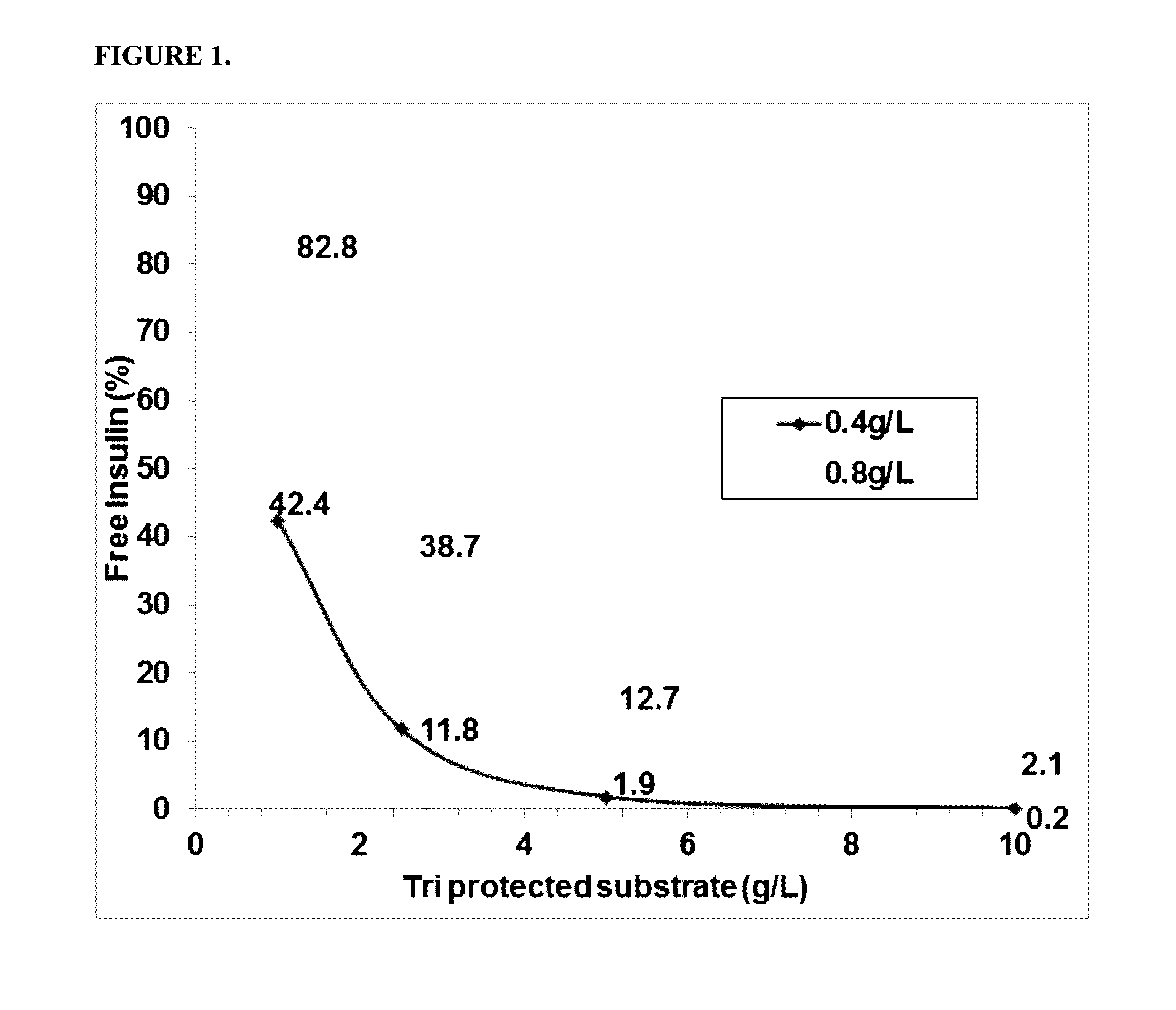
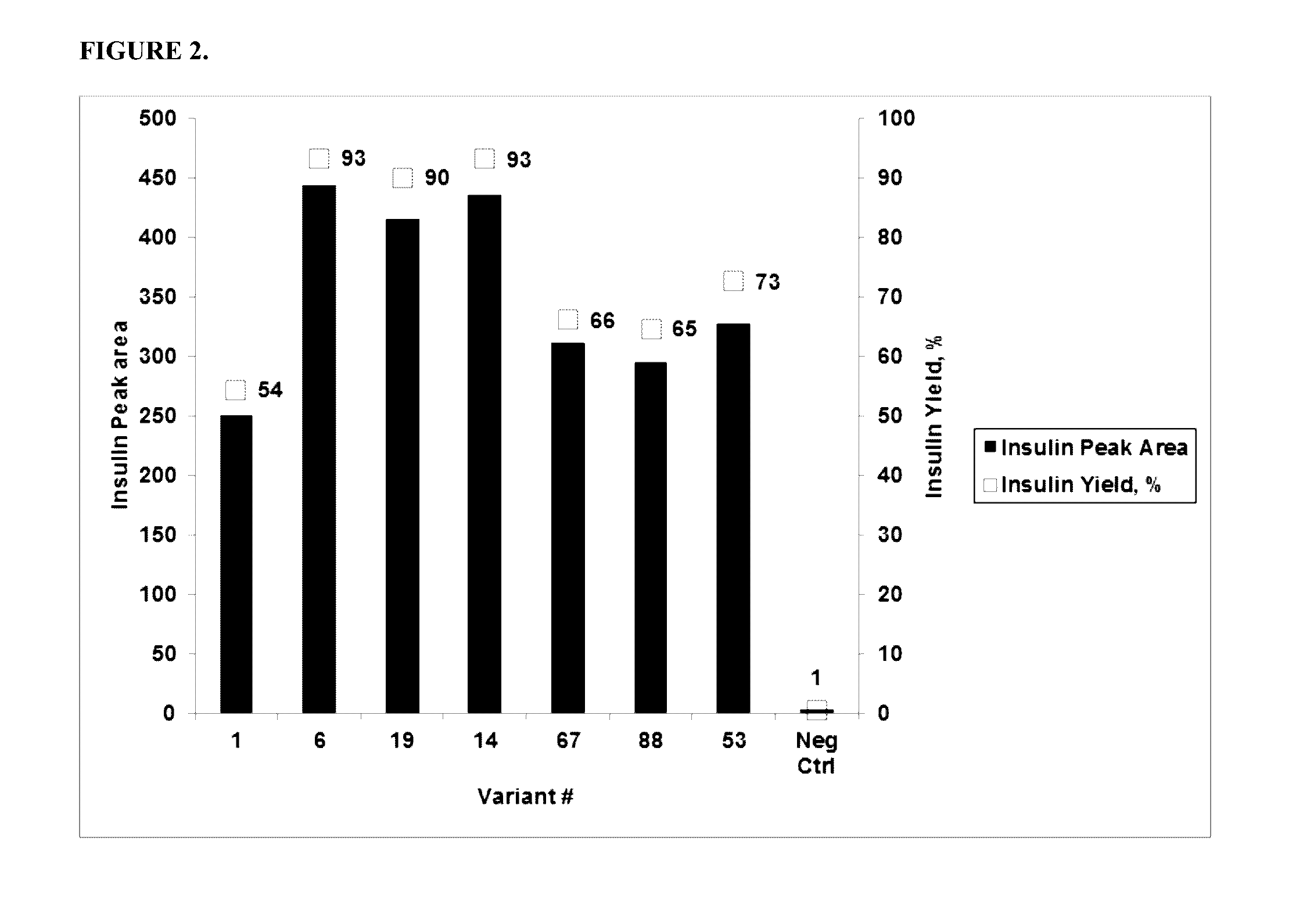
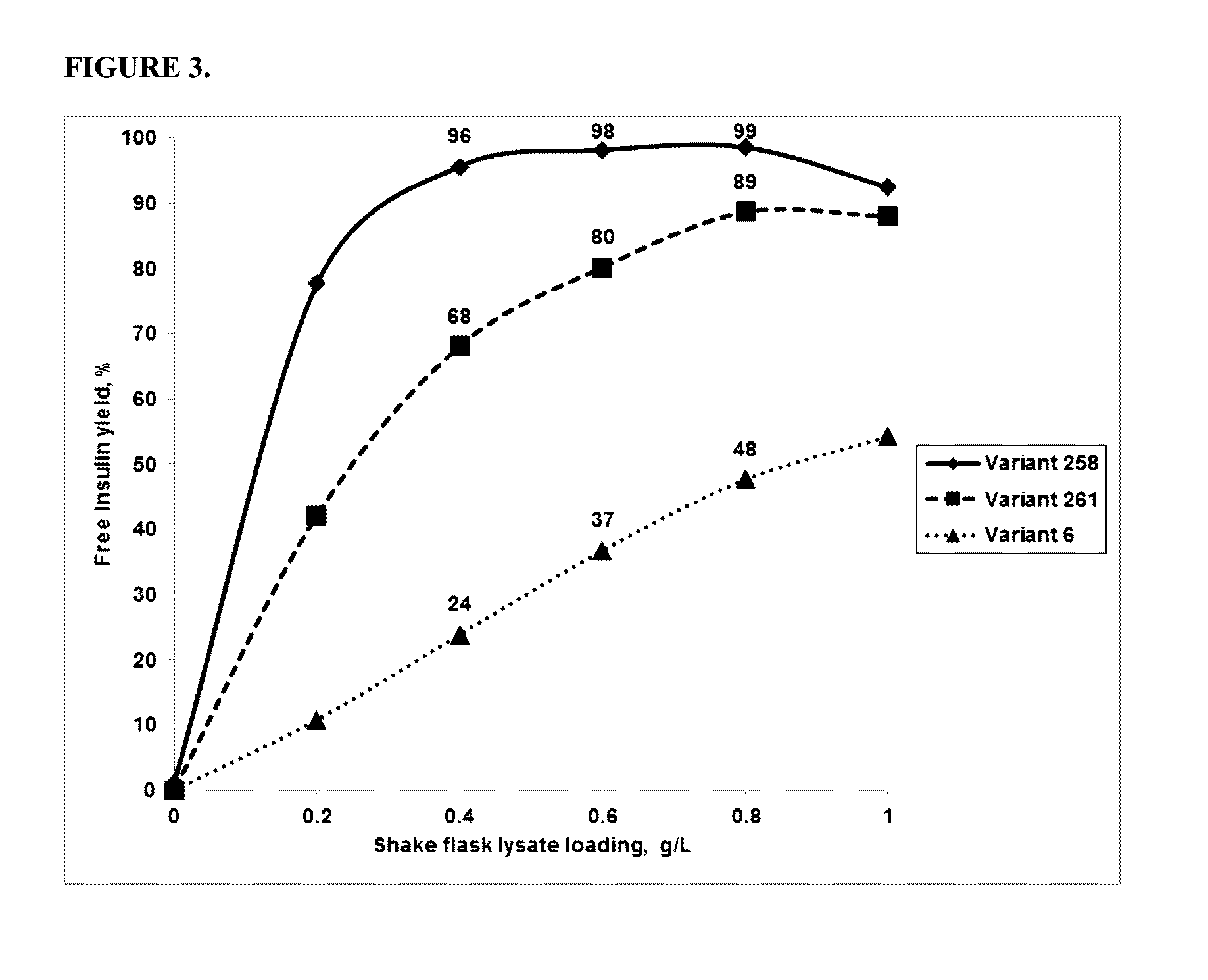
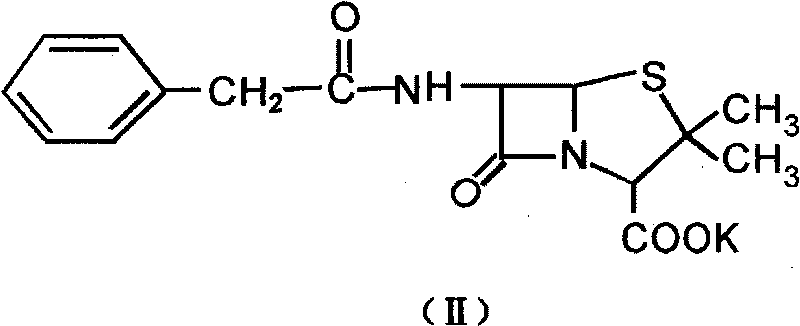
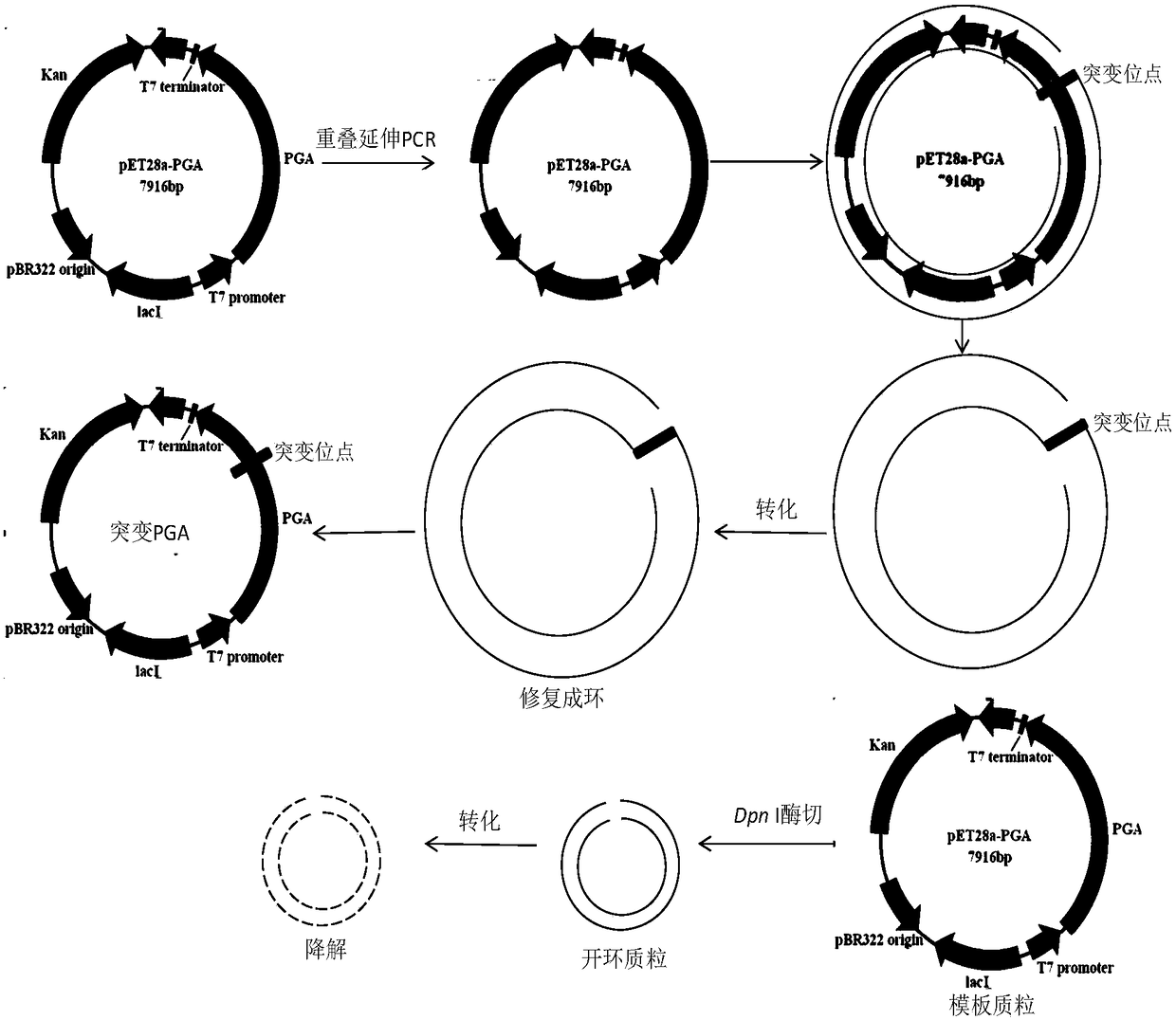
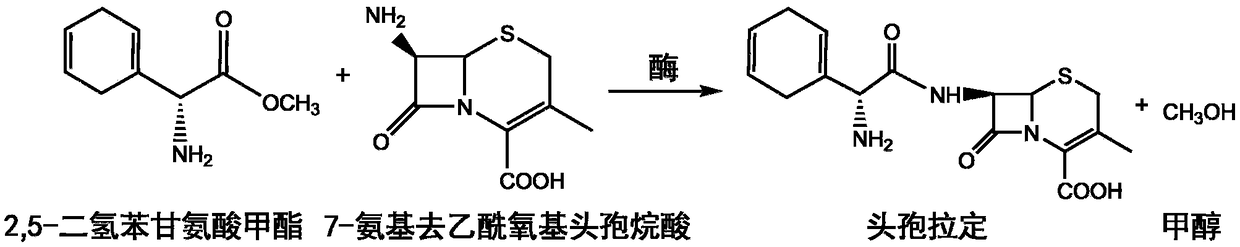
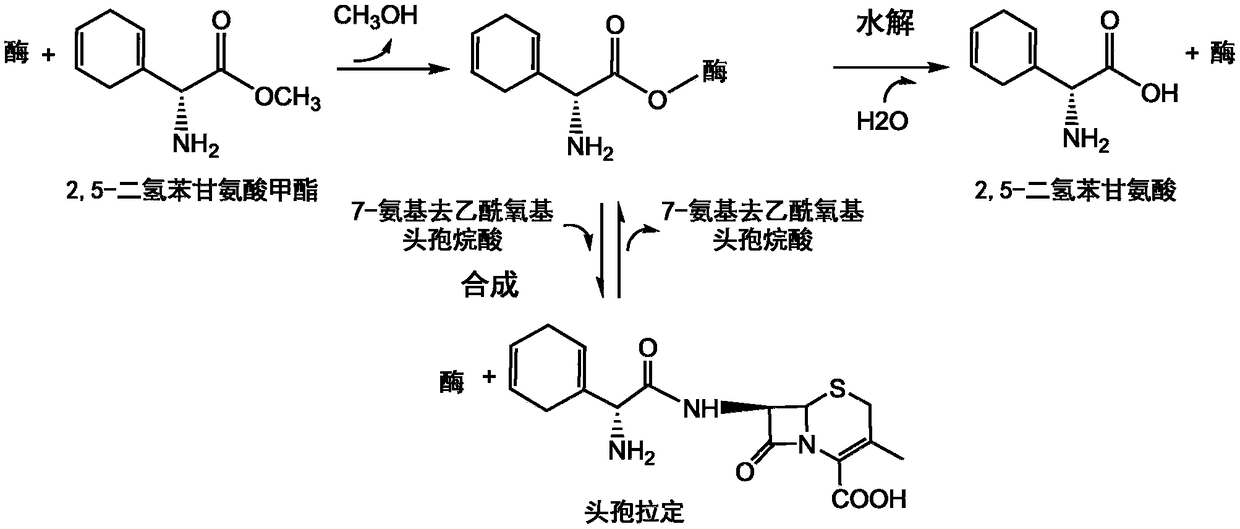
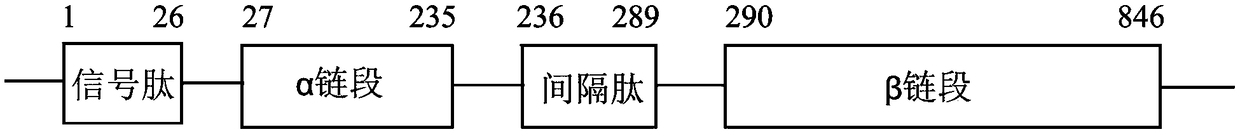
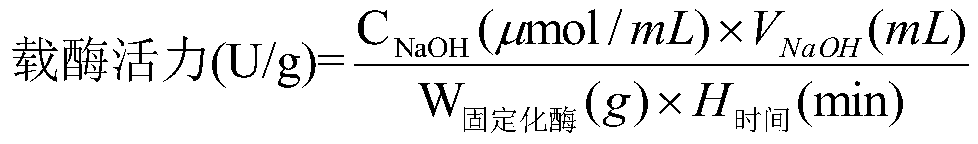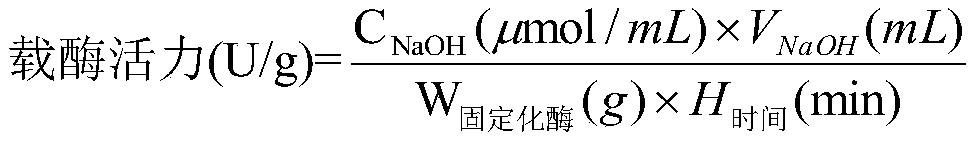Patents
Literature
69 results about "Penicillin G Acylase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
