Patents
Literature
127 results about "Transcriptional expression" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
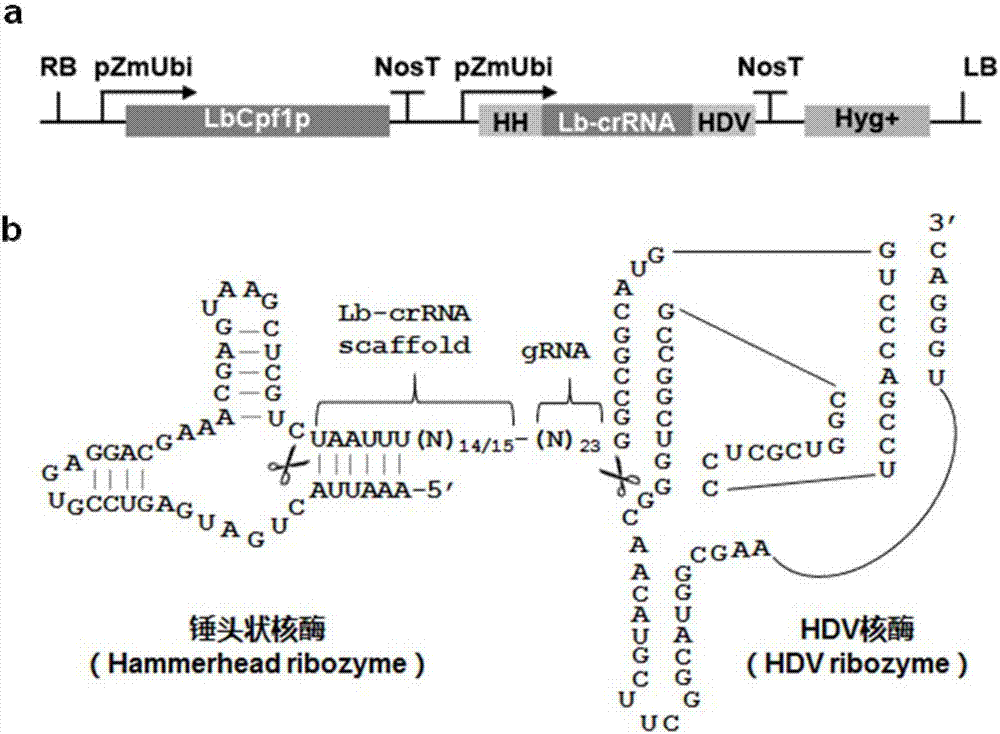
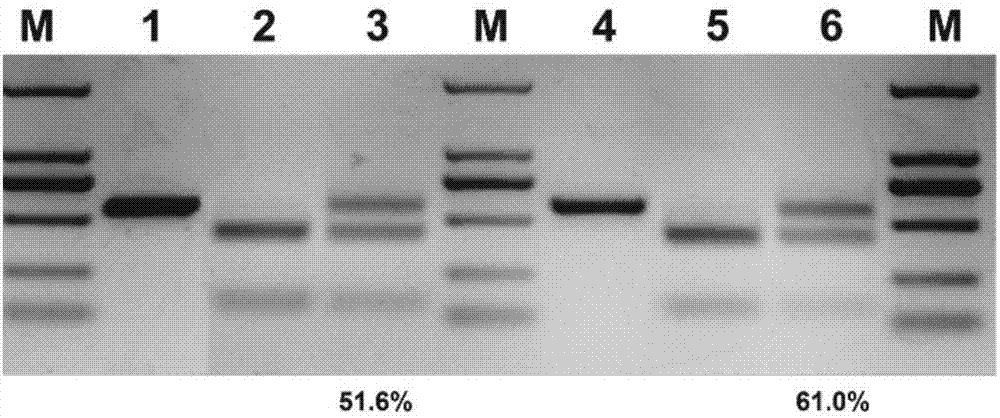
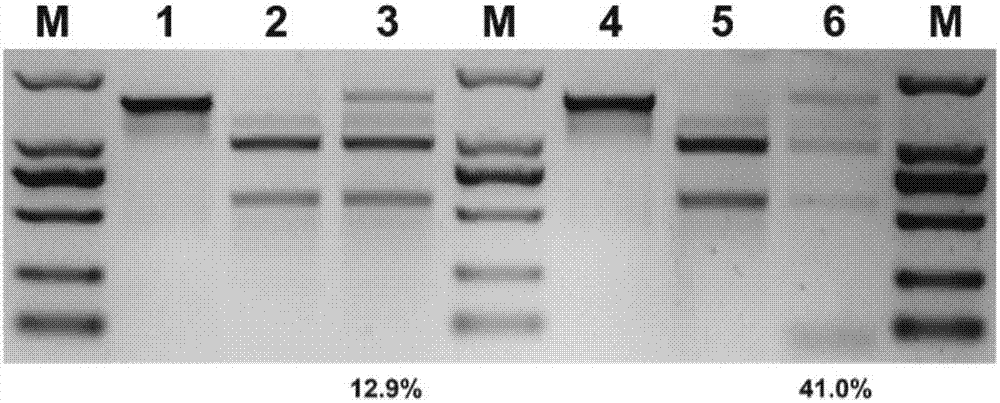
CRISPR/Cpf1 plant genome directional modification function unit, carrier comprising function unit, and application thereof
ActiveCN107012164AEfficient constructionDirectional modification shortcutVector-based foreign material introductionGene expressionNuclease
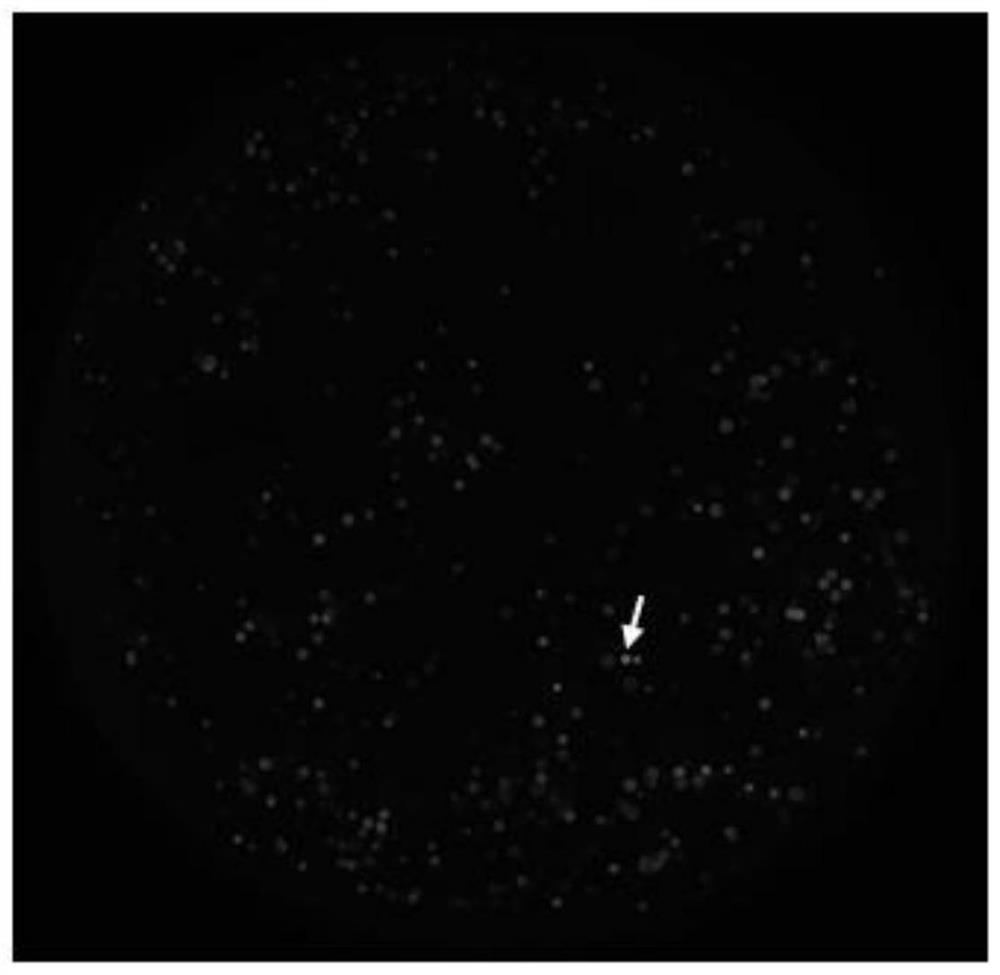
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, and concretely relates to a CRISPR / Cpf1 plant genome directional modification function unit, a carrier comprising the function unit, and application thereof. The invention aims to build an effective plant genome CRISPR / Cpf1 directional modification framework carrier according to an action principle of a CRISPR / Cpf1 system and a vegetable cell gene expression characteristic, and realize high-efficient application thereof in plant genome directional modification. The technical scheme provided by the invention is characterized by building the CRISPR / Cpf1 plant genome directional modification framework carrier formed by lachnospiraceae bacterium Cpf1 nuclease protein (LbCpf1) expression unit and a guiding crRNA transcription expression unit. The invention also provides a method for designing specificity-guided crRNA and building a CRISPR / Cpf1 recombinant expression vector aiming at rice genome target loci by adopting the CRISPR / Cpf1 plant genome directional modification framework carrier. The invention provides the high-efficient CRISPR / Cpf1 plant directional modification framework carrier, which can effectively realize simple, fast and high-efficient directional modification based on the CRISPR / Cpf1 system aiming at a plant genome target sequence.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
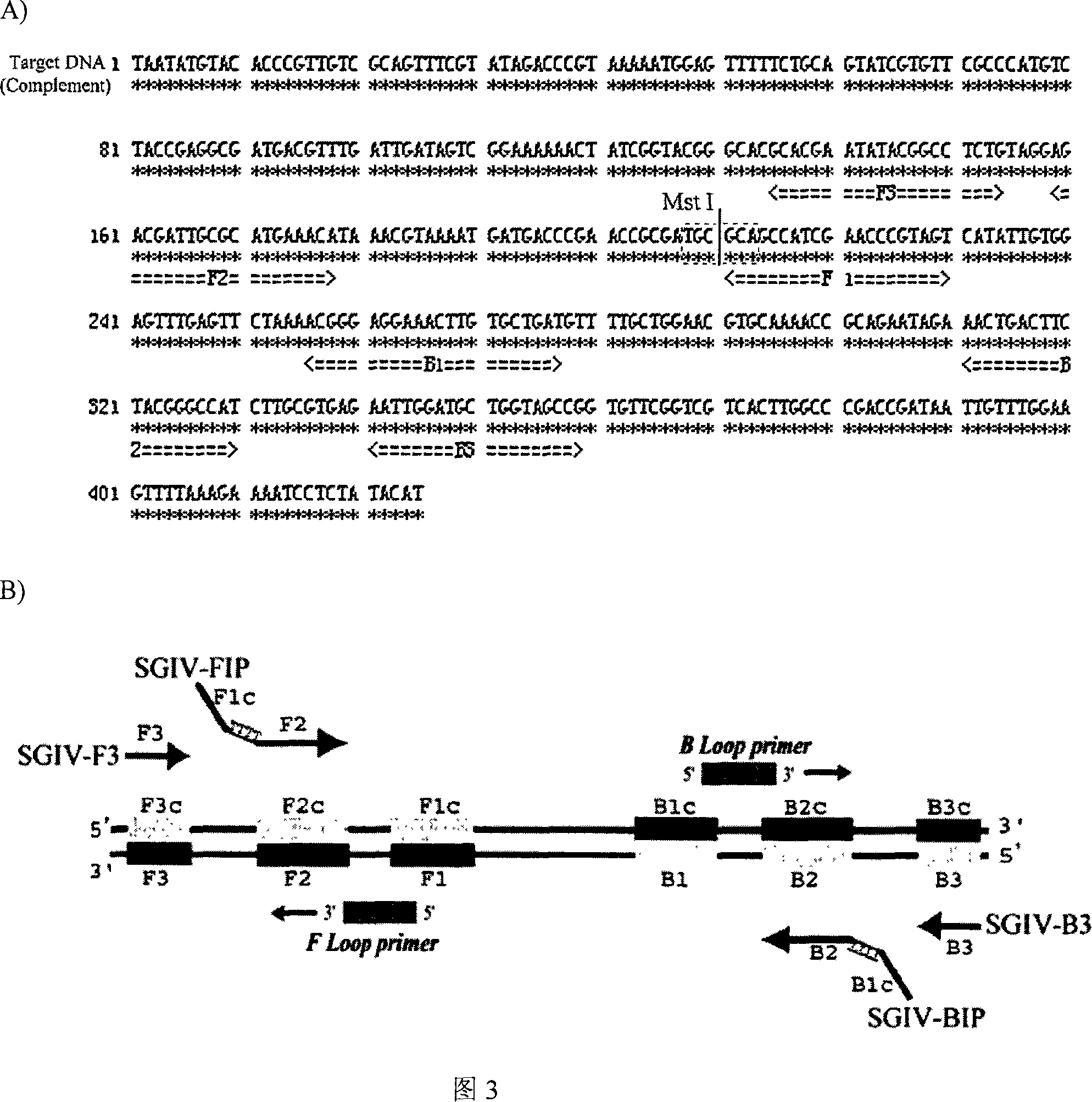
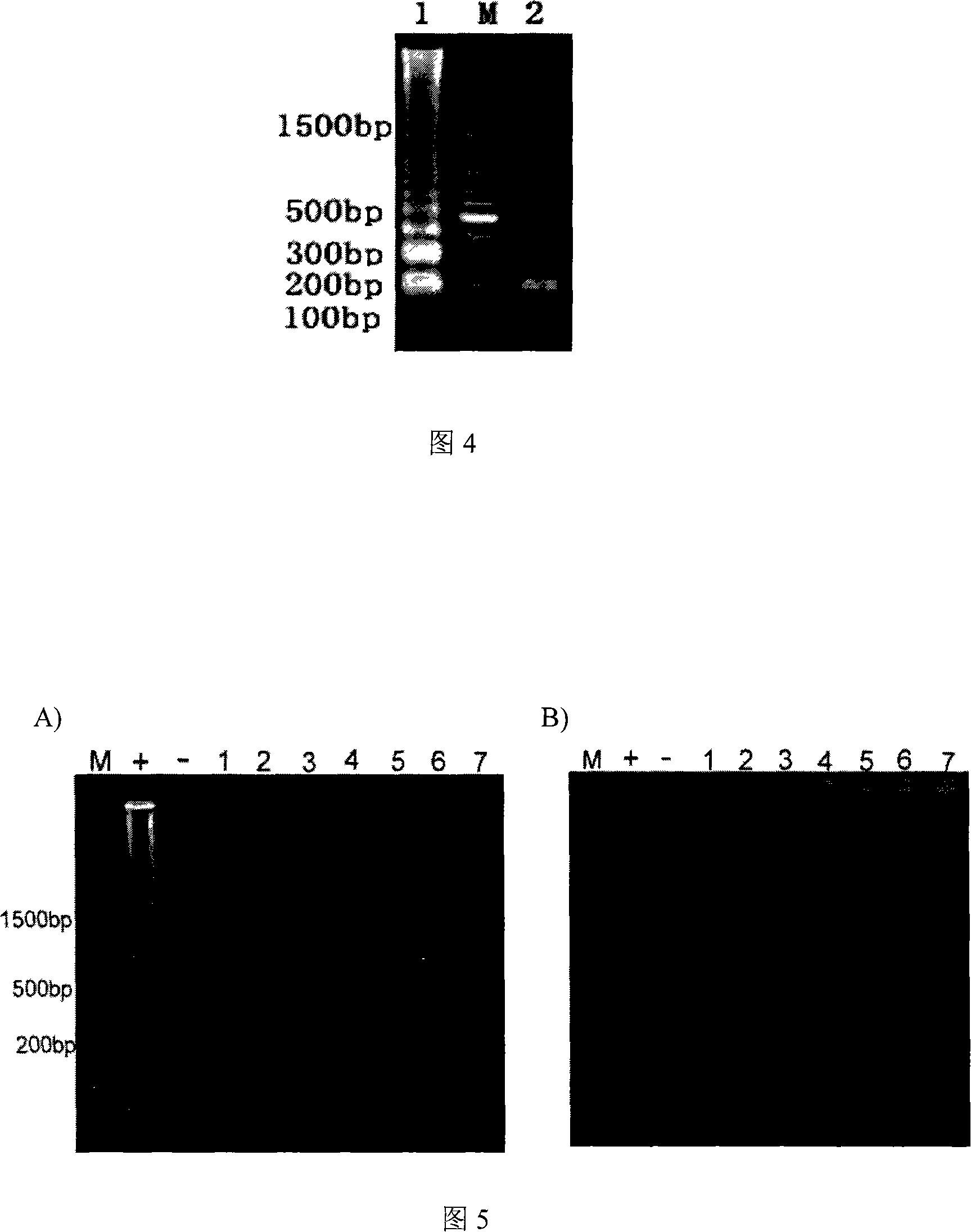
Method for rapidly detecting grouper irido virus
InactiveCN101173317AQuick checkHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementTranscriptional expressionReaction temperature
The invention discloses a fast detection method for grouper iridovirus, firstly proposing a loop-mediated isothermal nucleic acid amplifying detection applied for the detection of grouper iridovirus, which comprises the steps as follows: (1)a ORF-014L is cloned and a recombinant plasmid template containing ORF-014L is constructed; (2)primer design, primer sequence; (3)amplification, the reaction temperature is 63-65 DEG C, and the reaction time 20-60mins. The LAMP detection technique of the invention can rapidly detect SGIV, the transcriptional expression of SGV 014L in cells, the grouper tissue infected by SGIV, and the GP cells infected by SGIV; the sensitivity of the invention is three orders of magnitude higher than Nested PCR, reaching to six point six copies.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
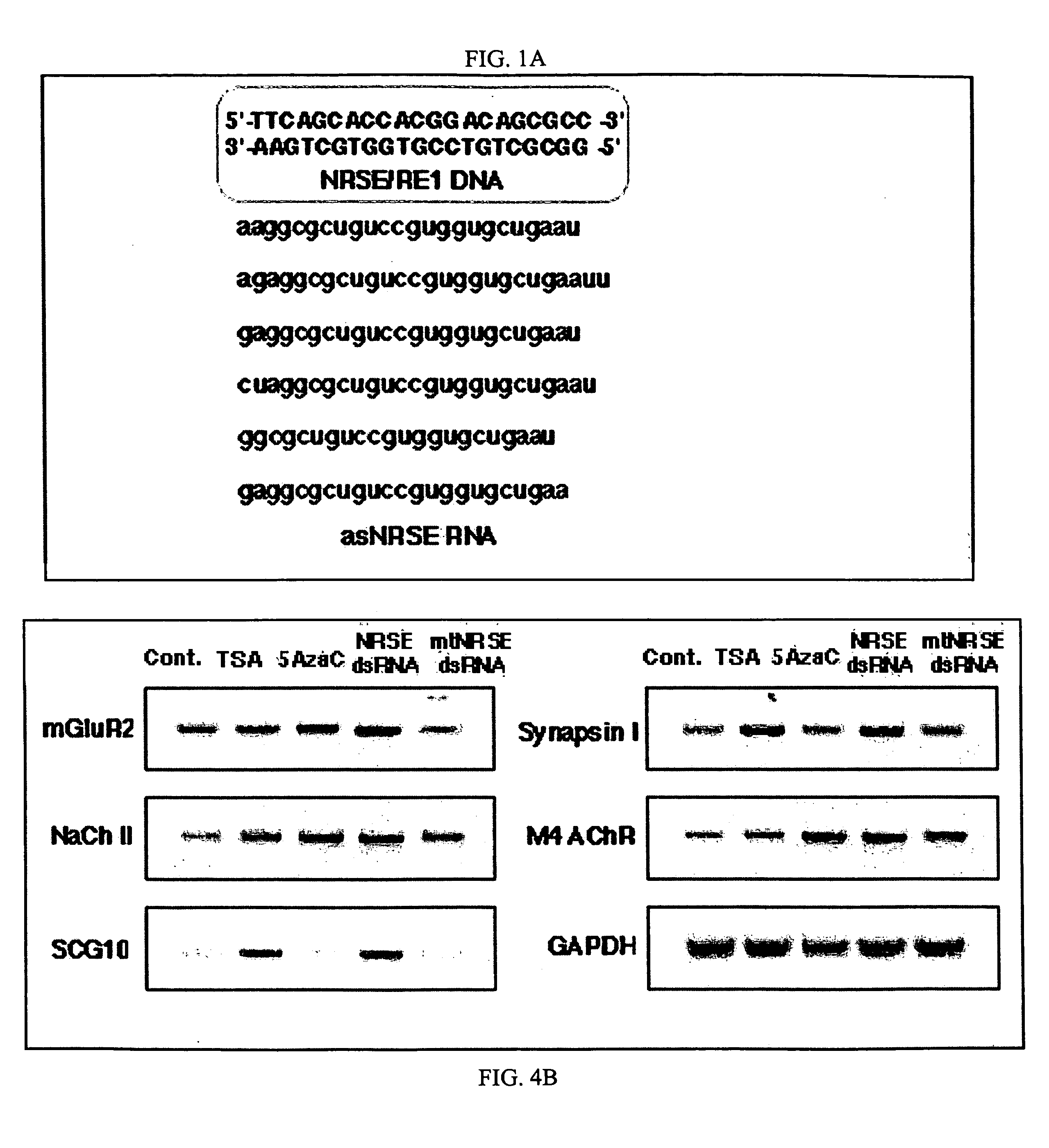
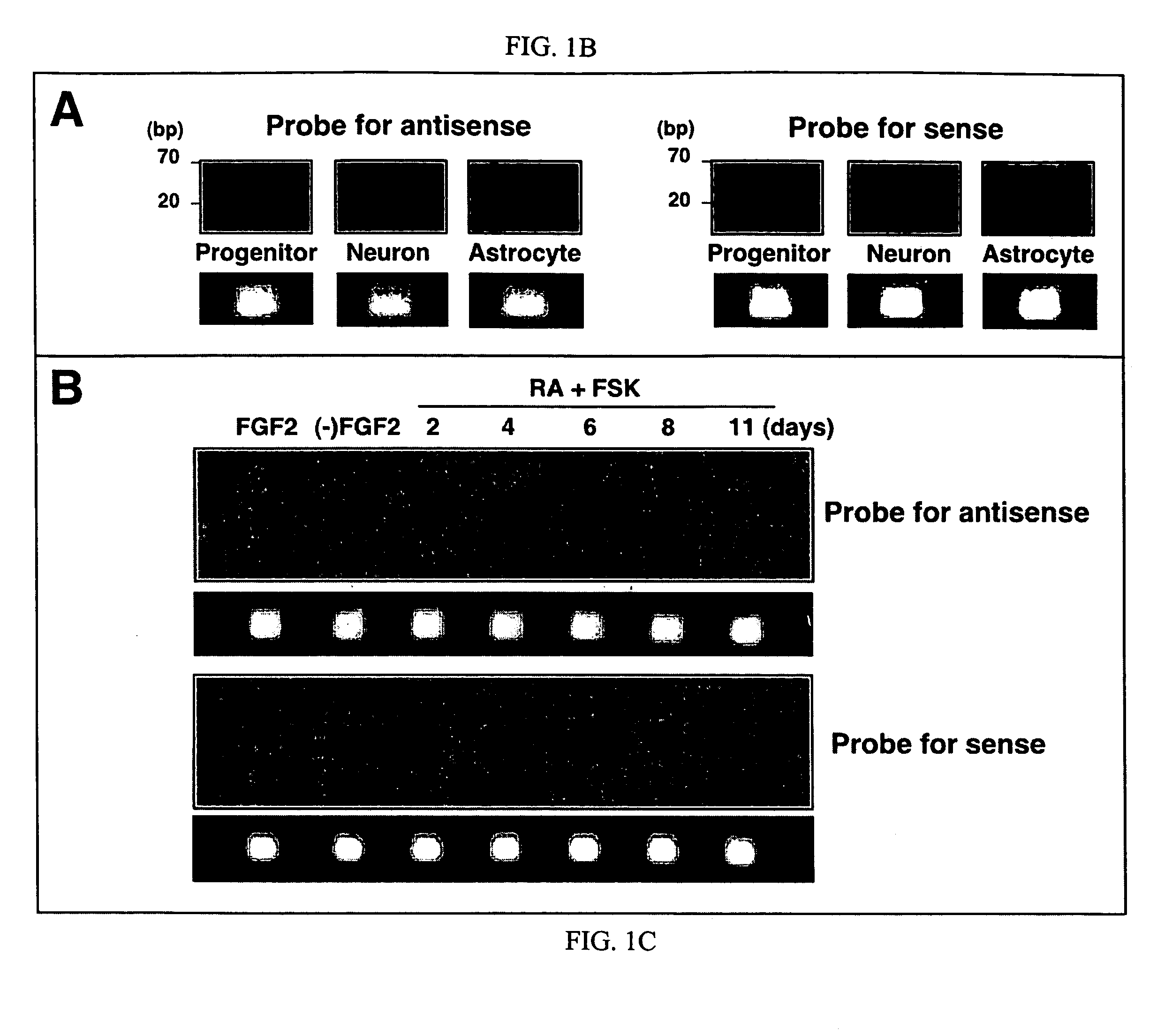
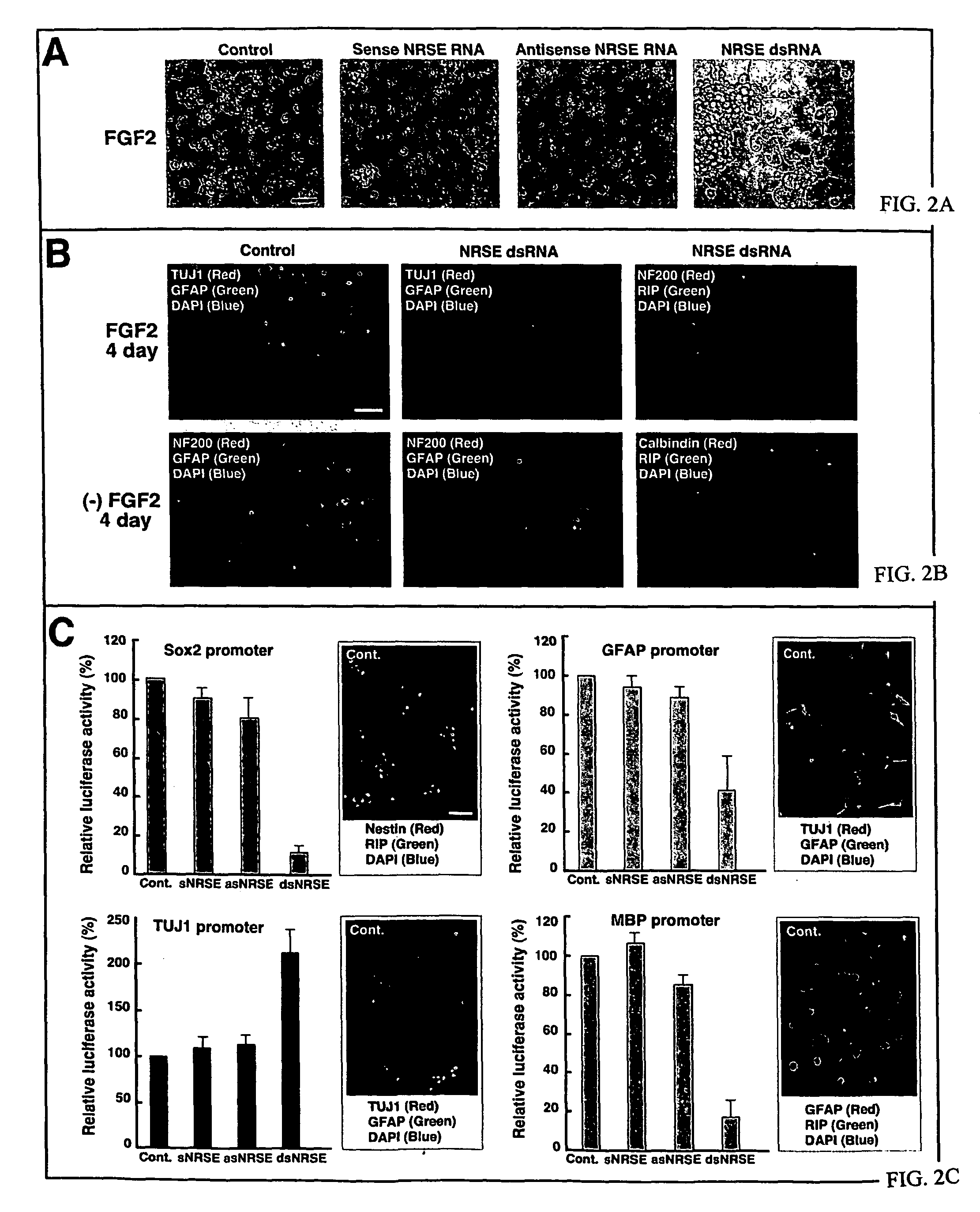
Transcriptional regulation of gene expression by small double-stranded modulatory RNA
The invention provides a method for modulating gene expression by contacting a cellular system with a double-stranded ribonucleic acid molecule capable of associating with a regulatory machinery that controls transcription of one or more genes, wherein the association results in altered expression of the one or more genes. The invention is further directed to method for directing the differentiation of neuronal stem cells into neurons by contacting a cellular system with a double-stranded ribonucleic acid molecule capable of associating with a regulatory machinery that controls transcription of one or more genes involved in neuronal differentiation and directing the transcription of the one or more genes. In related embodiments, the invention provides particular compositions of double-stranded ribonucleic acid molecules as well as therapeutic and screening applications of the invention.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Application of EB1 gene to detection of nosema bombycis
