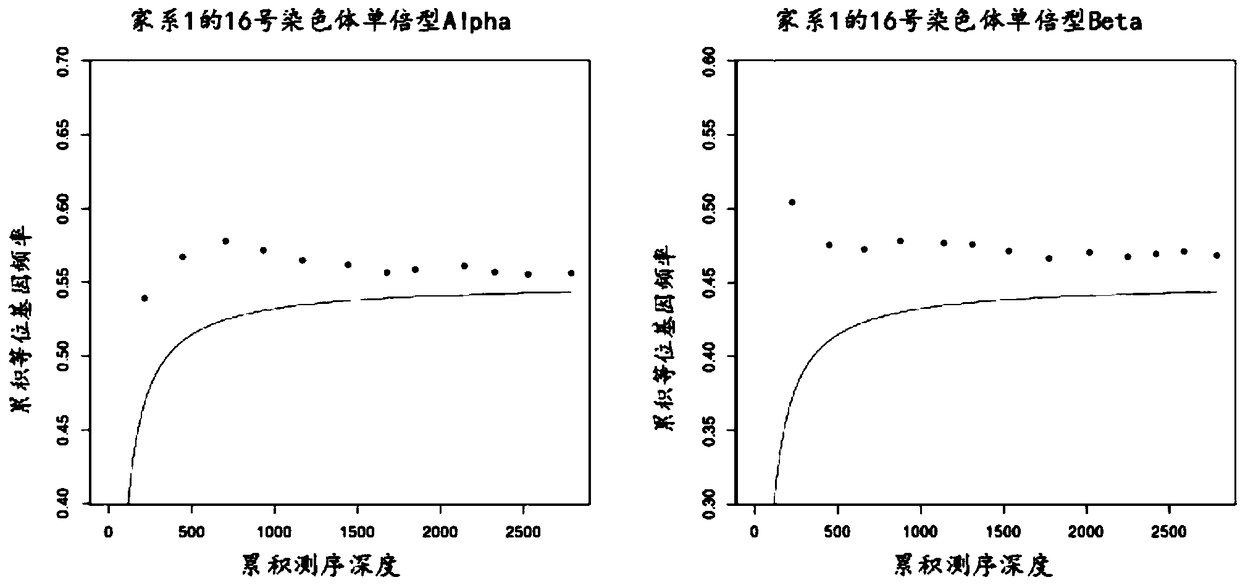
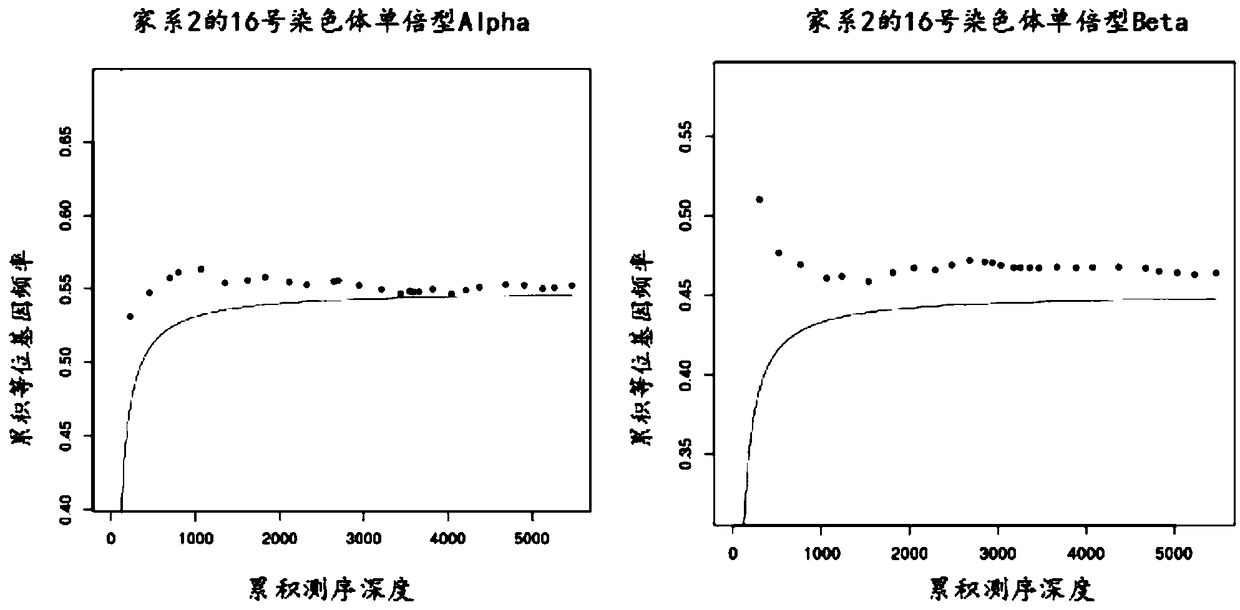
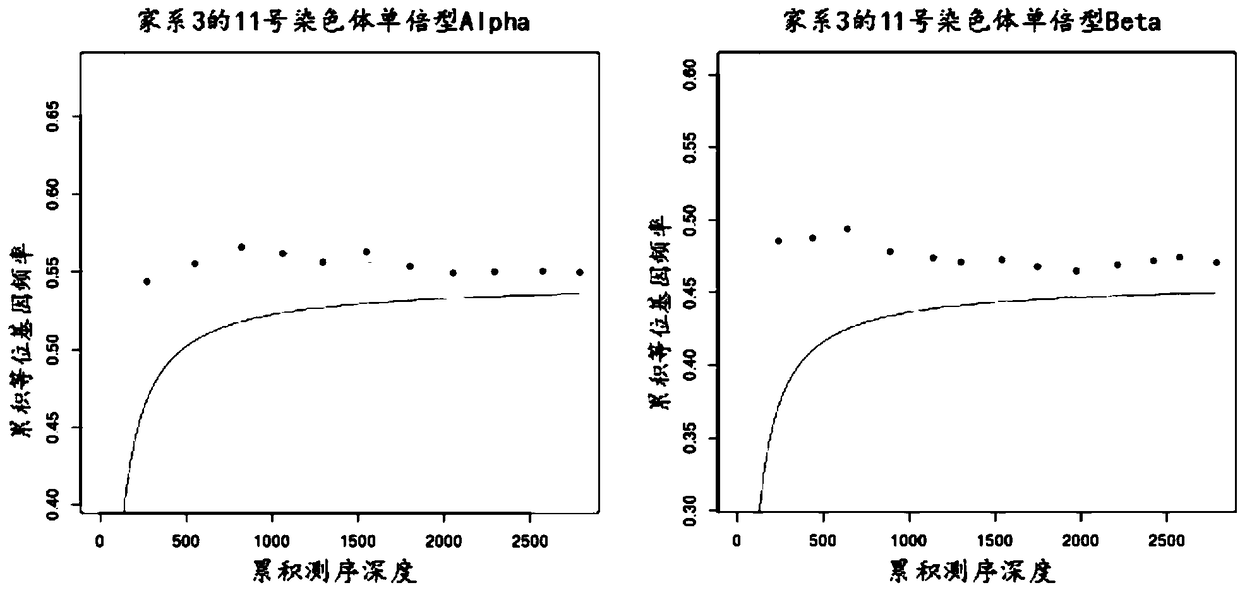
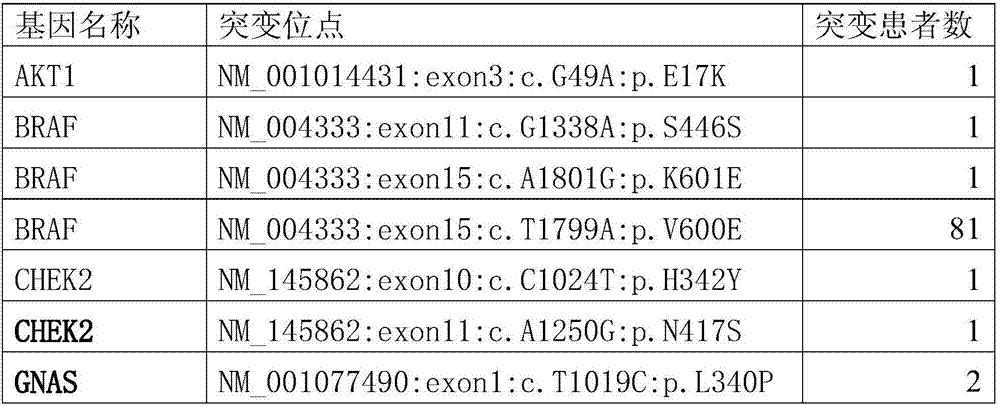
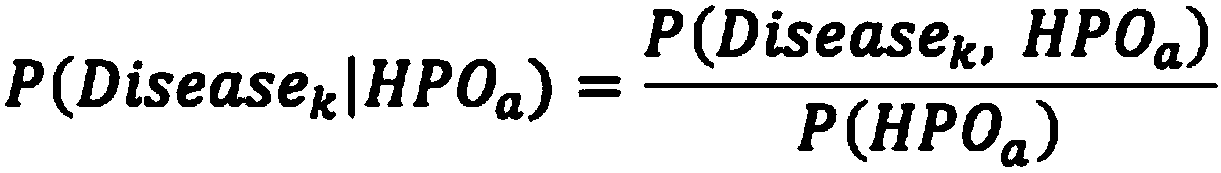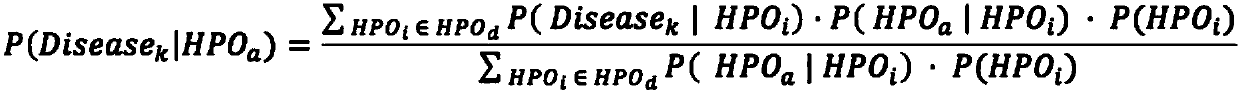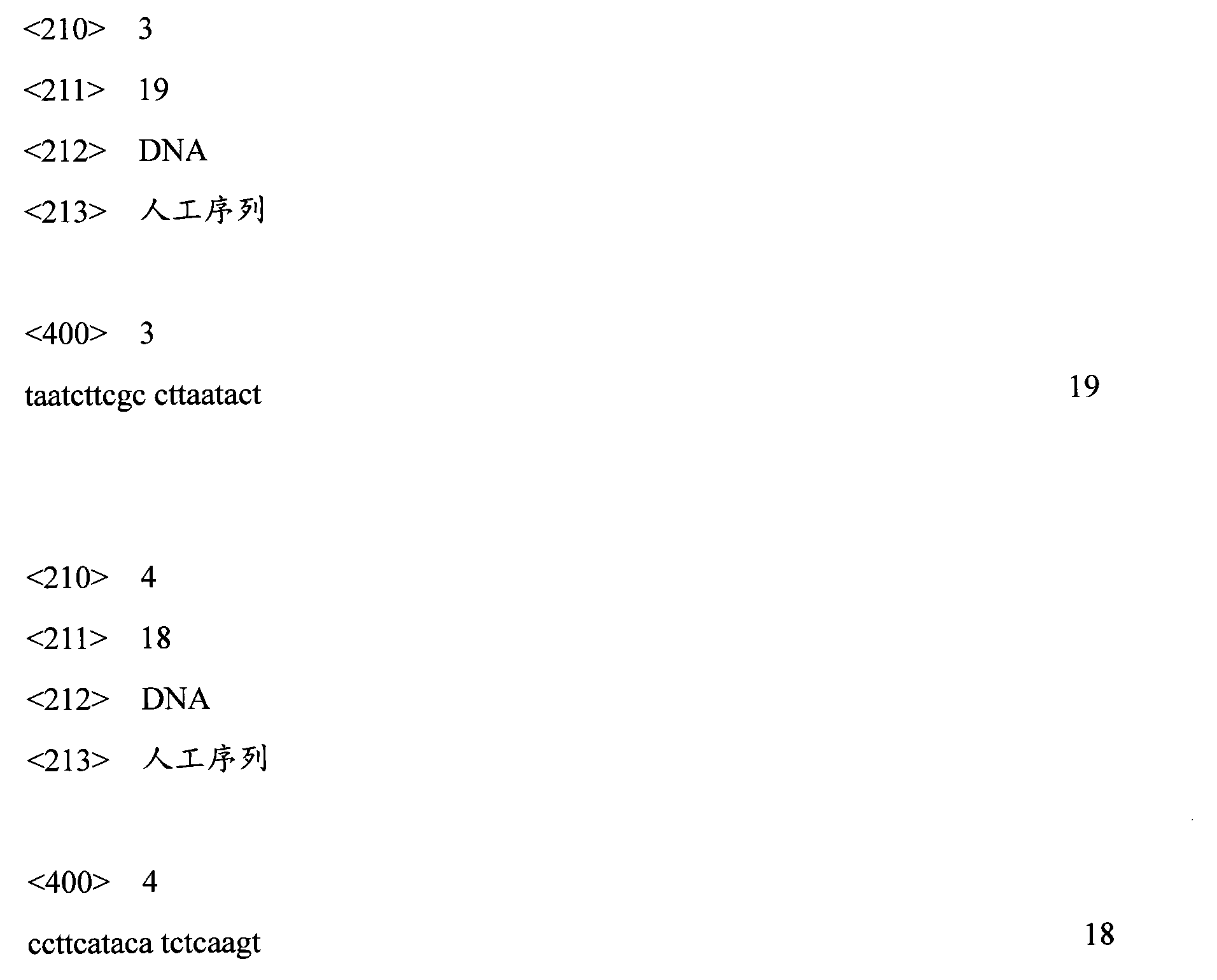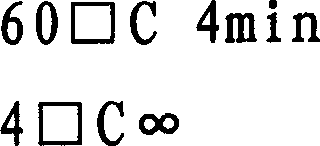Patents
Literature
443 results about "Pathogenic genes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pathogenic variant. listen (PA-thoh-JEH-nik VAYR-ee-unt) A genetic alteration that increases an individual’s susceptibility or predisposition to a certain disease or disorder. When such a variant (or mutation) is inherited, development of symptoms is more likely, but not certain.
