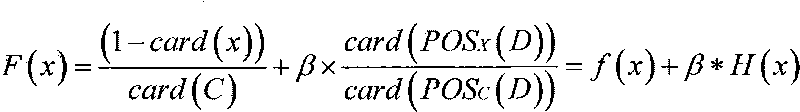Patents
Literature
59 results about "Gene Position" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The gene is the basic unit of heredity. A gene consists of a long sequence of DNA nucleotides which occupy a specific position (locus) on a chromosome (see Figure 1). Genes can carry the code for synthesizing proteins and RNA molecules, and also regulate the transcription of RNA sequences.
Primers for detecting plurality of newborn inherited metabolic disease causing genes and kit
ActiveCN105177160AQuick screeningConducive to screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyExon intron
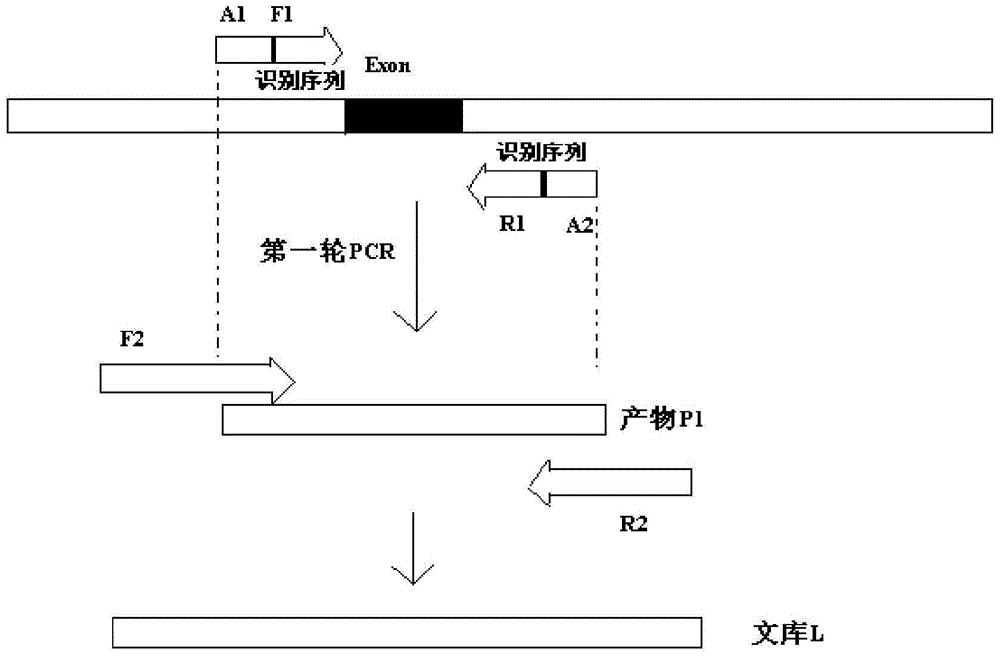
The invention discloses a design way of primers for in-vitro qualitative detection of newborn inherited metabolic disease genes. The design way comprises the following steps: (1) acquiring relevant disease-causing gene information of inherited diseases: acquiring the relevant disease-causing gene information, including gene location information and mutation site information of a plurality of inherited diseases through an OMIM (Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man) database, and acquiring exon and intron information of relevant genes from an NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information) database according to the obtained gene information; (2) designing primers specific to the relevant genes: designing corresponding specific primers F1 and R1 specific to an exon and an exon-intron combination area of each gene. The invention also discloses the first-round PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) primer sequence list of syndromic deafness, a first-round PCR primer list of G6PD genes, and a first-round PCR primer sequence list of SLC12A3 genes. The primers can be used for detecting relevant genes of 22 types of common newborn inherited diseases.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Major SNP marker capable of affecting pork aliphatic acid and application of major SNP marker in breeding pigs meat quality heredity improvement
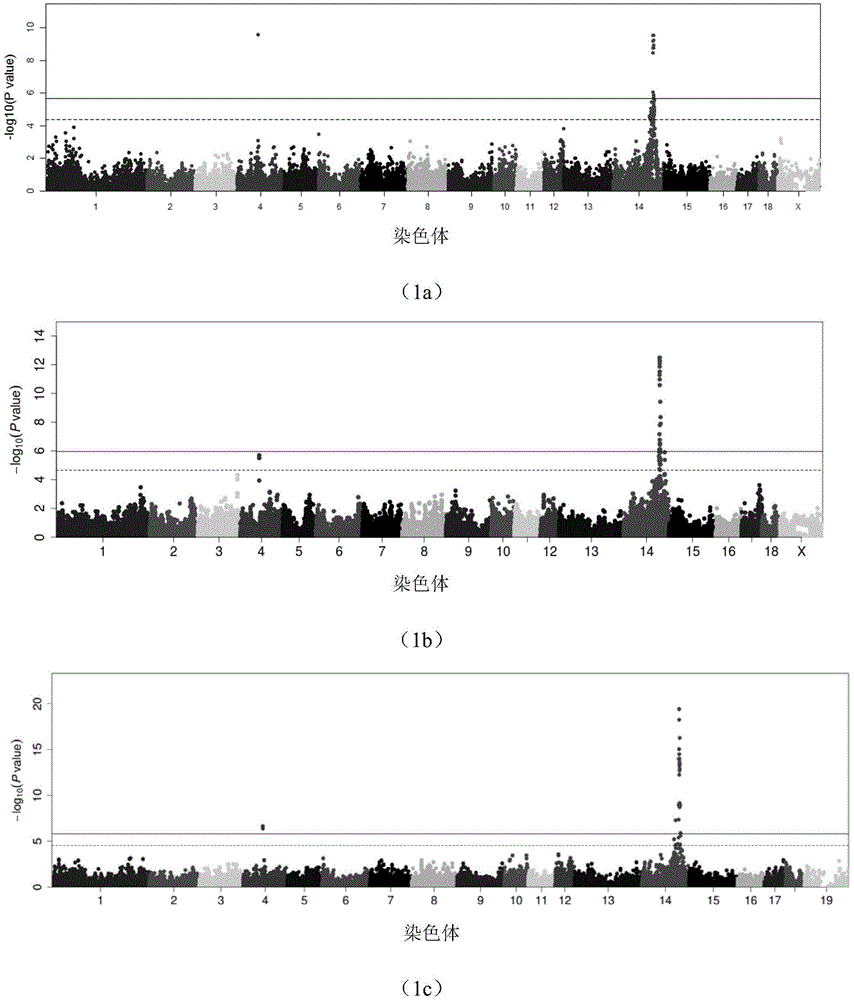
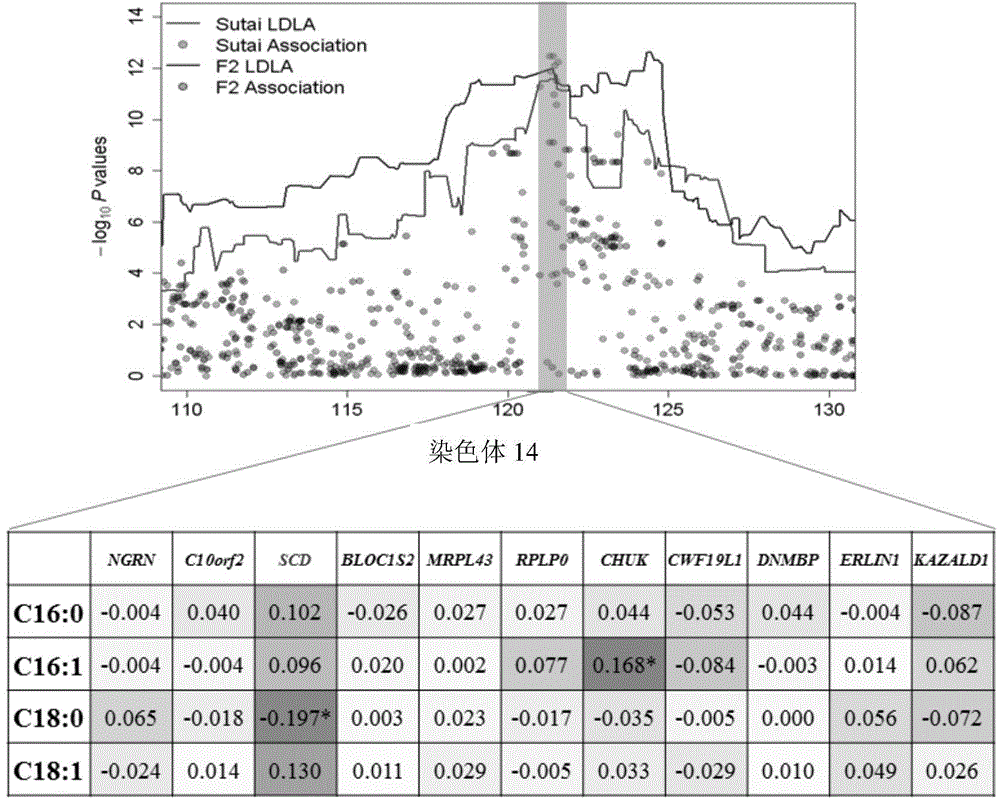
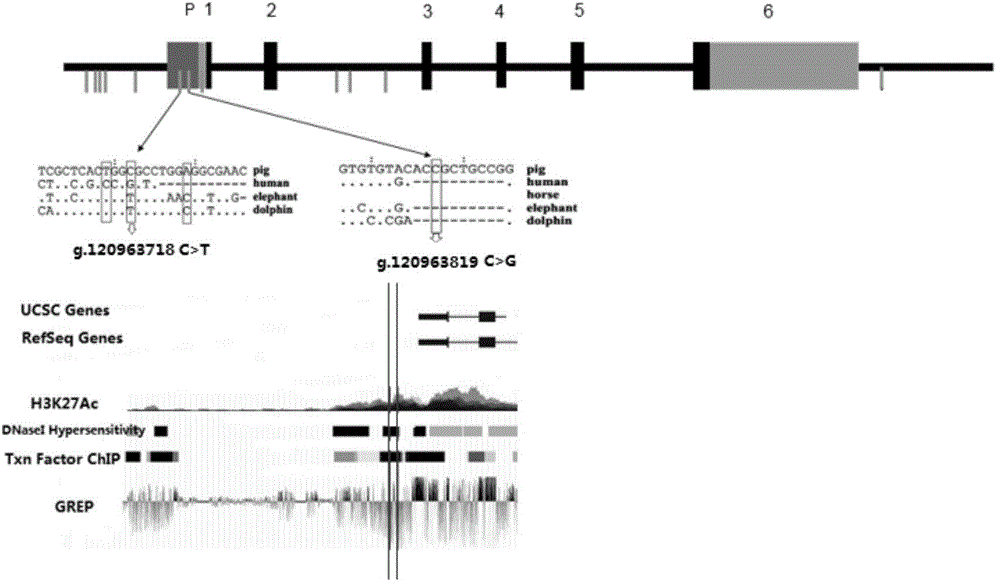
