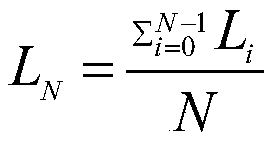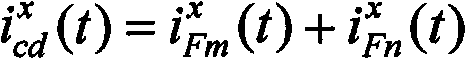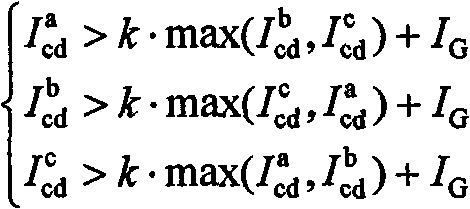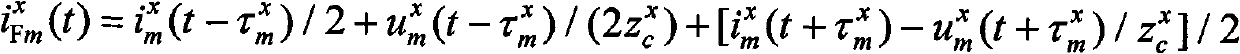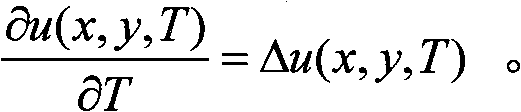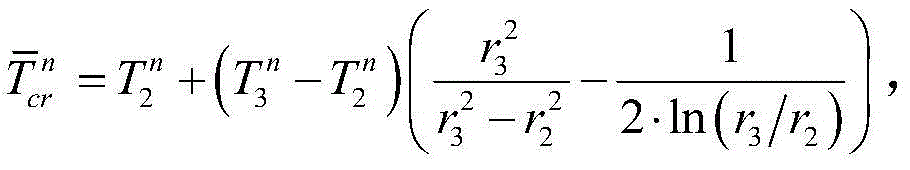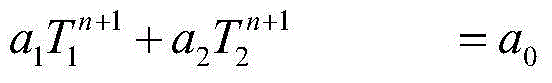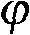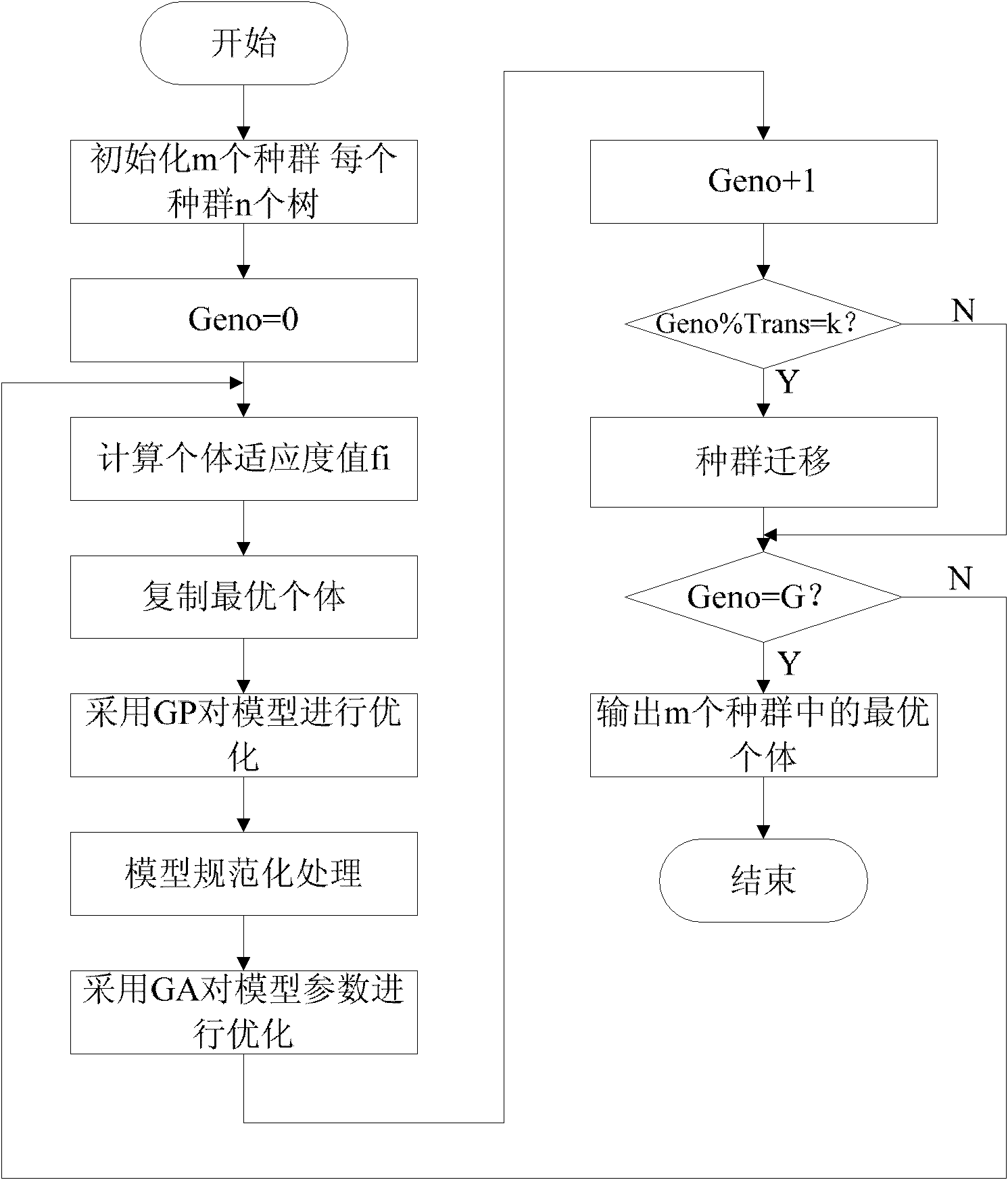Patents
Literature
213 results about "Ordinary differential equation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation (ODE) is a differential equation containing one or more functions of one independent variable and the derivatives of those functions. The term ordinary is used in contrast with the term partial differential equation which may be with respect to more than one independent variable.
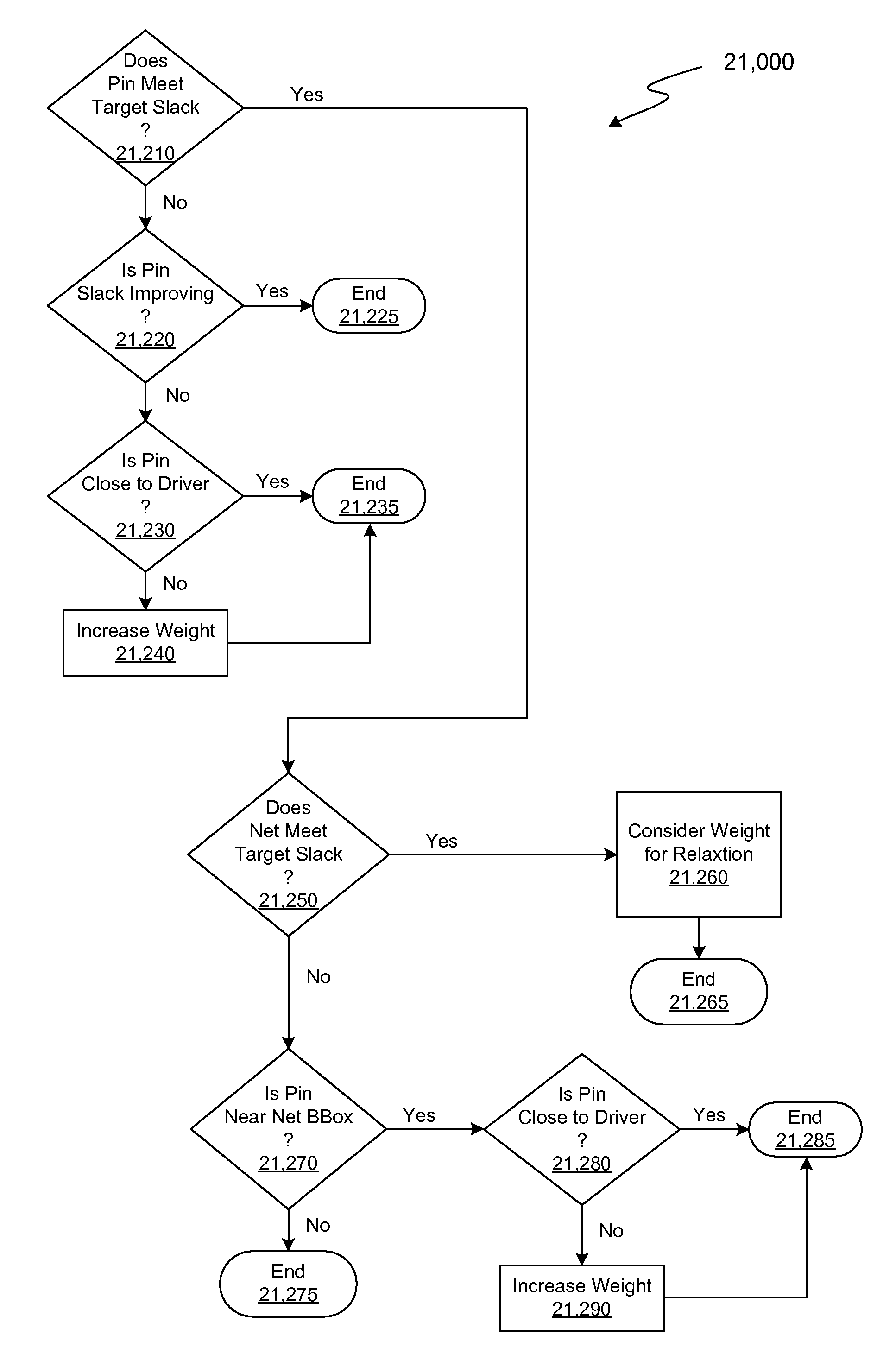
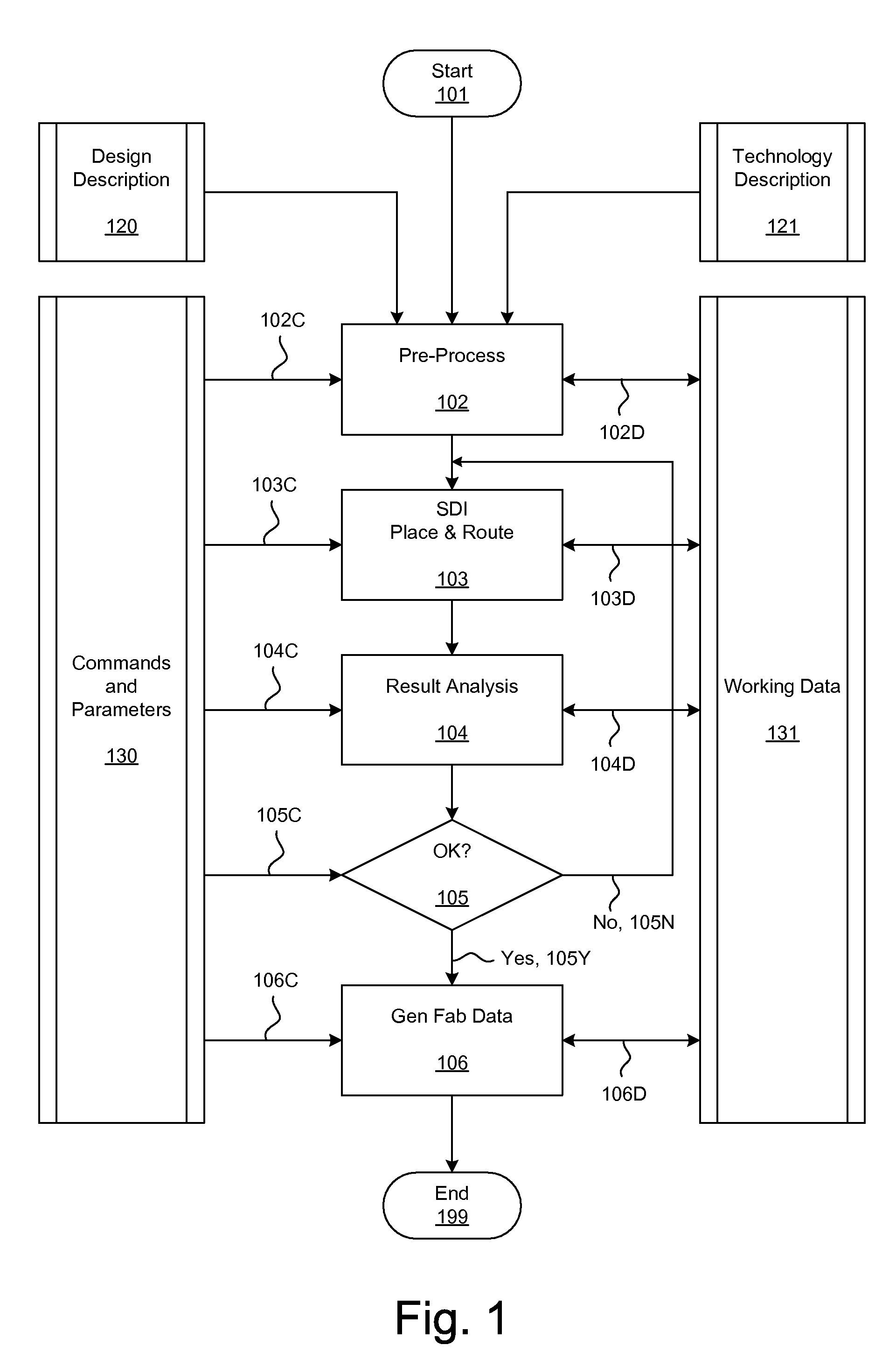
Incremental Relative Slack Timing Force Model
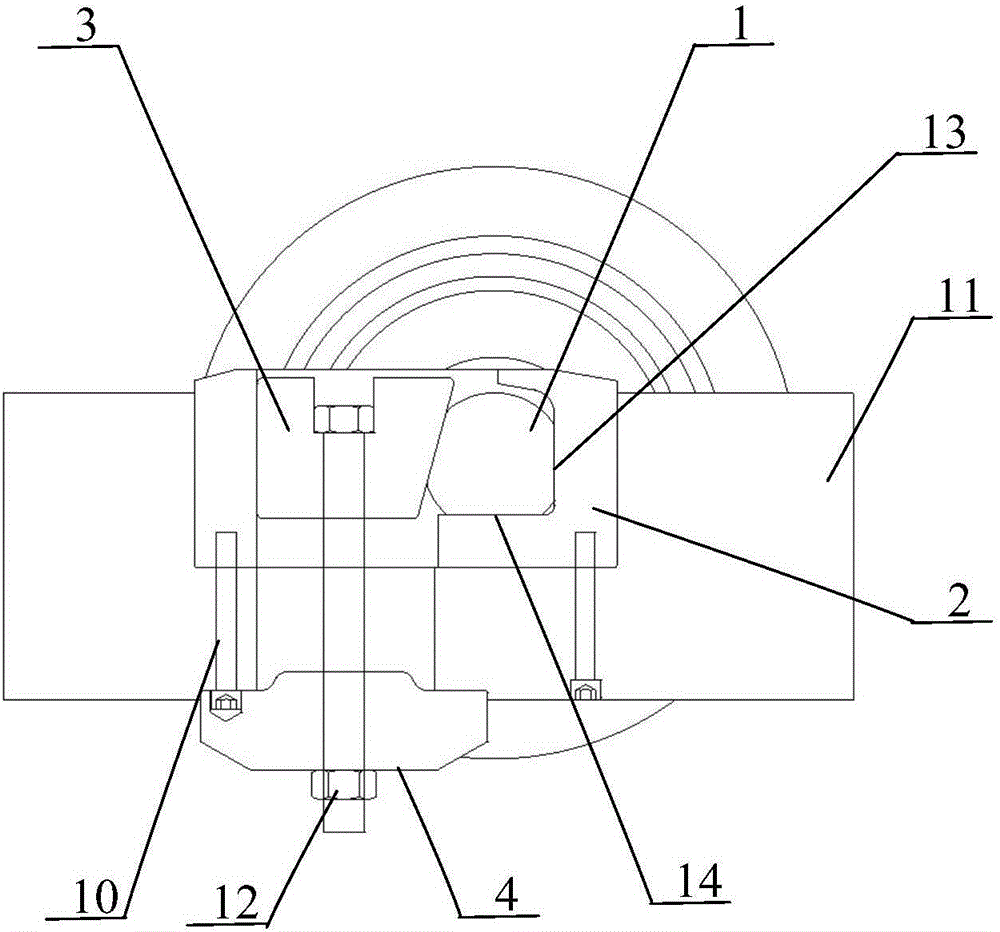
InactiveUS20080216040A1Influence optimizeImprove performanceCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsInterconnectionComputer science
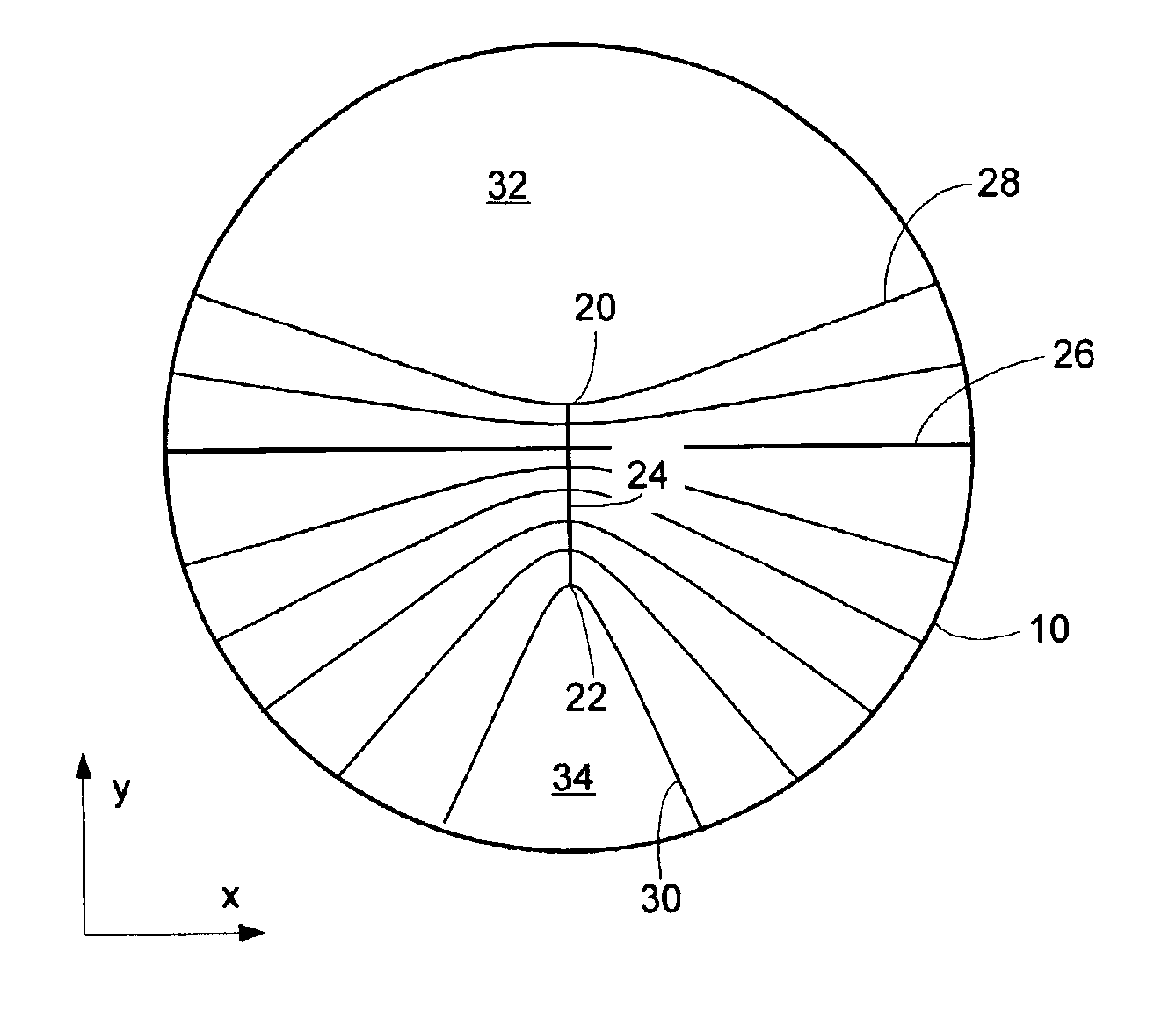
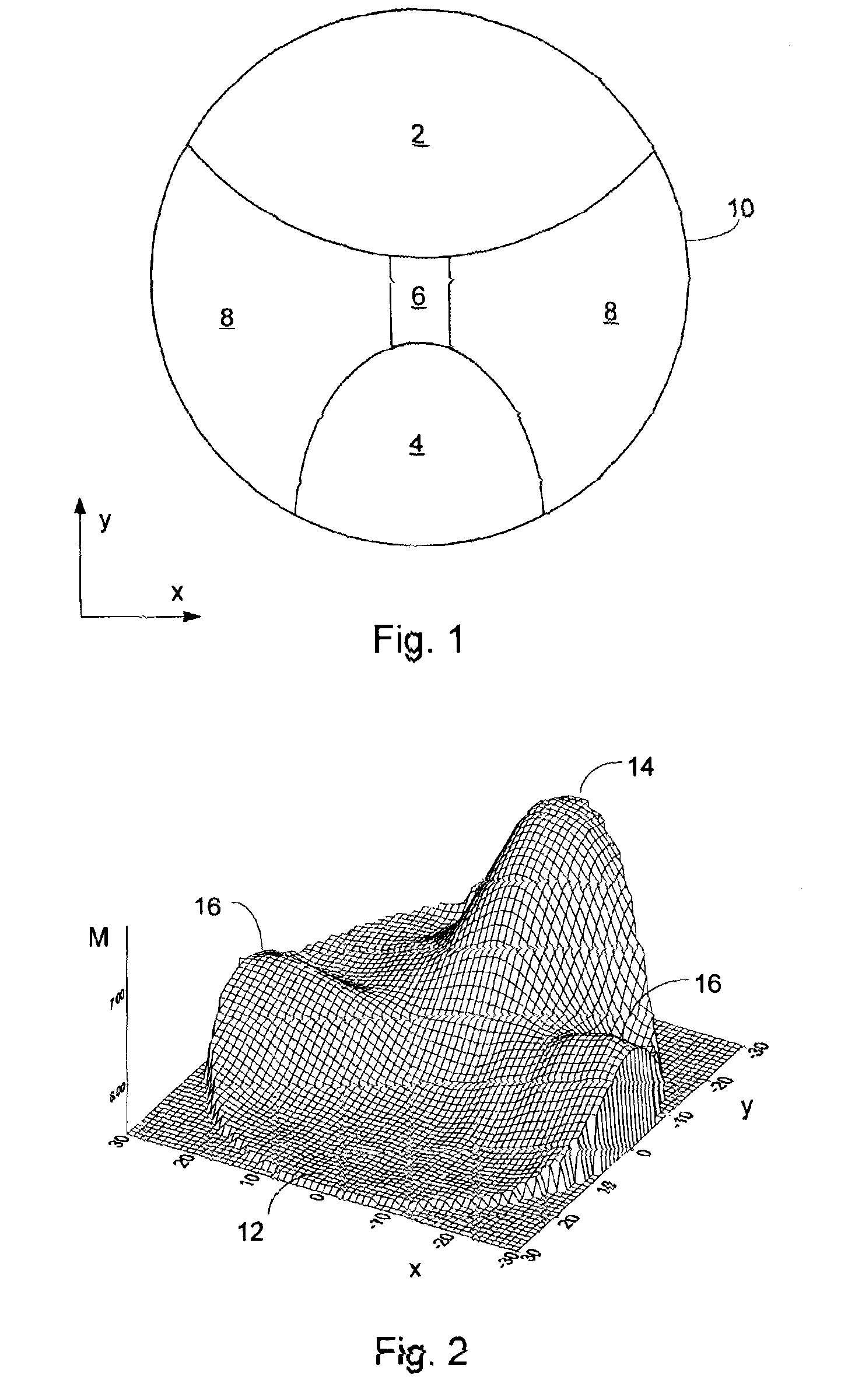
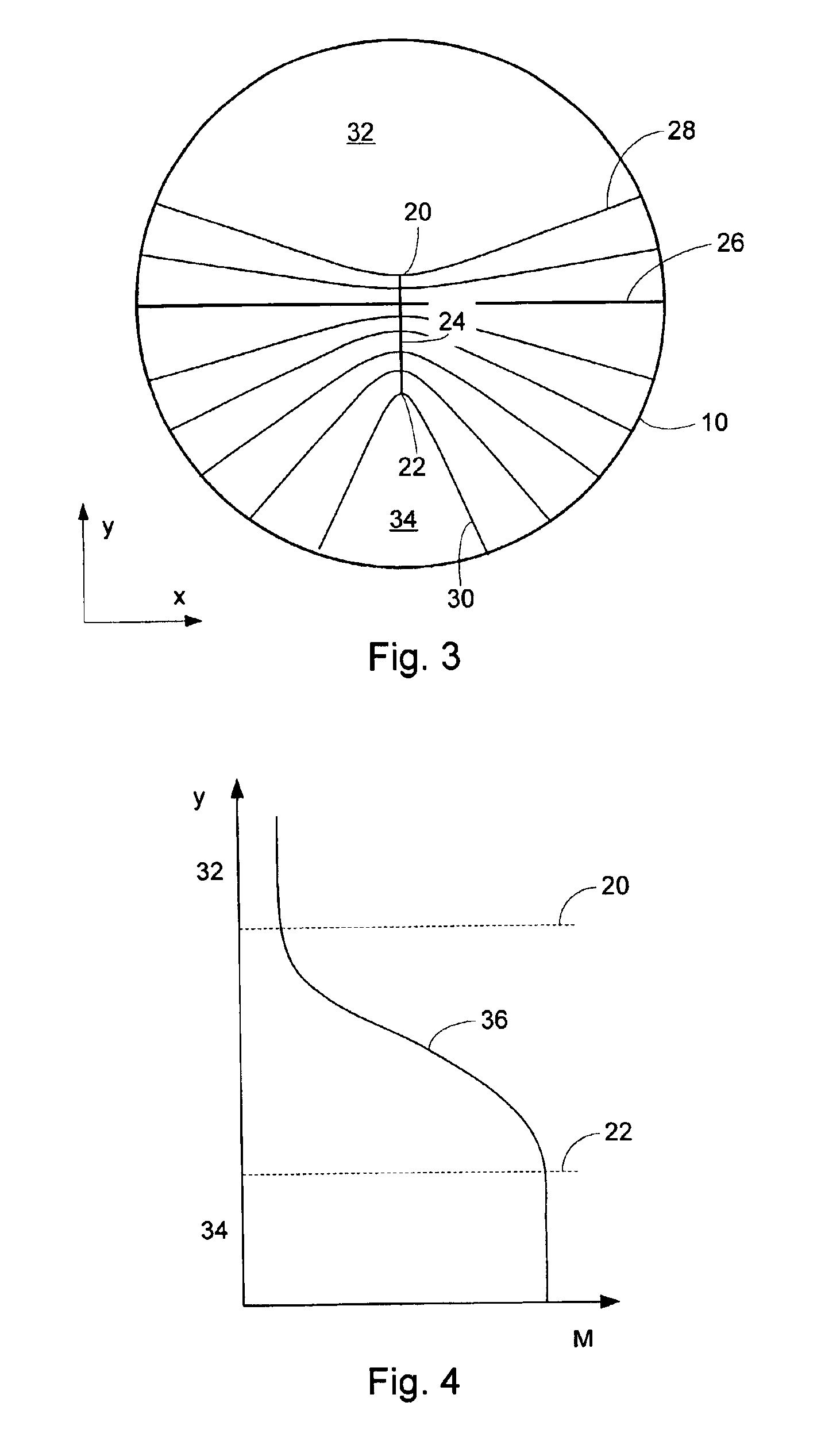
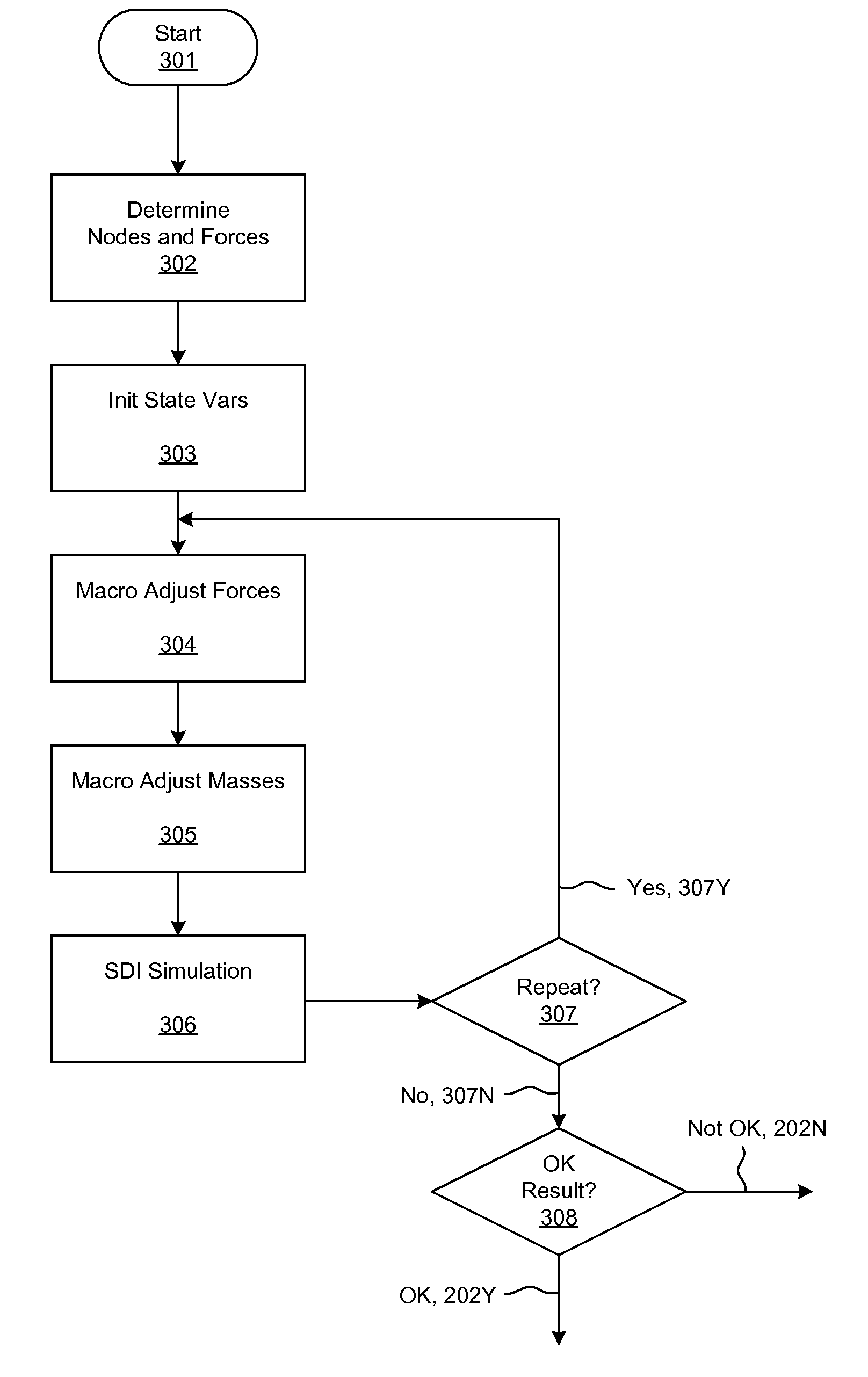
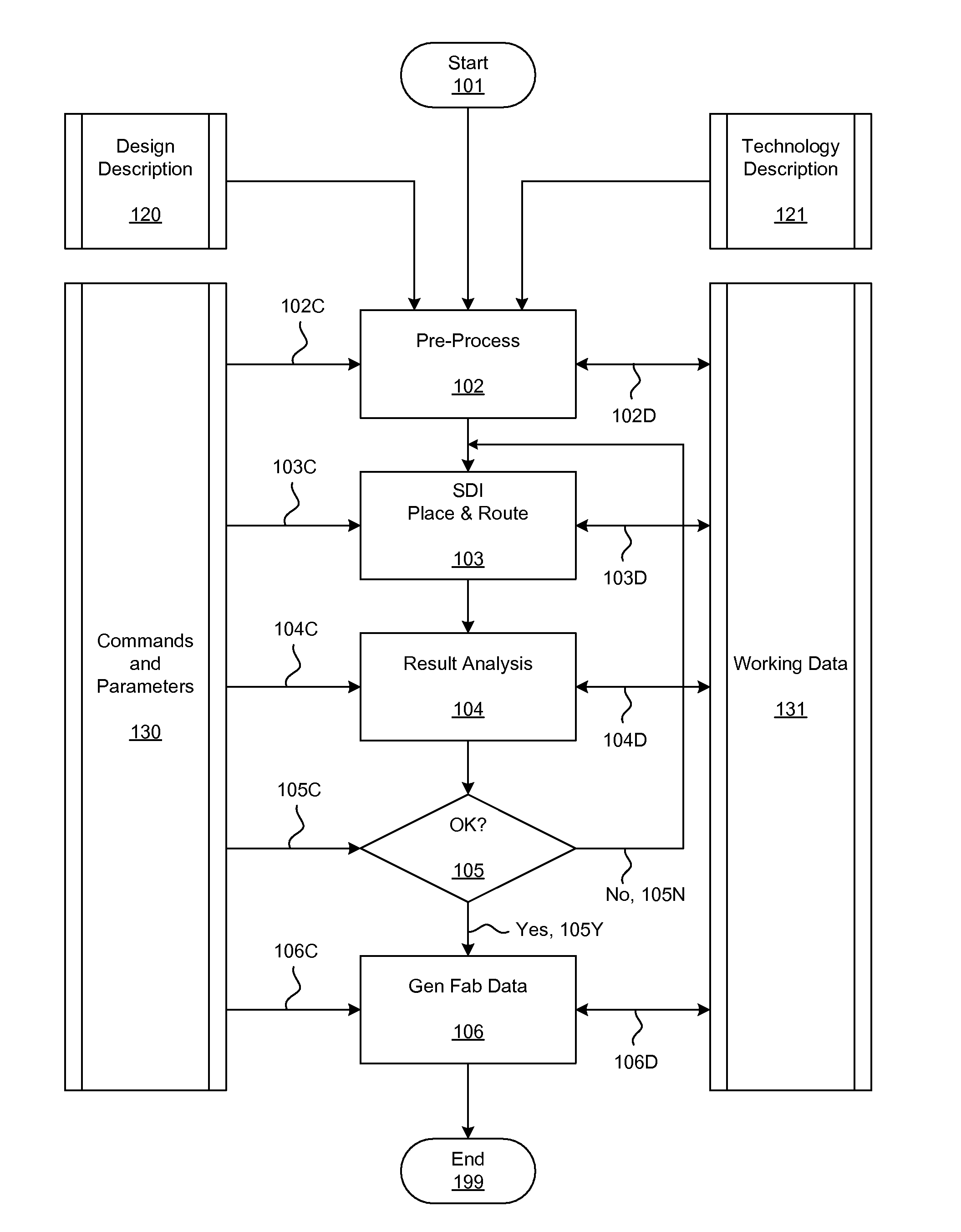
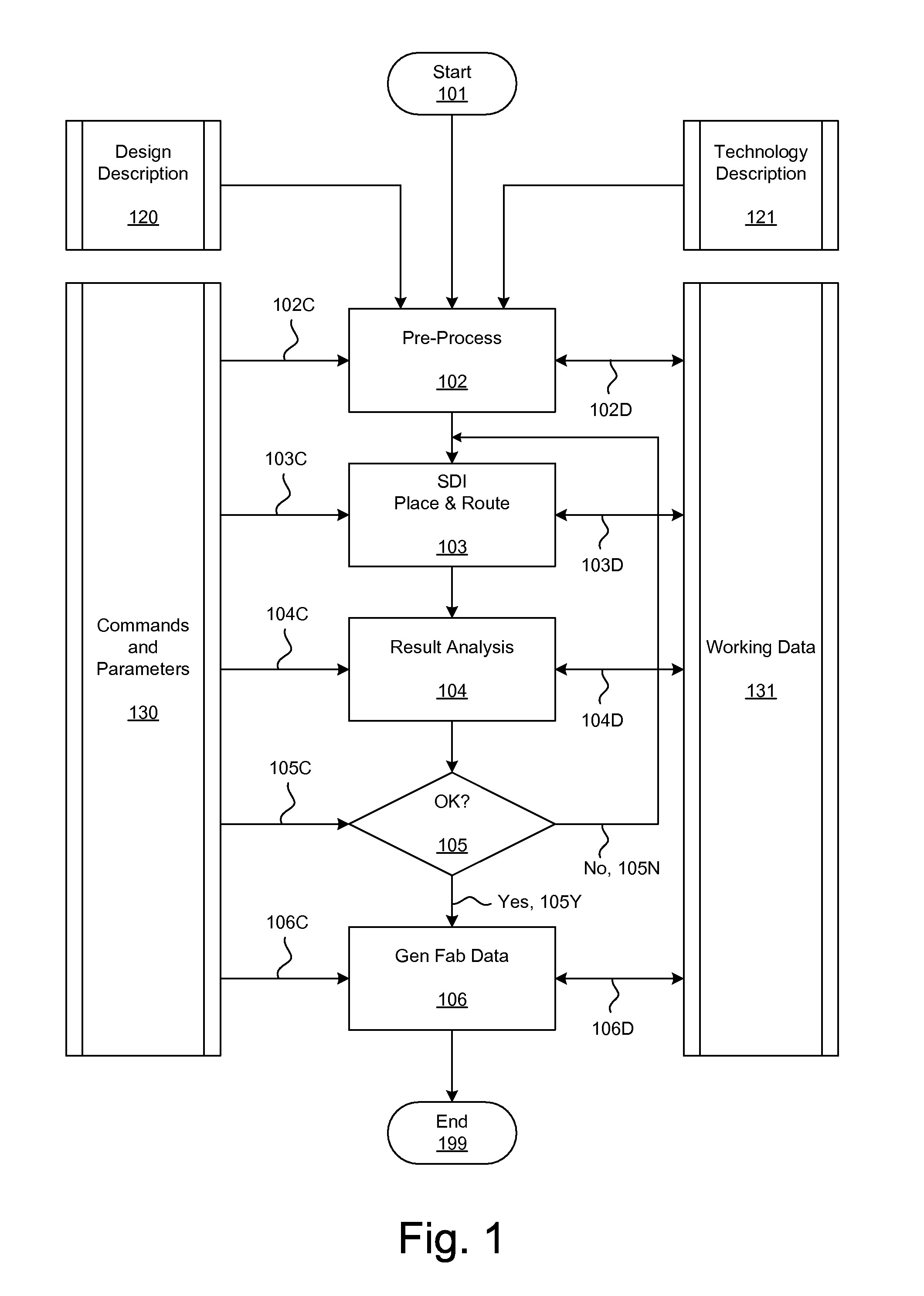
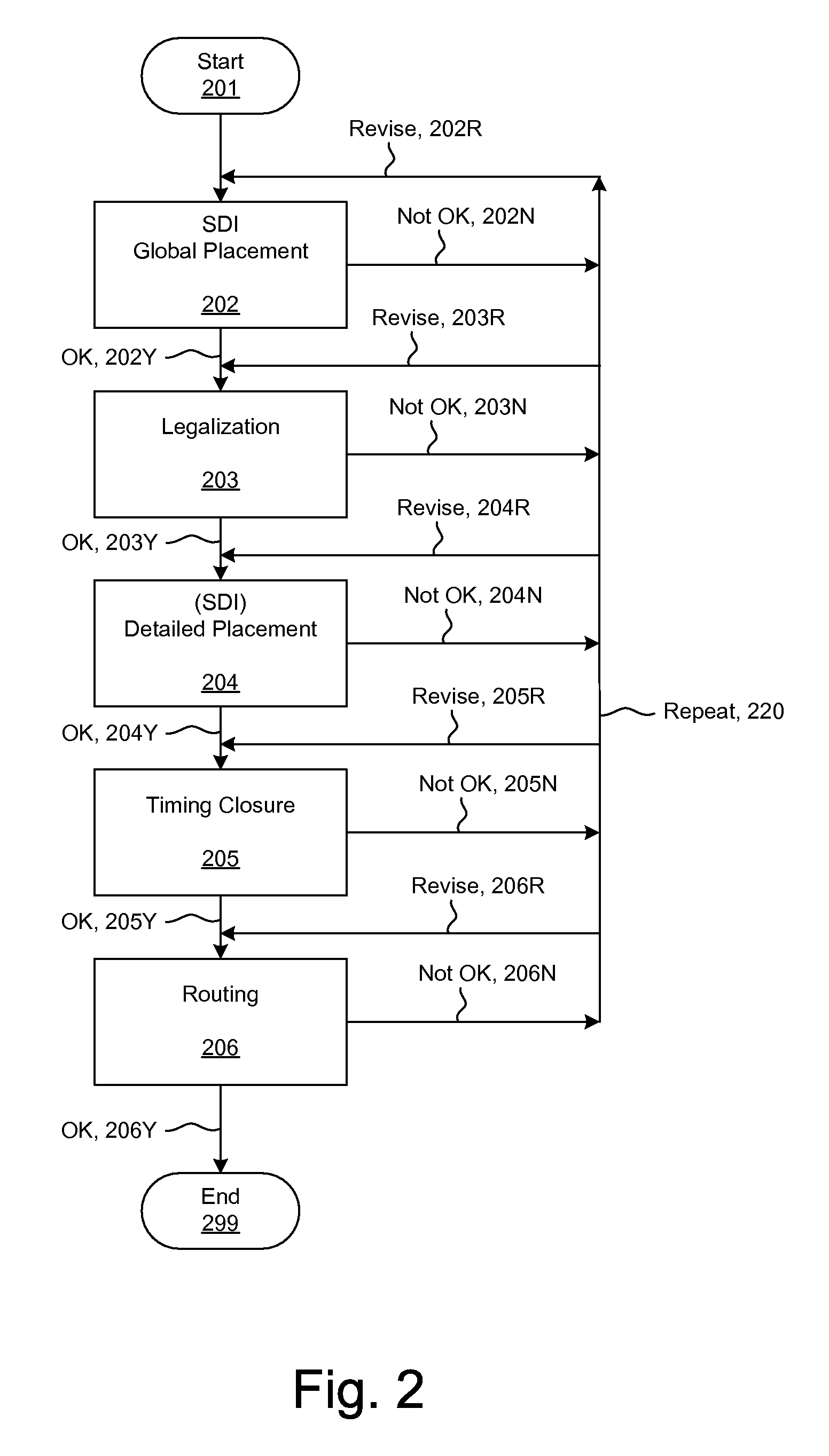
Simultaneous Dynamical Integration modeling techniques are applied to global placement of elements of integrated circuits as described by netlists specifying interconnection of morphable-devices. Solutions to a system of coupled ordinary differential equations in accordance with Newtonian mechanics are approximated by numerical integration. A resultant time-evolving system of nodes moves through a continuous location space in continuous time, and is used to derive placements of the morphable-devices having one-to-one correspondences with the nodes. Nodes under the influence of net attractive forces, computed based on the interconnections between the morphable devices, tend to coalesce into well-organized topologies. Nodes are also affected by spreading forces determined by density fields that are developed based on local spatial node populations.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