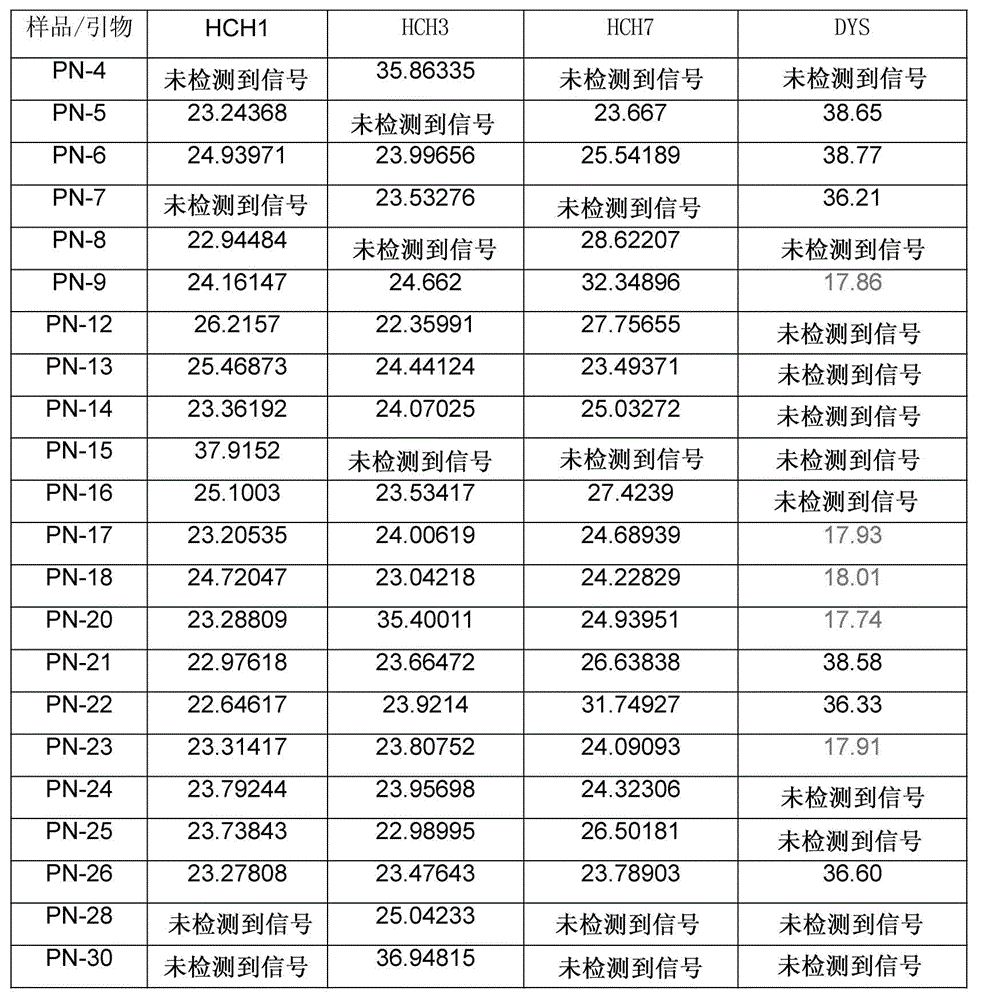
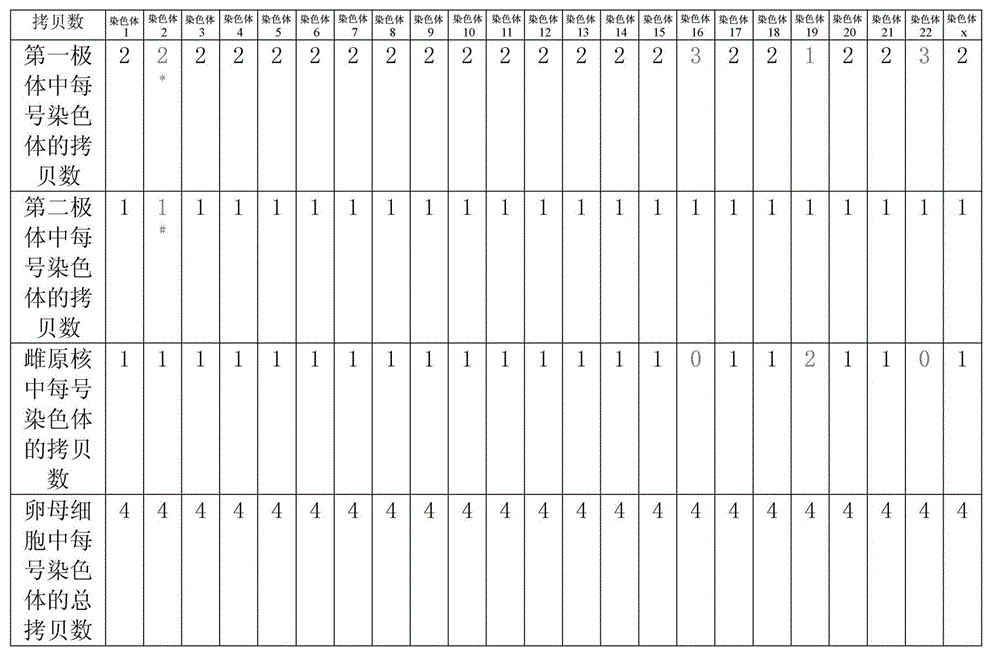
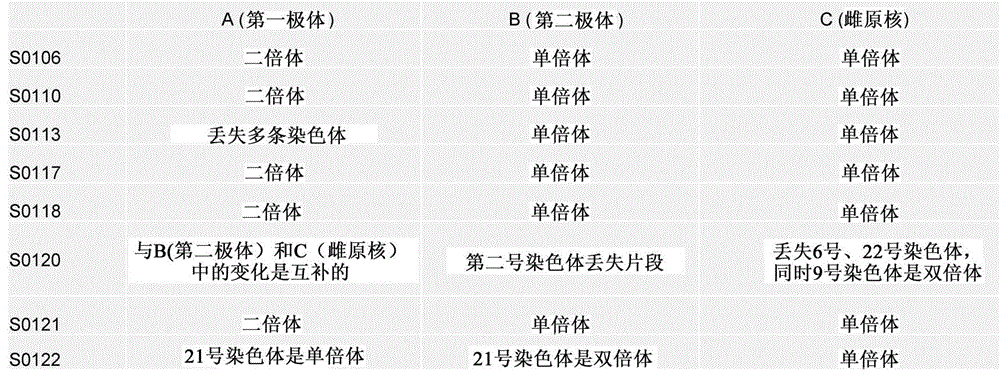
Selection of embryo of test tube baby through sequencing by single cell genome of polar body or embryo
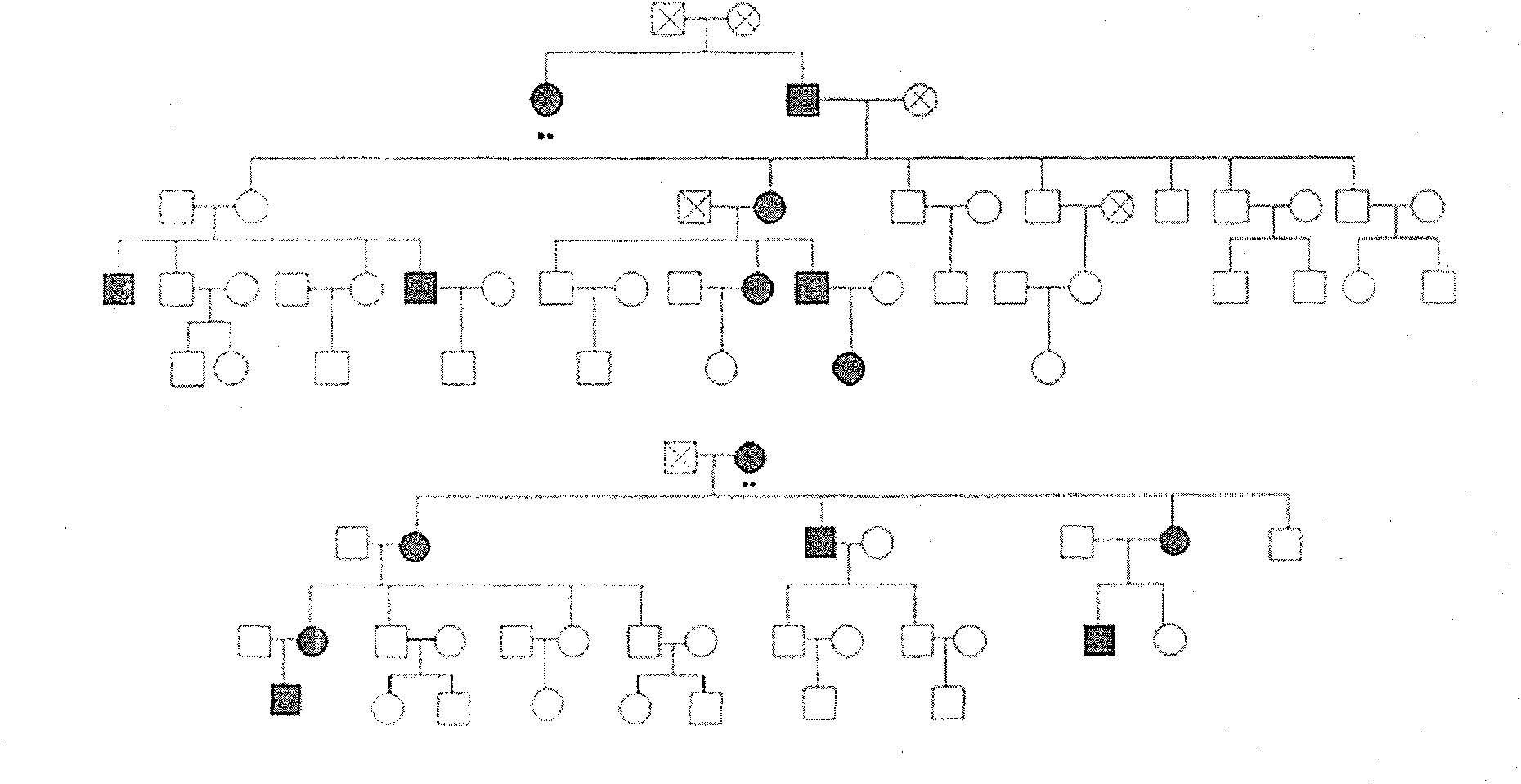
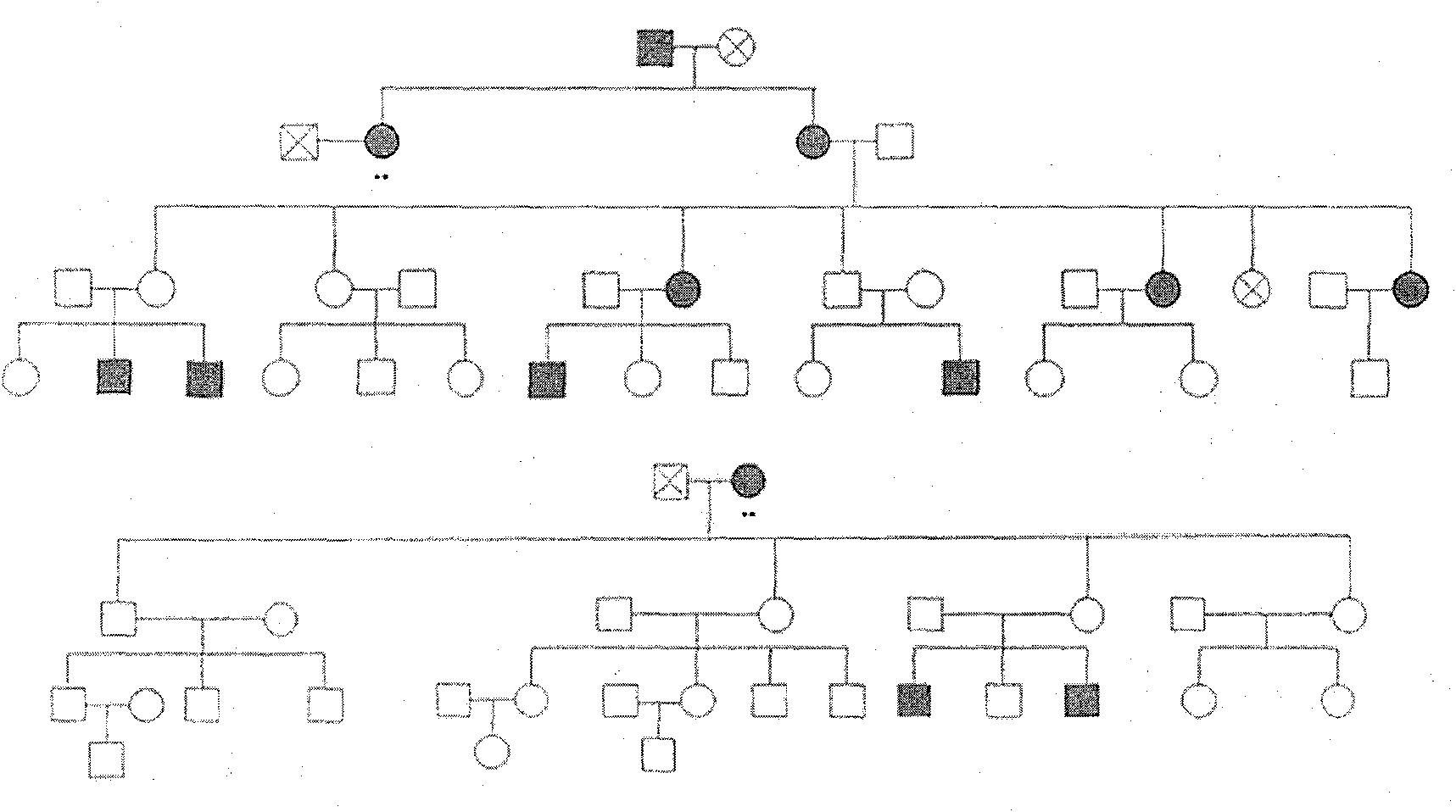
Disclosed is a method for using a first polar body and a second polar body as well as a single-cell embryo to carry out whole-genome non-exponential amplification and high-throughput genome sequencing, so as to perform preimplantation genetic diagnosis for genetic disease and testing for pathogenic genes causing repeated miscarriages. The method of the present invention comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining oocytes and embryos, and carrying out separation and genome amplification of first and second polar bodies and single-cell embryos; (2) establishing a genome sequencing library and sequencing, and carrying out bioinformatic analysis of the genome to obtain a gene spectrum and information concerning the number of copies of chromosomes and fragments thereof; (3) determining the chromosome ploidy of the polar bodies and embryos as well as information concerning defects, replication and point mutation in the chromosome fragments; (4) selecting normal or suitable embryos for implantation.
Owner:HARVARD UNIV +2
Gene chip for screening various ophthalmological hereditary diseases as well as preparation and usage method of gene chip
InactiveCN102978284AImprove efficiencyAccurate diagnosisNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementVirulent characteristicsIntein
The invention relates to the technical field of biological gene chips, and particularly relates to a gene chip for screening various ophthalmological hereditary diseases as well as preparation and a usage method of the gene chip. Specific oligonucleotide probes of gene sequences which are related to 261 ophthalmological hereditary diseases are fixed on the surface of a carrier of the gene chip for screening various ophthalmological hereditary diseases; and the gene chip which is related to the 261 ophthalmological hereditary diseases comprises the sequences of all coding region sequences of 954 related virulence genes or disease predisposing genes and introne sequences adjacent to the coding regions. As the specific oligonucleotide probes of the gene sequences which are related to 261 ophthalmological hereditary diseases and the sequences of all the coding region sequences of the related virulence genes or disease predisposing genes and the introne sequences adjacent to the coding regions are fixed on the surface of the carrier of the gene chip, the gene chip provided by the invention is capable of screening a plurality of ophthalmological hereditary diseases at the same time and then the efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:金子兵