The invention provides a major SNP marker capable of affecting pork aliphatic acid component, the SNP marker is positioned on a nucleotide sequence of pig SCD gene, the site marked by SNP is g.120963718 nucleotide site on international pig genome version 10.2 reference sequence pig No.14 chromosome, and is the mutation of C and T, which is corresponded to 4513rd site on SEQ ID NO: 1, the position marked by SNP is g.120963819 nucleotide site on international pig genome version 10.2 reference sequence pig No.14 chromosome, and is the mutation of C and G, which is corresponded to 4614th site on SEQ ID NO: 1, above two mentioned sites are completely linked; the SNP marker can increase the monounsaturated fatty acid content and / or reduce saturated fatty acid content of pig, the monounsaturated fatty acid is C18: 1 and / or C16: 1, and the saturated fatty acid is C18: 0 and / or C16: 0. The invention also provides a nucleotide sequence of SCD gene positioned on pig No.14 chromosome, and the application of the SNP marker and the nucleotide sequence in breeding pigs meat quality heredity improvement.
Owner:JIANGXI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
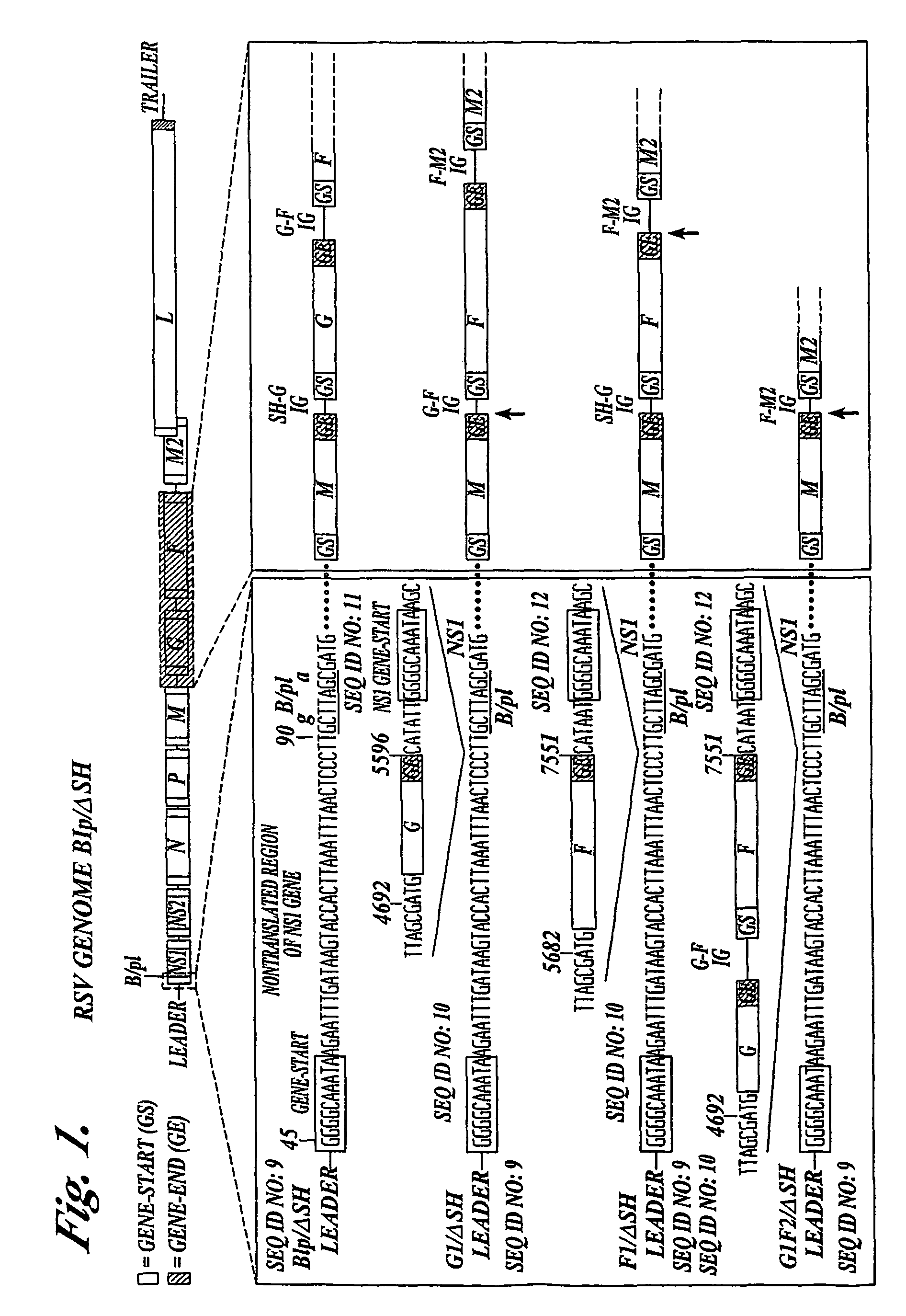
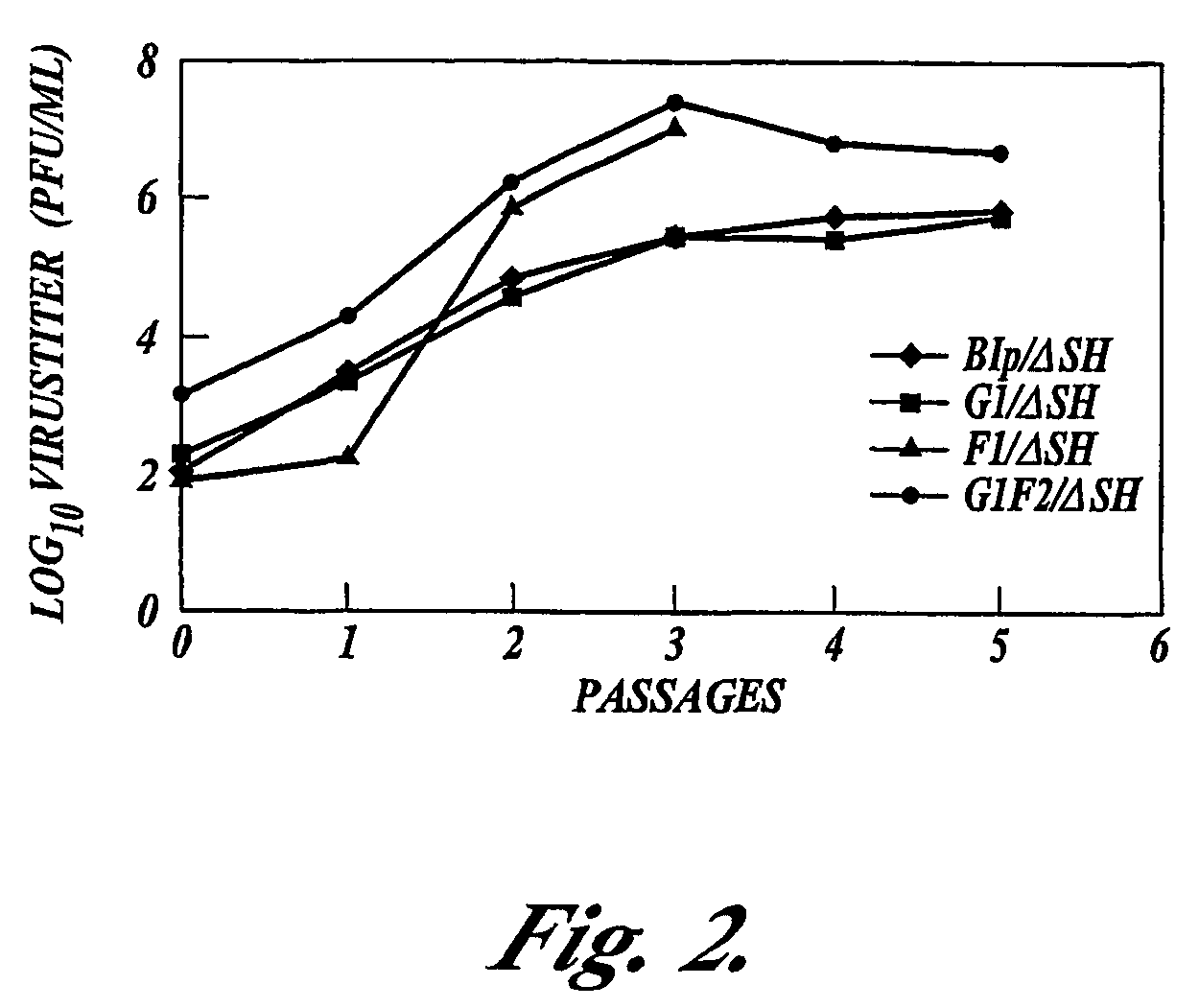
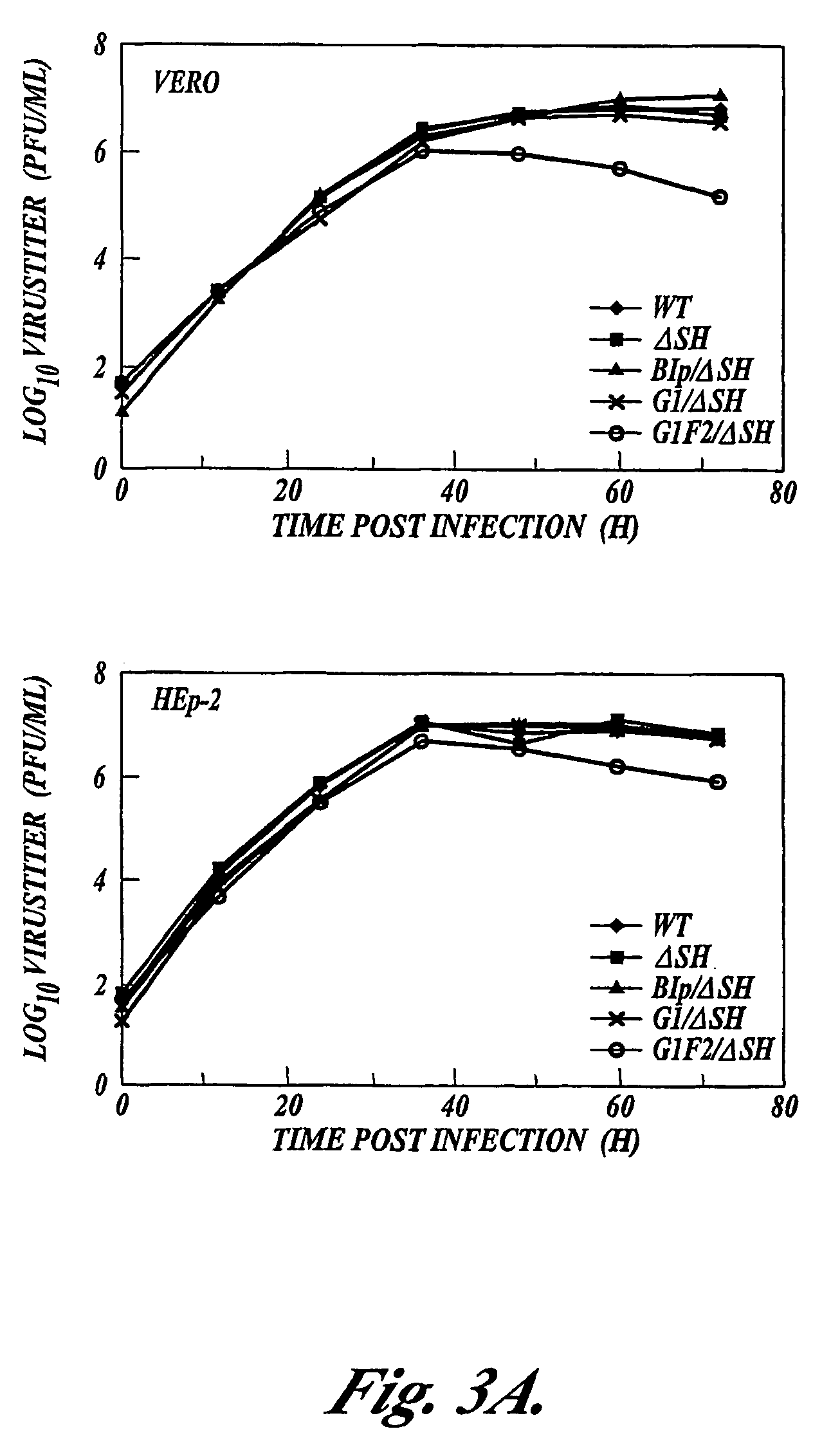
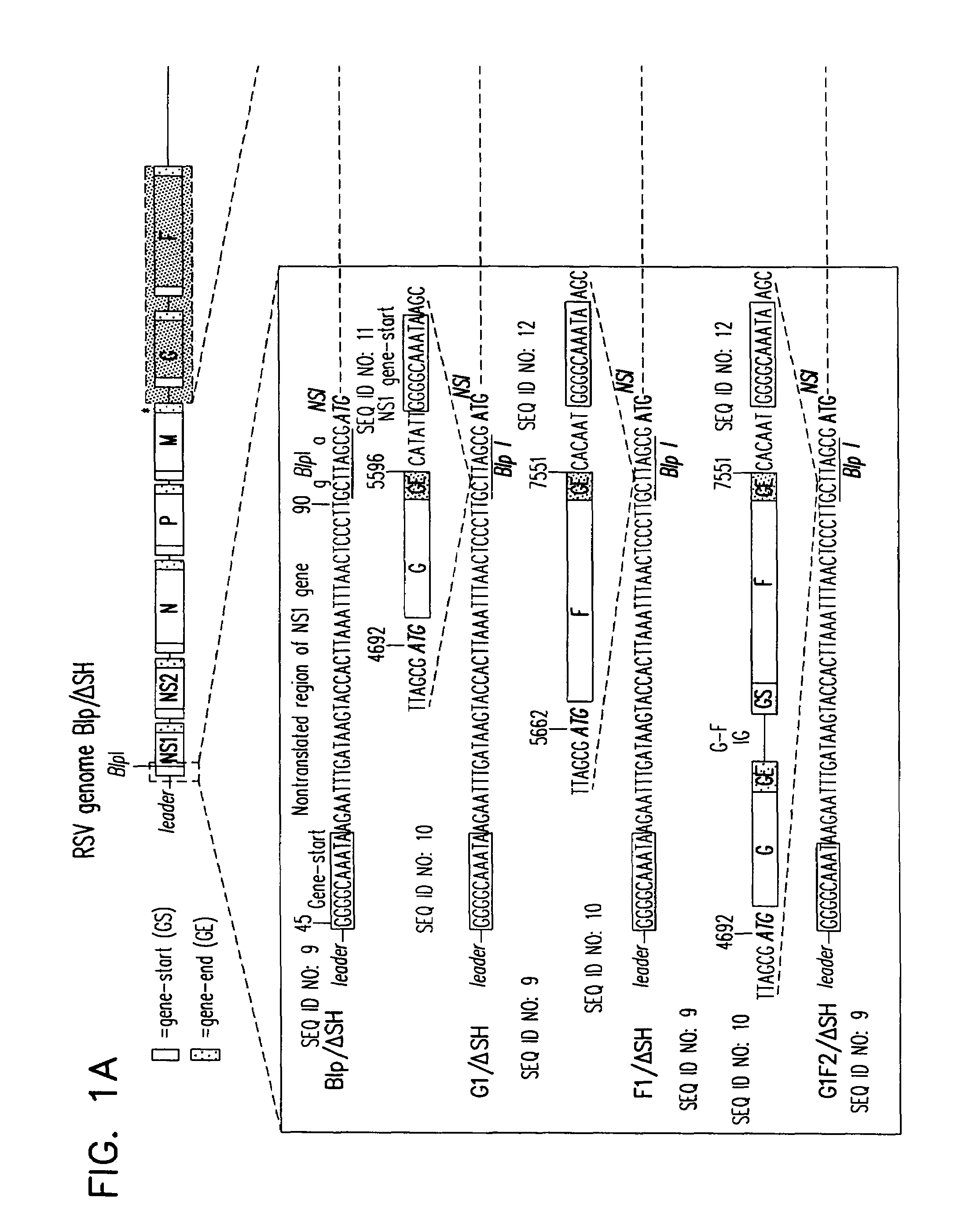
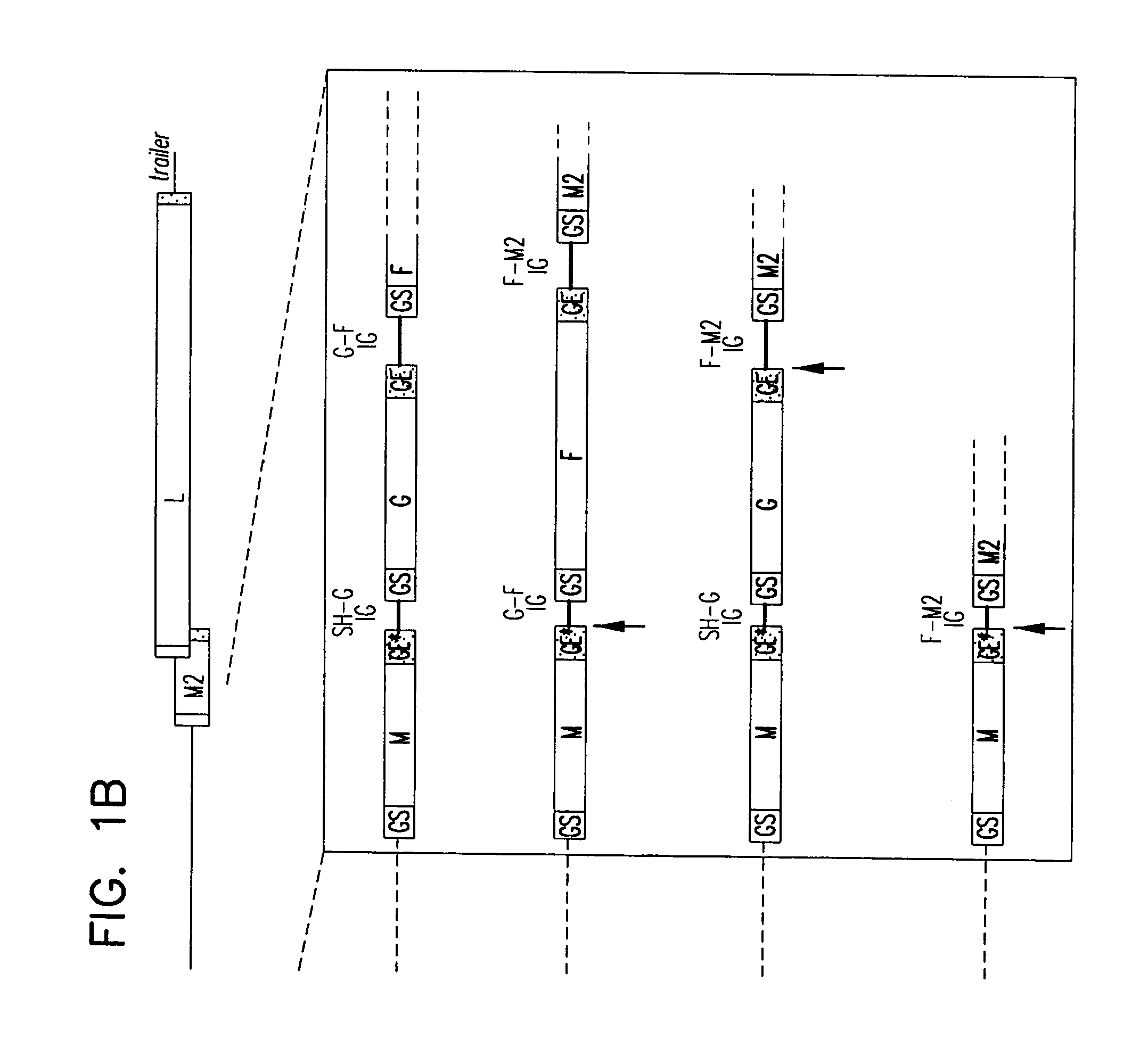
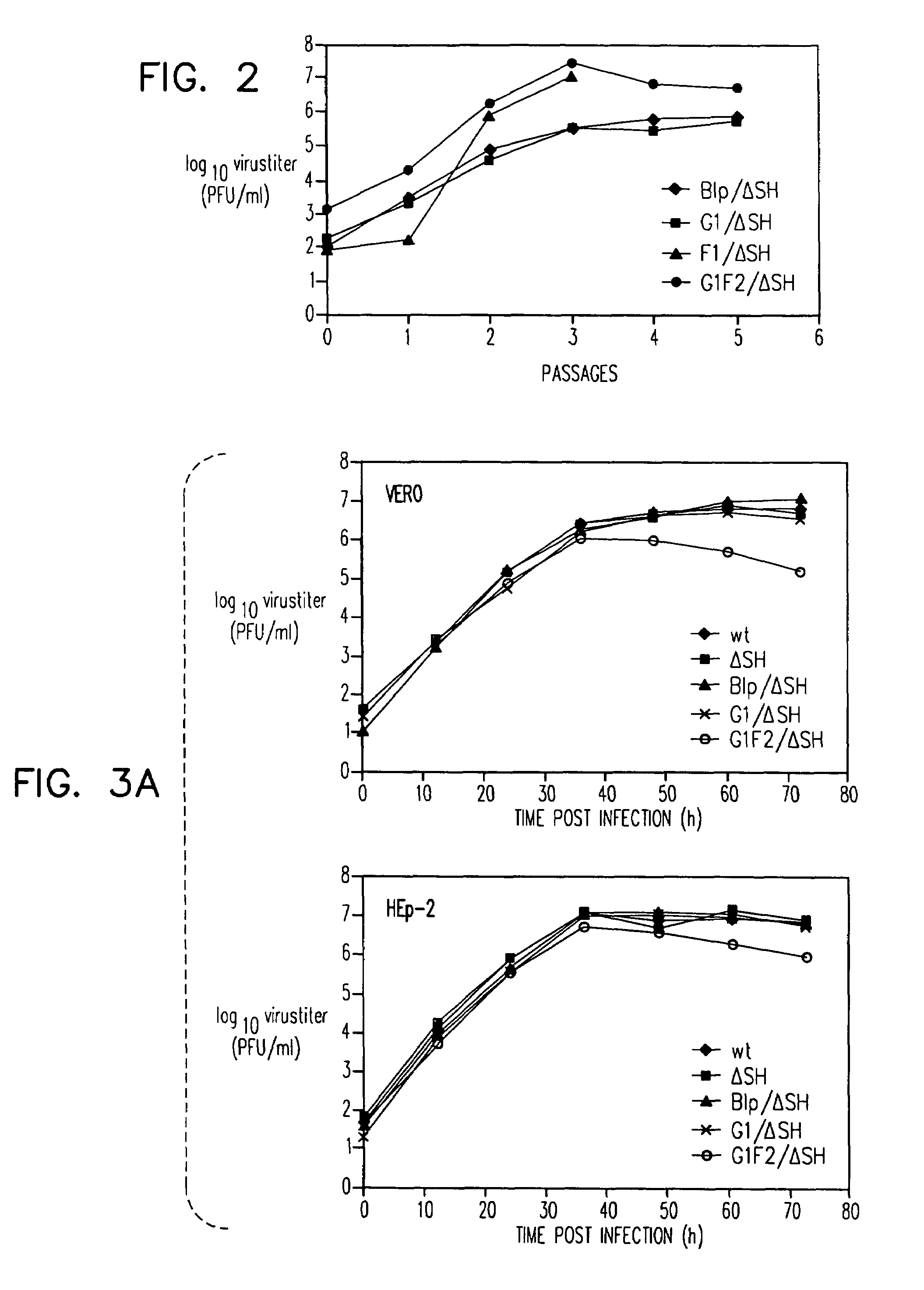
Respiratory syncytial virus vaccines expressing protective antigens from promoter-proximal genes
InactiveUS6923971B2Altered immunogenicitySmall sizeSsRNA viruses negative-senseSugar derivativesProtective antigenGene Position
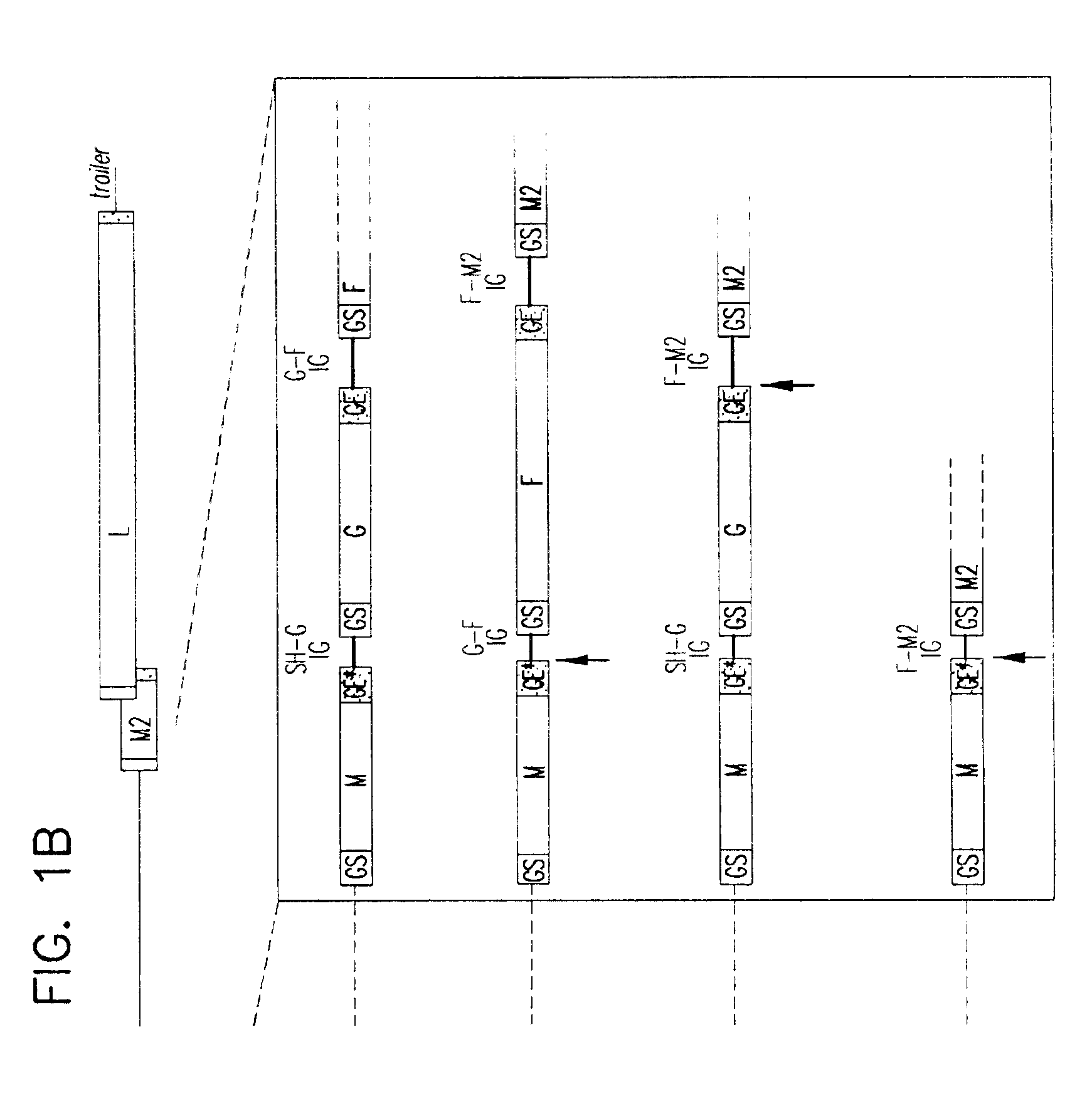
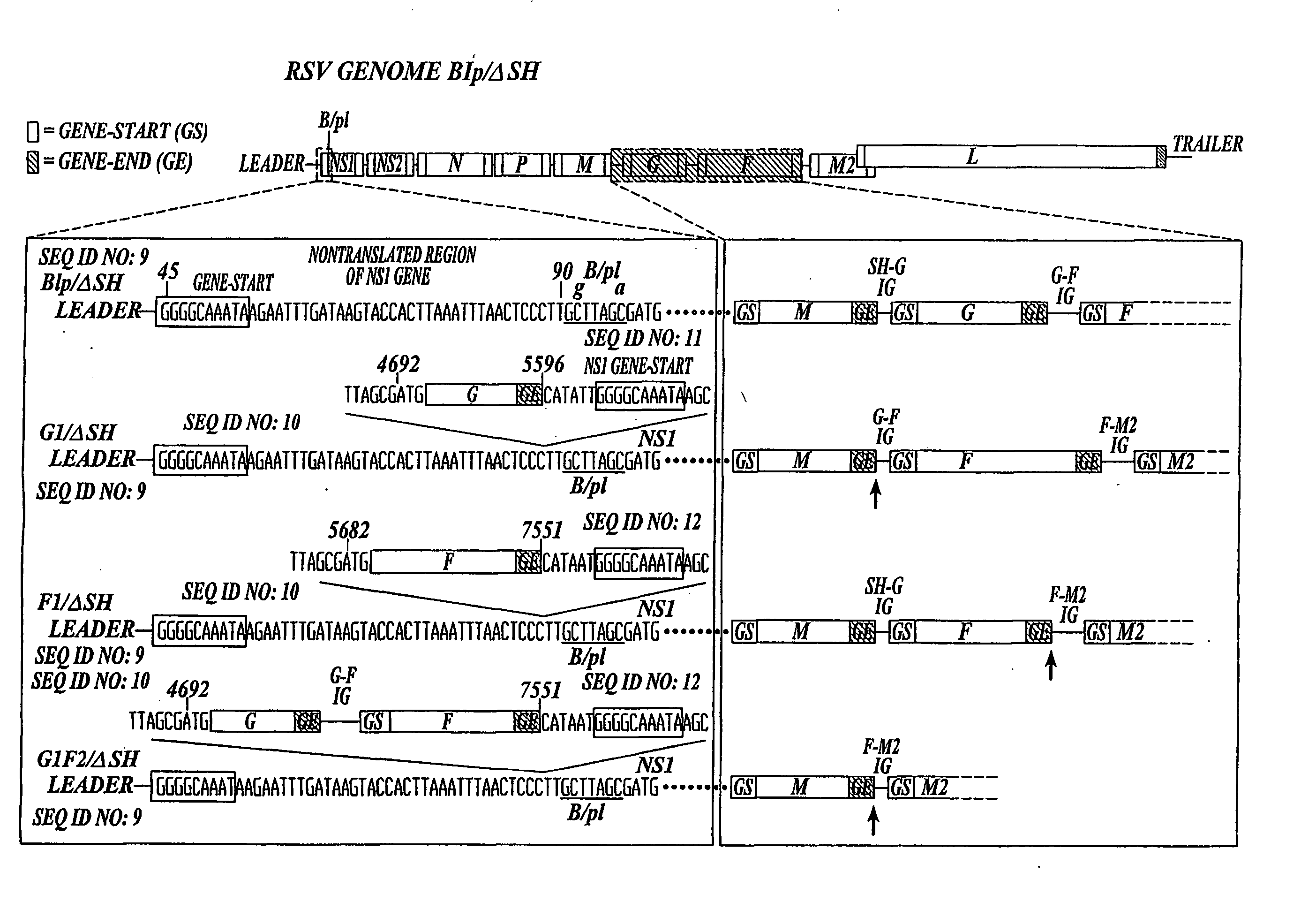
Recombinant respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) having the position of genes shifted within the genome or antigenome of the recombinant virus are constructed by insertion, deletion or rearrangement of genes or genome segments within the recombinant genome or antigenome and are useful for eliciting an anti-RSV immune response. Shifting the position of genes in this manner provides for a selected increase or decrease in expression of the gene. In one embodiment, expression of RSV glycoproteins is upregulated by shifting one or more glycoprotein-encoding genes to a more promoter-proximal position. Genes of interest for manipulation to create gene position-shifted RSV include any of the NS1, NS2, N, P, M, SH, M2(ORF1), M2(ORF2), L, F or G genes or a genome segment that may be part of a gene or extragenic. Additional mutations and nucleotide modifications are provided within gene position-shifted RSV to yield desired phenotypic and structural effects.
