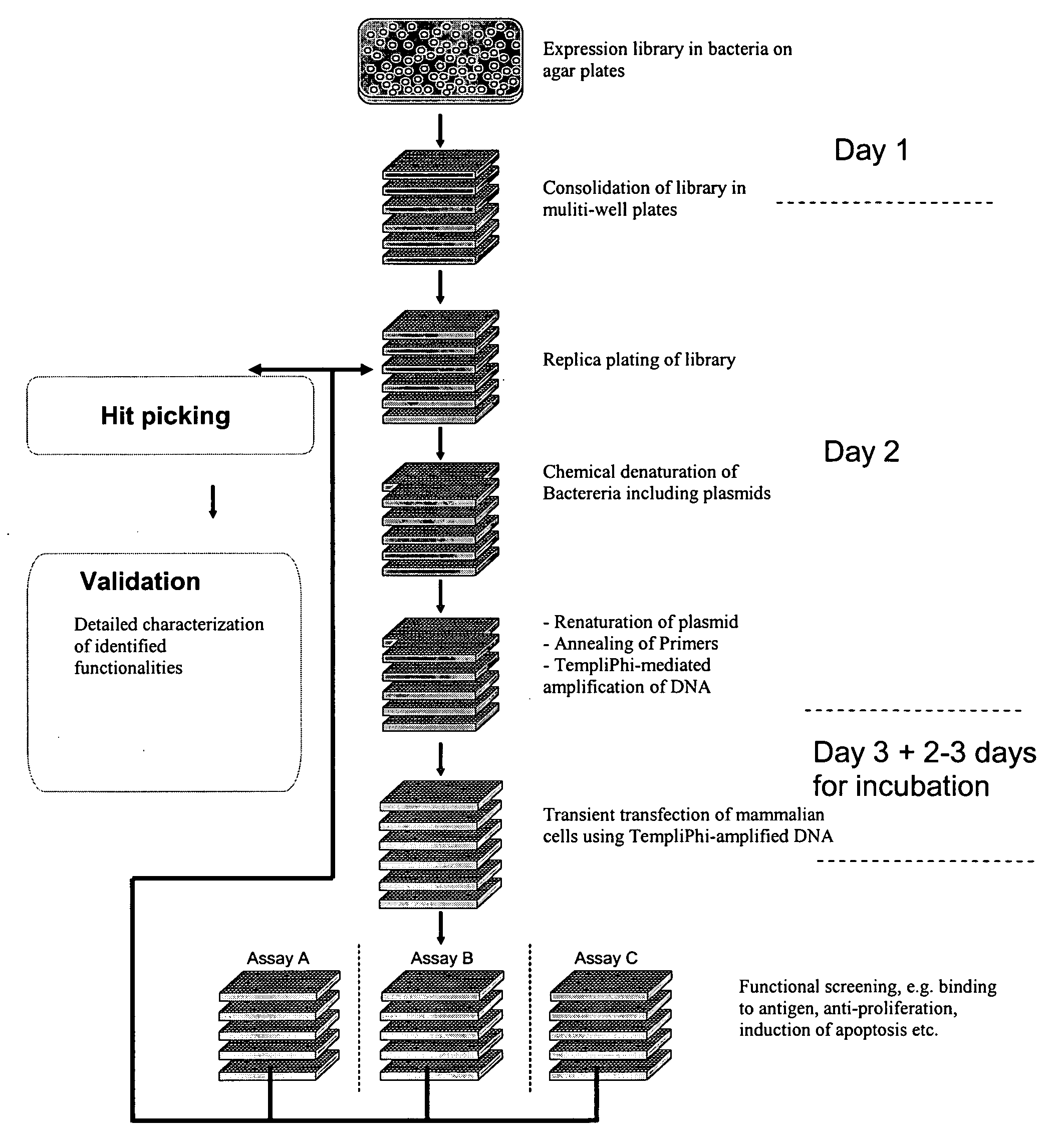
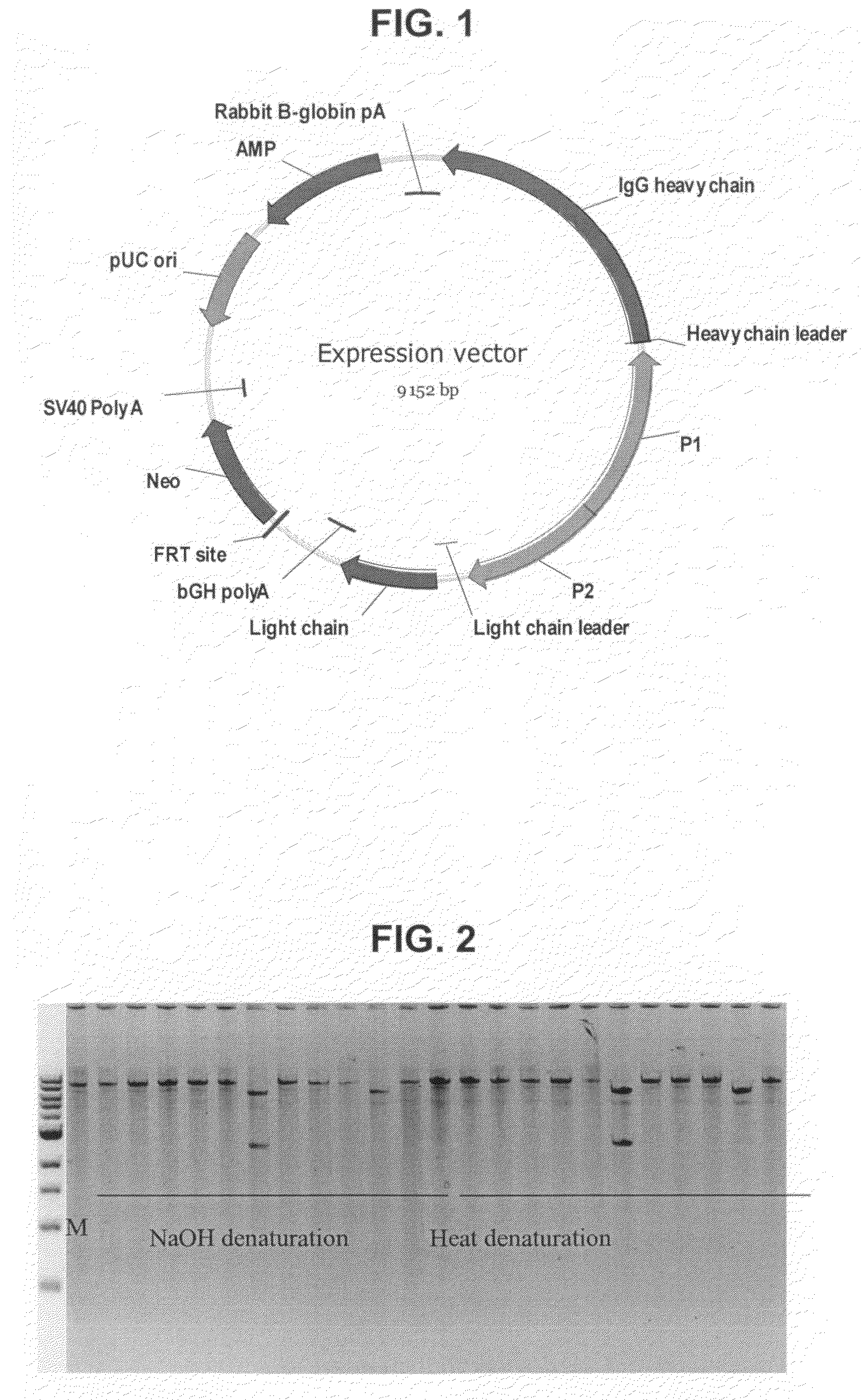
Patents
Literature
279 results about "Molecular cloning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
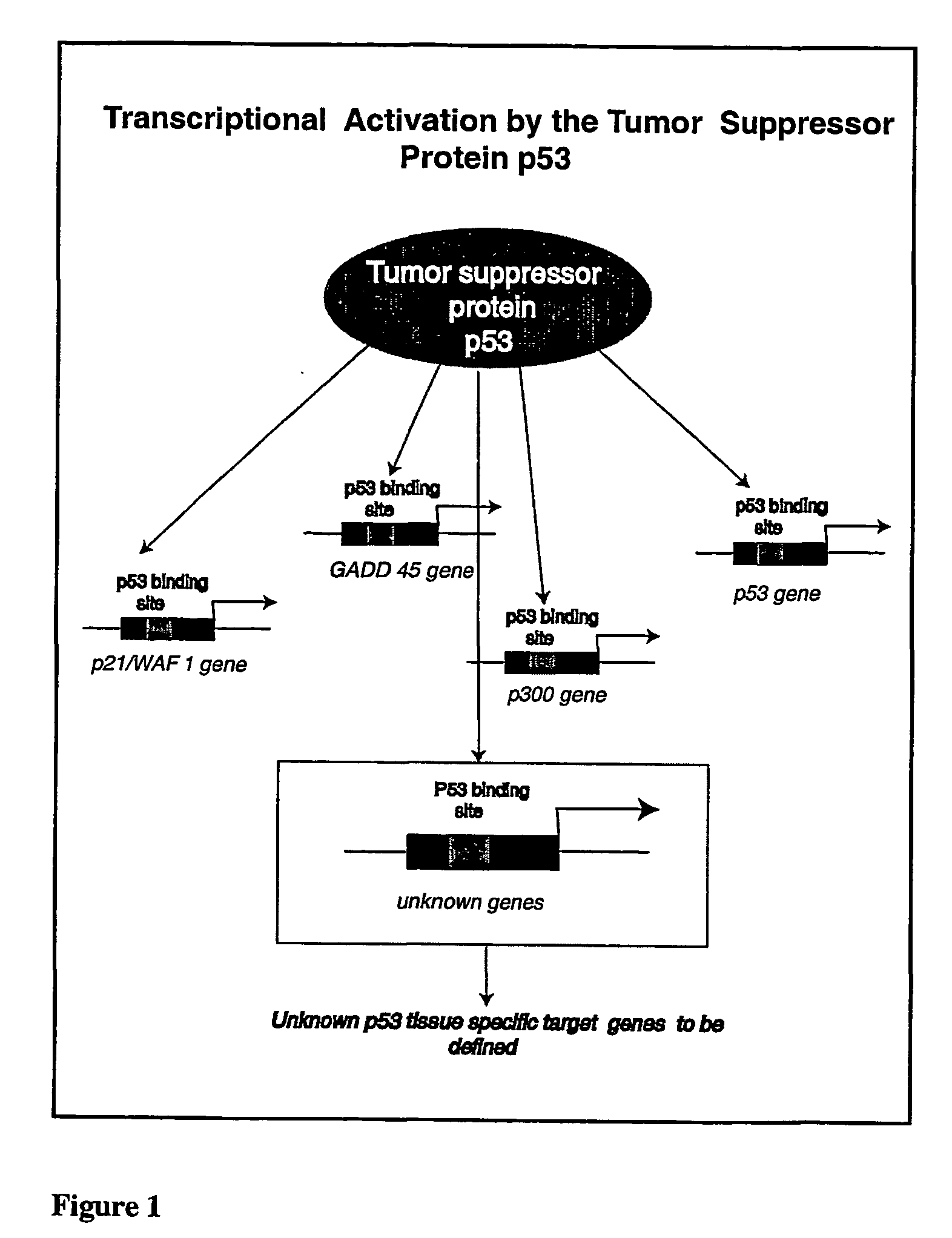
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word cloning refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine.
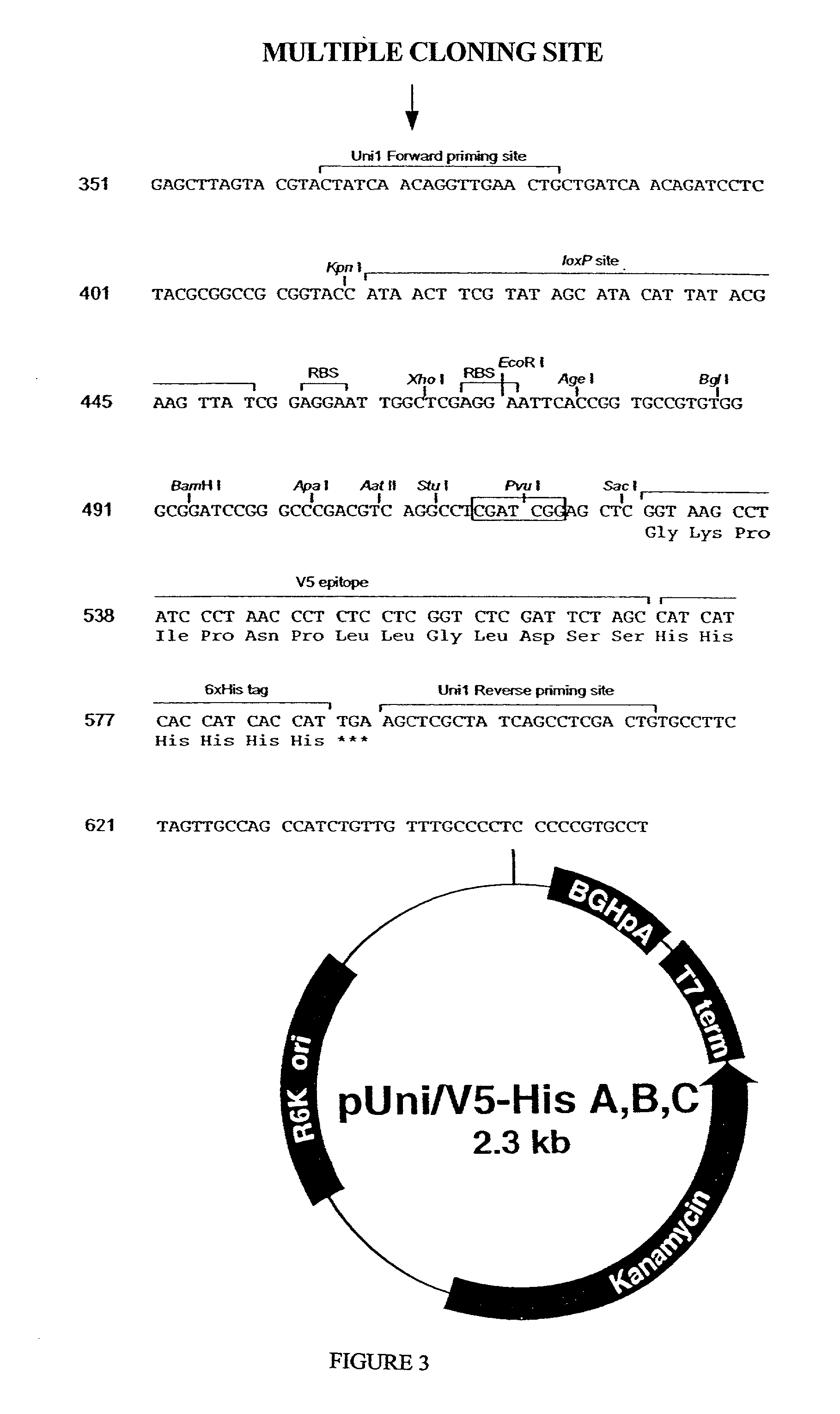
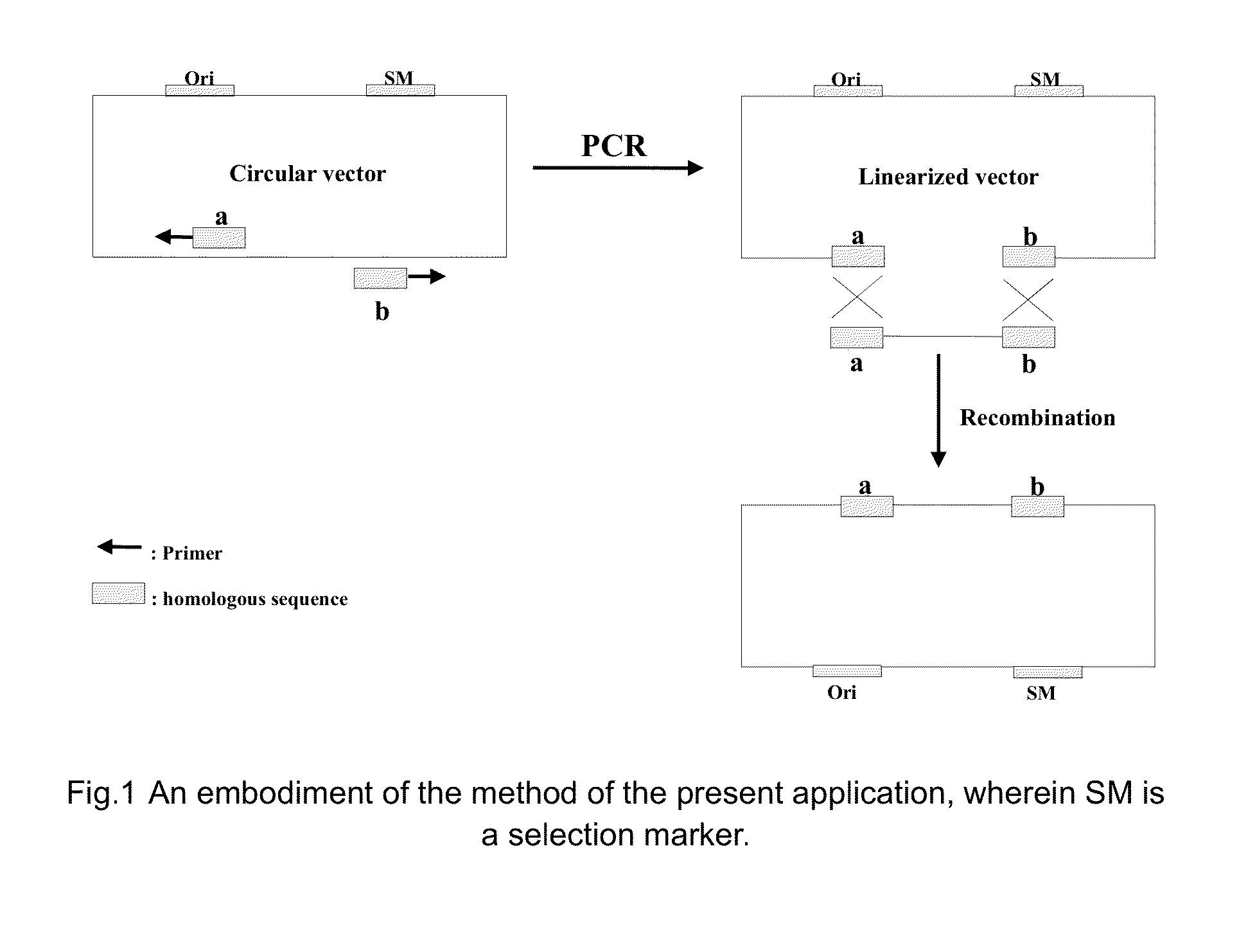
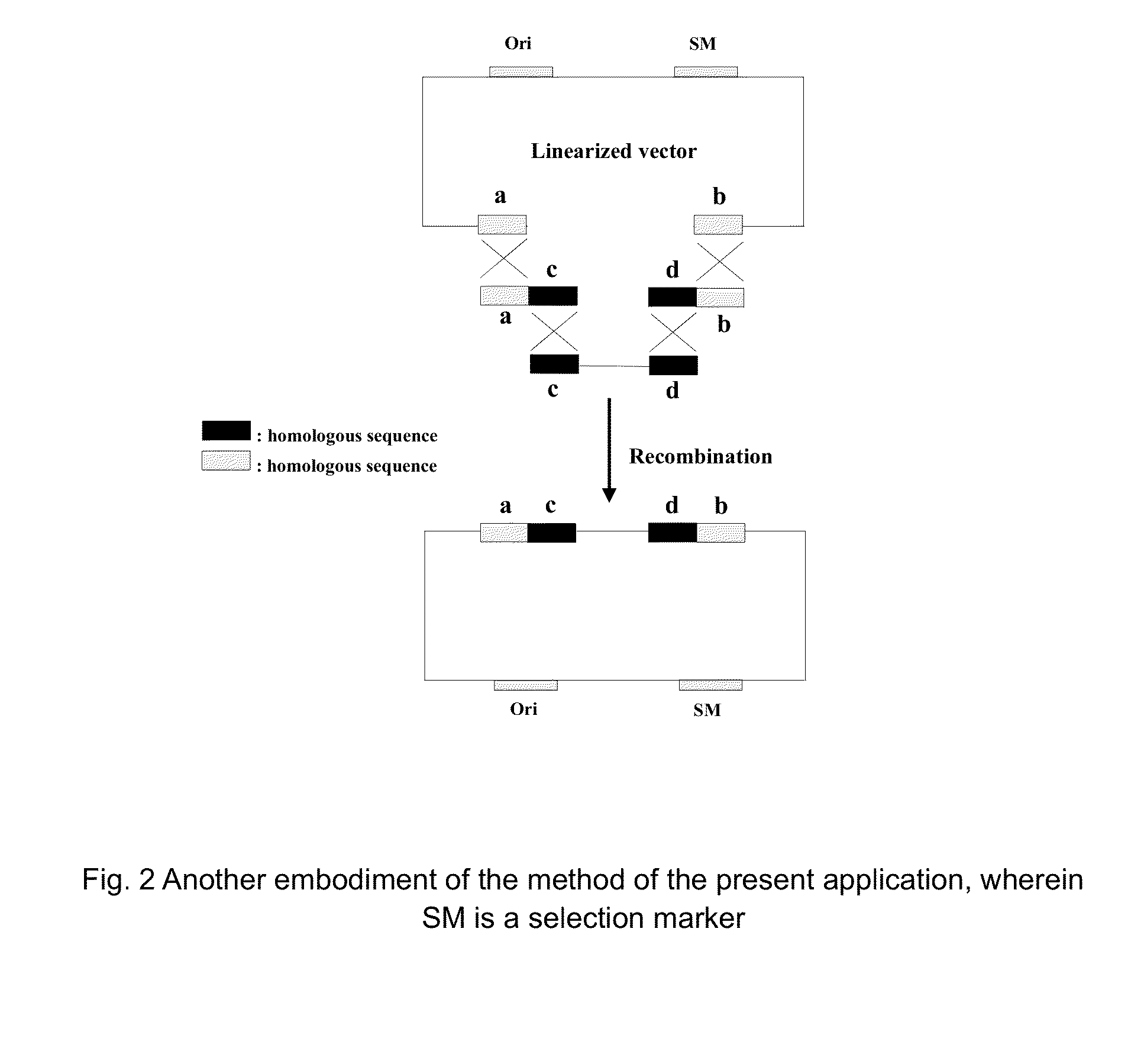
Methods and reagents for molecular cloning
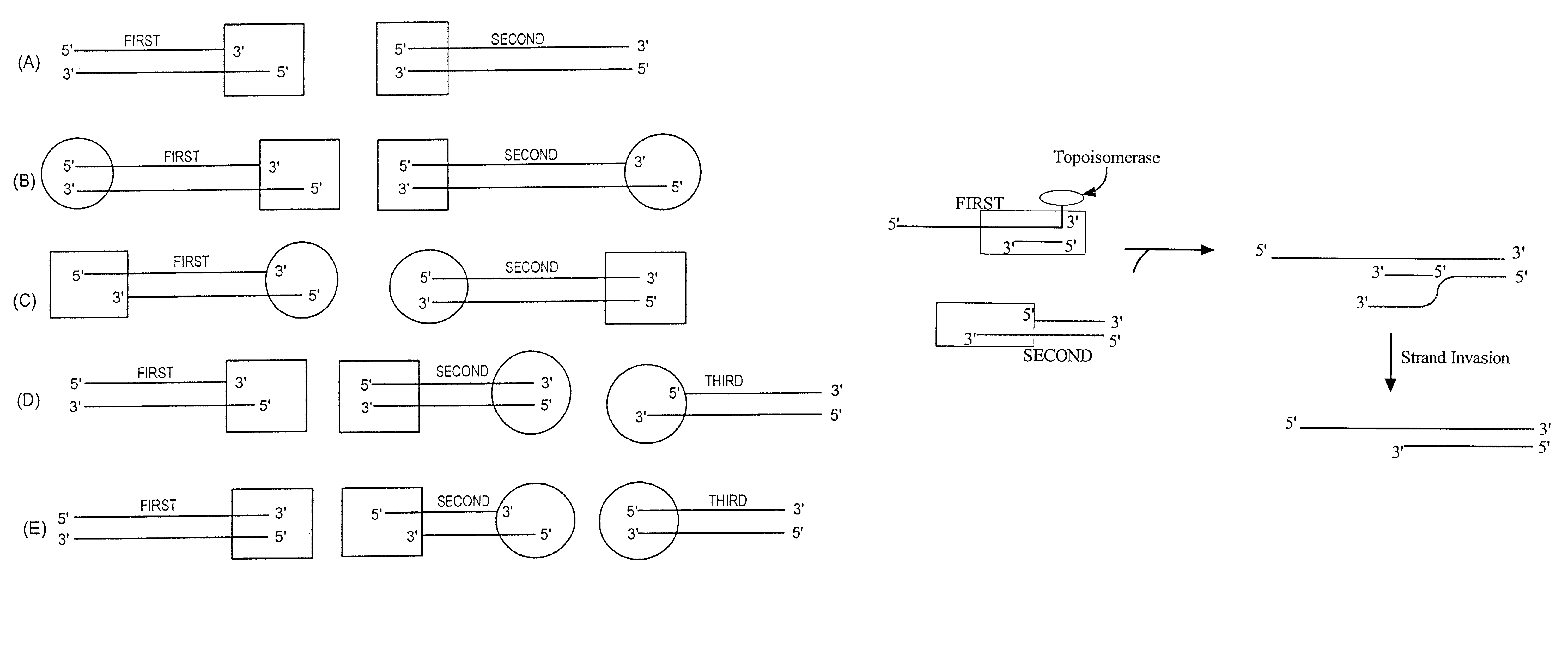
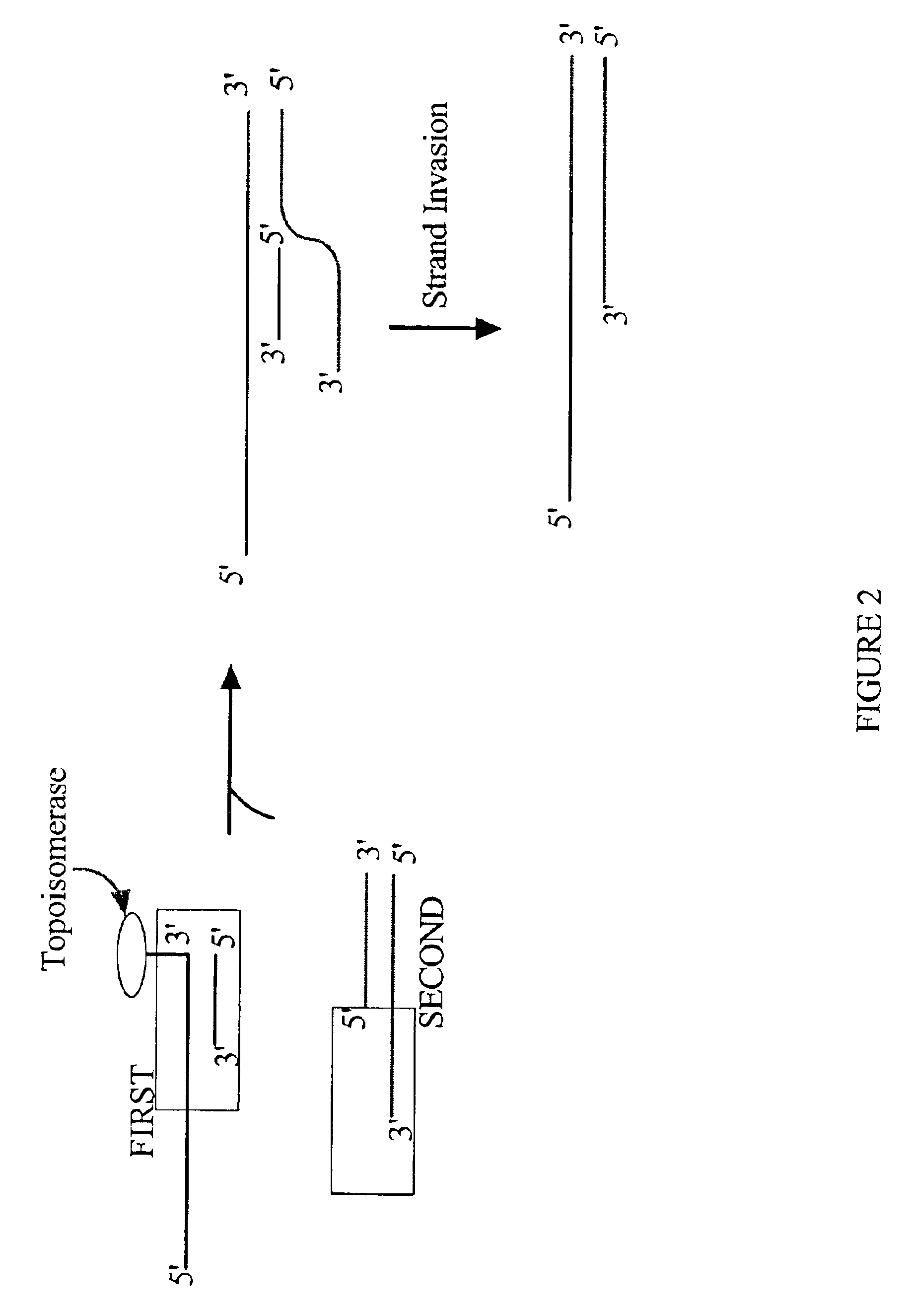
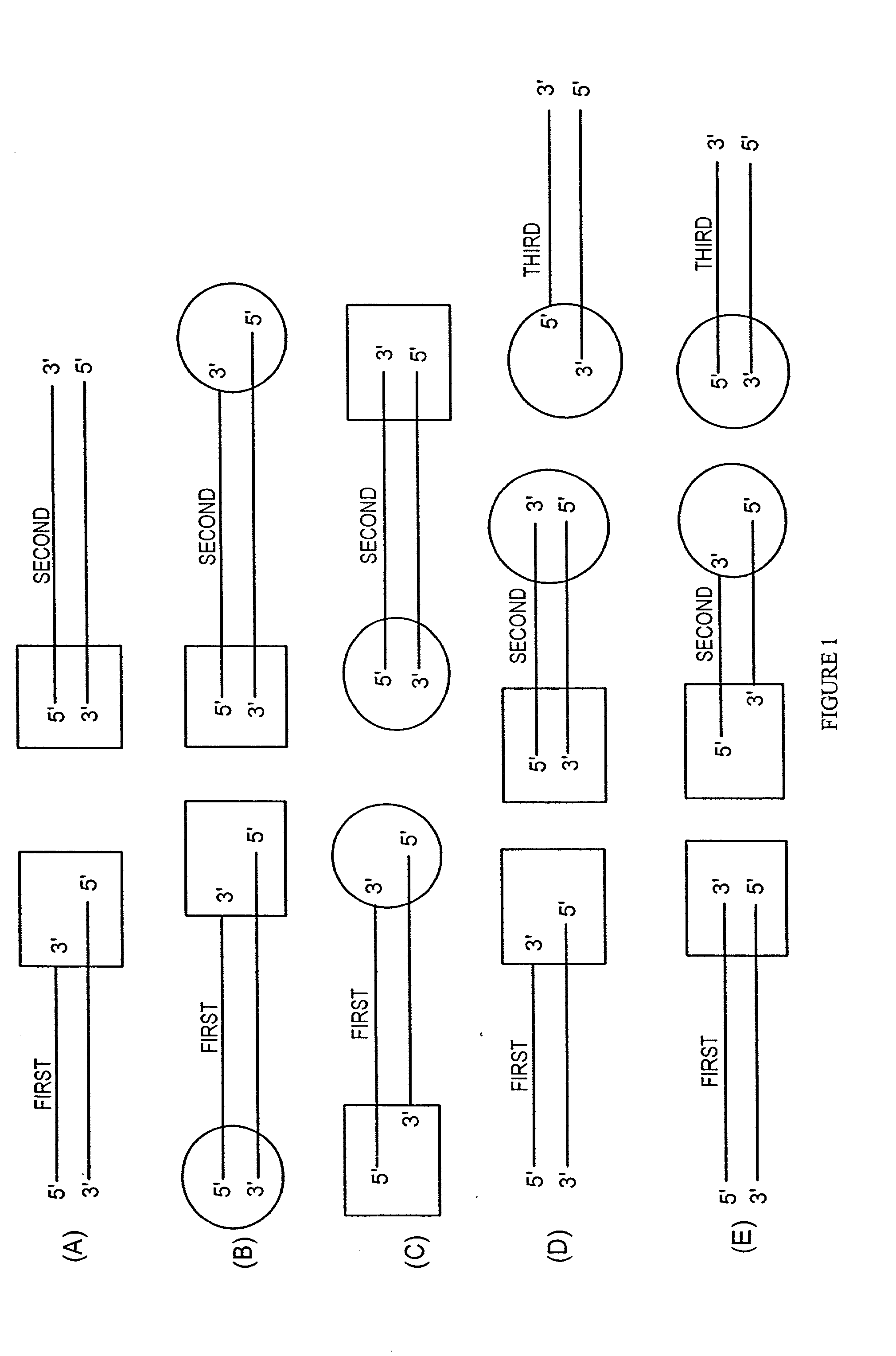
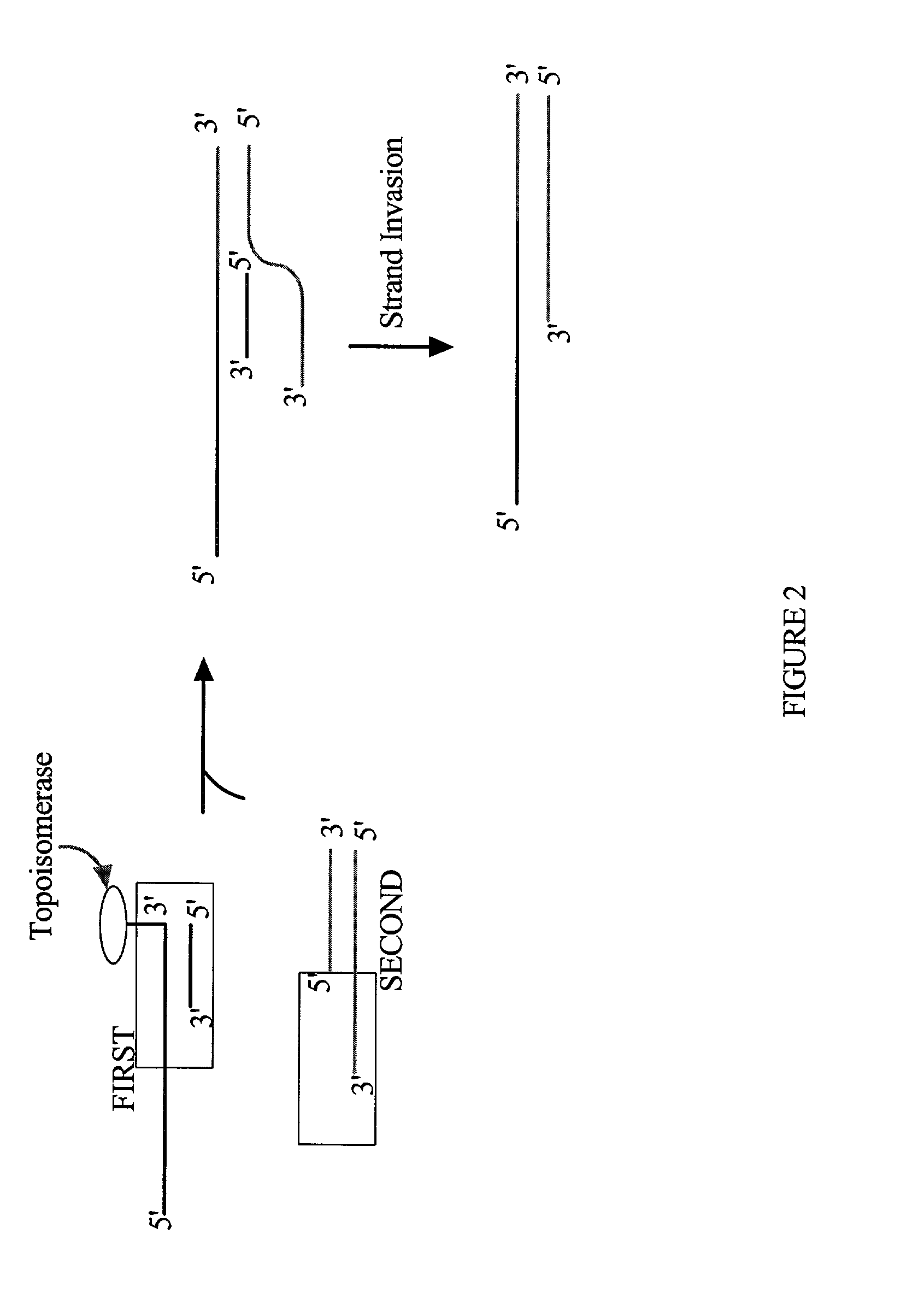
The present invention provides compositions, methods, and kits for covalently linking nucleic acid molecules. The methods include a strand invasion step, and the compositions and kits are useful for performing such methods. For example, a method of covalently linking double stranded (ds) nucleic acid molecules can include contacting a first ds nucleic acid molecule, which has a topoisomerase linked to a 3′ terminus of one end and has a single stranded 5′ overhang at the same end, with a second ds nucleic acid molecule having a blunt end, such that the 5′ overhang can hybridize to a complementary sequence of the blunt end of the second nucleic acid molecule, and the topoisomerase can covalently link the ds nucleic acid molecules. The methods are simpler and more efficient than previous methods for covalently linking nucleic acid sequences, and the compositions and kits facilitate practicing the methods, including methods of directionally linking two or more ds nucleic acid molecules.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES +1
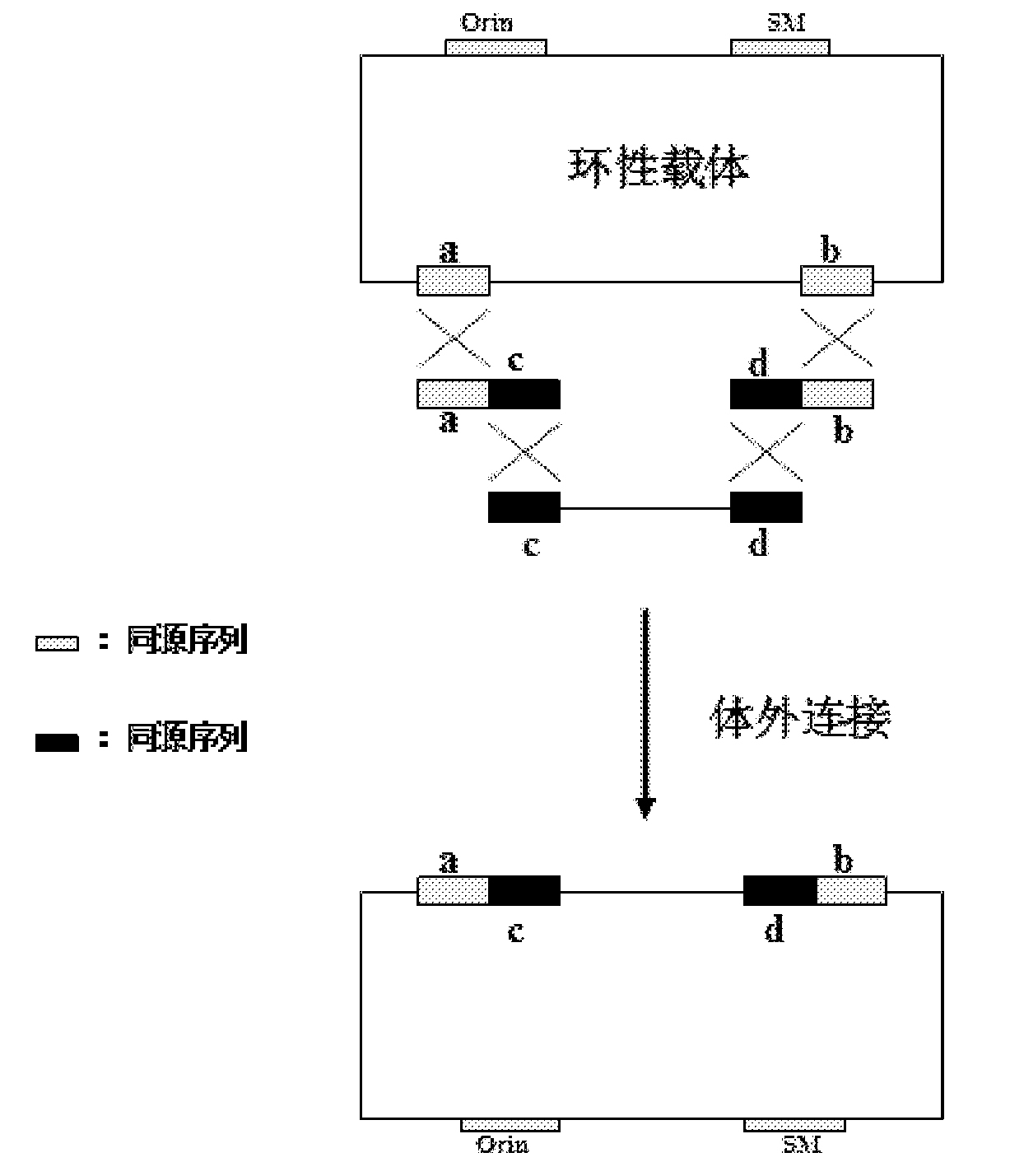
Molecular cloning method based on CRISPR/Cas9 and homologous recombination of saccharomyces cerevisiae cell endogenous genes
ActiveCN105624146AStrong specificityEasy to fragmentFungiVector-based foreign material introductionTime transformationDNA fragmentation
