Method for site-directed replacement of plant genome
A plant and plant cell technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of single mutation, low efficiency, and increased risk of gene editing.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0195] Example 1 Testing the editing effect of ABE7-10 in rice
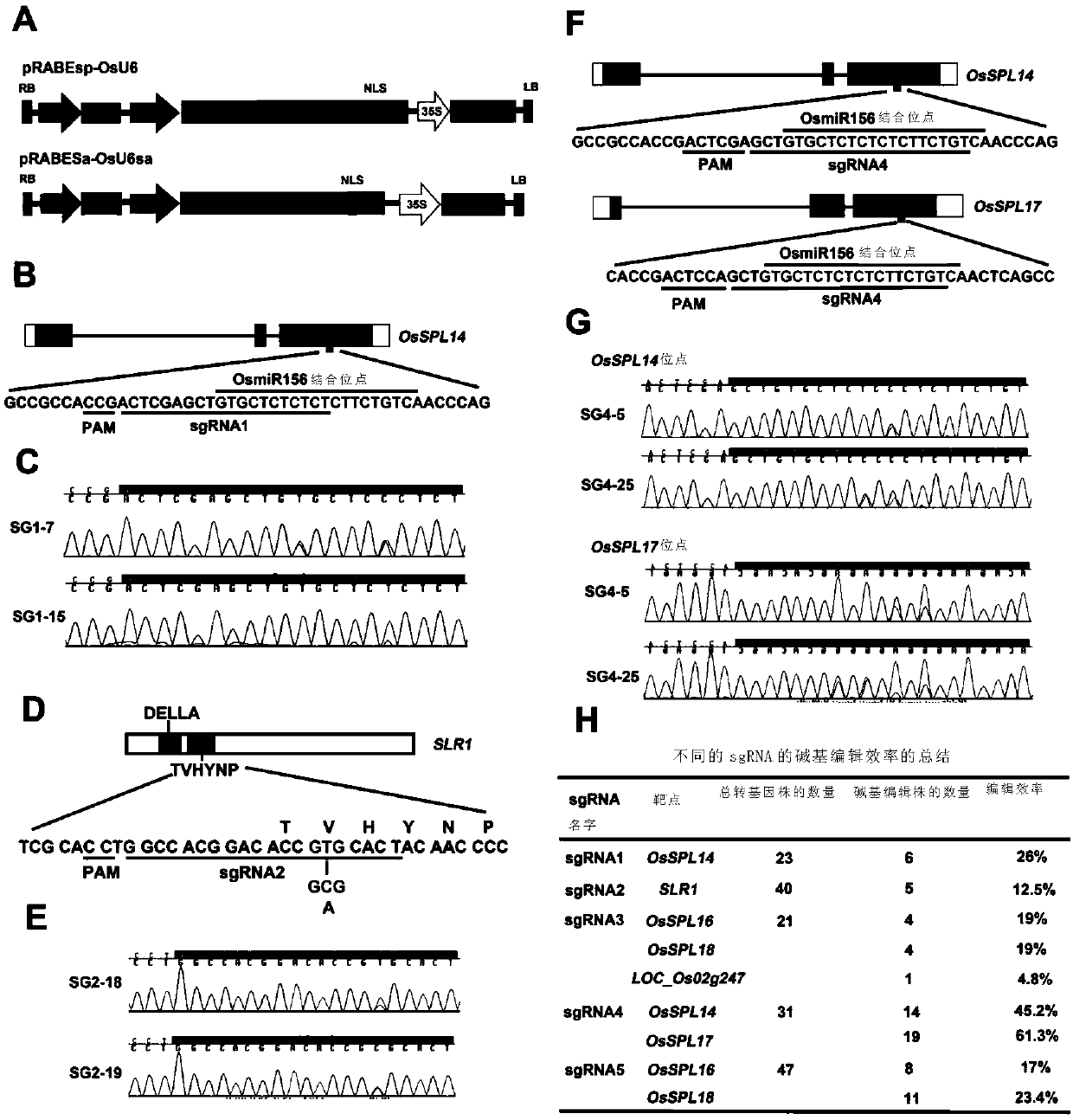
[0196]In this example, according to the general method, the present invention synthesized the coding sequences of wild-type ecTadA and its mutant form ecTadA*7.10. They were then linked together by using a linker coding sequence encoding 32 amino acid residues. Next, the coding sequence of the recombinant protein was fused to the N-terminus of the Cas9(D10A) nickase coding sequence with the same linker. Finally, the coding sequence of the VirD2 nuclear localization signal was ligated to the C-terminus of the Cas9(D10A) nickase to form ABE7-10. ABE7-10 was then cloned into a binary vector under the control of the maize ubiquitin promoter, and the sgRNA was driven by the rice U6 promoter to form the vector pRABEsp-OsU6 ( figure 1 A).
[0197] To test the editing effect of ABE7-10 in rice, we selected IPA1 (OsSPL14), which regulates the ideal plant type of rice, as the target gene ( figure 1 B).
