite radio beaconingHeadphonesControl system
Owner:BRAGI
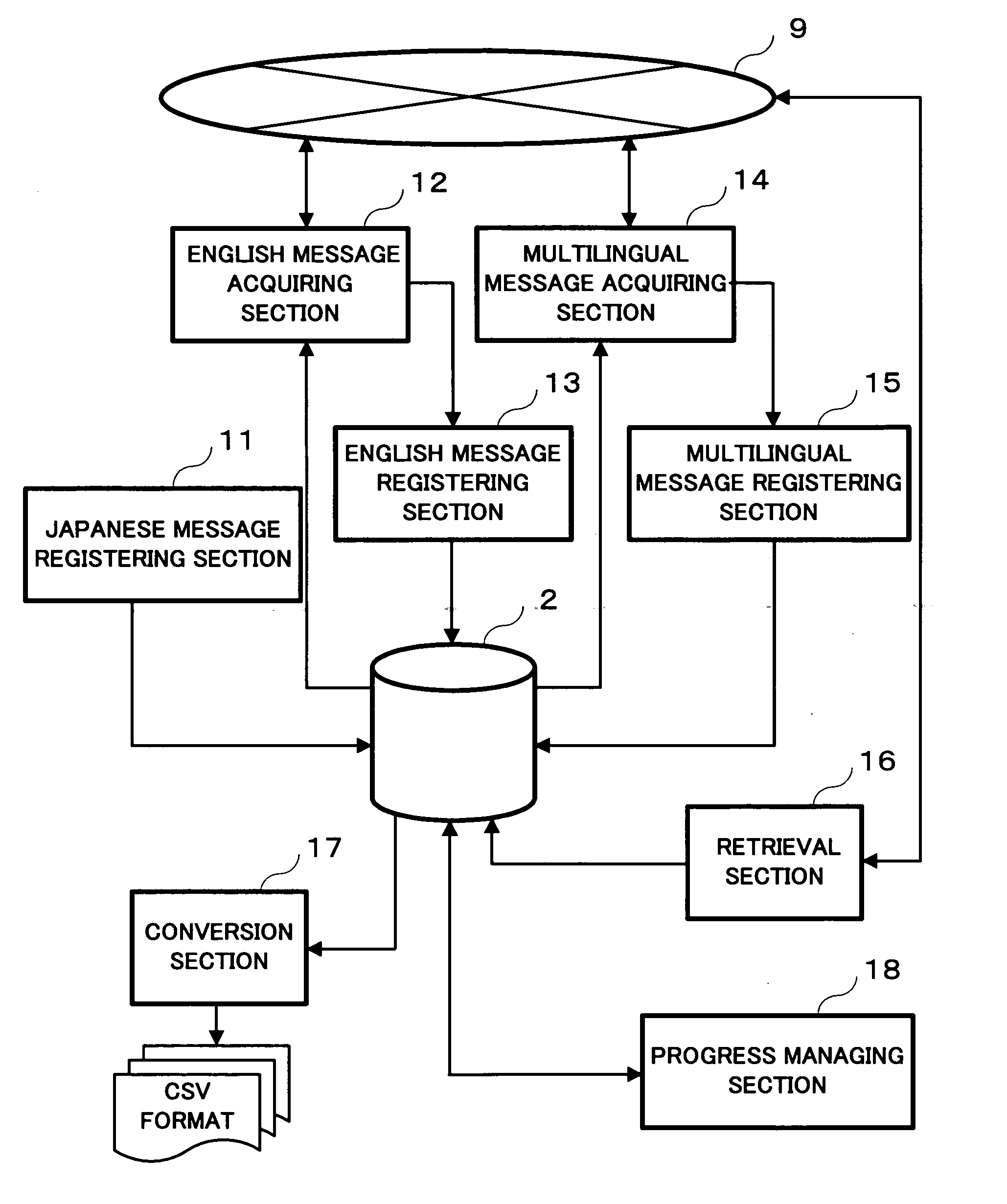
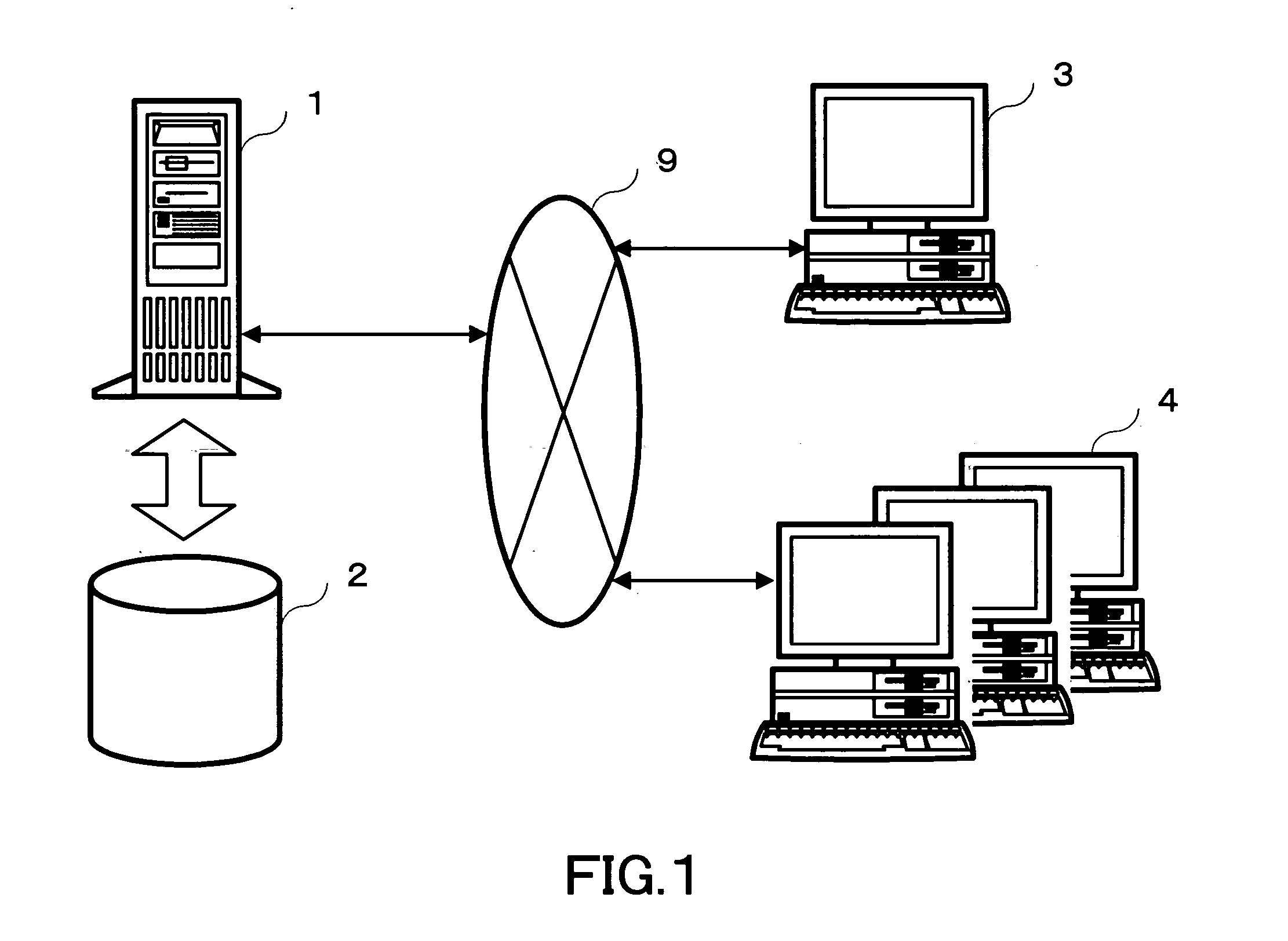
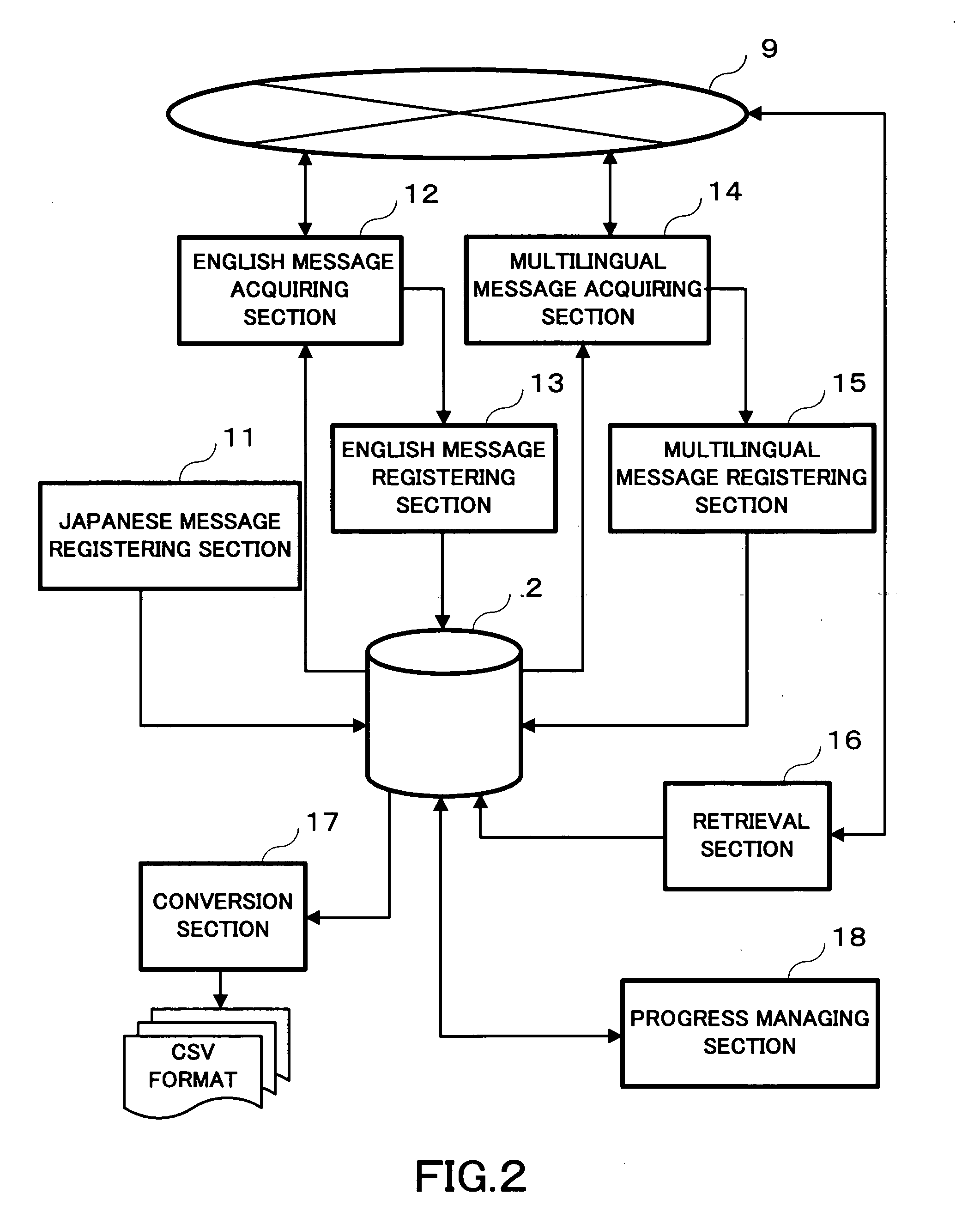
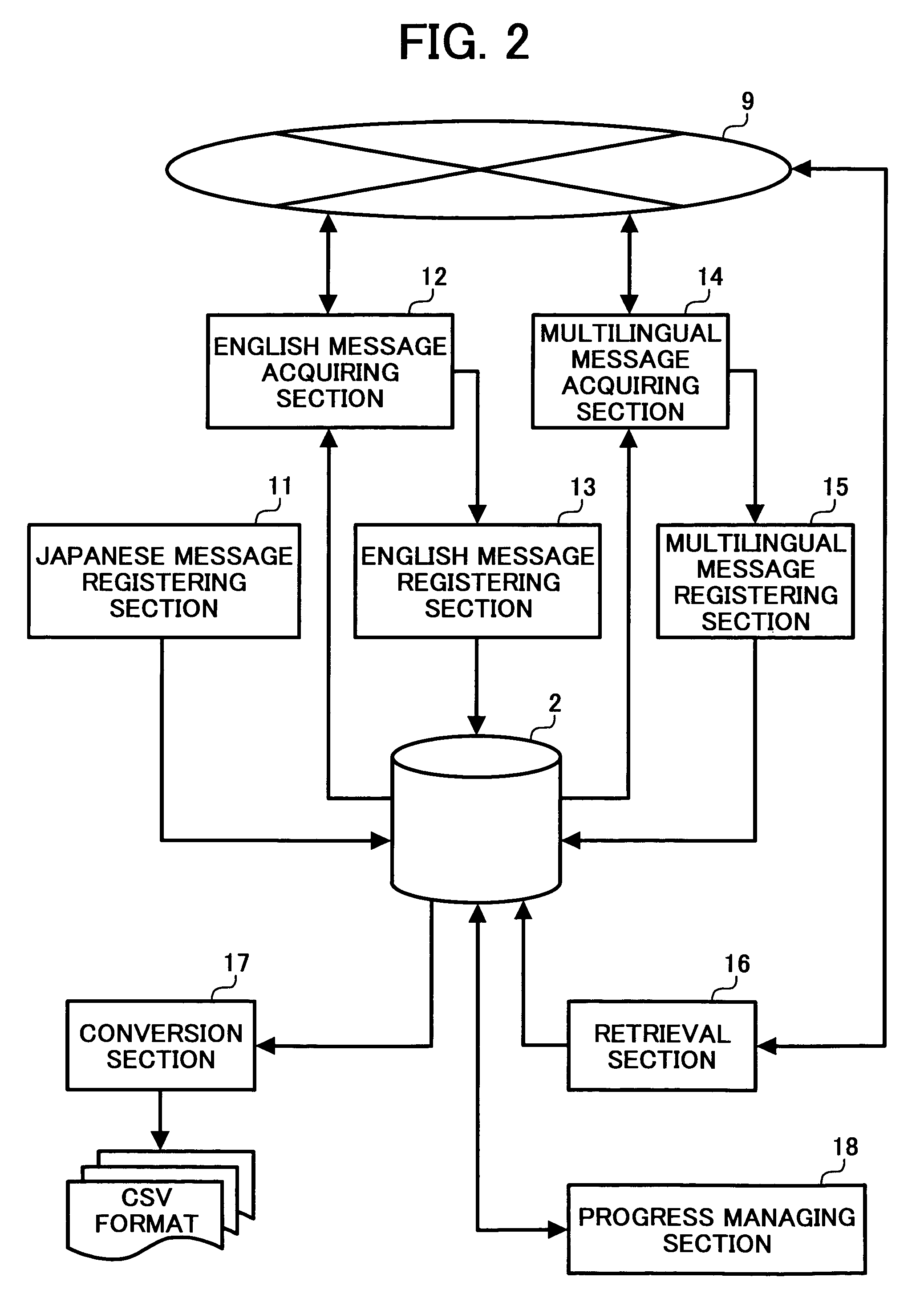
Translation support system, server, translation support method, recording medium and computer data signal
InactiveUS20050234702A1Quick translationNatural language translationDigital computer detailsSupporting systemData signal
A server having a database sequentially registers a plurality of Japanese messages to be translated into the database. In parallel to the registration, the server provides a first translation terminal with Japanese messages already registered, acquires English messages translated by the first translation terminal, and sequentially registers the acquired English messages in the database in association with corresponding Japanese messages. In parallel to the processes, the server provides individual second translation terminals with English messages already registered, acquires multilingual messages translated by the second translation terminals, and sequentially registers the acquired multilingual messages in the database in association with corresponding English messages.
Owner:RICOH KK
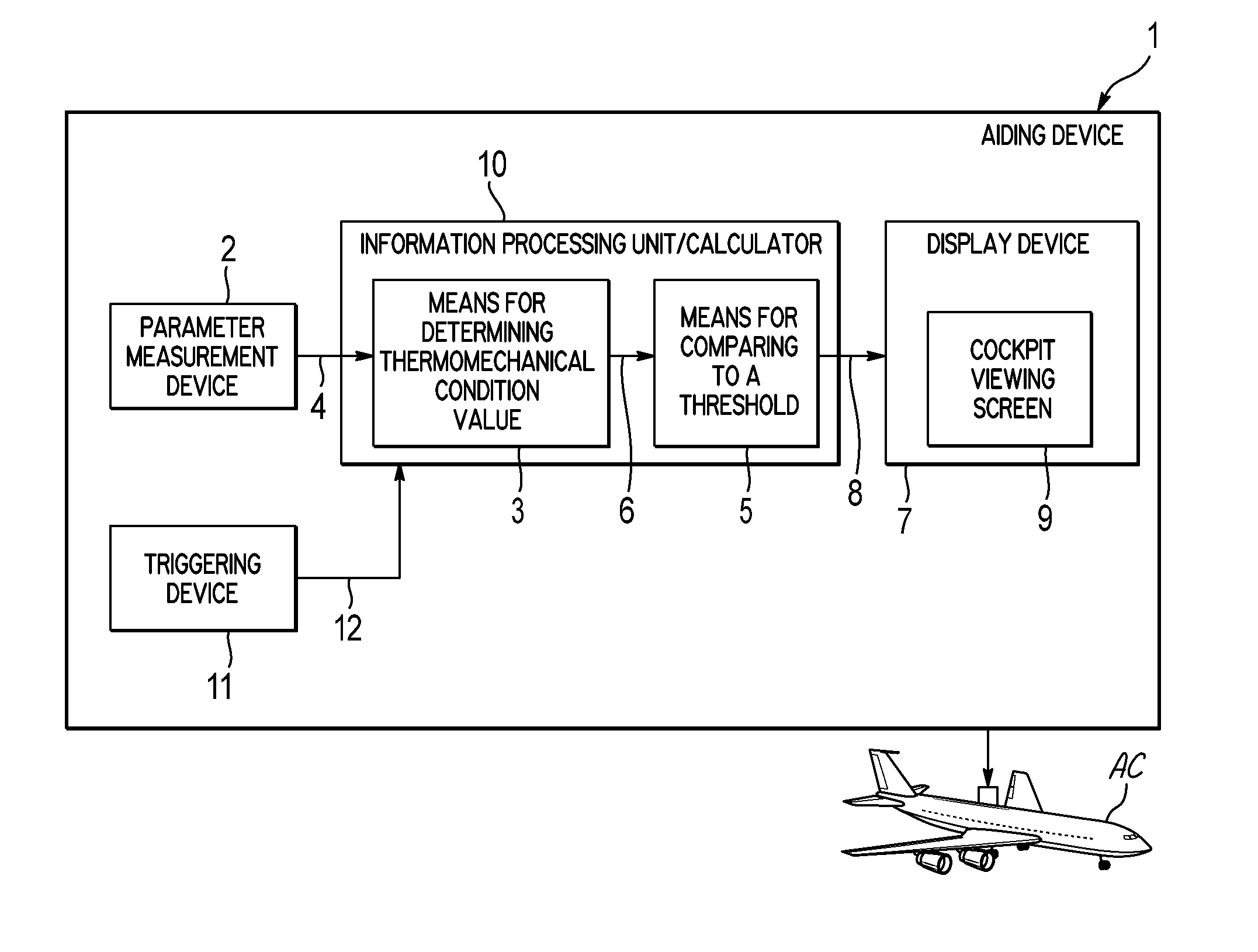
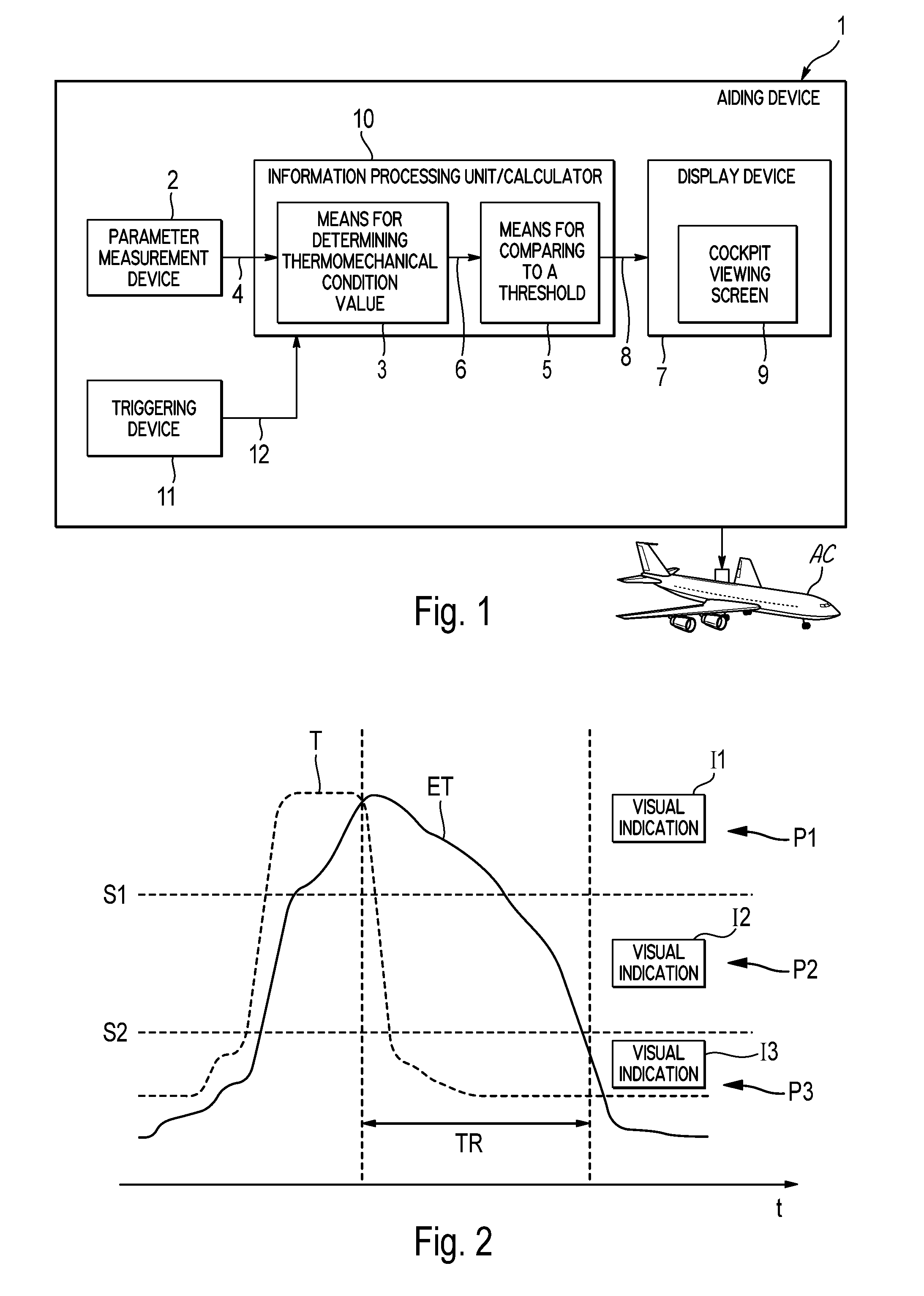
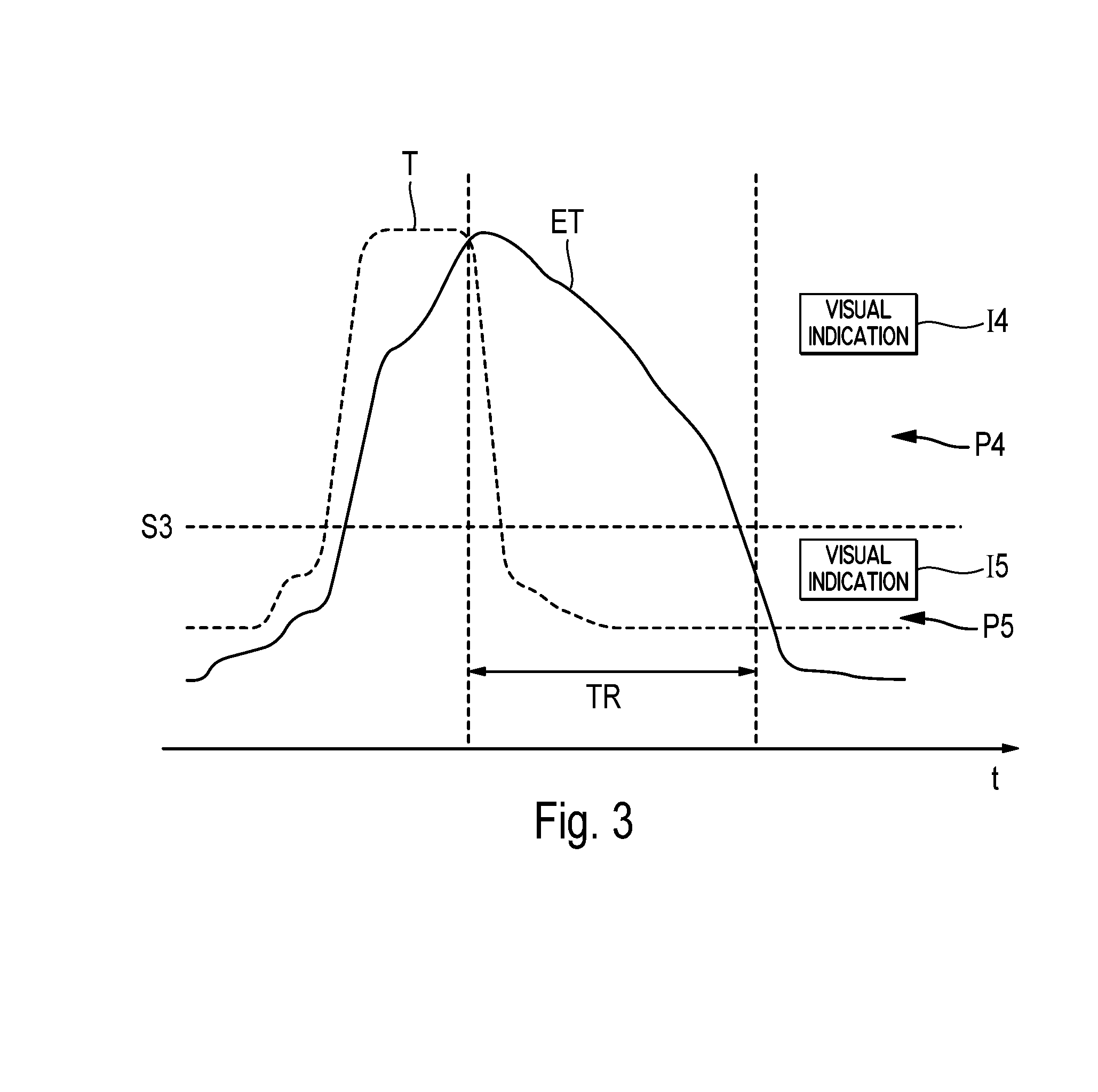
Method and device for monitoring a turbine engine of an aircraft
ActiveUS8918264B2Quick translationEasy to useAnalogue computers for vehiclesEngine fuctionsEngineeringTurbine
A method and device aids in monitoring at least one turbine engine in an aircraft. The method includes determining a value illustrating a thermomechanical state of the turbine engine, and comparing the determined value with at least one threshold. The method also includes displaying in the cockpit of the aircraft, at least one indication related to the operation of the turbine engine, according to this comparison. As a result, conditions that could result in mechanical degradation or failure of the turbine engine are identified for a crew of the aircraft.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS) +1
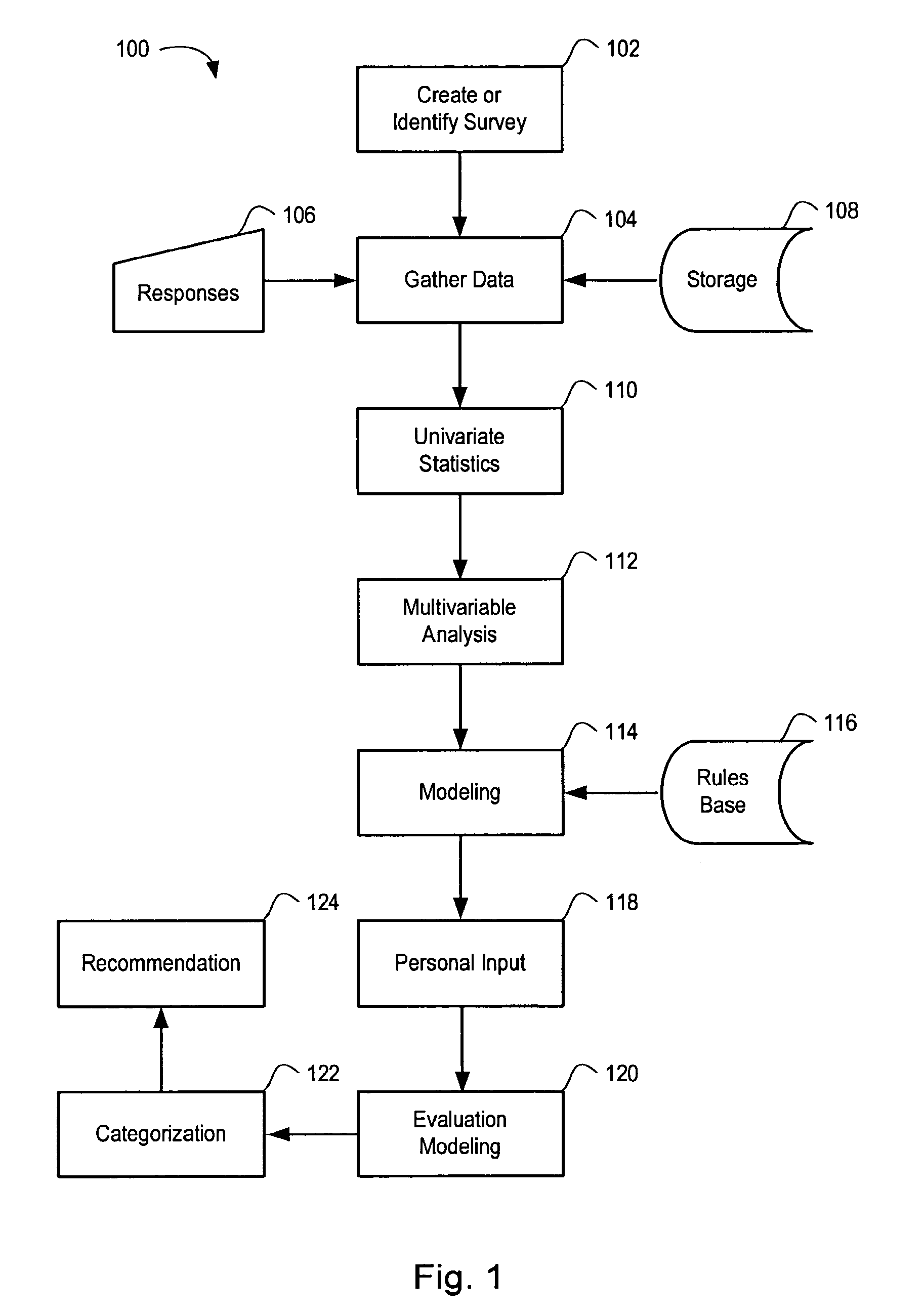
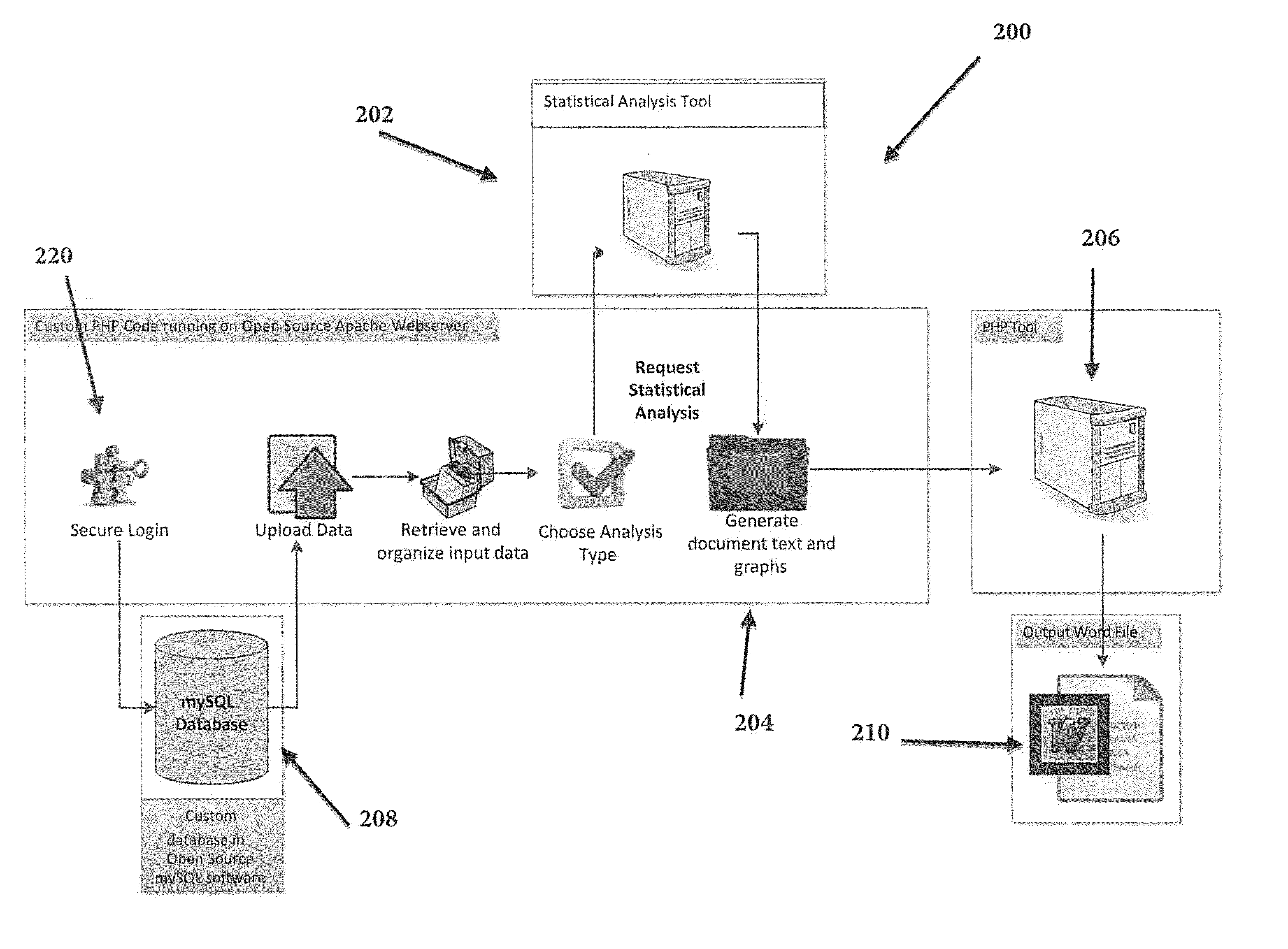
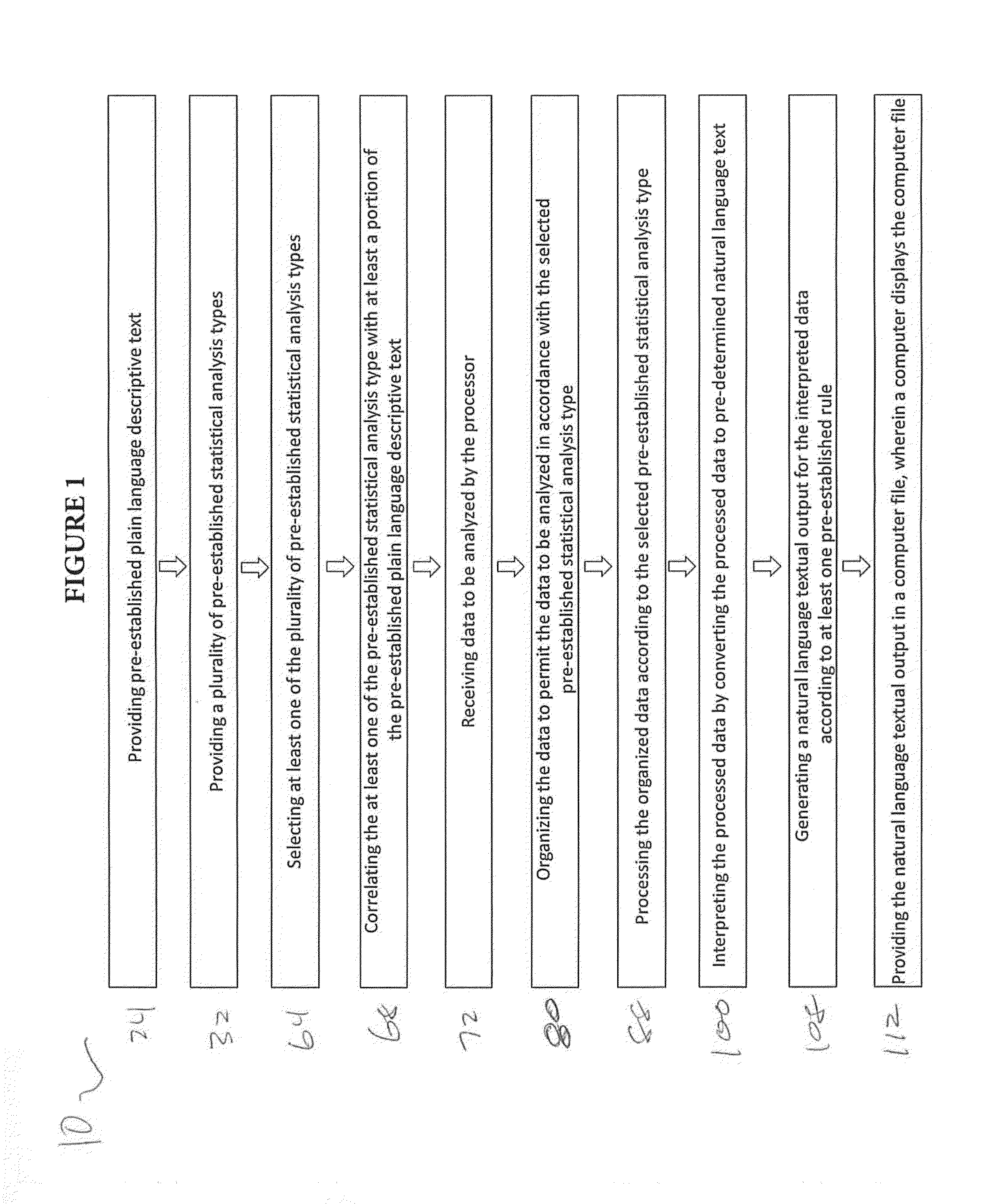
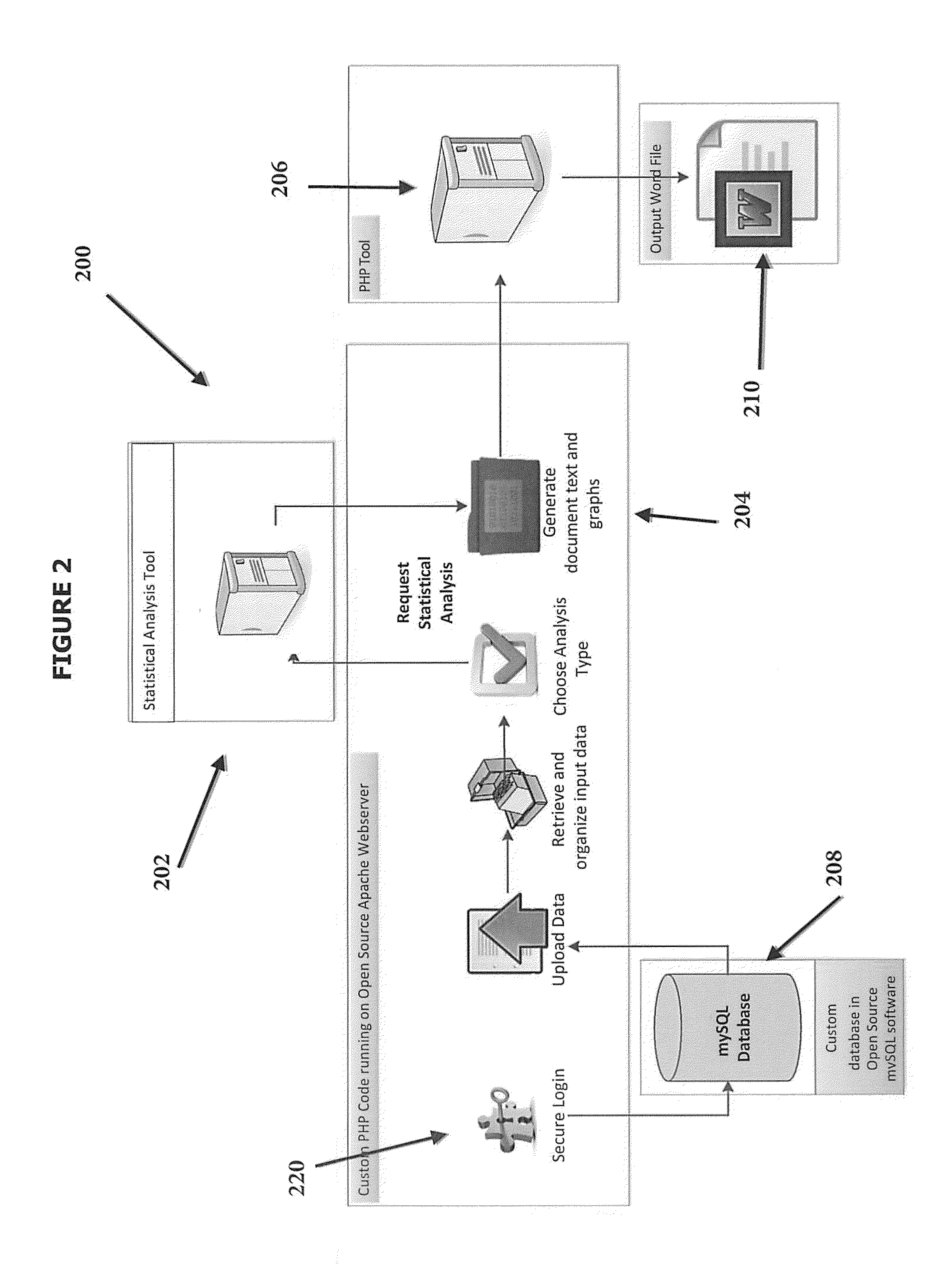
Method and System for Presenting Statistical Data in a Natural Language Format
InactiveUS20150095015A1Fast interpretationQuickly interpretingNatural language translationVisual data miningData conversionNatural language
A computer-implemented method for presenting statistical analysis in a natural language textual output comprising: receiving data to be analyzed by the processor; processing the data according to at least one of a plurality of pre-established statistical analysis types, thereby providing processed data; interpreting the processed data by converting the processed data to a pre-determined natural language text, thereby providing interpreted data; and generating a natural language textual output for the interpreted data according to at least one pre-established rule for converting the interpreted data to a natural language textual output.
