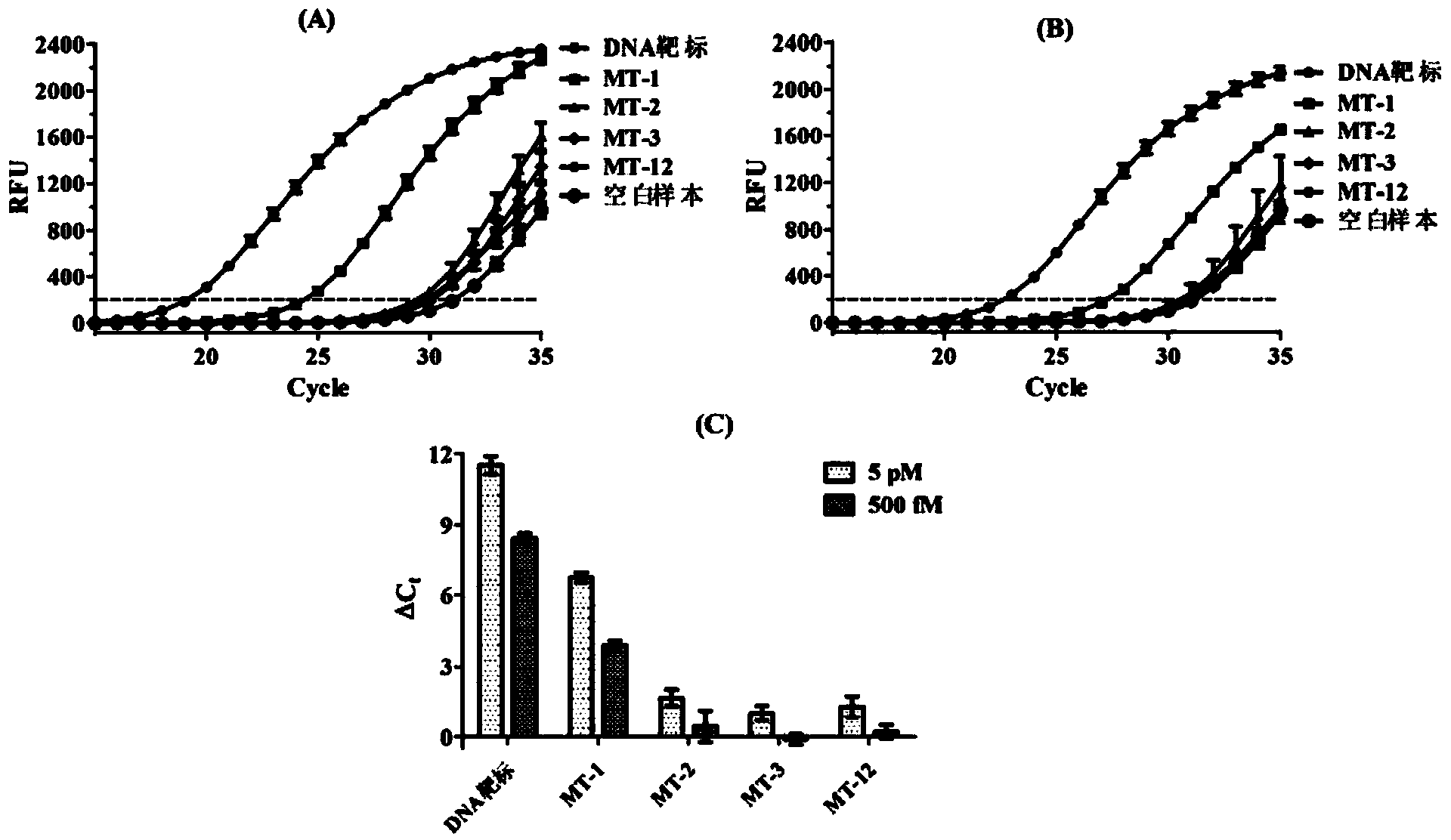
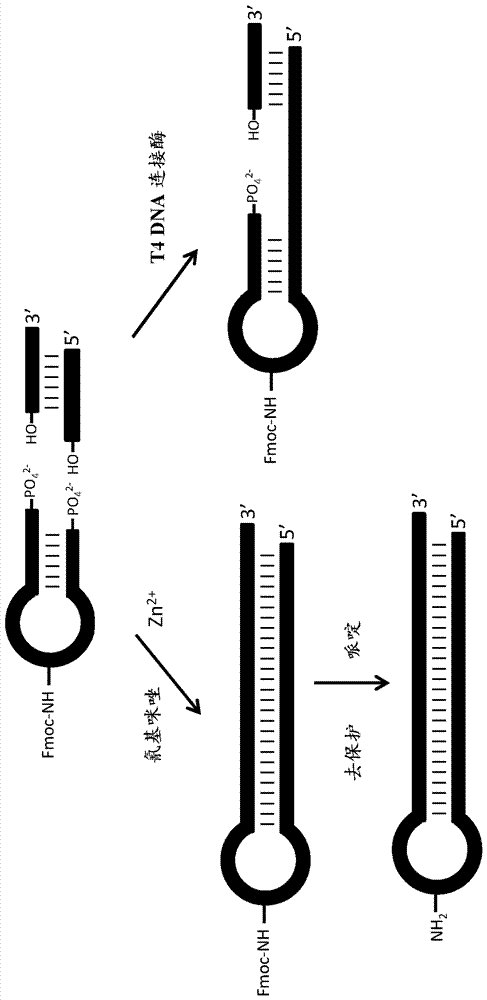
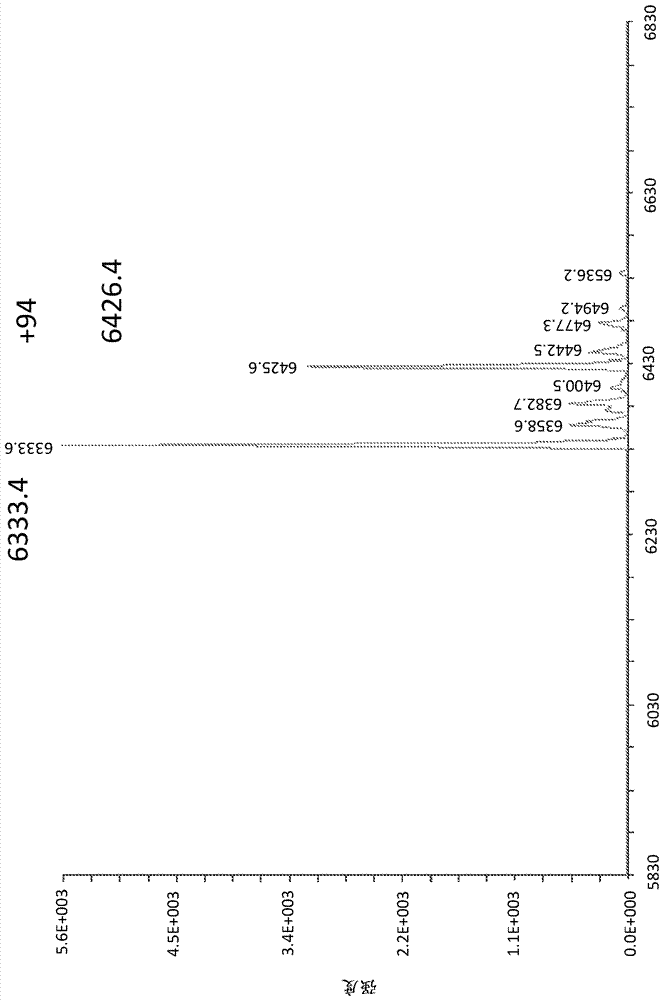
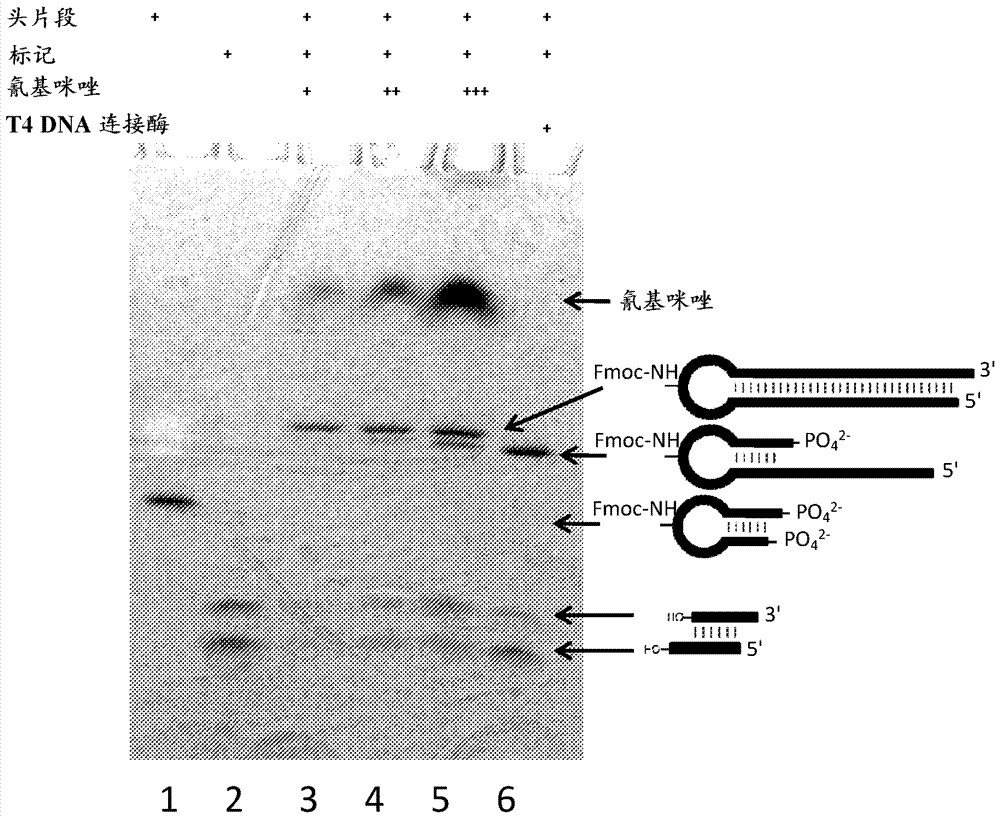
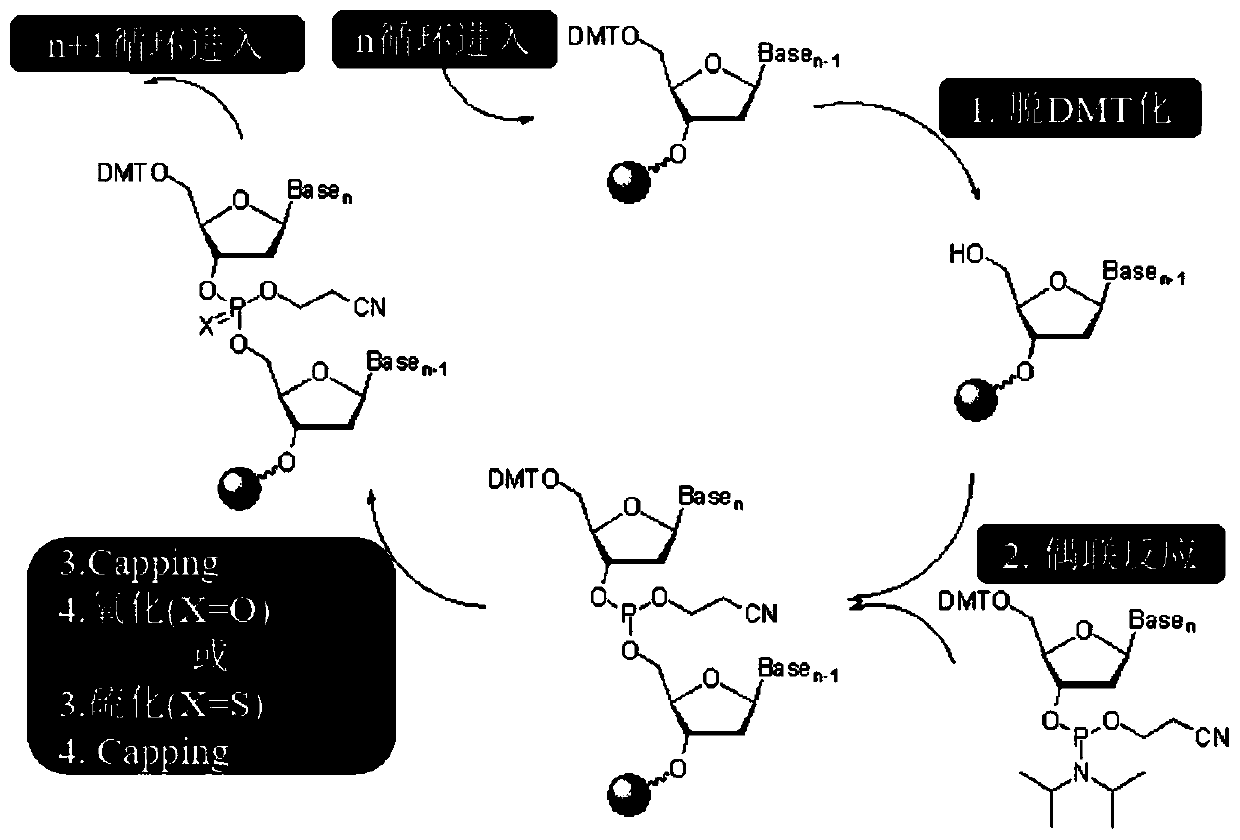
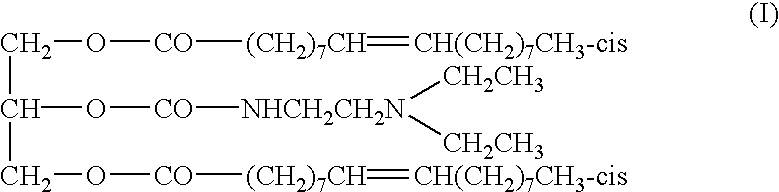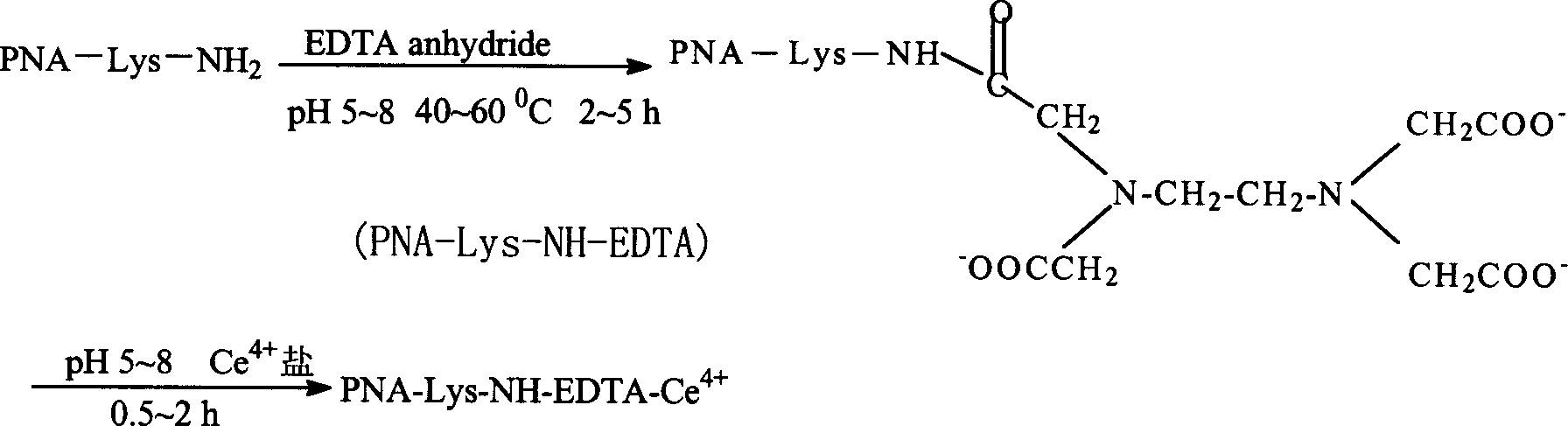