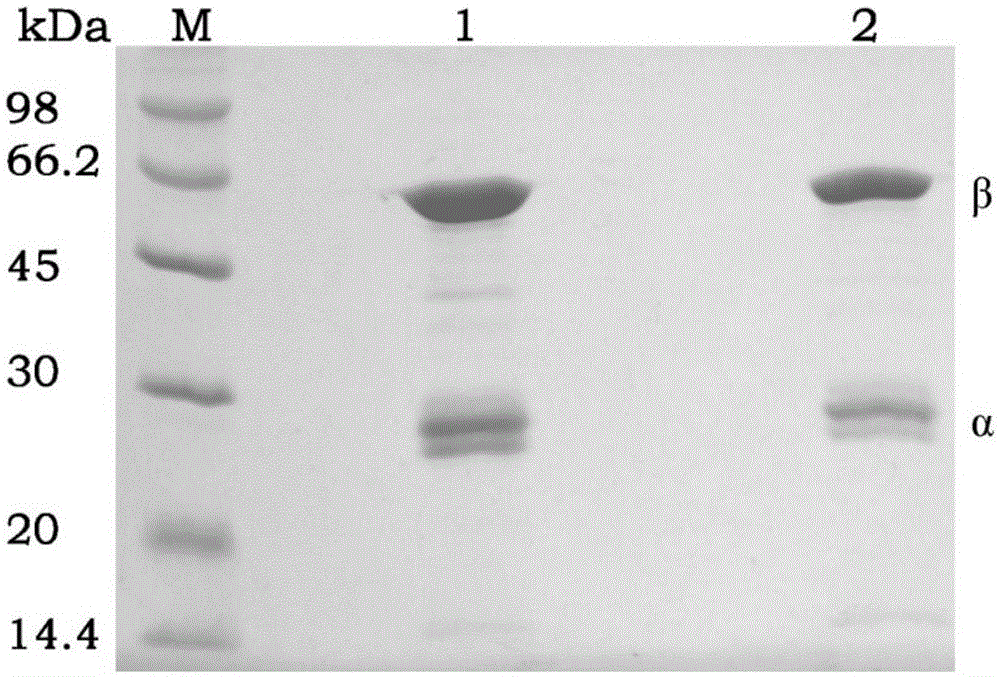
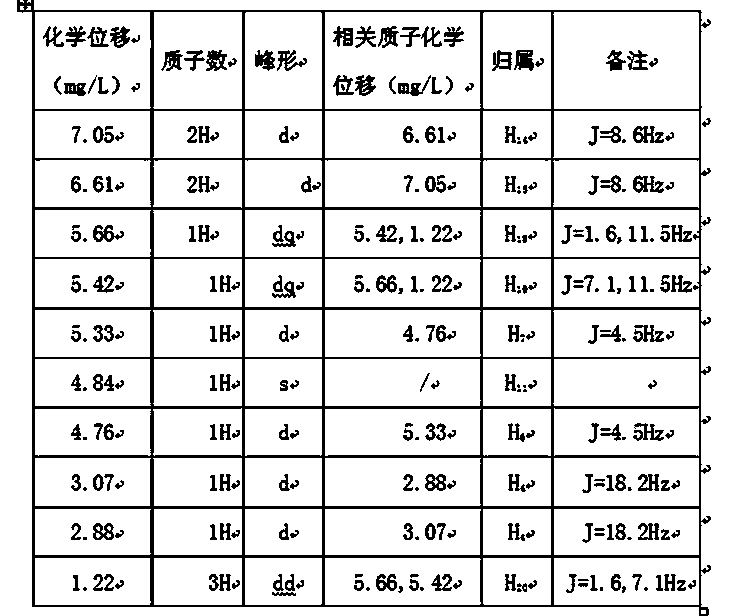
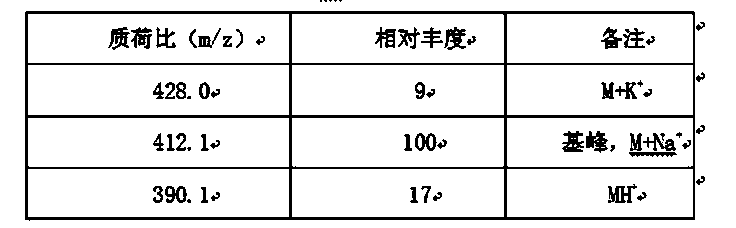
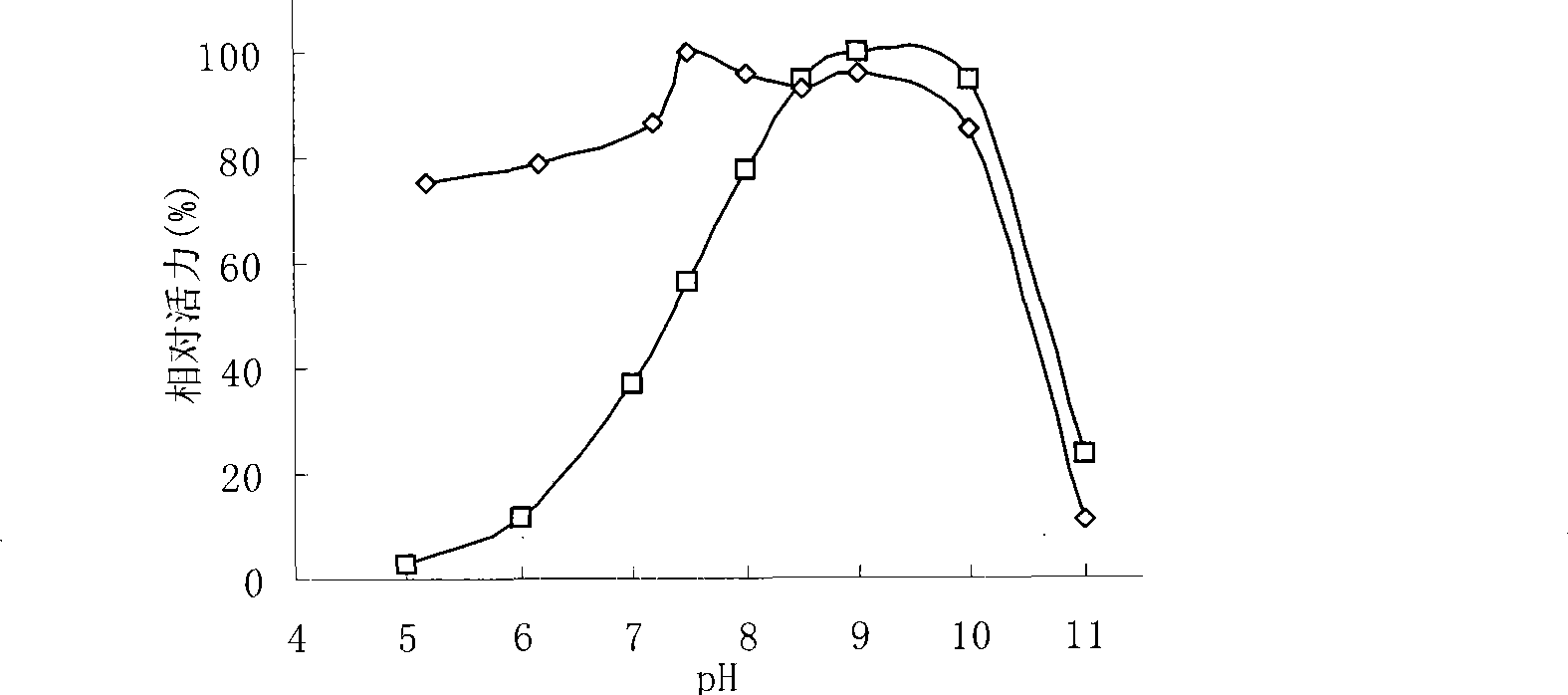
Penicillin G acylase (PDB ID: 1AJQ) is found in the organism Escherichia coli. Penicillin G acylase has a molecular weight of 94,642.59 Da, and its isoelectric point (pI) is 6.17. It is part of the larger family of penicillin acylases that come from such microorganisms as bacteria, yeast, and fungi.