ActiveCN104017890AReduce interferenceThe test result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNosema bombycis
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biotechnologies and particularly discloses an application of an EB1 gene to detection of nosema bombycis. Researches prove that the transcriptional expression of the EB1 gene is related to the cell division of the nosema bombycis and the development of a host. A specific primer is designed by taking the EB1 gene as a target gene, whether silkworm eggs are infected by the nosema bombycis is detected through PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification, and the detected result proves that if the EB1 gene is used as the detecting target gene, the interference effects of inhibiting substances in silkworm egg extracts to the effective PCR amplification of pathogenic gene DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) are very low, the detected result is more accurate and sensitive, and most importantly, whether the silkworm eggs are infected by the nosema bombycis can be rapidly detected at the early stage that the silkworm eggs are infected. The guarantee is provided for the detection and safe egg production of poisonous silkworm eggs in silkworm egg production.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
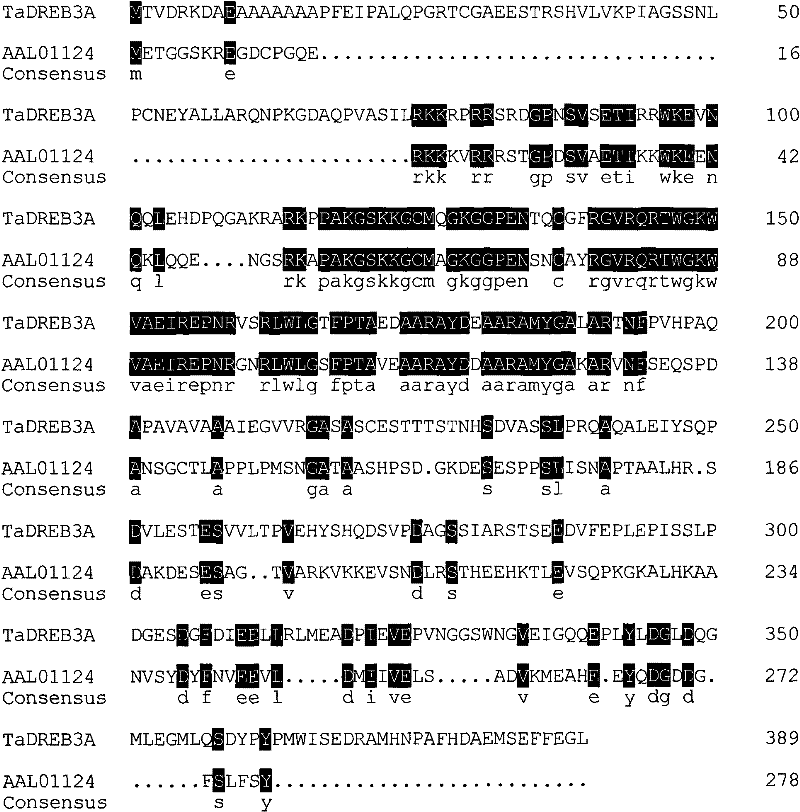
Plant stress-tolerance-associated protein TaDREB3A and coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN102234323AImprove drought resistanceImprove salt toleranceFungiBacteriaHuman controlProtein formation
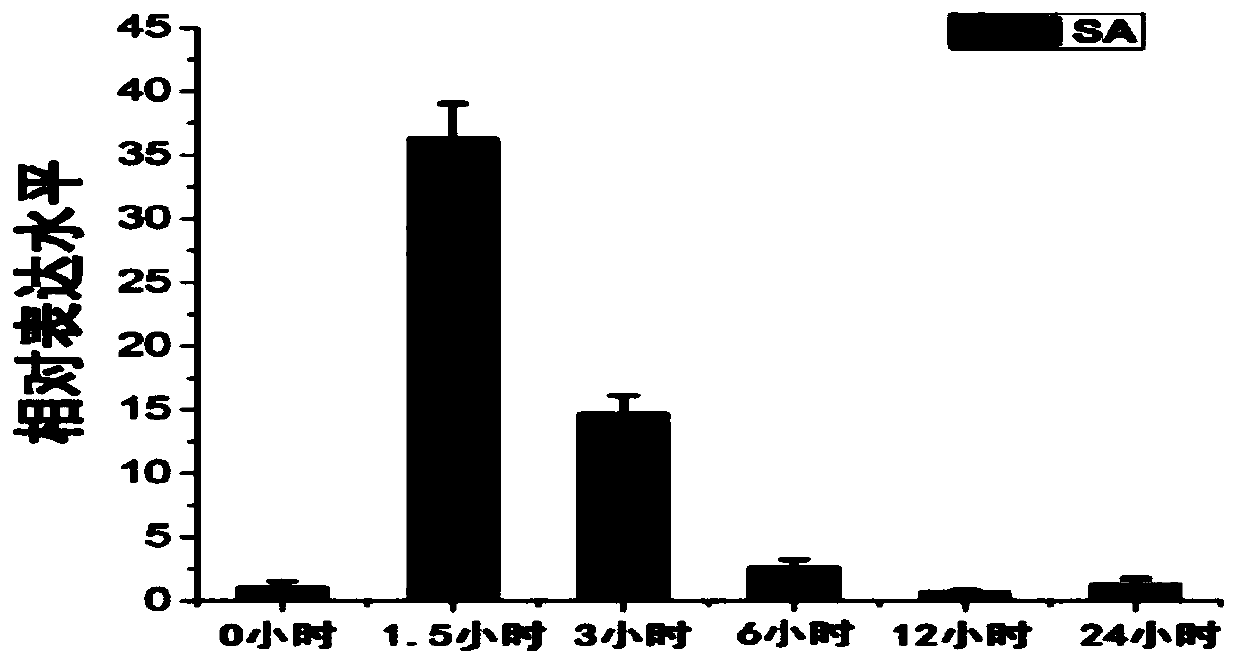
The invention discloses a plant stress-tolerance-associated protein TaDREB3A and a coding gene and application thereof. The protein provided by the invention is one of the following proteins: (a) a protein consisting of an amino acid sequence shown as a sequence 1 in a sequence list, and (b) a protein which is associated with plant stress tolerance and is derived from the sequence 1 by substituting and / or deleting and / or adding one or several amino acid residues for the amino acid sequence shown in the sequence 1. The TaDREB3A provided by the invention can express under the induction of drought, high salt, high temperature, low temperature, pathogenic bacteria, ABA (Abscisic Acid), ethylene, JA (Jasmonic Acid) and SA (Salicylic Acid), and can specifically regulate and control transcription expression of the gene containing a DRE / CRT (Dehydration-Responsive Element / C-Repeat) cis-element (core sequence: CCGAC); therefore, the drought resistance, the salt tolerance, the high temperature resistance and the resistance to the powdery mildew pathogen of the plant are improved. The TaDREB3A provided by the invention provides a base for artificially controlling the expression of genes related to the stress tolerance and the stress resistance, and is about to play an important role in cultivation of plants with enhanced stress tolerance and enhanced stress resistance.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A liver cancer PDX standardization model base
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV +1
Materials and methods for treating ocular-related disorders
InactiveUS20090041759A1Senses disorderHydroxy compound active ingredientsDiseaseTranscriptional expression
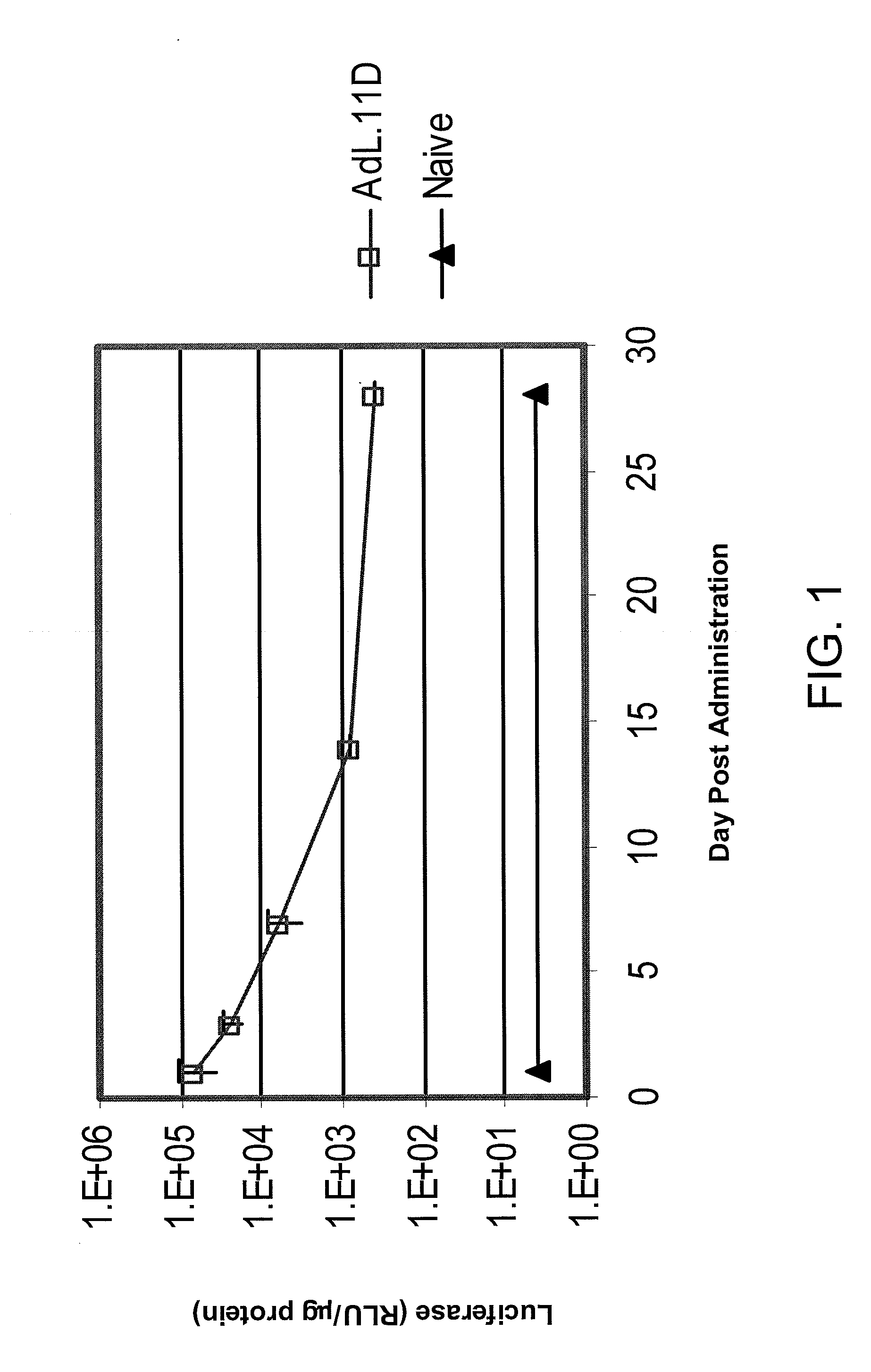
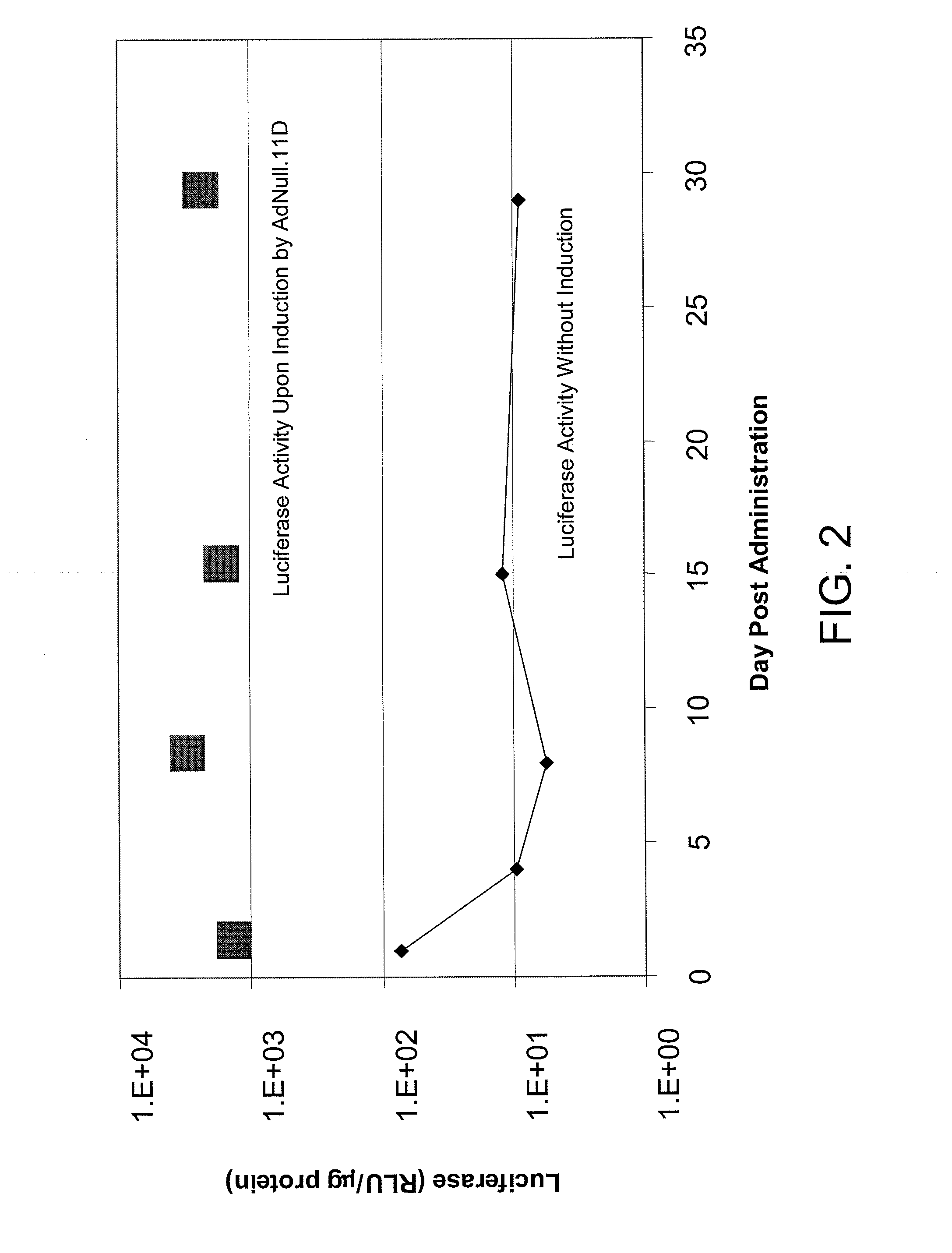