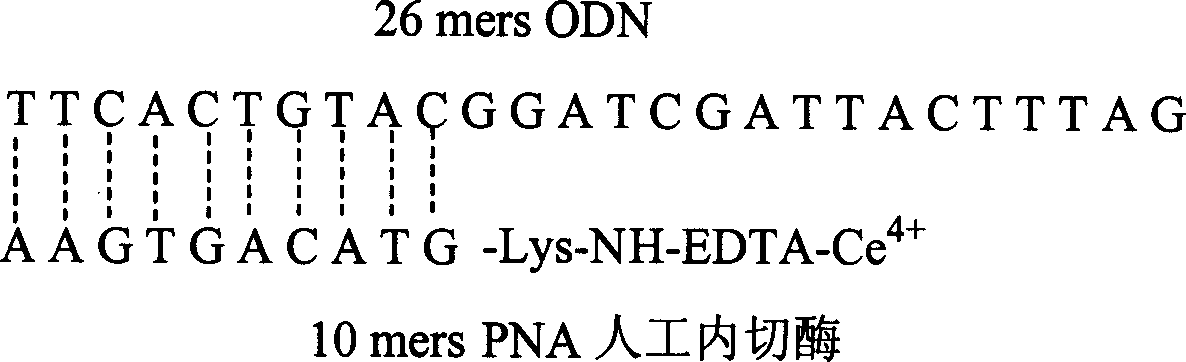Patents
Literature
77 results about "Phosphodiester bond" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
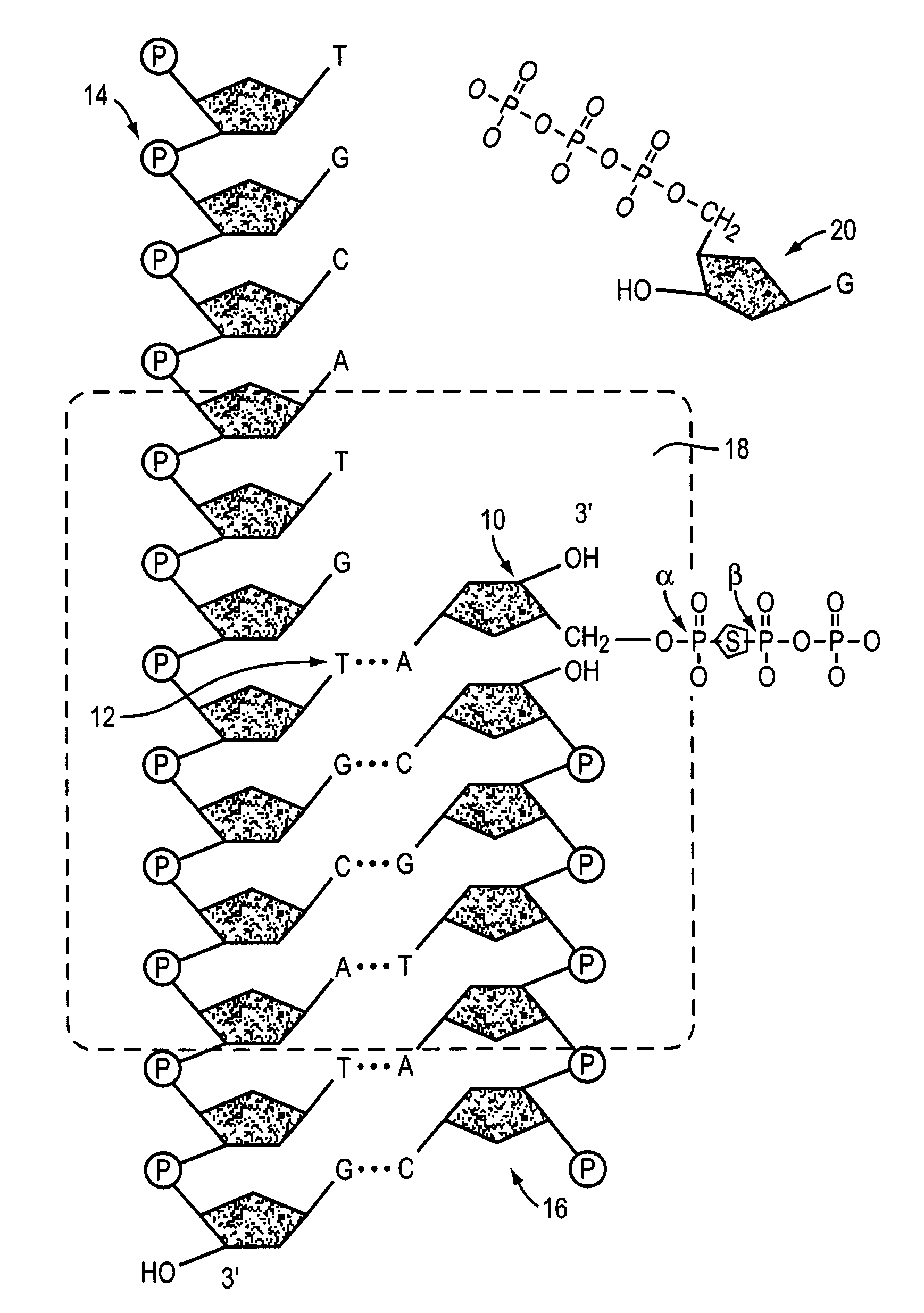
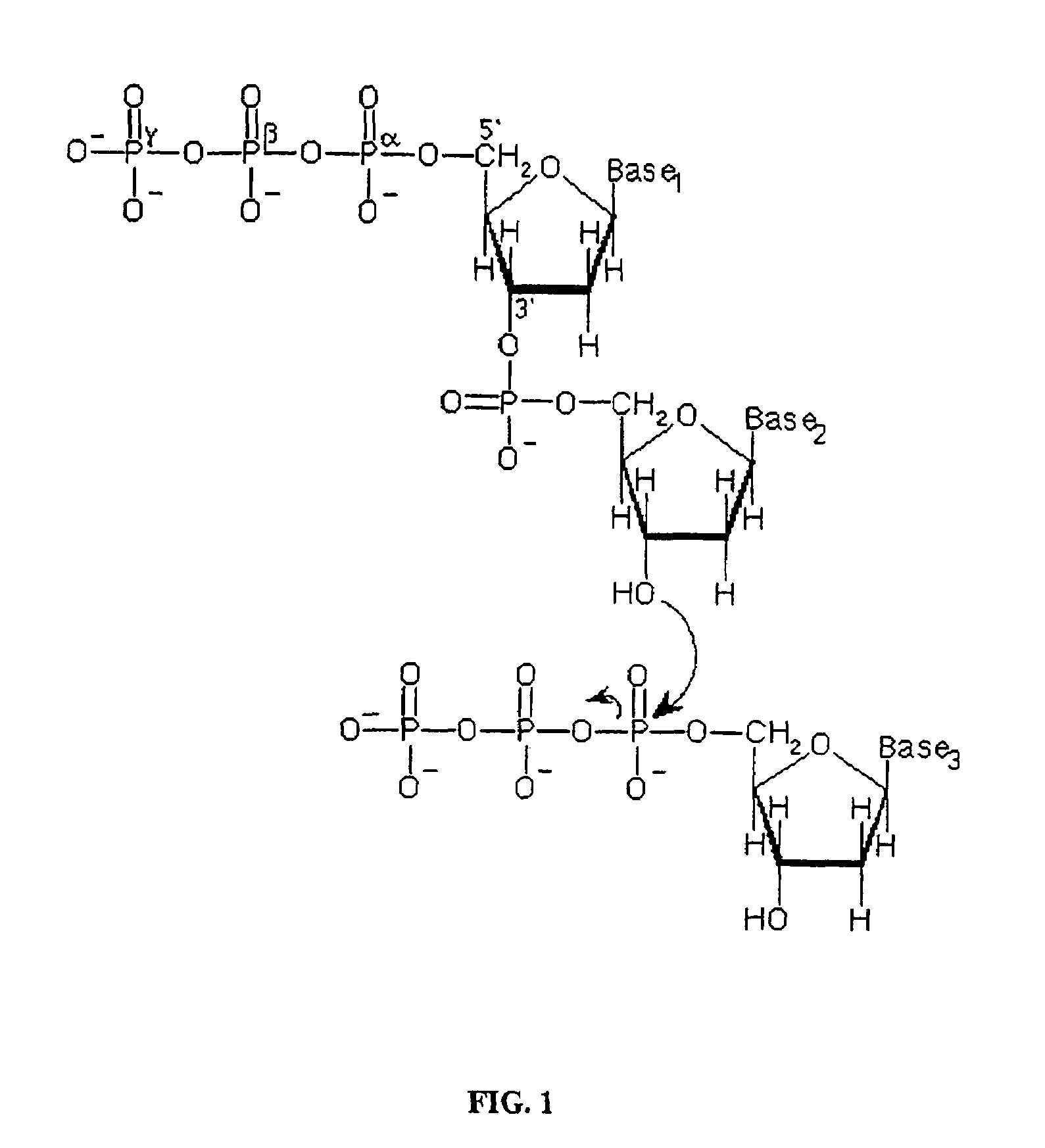
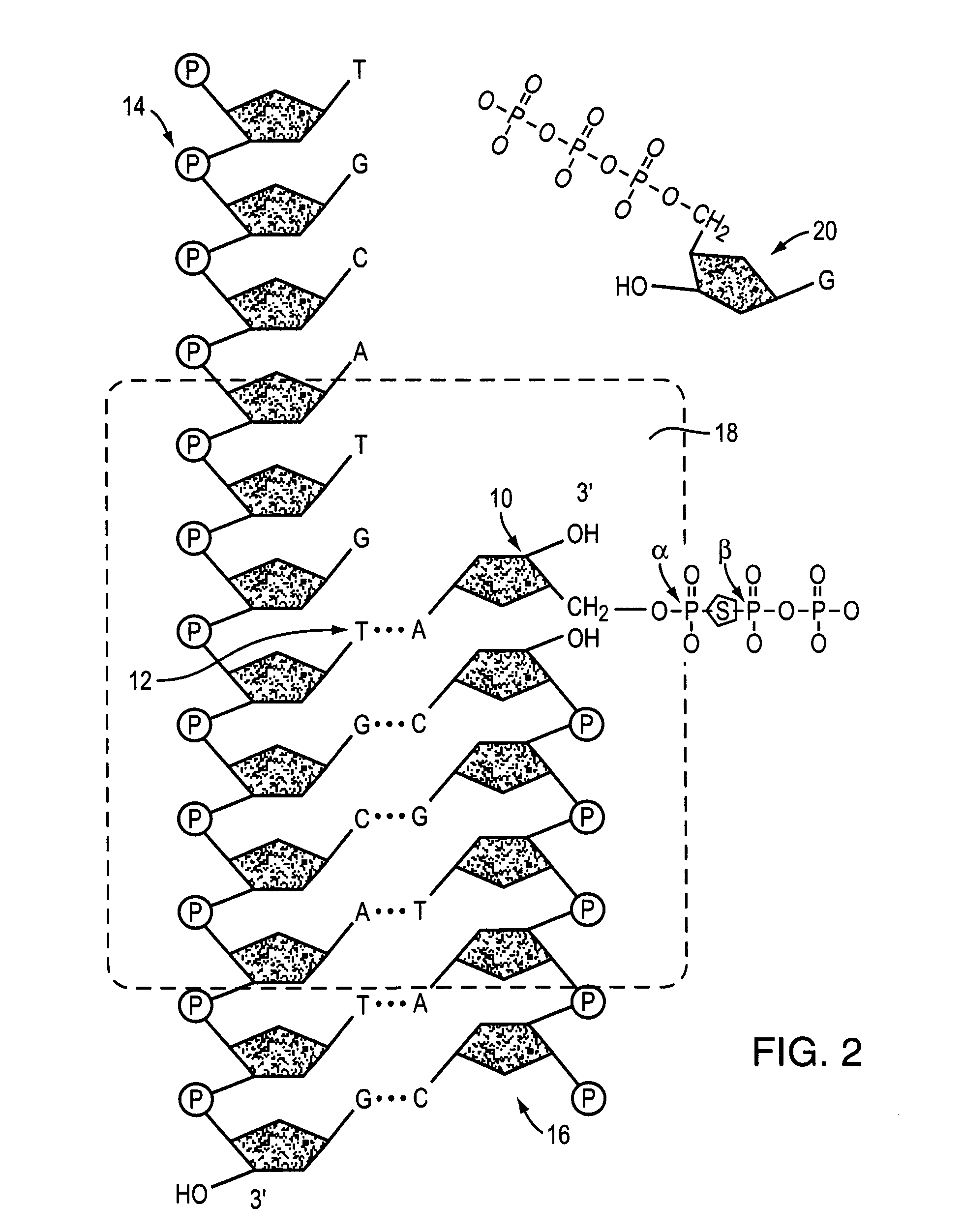