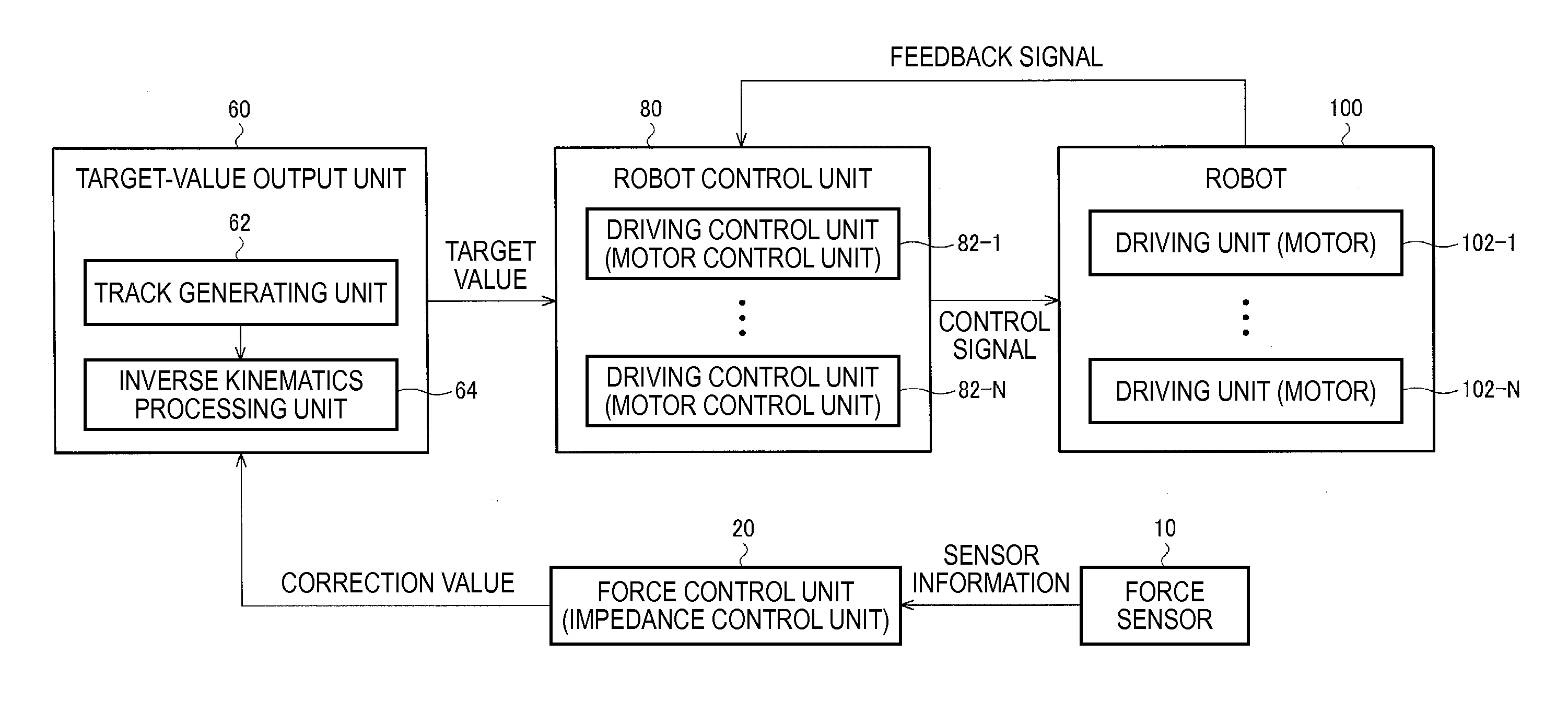
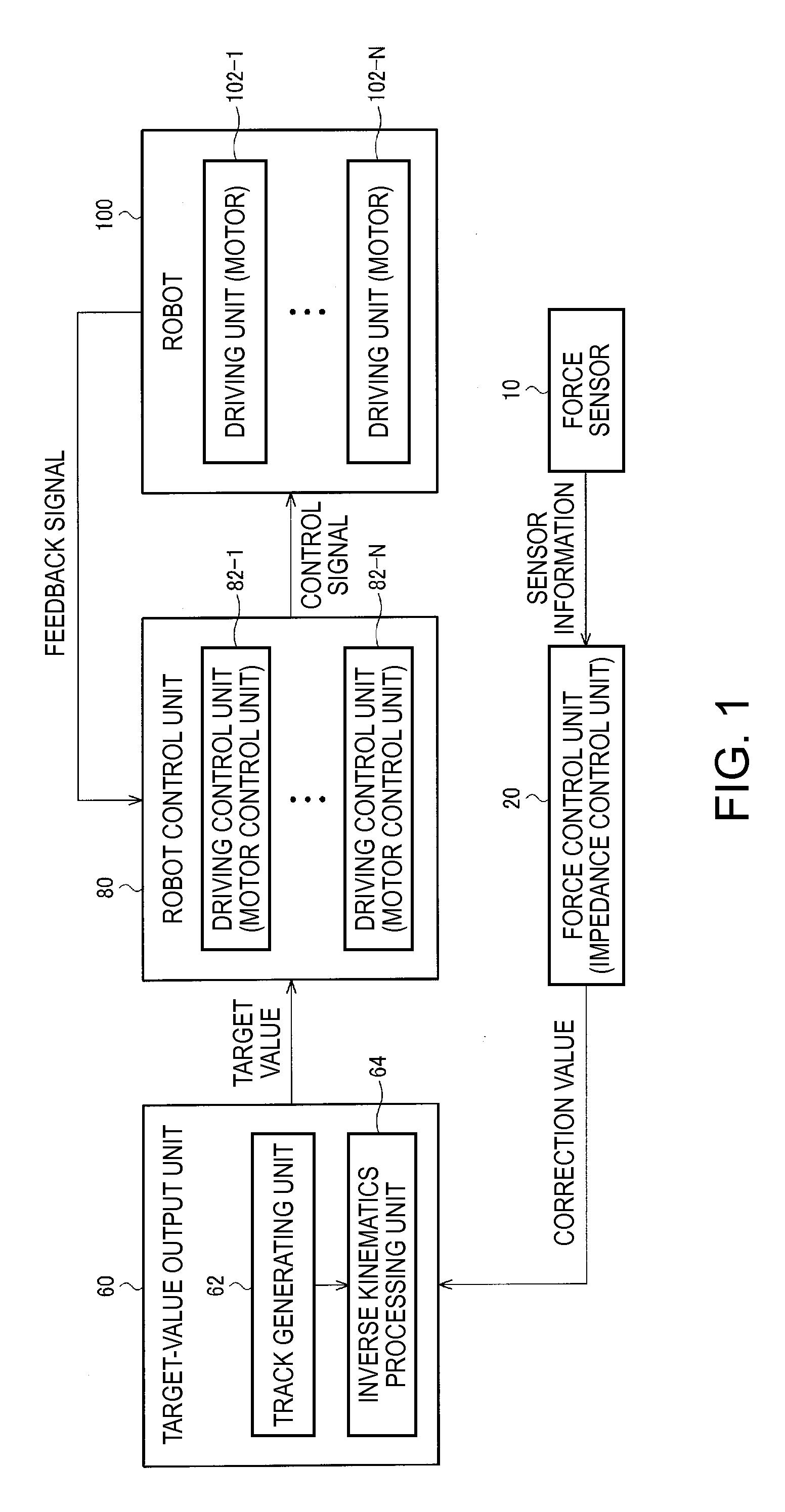
Robot control system, robot system, and sensor information processing apparatus
ActiveUS20130116827A1Facilitate of of responsivenessConvenient verificationProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorInformation processingRobotic systems
A robot control system includes a force control unit configured to output a correction value of a target track of a robot on the basis of sensor information acquired from a force sensor, a target-value output unit configured to apply correction processing based on the correction value to the target track to calculate a target value and output the calculated target value, and a robot control unit configured to perform feedback control of the robot on the basis of the target value. The force control unit includes a digital filter unit. The force control unit applies digital filter processing by the digital filter unit to the sensor information to calculate a solution of an ordinary differential equation in force control and outputs the correction value on the basis of the calculated solution.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Boring tool tracking fundamentally based on drill string length, pitch and roll
InactiveUS6868921B2Enhance corrected positionImprove accuracySurveyConstructionsEngineeringOrdinary differential equation
A boring tool moves having a pitch orientation, a yaw orientation and a roll orientation and is steerable underground using the roll orientation. A maximum drill string curvature is established for steering. The boring tool is advanced over a path segment. An averaged roll characteristic is determined for movement of the boring tool along the path segment. A path segment pitch orientation is established based on at least one measured pitch orientation along the path segment. Using the maximum drill string curvature in combination with the averaged roll characteristic and the path segment pitch orientation, the yaw orientation is determined. The averaged roll characteristic is determined based on a series of incremental roll measurements that are spaced across the path segment. A set of coupled ordinary differential equations is used to characterize movement of the boring tool.