Owner:STATISTICS SOLUTIONS +1
Handheld electronic apparatus with translation function and translation method using the same
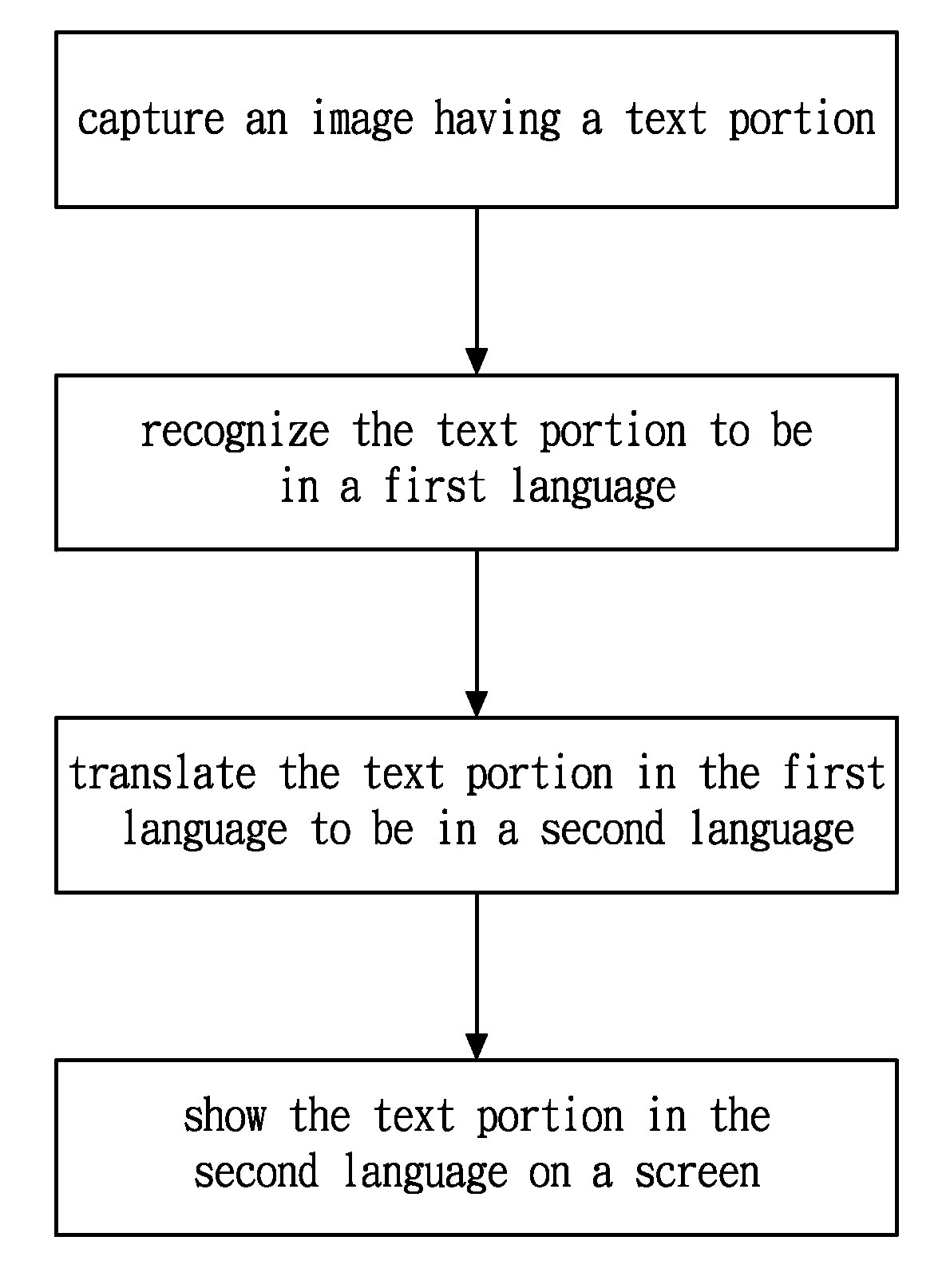
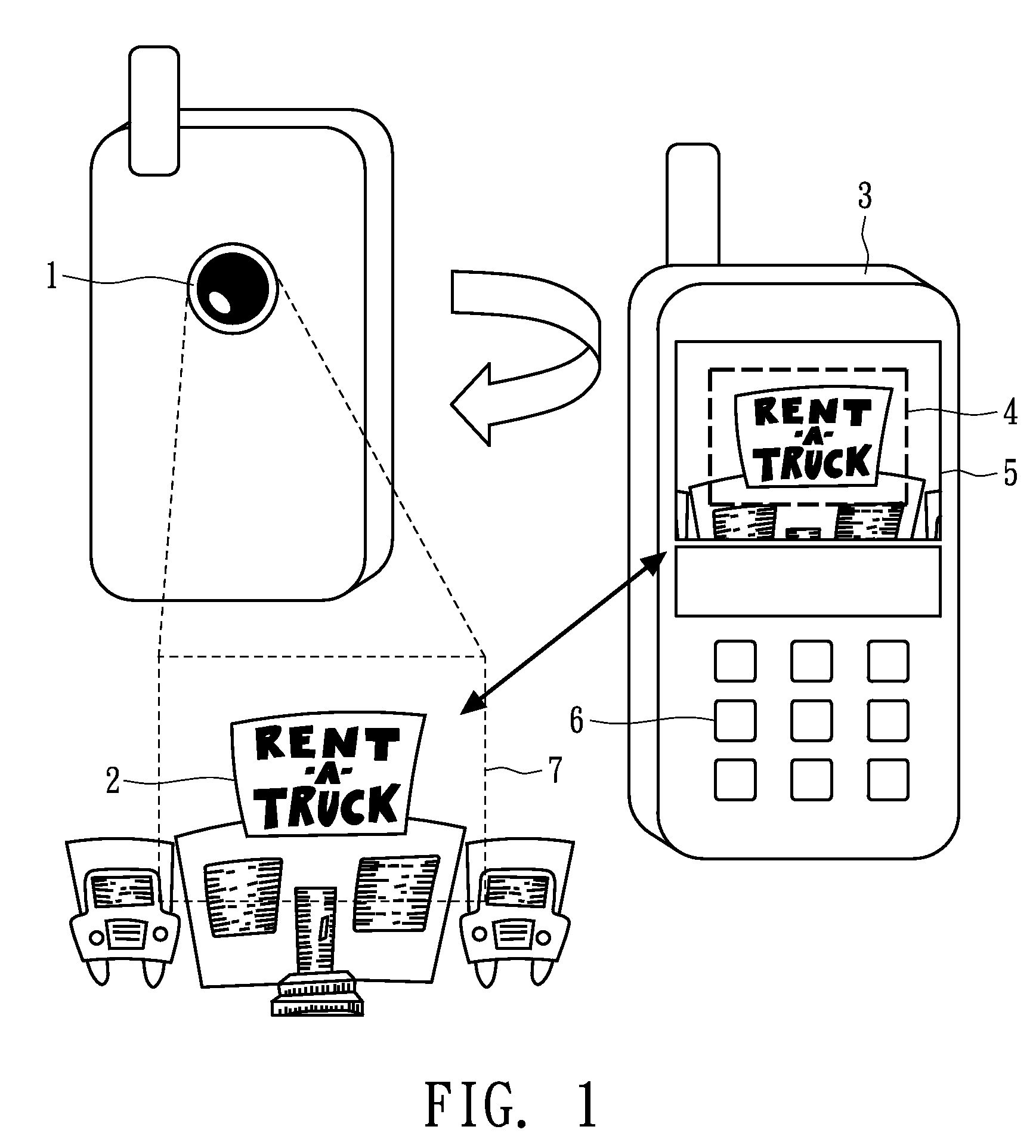
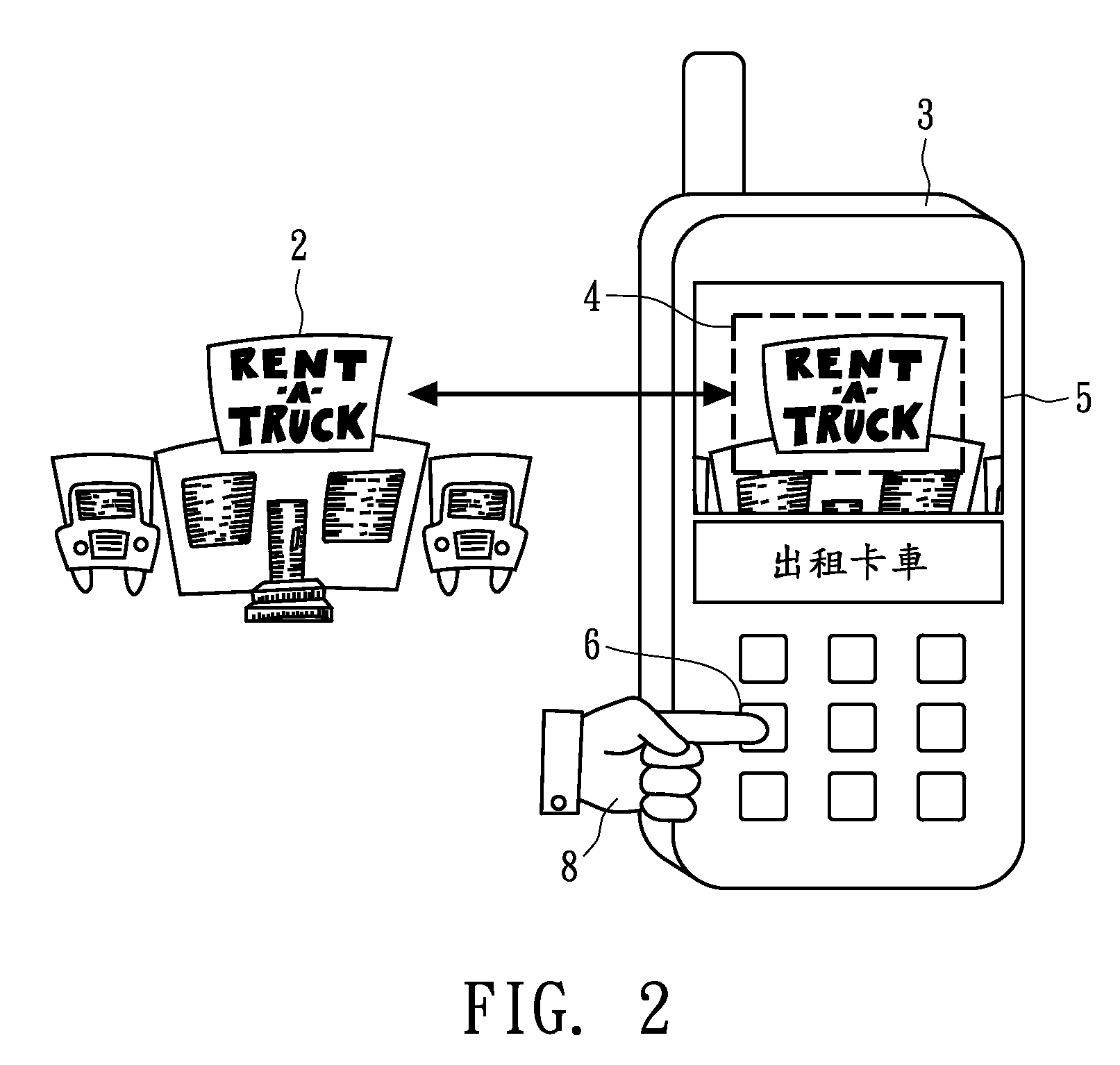
InactiveUS20090198486A1Convenient travelEasy to readNatural language translationCharacter and pattern recognitionDisplay deviceHand held
A handheld electronic apparatus with a translation function comprises an image-capturing device, an image recognition device, a language translator and a display device. The image-capturing device, e.g., a digital camera, is configured to take an image having a text portion of one or more words or sentences, and the image may be shown on the display device. The image recognition device is configured to recognize the text portion to be in a first language. For example, the recognition uses optical character recognition (OCR) technology. The language translator is configured to translate the text portion in the first language into a second language, and the text portion in the second language is shown on the display device.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Method and apparatus for fast performing MMU analog, and total system simulator
InactiveCN101246452AGood data localityImprove localityMemory adressing/allocation/relocationProgram loading/initiatingManagement unitComputerized system
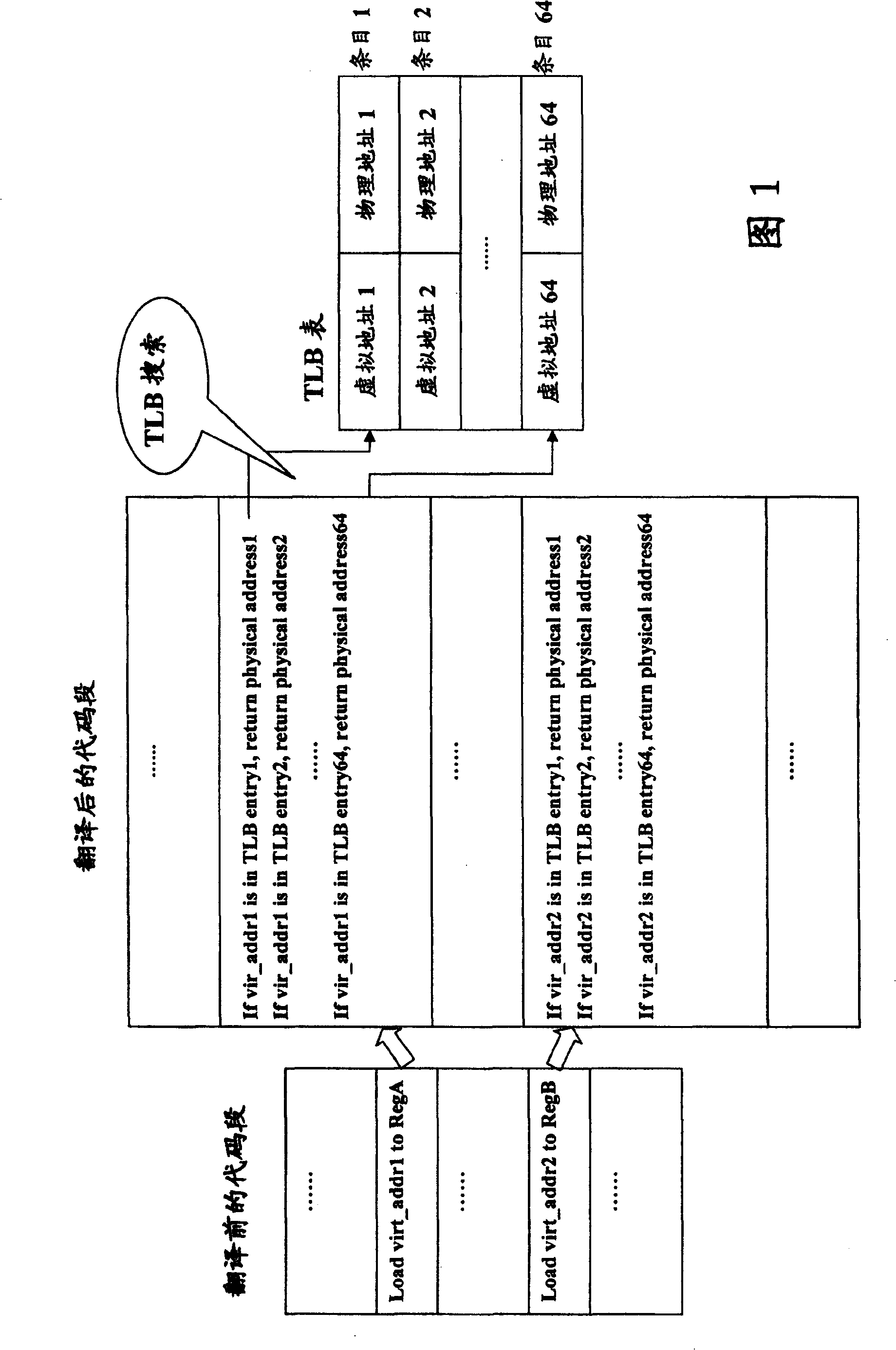
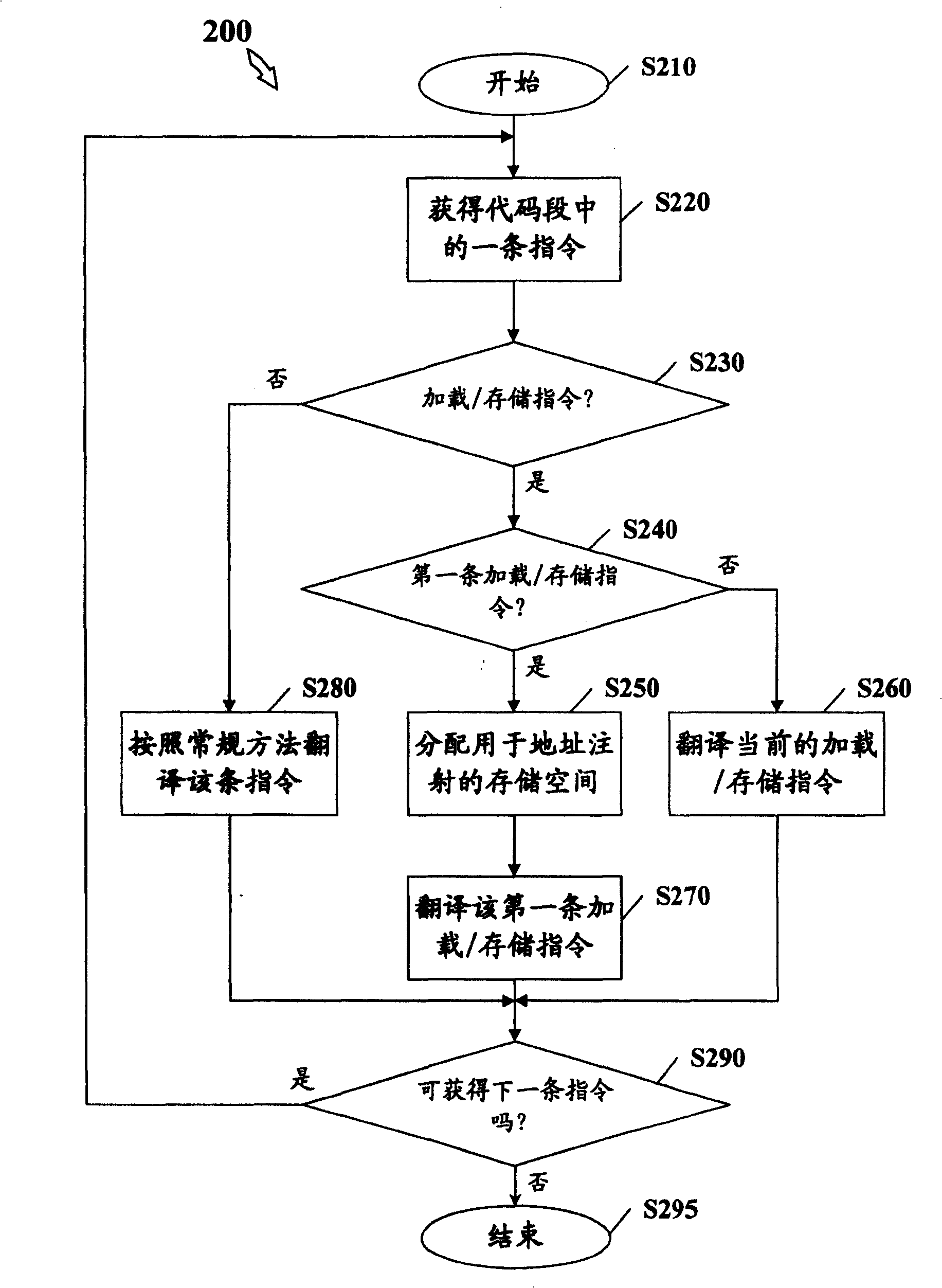
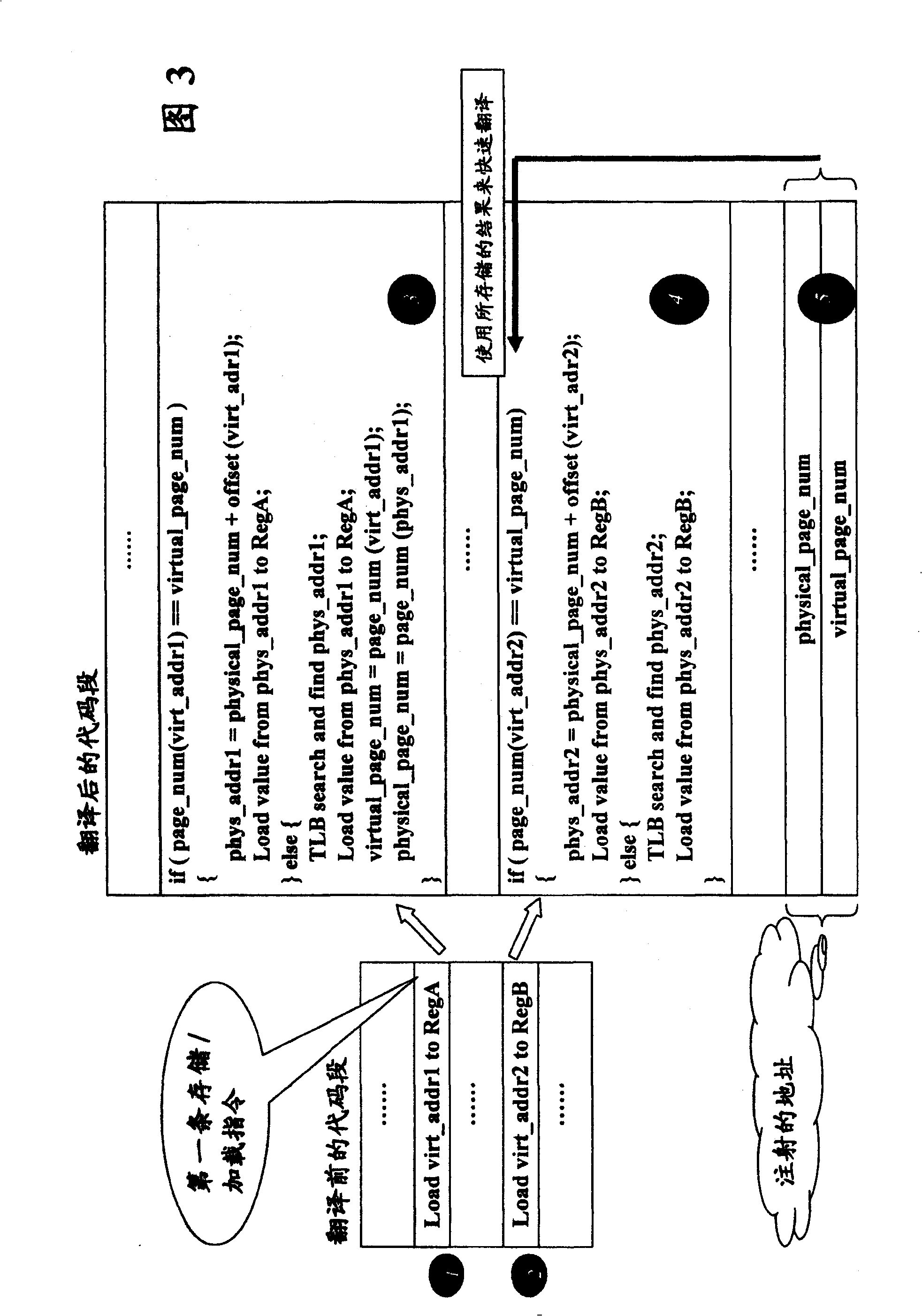
The invention provides a method for executing quick MMU simulation for computer program in computer system, wherein, a destined size address injection space in which virtual page number and corresponding physical page number are stored is allotted in the computer system. The method comprises the following steps: for the loading / storing instruction on a code sect of the computer program, comparing the virtual page number of virtual address of loading / storing instruction with the virtual page number stored in the address injection space, if the virtual page numbers being identical, obtaining corresponding physical address according to the physical page number stored in the address injection space, otherwise, executing address conversion by-pass buffer searching, that is TLB searching to obtain corresponding physical address, and reading data from the obtained corresponding physical address or writing data into the obtained corresponding physical address. The invention also discloses a device and a total system simulator for realizing the above method.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
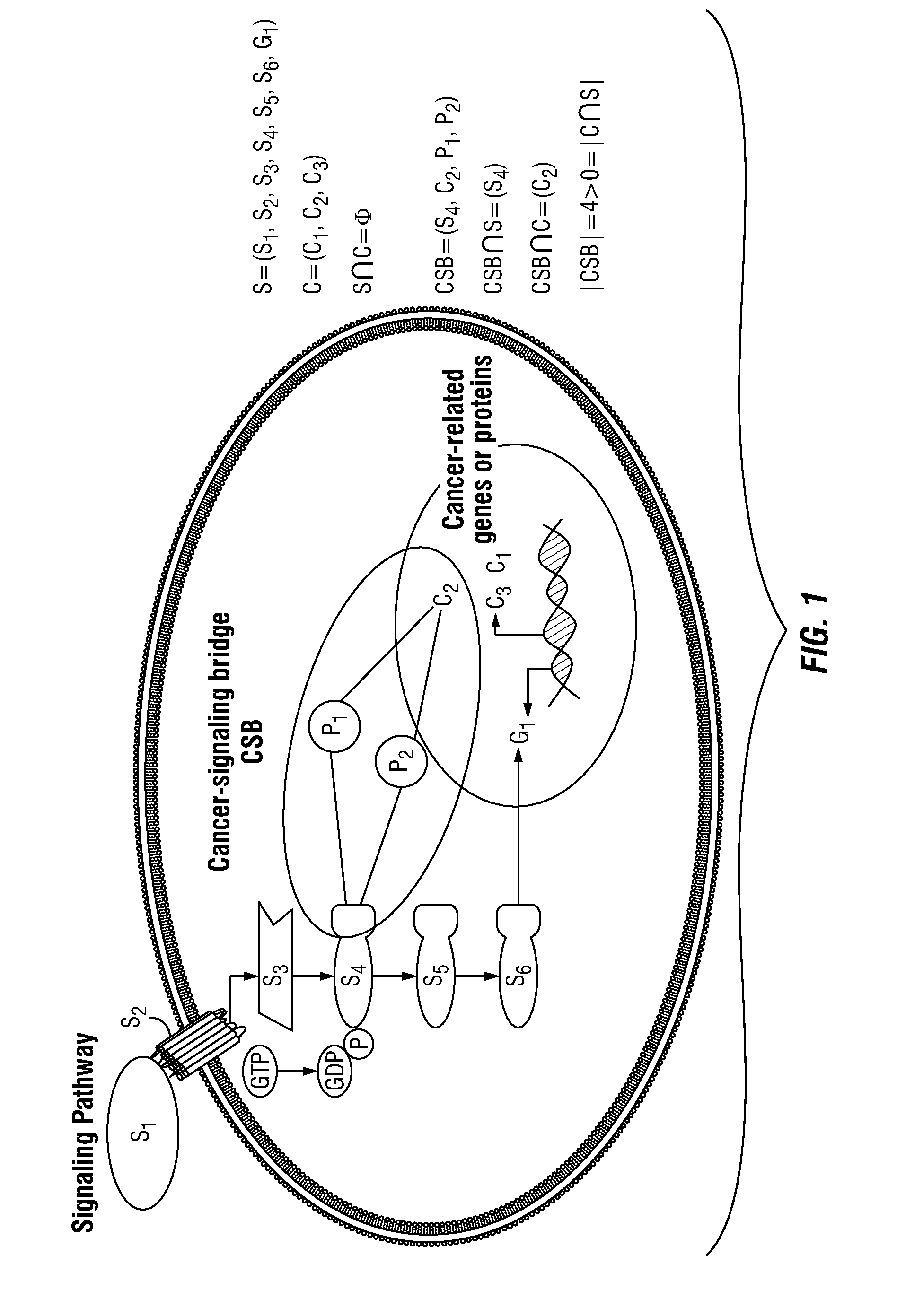
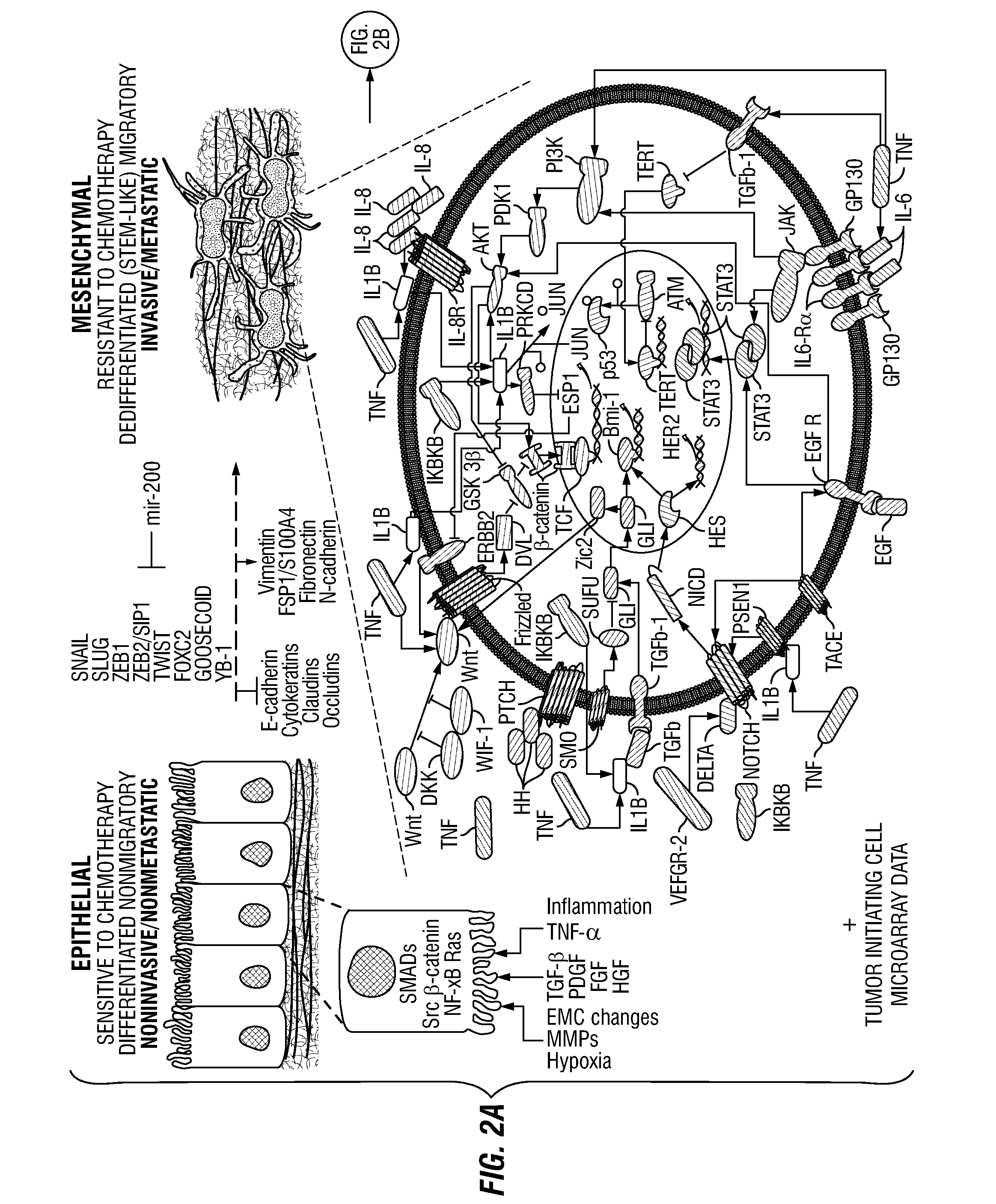
Drug Repositioning Methods For Targeting Breast Tumor Initiating Cells
InactiveUS20120296090A1Quick translationInhibit breast TICsMedical simulationOrganic chemistryOncologyPharmacology
Disclosed are systems biology-based methods for repositioning known pharmaceutical compounds to new indications, through the identification of network-based signatures. In particular, the invention provides new and useful methods for selecting drugs or combinations of drugs (and preferably previously-approved drugs) for use in new therapeutic indications. Also disclosed are methods for identifying anti-breast tumor initiating cell (TIC)-based therapeutics from within populations of target compounds. In illustrative embodiments, the invention provides methods and computer programs for the repositioning of FDA-approved pharmaceutical compounds to new indications using network-based signature analysis coupled with conventional in vitro and in vivo testing of identified drug candidates. The invention also allows identification of drugs or drug combinations for treating unmet medical needs including, for example, “orphan” diseases.