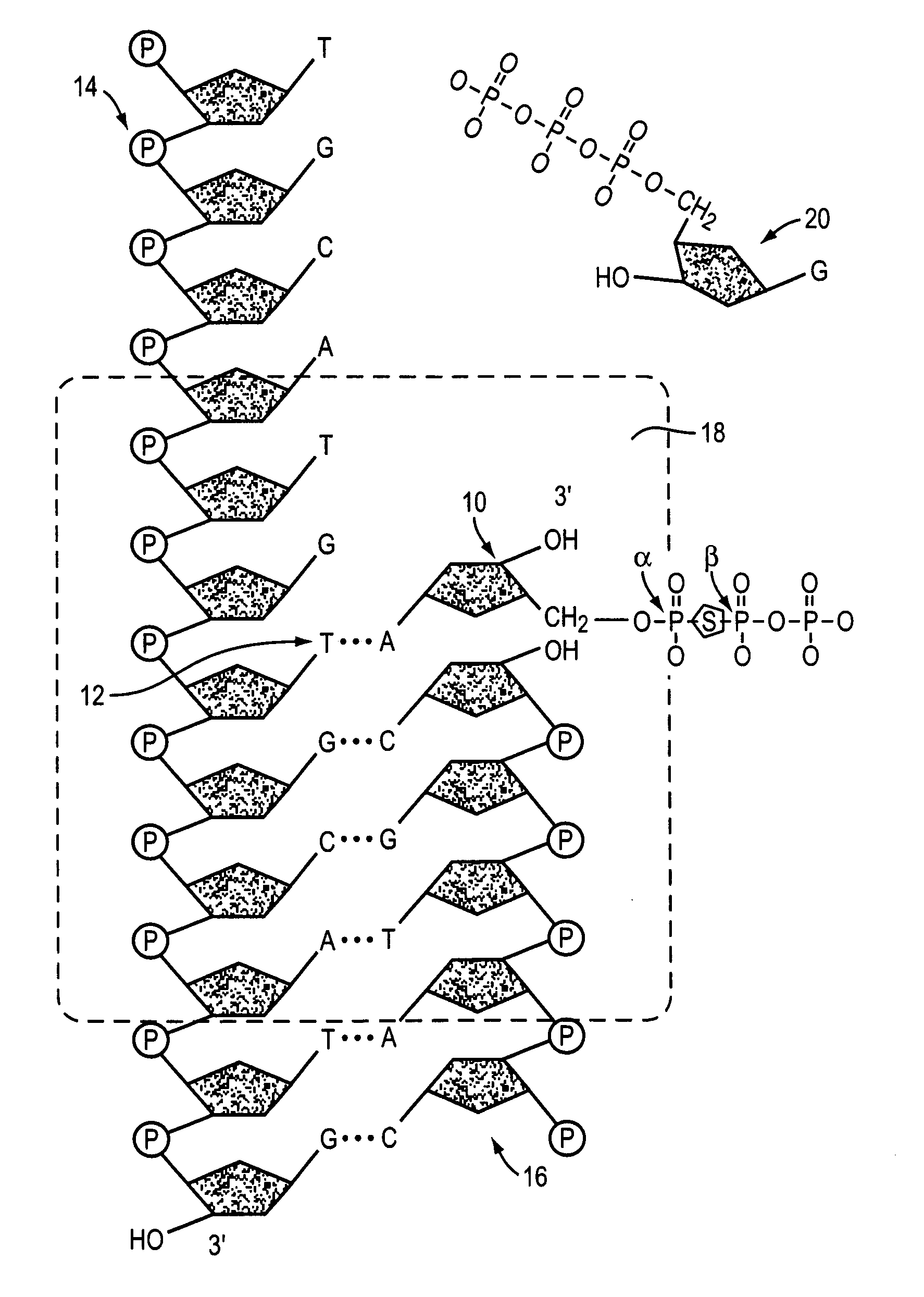
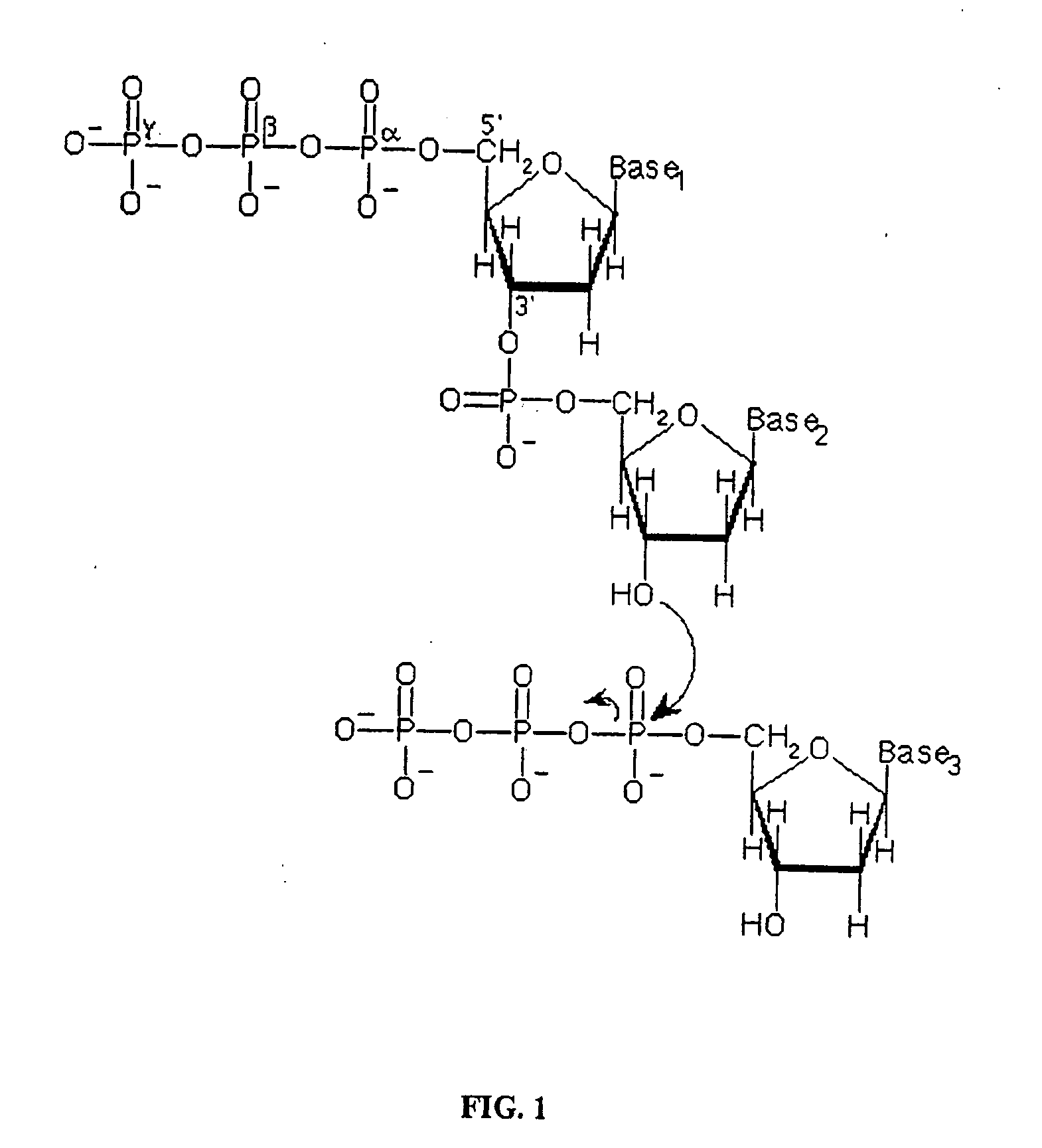
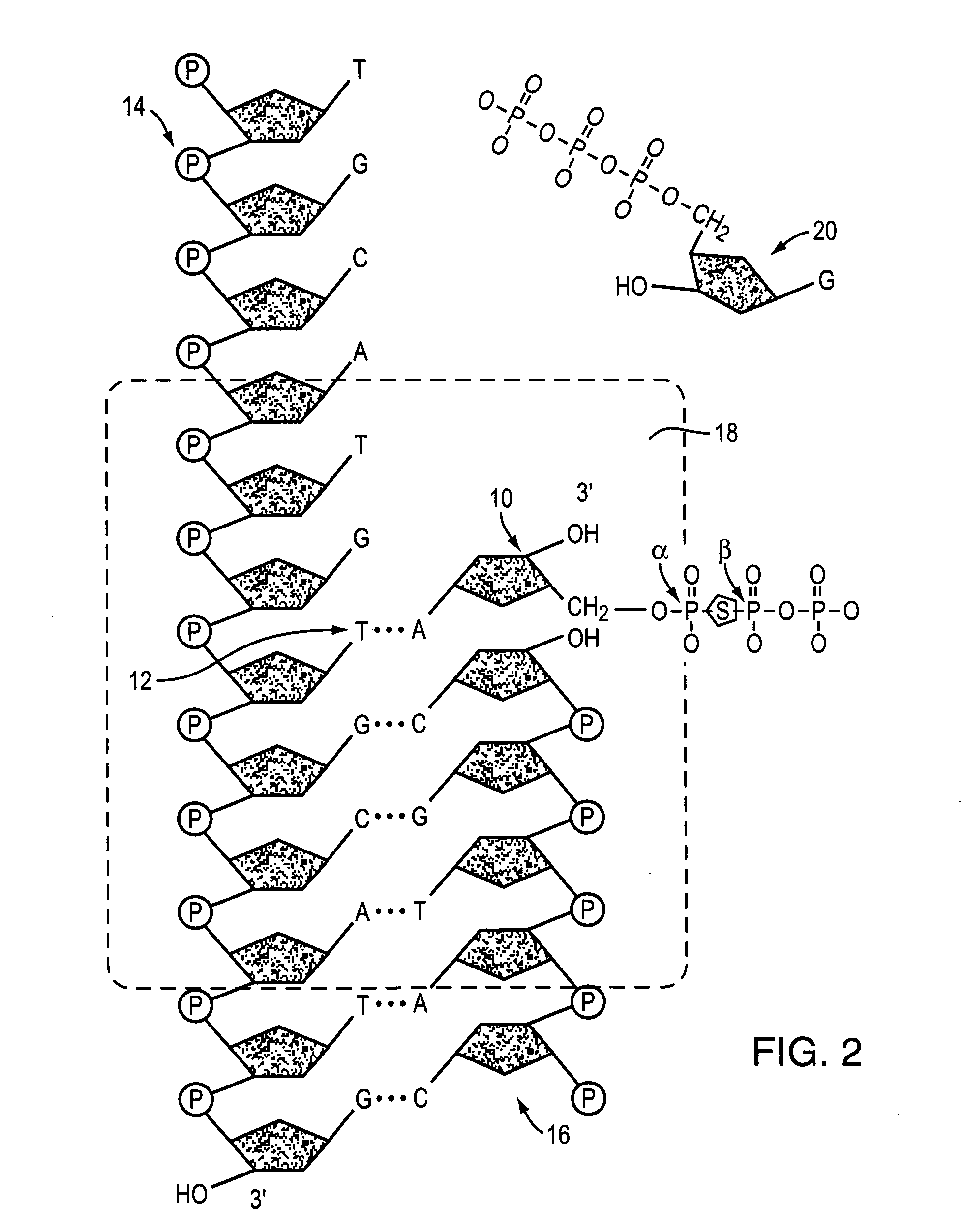
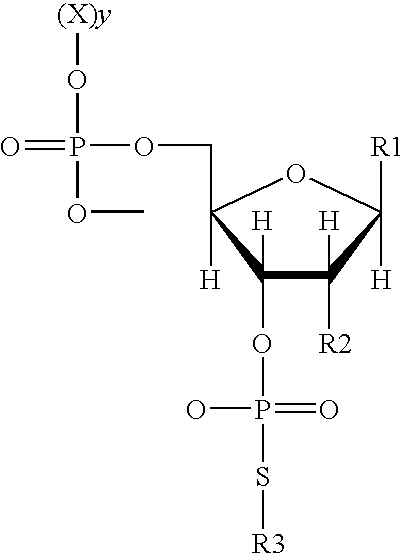
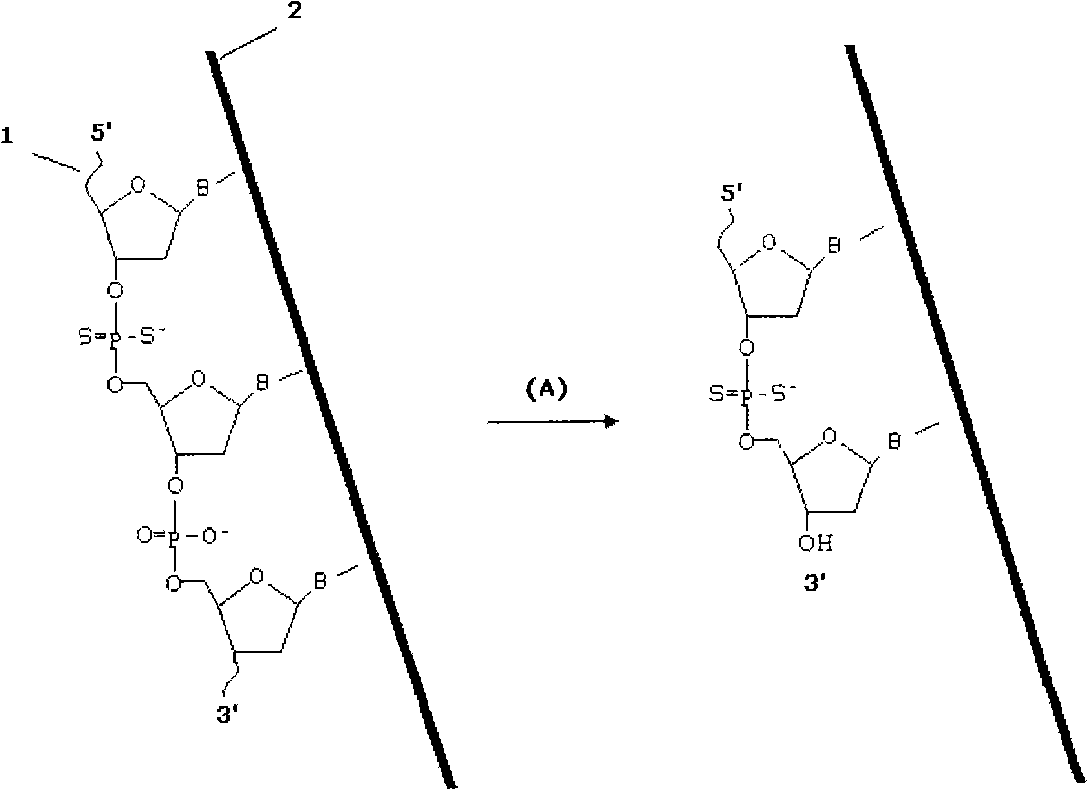
A phosphodiester bond occurs when exactly two of the hydroxyl groups in phosphoric acid react with hydroxyl groups on other molecules to form two ester bonds. Phosphodiester bonds are central to all life on Earth as they make up the backbone of the strands of nucleic acid. In DNA and RNA, the phosphodiester bond is the linkage between the 3' carbon atom of one sugar molecule and the 5' carbon atom of another, deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA. Strong covalent bonds form between the phosphate group and two 5-carbon ring carbohydrates (pentoses) over two ester bonds.