The invention relates to a novel molecular cloning method, and in particular to a method for obtaining recombinant vectors by modifying initial vectors through combined utilization of a CRISPR / Cas9 system and a saccharomyces cerevisiae cell endogenous gene homologous recombination system; only through one-time transformation and selection operations, the method can simultaneously complete insertion of ore or more target DNA fragments into the initial vectors, deletion of one or more DNA fragments from the initial vectors and / or substitution of one or more DNA fragments on the vectors for one or more target DNA fragments. The invention further relates to a reagent kit for conveniently and effectively applying the method provided by the invention.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods and reagents for molecular cloning
The present invention provides compositions, methods, and kits for covalently linking nucleic acid molecules. The methods include a strand invasion step, and the compositions and kits are useful for performing such methods. For example, a method of covalently linking double stranded (ds) nucleic acid molecules can include contacting a first ds nucleic acid molecule, which has a topoisomerase linked to a 3' terminus of one end and has a single stranded 5' overhang at the same end, with a second ds nucleic acid molecule having a blunt end, such that the 5' overhang can hybridize to a complementary sequence of the blunt end of the second nucleic acid molecule, and the topoisomerase can covalently link the ds nucleic acid molecules. The methods are simpler and more efficient than previous methods for covalently linking nucleic acid sequences, and the compositions and kits facilitate practicing the methods, including methods of directionally linking two or more ds nucleic acid molecules.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES +1
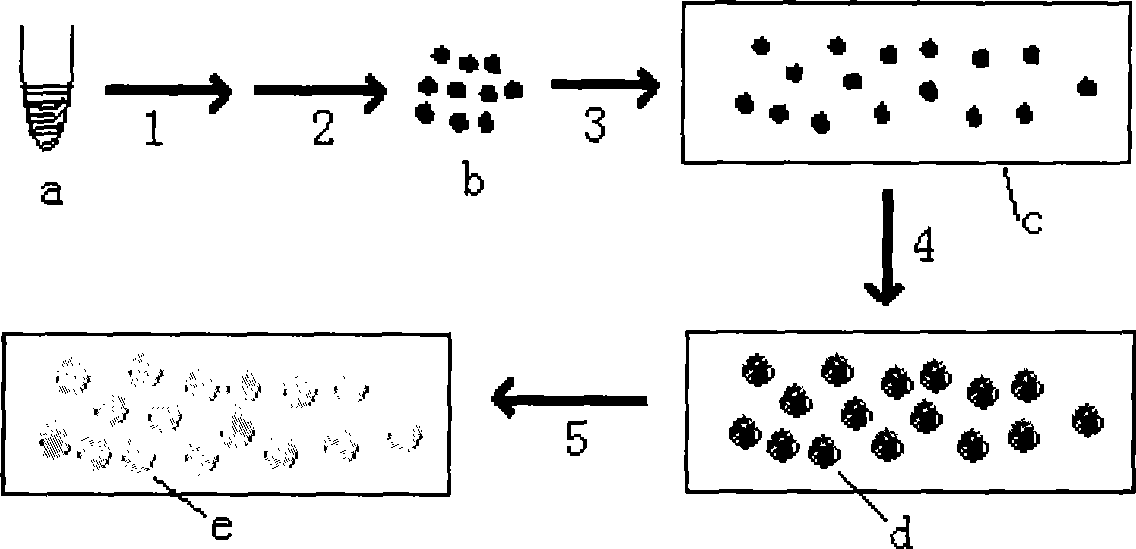
Method for preparing molecular cloning chip for high-throughput cloning of nucleic acid molecule
