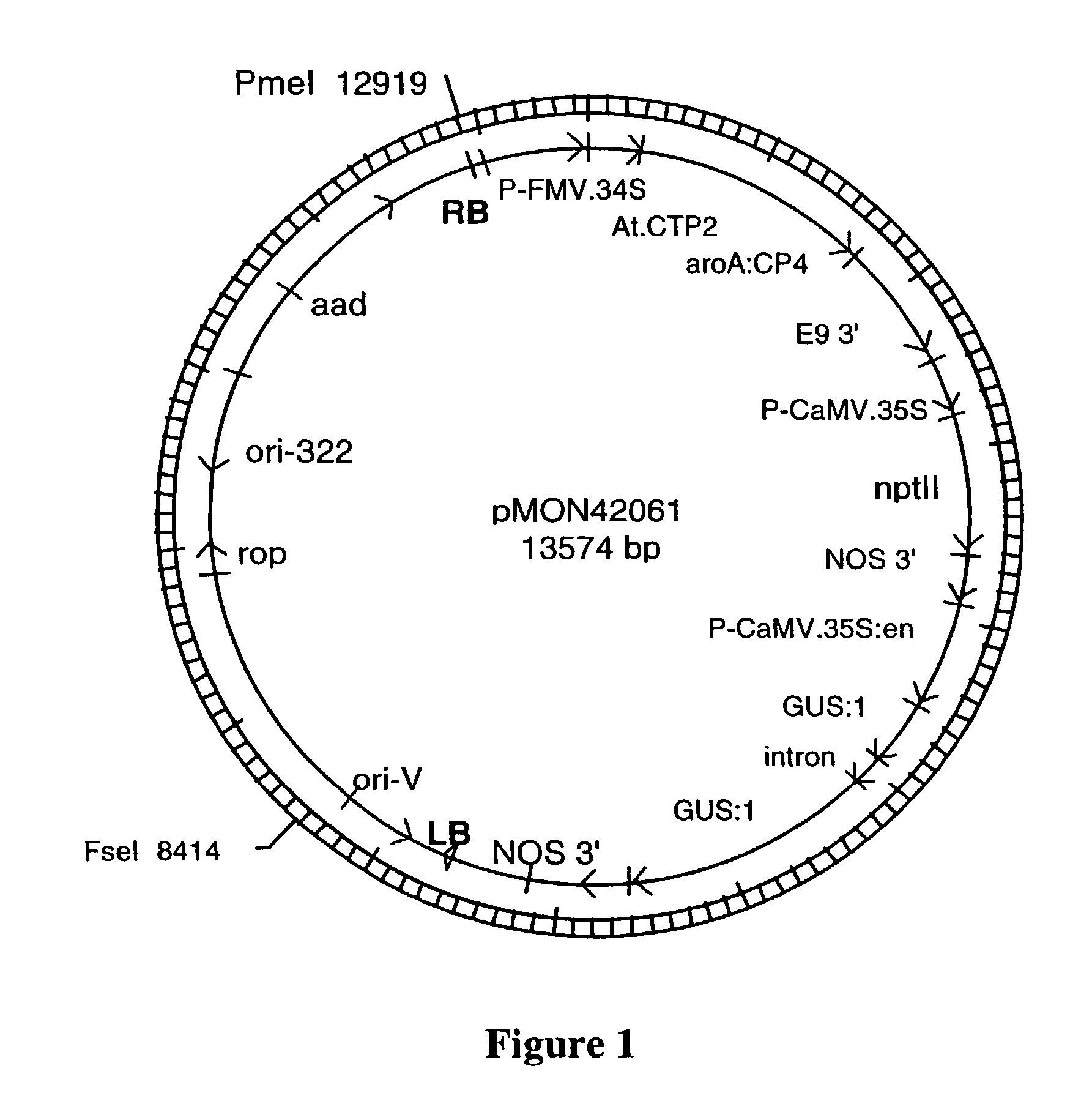
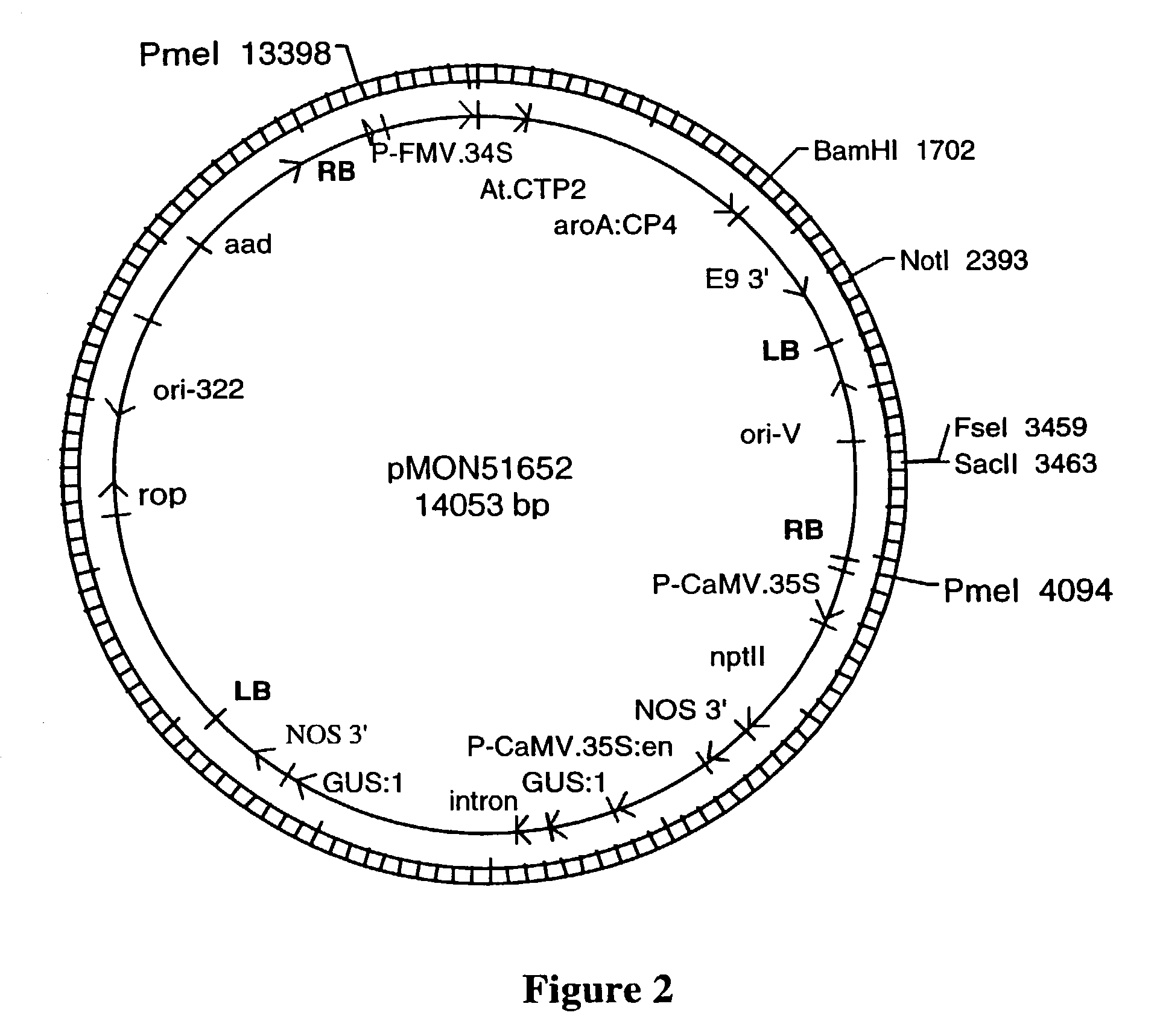
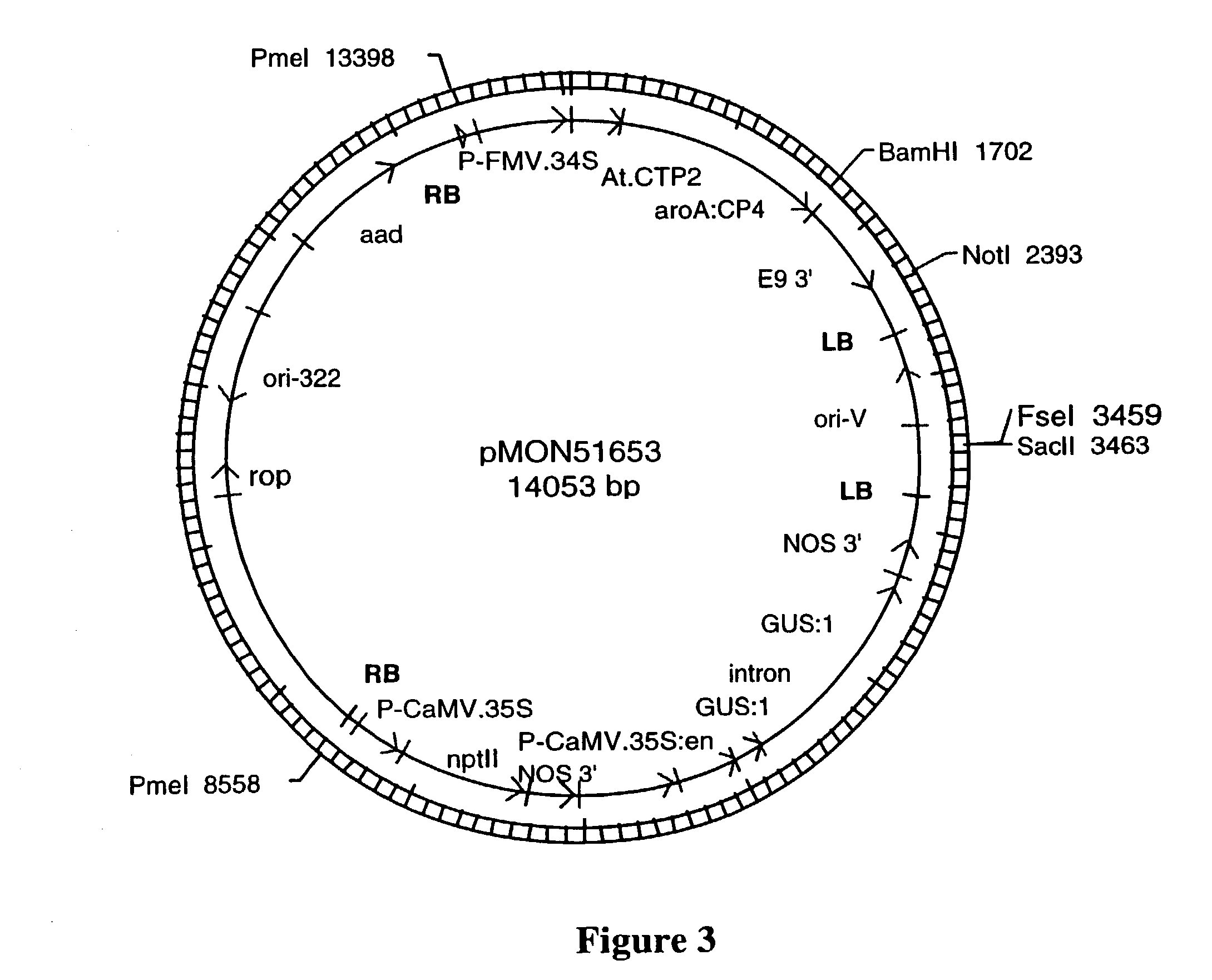
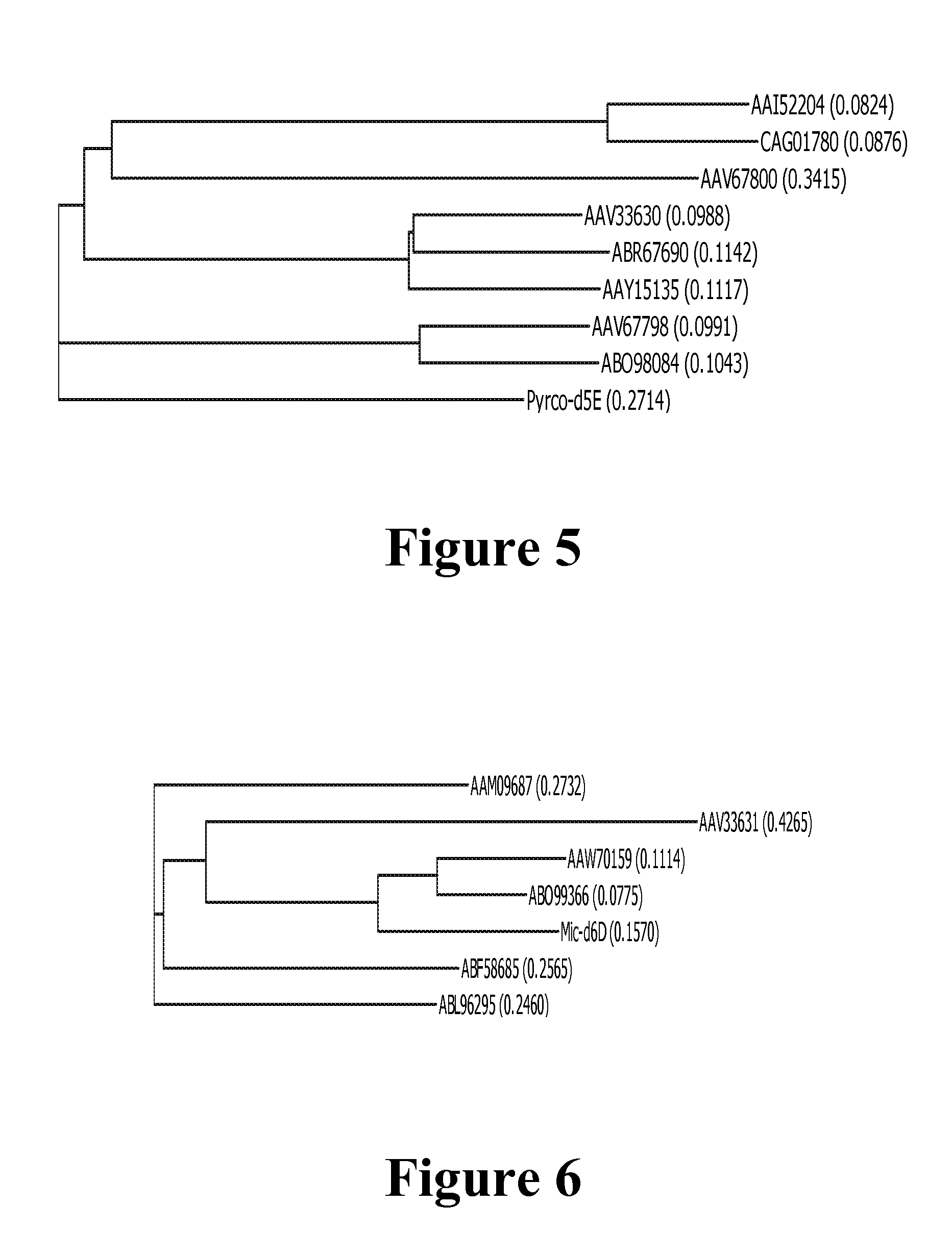
Patents
Literature
288 results about "Plant genomes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
This list of sequenced plant genomes contains plant species known to have publicly available complete genome sequences that have been assembled, annotated and published. Unassembled genomes are not included, nor are organelle only sequences. For all kingdoms, see the list of sequenced genomes Algae ...