Owner:MERLIN TECH INC
In-situ three-dimensional shape rendering from strain values obtained through optical fiber sensors
ActiveUS8970845B1Eliminate compoundEliminate needUsing optical meansTesting fibre optics/optical waveguide devicesFiber strainThree dimensional shape
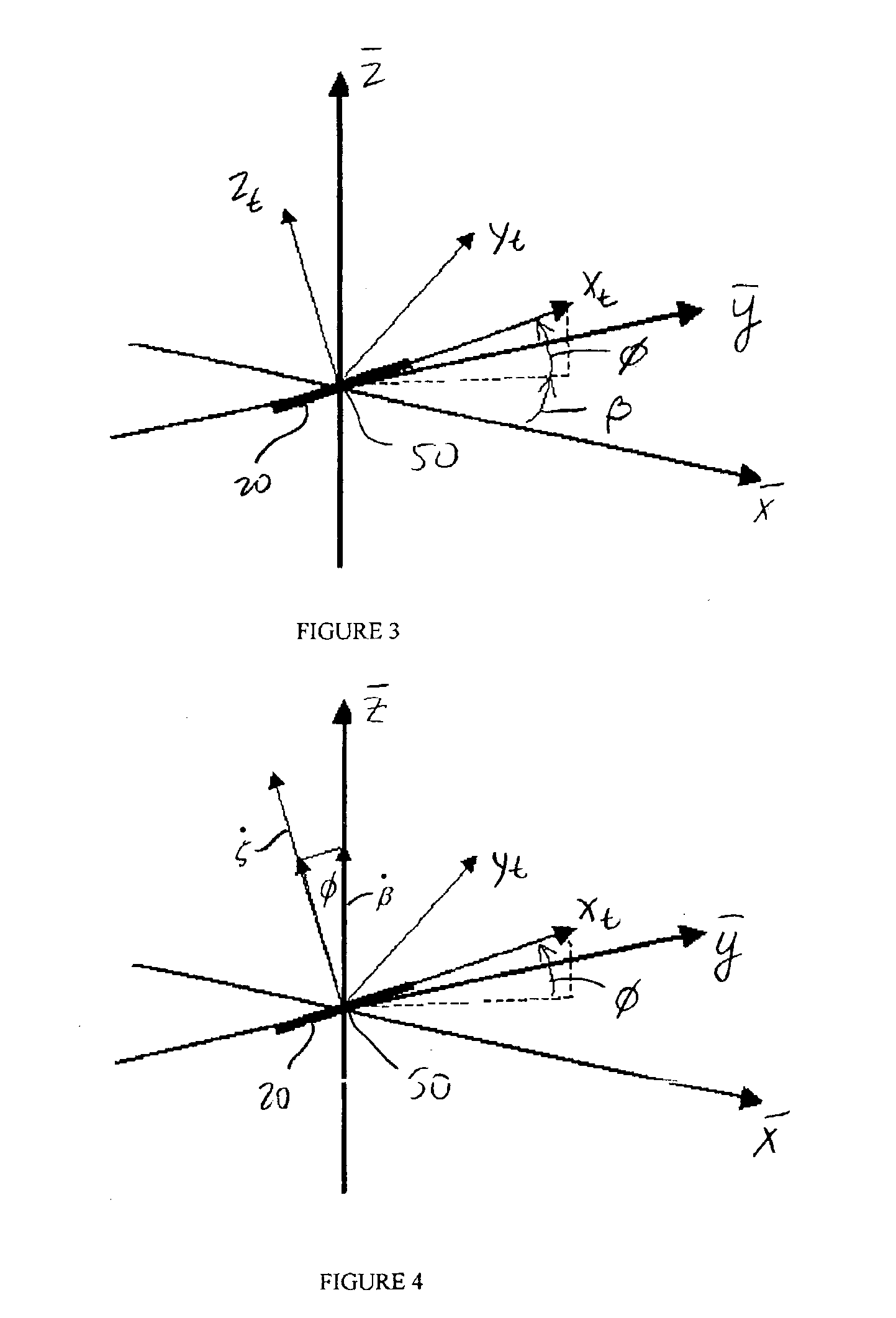
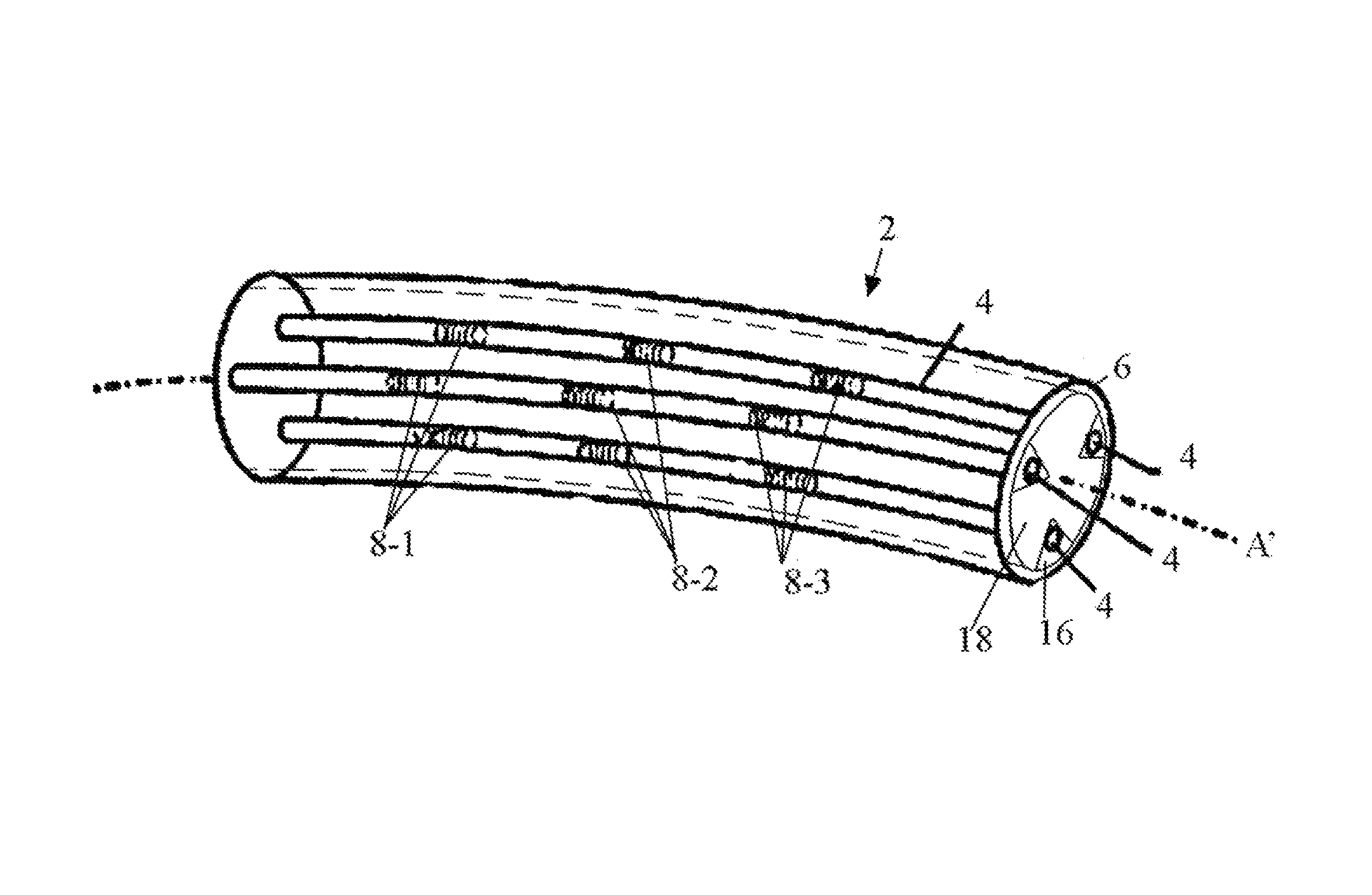
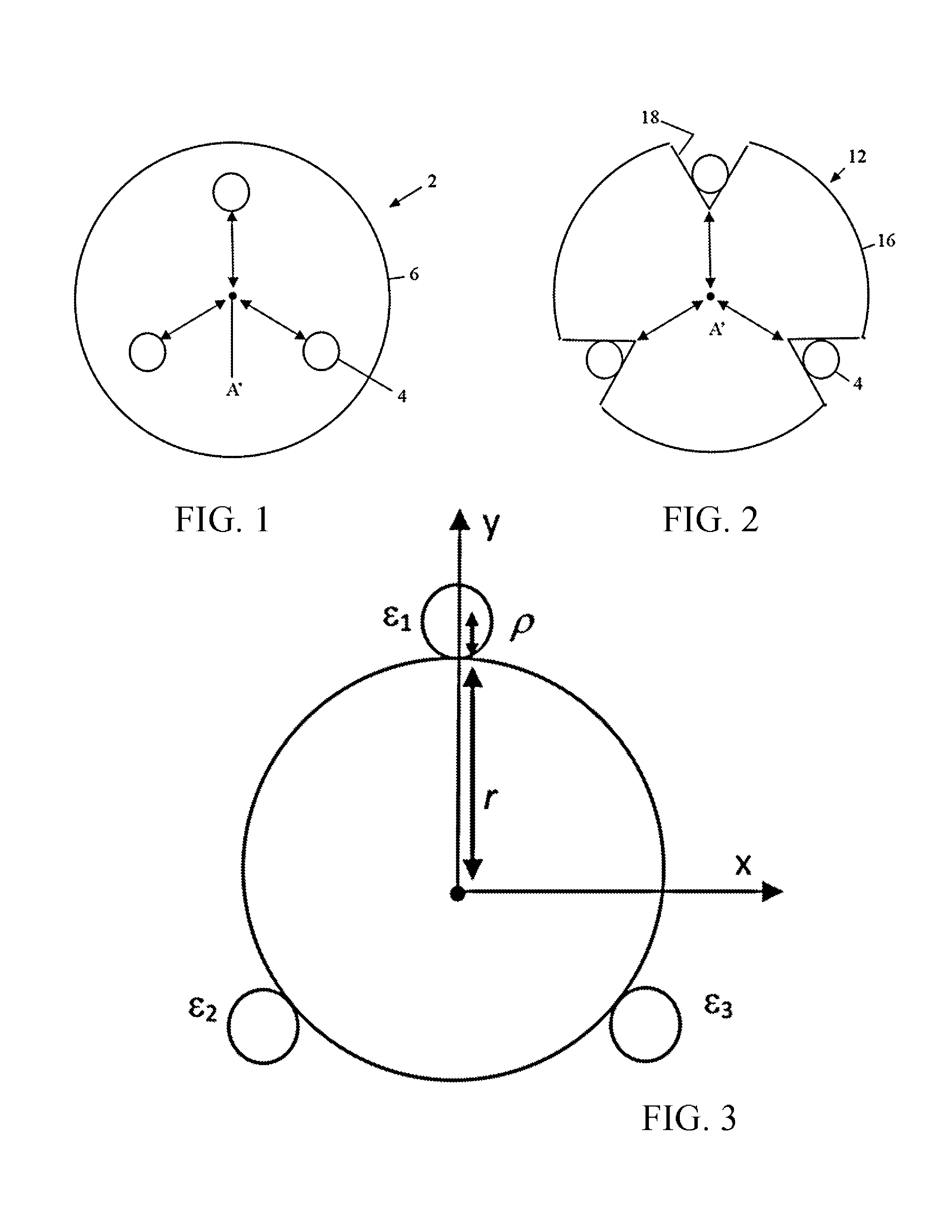
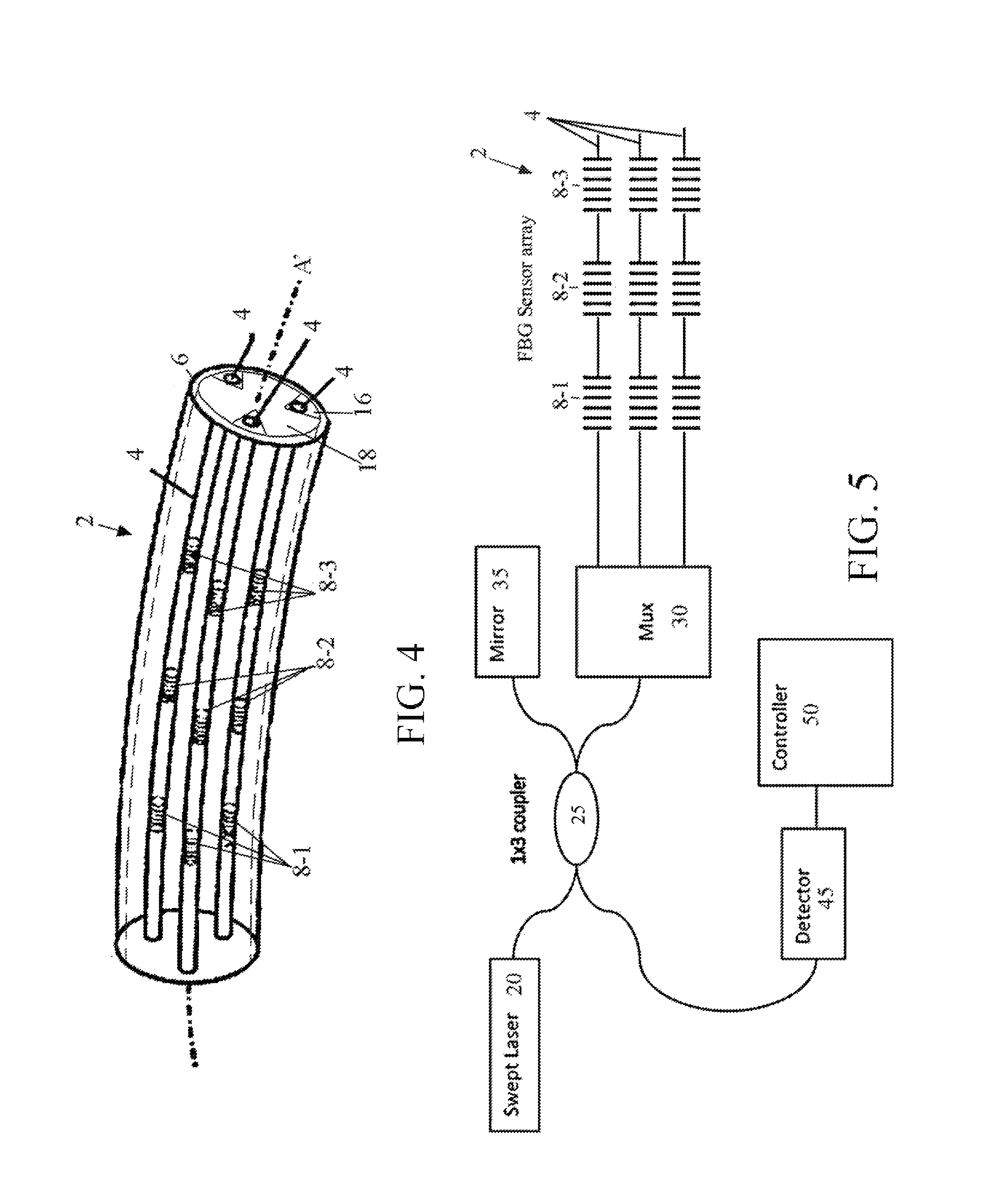
A method and system for rendering the shape of a multi-core optical fiber or multi-fiber bundle in three-dimensional space in real time based on measured fiber strain data. Three optical fiber cores arc arranged in parallel at 120° intervals about a central axis. A series of longitudinally co-located strain sensor triplets, typically fiber Bragg gratings, are positioned along the length of each fiber at known intervals. A tunable laser interrogates the sensors to detect strain on the fiber cores. Software determines the strain magnitude (ΔL / L) for each fiber at a given triplet, but then applies beam theory to calculate curvature, beading angle and torsion of the fiber bundle, and from there it determines the shape of the fiber in s Cartesian coordinate system by solving a series of ordinary differential equations expanded from the Frenet-Serrat equations. This approach eliminates the need for computationally time-intensive curve-tilting and allows the three-dimensional shape of the optical fiber assembly to be displayed in real-time.