Mutation penicillin G acylase, recombinant expression plasmid and transformation engineering strains thereof
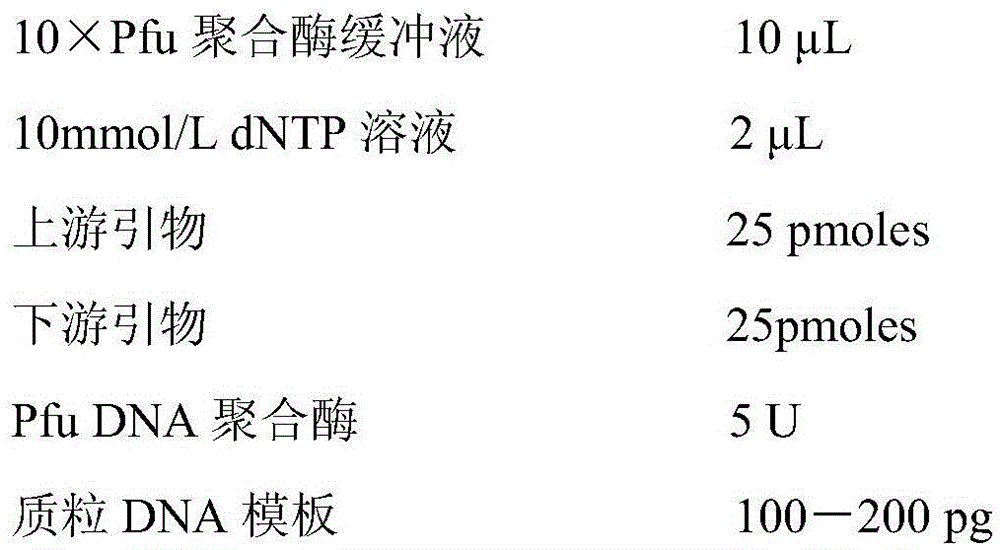
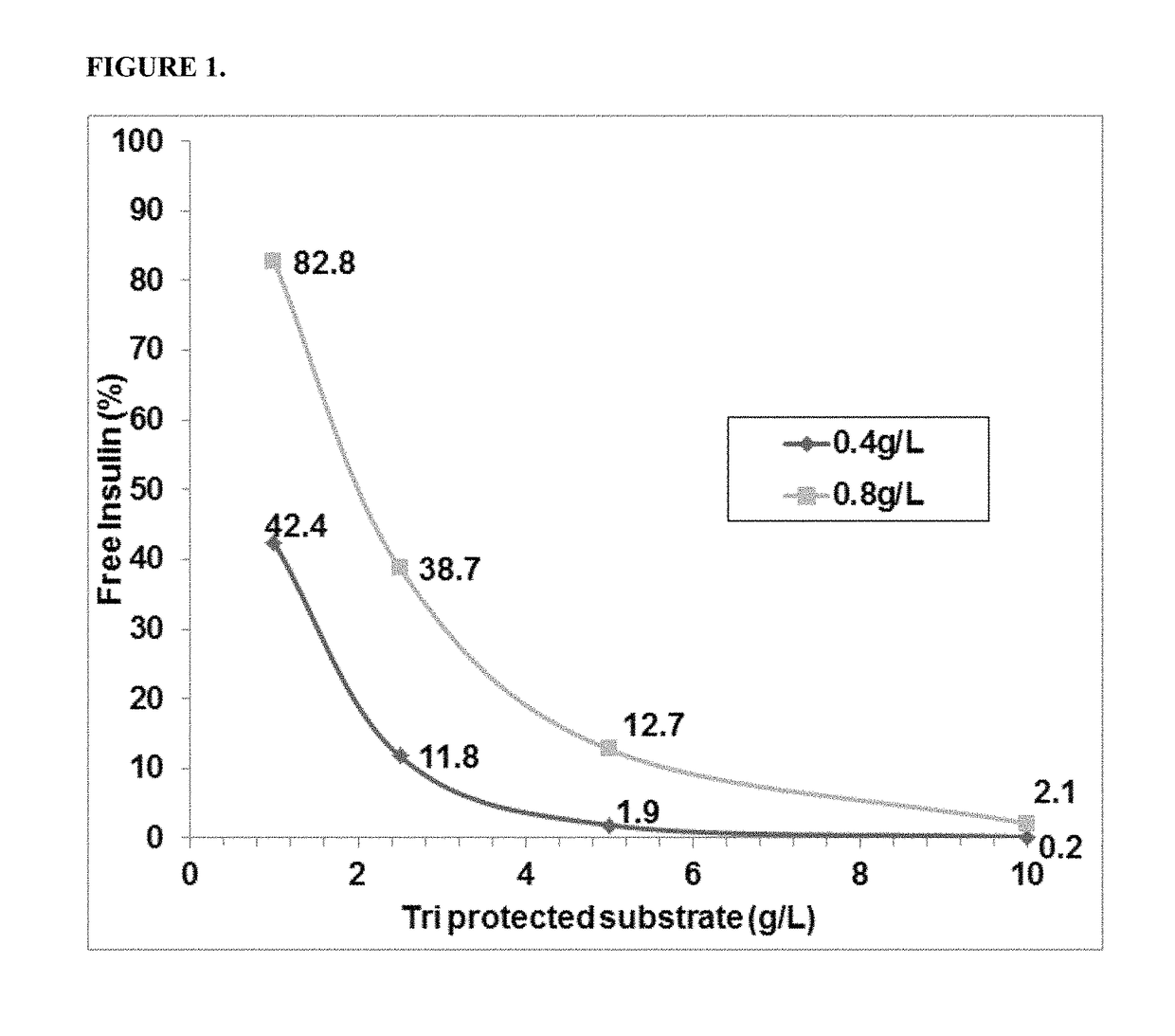
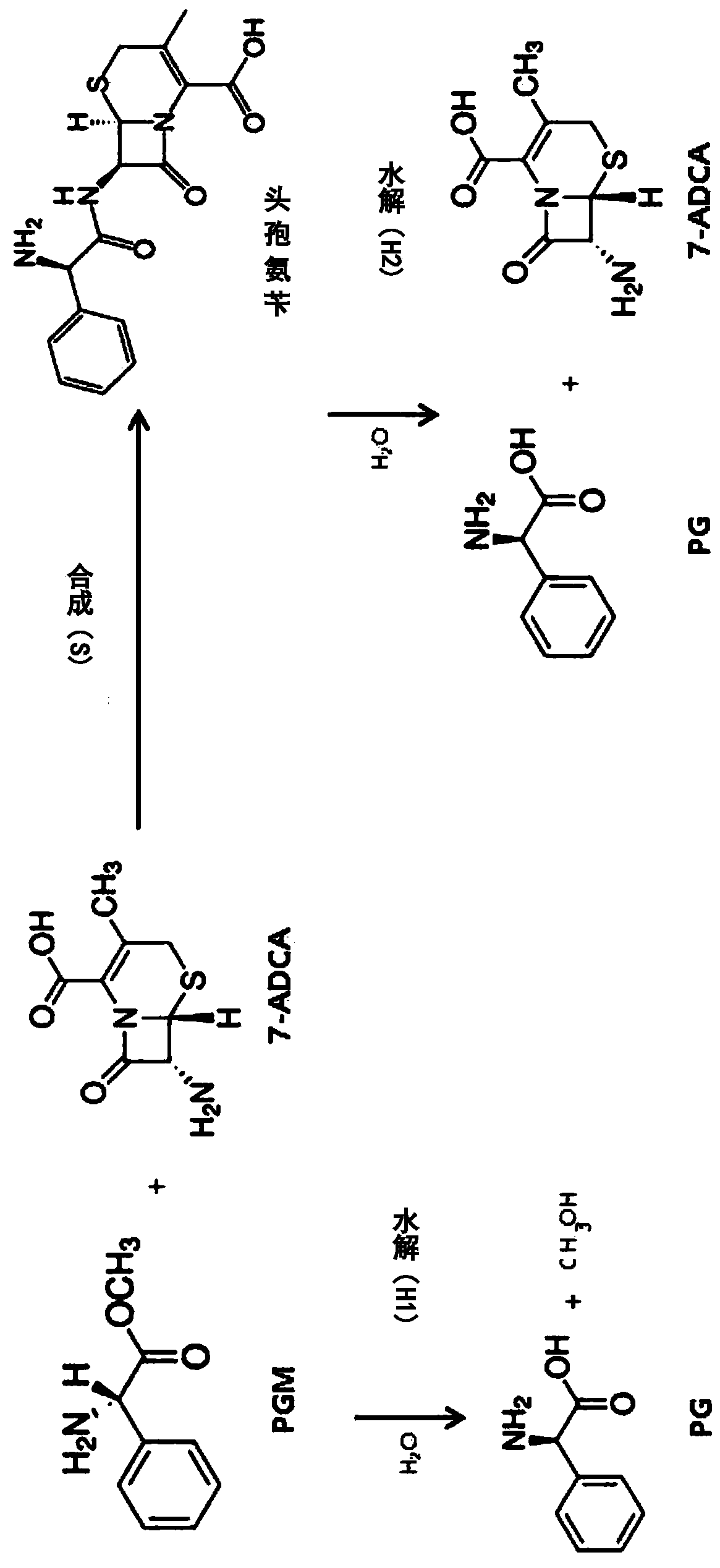
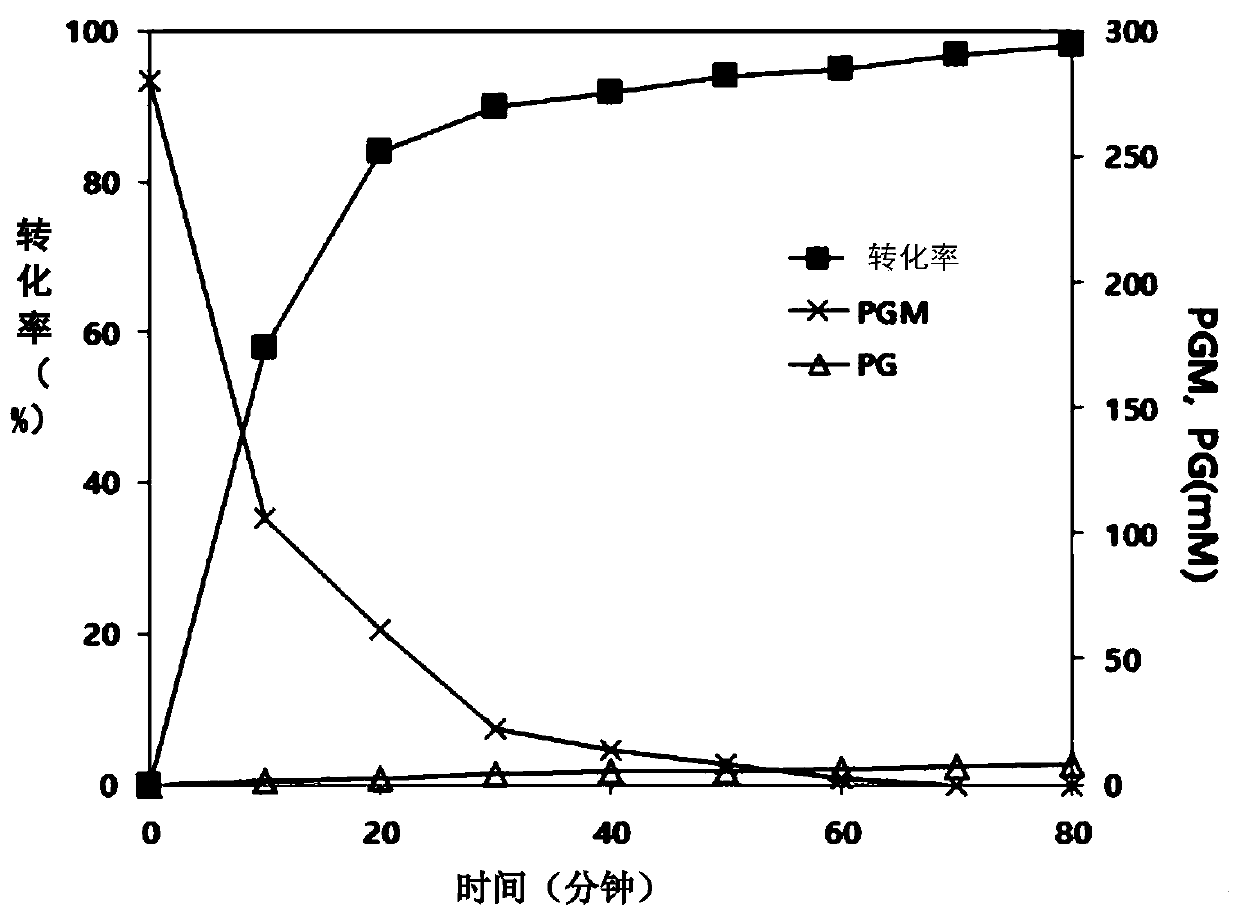
ActiveCN101177688AImprove synthesis abilityMaximum conversion rate increaseBacteriaHydrolasesHydrolysatePolymerase L
The invention relates to a gene, mutant plasmid and engineering bacteria which have improved synthesis performance to penicillin G acylase and are obtained by a gene site-directed mutagenesis method, and mutant enzyme can also be obtained with improved synthesis performance to penicillin G acylase by fermenting and purifying the engineering bacteria. Two enzymes Kpn I and Pst I are firstly used for cutting pUC18 by the invention, then T4 polymerase is adopted to make the ends blunt, and pZ01 is obtained through self-linkage; the enzyme of EcoR I is used for cutting pZ01, and then connected with pEES102 that is also cut by the enzyme of EcoR I, thereby obtaining the recombinant plasmid pY020; the pY020 is adopted as a template plasmid, and TaKaRa MuTanBEST Kit is utilized for conducting the site-directed mutagenesis to B.megaterium PGA, thereby obtaining the mutant plasmid with improved synthesis performance to the penicillin G acylase. The mutant plasmid is transformed to bacillus subtilis to obtain the required engineering bacteria. The engineering bacteria are amplified and fermented, and the mutant enzyme with improved maximum conversion rate of 7-ADCA and the ratio of synthetic product / hydrolysate can be obtained after the engineering bacteria are purified.
Owner:SHANXI WEIQIDA PHARMA IND
Penicillin G acylase immobilized with a crosslinked mixture of gelled gelatin and amino polymer
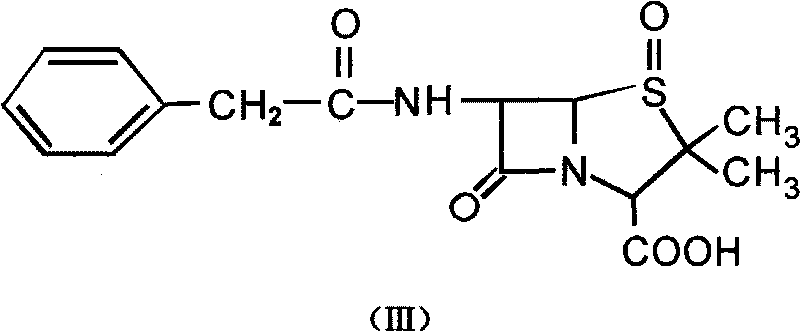
PCT No. PCT / EP96 / 03253 Sec. 371 Date Jan. 15, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jan. 15, 1998 PCT Filed Jul. 16, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 04086 PCT Pub. Date Feb. 6, 1997Penicillin G acylase is immobilized by covalent bonding to a crosslinked mixture of a gelled gelling agent such as gelatin and a polymer containing free amino groups such as alginate amine, chitosan or polyethylene imine. The immobilized penicillin G acylase provides a higher synthesis / hydrolysis ratio as compared to immobilizing with other carriers when producing beta -lactam derivatives by a condensing reaction of an amino beta -lactam with an acylating agent. The acylating agent may be a derivative of D-phenylglycine, a derivative of D-p-hydroxyphenylglycine or a derivative of D-2,5-dihydro-phenylglycine. Examples of beta -lactam derivatives that can be produced are amoxycillin, ampicillin, cephaclor, cephadroxil, cephprozil, cephalexin and cephradine.