The invention is directed to a method of delivering a gene product to an animal. The method comprises administering an expression vector comprising a nucleic acid sequence operably linked to a promoter and encoding a gene product, and upregulating transcription of the nucleic acid sequence in the ocular cell. The expression vector can be an adenoviral vector. The invention further provides a method of prophylactically or therapeutically treating an animal for at least one ocular-related disorder. The method comprises contacting an ocular cell with an expression vector comprising a nucleic acid sequence encoding an inhibitor of angiogenesis and / or a neurotrophic agent. In one aspect, the method further comprises upregulating transcription of the nucleic acid sequence. Preferably, if 2×108 adenoviral particles of the inventive method are administered to a mouse, the level of expression of the nucleic acid sequence is not diminished more than ten-fold at 28 days post-administration.
Owner:GENVEC INC
Survival motor neuron gene (SMN2) mRNA constructs for post-transcription regulation
InactiveUS9394539B1High expressionEliminate side effectsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsVectorsSpinal muscular atrophiesTranscriptional expression
The present invention provides compounds and assays for the identification and validation of compounds for use in the treatment of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), in which said compounds up-regulate the post-transcriptional expression of SMN1 or SMN2.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
Plant stress tolerance associated protein GmNF-YA17, and encoding gene and application thereof
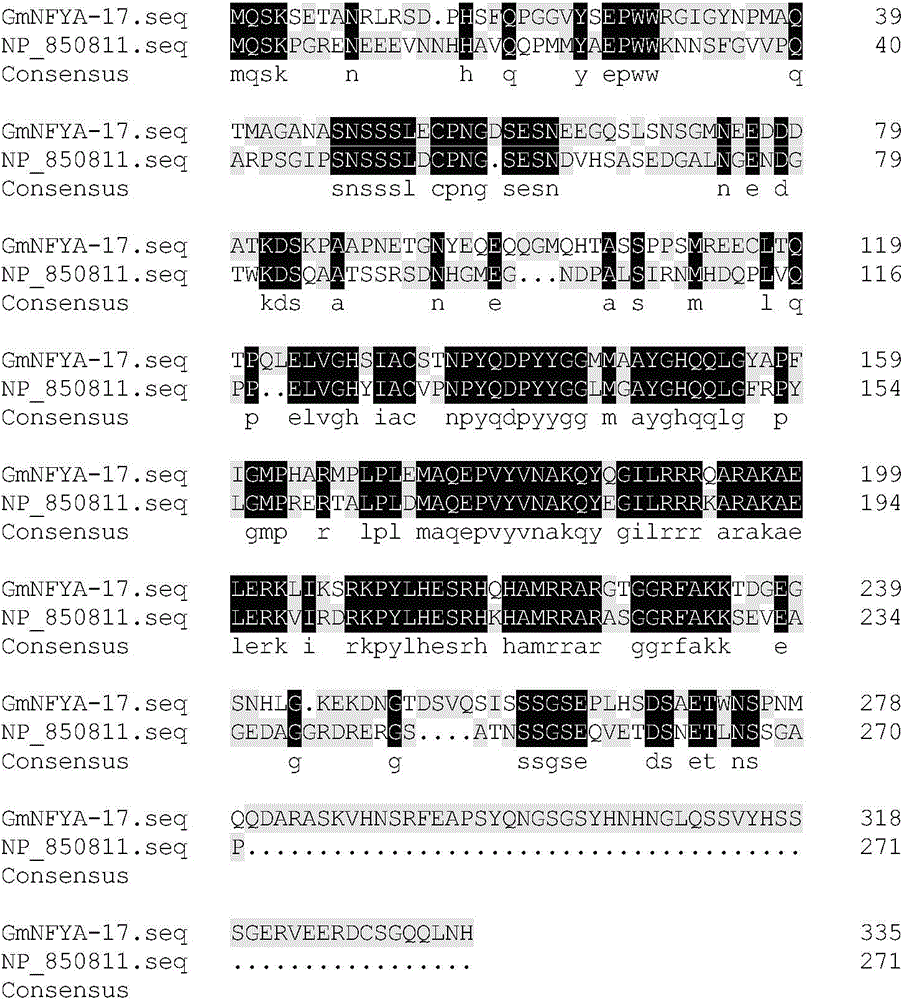
Plant stress tolerance associated protein GmNF-YA17, and an encoding gene and an application thereof. The protein is a protein (a) composed of an amino acid sequence represented by sequence 1 in a sequence table, or a protein (b) obtained by substituting and / or deleting and / or adding one or more amino acid residues to the protein (a), associating with the plant stress tolerance and derived from the sequence 1. Experiments prove that gene GmNF-YA17 can be obtained through cloning from soybeans, is expressed under induction of drought, salt, ABA and ethylene, positions the coded protein to a nucleus, and can specifically regulate the transcription expression of gene containing a CCAAT-box cis-element. The GmNF-YA17 can improve the drought resistance of plants, provides a foundation for artificial control of expression of stress resistance and stress tolerance associated genes, and plays a great role in the cultivation of stress resistance and stress tolerance reinforced plant.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Mesothelin-targeted replication-defective recombinant lentivirus CAR-T transgenic carrier as well as establishment method and application thereof
ActiveCN105969805APromote secretionImprove in vitro killing effectMammal material medical ingredientsNucleic acid vectorEucaryotic cellFluorescence
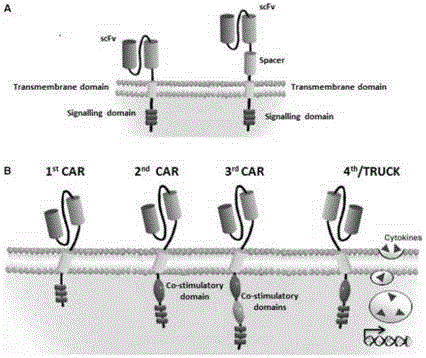
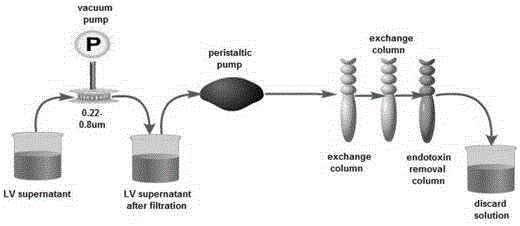
The invention discloses a Mesothelin-targeted replication-defective recombinant lentivirus CAR-T transgenic carrier which comprises a pronucleus replicon pUC Ori sequence for plasmid replication, an amicillin resistance gene AmpR containing sequence for mass amplification of target strain, virus replicon SV40Ori sequence for enhancing replication in eukaryocyte, a lentivirus packaging cis-element for lentivirus packaging, a ZsGreen1 green fluorescent protein for green fluorescence expression of eukaryocyte, an IRES ribosome combination sequence for joint transcriptional expression of protein, a human EF1(alpha) promoter for the eukaryotic transcription of chimeric antigen receptor gene, a chimeric antigen receptor for forming a second-generation CAR or third-generation CAR integrating identification, transfer and start, and an eWPRE element for improving the transgenic expression efficiency. Moreover, the invention also discloses an establishment method and application of the carrier. In the invention, the secretion of cell factors and the in-vitro killing effect of CAR-T cells can be remarkably enhanced, and the effect of clinical treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma and pancreatic cancer is outstanding.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNICAR THERAPY BIOPHARM TECH CO LTD
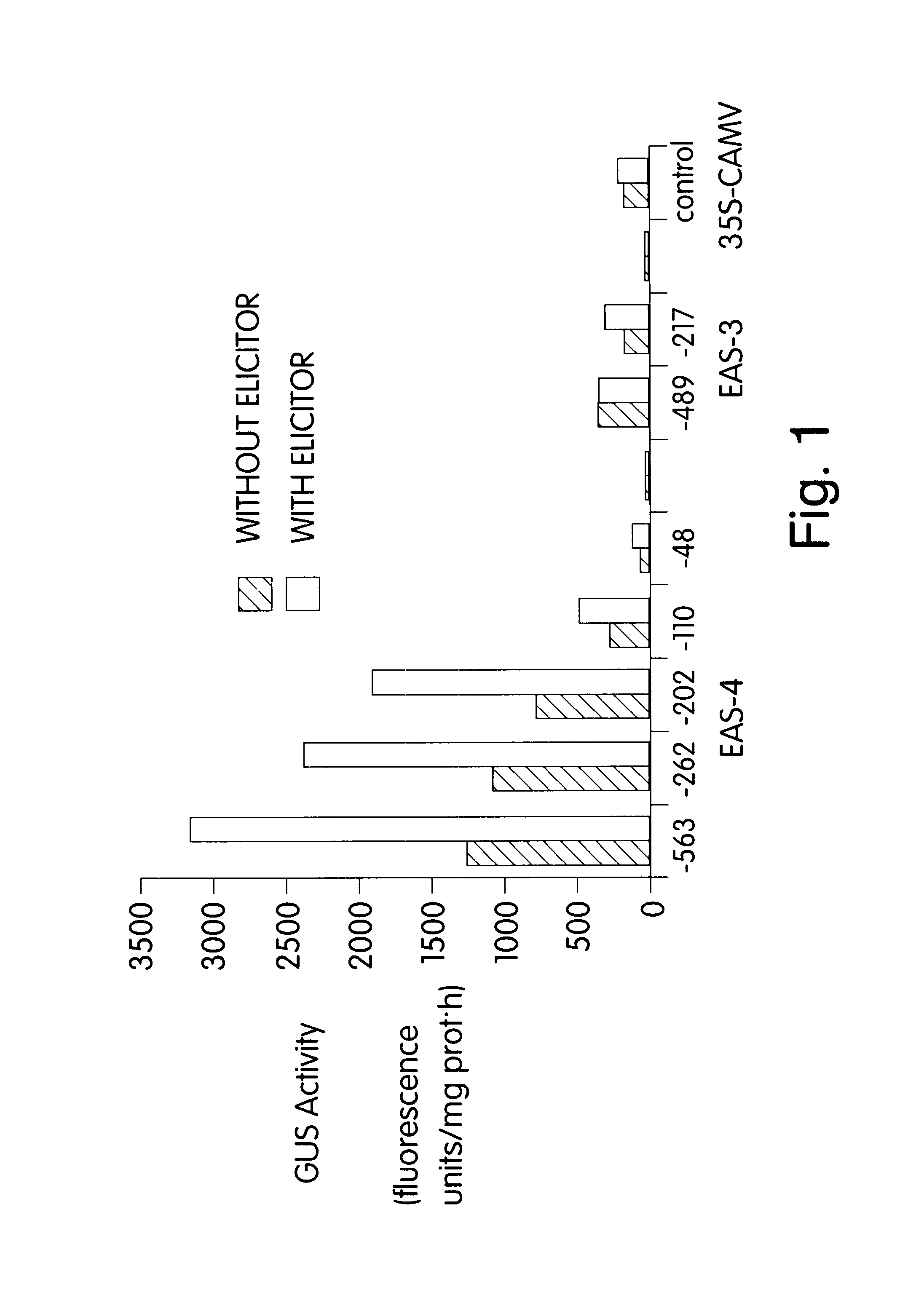