Owner:THE METHODIST HOSPITAL RES INST
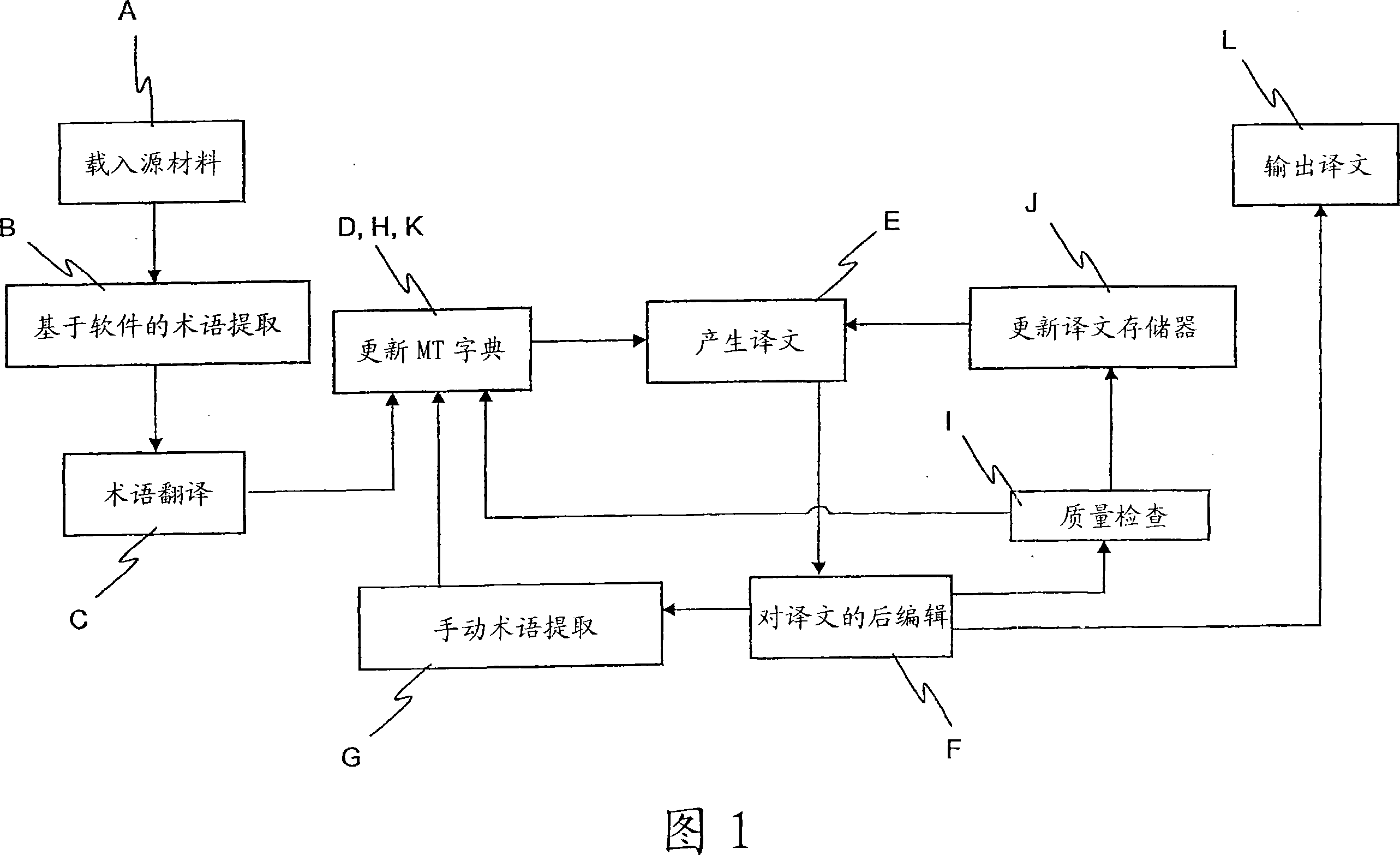
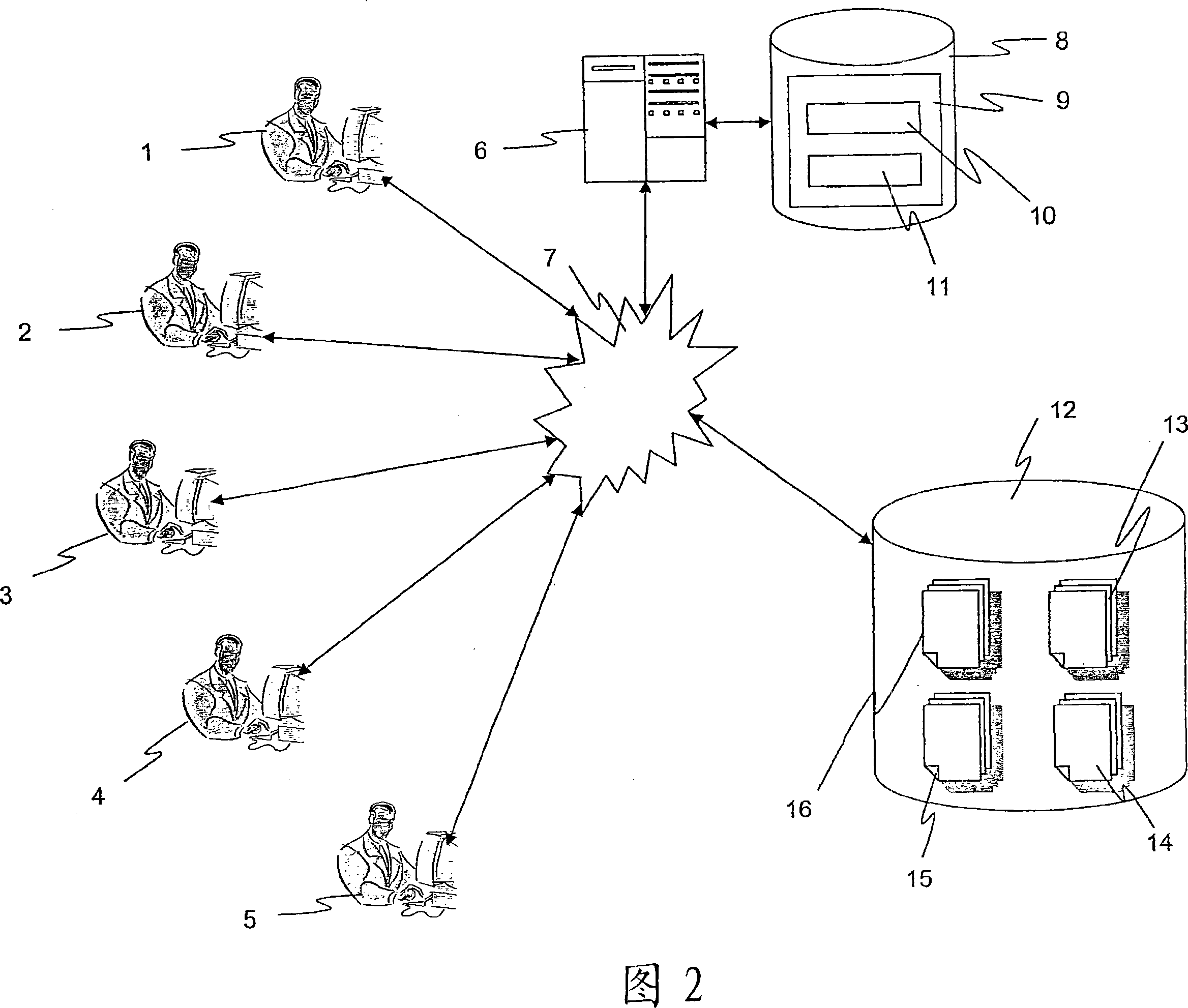
Computer-implemented method for use in a translation system
InactiveCN101019113AEasy to useEfficient identificationNatural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsSource materialMachine translation
The invention provides a computer implemented method for use in a translation system. A computer-implemented method for use in natural language translation. The method involves attaching pieces of linguistic information to two or more source language elements in a source material in a first natural language. The pieces of linguistic information are matched to one or more predetermined parse rules. Associations are then formed between the two or more source language elements to form terminology candidates, which are then presented to human reviewers. Terminology candidates are subsequently validated by a user, becoming validated terminology which is then translated into a second, different, natural language, becoming translated terminology. The translated terminology can then be loaded into a machine-translation dictionary which can be used during subsequent machine-assisted translations.
Owner:SDI NORTH AMERICA INC
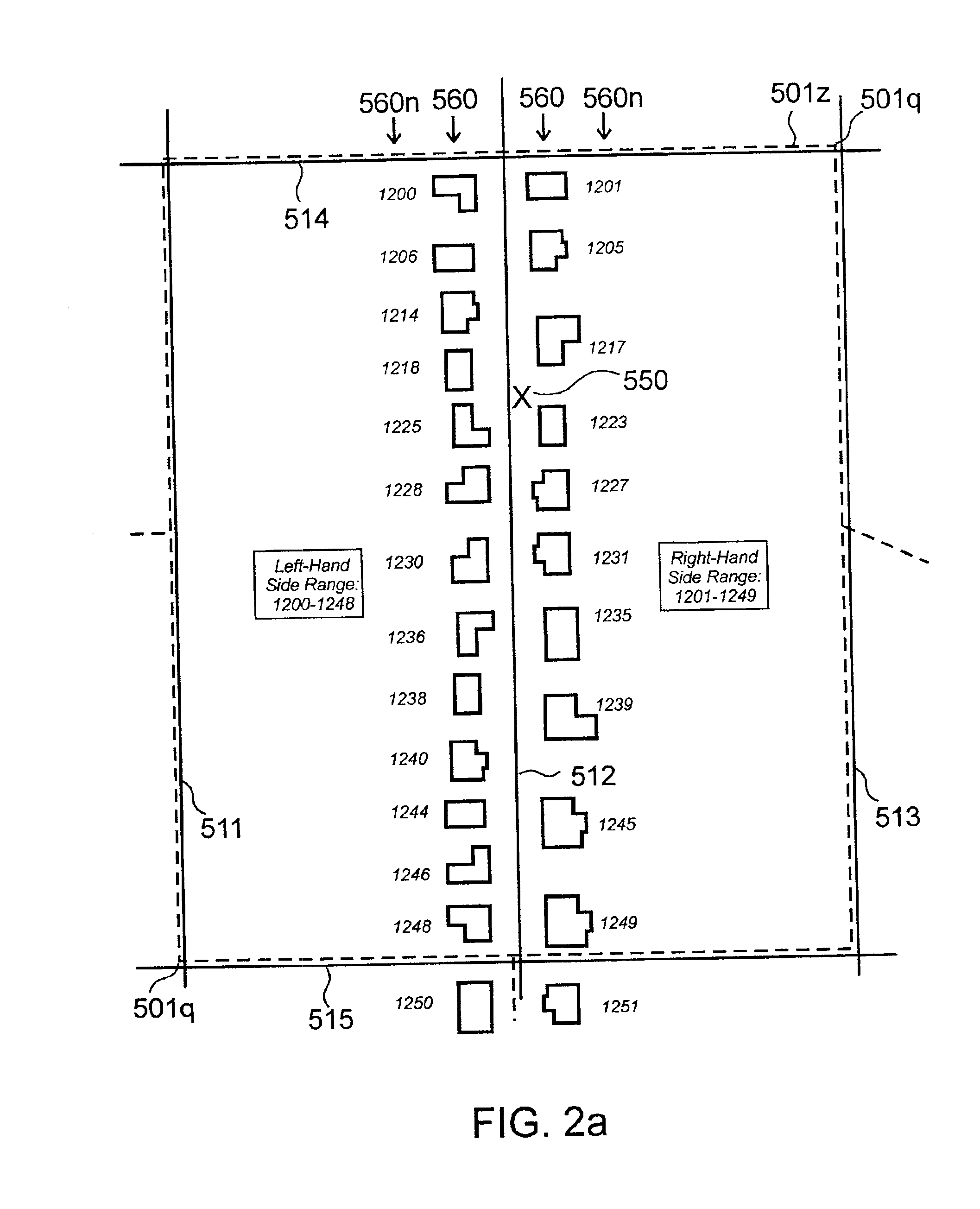
System and method for spatial point-of-interest generation and automated trip segmentation using location data
InactiveUS8843315B1Quick translationInhibit scalabilityInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlData processing systemTime segment
This present invention is a spatial data processing system and method that allows the automatic, rapid, scalable analysis and transformation of large amounts of travel behavior data (e.g., tracking data points) into individual “points-of-interest” and discrete trips stored in a spatial database. Each trip has a point-of-interest as a starting and ending location, and contains multiple positions (e.g. latitude and longitudes) which define the travel path of the user / device during that time period.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
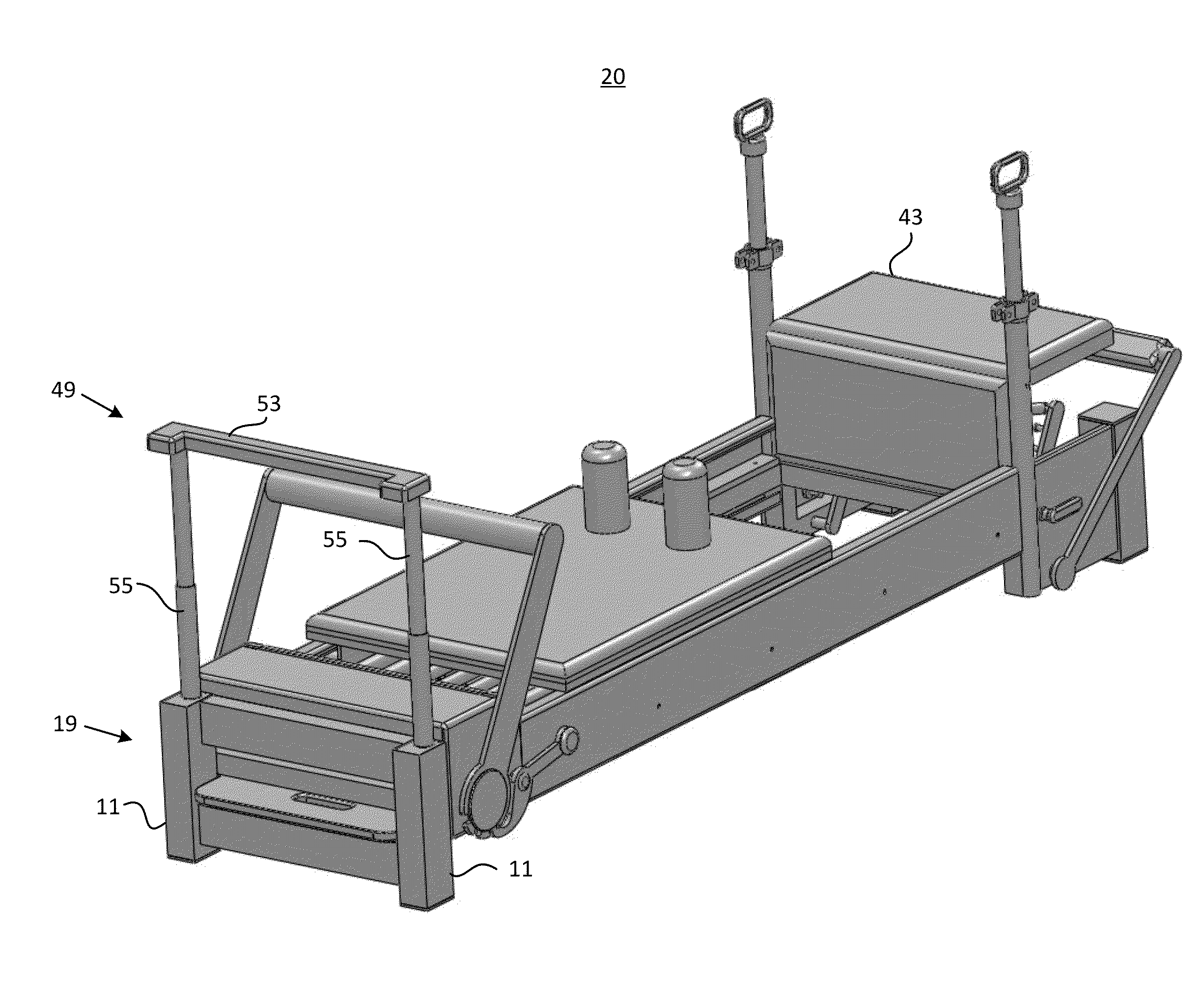
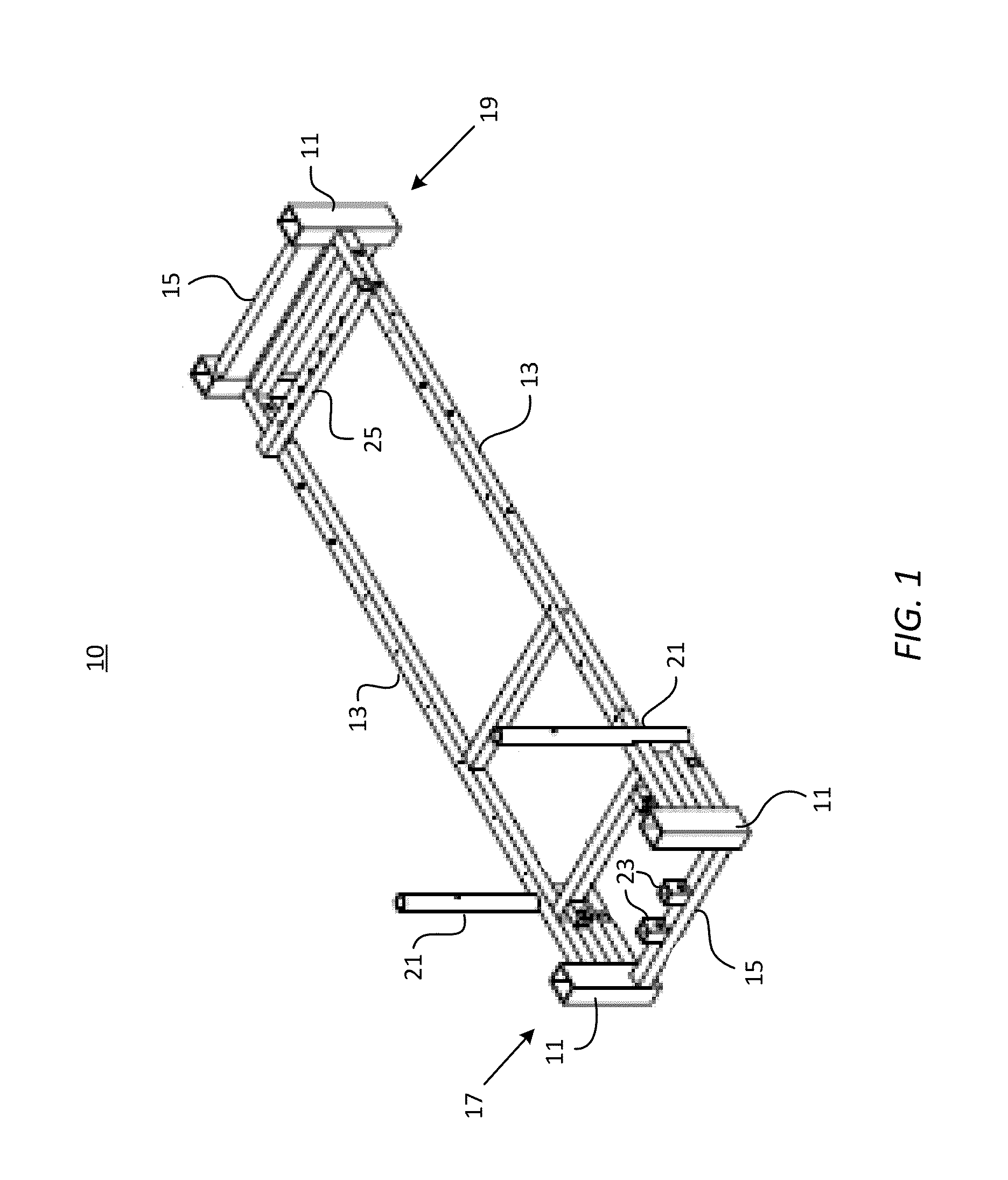
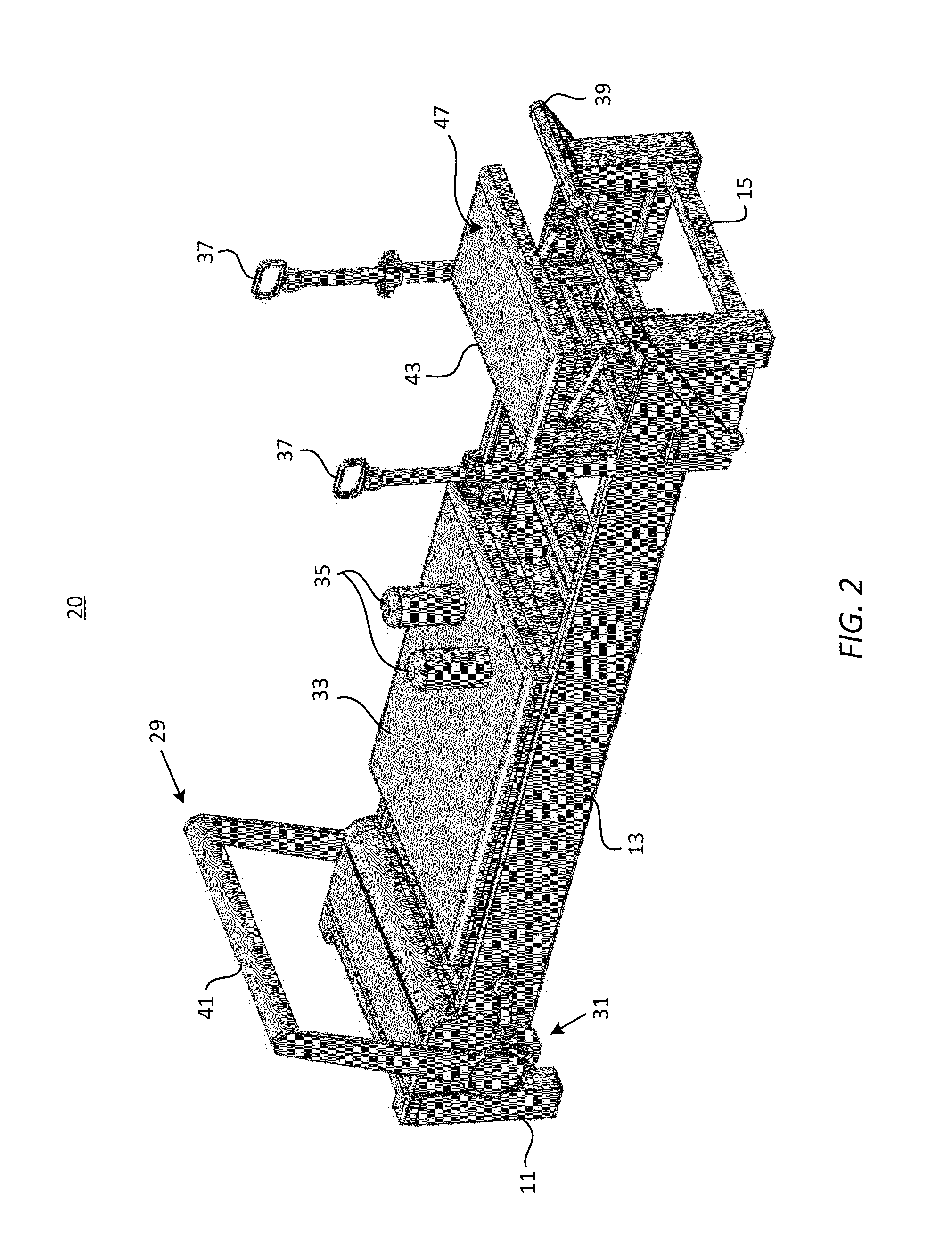
Reformer apparatus having integral ergonomic purchase translatable into deployed and stowed positions
ActiveUS8602953B2Quick translationSmall volumeResilient force resistorsSpace saving gamesCarriageMechanical engineering
A Pilates reformer includes a rectangular frame having two transverse ends connected by longitudinal rails, each transverse end comprising a pair of bases and an interconnecting transverse member. A planar carriage attaches to the frame by springs, and is moveable horizontally against force of the springs by means of rollers along the longitudinal rails. An ergonomic purchase confined to the frame is translatable into a stowed position for spatial efficiency, and into a deployed position that enables a user mounted on the carriage to reach the purchase, one of the transverse ends arresting the purchase when fully translated to the stowed or deployed position. The purchase may be a rotatable bench, a slidable and rotatable jump board, a vertically adjustable ballet bar, or the reformer may include a combination of these purchases.