Owner:GIST BROCADES NV
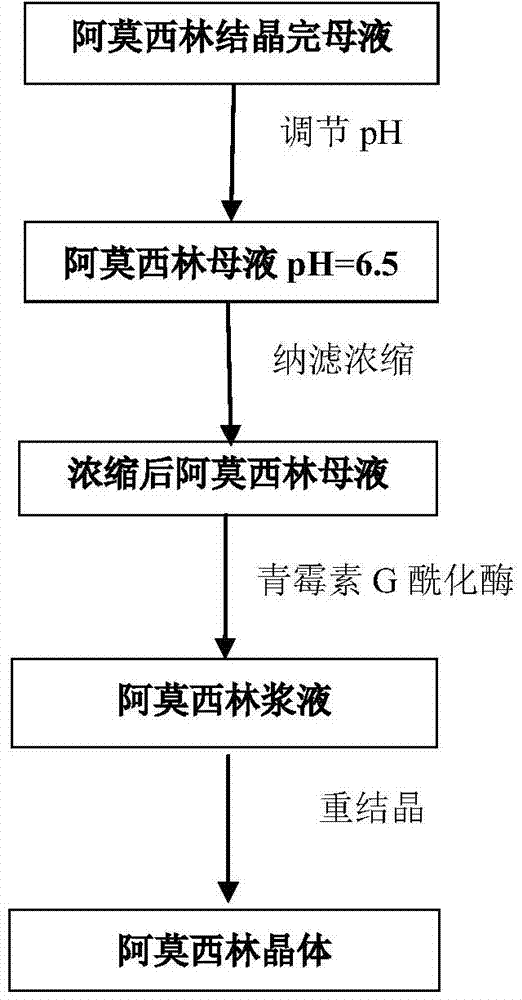
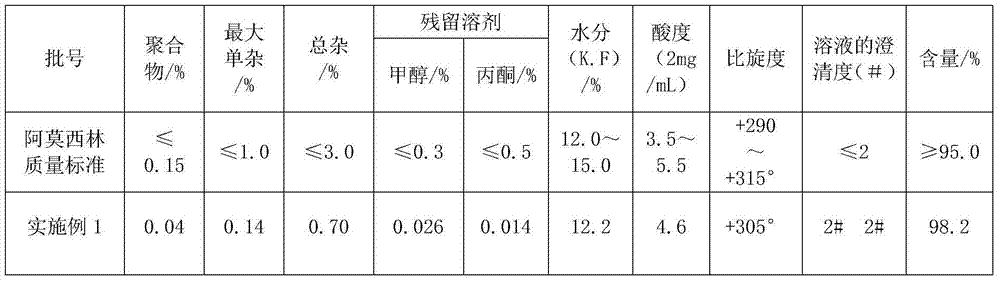
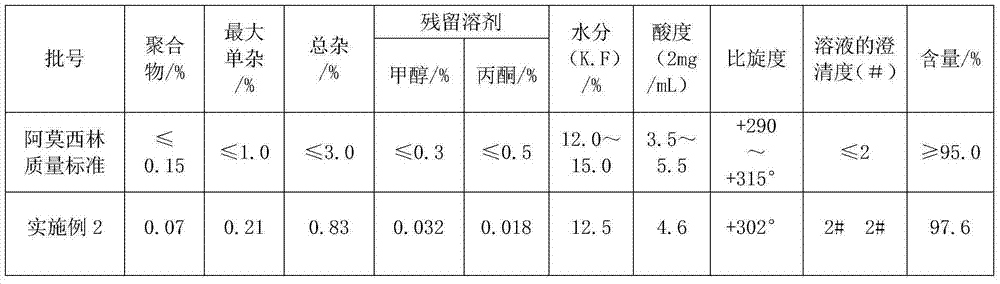
Improved method for preparing amoxicillin by enzymic method
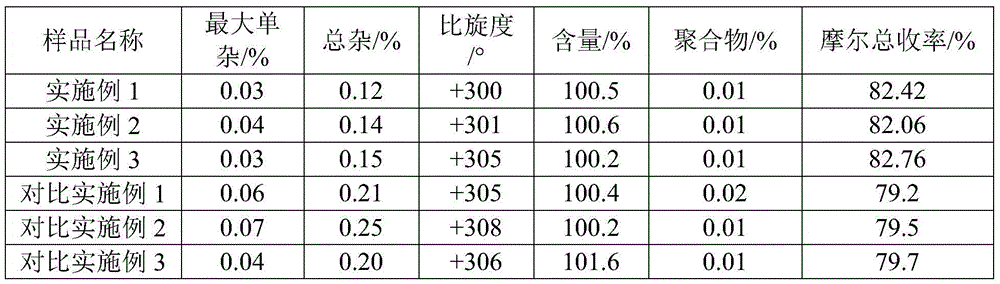
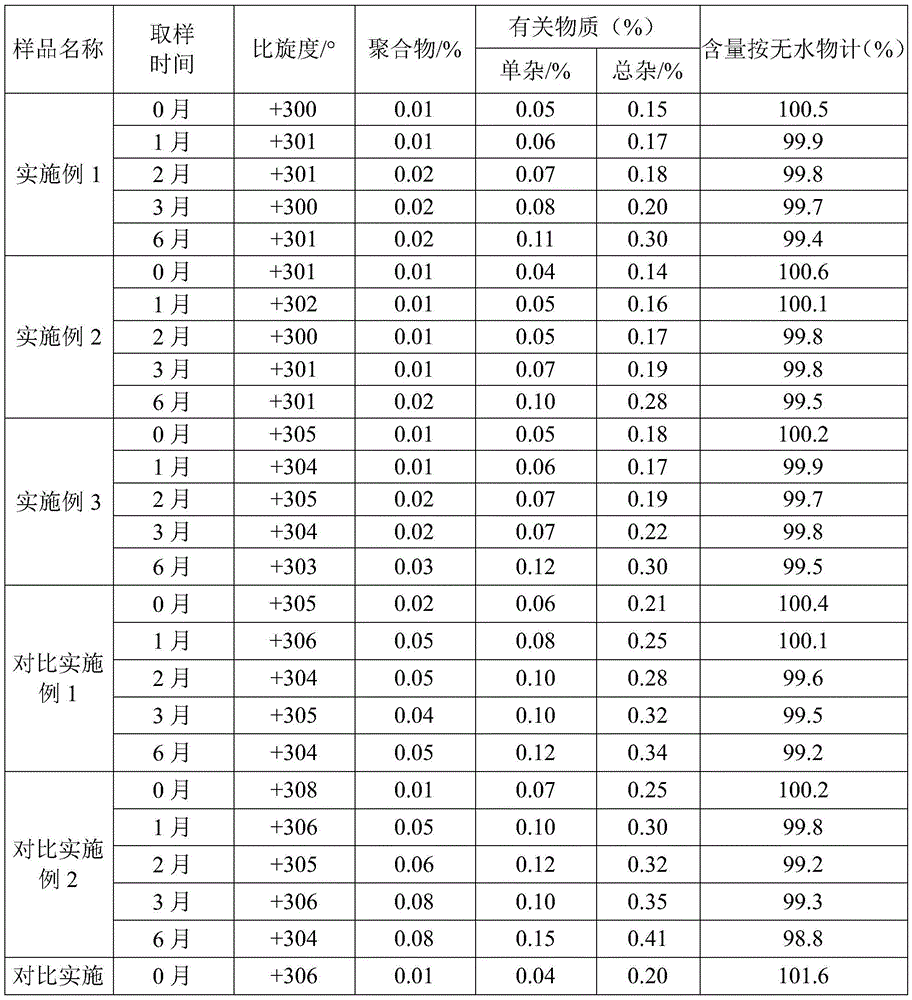
The invention relates to the field of pharmacy, and provides an improved method for preparing amoxicillin by an enzymic method, and a product obtained by the improved method for preparing amoxicillin by the enzymic method. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) dissolving 6-aminopenicillanic acid (6-APA) at the temperature of between 10 and 20 DEG C by using water or / and aqueous solution of ammonia which has the pH value of 7.0 to 8.0, and adding D-p-Hydroxyphenylglycine methyl ester hydrochlorid and penicillin G acyltransferase; 2) adjusting the pH value of a solution obtained in the step 1) to be 6.0 to 6.5, and reacting at the temperature of between 21 and 30 DEG C until the content of 6-APA is less than 5mg / ml to obtain a solution of an amoxicillin product; and 3) separating the penicillin G acyltransferase from the solution of the amoxicillin product, adjusting by using hydrochloric acid until the solution of the amoxicillin product is clarified, adding the aqueous solution of ammonia, adjusting the pH value to be 5.5 to 6.5, and crystallizing at the temperature of between 0 and 5 DEG C to obtain amoxicillin. By the improved method for preparing amoxicillin by the enzymic method, the quality of the amoxicillin product is greatly improved, and the medication safety of the amoxicillin product is further improved.
Owner:UNITED LAB INNER MONGOLIA CO LTD
Penicillin-g acylases
The present disclosure relates to engineered penicillin G acylase (PGA) enzymes having improved properties, polynucleotides encoding such enzymes, compositions including the enzymes, and methods of using the enzymes.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
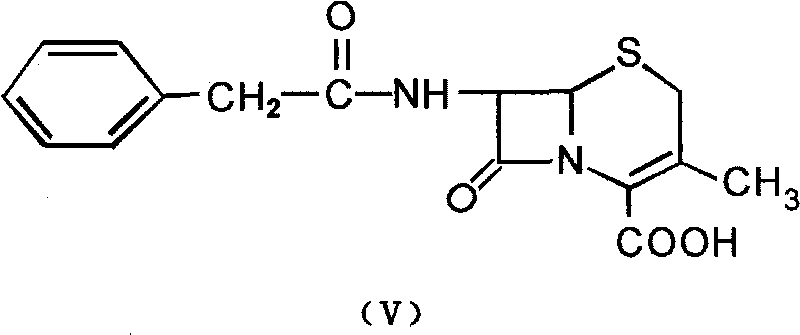
Method for preparing cephalosporin intermediate 7-ADCA
InactiveCN101735246AEasy to buy raw materialsHigh reaction yieldOrganic chemistryPyridiniumPenicillin G sulfoxide
The invention discloses a method for preparing cephalosporin intermediate 7-ADCA. The preparation method has the advantages of high reaction yield and good quality. In the method, penicillin G sylvite is taken as a raw material and is oxidized into penicillin G sulfoxide by peracetic acid, wherein the mass yield reaches over 85 percent; hydrobromic acid-pyridinium is taken as a catalyst and bis(trimethylsily) urea is taken as a carboxyl protective reagent, and cephalosporin G acid is obtained through ring expansion and rearrangement, wherein the mass yield of a coarse product reaches 90 percent; and side chains are catalyzed and hydrolyzed by immobilized penicillin G acylase to prepare the 7-ADCA. On the basis of the penicillin G sylvite, the total mass yield reaches over 40 percent.
Owner:杨石
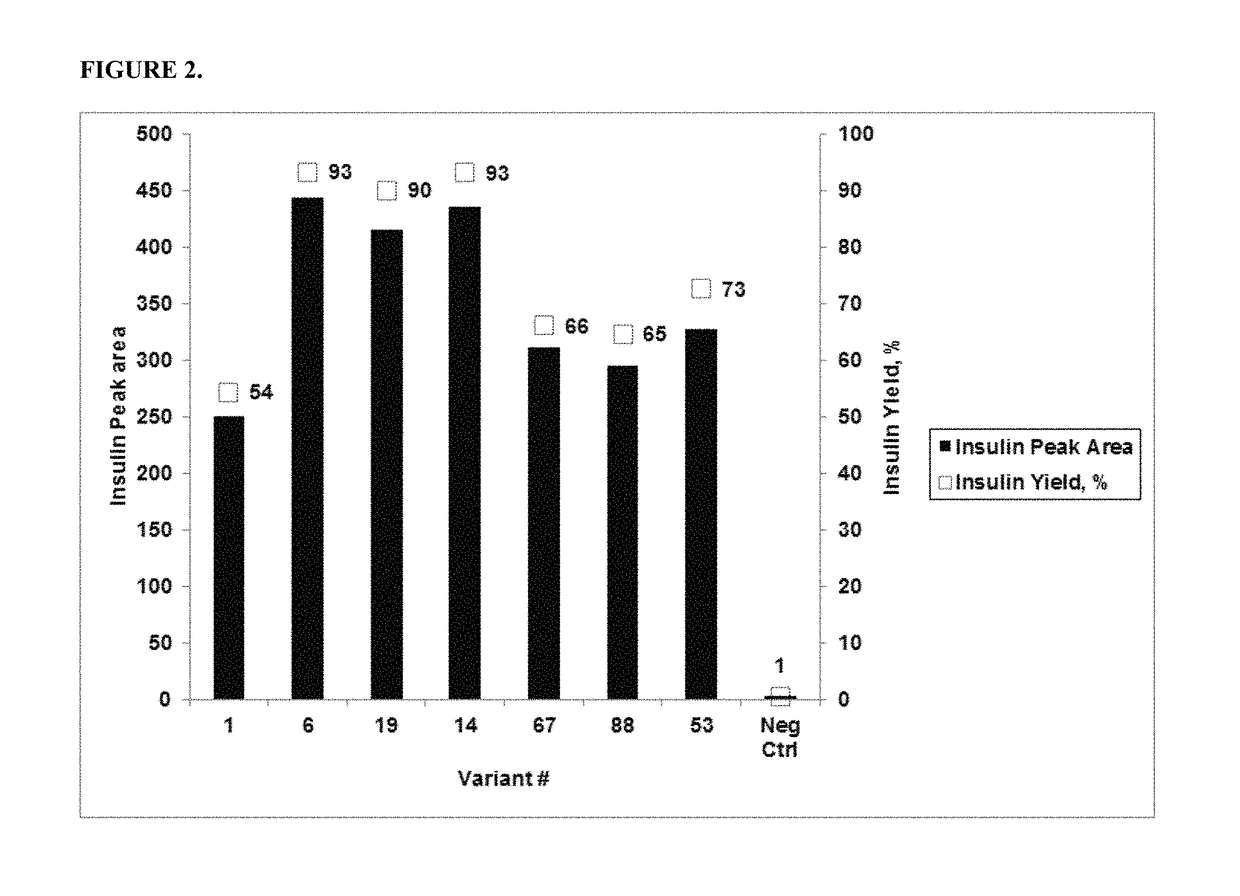
Mutant of penicillin G acylase (PGA) and preparation method and application of mutant
ActiveCN105087533AStrong concentration toleranceIncreased concentration toleranceHydrolasesFermentationPhenyl acetic acidEscherichia coli
The invention provides a mutant of penicillin G acylase (PGA) and a preparation method and application of the mutant. The non-rationally and semi-rationally designed enzyme engineering reconstruction technology is adopted for mutation of penicillin G acylase obtained from Escherichia coli ATCC 11105, so that a PGA mutant with higher reactivity, higher reaction rate, better conversion rate, stronger in penicillihe concentration tolerance, less substrate residue, and higher in phenyl acetic acid concentration tolerance; meanwhile, the mutant is subjected to recombinant expression, bacteria strain construction, fermenting cultivation, immobilization and application to prepare 6-amino-penicillanic acid (6-APA). The activity of the PGA-6 mutant prepared by the invention is increased by 102 times, the substrate penicillihe concentration tolerance is increased to 30%, and the phenyl acetic acid concentration tolerance is increased to 20 mmol / L; meanwhile, the immobilized PGA-6 mutant is used to decompose penicillihe with a concentration of 25% under the condition of pH 8.0 and 25 DEG C so as to prepare 6-APA, and the reaction time is shortened to 55 minutes, the substrate conversion rate is 98% or above, and after being used for 600 batches and above, the activity is not lost obviously, therefore, good operation stability is achieved.