Owner:DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES THE GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC THE +1
Preparation method of completely humanized antibody of infectious disease pathogen
InactiveCN103045607AFully humanizedNo rejectionImmunoglobulins against bacteriaImmunoglobulins against virusesHumanized antibodyInfectious illness
The invention relates to a preparation method of the completely humanized antibody of a infectious disease pathogen, which mainly comprises the following steps of: preparing an infectious disease pathogen antigen; fluorescently labeling an infectious disease pathogen antibody; concentrating and purifying the peripheral B cells of an infectious disease patient; combining the labeled pathogen antigen and the antigenic-specificity B cells; screening antigenic-specificity single B cells through a flow cytometer; carrying out single cell RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification on genes positioned in the heavy chain and light chain variable region of the infectious disease pathogen antibody; connecting with a heavy chain and light chain constant region to construct the eukaryotic expression vector of the humanized antibody; and carrying out the high-efficiency expression and purification of a recombined antibody in an eukaryotic cell. The humanized monoclonal antibody prepared through the method disclosed by the invention can be used for the infectious disease diagnosis and the infectious disease treatment.
Owner:李福胜
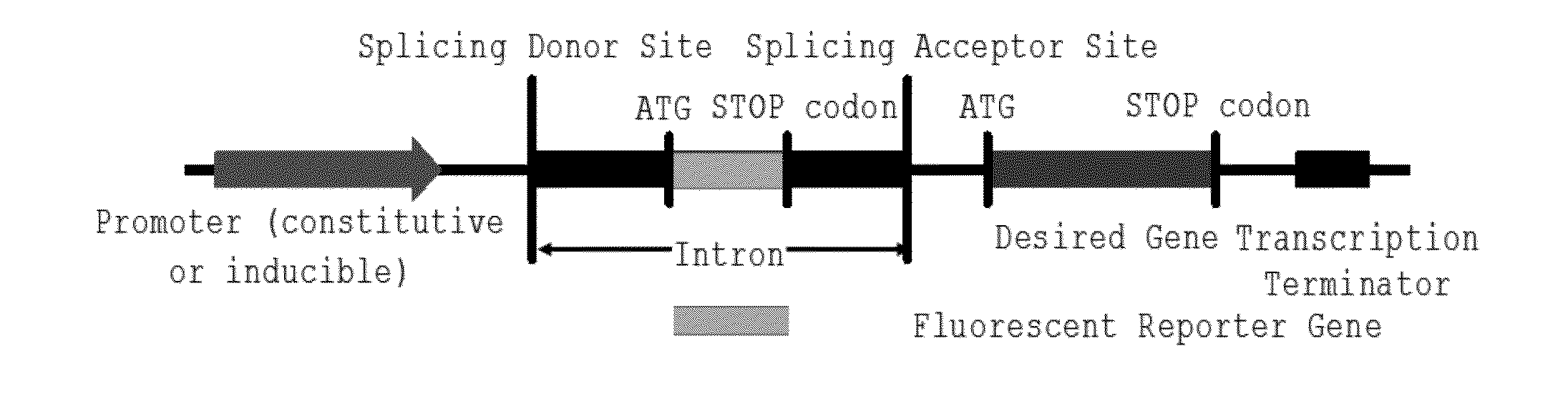
DNA construct and method for transgene expression
InactiveUS20160040186A1Easy to identifyRapidly and conveniently performVectorsMicroorganismsGene PositionDNA construct
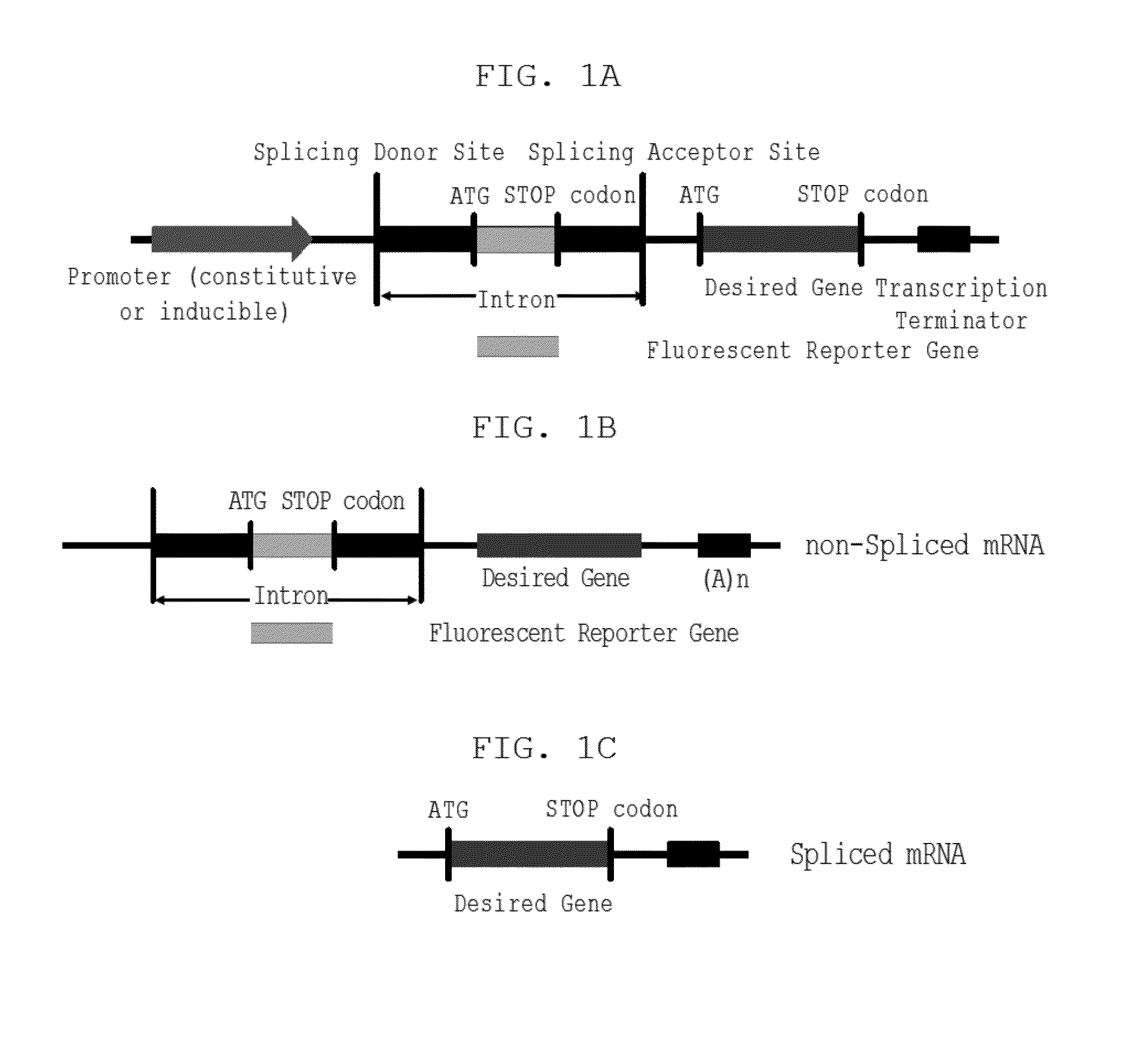
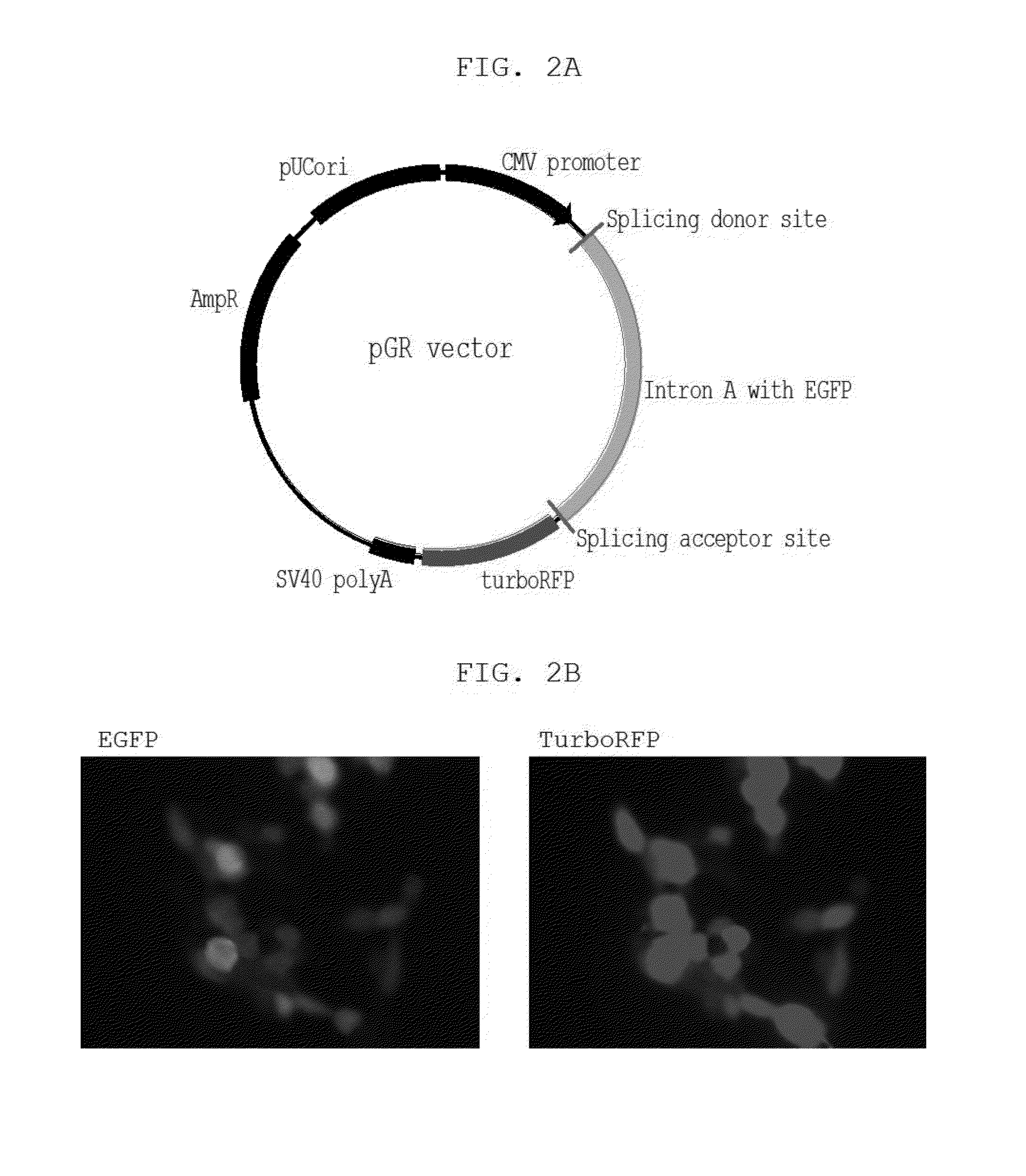
This invention relates to a DNA construct that is capable of expressing a desired transgene in a trackable manner. The construct comprises in 5′ to 3′ downstream direction: a promoter; a fluorescent reporter gene positioned within an intron defined by a 5′-donor splice site comprising a splice donor sequence and a 3′-acceptor splice site comprising a splice acceptor sequence; a desired gene and a transcription terminator. A method of producing a transgenic host cell having a desired product is also disclosed.
Owner:LIU XIAOYUN
Rough set attribute reduction method based on genetic algorithm
InactiveCN101763529AFast convergenceSimple codingGenetic modelsKnowledge based modelsGene PositionMutation operator
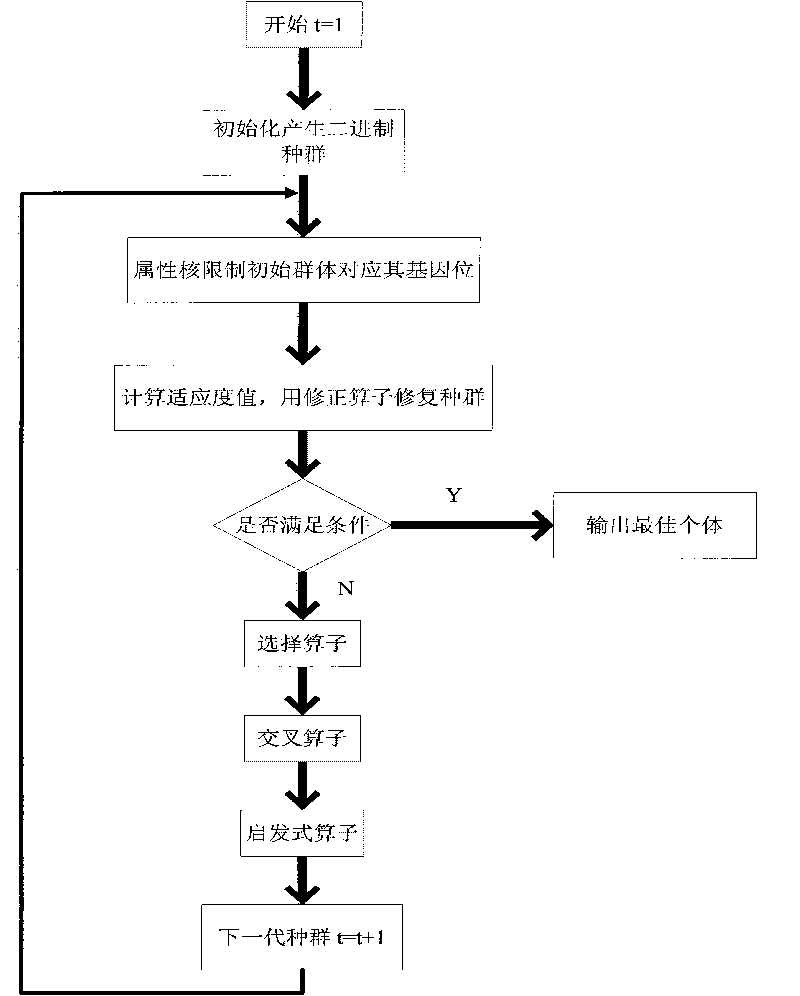
The invention discloses a rough set attribute reduction method based on genetic algorithm. The method comprises: (1) obtaining a core of a decision table, and generating an initial population randomly by initialization; (2) controlling the initial population to correspond to the gene position thereof through the attribute core, and calculating a fit value according to fitness function; (3) repairing the population by adopting modification operator; (4) judging whether to satisfy the algorithm terminating condition, if yes, outputting the best individual, and if no, proceeding to (5); (5) performing survival-of-the-fittest operation to individuals in the population by using a selection operator in the genetic algorithm; (6) performing interlace operation to the population with interlace probability by adopting one-point interlace rule; and (7) performing mutation operation to the population according to a heuristic mutation operator with the gene position corresponding to the attribute core not mutated. The technical scheme of the invention is designed to rapidly and efficiently obtain the smallest reduction of attribute in the decision table and efficiently improve information accuracy.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for auxiliary screening of high-oil corn and dedicated quantitative character gene locus therefor
InactiveCN1880481AAccurate identificationQuick Selection MethodMicrobiological testing/measurementGene PositionScreening method
The invention discloses an auxiliary screening method and specific quantity property gene position for high-oil maize, which is characterized by the following: adopting gene group DNA of detected maize and high-oil maize gene group DNA of known seed oil content as form; proceeding PCR augmentation through primer p-bnlg1142 and or p-umc2313 and or p-bnlg1188 and or p-bnlg107; setting the detected maize as candidate high-oil maize kind if the band type of detected maize augmentation product is the same as the band type of known seed. The invention can detect generation high-oil individual, which adopts seed color as phenotype mark.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
A gene automatic deletion binary system and its related plant expression vector for biosafety control of exogenous genes in sexually propagated plants