Owner:WUNDAFORMER
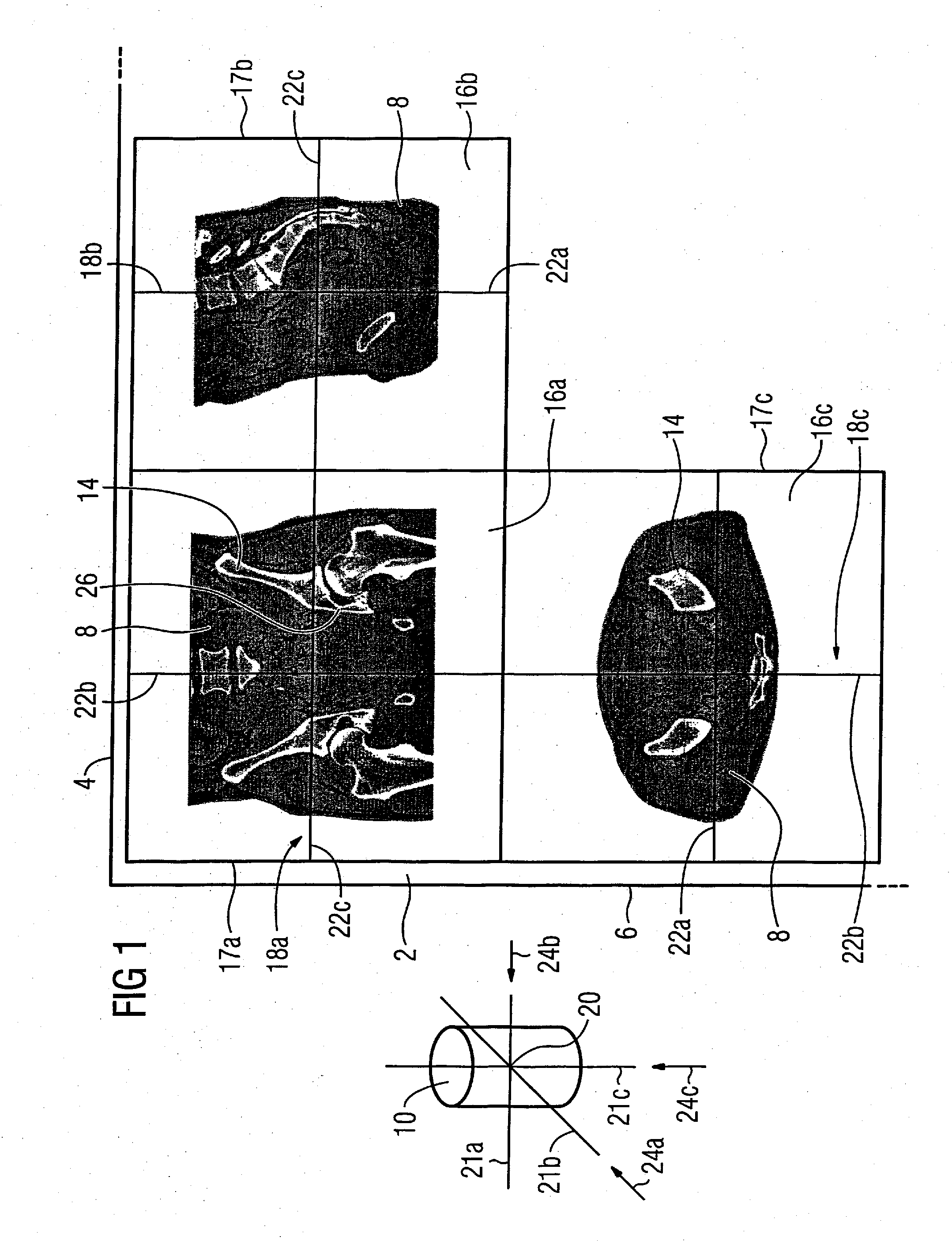
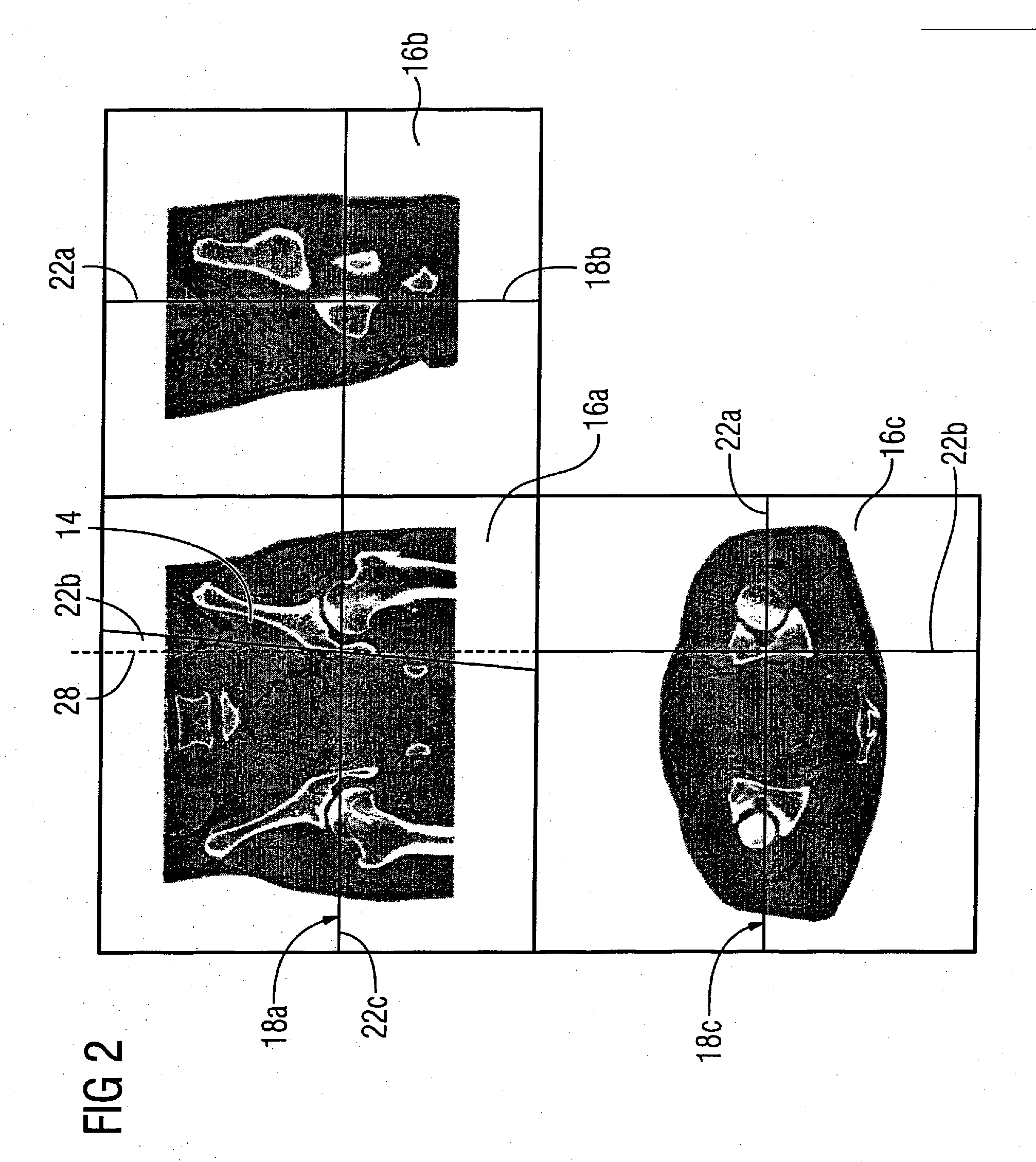
Method for display of medical 3D image data on a monitor
InactiveUS20080074427A1Intuitive interpretationQuick identificationDiagnosticsSurgical systems user interface3d imageComputer science
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Device and method for foreign words translation on hand-hold equipment based on photograph
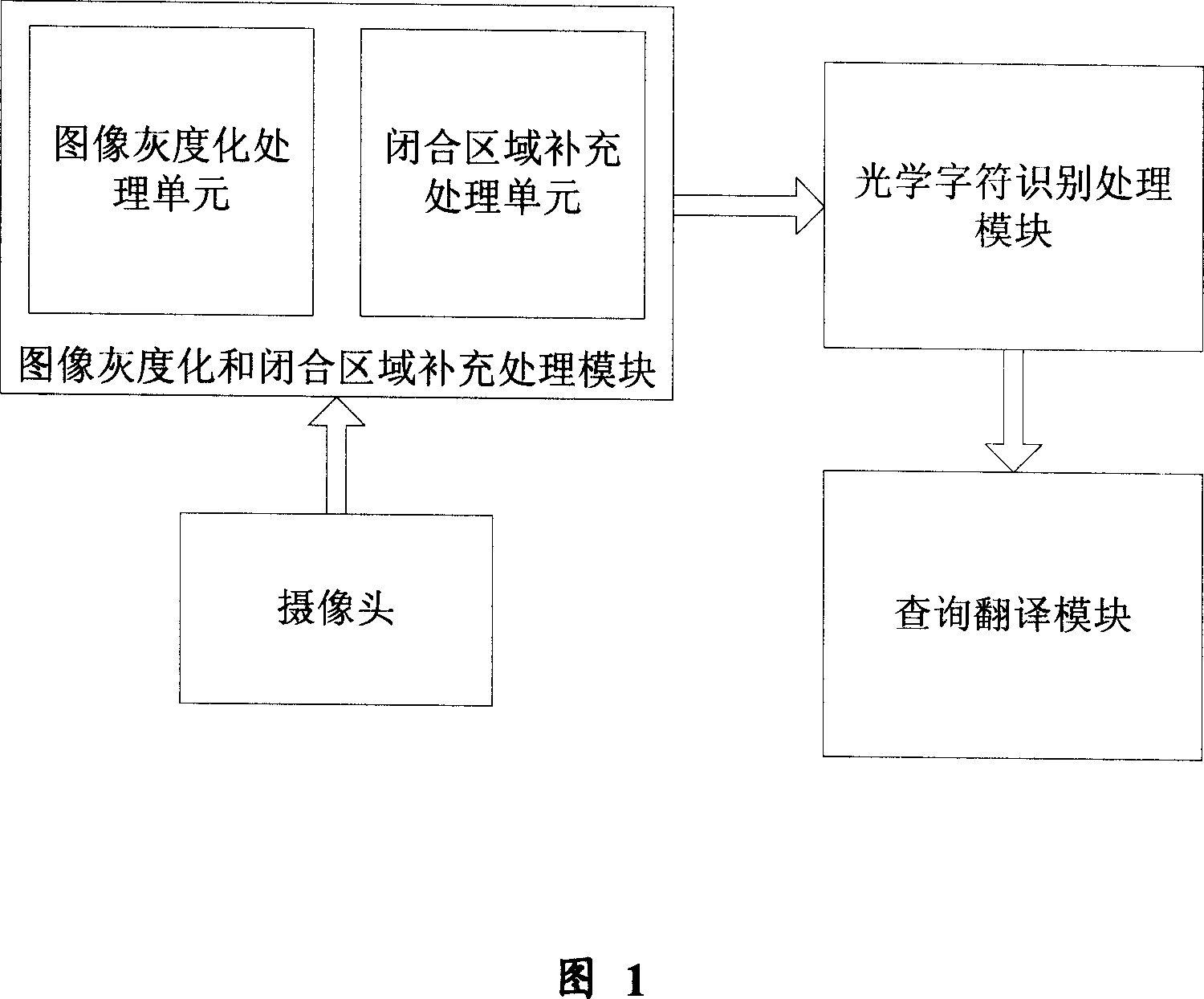
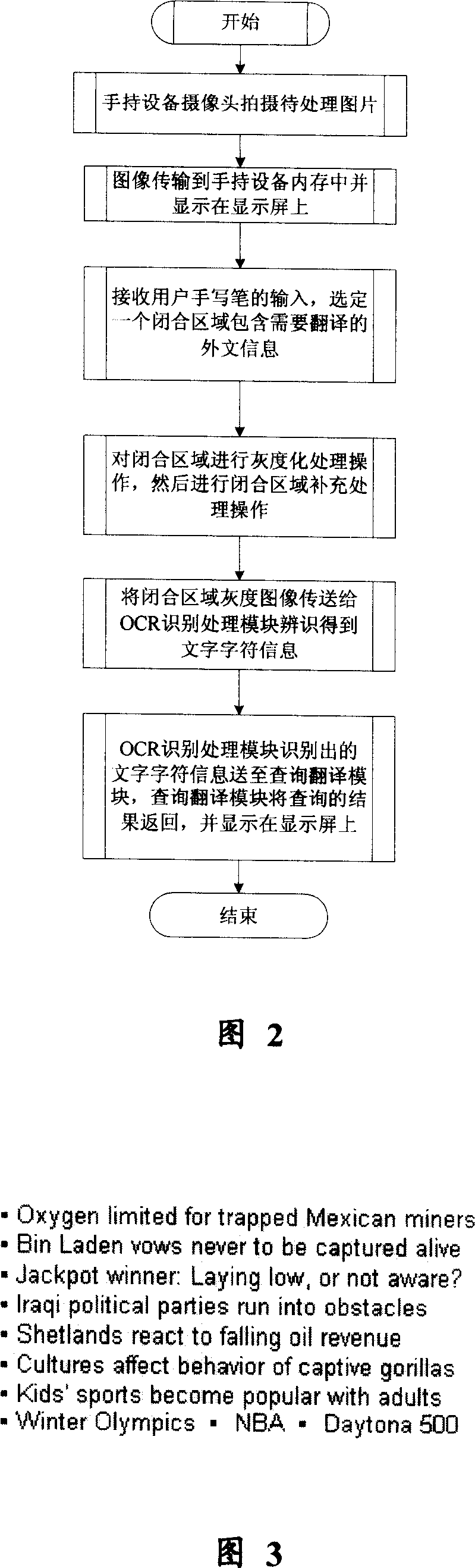
ActiveCN101082956AQuick translationEasy to operateCharacter and pattern recognitionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCharacter recognitionTextual information
The invention discloses a translating device and method of foreign language based image on the hand-held equipment, which comprises the following parts: cam, image graying and seal area supplementing processing mode, optical character identifying processing mode and inquiry translation mode, wherein the cam connects image graying and seal area supplementing processing mode, optical character identifying processing mode and inquiry translation mode sequently. The method comprises the following steps: shooting the translated information picture of foreign language; selecting a seal area in the picture; graying the information in the seal area; supplementing the seal area; identifying the character; inquiring; translating; processing; displaying the translation result. The invention is convenient to operate with high translating efficiency, which improves the stability and reliability of identifying inquiry property with wide fitting scale.
Owner:YINGHUADA (SHANGHAI) ELECTRONIC CO LTD
Partially-ordered cams used in ternary hierarchical address searching/sorting
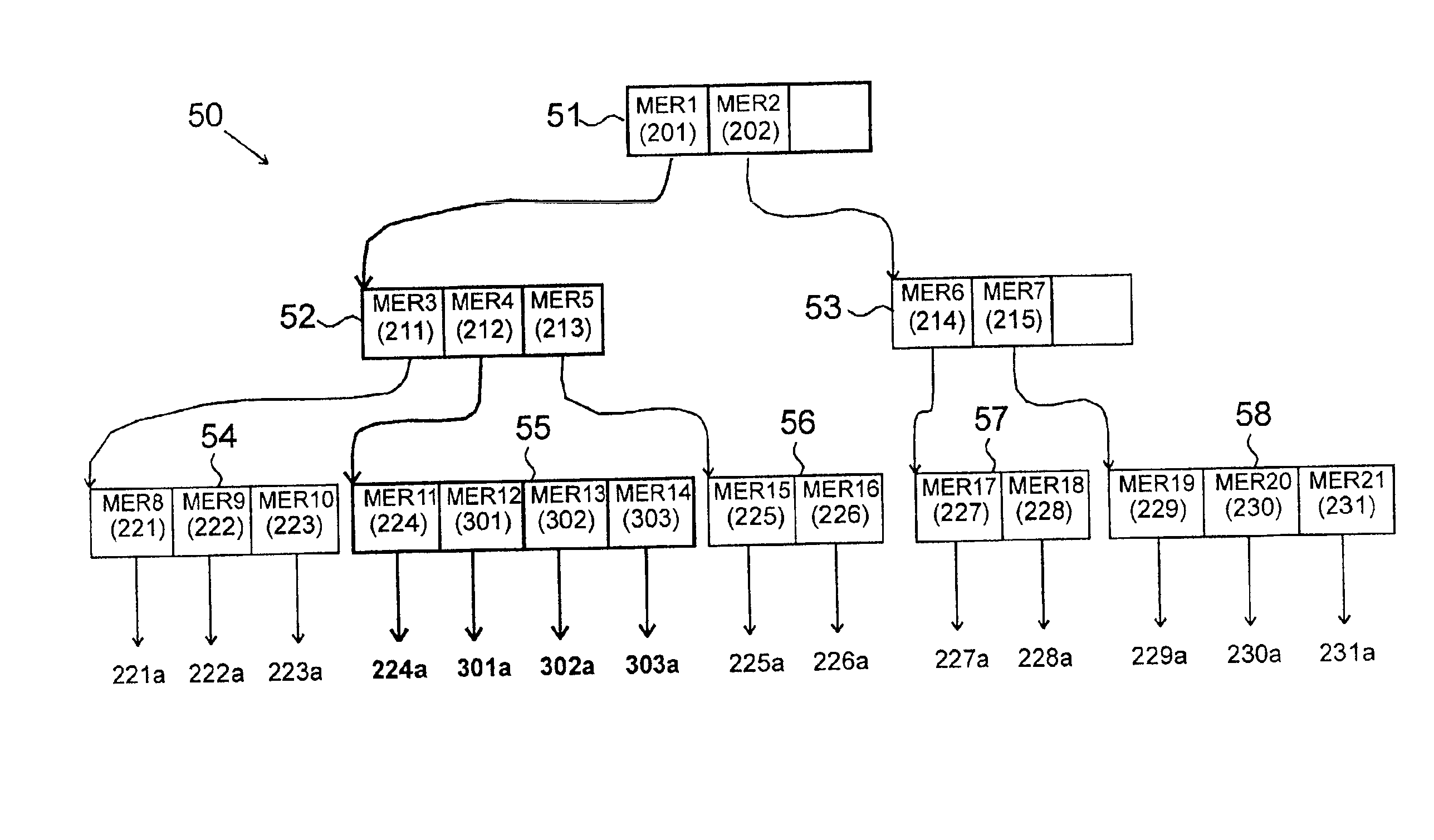
