Non-coded RNA and disease association prediction method based on sparse subspace learning
A technology of subspace learning and prediction method, applied in the field of non-coding RNA and disease association prediction, which can solve the problems of expensive, time-consuming, and high false positives of transition components
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
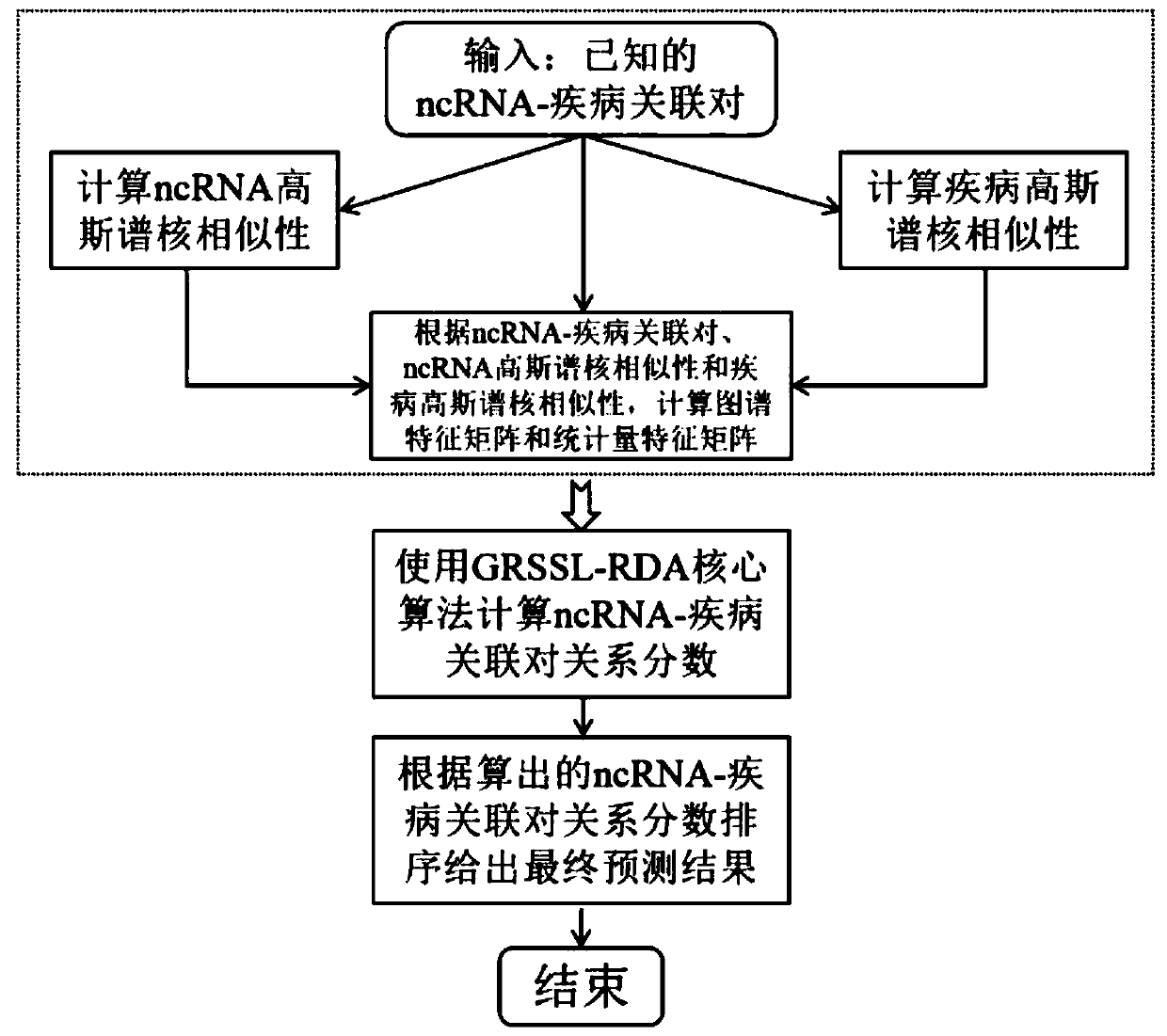
[0072] The technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention will be clearly and completely described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments are only some of the embodiments of the present invention about miRNA, not all of them. Example (ncRNA also includes other types, such as lncRNA, circRNA, etc.). Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without making creative efforts belong to the protection scope of the present invention.