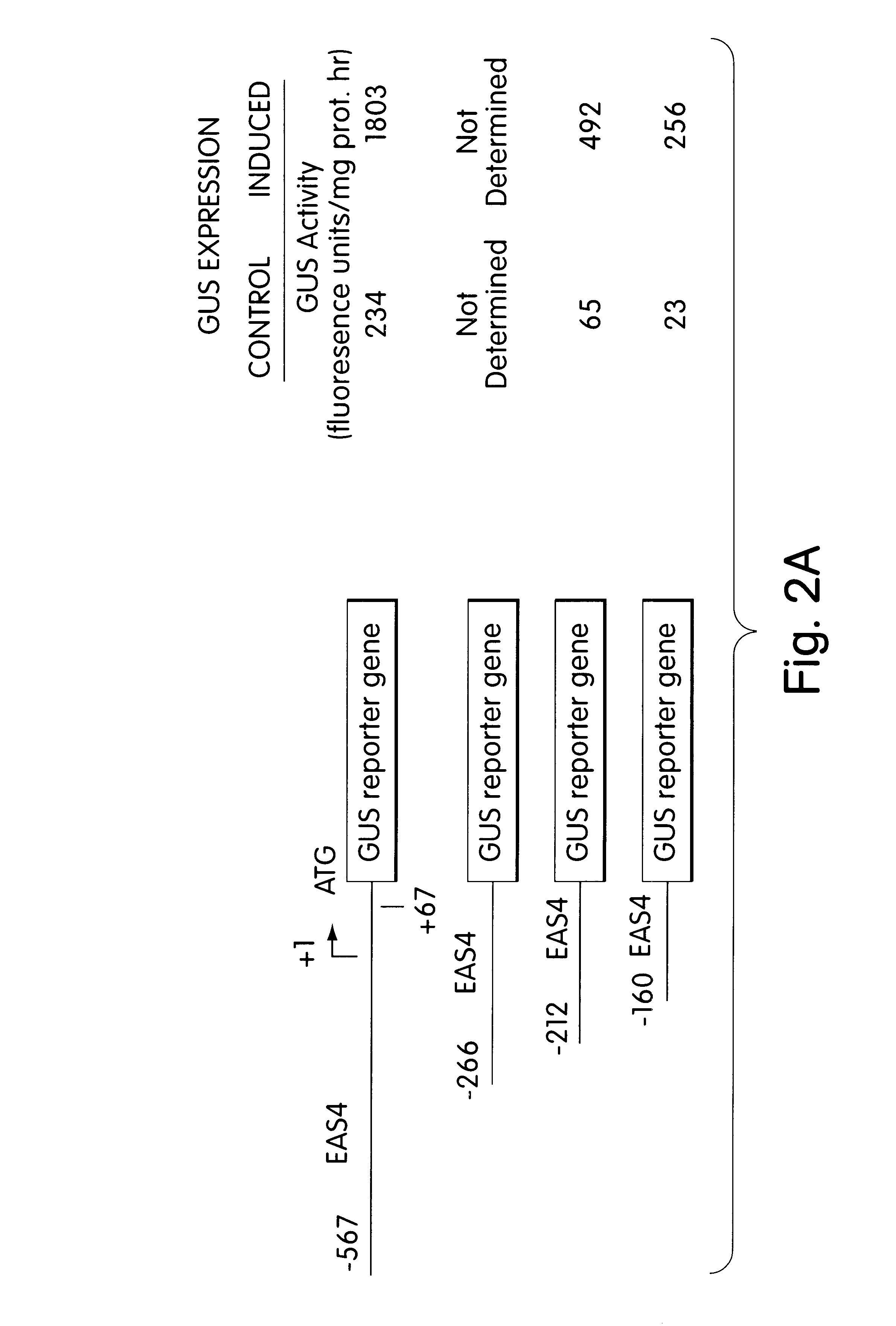
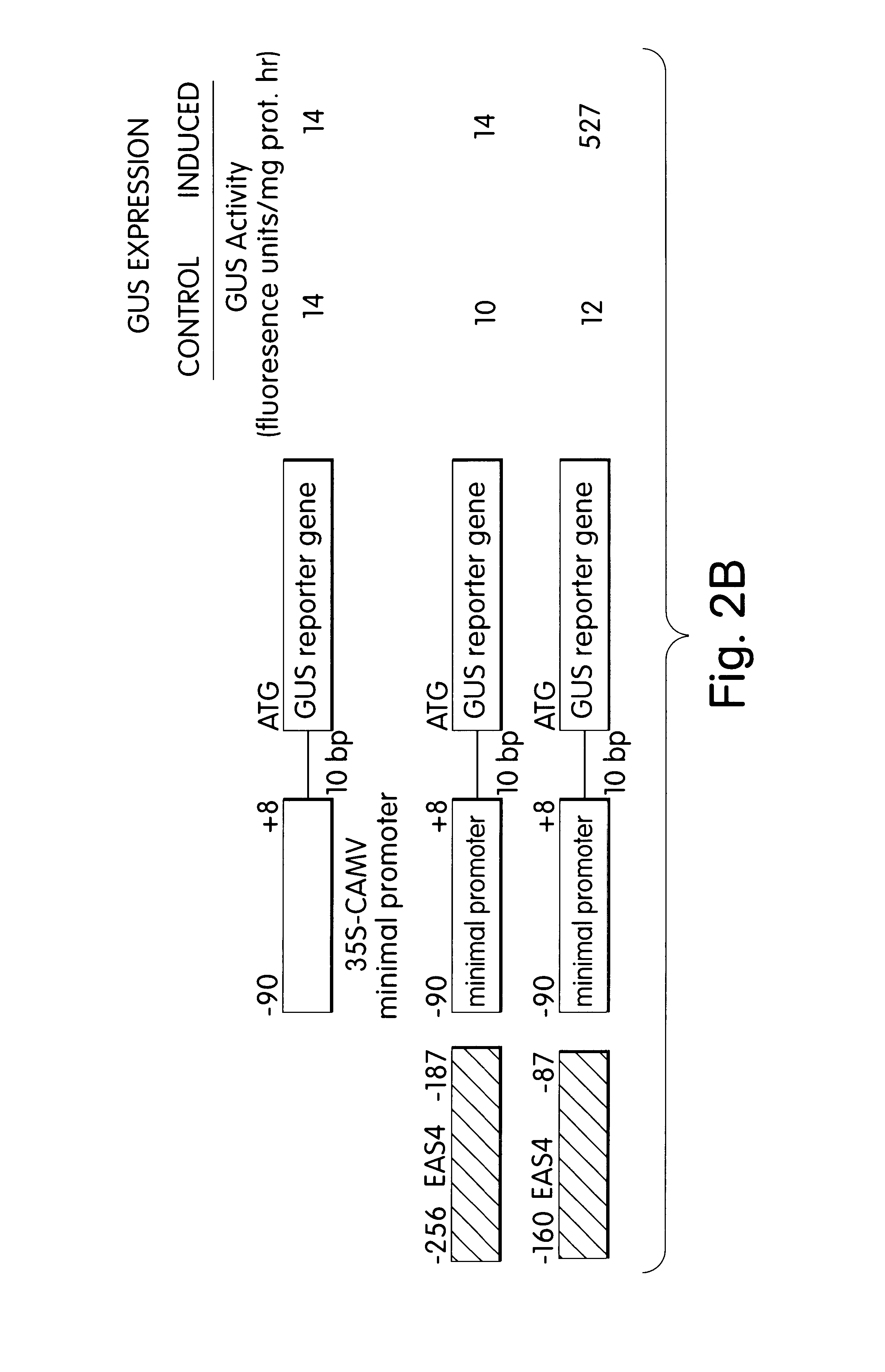
Pathogen- or elicitor-inducible transcription regulatory element from the tobacco 5-EPI-aristolochene synthase gene and plants transformed therewith
A tobacco epi-5-aristolochene synthase transcriptional regulatory element functional in plants, plant tissue and in plant cells for pathogen inducible gene expression and a method for increasing the transcriptional expression of downstream genetic information in plants, plant tissue and plant cells are disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
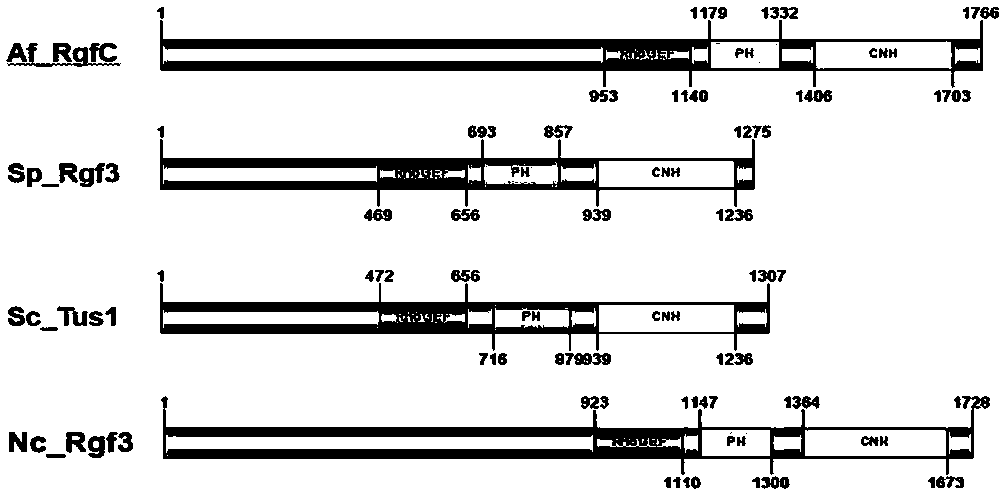
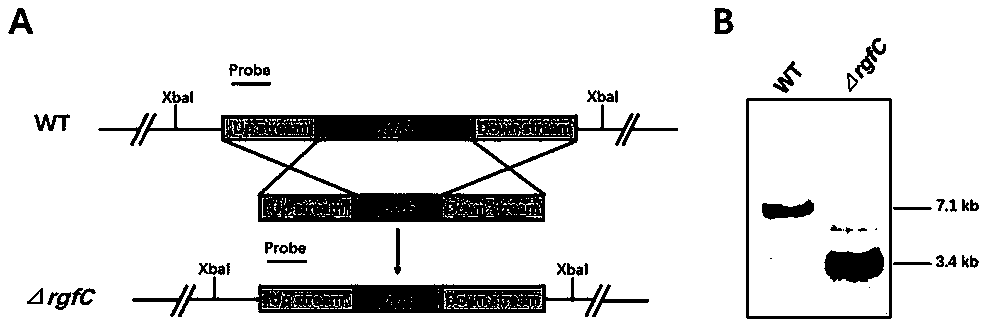
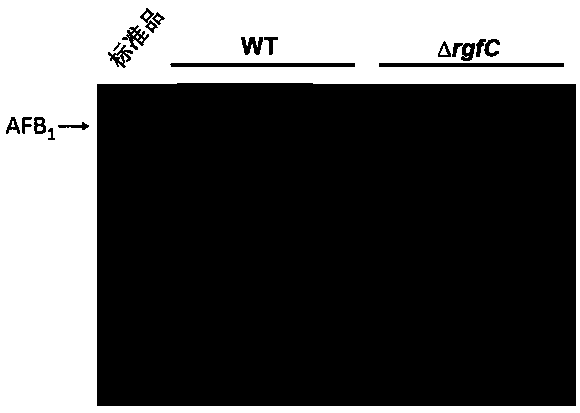
Aspergillus flavus pathogenic gene rgfC and application thereof
ActiveCN107904250AReduce usageReduce pollutionMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptidesAspergillus welwitschiaeTranscriptional expression
The invention provides an aspergillus flavus pathogenic gene rgfC and an application thereof in screening of medicines used for preventing and treating aspergillus flavus contamination. The inventionalso discloses a method for screening and inhibiting pathogenicity of aspergillus flavus or screening medicines capable of preventing and treating aspergillus flavus contamination. More specifically,the method disclosed by the invention contains the following steps: adding a to-be-screened candidate into an aspergillus flavus culture system, detecting transcriptional expression level of an rgfC gene in aspergillus flavus, comparing with a control group which is not added with the candidate, and determining the candidate is a potential medicine capable of inhibiting the pathogenicity of aspergillus flavus or preventing and treating the aspergillus flavus contamination if the transcriptional expression level of the rgfC gene in a test group is lower than that of the control group statistically.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
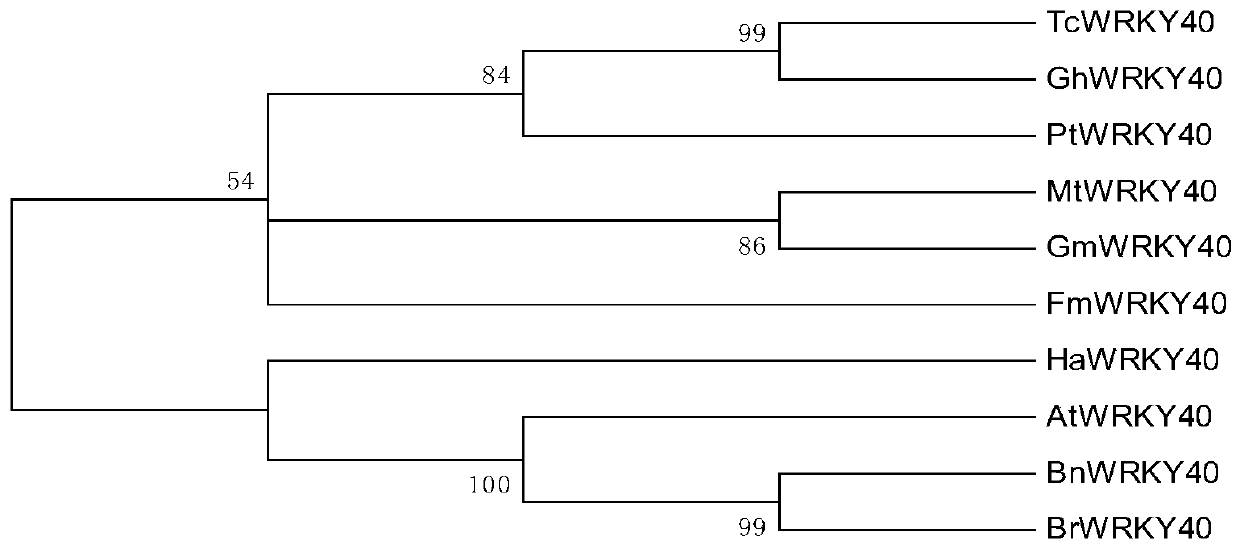
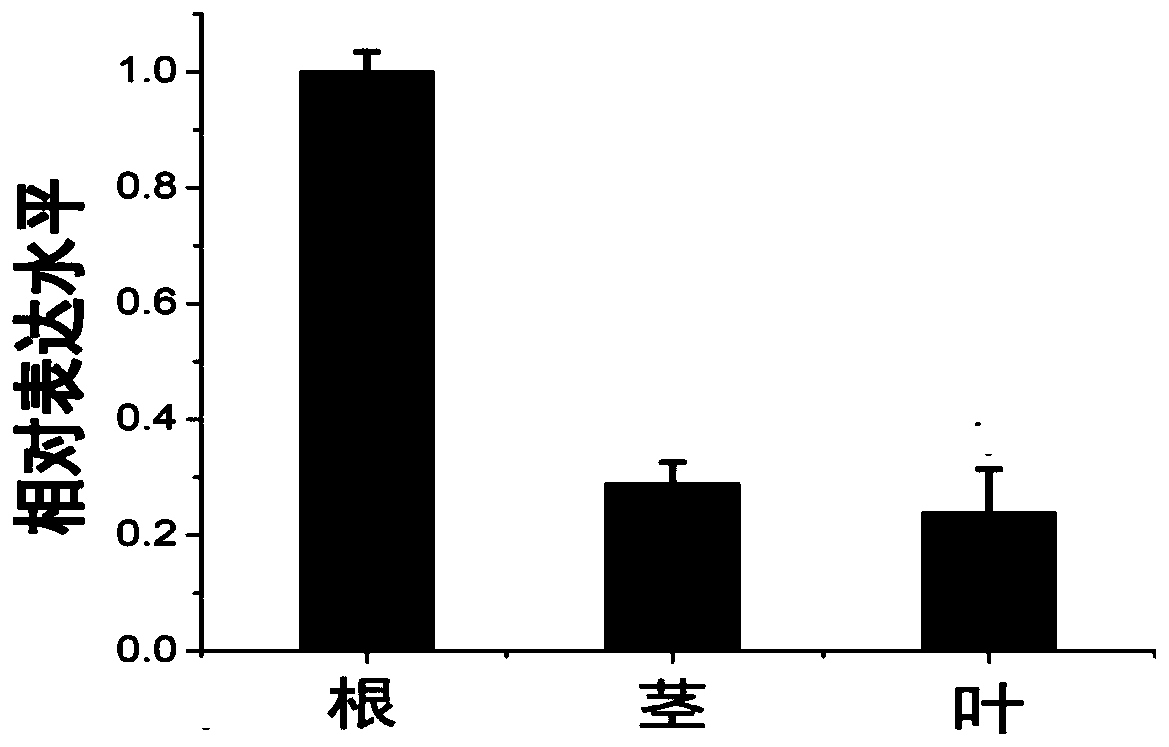
Plant disease-resistant protein GhWRKY40, coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN110256549AImprove disease resistanceImprove resistance to damagePlant peptidesFermentationPathogenAmino acid
The invention discloses a protein, the name of which is GhWRKY40, which is a protein shown in (a) or (b) or (c): (a) a protein with the amino acid sequence shown in sequence 2 in a sequence table; (b) a fusion protein obtained by connecting tags at the N end or / and the C end of the protein shown in the sequence 2 in the sequence table; and a protein with the function or activity of GhWRKY40 transcription factors which is obtained by deriving the protein shown in (a) or (b) through substitution, deletion or / and insertion of one or more amino acids. The gene has the advantages that the GhWRKY40 regulates transcription expression of specific genes, causes physiological and biochemical changes of plants, increases resistance of plants to pathogen invasion, so as to protect growth and development of plants, and has important significance in application of improving response of plants to pathogens.
Owner:九圣禾种业股份有限公司
Methods of screening for compounds for treating muscular dystrophy using mIGF1 mRNA translation regulation
InactiveUS8741572B1Increase productionIncrease and enhance expressionIntegrin superfamilyMicrobiological testing/measurementITGA7Transcriptional expression
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
Methods of screening for compounds for treating muscular dystrophy using UTRN mRNA translation regulation
InactiveUS8283115B1Good curative effectLow toxicityIntegrin superfamilyMicrobiological testing/measurementITGA7Transcriptional expression
The present invention provides compounds and assays for the identification and validation of compounds for use in the treatment of muscular dystrophy (MD), or a form thereof, in which said compounds increase the post-transcriptional expression of a target gene (i.e., mIGF1, ITGA7, or UTRN).