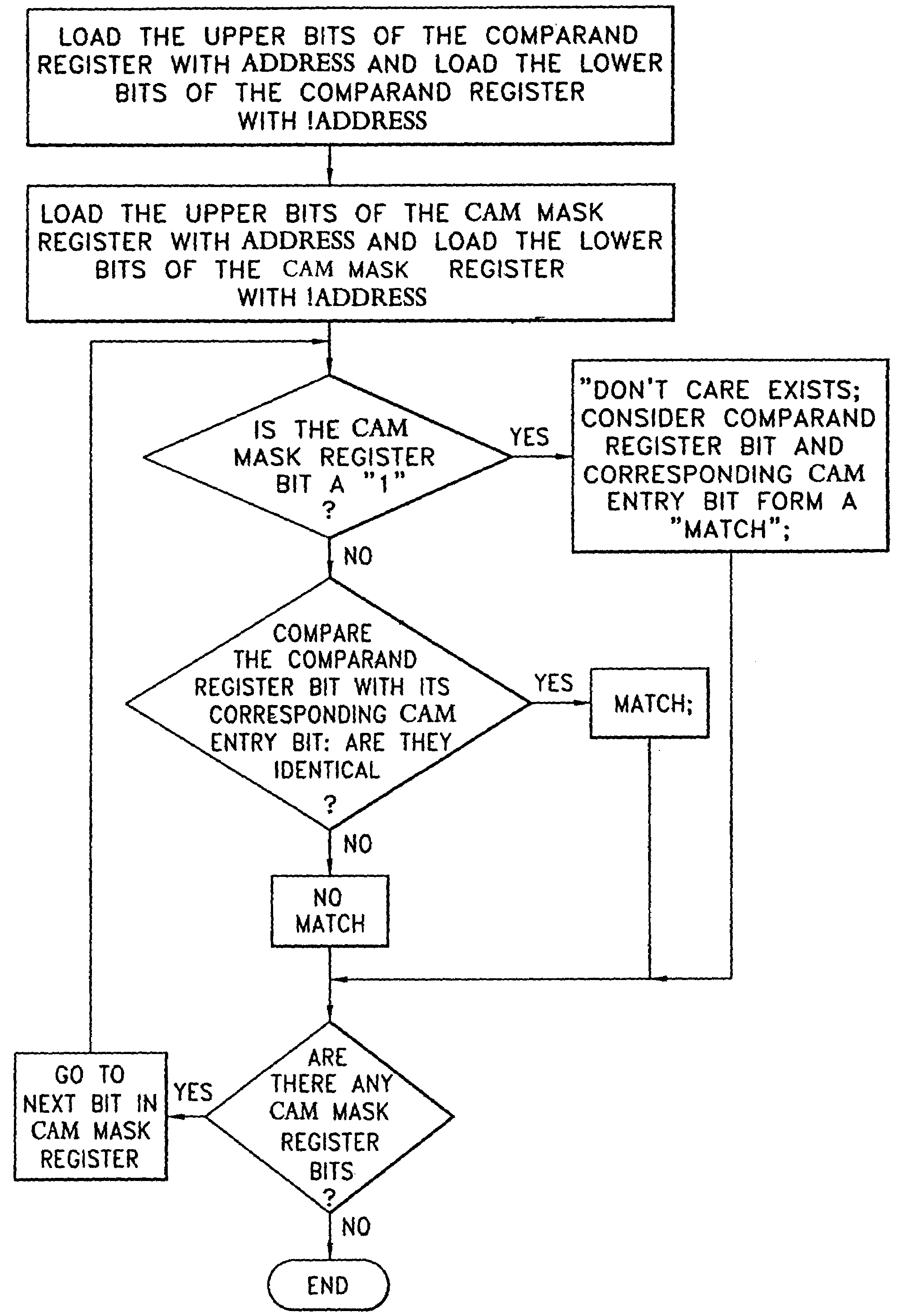
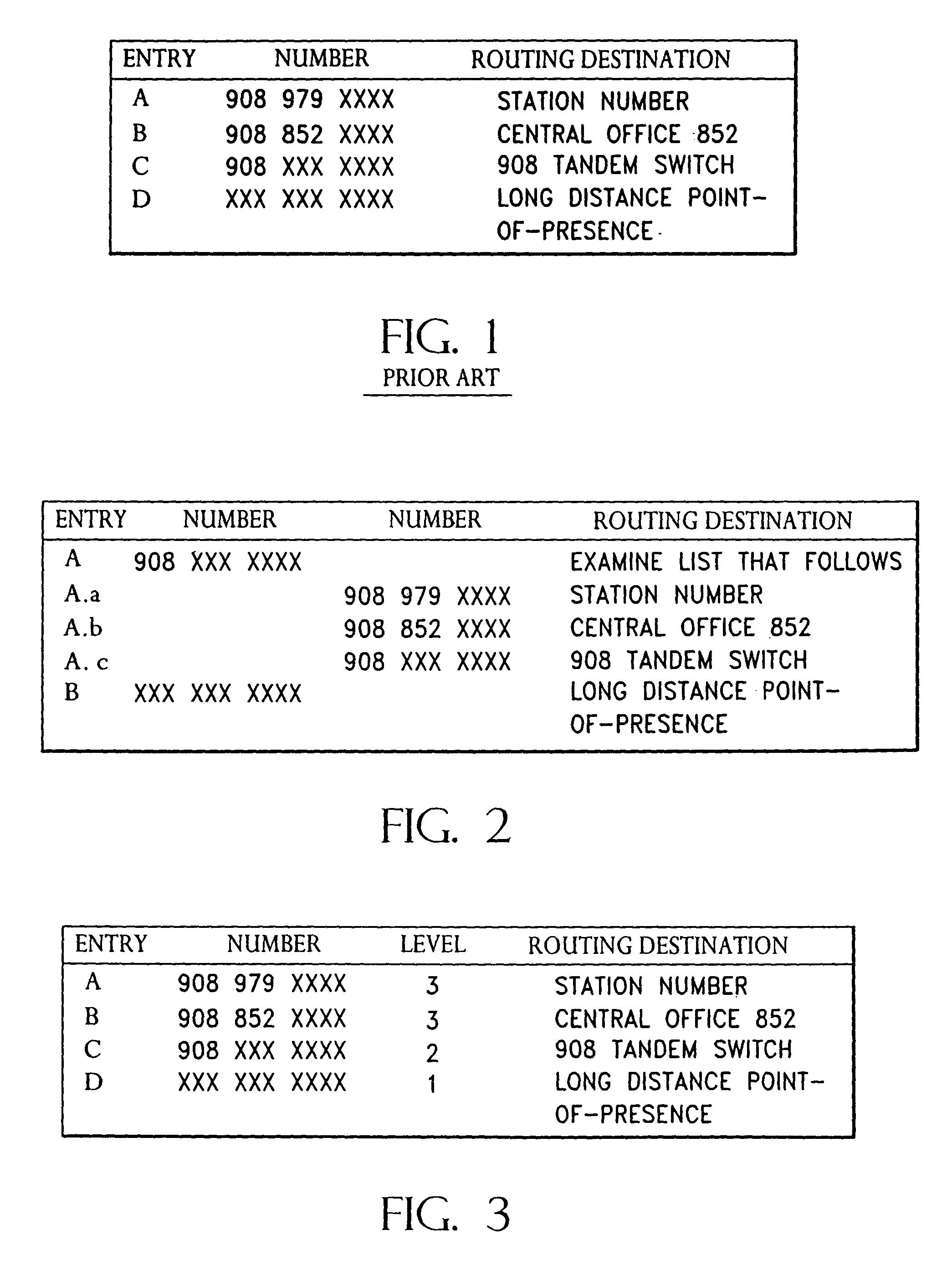
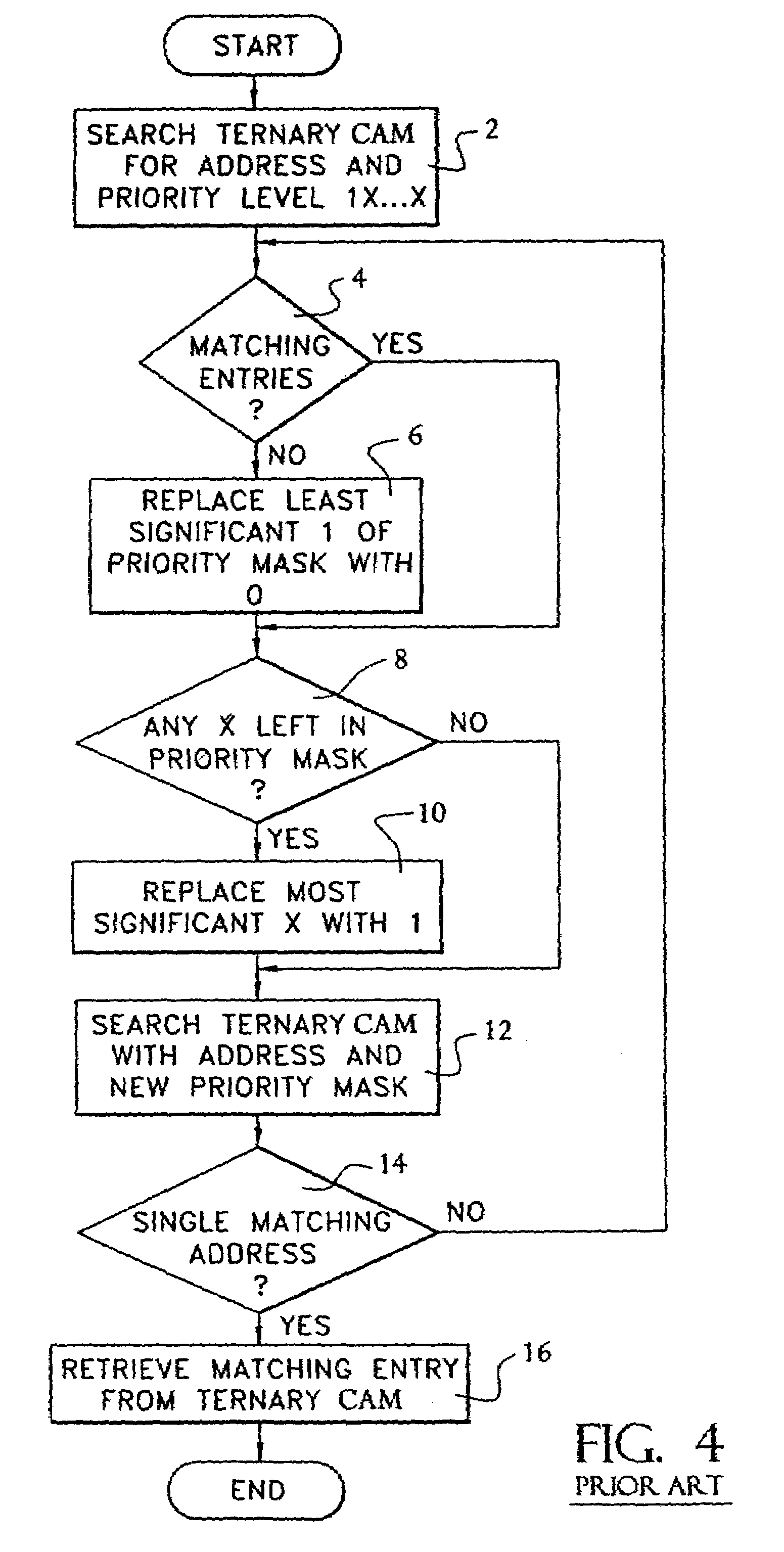
InactiveUS7139867B2Quick translationDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer hardwareCommunications system
An apparatus and method that utilizes partial ordering of ternary hierarchical addresses and their associated masks entries in both binary and ternary content addressable memories (CAMs) for providing fast searches and while reducing address table size used in the processing of communication system (e.g., Internet Protocol (IP), layer-3 switches and ATM switches using E.164 addressing) addresses for identifying the source and destination of each digital packet data.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
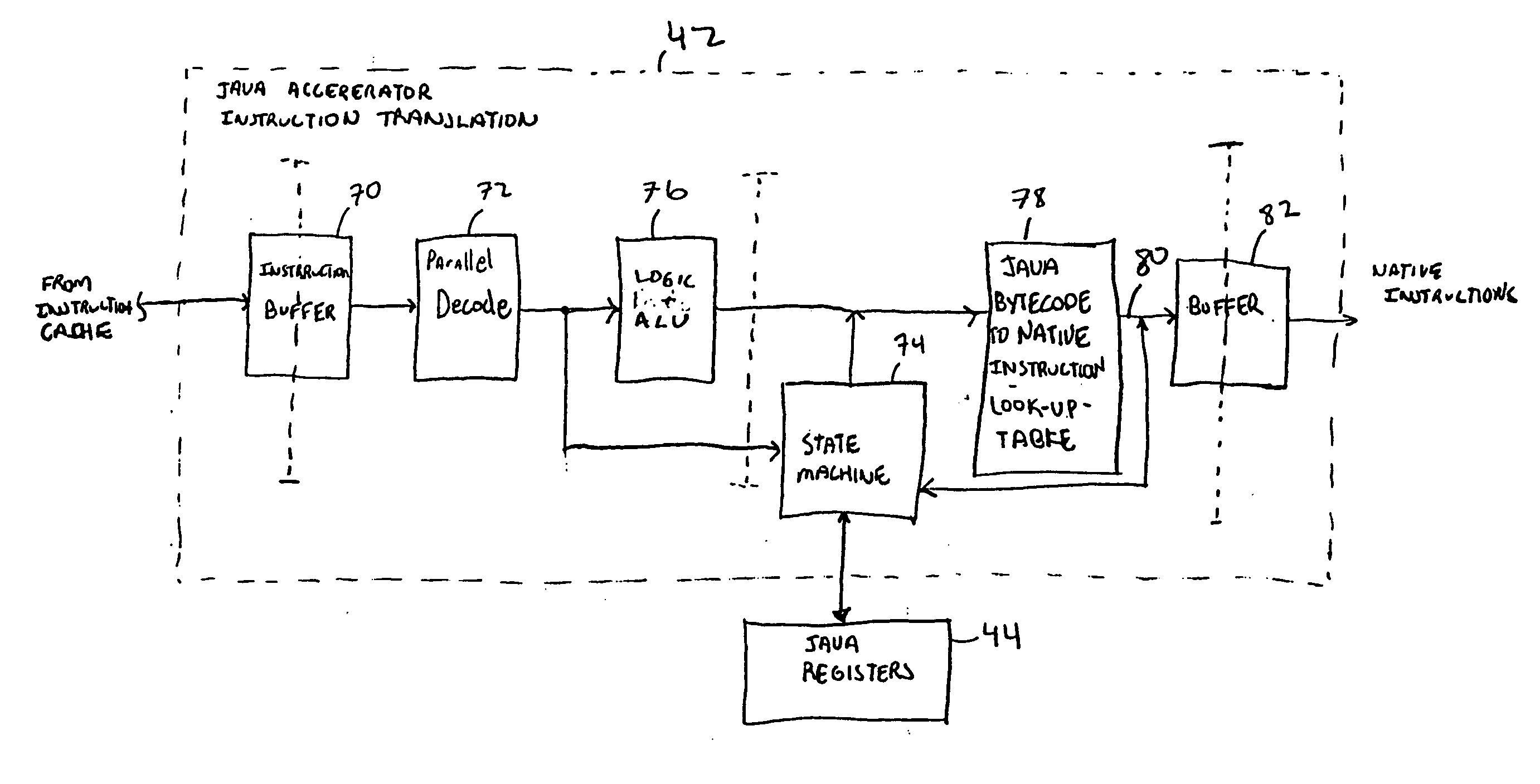
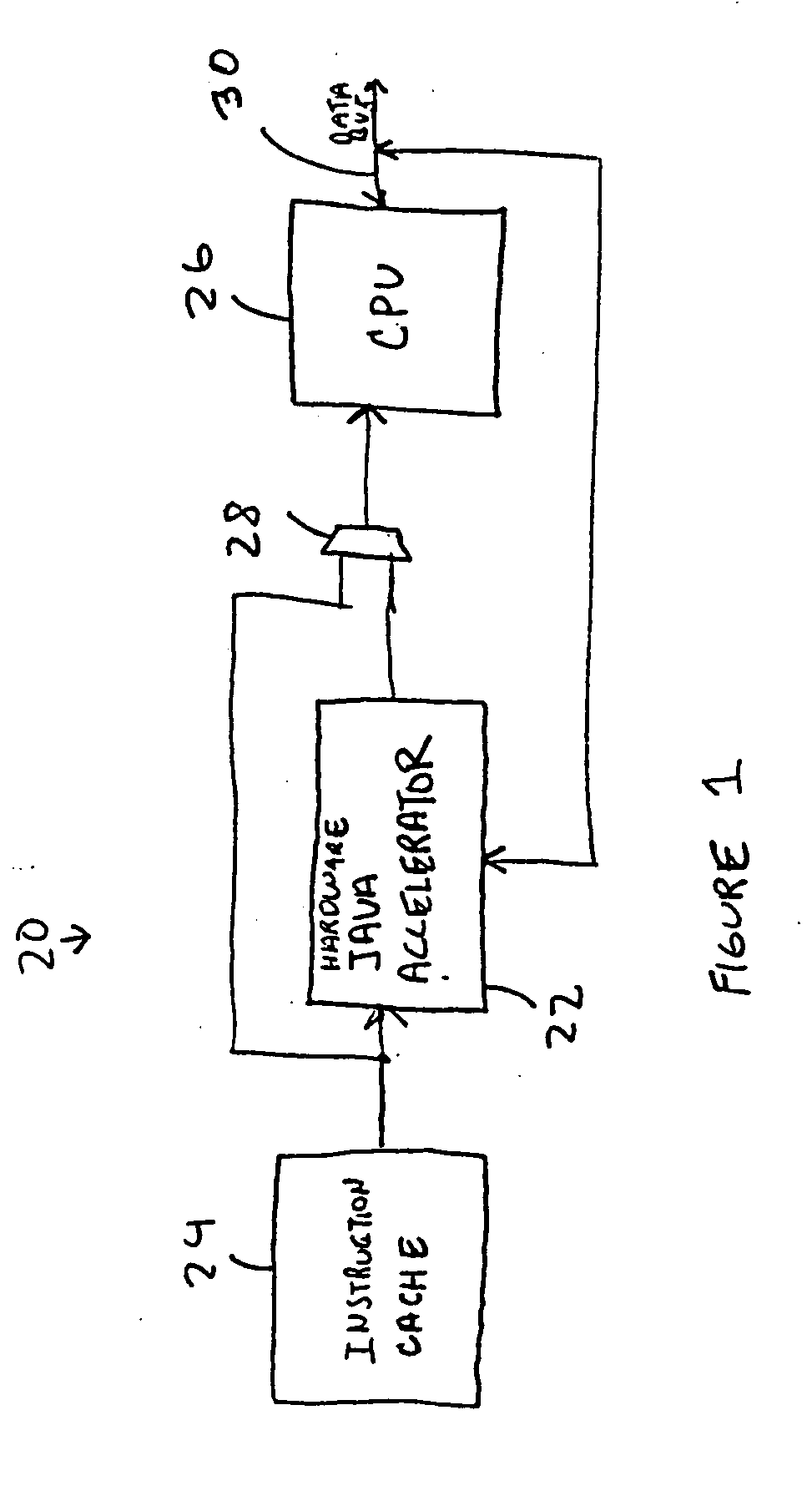
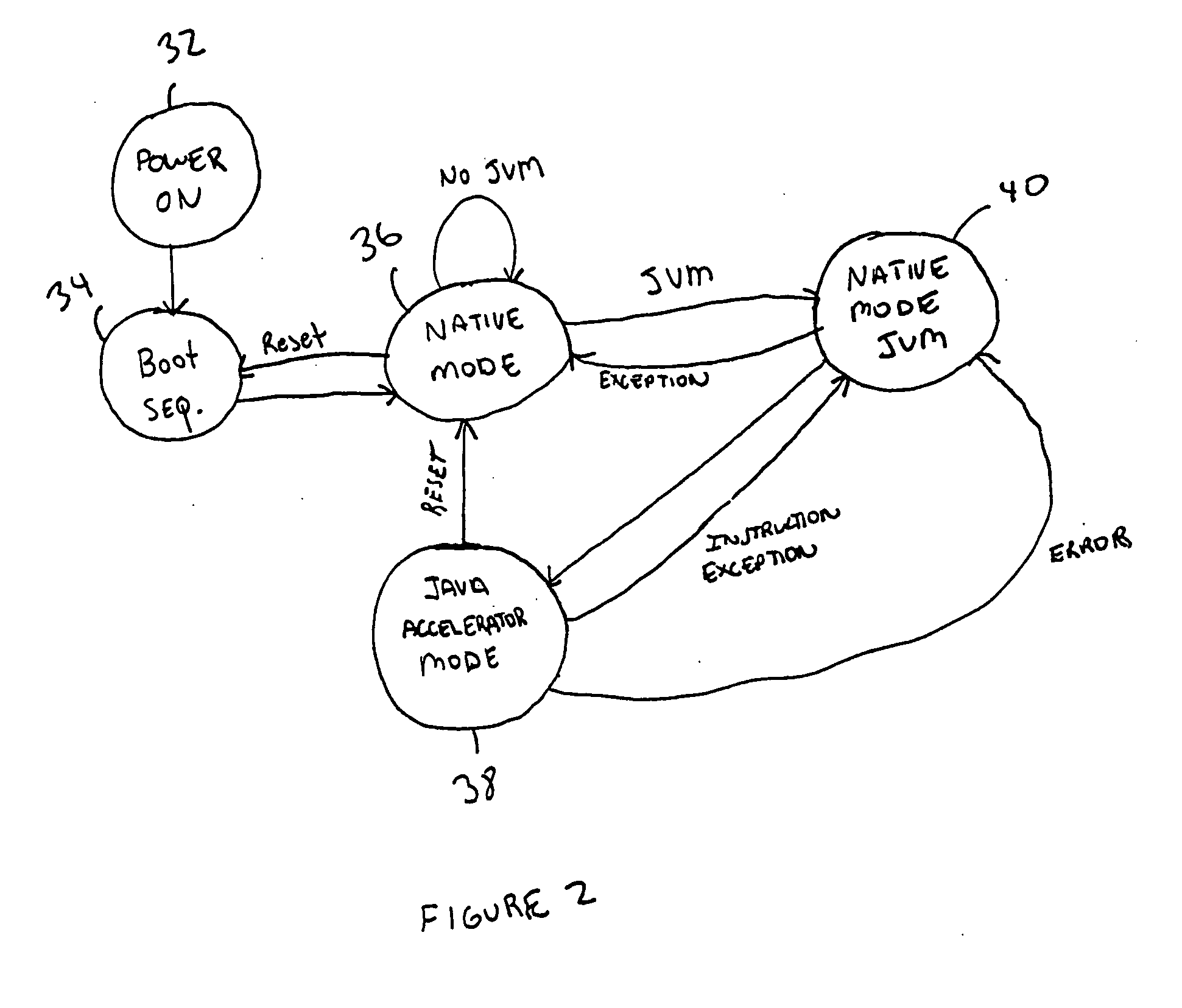
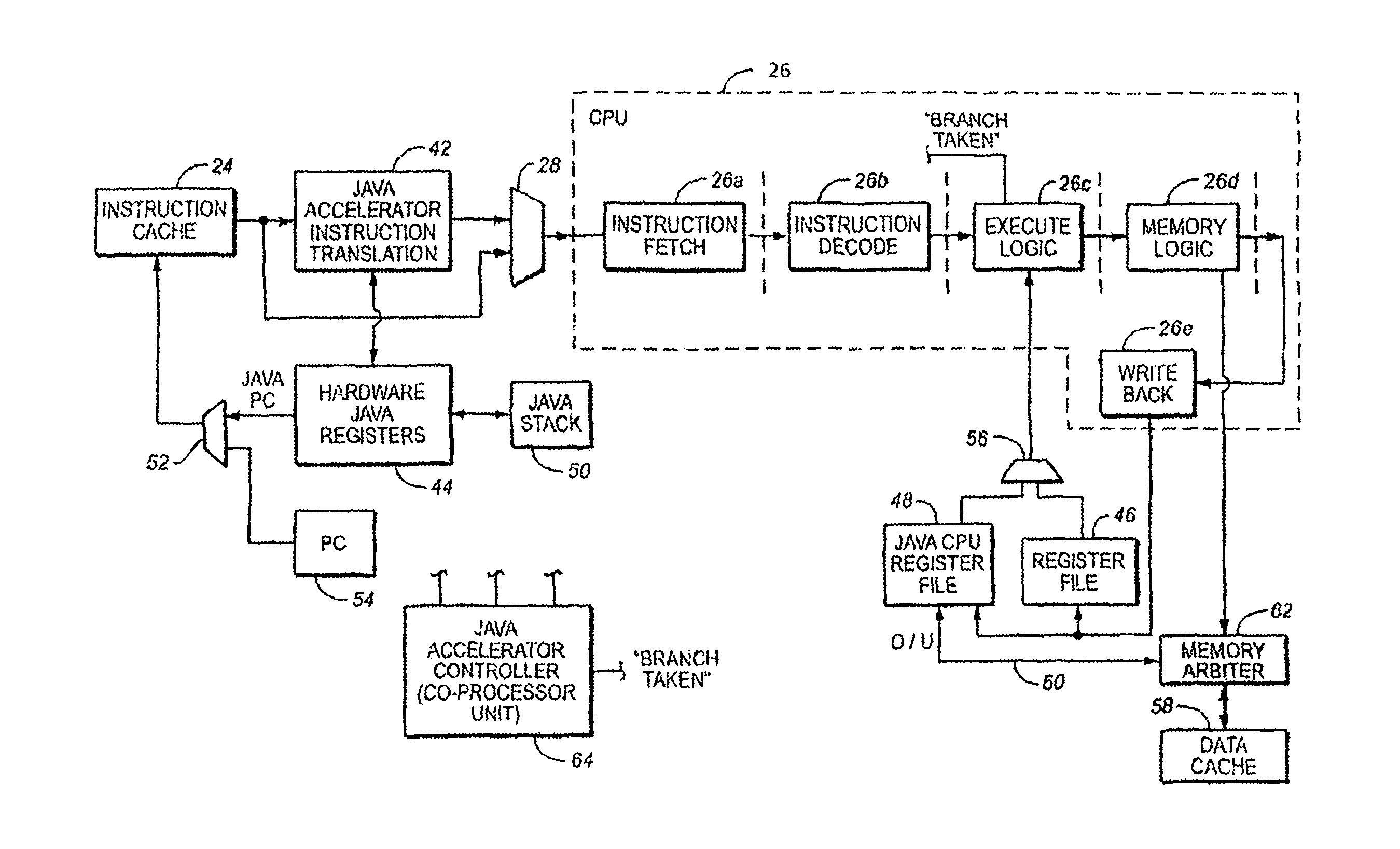
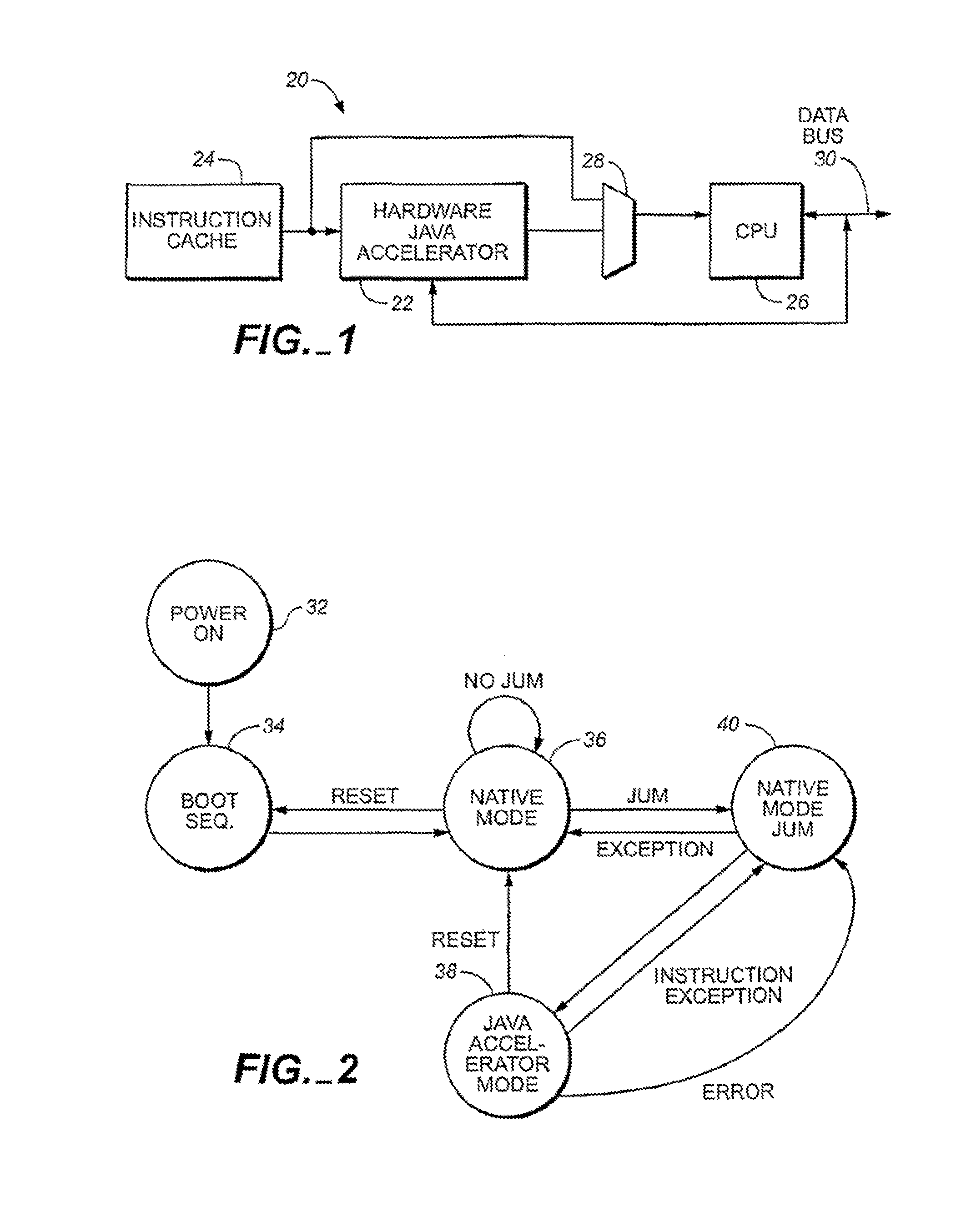
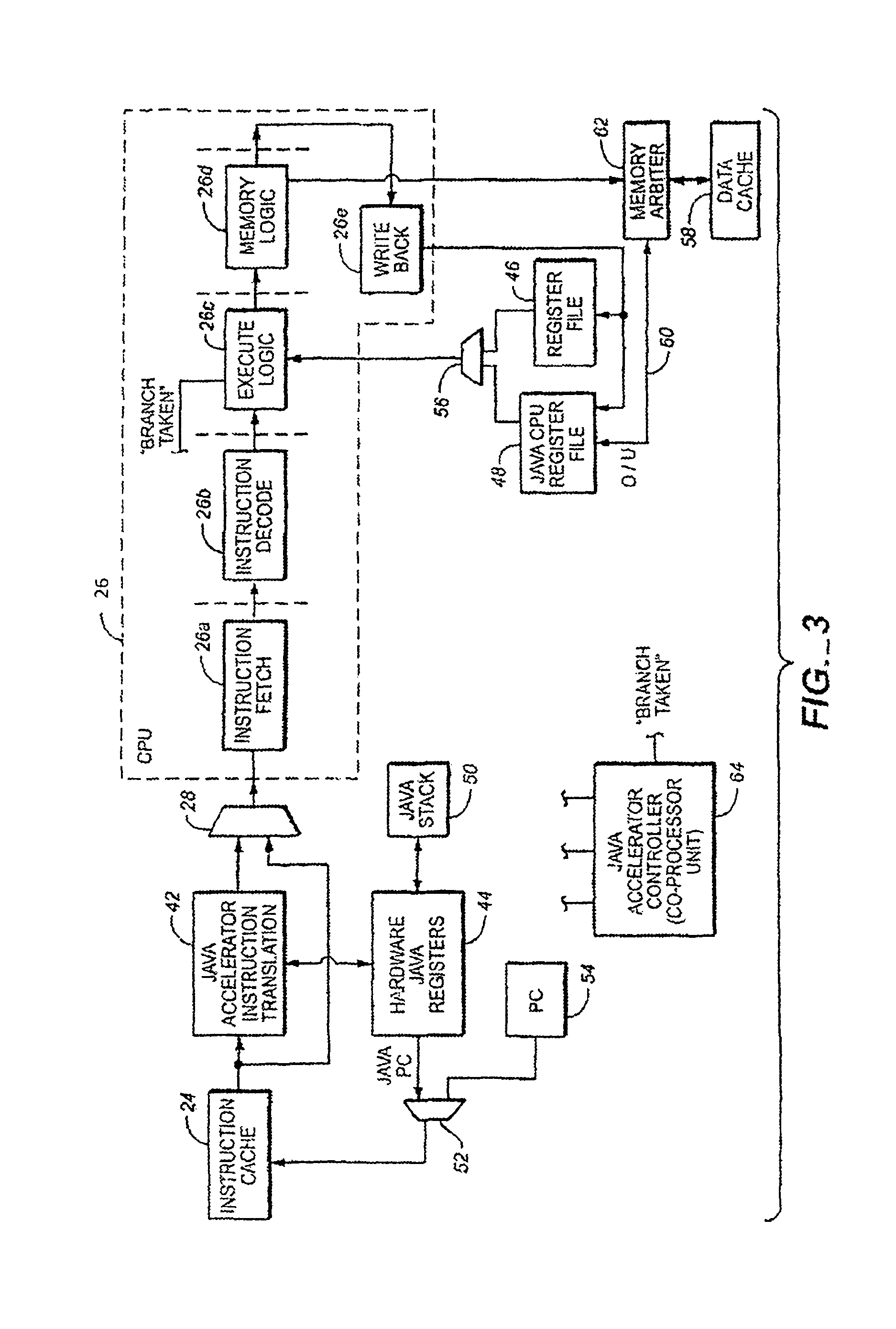
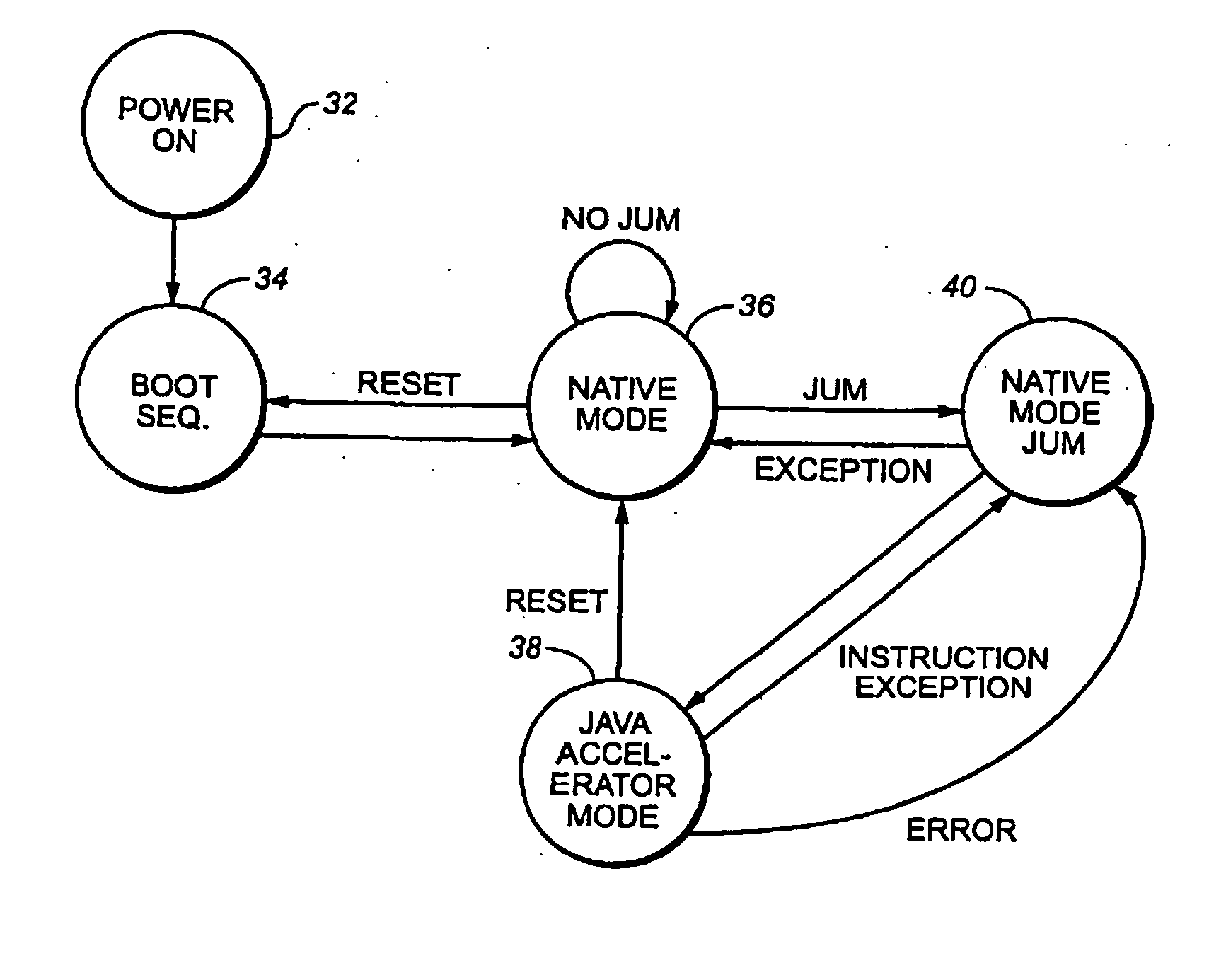
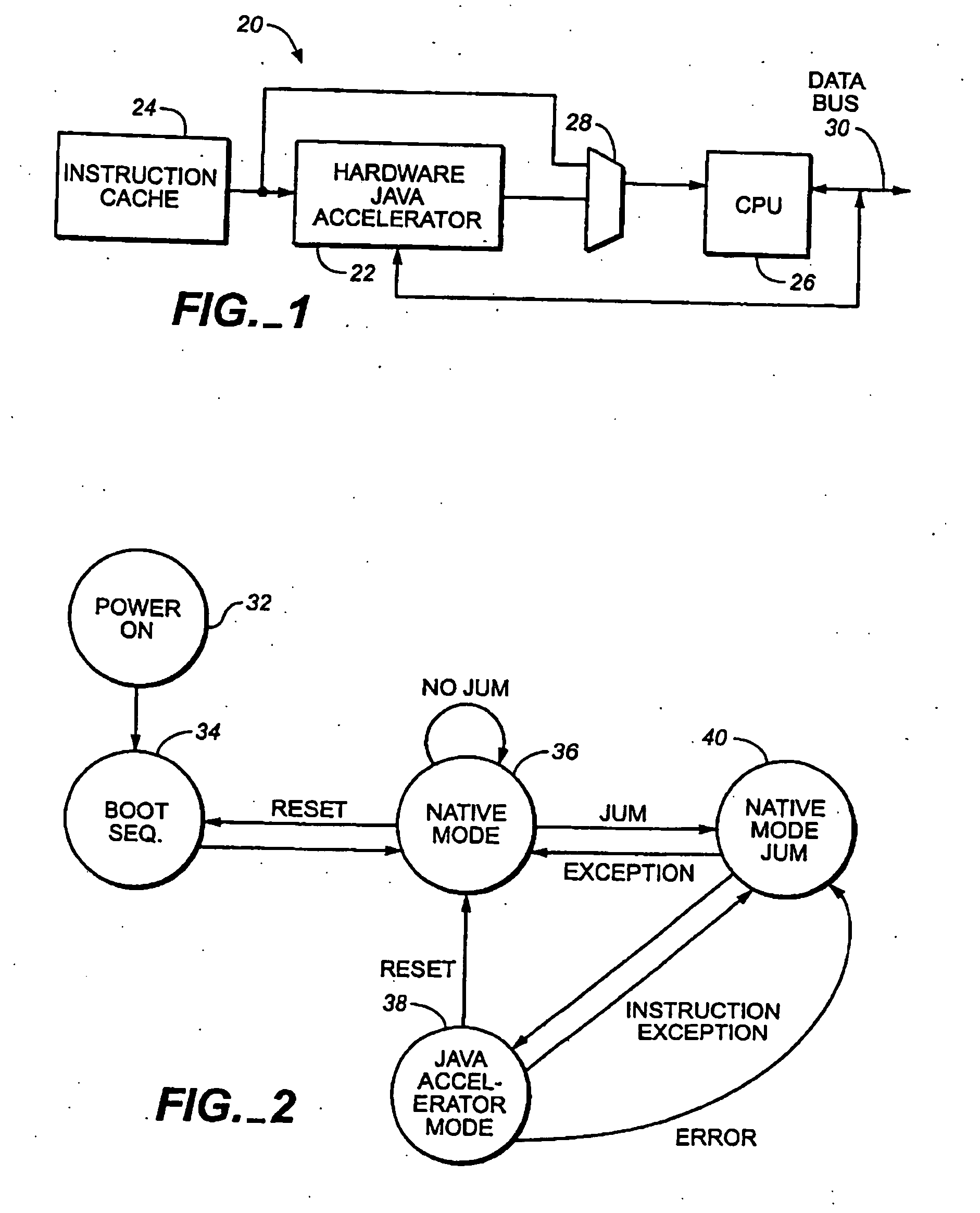
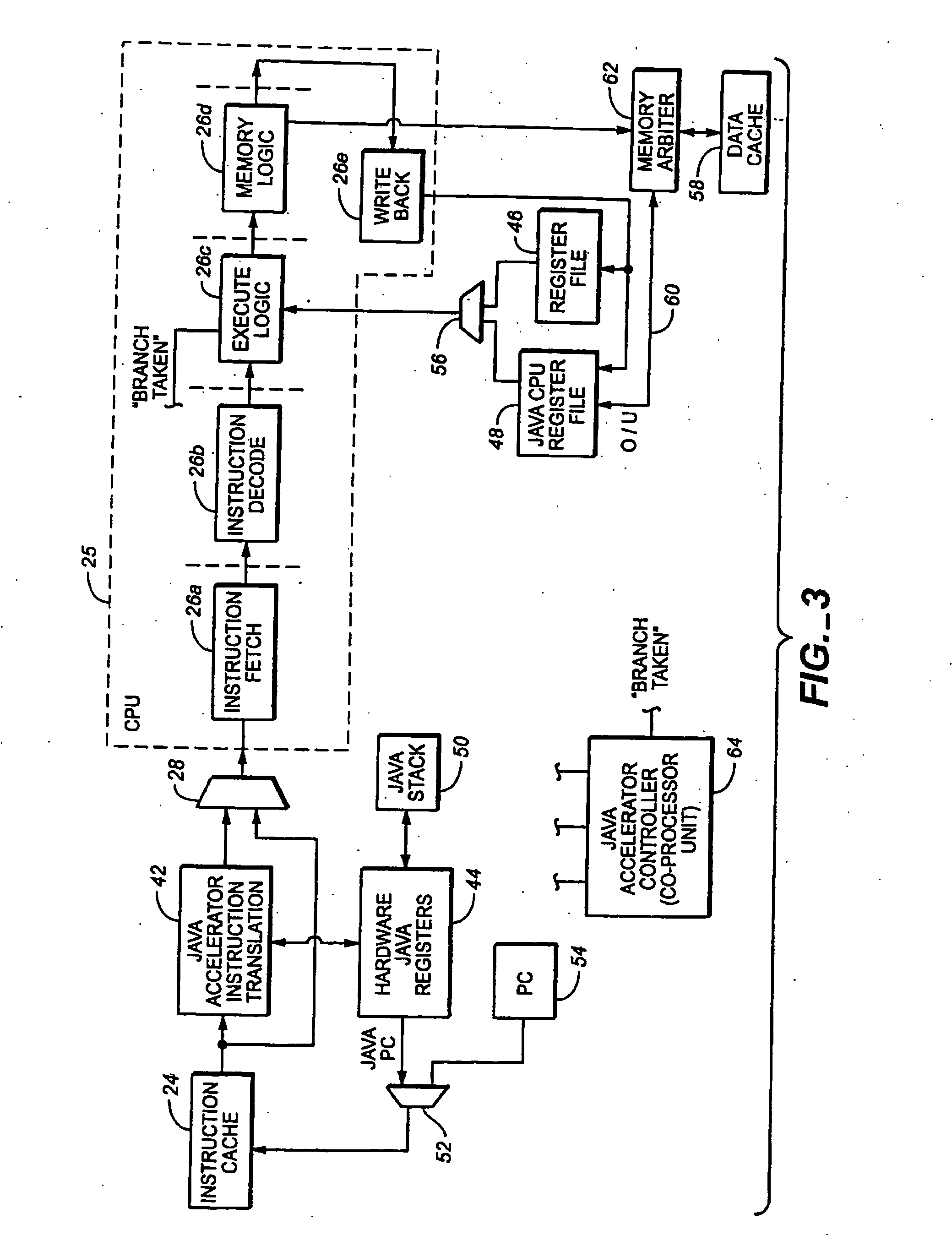
Java hardware accelerator using microcode engine
InactiveUS20050240915A1Quick translationProcess can be speededSpecific program execution arrangementsMemory systemsJava bytecodeHardware acceleration
A hardware Java accelerator is provided to implement portions of the Java virtual machine in hardware in order to accelerate the operation of the system on Java bytecodes. The Java hardware accelerator preferably includes Java bytecode translation into native CPU instructions. The combination of the Java hardware accelerator and a CPU provides a embedded solution which results in an inexpensive system to run Java programs for use in commercial appliances.