InactiveCN102286511ASolve the technical problem of stable inheritanceStable Genetic RealizationVector-based foreign material introductionPlant genotype modificationMolecular switchOrganism
The invention constructs a new gene-auto-excision binary system for biological safety control of exogenous gene in a sexual reproduction plant. The use of a transcription system as a molecular switch to control a recombinase deletion system, on one hand, keeps a recombinase gene positioned between recombinase identification loci silenced in sexual generations of a plant and realizes the stable inheritance of an exogenous gene transferred by a 'GM-gene-deletor' technique in sexual generations of a plant; on the other hand, the hybridizing of parent plants carrying an effector element and an activator element respectively closes two matched elements in the transcription system. Thus, the activity of a transcription activator is demonstrated and the deletion of the exogenous gene is realizedby promoting the expression of the recombinase by a plant tissue specific promoter to obtain a safe transgenic plant; and the biological safety hazard problem the exogenous gene may brings is solved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
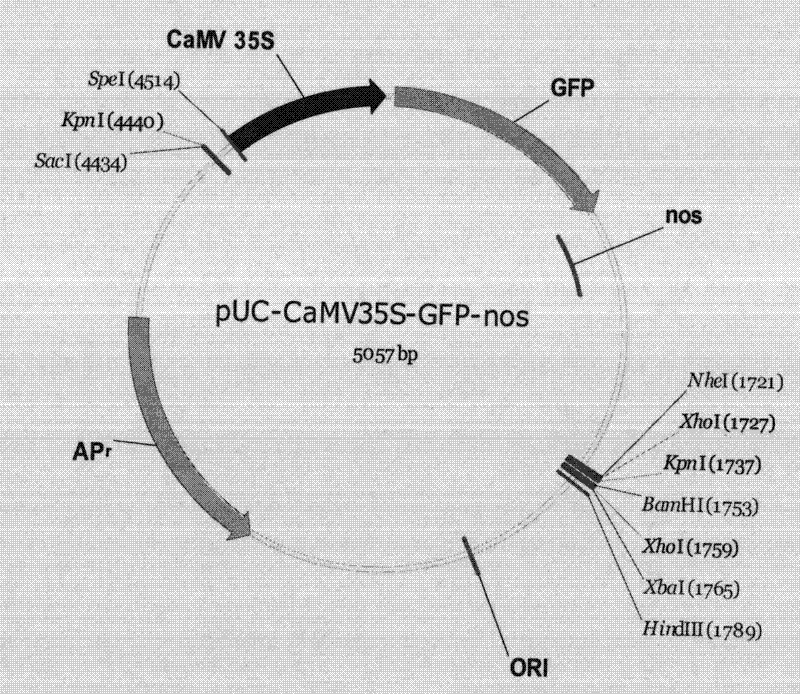
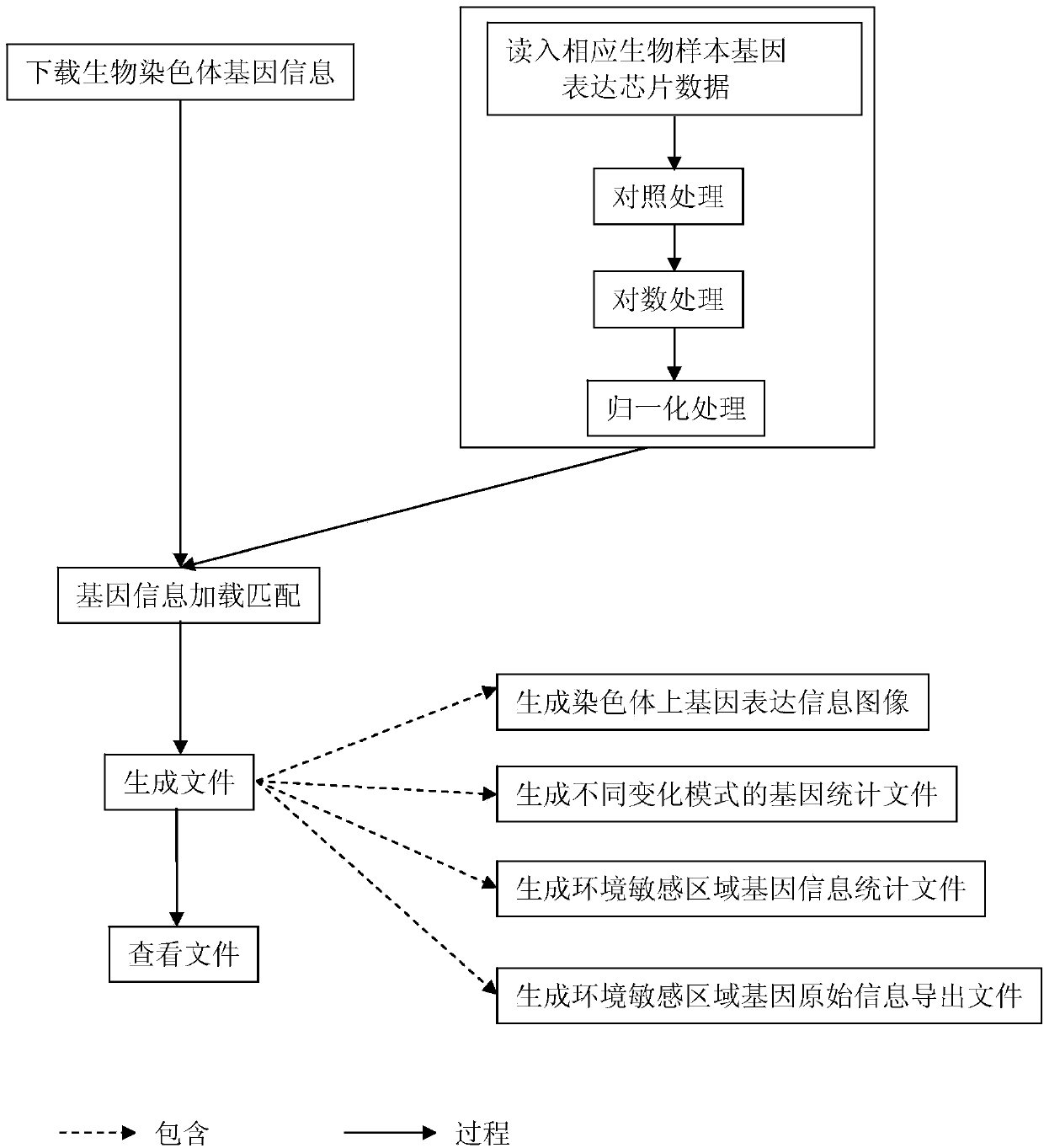
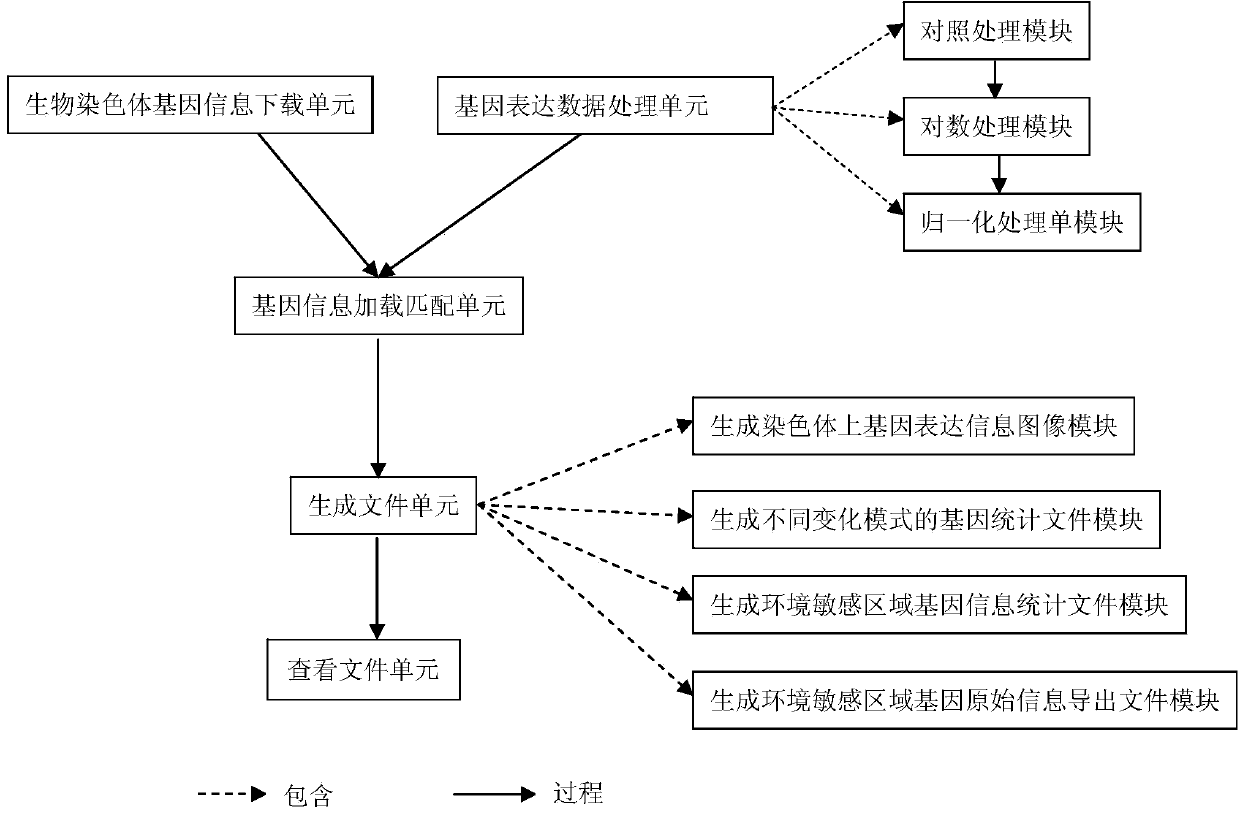
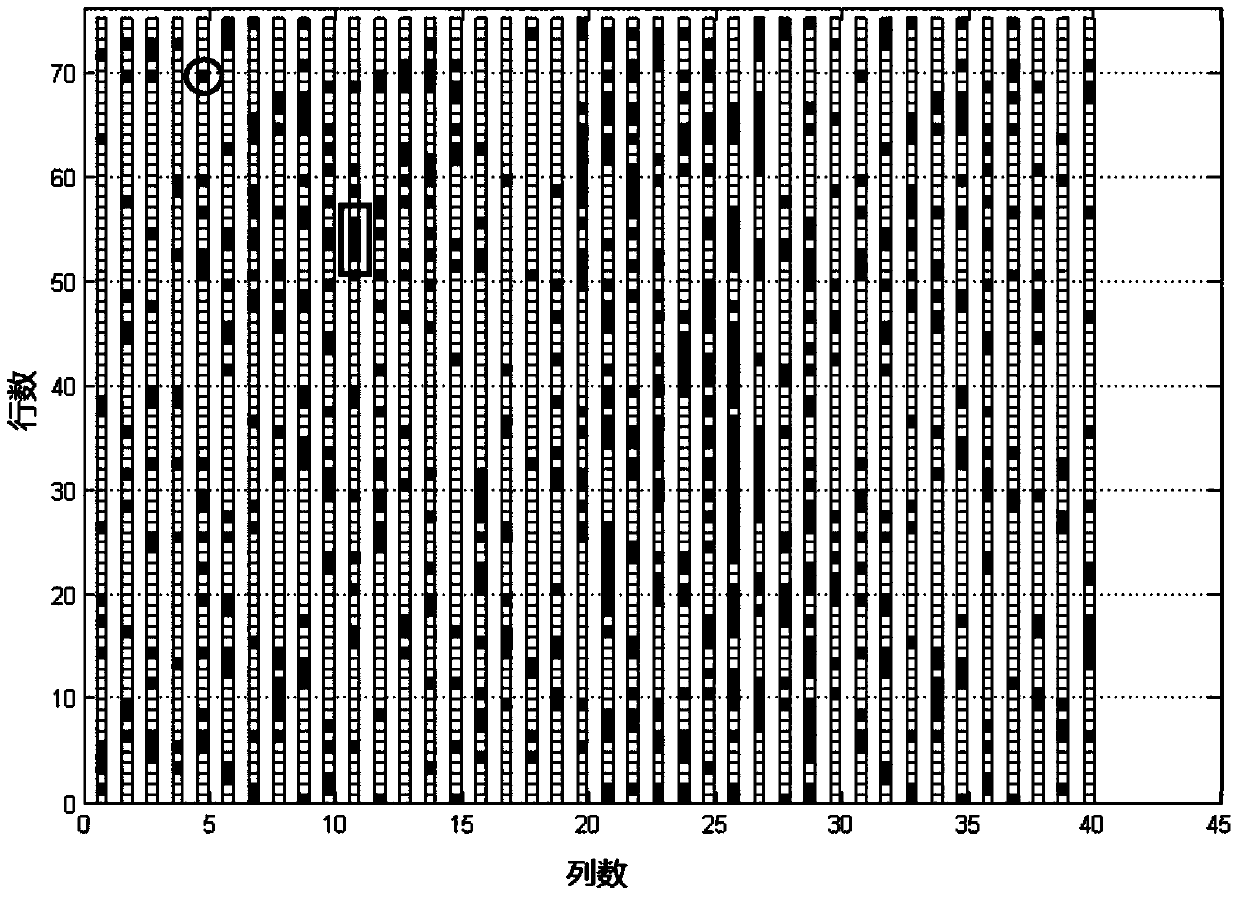
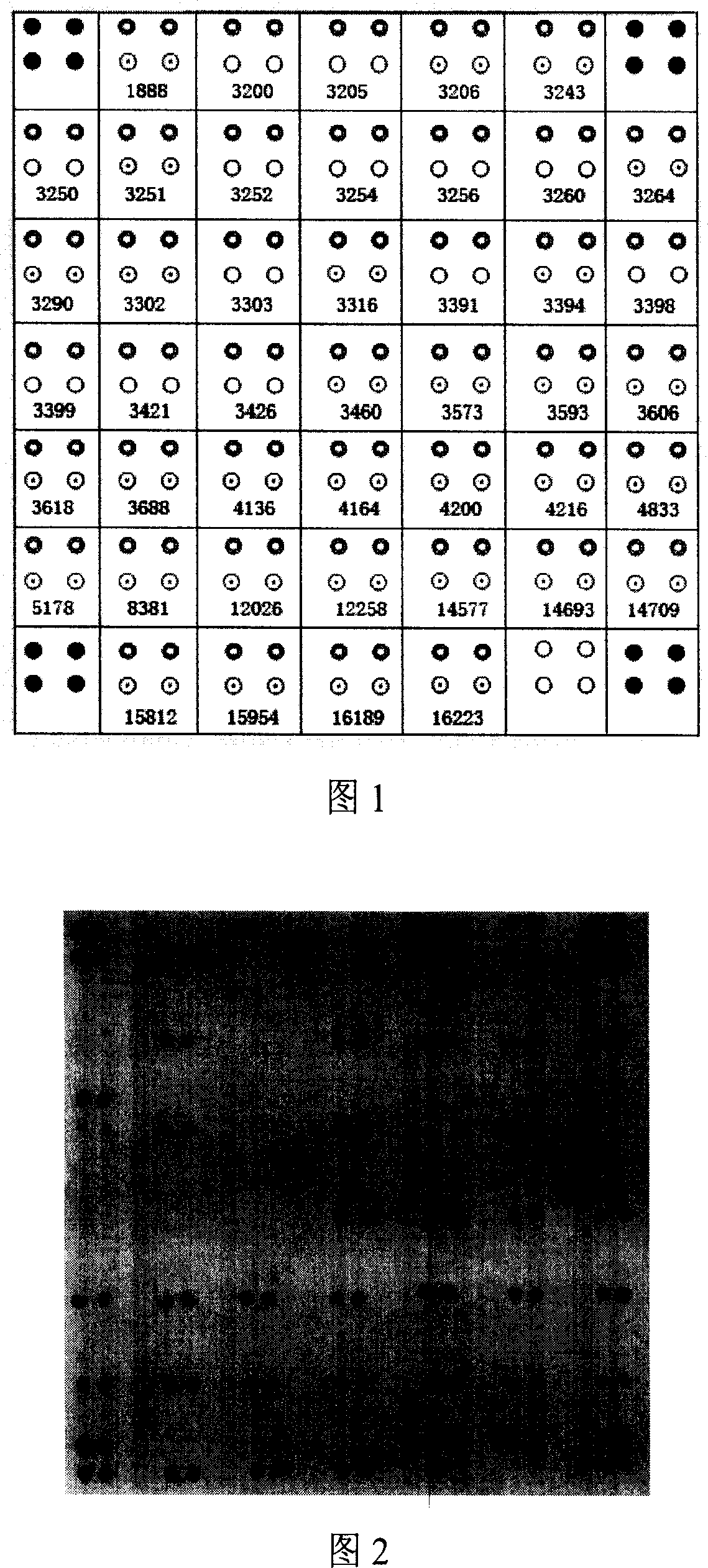
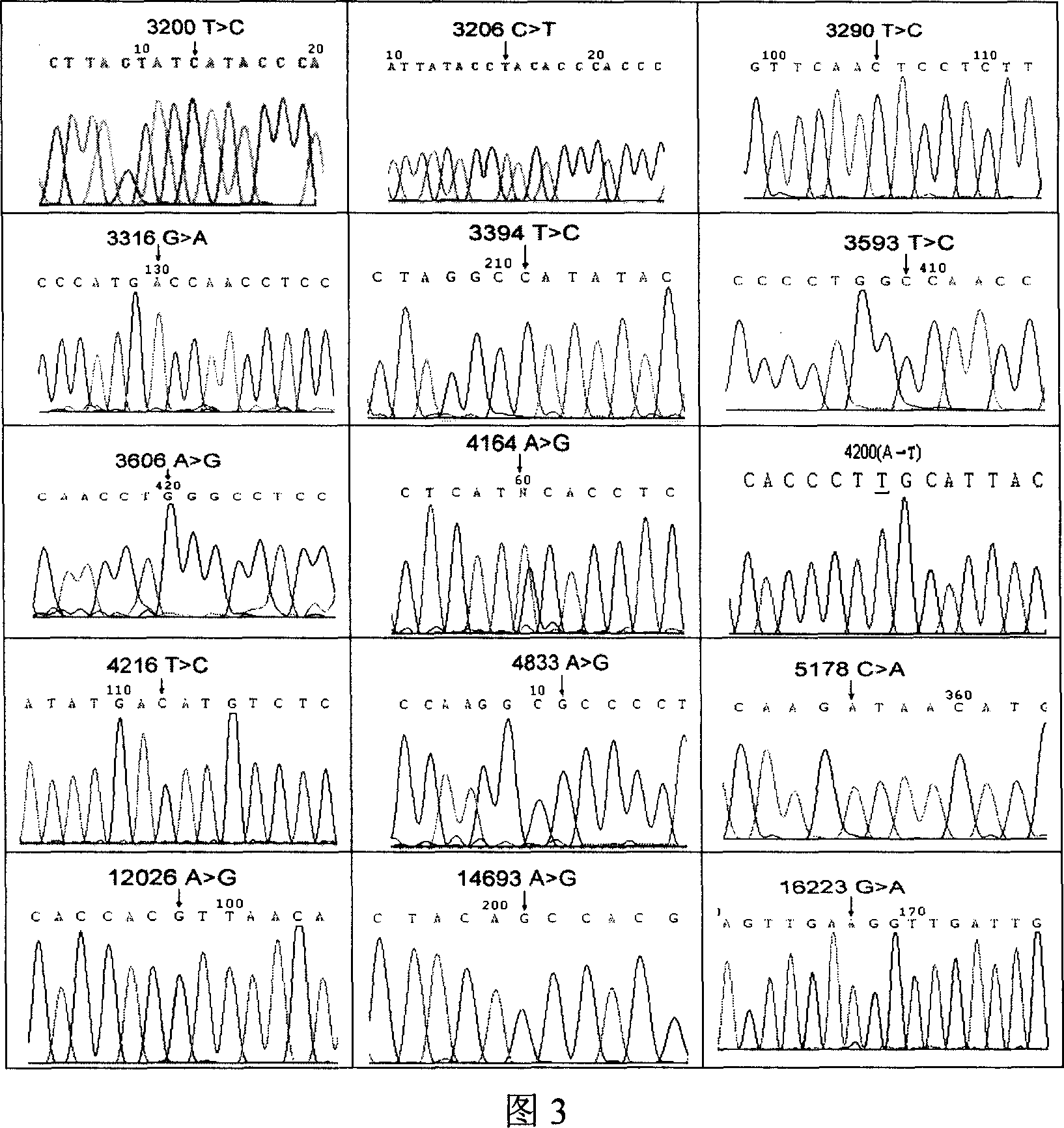
Method for positioning and displaying biological gene expression information and environmental sensitive area on chromosomes
InactiveCN104182656ARealize the visualization functionSpecial data processing applicationsGene PositionGene expression microarray data
The invention provides a method for positioning and displaying biological gene expression information and environmental sensitive area on chromosomes. The method comprises the following steps: downloading genomic sequence of biological chromosomes; reading in the gene expression microarray data of the corresponding biological sample and then performing contrast treatment, logarithm processing and normalization processing to obtain environmental condition value; matching gene names in the gene expression microarray data matrix with the downloaded gene names in gene sequence of the biological chromosomes and then positioning the environmental condition value of the gene on the corresponding gene position in the biological genomic sequence; obtaining gene expression images and environmental sensitive areas on the biological chromosome genome according to the positioned environmental condition value. According to the method, the visualization function of distribution characteristics of expressed variant genes on the chromosomes is achieved, the distribution characteristic data of the genes in the environmental sensitive areas is obtained, which provides effective help for analysis of expressed variant sensitive areas of genes on the chromosomes and speculation of environmental sensitive transcription factors.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
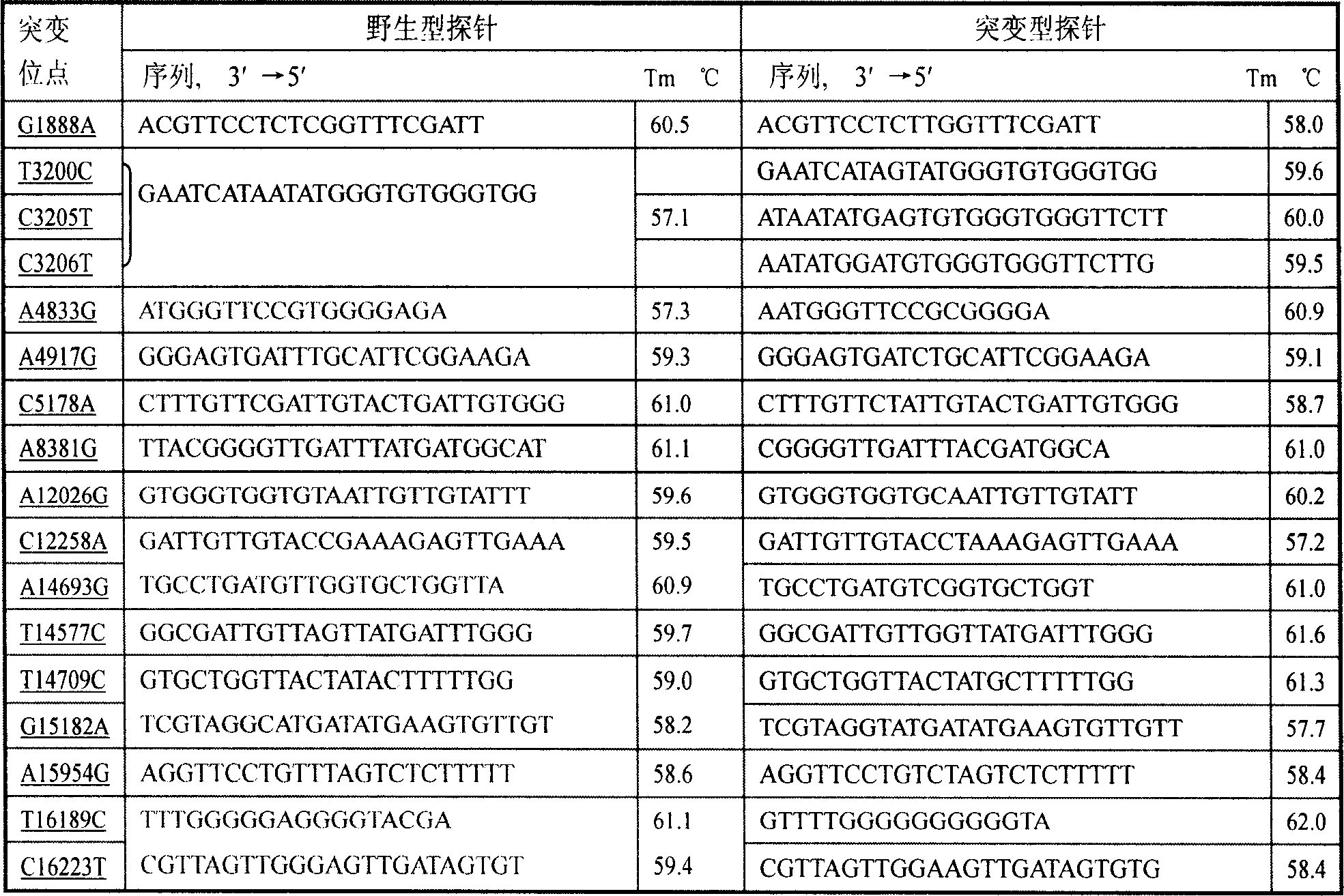
Membrane chip for detecting 45 gene locus of mitochondria diabetes
InactiveCN1970791AHelp in correct diagnosisHelpful for classificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationHigh risk populationsGene Position
The invention discloses a detecting method of mitochondria diabetic 45-gene position film chip, which comprises the following steps: adopting nylon film as carrier; designing primer and probe; distributing chip lattice; sampling and fixing chip. The chip monitoring system is composed of negative comparison, positive comparison and paralleling comparison of base mutation position. The detecting system is wild-typed and mutation-typed probe of detected mtDNA45 with 90 probes and 196 sampling points on each chip. The invention simplifies operating flow path, which can detects 45 mtDNA positioins.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Respiratory syncytial virus vaccines expressing protective antigens from promotor-proximal genes
InactiveUS7744902B2Altered immunogenicitySmall sizeSsRNA viruses negative-senseSugar derivativesProtective antigenMammal