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
Gluconobacter oxydans nonresistant marker gene knockout system
ActiveCN103805545AAvoid polarityBacteriaVector-based foreign material introductionKanamycinTranscriptional expression
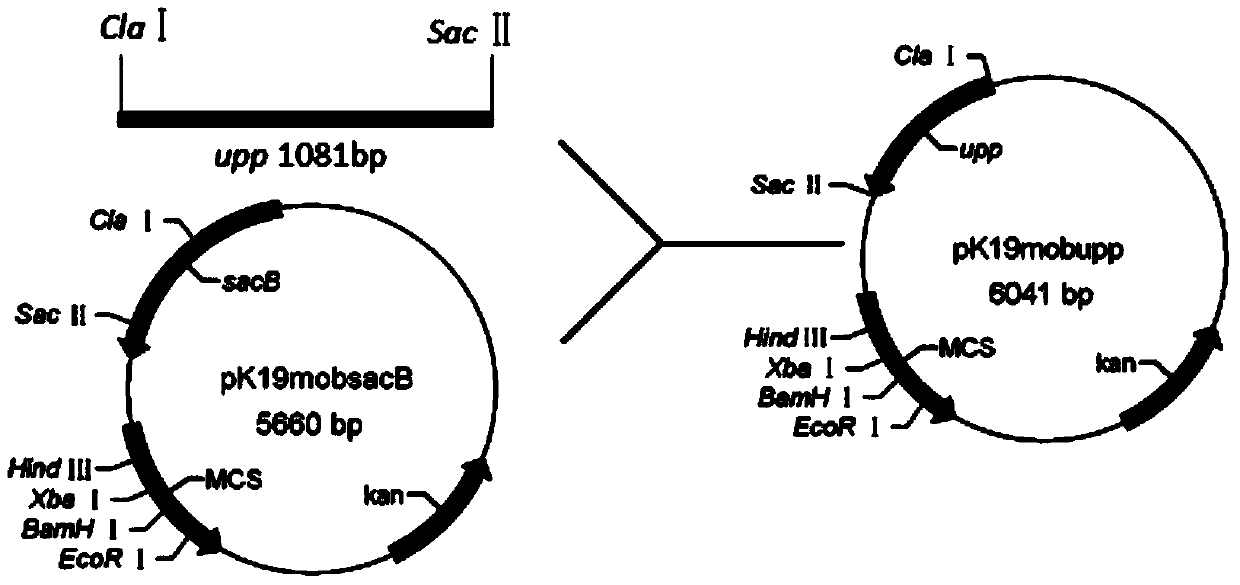
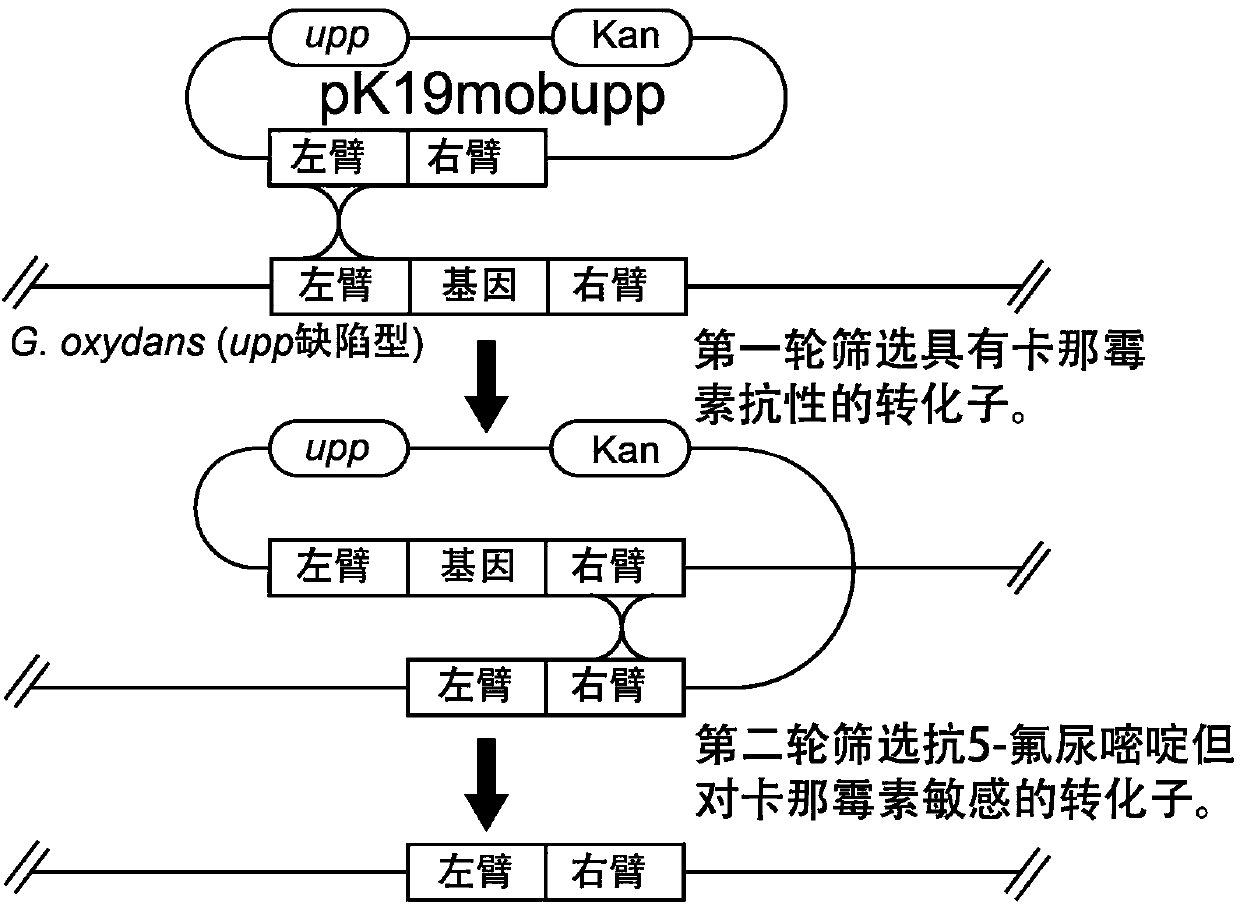
The invention discloses a gluconobacter oxydans nonresistant marker gene knockout system, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. According to the invention, through a homologous recombination technique, upp genes in G.o xydans are knocked out, so that a upp genetic deficient strain is obtained; a recombinant integrating plasmid containing a upp gene which can be subjected to good transcribed expression in G.o xydans and has a conditional lethal function, a resistance maker kanamycin resistant marker gene for the transformant selection of G.o xydans and an MCS polycloning site is built. The plasmid is applicable to the knockout and replacement of G.o xydans chromosome genes; compared with gene knockout implemented by taking a resistant marker gene as a selection marker, the system disclosed by the invention has the following two advantages: no resistant gene is introduced to a G.o xydans genome, so that a polar effect of the resistant gene on upstream and downstream genes is avoided; by using the knockout system, the multiple knockout and replacement of chromosome genes can be performed in a same strain.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
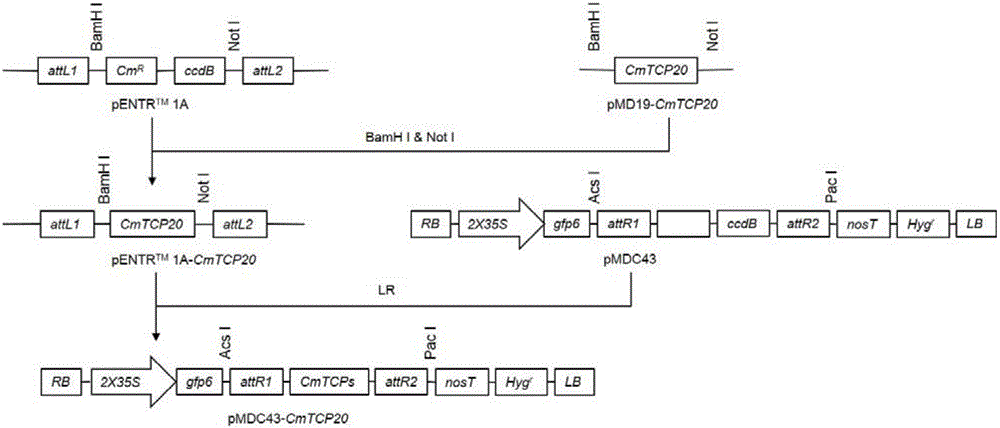
Method for regulating and controlling growth of chrysanthemum petals through conversion of CmTCP20 gene
ActiveCN105671056APromote growthMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesTranscriptional expressionPetal
The invention belongs to the field of plant genetic engineering and transgenic breeding and relates to a method for regulating and controlling growth of chrysanthemum petals through conversion of the CmTCP20 gene.The method includes the following steps that the CmTCP20 gene is cloned from florist's chrysanthemum 'ShenMa'; a plant expression vector of the CmTCP20 gene is constructed; the plant expression vector is transferred into chrysanthemum through an agrobacterium-mediated method, culturing is conducted, and a resistant plant is preliminarily obtained; the converted plant is subjected to PCR and quantitative RT-PCR detection to verify that the CmTCP20 endogenous gene is integrated to a genome DNA of the transgenic plant and subjected to transcription; the transgenic plant is subjected to phenotypic observation and statistic analysis, and it is found that compared with a plant not subjected to transgenosis, the petal growth amount of the transgenic plant is obviously increased.According to the method, the endogenous CmTCP20 transcription factors are converted and subjected to normal transcriptional expression, so that growth of the chrysanthemum petals is regulated and controlled, a novel and practical method is provided for improving ornamental quality of chrysanthemum through a genetic engineering technology, and the chrysanthemum biotechnology breeding process can be effectively promoted.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
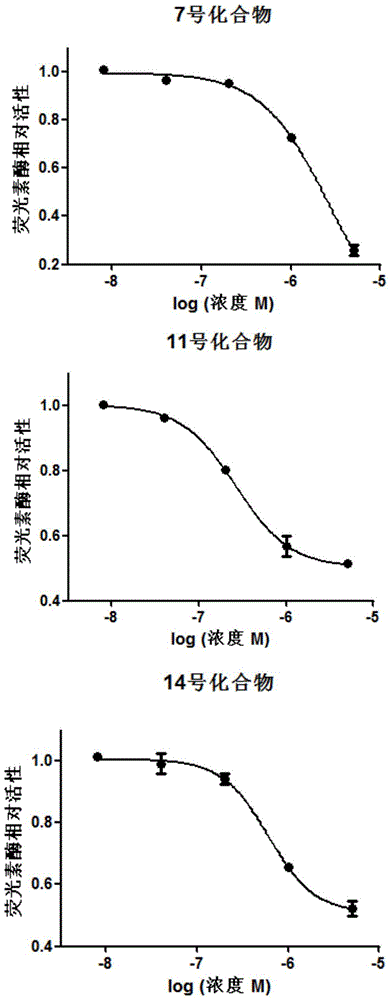
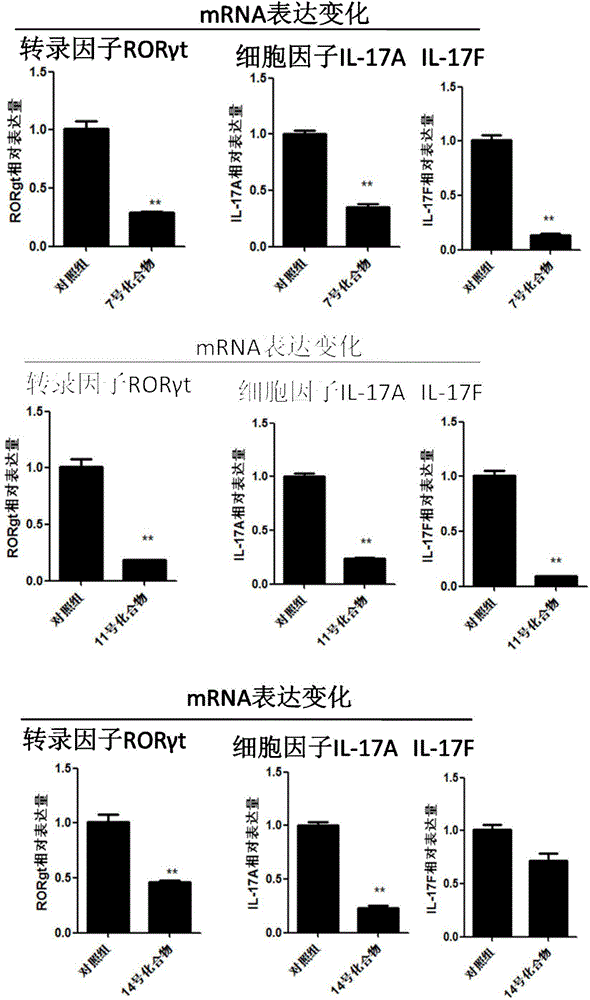
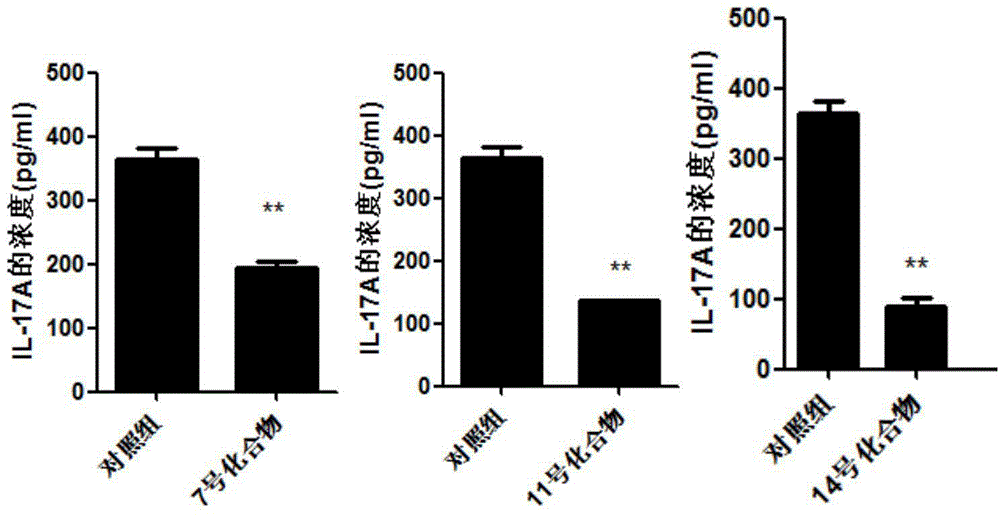
Application of 4N heterocyclic compound as inhibitor for Th17 cell differentiation
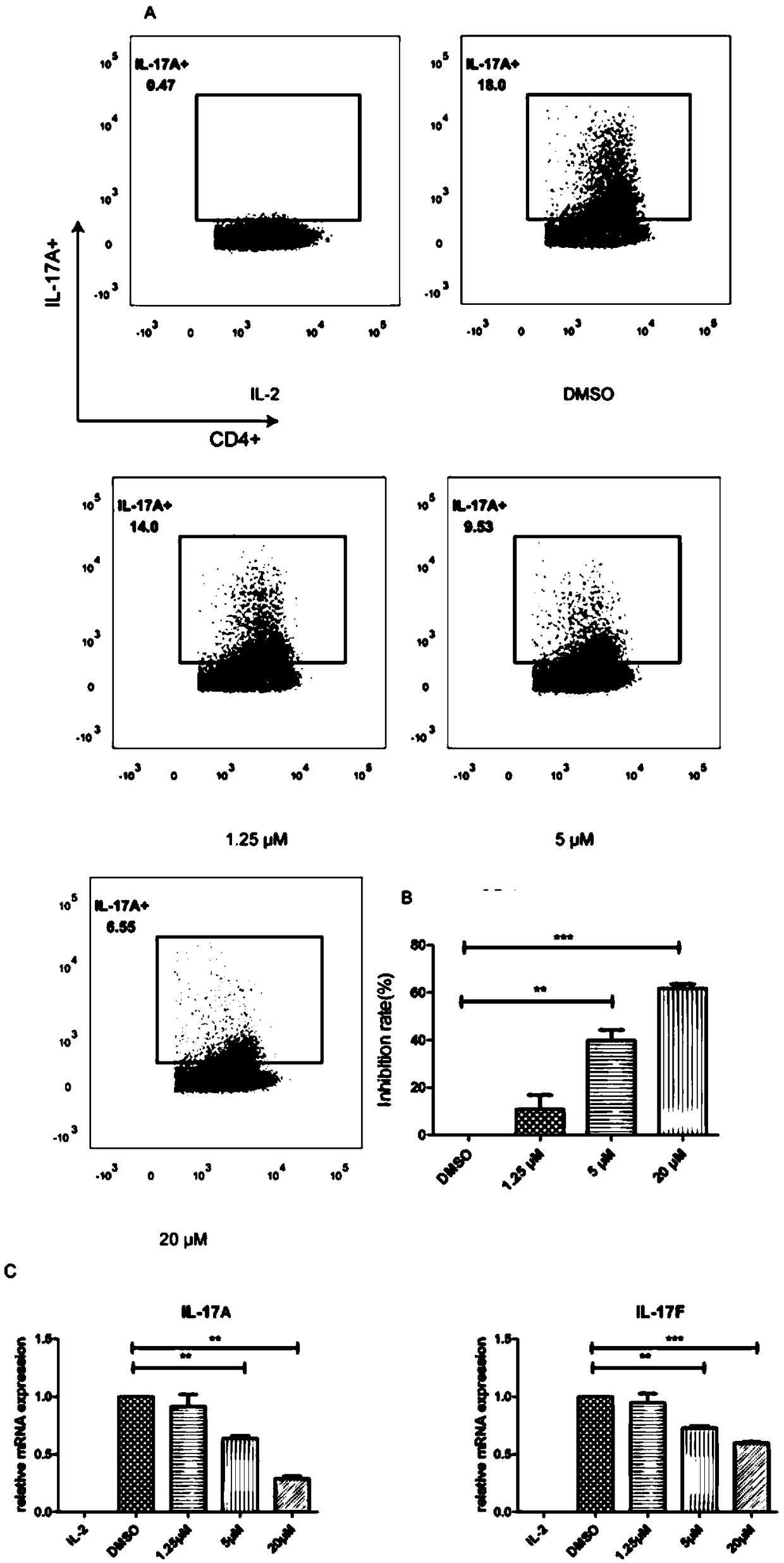
ActiveCN104814962AOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAutoimmune conditionTranscription factor activity
The invention discloses application of a 4N heterocyclic compound as an inhibitor for Th17 cell differentiation. In virtue of a luciferase activity screening system based on the activity of transcription factors, it is found that the 4N heterocyclic compound with a general formula as described in the specification has capability in inhibiting the key transcription factor ROR gamma t of Th17 cell differentiation and the inhibition capability EC50 is in a range of 0.2 to 1.5 [mu]M. In-vitro Th17 cell differentiation experiments prove that the 4N heterocyclic compound is capable of inhibiting Th17 differentiation, including substantially reducing the transcription expression of ROR gamma t, inhibiting the transcription expression of the effector molecules IL17A and IL17F of Th17 and obviously inhibiting the secretion level of IL17A cytokines in a culture. The 4N heterocyclic compound is expected to be developed into a drug used for treating autoimmune diseases, especially psoriasis, systematic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, asthma or inflammatory intestinal diseases.
