Artificially designed penicillin G acylase proenzyme and coding sequence and applications thereof
A technology of pro-acylase and penicillin, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of low synthase activity, low synthase activity/hydrolase activity, limited increase of synthase activity/hydrolase activity, etc. Enhances hydrophobicity and reduces the effect of water molecule binding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Codon optimization of wild-type penicillin G acylase proenzyme
[0050] Escherichia coli penicillin G acylase proenzyme (NCBI: WP_062871965.1) consists of a signal peptide sequence (26 amino acid residues), an α subunit (209 amino acid residues), a connecting peptide (54 amino acid residues) and a β subunit (557 amino acid residues), after the proenzyme of penicillin G acylase is expressed in E. The proenzyme is folded and protein modified and cleaved, and the connecting peptide is cut off to form a penicillin G acylase mature enzyme composed of α subunit and β subunit, which is a dimer enzyme.
[0051] By analyzing the nucleotide sequence of the wild-type penicillin G acylase proenzyme, its codon usage has a certain bias, and it is necessary to optimize the nucleotide sequence of the wild-type penicillin G acylase proenzyme. These amino acid sequences are converted into nucleotide sequences according to the codon table. During the conversion process, according to the ...
Embodiment 2
[0054] The construction of embodiment 2 recombinant expression vector
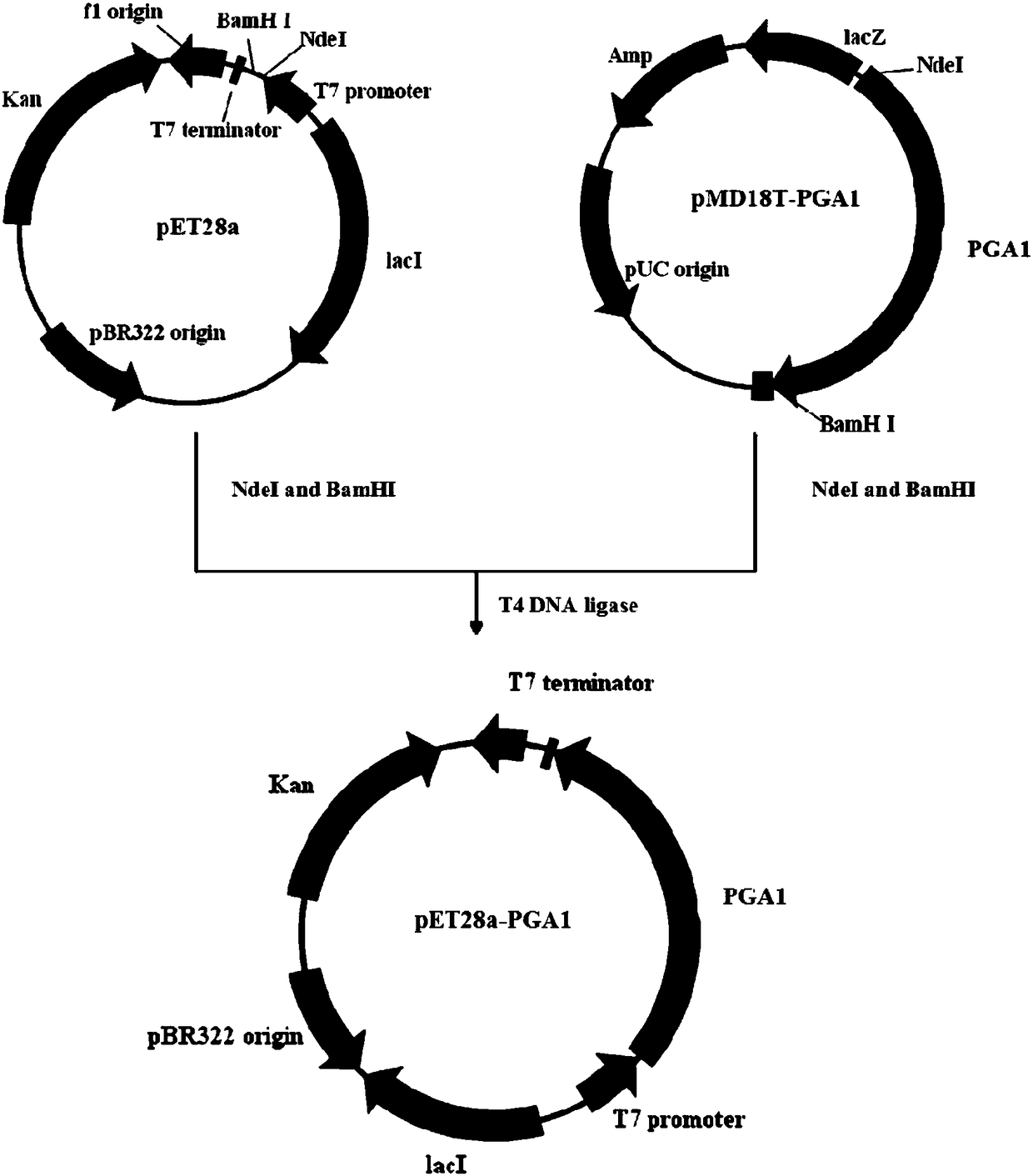
[0055] The pET series vectors developed by Novagen use the T7 promoter with strong starting ability to efficiently drive the expression of target genes, and have become one of the most commonly used prokaryotic expression vectors. The vector pET28a(+) selected by the present invention uses a T7lac composite promoter, which can freely turn off and turn on the expression of genes, and the genes are basically not expressed before induction, which greatly reduces the load on the host bacteria, and can quickly express a large number of target proteins after induction.