Recombinant respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) having the position of genes shifted within the genome or antigenome of the recombinant virus are infectious and attenuated in humans and other mammals. Gene shifted RSV are constructed by insertion, deletion or rearrangement of genes or genome segments within the recombinant genome or antigenome and are useful in vaccine formulations for eliciting an anti-RSV immune response. Also provided are isolated polynucleotide molecules and vectors incorporating a recombinant RSV genome or antigenome wherein a gene or gene segment is shifted to a more promoter-proximal or promoter-distal position within the genome or antigenome compared to a wild type position of the gene in the RSV gene map. Shifting the position of genes in this manner provides for a selected increase or decrease in expression of the gene, depending on the nature and degree of the positional shift. In one embodiment, RSV glycoproteins are upregulated by shifting one or more glycoprotein-encoding genes to a more promoter-proximal position. Genes of interest for manipulation to create gene position-shifted RSV include any of the NS1, NS2, N, P, M, SH, M2(ORF1), M2(ORF2), L, F or G genes or a genome segment that may be part of a gene or extragenic. A variety of additional mutations and nucleotide modifications are provided within the gene position-shifted RSV of the invention to yield desired phenotypic and structural effects.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Molecular marker related to chicken growth and development and application thereof
ActiveCN111910008AIncrease selection strengthImprove breeding efficiencyFood processingMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyGenes mutation
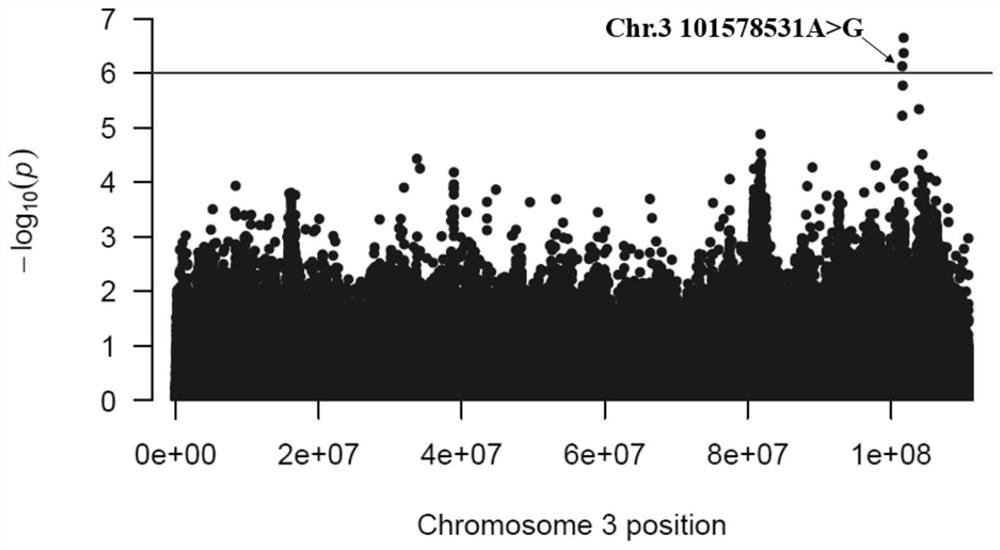
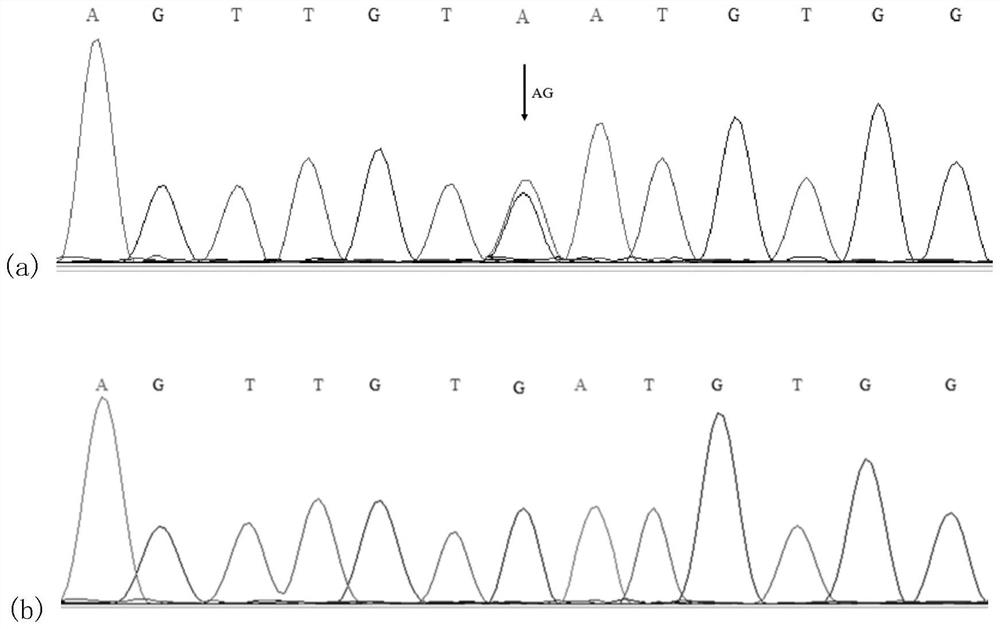
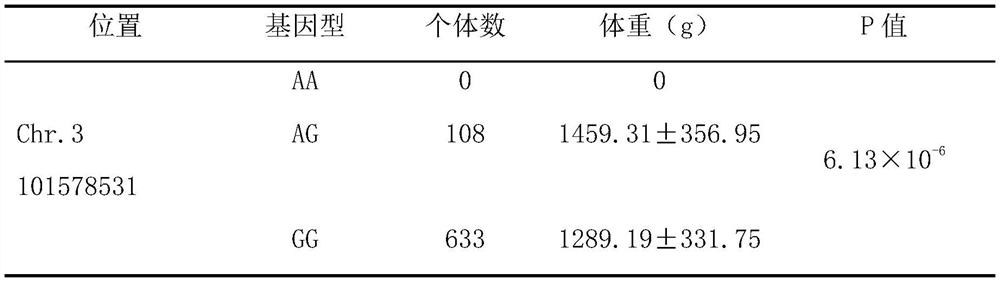
The invention discloses a molecular marker related to chicken growth and development and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of molecular marker-assisted selection and animal genetic breeding. The molecular marker is obtained by performing genome-wide association (GWAS) analysis on 741 test chickens of F2-generation resource groups established by Daweishan mini chickens and recessive Bailuoke broilers, a nucleotide single base mutation (named as Chr.3101578531A>G) of A >G exists at the 101578531bp position on the chromosome 3 of the version Gallus_gallus.GRCg6a of a chickenreference genome, a gene positioned in the nearby area is an RNA binding protein PUM2 (pumilio RNA binding family member 2) gene, and the mutation remarkably influences the weight of the chickens. The invention discloses obtaining and application of the molecular marker. The invention further provides a molecular marker genotyping detection method influencing chicken growth and development. By means of the method, an efficient and accurate molecular marker-assisted breeding technology can be established and applied to chicken growth and development genetic improvement, and therefore chicken growth and development are improved.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Baculovirus expression vector capable of quickly determining titer and construction and application thereof
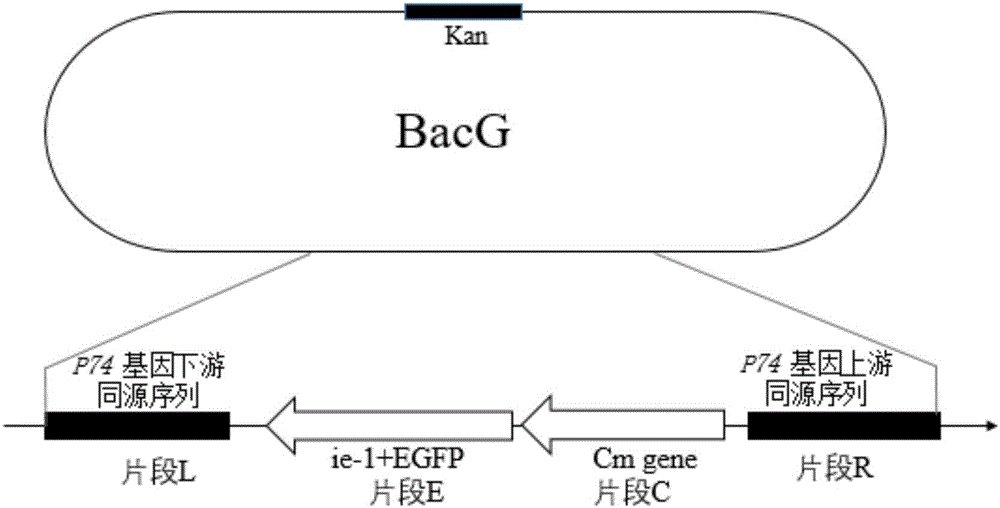
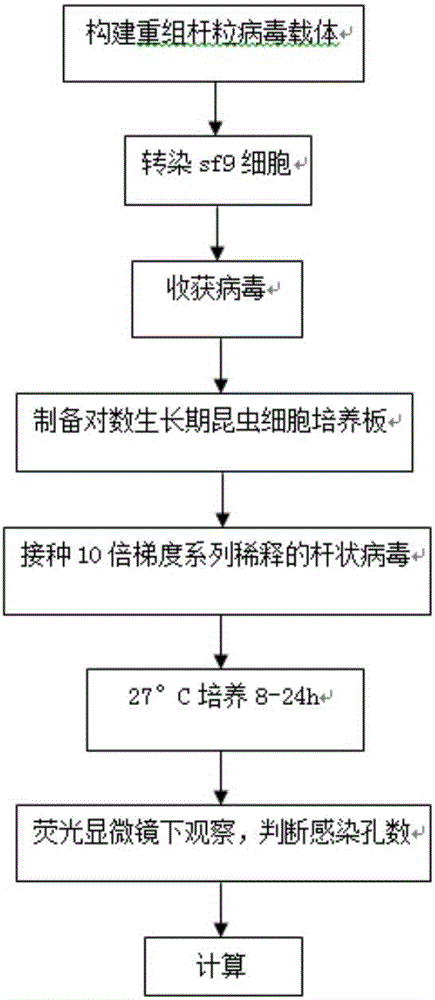
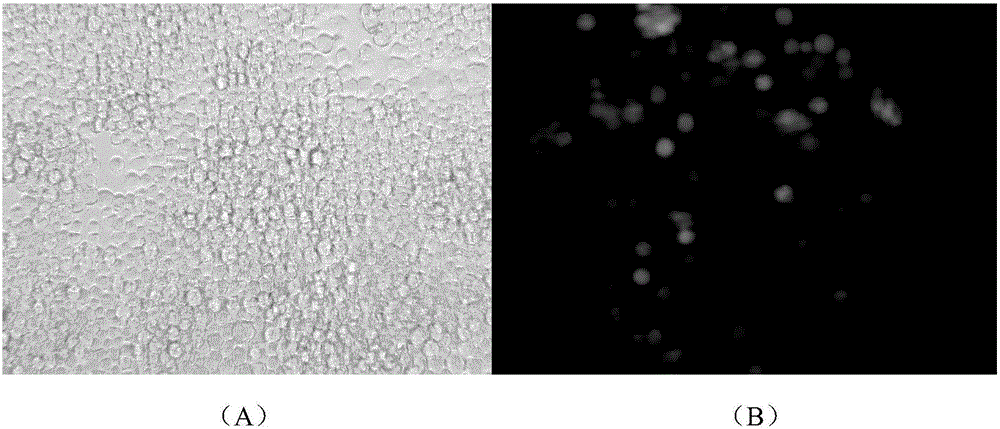
ActiveCN106497974AQuantitative quickShort detection cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBaculovirus expressionGene Position
The invention discloses a baculovirus expression vector capable of quickly determining titer and construction and application thereof. The vector is named BacG, and is obtained by inserting a green fluorescent protein gene regulated by a baculovirus extremely early promoter ie-1 on a nonessential gene position on a genome of a baculovirus expression vector Bacmid bMON14272. The baculovirus expression vector keeps a complete green protein expression ability of the Bacmid bMON14272, meanwhile because of recombinant baculovirus produced by the baculovirus expression vector, the tilter of the baculovirus can be quickly determined by observing the expression of the green fluorescent protein under a fluorescence microscope, and thus the time for determining the tilter of the recombinant baculovirus is shortened to 24 hours.
Owner:GUANGXI BOTANICAL GARDEN OF MEDICINAL PLANTS
Enhanced Gene Expression
InactiveUS20180305686A1Increase gene expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementStable introduction of DNAIntegrasesInstability
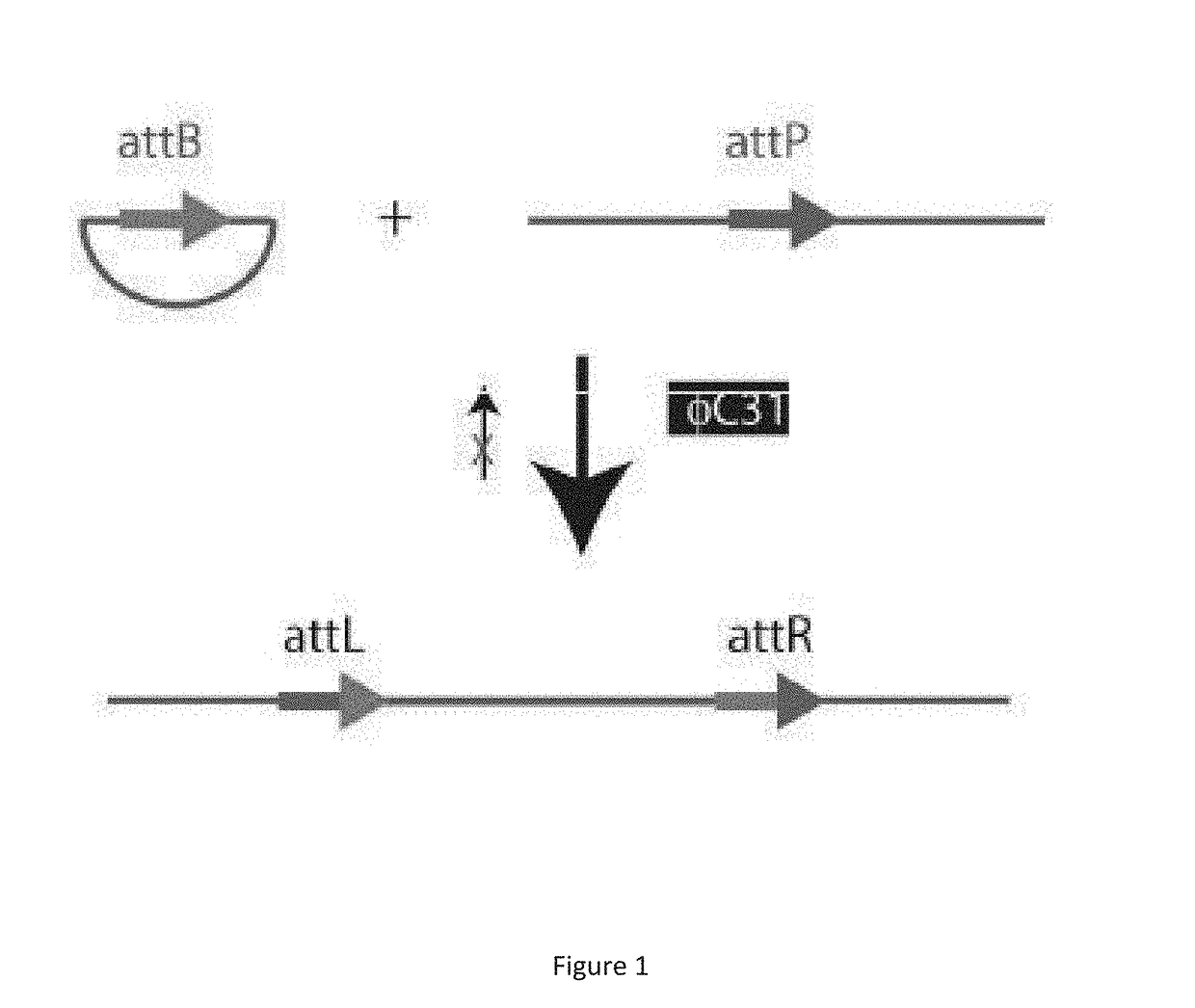
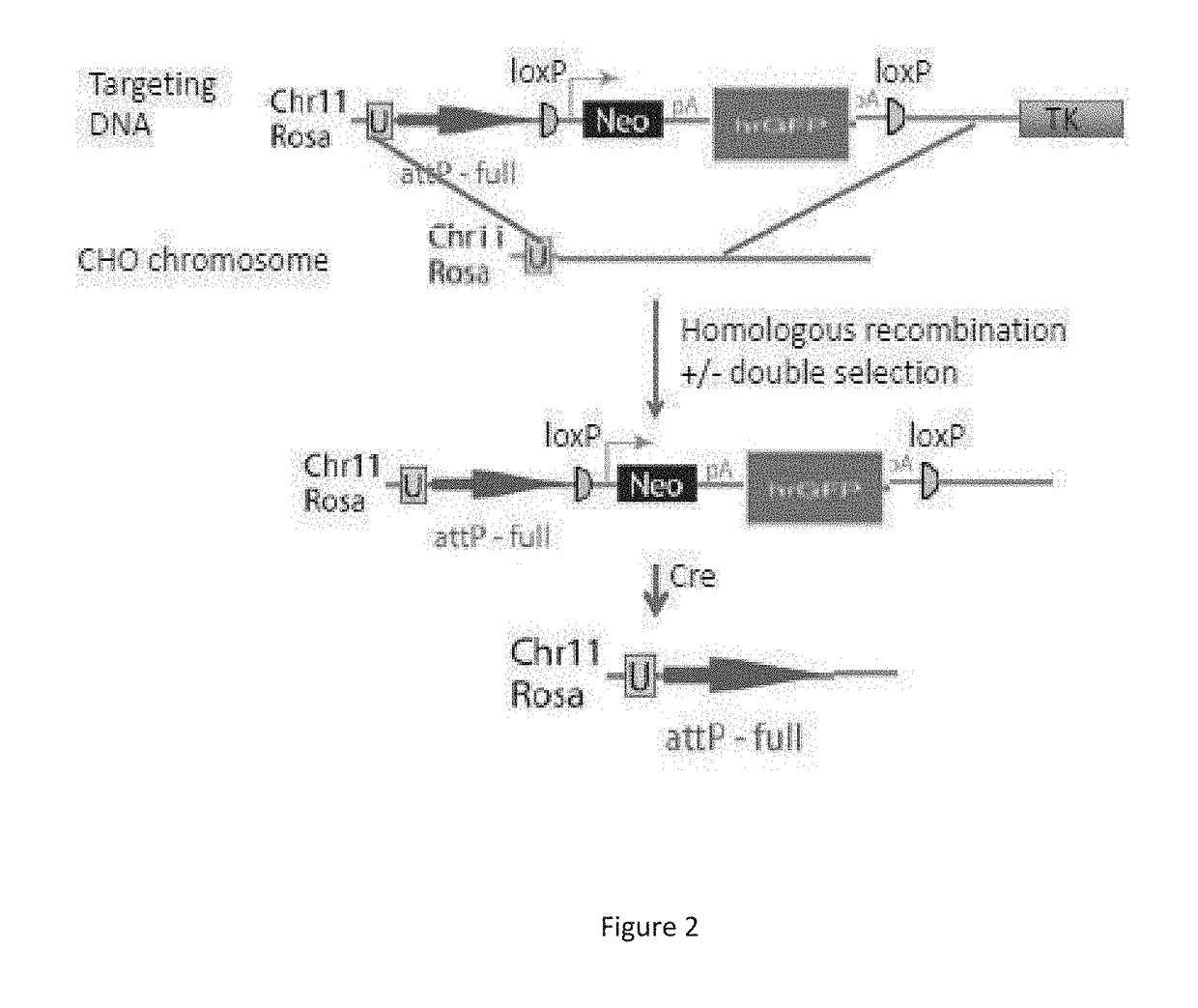
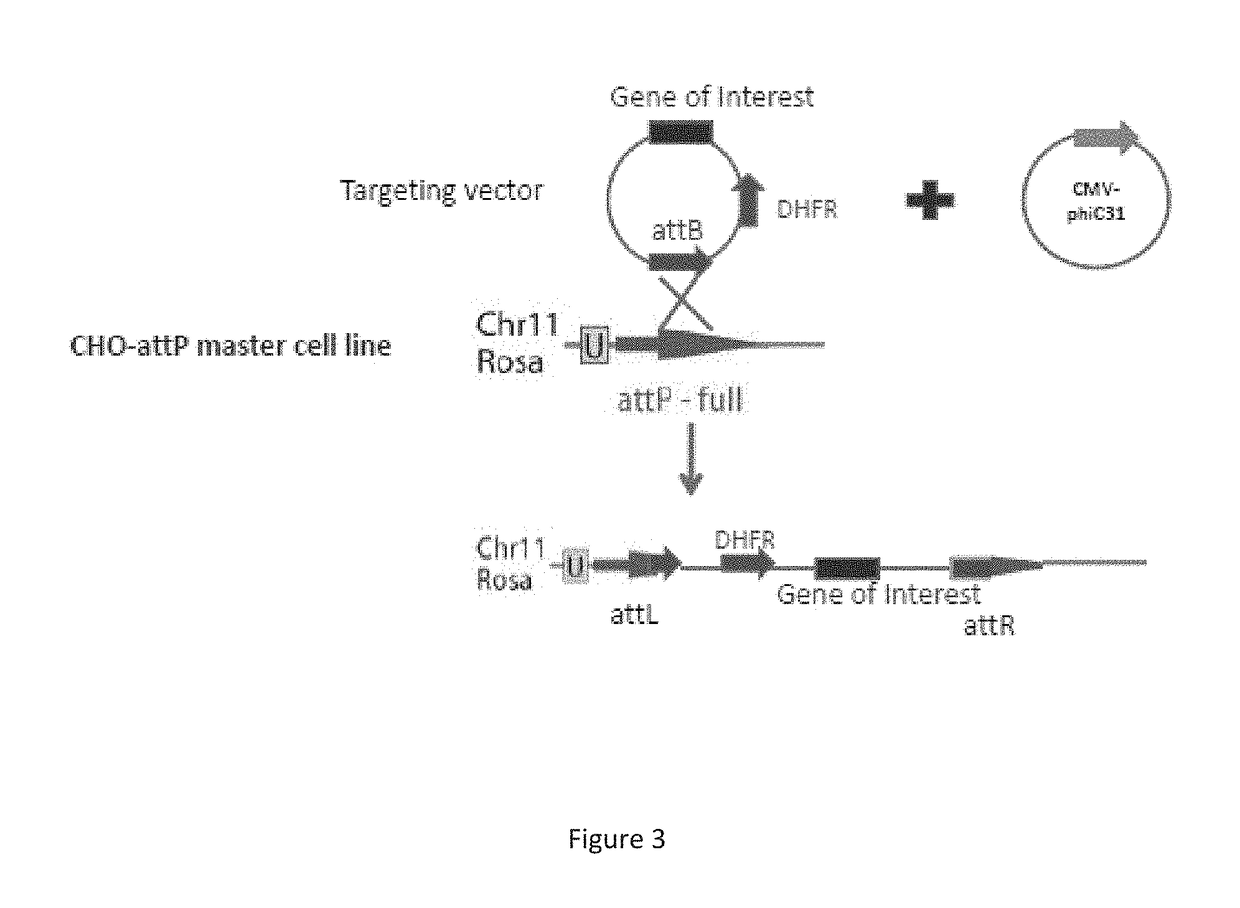
The present disclosure is directed to a novel, unexpected approach of expressing exogenous gene(s) at increased levels by predictably, optionally irreversibly, incorporating the gene(s) into a region of increased gene expression (RIDGE) on a chromosome of a host cell. This approach is accomplished by identification of RIDGE(s). and further by integration of integrase-specific sites (e.g., attP or attB) in the presence of or mediated by integrase. The approach renders a high level of gene expression; predictability of the location of the exogenous genes, elimination of genetic instability or unwanted phenotype; and reduction of time and cost in optimizing protein production in host cells, which will be every useful in the production of therapeutic, prophylactic, and diagnostic proteins.