Owner:NAZOMI COMM
Translator support system, server, method and recording medium
InactiveUS7933857B2Quick translationNatural language translationDigital computer detailsSupporting systemRecording media
Owner:RICOH KK
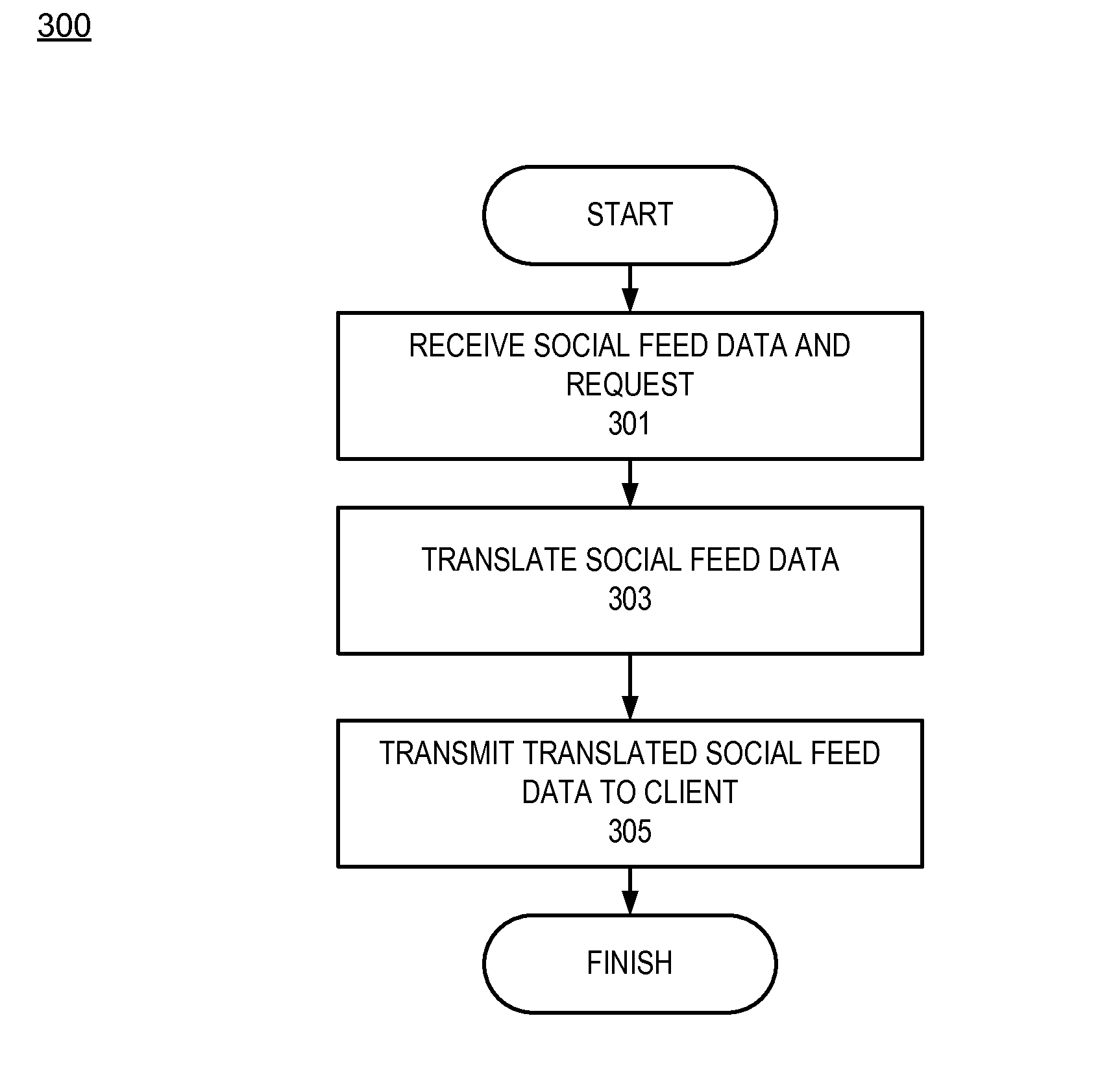
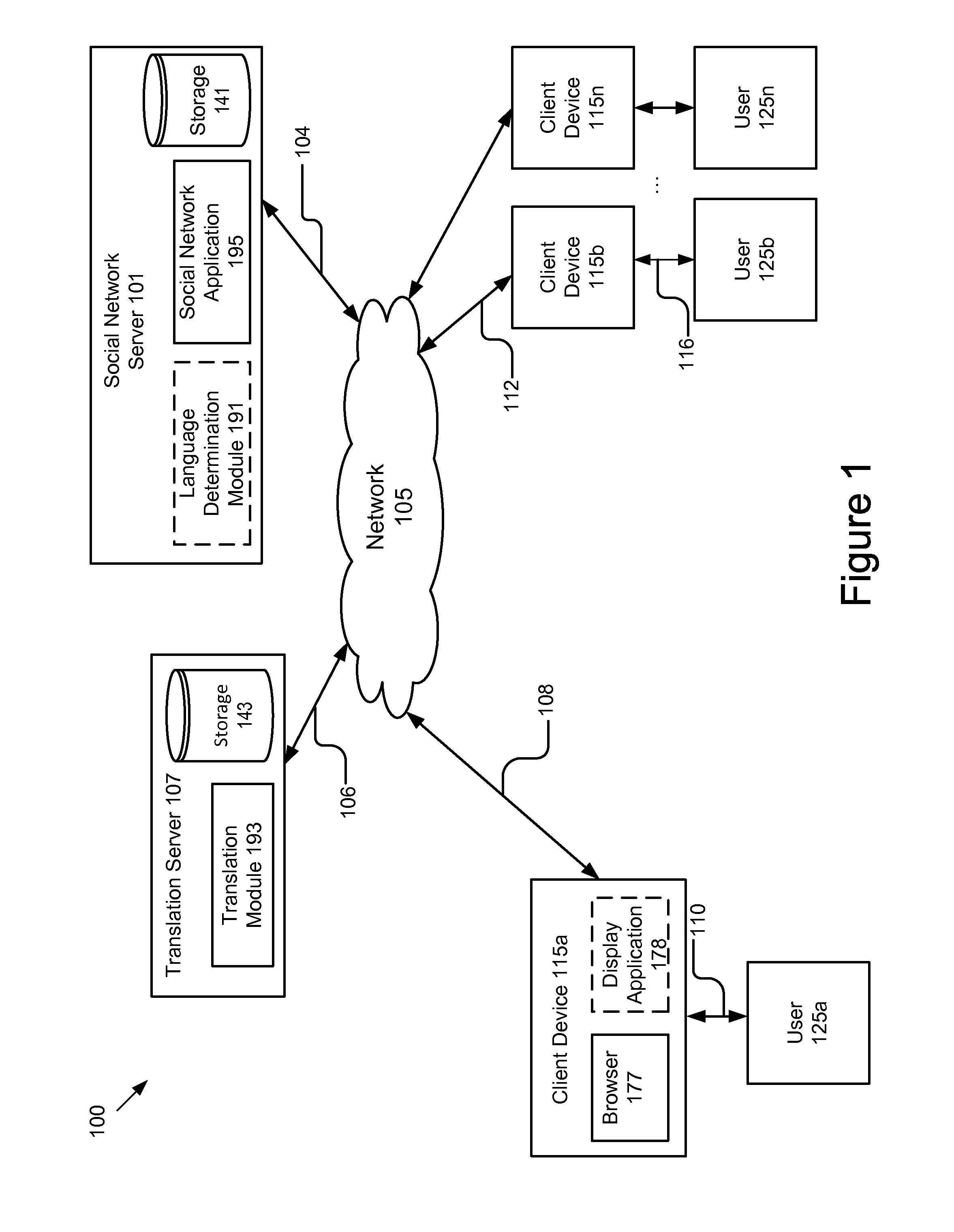
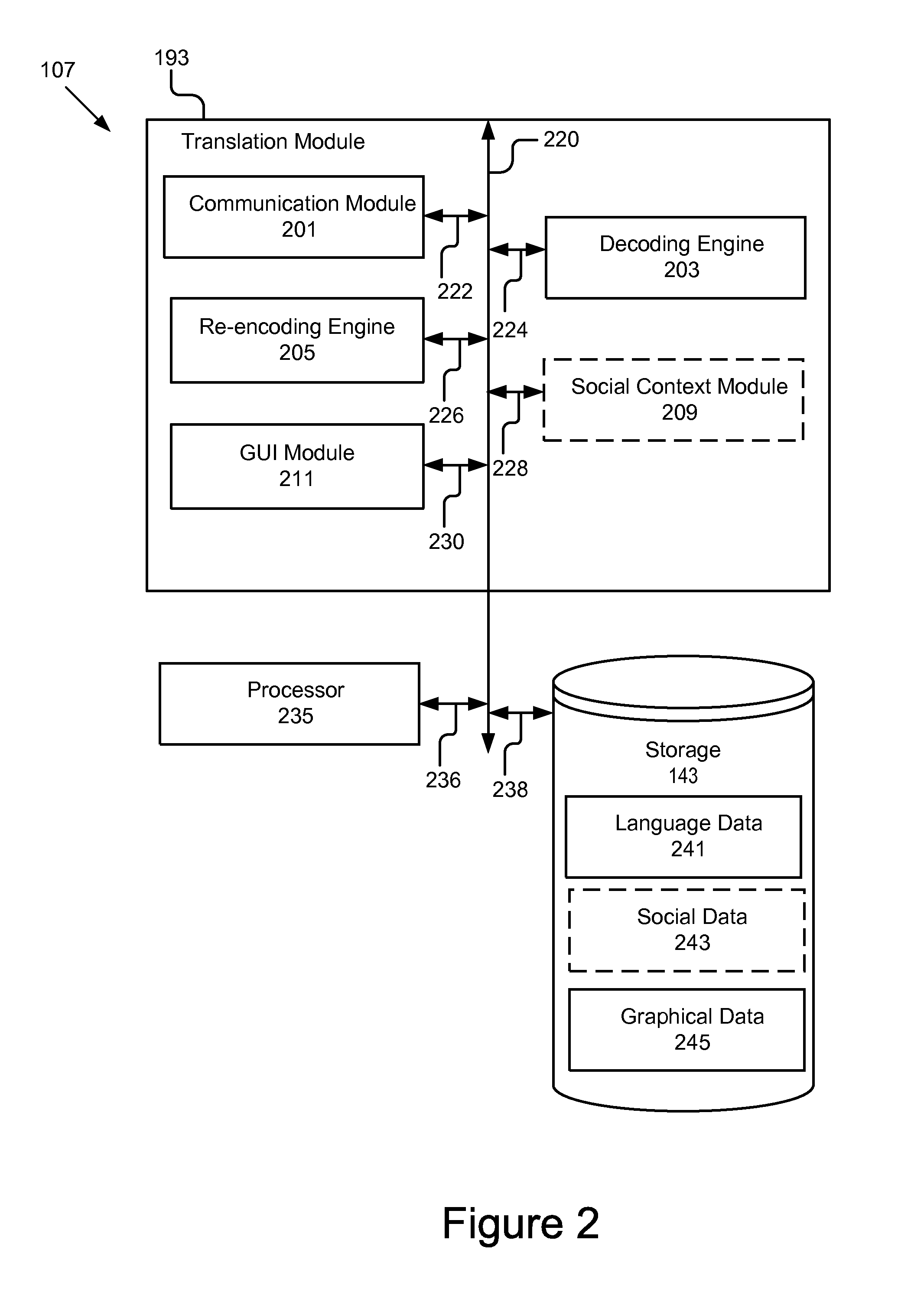
Feed translation for a social network
InactiveUS8412512B1Efficient and simplisticQuick translationNatural language translationWeb data retrievalClient-sideSocial web
A system and method for translating a social feed is disclosed. The system comprises a communication module, a decoding engine and a re-encoding engine. The communication module receives social feed data and a request from a social network application. The social feed data is configured to cause a client to display a social feed in a first language. The request includes data indicating that the social feed should be displayed in a second language. The decoding engine decodes the social feed data to generate decoded social feed data. The re-encoding engine re-encodes the decoded social feed data to cause the client to display the social feed in the second language based at least in part on the request. The communication module sends the translated social feed data to the client.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
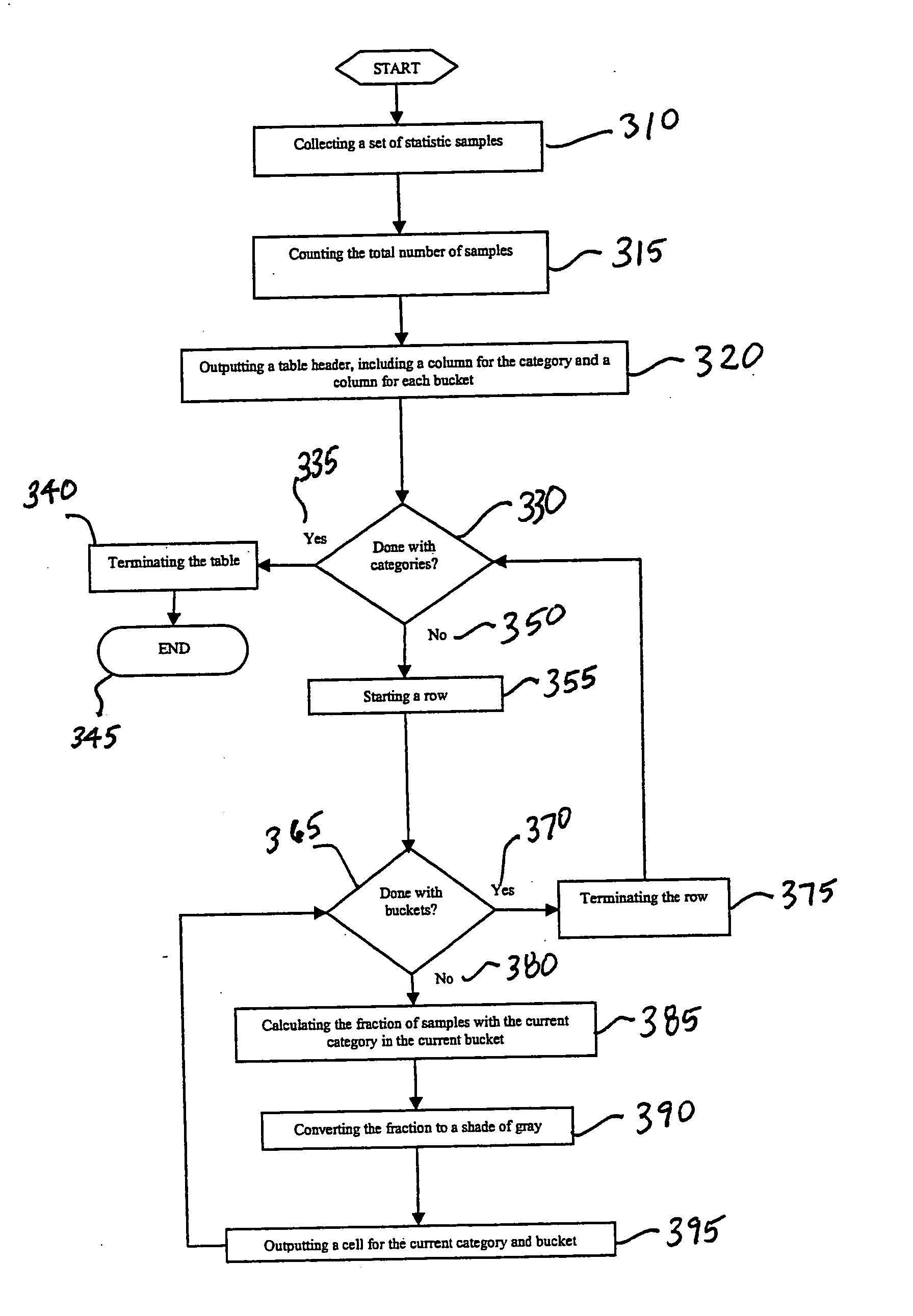
Method for superimposing statistical information on tabular data
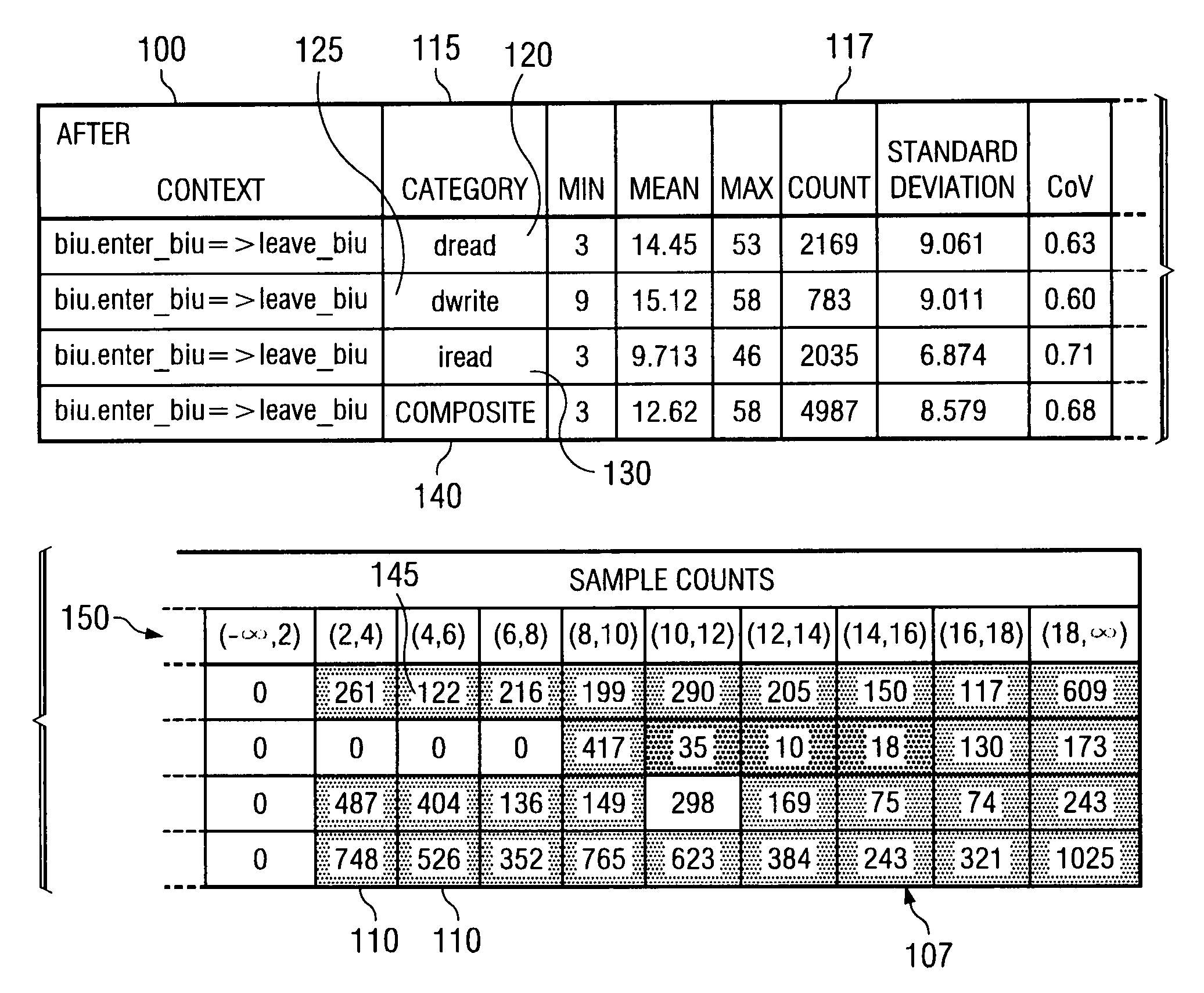
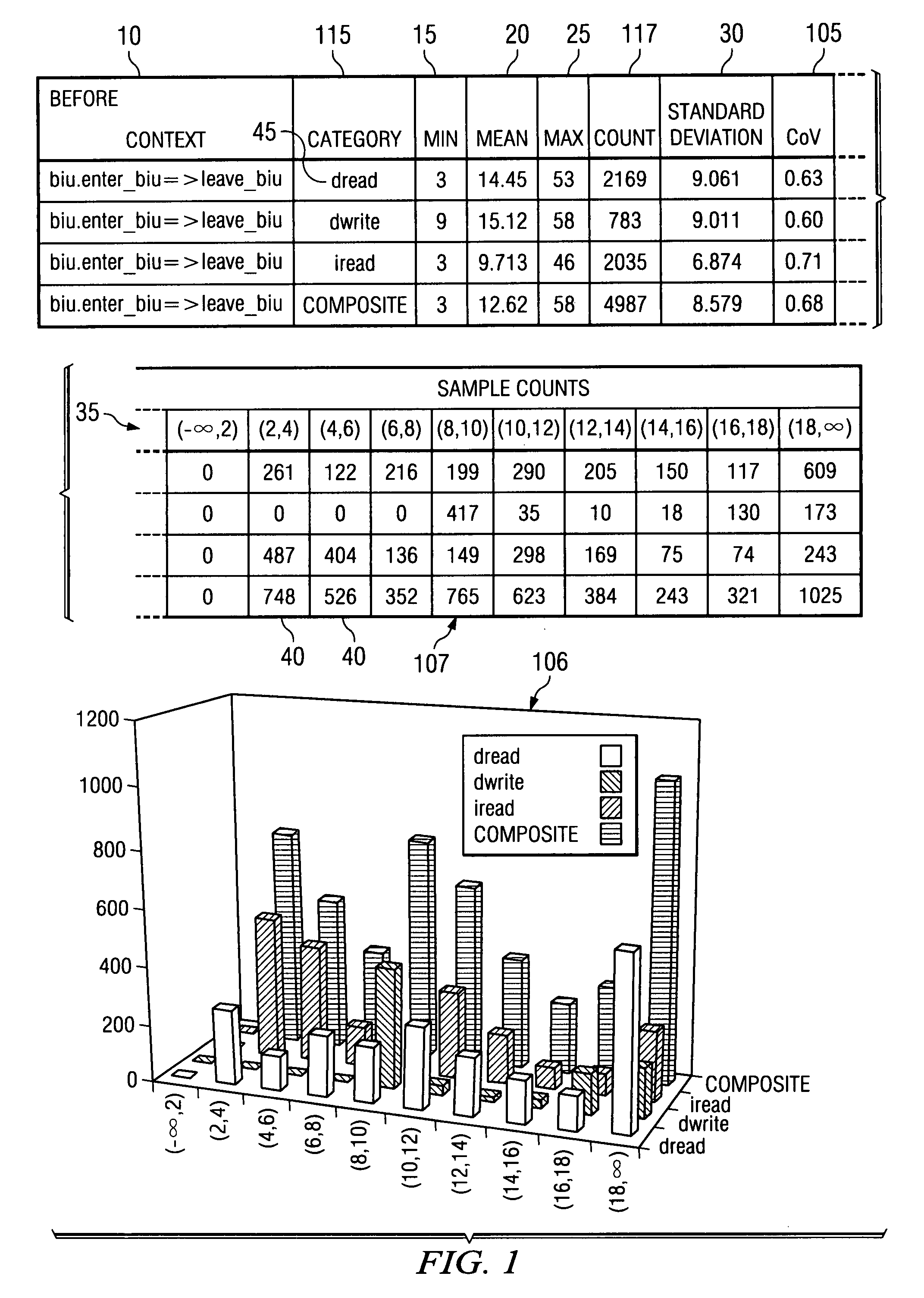
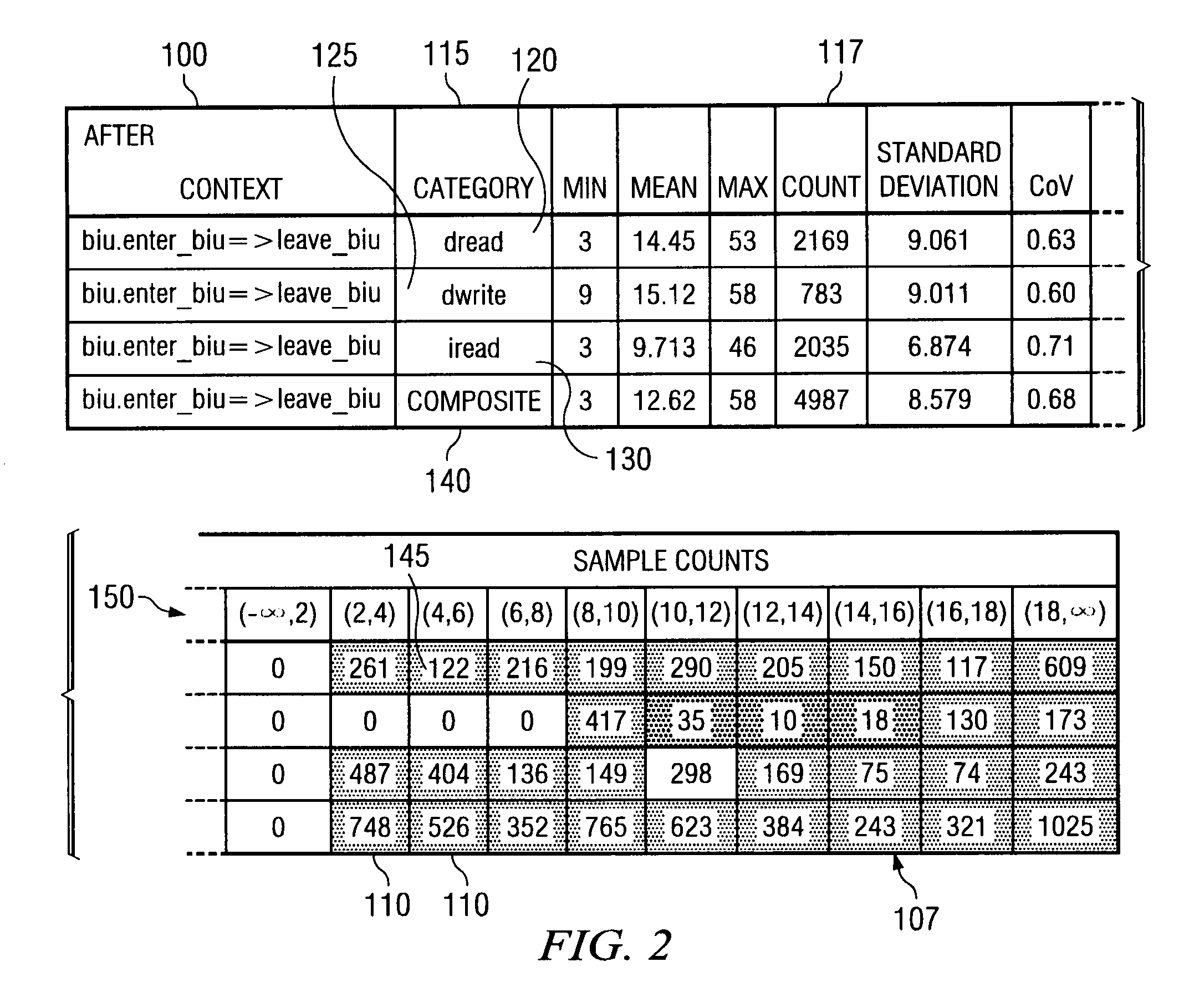
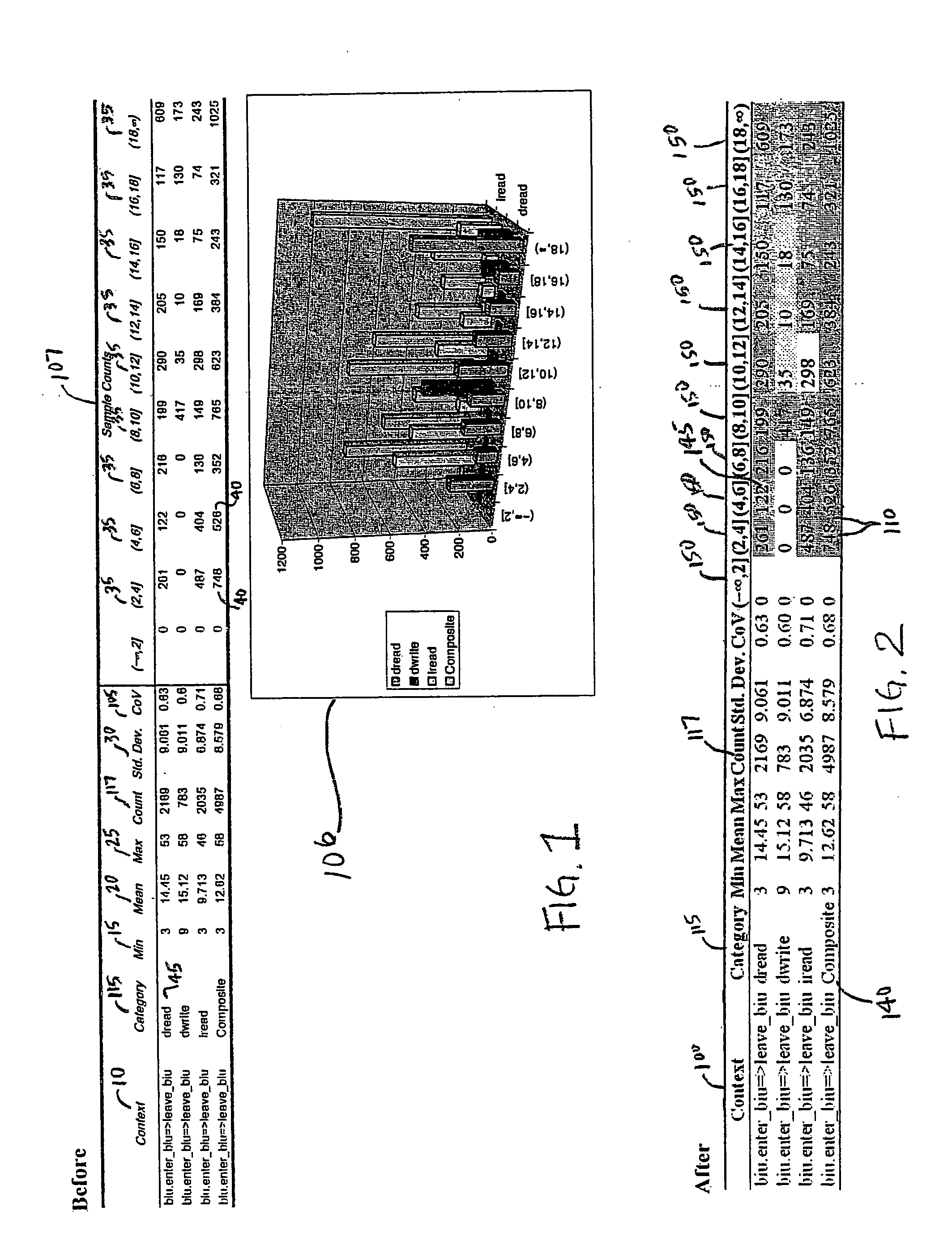
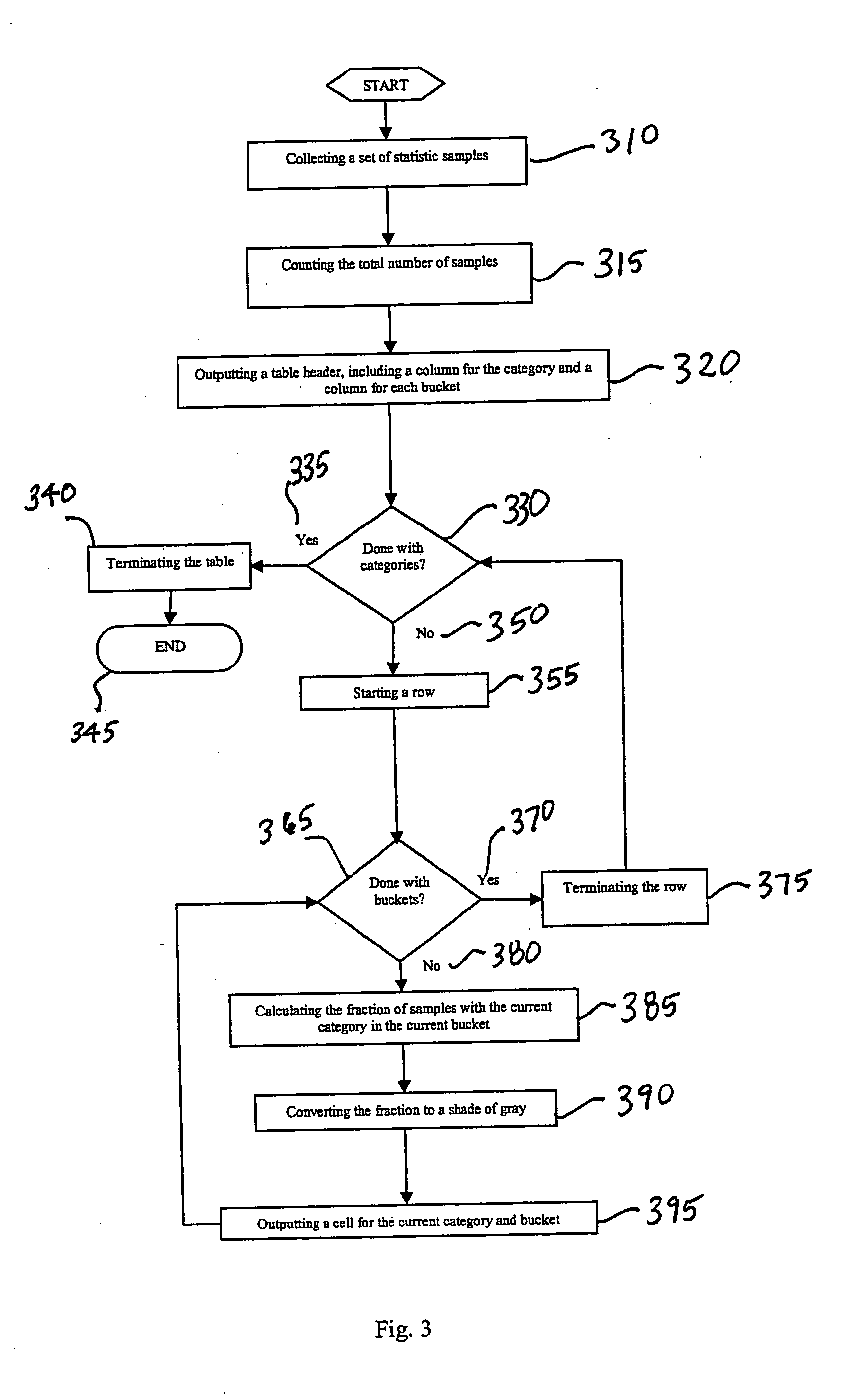
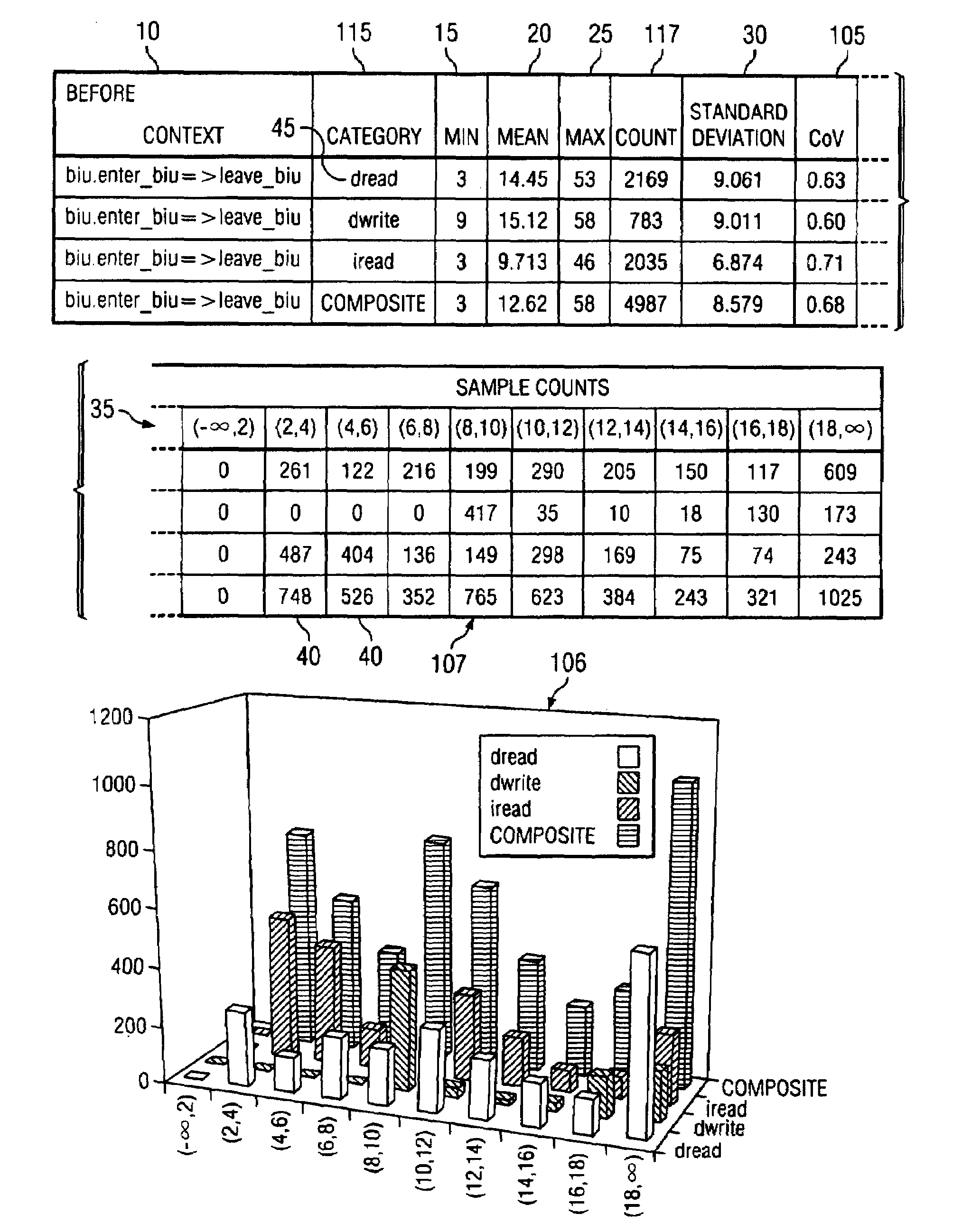
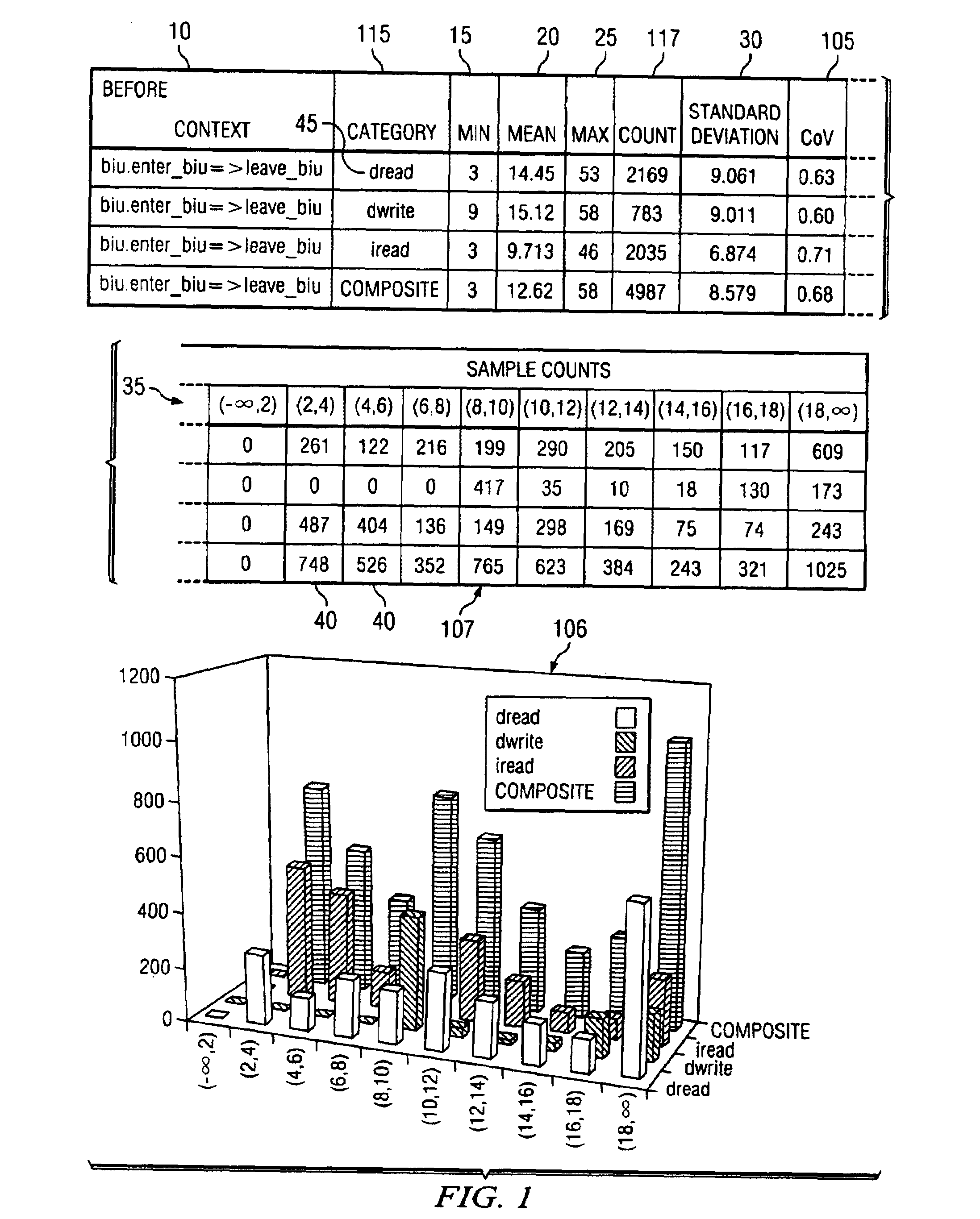
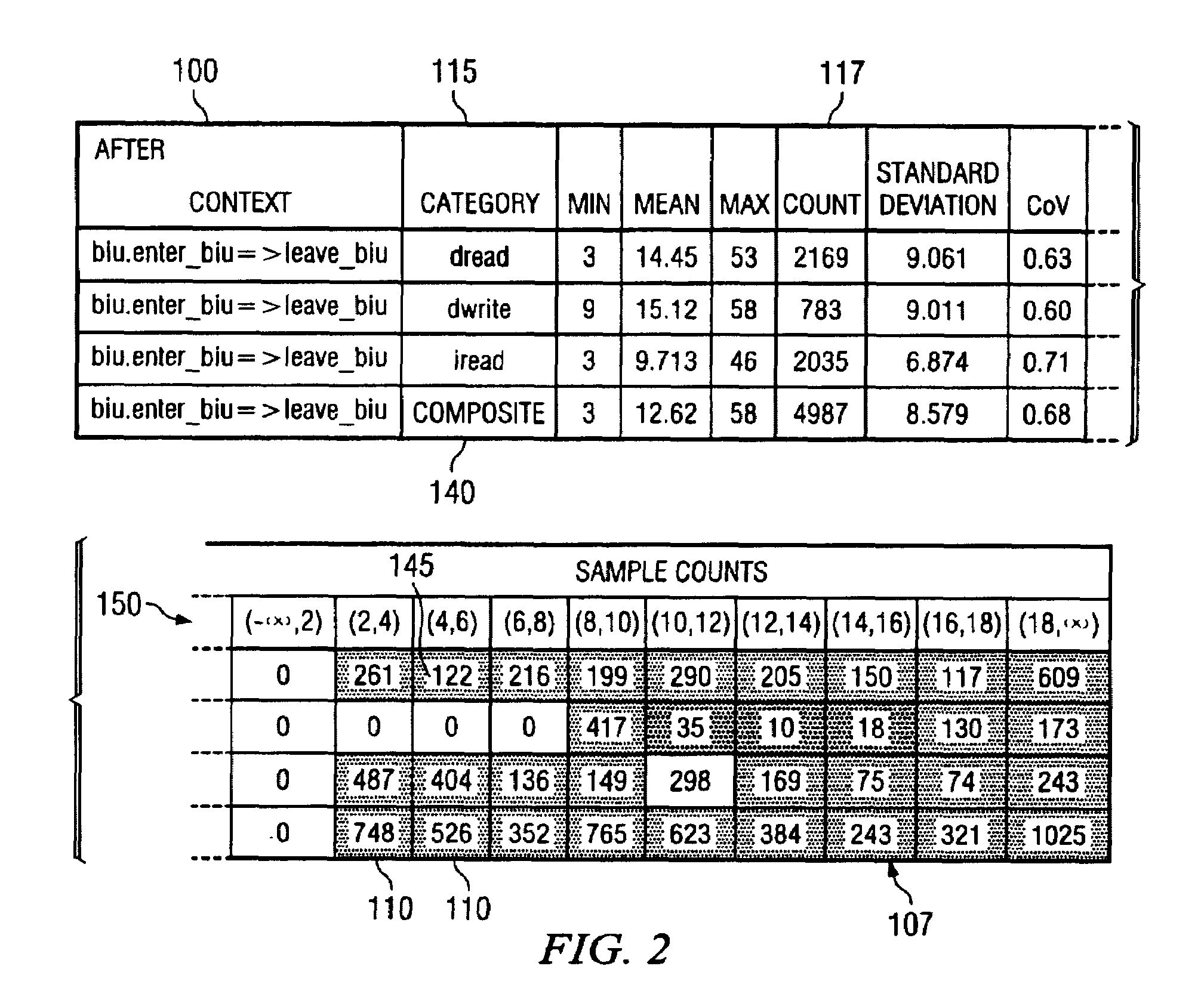
ActiveUS20090009517A1Easy to explainCompact representationDrawing from basic elementsHistogramCLARITY
A method is disclosed for displaying a plurality of statistical data usually presented in a histogram, such as sample counts and percentages of a collection of categorized samples, in a compact single table. The method comprises presenting grouped statistical data that exists within a collection of “buckets” and presenting the sample count for the collected data as an integer in a corresponding cell in the table. Additionally, as disclosed by the present invention, the percentage value of the samples located in each bucket data cell is represented in the data cell as a superimposed gray-scale representation. Presenting the percentages in gray-scale provides overall clarity to the table, assists in ensuring that data can be quickly and easily interpreted and not be subject to misinterpretation, and further allows for the compact display of such information in a single table and subsequent manipulation by automated analysis tools.
Owner:HYPERFORMIX
Virtual machine hardware for RISC and CISC processors
InactiveUS8769508B2Quick translationSpeedSpecific program execution arrangementsMemory systemsParallel computingHardware acceleration
A hardware Java™ accelerator is comprised of a decode stage and a microcode stage. Separating into the decode and microcode stage allows the decode stage to implement instruction level parallelism while the microcode stage allows the conversion of a single Java™ bytecode into multiple native instructions. A reissue buffer is provided which stores the converted instructions and reissues them when the system returns from an interrupt. In this manner, the hardware accelerator need not be flushed upon an interrupt. A native PC monitor is also used. While the native PC is within a specific range, the hardware accelerator is enabled to convert the Java™ bytecodes into native instructions. When the native PC is outside the range, the hardware accelerator is disabled and the CPU operates on native instructions obtained from the memory.
Owner:NAZOMI COMM
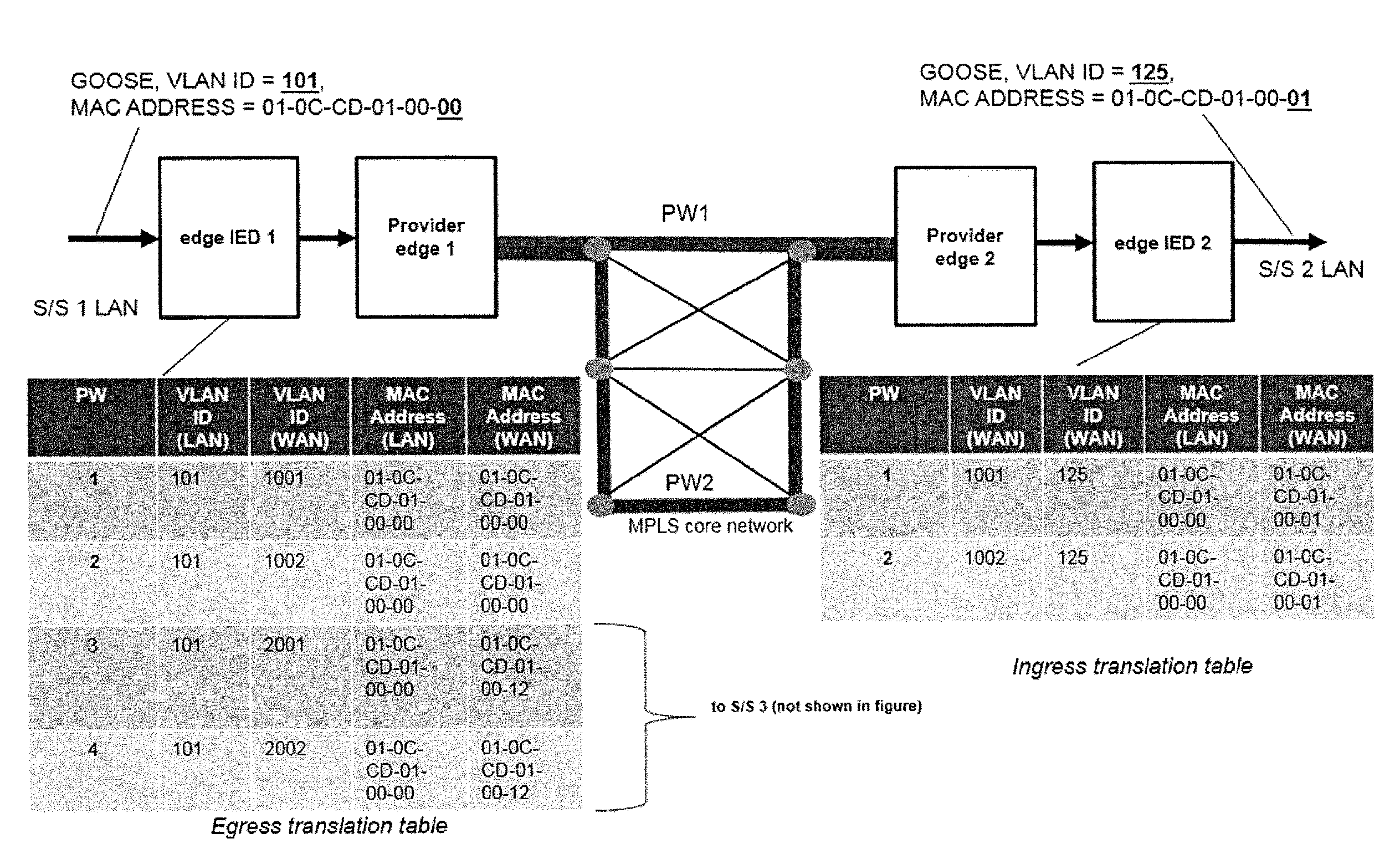
Tunnelling time-critical messages between substations over wan