InactiveCN101413034AEasy to manufactureMiscellaneous transactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationOil phaseWater in oil emulsion
The invention provides a method for preparing a molecular cloning chip by cloning high flux nucleic acid molecule. The method comprises the following steps: a. a cloning nucleic acid molecule template is mixed with a nucleic acid amplification reaction system reagent to obtain an amplification mixture solution; b. the amplification mixture solution is added with a high molecular compound; c. the solution is added with oil phase, of which the volume is two times of the volume of the solution for emulsification to obtain water-in-oil emulsion; d. the emulsion is placed in a PCR meter or a thermostat to undergo a nucleic acid amplification reaction; e. after the nucleic acid amplification reaction, the emulsion is cooled down to form nucleic acid molecule cloning grains; f. the nucleic acid molecule cloning grains are separated; and g. the nucleic acid molecule cloning grains are randomly dispersed on a solid phase carrier to fix the nucleic acid amplification products in the solution on the solid phase carrier and form a nucleic acid molecule cloning array on the surface of the solid phase carrier and thus the cloning chip is obtained. The method has the advantages of improving preparation sequencing template, ensuring high flux of sequencing and lowering sequencing cost.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
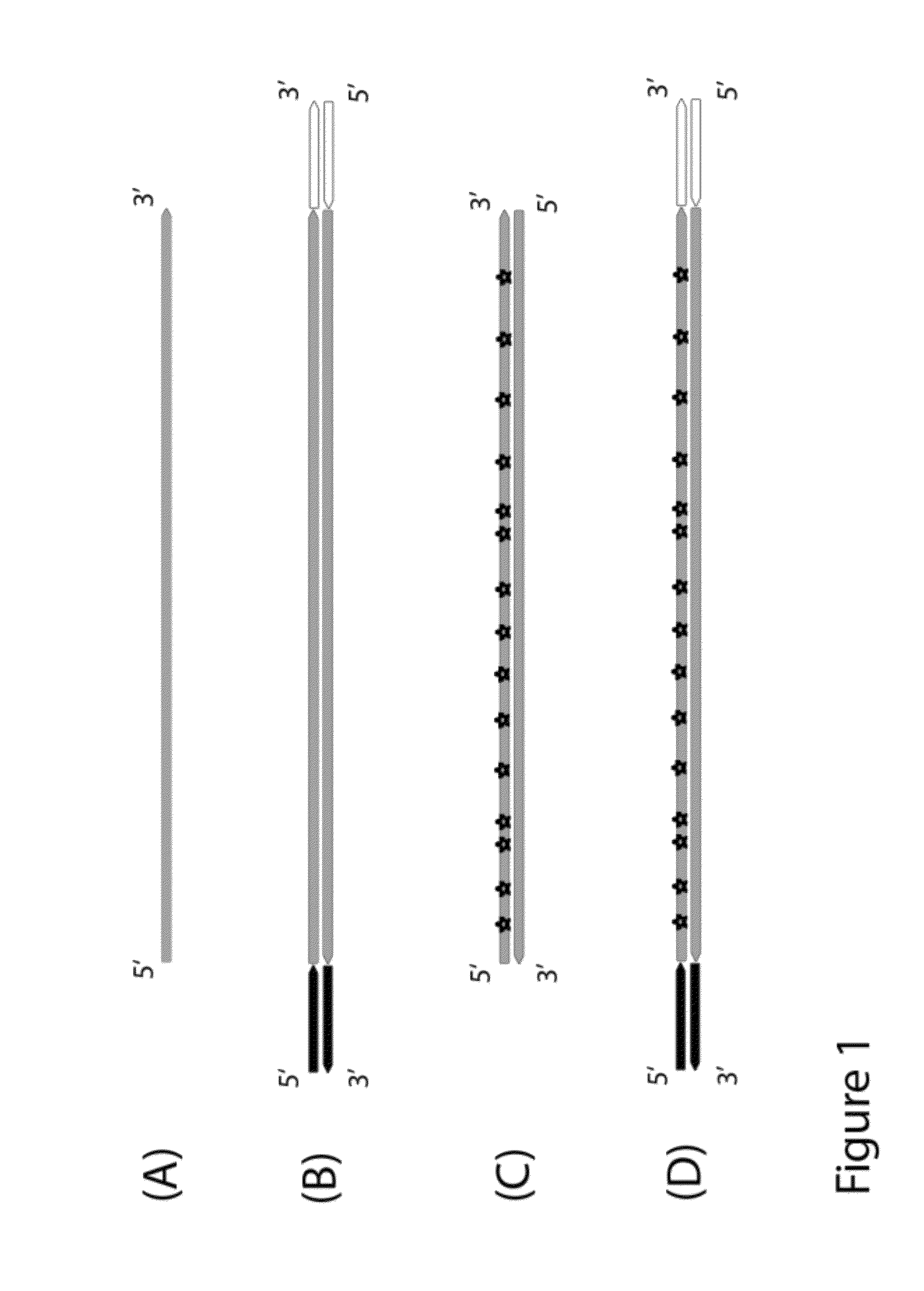
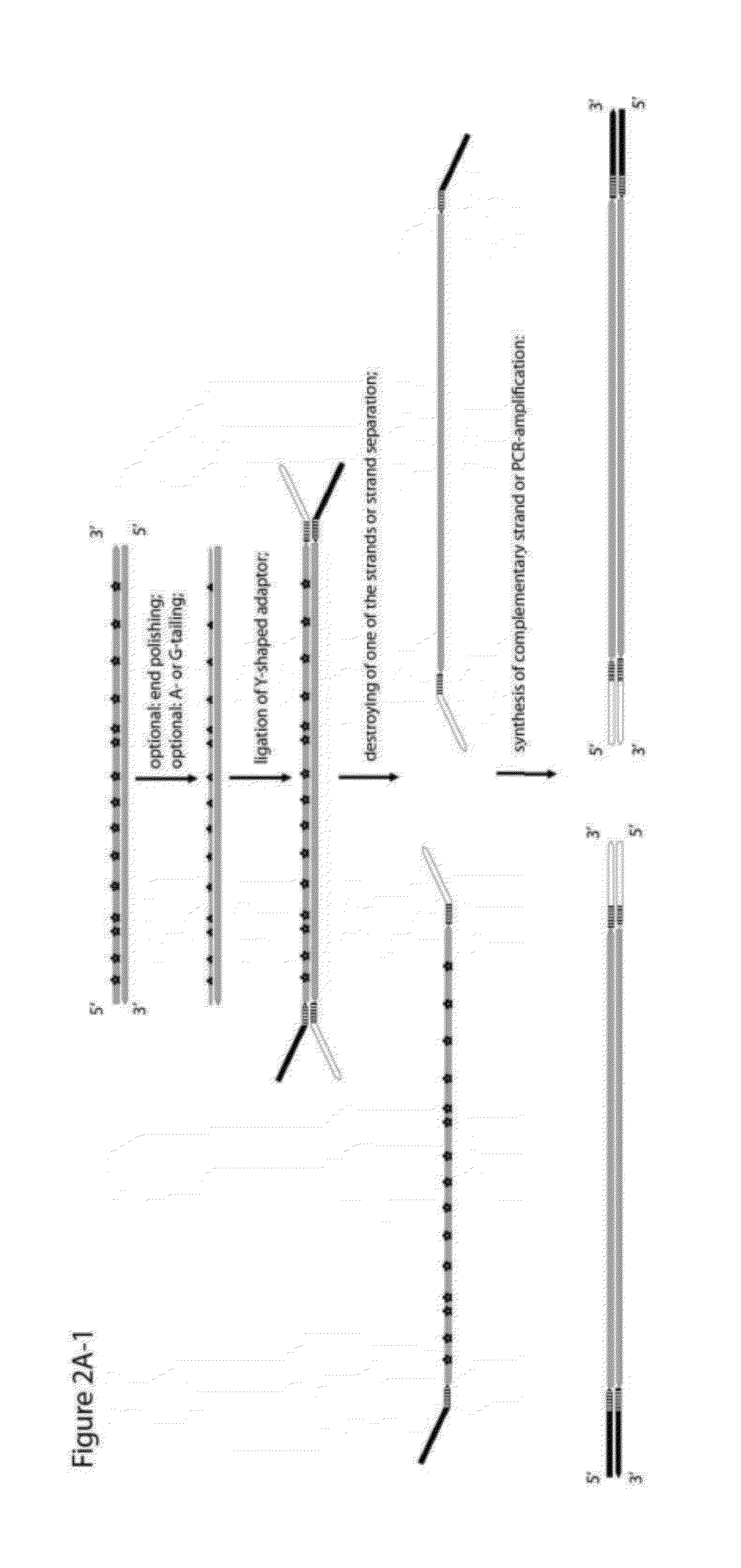
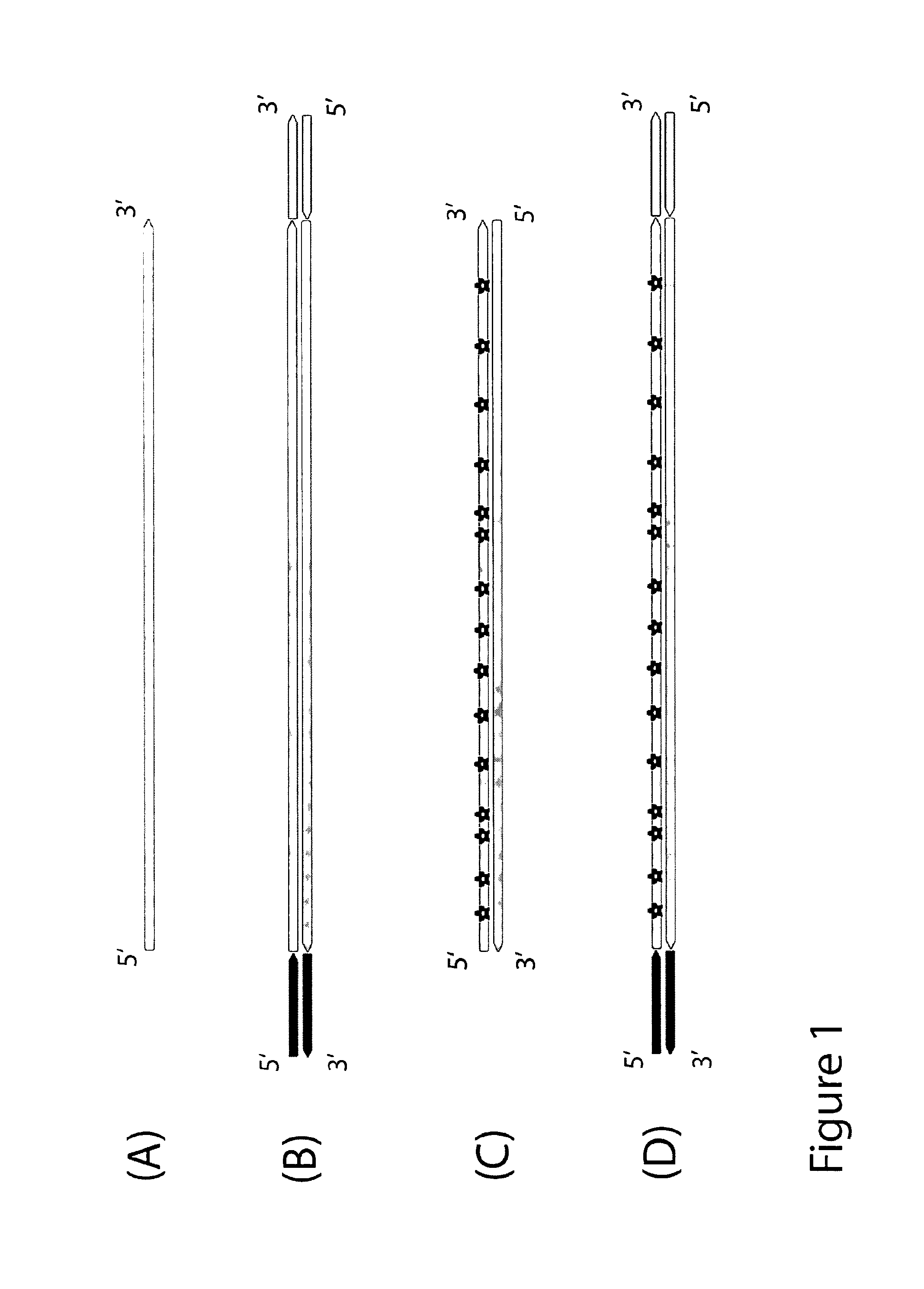
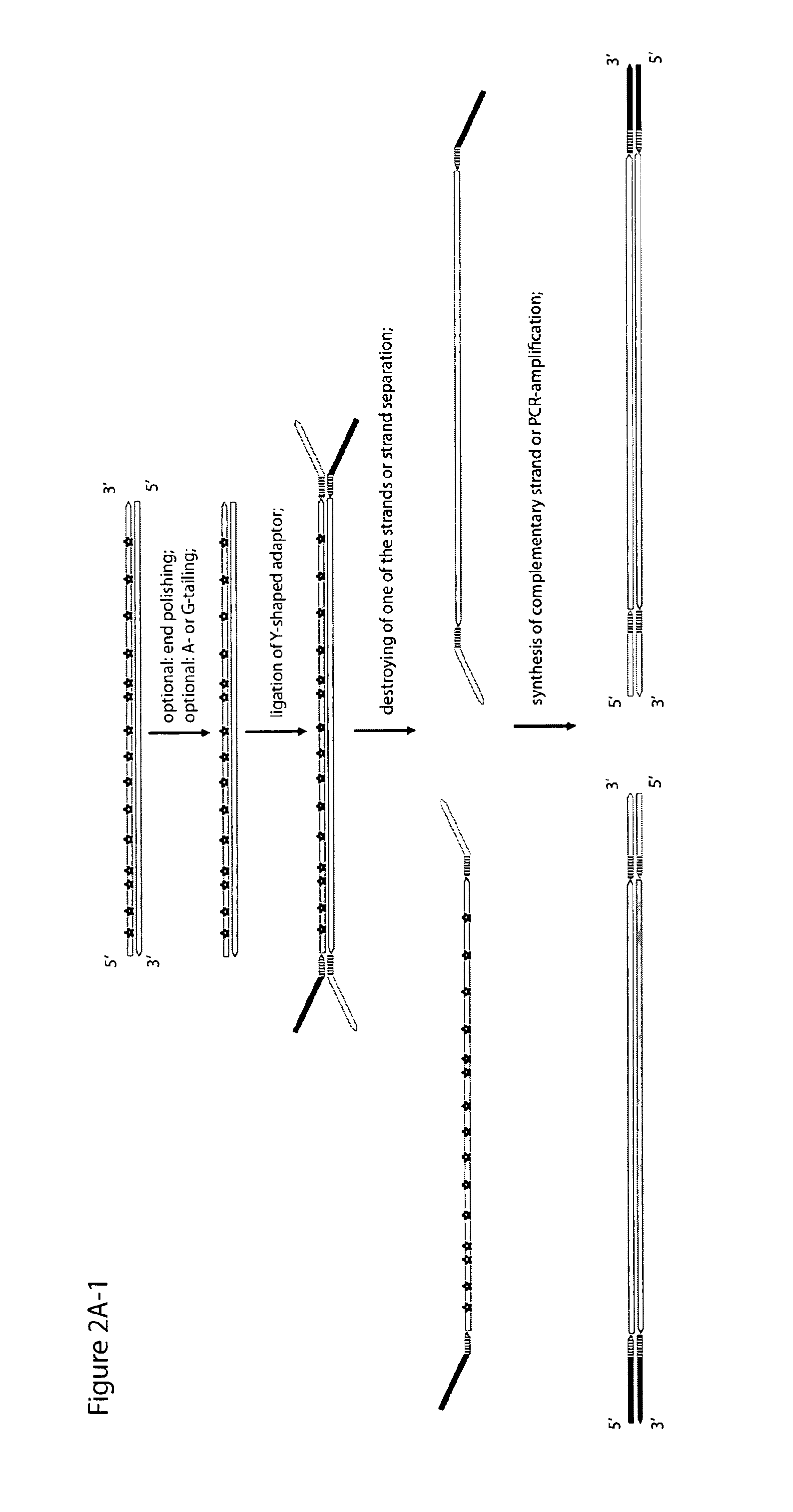
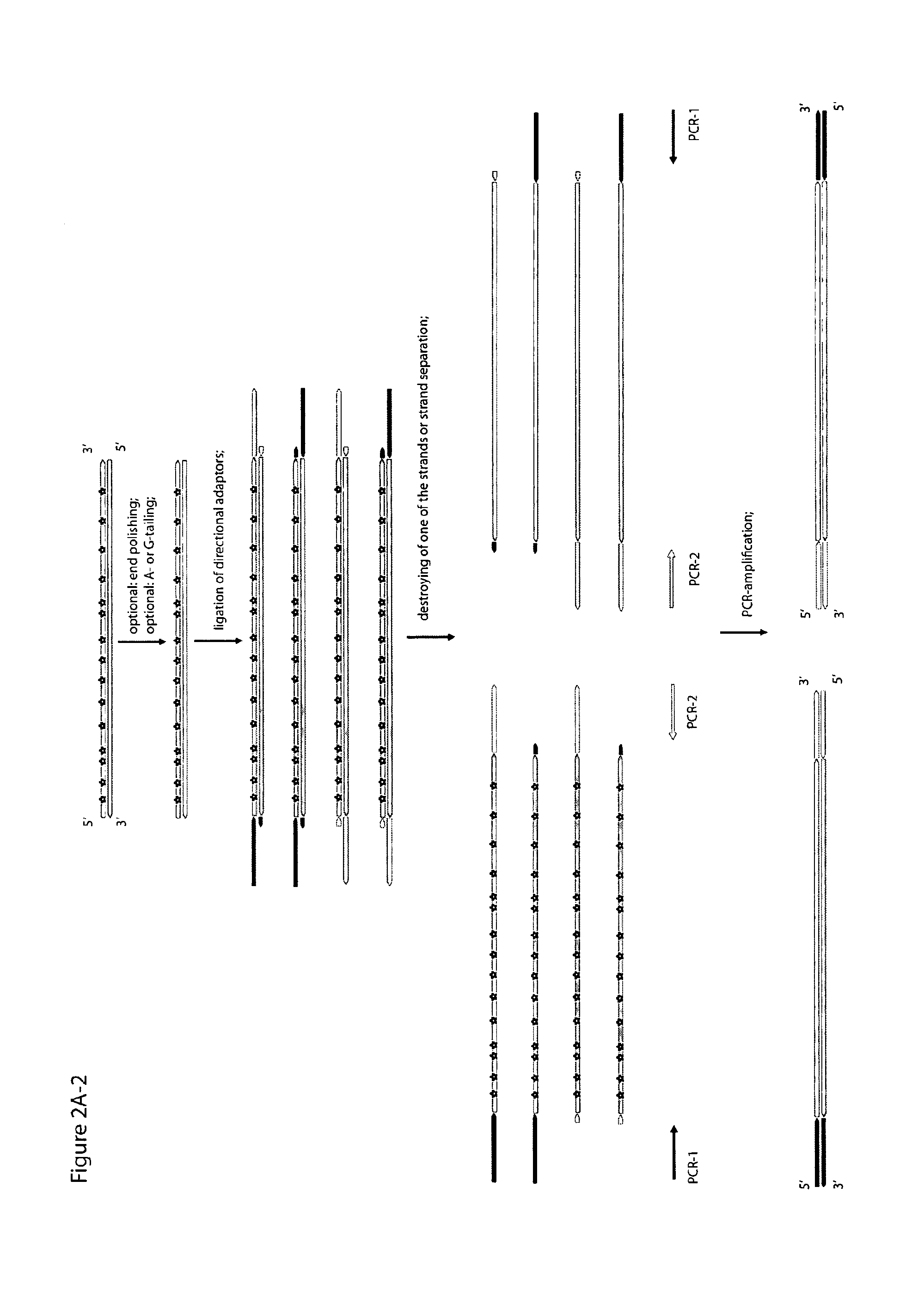
Method for differentiation of polynucleotide strands
ActiveUS20120237943A1Easy to implementImprove reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisLibrary preparationPolynucleotide