Owner:ASC THERAPEUTICS INC
Application of Ghd7 gene in regulating rice flag leaf chlorophyll content
InactiveCN106148354AReduce chlorophyll contentFermentationGenetic engineeringAgricultural scienceChloroplast
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. It is found that a significant hot spot region exists in the range of 9.13 Mb to 9.17 Mb of a chromosome 7 through genome-wide association study (GWAS), nine signal peak values which have an extremely significant effect on the rice flag leaf chlorophyll content from different GWAS can be detected repeatedly, and the peak values correspond to Ghd7 gene positions. It is verified through near-isogenic lines and genetically modified materials that Ghd 7 serves as a main natural variation site to regulate the rice flag leaf chlorophyll content by down-regulating related gene expressions such as chlorophyll metabolism and chloroplast synthesis. The Ghd 7 has important breeding value in optimizing the rice flag leaf chlorophyll content.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
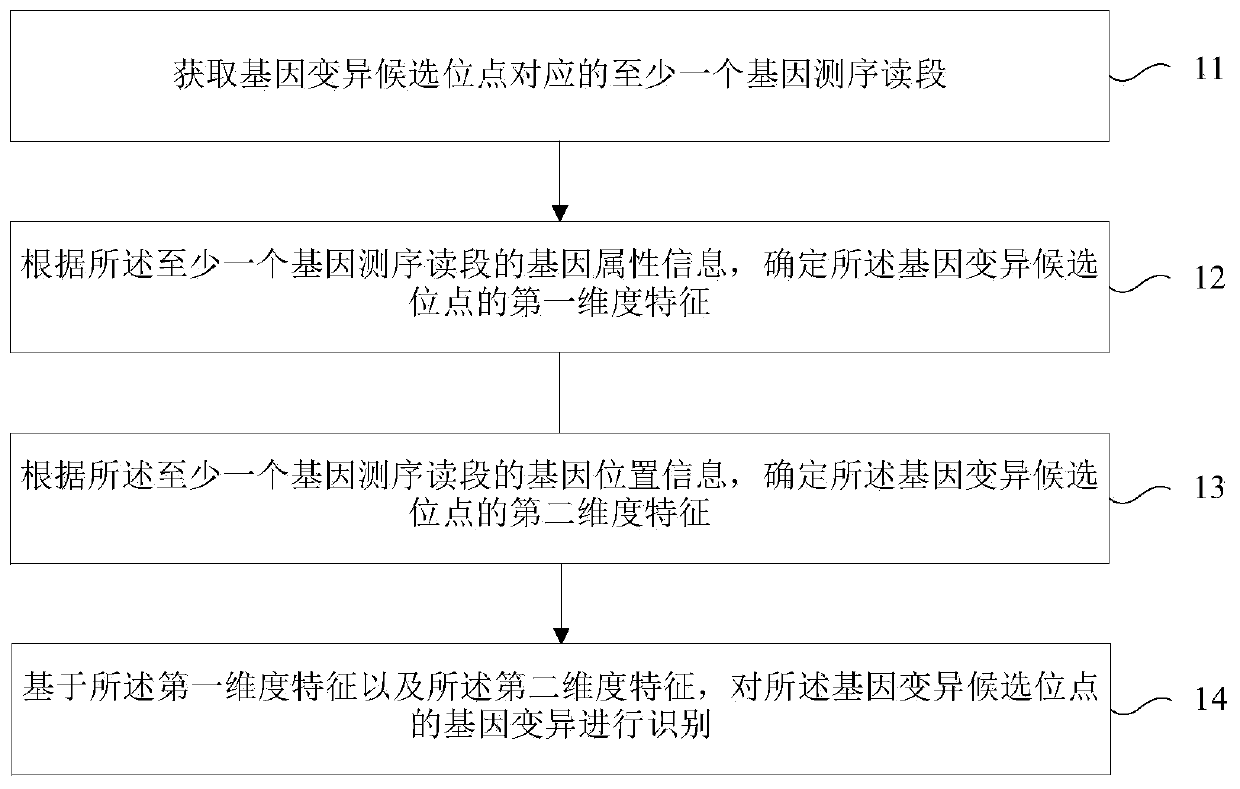
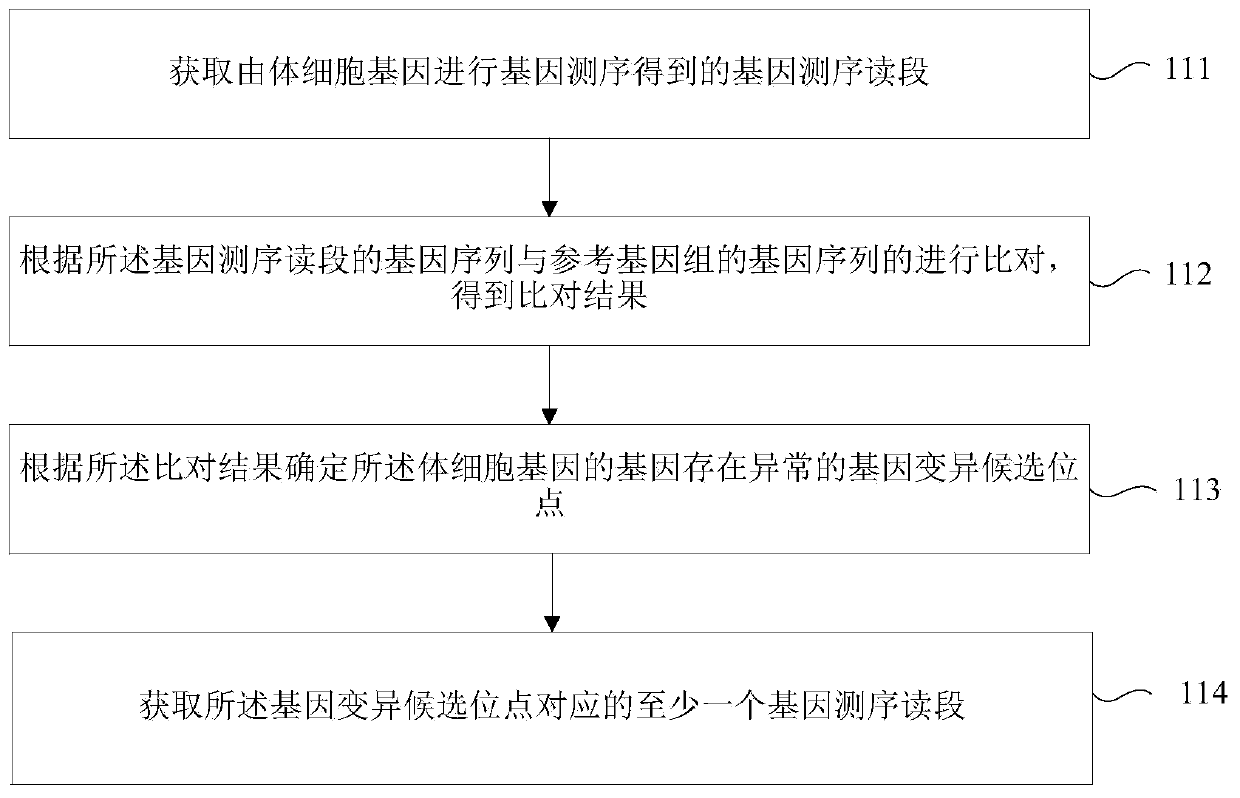
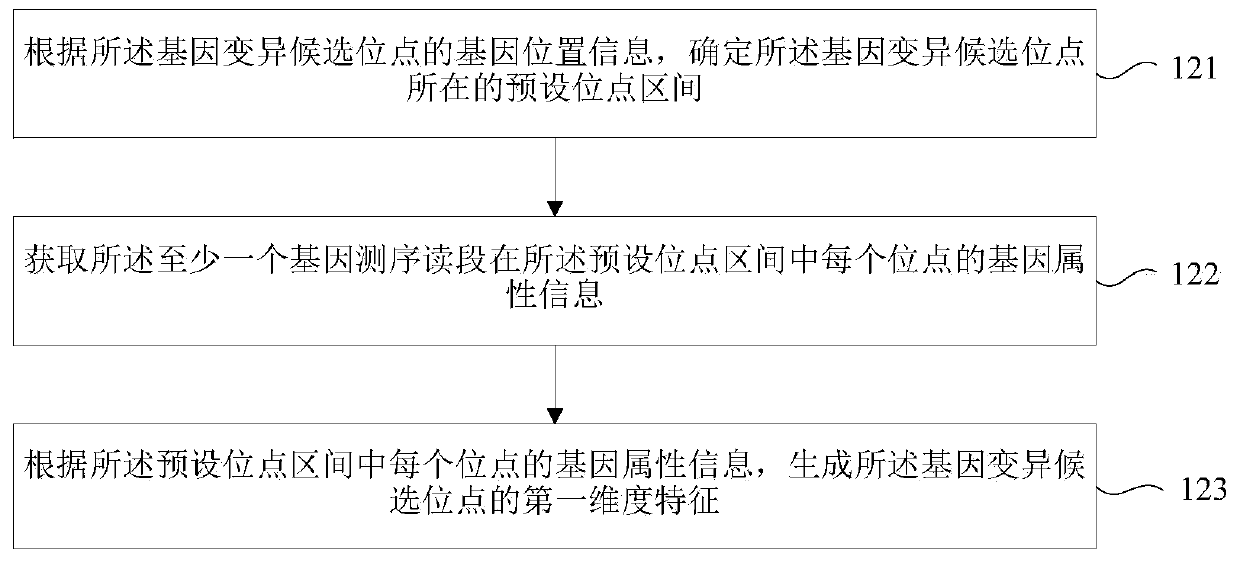
Gene variation identifying method, device and storage medium
The invention relates to a gene variation identifying method, a device and a storage medium, wherein the gene variation identifying method comprises the steps of acquiring at least one gene sequencingread segment which corresponds with a gene variation candidate site; according to the gene attribute information of at least one gene sequencing read segment, determining a first dimension characteristic of the gene variation candidate site; according to the gene position information of at least one gene sequencing read segment, determining a second dimension characteristic of the gene variationcandidate site; and based on the first dimension characteristic and the second dimension characteristic, identifying the gene variation of the gene variation candidate site. According to the gene variation identifying method, the device and the storage medium, the gene variation is identified through the two dimension characteristics, thereby improving gene variation identifying accuracy.
Owner:BEIJING SENSETIME TECH DEV CO LTD
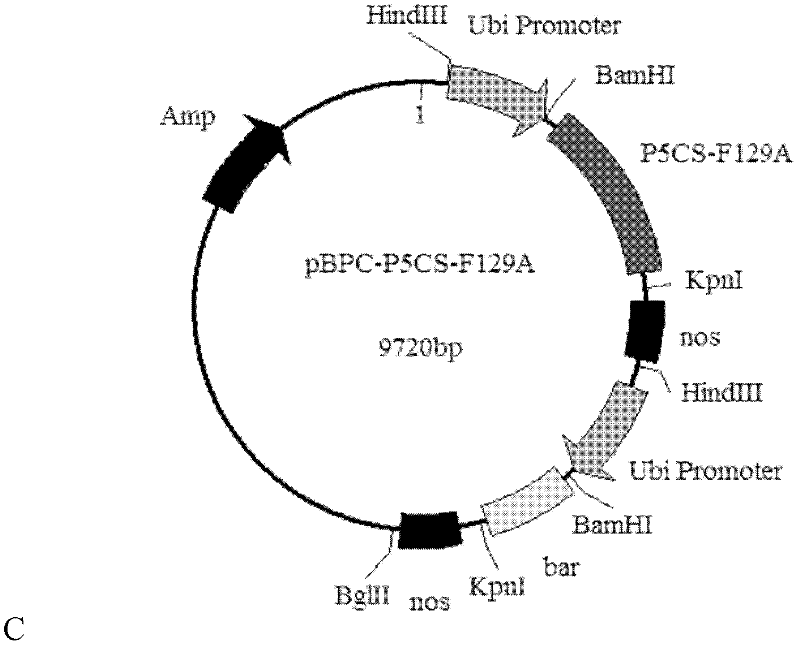
Application of Cre/loxP recombinant enzyme system in transgenic breeding of chrysanthemum
InactiveCN102559742AThe result is accurateVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsGene PositionLow temperature treatment
The invention relates to the application of a Cre / loxP recombinant enzyme system in transgenic breeding of chrysanthemum. According to the invention, a particle bombardment method is adopted to convert plant expression vectors that respectively carry exogenous P5CS (Pyrroline 5 Carboxylate Synthetase), NP-1 (Nuclear Protein-1) genes and Cre / loxP to together into ground-cover chrysanthemum, and transgenic lines adopting polygenic integration transformation are determined and obtained through hybridization detection of PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) and Southern; and then low temperature treatment is performed at the temperature of 4 DEG C, and Cre can express, so that a selectable marker gene positioned between two equidirectional loxP sites is deleted, detection is carried out through a molecular method to prove that the obtained results are correct, and the ground-cover chrysanthemum transgenic lines that do not contain marker genes npt-II are obtained.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Seed selection method of high stigma exsertion rate japonica two-line sterile line
ActiveCN104170716AImprove fertilityImprove breeding efficiencyPlant genotype modificationGene PositionGreenhouse
A seed selection method of a high stigma exsertion rate japonica two-line sterile line belongs to the fields of two-line hybrid japonica rice genetic breeding and seed production. The method comprises the following steps: 1 choosing a two-line sterile line with a high stigma exsertion rate as a donor parent; 2, hybridizing the donor parent with a japonica two-line sterile line; 3, selecting individual plants with the stigma exsertion rate reaching above 95% from the above obtained F2 generation; 4, selecting materials with high stigma exsertion rate and stable and consistent group properties from the above obtained F3 to F7 generations; 5, carrying out high stigma exsertion rate gene positioning on the obtained materials, and selecting low initial temperature materials by using a greenhouse; 6, hybridizing the materials obtained in step 5 with conventional japonica rice, backcrossing the F2, selecting thoroughly abortive individual plants from BC1F2, cutting spikes, and collecting seeds; 7, continuously inbreeding the obtained materials in Hainan to F4, experimentally planting the BC1F5 in different latitude regions, selecting temperature and light-insensitive sterile individual plants, cutting spikes, and collecting seeds; and 8, carrying out stigma exsertion gene detection on the obtained materials, and finally screening a two-line sterile line material with a high stigma exsertion rate. The method can significantly improve the breeding efficiency and the seed yield.
