Site-specific modification method for plant genome
A plant genome, site-specific modification technology, applied in the field of plant genome site-specific modification, can solve problems such as successful development and application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
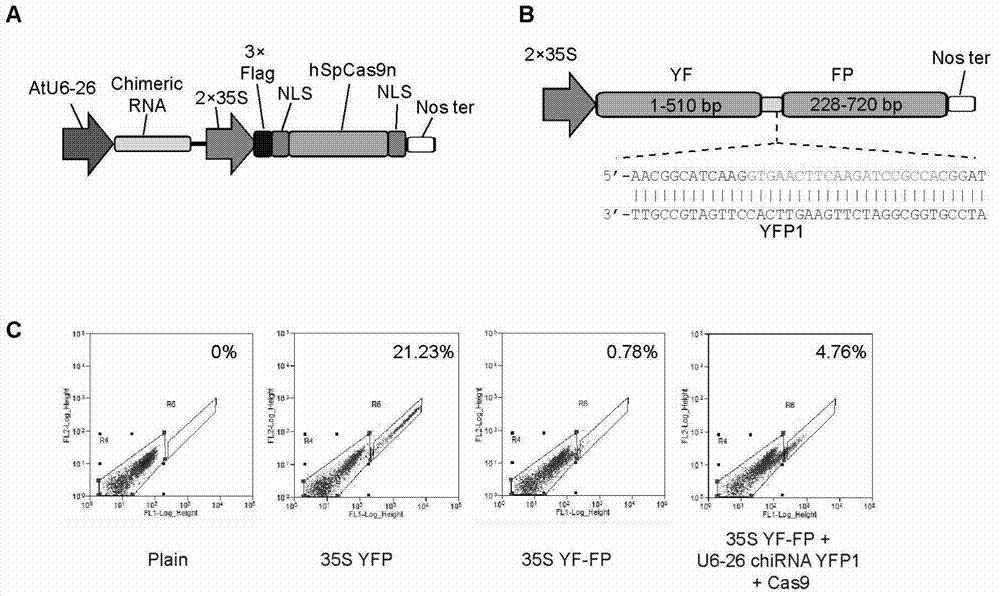
[0236] CRISPR / Cas9 using Streptococcus pyogenes SF370 causes site-directed DNA double-strand breaks in Arabidopsis protoplasts.
[0237] The result is as figure 1 shown. The oligos for constructing YFP1 target site chiRNA are YF-FP F and YF-FP R in Table 1. The results showed that when the YF-FP reporter gene and CRISPR / Cas vector were co-transfected into Arabidopsis protoplasts, a strong YFP signal could be obtained, and the gene repair efficiency based on homologous recombination was as high as 18.8% [(4.76%-0.78% ) / 21.23%]. This shows that the constructed CRISPR / Cas system functions and can efficiently cut DNA sequences in plant cells to generate double-strand breaks.
Embodiment 2
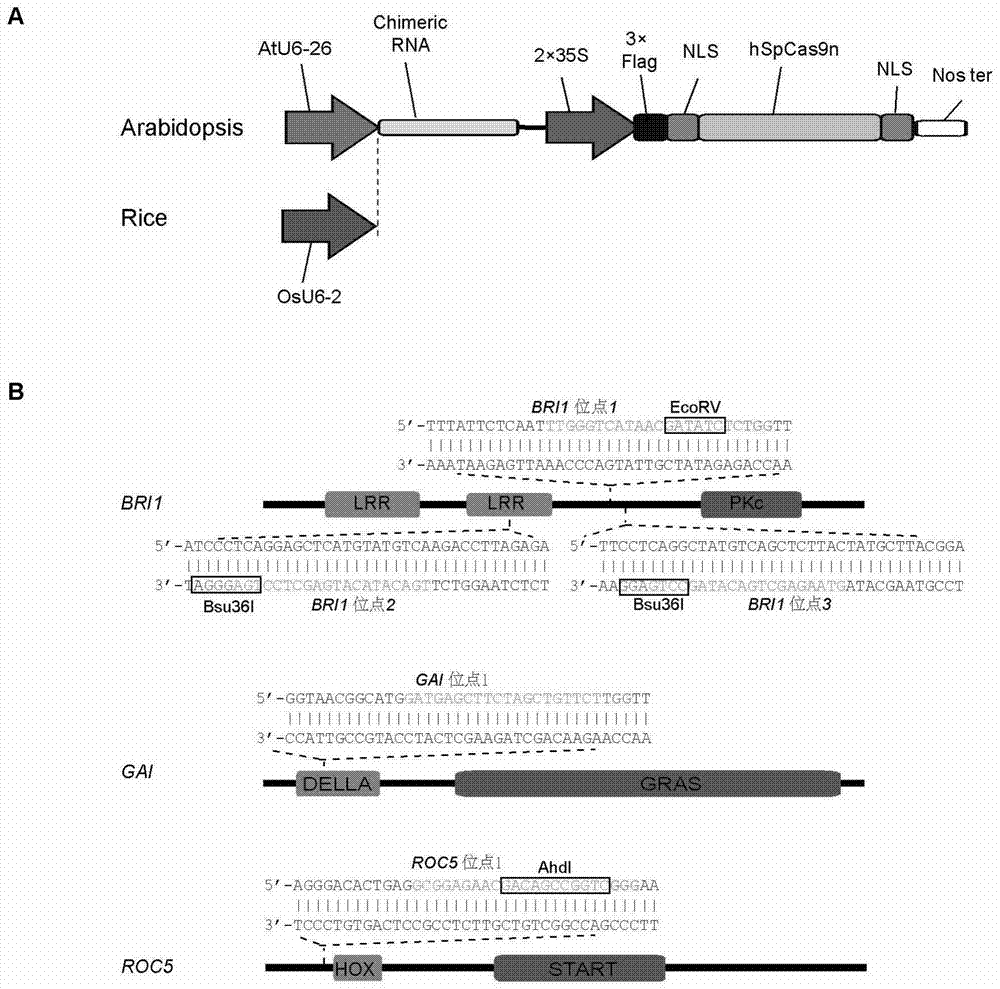
[0239] A single binary vector for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis and rice was constructed to express chiRNA and hSpCas9, and two Arabidopsis genes BRI1 and GAI and one rice gene ROC5 were selected to design target sites.