Objective of the present invention is to provide a method for keeping of directional information in double-stranded DNA. We suggest to convert polynucleotide into a hybrid double-stranded DNA. One particular strand of this hybrid double-stranded DNA should be synthesised using at least one modified nucleotide. Thus, this particular strand would contain modified nucleotides along the whole length. Density of directional markers would not depend on the length of polynucleotides. Any internal fragments of the hybrid double-stranded DNA would have directional information. When it is necessary the modified strand may be easily degraded or separated from the other strand. It was found that such hybrid double-stranded DNA may be easily generated in a number of molecular biology tasks and may be used for molecular cloning, library preparation and strand separation.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Novel chimeric antigen receptor and application thereof
ActiveCN106279438AImprove securityAdd control switchFermentationHybrid peptidesAntigenAntigen receptors
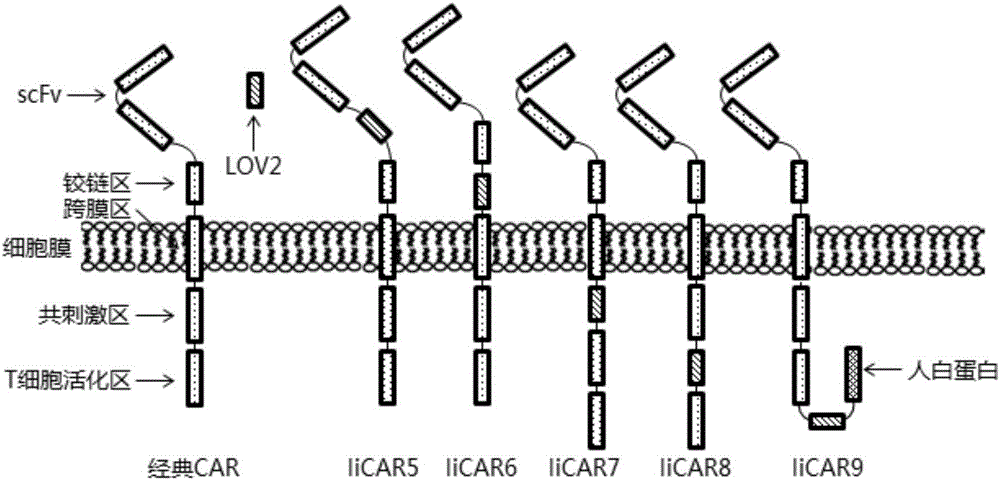
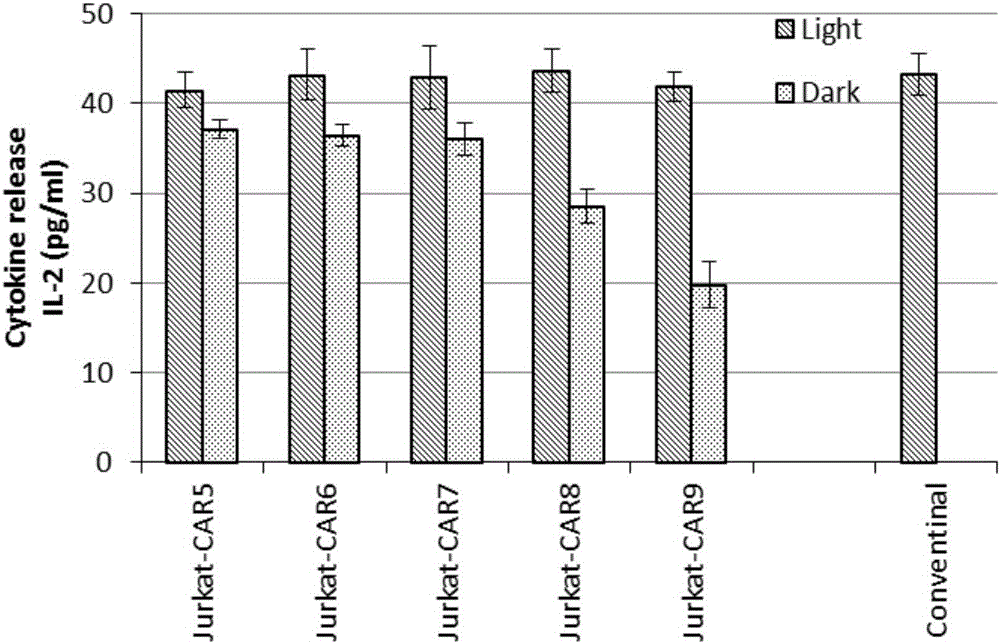
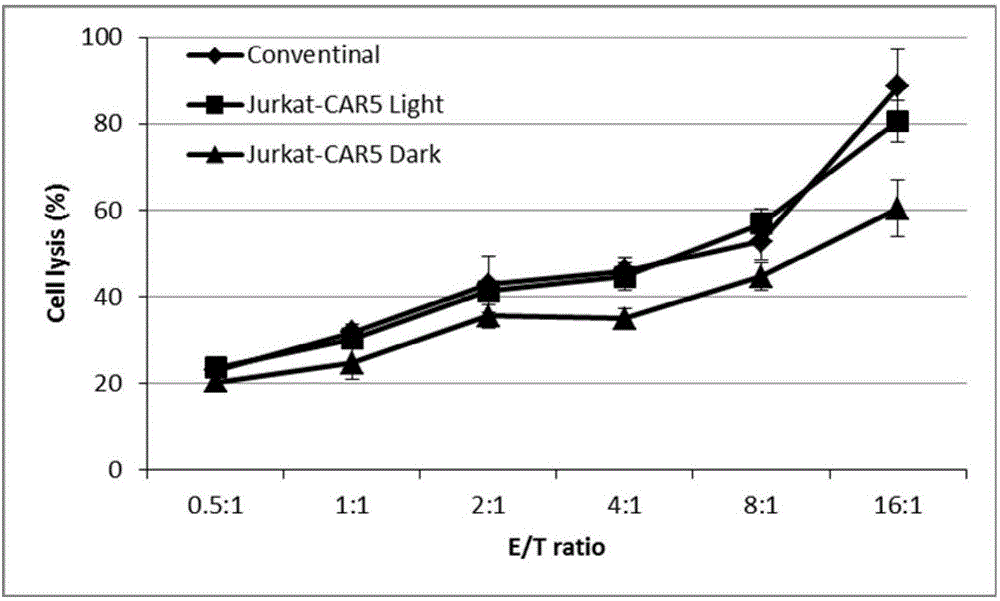
The invention discloses a recombined chimeric antigen receptor with a photoinduction element. The chimeric antigen receptor comprises an antigen combining area, a transmembrane structure area, a co-stimulatory signal transduction area and T cell signal transduction area functional structure domains, wherein the photoinduction element is inserted at the N terminal or C terminal of the recombined chimeric antigen receptor or between the functional structure domains. According to the chimeric antigen receptor, photoinduction element LOV2 genes are cloned into plasmids Lenti-EF1alpha-CD19CAR with a molecular cloning method to establish a co-expression vector of the recombined chimeric antigen receptor with the photoinduction element, 293T cells are used for packaging to obtain a lentiviral vector with photoinduction CAR molecules. After the recombined chimeric antigen receptor is expressed in T cells through the lentiviral vector, the damage toxicity of T cells is reversely controlled by LOV2, and an importable approach is provided for improving the safety of CAR-T in treating cancer clinically.