Owner:天津天隆科技股份有限公司
Respiratory syncytial virus vaccines expressing protective antigens from promoter-proximal genes
InactiveUS7662397B2Altered immunogenicitySmall sizeSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsProtective antigenNucleotide
Recombinant respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) having the position of genes shifted within the genome or antigenome of the recombinant virus are infectious and attenuated in humans and other mammals. Gene shifted RSV are constructed by insertion, deletion or rearrangement of genes or genome segments within the recombinant genome or antigenome and are useful in vaccine formulations for eliciting an anti-RSV immune response. Also provided are isolated polynucleotide molecules and vectors incorporating a recombinant RSV genome or antigenome wherein a gene or gene segment is shifted to a more promoter-proximal or promoter-distal position within the genome or antigenome compared to a wild type position of the gene in the RSV gene map. Shifting the position of genes in this manner provides for a selected increase or decrease in expression of the gene, depending on the nature and degree of the positional shift.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Molecular identification method for China rana rugulosa and Thailand rana rugulosa
InactiveCN103667482AStrong specificitySimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular identificationGene Position
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Microbiology method for detecting metallic arsenic in water body
ActiveCN104911200AReduce the background valueHigh background valueBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliFluorescence
The invention relates to a microbiology method for detecting metallic arsenic in water body, which more specifically relates to an Escherichia coli report bacterial strain construction method through gene engineering reconstruction, and relates to a method for establishing arsenic in water body. According to the construction of detection bacterial strain, a Red recombination system is employed for deleting wild type escherichia coli MC4100 arsenic resistance arsB gene, and then a gene integration technology is employed for displacing pars-arsR-gfpmut2 reporter gene to the araB coding gene position. The biological detection bacterial strain is named as E.coli WMC-011p, and a lowest detection scope for arsenic accords with a sewage integration discharge standard-GB8978-1996. The bacterial strain overcomes the disadvantages of high fluorescence background value, unstable detection signal and inaccurate result of the biological detection bacterial strain based on a plasmid carrier, and has the characteristics of strong specificity, high sensitivity and low cost.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
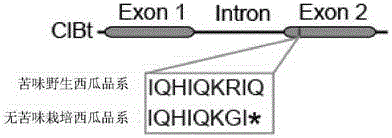
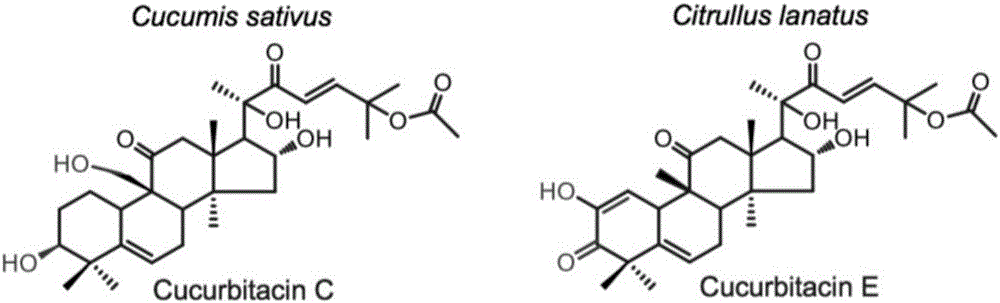
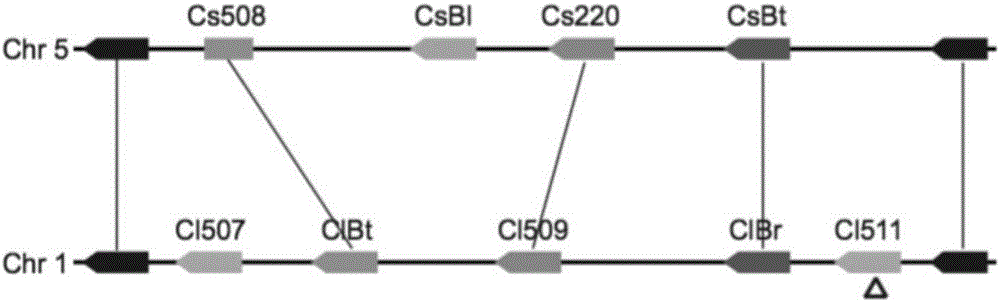
Transcription factor participating in regulating watermelon bitter principle and application thereof
ActiveCN106518994ATranslation terminated earlyMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesYeastGene Position
The invention provides a transcription factor participating in regulating watermelon bitter principle and an application thereof. Two bHLH transcription factors ClBr and ClBt controlling bitterness synthesis are discovered in watermelon genome for the first time by use of comparative genomics, wherein the two bHLH transcription factors control the formation of bitterness in the root and wild fruits respectively. The yeast one-hybrid technology, gel retardation experiment and tobacco transient expression system prove that the two transcription factors can be directly combined to the promoter area of the bitter principle synthesis gene and activate the expression of the synthesis gene; and meanwhile, through the transient expression of watermelon cotyledon, the overexpression of ClBr and ClBt is genetically proven to activate the expression of the bitterness synthesis gene so that the bitterless cotyledon obtains a bitterness phenotype. The ClBt gene encodes the mutation of an SNP so that the bitter fruit loses bitterness; and moreover, the gene positioned in an acclimation area is an acclimation gene. The invention further discloses a molecular mechanism forming watermelon bitterness and provides a theoretical basis for bitterless watermelon breeding.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
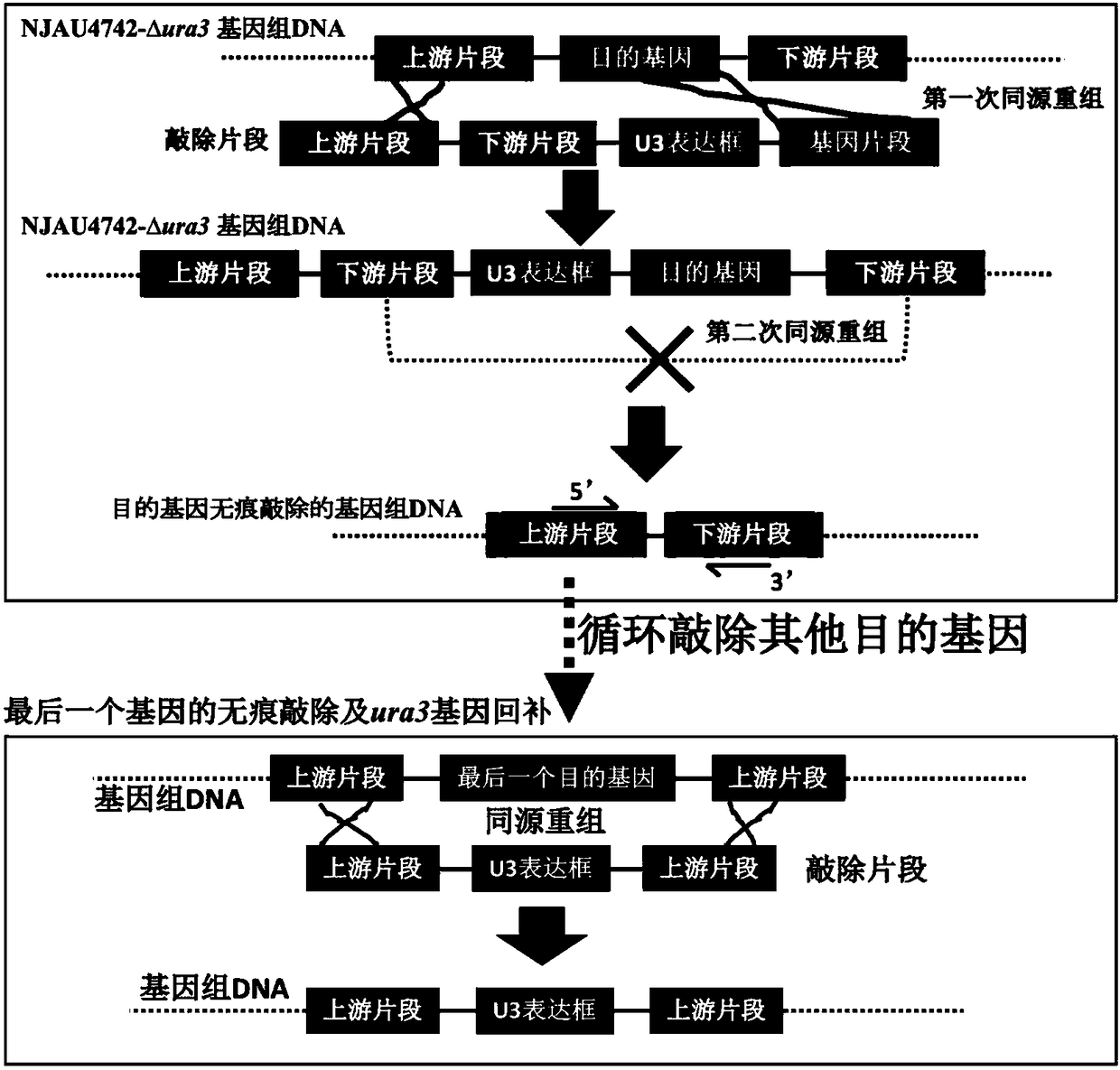
Traceless gene editing method for trichoderma fungi
ActiveCN108384797ASolve scientific research problems that are extremely difficult to operateRealize traceless recyclable operationFungiStable introduction of DNAHygromycin BGene Position
The invention relates to a traceless gene editing method for trichoderma fungi. According to the method, the traceless knockout mutant of the trichoderma guizhouense ura3 gene is obtained through twotimes of homologous recombination events and in combination with the resistance screening strategy of hygromycin B and the lethal strategy of 5-FOA; based on the mutant, the knockout fragment containing the ura3 gene expression cassette is inserted at the position of the target gene through the homologous recombination method, and the mutant having the first-time homologous recombination is screened by utilizing the nutrition defect feature of the ura3 traceless mutant; after the second-time homologous recombination, the ura3 gene and the target gene are removed through recombination, at the time, inverse screening is carried out by utilizing the lethal feature of 5-FOA, and thus the traceless mutant with the target gene completely deleted is obtained. The system is optimized sufficiently,the homologous recombination ratio is 15% or above, the single-gene traceless operating period is shortened to be within 15 days, meanwhile, the traceless overexpression of the target gene can be realized, and no exogenous fragments are introduced during the process.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
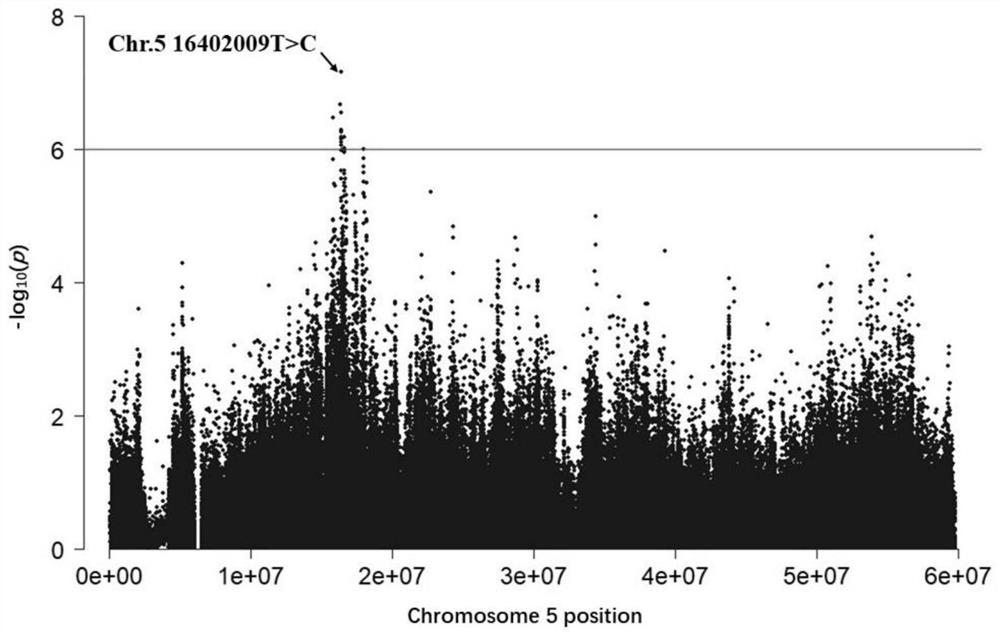
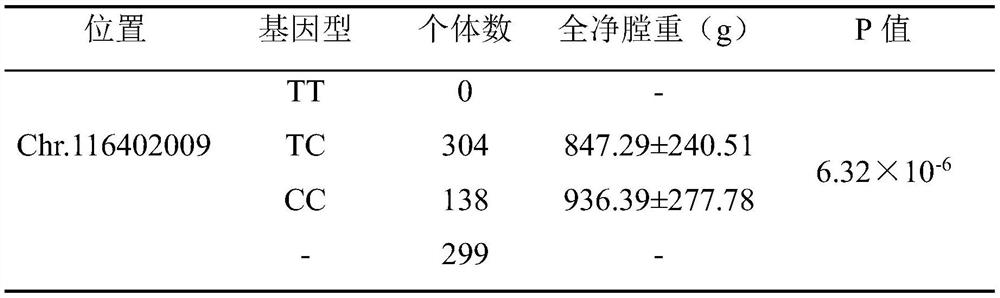
Molecular marker influencing oblique length of chicken body and application thereof
ActiveCN111926086AIncrease selection strengthImprove breeding efficiencyFood processingMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyGenes mutation
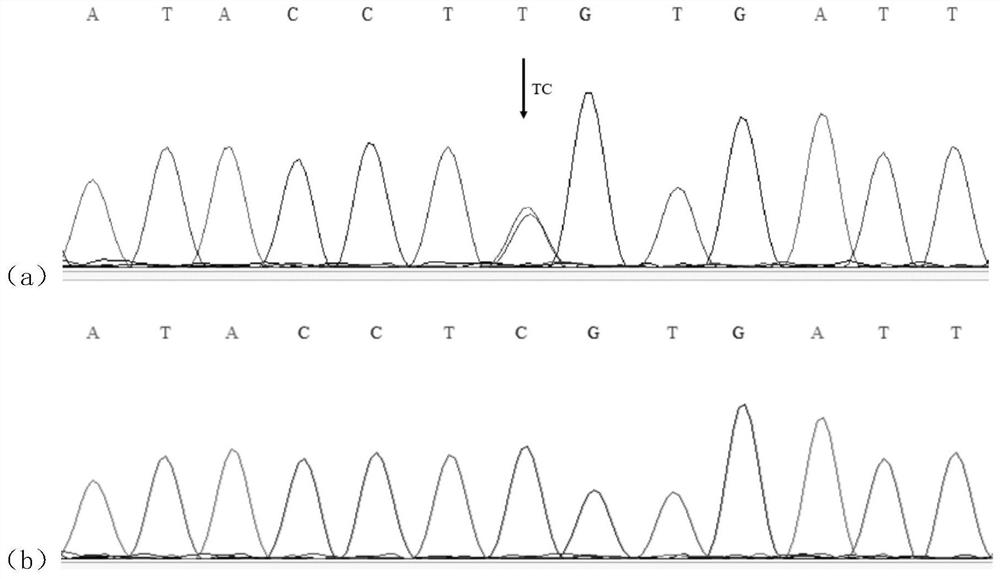
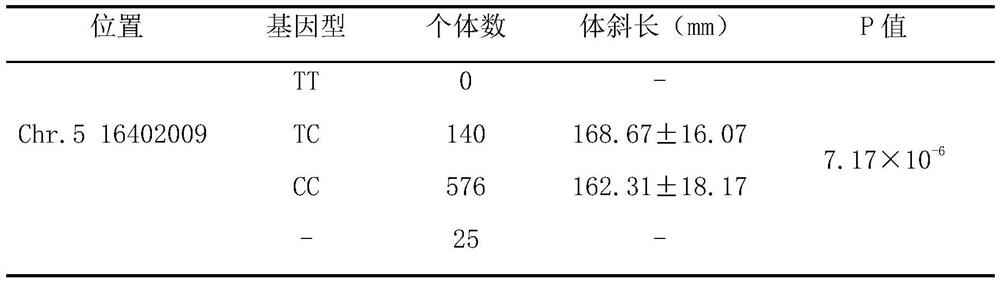
The invention discloses a molecular marker influencing the oblique length of a chicken body and application of the molecular marker, and belongs to the technical field of molecular marker assisted selection and animal genetic breeding. The molecular marker disclosed by the invention is obtained by carrying out genome wide association study (GWAS) analysis on 741 test chickens in F2-generation resource groups established by Dawei Mountain miniature chickens and WRR broilers; a nucleotide single-base mutation (named as Chr.16402009T>C) of T>C exists at the 16402009bp position of a chromosome V of a chicken reference genome Gallus_gallus.GRCg6a version. A gene positioned near the nucleotide single-base mutation is a lysine methyltransferase 5B (KMT5B) gene, and the oblique body length of thechicken is obviously influenced by mutation. The invention discloses acquisition and application of the molecular marker. The invention further provides an SNP molecular marker genotyping detection method influencing the oblique length of the chicken body, an efficient and accurate molecular marker assisted breeding technology can be established by utilizing the method, and the molecular marker assisted breeding technology is applied to chicken growth and development genetic improvement, so that the growth and development of the chicken are improved.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Whole genome association analysis method based on comparison of multiple genomes and next-generation sequencing data
ActiveCN113628685AImplementation of association analysisEasy to understandProteomicsGenomicsGene PositionWhole Genome Association Analysis
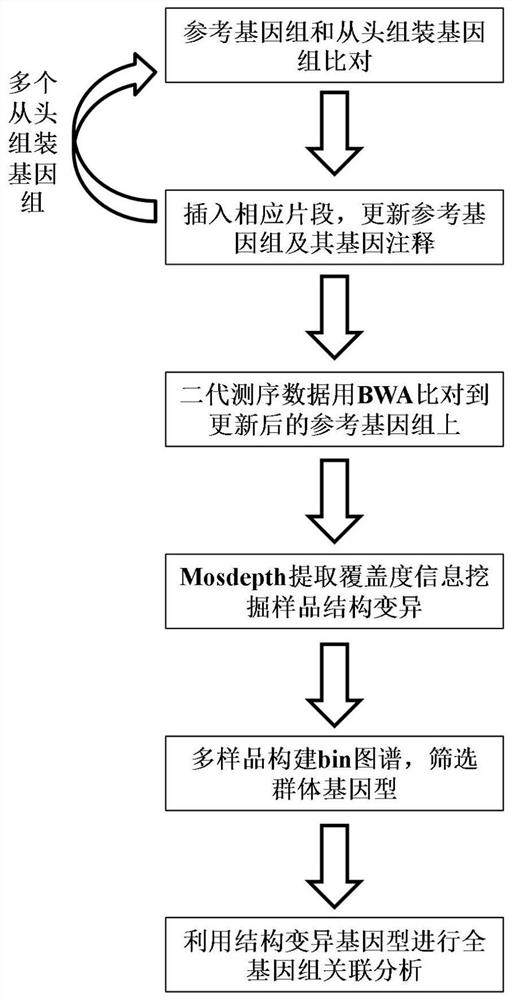
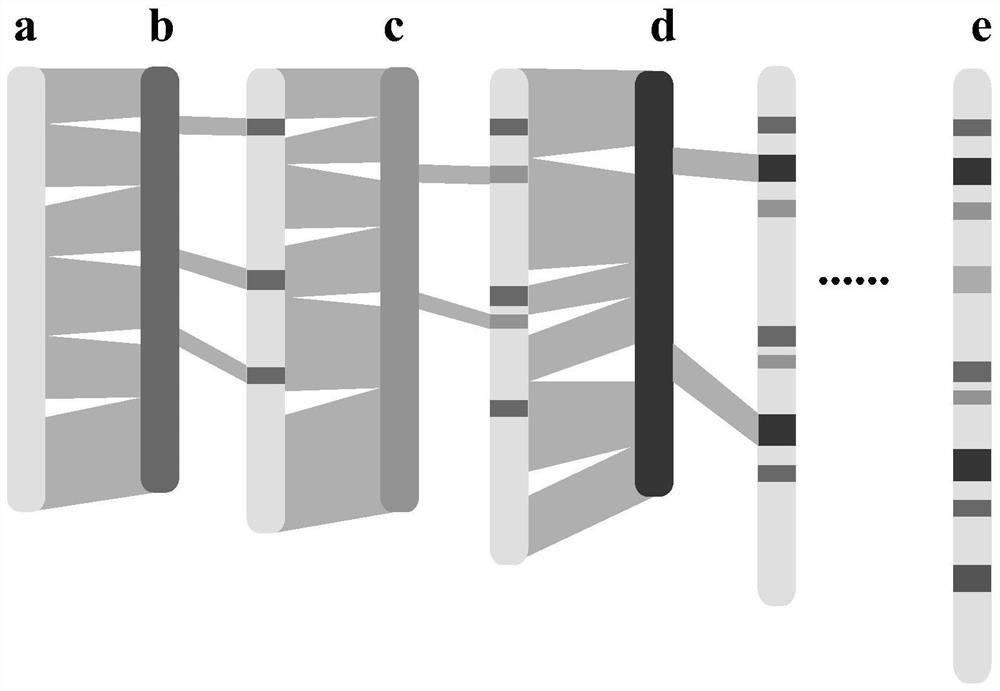
The invention discloses a whole genome association analysis method based on comparison of multiple genomes and next-generation sequencing data, which comprises the following steps of: 1, comparing a reference genome with a de novo assembly genome file by using comparison software; and updating the annotation gene positions or structures in the reference genomes; 3, if a plurality of de novo assembly genomes exist, sequentially iteratively updating the reference genomes; 4, comparing the next-generation sequencing data of the samples to the updated reference genome by using comparison software; 5, collecting demarcation point position information of all structural variations of all the samples into a set, constructing a population genotype; and 6, performing functional gene candidate according to the association site and the updated reference genome annotation file. According to the method, the whole genome association analysis is performed by using the structure variation genotype data.