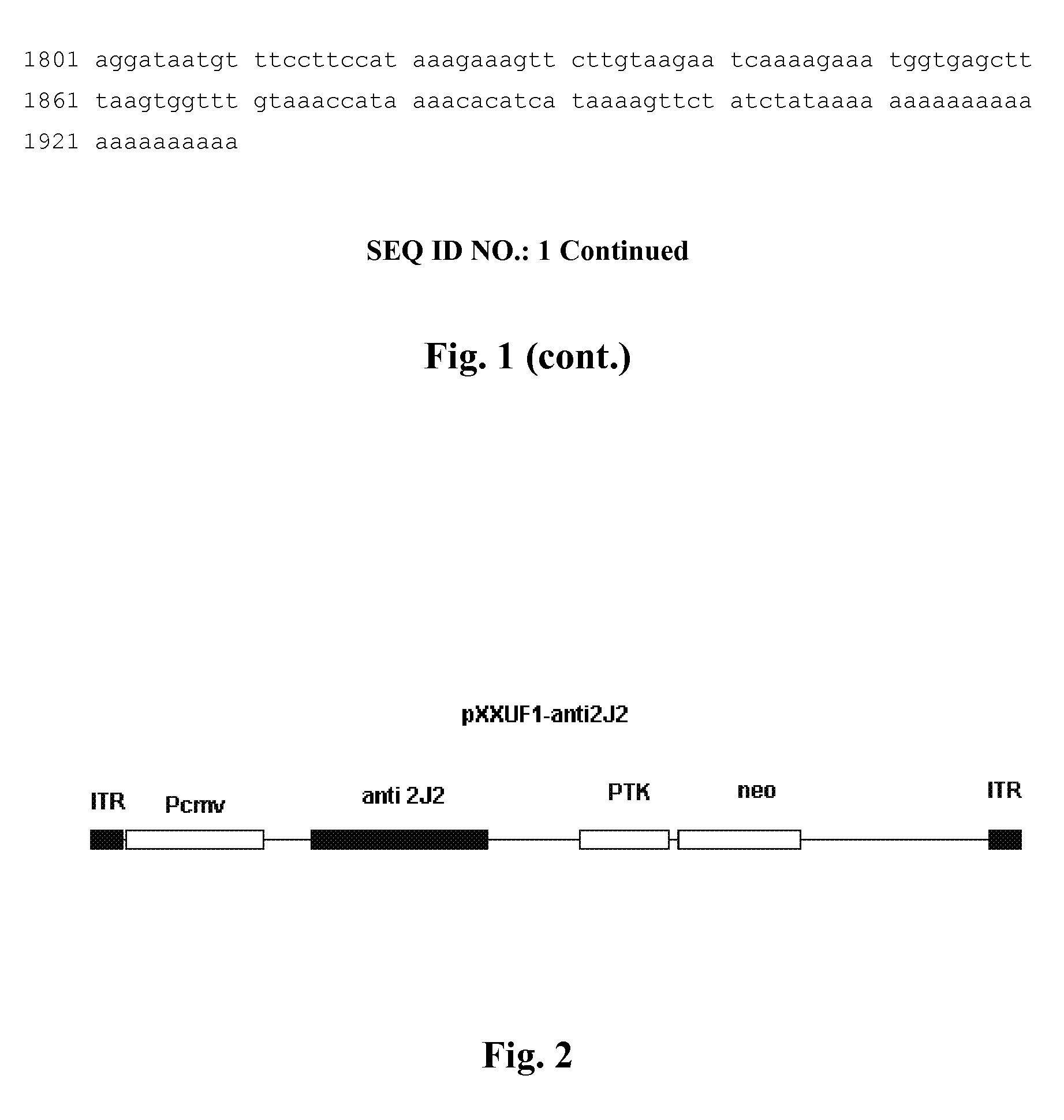
Recombinant adeno-associated virus expressing human antisense gene CyP2J2 and its preparation methods
ActiveUS8273344B2Inhibit proliferation and migrationPromote apoptosisBiocideGenetic material ingredientsNucleotideGenetics
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV
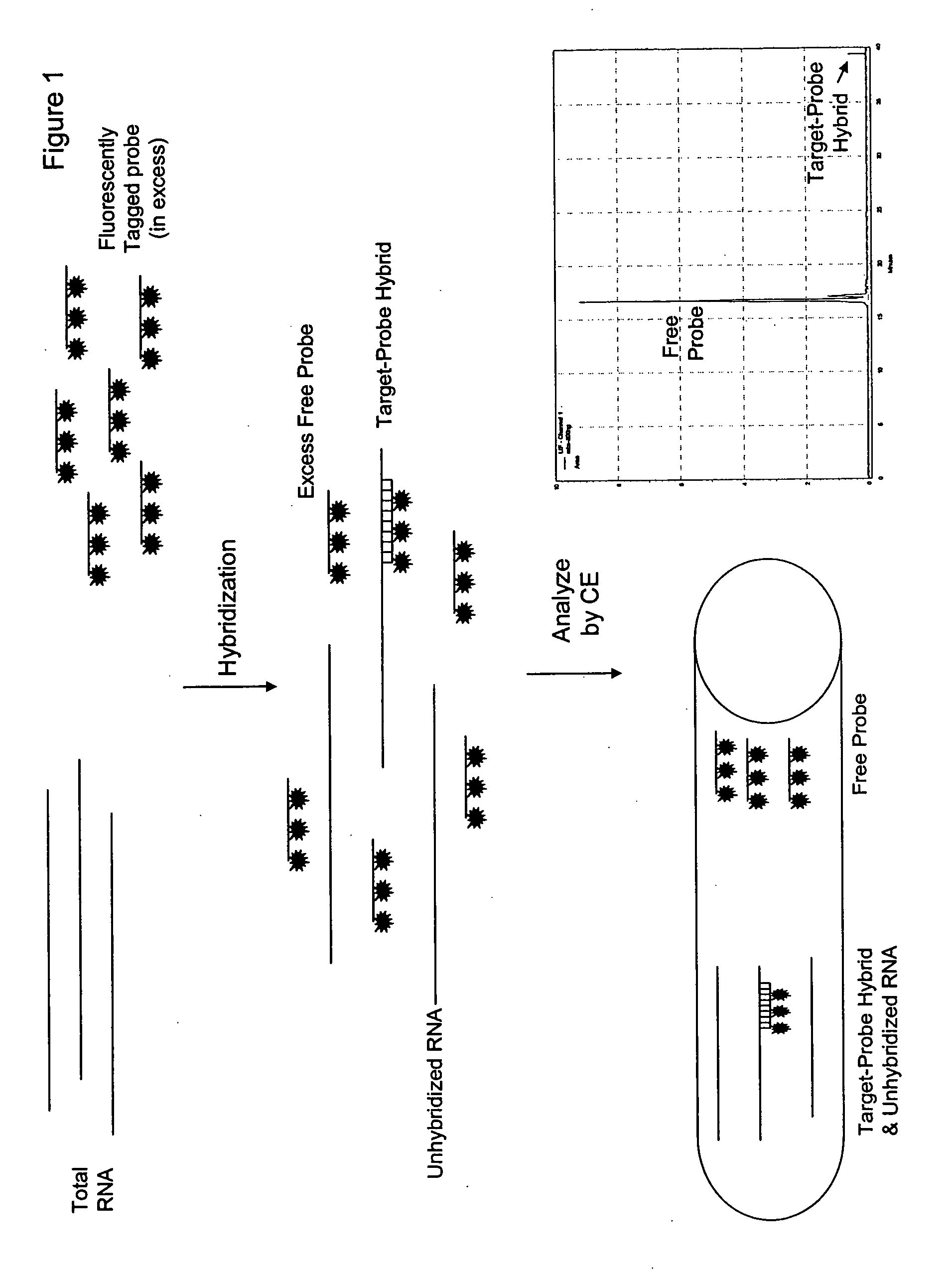
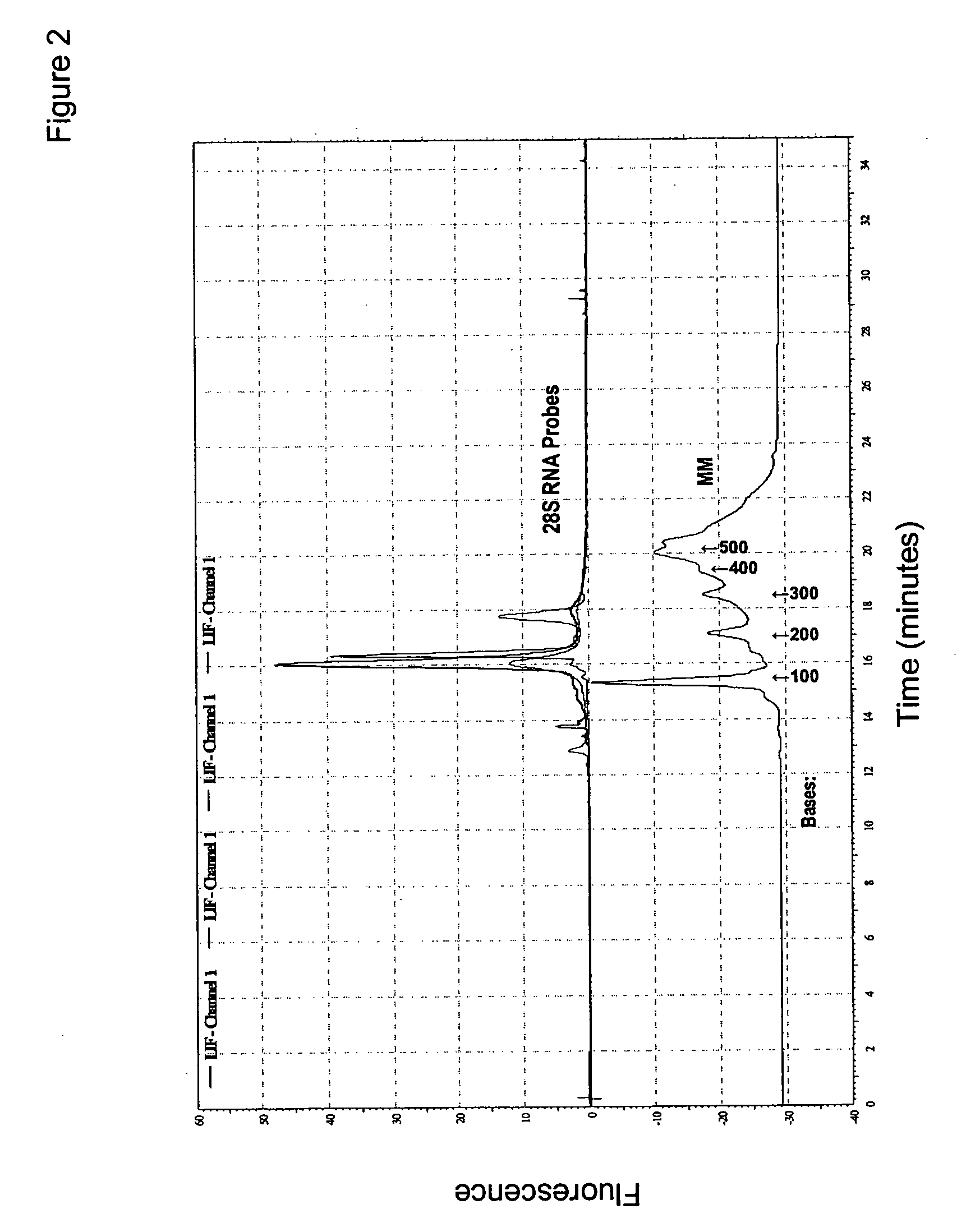
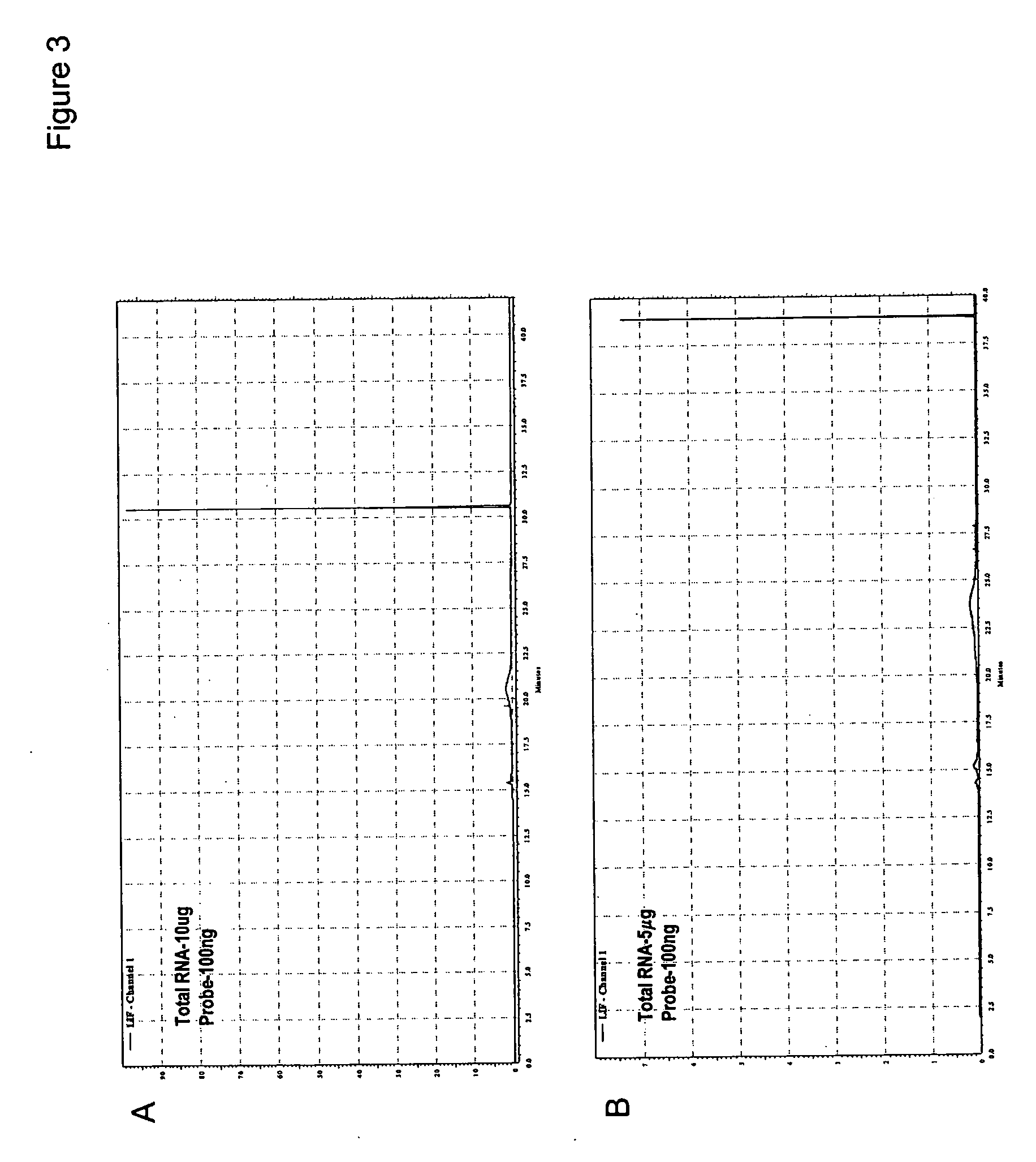
Direct quantification of gene expression using capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence
InactiveUS20060286552A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCapillary electrophoresisElectrophoresis
Provided is a method for direct quantification of gene expression using capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence to measure RNA in a sample. Also provided is a method of diagnosing a disease in a subject, wherein the disease is caused by increased or decreased expression of a causative gene.
Owner:SOUTH CAROLINA UNIV OF
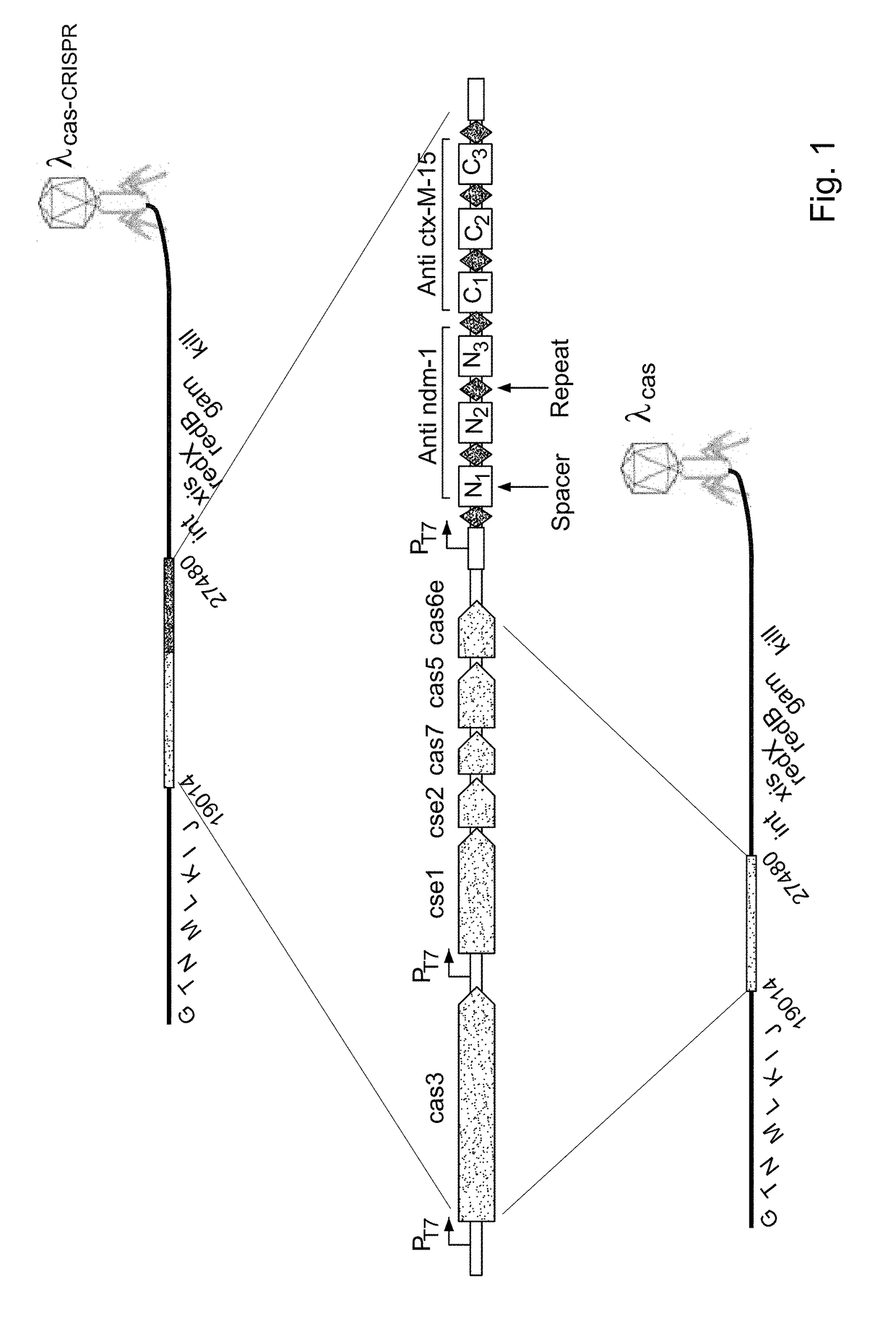
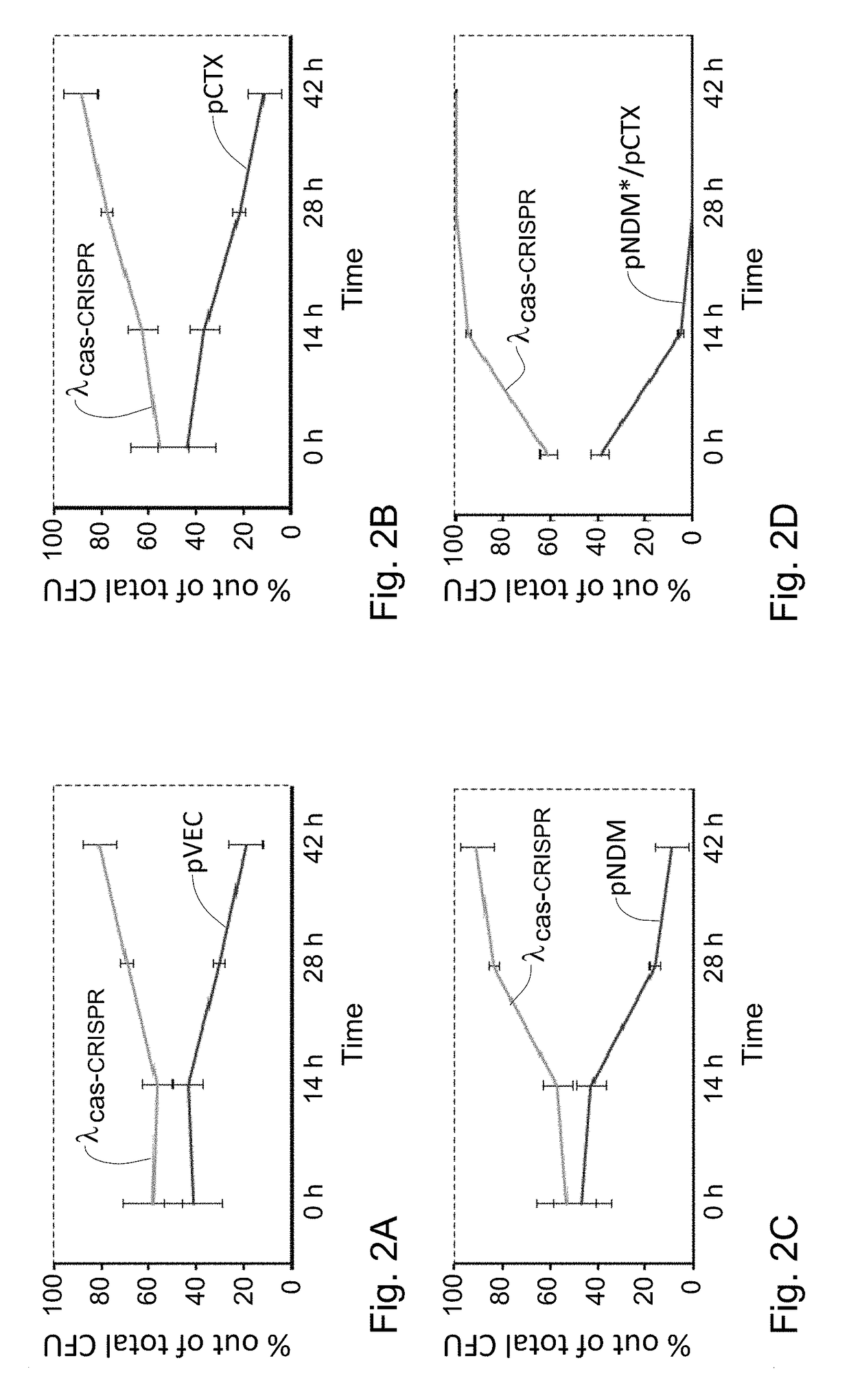
Targeted elimination of bacterial genes
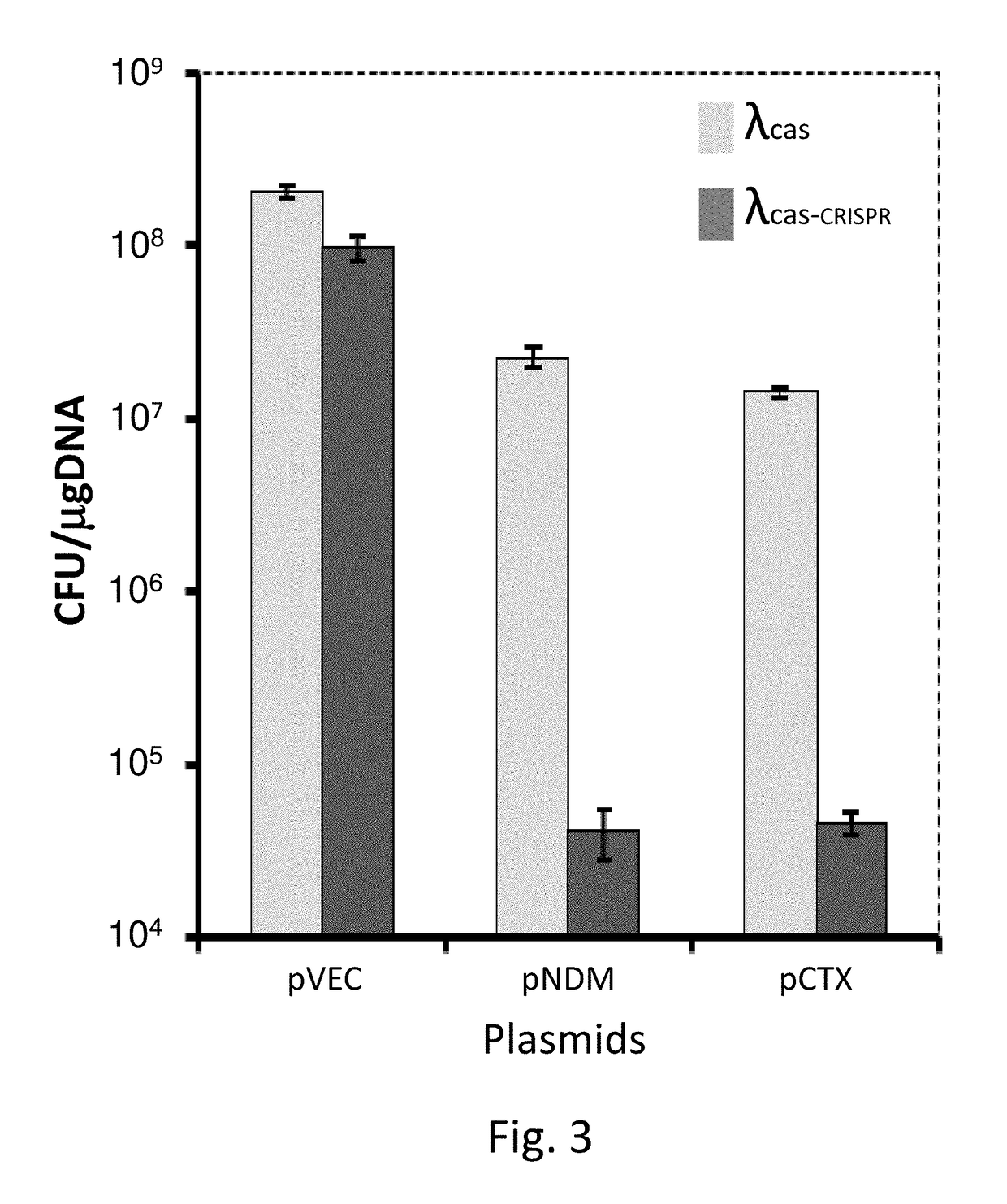
Provided is a kit or a system including two elements or components. The first component (i) is a selective component including a nucleic acid sequence and at least one proto-spacer. The second component (ii) includes at least one sensitizing component including at least one cas gene and at least one CRISPR array. At least one spacer of the CRISPR targets a proto-spacer included within a pathogenic gene of a bacterium so as to specifically inactivate said pathogenic gene in said bacterium and wherein at least one spacer of said CRISPR targets a proto-spacer included within said selective component of (i) so as to specifically inactivate said selective component. Further provided is a method using the components or kits of the invention for interference with a horizontal transfer of a pathogenic gene between bacteria and for preventing a pathologic condition in a mammalian subject caused by a bacterial infection.
Owner:TECH INNOVATION MOMENTUM FUND ISRAEL
Human idiopathic basal ganglia calcification pathogenic gene and detection method thereof
ActiveCN106834299AEfficient and comprehensive acquisitionAccurate acquisitionMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringNervous systemInformation analysis
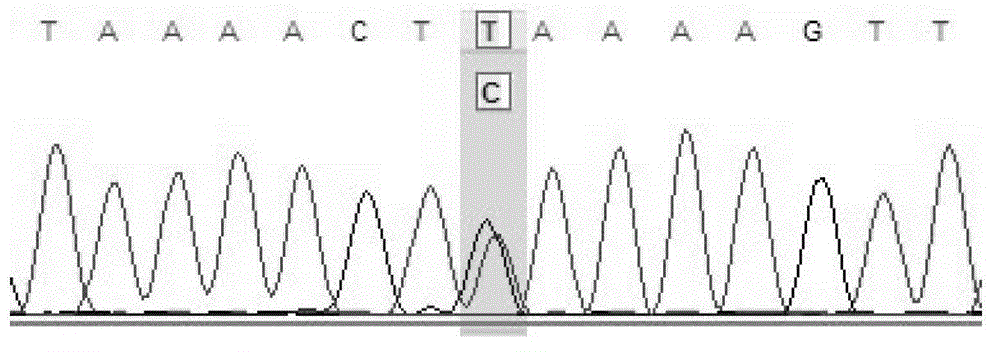
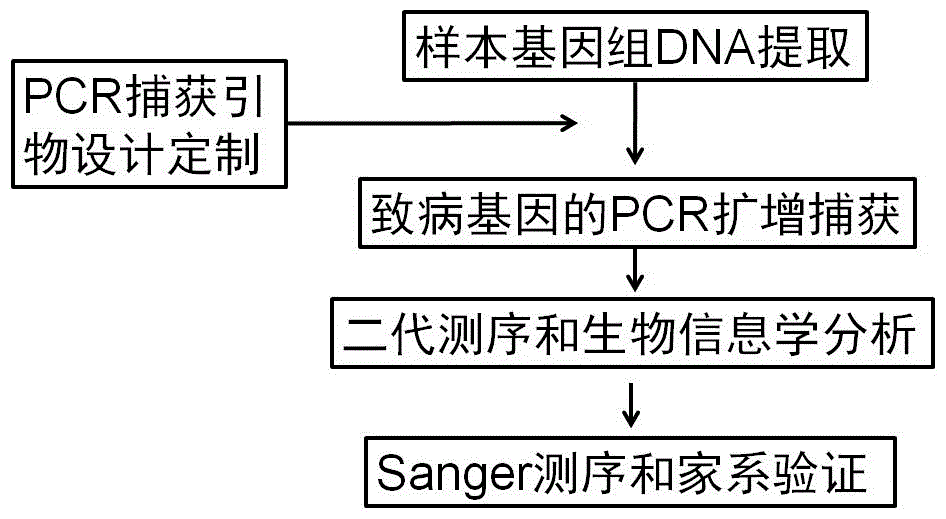
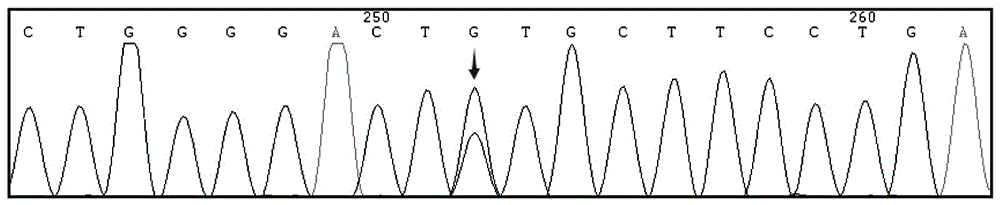
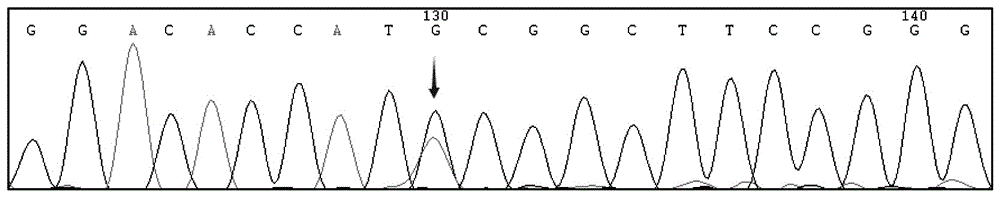