Owner:CELLREGEN BEIJING LIFE SCI & TECH CO LTD
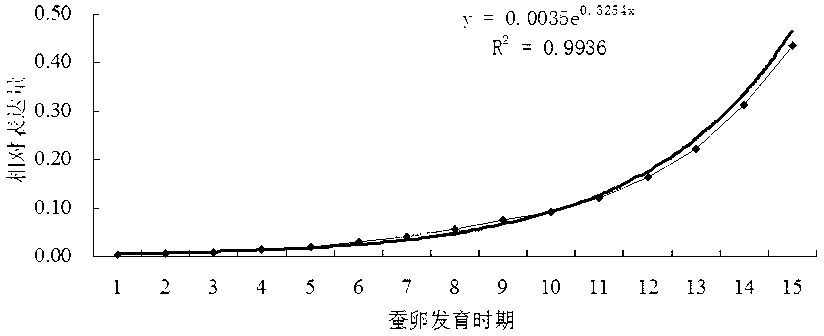
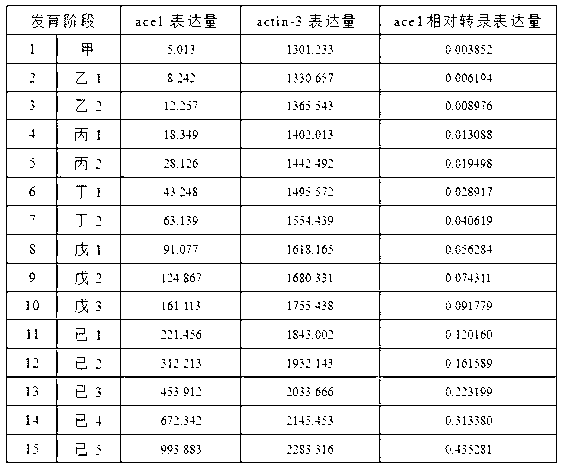
Method for testing development process of silkworm embryos
InactiveCN103070141AAccurate measurementAvoid judgment errorsAnimal husbandryBiotechnologyTranscriptional expression
The invention discloses a method for testing the development process of silkworm embryos. The method specifically comprises the following steps of: (1), establishing a model expressing the incidence relation between the relative transcription expression quantity of the acetylcholine esterase type 1 (ace1) of a to-be-tested variety of the silkworm embryos and the development process of the embryos; (2), selecting at least one embryo from the to-be-tested silkworm embryos to use as a sample, testing the relative transcription expression quantity of the ace1 of the sample, and then contrasting with the model obtained in step (1) to determine the development process of the silkworm embryos according to the relative transcription expression quantity of the ace1 of the to-be-tested sample. The development stage of a whole graine can be accurately determined by the method through the test on the development process of a small quantity of silkworm embryos. Manual operation errors can be reduced, the test process is simplified, and a development process identification method is provided for molecular biology study of the silkworm embryos.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
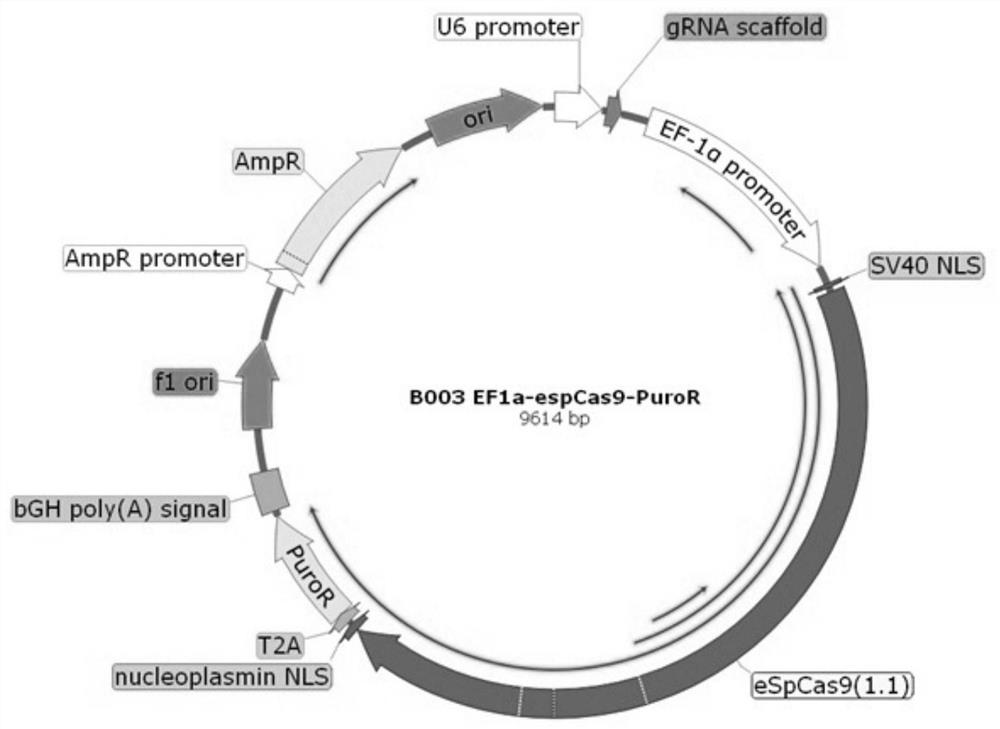
Human iPS cell gene editing and screening method
PendingCN112266935AAvoid stabilityEdit rate increaseHydrolasesGenetically modified cellsIntracellularTranscriptional expression
The invention discloses a human iPS cell gene editing and screening method. The method comprises the following steps: introducing editing plasmids into iPS cells by an electroporation method; producing gene-edited cells through resistance screening and enrichment; and performing low-density passage, and selecting monoclonal cell colonies for enlarged culture and identification. An EF1 alpha promoter is used for promoting free plasmids capable of simultaneously promoting Cas9 and screening resistance protein expression in human iPS cells, after the plasmids enter the human iPS cells, Cas9 protein and resistance protein can be transiently and stably expressed in the cells at the same time, and in the most vigorous time period of plasmid transcriptional expression, screened substances are added into a culture environment. The iPS cells which obtain exogenous plasmids and express the resistance protein survive, besides, the expressed Cas9 protein is guided by sgRNA to be subjected to double-strand cleavage at the target sequence position of a genome for gene editing, and the cells which do not obtain the exogenous plasmids or are not expressed by the plasmids die due to the fact that the cells do not contain resistance. Use of a flow cytometry or insertion of exogenous genes into the cell genome is avoided.
Owner:UNION STEMCELL & GENE ENG
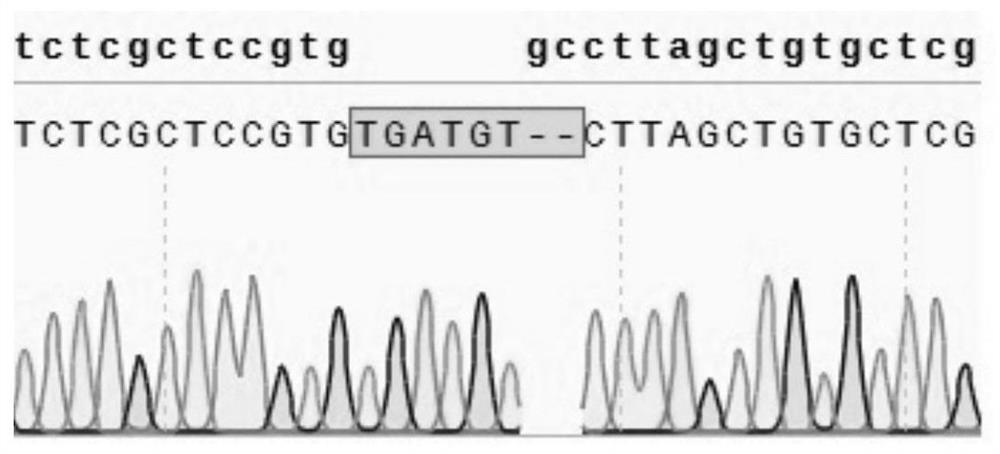
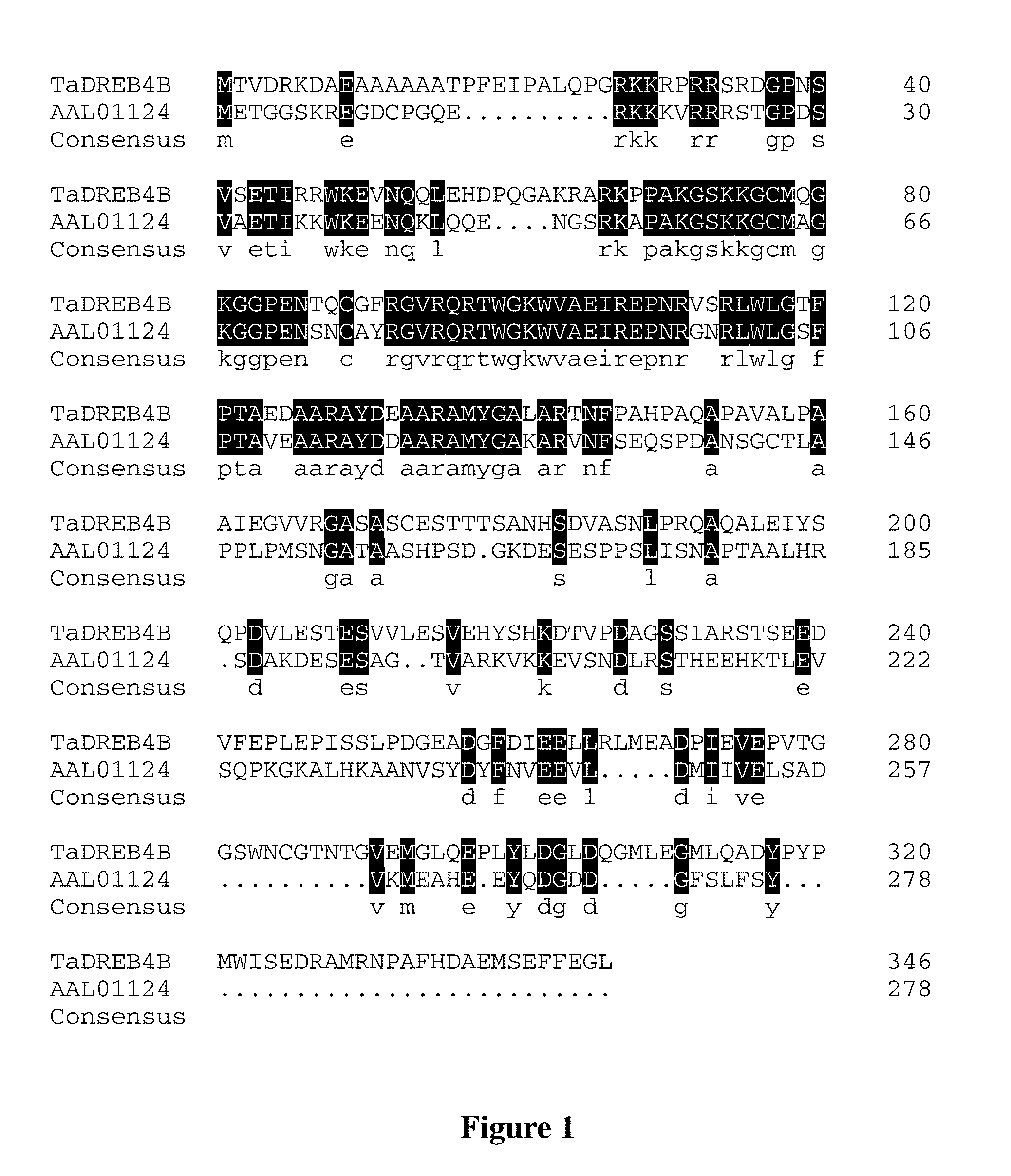
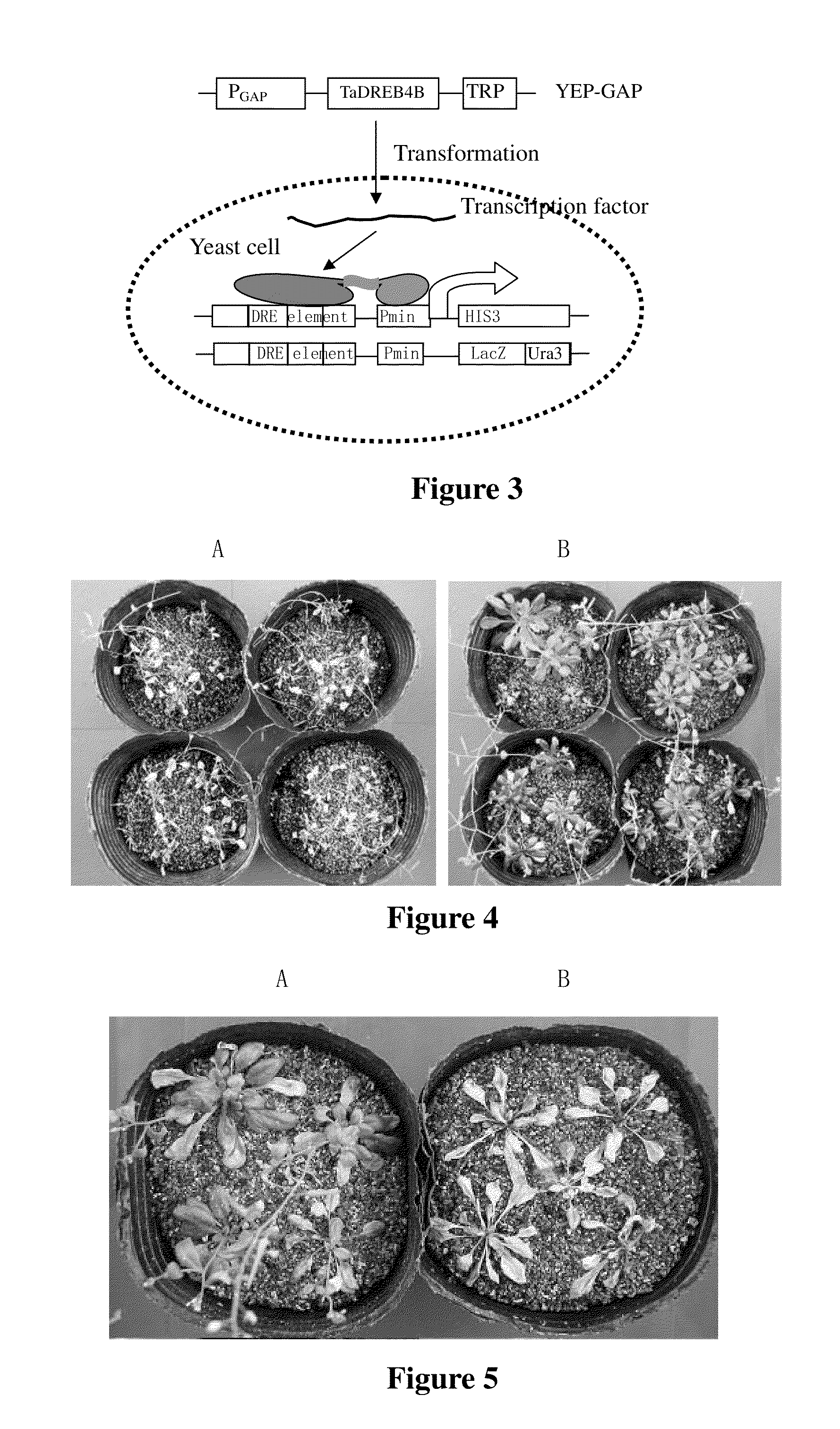
Plant Stress Tolerance Related Protein TaDREB4B and Encoding Gene and Use Thereof
InactiveUS20130152225A1Convenient identificationConducive to screeningBacteriaImmunoglobulinsTranscriptional expressionPathogenic bacteria
Provided are a plant stress tolerance related protein TaDREB4B and encoding gene and use thereof. The TaDREB4B protein has the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1, which can be expressed under induction by drought, high salt, high temperature, low temperature, pathogenic bacteria, ABA, ethylene, JA and SA, and can specially regulate the transcriptional expression of gene comprising the DRE / CRT cis element (core sequence: CCGAC), thereby enhancing the drought resistance, salt tolerance, high temperature tolerance and resistance to pathogenic bacteria of powdery mildew of plant.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