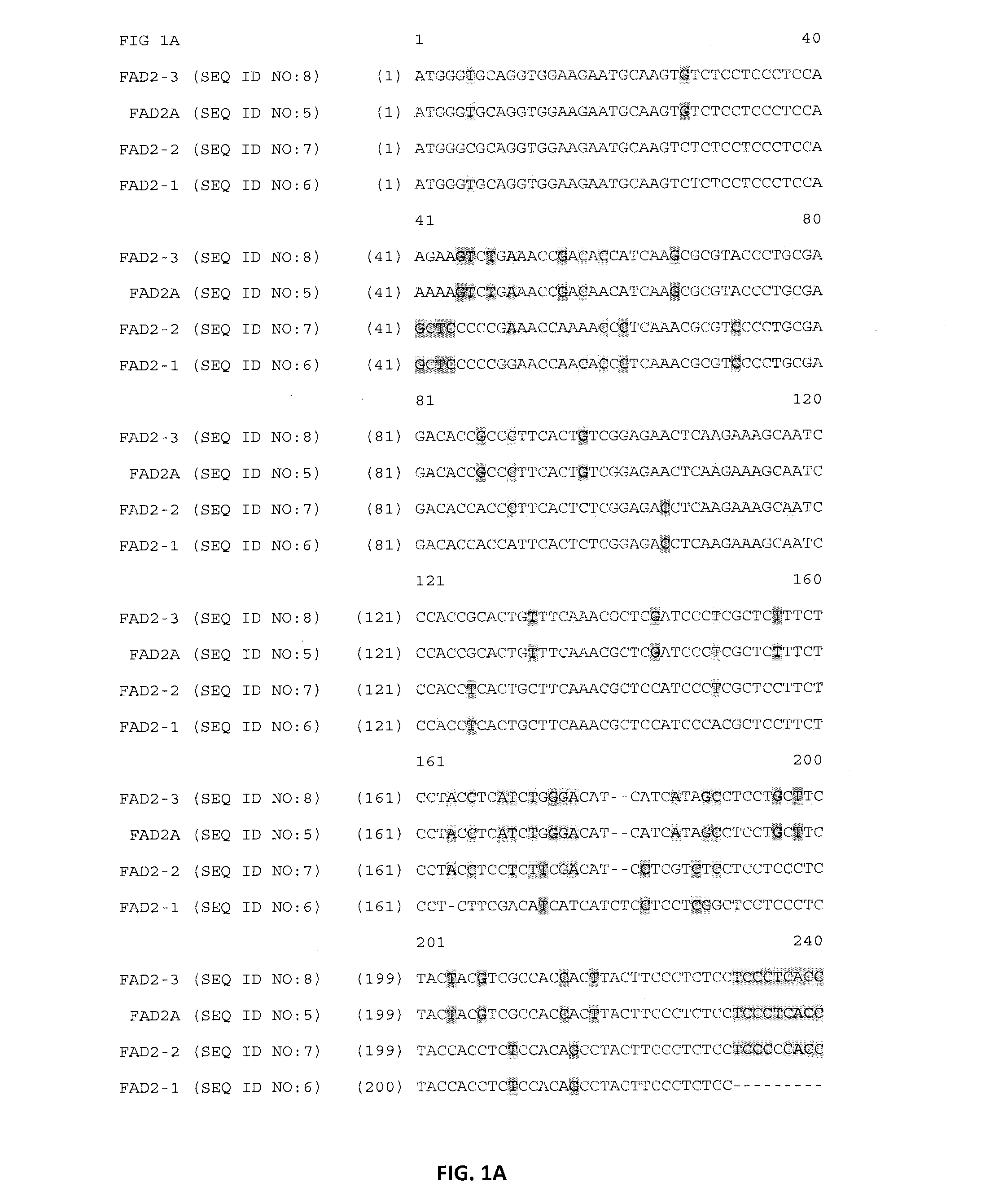
Plant genome sequence and uses thereof
InactiveUS7868149B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementADAMTS ProteinsPlant biochemistry
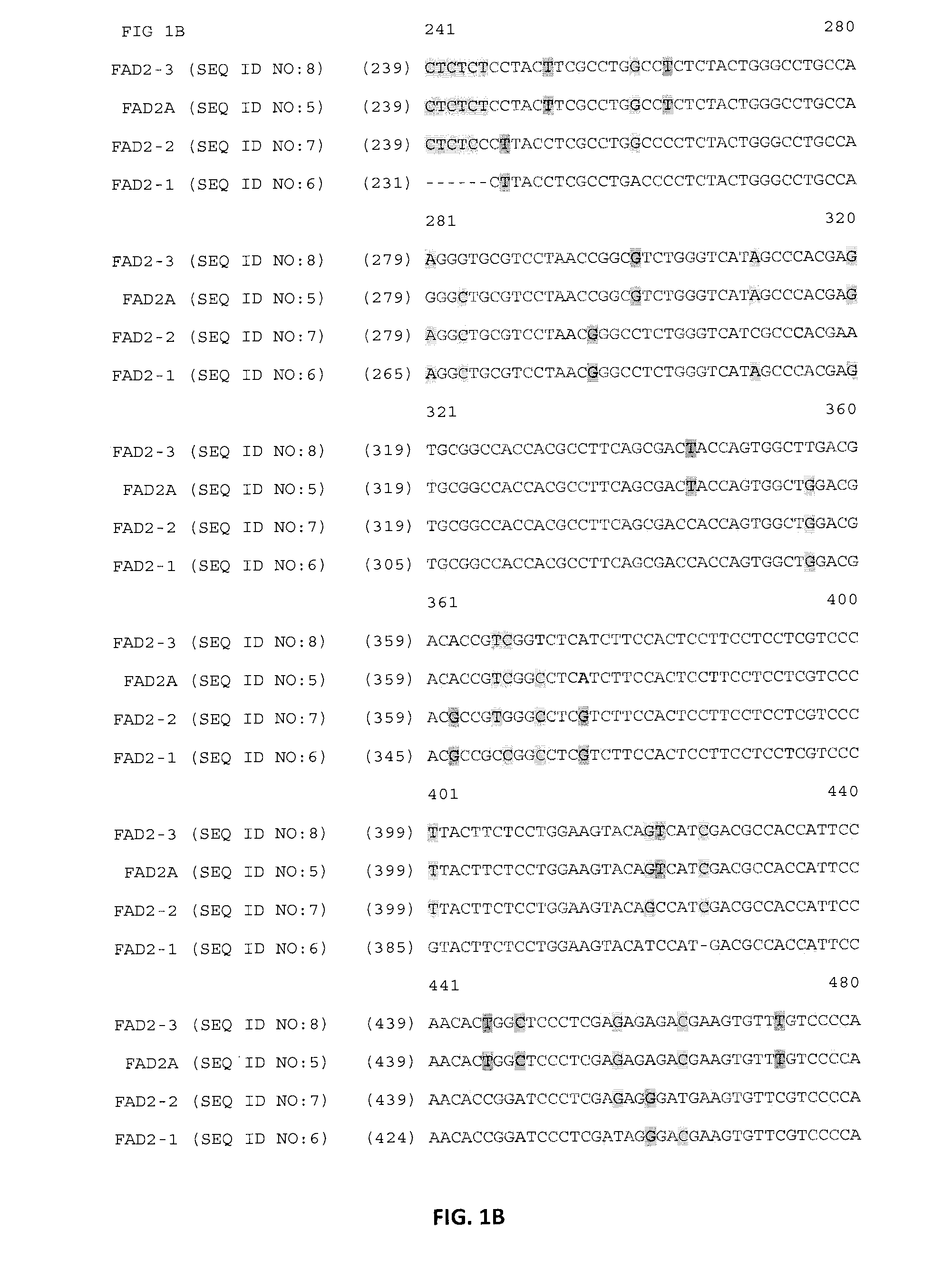
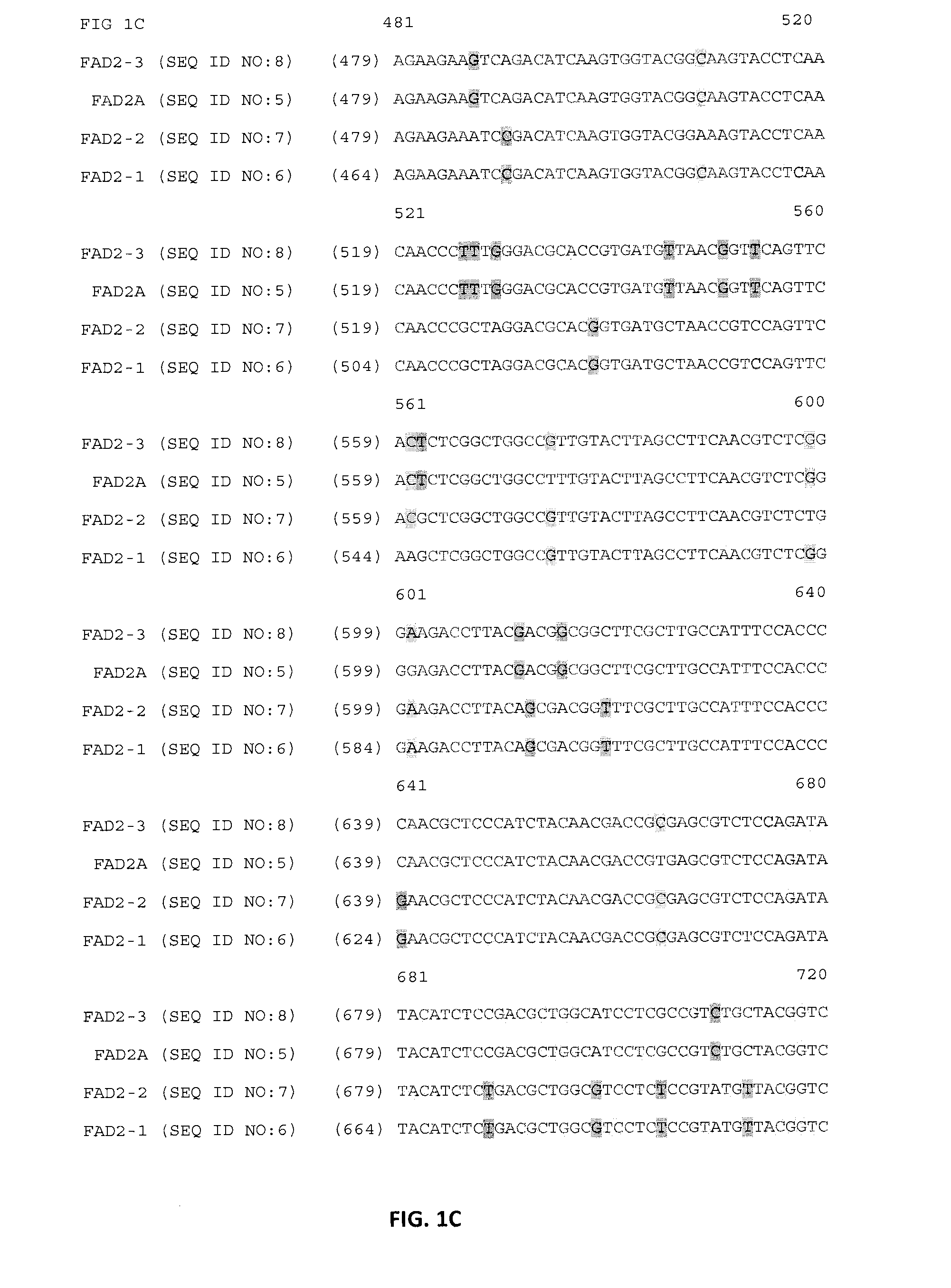
The present invention is in the field of plant biochemistry and genetics. More specifically the invention relates to nucleic acid molecules from plant cells, in particular, genomic DNA sequences from rice plants and nucleic acid molecules that contain markers, in particular, single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and repetitive element markers. In addition, the present invention provides nucleic acid molecules having regulatory elements or encoding proteins or fragments thereof. The invention also relates to proteins and fragments of proteins so encoded and antibodies capable of binding the proteins. The invention also relates to methods of using the nucleic acid molecules, markers, repetitive elements and fragments of repetitive elements, regulatory elements, proteins and fragments of proteins, and antibodies, for example for genome mapping, gene identification and analysis, plant breeding, preparation of constructs for use in plant gene expression, and transgenic plants.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Plant genome sequence and uses thereof
InactiveUS20070039076A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesRice plantsGenomic DNA
The present invention is in the field of plant biochemistry and genetics. More specifically the invention relates to nucleic acid molecules from plant cells, in particular, genomic DNA sequences from rice plants and nucleic acid molecules that contain markers, in particular, single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and repetitive element markers. In addition, the present invention provides nucleic acid molecules having regulatory elements or encoding proteins or fragments thereof. The invention also relates to proteins and fragments of proteins so encoded and antibodies capable of binding the proteins. The invention also relates to methods of using the nucleic acid molecules, markers, repetitive elements and fragments of repetitive elements, regulatory elements, proteins and fragments of proteins, and antibodies, for example for genome mapping, gene identification and analysis, plant breeding, preparation of constructs for use in plant gene expression, and transgenic plants.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Gene targeting and genetic modification of plants via rna-guided genome editing
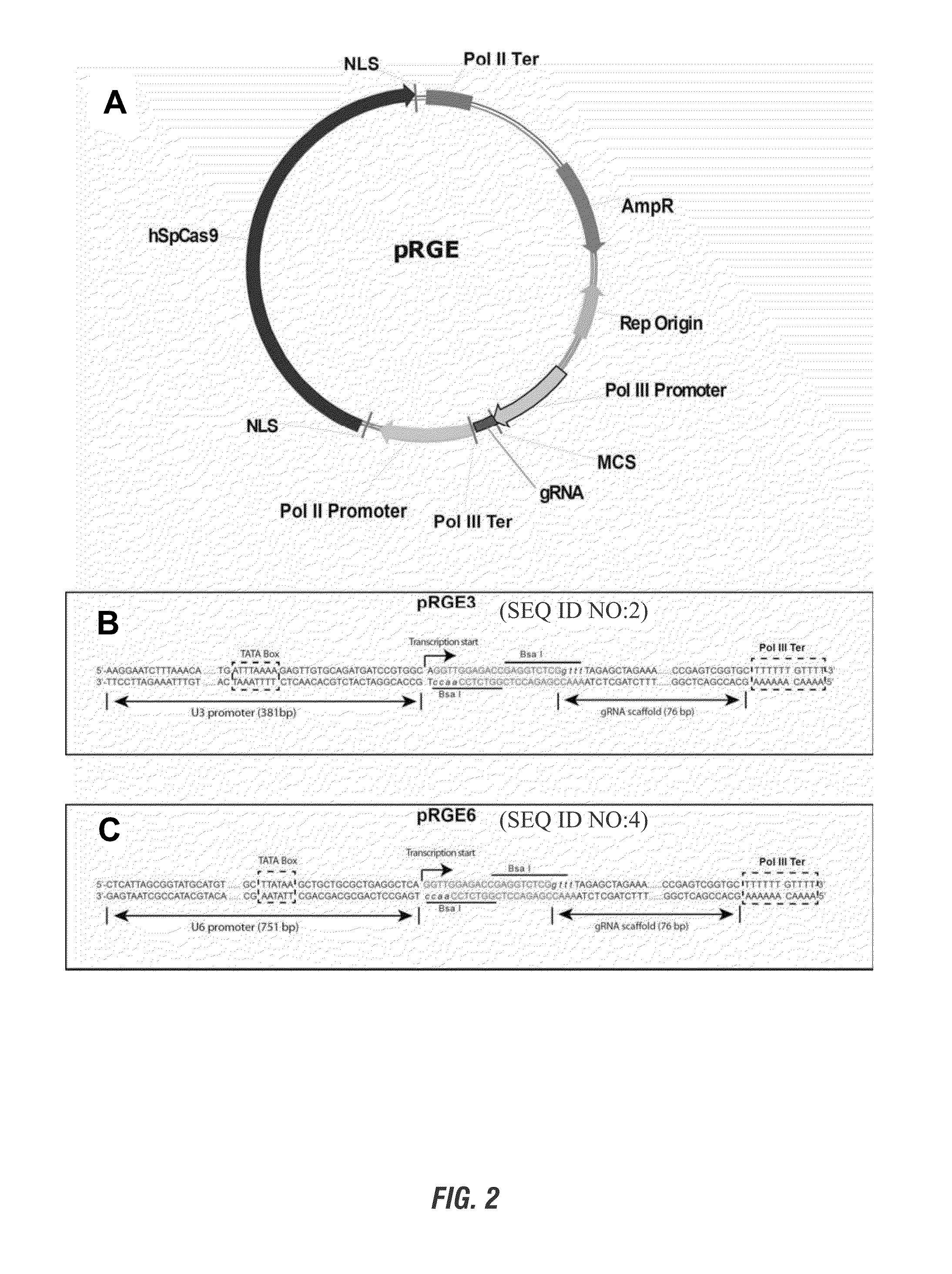
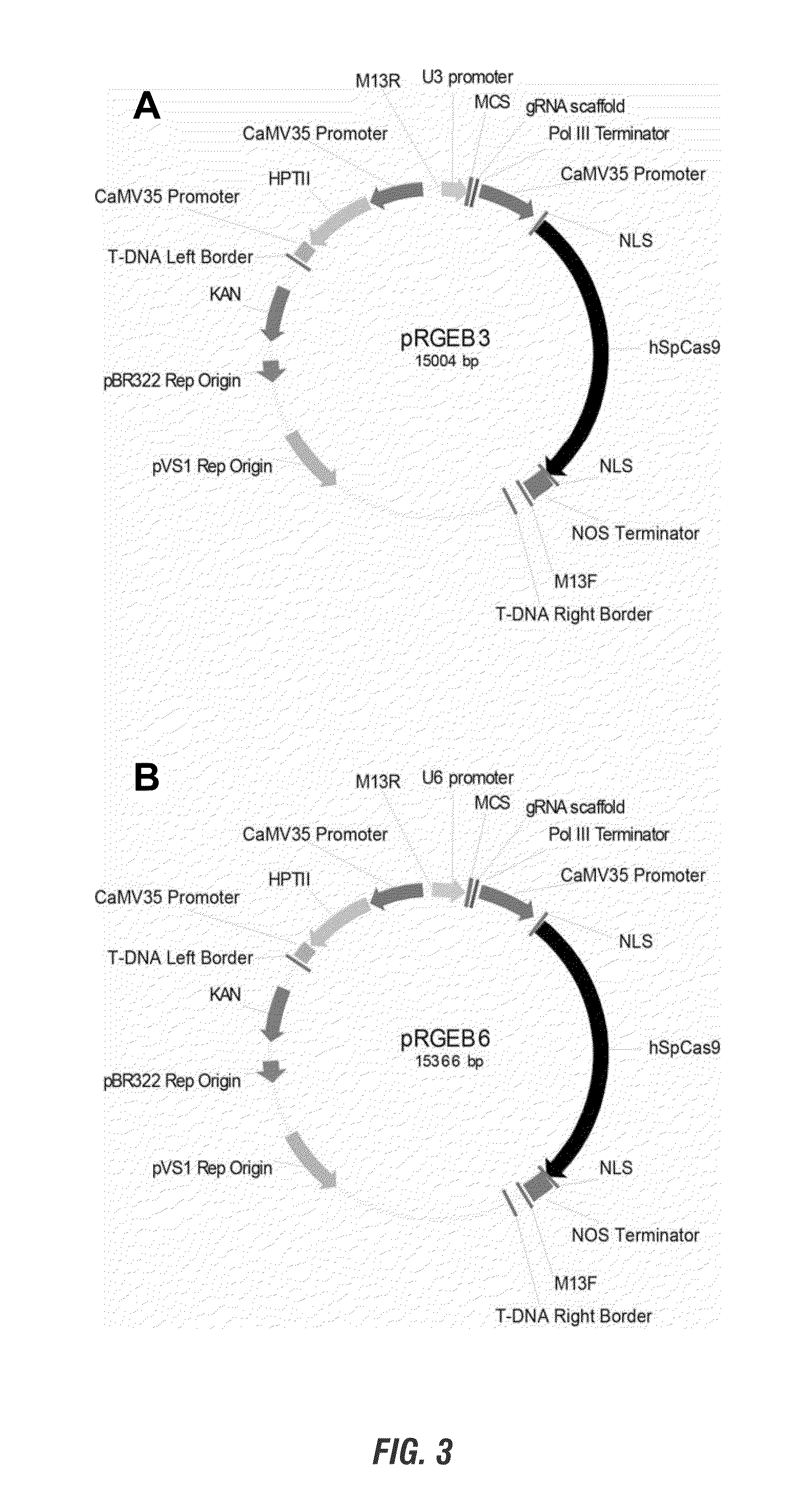
InactiveUS20150067922A1Improve stateFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGenome editingGenetically modified crops
The present invention provides compositions and methods for specific gene targeting and precise editing of DNA sequences in plant genomes using the CRISPR (cluster regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) associated nuclease. Non-transgenic, genetically modified crops can be produced using these compositions and methods.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
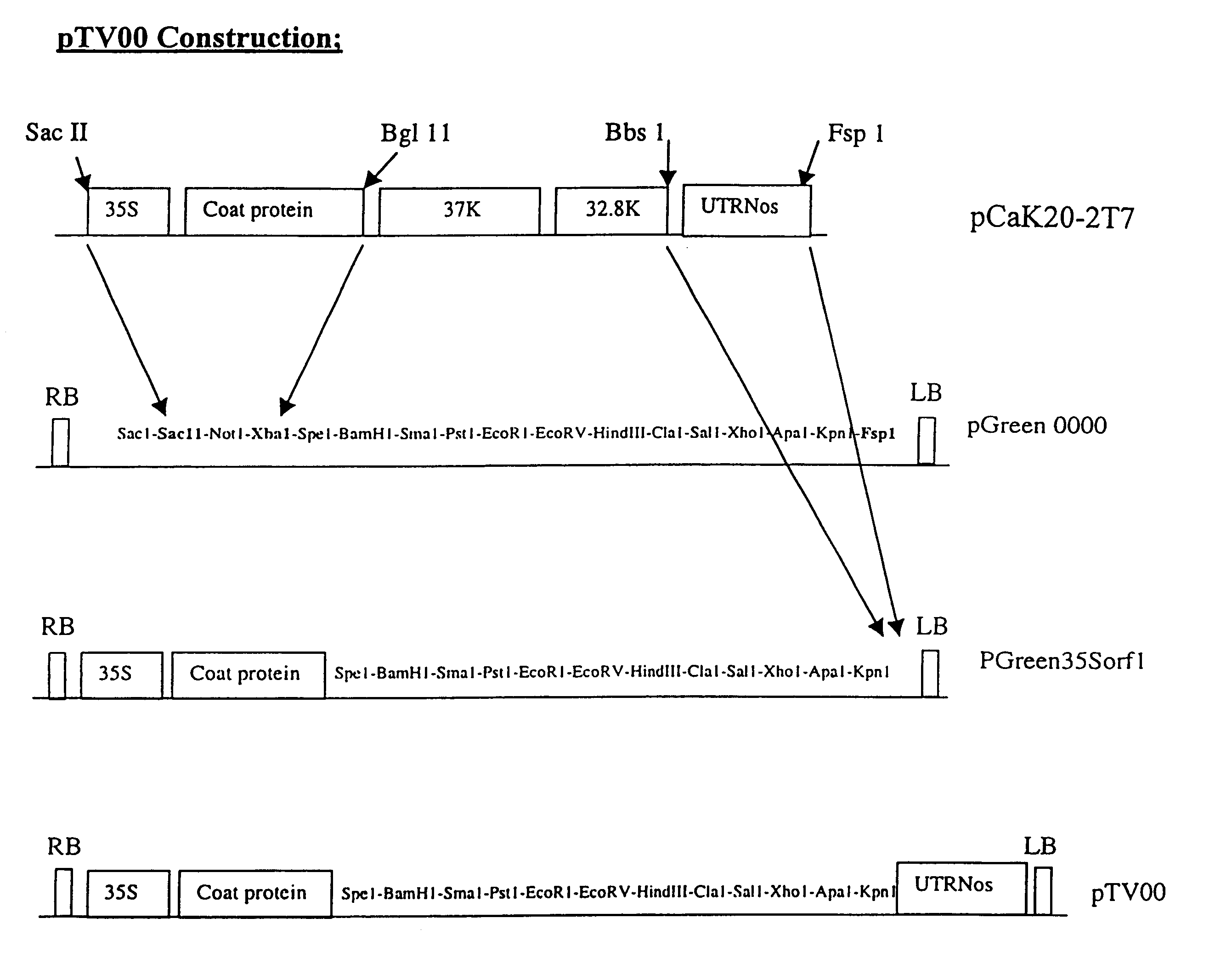
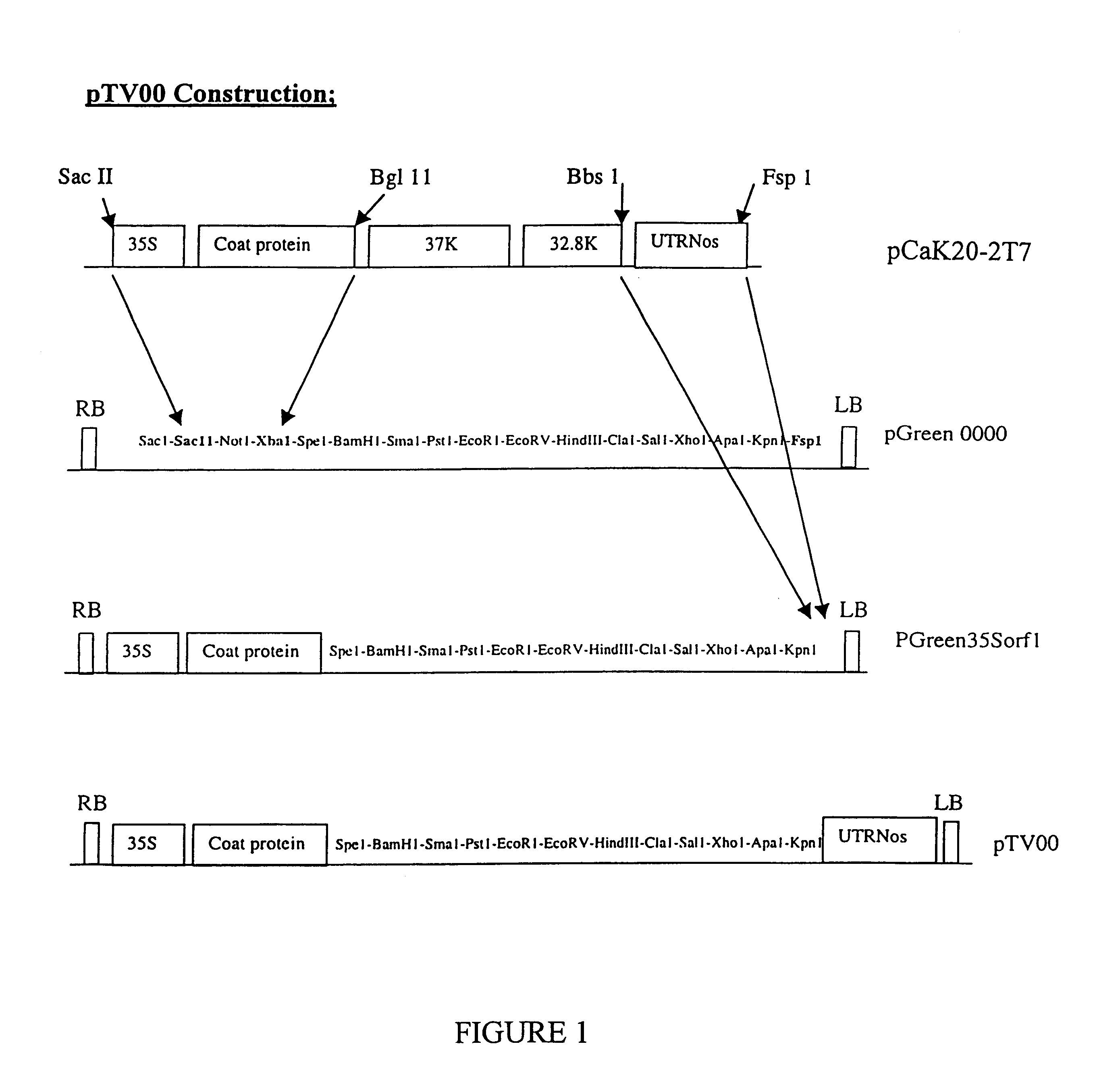
Recombinant plant viral vectors
Disclosed are nucleic acid vectors which comprise: (a) a transfer nucleotide sequence comprising (i) a plant active promoter, operably linked to (ii) a recombinant tobacco rattle virus (TRV) cDNA (preferably derived from TRV RNA2) which includes at least cis acting elements permitting replication of the cDNA; a subgenomic promoter operably linked to a sequence encoding a TRV coat protein; and a heterologous nucleotide sequence which is foreign to the virus;(b) border sequences which permit the transfer of the transfer nucleotide sequence into a plant genome. Such vectors may be used as expression vectors or for achieving viral induced gene silencing (VIGS) of a target gene, wherein the heterologous nucleotide sequence is a targeting sequence which corresponding to that gene. Example vectors include pTV00 and vectors which are derived from PTV00 and have the characteristics thereof. Also disclosed are associated processes, methods, viruses or viral particle, kits, host cells and plant tissues.