The invention relates to a human idiopathic basal ganglia calcification pathogenic gene and a detection method thereof. Human idiopathic basal ganglia calcification, namely IBGC is a neurodegenerative genetic disease. The invention provides seven mutation forms of four pathogenic genes including SLC20A2 (Sodium-dependent phosphate transporter 2), PDGFRB (Platelet-derived Growth Factor Receptor Beta), PDGFB (Platelet-derived Growth Factor Subunit B) and XPR1 (Xenotropic and Polytropic Retrovirus Receptor 1) and sequences of the seven mutation forms are shown as SEQ ID NO.1 to SEQ ID NO.7. The form of the pathogenic gene provided by the invention is not reported until now and can provide evidence and lay a foundation for analysis and medicine development of a pathogenic mechanism, pathogenic gene screening and detection, formulation of a therapeutic regimen and the like. Meanwhile, the invention constructs a pathogenic gene detection method; the pathogenic gene detection method comprises the following steps: firstly, capturing a pathogenic gene exon region by utilizing multi-PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction); carrying out next generation sequencing on the pathogenic gene exon region and carrying out information analysis to find out mutation; finally, identifying the mutation by utilizing Sanger sequencing, wherein a PCR captured primer group comprises amplification primer sequences SEQ ID NO.12 to SEQ ID NO.23, and amplification primer sequences of a Sanger sequencing segment are shown as SEQ ID NO.24 to SEQ ID NO.35. The detection method provided by the invention covers all exons of the four pathogenic genes and can be used for efficiently, comprehensively, rapidly and accurately acquiring mutation information.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV
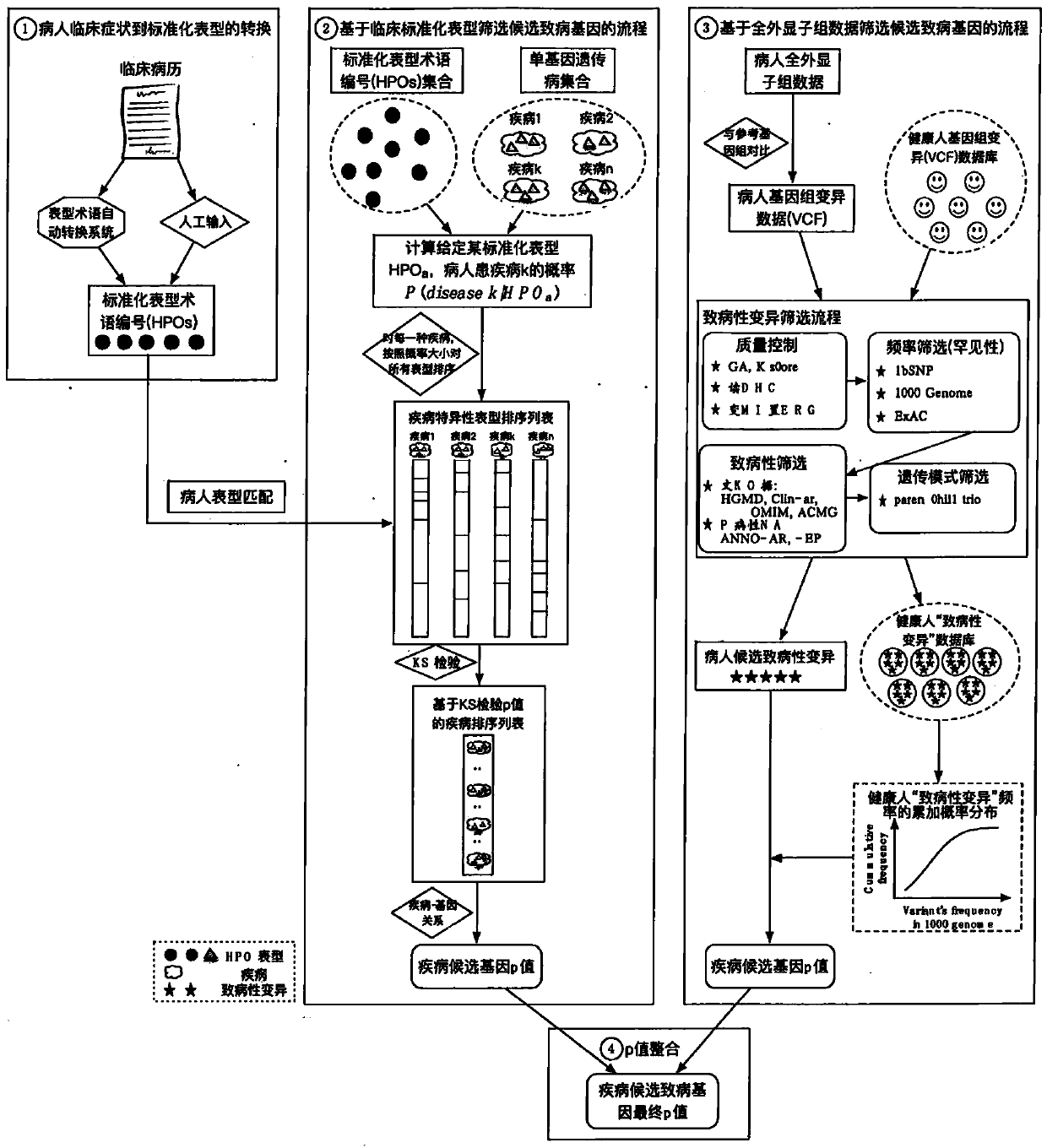
Analysis detection system for screening single gene hereditary disease pathogenic gene based on patient clinical symptom data and whole exome sequencing data
The invention relates to an automated analysis system for automatically screening the single gene disease and hereditary disease pathogenic gene based on patient clinical phenotype information and whole exome sequencing data. The system comprises four automatic analysis modules: (1) an automatic transferring subsystem for automatic transferring from patient clinical report to standardized phenotype term (HPO, human phenotype ontology); (2) an automatic analysis system for screening disease pathogenic gene based on patient standardized phenotype; (3) an automatic analysis system for screening disease pathogenic gene based on patient whole exome sequencing data; and (4) a p value integration system. The system adopts a possibility model to calculate the possibility of developing a certain single gene hereditary disease under the situation that a certain standard phenotype of the patient is provided, and utilizes a computer statistic check method to systematically evaluate the significance level of developing a certain single gene hereditary disease after all standard phenotype of the patient are provided, so as to accordingly achieve the purpose of screening candidate disease pathogenic gene based on clinical standard phenotype.