[0240] The result is as figure 2 shown. The Cas9 expression cassette of the vector is identical. For the chiRNA expression cassette, the AtU6-26 promoter was used for Arabidopsis transformation, and the OsU6-2 promoter was used for rice transformation. The oligos corresponding to the chiRNA construction of BRI1 sites 1, 2, and 3 are BRI1chiRNA1F and BRI1chiRNA1R, BRI1chiRNA2F and BRI1chiRNA2R, BRI1chiRNA3F and BRI1chiRNA3R in Table 1, respectively. The oligos corresponding to the chiRNA construction of GAI site 1 are GAI chiRNA1F and GAI chiRNA1R in Table 1. The oligos corresponding to the chiRNA construction of ROC5 site 1 are ROC5chiRNA1F and ROC5chiRNA1R in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
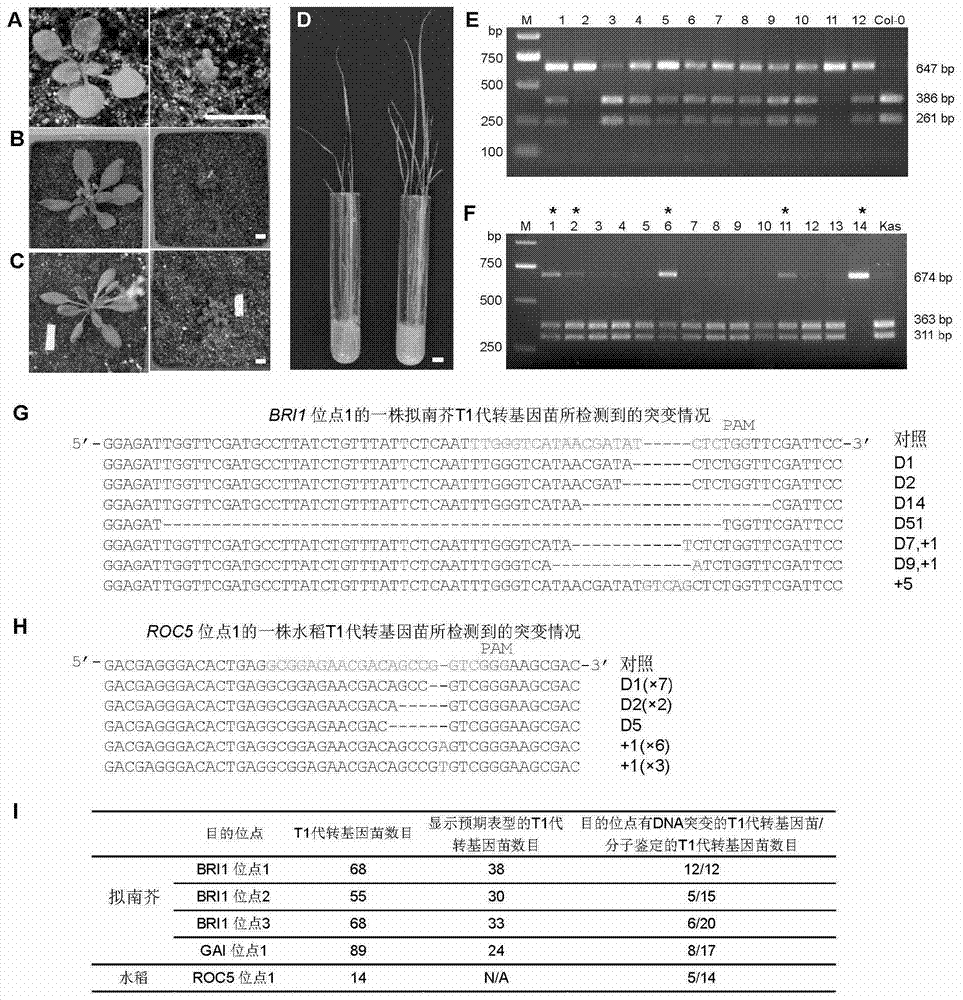
[0242] Generation of stable transgenic plants in Arabidopsis and rice via target loci.
[0243] The result is as image 3 shown. The PCR primers for RFLP identification of BRI1 locus 1 and 3 transgenic plants are BRI1 1F and BRI1 1R in Table 1, and the PCR primers for RFLP identification of BRI1 locus 2 transgenic plants are BRI1 2F and BRI1 2R in Table 1. The PCR primers for RFLP identification of transgenic plants at GAI locus 1 are GAI F and GAI R in Table 1. The PCR primers for RFLP identification of transgenic plants at ROC5 locus 1 are ROC5F and ROC5R in Table 1.
[0244] The results showed that a large proportion of Arabidopsis transgenic T1 plants showed phenotypes similar to the homozygous mutation of the target gene locus in the early growth stage. RFLP restriction analysis showed that the PCR products at the target sites in some transgenic plants had obvious fragments that could not be digested, indicating that the natural restriction sites at the target sites in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com