Owner:PLANT BIOSCI LTD
Insect resistant plants
InactiveUS6943282B1Stably replicatedEliminating instanceClimate change adaptationDepsipeptidesBacteroidesAureobasidium sp.
A method for expressing insecticidal protein structural genes in plant genomes is provided. In the preferred embodiments this invention comprises placing a structural gene for the Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein under control of a plant or a T-DNA promoter and ahead of a polyadenylation site followed by insertion of said promoter / structural gene combination into a plant genome by utilizing an Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid-based transformation system. The modified Ti plasmid is then used to transform recipient plant cells. Also provided are the plants and tissues produced by this method and bacterial strains, plasmids, and vectors useful for execution of this invention.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Engineered transgene integration platform (ETIP) for gene targeting and trait stacking
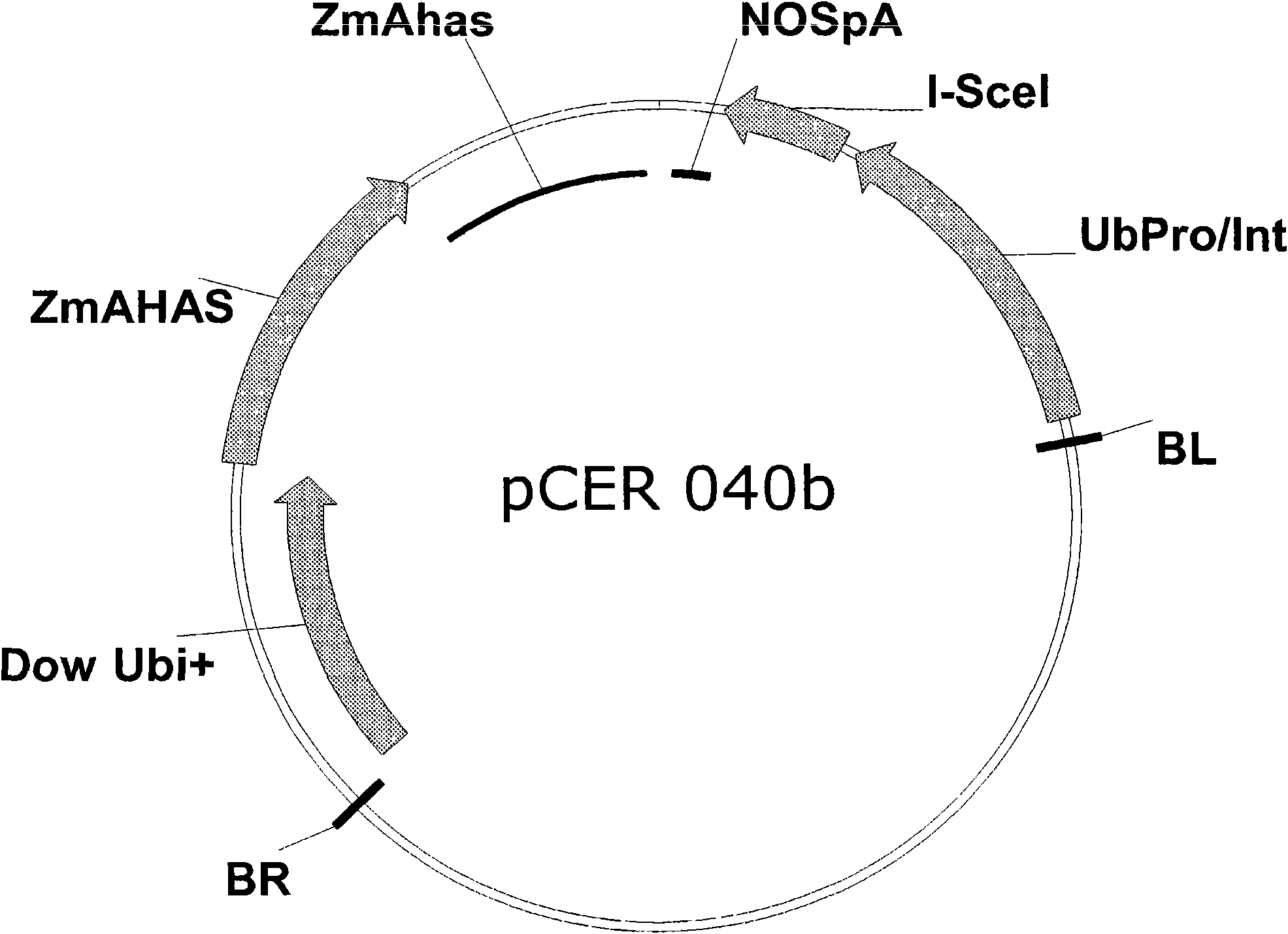
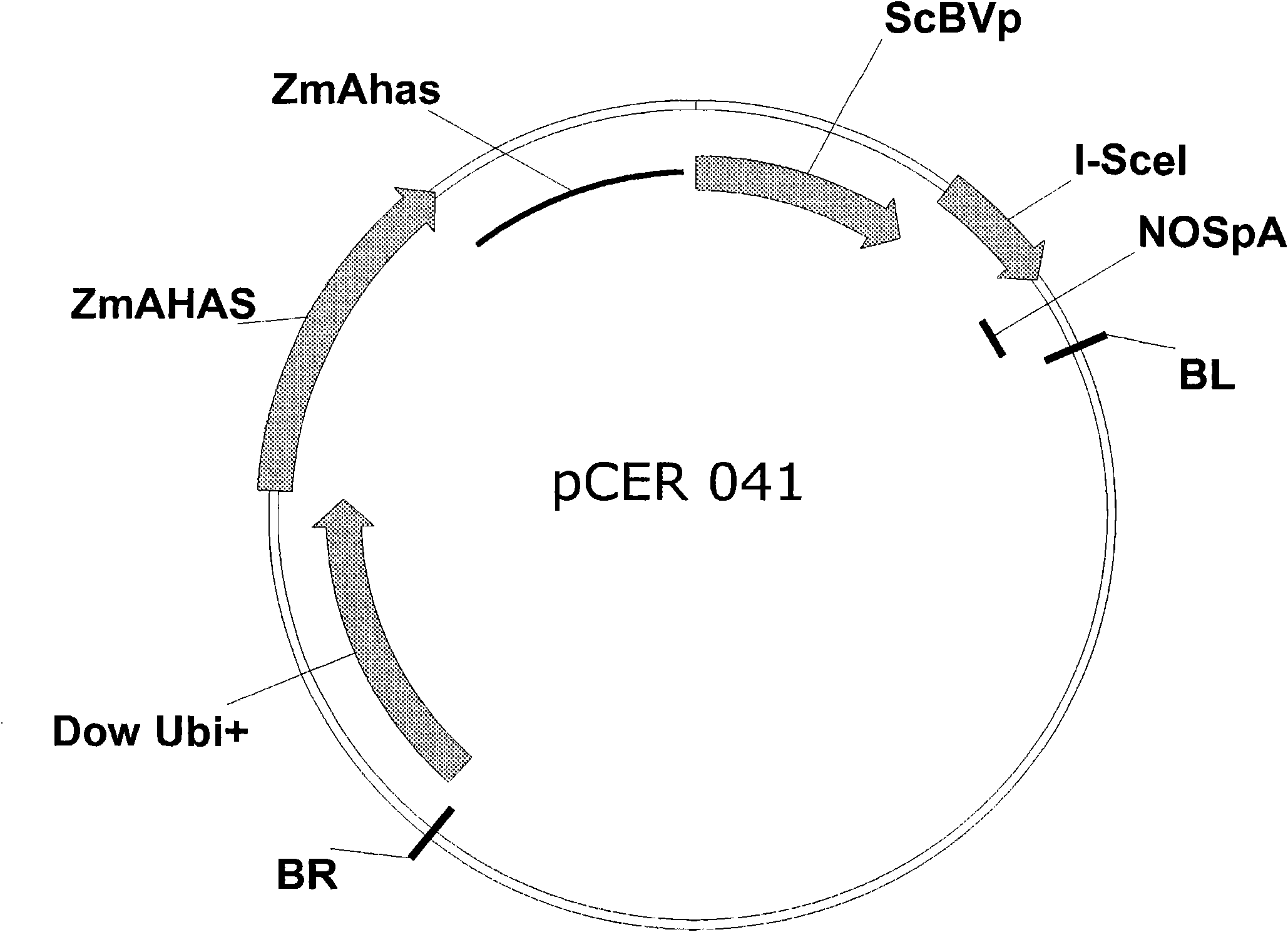
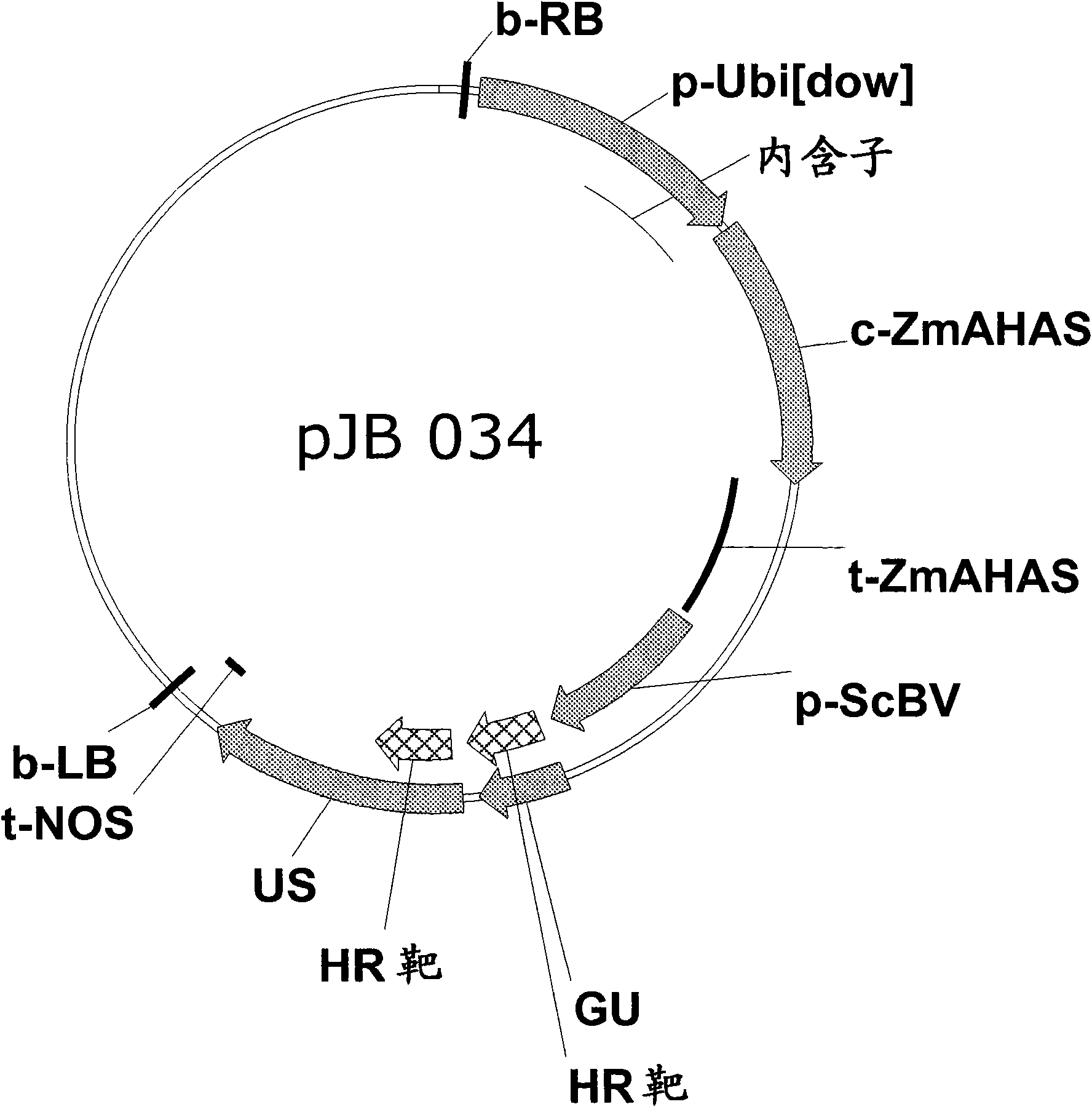
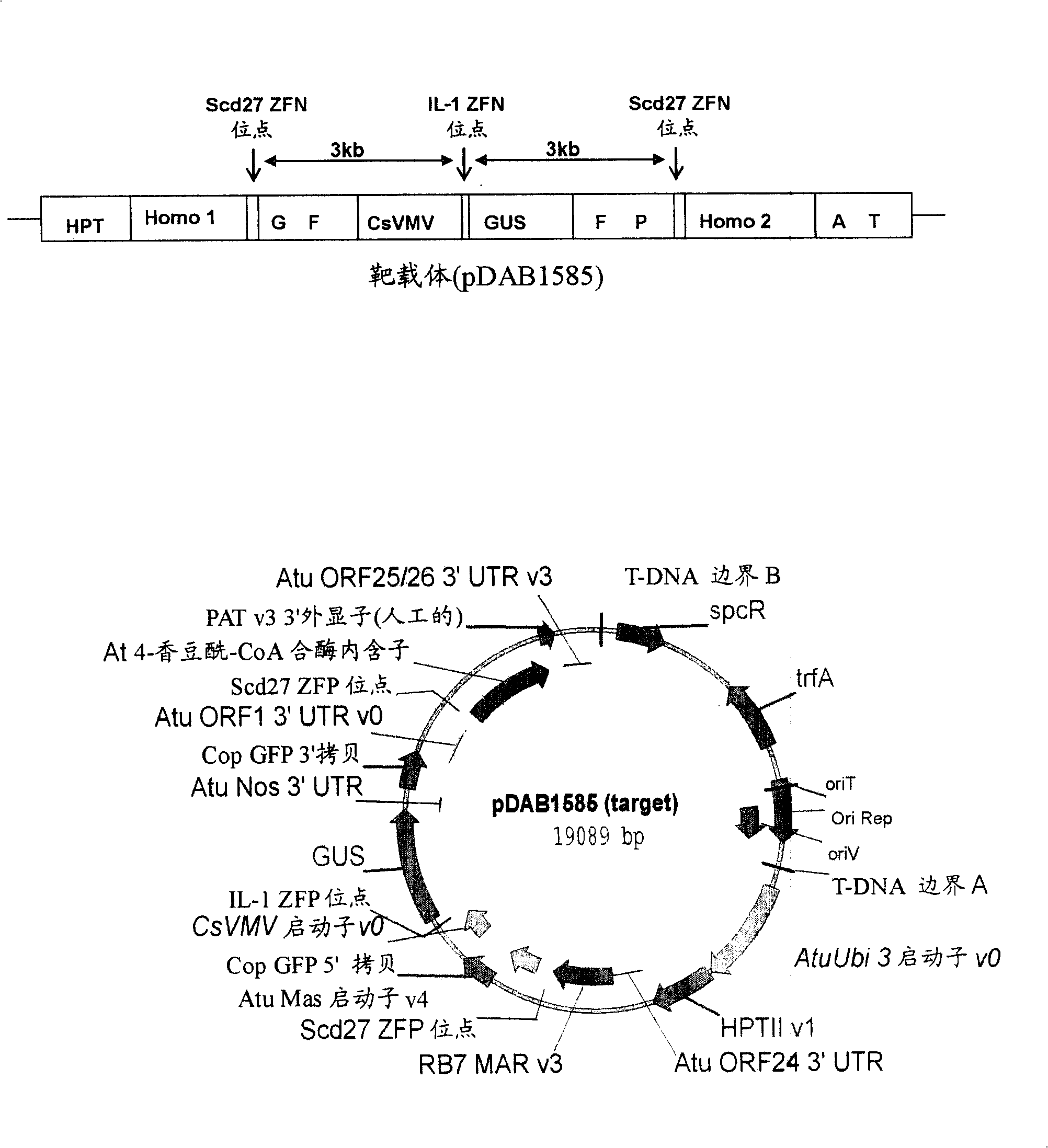
An Engineered Transgene Integration Platform (ETIP) is described that can be inserted randomly or at targeted locations in plant genomes to facilitate rapid selection and detection of a GOI that is perfectly targeted (both the 5′ and 3′ ends) at the ETIP genomic location. One element in the subject disclosure is the introduction of specific double stranded breaks within the ETIP. In some embodiments, an ETIP is described using zinc finger nuclease binding sites, but may utilize other targeting technologies such as meganucleases, CRISPRs, TALs, or leucine zippers. Also described are compositions of, and methods for producing, transgenic plants wherein the donor or payload DNA expresses one or more products of an exogenous nucleic acid sequence (e.g. protein or RNA) that has been stably-integrated into an ETIP in a plant cell. In embodiments, the ETIP facilitates testing of gene candidates and plant expression vectors from ideation through Development phases.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
DNA encoding a plant deoxyhypusine synthase, a plant eukaryotic initiation factor 5A, transgenic plants and a method for controlling senescence programmed and cell death in plants
InactiveUS6538182B1Lower Level RequirementsExtended shelf lifeBacteriaOxidoreductasesAntisense OrientationApoptotic programmed cell death
Regulation of expression of programmed cell death, including senescence, in plants is achieved by integration of a gene or gene fragment encoding senescence-induced deoxyhypusine synthase, senescence-induced eIF-5A or both into the plant genome in antisense orientation. Plant genes encoding senescence-induced deoxyhypusine synthase and senescence-induced eIF-5A are identified and the nucleotide sequences of each, alone and in combination are used to modify senescence in transgenic plants.