ActiveUS20160373274A1Less reconfigurationReduce distractionsNetworks interconnectionTime criticalTunneling time
The present invention discloses a method of transmitting time-critical messages in an OSI layer 2 network tunnel from a first TED in a first substation to a second IED in a second substation over a WAN, wherein each of the first and second substation comprises an edge IED and is associated with a substation LAN, wherein each of the time-critical messages comprises message parameters. The method comprises the steps of: a) creating a translation table comprising corresponding values of the message parameters, between the LANs and the WAN, b) defining a virtual FED in the second substation using the translated values of the message parameters, to impersonate the first IED, c) translating the message parameters according to the translation table, by the edge IED of the first and second substation, d) forwarding the time-critical messages from the first IED in the first substation to the WAN, and e) receiving the time-critical messages by the second IED in the second substation from the WAN.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
Method for superimposing statistical information on tabular data
ActiveUS20050240862A1Easy to explainCompact representationDrawing from basic elementsText processingCLARITYAnalysis tools
A method is disclosed for displaying a plurality of statistical data usually presented in a histogram, such as sample counts and percentages of a collection of categorized samples, in a compact single table. The method comprises presenting grouped statistical data that exists within a collection of “buckets” and presenting the sample count for the collected data as an integer in a corresponding cell in the table. Additionally, as disclosed by the present invention, the percentage value of the samples located in each bucket data cell is represented in the data cell as a superimposed gray-scale representation. Presenting the percentages in gray-scale provides overall clarity to the table, assists in ensuring that data can be quickly and easily interpreted and not be subject to misinterpretation, and further allows for the compact display of such information in a single table and subsequent manipulation by automated analysis tools.
Owner:HYPERFORMIX
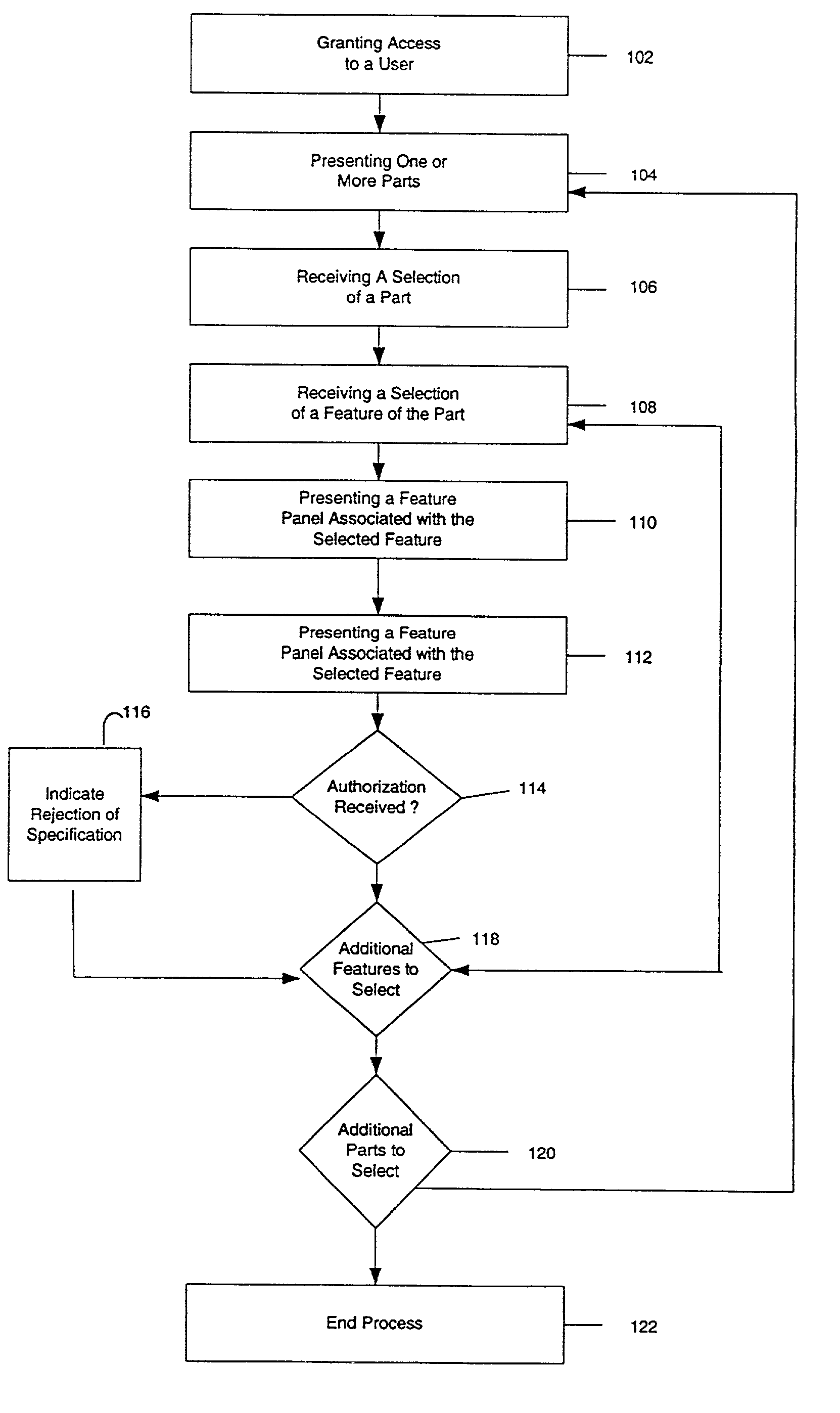
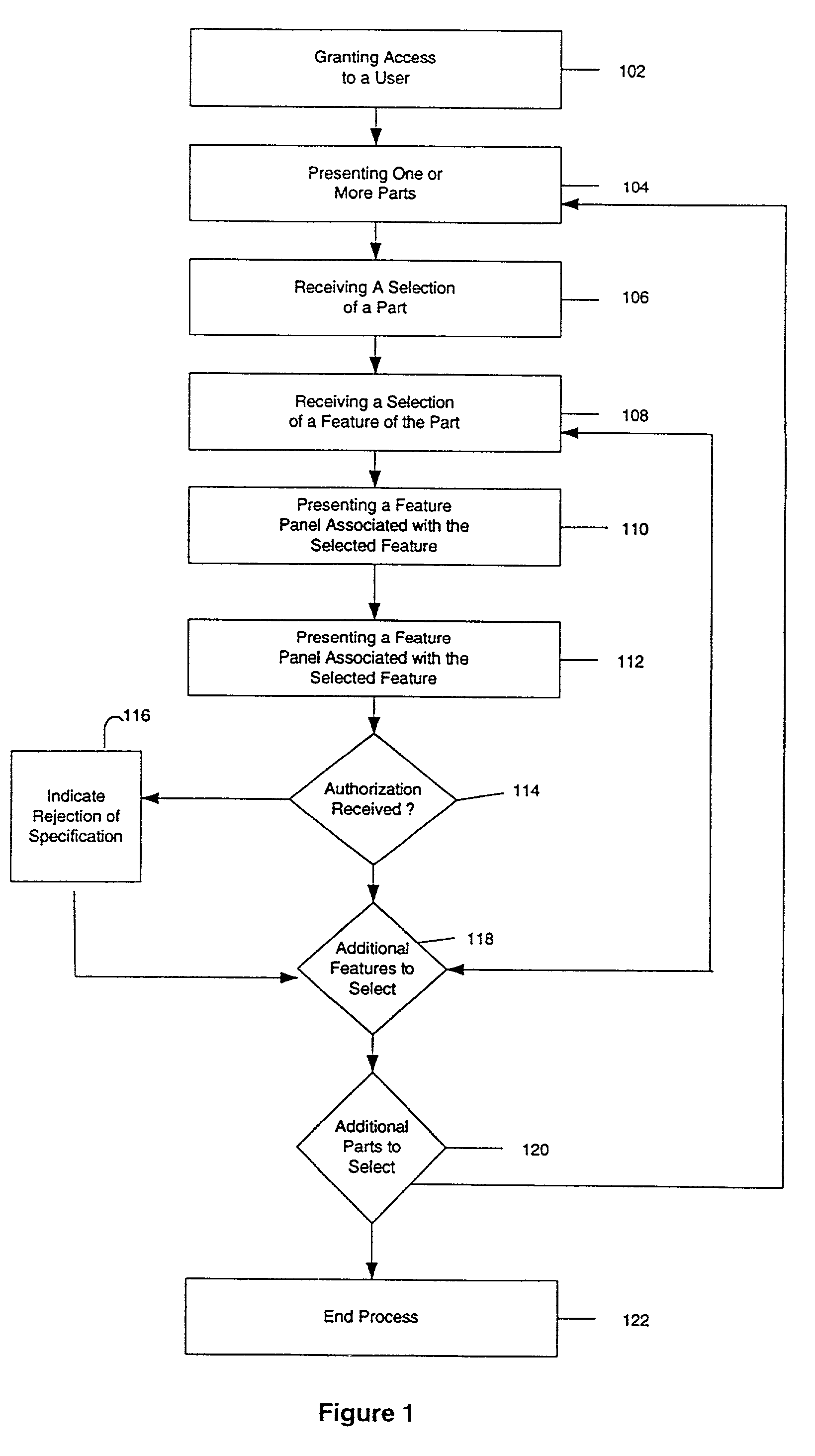
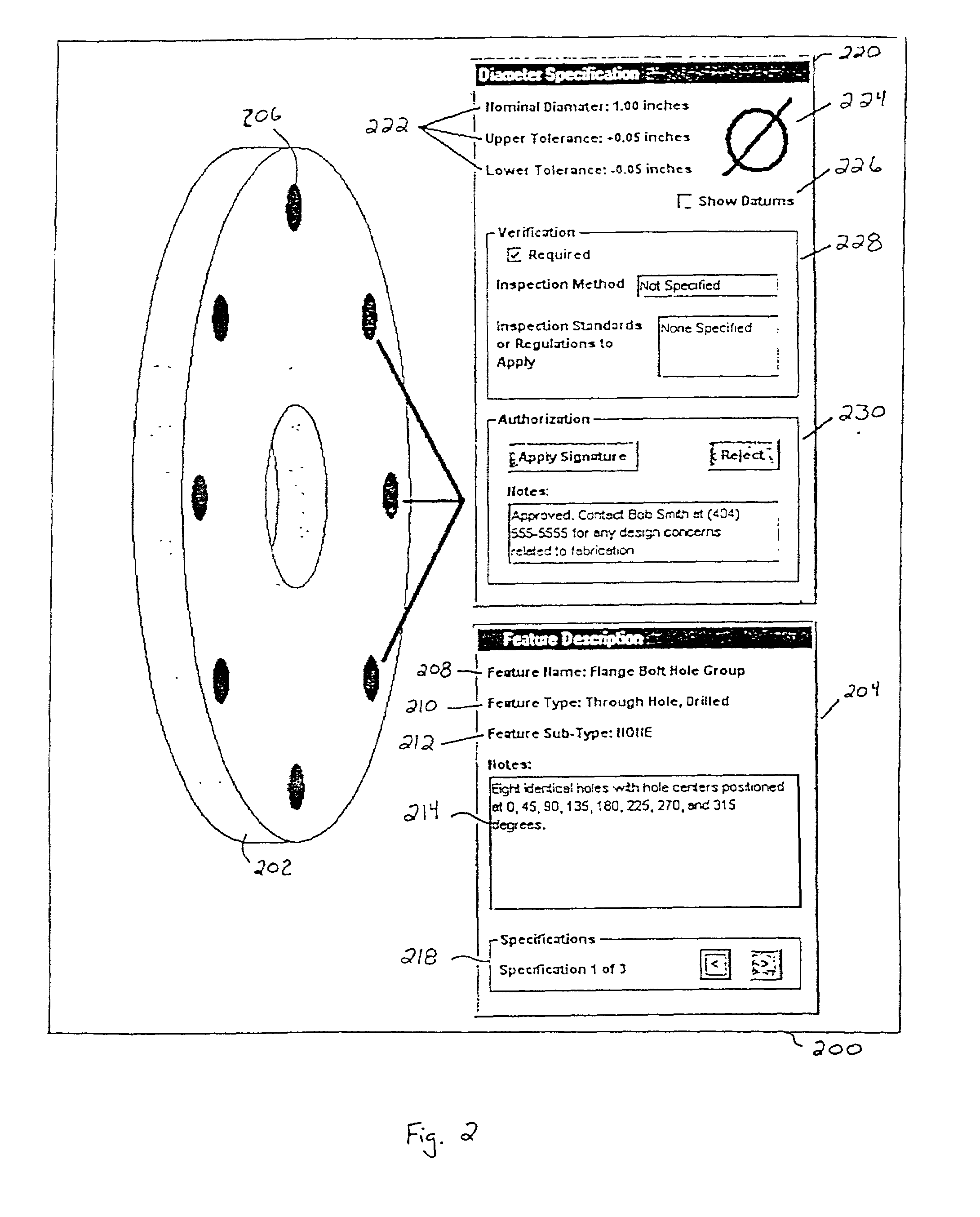
System and process for facilitating efficient communication of specifications for parts and assemblies with a mechanism for assigning responsibility selection
InactiveUS7069093B2Reduce errorsImprove abilitiesUser identity/authority verificationComputer security arrangementsDigital signatureVirtual collaboration
The present invention relates generally to a comprehensive, integrated computer-based process and method for undertaking an engineering design and development effort in a virtual collaborative environment by facilitating communication of specifications for parts and assemblies for review and approval. Specifications for the fabrication of parts may be presented and reviewed by the user. By accepting or validating the specifications, the user may apply his / her digital signature, thereby confirming an understanding of the specifications and, according to an embodiment of the invention, creating a binding contract.
Owner:THACKSTON JAMES D
Java Virtual Machine hardware for RISC and CISC processors
InactiveUS20060200801A1Quick translationProcess can be speededTransformation of program codeConcurrent instruction executionParallel computingJava bytecode
A hardware Java accelerator is provided to implement portions of the Java virtual machine in hardware in order to accelerate the operation of the system on Java bytecodes. The Java hardware accelerator preferably includes Java bytecode translation into native CPU instructions. The combination of the Java hardware accelerator and a CPU provides a embedded solution which results in an inexpensive system to run Java programs for use in commercial appliances.