Owner:HUNAN FLAG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
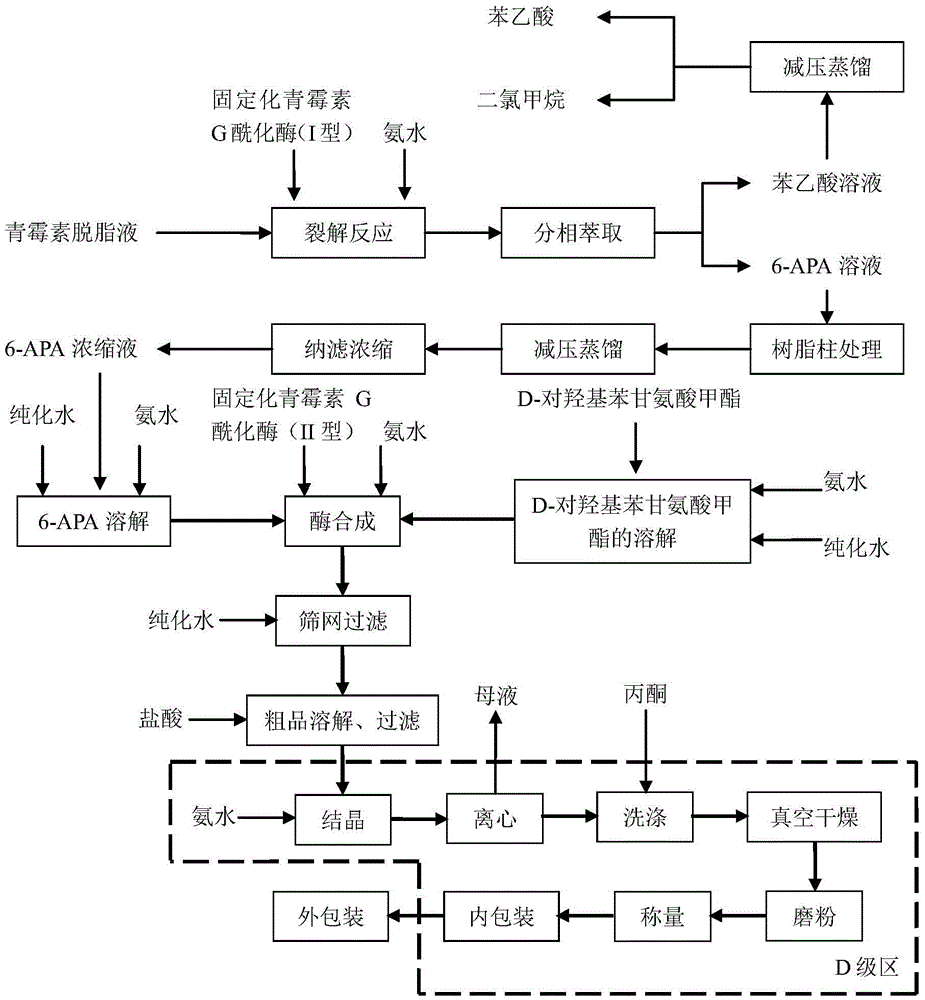
Process for direct preparation of amoxicillin by liquid 6-APA (amino penicillanic acid)
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine preparation and relates to a process for direct preparation of amoxicillin by liquid 6-APA (amino penicillanic acid). The process includes: taking penicillin degreasing solution as an initial material, sequentially performing cracking reaction, extraction, phase splitting, resin column adsorptive purification, distillation and concentration to obtain a 6-APA solution with the concentration being 80-100g / L, and synthesizing with p-hydroxyphenylglycine methyl ester under a catalytic action of type-II penicillin G acylase to obtain the amoxicillin. Compared with a traditional method, the process has the advantages that subsequent steps of 6-APA crystallization, centrifuging, drying and the like are avoided, investment of fixed assets is reduced, energy loss, equipment loss and cost are reduced, profits are increased, and physical injuries of staffs are reduced. Compared with existing direct amoxicillin preparation methods, the process has the advantages that by adoption of dichloromethane as an extracting agent, total mole yield of amoxicillin is higher relatively, the extracting agent is easy for distillation separation, the content of residual solvents in products is greatly reduced, medication safety is improved, and the process is worthy of popularization in production.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA CHANGSHENG PHARMA
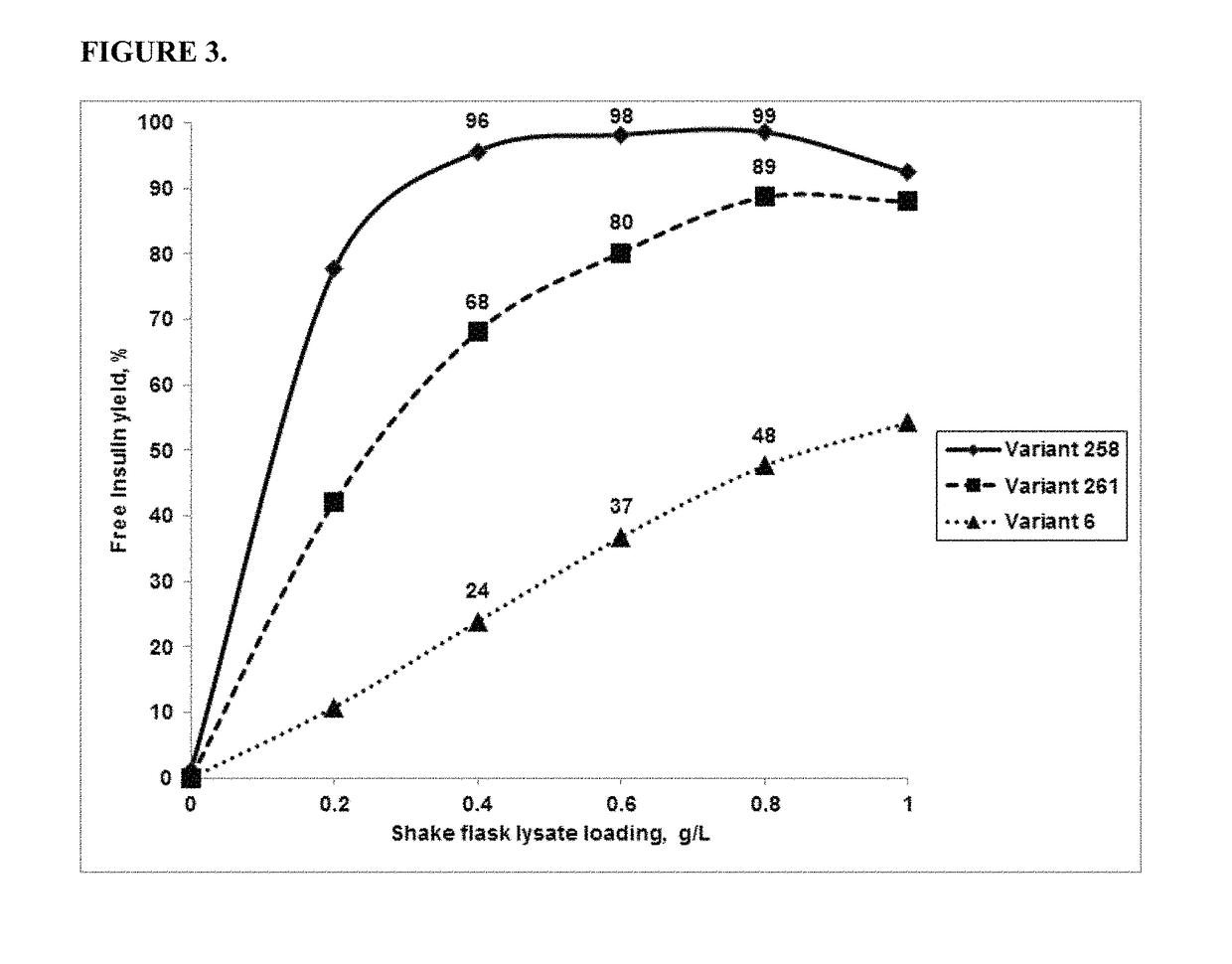
Penicillin G acylase mutant for synthesis and application thereof in preparation of amoxicillin
ActiveCN105274082ASynthetic activity is goodImprove stabilityHydrolasesFermentationContinuous useOrthogenesis
The invention provides a penicillin G acylase mutant for synthesis and an application thereof in the preparation of amoxicillin. Penicillin G acylase of Achromobacter xylosoxidans origin is mutated by computer aided design in connection with semi-rational design of site-saturation mutagenesis technique and enzyme engineering modification of orthogenesis, thus acquiring the penicillin G acylase mutant lower in hydrolytic activity, better in synthetic activity, higher in synthesis-hydrolysis ratio (S / H), higher in acid resistance and better in stability, and amoxicillin can be catalytically synthesized more effectively and quickly. Immobilized enzyme hydrolytic activity of the mutant SPGA-4 obtained is decreased by 8.7 times, synthetic activity is increased by 5.6 times, the S / H ratio is increased by 8 times, the activity remains at 79% for 60 min under the condition of pH 2.0, amoxicillin is catalytically synthesized by a solid method at 10 DEG C or 20 DEG C, substrates 6-APA and D-HPM are directly charged in a solid form without dissolving, reaction pH need not be controlled, substrate conversion rate is higher than 99%, continuous use is available in more than 300 batches, and good operational stability is given.
Owner:HUNAN FLAG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Penicillin G acylase containing one or a plurality of point mutation
ActiveCN103074320ASavings and time costsHigh enzyme productionFungiBacteriaAmoxicillinPenicillin G Acylase
The present invention relates to a new penicillin G acylase mutant, nucleic acid for encoding the mutant, a related expression vector, host cells, and a use of the mutant in amoxicillin synthesis.
Owner:CSPC ZHONGQI PHARM TECH (SHIJIAZHUANG) CO LTD
Penicillin G acylase mutant, and coding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a penicillin G acylase mutant, and coding gene and application thereof; the amino acid sequence of the penicillin G acylase mutant is displayed by SE Q ID NO.1; the nucleotide sequence of the coding gene is presented by the SEQ ID NO.2; the invention also provides the application of the penicillin G acylase mutant in synthesis of cephalo-type antibiotic. Compared with wild type, the novel penicillin G acylase mutant has higher activity in synthesis of the cephalo-type antibiotic like cephalosporin propylene, cofactor or cephalosporin amoxicillin, and has highly improved enzyme vitality when catalyzing 7-APRA and side chain 2-hydroxy ethyl to react with hydroxy benzenes glycine ester so as to synthesis the cephalosporin propylene; specific vitality is improved from 1.5U / mg to 35U / mg, and synthesis hydrolysis vitality ratio is not reduced, and the synthesis hydrolysis vitality ratio can reach 1.8.
Owner:ZHEJIANG APELOA TOSPO PHARMA +1
Penicillin G acylase mutant
ActiveCN105483105AHigh catalytic efficiencyHydrolasesMicroorganismsBeta lactam antibioticHydrolysate
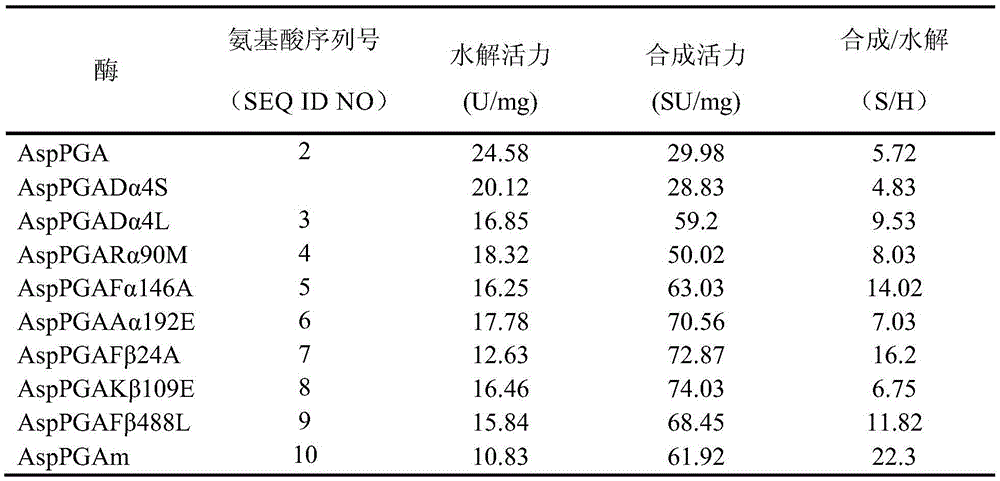
The invention relates to a penicillin G acylase mutant constructed by genetic engineering. In comparison with wild type penicillin G acylase from achromobacter (Achromobacter sp.CCM 4824), the synthesis performance of the penicillin G acylase mutant is improved substantially, the maximum synthetic product / hydrolysate value S / H reaches 22.3 and is 3.9 times that of wild type enzyme, and various beta-lactam antibiotics can be efficiently synthesized catalytically. When the ratio of side chains to mother nucleus is 1.05:1, the conversion rate of the mother nucleus 6-APA, 7-ADCA, 7-ACCA and 7-APRA reaches 99.0% or above, and the penicillin G acylase mutant has wide industrial application prospects.
Owner:山西双雁生物科技有限公司
Synthetic method of aztreonam intermediate
The invention relates to a synthetic method of an aztreonam intermediate, and particularly relates to a method for removing a phenylacetyl protective group at a 3-amino position of an aztreonam main ring intermediate. The invention comprises the following steps: preparing phenylacetyl-L-threoninamide from L-threonine, performing sulfonylation of a beta-position hydroxyl, and sulfonation of an end amino, then preparing the aztreonam main ring intermediate with the amino protected by the phenylacetyl protective group through cyclization, performing hydrolysis in the presence of penicillin G acylase, and removing the protective group on the amino to obtain the aztreonam main ring intermediate. The method of the invention has the advantages of mild process conditions, simple post-treatment, high finished product purity, and high yield, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:CHONGQING SHENGHUAXI PHARMA CO LTD +1
Method for enzymatic synthesis of cefprozil in recyclable aqueous two-phase system by using immobilized penicillin acylase
The invention discloses a method for the enzymatic synthesis of cefprozil in a recyclable aqueous two-phase system by using immobilized penicillin acylase. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving a cefprozil parent nucleus and an acylation reagent in an aqueous two-phase polymer solution, wherein the molar ratio of the parent nucleus to the acylation reagent is 1: (1-4); and adding immobilized penicillin G acylase, then adding a two-phase distribution conditioning agent, adjusting the pH value to 4.5-7, and reacting for 1 to 80 hours at the temperature of 5-30 DEG C, wherein the concentration of enzyme in a reaction system is 50-150U / ml. By adopting the method, the hydrolytic activity of the penicillin acylase can be effectively inhibited, thus the hydrolysis degrees of the acylation reagent and the cefprozil product can be reduced. Compared with a method using water as a medium, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the product and the enzyme are distributed in two different water phases, a reactant is fully in contact with the enzyme, so that a synthesis / hydrolysis specific value is greatly increased, the yield of the cefprozil can be increased by 20%, and the highest yield can reach 78%; the adopted novel recyclable aqueous two-phase system can be recycled, so that the production cost is reduced.