Owner:SENESCO TECHNOLOGIES INC
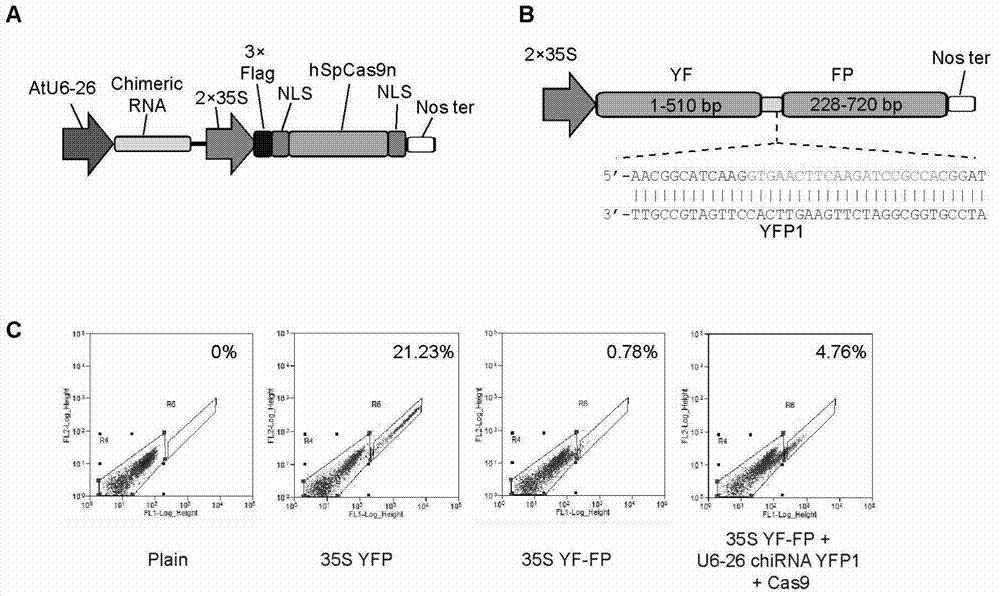
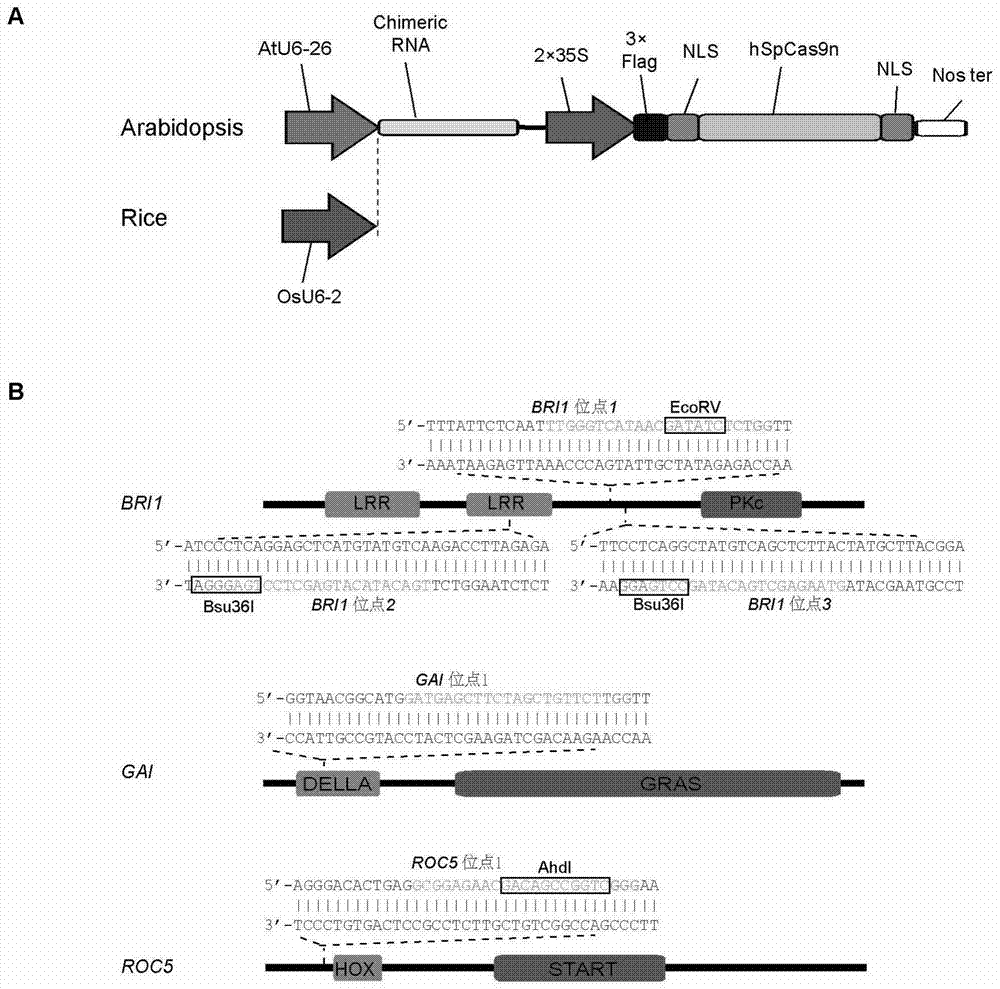
Application of CRISPR/nCas9 mediated site-directed base substitution in plant
ActiveCN107043779ARapid improvement of agronomic traitsImproved agronomic traitsVectorsVector-based foreign material introductionUracil-DNA glycosylaseSubstitution method
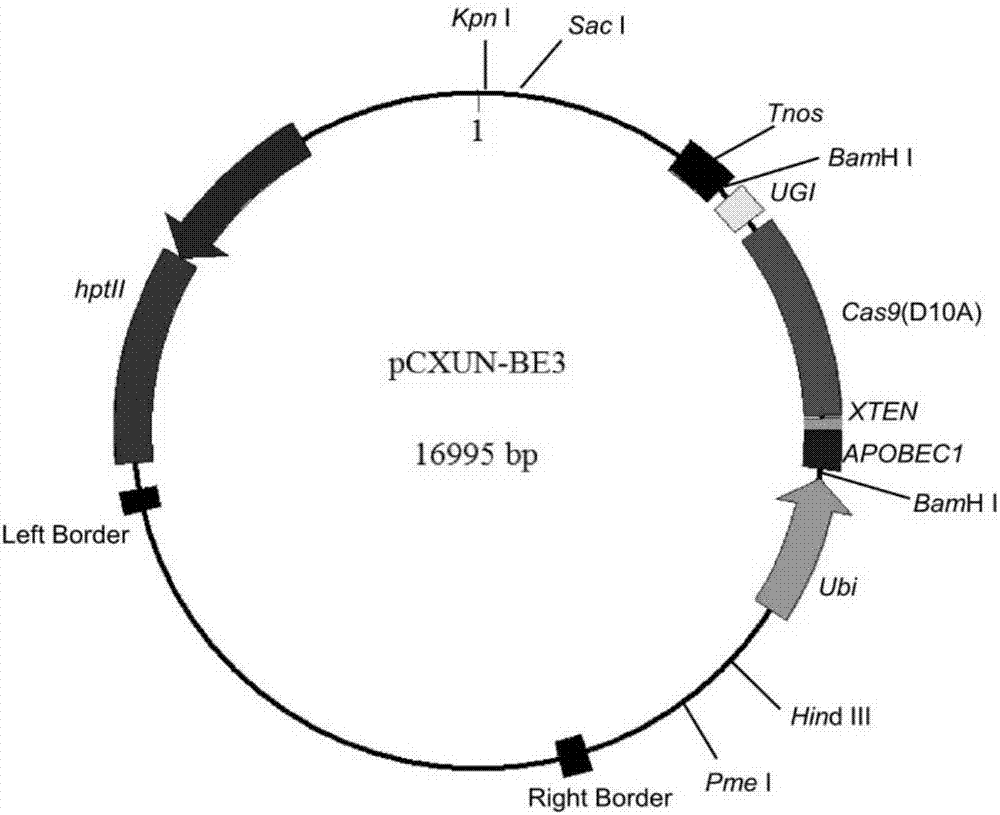
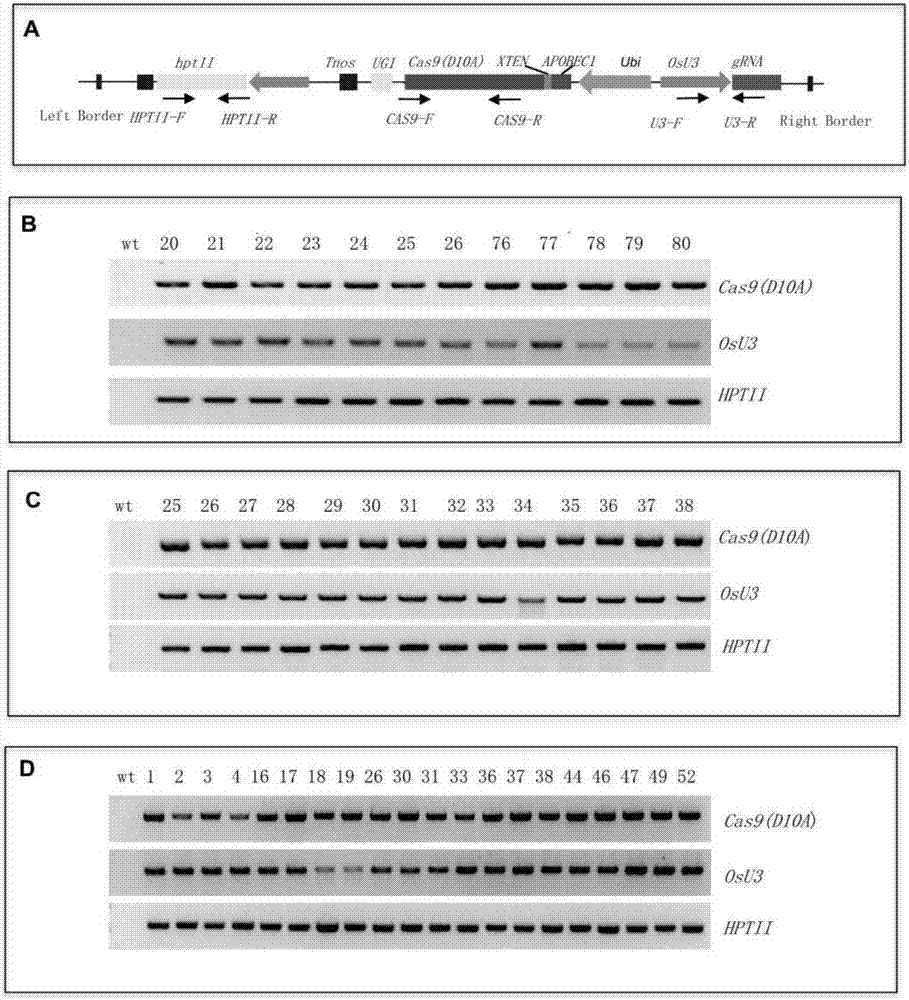
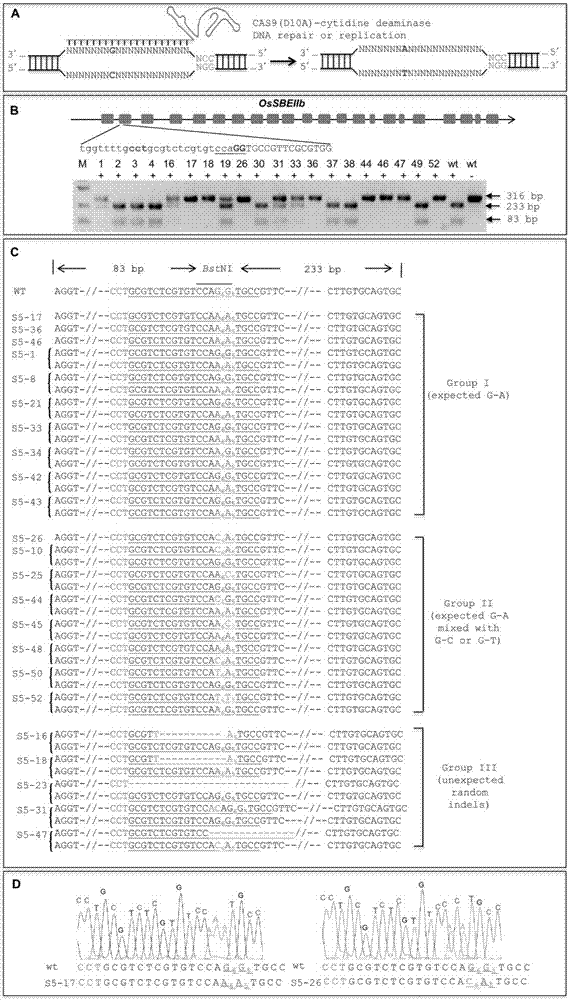
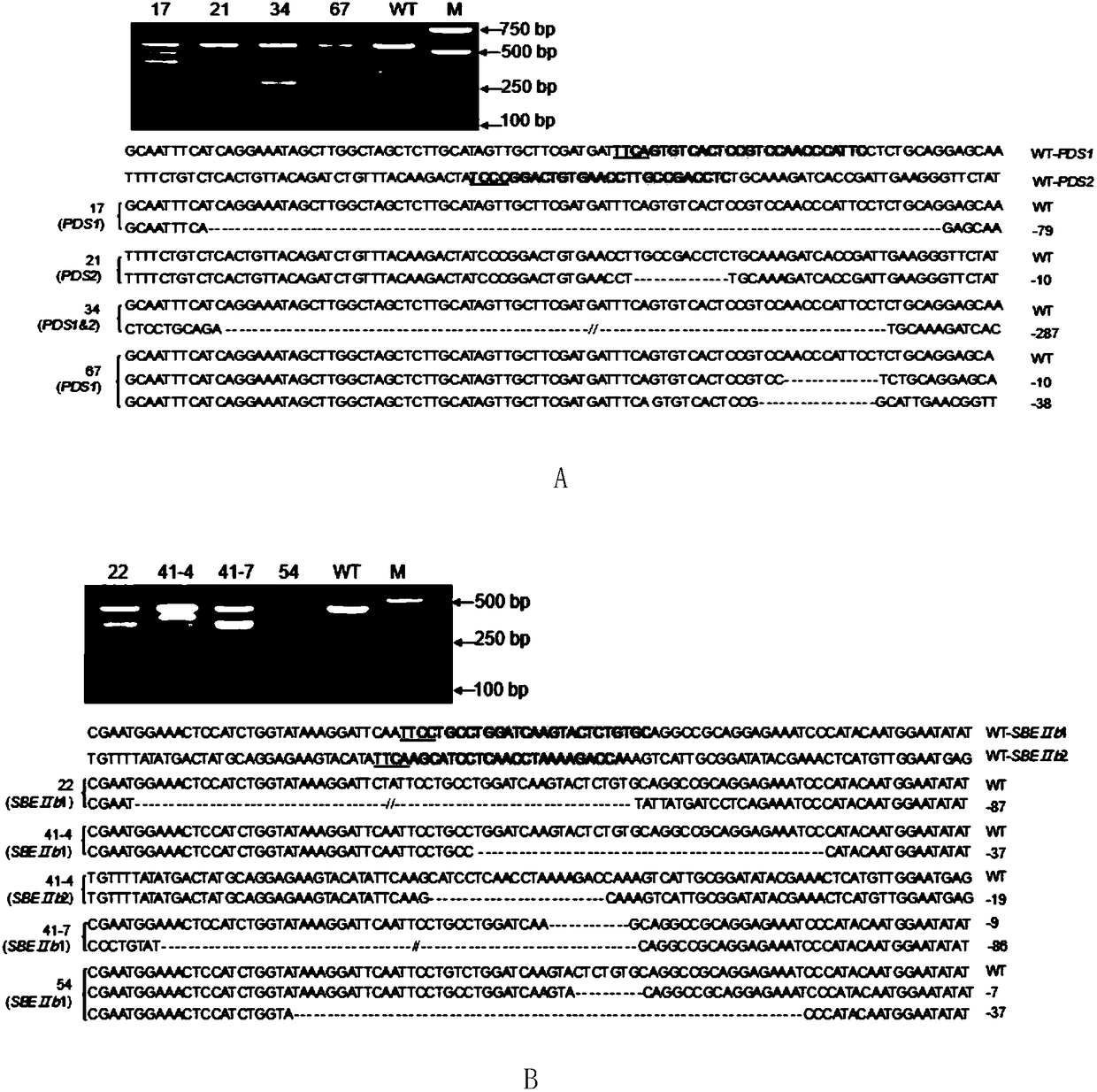
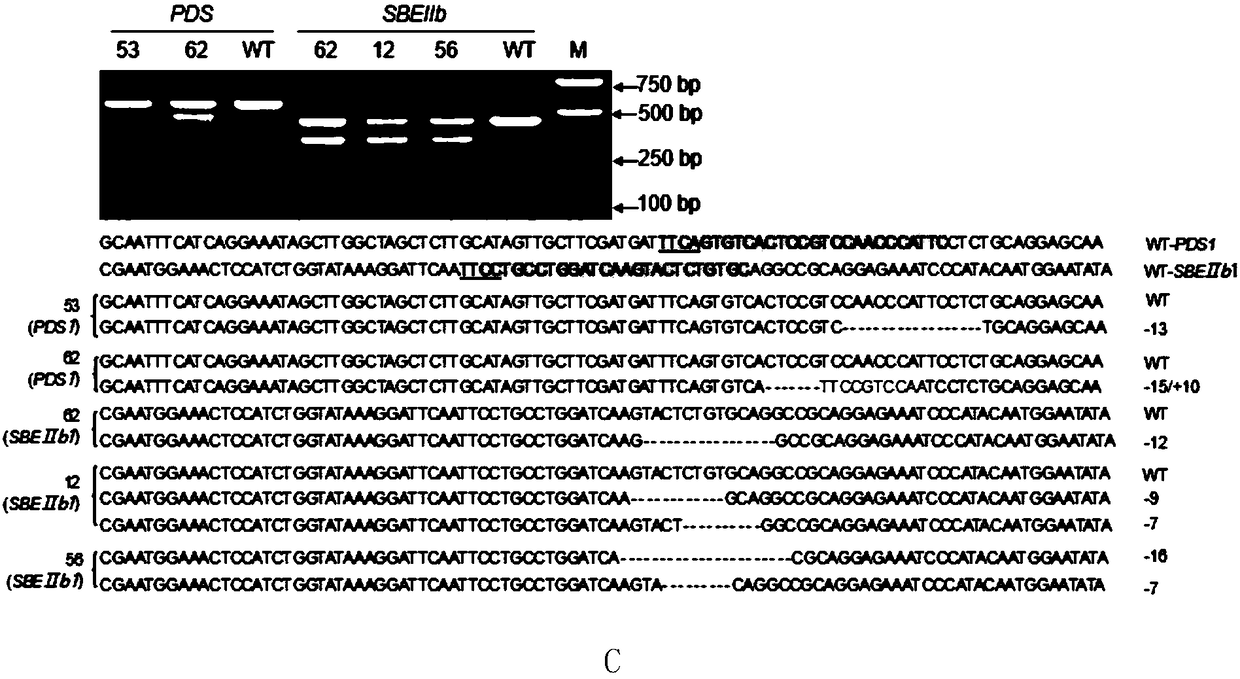
The invention discloses application of CRISPR / nCas9 mediated site-directed base substitution in a plant. The invention provides a plant genome site-directed edition system. The system comprises a BE3 plant expression carrier (expressing a fusion protein composed of nCas9(D10A), deaminase and a uracil DNA glycosylase inhibitory protein), and rice OsPDS and OsSBEIIb are taken as target genes for verifying the system. Results show that an expected site-directed mutant plant is respectively obtained in the three selected target spots, accurate site mutation of a base is realized in rice, and the highest efficiency reaches about 20%, so that a feasible and effective base substitution method is provided for crop breeding, the method has strong application potential in the aspect of agricultural breeding, and a foundation is provided for rapidly improving important agronomic traits of crops.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
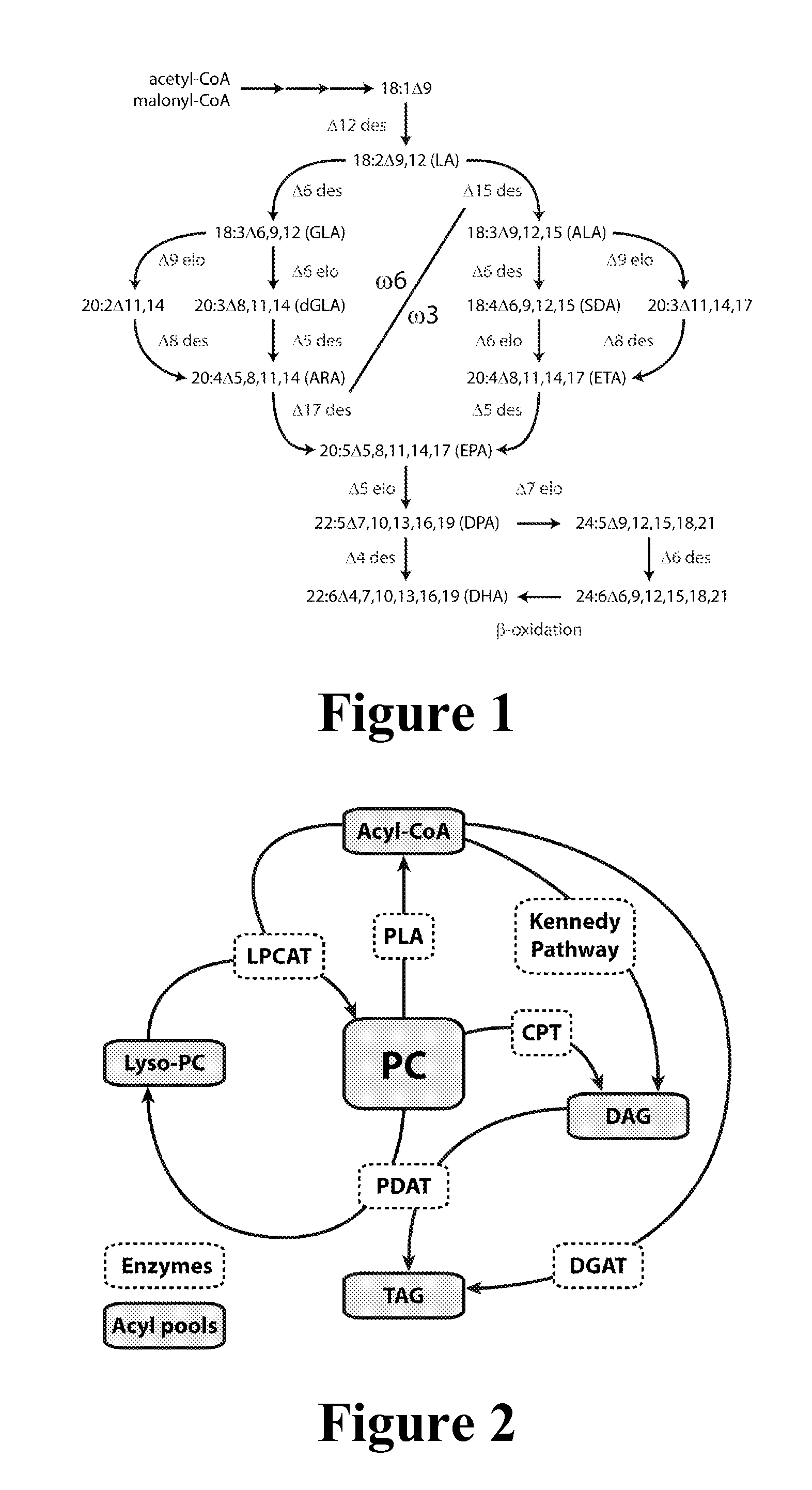
Enzymes and methods for producing omega-3 fatty acids
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG +1
DNA encoding a plant deoxyhypusine synthase, a plant eukaryotic initiation factor 5A, transgenic plants and a method for controlling senescence programmed and cell death in plants
InactiveUS6878860B1Lower Level RequirementsReduce and prevent expression of geneBacteriaOxidoreductasesAntisense OrientationApoptotic programmed cell death
Regulation of expression of programmed cell death, including senescence, in plants is achieved by integration of a gene or gene fragment encoding senescence-induced deoxyhypusine synthase, senescence-induced elF-5A or both into the plant genome in antisense orientation. Plant genes encoding senescence-induced deoxyhypusine synthase and senescence-induced elF-5A are identified and the nucleotide sequences of each, alone and in combination are used to modify senescence in transgenic plants.