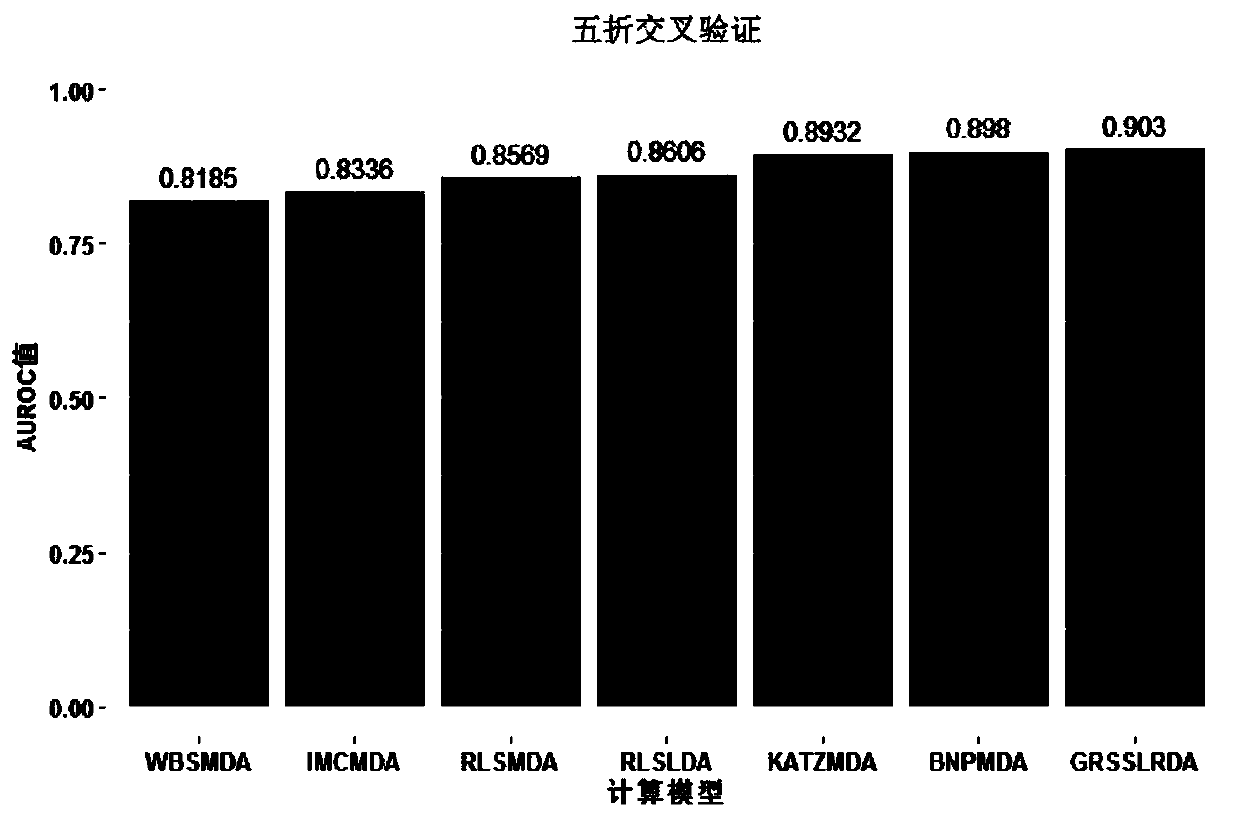
[0073] The known human miRNA-disease association data used in the embodiments of the present invention are retrieved from the database HMDDV2.0 and then downloaded (website http: / / www.cuilab.cn / hmdd), and the downloaded data are After cleaning, classification and normalization, 5430 experimentally validated human miRNA-disease associations, including 383 diseases ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com