Owner:南通康鑫药业有限公司 +1
Mutant penicillin G acylases
ActiveUS8541199B2High synthetic activityRaise the ratioSugar derivativesBacteriaEscherichia coliPenicillin
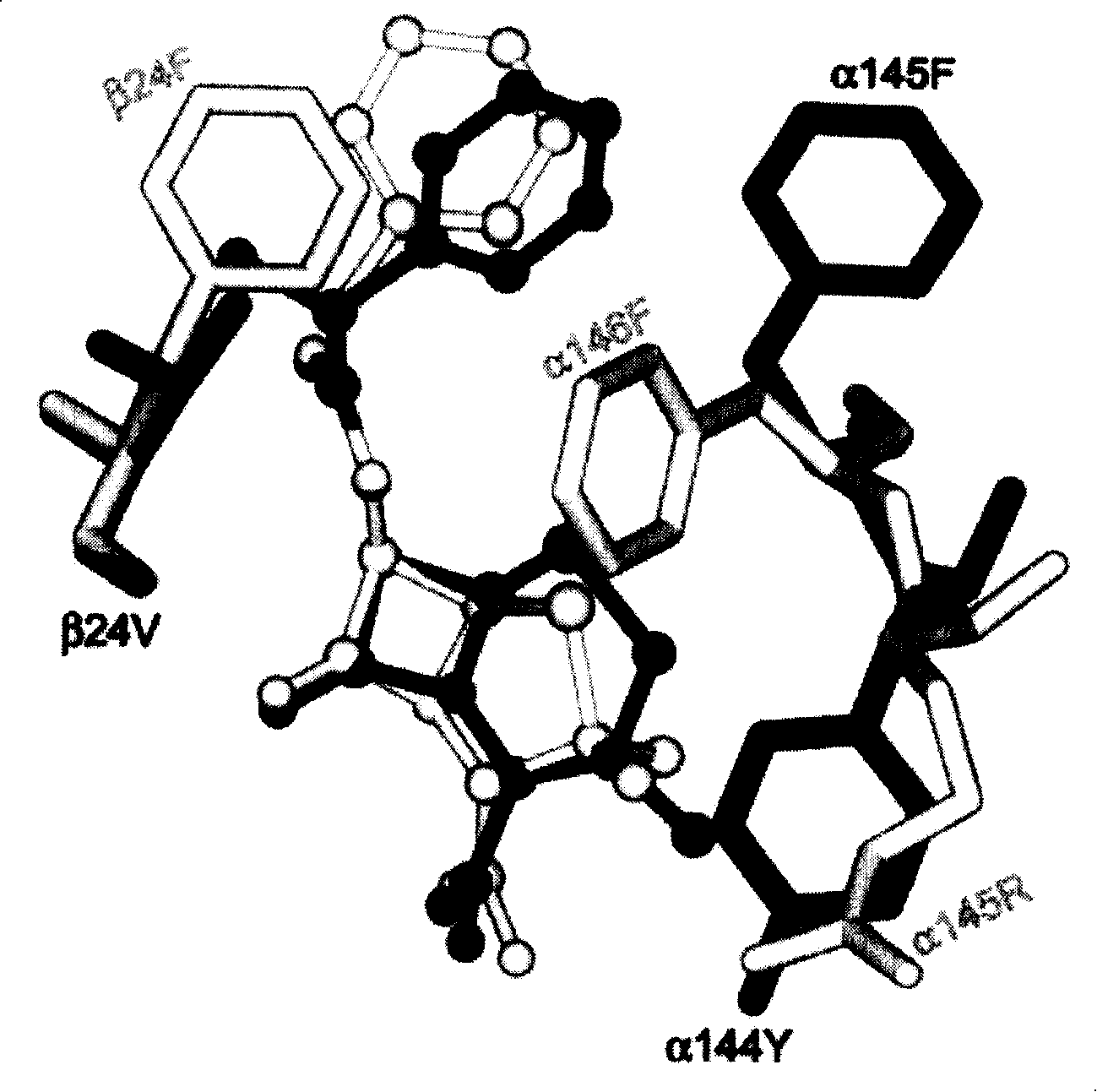
The present invention relates to a mutant prokaryotic penicillin G acylase derived from a wild-type penicillin G acylase characterized in that the mutant is having an amino acid substitution at one or more amino acid positions selected from the group consisting of amino acid positions A3, A77, A90, A144 A192, B24, B109, B148, B313, B460 and B488 according to the amino acid numbering of the Escherichia coli penicillin G acylase having the amino acid sequence depicted in SEQ ID No: 1.
Owner:DSM SINOCHEM PHARMA NETHERLANDS
Immobilization method of alcaligenes faecalis penicillin G acylase
InactiveCN101381718AIncrease vitalityImprove performanceImmobilised enzymesHydrolasesOperational stabilityPenicillin K
The invention relates to a process for immobilizing an enzyme in biological chemistry, in particular to a method for immobilizing a bacillus foecalis alkaligenes penicillin G acylase. The carrier for immobilizing the bacillus foecalis alkaligenes penicillin G acylase is ZH-EP. In a buffer solution system, when the ZH-EP is used to immobilize, the concentration of the enzyme is between 100 and 160 mg / ml, the immobilizing time is between 106 and 120 hours, the pH value of the buffer solution is between 8.5 and 10.0, the concentration of salt in the reaction system is between 1.0 and 1.5M, and the weight volume ratio of the carrier to the buffer solution is 1g : 4 to 6ml. The method improves the temperature and the pH stability of the immobilized enzyme compared with a free enzyme. Through continuous batches of hydrolysis of penicillin G kali salt, the immobilized bacillus foecalis alkaligenes penicillin G acylase shows the excellent operation stability and the superiority to the free enzyme.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Technology for preparing ampicillin by adopting enzymic method
The invention discloses a technology for preparing ampicillin by adopting an enzymic method. The technology comprises the following steps of (a) mixing 6-aminopenicillanic acid, a phenylglycine derivative and penicillin G acylase into water to obtain mixed liquid; (b) adjusting and controlling the pH value of the mixed liquid to be 5.5-6.1 through acid or alkaline, and reacting under the temperature of 0-40 DEG C; (c) after the reaction is finished, performing separation, cleaning reaction liquid containing a coarse ampicillin product through the acid, crystallizing the reaction liquid through the alkaline, and performing grain cultivation, washing and drying to obtain an ampicillin product. The preparation technology provided by the invention is simple, convenient to operate, low in energy consumption, high in safety and high in stability; furthermore, the pH value required by a reaction system is easy to control, the reaction time is short, the conversion rate is up to over 99 percent, the product purity is high, and a solvent does not need to be recycled; and therefore, the low-cost and high-efficiency production technology can be popularized and applied in the industrial production.
Owner:NORTH CHINA PHARM GRP SEMISYNTECH CO LTD
Recycling process of amoxicillin in enzymatically synthesized amoxicillin mother liquor
The invention discloses a recycling process of amoxicillin in enzymatically synthesized amoxicillin mother liquor. The process comprises the following steps: concentrating the amoxicillin mother liquor through the adoption of nanofiltration membrane high-power concentration equipment, feeding the concentrated liquor in a reaction tank, sufficiently reacting the 6-APA in the concentrated liquor with methyl D-(-)-4-hydroxy-phenylglycinate under the effect of penicillin G acylase so as to generate the amoxicillin. The recycling process disclosed by the invention has the advantages that through the nanofiltration concentration, not only the amoxicillin in the mother liquor is recycled, but also the 6-APA contained in the mother liquor participates the enzymatic synthesis reaction to be translated into the amoxicillin, the aim of extremely recycling the amoxicillin in the mother liquor is achieved, and the recycling process has more economy.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA CHANGSHENG PHARMA
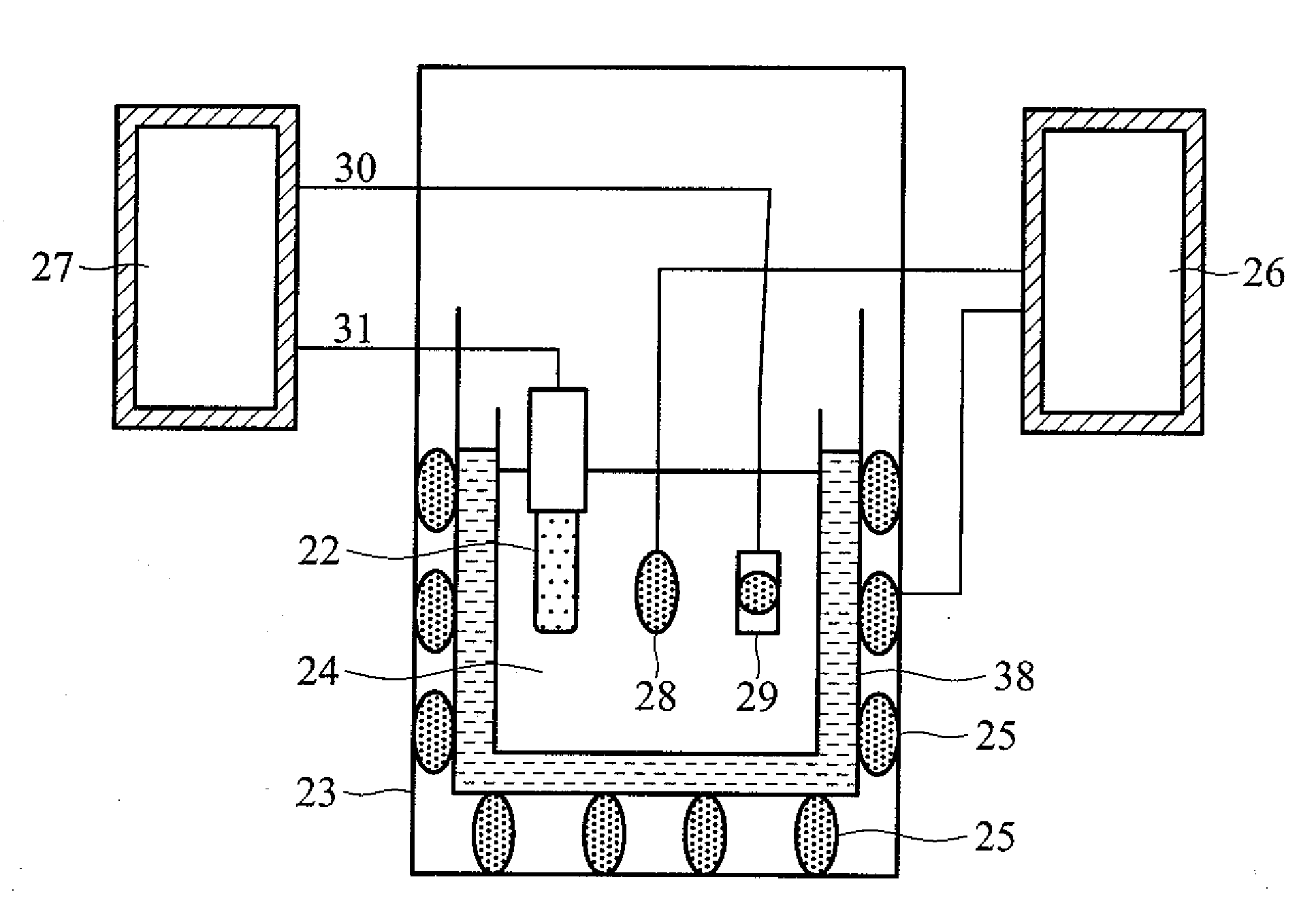
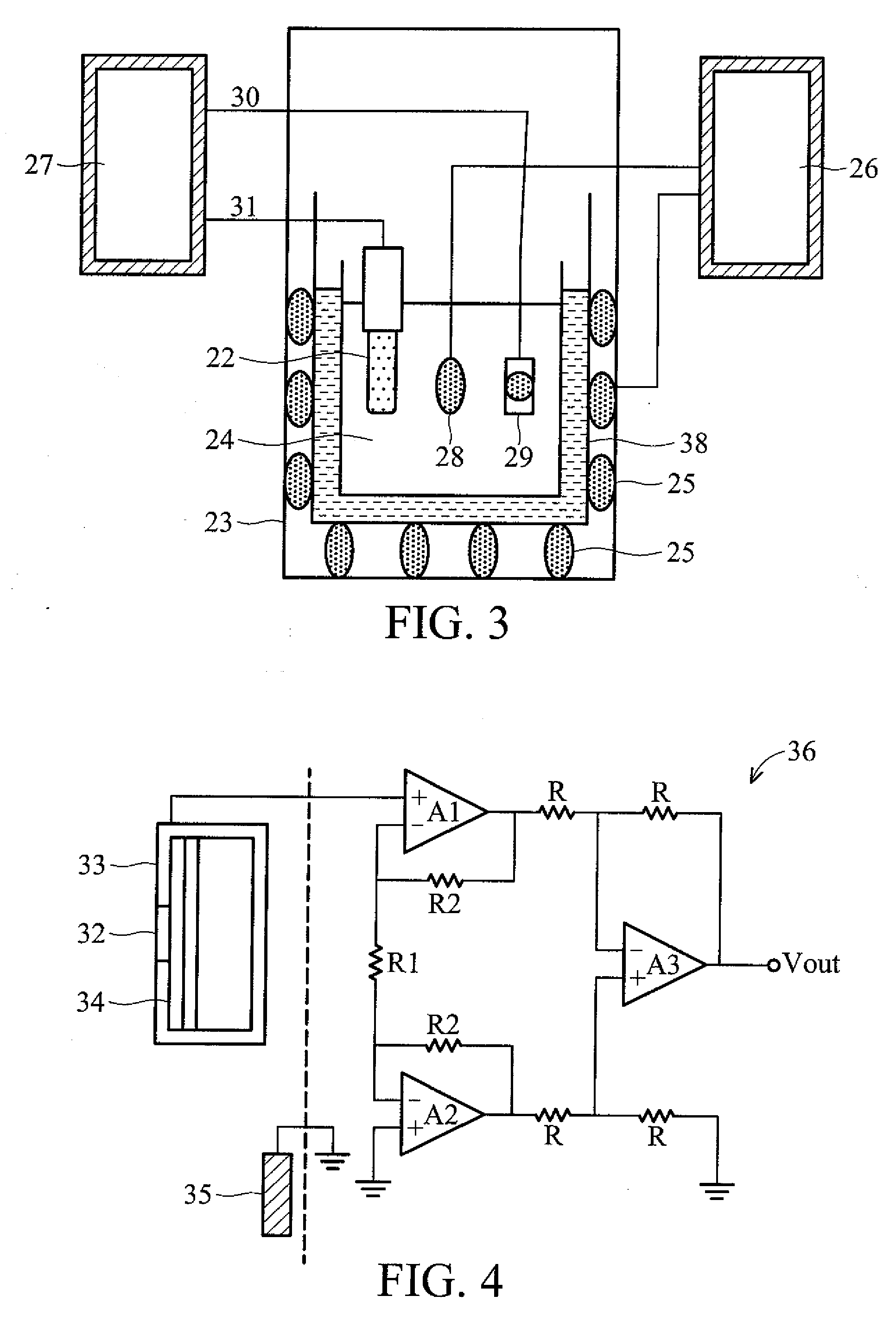
Penicillin g biosensor, systems comprising the same, and measurement using the systems
InactiveUS20090145776A1Low costHigh sensitivityWeather/light/corrosion resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementMOSFETField-effect transistor
A penicillin G biosensor, systems comprising the same, and measurement using the systems. The penicillin G biosensor has an extended gate field effect transistor (EGFET) structure and comprises a metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) on a semiconductor substrate, a sensing unit comprising a substrate, a tin oxide film on the substrate, and a penicillin G acylase film immobilized on the tin oxide film, and a conductive wire connecting the MOSFET and the sensing unit.
Owner:CHOU JUNG CHUAN +2
Artificially designed penicillin G acylase proenzyme and coding sequence and applications thereof
ActiveCN108660127AAvoid steric hindrance effect position effectIncrease reaction rateBacteriaHydrolasesZymogenSide chain
The invention discloses artificially designed penicillin G acylase proenzyme and a coding sequence and applications thereof. Substrate combining steric effects can be reduced and the substrate can beurged to rapidly enter an active pocket by mutating more than one of large side chain amino acids near a substrate binding pocket of wild penicillin G acylase proenzyme into side chain amino acids which are smaller than the amino acids before mutation; and at the same time, through the mutation of more than one of key hydrophilic amino acids or weakly hydrophobic amino acids in the active pocket near a substrate-active center into the amino acids whose hydrophobicity is stronger than that of amino acids before the mutation, the hydrophobicity around the substrate binding pocket can be increased, the combination of water molecules can be reduced, hydrolysis can be reduced, S / H can be increased from reducing hydrolysis and increasing synthesis, and the capability of synthesizing penicillin Gacylase into amoxicillin can be greatly enhanced. The penicillin G acylase proenzyme with the highest S / H so far is provided, and the penicillin G acylase proenzyme has great potential in amoxicillinsynthesis.
Owner:ZHUHAI UNITED LAB
Mutant penicillin g acylases
ActiveUS20110256585A1High synthetic activityRaise the ratioSugar derivativesBacteriaEscherichia coliPenicillin
The present invention relates to a mutant prokaryotic penicillin G acylase derived from a wild-type penicillin G acylase characterized in that the mutant is having an amino acid substitution at one or more amino acid positions selected from the group consisting of amino acid positions A3, A77, A90, A144 A192, B24, B109, B148, B313, B460 and B488 according to the amino acid numbering of the Escherichia coli penicillin G acylase having the amino acid sequence depicted in SEQ ID No: 1.