Owner:上海睿视健康科技有限公司
Screening method of inherited metabolic disorder gene
InactiveCN103305618AAccurate diagnosisReduce harmMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening methodGenomic library
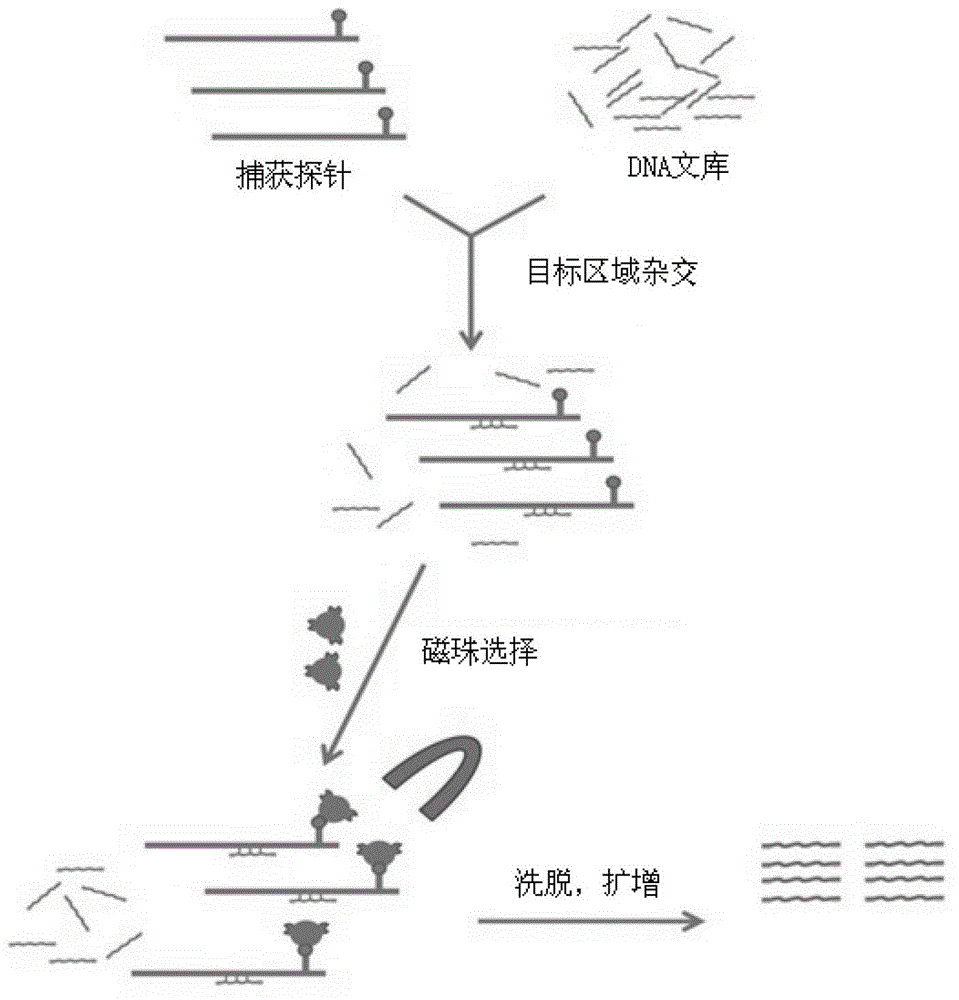
The invention provides a screening method of all inherited metabolic disorder genes for genetic diagnosis within an exon area, which is fast and accurate and can cover the newest inherited metabolic disorder genes. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: drawing 3-5ml of blood from an individual, extracting 3-5 microgrammes of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) from the blood, interrupting and amplifying the DNA to construct a whole genome library for the patient, capturing the virulence genes by using an inherited metabolic disorder gene scanning kit provided by the invention, carrying out high-throughput sequencing by using a sequencing machine, and analyzing and finding mutation information relevant to the genes so as to obtain the mutation conditions of the inherited metabolic disorder genes of the individual to reach the purpose of accurate genetic diagnosis. Dozens of to thousands of genes and millions of loci can be captured and detected once by taking advantage of the high-throughput sequencing, and the screening method covers known 700 inherited metabolic disorders.
Owner:北京迈基诺基因科技股份有限公司
Method for simultaneously completing gene locus, chromosome and linkage analysis
ActiveCN105543339AEasy to operateStrong practical feasibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementEmbryoRecurrent abortion
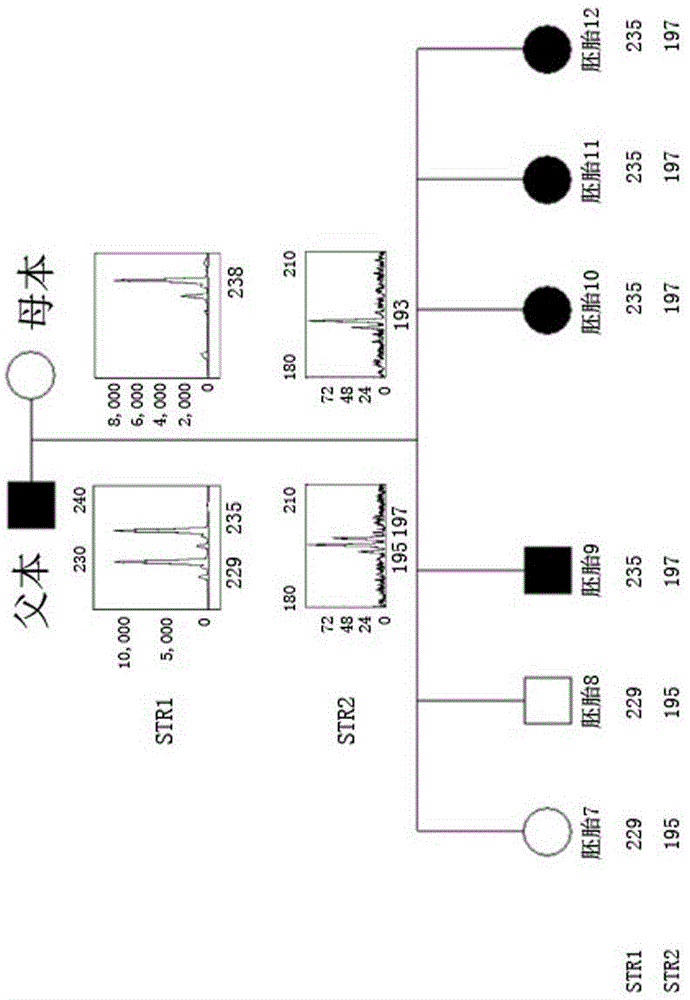
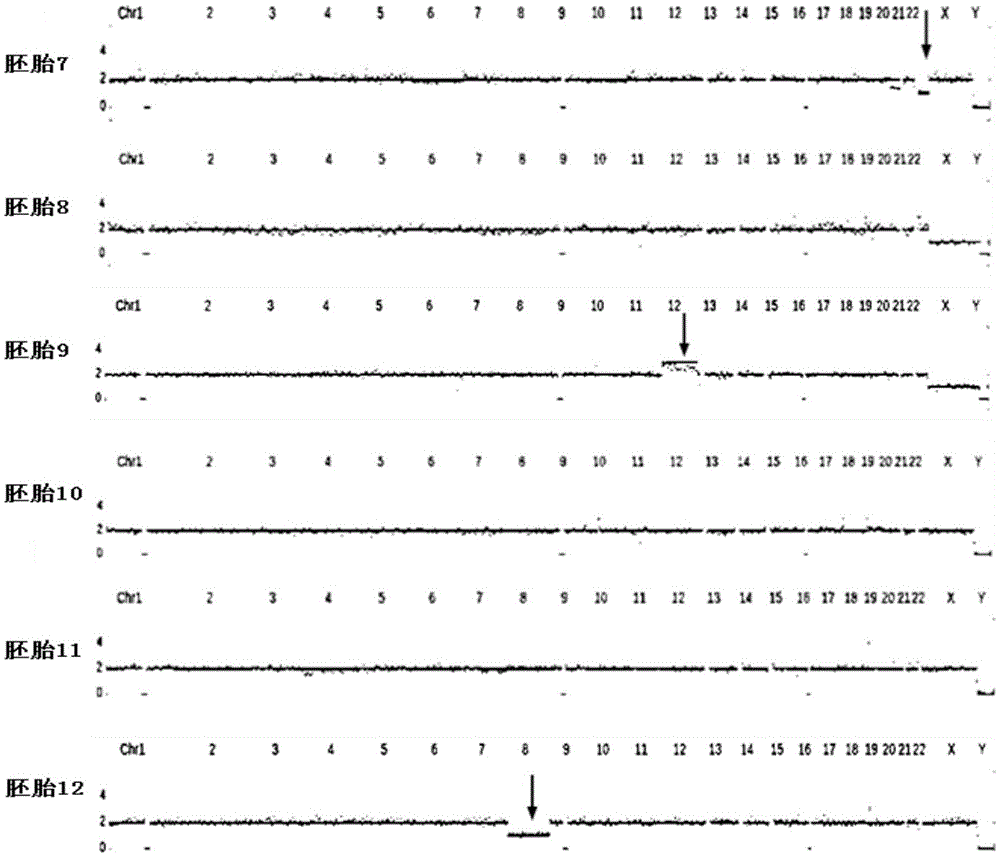
The invention relates to a method for simultaneously completing gene locus, chromosome and linkage analysis. The method concretely and mainly comprises the following steps: collecting an embryo cell sample, amplifying a whole genome, amplifying a target gene mutation locus, establishing a whole genome and target gene mutation locus library, carrying out high flux sequencing, and carrying out data analysis. Multiple-item comprehensive detection is completed through one step by combining a whole genome amplification technology with the high flux sequencing, so respective detection of single-gene genetic disease mutation site, chromosome diseases and linkage analysis through using multiple methods and multiple steps is avoided. The method provided by the invention provides favorable conditions for a tiny amount of a sample, can be used for PGD detection to determine whether an embryo carries a pathogenic gene and chromosome copy number abnormity or not, is also suitable for genetic screening of embryos of recurrent abortion older women, and realizes multi-item detection of a plurality of single samples through one step. The method has the advantages of simple operation, short period and strong feasibility, so promotion and application of the method are facilitated.
Owner:SHANGHAI XUKANG MEDICAL TECH CO LTD +2
Non-treatment-purpose method for screening mutation of pathogenic genes relevant with hypertrophic cardiac myopathy
ActiveCN105695606AThe method is simple and fastLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyMyopathy
The invention relates to the technical field of biology and particularly relates to a non-treatment-purpose method for screening mutation of pathogenic genes relevant with hypertrophic cardiac myopathy. The method comprises the following steps: (1) extracting genomes; (2) carrying out multiplex PCR amplification on target genes; (3) constructing a target gene library; and (4) sequencing the target gene library by virtue of a next-generation semiconductor sequencing platform, and screening gene mutation sites relevant with the hypertrophic cardiac myopathy. The method is simple, convenient, rapid and low in cost, multiple samples can be detected once, the foundation is laid for the screening of the hypertrophic cardiac myopathy, and the road is exploited for the clinic molecular diagnosis.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Chinese population linkage analysis single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) marker sets and use method and application thereof
InactiveCN102121046AEnsure reliabilityEnsure comprehensivenessMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenetic linkage disequilibriumInternational HapMap Project
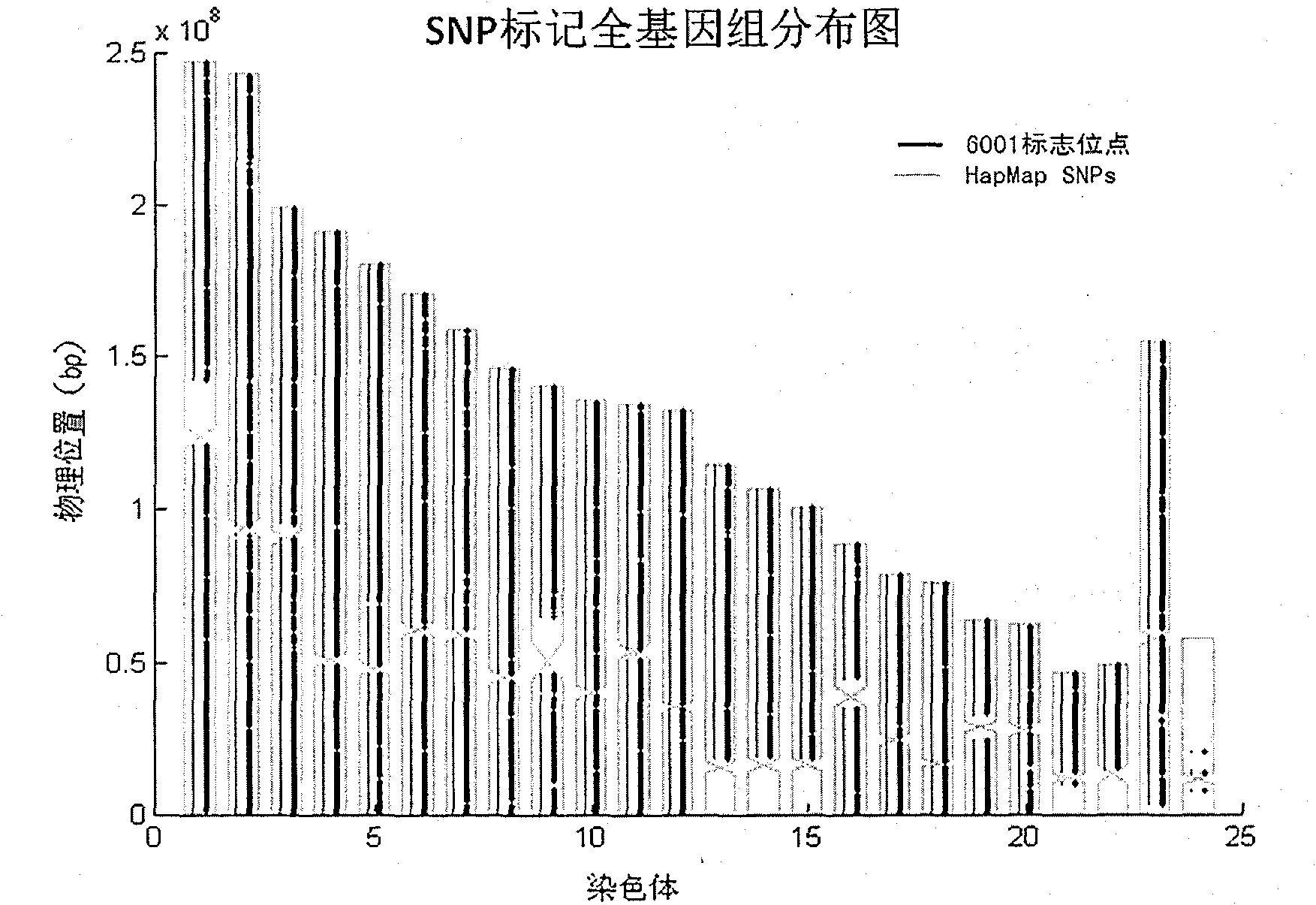
The invention relates to Chinese population linkage analysis single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) marker sets and a use method and application thereof. On the basis of hundreds of millions of Chinese Han population data results in the mass data of the International HapMap Project, medium-density and high-density SNP marker sets for linkage analysis are constructed and optimized, according to the statistical comparisons of multiple parameters such as the linkage disequilibrium, the polymorphism level, the typing success rate, the distribution position and density of genomes and the functional characteristic, and the multi-level selections and experimental verifications. The two marker sets separately contain 3000 and 6001 loci, wherein the 6001 loci contain the 3000 loci. The SNP sets aim at the Han genetic background in design, have high polymorphism in Chinese and can realize the aim of efficiently marking the Chinese family sample genomes. The selection of polymorphic loci is based on the neutral evolution principle, and all the loci are in a non-gene function region, thus the influence of evolution on the gene function can be avoided. Meanwhile, the characteristics that the marking loci have high typing detectability and can uniformly cover the whole genomes can ensure that the whole genomes can be screened completely and new pathogenic genes can be located and found. The two sets of SNP markers are used to customize probes or chips and perform whole-genome genotyping to family samples; and the typing data are used for linkage analysis, and the haplotyping and fine locating of the linkage candidate region are also adopted, thus the use method has more accurate locating result than the traditional method while the cost is lower and the speed is higher. The distribution and coverage of the 6001 SNP marker set in human chromosomes are shown in the appended drawings.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION +1
Oral squarmous cell carcinomas pathogenic gene BPIFB2 and application thereof
InactiveCN104059982AGood correlationConvenient for clinical operationMicrobiological testing/measurementTumour tissuePcr method
The invention relates to an oral squarmous cell carcinomas pathogenic gene BPIFB2 and application of the oral squarmous cell carcinomas pathogenic gene BPIFB2. RNA is extracted from oral squarmous tissue, tissue adjacent to the oral squarmous cell carcinomas and normal tissue, deep sequencing and analyzing are performed on a transcriptome, the oral squarmous cell carcinomas relevant gene BPIFB2 is obtained through screening, an RT-PCR method is adopted for analyzing the expression conditions, on the carcinomas tissue and the tissue adjacent to the carcinomas of a patient with the oral squarmous cell carcinomas, of the screened BPIFB2, and the result shows that the obtained BPIFB2 through screening has good relevance to the oral squarmous cell carcinomas and can be used for preparing an oral squarmous cell carcinomas auxiliary diagnosis preparation or a pregnosis preparation. The invention further discloses a fluorogenic quantitative PCR kit and a using method of the fluorogenic quantitative PCR kit. The kit can detect the expression level of the BPIFB2 in oral squarmous cell carcinomas tissue sensitively, rapidly, quantitatively, accurately and stably and has good application prospects.