Methods and compositions for improving fidelity in a nucleic acid synthesis reaction
InactiveUS7482120B2Improve fidelityInhibition formationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotidePerylene derivatives
The invention provides methods and compositions for improving the fidelity of a sequencing-by-synthesis reaction by using a nucleotide derivative that forms a hydrogen bond with a complementary nucleotide on a template, but fails to form a phosphodiester bond with the 3′ hydroxyl group of a primer under conditions otherwise suitable for a polymerization reaction; thereby blocking incorporation of a mismatched nucleotide.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Compound for detecting and modulating RNA activity and gene expression
InactiveUS6262241B1Tightly boundEfficient executionSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsBond cleavageMinor groove
Compositions and methods for modulating the activity of RNA and DNA are disclosed. In accordance with preferred embodiments, antisense compositions are prepared comprising targeting and reactive portions. Reactive portions which act, alternatively, through phosphorodiester bond cleavage, through backbone sugar bond cleavage or through base modification are preferrably employed. Groups which improve the pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties of the oligonucleotides are also useful in accordance with certain embodiments of this invention. Delivery of the reactive or non-reactive functionalities into the minor groove formed by the hybridization of the composition with the target RNA is also preferrably accomplished. Therapeutics, diagnostics and research methods and also disclosed. Synthetic nucleosides and nucleoside fragments are also provided useful for elaboration of oligonucleotides and oligonucleotide analogs for such purposes.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Antisense inhibition of ras gene with chimeric and alternating oligonucleotides
InactiveUS6359124B1Loss of expressionEnhanced cellular uptakeOrganic active ingredientsBiocideBiological activationH-ras Genes
Compositions and methods are provided for the modulation of expression of the human ras gene in both the normal and activated forms. Oligonucleotides are provided that have methylene(methylimino) linkages alternating with phosphorothioate or phosphodiester linkages. Further oligonucleotides are provide that have a first region having a methylene(methylimino) linkage alternating with a phosphorothioate or phosphodiester linkage and a second region having phosphorothioate linkages. Such oligonucleotides can be used for diagnostics as well as for research purposes including methods for diagnosis, detection and treatment of conditions arising from the activation of the H-ras gene.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