Owner:DSM SINOCHEM PHARMA NETHERLANDS
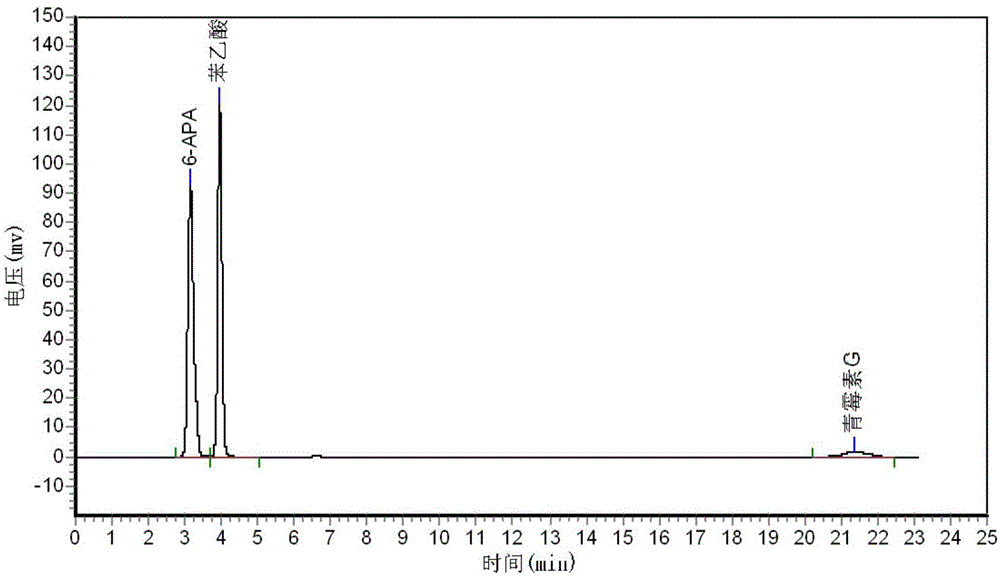
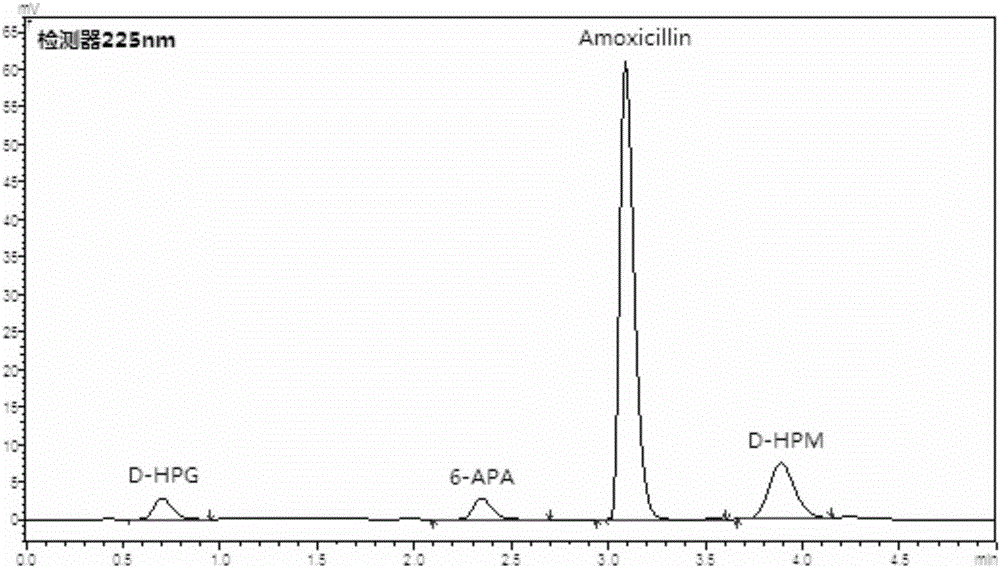
Detection method for vestigial protein in amoxicillin prepared by using enzymic method
The invention relates to the field of pharmacy, provides a detection method for vestigial protein in amoxicillin prepared by using an enzymic method, and comprises obtaining penicillin G acyltransferase standard substances, and using 0.05mol / L of phosphate buffer with the potential of hydrogen (pH) value of 7.0 for diluting to obtain standard substance liquid; obtaining products for testing, accurately weighting and placing the products for testing in a measuring flask, adding 0.05mol / L of phosphate buffer with the pH value of 7.0, adding 0.1mol / L of sodium hydroxide solution until the products for testing are dissolved and solution is clear, and using 0.05mol / L of phosphate buffer with the pH value of 7.0 for diluting to obtain product solution for testing; respectively and accurately measuring and obtaining 100mu L of the solution and injecting the solution in a high performance liquid chromatograph, and recording the peak area and measuring content of the vestigial protein by using an external standard method. The detection method can effectively detect the content of the vestigial protein in amoxicillin products, thereby being capable of effectively detecting quality of the products and improving pharmacy safety of medicines.
Owner:内蒙古联邦动保药品有限公司
Cefradine synthase mutant and coding gene thereof
ActiveCN107099523AIncrease enzyme activityIncrease vitalityHydrolasesFermentationEscherichia coliCefradine
The invention discloses a cefradine synthetase mutant and a coding gene thereof. A protein shown as A) or B) or C) is provided, wherein A) is obtained by substitution of twenty-fourth-site phenylalanine of the beta chain of Escherichia coli natural penicillin G acylase into alanine and substitution of sixty-seventh-site serine of the beta chain of the Escherichia coli natural penicillin G acylase into the alanine; B) is obtained by substitution of 142nd-site methionine the alpha chain of the Escherichia coli natural penicillin G acylase into leucine, substitution of twenty-fourth-site phenylalanine of the beta chain into the alanine, and substitution of sixty-seventh-site serine of the beta chain into the alanine; and C) is a protein derived from the A) or B) by substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or a plurality of amino acid residue of the protein defined by the A) or B), and has the ability of synthesis of cefradine. The protein provided on has high activity for synthesis of the cefradine and Vs / Vh and lower alpha, and lays a foundation for the industrialization of the enzyme method synthesis of the cefradine.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Penicillin-G acylases
The present disclosure relates to engineered penicillin G acylase (PGA) enzymes having improved properties, polynucleotides encoding such enzymes, compositions including the enzymes, and methods of using the enzymes.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
Primary amine immobilized enzyme carrier and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107641623ALarge apertureGood enzyme activityOn/in organic carrierFermentationPoly methacrylateAmination
The invention discloses a primary amine immobilized enzyme carrier and a preparation method thereof. Positive suspension polarization is performed to obtain a crude macroporous polymethacrylate-diallylamine carrier; washing the crude carrier, and grading; performing amination to obtain the primary amine-containing immobilized enzyme carrier. The primary amine immobilized enzyme carrier according to the technical scheme of the invention is applicable to immobilization of various biological enzymes, provides effective immobilization for penicillin G acylase, D-amino acid oxidase, Gl-7-ACA acylase and the like, and has high enzyme-carrying activity, good mechanical strength and good storage stability. The preparation method is simple and has low cost, and the carrier has significantly improved storage stability and is expectedly applicable to industrial large-scale production.
Owner:天津南开和成科技有限公司
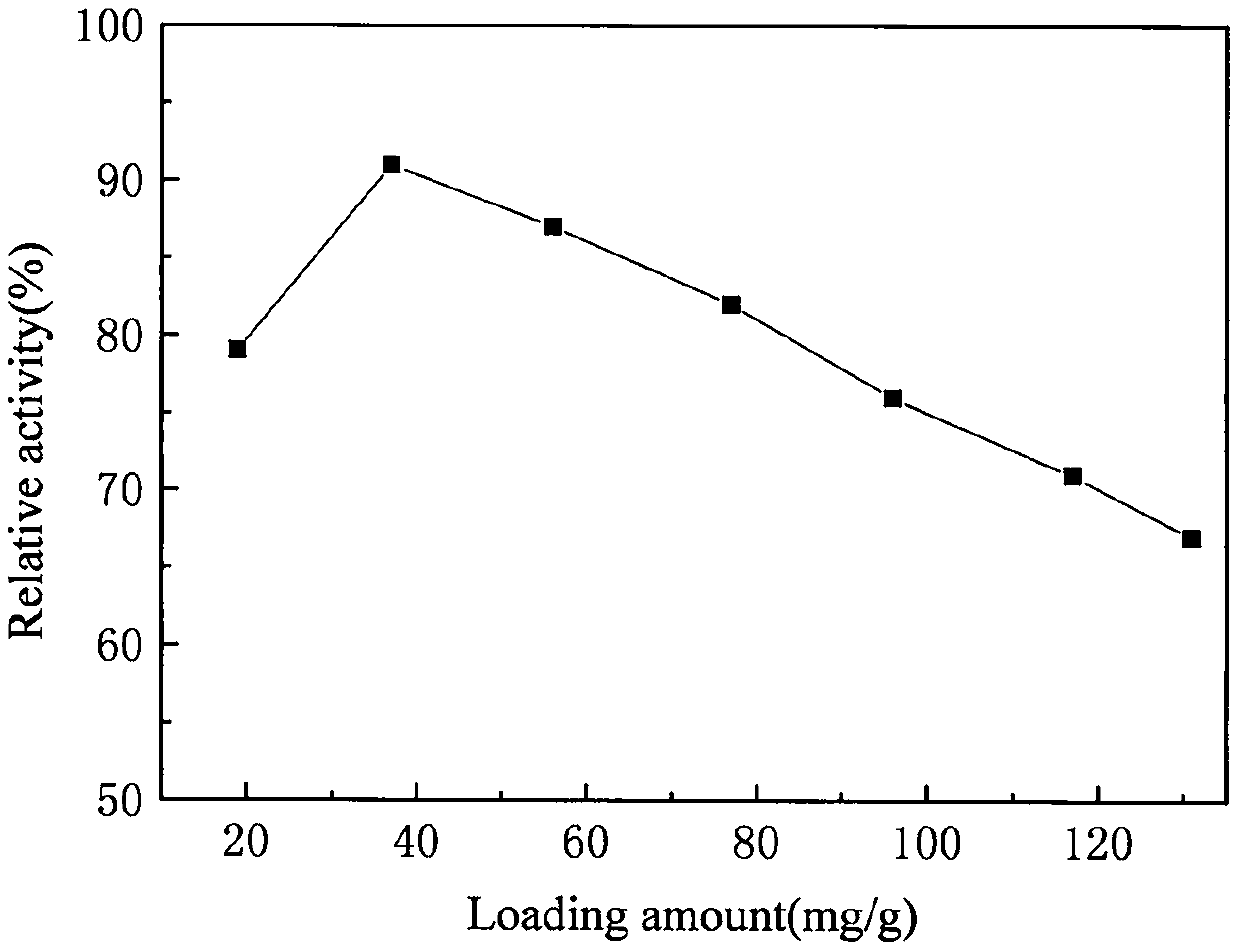
Co-crosslinking immobilization method of penicillin G acylase
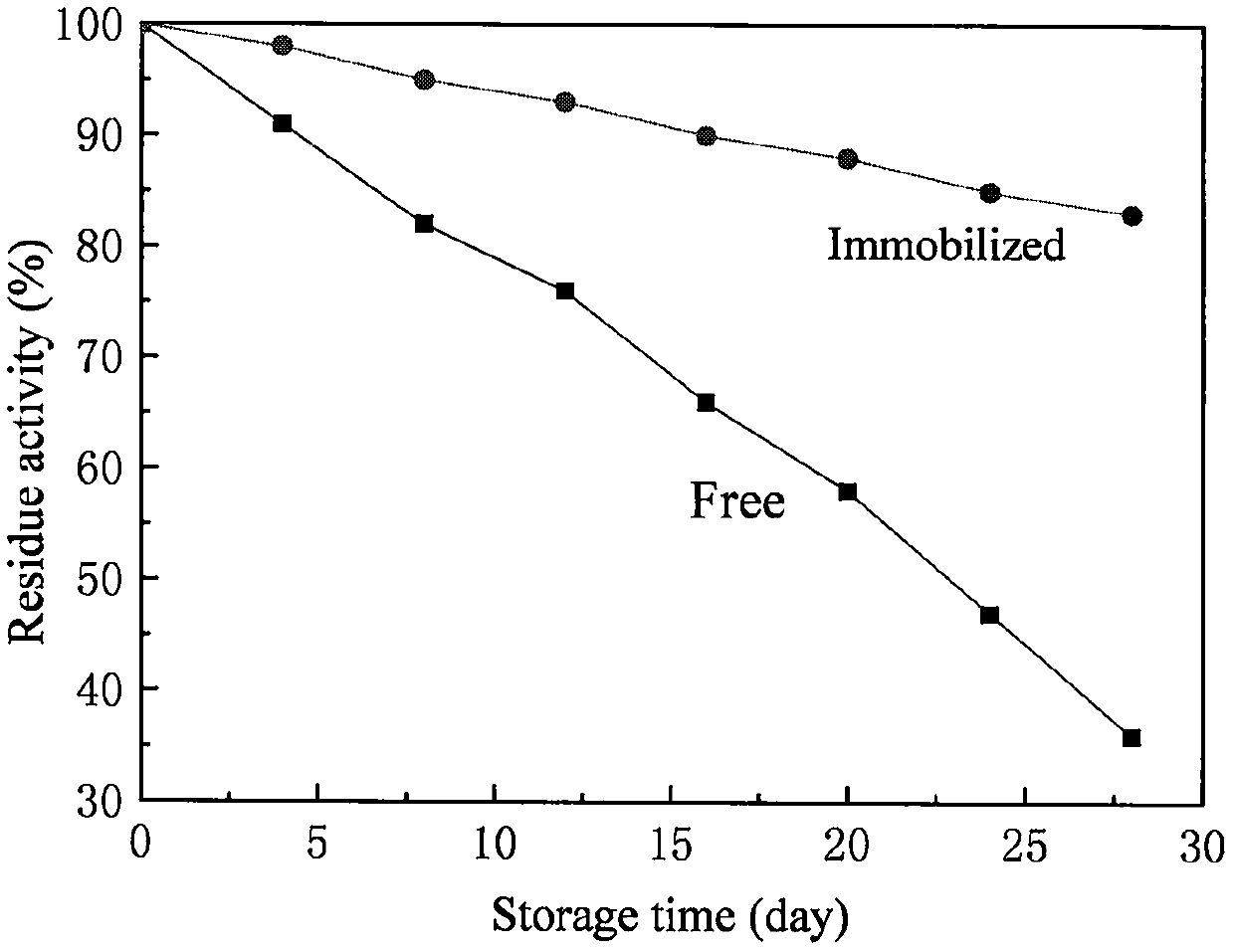
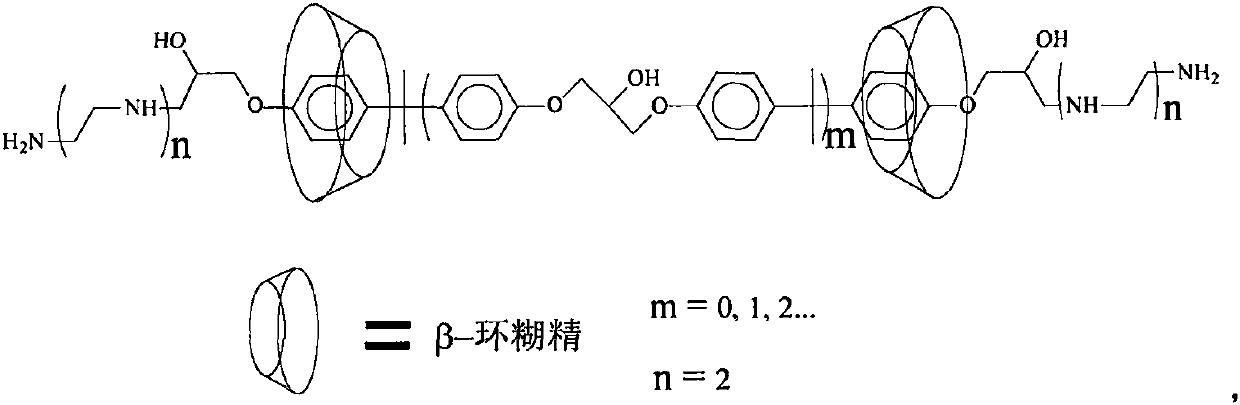
ActiveCN110760496AImprove microenvironmentHigh catalytic activityHydrolasesChemical industryEpoxyPolymer science
The invention discloses a co-crosslinking immobilization method of penicillin G acylase. According to the co-crosslinking immobilization method of the penicillin G acylase, oil-soluble butanediol diacrylate is used as a crosslinking agent; penicillin G acylase containing amino groups, as well as a supramolecular complex formed by aminated epoxy resin and beta-cyclodextrin are used as reactants inan aqueous phase; and then, through a Michael addition reaction of the amino groups with double bonds, co-crosslinking polymerization is conducted at a relatively low temperature so as to prepare immobilized penicillin G acylase with different loading capacity. With crosslinking degree controlled, dispersivity enhanced and internal mass transfer microenvironment improved, the immobilized penicillin G acylase has relatively high catalytic activity that relative activity of the immobilized penicillin G acylase can be up to 91% of that of free enzyme when the loading capacity is 37 milligrams ofthe immobilized penicillin G acylase per gram of carrier.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
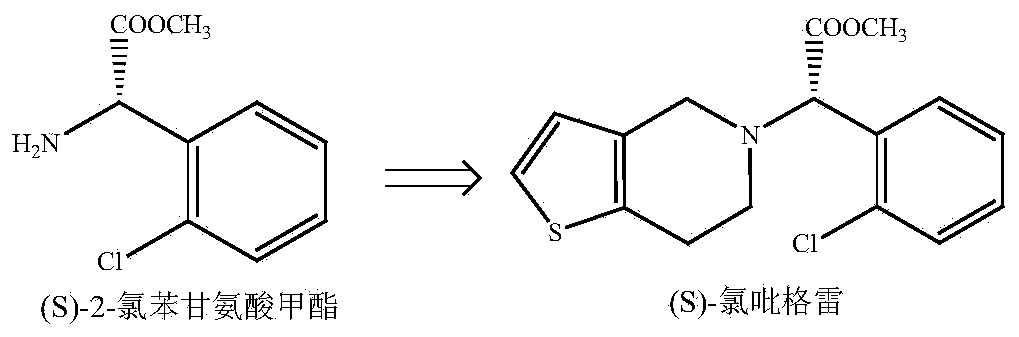
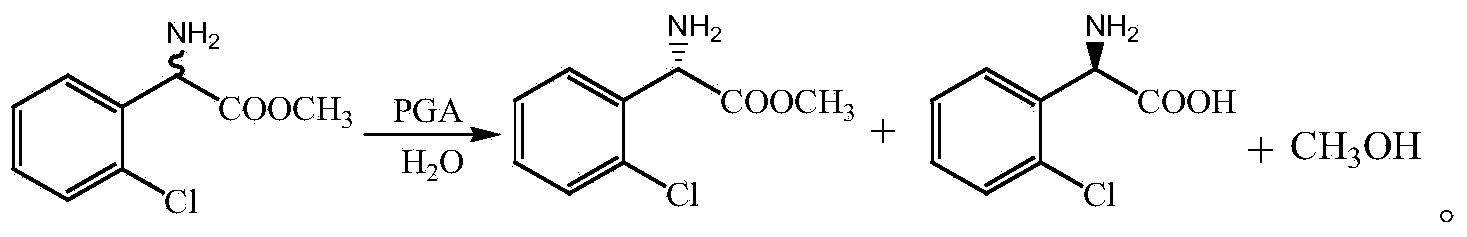
Method for preparing (S)-2-chlorophenylglycine methyl ester single enantiomer by virtue of biological enzyme catalysis