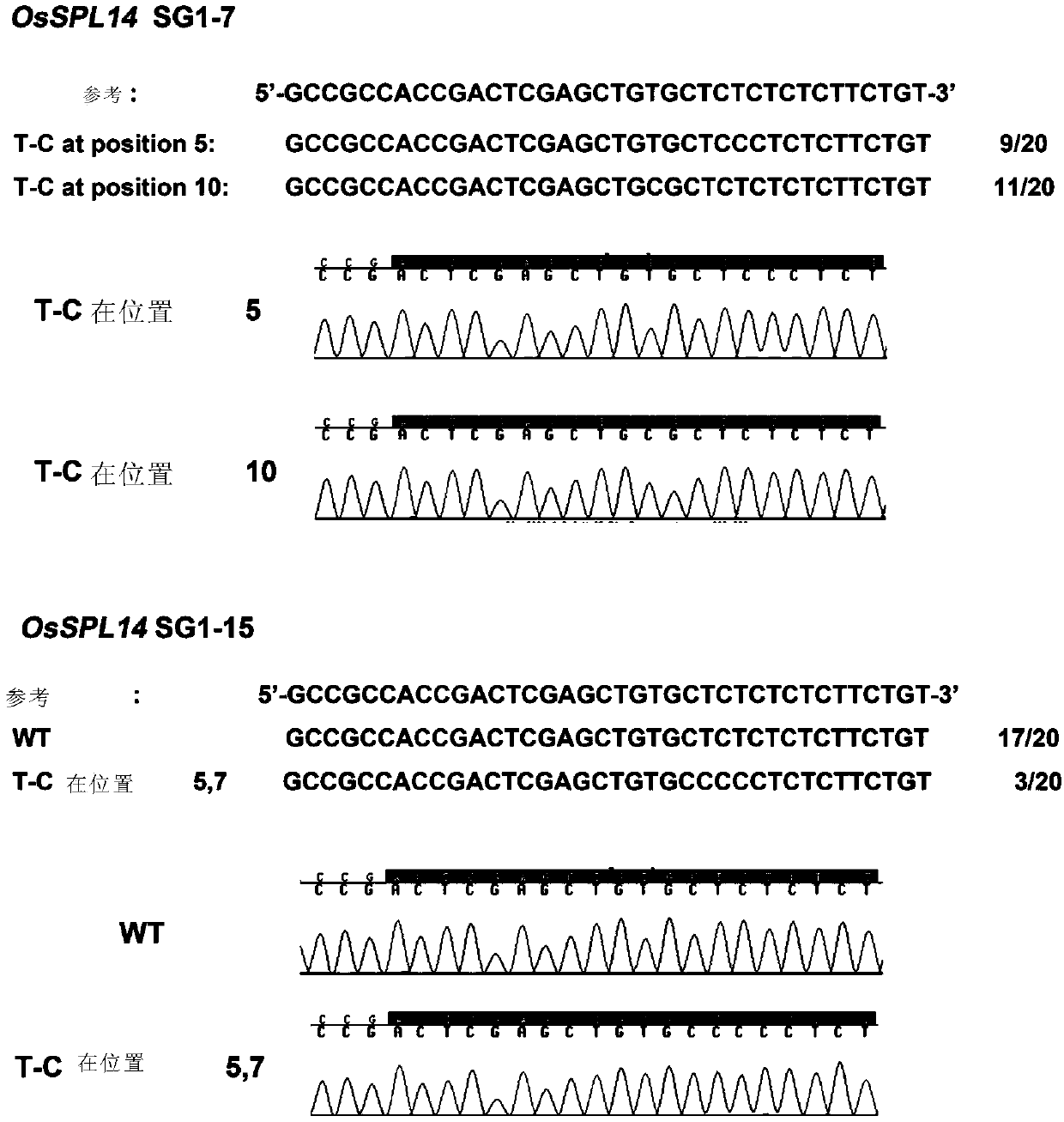
[0198] The pr...
Embodiment 2
[0212] Example 2 Testing the editing ability of the adenine base editing system in rice
[0213] In order to further test the editing ability of the adenine base editing system in rice, further experiments were performed on the SLR1 locus. SLR1 encodes a DELLA protein in rice that acts as a repressor in the GA signaling pathway.
[0214] The present invention designs an sgRNA (sgRNA2) targeting the TVHYNP domain of SLR1. The primers corresponding to the sgRNA2 vector construction are sgRNA2F and sgRNA2R in Table 3. The T-C base substitution at position 6 of Protospacer can lead to the V92A substitution in the TVHYNP motif ( figure 1 D).
[0215] From the obtained 40 transgenic lines, 5 lines had the expected T-C substitution at position 6 of the protospacer ( figure 1 E, 1H). Target region amplification primers are SLR-seq-F and SLR-seq-R in Table 3. Since there is only one editable T in the base editing window of SLR1, no other mutant forms were found in the target locus...