Owner:NASA
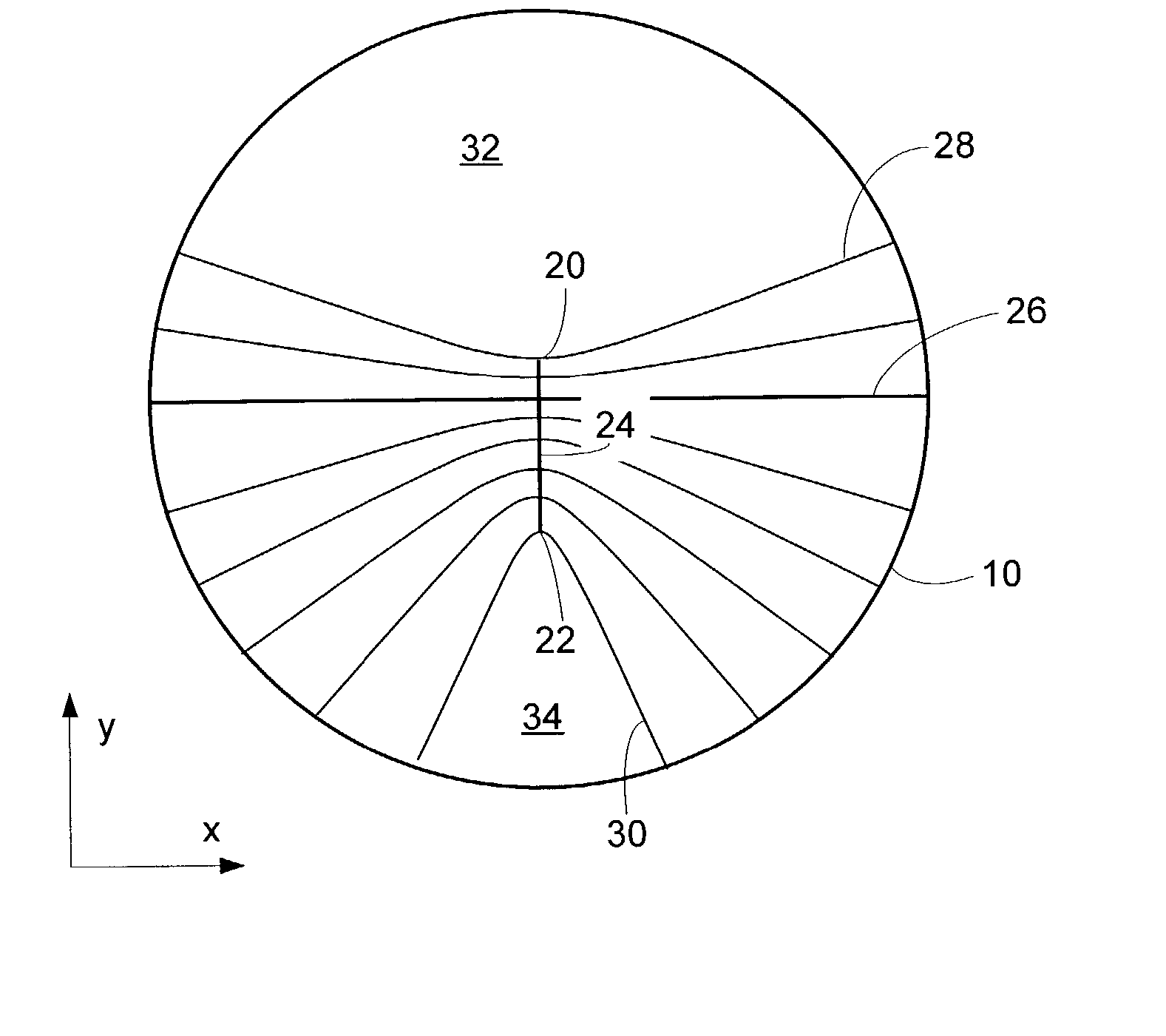
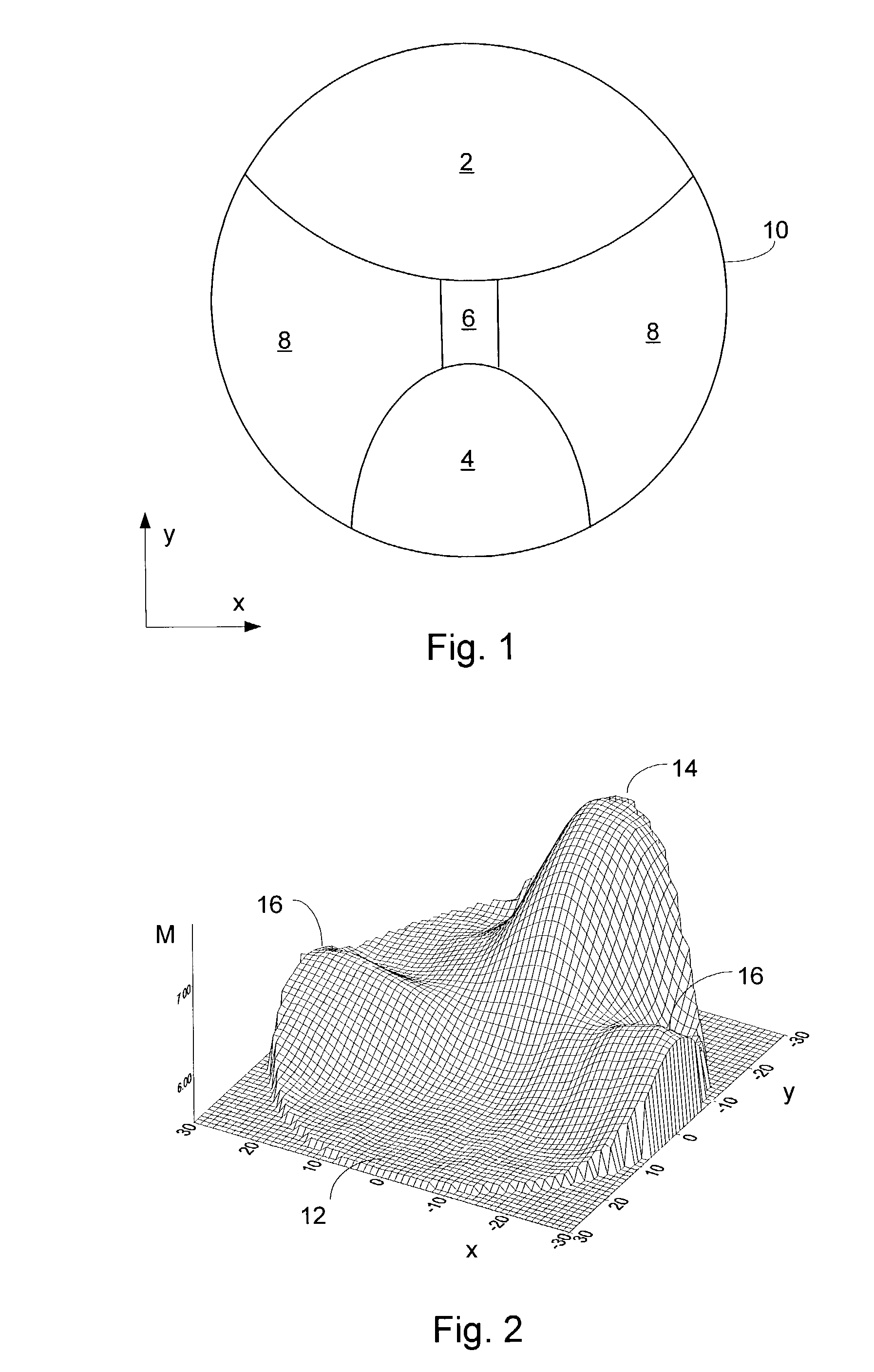
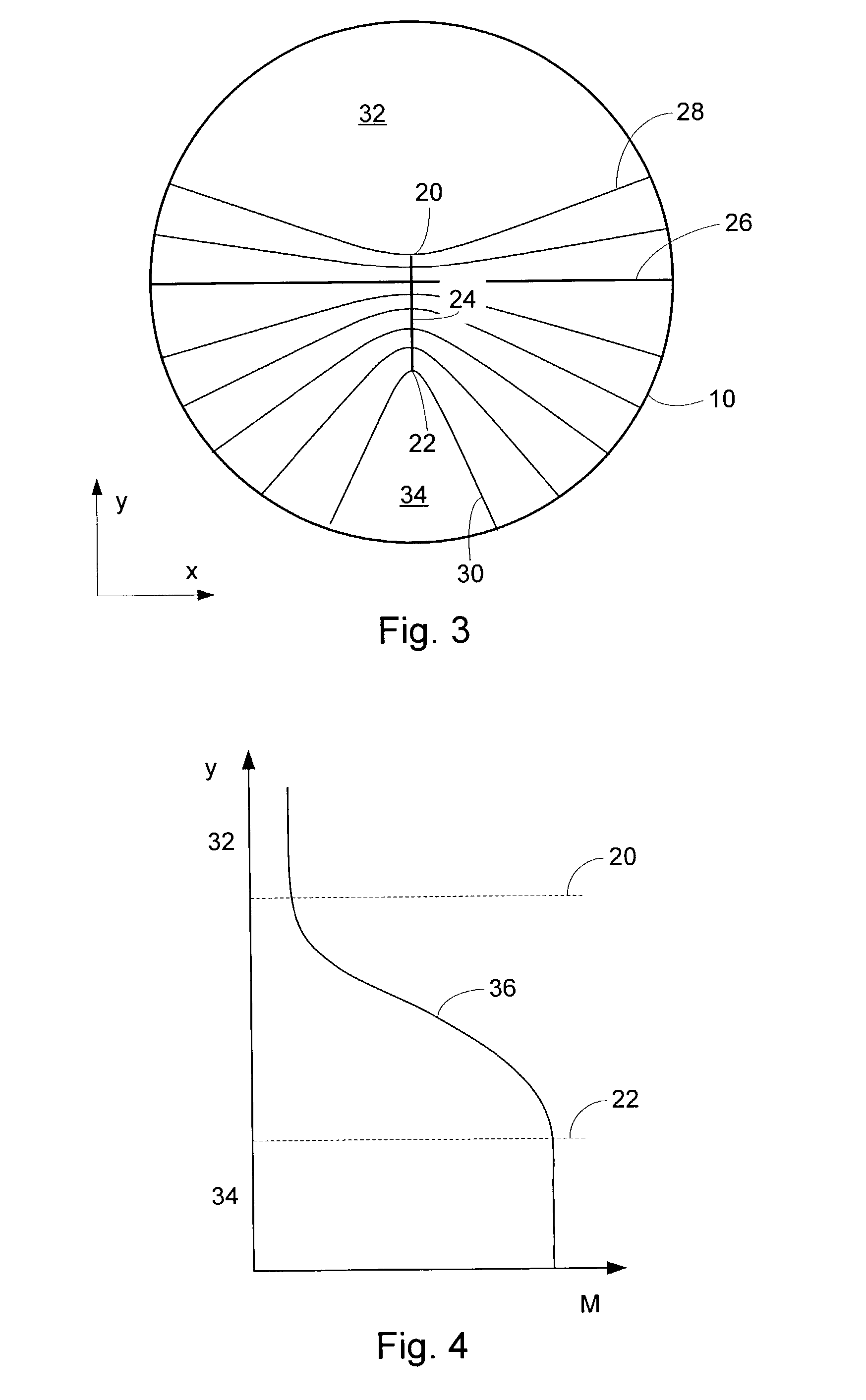
Progressive addition power lens
A system and method for designing a progressive lens. Mean power is specified at points distributed over the entire surface of the lens and lens height is specified around the edge of the lens. Lens height is determined at the points consistent with the specified mean power and the lens edge height in part by solving a partial differential equation of the elliptic type subject to the lens edge height as a boundary condition. A successive over-relaxation technique may be employed to converge on the solution to the partial differential equation, and an over-relaxation factor may be determined to most efficiently relax the equation.
Owner:CROSSBOWS OPTICAL
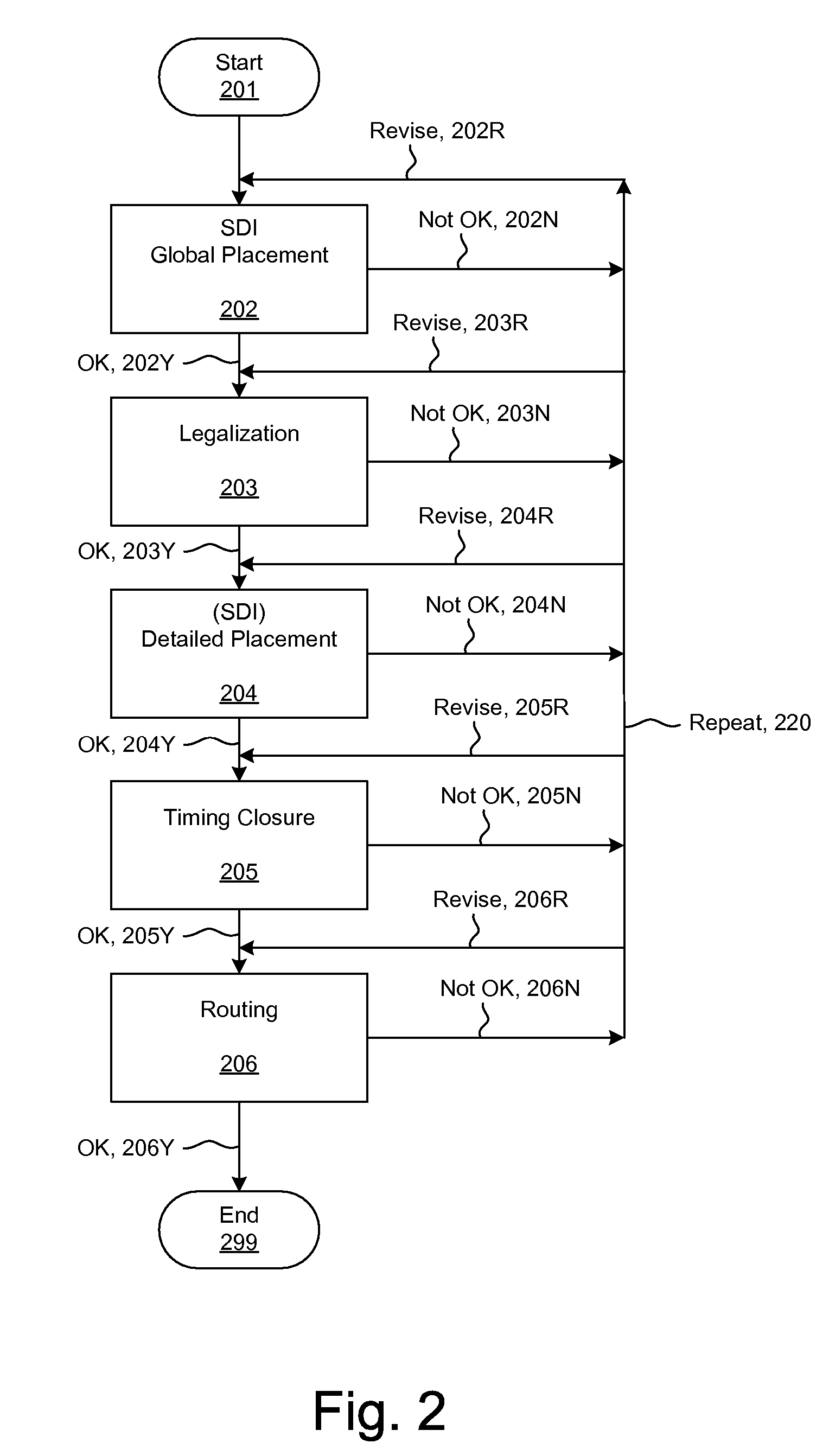
Methods and systems for placement
Simultaneous Dynamical Integration modeling techniques are applied to placement of elements of integrated circuits as described by netlists specifying interconnection of devices. Solutions to a system of coupled ordinary differential equations in accordance with Newtonian mechanics are approximated by numerical integration. A resultant time-evolving system of nodes moves through a continuous location space in continuous time, and is used to derive placements of the devices having one-to-one correspondences with the nodes. Nodes under the influence of net attractive forces, computed based on the interconnections between the morphable devices, tend to coalesce into well-organized topologies. Nodes are also affected by spreading forces determined by density fields that are developed based on local spatial node populations. The forces are optionally selectively modulated as a function of simulation time. The placements of the devices are compatible with various design flows, such as standard cell, structured array, gate array, and field-programmable gate array.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
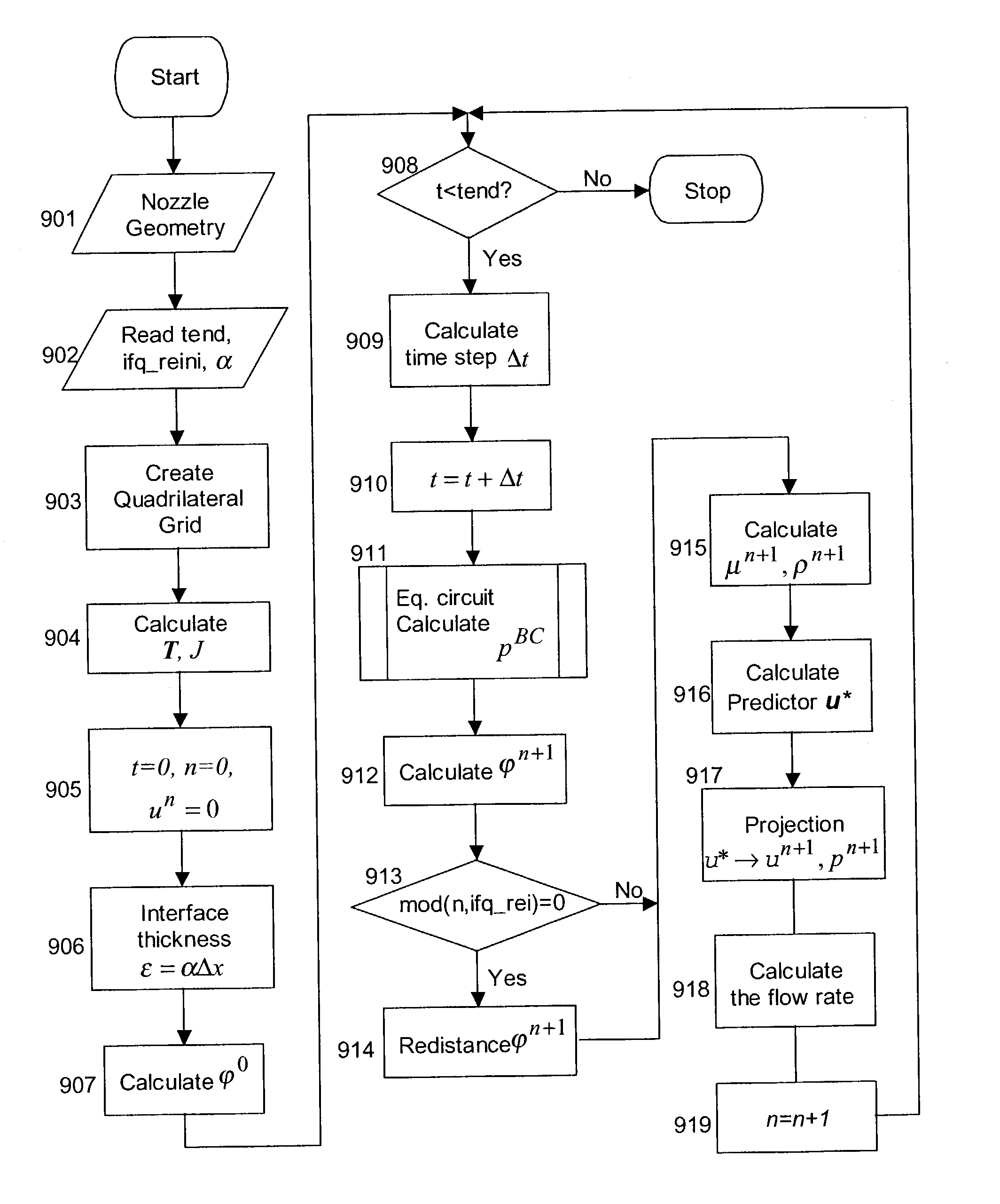
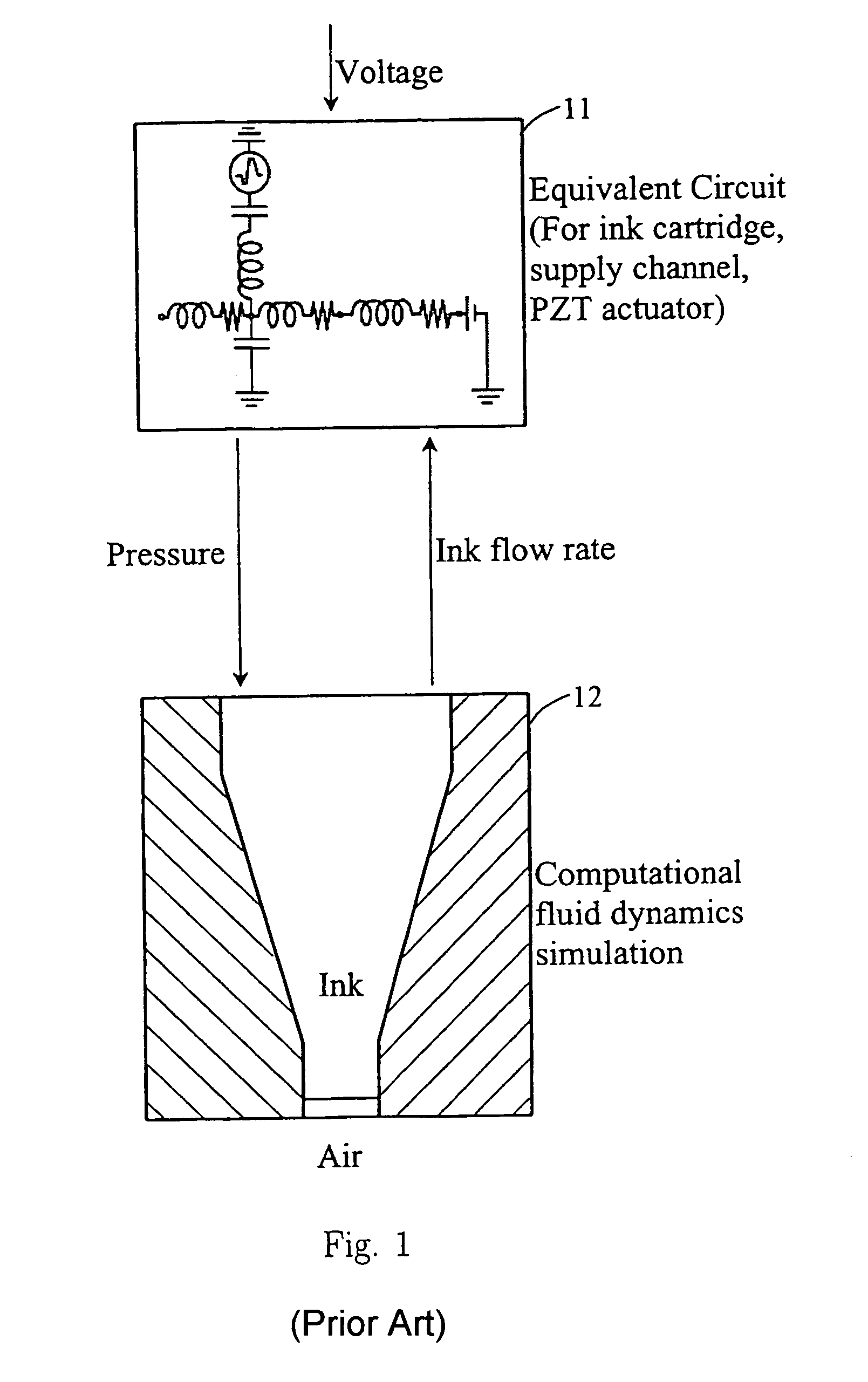
Coupled quadrilateral grid level set scheme for piezoelectric ink-jet simulation
ActiveUS7117138B2Easy to controlOvercome problemsElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingTesting/calibration apparatusPhysical spaceHyperbolic partial differential equation
Methods for finite-difference-based inkjet simulation enable more precise control of ink droplet size and shape. A discrete transformation (mapping) is constructed so that a quadrilateral grid in physical space is transferred to the uniform square grid in a computational space. Since the grid in the computational space is square, numerical finite difference differentiation can be easily done. Governing partial differential equations, including a viscosity term, a surface tension term, and a level set convection equation for two-phase flows, are derived on the quadrilateral grid and then transformed to the computational space for application on the uniform square grid. A stable and powerful numerical algorithm is developed to solve the derived and transformed equations to enable finite-difference-based ink-jet simulation.
Owner:KATEEVA
Anti-sway control of a crane under operator's command
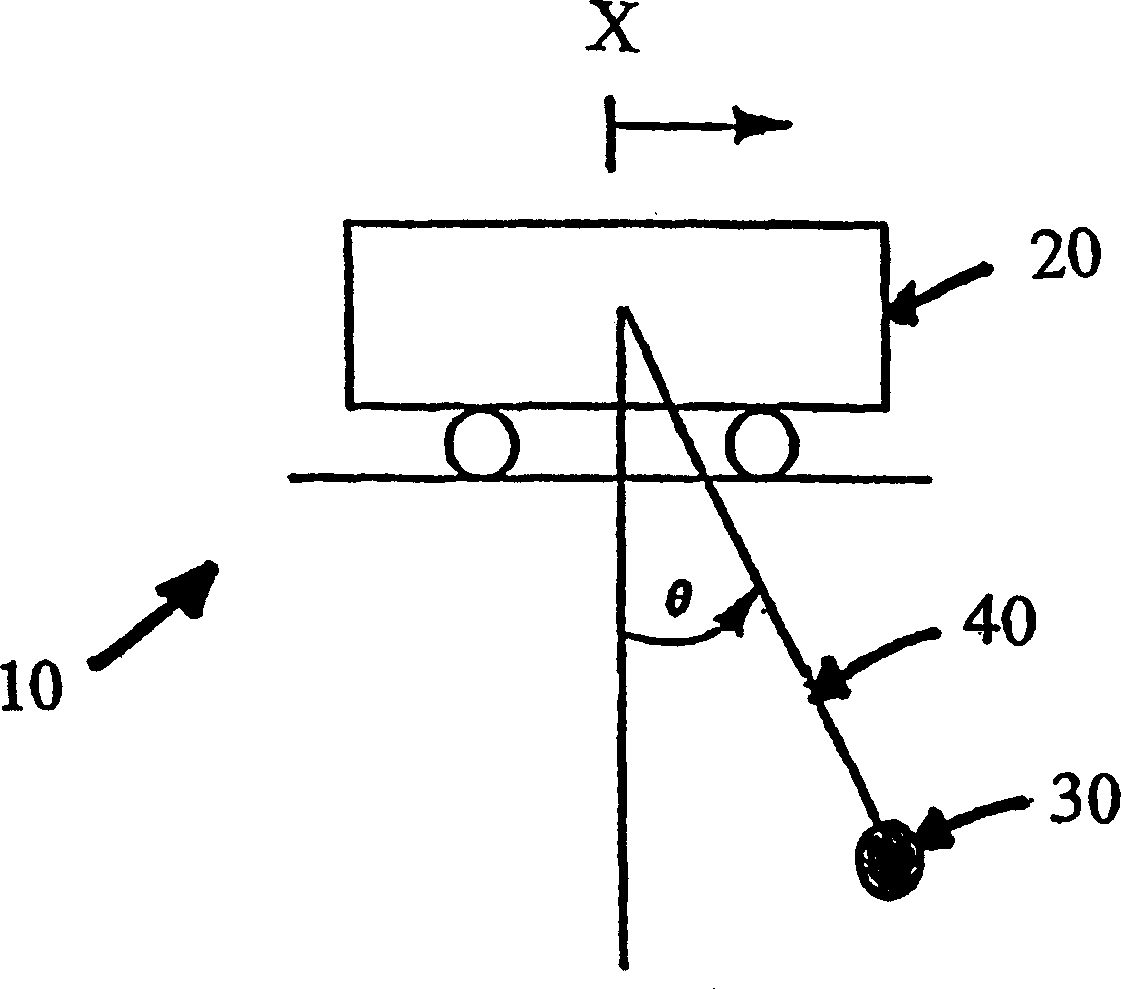
InactiveCN1505590AMake sure it works correctlyResidual Swing EliminationTrolley cranesLoad-engaging elementsEngineeringKey factors
A system (10) is disclosed for eliminating sway of a load (30) in a crane or crane-like system subject to operator's command. The load is suspended by a cable (40) from a horizontally movable trolley (20) and can be hoisted vertically. The system uses the principle of cancellation to eliminate sway even when the crane has simultaneous trolley and hoisting motions. The system takes into account the full dynamical effect in computing cancellation signals. The use of a family of ordinary differential equations for the computation of the cancellation controls is a key component of the invention. In computing these controls, the differential equations are solved in real time using sensory measurement of the cable length and its time derivative. The cancellation controls handle the sway induced by the operator's command. Sway can also be induced by other factors, like wind load and external disturbances. This system also includes a feedback mechanism for eliminating sway due to such factors. The system ensures saturation limits, corresponding to the velocity and acceleration limits of the drive system of the trolley are not exceeded for proper functioning of the system.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
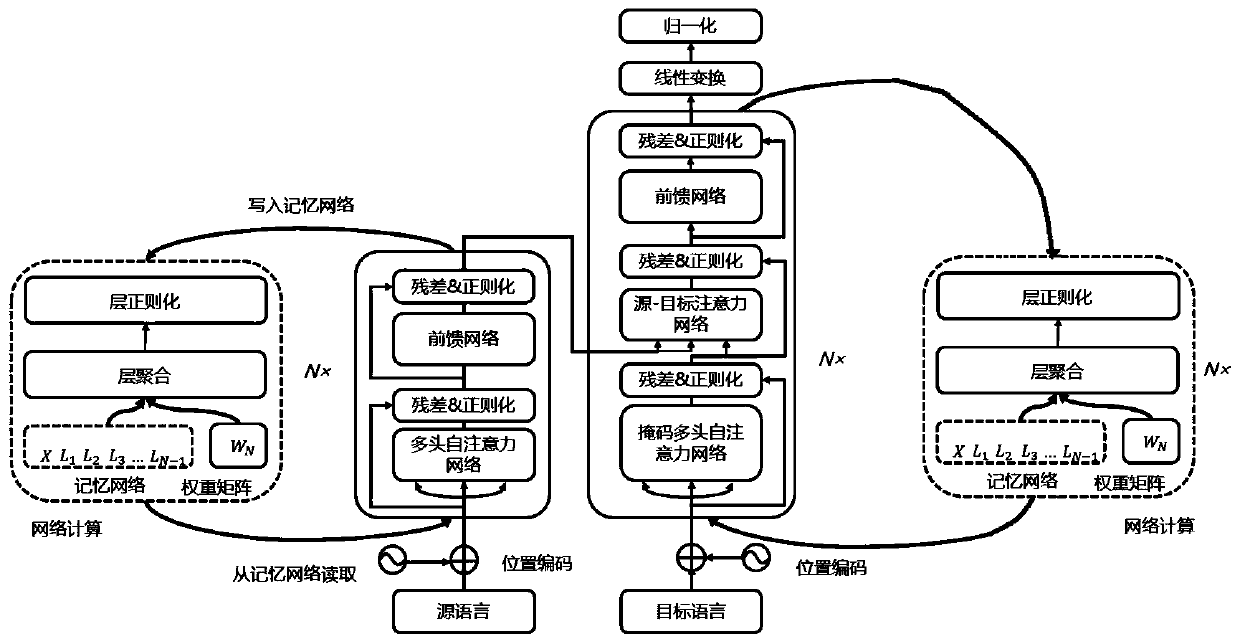
Deep neural machine translation method based on dynamic linear aggregation
ActiveCN109783827AStacked deepImprove delivery efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsNeural learning methodsHidden layerFeature vector
The invention discloses a deep neural machine translation method based on dynamic linear aggregation. Based on a Transformer model, a memory network is added to a coding end and a decoding end of theTransformer model at the same time to store the output of a previous middle lamination. The memory network is accessed before the next laminated network calculation. A linear multi-step method based on an ordinary differential equation aggregates dense vectors stored in a memory network and semantic vectors of all previous laminates to obtain a hidden layer representation for aggregating characteristics of each layer, and the hidden layer representation obtains a semantic vector of which parameters obey standard regularization as input of a next lamination through layer regularization operation. In this way, the feature vectors extracted by all previous laminated networks are fully considered when the current laminated network is calculated, so that a deeper model is trained to improve therepresentation ability of the model, and the performance of machine translation is improved.