Owner:NAZOMI COMM
Processing Sensing Measurements
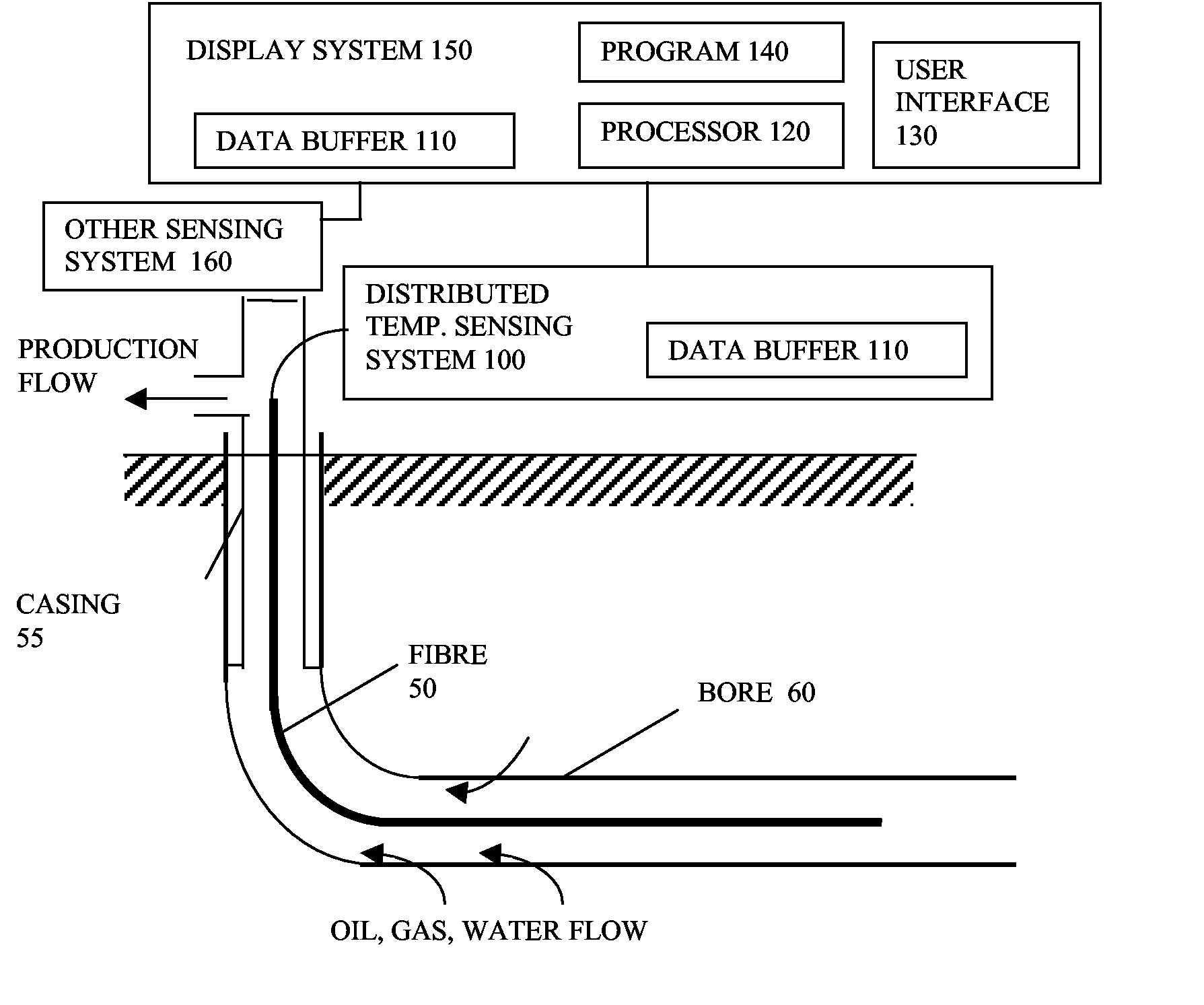
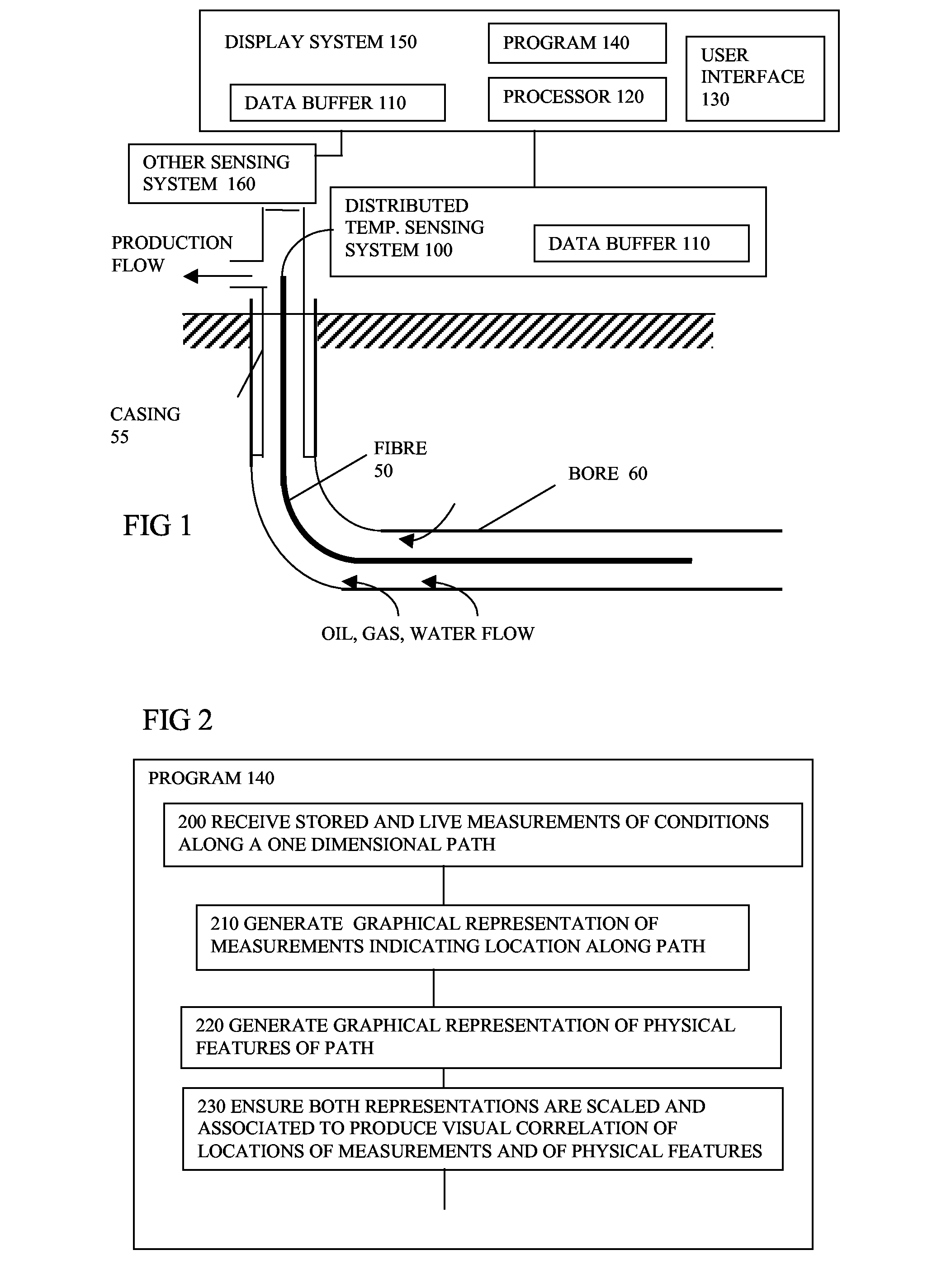
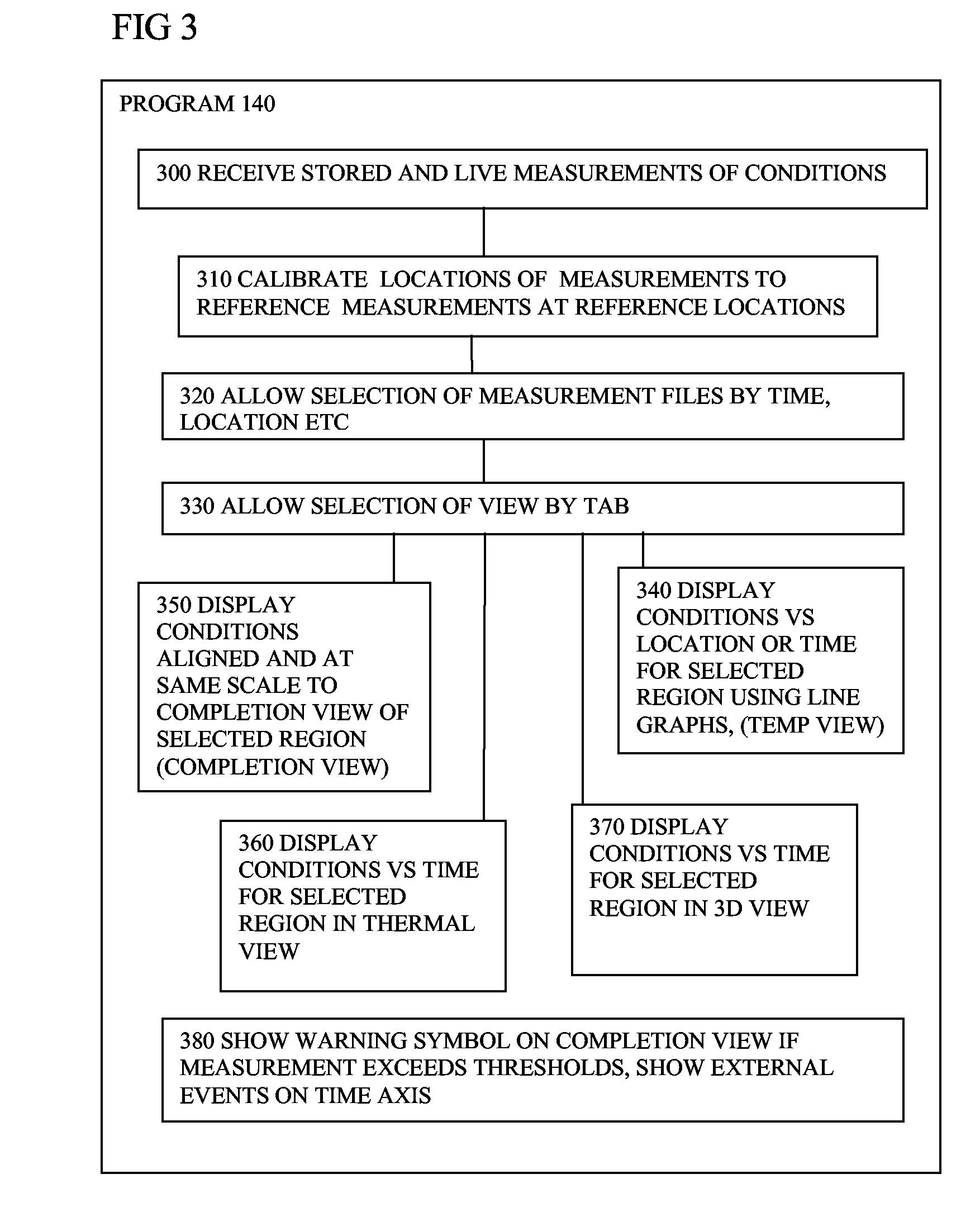
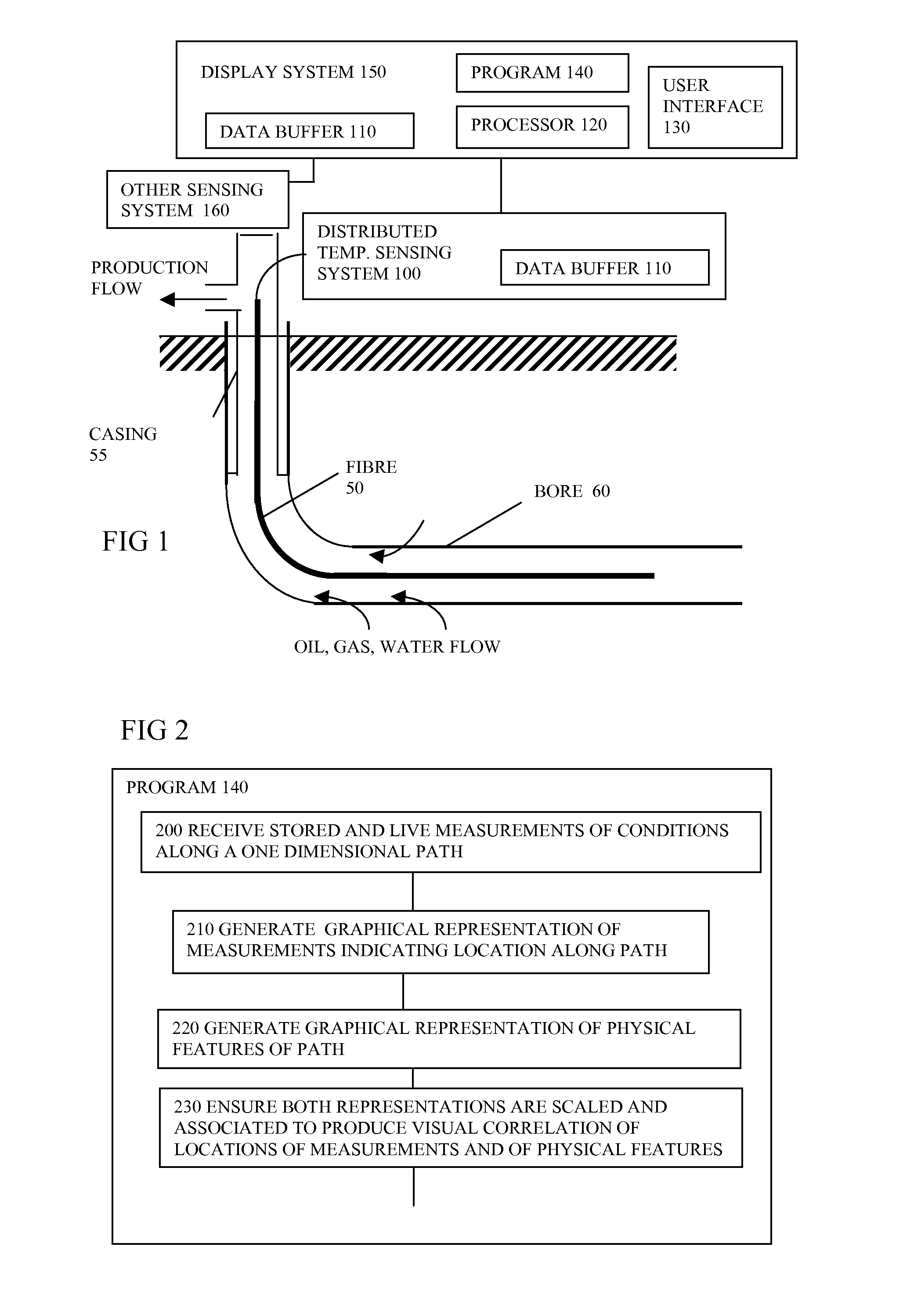
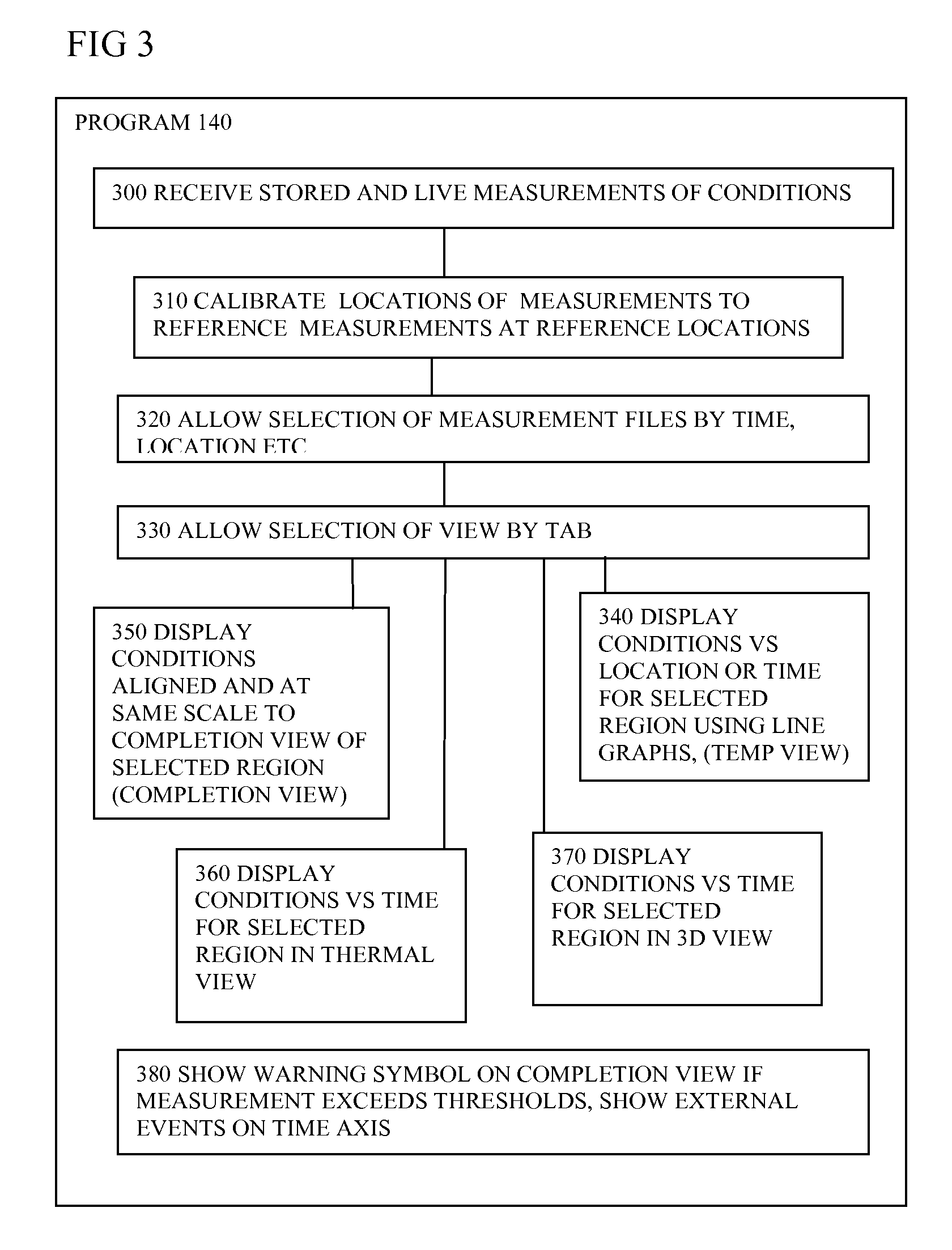
ActiveUS20080065344A1Avoid difficult choicesEasy to measureSurveyAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGraphicsRemedial action
Software (140) for processing measurements from a distributed sensing system (100) receives the measurements, and generates a graphical representation of the measurements indicating their location or time sequence, and a representation of locations of physical features along the path (50), or times of external events, the representations being scaled and associated to provide a visual correlation between the locations of the measurements and locations of the physical features, or between times of measurements and times of external events. The enhanced visual correlation can lead to cost savings if more rapid interpretation of large volumes of measurements can give warning of changes such as subsidence of structures, or of ingress of water into oil wells, for example in time for remedial action to be taken.
Owner:SENSORNET
Motor drive for a camper jack
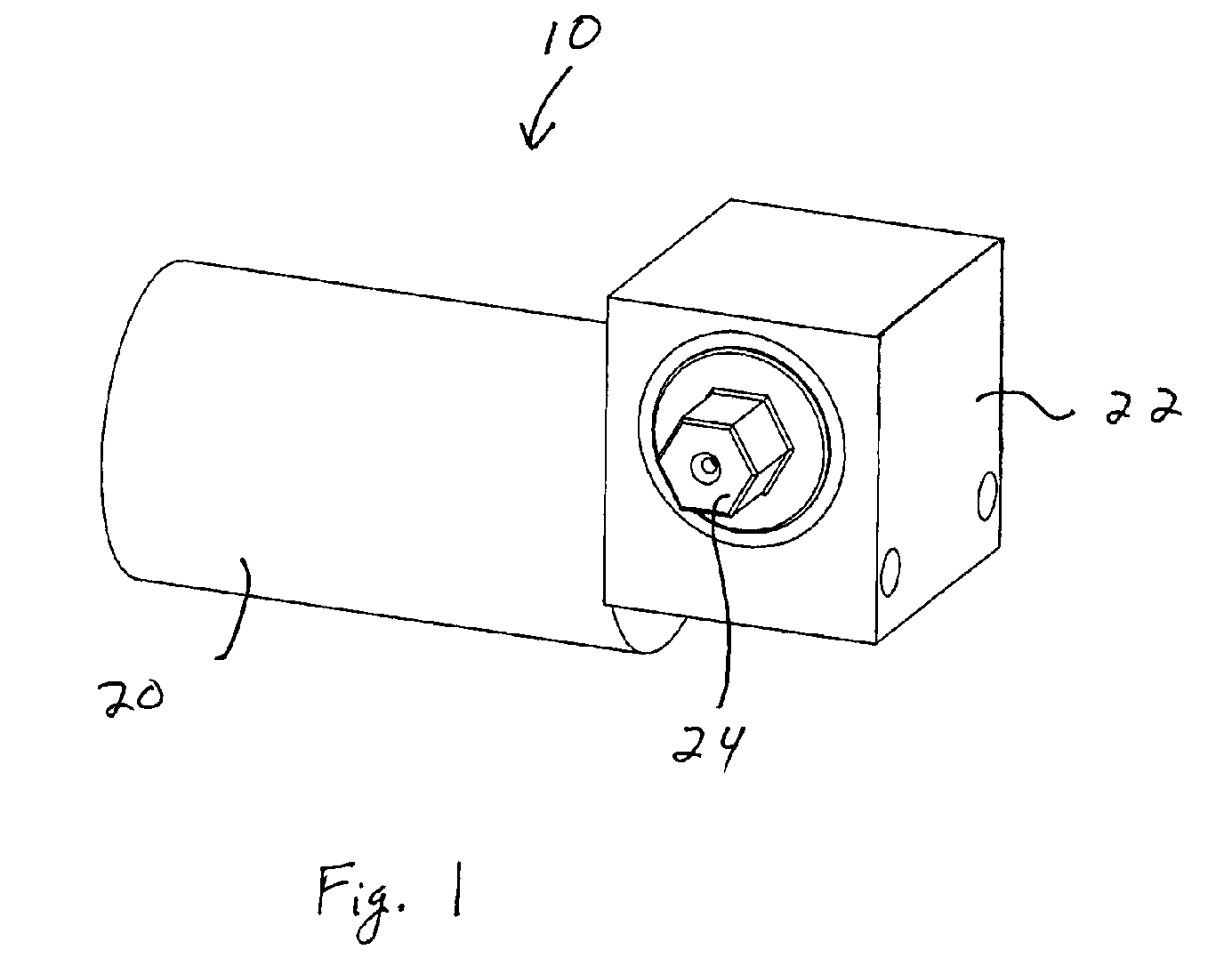
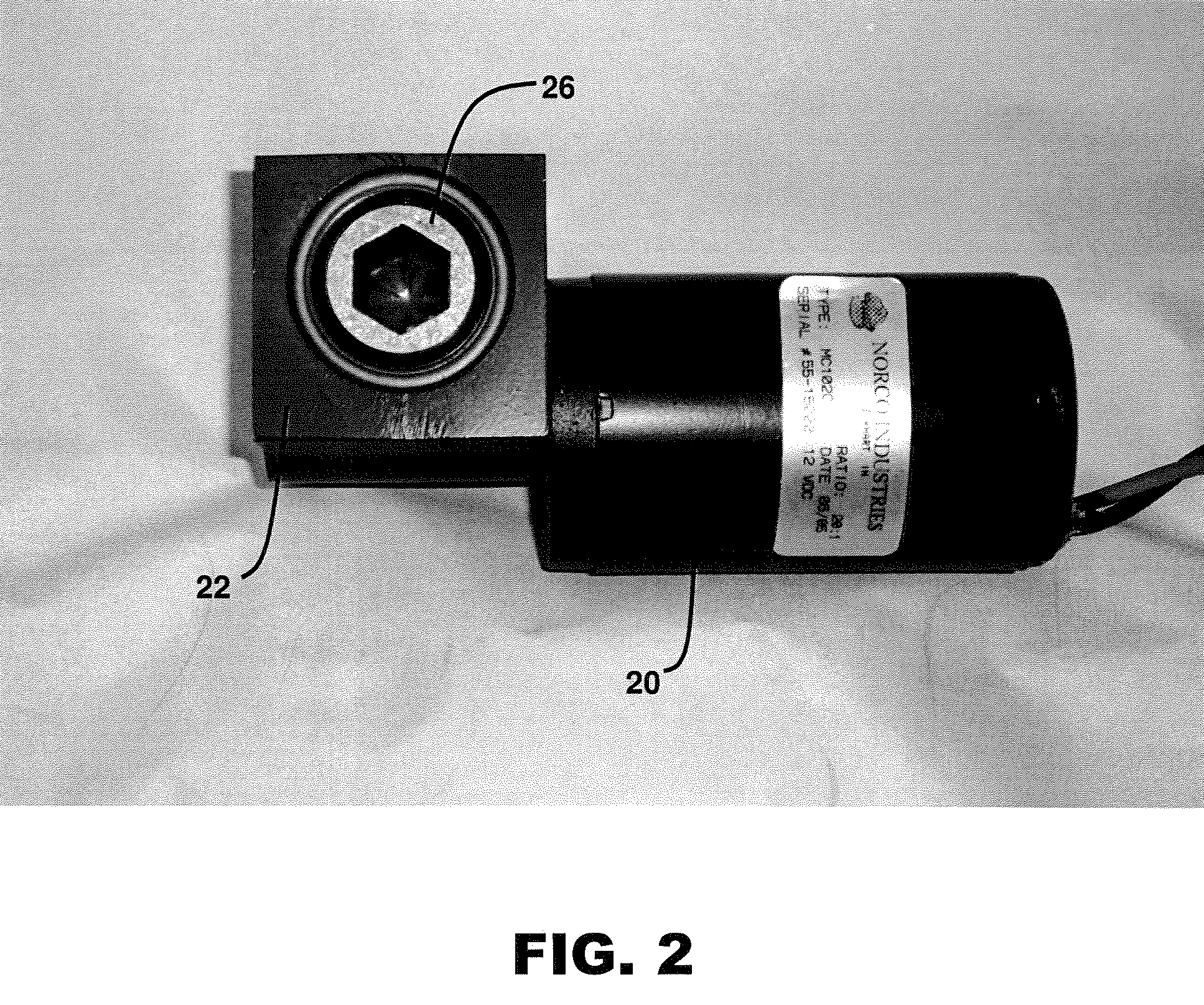
A motor drive for camper jacks or screw jacks that rapidly operates the screw jack between a retracted position and an extended no load position. A manual operator then operates the screw jack between the extended no load position and an extended loaded position. The motor drive and manual operator share a right angle gear mechanism.
Owner:NORCO INDS
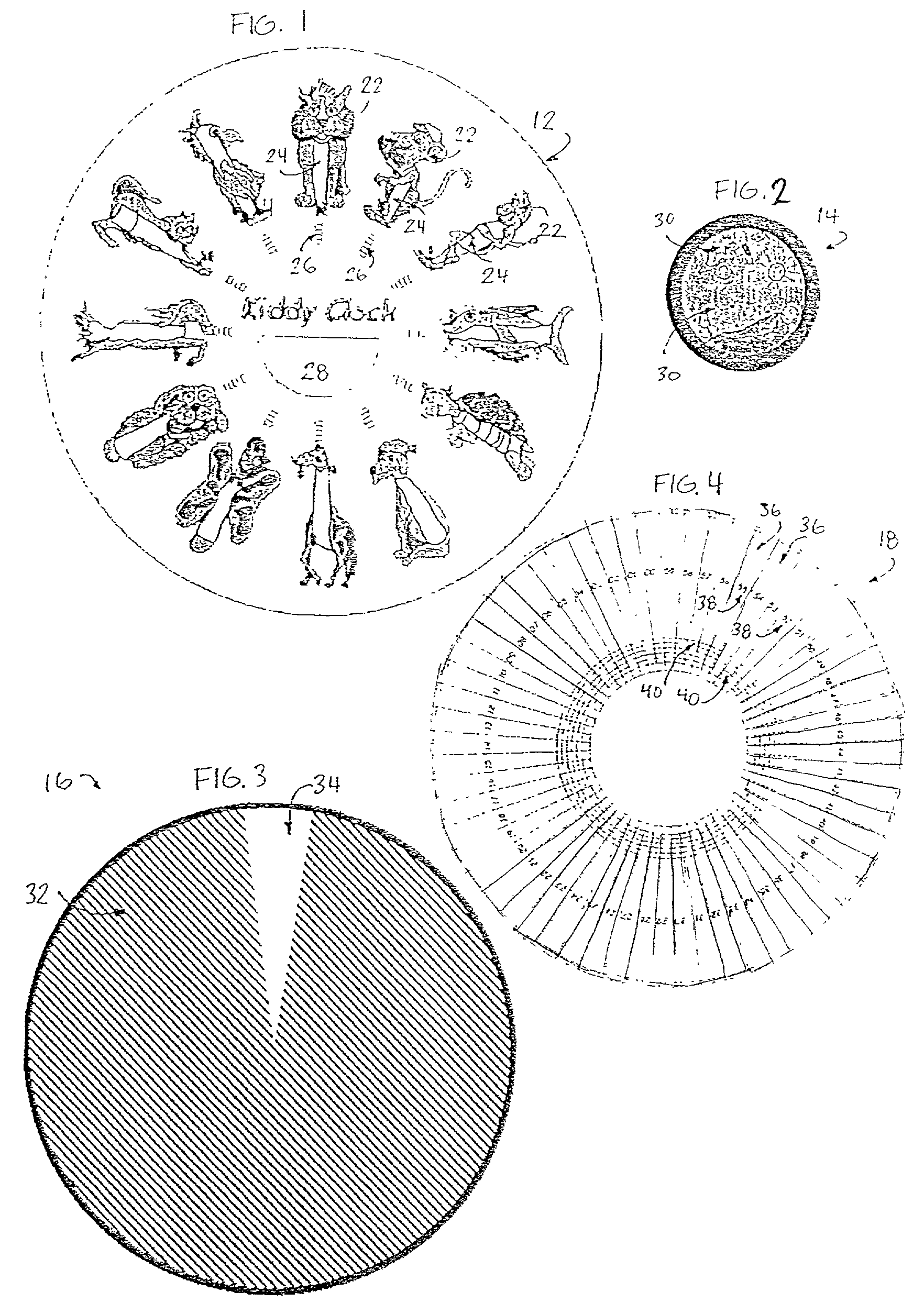
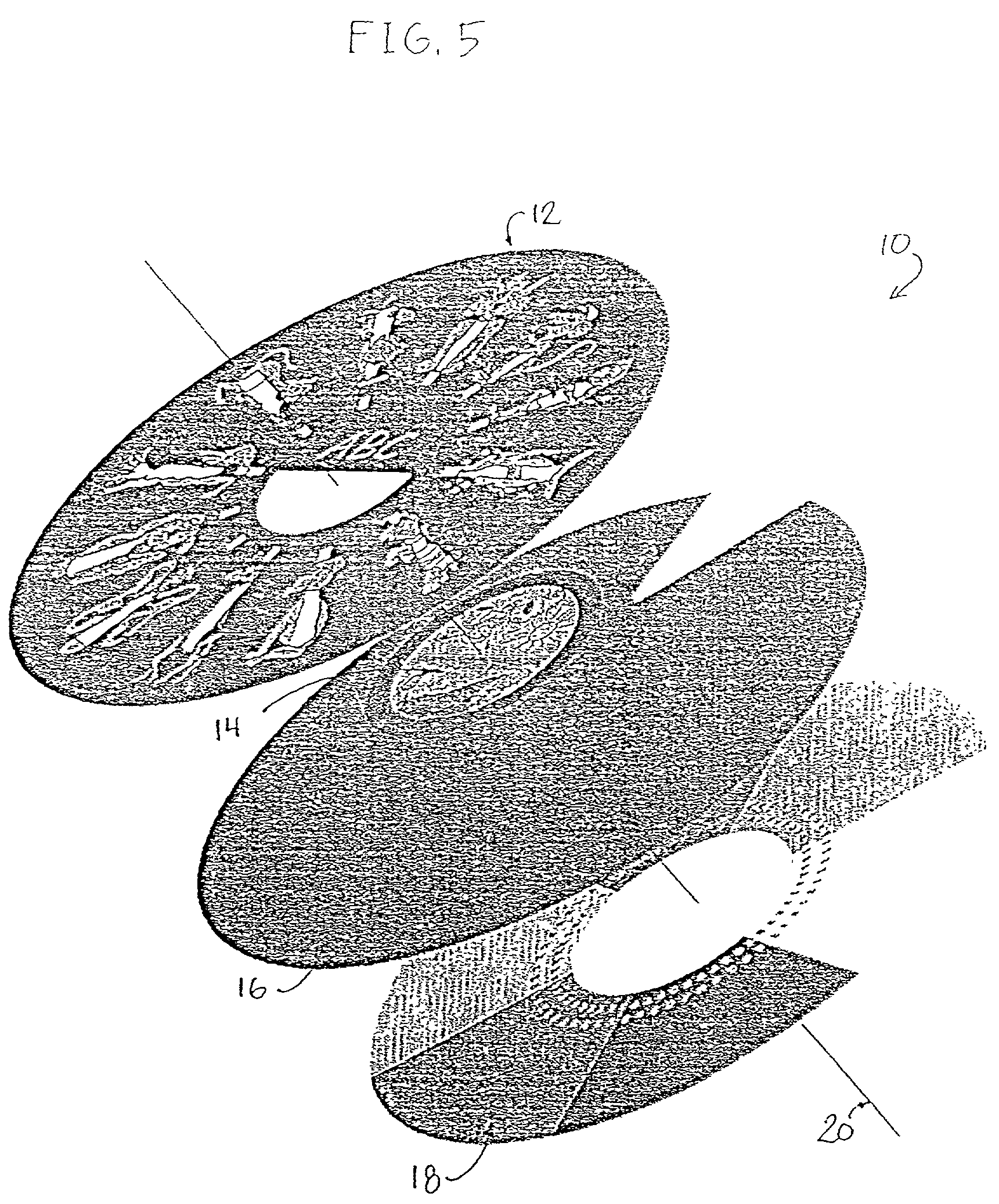
Clock for children
Owner:LUDOVIQ
Processing sensing measurements
ActiveUS7813898B2Improve understandingConfidenceSurveyAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceGraphicsRemedial action
Software (140) for processing measurements from a distributed sensing system (100) receives the measurements, and generates a graphical representation of the measurements indicating their location or time sequence, and a representation of locations of physical features along the path (50), or times of external events, the representations being scaled and associated to provide a visual correlation between the locations of the measurements and locations of the physical features, or between times of measurements and times of external events. The enhanced visual correlation can lead to cost savings if more rapid interpretation of large volumes of measurements can give warning of changes such as subsidence of structures, or of ingress of water into oil wells, for example in time for remedial action to be taken.
Owner:SENSORNET
Method for superimposing statistical information on tabular data
InactiveUS7256784B2Easy to explainCompact representationDrawing from basic elementsText processingCLARITYAnalysis tools
A method is disclosed for displaying a plurality of statistical data usually presented in a histogram, such as sample counts and percentages of a collection of categorized samples, in a compact single table. The method comprises presenting grouped statistical data that exists within a collection of “buckets” and presenting the sample count for the collected data as an integer in a corresponding cell in the table. Additionally, as disclosed by the present invention, the percentage value of the samples located in each bucket data cell is represented in the data cell as a superimposed gray-scale representation. Presenting the percentages in gray-scale provides overall clarity to the table, assists in ensuring that data can be quickly and easily interpreted and not be subject to misinterpretation, and further allows for the compact display of such information in a single table and subsequent manipulation by automated analysis tools.
Owner:HYPERFORMIX
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com