Owner:北京领柯生物科技有限公司
Molecular clones with mutated HIV gag/pol, SIV gag and SIV env genes
Nucleic acid constructs containing HIV-1 gag / pol and SIV gag or SIV env genes which have been mutated to remove or reduce inhibitory / instability sequences are disclosed. Viral particles and host cells containing these constructs and / or viral particles are also disclosed. The exemplified constructs and viral particles of the invention may be useful in gene therapy for numerous disorders, including HIV infection, or as a vaccine for HIV-1 immunotherapy and immunoprophylaxis.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Homologous recombination-based DNA cloning methods and compositions
Methods and compositions for cloning a donor DNA molecule into an acceptor vector at a predetermined location are described. The methods are based on homologous recombination mediated by in vitro treatment of the donor DNA and the acceptor vector with an enzyme cocktail containing an exonuclease and a single-stranded DNA binding protein.
Owner:NANJING GENSCRIPT BIOTECH CO LTD
GA 20-oxidase gene sequences
InactiveUS6198021B1High copy numberIncrease the number ofBacteriaSugar derivativesOxygenase activityFhit gene
The invention relates to the molecular cloning and expression of a gibberellin (GA) 20-oxidase gene and its use, for example in transgenic plants. Aspects of the invention include recombinant DNA which encodes a polypeptide exhibiting GA 20-oxidase activity, a recombinant polypeptide exhibiting GA 20-oxidase activity, and transgenic plants which express a GA 20-oxidase gene or reverse GA 20-oxidase sequences.
Owner:ROTHAMSTED RES LTD
Plasmid control molecule for detection of transgenic soybean and building method thereof
InactiveCN101775440AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionEnzyme digestionPositive control
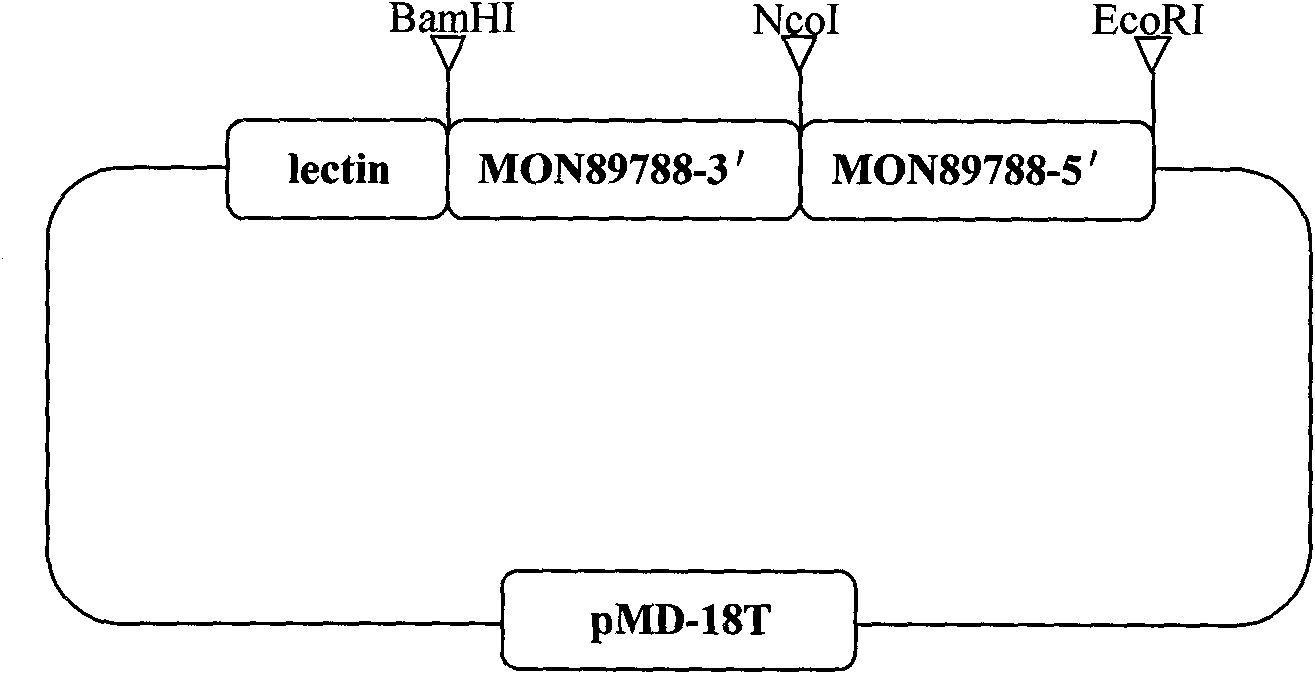
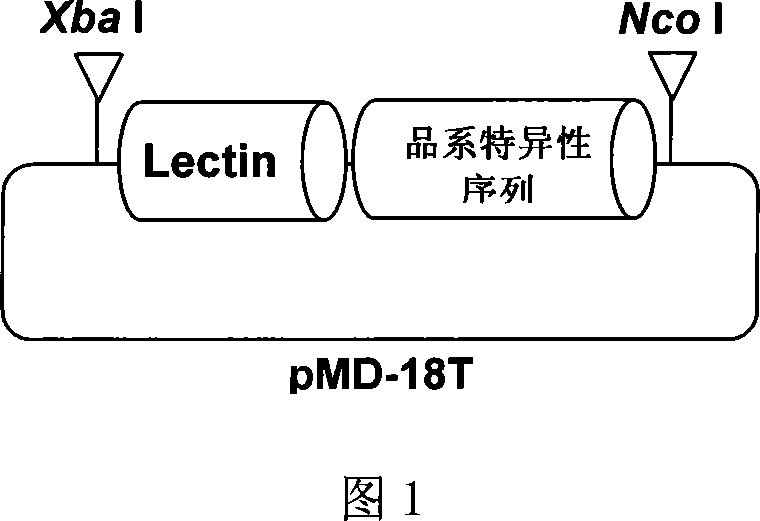
The invention relates to a plasmid control molecule for detection of transgenic soybean and a building method thereof. The plasmid control molecule contains a control gene lectin specific sequence in soybean, a 3' end transformant specific sequence and a 5' end transformant specific sequence of transgenic soybean MON89788. Through designing a specific qualitative PCR primer, the lectin gene specific sequence, the 3' end transformant specific sequence and the 5' end transformant specific sequence of the MON89788 are obtained through amplification. Through molecular cloning techniques such as enzyme digestion, connection, transformation and the like, the three specific sequence segments are built into a plasmid molecule to obtain an artificially recombined plasmid control molecule pMD-LM3M5. According to tests, the plasmid control molecule built in the invention can fully substitute for the positive control of the transgenic soybean MON89788 and is suitable for the transformant specific qualitative and quantitative PCR analysis and detection of the MON89788 soybean.
Owner:JILIN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
GA 20-oxidase gene sequences
InactiveUS6455675B1High copy numberIncrease the number ofBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementOxygenase activityFhit gene
The invention relates to the molecular cloning and expression of a gibberellin (GA) 20-oxidase gene and its use, for example in transgenic plants. Aspects of the invention include recombinant DNA which encodes a polypeptide exhibiting GA 20-oxidase activity, a recombinant polypeptide exhibiting GA 20-oxidase activity, and transgenic plants which express a GA 20-oxidase gene or reverse GA 20-oxidase sequences.
Owner:ROTHAMSTED RES LTD
Method for analysis of substances in tissue or in cells
InactiveUS20040137420A1Potent contracting activityParticle separator tubesMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical structureIntracellular
An improved method for directly identifying a chemical structure of a substance present in tissue or cells of organisms is disclosed. In particularly, the method for directly identifying a chemical structure of a substance present in tissue or cells of various kind of organisms comprises the following steps: (1) a step irradiating a laser to a certain intracellular region of a sample tissue slice or a cell, and analyzing the generating mass ions to obtain mass spectrum of the substance present at the cite, (2) a step analyzing the mass spectrum to obtain a mass profile of the substance existing at the intracellular region of the sample tissue slice or in cell, and (3) a step determining the chemical structure of the substance corresponding a certain molecular weight appeared in the mass profile. The method of this invention is conducted by utilizing the combined techniques of matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS), and on-line capillary reversed-phase HPLC / quadrupole orthogonal acceleration time-of-flight (Q-Tof)-MS, and molecular cloning, is disclosed.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Standard plasmid molecule for detection of genetic improved soybean strain GTS40-3-2 and constructing method thereof
InactiveCN101063171AAvoid missingThe analysis result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringInternal standardPlasmid
The invention discloses a standard plasmid molecule to check genetic improved soybean strain GTS40-3-2 and constructing method, which comprises the following steps: incorporating strain special fragment of the genetic improved soybean strain GTS40-3-2 and special fragment of soybean internal standard gene Lectin; analyzing exogenesis inserting carrier by-pass ortho gene sequence of genetic improved soybean strain GTS40-3-2; designing strain special PCR primer; augmenting; getting strain special fragment of genetic improved soybean strain GTS40-3-2 and soybean internal standard gene special sequence; constructing into a plasmid molecule with molecular cloning method; getting artificial retooling plasmid molecule pMD-RRS. This standard plasmid molecule can be fit for strain special quantitative PCR analysis and check of genetic improved soybean strain GTS40-3-2 sample.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Application of cell penetrating peptide Tat-mediated growth factor in transdermal transfer
ActiveCN101711874AIncrease speedIncrease the number ofCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunodeficiency virusActive protein
The invention discloses an application of a growth factor series mediated by an active factor Tat protein transcribed by an immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) in the transdermal transfer, in particular to an application in the fields of transdermal administration and cosmetics. The application is achieved by the following steps of: constructing a fusion protein recombinant expression vector of Tat and a series of active proteins in the growth factor family by the general molecule clone method, purifying with different chromatographic columns to obtain a fusion protein, or linking the Tat to a natural or synthetic phosphatide by the chemical and (or) physical method to prepare a liposome coating the growth factor, forming a transdermal transfer system for the Tat-mediated liposome, matching with proper pharmaceutical or cosmetic auxiliary materials to prepare finished products used for a transdermal administration system or a cosmetics system. The invention can effectively transfer the active proteins of the growth factor with macromolecules through the skin by the Tat mediation and fully exert the effect. The invention provides a novel platform to the application of Tat.
Owner:BIOPHARM RES & DEV CENT JINAN +1
Use of phosphorothiolate polynucleotides in ligating nucleic acids
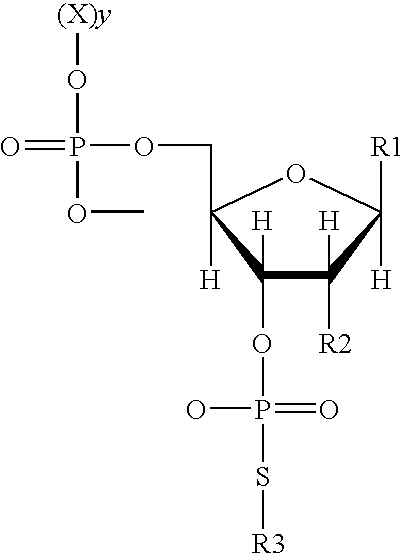
The invention provides a method of nonenzymatic ligation of a nucleic acid. The method consists of contacting a polynucleotide-3′ phosphorothiolate with an acceptor polynucleotide under conditions that allow formation of a phosphodiester bond between the polynucleotide-3′ phosphorothiolate and the acceptor polynucleotide. The invention also provides methods of molecular cloning. In one embodiment, the method consists of contacting an insert comprising a polynucleotide-3′ phosphorothiolate with an acceptor vector under conditions that allow formation of a phosphodiester bond between the insert and the acceptor vector to generate a vector comprising an insert polynucleotide. The invention further provides a compound consisting of a polynucleotide-3′ phosphorothiolate and a kit containing a polynucleotide-3′ phosphorothiolate. Also provided is a method of ligating a nucleic acid using a non-sequence specific topoisomerase.