Owner:沈阳雅译网络技术有限公司
Traveling-wave differential protection method suitable for series capacitor compensation circuit
ActiveCN101662142ASmall differential operating currentImprove securityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsCapacitanceMatrix differential equation
The invention discloses a traveling-wave differential protection method suitable for a series capacitor compensation circuit. The method comprises the steps: 1) current calculation under a mold domain, calculating mold currents im<x> and in<x> flowing into a series capacitor device from onside and offside; 2) establishment of differential equation; 3) resolution of differential currents, utilizingthe reverse transformation of phase molds to solve vectors icd<phi> of the differential currents of each fault phase and each non-fault phase; 4) action judgment of a differential relay: utilizing the fault-phase action amount as braking, and adding an appropriate fixing threshold. The invention can effectively solve the effect of capacitor current on differential protection of long-distance transmission lines, can be well suitable for the series capacitor compensation circuit, and enhances the sensitivity of differential protection.
Owner:NANJING GUODIAN NANZI POWER GRID AUTOMATION CO LTD
Method for constructing reduced-order models of systems
InactiveUS6188974B1Computing operations for integral formationAnalogue computers for electric apparatusTime delaysAlgorithm
A method comprising a computational procedure for obtaining reduced-order models of partial element equivalent circuit (PEEC) models of very large scale integrated (VLSI) interconnects. The methodology is not limited to PEEC applications, and can be used for generating reduced-order models of other systems which can be modeled with linear, time-invariant systems of ordinary differential equations with time delays.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for de-noising dual-tree complex wavelet image on basis of partial differential equation
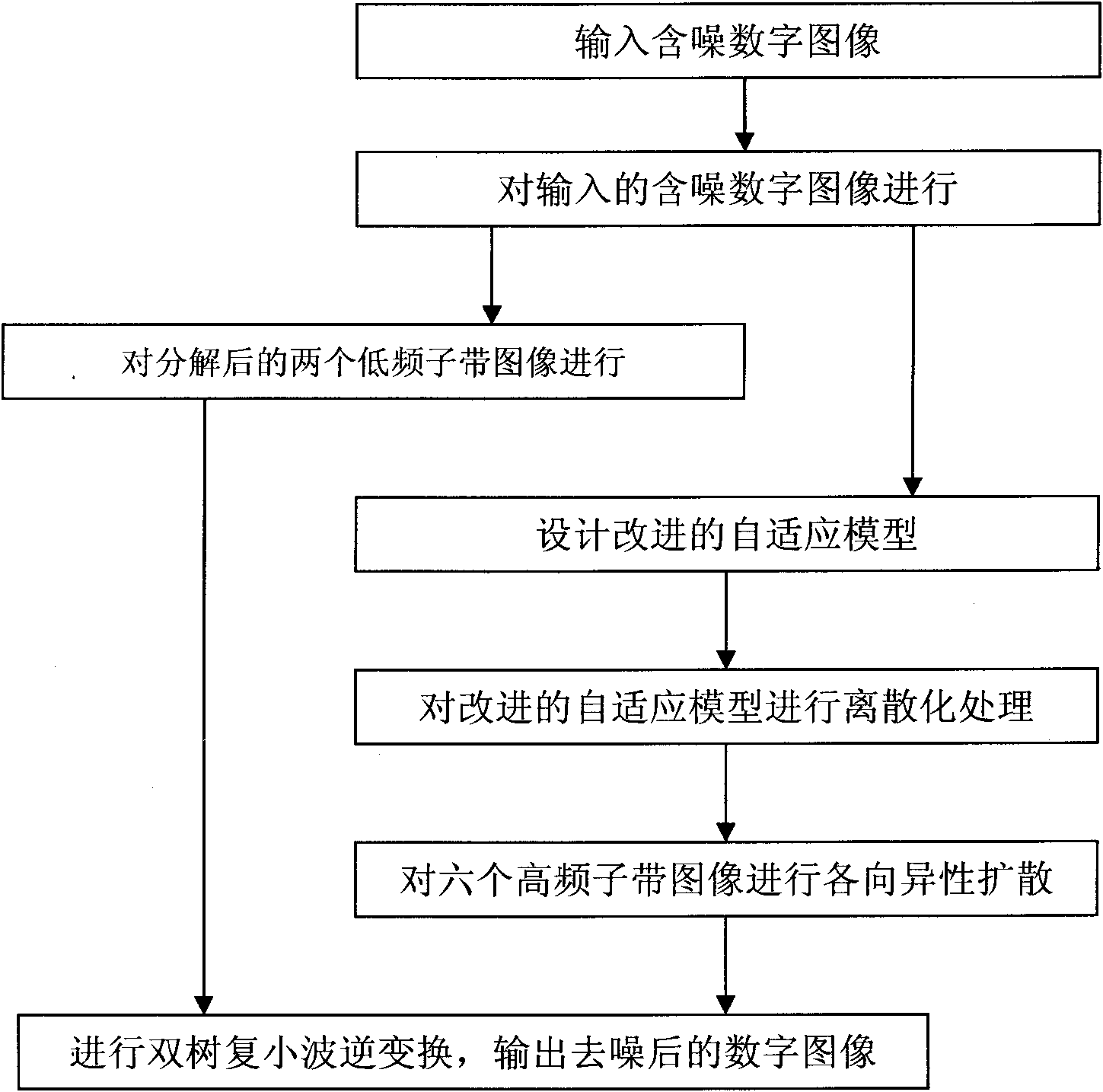
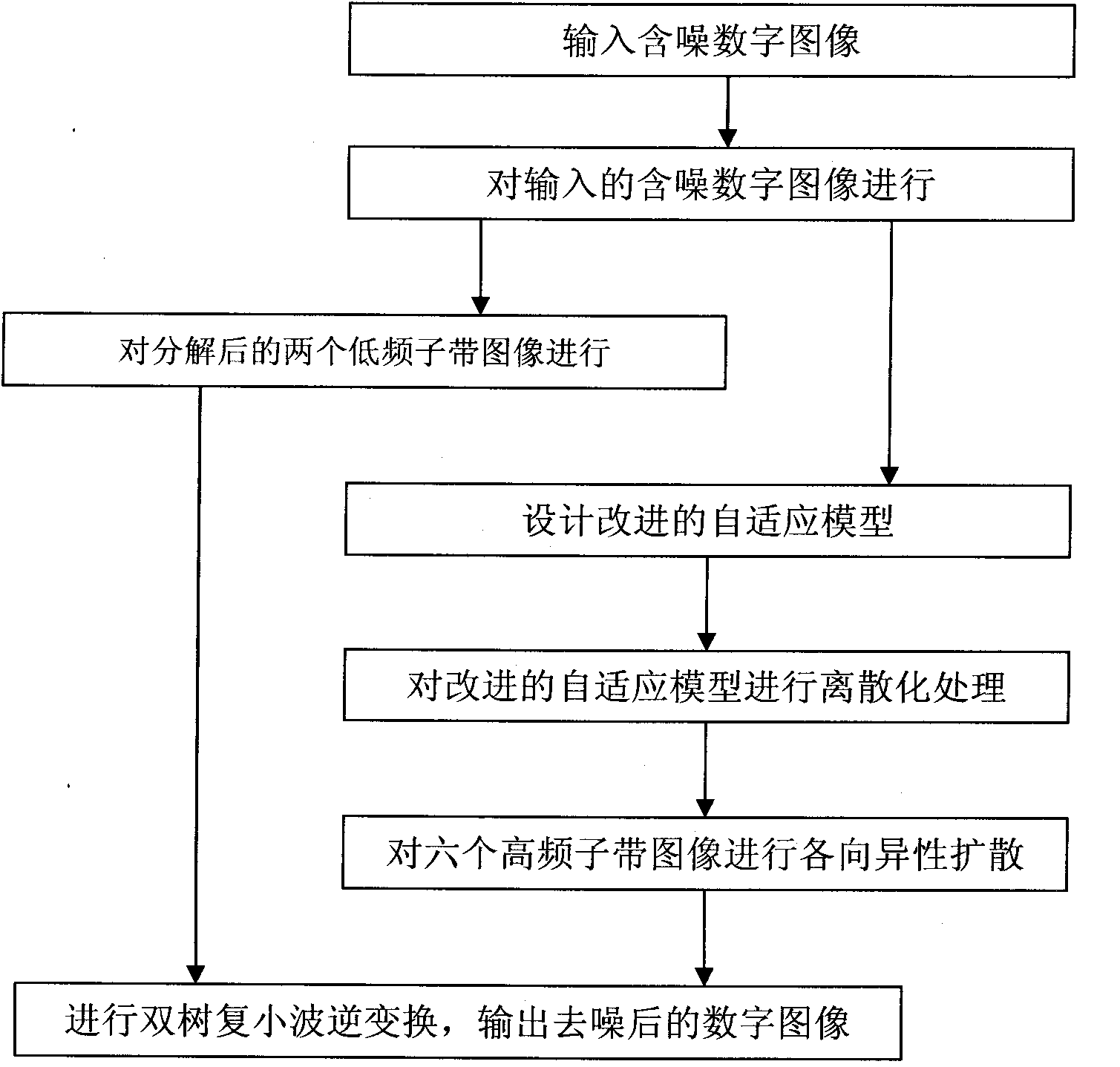
InactiveCN101777179AHigh denoising speedSuppression of Pseudo-Gibbs PhenomenoImage enhancementHigh rateDecomposition
The invention relates to a method for de-noising a dual-tree complex wavelet image on the basis of partial differential equation. The method comprises the following steps: inputting a noised digital image; carrying out the dual-tree complex wavelet transform decomposition on the inputted noised digital image to obtain two low-frequency sub-band images and six high-frequency detailed sub-band images; carrying out the isotropic diffusion on the two decomposed low-frequency sub-band images; designing an improved adaptive model; calculating the dual-tree complex wavelet transform modulus and gradient modulus of the high-frequency detain sub-band images on each direction, and designing an adaptive diffusion coefficient function to improve the P-M (Perona-Malik) model (i.e., the isotropic diffusion model) by using the weighted average of the dual-tree complex wavelet transform modulus and gradient modulus; carrying out the diffusion processing on the improved adaptive model; carrying out the isotropic diffusion on the six high-frequency sub-band images; and carrying out the dual-tree complex wavelet transform, and outputting the de-noised digital image. The invention has the beneficial effect that more detailed information of the image can be preserved on the premise that the higher rate of image de-noising is maintained.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
TBM hobbing cutter stress online real-time monitoring apparatus and monitoring method
ActiveCN106370333AWon't fall offHigh precisionApparatus for force/torque/work measurementStress conditionsHobbing
The invention discloses a TBM hobbing cutter stress online real-time monitoring apparatus and monitoring method. The apparatus comprises a support cushion block, an upper compaction block, a strain gauge, a strain instrument, a wireless emission module, a wireless receiving module and a monitoring computer. According to the monitoring method, by use of strain data of the support cushion block, obtained by the apparatus, through the monitoring computer, by use of a hobbing cutter system vibration differential equation established through a hobbing cutter vertical and swing-direction coupling vibration mechanical model, stress of a hobbing cutter during work is calculated, such that work personnel can monitor the stress condition of the hobbing cutter in real time and adjust driving parameters based thereon, damage is reduced, vibration is mitigated, and the driving efficiency is improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Progressive addition power lens
A system and method for designing a progressive lens. Mean power is specified at points distributed over the entire surface of the lens and lens height is specified around the edge of the lens. Lens height is determined at the points consistent with the specified mean power and the lens edge height in part by solving a partial differential equation of the elliptic type subject to the lens edge height as a boundary condition. A successive over-relaxation technique may be employed to converge on the solution to the partial differential equation, and an over-relaxation factor may be determined to most efficiently relax the equation.
Owner:CROSSBOWS OPTICAL
Node Spreading via Artificial Density Enhancement to Reduce Routing Congestion
ActiveUS20080216039A1Influence optimizeImprove performanceCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsInterconnectionRouting congestion
Simultaneous Dynamical Integration modeling techniques are applied to global placement of elements of integrated circuits as described by netlists specifying interconnection of morphable-devices. Solutions to a system of coupled ordinary differential equations in accordance with Newtonian mechanics are approximated by numerical integration. A resultant time-evolving system of nodes moves through a continuous location space in continuous time, and is used to derive placements of the morphable-devices having one-to-one correspondences with the nodes. Nodes under the influence of net attractive forces, computed based on the interconnections between the morphable devices, tend to coalesce into well-organized topologies. Nodes are also affected by spreading forces determined by density fields that are developed based on local spatial node populations.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
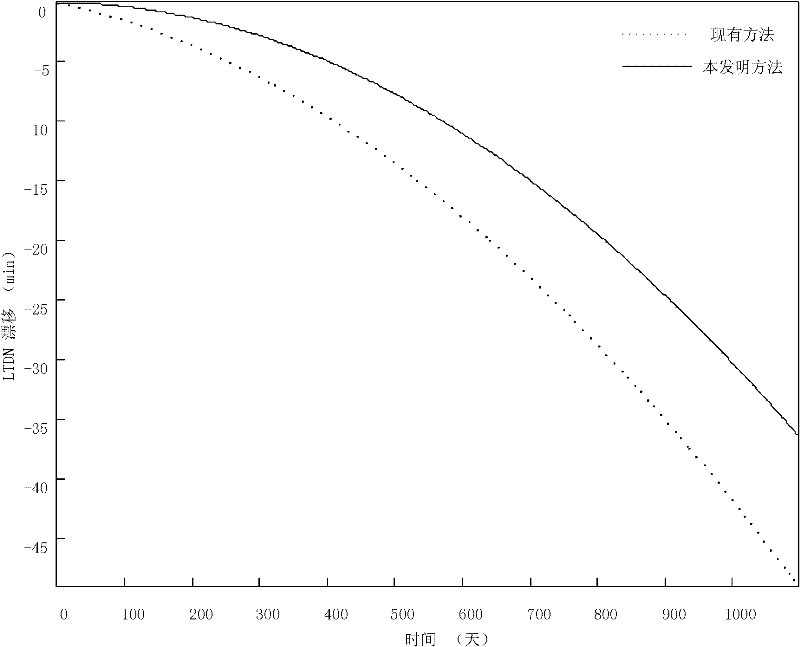
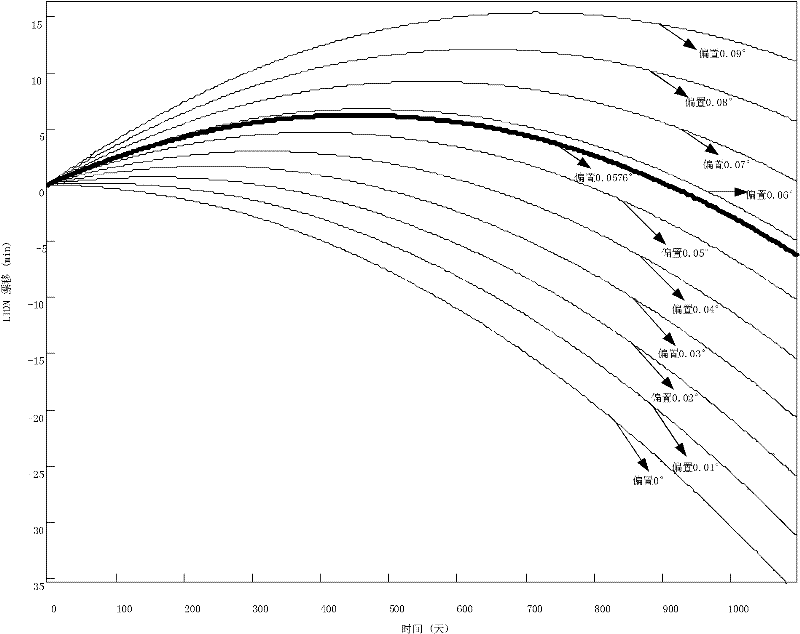
Acquisition method of inclination biased quantity for sun synchronous orbit
InactiveCN102495950AHigh precisionImprove controlSpecial data processing applicationsOrbitRight ascension
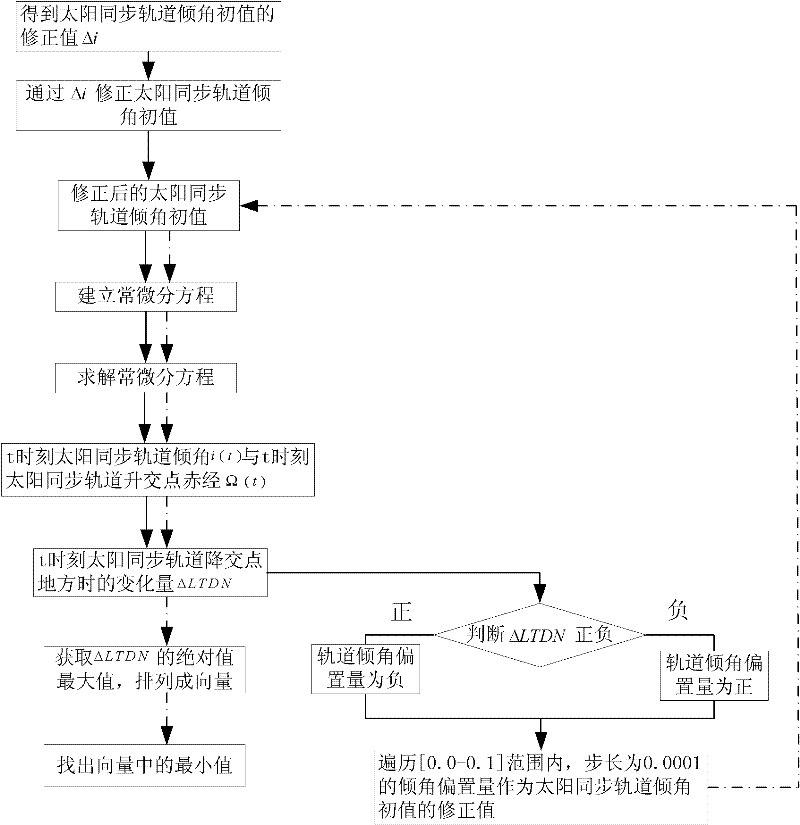
The invention discloses an acquisition method of inclination biased quantity for sun synchronous orbit. The method comprises the following steps: 1, correcting an initial value i0 of an orbit inclination by virtue of a correction value delta I of the initial value of the orbit inclination; 2, establishing an ordinary differential equation to acquire an orbit inclination at moment t and orbit right ascension of ascending node, and variation delta LTDN of local time of descending node at moment t; 3, judging the orbit drifting direction, wherein the biased quantity of the orbit inclination is negative if the direction is toward east, while the biased quantity of the orbit inclination is positive if the direction is toward west; and 4, traversing inclination biased quantities with step length of 0.0001 degree in a range from 0.0 to 0.1 degree, and respectively adding the corrected initial value of the sun synchronous orbit inclination in the step 1 to serve as an orbit initial value with inclination biased quantity, and carrying out the step 2 to obtain the variation of the local time of descending node at the moment t, arranging the maximum values of absolute values of variations into vectors according to a sequence, and the minimum value in the vectors is the inclination biased quantity. According to the method, the defect of low calculation accuracy of inclination biased quantity of the conventional sun synchronous orbit inclination biased quantity is overcome, and the orbit control capability is effectively improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