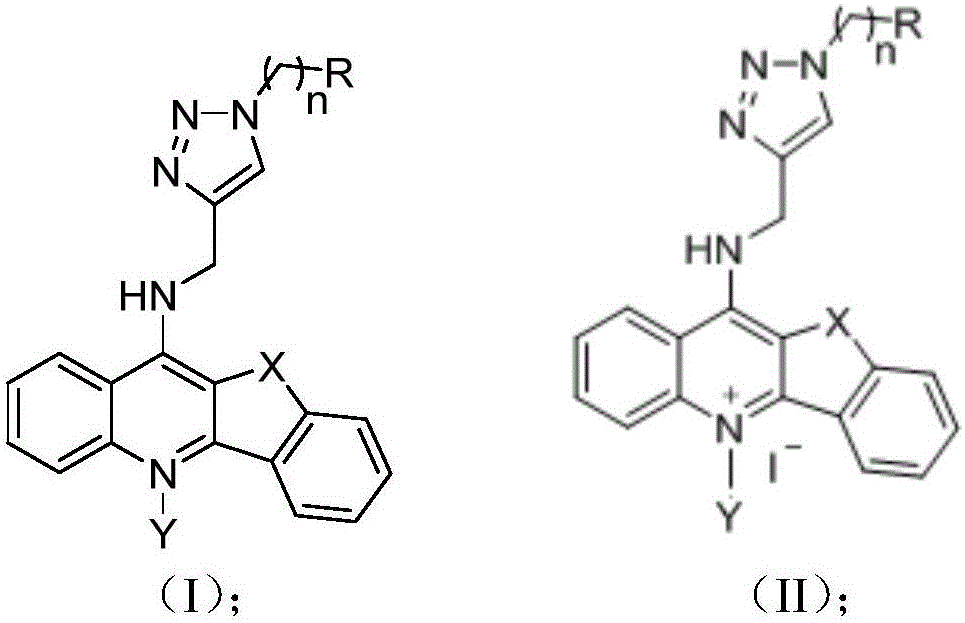
Quinolines derivative and preparation method thereof and application of quinolines derivative to preparation of anti-tumor medicine
ActiveCN106279189AInhibition of transcriptional expressionStrong growth inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCancer cellTranscriptional expression
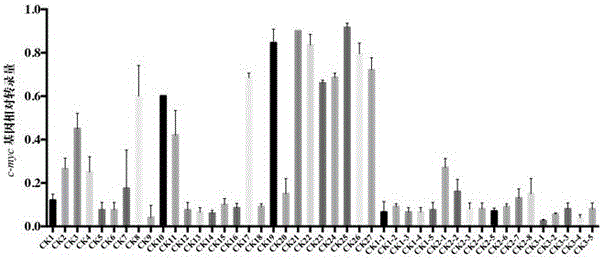
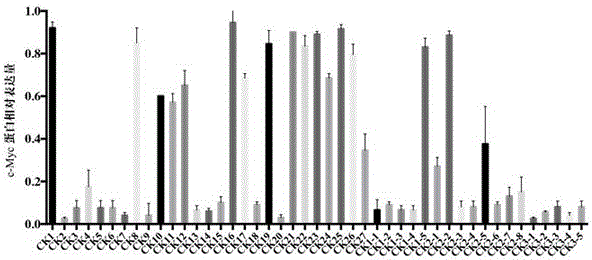
The invention discloses a quinolines derivative. The structural formula of the quinolines derivative is shown as the formula (I) or the formula (II) in the description, wherein R represents hydroxyl, phenyl, substituted phenyl, naphthenic base, amino, substituted amino, pentabasic or hexabasic heterocyclic group, C1 to C8 alkyl or substituted C1 to C8 alkyl, halogeno or glycosyl; X is N, O or S; Y is C1 to C3 alkyl or hydrogen and n is an integer from 0 to 6. The invention further discloses a preparation method and application of the quinolines derivative. The quinolines derivative provided by the invention has a very strong inhibition effect on transcription expression of a cancer gene c-myc and has a remarkable inhibition effect on a plurality of cancer cell plants and particularly has a relatively strong inhibition effect on lymphoma cells; the quinolines derivative has small toxicity on normal cells and has a wide application space in the preparation of an anti-tumor medicine.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
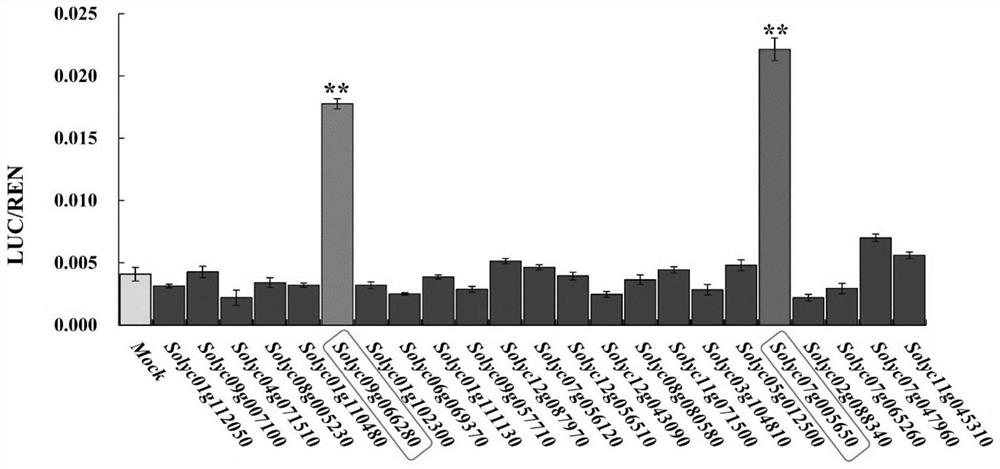
WRKY32 regulated YFT1 expression affected tomato fruit color and application of WRKY32 in tomato quality improvement
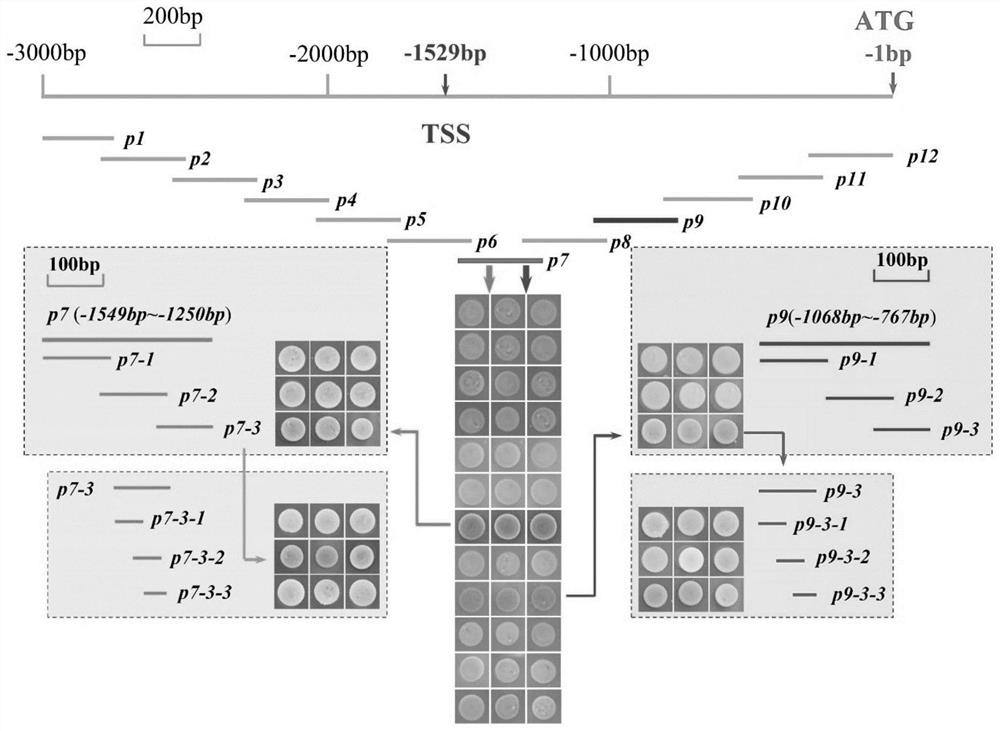
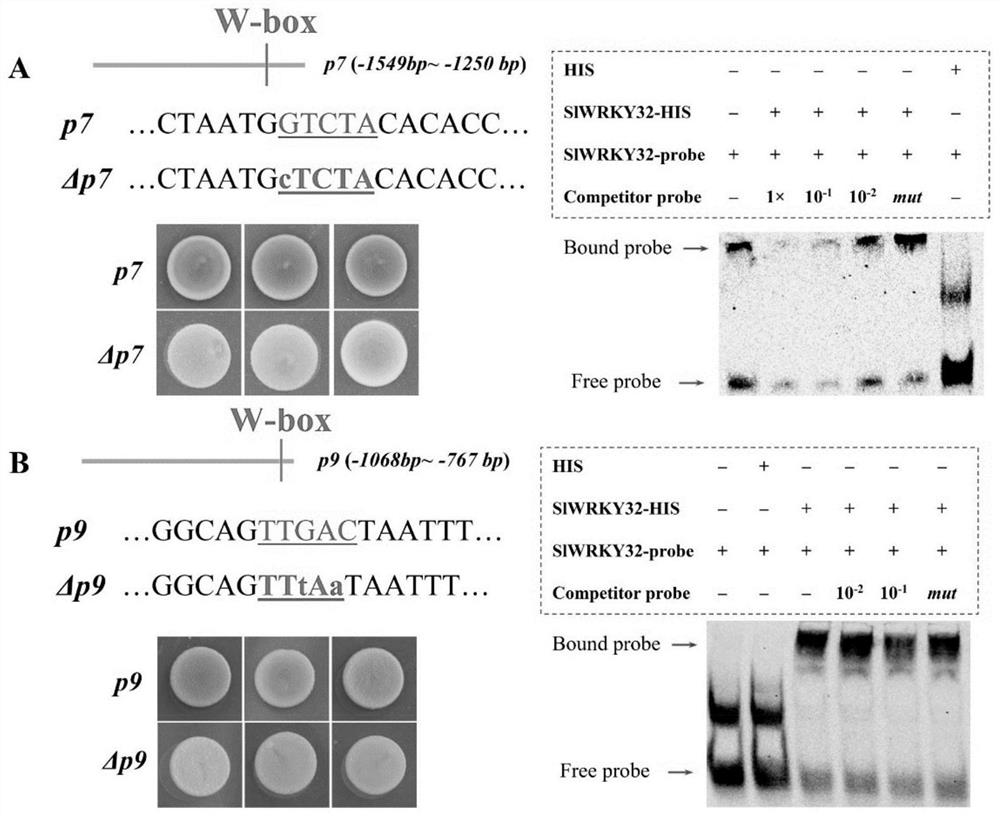
ActiveCN112430261APrecise and mature regulationImprove qualityPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyStart codon
The invention discloses a WRKY32 regulated YFT1 expression affected tomato fruit color and application of WRKY32 in tomato quality improvement. Specifically, the WRKY32 regulates the transcription expression of the YFT1 by combining a W-box (TTGAC, -784bp--780bp) motif (GTCTA, -1306bp--1302bp) in a YFT1 promoter region (defining the first nucleotide at the upstream of an initiation codon ATG of the YFT1 as -1bp). WRKY32 down-regulation expression tomatoes (WRKY32RNAi) are created through an RNAi technology, the fruit form and chemical phenotype of the WRKY32RNAi tomatoes are analyzed, and solid genetic evidences are provided for fruit ethylene release and signal transduction inhibition, carotenoid content reduction, chromosome development and fruit softening speed delay.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Vitro method for the prognosis or prediction of the response in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with agents that recognize the cd20 membrane receptor in b lymphocytes
InactiveUS20120225790A1Reduce riskMinimally invasiveMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCD20Transcriptional expression
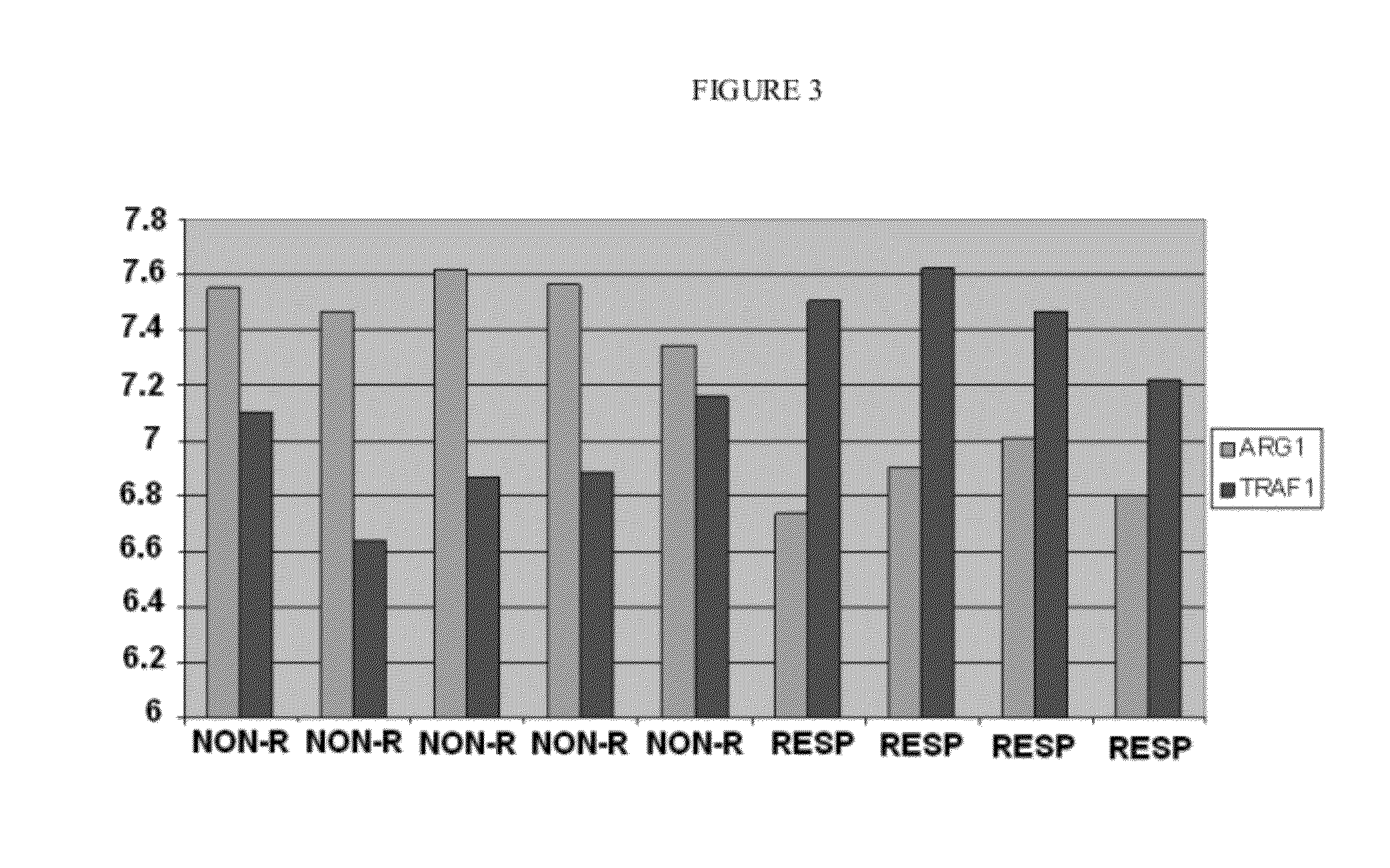
An in vitro method for the prognosis or prediction of response in patients with rheumatoid arthritis to treatment with agents recognising the B-lymphocyte CD20 membrane receptor. The method of the invention comprises an assay in a blood sample from these patients and measuring, before starting the treatment, the transcriptional expression level (mRNA) of at least one of the genes selected from the group: ARG1, CPD, TRAF1, C1QA, LRRN3, HLA-DQA1, NLK, TLR4, LOC89944, TOM1L1, BACH, NCALD, EIF2C2, NFIC, PCDHB7, FLJ32770, ARID3A, C14ORF9, CSNK1E, BCAS1, TEAD2, C6orfl45 and SNTA1; and the comparison of this expression level to the expression values previously obtained in patients who responded and who did not respond to the treatment.