The invention discloses a method for preparing an (S)-2-chlorophenylglycine methyl ester single enantiomer by virtue of biological enzyme catalysis. The method comprises the following steps: adding racemized 2-chlorophenylglycine methyl ester and a sodium phosphate buffer solution into a reactor with the water bath constant temperature of 30 DEG C, stirring, then adding penicillin G acylase, controlling the stirring rotating speed to be 100-500r / min, controlling the reaction time to be 20-60 hours, continuously stirring until reaction ends, and finally recycling penicillin G acylase. The method disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that PGA is adopted as a catalyst, and reaction under normal temperature and normal pressure by using the activity, high selectivity and specificity to substrates of PGA to prepare (S)-2-chlorophenylglycine methyl ester through one-step, so that protection and deprotection processes of reactive groups in chlorophenylglycine can be saved, the (S)-2-chlorophenylglycine methyl ester single enantiomer with higher optical purity also can be obtained, and the enantiomer excess can reach more than 95%; and the method is simple and easily-controllable in operation process, is low in energy consumption in a preparation process, is low in emission, and is of an environment-friendly preparation method.
Owner:NINGXIA UNIVERSITY
Preparation of magnetic immobilized penicillin G acylase doped with divalent manganese ions
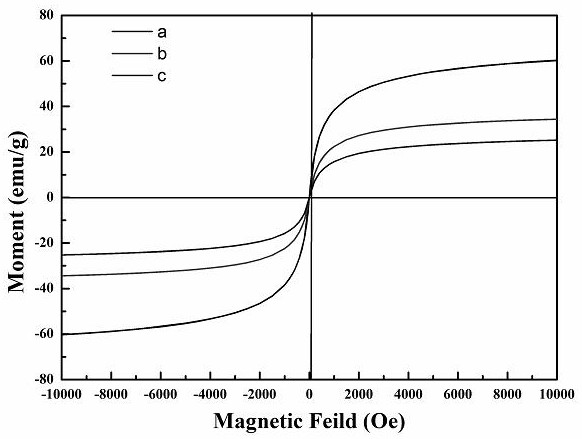
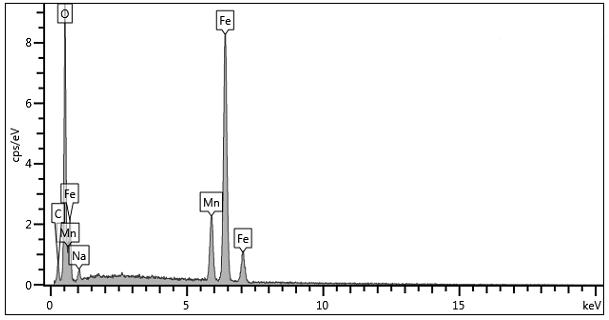
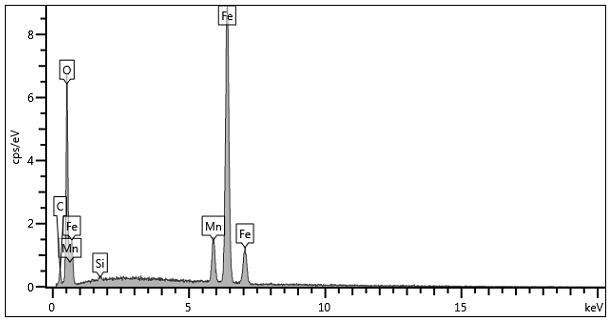
PendingCN113462680ASmall particle sizeSmall specific surface areaHydrolasesOn/in organic carrierCyclodextrinMagnetite Nanoparticles
The invention relates to preparation of magnetic immobilized penicillin G acylase doped with divalent manganese ions. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing magnetic nanoparticles ferroferric oxide@beta-cyclodextrin doped with divalent manganese ions; (2) carrying out mixed reaction on an ethanol solution of 3-glycidyl ether oxypropyl trimethoxy silane with the magnetic nanoparticle ferroferric oxide@beta-cyclodextrin doped with the divalent manganese ionst, so as to obtain a magnetic nanoparticle ferroferric oxide@beta-cyclodextrin-g-3-glycidyl ether oxypropyl trimethoxy silane carrier doped with the divalent manganese ions; and (3) adding the divalent manganese ion-doped magnetic nanoparticle ferroferric oxide@beta-cyclodextrin-g-3-glycidyl ether oxypropyl trimethoxy silane carrier dissolved in a phosphate buffer solution into a free penicillin G acylase solution, carrying out oscillatory reaction, and then carrying out vacuum drying to obtain the magnetic immobilized penicillin G acylase carrier doped with the divalent manganese ions. The method can effectively improve the enzyme activity recovery rate.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
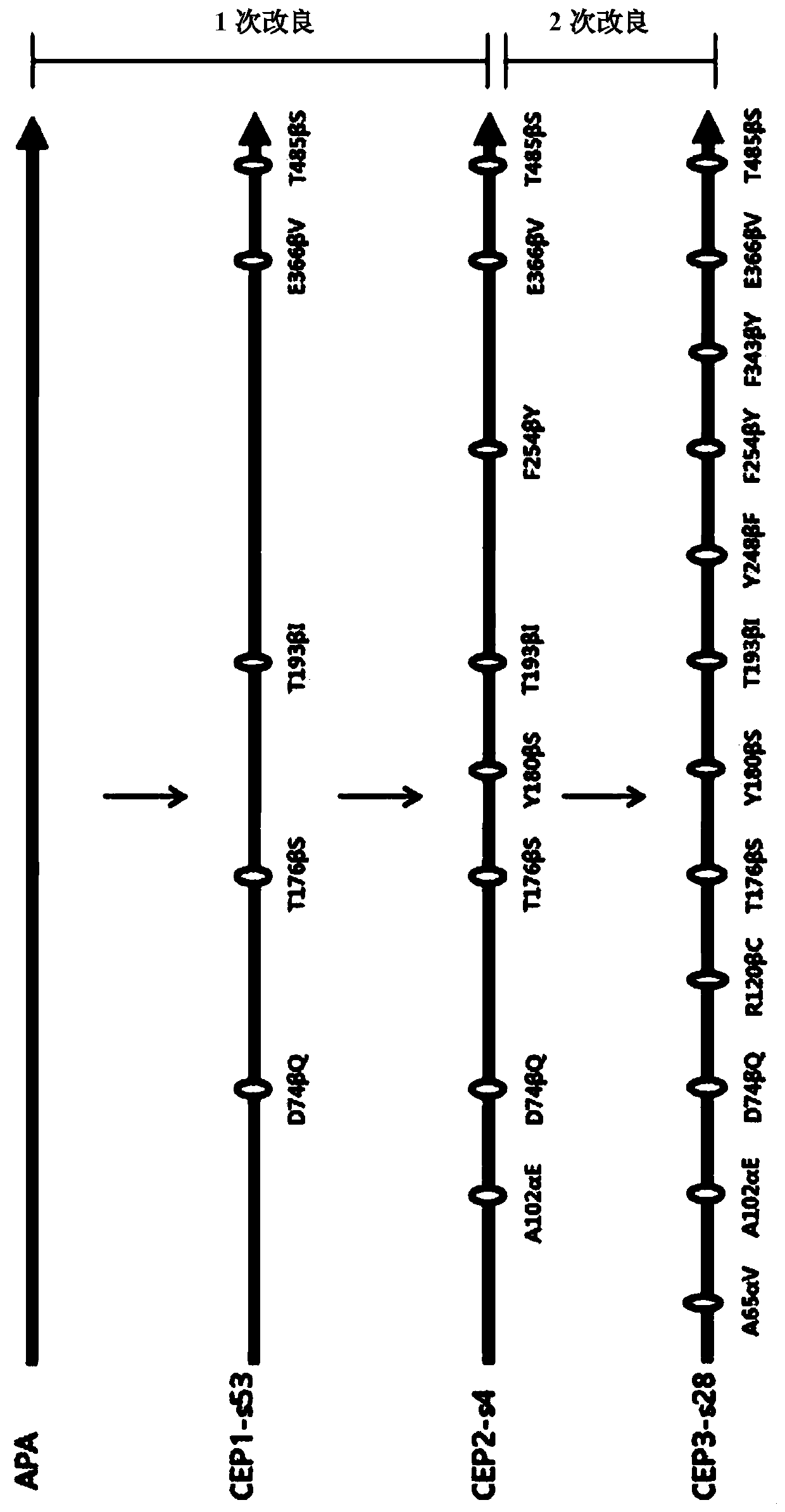
Mutants of penicillin G acylase from Achromobacter sp. CCM 4824 and uses thereof
ActiveCN109971743AHigh synthetic activityIncrease productionBacteriaHydrolasesGenus AchromobacterBeta lactam antibiotic
The present invention relates to mutants of penicillin G acylase from Achromobacter sp. CCM 4824 and uses thereof, and more specifically relates to Mutants of penicillin G acylase in a wild type penicillin G acylase protein sequence including an Alpha subunit shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and a Beta subunit shown in SEQ ID NO.2 and a method of preparing (synthesizing) Beta-Lactam antibiotics by using theMutants of penicillin G acylase, wherein the Mutants of penicillin G acylase select at least one mutation from a population consisting of A65AlphaV, A102AlphaE, A106AlphaT, D74BetaQ, R120BetaC, T176BetaS, Y180BetaS, T193BetaI, Y248BetaF, F254BetaY, T292BetaS, F343BetaY, E366BetaV and T485BetaS as the feature. The Mutants of penicillin G acylase from Achromobacter sp. CCM 4824, having a specific mutation form, are characterized by multiple syntheses with high efficiency for multiple semi-synthesized Beta-Lactam antibiotics.
Owner:艾美科健株式会社
Primary amino group immobilized enzyme carrier and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107641623BLarge apertureIncrease enzyme activityImmobilised enzymesFermentationOxidative enzymeCombinatorial chemistry
The invention discloses a primary amine immobilized enzyme carrier and a preparation method thereof. Positive suspension polarization is performed to obtain a crude macroporous polymethacrylate-diallylamine carrier; washing the crude carrier, and grading; performing amination to obtain the primary amine-containing immobilized enzyme carrier. The primary amine immobilized enzyme carrier according to the technical scheme of the invention is applicable to immobilization of various biological enzymes, provides effective immobilization for penicillin G acylase, D-amino acid oxidase, Gl-7-ACA acylase and the like, and has high enzyme-carrying activity, good mechanical strength and good storage stability. The preparation method is simple and has low cost, and the carrier has significantly improved storage stability and is expectedly applicable to industrial large-scale production.
Owner:天津南开和成科技有限公司
High-selectivity mutant of cefradine synthesizing enzyme and coding gene thereof
The invention discloses high-selectivity mutant of cefradine synthesizing enzyme and a coding gene thereof. The invention provides the following protein obtained by the steps of substituting 142-sitemethionine of an alpha chain of natural penicillin G acylase of escherichia coli with phenylalanine, substituting 24-site phenylalanine of a beta chain with alanine and substituting 67-site serine ofthe beta chain with alanine. The protein provided by the invention has higher activity and Vs / Vh for synthesizing the cefradine and lower alpha and lays foundation for industrialization of enzymatic synthesis of the cefradine.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com