Embodiment 3
[0216] Example 3 Detection of whether the base editing system of the present invention can simultaneously edit two or more sites in the rice genome
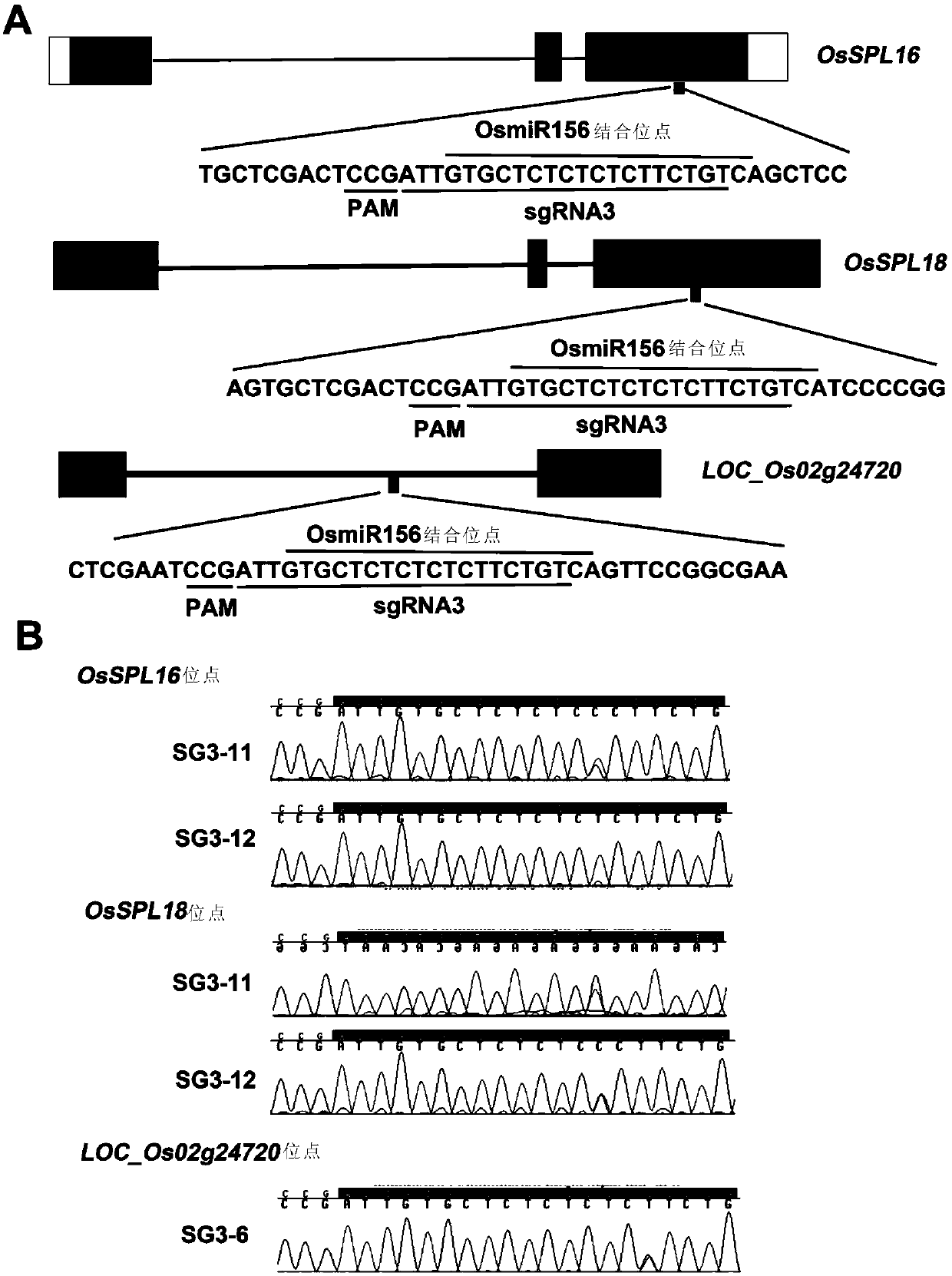
[0217] In order to detect whether the base editing system of the present invention can simultaneously edit two or more sites in the rice genome, a third sgRNA (sgRNAs3) was designed to simultaneously target the OsmiR156 binding site of OsSPL16 and OsSPL18 ( image 3 , A and B). The primers corresponding to the sgRNA3 vector construction are sgRNA3F and sgRNA3R in Table 3. In addition, an off-target site with 100% match to the sgRNA3 sequence was found in the intron of the LOC_Os02g24720 gene ( image 3 , A and B). Therefore, sgRNA3 can simultaneously target three sites in the rice genome. The present invention has carried out genotype identification on these three target sites in 21 transgenic lines. Four transgenic lines each displayed T-C substitutions in the OsSPL16 and OsSPL18 targeted regions. However, only one line con...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com