Owner:AGRIBODY TECH INC
Methods for enhancing segregation of transgenes in plants and compositions thereof
ActiveUS7288694B2Increase nutritionIncrease productionSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesSTATH genePositive selection
The compositions and methods are provided that enhance the selection of transgenic plants having two T-DNA molecules integrated into a plant genome at different physical and genetic loci. The compositions are DNA constructs that comprise novel arrangements of T-DNA molecules containing genes of interest, positive selectable marker genes, and conditional lethal genes. The methods disclosed herein comprises transforming a plant cell to comprise the DNA constructs of the present invention, regenerating the plant cell into a plant and identifying independant transgene loci, where the selectable marker genes or transgenic elements can be segregated in the progeny.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
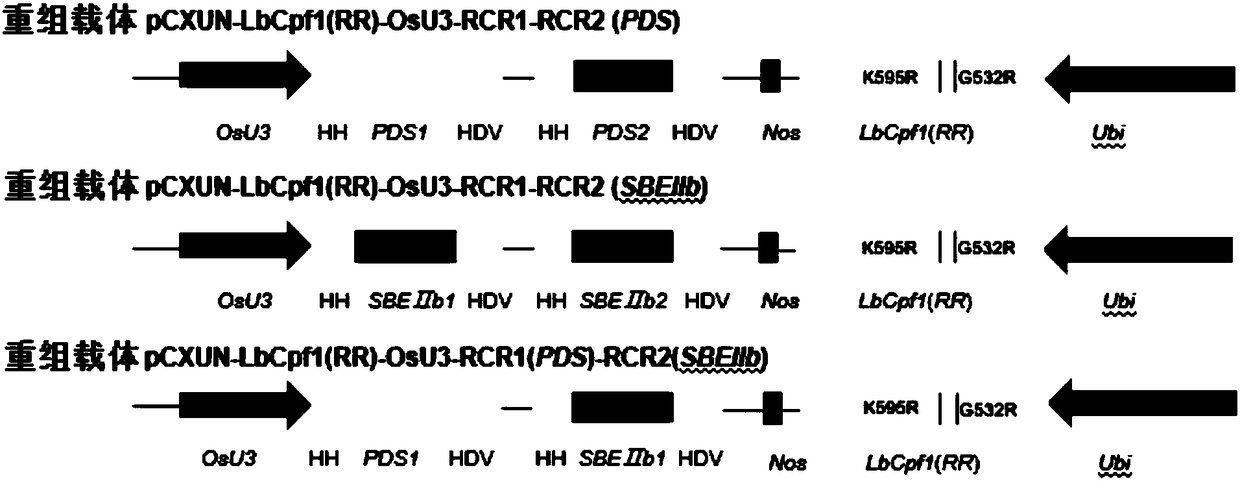
Application for using LbCpf1-RR mutant in CRISPR/Cpf1 system in plant gene editing
ActiveCN108486146AExpand the scope of editingAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleic acid vectorRice plantsMutant
The invention discloses application for using an LbCpf1 - RR mutant in a CRISPR / Cpf1 system in plant gene editing. The application for using the LbCpf1 - RR mutant in the CRISPR / Cpf1 system in plant gene editing uses an OsPDS gene and an OsSBEIIb gene as target genes, constructs a target double loci of one gene and a series of vectors of two genes, and utilizes an agrobacterium-mediated transformation method to import the vectors into rice callus, and rice plants with the target gene knockout are successfully obtained by using the LbCpf1-RR mutant. The only difference between the LbCpf1-RR mutant and the protein LbCpf1 is that the 532nd amino acid changes from G to R, and the 595th amino acid changes from K to R. The LbCpf1-RR mutant provided by the application for using the LbCpf1 - RR mutant in the CRISPR / Cpf1 system in plant gene editing expands the PAM site sequence identified by the LbCpf1-RR mutant, so that the editing range of the CRISPR / Cpf1 system in rice genome is expanded, great significance for promoting the application of the system in the field of plant genome editing is achieved. The application for using the LbCpf1 - RR mutant in the CRISPR / Cpf1 system in plant geneediting has great application value.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Plant Genome Sequence and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20080113342A1Microbiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsGenomic DNAPlant cell
The present invention is in the field of plant biochemistry and genetics. More specifically the invention relates to nucleic acid sequences from plant cells, in particular, genomic DNA sequences from Arabidopsis thaliana plants. The invention encompasses nucleic acid molecules present in non-coding regions as well as nucleic acid molecules that encode proteins and fragments of proteins. In addition, the invention also encompasses proteins and fragments of proteins so encoded and antibodies capable of binding these proteins or fragments. The invention also relates to methods of using the nucleic acid molecules, proteins and fragments of proteins, and antibodies, for example for genome mapping, gene identification and analysis, plant breeding, preparation of constructs for use in plant gene expression, and transgenic plants.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Plant genome sequences and uses thereof
The present invention is in the field of plant biochemistry and genetics. More specifically the invention relates to nucleic acid sequences from plant cells, in particular, genomic DNA sequences from Arabidopsis thaliana plants. The invention encompasses nucleic acid molecules present in non-coding regions as well as nucleic acid molecules that encode proteins and fragments of proteins. In addition, the invention also encompasses proteins and fragments of proteins so encoded and antibodies capable of binding these proteins or fragments. The invention also relates to methods of using the nucleic acid molecules, proteins and fragments of proteins, and antibodies, for example for genome mapping, gene identification and analysis, plant breeding, preparation of constructs for use in plant gene expression, and transgenic plants.
Owner:CAO YONGWEI +1
Targeted manipulation of genes in plants
Methods and compositions for altering a nucleotide sequence of interest in a plant is provided. The method involves introducing a chimeric oligonucleotide into a plant cell, wherein the oligonucleotide comprises at least two intervening blocks of RNA residues with intervening DNA residues. The RNA blocks are homologous to a plant nucleotide sequence. The chimeric oligonucleotide is capable of folding to form a duplex oligonucleotide. The chimeric oligonucleotide is maintained within the nucleus of the plant whereby the alteration is introduced into the target sequences of the plant genome.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Enzymes and methods for producing omega-3 fatty acids
ActiveUS20120016144A1Efficient production of LC-PUFAValid conversionSenses disorderNervous disorderHeterologousBiotechnology
The present invention relates generally to the field of recombinant fatty acid synthesis, particularly in transgenic plants. The application describes genes involved in fatty acid synthesis and provides methods and vectors for the manipulation of fatty acid composition of plant oils. In particular, the invention provides constructs for achieving the integration of multiple heterologous genes involved in fatty acid synthesis into the plant genome, such that the resulting plants produce altered levels of polyunsaturated fatty acids. Also described are methods for enhancing the expression of fatty acid biosynthesis enzymes by co-expressing a silencing suppressor within the plant storage organ.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG +1
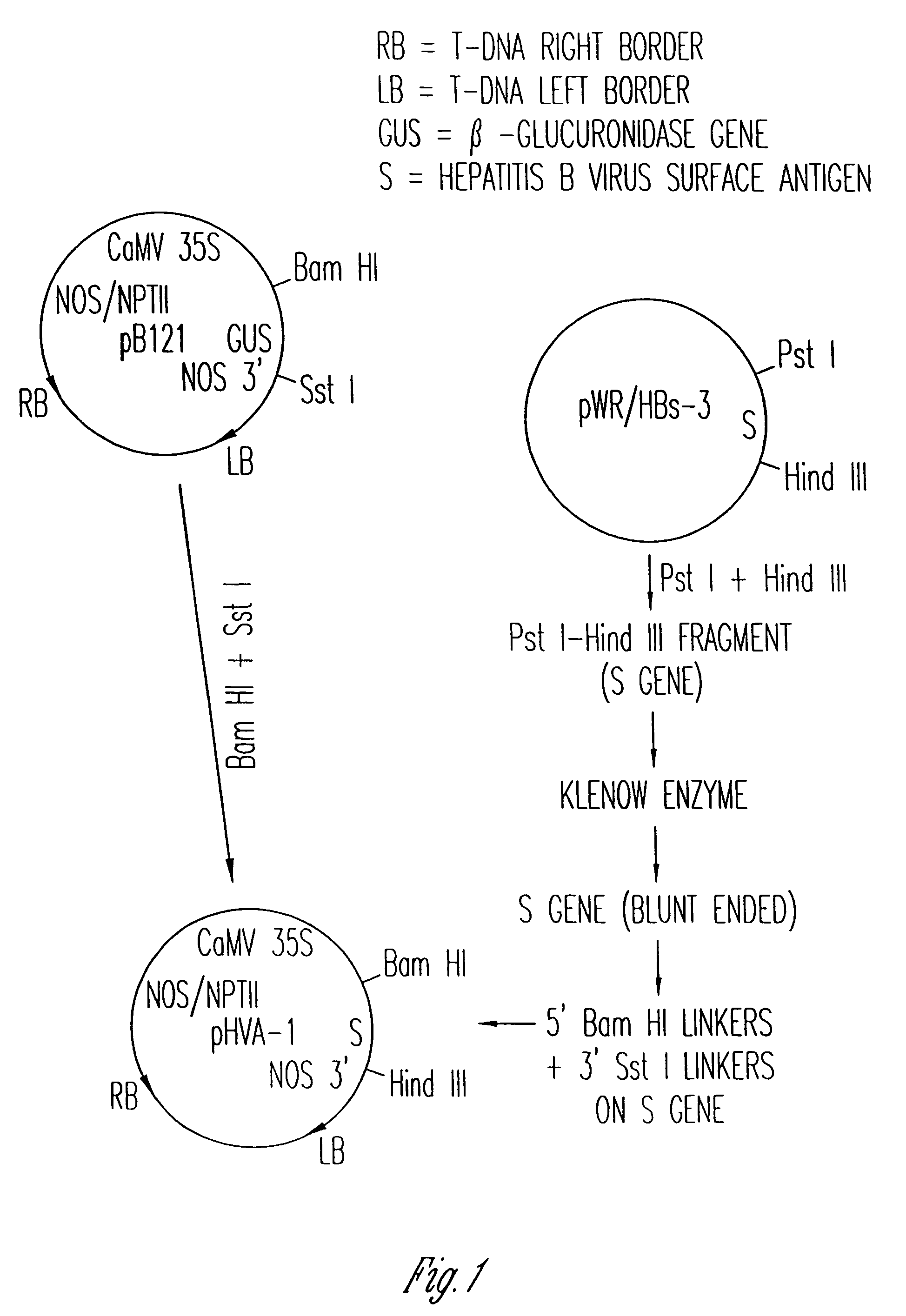
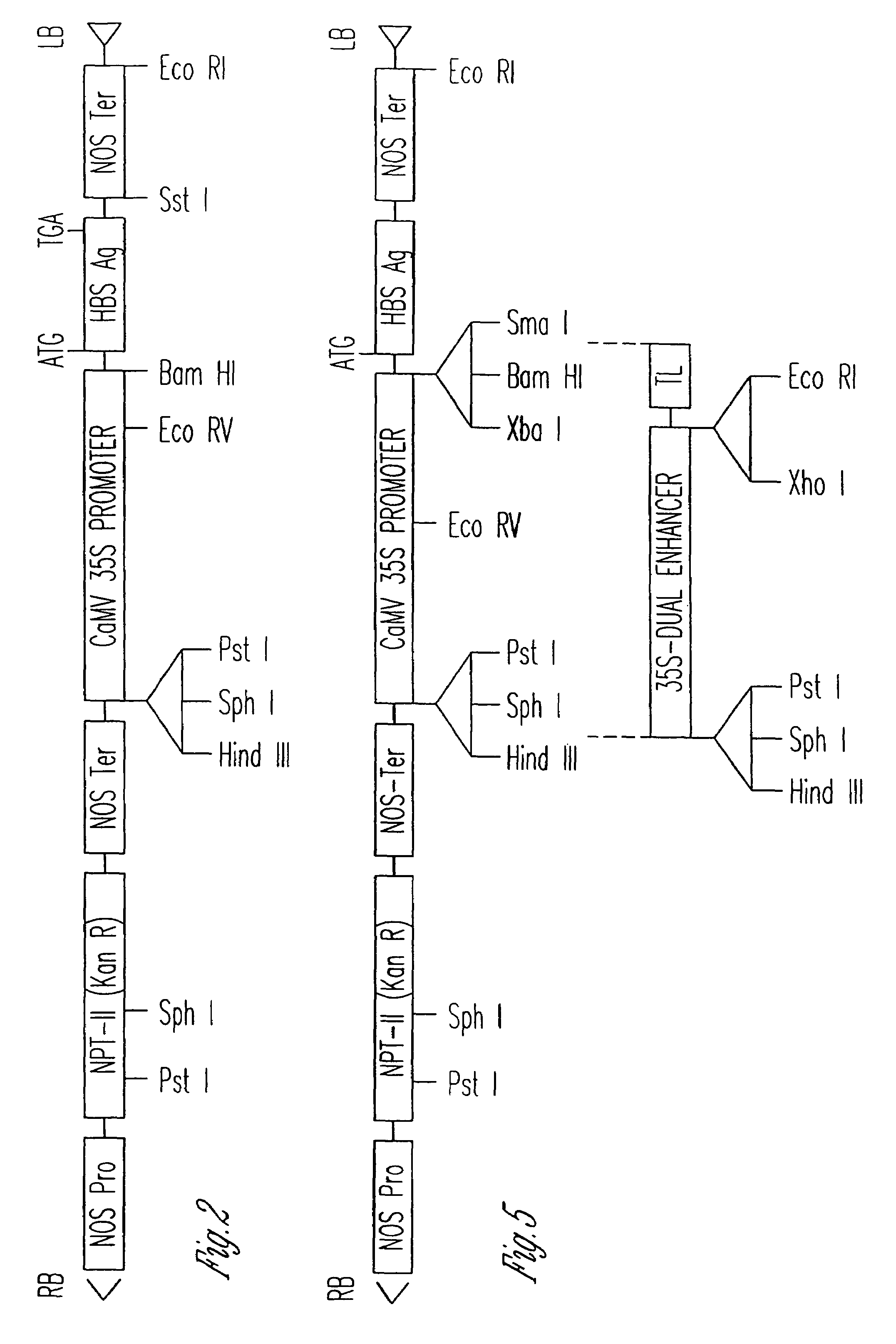
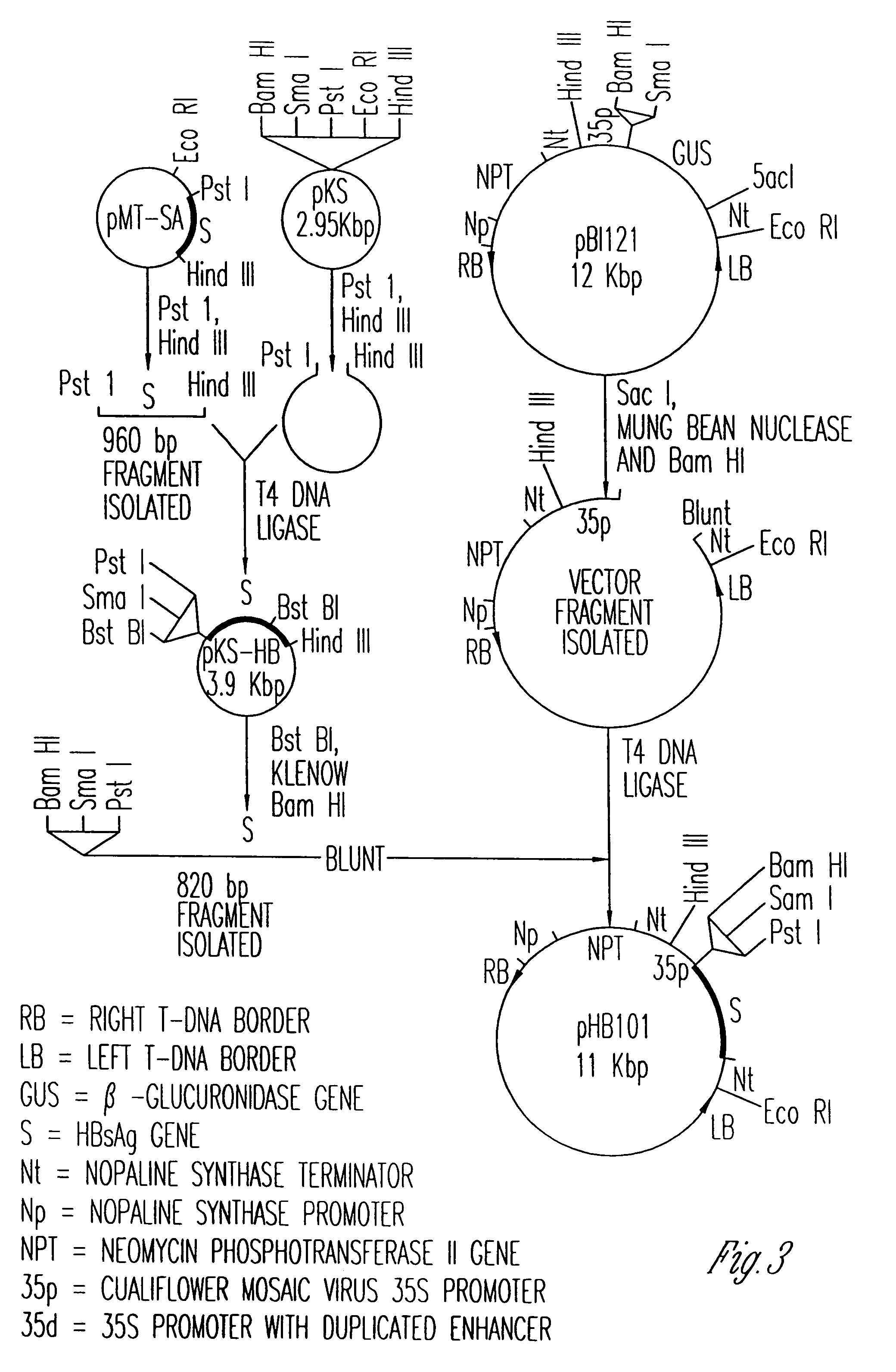
Vaccines expressed in plants
The anti-viral vaccine of the present invention is produced in transgenic plants and then administered through standard vaccine introduction method or through the consumption of the edible portion of those plants. A DNA sequence encoding for the expression of a surface antigen of a viral pathogen is isolated and ligated to a promoter which can regulate the production of the surface antigen in a transgenic plant. This gene is then transferred to plant cells using a procedure that results in its integration into the plant genome, such as through the use of an Agrobacterium tumenfaciens plasmid vector system. Preferably, the foreign gene is expressed in an portion of the plant that is edible by humans or animals. In a preferred procedure, the vaccine is administered through the consumption of the edible plant as food, preferably in the form of a fruit or vegetable juice which can be taken orally.
