Mutation penicillin G acylase, recombinant expression plasmid and transformation engineering strains thereof
A technology of acylase and penicillin, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of reduction of antibiotics, low ratio, low conversion rate of mother nucleus, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1 , Determine the sequence of the site-directed mutation gene
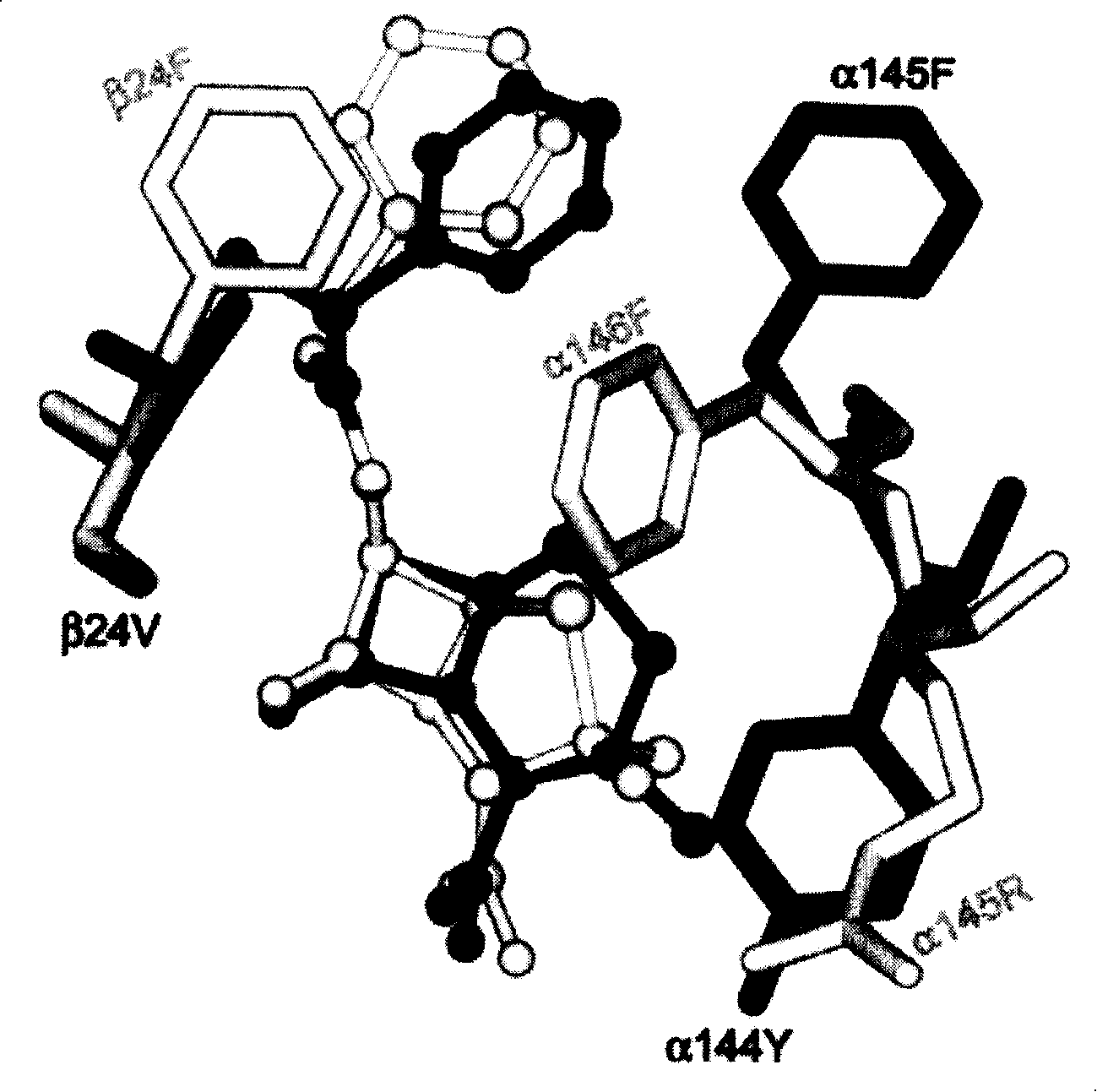
[0044] 1.1. Structural modeling of BmPGA-ligand complex
[0045] With the structure of penicillin G acylase derived from Escherichia coli (E.coli) and Presdenia (Providencia rettgeri) as template, utilize the Swiss-Model model (Kaplan and Littlejohn, Swiss-PDB Viewer, 2001, http: / / www.expasy.org / spdbv / ), to model PGA (BmPGA) derived from Bacillus megaterium; then using the modeled complex structure of E.coli PGA and penicillin G, by overlaying (PG) The complex structure of BmPGA-PG was obtained.
[0046] 1.2. Selection of mutation sites
[0047] BmPGA- The structure of the PG complex was energy-optimized to select suitable mutation sites and mutation directions.
[0048] The results of modeling and optimization are as follows figure 1 shown, according to figure 1 As a result, it was determined that the site-directed mutation sites were: α144, α145 and β24, and the mutation direction was: th...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2 , Construction of mutant plasmids
[0050] 2.1. Primer design
[0051] According to the gene sequence (SEQ ID NO: 1) of PGA derived from Bacillus megaterium, and the selected mutation sites α144, α145, β24, the following 7 mutation primers were designed:
[0052] α144R: 5`-G AGA TTT ATG GAT AAT CAC CAG GAG TTA-3`;
[0053] α145Y: 5`-G TAT TAT ATG GAT AAT CAC CAG GAG TTA-3`;
[0054] α145A: 5`-G TAT GCT ATG GAT AAT CAC CAG GAG TTA-3`;
[0055] α145L:5`-G TAT CTT ATG GAT AAT CAC CAG GAG TTA-3`;
[0056] β24F2:5`-AA TTT GGT TTT GTT GCT CCT GGA TTT-3`;
[0057] #145U:5`-GT CAT CGA TAC CAT ATA AAC ACG GAC A-3`;
[0058] (Cla I)
[0059] β24F1:5`-G GGG CCC ACT GAA TAA TAA AGC ATT T-3`;
[0060] (Apa I)
[0061]Wherein, the underline in the primer indicates the introduced mutant sequence. Primers α145U and β24F1 are synonymous mutations, which are used to identify whether the mutation is successful.
[0062] 2.2. Construction of recombi...
Embodiment 3
[0087] Example 3 , the acquisition of engineered bacteria
[0088] According to the operation manual of TAKARA company, the mutated four kinds of plasmids (BmPGA α144R, BmPGAα145Y, BmPGAβ24F, BmPGAα144R+β24F) were digested with EcoR I, extracted with phenol chloroform, precipitated with ethanol, and then self-cyclized with T4 ligase e , and then transform Bacillus subtilis competent cells WB600 to obtain genetically engineered strains BmPGAα144R / WB600, BmPGAα145Y / WB600, BmPGAβ24F / WB600 and BmPGAα144R+β24F / WB600, as follows:
[0089] 3.1. Circularization of mutant plasmids
[0090] 1) Under the condition of 37°C, in 100 μl EcoR I enzyme digestion system (30 μl to obtain the mutant plasmid, 1 / 10 volume of H buffer from TaKaRa Company, EcoR I enzyme (final concentration is 0.05U / μl), supplemented with double Distilled water into 100 μl), digested the mutant plasmid, ran agarose gel electrophoresis after 2 hours, and recovered a 6.3 kb fragment with the gel recovery kit of Huas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com