Owner:SAN DIEGO STATE UNIVERSITY +1
Monoclonal antibodies to antigens expressed by hematopoietic facilitatory cells
InactiveUS6013519AImprove abilitiesQuick identificationAnimal cellsHybrid cell preparationHigh level expressionMonoclonal antibody
The present invention relates to monoclonal antibodies (MAb) to hematopoietic facilitatory cells (FC). In particular, it relates to MAb against antigens expressed by murine FC, methods of generating the antibodies, and methods of using the same. MAb directed to markers that are expressed specifically or at higher levels by FC than by most other bone marrow cells have a wide range of applications, including but not limited to, rapid isolation of FC, identification of FC in a donor cell preparation, and molecular cloning of the genes encoding the corresponding target antigens.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Method for enriching and separating endogenous transcription factors and compounds thereof and concatenated transcription factor response elements special for method
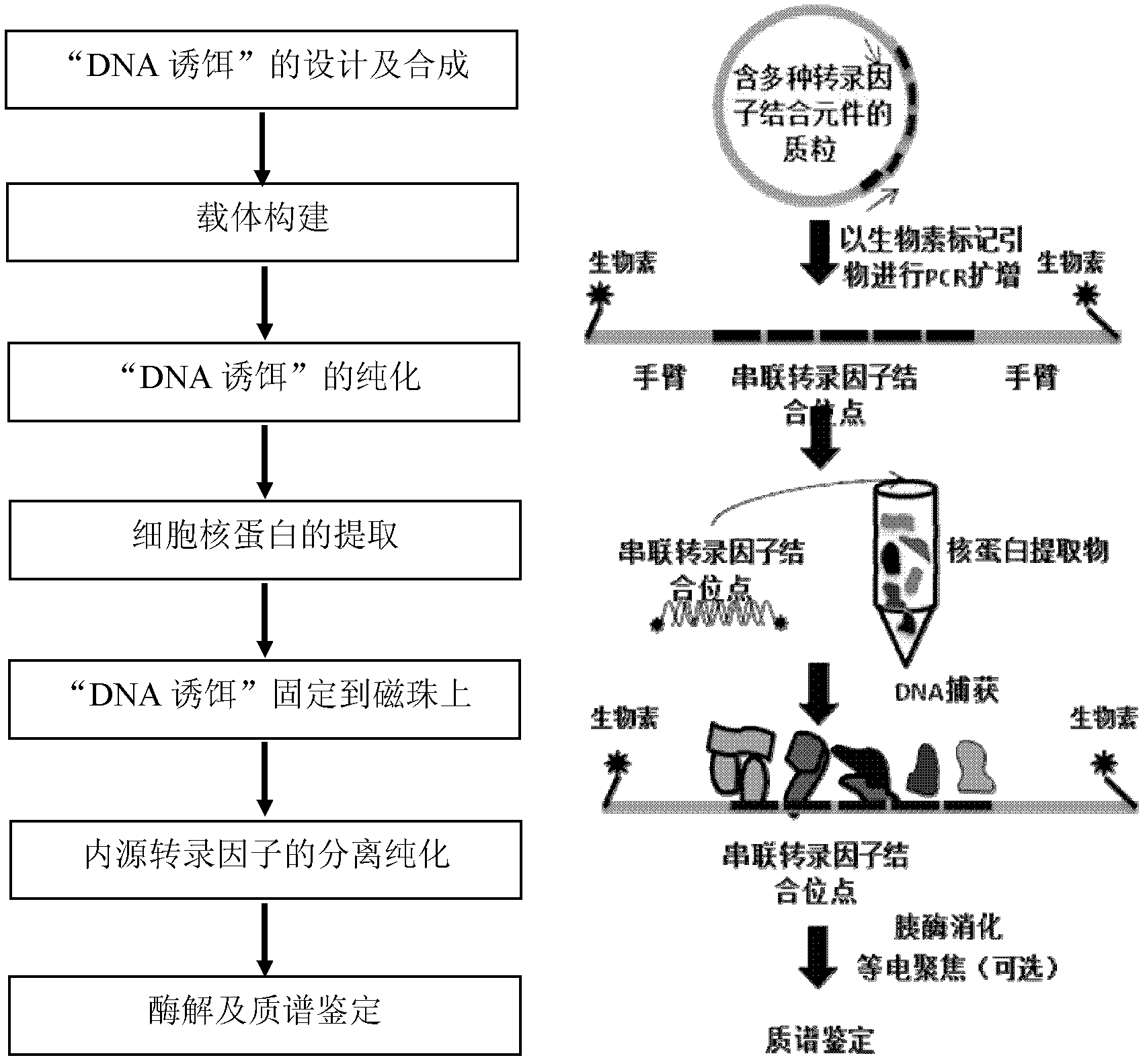
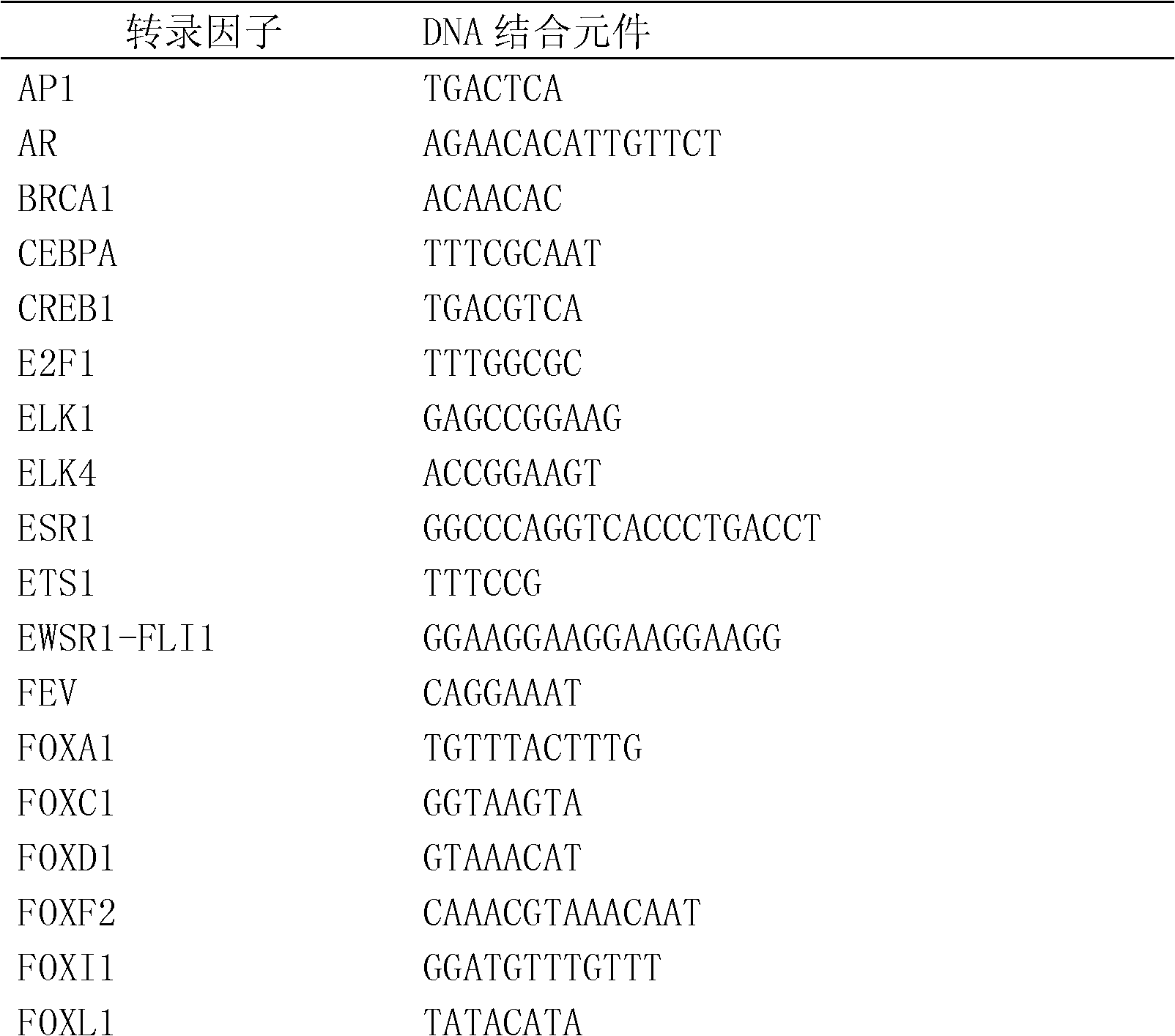
ActiveCN102517282AMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsBiotin-streptavidin complexMagnetic bead
The invention discloses a method for enriching and separating endogenous transcription factors and compounds thereof and concatenated transcription factor response elements special for the method. The method includes of designing multi-copy double-stranded DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) binding elements according to the characteristic that transcription factors are bound with sequence-specific DNA elements, adding double-stranded DNA arms labeled with biotin to two ends of each DNA binding element by the aid of molecular cloning technology to form 'DNA baits', coupling the biotinylated DNA baits which are purified onto magnetic beads enveloped by streptavidin when in separation and purification of the endogenous transcription factors and compounds thereof, incubating the magnetic beads together with the prepared nucleoprotein, and finally separating and purifying the endogenous transcription factors and the compounds thereof from the nucleoprotein. Further, after the endogenous transcription factors and the compounds thereof are separated and purified, protein identification and function analysis of the transcription factors can be performed subsequently.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA +1
Porcine circovirus I type infectious clone and virus rescued thereby and application thereof
InactiveCN101423836ASimple and fast operationInfectious cloneViruses/bacteriophagesFermentationViral antibodyPorcine circovirus type 1
The invention discloses infective clone for porcine circovirus type 1 and rescued virus and application thereof. Two genomes of the porcine circovirus type 1 are connected in cis and inserted into a vector to construct and obtain an infective molecular clone. A Sal I enzyme cutting site as a molecular target is inserted in the infective molecular clone. A rescued recombinant virus (PCV1 / G strains) carries a molecular marker, and the preservation number of the rescued recombinant virus is CGMCC NO.2658. An antigen of the recombinant virus is only reacted with a univalent specific antibody of PCV1 / Cap protein, but has no cross with an antibody against PCV2 / Cap protein. The recombinant virus and a parental virus are identified by combination of PCR and RFLP. The virus strain cultured in vitro has stable propagation property and high virus titer, and the rescued virus strain can be used for detecting the antibody of the virus. The invention lays a foundation for research such as genesis and evolution, genetic variation rule, molecular differential diagnosis, and the like for porcine circovirus in future.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for preparing molecular cloning chip for high-throughput cloning of nucleic acid molecule
InactiveCN101413034BEasy to manufactureMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationOil phaseThermostat
The invention provides a method for preparing a molecular cloning chip by cloning high flux nucleic acid molecule. The method comprises the following steps: a. a cloning nucleic acid molecule template is mixed with a nucleic acid amplification reaction system reagent to obtain an amplification mixture solution; b. the amplification mixture solution is added with a high molecular compound; c. the solution is added with oil phase, of which the volume is two times of the volume of the solution for emulsification to obtain water-in-oil emulsion; d. the emulsion is placed in a PCR meter or a thermostat to undergo a nucleic acid amplification reaction; e. after the nucleic acid amplification reaction, the emulsion is cooled down to form nucleic acid molecule cloning grains; f. the nucleic acid molecule cloning grains are separated; and g. the nucleic acid molecule cloning grains are randomly dispersed on a solid phase carrier to fix the nucleic acid amplification products in the solution onthe solid phase carrier and form a nucleic acid molecule cloning array on the surface of the solid phase carrier and thus the cloning chip is obtained. The method has the advantages of improving preparation sequencing template, ensuring high flux of sequencing and lowering sequencing cost.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
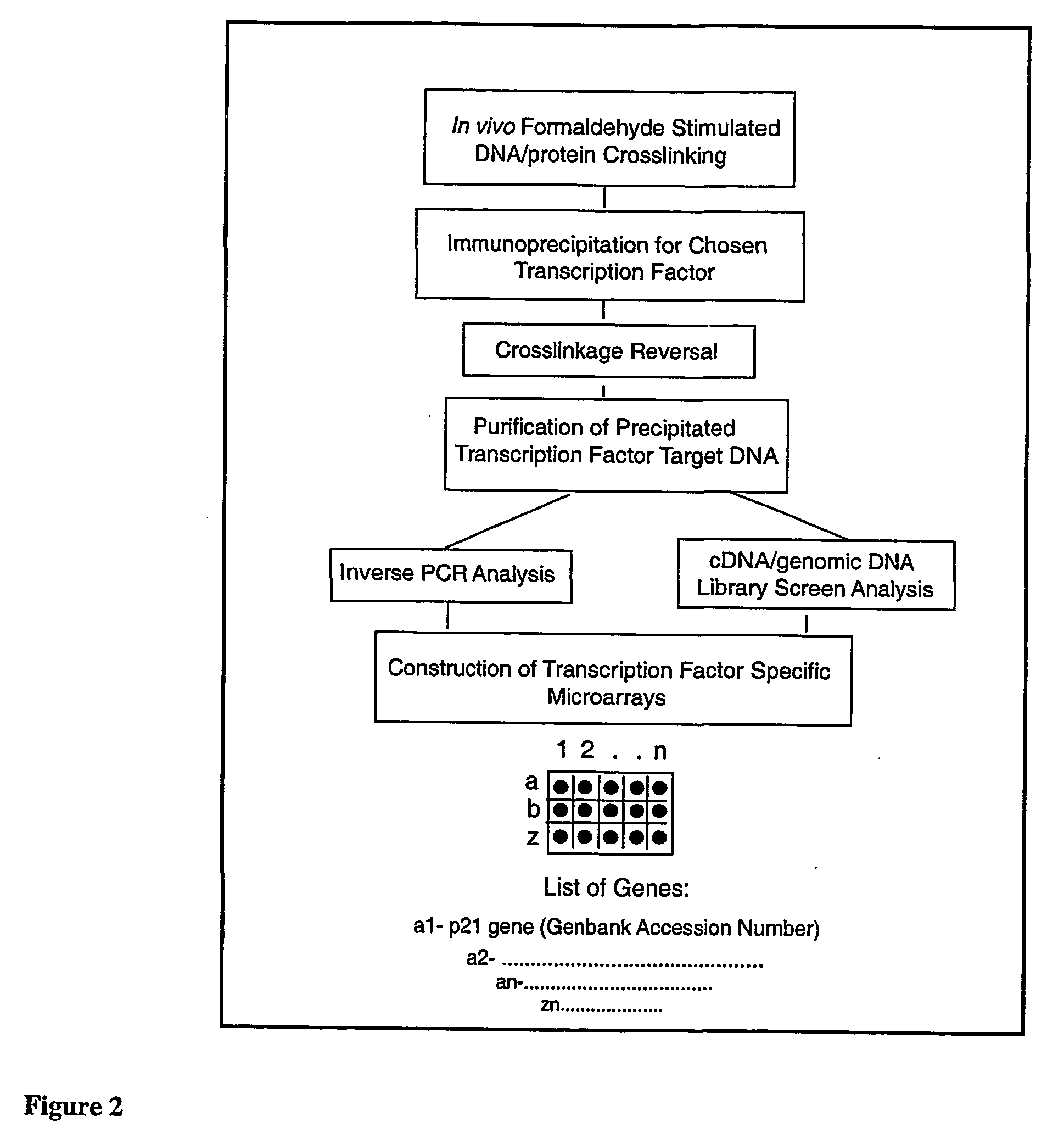
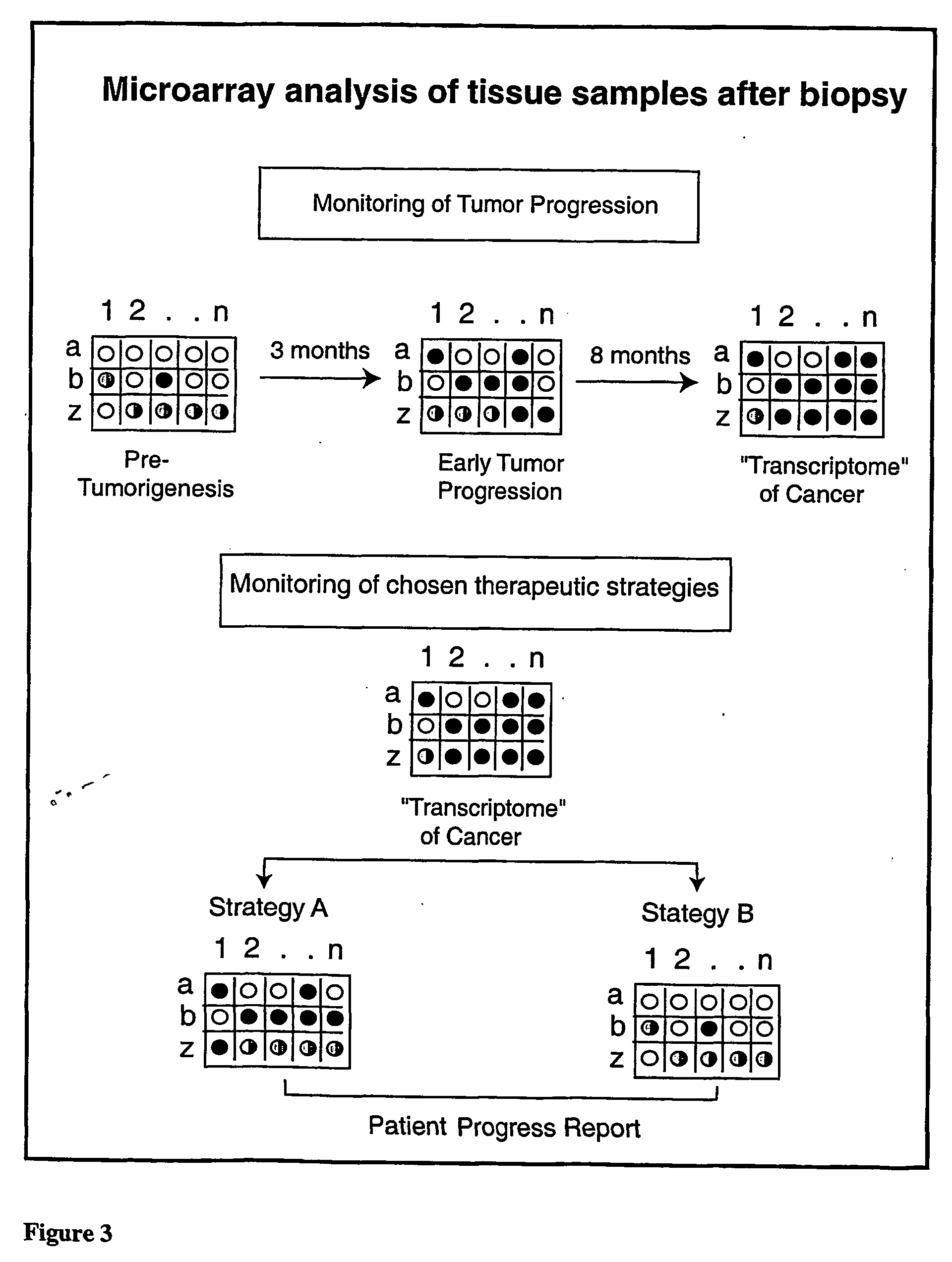
Micro-arrayed organization of transcription factor target genes
InactiveUS20050079492A1Decreasing acquisitionDecreased background random sequenceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationProtein targetImmunoprecipitation
The following invention outlines methodologies for the construction and utilization of transcription factor direct target gene microarrays of both DNA and corresponding protein / peptide target origin. The technology entails the array / microarray annotation and organization of transcription factor direct loci and corresponding protein products identified through modified and improved versions of chromosomal immunoprecipitation (CHIP) and molecular cloning procedures. It allows for the formulation of physiologically directed arrays which result in a thorough, focused characterization of the genetic and biochemical regulation occurring within a give population of cells or a given tissue. Arrays and microarrays of direct targets for any given transcription factor created utilizing this technology are substantially more clinically relevant for purposes of medical diagnostics and patient prognostics than conventional microarrays due to the physiologically focused nature and the transcription factor targets. In addition, the characterization and array organization of transcription factor target protein products and the assessment of their interactions with other proteins and / or small molecules is of critical importance for the purposes of understanding cellular and ultimately the design of therapeutics for human anomalies.