Owner:PRODI GENE INC
Plant Genome Sequence and Uses Thereof
The present invention is in the field of plant biochemistry and genetics. More specifically the invention relates to nucleic acid molecules from plant cells, in particular, genomic DNA sequences from rice plants and nucleic acid molecules that contain markers, in particular, single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and repetitive element markers. In addition, the present invention provides nucleic acid molecules having regulatory elements or encoding proteins or fragments thereof. The invention also relates to proteins and fragments of proteins so encoded and antibodies capable of binding the proteins. The invention also relates to methods of using the nucleic acid molecules, markers, repetitive elements and fragments of repetitive elements, regulatory elements, proteins and fragments of proteins, and antibodies, for example for genome mapping, gene identification and analysis, plant breeding, preparation of constructs for use in plant gene expression, and transgenic plants.
Owner:BOUKHAROV ANDREY +5
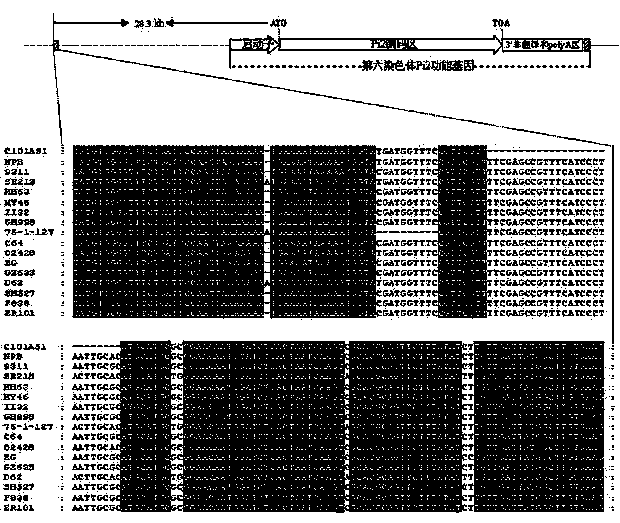
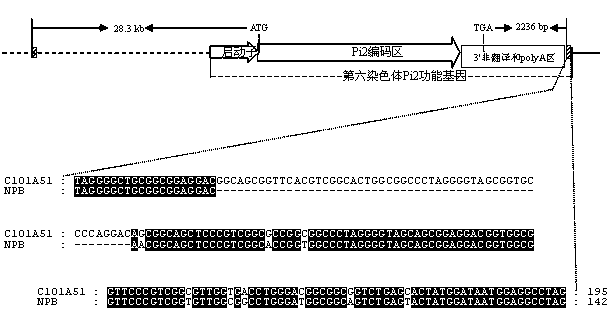
Molecular marker of rice-blast-resistant gene Pi2 and application of molecular marker
InactiveCN104073487AChoose a clear goalImprove selection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention belongs to the field of crop biotechnology and in particular relates to a molecular marker of a rice-blast-resistant gene Pi2 and application of the molecular marker. The upstream and downstream molecular markers are based on specific insertion / deletion loci polymorphism of nucleotide sequences shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2. The two molecular markers are co-dominant molecular markers developed for close linkage regions on two sides of the functional gene Pi2, and have the advantages of being high in accuracy and capable of being widely applied to different breeding parents. By detecting the two molecular markers, whether a detected rice material has the rice-blast-resistant gene Pi2 or not can be accurately judged. By virtue of a molecular marker combination, whether a hybrid transferred progeny plant genome of a parent of the functional gene Pi2 and other parents has the functional gene Pi2 or not and the homozygous state of the functional gene Pi2 can be accurately detected, and the breeding efficiency of a rice-blast-resistant rice variety with the functional gene Pi2 is improved.
Owner:BIOLOGICAL TECH INST OF FUJIAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
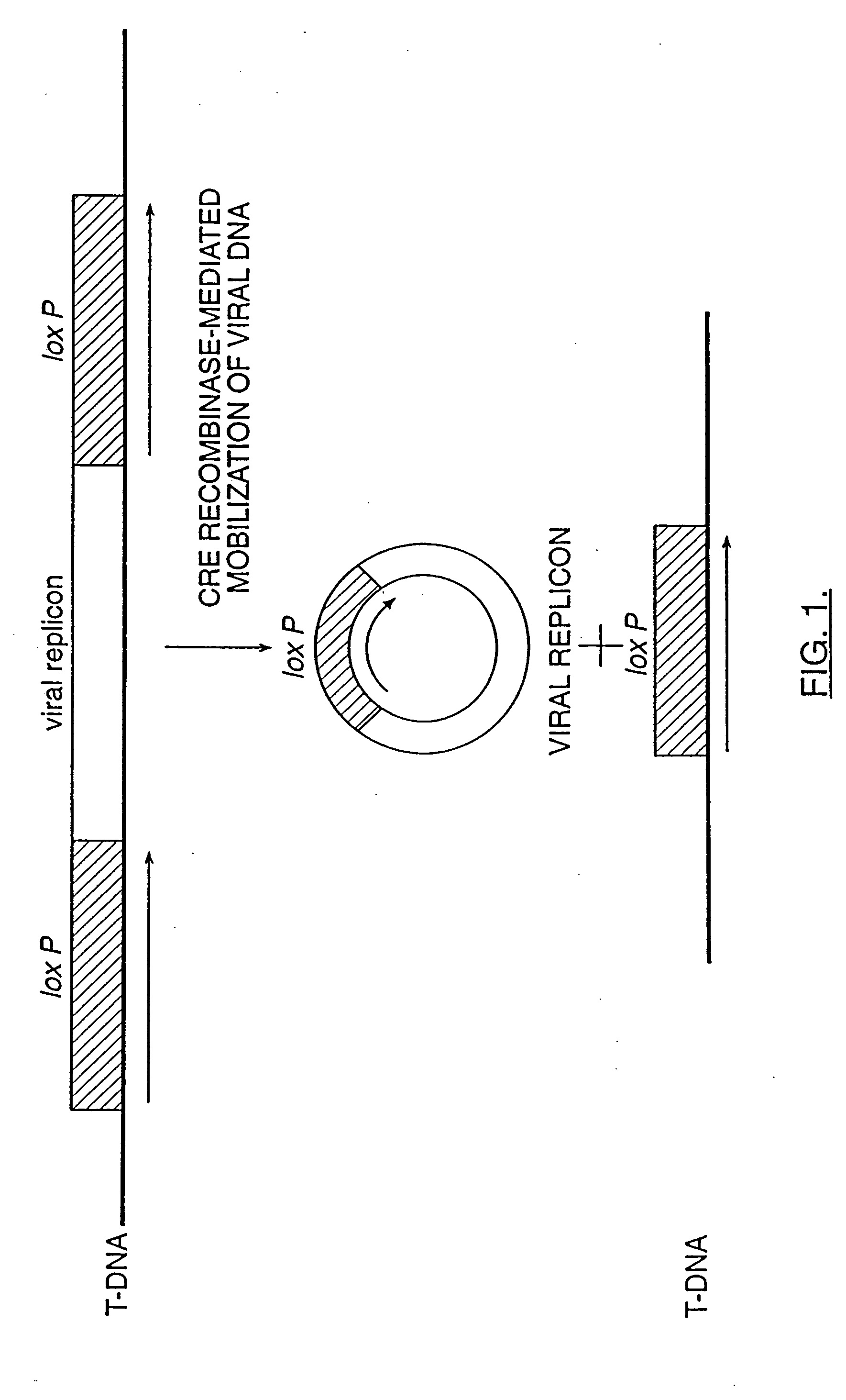
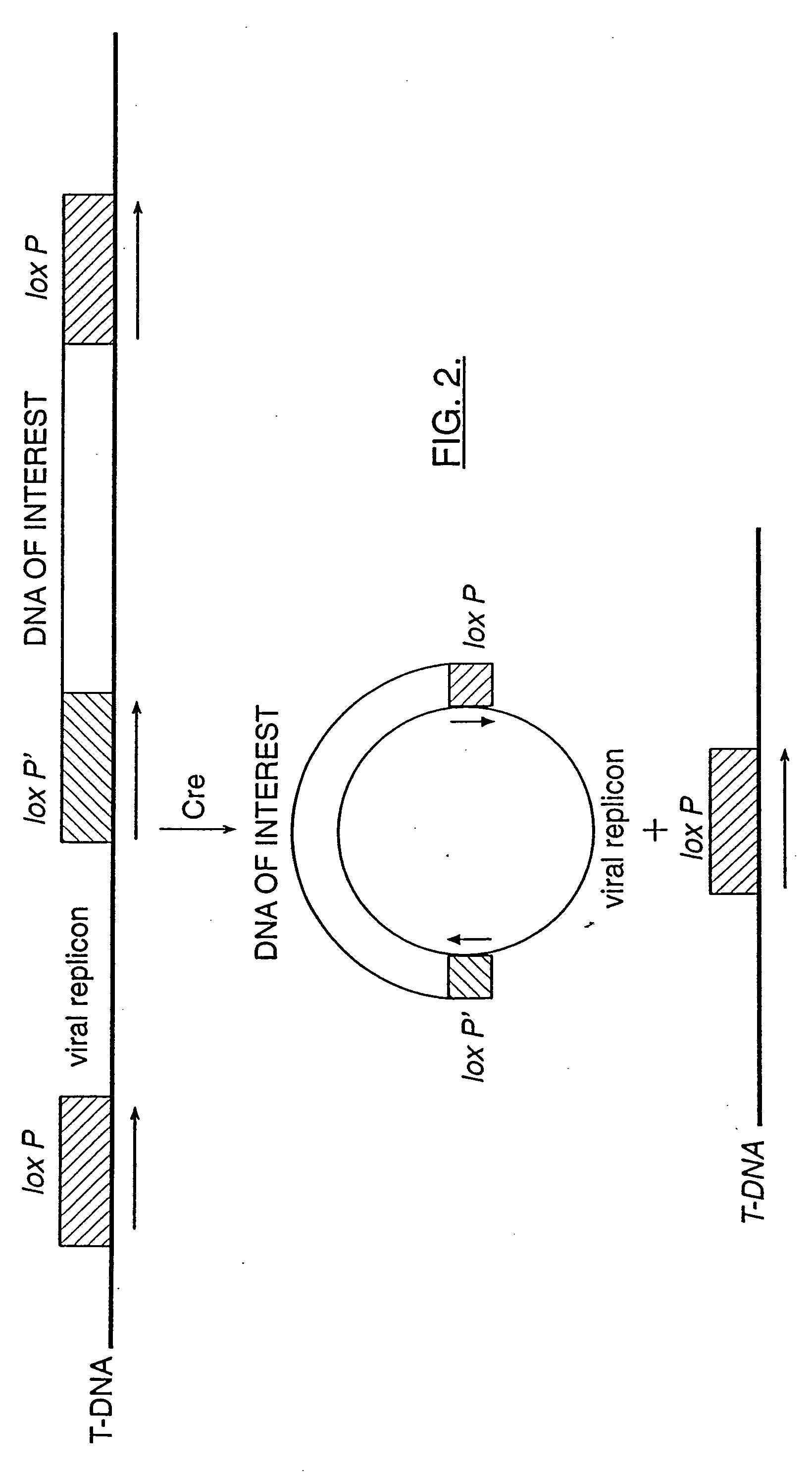
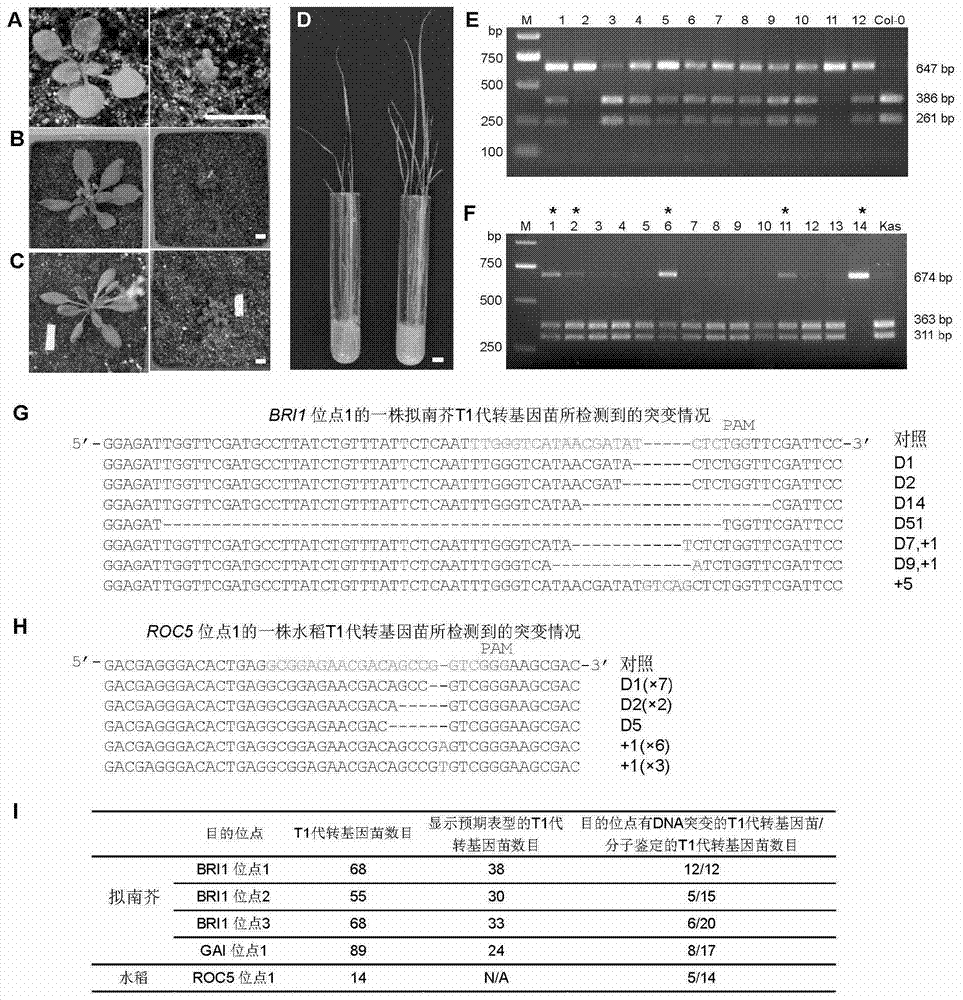
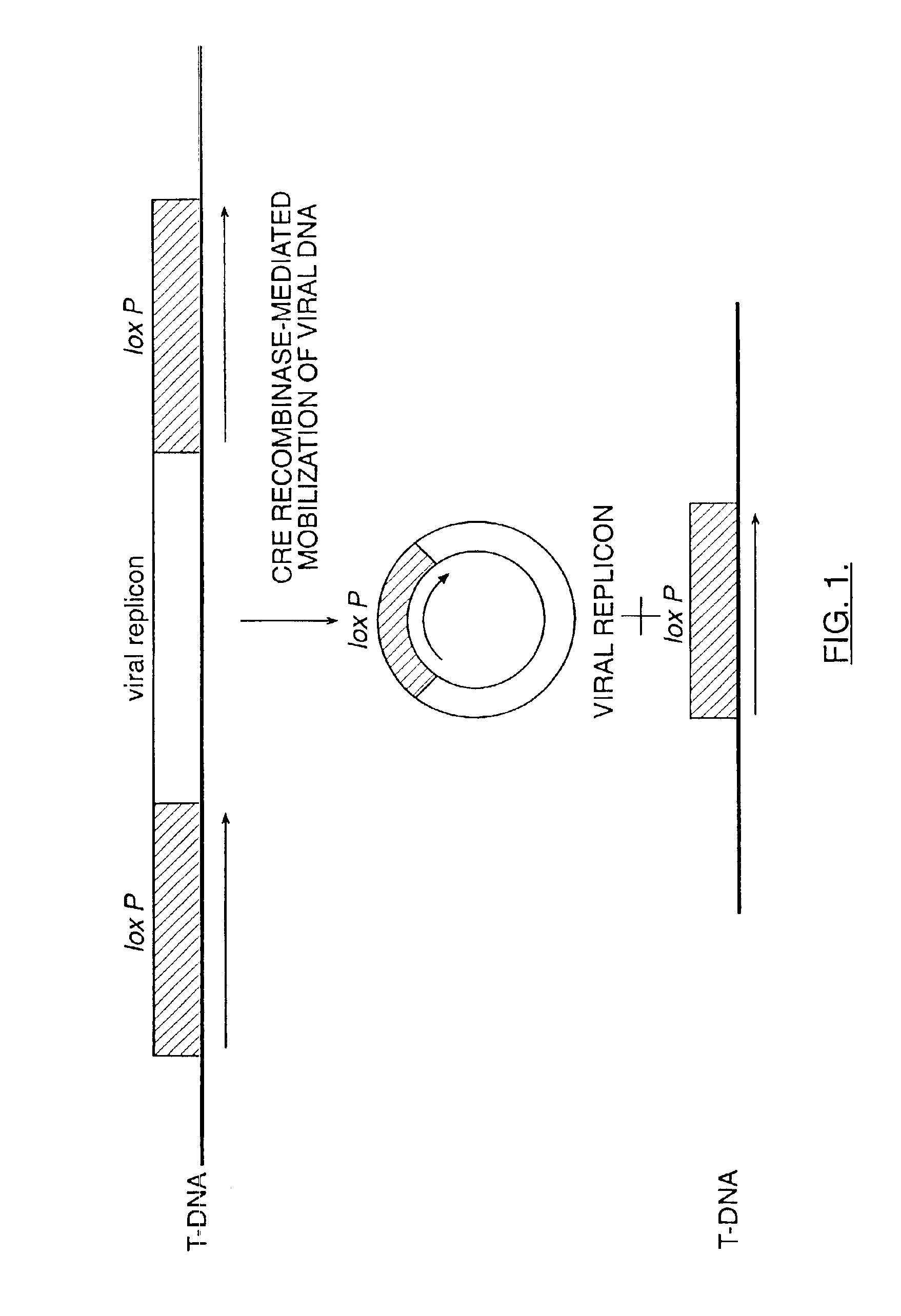
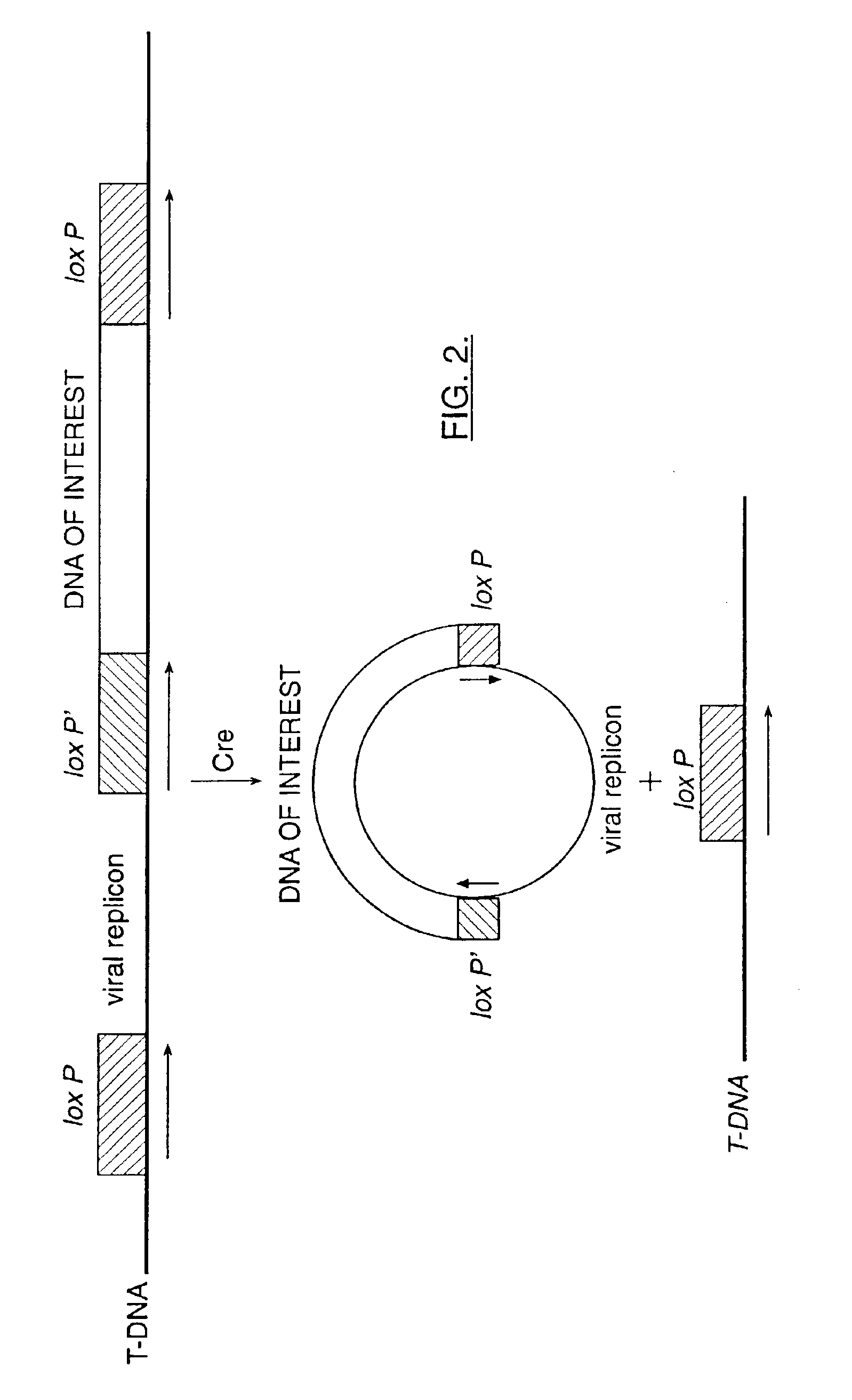
Mobilization of viral genomes from T-DNA using site-specific recombination systems
InactiveUS20060253939A1Easy constructionSimplifying stable maintenanceBacteriaSugar derivativesSite-specific recombinationPlant cell
The invention relates to methods and compositions for site-specific recombinase-mediated mobilization of viral replicons and associated DNAs of interest from T-DNA. The methods of the invention comprise Agrobacterium-mediated transfer of T-DNA to a plant cell, wherein the T-DNA contains a viral replicon flanked by directly repeated target sites for a site-specific recombinase and optionally a DNA of interest linked to the viral replicon. The DNA of interest may also contain a non-identical target site for the recombinase. An expression cassette for the site-specific recombinase is present on the T-DNA or the plant genome, or is transiently introduced into the plant cell. Expression of the site-specific recombinase in the plant cell results in excision of the viral replicon and the associated DNA of interest. The viral replicon and DNA of interest are then replicated to high copy number in the host plant cell. The compositions of the invention comprise nucleic acids, such as T-DNAs containing a viral DNA flanked by directly repeated target sites for a site-specific recombinase. The nucleic acids of the invention may additionally contain expression cassettes encoding the cognate site-specific recombinase for the target sites flanking the viral genome. The compositions of the invention further comprise Agrobacterium containing the nucleic acids of the invention. The compositions and methods of the invention have use in increasing the efficiency of agroinfection, providing high copy numbers of a DNA of interest for transient expression or for integration into a plant chromosome, and in simplifying the construction and stable maintenance of vectors for agroinfection and transformation.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Site-specific modification method for plant genome
Provided is a method for plant genome site-directed modification. Specifically, a method for plant genome site-directed modification introduced by RNA is provided. By utilizing nucleic acid construct with particular structure, site-directed modification may be performed at pre-determined site in plant genome with high efficiency. Useful for screening plant with improved traits efficiently.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Mobilization of viral genomes from T-DNA using site-specific recombination systems
InactiveUS7179599B2Simplifying construction and stable maintenanceImprove efficiencyBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSite-specific recombinationPlant cell