Owner:RICE RES INST GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Respiratory syncytial virus vaccines expressing protective antigens from promotor-proximal genes
InactiveUS20060024797A1Promote growthImprove the attenuation effectSsRNA viruses negative-senseSugar derivativesAntigenGenomic Segment
Recombinant respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) having the position of genes shifted within the genome or antigenome of the recombinant virus are infectious and attenuated in humans and other mammals. Gene shifted RSV are constructed by insertion, deletion or rearrangement of genes or genome segments within the recombinant genome or antigenome and are useful in vaccine formulations for eliciting an anti-RSV immune response. Also provided are isolated polynucleotide molecules and vectors incorporating a recombinant RSV genome or antigenome wherein a gene or gene segment is shifted to a more promoter-proximal or promoter-distal position within the genome or antigenome compared to a wild type position of the gene in the RSV gene map. Shifting the position of genes in this manner provides for a selected increase or decrease in expression of the gene, depending on the nature and degree of the positional shift. In one embodiment, RSV glycoproteins are upregulated by shifting one or more glycoprotein-encoding genes to a more promoter-proximal position. Genes of interest for manipulation to create gene position-shifted RSV include any of the NS1, NS2, N, P, M, SH, M2(ORF1), M2(ORF2), L, F or G genes or a genome segment that may be part of a gene or extragenic. A variety of additional mutations and nucleotide modifications are provided within the gene position-shifted RSV of the invention to yield desired phenotypic and structural effects.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Method for providing recombinant baculovirus with polyhedrosis coatings
InactiveCN101205535AImprove labor efficiencyRecombinant DNA-technologyViruses/bacteriophagesGene PositionBiotechnology
The invention provides a method for obtaining polyhedron by recombining baculovirus and utilizing the obtained polyhedron to feed, wherein, silkworm baculovirus polyhedron genes are transposed onto chromosomes of silkworm cells; recombined silkworm baculoviruses are infected the silkworm cells after modification; the polyhedron genes positioned on the chromosomes of the silkworm cells express along with stimulus of expression of virogenes, thereby the recombined baculoviruses can be embedded into the polyhedron; the polyhedron is then sprayed on mulberry leaves, and silkworm larvae can be infected after eating the mulberry leaves, thereby work efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method for transforming schizosaccharomyces pombe, transformant of schizosaccharomyces pombe and method for producing heterologous protein
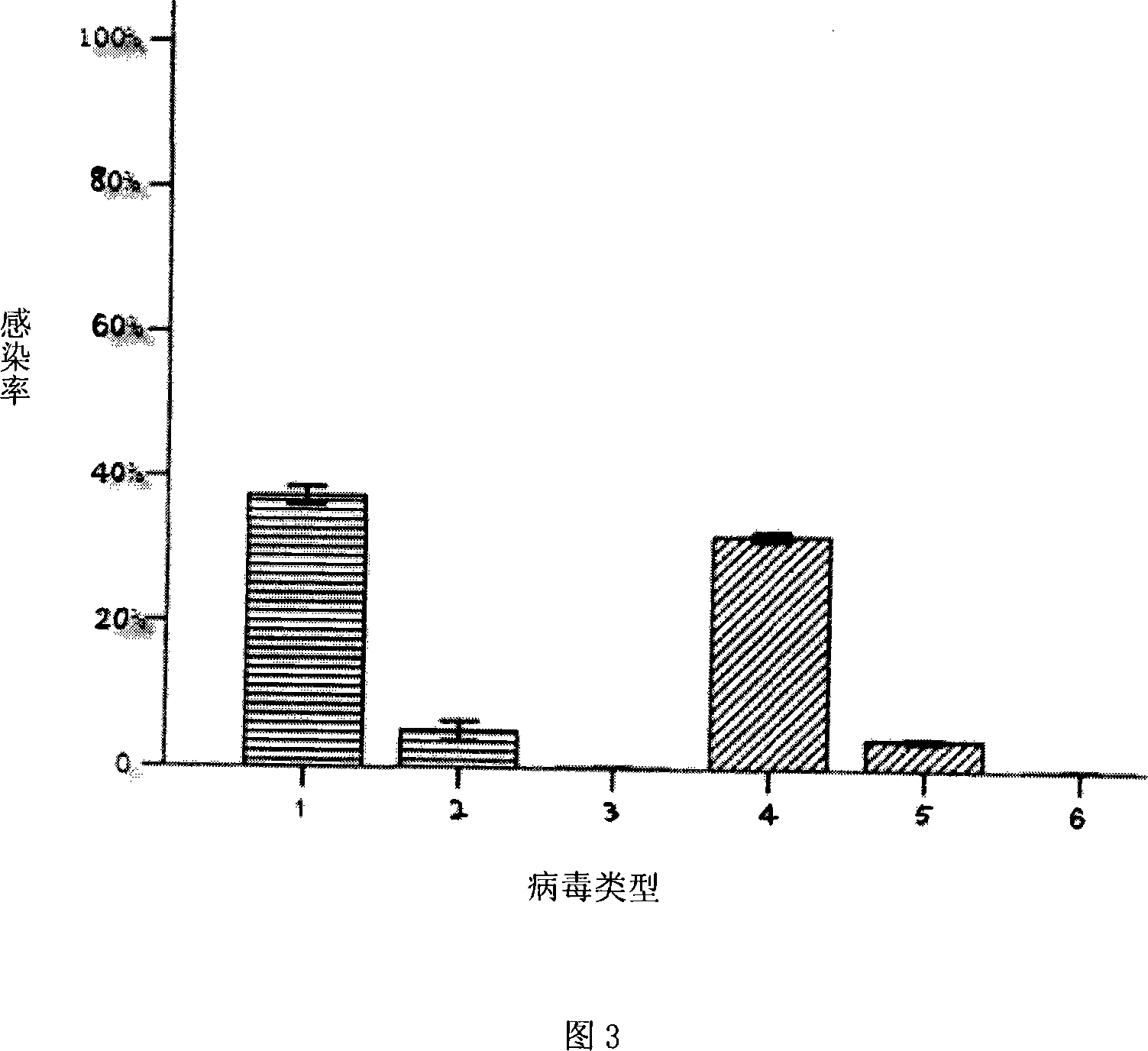
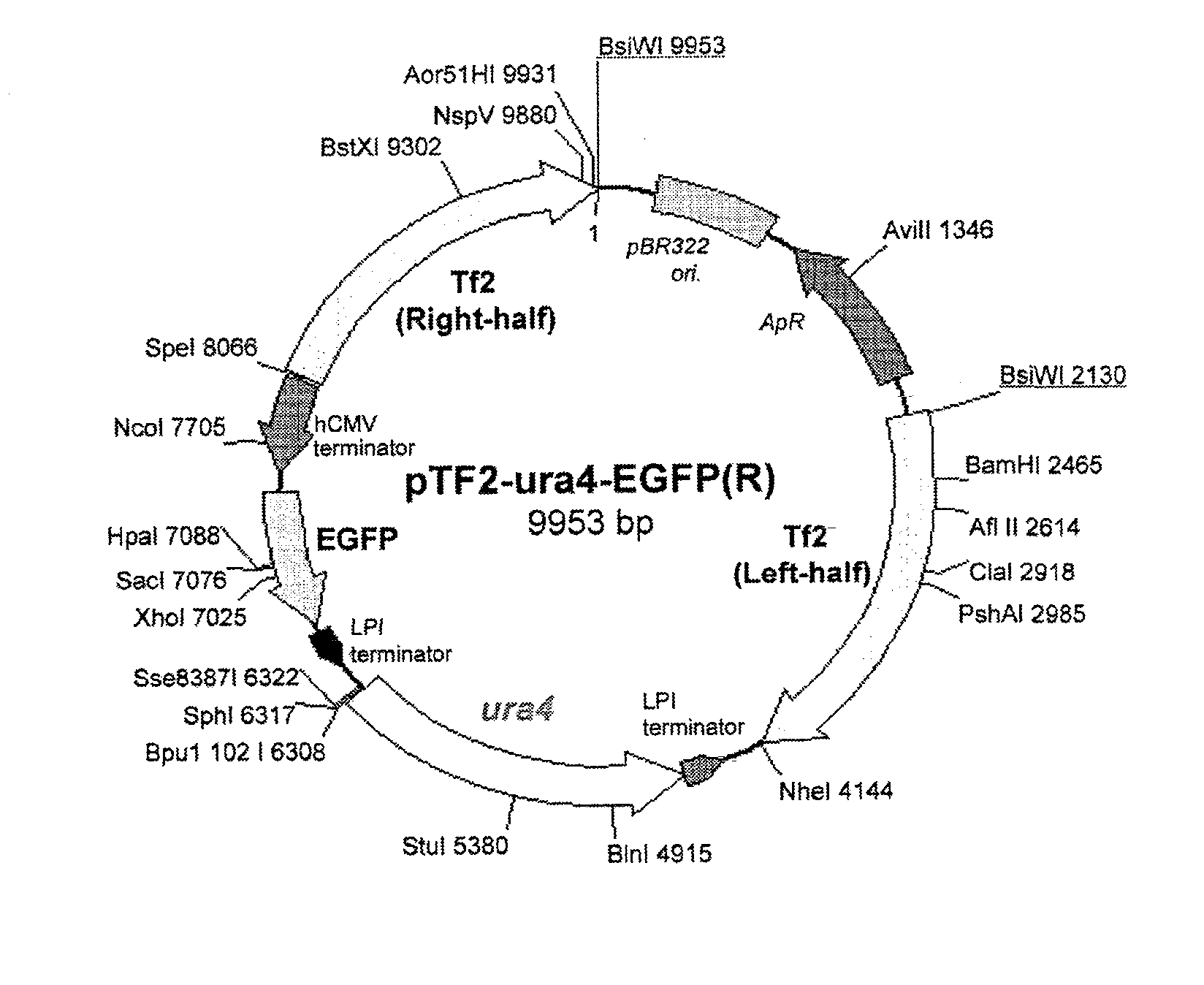
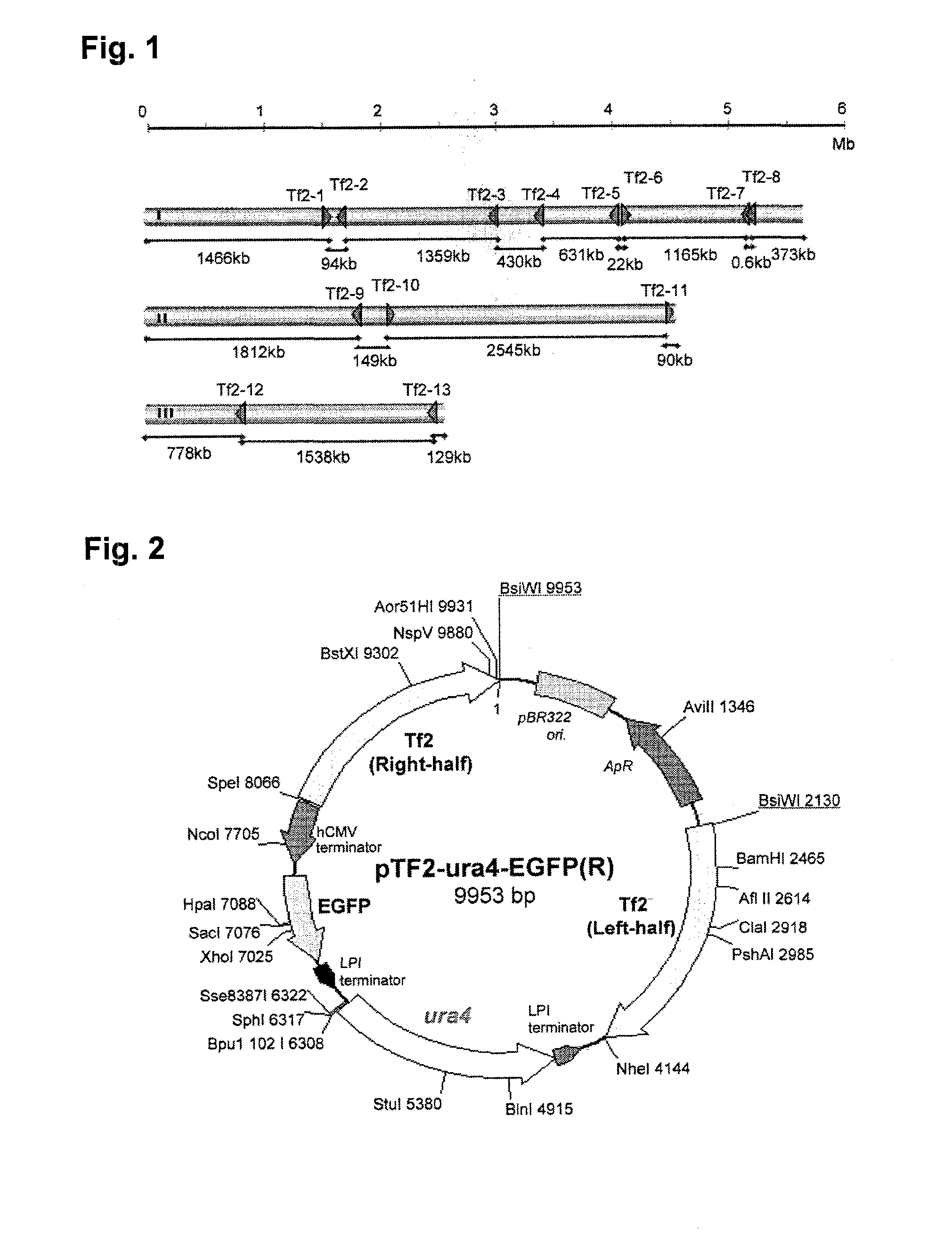
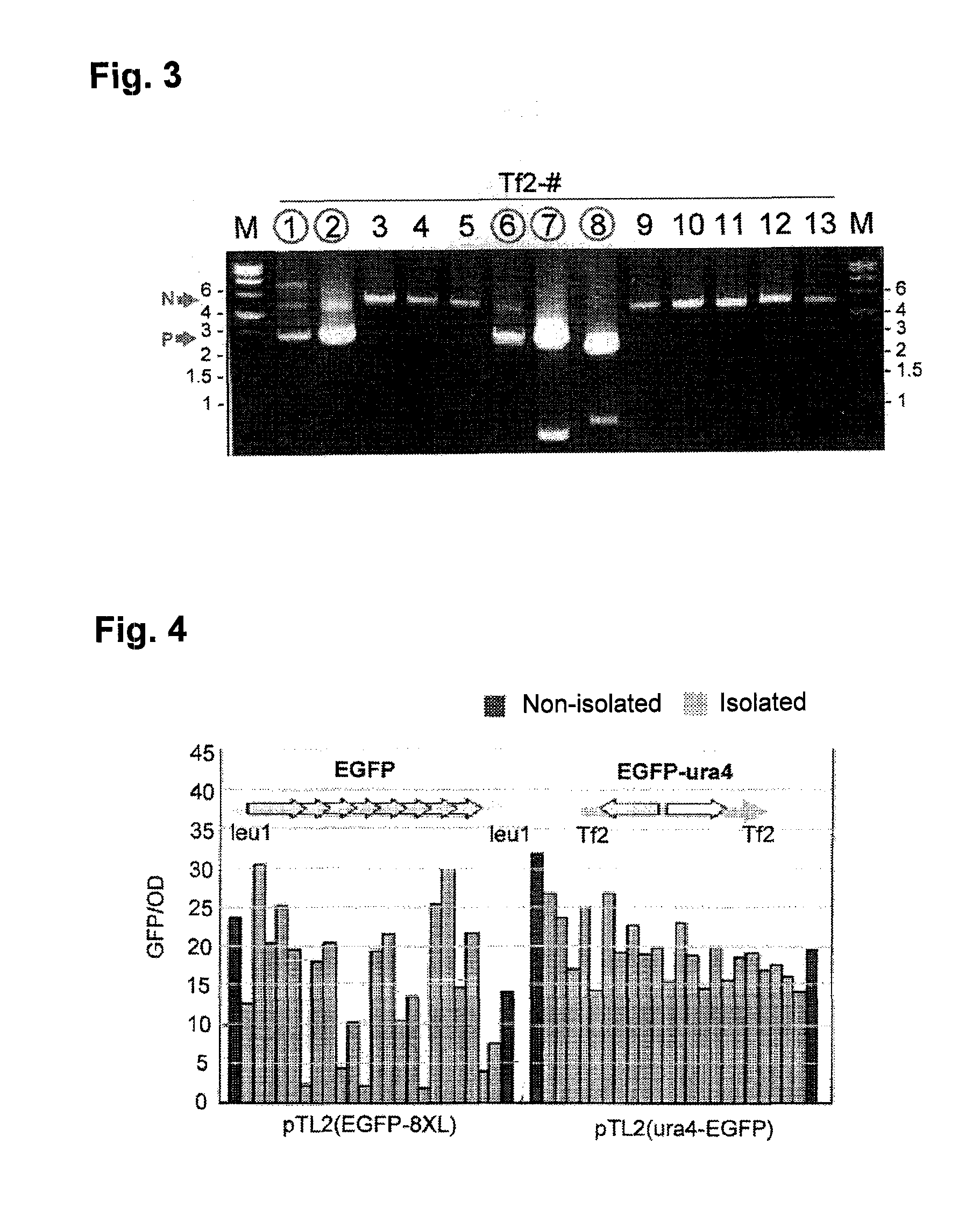
To provide a method for transforming S. pombe for creating a transformant with a high stability of maintenance after passage and enables the steady production of a heterologous protein of interest, a transformant produced by the method and a method for producing a heterologous protein using the resultant transformant.A method for transforming Schizosaccharomyces pombe by using a vector carrying an expression cassette (containing a promoter capable of functioning in Schizosaccharomyces pombe, a heterologous protein structural gene and a terminator), and having recombination region(s) at which homologous recombination with each chromosome of Schizosaccharomyces pombe is to be achieved, which comprises integrating the expression cassette into the Tf2 transposon gene position(s) in the chromosome(s) of Schizosaccharomyces pombe by homologous recombination, a transformant created by the method and a method for producing a heterologous protein using the resultant transformant.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Primer pair for detecting rice brown planthopper resistance gene Bph14 and application thereof
InactiveCN109913576AQuick filterImprove breeding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerRice plants
The invention discloses a primer pair for detecting a rice brown planthopper resistance gene Bph14 and an application thereof. The primer pair for detecting the rice brown planthopper resistance geneBph14 is a co-dominance marker primer B14InD. The co-dominance marker primer B14InD is as follows: a forward primer sequence: CTACTGATTGCAGATTGACG; and a reverse primer sequence: CACTTGGTGAACTTATTCCCTT. The primer pair for detecting the rice brown planthopper resistance gene Bph14 is used for performing PCR amplification to obtain a Bph14 specificity co-dominance molecular marker, and the brown planthopper resistance gene positioned by the Bph14 specificity co-dominance molecular marker is clear in position. Through detecting the specificity co-dominance molecular marker of the Bph14 gene, namely genetype detection applied to rice varieties or strains, brown planthopper resistance of a rice plant can be forecasted, and it is beneficial to improve seed breeding efficiency of brown planthopper resistance rice.
Owner:武汉禾泰青生物科技有限公司
Molecular marker affecting eriscerated yield of chicken and application of molecular marker
ActiveCN111961732AIncrease selection strengthImprove breeding efficiencyFood processingMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyGenes mutation
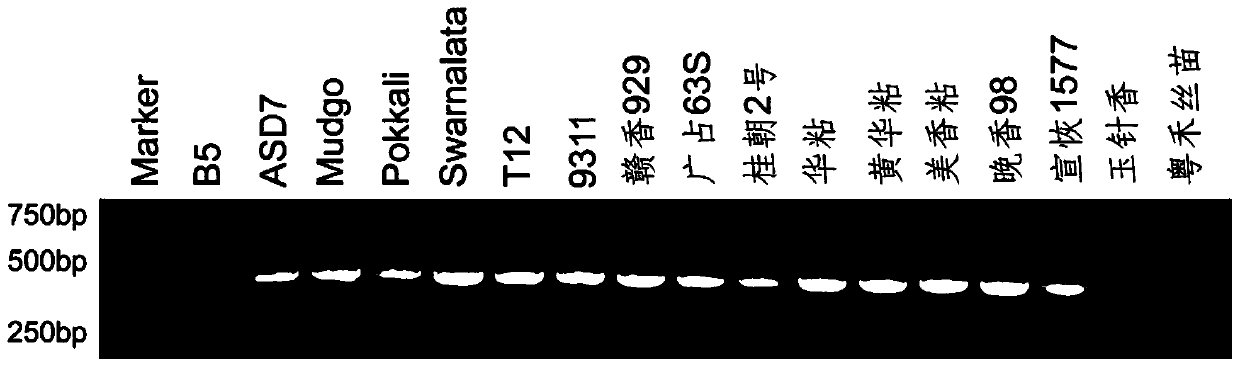
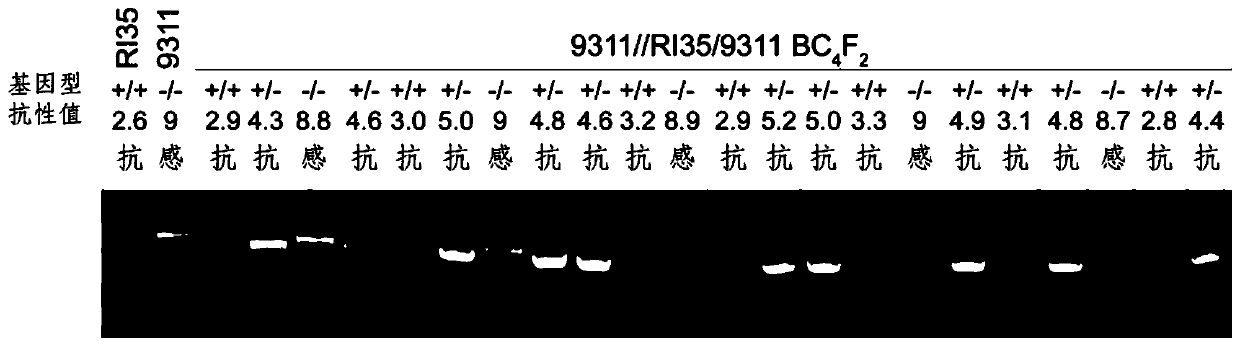
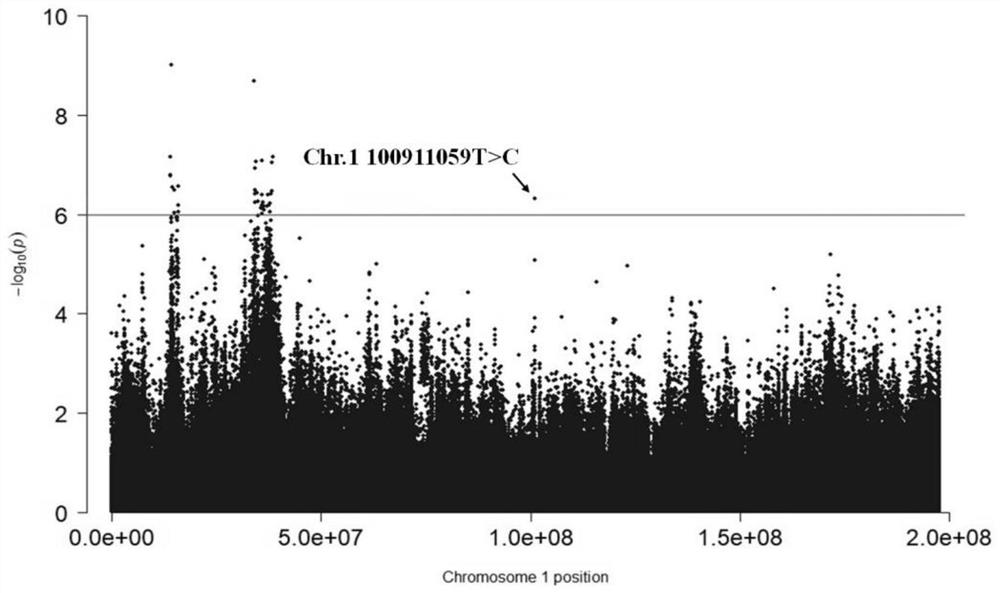
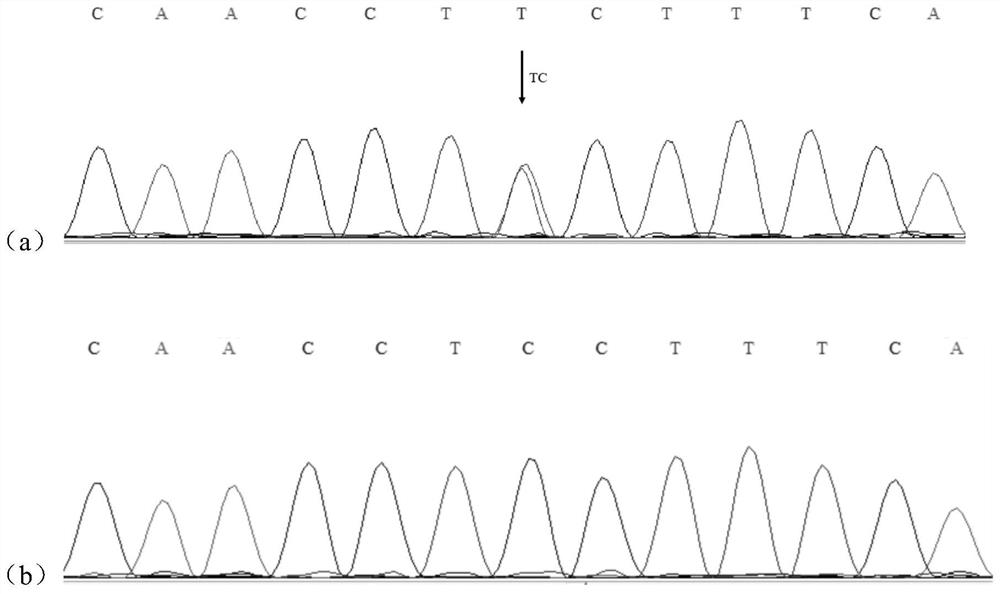
The invention discloses a molecular marker affecting the eriscerated yield of chicken and application of the molecular marker, and belongs to the technical fields of molecular marker-assisted selection and animal genetics and breeding. The molecular marker affecting the eriscerated yield of chicken is obtained by genome-wide association (GWAS) analysis on 741 test chickens from F2 generation resource population formed by Daweishan miniature chickens and recessive white plymouth rock, nucleotide single base mutation T>C (named: Chr.1 100911059T>C) exists at 100911059bp on chromosome 1 of the chicken ginseng genome Gallus_gallus. GRCg6a version, a gene positioned nearby the nucleotide single base mutation is gene of CHODL (chondrolectin), and the chicken eriscerated yield is significantly affected by mutation. The invention discloses acquisition and application of the molecular marker. The invention also provides a genotyping detection method for the molecular marker affecting the chicken eriscerated yield. An efficient and accurate molecular marker-assisted breeding technology can be established by the method, and is applied to genetic improvement of chicken meat production performance, so that chicken meat production is increased.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com