Owner:FUNDACIO INST DE RECERCA DE LHOSPITAL UNIVRI VALL DHEBRON
Combinatorial expression of split caspase molecules
InactiveUS20070026428A1Inhibition effectGreat ability to targetVectorsSugar derivativesBiological bodyPromoter activity
The present invention relates to the use of split caspase proteins to determine whether or not promoters are coordinately active, whereby the transcriptional expression of incomplete portions of a caspase protein is controlled by different promoters and coordinate (not necessarily contemporaneous) promoter activity results in formation of an activated caspase protein and, consequently, apoptotic cell death. The present invention further provides for the use of an additional promoter element controlling expression of a “caspase neutralizing protein,” which, when present, inhibits the apoptotic effect of the assembled caspase subunits. Rescue of cells that actively transcribe the complementary caspase subunits indicates that all promoters of the system are coordinately active. The present invention, in non-limiting embodiments, may be used to selectively ablate cells in the context of cultures as well as intact organisms, and provides means of demonstrating coordinate activity of multiple promoters.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Thinopyrum intermedium ERF-transcription factor and its coding gene and use
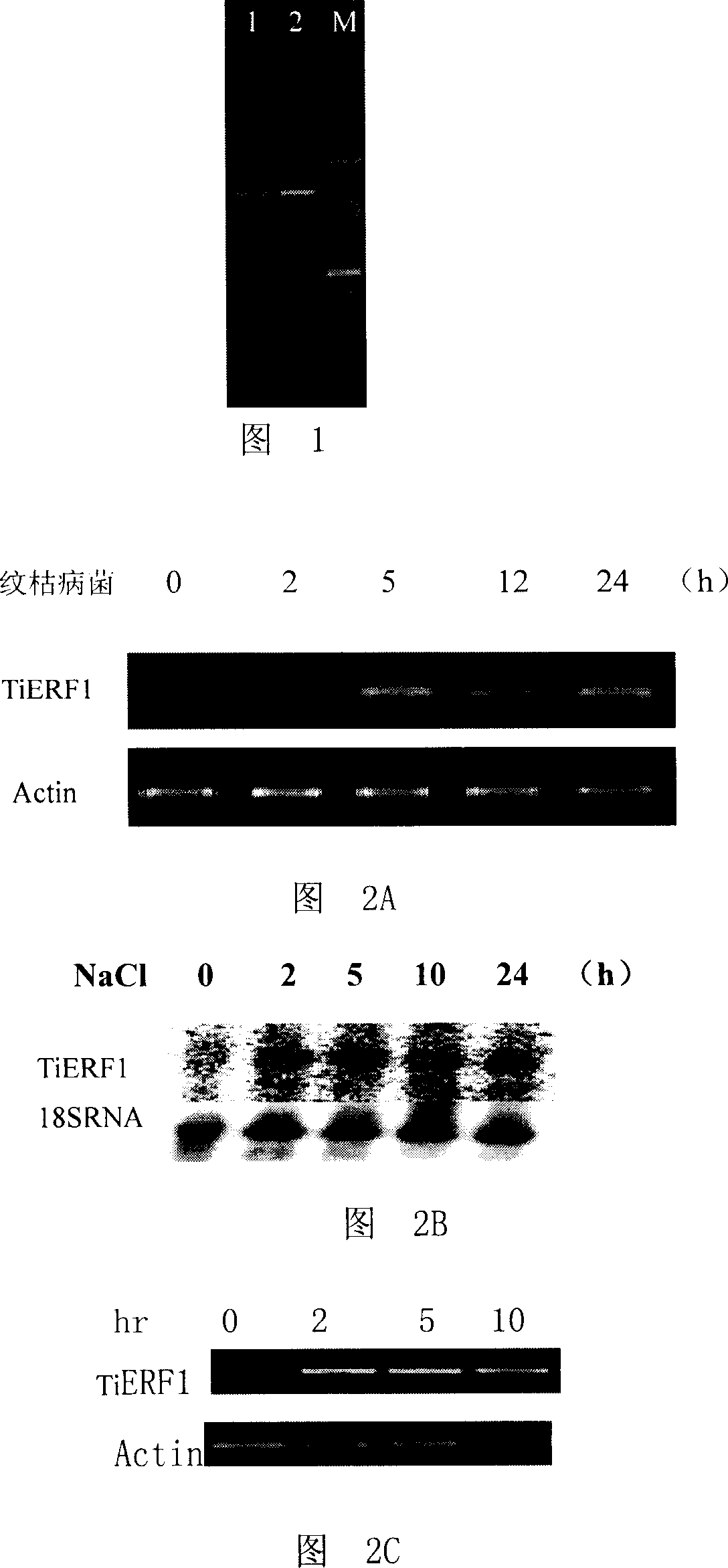
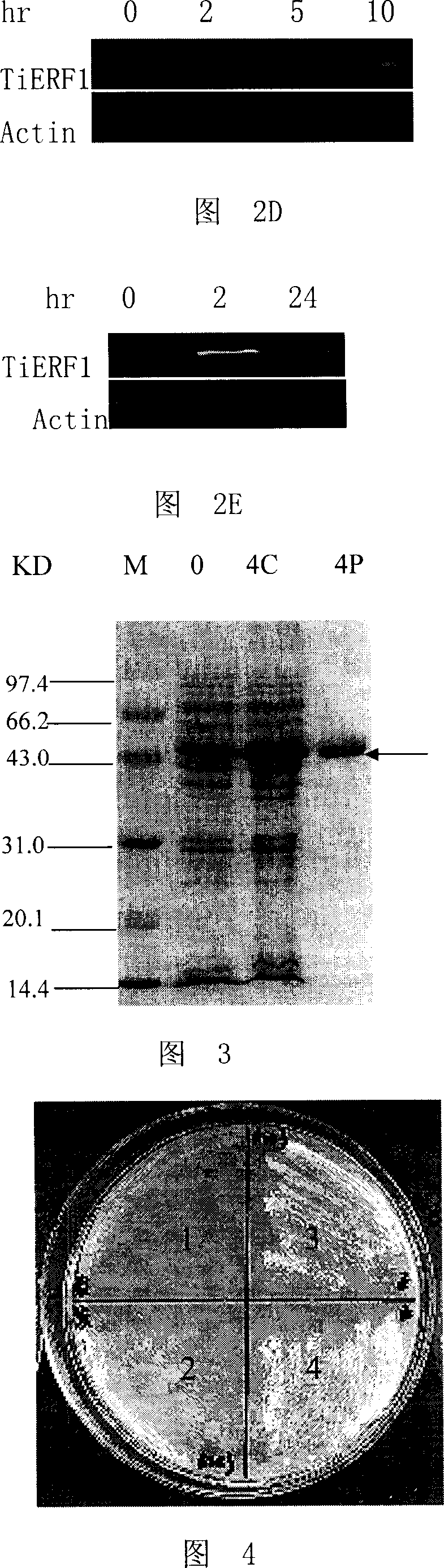
The invention discloses a middle couch grass ERF transcription factor and its coding gene. The middle couch grass ERF transcription factor can be the protein with one of the following amino acid residues sequences that SEQ ID No: 2 in sequence list; or its amino acid residues sequence which is replaced and / or missed and / or added with one or many amino acid residues, and relevant to plant against disease against reverse performance. The transcription expression of the coding gene is greatly induced by rhizoctonia cerealis, salt, cold, ethylene etc. The TiERF1 of the invention supplies the base for the relevant gene expression, gene resources for gene engineering breeding, and will play an importance role in increasing plant against disease against reverse performance for gene engineering breeding.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Polynucleotides having promoter activity and applications thereof in production of amino acids
ActiveCN113201536AHigh promoter activityImprove expression strengthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPromoter activityTranscriptional expression
The present disclosure relates to polynucleotides having promoter activity and applications thereof in the production of amino acids. Specifically, the present disclosure relates to a polynucleotide having promoter activity, a transcription expression cassette containing the polynucleotide, a recombinant expression vector, a recombinant host cell, a method for enhancing expression of a target gene, a method for preparing a protein, and a method for producing an amino acid. The polynucleotide with the promoter activity is a mutant of the polynucleotide with the sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 9, compared with the polynucleotide with the sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 9, the promoter activity of the mutant is remarkably enhanced, stable and efficient expression of a target gene can be promoted, and then downstream products can be stably and efficiently produced.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Application of oleanolic acid in preparation of drugs for treatment of autoimmune diseases
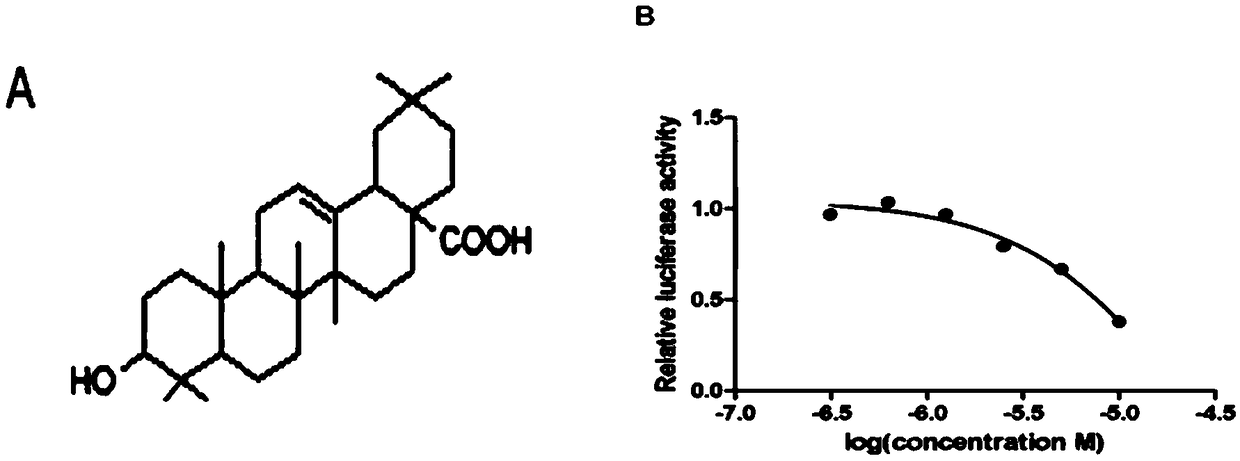
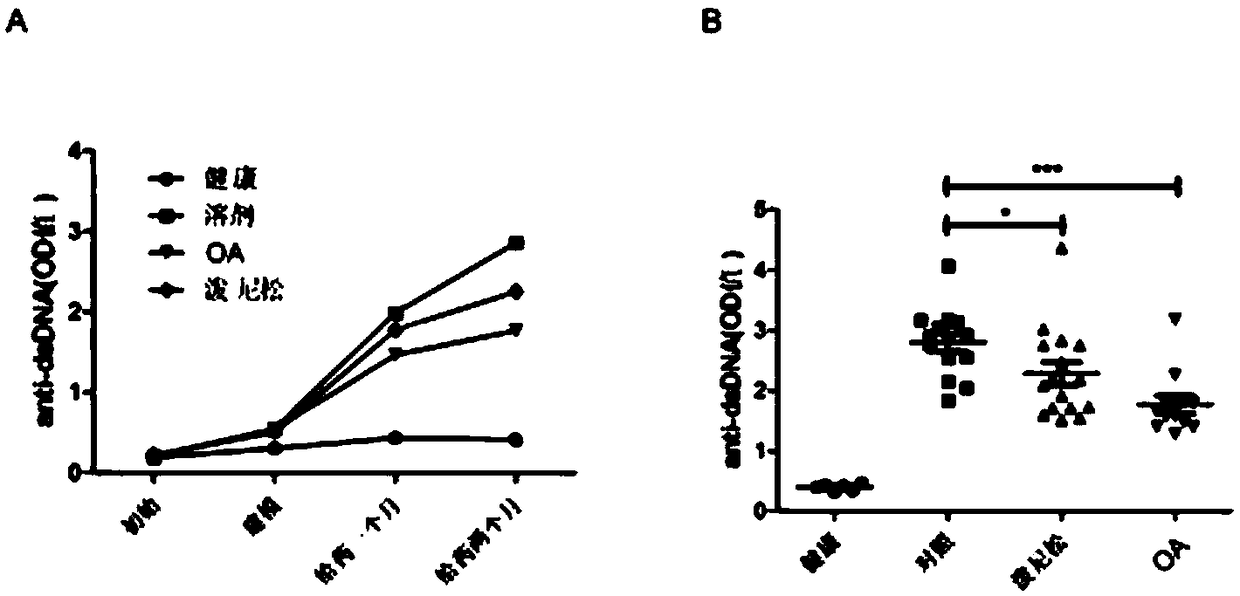
InactiveCN109223805AActive inhibitory functionInhibition of differentiationOrganic active ingredientsImmunological disordersTranscriptional expressionAutoimmune disease
The invention relates to application of oleanolic acid in preparation of drugs for treatment autoimmune diseases, and belongs to the technical field of biomedicine. The oleanolic acid can inhibit thefunction of the transcription factor ROR[gamma]t, inhibit the differentiation of Th17 cells, and inhibit the transcriptional expression of the target genes IL-17A and IL-17F of ROR[gamma]t at the RNAlevel, and inhibit IL-17A cytokines. The secretion inhibits the level of anti-dsDNA antibodies in the serum; the oleanolic acid of the present invention has an obvious Th17 cell activity inhibitory function, and provides a lead structure for the development of new drugs for the treatment of autoimmune diseases.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Novel resistant gene of chloromycetin and application of novel resistant gene of chloromycetin
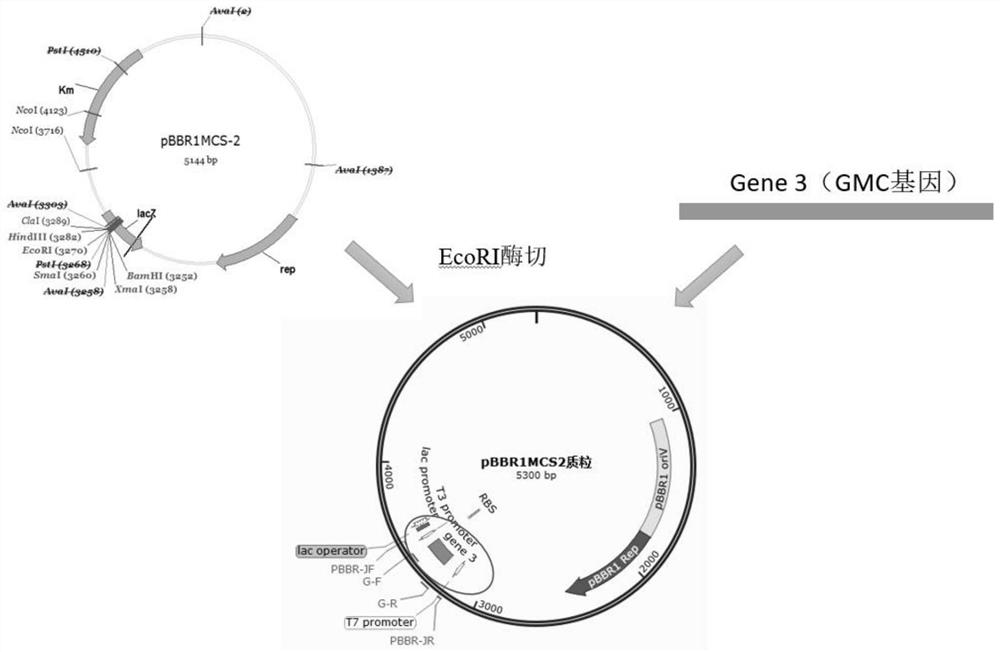
The invention provides a novel resistant gene of chloromycetin and application of the novel resistant gene of chloromycetin. The resistant gene has a sequence shown in SEQ ID No. 1 and is called aftera gene GMC; after tertiary sequencing of a genome, a drug-resistant gene known at present is not discovered on the genome, and then, through sequencing of RNA, it is discovered that GMC-encoded oxidoreductase has a very high transcription expression level in the presence of antibiotics. According to the novel resistant gene provided by the invention, a potential drug-resistant gene of the chloromycetin is discovered, help is provided for learning about a drug resisting mechanism of the chloromycetin and supplementing a drug resisting database, and a target point is provided for resisting drugresistance to the chloromycetin afterwards.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Influenza virus carried HCV nucleic acid test quality control product and preparation method thereof
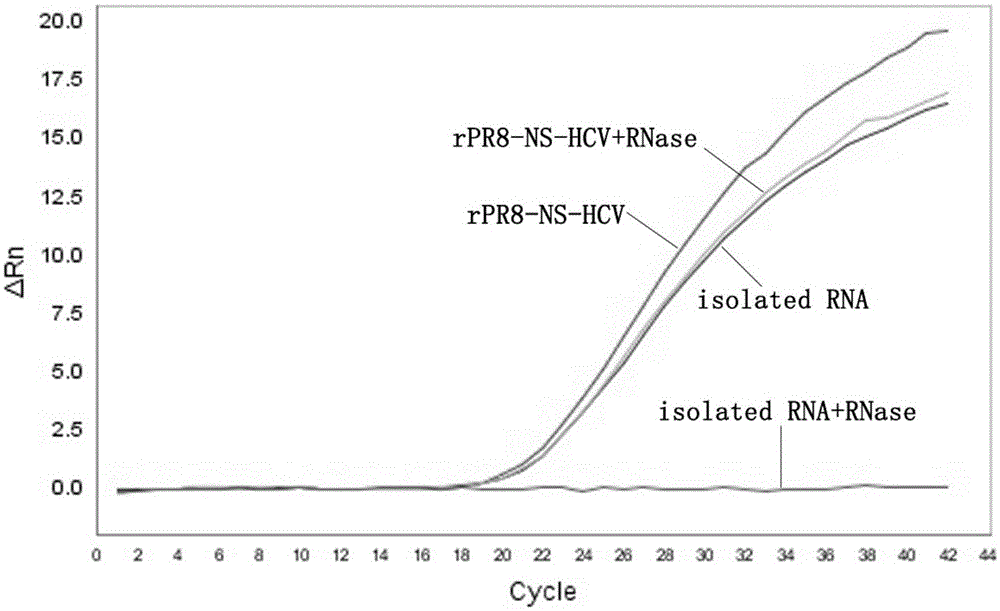
ActiveCN105132583ALow costGood for mass manufacturingMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNucleic acid detectionTranscriptional expression
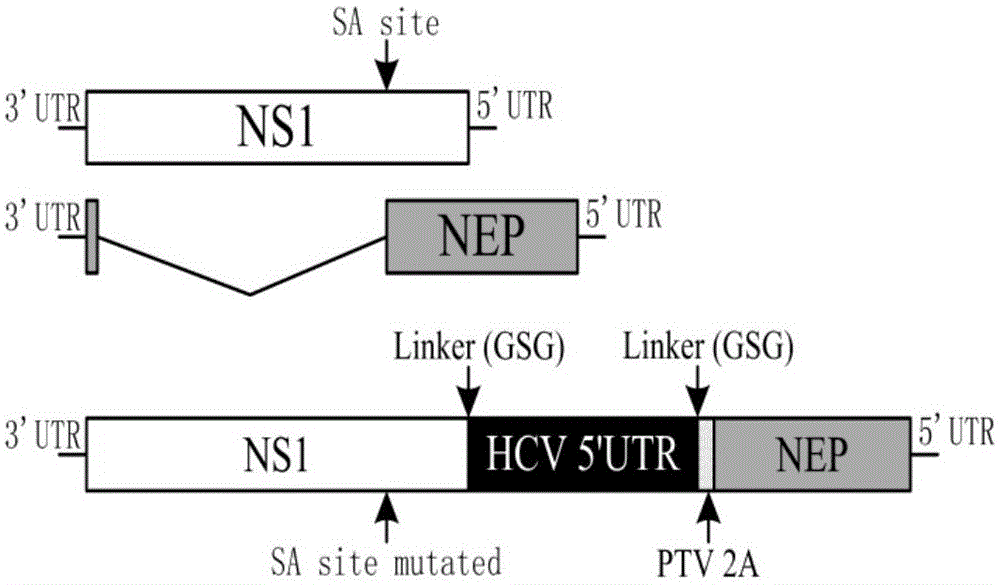
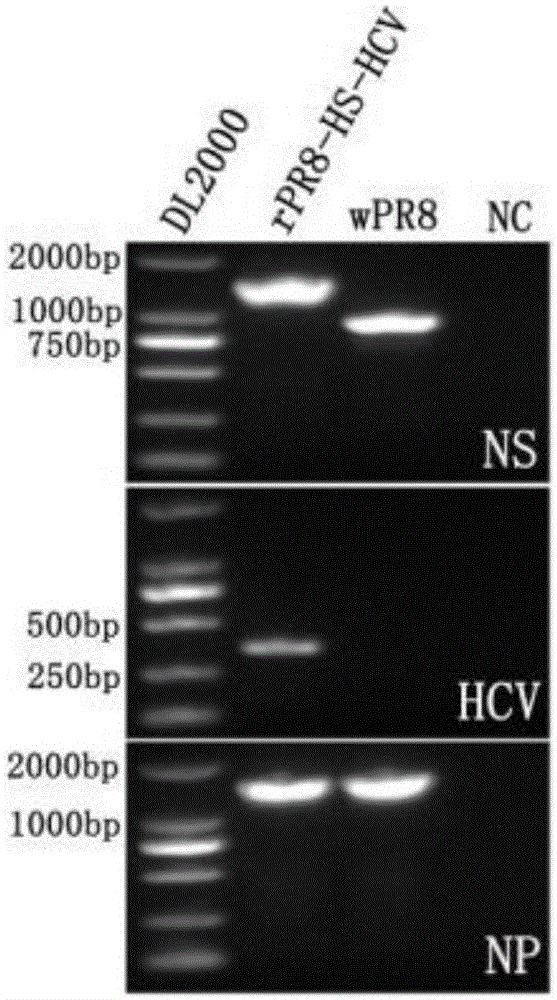
The invention relates to an influenza virus carried HCV nucleic acid test quality control product and a preparation method thereof; the quality control product is prepared from HCV conserved gene carried recombinant influenza virus through enlarged culture, inactivation and purification; the preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) constructing a plasmid which is used for rescuing influenza virus and is interpolated with HCV conserved gene in PR8 virus NS gene; (2) co-transfecting 293T cell to the constructed plasmid with plasmids which are respectively used for transcriptional expression of PR8 viruses PB2, PB1, PA, HA, NP, NA and M, so as to rescue and obtain HCV 5' UTR carried recombinant influenza virus; and (3) enlarged-culturing, inactivating and purifying the recombinant influenza virus so as to obtain the quality control product. The quality control product disclosed by the invention can be used for really simulating HCV pathogens and achieving all-around monitoring on HCV detection; and the quality control product is easy in large-scale preparation, low in cost, good in stability, easy in storage and transportation, and good in application prospect.
Owner:上海市临床检验中心
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com