Owner:BEIJING MEDINTELL BIOMED CO LTD
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) library for detecting cholestatic jaundice pathogenic genes and application thereof
ActiveCN104313698AFree from painSuitable for testingNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementA-DNAExon
The invention discloses a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) library for detecting cholestatic jaundice pathogenic genes by virtue of a high-throughput sequencing technology and application thereof and in particular relates to a super-multiplet PCR primer which can cover the exon and adjacent areas of the genes according to 60 cholestatic jaundice pathogenic genes. The genome DNA of the sample is subjected to super-multiplet PCR amplification, the amplification product is sequenced by utilizing the high-throughput sequencing technology, the pathogenic mutation is searched, the genetic etiology of the cholestatic jaundice is clear, and a theoretical basis of genetics and molecular biology is provided for clinical diagnosis. The DNA library has the characteristics of accuracy, flexibility, rapidness and low cost. Moreover, according to the detection area of 60 genes, 15 common cholestatic genetic defects can be detected, and the DNA library has significance and clinical values on differential diagnosis of the cholestatic jaundice.
Owner:TONGJI HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI TECH
Multiple target point small interference RNA cocktail agent for treating ophthalmic disease and preparing method thereof
The invention discloses a multi-target small-interfering RNA cocktail preparation for treating ophthalmic diseases and the preparation method. The multi-target small-interfering-RNA cocktail preparation is composed of three or more than three small-interfering RNA aiming to three or more than three different genes and knocking down simultaneously a plurality of pathogenic genes; the multi-target small-interfering-RNA cocktail preparation is prepared by a plurality of small-interfering RNA in a certain proportion according to different diseases. The multi-target small-interfering-RNA cocktail preparation is a plurality of double-bond RNA molecules of different lengths from 19to 27nt, with blunt ends or overhanging ends; the RNA sequence in the multi-target small-interfering-RNA cocktail preparation has the homology to the gene targets of human, rat and other nonhuman primate; . The multi-target small-interfering-RNA cocktail preparation aiming to the following gene sequences: (1) virus-affection-related gene; (2) inflammation-arosing gene; (3) neovescular-related gene. The invention provides a novel treatment for a plurality of ophthalmic diseases, including retinopathy of prematurity, senile fundus macula lutea, retinopathy caused by senile diabetes, herpes simplex corneal stromal opacification and uveitis.
Owner:广州拓谱基因技术有限公司
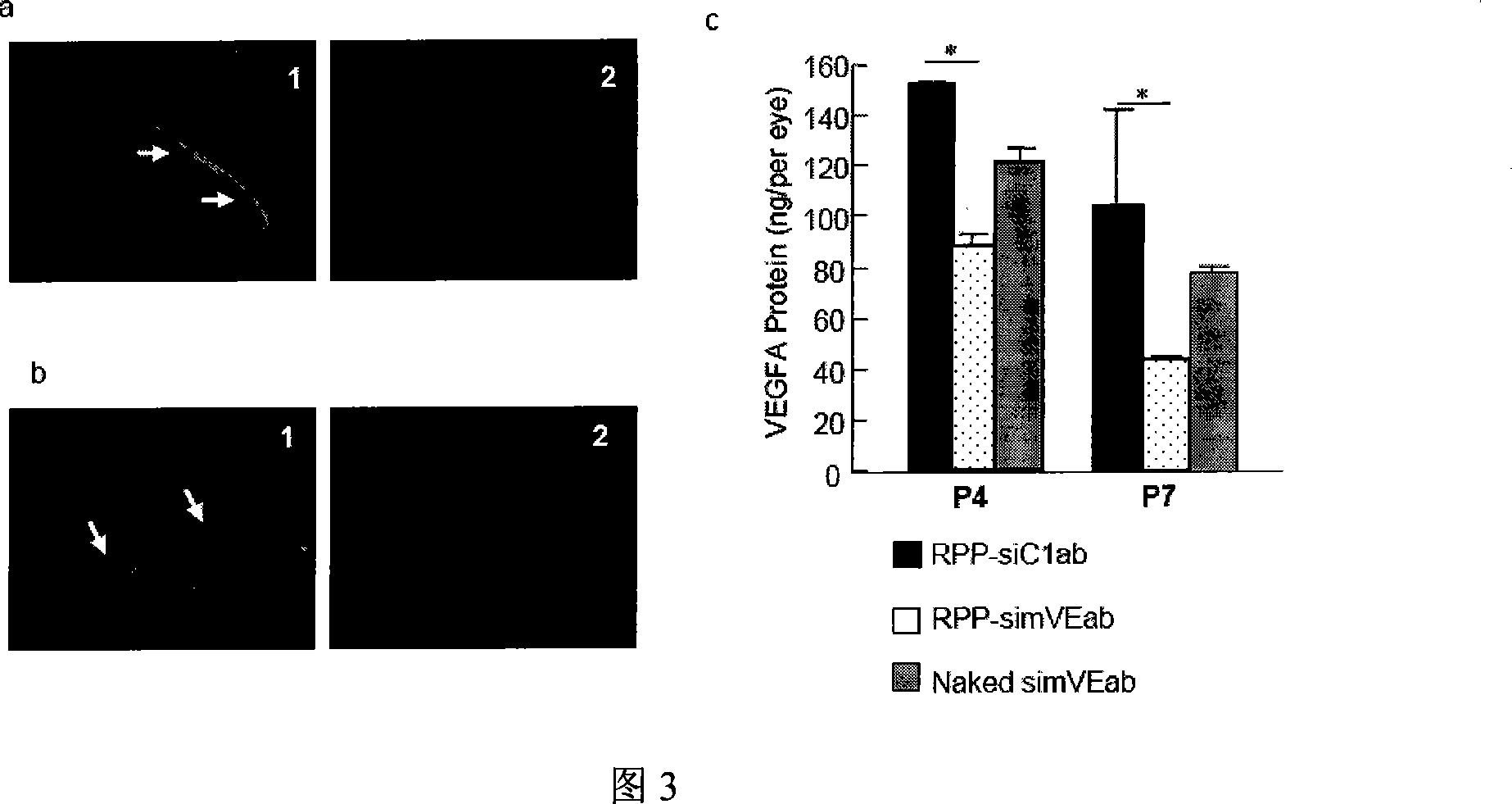
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) library for detecting disease causing genes of aoreic dissection diseases and application thereof
InactiveCN105442052AWide coverageLow costNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementMultiplex pcrsLoeys–Dietz syndrome
The invention discloses a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) library for detecting disease causing genes of aoreic dissection diseases through a targeted high-flux semiconductor sequencing technology and application thereof. In particular, a primer pond is designed according to 33 disease-causing genes of aoreic dissection diseases, a sample genome DNA is subjected to super-multiple polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification, and amplification products are sequenced by using the high-flux semiconductor sequence technology in order to find disease-causing mutation and lay theoretical bases on the aspects of genetics and molecular biology for clinical diagnosis. The DNA library has the advantages of accuracy, rapidness, flexibility and low cost. Through 33 gene detection areas, various common aoreic dissection relevant diseases such as familial aortic aneurysms or dissections (FTAAD), Marfan syndrome (MFS), Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS), Loeys-Dietz syndrome (LDS) and aortic torsion syndrome (ATS) can be detected. The DNA library has important significance and a clinical value to diagnosis and identification of the aoreic dissections.
Owner:TONGJI HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI TECH
Method for detecting fetal thalassemia pathogenic gene and kit
ActiveCN108642160AEnable prenatal testingSmall sample sizeMicrobiological testing/measurementThalassemiaGenomic DNA
The invention discloses a method for detecting a fetal thalassemia pathogenic gene, which comprises the following steps of: (1) screening SNP sites, wherein the SNP sites are used for designing a primer pool of the thalassemia gene in an amplification genome and for capturing the probe of the thalassemia gene of the free DNA in the plasma of a pregnant woman; (2) extracting the free DNA in the plasma of the pregnant woman and the whole blood genomic DNA of the father, the mother and a born sibling and constructing a corresponding DNA library, and carrying out template preparation and enrichment; (3) sequencing the free DNA and the whole blood genomic DNA library in step (2); (4) constructing the haploid genotype of the SNP sites on the thalassemia gene, combining the sequencing informationof the free DNA and the whole blood genomic DNA library, analyzing the genetic condition of the parent source and the genetic condition of the parent source, so as to determine the corresponding genotype of the SNP sites of the fetal. According to the method, target area capture and high-throughput sequencing technology are used, so that the noninvasive antepartum detection of the thalassemia isrealized; the required sample amount is small; on the basis of detecting the mutation of the parent source, the method can realize the detection of the gene mutation of the maternal source of the fetal.
Owner:GUANGZHOU DARUI BIOTECH +1
Gene polymorphism sites related to thyroid cancer and application thereof
PendingCN107164496AStrong specificityExcellent diagnostic valueMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisGenes mutationSomatic cell
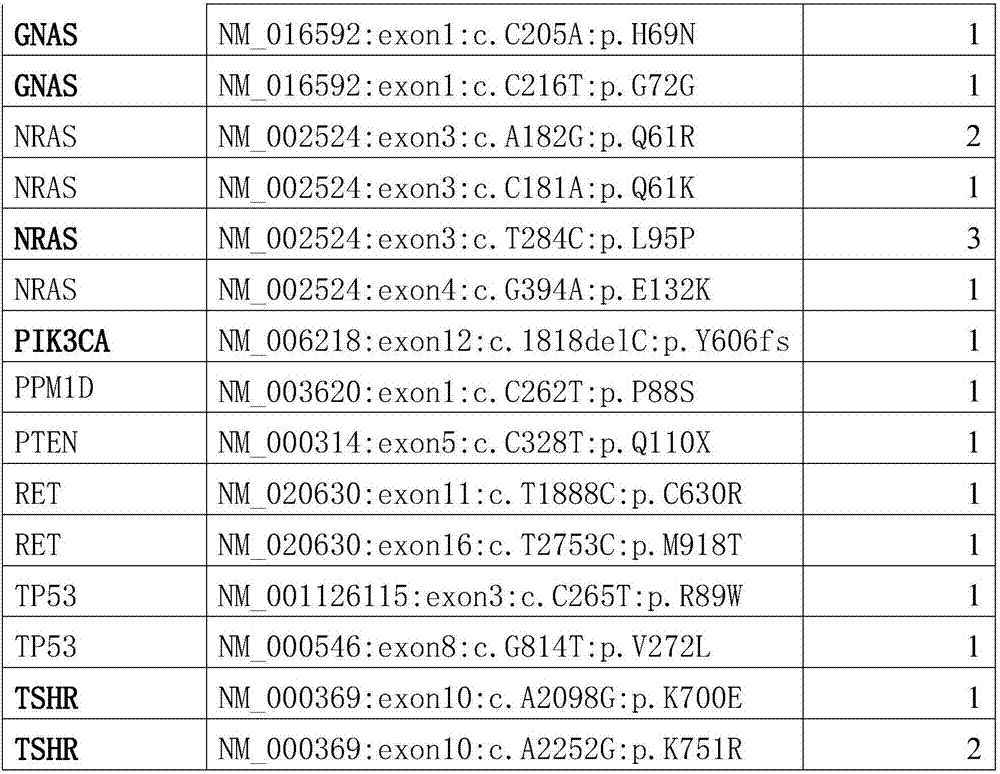
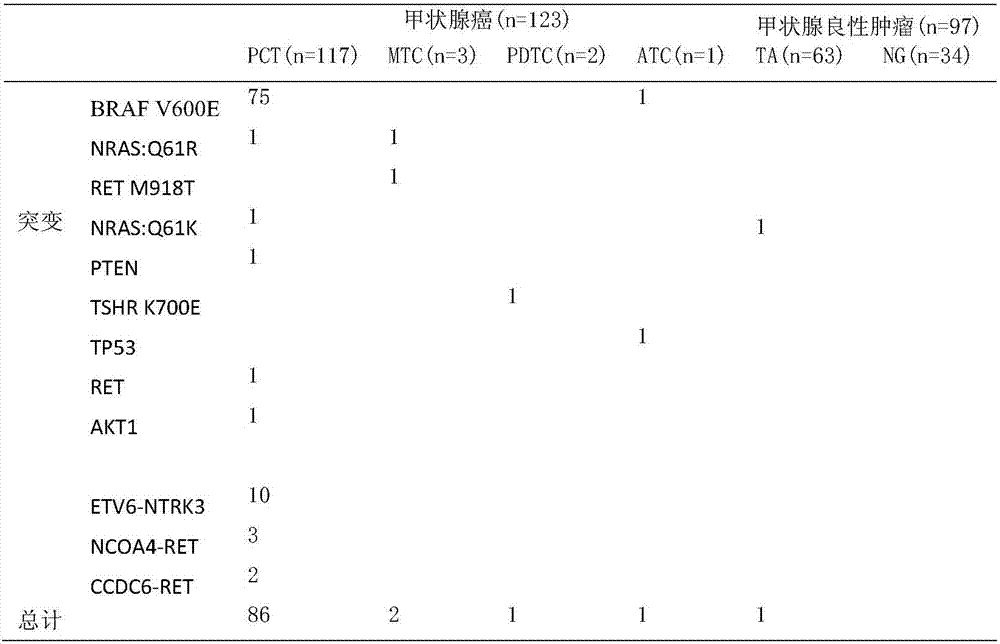
The invention provides somatic mutation sites of pathogenic genes of the thyroid cancer and application thereof, specifically to a group of mutation sites of the pathogenic genes of the thyroid cancer. The mutation sites are composed of a GNAS gene mutation site, a NRAS gene mutation site, a TSHR gene mutation site, etc. The gene mutation sites provided by the invention can be used as markers for identification of benign and malignant thyroid nodules.
Owner:上海安甲生物科技有限公司
Primers for detecting plurality of newborn inherited metabolic disease causing genes and kit
ActiveCN105177160AQuick screeningConducive to screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyExon intron
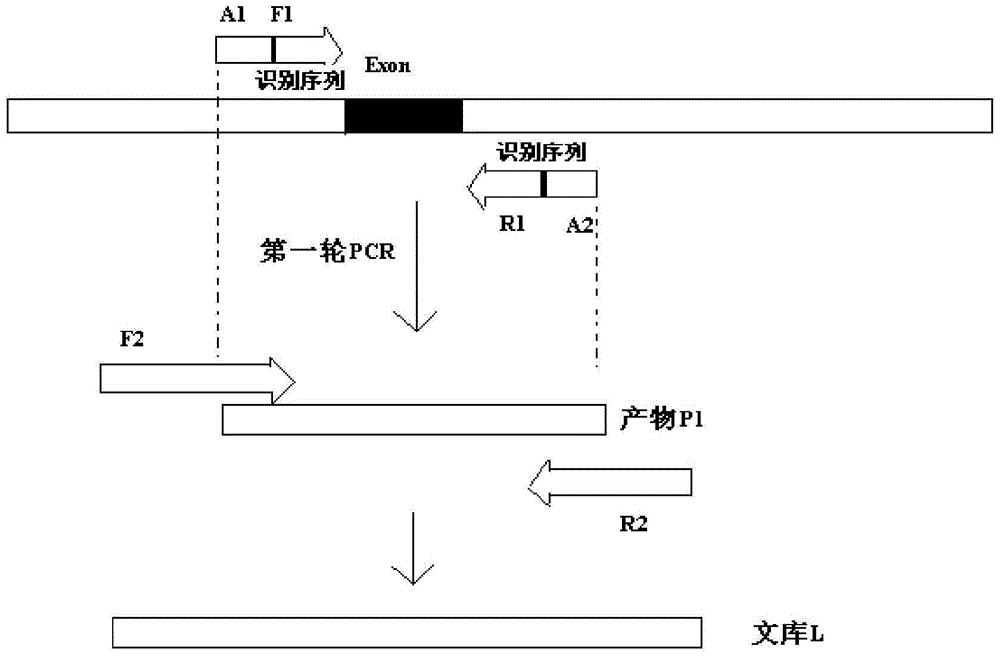
The invention discloses a design way of primers for in-vitro qualitative detection of newborn inherited metabolic disease genes. The design way comprises the following steps: (1) acquiring relevant disease-causing gene information of inherited diseases: acquiring the relevant disease-causing gene information, including gene location information and mutation site information of a plurality of inherited diseases through an OMIM (Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man) database, and acquiring exon and intron information of relevant genes from an NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information) database according to the obtained gene information; (2) designing primers specific to the relevant genes: designing corresponding specific primers F1 and R1 specific to an exon and an exon-intron combination area of each gene. The invention also discloses the first-round PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) primer sequence list of syndromic deafness, a first-round PCR primer list of G6PD genes, and a first-round PCR primer sequence list of SLC12A3 genes. The primers can be used for detecting relevant genes of 22 types of common newborn inherited diseases.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Application of EB1 gene to detection of nosema bombycis
ActiveCN104017890AReduce interferenceThe test result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNosema bombycis
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biotechnologies and particularly discloses an application of an EB1 gene to detection of nosema bombycis. Researches prove that the transcriptional expression of the EB1 gene is related to the cell division of the nosema bombycis and the development of a host. A specific primer is designed by taking the EB1 gene as a target gene, whether silkworm eggs are infected by the nosema bombycis is detected through PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification, and the detected result proves that if the EB1 gene is used as the detecting target gene, the interference effects of inhibiting substances in silkworm egg extracts to the effective PCR amplification of pathogenic gene DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) are very low, the detected result is more accurate and sensitive, and most importantly, whether the silkworm eggs are infected by the nosema bombycis can be rapidly detected at the early stage that the silkworm eggs are infected. The guarantee is provided for the detection and safe egg production of poisonous silkworm eggs in silkworm egg production.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Parkinson's disease gene diagnosis kit
ActiveCN104928373AGuaranteed speedGuaranteed accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease riskDisease injury
The invention discloses a Parkinson's disease gene diagnosis kit which comprises 11 pathogenic genes of the Parkinson's disease namely SNCA,Parkin,Pink1,UCHL-1,DJ-1,ATP13A2,GIGYF2,HTRA2,FBX07,Vps35 and MAPT. A detection method comprises the following steps: designing and synthesizing specific primers of all genes, collecting specimens of individuals to be detected, sequencing specific DNA fragments obtained by all genes through a RT-PCR technology, comparing the gene sequence with a normal gene sequence, and analyzing whether deleterious mutations exit or not to evaluate disease risks of the individuals. By adopting the Parkinson's disease gene diagnosis kit disclosed by the invention, different deleterious mutations of a pathogenic gene protein coding region (CDS) can be detected at a time, the method is simple, convenient and rapid, the specificity is good, the sensitivity is high and the Parkinson's disease gene diagnosis kit can be used for pathogenic gene screening and early diagnosis of the Parkinson's disease.