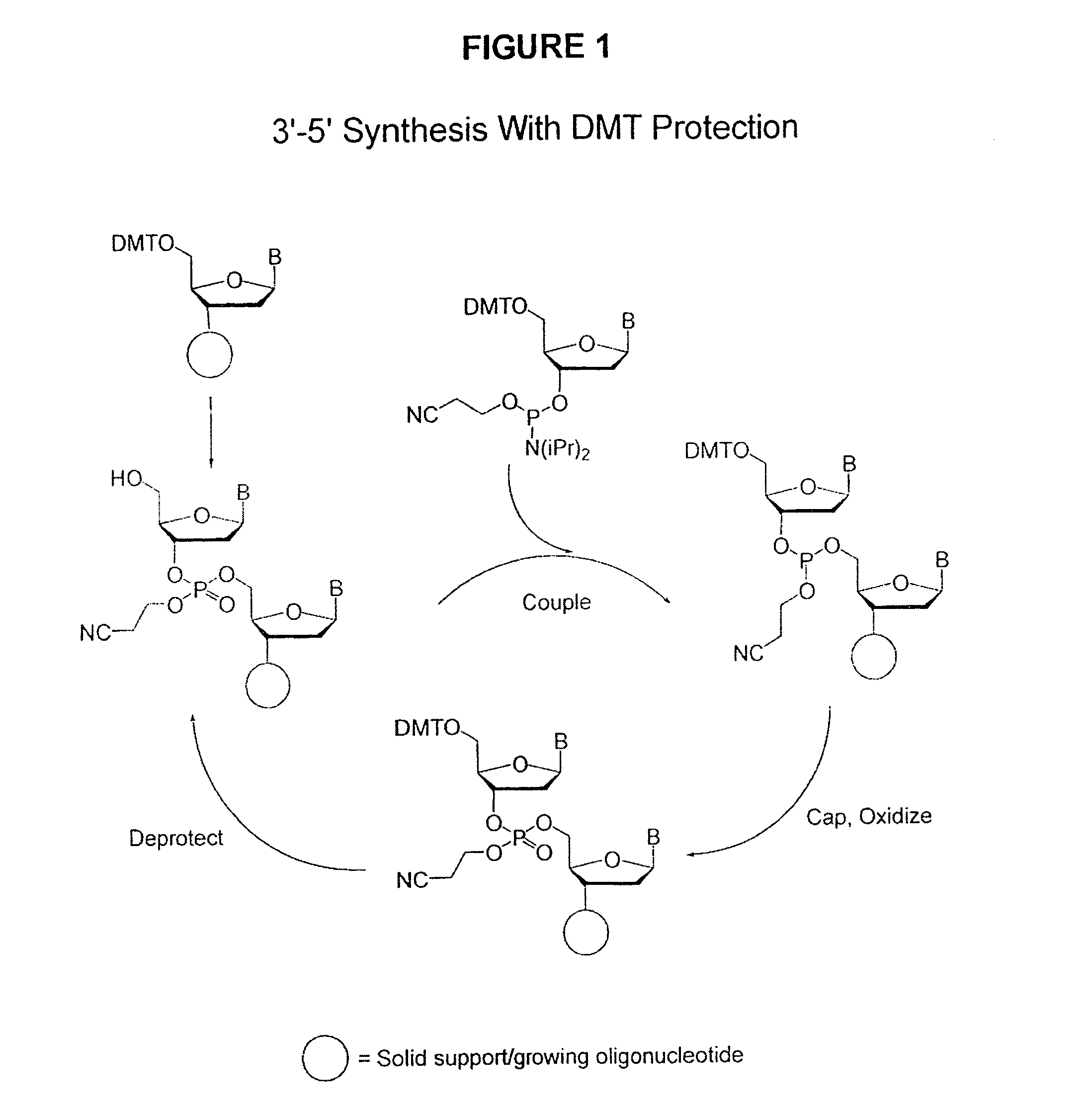
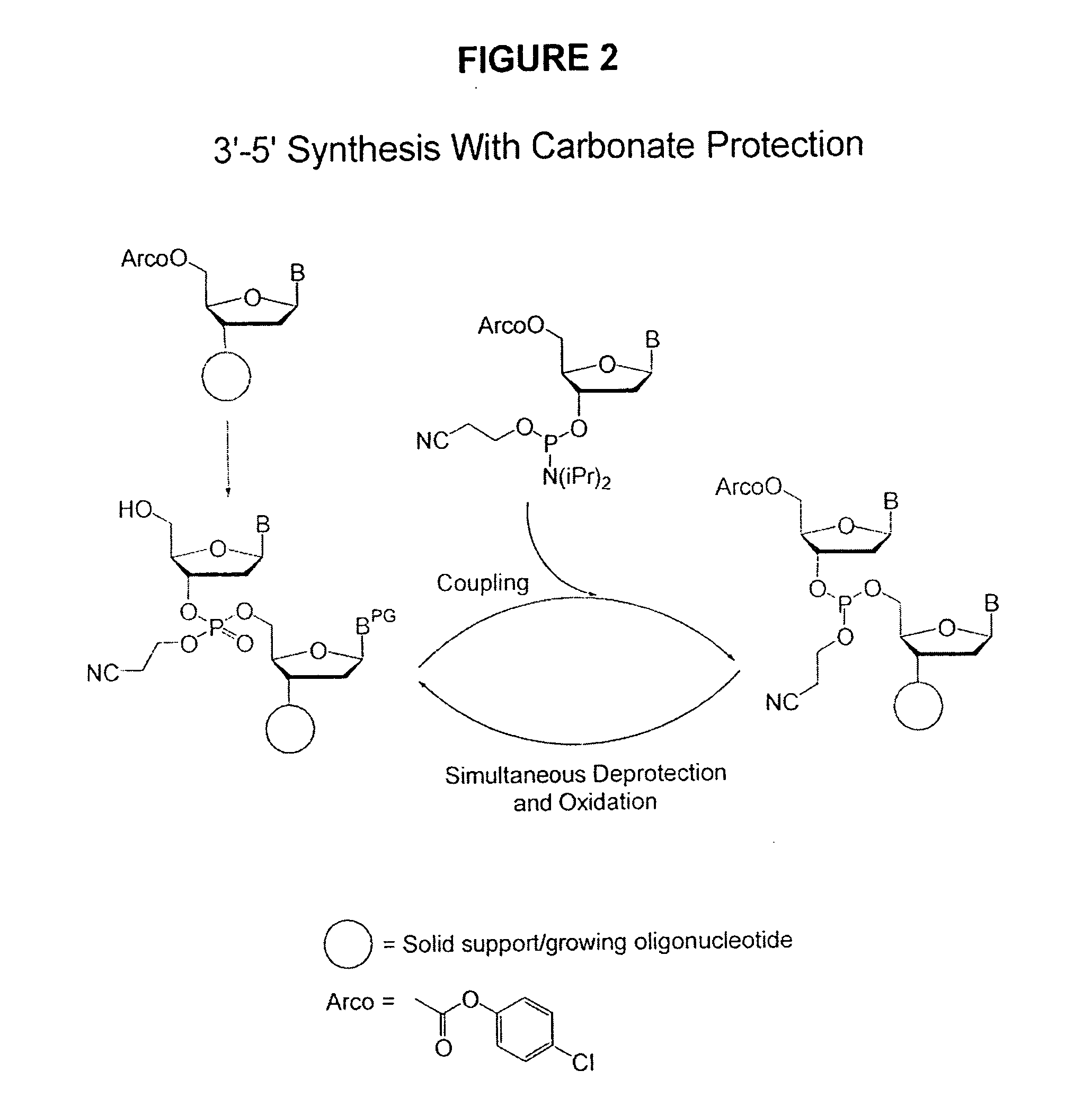
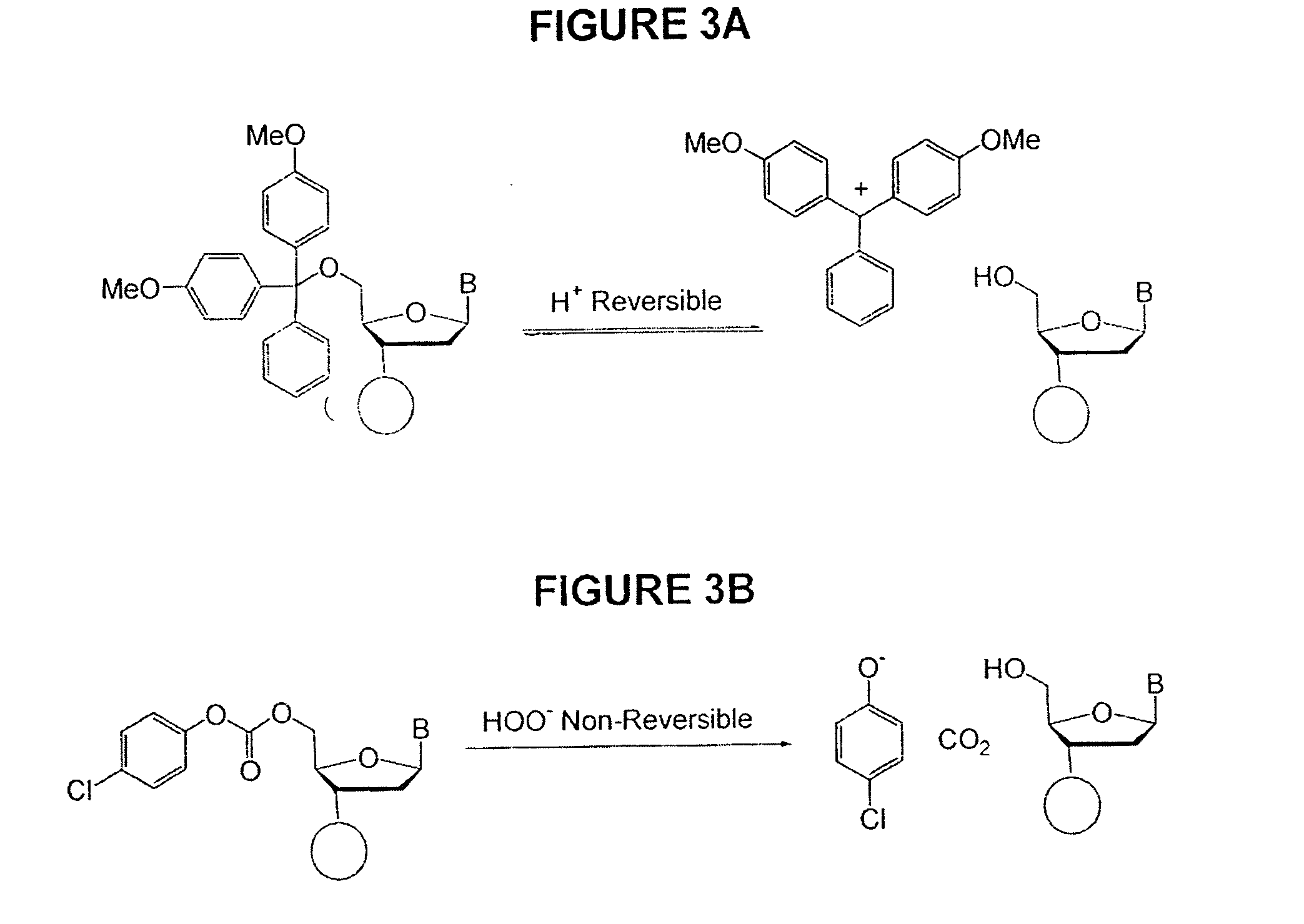
Methods of synthesizing oligonucleotides using carbonate protecting groups and alpha-effect nucleophile deprotection
The invention provides methods for synthesizing oligonucleotides using nucleoside monomers having carbonate protected hydroxyl groups that are deprotected with α-effect nucleophiles. The α-effect nucleophile irreversibly cleave the carbonate protecting groups while simultaneously oxidizing the internucleotide phosphite triester linkage to a phosphodiester linkage. The procedure may be carried out in aqueous solution at neutral to mildly basic pH. The method eliminates the need for separate deprotection and oxidation steps, and, since the use of acid to remove protecting groups is unnecessary, acid-induced depurination is avoided. Fluorescent or other readily detectable carbonate protecting groups can be used, enabling monitoring of individual reaction steps during oligonucleotide synthesis. The invention is particularly useful in the highly parallel, microscale synthesis of oligonucleotides.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC +1
Method of nucleic acid sequence determination
ActiveUS20170314072A1Unable to formatMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesNucleotideFluorescence
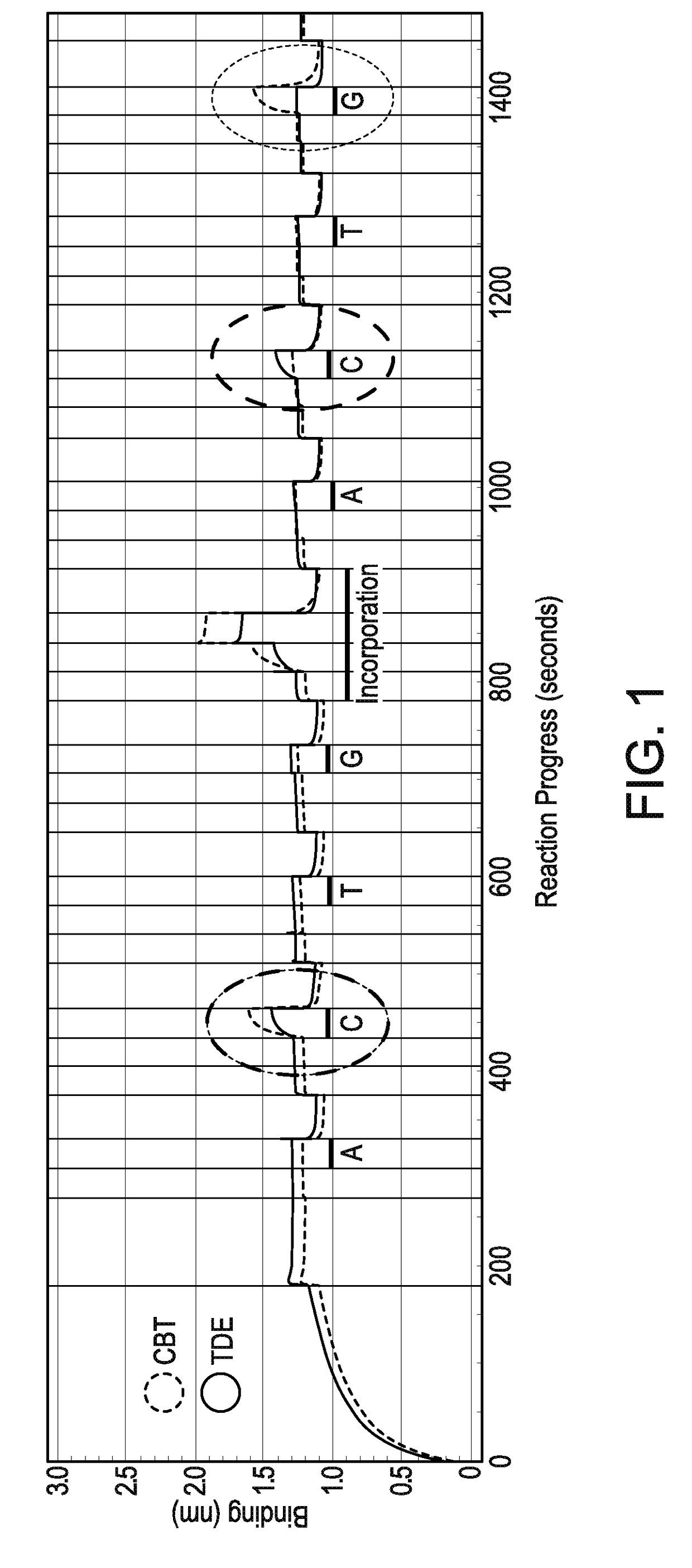
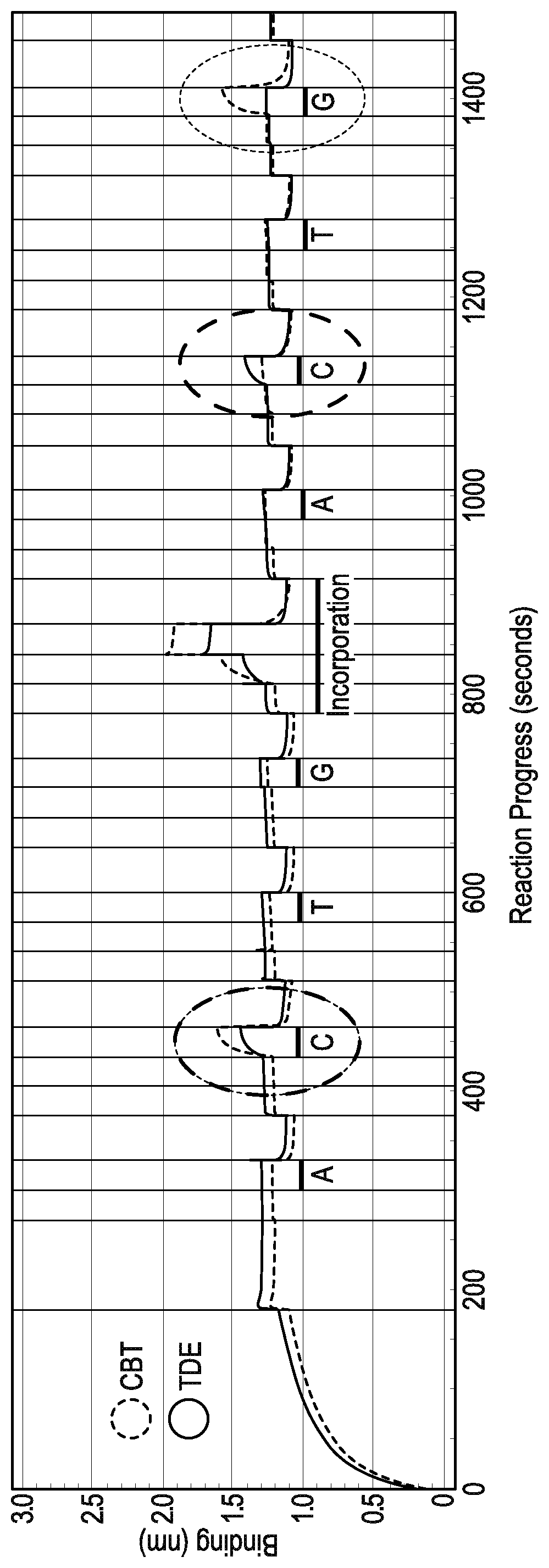
Provided are sequencing-by-binding methods of detecting cognate nucleotides using a crippled DNA polymerizing enzyme that possesses the ability to bind the next correct nucleotide downstream of a primer in a template-dependent fashion, but does not possess the activity needed to promote phosphodiester bond formation. Use of the crippled DNA polymerase permits interrogation of one nucleotide at a time, without incorporation of any nucleotide. Labeled nucleotides, such as fluorescently labeled nucleotides, can be used in conjunction with the crippled DNA polymerase to establish cognate nucleotide identity in a rapid manner.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Chain-shortened polynucleotide and method for preparation thereof
InactiveUS6780429B1Convenient lengthSure easyOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesNucleotidePolynucleotide
The present invention provides a chain-shortened polynucleotide wherein the proportion of a 2'-5' phosphodiester bond is up to 3% based on the whole phosphodiester bonds or a salt thereof and a pharmaceutical composition containing the same, and a method for producing the same.
Owner:NIPPON SHINYAKU CO LTD
Binder compositions with polyvalent phosphorus crosslinking agents
ActiveUS20130023174A1Readily availableLow costStarch dervative coatingsStarch adhesivesFiberProcedure Agents