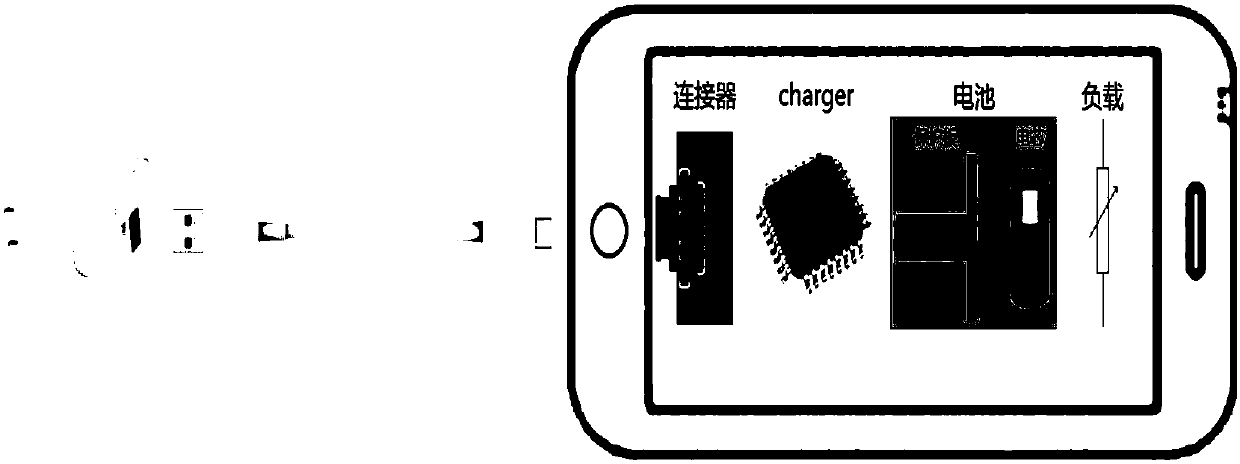
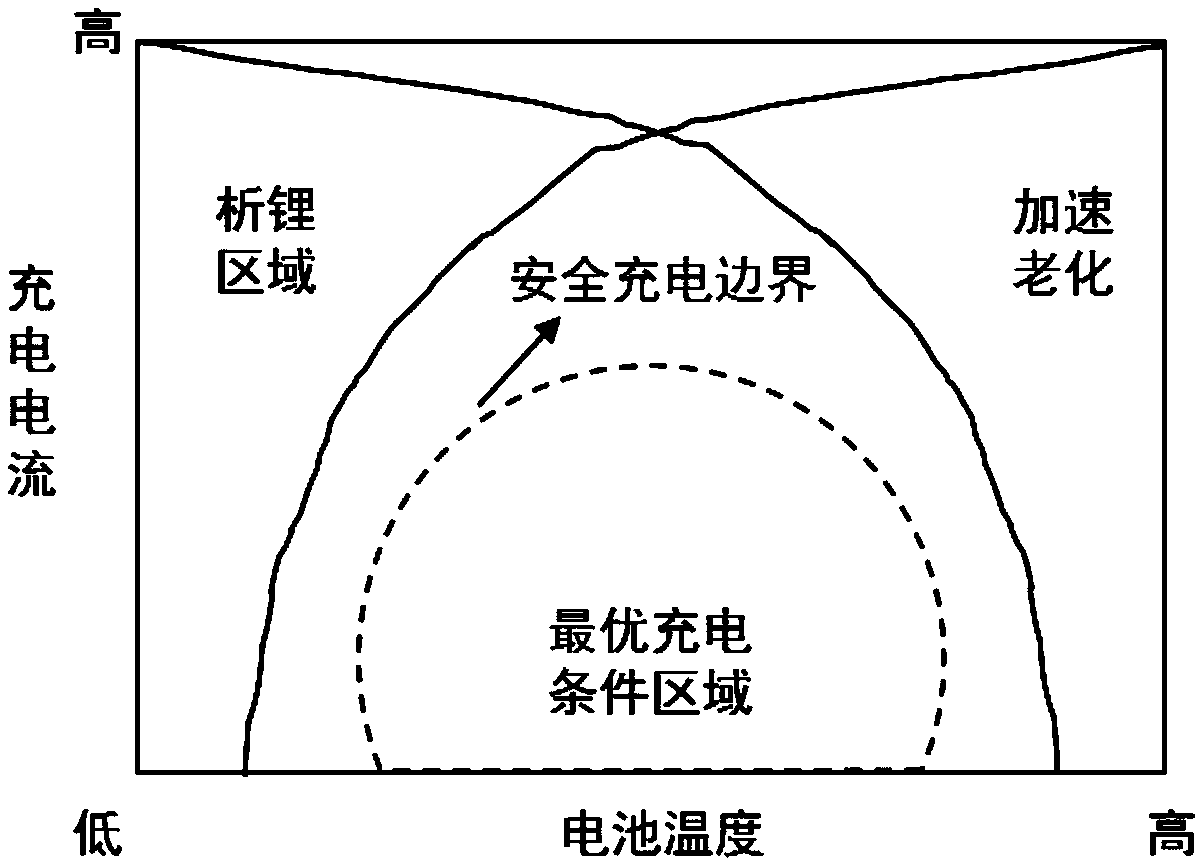
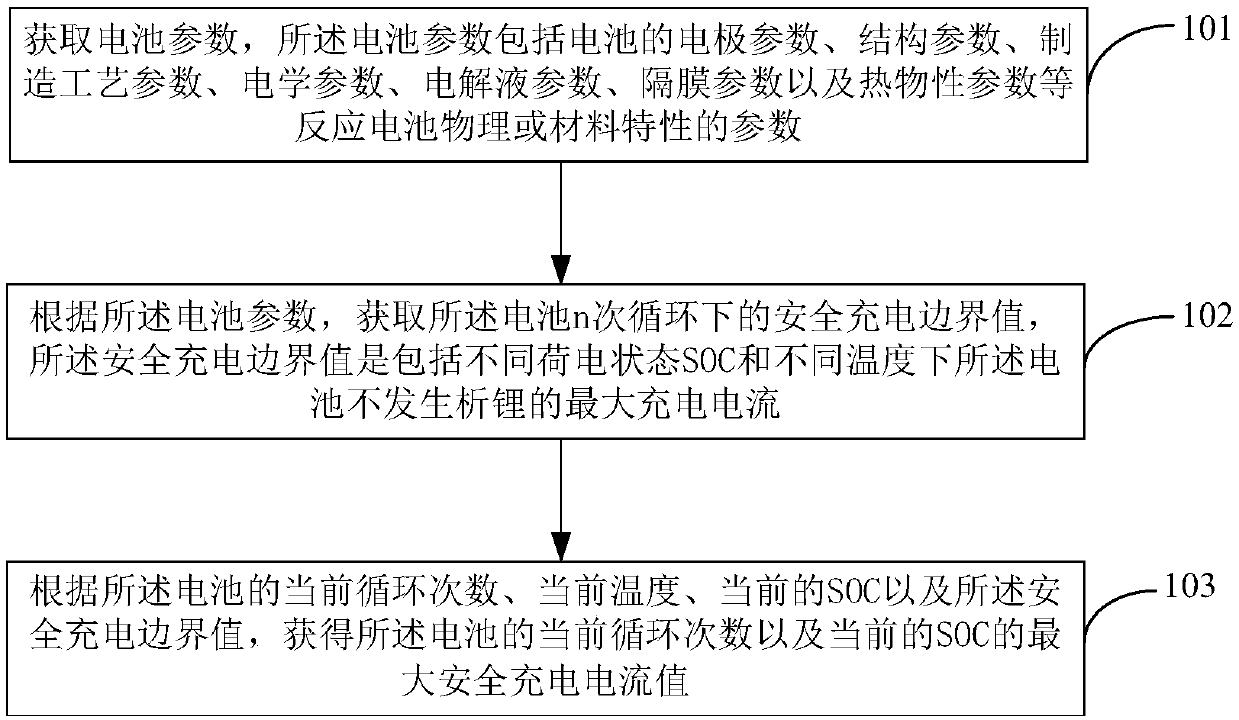
Charging method and device of battery
PendingCN109586373ADelay agingImprove fast charging speedCircuit monitoring/indicationSecondary cells charging/dischargingLithiumCharge current
The invention relates to a charging method of a battery. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a battery parameter, wherein the battery parameter comprises an electrode parameter of the battery;inputting a battery model expressed by ordinary differential equation according to the battery parameter; acquiring a safety charging boundary value of the battery under circulation for n times, wherein the parameter also comprises one or more of a structure parameter of the battery, a manufacturing process parameter, an electrical parameter, an electrolyte parameter, a separator parameter and athermo-physical property parameter, the safety boundary value is maximum charging current which the battery does not generate lithium separation under different states of charge (SOC) and different temperatures, n is larger than or equal to 2 but smaller than or equal to N, N is cycle lifetime of the battery, and circulation for n times is n(th) circulation selected from 0(th) circulation to N(th)circulation; and finally, acquiring maximum safety charging current value of the battery under current circulation frequency and current SOC according to the current circulation frequency, a currenttemperature, current SOC and the safety charging boundary value of the battery.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
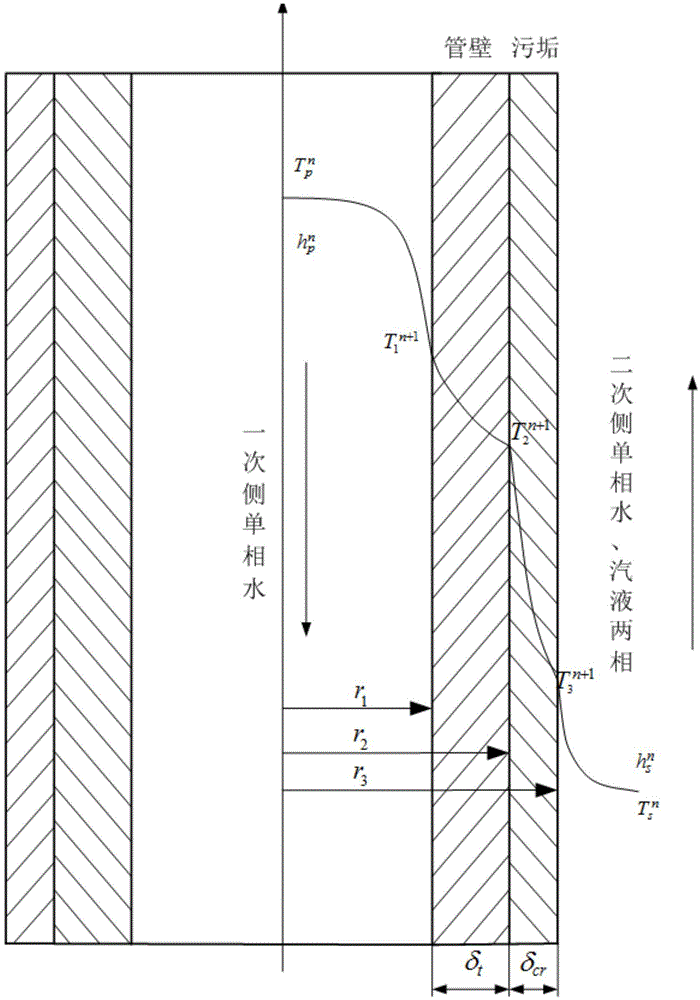
Heat conduction modeling and calculating method for natural circulation vapor generator
InactiveCN104091036AGuaranteed accuracyReduce workloadSpecial data processing applicationsNuclear powerPartial differential equation
The invention discloses a heat conduction modeling and calculating method for a natural circulation vapor generator. On the basis of a cylinder wall no-internal-heat-source one-dimensional heat conduction differential equation, distribution of the temperature in a heat transfer pipe in the natural circulation vapor generator and distribution of the temperature in dirt are expressed as a function of the primary side wall temperature and a function of the secondary side wall temperature of the heat transfer pipe, and a function of the outer surface temperature of the dirt, it is supposed that the heat transfer pipe and the dirt are in a quasi stable state in the dynamic process, and the problem of solving a partial differential equation is converted into the problem of solving an ordinary differential equation; in addition, when heat conduction and fluid thermotechnical hydraulic power are coupled, a loose coupling calculation method is adopted, on the basis of ensuring the model precision, the workloads of simulating calculation are greatly reduced, heat conduction of the natural circulation vapor generator is calculated fast, and the method is beneficial for achieving high-precision real-time simulating calculation of the natural circulation vapor generator and a nuclear power unit device, and has the great significance in guiding a nuclear power plant unit to operate safely and reliably.
Owner:NO 719 RES INST CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND
Spherical motor rotor position detection method based on MEMS sensor
InactiveCN108061855ASimple hardware structureEliminate errorsDynamo-electric machine testingOriginal dataComplementary filter
The invention relates to a spherical motor rotor position detection method based on an MEMS (Micro Electron Mechanical Systems) sensor. The method comprises steps: the original data of the MEMS sensorare acquired; zero bias error compensation is carried out on an angular velocity, and ellipsoid fitting compensation is carried out on an acceleration and a magnetic induction intensity; the angularvelocity, the acceleration and the magnetic induction intensity data after compensation are subjected to complementary filter-based data fusion and are substituted to a quaternion differential equation to obtain an attitude updating quaternion; the attitude updating quaternion is converted to an Euler angle, the change characteristics of the Euler angle in different intervals are combined, accurate interval transfer judgment is made, and conversion of the Euler angle in a full angle range change condition can be realized.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
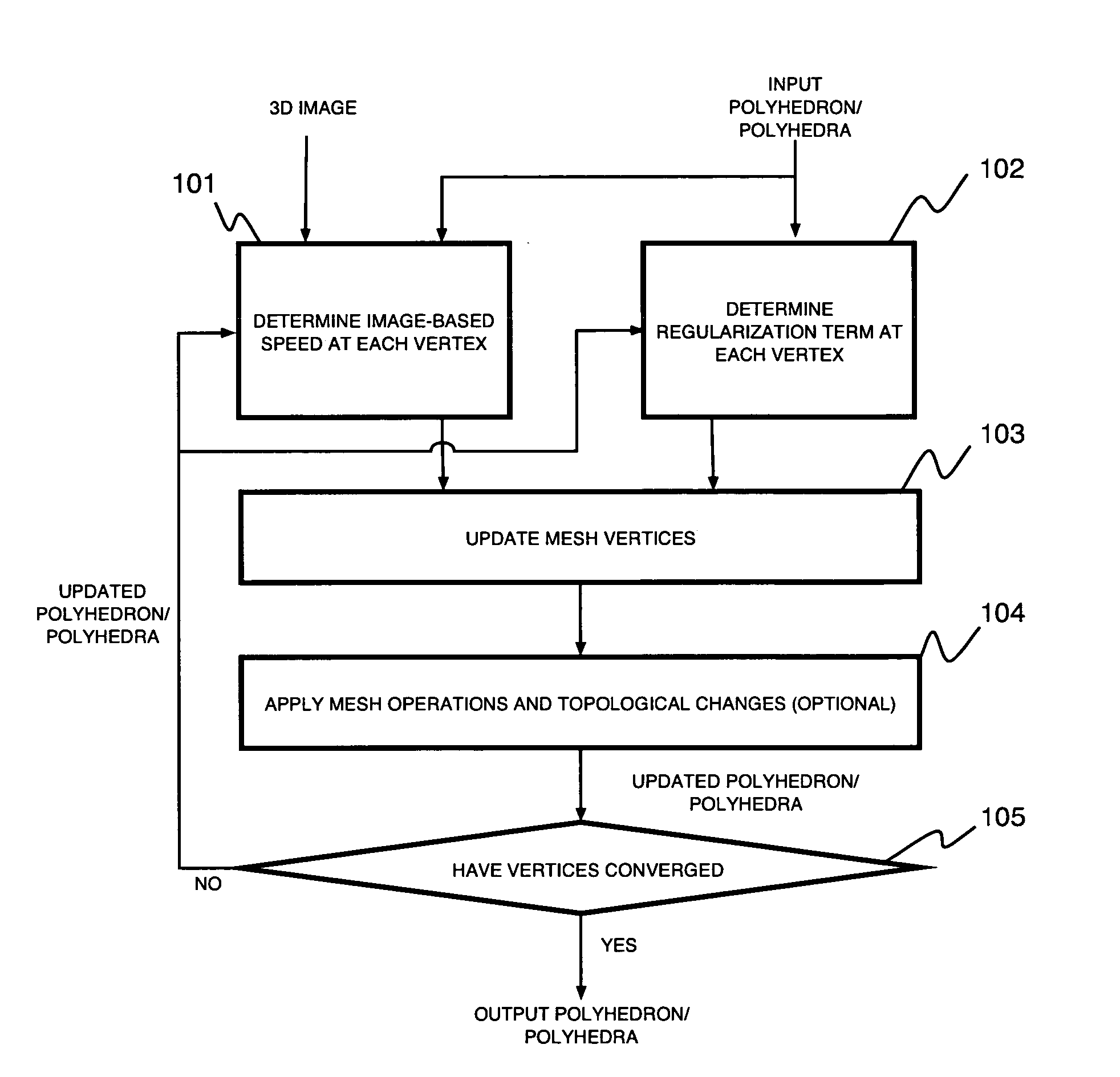
Active polyhedron for 3D image segmentation
InactiveUS20050195185A1Improve noiseEfficiently provideImage analysis3D-image renderingComputer graphics (images)3d image
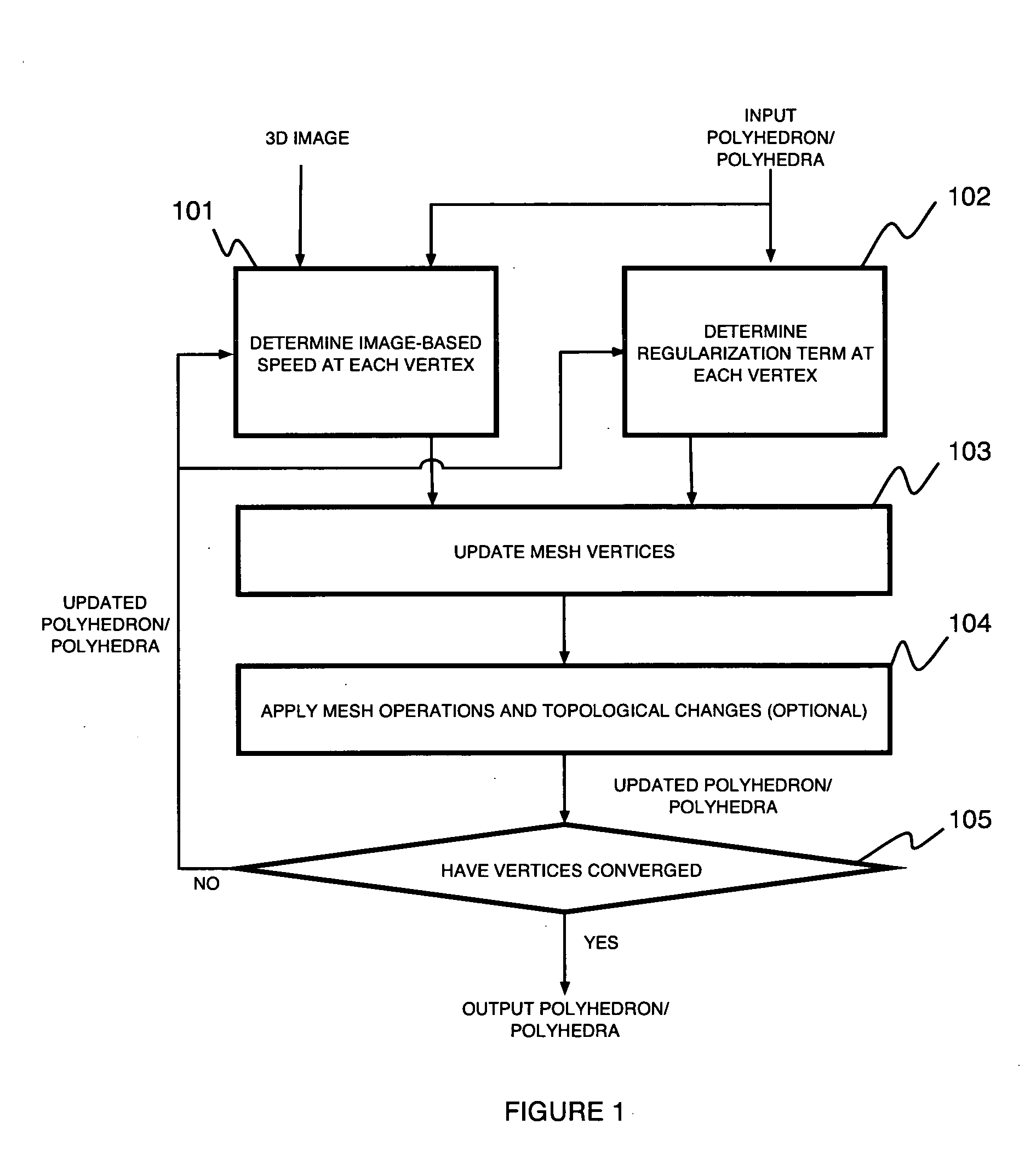
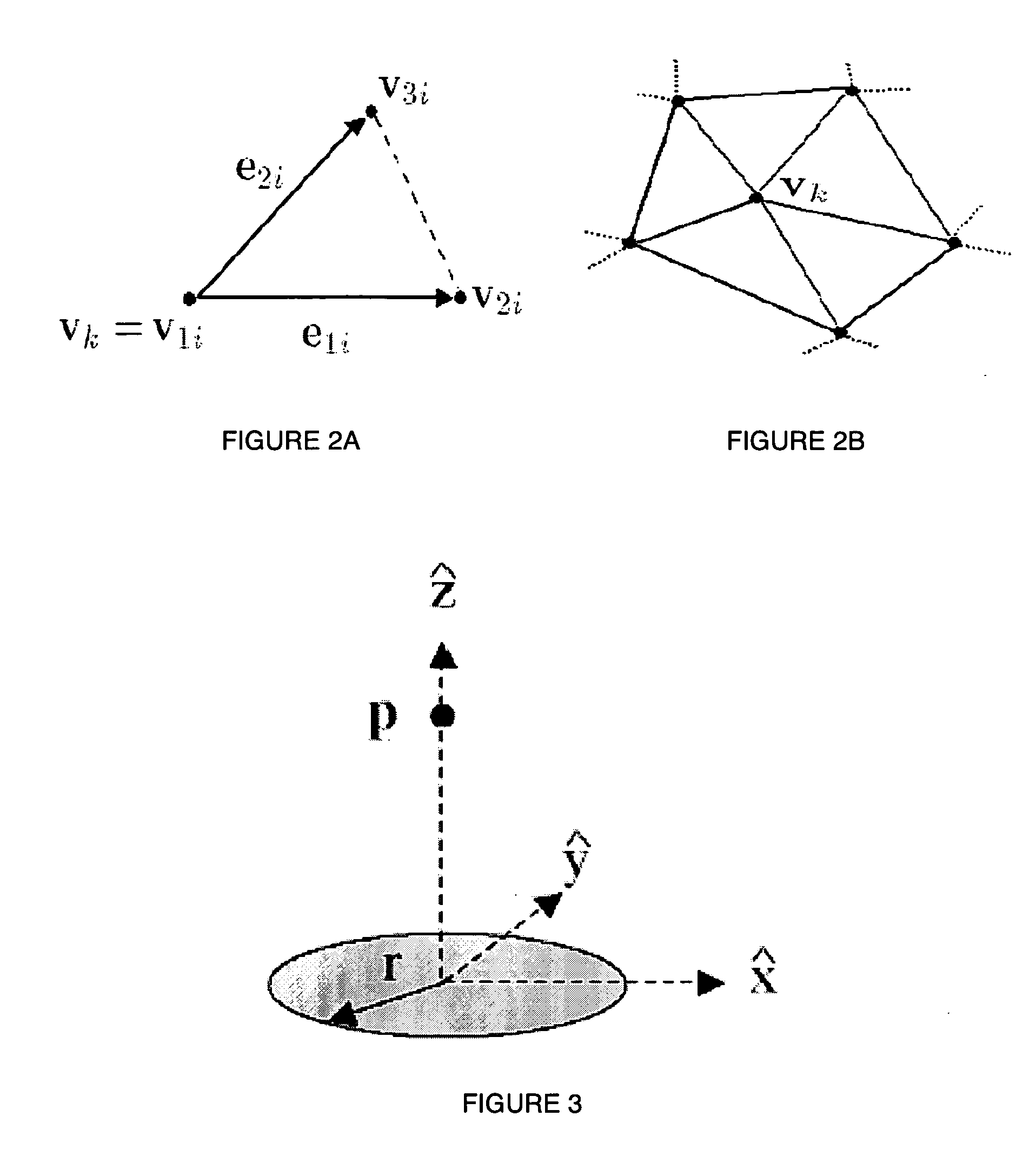
A method for three dimensional image segmentation of a volume of interest includes providing a three dimensional image of the volume of interest, providing an initial polyhedron having a plurality of mesh vertices within the three dimension image and determining an image-based speed at each vertex of the polyhedron using an ordinary differential equation (ODE) that describes the vertex motion of the polyhedron. The method further includes determining a regularization term at each vertex of the polyhedron, updating the plurality of mesh vertices of the polyhedron, integrating the image-based speed of each vertex over a face of the polyhedron, and determining an output polyhedron approximating a shape of the volume of interest.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Denoising method of strong noise pollution image on basis of partial differential equation
InactiveCN101916433AImprove denoising effectReduce distractionsImage enhancementPattern recognitionDiffusion
The invention discloses a denoising method of a strong noise pollution image on the basis of partial differential equation, mainly solving the problem of poor traditional denoising effect of the strong noise pollution image. The realization process comprises: (1) pretreating an input noise image u0, and recording the result as u; (2) calculating the partial derivative sum of the image u; (3) calculating the gradient module value of the image u; (4) according to the gradient and the gradient module value, building the partial differential equation; (5) calculating diffusion coefficients and psi in the partial differential equation; (6) utilizing the coefficients and psi, solving the partial differential equation to obtain a filter image; (7) calculating the peak signal to noise ratio PSNR of the filter image; and (8) repeating steps 2 to 7, when the PSNR value of the filter image output iteratively one time is smaller than that output iteratively in the previous time, stopping iteration, and outputting the previously iterated filter image. The invention has simple calculation and high operation speed, can better keep image texture details while smoothening strong noise and can be used for denoising a natural image with strong noise pollution.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Parametric elastic vibration analysis method of rotating annular periodic structure