[0056] The recombinant vector pMD18T-PGA1 was double-digested with restriction enzymes NdeI and BamHI from TaKaRa Company, and 5 μL of the digested product was analyzed by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis with a mass-volume ratio. After the digestion was complete, all The digested product was subjected to 0.8% agarose electrophoresis with a mass v...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Embodiment 3 site-directed mutagenesis obtains mutant penicillin G acylase
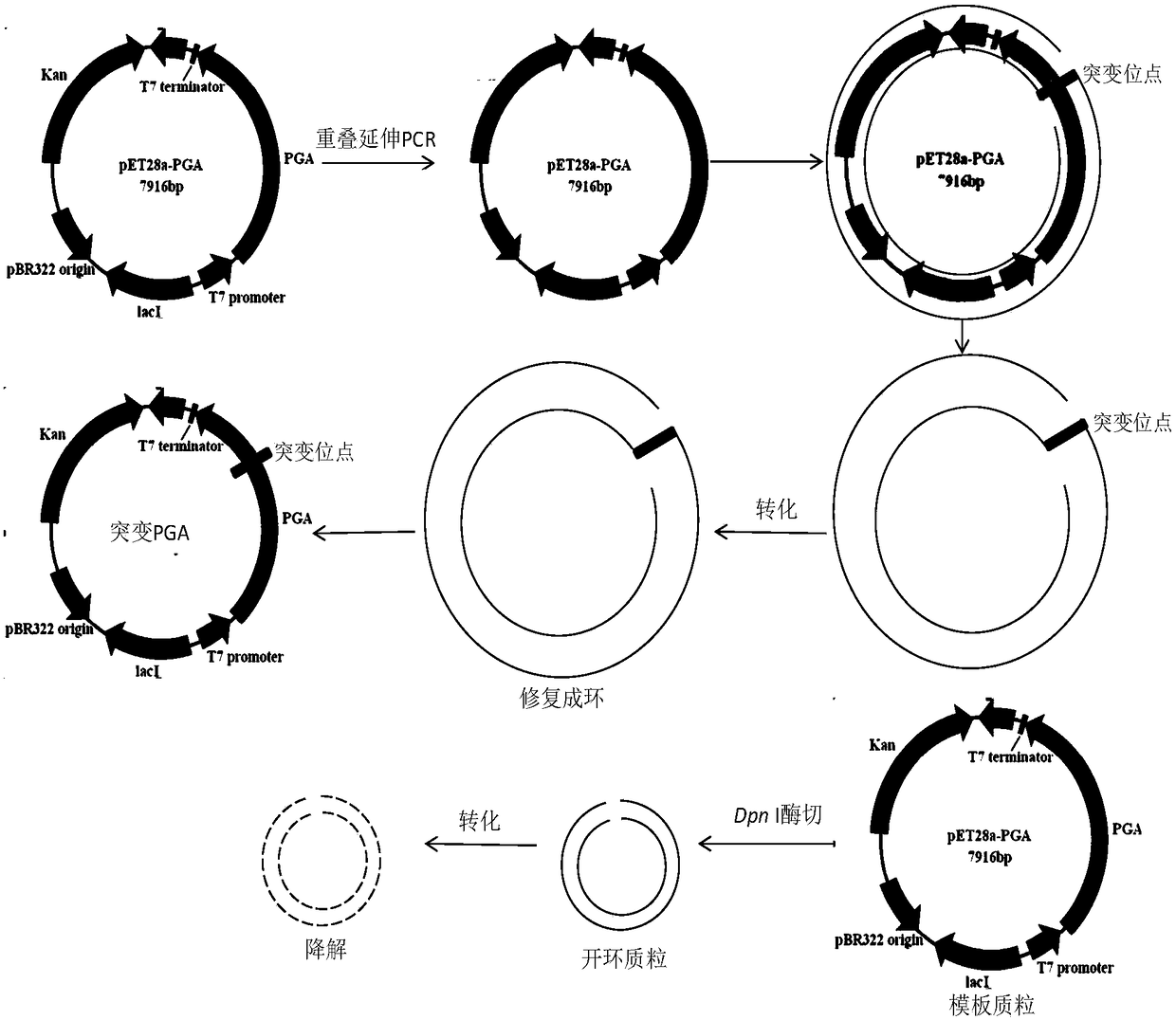
[0058] 1. Obtaining mutant penicillin G acylase PGA2 by site-directed mutagenesis
[0059] Using site-directed mutagenesis technology, using pET28a-PGA1 plasmid as a template, using point mutation primers to perform overlap extension PCR to obtain mutant fragments, and recovering PCR products according to the instructions of the Tiangen nucleic acid purification kit. Use commercial DpnI enzyme to digest and recover PCR products according to the instructions, DpnI can cut off adenine methylated G m The ATC sequence can eliminate the unmutated template, and the PCR product that is not digested by Dpn I enzyme is the mutant plasmid. Add the PCR product digested with Dpn I enzyme directly to 80 μL with CaCl 2coli Top10F' (purchased from Invitrogen) competent cells prepared by the method (the third edition of "Molecular Cloning Experiment Guide" published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, USA), tr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com