Owner:江苏雄鸣医药科技有限公司
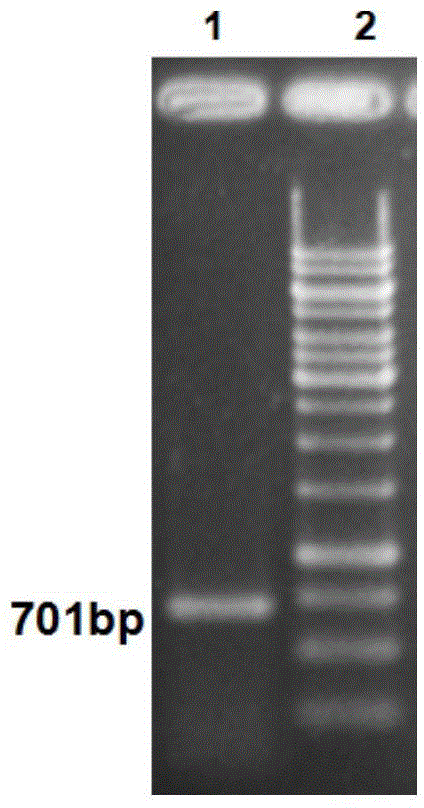
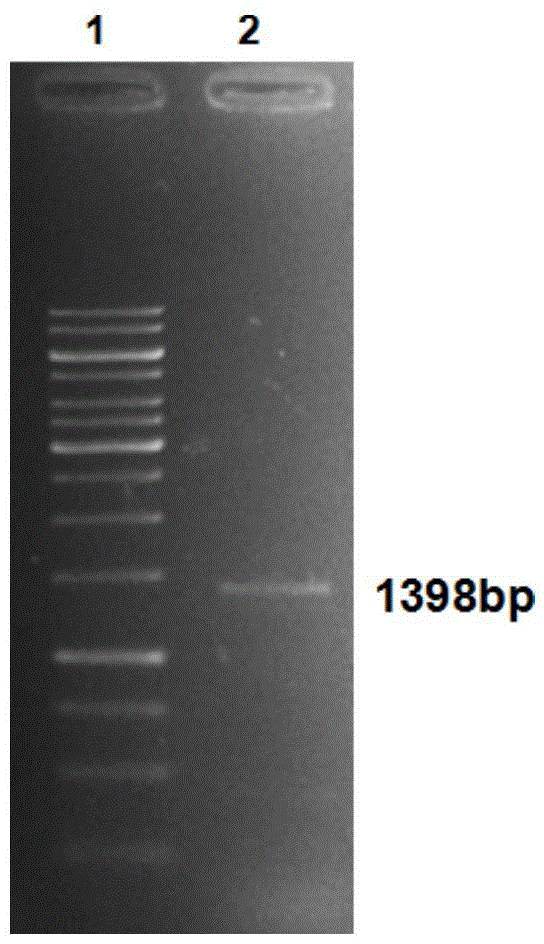
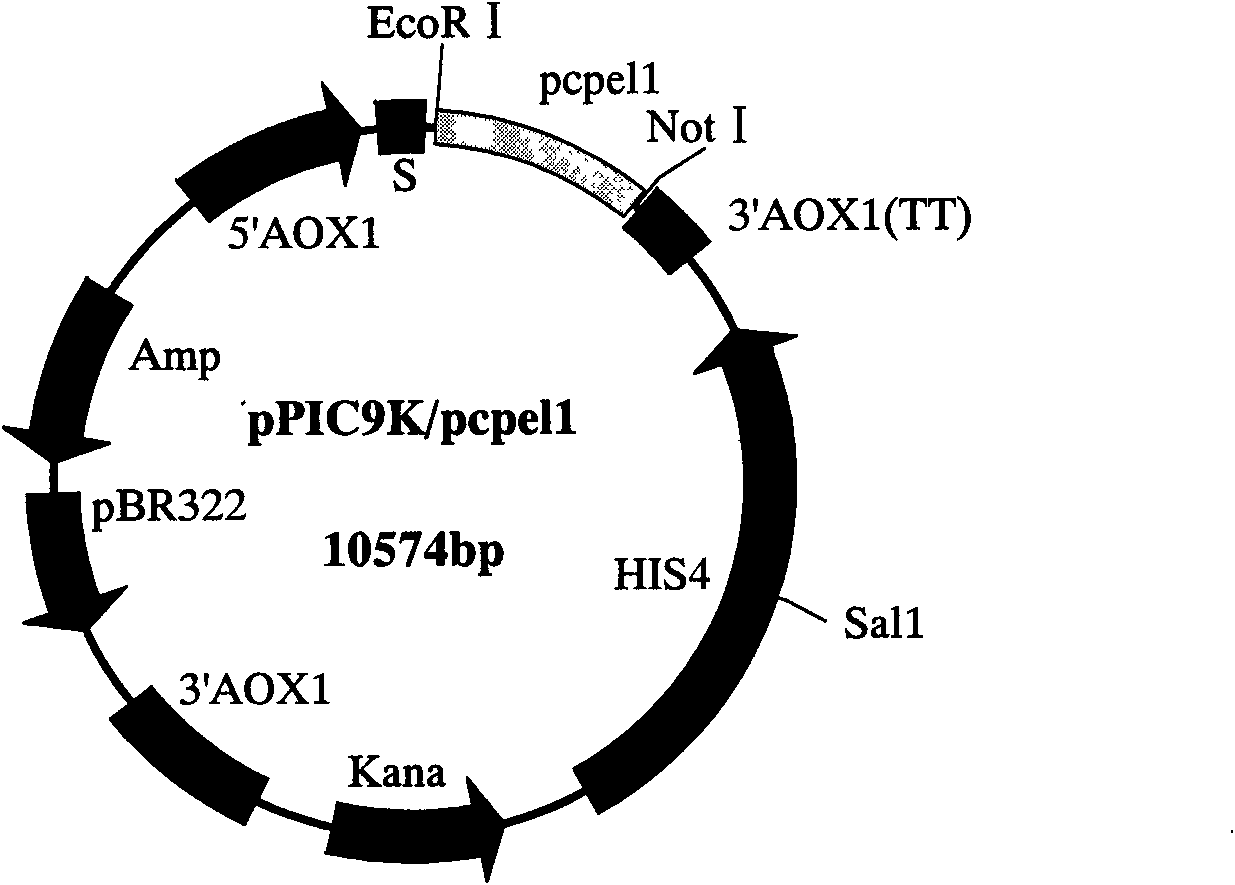
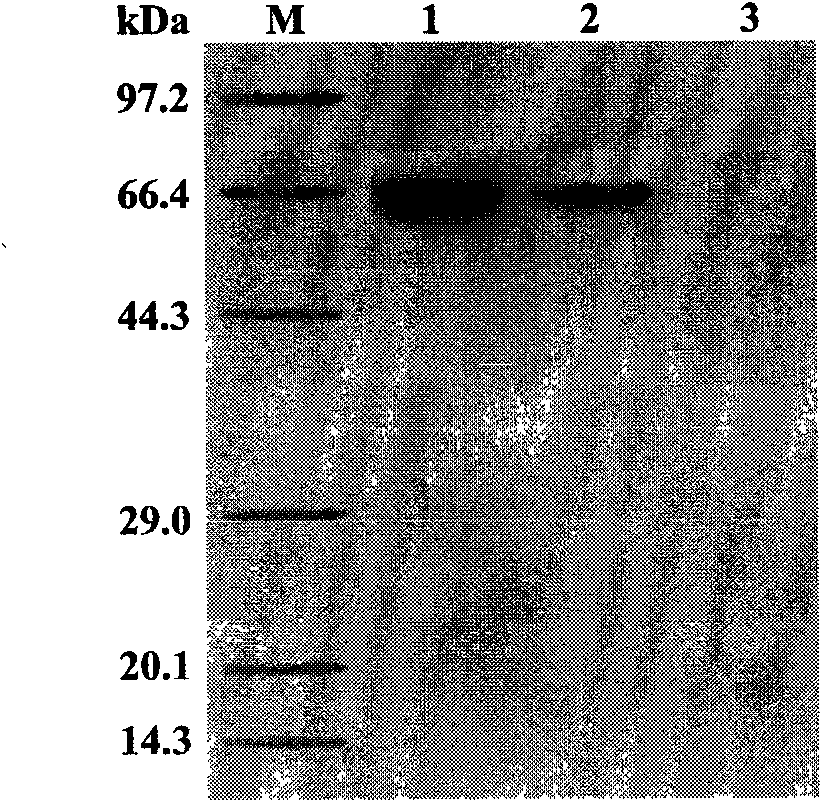
Phytophthora capsici pectate lyase (PL) Pcpel1 gene, protein preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101638663AObvious symptomsSufficient technical reservesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesCytochemistryPlant pathology
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and in particular provides a pectate lyase (PL) gene Pcpel1 which is cloned from phytophthora capsici and protein preparation technology thereof. Gene and protein levels prove that the gene is effectively involved in the process that the phytophthora capsici infects hot pepper hosts and results in occurrence of the course of diseases on hot pepper leaves. Plant pathology and cytochemistry technology further prove that after the protein coded by the gene is inoculated onto the hot pepper leaves, obvious withering and shrinking occur on theinoculated parts of the leaves and the cell walls on the affected parts of the leaves are obviously degraded, namely the gene code is an important protein related to the course of diseases or is possibly an important target pathogenic gene of a phytophthora capsici PL gene cluster. The invention provides important technical reserve for further developing phytophthora capsici molecule detection technology.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
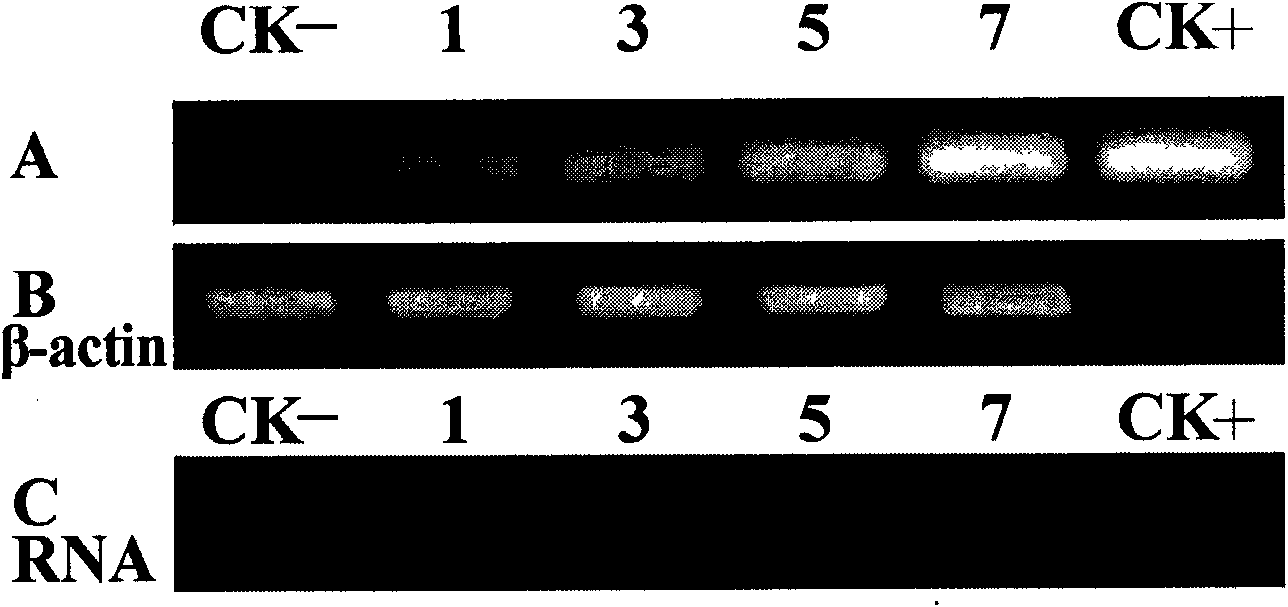
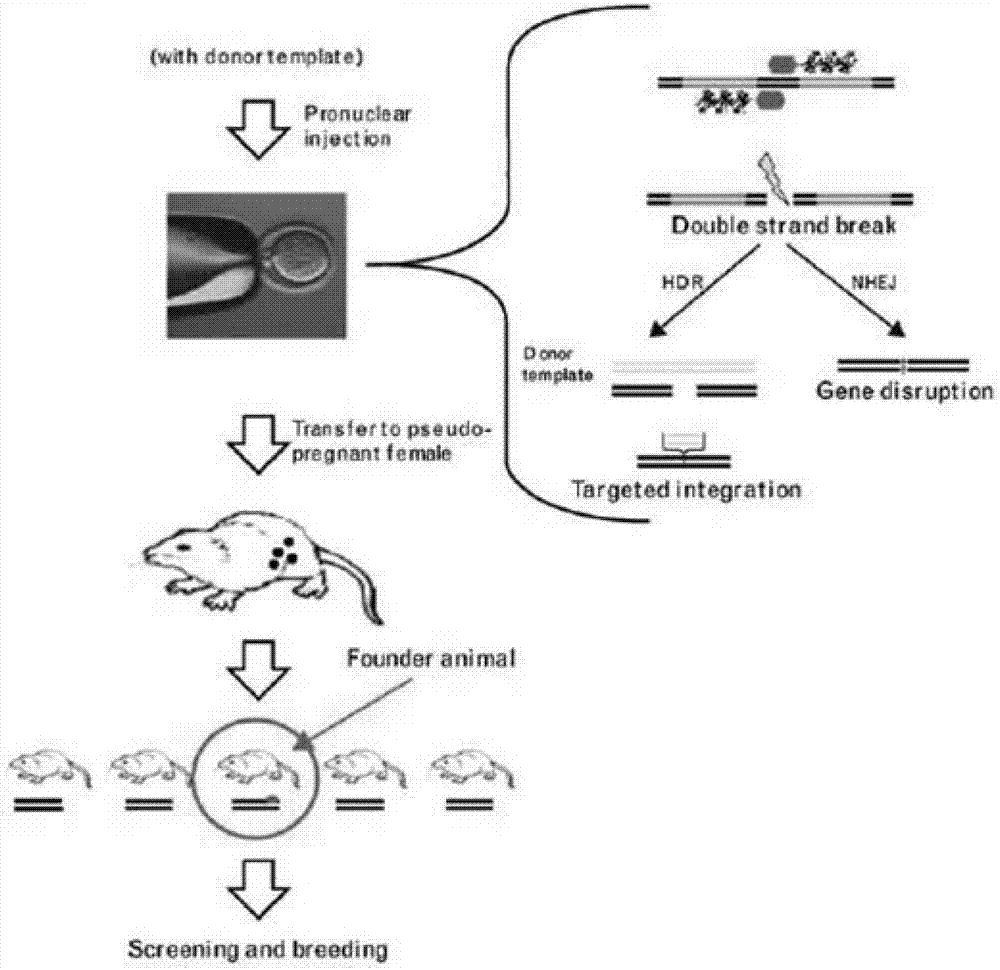
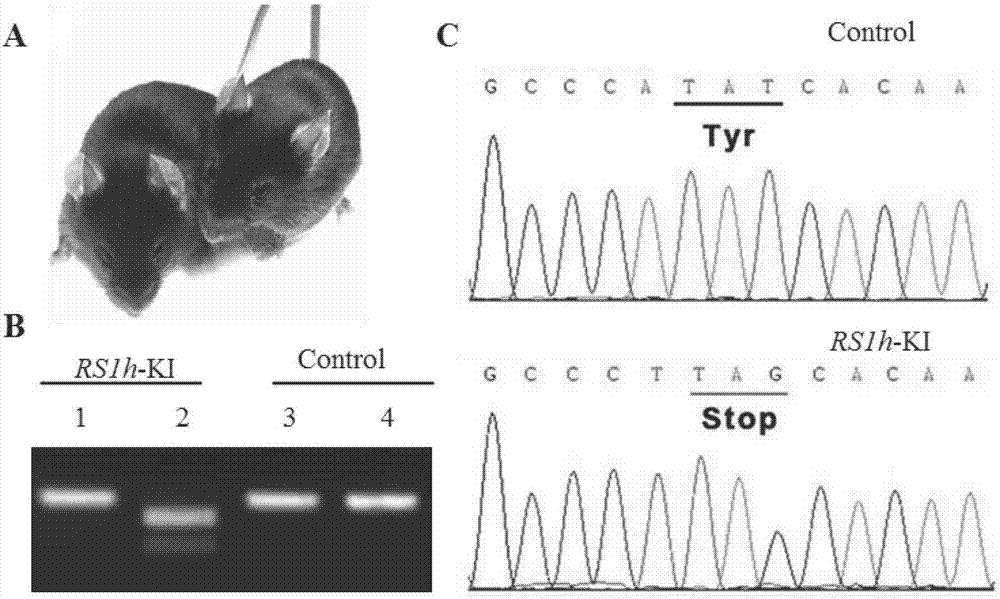
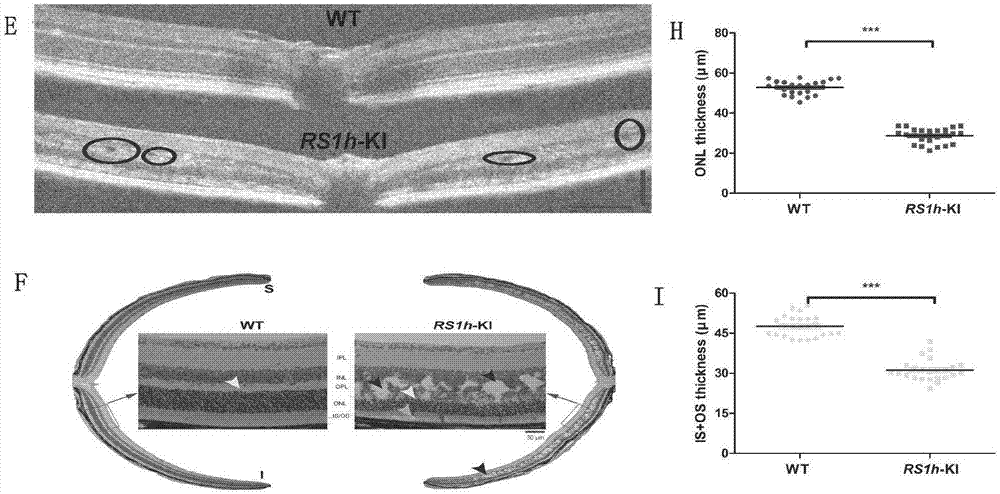
Human-derived retinoschisis transgenic mice model and construction method thereof
The invention provides a method for constructing a human-derived retinoschisis transgenic mice model. The method comprises the following steps: taking human-derived RS1 genes as basis, screening human pathogenic genes to be knocked in mice through gene editing means, thereby obtaining RS1h-KI mouse disease model.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Kit for detecting disease-causing genic mutation of neural tube defect of neonatus and application thereof
InactiveCN102181569AReduce morbidityQuick and easy detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceDiseasePrenatal diagnosis
The invention discloses a kit for detecting whether mutation occurs at a relevant single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) locus on a disease-causing gene of a neural tube defect of a neonatus. The kit mainly comprises a specific primer pair and a specific fluorescent probe pair which are used for detecting a No.rs1801133 SNP locus polymorphism genotype and a No.rs1801131 SNP locus polymorphism genotype on a methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene and a No.rs1801394 SNP locus polymorphism genotype on a methionine synthase reductase (MTRR) gene, and the conventional fluorescent quantitative PCR reaction reagent. The kit is used for detecting a mutant of the disease-causing gene of the neural tube defect of the neonatus, can be used for quickly and conveniently searching a carrier with the disease-causing gene, can be applied to antenatal diagnosis and timely treatment, and reduces the morbidity of the neutral tube defect of the neonatus so as to fulfill the aims of promoting good prenatal and postnatal care.