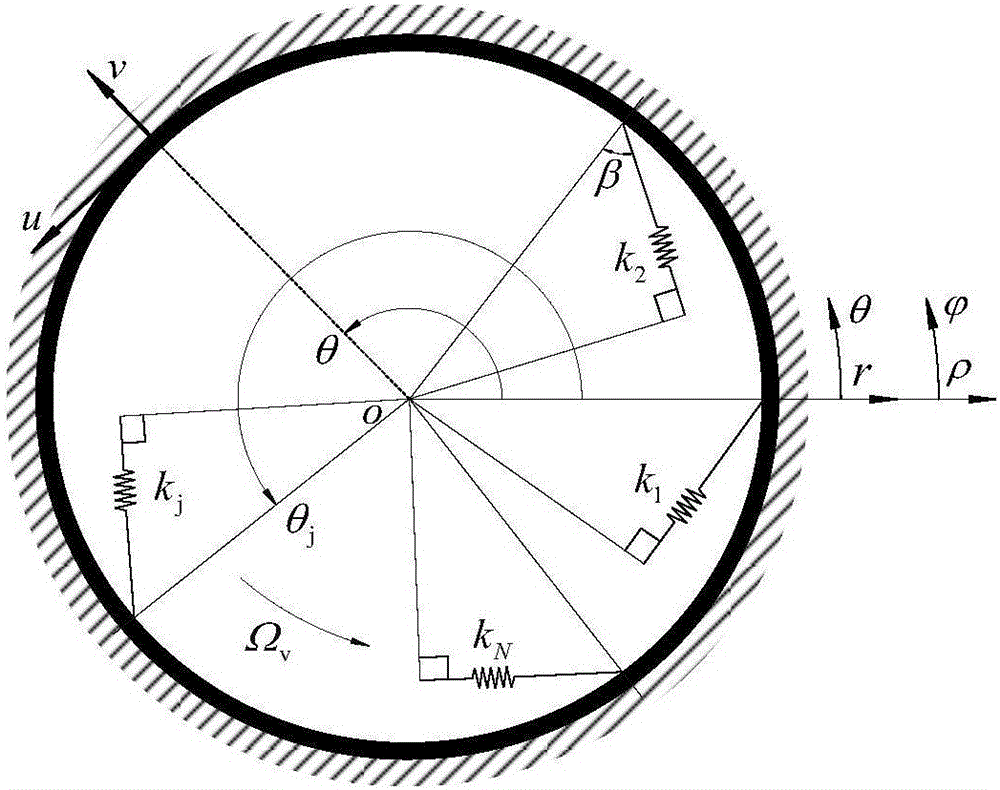
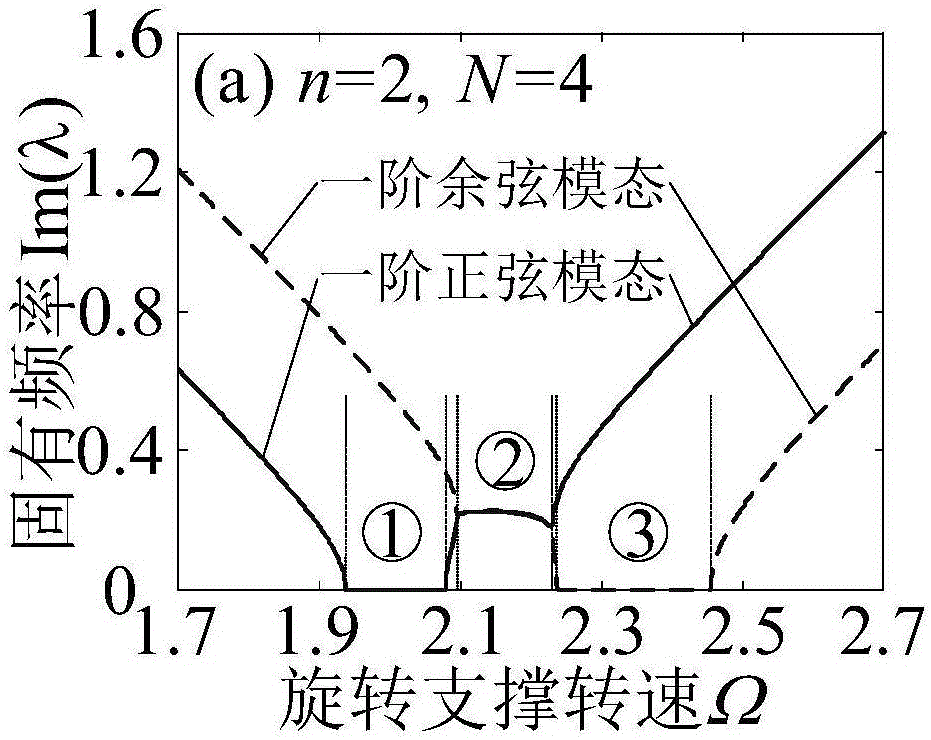
ActiveCN106547957AStable structural designOvercoming inefficienciesGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsDynamic modelsDynamic equation
A parametric elastic vibration analysis method of a rotating annular periodic structure comprises the steps of building a rigid-elastic coupling dynamic model of the rotating annular periodic structure according to a Hamilton principle under a global stationary coordinate system; introducing coordinate conversion, and converting the dynamic model to a support follow-up coordinate system so that a parametric item in an original equation is eliminated; performing discrete processing on a partial differential constant coefficient dynamic equation under the rotating support follow-up coordinate system by a Galerkin method to obtain an ordinary differential matrix equation; analyzing a characteristic value of the ordinary differential matrix equation by using a classical vibration theory; and respectively analyzing mode characteristic of the rotating annular periodic structure and a dynamic stability rule of parametric elastic vibration by employing an imaginary part and a real part of the characteristic value of the ordinary differential matrix equation. The parametric elastic vibration analysis method can be used for dynamic analysis of rotating machinery, calculation and solution of the mode characteristic of a system, and analysis on the dynamic stability and the dynamic response of the system.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Under-actuated release control method based on nonlinear space tether system
ActiveCN106054906AHas non-linear propertiesVerify stabilityAttitude controlIn planePartial differential equation
The invention provides an under-actuated release control method based on a nonlinear space tether system. The method comprises the following steps: 1, a dumbbell model is adopted, system dynamics differential equations are built according to a second kind Lagrange equation, and a dimensionless form is introduced in the differential equations; 2, based on a normal form expression for the above dynamics differential equations, expected values for a system in-plane pitching angle and an out-plane rolling angle are set, and the balance position of the system in the release process is obtained; 3, starting from the balance position of the system, a tether length change control law for realizing tether release is deduced and obtained; and 4, the range for the expected in-plane pitching angle is determined to ensure the tether release process to be asymptotically stable under effects of the control law. Numerical simulations show that the space tether can be released asymptotically stably under effects of the release control method provided by the invention, and an attractor capable of covering the balance point and an attraction domain with enough thickness can be found out.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Electronic power switch interpolation real-time simulation method
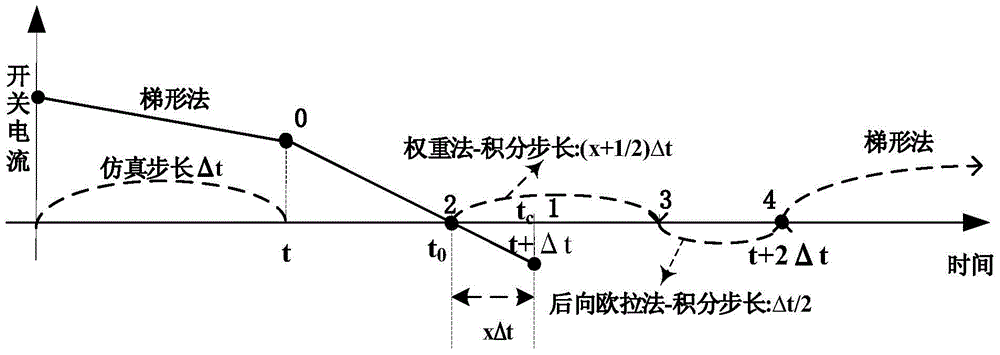
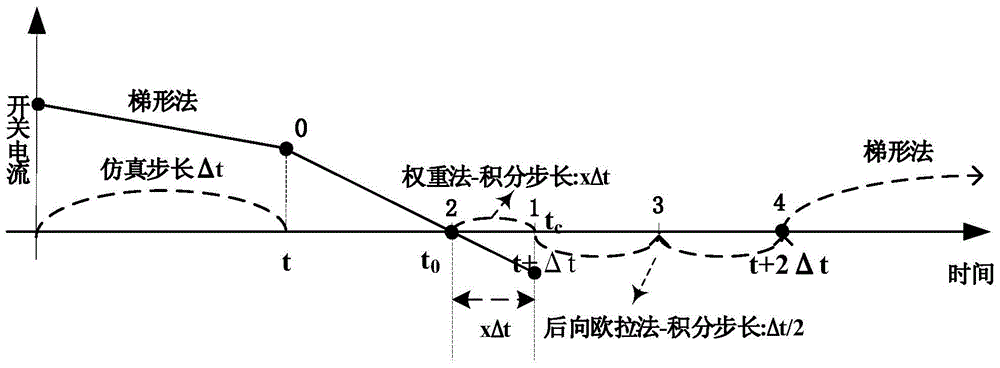
ActiveCN104462661ASolving Traditional Challenges of Electromagnetic Transient Simulation EfficiencySolve the problem of not being able to combineSpecial data processing applicationsElectric power systemTime moment
The invention discloses an electronic power switch interpolation real-time simulation method based on backward euler-trapezoidal weighted integral method. The electronic power switch interpolation real-time simulation method comprises the steps that at the turn-off time of an electronic power switch, linear interpolation is adopted for determining the accurate switch action time point and relevant state variables; according to the position of the switch action time point in the single-step simulation step size, an ordinary differential equation backward euler-trapezoidal weighted integral method is utilized for building a piecewise function, and the numerical solution of the system whole-step stimulation time point is obtained through integration, wherein in the process, all amounts of the system are reinitialized, and therefore the accurate network topology and system initial value at the time moment are obtained. A traditional problem that the electromagnetic transient stimulation efficiency is affected due to the fact that system topology high frequency changes are caused when the electronic power switch frequently acts during power system electromagnetic transient simulation is effectively solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Short-term climate forecast method based on Kalman filtering and evolution modeling
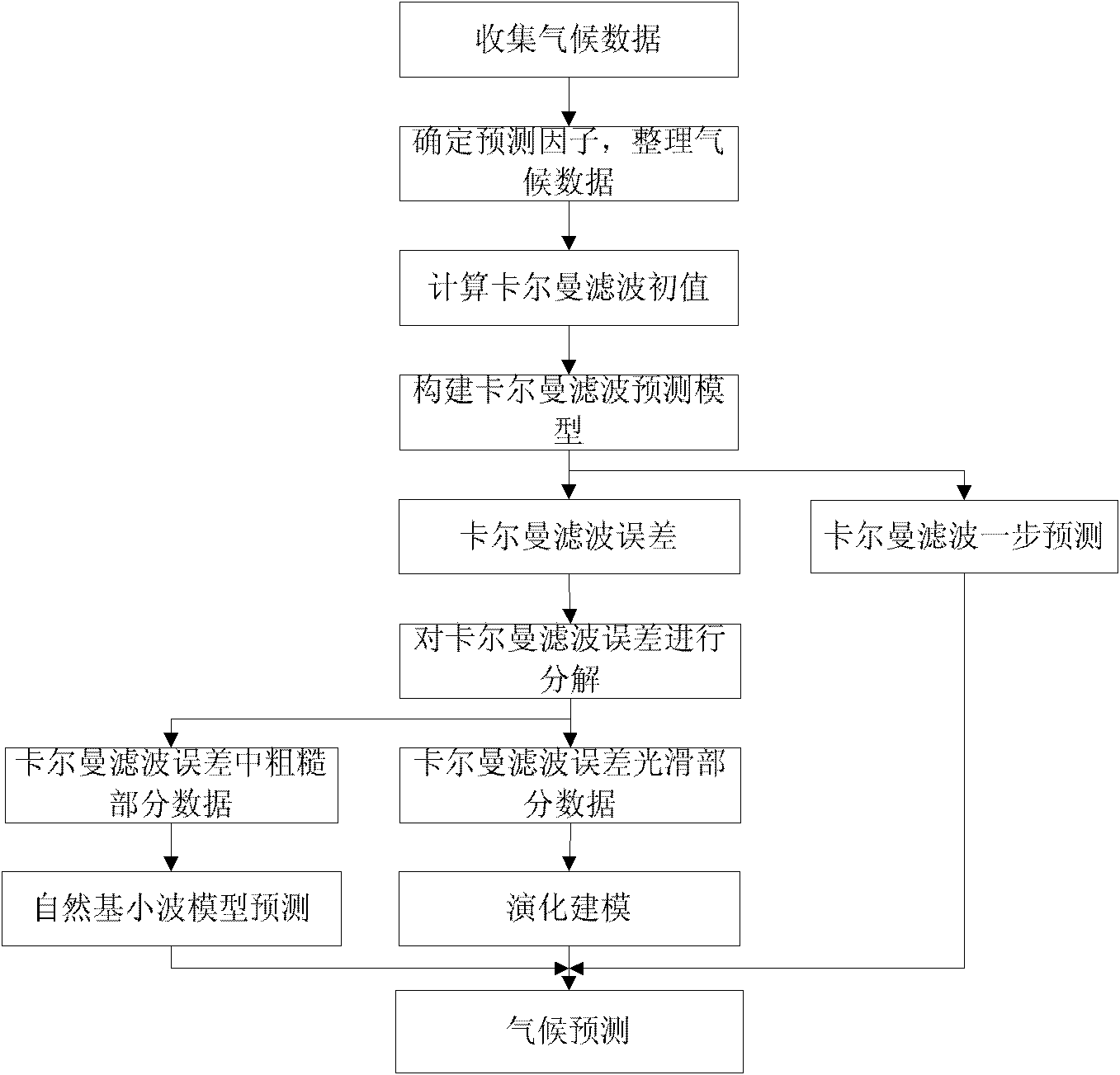
ActiveCN102183802AImprove forecast accuracyWeather condition predictionPredictive methodsShort terms
The invention discloses a short-term climate forecast method based on Kalman filtering and evolution modeling. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a linear model about a forecast factor by the Kalman filtering at first; and simulating an error sequence approaching the Kalman filtering by using a non-linear ordinary differential equation math model on the basis of the linear model a, and performing error forecast. An evolution algorithm is an evolution process for simulating the nature by using a computer, in particular a calculation method for solving complicated problems by simulating biological evolution processes, and has the intelligent characteristics of self-adaptation, self-organization, self-learning, internal parallelism and the like. The two algorithms are combined with each other, so the natural characteristic of the climate can be simulated better than being simulated by a pure linear model, so the climate forecast precision is enhanced. By the method, short-term sunshine duration, temperature and rainfall can be forecast, so future knowledge of the short-term climate can be provided.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
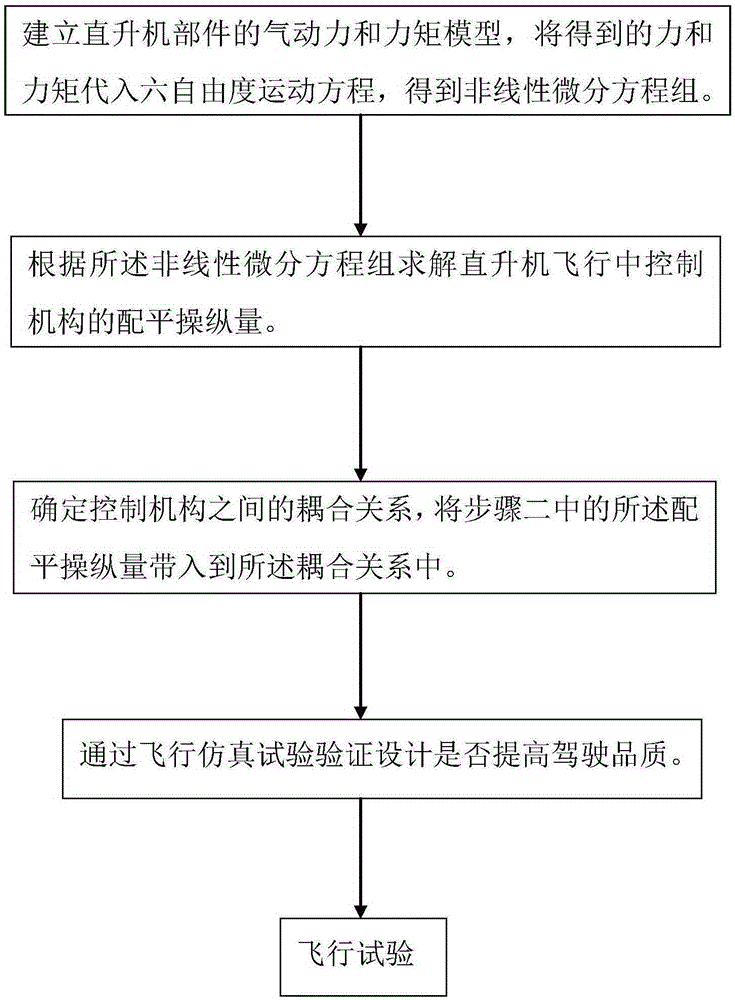
Decoupling design method for helicopter control
ActiveCN105260566AReduce driving skill requirementsReduce workloadSpecial data processing applicationsDriving skillsSystem of differential equations
The invention discloses a decoupling design method for helicopter control, relating to the technical field of helicopters. The decoupling design method for a helicopter comprises the following steps: 1, establishing an aerodynamic force and moment model for a helicopter component, and substituting the obtained force and moment into a movement equation of six freedom degree to obtain a nonlinear differential equation set; 2, solving trim control amounts of control mechanisms in helicopter flight according to the nonlinear differential equation set; 3, determining a coupling relationship between the control mechanisms, and substituting the trim control amounts in the step 2 into the coupling relationship; 4, verifying that whether the design improves the driving quality or not via a flight simulation test; 5, carrying out flight testing. The decoupling design method disclosed by the invention has the advantage that in the flight process, the tail rotor tension and the horizontal trim can be automatically adjusted just by the total pulling moment. The control correction precision is improved, the workload of a pilot is reduced, and the requirements on driving skills of the helicopter are reduced.