Owner:BURS JR ROBERT M +2
Method for differentiation of polynucleotide strands
ActiveUS8999677B1Easy to implementImprove reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotideLibrary preparation
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
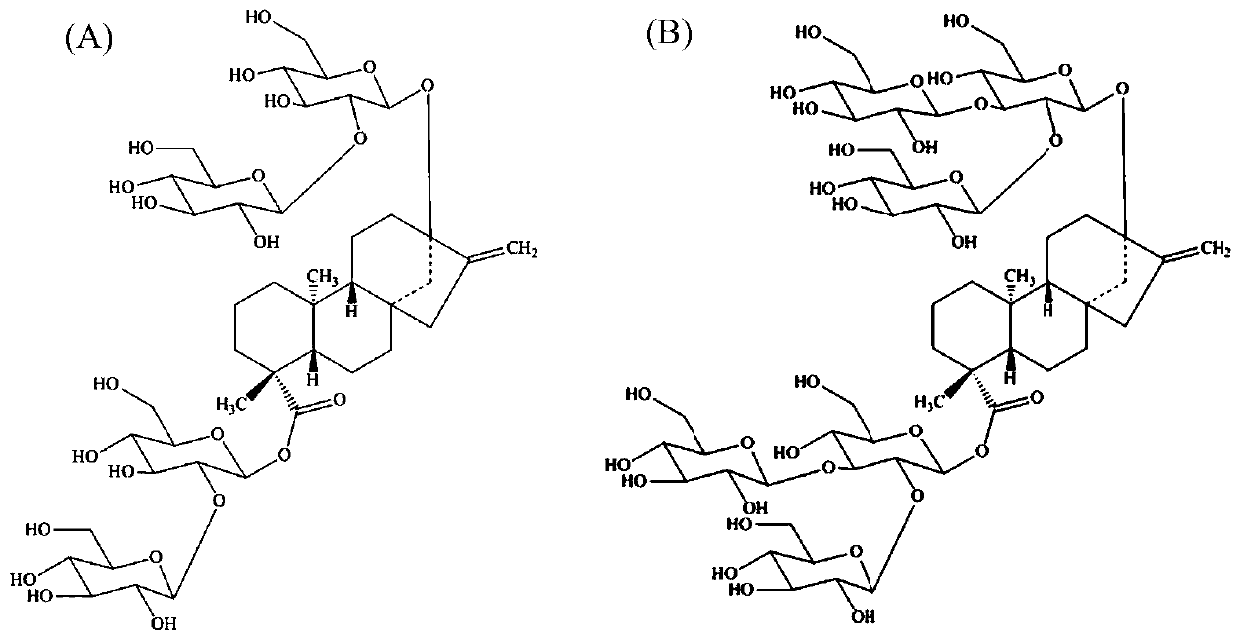
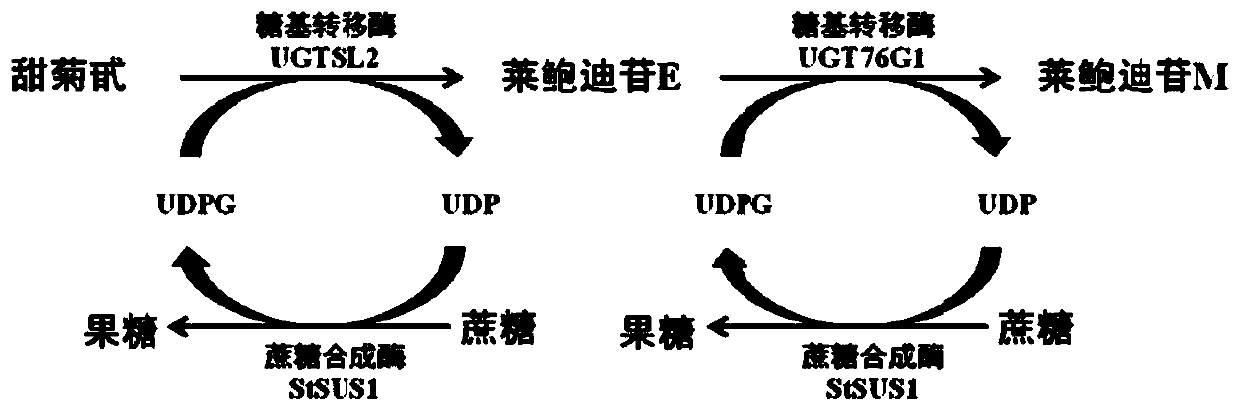
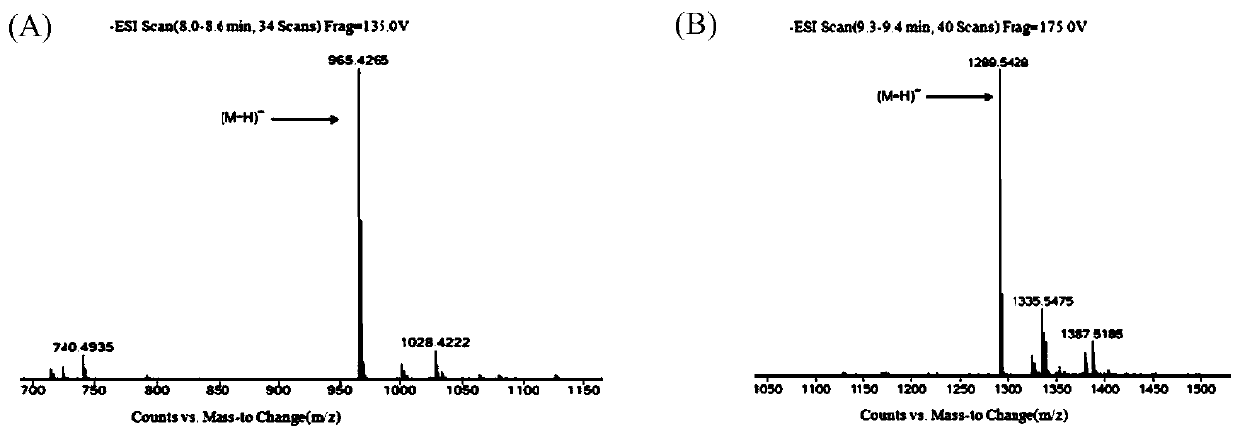
Biocatalytic method for synthesis of rebaudioside M
The invention discloses a biocatalytic method for synthesis of rebaudioside M. Firstly, rebaudioside E is synthesized by a glycosylation reaction of stevioside with UDP-glycosyltransferase from tomatos and sucrose synthetase from potatoes; then, rebaudioside M is synthesized by a glycosylation reaction of rebaudioside E with UDP-glycosyltransferase from stevia rebaudiana and sucrose synthetase from potatoes. The method uses a molecular cloning technique, escherichia coli genetically engineered bacteria for heterologous expression of UDP-glycosyltransferase and sucrose synthetase are obtained,after fermentation and enzyme production, crude extract of cells is directly used for a catalytic reaction, addditionally added saccharose is decomposed with sucrose synthetase to obtain UDP-glucose,UDP in the crude extract and the UDP-glucose serve as raw materials for the glycosylation reaction, a double-enzyme cycle reaction system is established, and the rebaudioside M is produced by effectively catalyzing stevioside. The cost of raw materials is lower, the processing steps are simple, and the method has an important application value.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
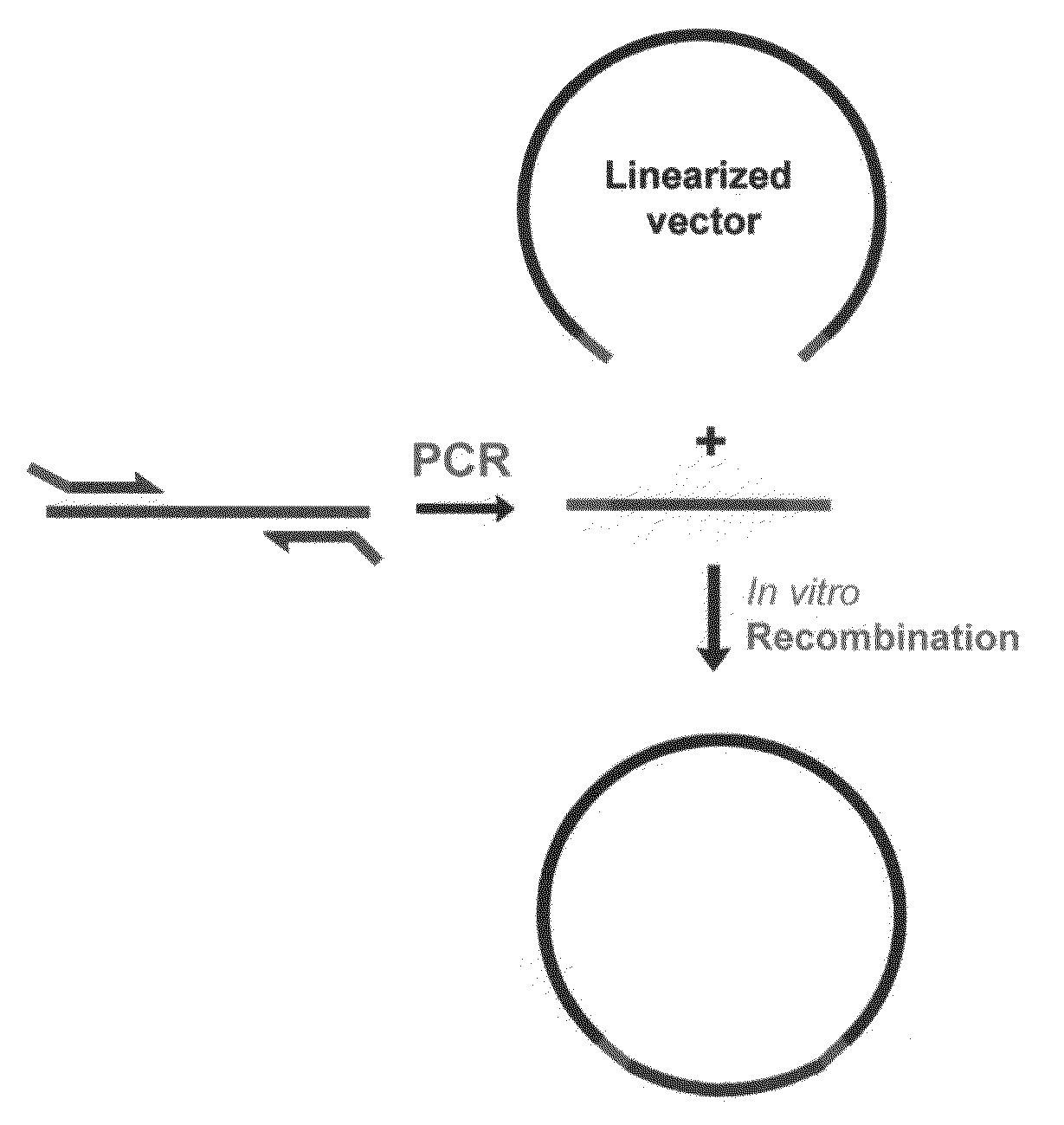
Nucleic acid molecular cloning method and related kit based on homologous recombination
InactiveCN102634534ASize limitAvoid the contradiction of low conversion rateVector-based foreign material introductionDNA preparationNucleotideMolecular cloning
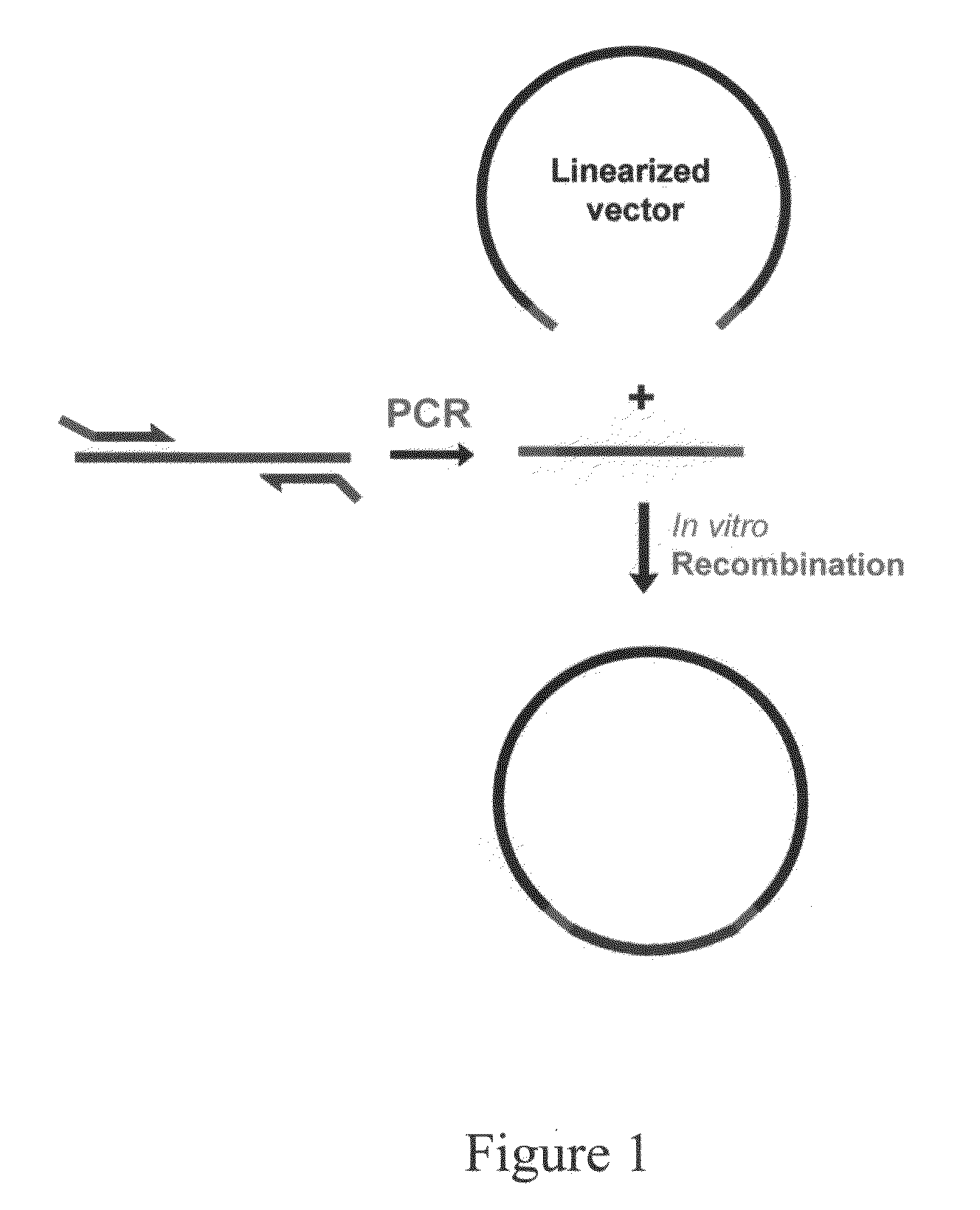
The invention provides a nucleic acid molecular cloning method based on homologous recombination. According to the method provided by the invention, a target DNA is cloned to a vector by the homologous recombination through providing a linearizing vector with two ends respectively added with sequences(namely specific homologous arm of the target DNA) homologous with sequences at the two ends of the target DNA or the flanking sequence of the target DNA or utilizing a connecting section containing the specific homologous arm of the target DNA as well as the specific homologous arm of the vector (sequence homologous with the specific region of the vector). The nucleic acid molecular cloning method provided by the invention is especially suitable for the clone of large DNA section and polymorphism researches of mononucleotide. The invention further provides a related kit.