The invention relates to methods and compositions for site-specific recombinase-mediated mobilization of viral replicons and associated DNAs of interest from T-DNA. The methods of the invention comprise Agrobacterium-mediated transfer of T-DNA to a plant cell, wherein the T-DNA contains a viral replicon flanked by directly repeated target sites for a site-specific recombinase and optionally a DNA of interest linked to the viral replicon. The DNA of interest may also contain a non-identical target site for the recombinase. An expression cassette for the site-specific recombinase is present on the T-DNA or the plant genome, or is transiently introduced into the plant cell. Expression of the site-specific recombinase in the plant cell results in excision of the viral replicon and the associated DNA of interest. The viral replicon and DNA of interest are then replicated to high copy number in the host plant cell. The compositions of the invention comprise nucleic acids, such as T-DNAs containing a viral DNA flanked by directly repeated target sites for a site-specific recombinase. The nucleic acids of the invention may additionally contain expression cassettes encoding the cognate site-specific recombinase for the target sites flanking the viral genome. The compositions of the invention further comprise Agrobacterium containing the nucleic acids of the invention. The compositions and methods of the invention have use in increasing the efficiency of agroinfection, providing high copy numbers of a DNA of interest for transient expression or for integration into a plant chromosome, and in simplifying the construction and stable maintenance of vectors for agroinfection and transformation.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
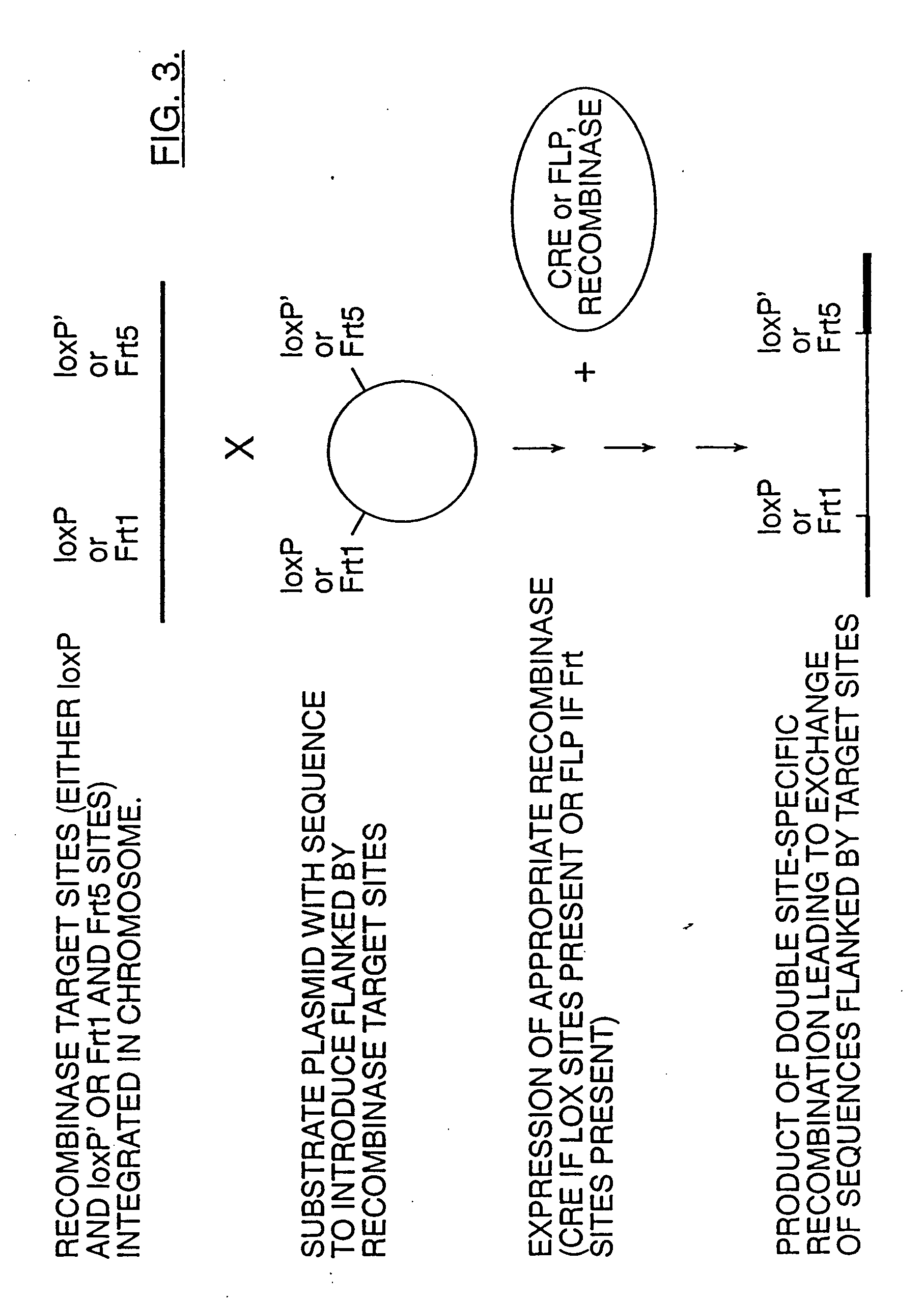
Method of excising a nucleic acid sequence from a plant genome
The present invention relates to a method for excising a nucleic acid sequence from the genome of a plant or a plant cell. This method is based on the steps of transforming a plant cell with a construct encoding a DNA double strand break inducingenzyme (DSBI), generating a transgenic plant line, performing a transient assay to analyze the functionality of the transgenic enzyme, crossing the plant line with a line containing a nucleic acid sequence to be excised and performing an immature embryo conversion or a tissue culture regeneration through callus formation. The method can also be reversed, which means that a plant cell is transformed with a construct encoding a nucleic acid sequence to be excised, and the crossing is performed witha plant line containing a DSBI. As an alternative to the crossing step, a re-transformation of a transgenic plant line with a second construct can also be performed. The invention is also directed to a plant obtained by this method, or progeny, propagation material, part, tissue, cell or cell culture, derived from such a plant. Finally, the invention relates to the use of a plant or progeny, propagation material, part, tissue, cell or cell culture, derived from this method, as aliment, fodder or seeds or for the production of pharmaceuticals or chemicals.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
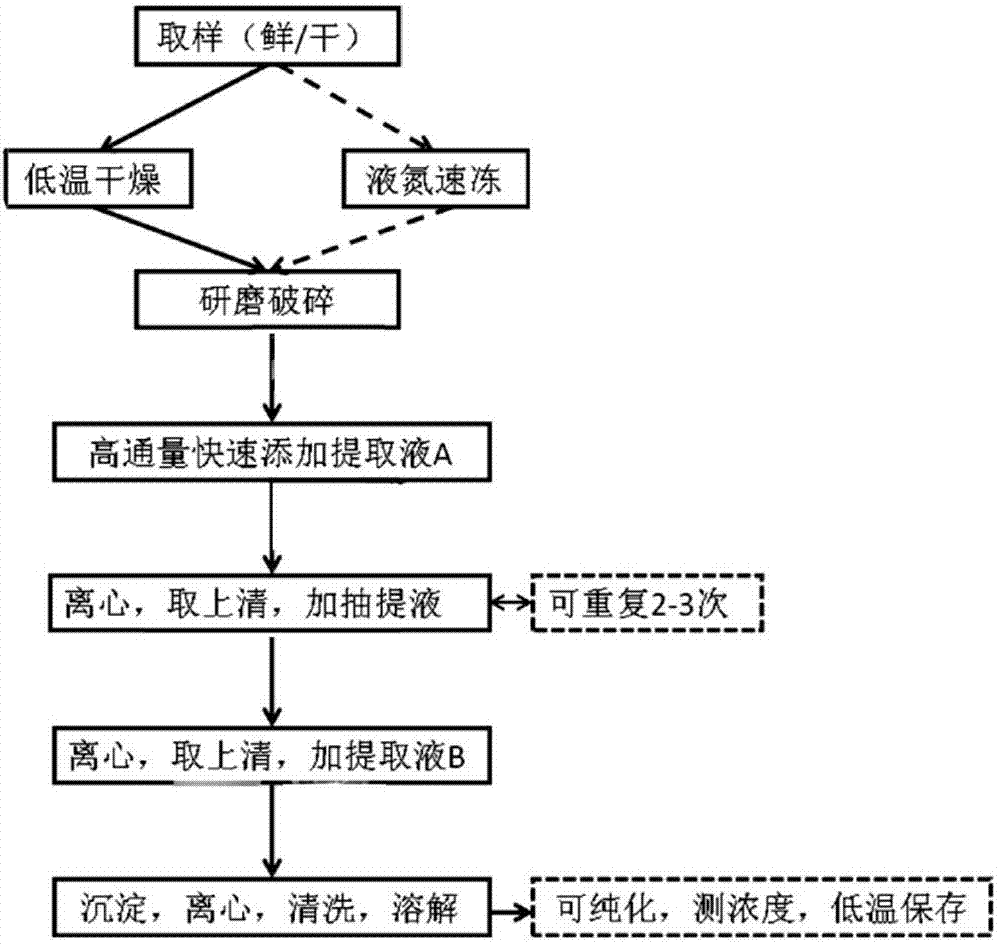
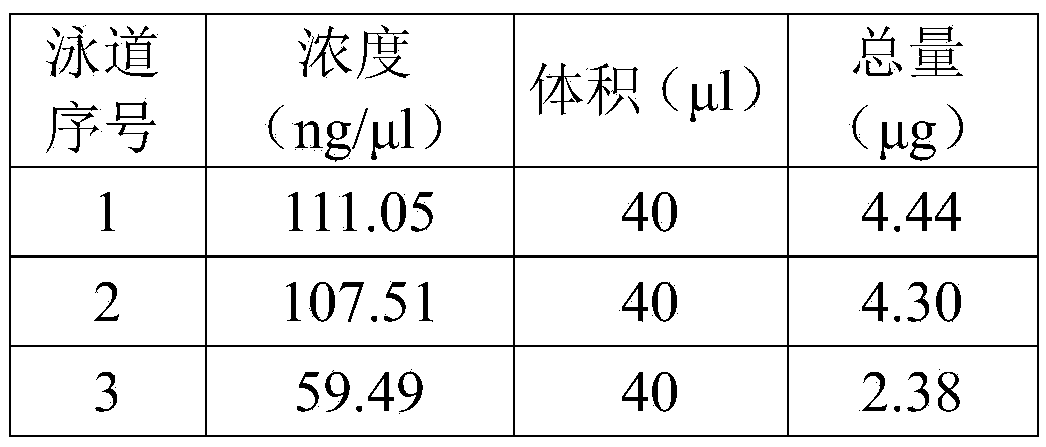
Method for rapidly extracting DNA (Desoxvribose Nucleic Acid) of plant genome with high flux
The invention discloses a method for rapidly extracting DNA (Desoxvribose Nucleic Acid) of a plant genome with a high flux. The method comprises the following steps: respectively putting plant materials to be extracted in hole plates 96; then putting a steel ball in each hole and performing liquid nitrogen flash freezing on each hole; fully grinding the plant materials to be extracted in the hole plates 96 by virtue of a crusher; and finally, extracting the DNA from the grinding powder via an improved NaOH, CTAB (Cetyltrimethyl Ammonium Bromide) or SDS (Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate) method, wherein various reagents are all added by utilizing channels 96 of a Zephyr MBW nucleic acid workstation during the DNA extracting process. The method has the advantages of high flux, low cost, rapid speed and the like. In addition, the extraction method is simple; and the obtained DNA of the plant genome is high purity and good in stability.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Extracting method of polysaccharide and polyphenol plant genomes
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology and discloses an extracting method of polysaccharide and polyphenol plant genomes. The method includes: grinding plant materials, then adding a nucleic acid separation buffer solution and 2-mercaptoethanol, well mixing, and placing into water bath; centrifuging in a centrifuge, and then discarding supernate; adding a 1x PBS solution, well mixing on a grinding instrument in an oscillation manner, and discarding supernate after centrifuging; adding preheated 3x CTAB lysate into sediment, well mixing, and performing splitting decomposition under water bath; adding equal-volume phenol / chloroform / isoamyl alcohol mixed liquor, well mixing and centrifuging; taking supernate, adding equal-volume chloroform / isoamyl alcohol mixed liquor, well mixing and centrifuging; taking supernate, adding NaCl and icy isopropanol, well mixing, and precipitating for 1-3 hours; taking out and centrifuging, then washing sediment with ethanol, and adding TE for dissolving after air drying so as to complete the extracting process. The extracting method has the advantages that polysaccharides and polyphenols can be removed effectively, the influence of the polysaccharides and polyphenols on nucleic acid extraction is reduced, and DNA quality and concentration are increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI PASSION BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
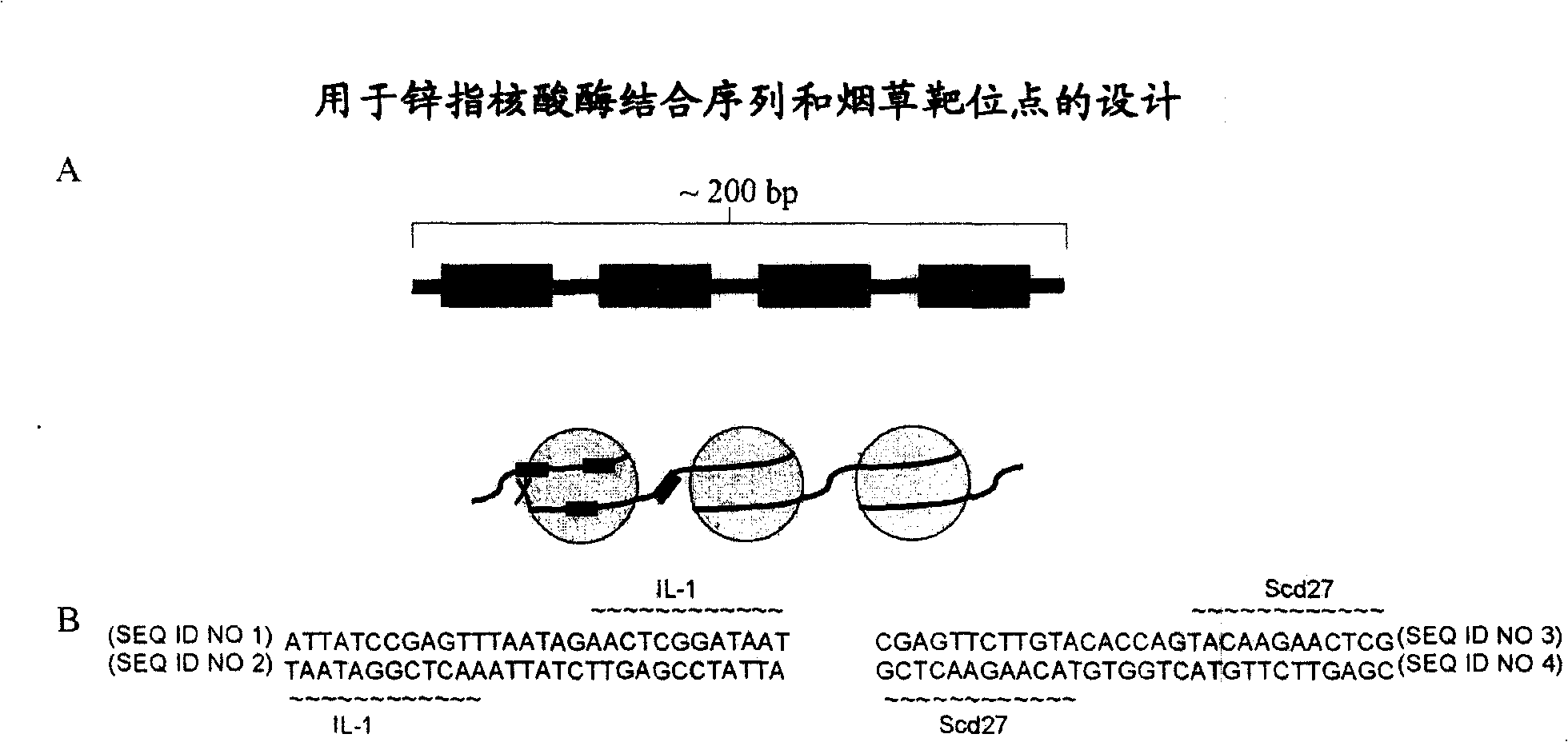
Zinc finger nuclease-mediated homologous recombination
The present invention discloses methods and compositions for targeted integration of an exogenous sequence into a predetermined target site in a plant genome.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC +1
Method for site-directed replacement of plant genome
The present invention provides a method for site-directed replacement of a plant genome, and particularly relates to a nucleic acid construct. The nucleic acid construct of a specific structure is adopted to successfully achieve sgRNA-directed base site-directed mutagenesis in plants for the first time (for example, T mutates into C, or A mutates into G).