Owner:CHINA HELICOPTER RES & DEV INST
Nonlinear initial alignment method for all-altitude strapdown inertial navigation system
ActiveCN106153073AAvoid double countingTo achieve the purpose of navigation solutionMeasurement devicesNonlinear filterMatrix differential equation
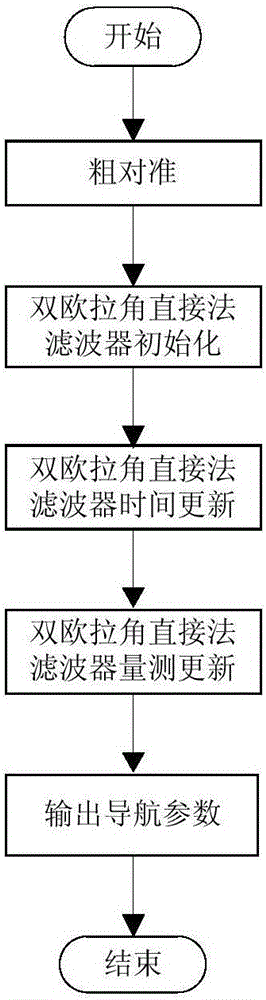
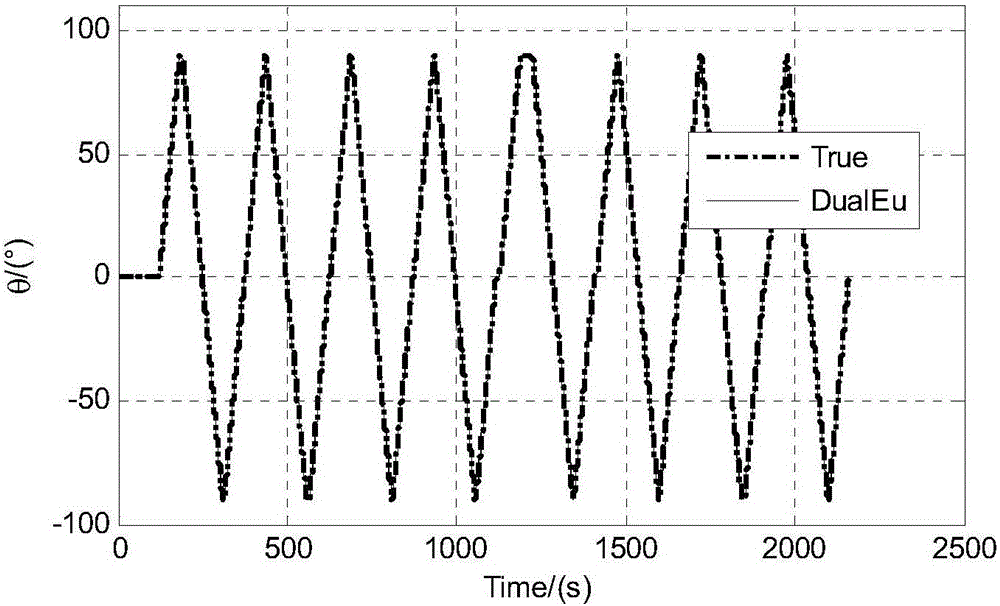
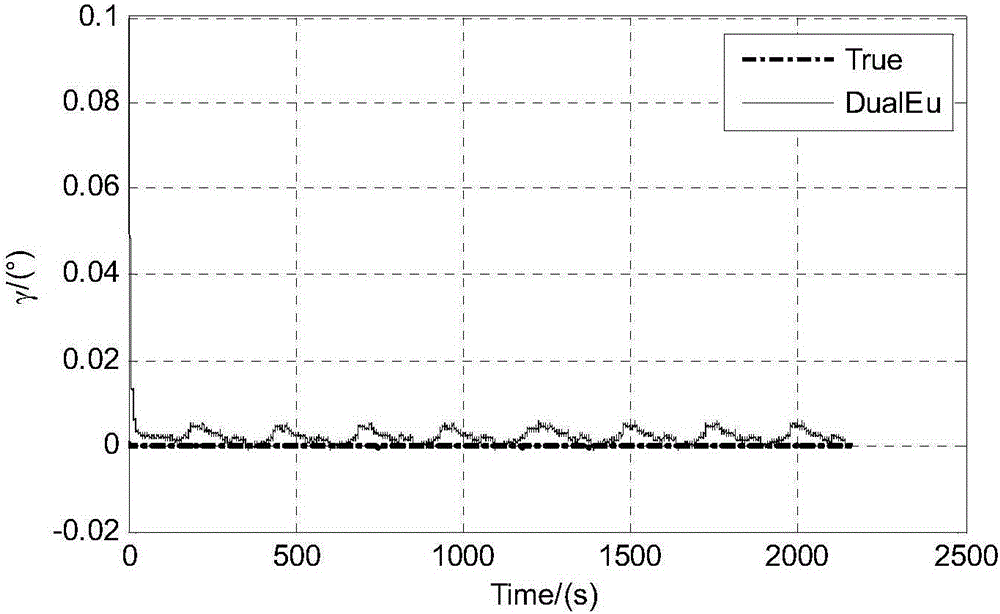
The invention discloses a nonlinear initial alignment method for an all-altitude strapdown inertial navigation system, including the main steps of roughly aligning the strapdown inertial navigation system; initiating a double-Euler-angle direct method nonlinear filter of the strapdown inertial navigation system, updating time, measuring measurements, and switching forward and reverse Euler-angle direct methods. The double-Euler-angle direct method and the direct method are fused, the problem of singularity in the single-Euler-angle direct method is solved, the nonlinear initial alignment method is applicable to cases with high carrier dynamics; system equations are mainly velocity differential equations and Euler-angle differential equations, and models are more precise than first approximation of the direct method; navigation resolution is implemented in the filtering process, filtering outputs are navigation parameters, repeated calculations in mechanically arranged equations are avoided, and an algorithm is simpler than the direct method; compared with quaternion direct method, the nonlinear initial alignment method has no need for filtering step modification, and the algorithm is simple.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Industrial process dynamic optimization system and method based on nonlinear conjugate gradient method
InactiveCN101763087AThe optimization process is accurateEfficient optimization processTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlProcess dynamicsConjugate gradient method
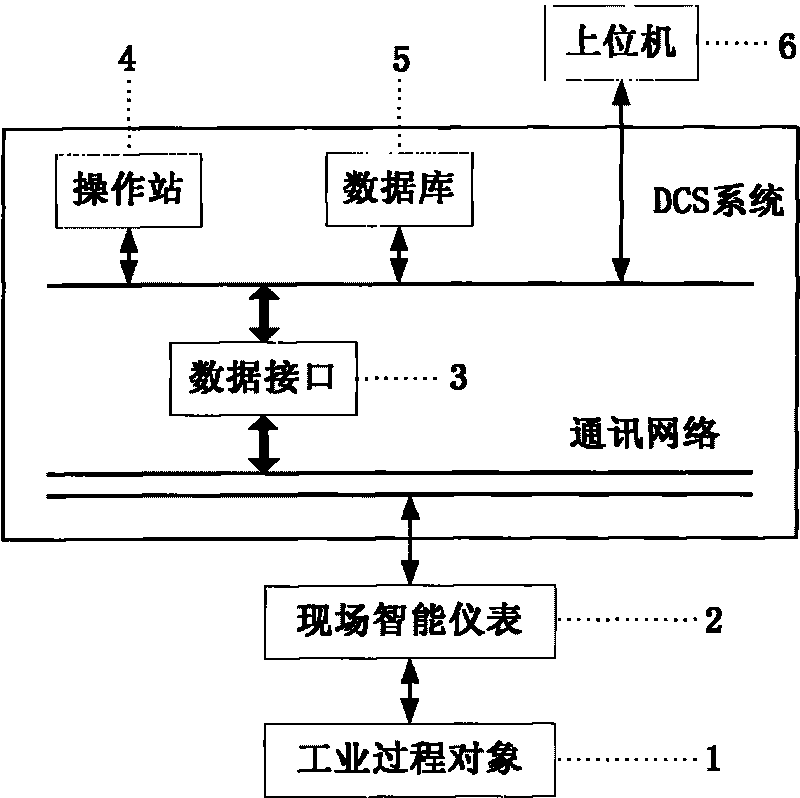
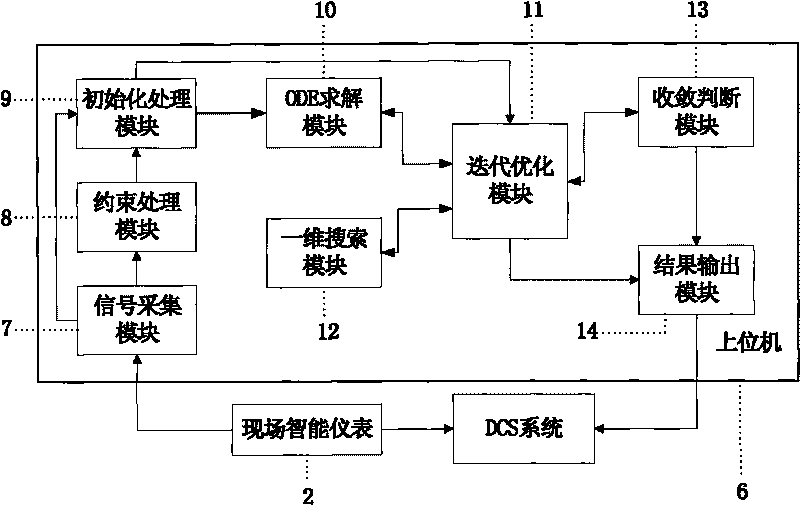
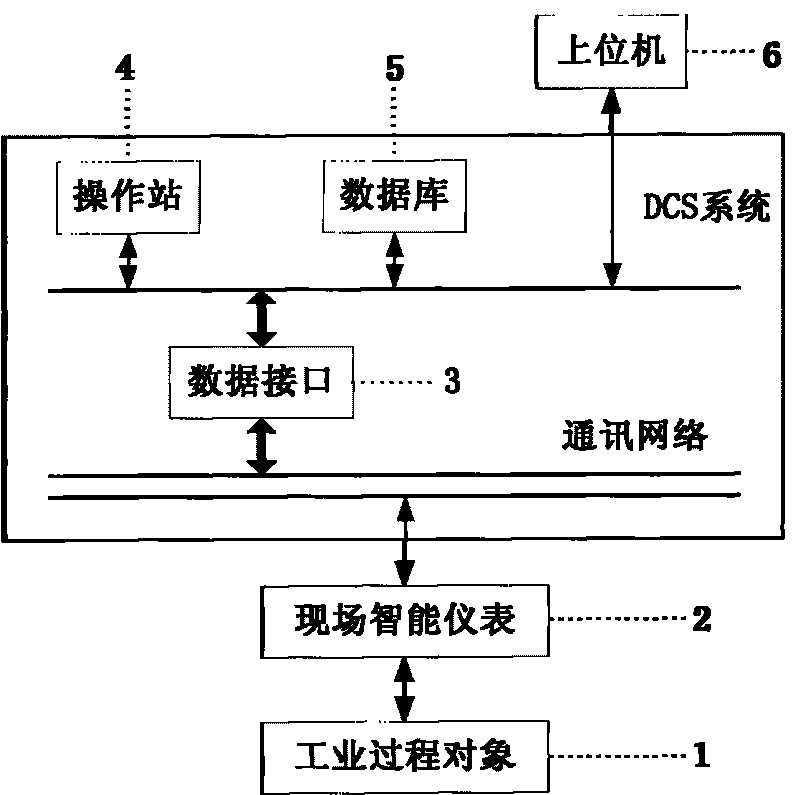
The invention provides an industrial process dynamic optimization system based on a nonlinear conjugate gradient method, which comprises an in-site intelligent meter, a DCS system and a host machine, wherein the in-site intelligent meter is connected with an industrial process object, the host machine comprises a restriction processing module, an initialization processing module, an ODE solving module, an iteration optimization module and a convergence judgment module, the restriction processing module is used for processing the control variable boundary restriction in the optimization process, the initialization processing module is used for setting initialization parameters, the OED solving module is used for solving ordinary differential equation groups of a dynamic optimization question, the iteration optimization module is used for searching a decision vector w which makes a target function J optimum, the convergence judgment module is used for judging whether the error absolute value of the target value obtained by the current convergence and the target value obtained by the former convergence is smaller than or equal to the set convergence precision omicron, and the current optimum vector w*, the current optimum target value J* and the current convergence time number k are stored if the error absolute value of the target value obtained by the current convergence and the target value obtained by the former convergence is smaller than or equal to the set convergence precision omicron. The invention also provides an industrial process dynamic optimization method based on the nonlinear conjugate gradient method. The invention can simultaneously meet the requirements of high efficiency and high precision of the on-line dynamic optimization solving.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Reusable parameter module model building method for space contineous deformation MEMS
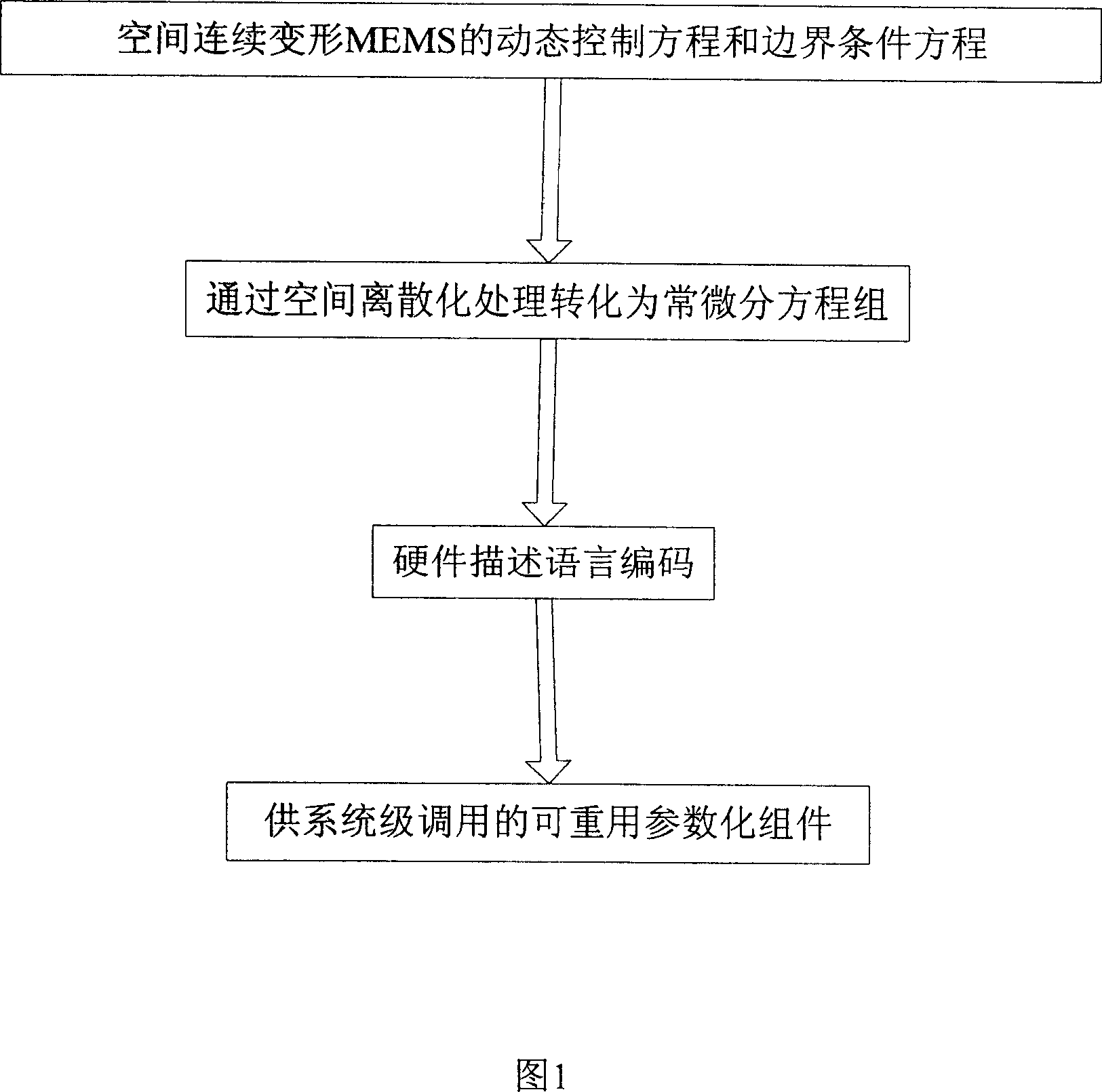
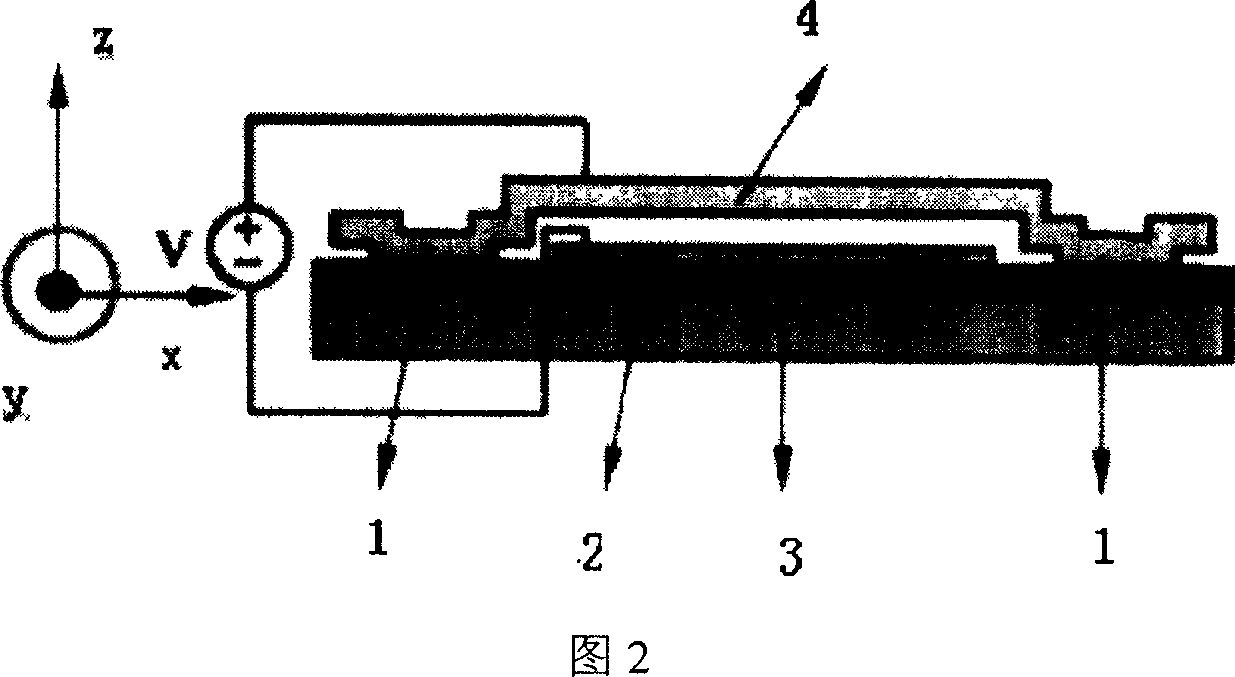
InactiveCN101051328AConvenient characteristic simulation analysisSemi-permeable membranesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesDynamic equationDiscretization
A modeling method of reusable parameterized component for space continuous deformation MEMS includes confirming each dynamic control equation and boundary condition equation of MEMS device, carrying out space discretization on dynamic control equation and converting said control equation to be constant-differential equation set, utilizing hardware description language of analog and mixed signal to carry out coding for realizing function description, plotting schematic diagram of MEMS device and connecting said diagram with code to form MEMS device being called in system modeling and in simulation analysis.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method and apparatus for executing high performance computation to solve partial differential equations and for outputting three-dimensional interactive images in collaboration with graphic processing unit, computer readable recording medium, and computer program product
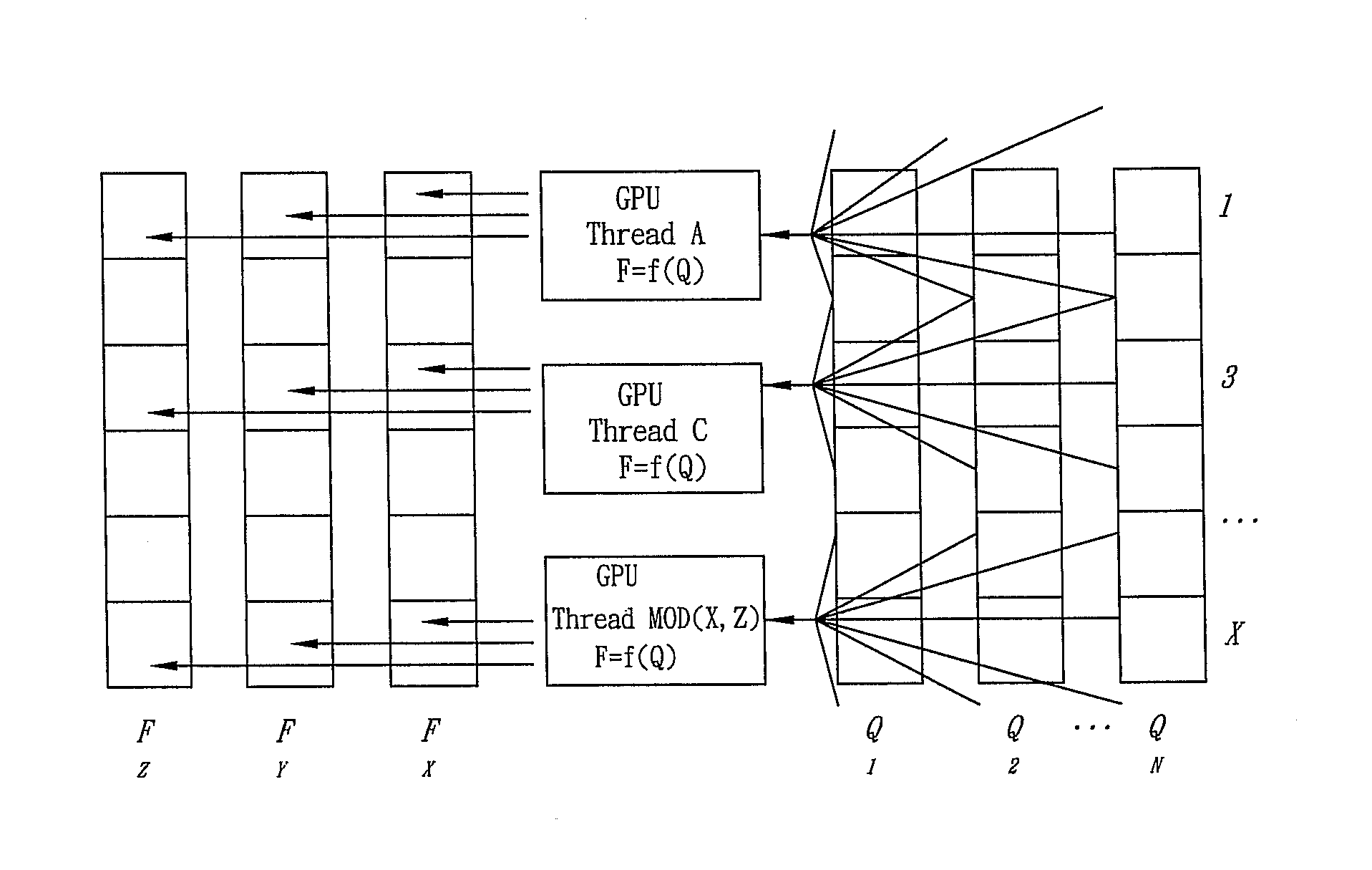
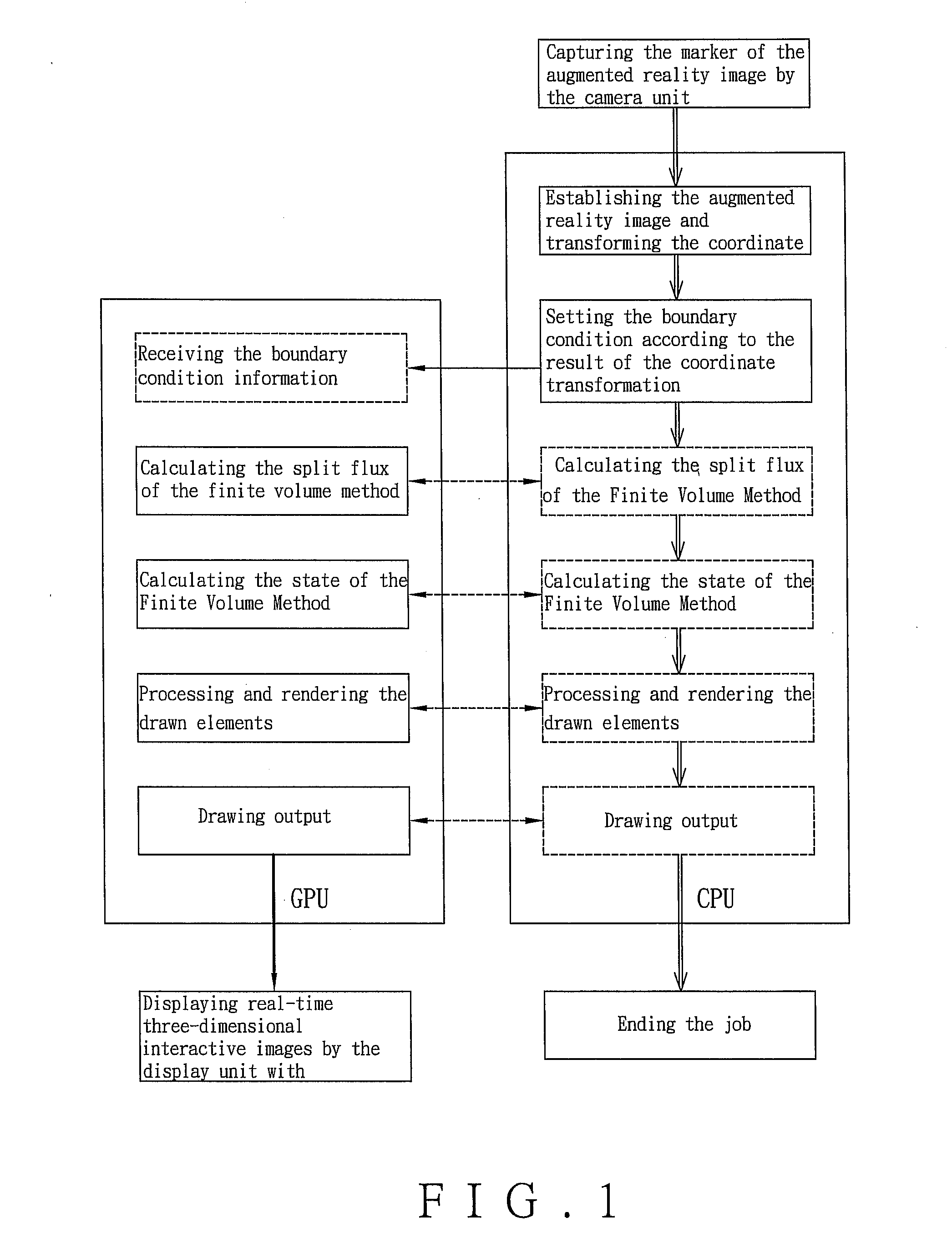
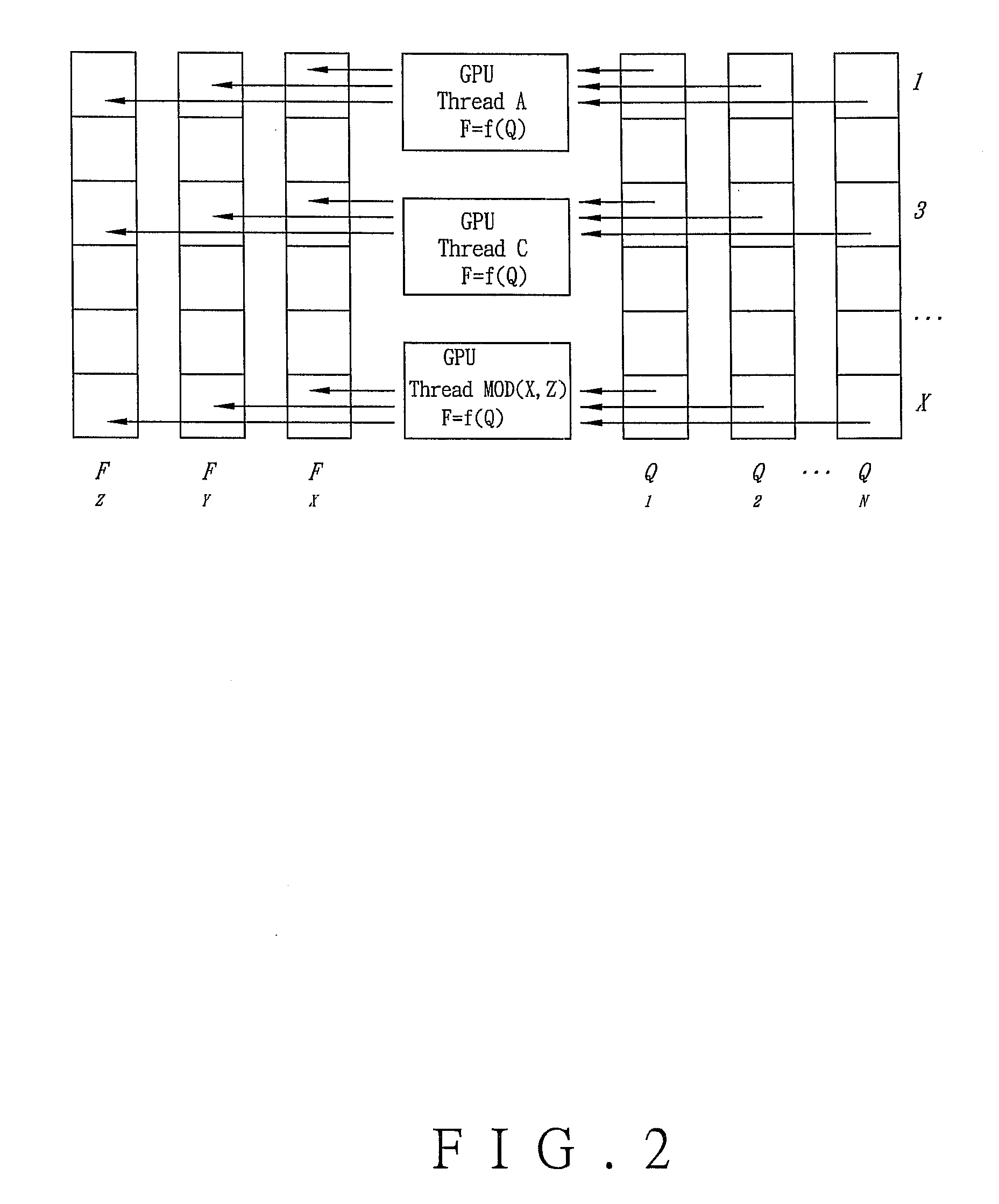
InactiveUS20130147786A1High performance computationIncrease speedImage generationComplex mathematical operationsPartial differential equationVisual perception
A method and apparatus for executing high performance computation to solve PDEs and for outputting three-dimensional interactive images in collaboration with a GPU is disclosed. The method includes: (A) executing a coordinate transformation to a three-dimensional image by the CPU, setting a boundary condition required by a simulation according to a coordinate transformation result, and inputting the boundary condition to the GPU; (B) executing a numerical simulation of the PDEs and the boundary condition in the step (A); (C) processing and rendering each drawn element by the GPU according to a numerical simulation result to draw a visual image featured with physical quantity variation and overlapping the visual image on the three-dimensional image to form the three-dimensional interactive images.
Owner:NAT APPLIED RES LAB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com