Owner:SHENZHEN ZHONGLIAN BIOLOGICAL TECH DEV
Method for extracting total RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) from woody mangrove plants and special extracting solution thereof
The invention discloses a method for extracting total RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) from woody mangrove plants and special extracting solution thereof. The extracting solution provided in the invention comprises Tris-HCl, EDTA (Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid), NaCl, SDS (Sodium Dodecyl Sulfonate), DTT (Dithiothreitol), beta-mercaptoethanol and water, wherein the final concentration of the Tris-HCl is 75-125 mmol / L, the final concentration of the EDTA is 400-600 mmol / L, the final concentration of the NaCl is 400-600 mmol / L, the final concentration of the SDS is 1%-3% (in weight percent), the final concentration of the DTT is 3-8 mmol / L, and the final concentration of the beta-mercaptoethanol is 1%-3% (in weight percent); and the pH value is 8-9. The method provided in the invention is used for extracting the total RNA from the woody mangrove plants by using the extracting solution. The RNA extracted by the method can be directly used for synthesizing cDNA (complementary Desoxyribonucleic Acid) and carrying out molecular biology operations, such as library establishment, molecular clone and the like.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Screening for expressible transfectants in a eukaryotic system
InactiveUS20080299581A1Easy to identifyEfficient screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDna transfectionExpression cloning
The present invention relates to the field of molecular cloning and to the field of expression cloning in higher, eukaryotic cells. In particular, the present invention relates to a method for fast and reliable identification of vectors and vector DNA which will be capable of providing a desired expression product if a eukaryotic host cell is transfected with the vector DNA.
Owner:SYMPHOGEN AS
Method for extracting total ribonucleic acid from plants with polysaccharide and polyphenol by using silica membrane
The invention relates to a method for extracting total ribonucleic acid from plants with polysaccharide and polyphenol by using a silica membrane, and belongs to the field of nucleic acid purification. The method comprises the following steps of: adding a lysis solution for the plants with polysaccharide and polyphenol into a plant material with polysaccharide and polyphenol, which is ground by liquid nitrogen, performing centrifugal separation on the mixture, taking the supernate obtained through centrifugal separation out, transferring into a filtration column for filtration, adding absolute ethanol into filtrate, uniformly mixing, transferring into a silica membrane adsorbing column for adsorbing centrifugation, adding a protein removing solution and a deoxyribonuclease solution for protein removal centrifugation twice, adding a rinsing solution for desalting centrifugation, performing drying centrifugation, and adding deoxyribonuclease water for rinsing centrifugation to obtain a ribonucleic acid solution. The method has the characteristics of high efficiency, quickness and conciseness; and the purified ribonucleic acid (RNA) can be used for various downstream experiments suchas microarray analysis, in vitro translation, molecular cloning and the like.
Owner:TIANGEN BIOTECH BEIJING
DNA molecular marking method for researching fish genetic relation
ActiveCN1884529ASugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA fragmentationHigh-mobility group
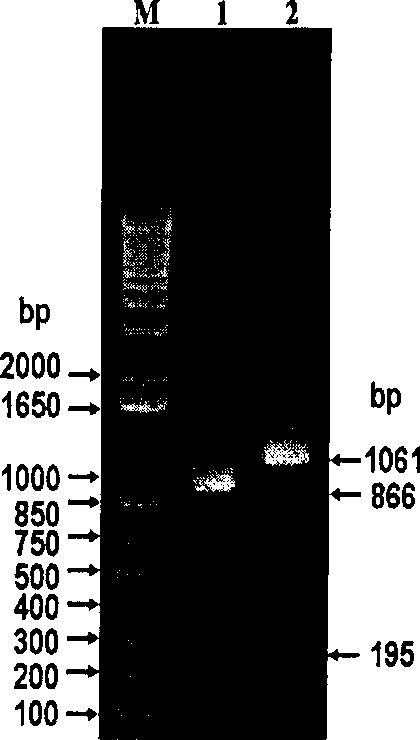
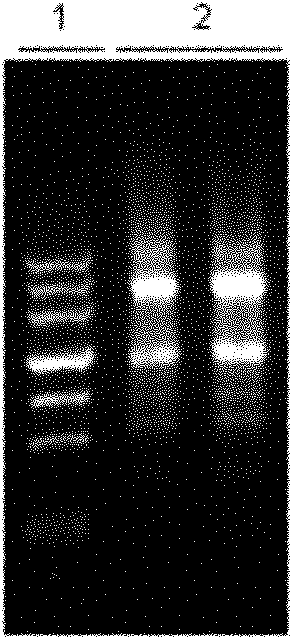
The invention relates to a fish DNA molecular labeling technique. The invention selects Sox gene HMG (High mobility group) conservative area as colony-molecular goal, designs unique degenerate goal, obtains DNA fragments of Sox genes which are different in numbers and species with PCR and agarose gel electrophoresis, and uses this specific DNA molecules to decide and analyze hereditary characteristic and hereditary connection of diversity fishes. The method can analyze fish hereditary connection quickly and exactly and can also be used in hereditary connection analysis of other animals.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for rapidly extracting total ribonucleic acid from blood
The invention relates to a method for rapidly extracting total ribonucleic acid from blood, belonging to the field of nucleic acid purification. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, adding a rapid erythrocyte lysing solution into whole blood; performing centrifugal separation on a mixture of the rapid erythrocyte lysing solution and the whole blood; taking precipitate formed by the centrifugal separation out; adding suspension into the precipitate; adding a lysing solution and a protease K solution in sequence; uniformly mixing and then adding absolute ethyl alcohol; uniformly mixing and transferring into a silicon membrane adsorption column to perform adsorptive centrifugation; adding a deproteinizing solution and a deoxyribonuclease solution; performing deproteinizing centrifugation twice; adding a rinsing solution to perform desalting centrifugation; and finally performing drying centrifugation and adding water without ribonuclease, and eluting and centrifuging so as to obtain a ribonucleic acid solution. The method provided by the invention has the characteristics of high efficiency, rapidness and simplicity; and purified RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) can be used for various downstream experiments such as chip analysis, in vitro translation, molecular cloning and the like.
Owner:TIANGEN BIOTECH BEIJING
Homologous recombination-based nucleic acid molecular cloning method and related kit
This invention provides a homologous recombination-based nucleic acid molecular cloning method. According to the method of the present invention, a target DNA is cloned into a vector through homologous recombination by providing a linearized vector with both ends respectively added with a sequence (namely, a target DNA-specific homologous arm) homologous with sequences of both ends of the target DNA or a flank sequence thereof, or by utilizing a ligation fragment containing both the target DNA-specific homologous arm and a vector-specific homologous arm (a sequence homologous with a specific region of the vector). The method of the present invention is especially applicable to the cloning of a large DNA fragment and to the studies of single nucleotide polymorphism. The present invention further provides a related kit.
Owner:SHENZHEN ZHONGLIAN BIOLOGICAL TECH DEV
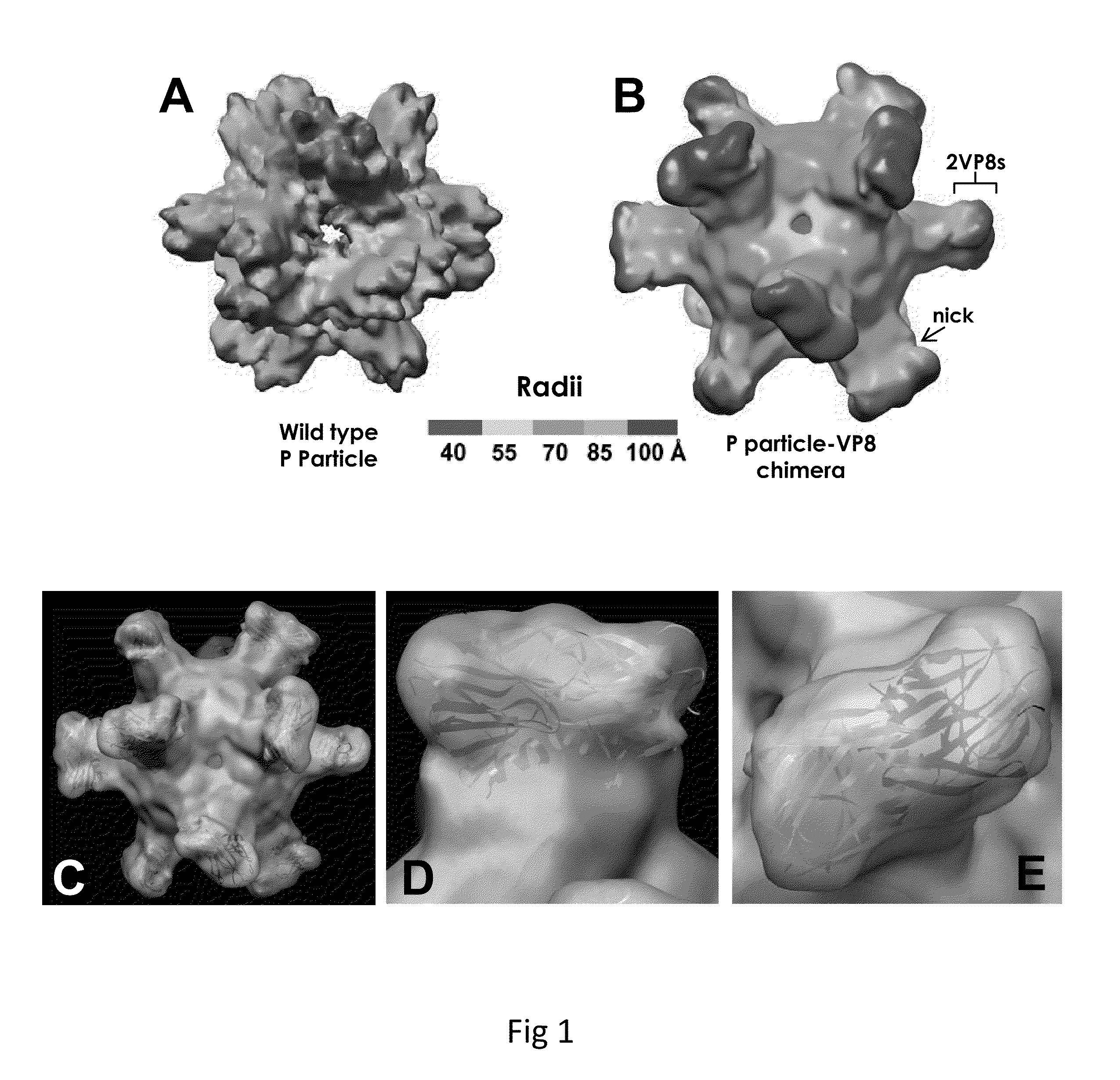
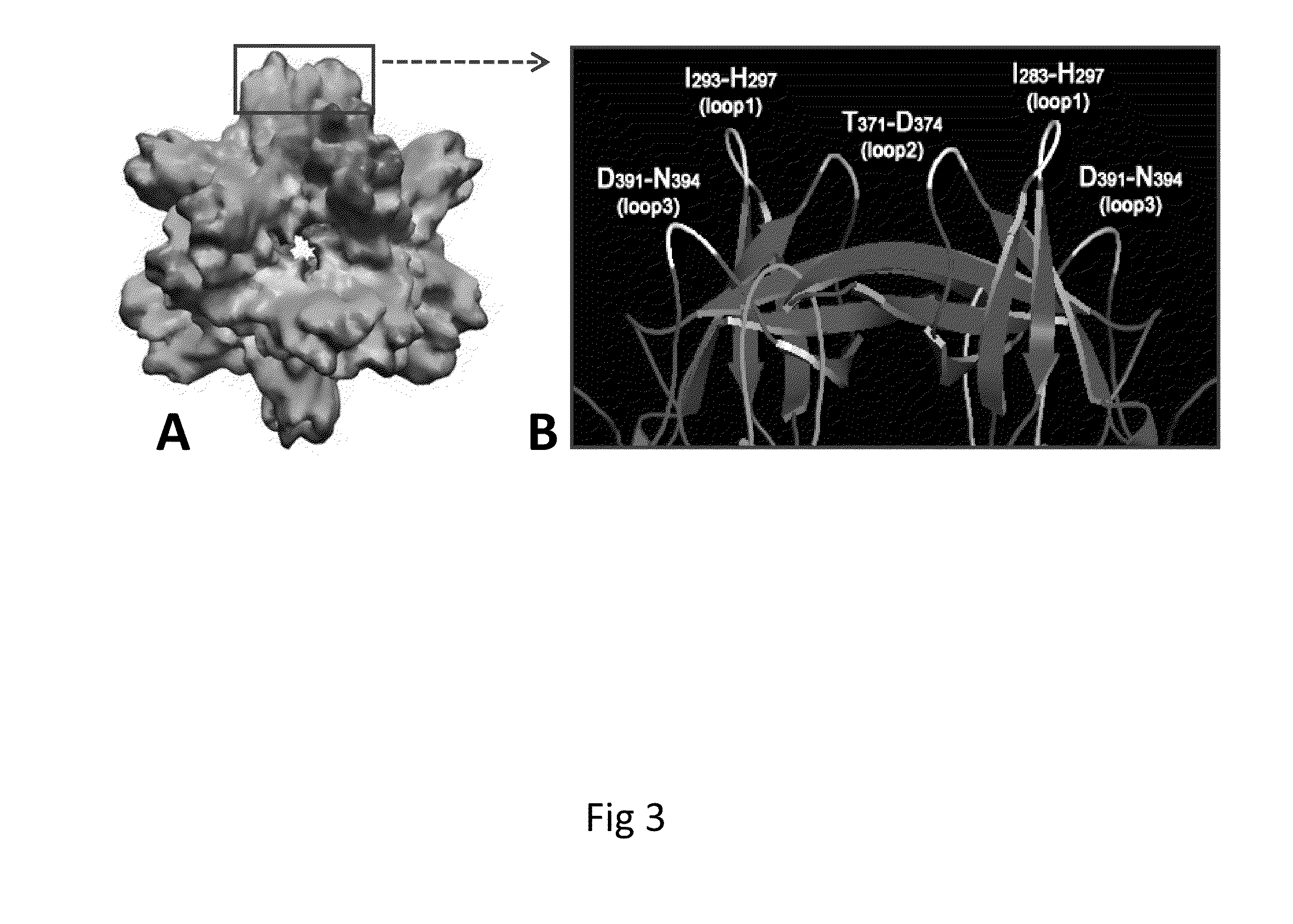
Antigen-norovirus P-domain monomers and dimers, antigen-norovirus P-particle molecules, and methods for their making and use
ActiveUS8486421B2Easy to produceImproving immunogenicitySsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAntigen
A substituted Norovirus capsid protein monomer, having only the P-domain and called an antigen-Norovirus P-domain monomer, includes a foreign antigen inserted into one or more of three surface loops present on each P-domain monomer by molecular cloning. The antigen-P-domain monomer can assemble spontaneously into an octahedral form, called an antigen-Norovirus P-particle, that is composed of 24 copies of the antigen-P-domain monomer. Each substituted P-domain monomer will contain one to three copies of the foreign antigen, for a total of 24-72 antigen copies on each antigen-P-particle. The antigen-P-particle is useful in methods for diagnosing, immunizing and treating individuals infected with a foreign virus, for example Rotavirus, and can serve as a carrier for presentation of foreign antigens for development of novel vaccines against many infectious and non-infectious diseases. The substituted Norovirus P-particles can be readily produced in E. coli and yeast, are highly stable and tolerate a wide range of physio-chemical conditions. A modified Norovirus P-domain monomer includes one or more restriction recognition sites inserted within one or more of the three loops of the P-domain monomers, to provide user-friendly cloning cassettes for conveniently inserting candidate foreign antigens into the surface loops. The P-particle-VP8 chimeras may also serve as a dual vaccine against both rotavirus and norovirus.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com