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Method Of Excising A Nucleic Acid Sequence From A Plant Genome
The present invention relates to a method for excising a nucleic acid sequence from the genome of a plant or a plant cell. This method is based on the steps of transforming a plant cell with a construct encoding a DNA double strand break inducing enzyme (DSBI), generating a transgenic plant line, performing a transient assay to analyze the functionality of the transgenic enzyme, crossing the plant line with a line containing a nucleic acid sequence to be excised and performing an immature embryo conversion or a tissue culture regeneration through callus formation. The method can also be reversed, which means that a plant cell is transformed with a construct encoding a nucleic acid sequence to be excised, and the crossing is performed with a plant line containing a DSBI. As an alternative to the crossing step, a re-transformation of a transgenic plant line with a second construct can also be performed. The invention is also directed to a plant obtained by this method, or progeny, propagation material, part, tissue, cell or cell culture, derived from such a plant. Finally, the invention relates to the use of a plant or progeny, propagation material, part, tissue, cell or cell culture, derived from this method, as aliment, fodder or seeds or for the production of pharmaceuticals or chemicals.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
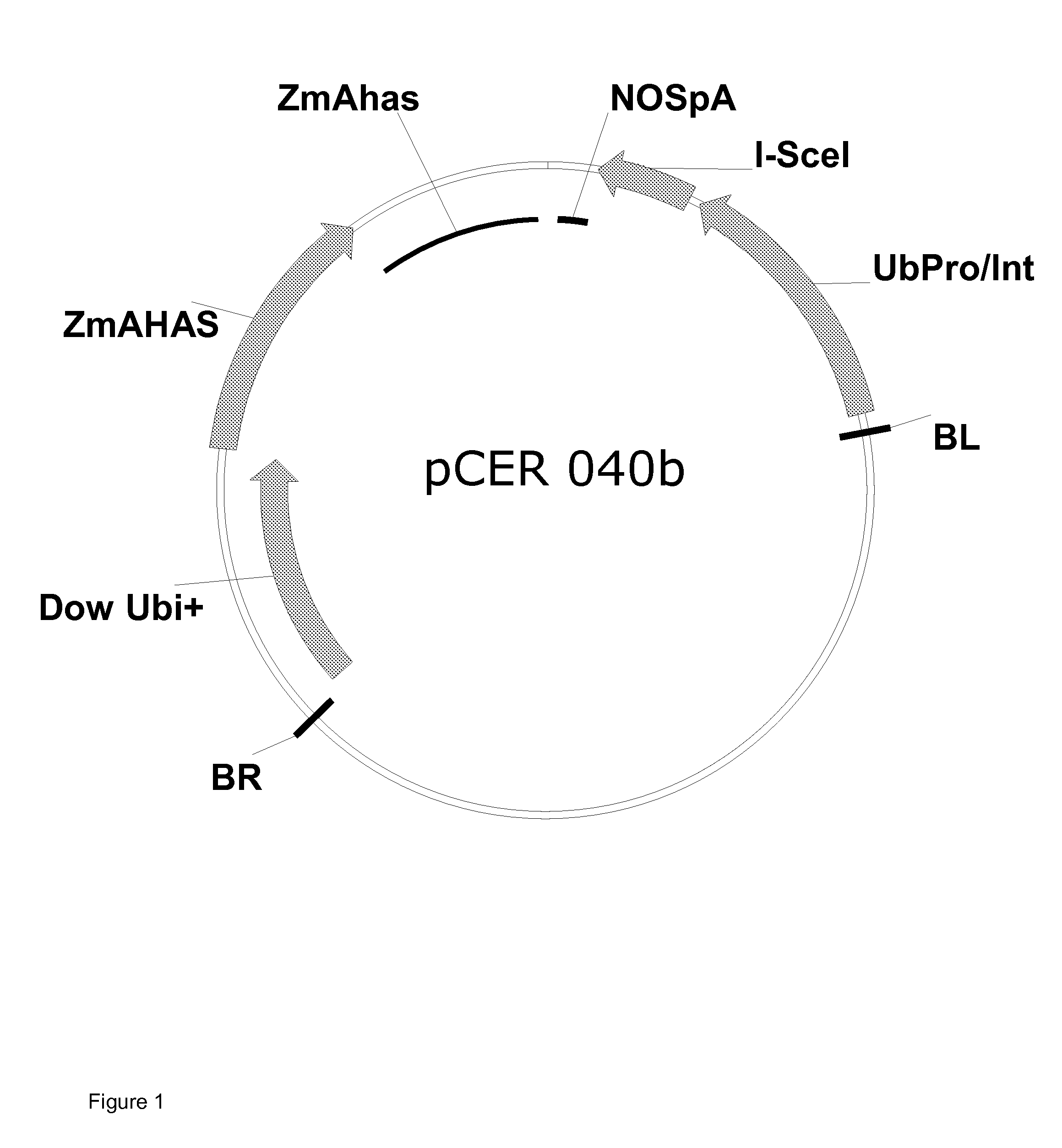
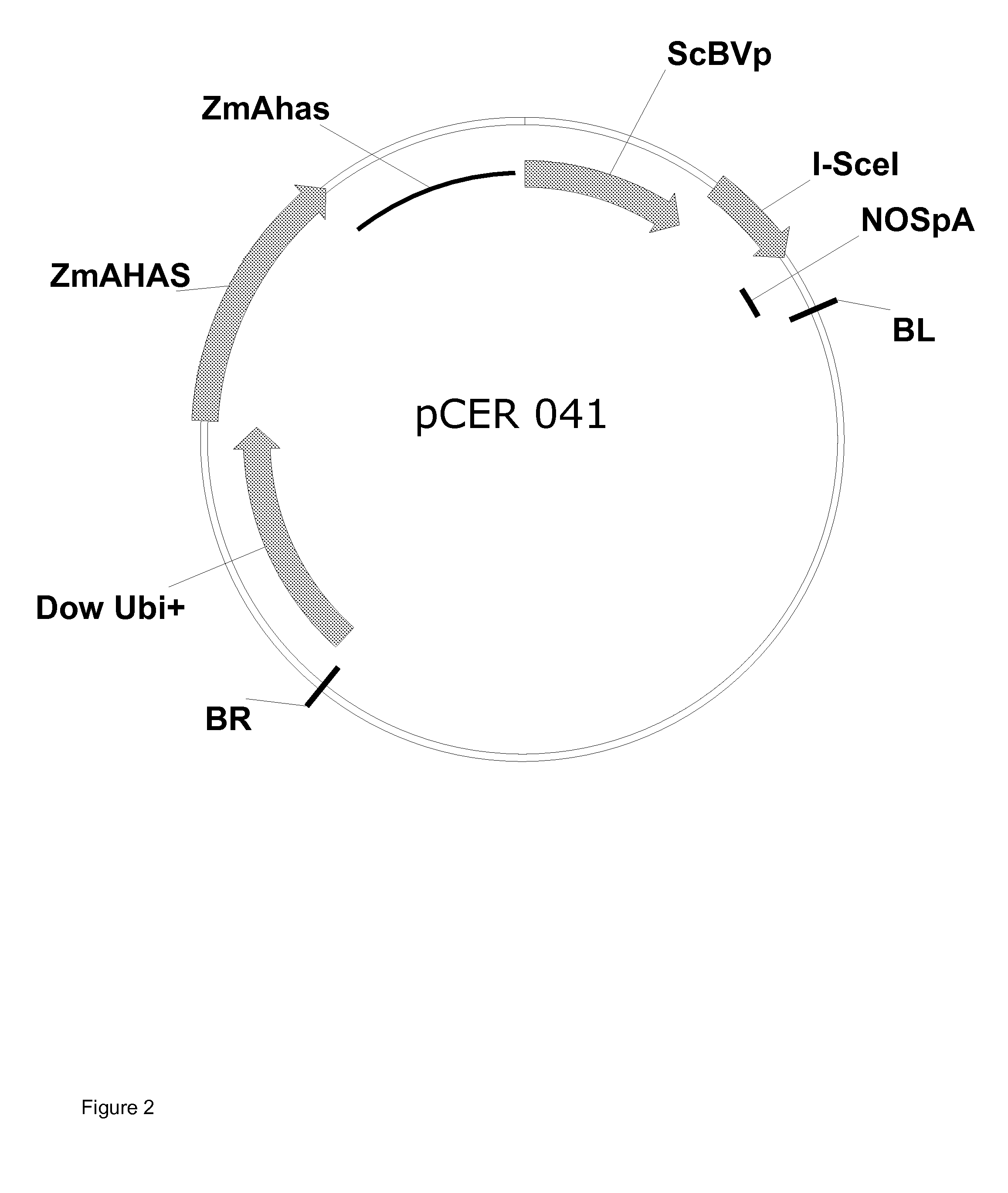
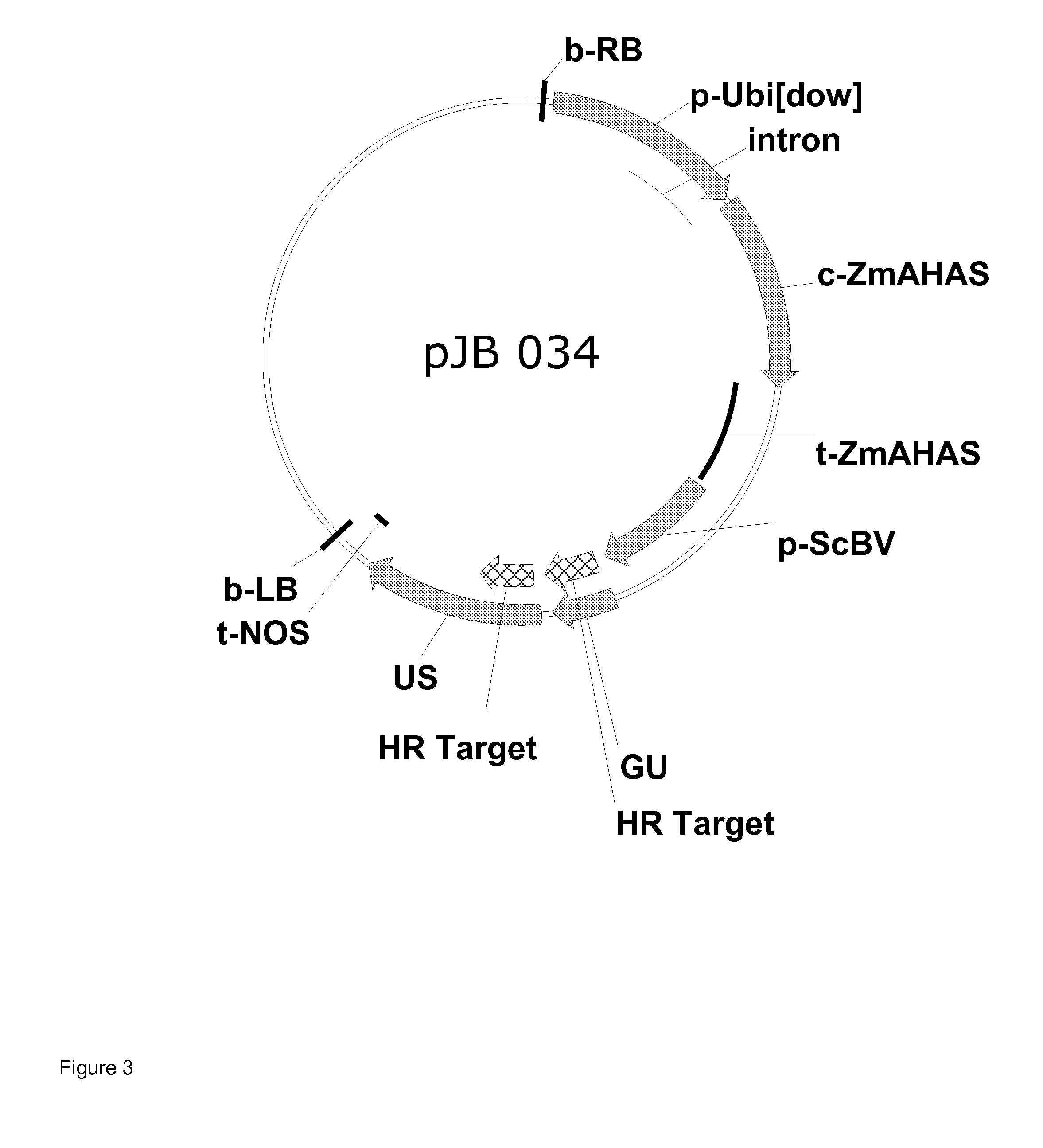
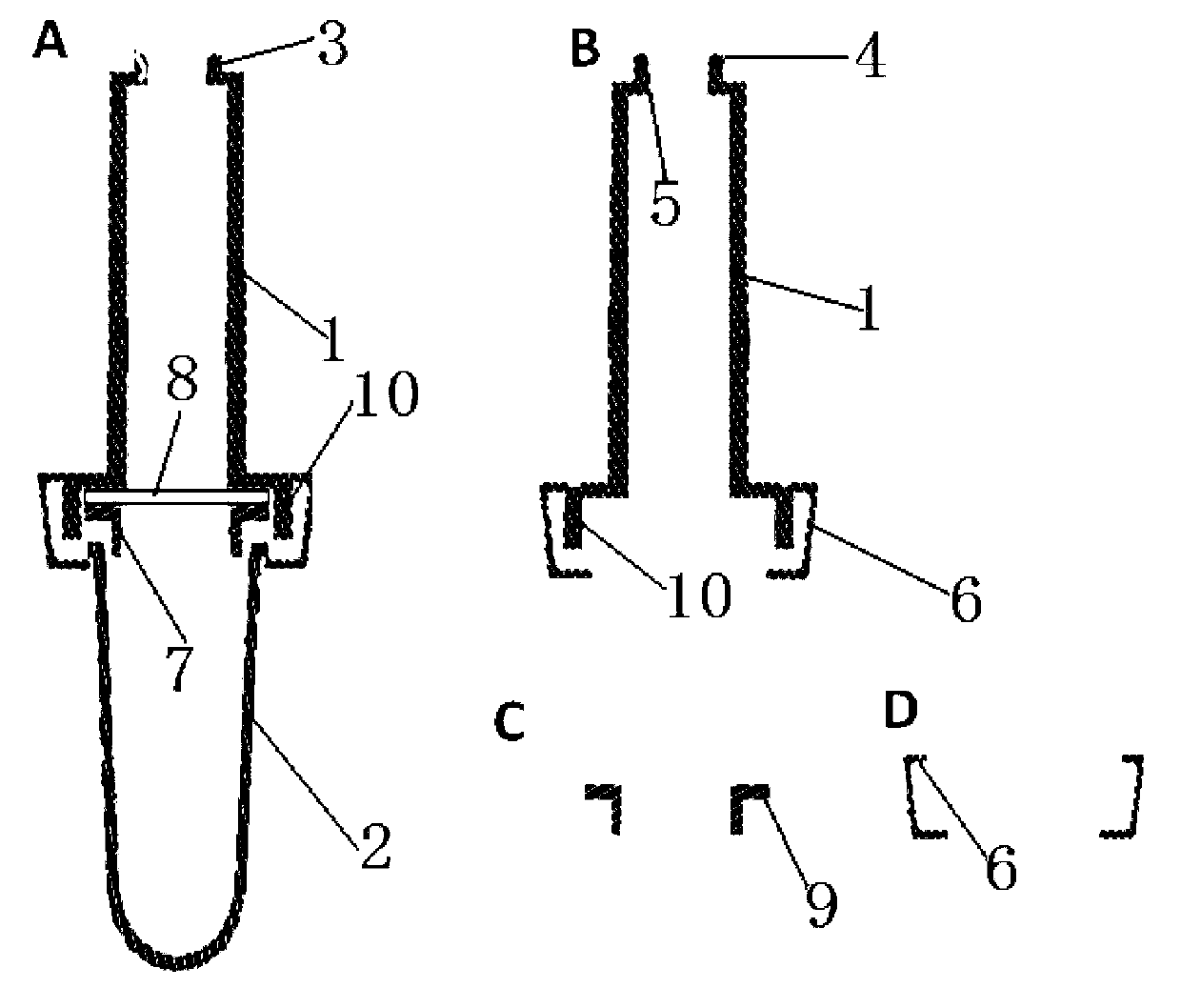
Plant genomes deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) quick extraction device and testing method thereof
InactiveCN103131628ANo dependencyAchieve the purpose of extractionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsInjection portEngineering
The invention relates to a plant genomes deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) quick extraction device and a testing method thereof. The plant genomes DNA quick extraction device is composed of a plurality of injectors with sponges on the bottoms, extraction pillars, and a plurality of centrifugal tubes, wherein the upper end portion of each of the extraction pillars can be connected with an injection port of each of the injectors in a sealing mode, the lower end portion of each of the extraction pillars can be connected with each of the centrifugal tubes, a loading seal cover is connected on the end portion of each of the extraction pillars, the loading seal cover is loaded with a silica film and is embedded in the inner side of the lower end portion of each of the extraction pillars in a clamping mode, and a through hole is formed in the center of the loading seal cover. According to the plant genomes DNA quick extraction device and the testing method thereof, compared with the prior art, large instruments of a centrifugal machine and the like are replaced by an air pressure method, the silica film is used for combining nucleic acid molecules, the plant genomes DNA quick extraction device is simple and effective, an extraction process is simple and convenient without any dependency of valuable instruments, testing time is short, the testing method is high in sensitivity, and the problem of quick testing of transgenetic products on site is resolved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com