Owner:XINBAXIANG SHANGHAI MOLECULAR MEDICAL TECH SHANGHAI
CYP4V2 gene mutant and application thereof
InactiveCN103374575AEfficient screeningScreening treatment is effectiveBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBIETTI CRYSTALLINE DYSTROPHYCYP4V2 gene
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Single-gene genetic kidney disease gene combined screening method, kit and preparation method of kit
InactiveCN109161591AAccurate mutation information siteAccurately find out the mutation information siteMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening methodExon
The invention discloses a single-gene genetic kidney disease gene combined screening method, a kit and a preparation method of the kit. The kit comprises a probe for capturing specific oligonucleotides of all the exon sequences in various genetic kidney disease related disease-causing genes or disease susceptible genes. A whole-genome DNA library of a subject is constructed, a target gene sequenceis captured by the prepared single-gen genetic kidney disease gene screening kit, a sample is detected through a double-end 150bp sequencing mode of a high-flux sequencing platform, and a data resultis analyzed through bioinformatics, so that mutation information sites of genetic kidney disease related genes can be found out rapidly and accurately, the aim of gene diagnosis is fulfilled, and theexon area of all the genetic kidney disease genes which are known at present can be covered.
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Method and kit for non-invasive measurement on fetus deaf pathogenic gene mutation
PendingCN105087756AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationNon invasiveHigh throughput sequence
The present invention is directed to a method, kit and primers for detecting fetal deafness pathogenic gene mutations. The method of the invention comprises: (a) designing primers according to the pre-determined mutation loci of deafness pathogenic genes; (b) extracting plasma DNAs in a pregnant woman; (c) connecting the extracted plasma DNAs with pre-amplification linkers to obtain connected products; (d) PCR pre-amplifying the connected product to obtain pre-amplified products; (e) cyclizing the pre-amplified products to obtain cyclised DNAs; (f) PCR amplifying the cyclised DNAs using the designed primers to obtain amplified products; and (g) high throughput sequencing the amplified products and analyzing the mutations of the fetal deafness pathogenic genes. The invention can effectively determine whether the pre-determined loci on deafness pathogenic genes have been mutated as well as the mutation type.
Owner:BERRYGENOMICS CO LTD
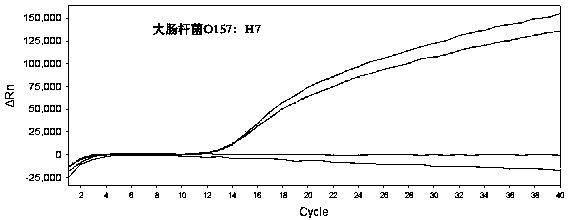
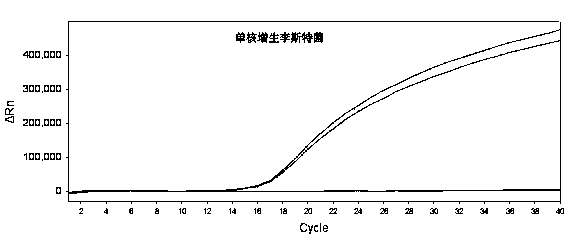
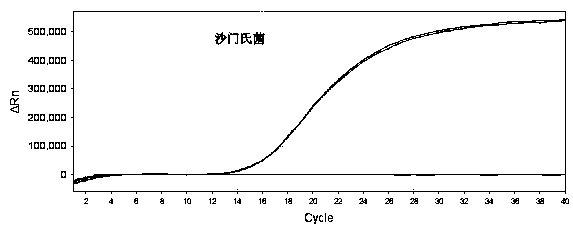
Method for detecting fluorescent quantitative PCR of 12 pathogenic bacteria in real time at the same time
PendingCN109182567AStrong specificityReactiveMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesStaphylococcus aureus
The invention provides a method for detecting fluorescent quantitative PCR of 12 pathogenic bacteria in real time at the same time, including the steps: collecting specific pathogenic gene or toxin gene of the target pathogen and using it as a target gene to design primers and probes so as to make the reaction conditions consistent; extracting a genome template of a sample to be detected; adding the template respectively into tubules equipped with different specific upstream and downstream primers and probes, and then adding the corresponding fluorescent quantitative PCR reagents; under the same cycle of fluorescent quantitative PCR, the corresponding primers and probes are used to detect the samples simultaneously, quickly and quantitatively in their respective reaction tubes. Easier, Quick and efficient, Twelve common pathogenic bacteria (Escherichia coli O157: H7, Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Streptococcus betae, Yersinia enterocolitica, Streptococcusfaecalis, Shigella, Proteus mirabilis, Vibrio fluvialis, Campylobacter jejuni, Staphylococcus aureus) can be detected simultaneously in drinking water and food economically.
Owner:INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE & OCCUPATIONAL MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY SCI
Detection kit and method for copy number of spinal muscular atrophy pathogenic gene SMN1 based on real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technique
InactiveCN108396060AIncrease TM valueImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genesFluorescence
The invention discloses a detection kit and a method for copy number of spinal muscular atrophy pathogenic gene SMN1 based on a real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technique. The detection kit comprises specific primers SMN1-F (SEQ ID NO.1) and SMN1-R (SEQ ID NO.2) modified by NO.7 exon locked nucleic acid of a pair of target genes SMN1, an SMN1 detection probe (SEQID NO.3), an SMN2 gene closed probe SMN2-B (SEQ ID NO.4) modified by SMN-P locked nucleic acid and 3'end C3Spacer, gene primers ALB-F (SEQ ID NO.5) and ALB-R (SEQ ID NO.6) of a reference gene ALB andan ALB detection probe ALB-P (SEQ ID NO.7). The amplification specificity and amplification efficiency of the SMN1 gene are enhanced by using locked nucleic acid modification; a stable reaction system for double amplification of the target genes and the reference gene is established by using a multi-PCR principle and optimizing reaction systems and conditions, and further quantitative accuracy and reliability of the copy number of the SMN1 can be ensured; good repeatability and high operability are obtained.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
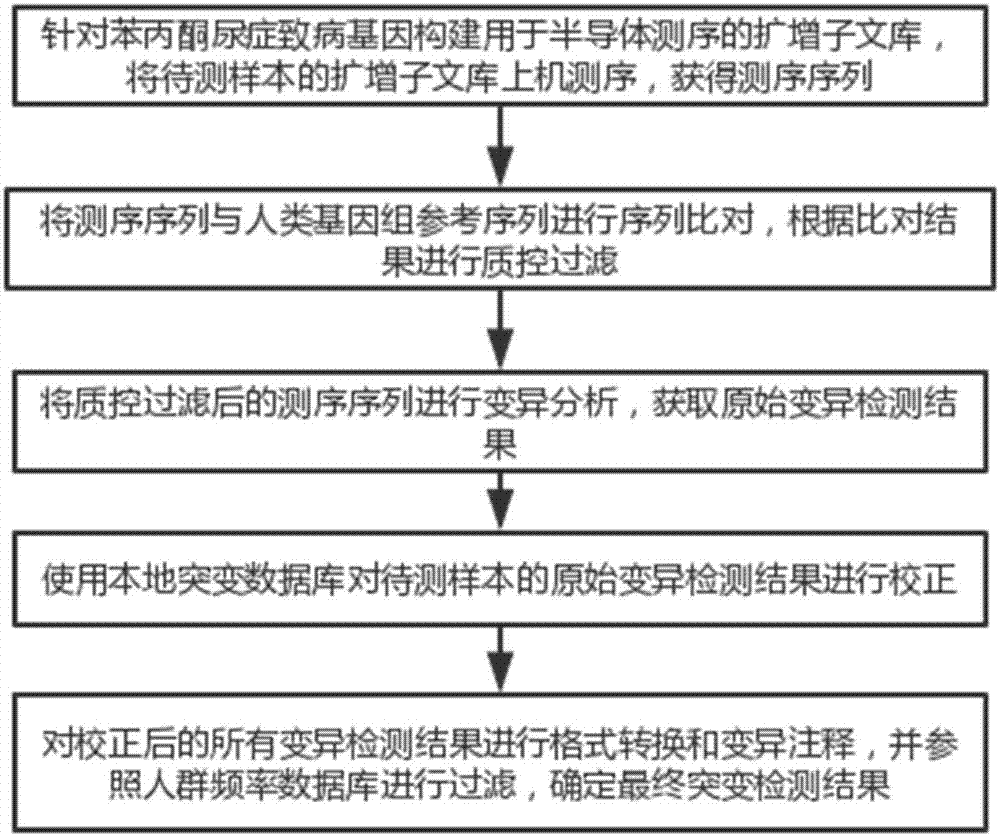
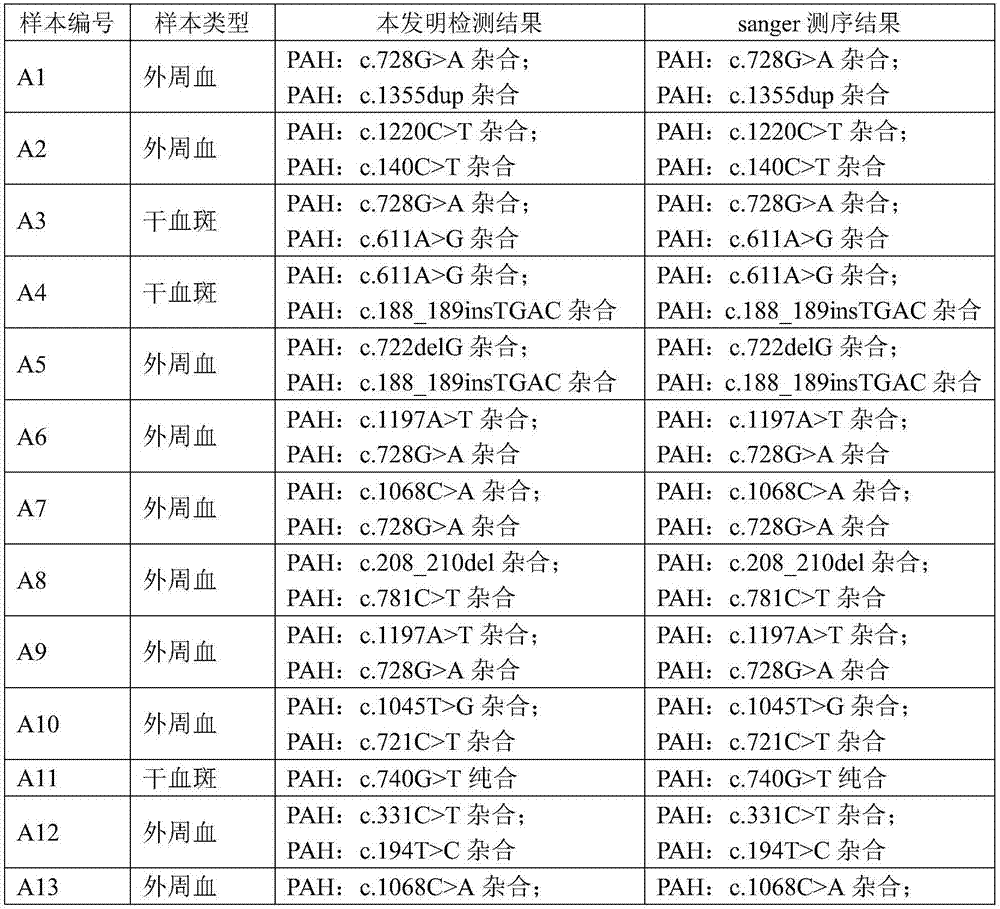
PKU (Phenylketonuria) pathogenic gene mutation detection method and device based on semiconductor sequencing
ActiveCN107974490ASolve the problem of detecting large background noiseEffectively distinguish between true and false positivesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMutation detectionProton
The invention discloses a PKU (Phenylketonuria) pathogenic gene mutation detection method and device based on semiconductor sequencing. A local mutation database is constructed to comprehensively reflect background noise which possibly exists in a detection range and true and false positive results of mutation can be effectively distinguished; the problem that the background noises of PKU detection are great, caused by inherent homopolymerize basic group sequencing errors of a semiconductor sequencing platform, is solved; influences of different batches sequencing quality can be controlled relatively well and the accuracy and stability of detection are improved; the PKU pathogenic gene mutation detection method and device are especially suitable for a Proton platform.
Owner:CAPITALBIO GENOMICS
Novel pathogenetic gene mutation of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and use thereof
InactiveCN1865440AMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringHypertrophic cardiomyopathyNew mutation
The invention relates to several new mutations of pathogenic genes for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and their use in the treatment and diagnosis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Owner:FUWAI HOSPITAL OF CARDIOVASCULAR DESEASE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com