An fibrous insulation product is provided that includes a binder comprising a polyol and a phosphorus crosslinking agent derived from a phosphonic or phosphoric acid, salt, ester or anhydride to form crosslinked phosphodiester linkages. The polyol is polyvalent, but may be monomeric or preferably polymeric; and may be synthetic or natural in origin. Carbohydrate polysaccharides are exemplary polyols, including water-soluble polysaccharides such as dextrin, maltodextrin, starch, modified starch, etc. Additionally, the carbohydrate polymer may have a dextrose equivalent (DE) number from 2 to 20. In exemplary embodiments, the binder may also include a catalyst, a coupling agent, a process aid, and other additives. The environmentally friendly, formaldehyde-free binder may be used in the formation of residential and commercial insulation materials and non-woven chopped strand mats. A method of making fibrous products is also provided.
Owner:OWENS CORNING INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL LLC
Methods and compositions for improving fidelity in a nucleic acid synthesis reaction
InactiveUS20060172313A1Improve fidelityInhibition formationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationOrganic chemistryPolymerization
The invention provides methods and compositions for improving the fidelity of a sequencing-by-synthesis reaction by using a nucleotide derivative that forms a hydrogen bond with a complementary nucleotide on a template, but fails to form a phosphodiester bond with the 3′ hydroxyl group of a primer under conditions otherwise suitable for a polymerization reaction; thereby blocking incorporation of a mismatched nucleotide.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Use of phosphorothiolate polynucleotides in ligating nucleic acids
The invention provides a method of nonenzymatic ligation of a nucleic acid. The method consists of contacting a polynucleotide-3′ phosphorothiolate with an acceptor polynucleotide under conditions that allow formation of a phosphodiester bond between the polynucleotide-3′ phosphorothiolate and the acceptor polynucleotide. The invention also provides methods of molecular cloning. In one embodiment, the method consists of contacting an insert comprising a polynucleotide-3′ phosphorothiolate with an acceptor vector under conditions that allow formation of a phosphodiester bond between the insert and the acceptor vector to generate a vector comprising an insert polynucleotide. The invention further provides a compound consisting of a polynucleotide-3′ phosphorothiolate and a kit containing a polynucleotide-3′ phosphorothiolate. Also provided is a method of ligating a nucleic acid using a non-sequence specific topoisomerase.
Owner:SAN DIEGO STATE UNIVERSITY +1
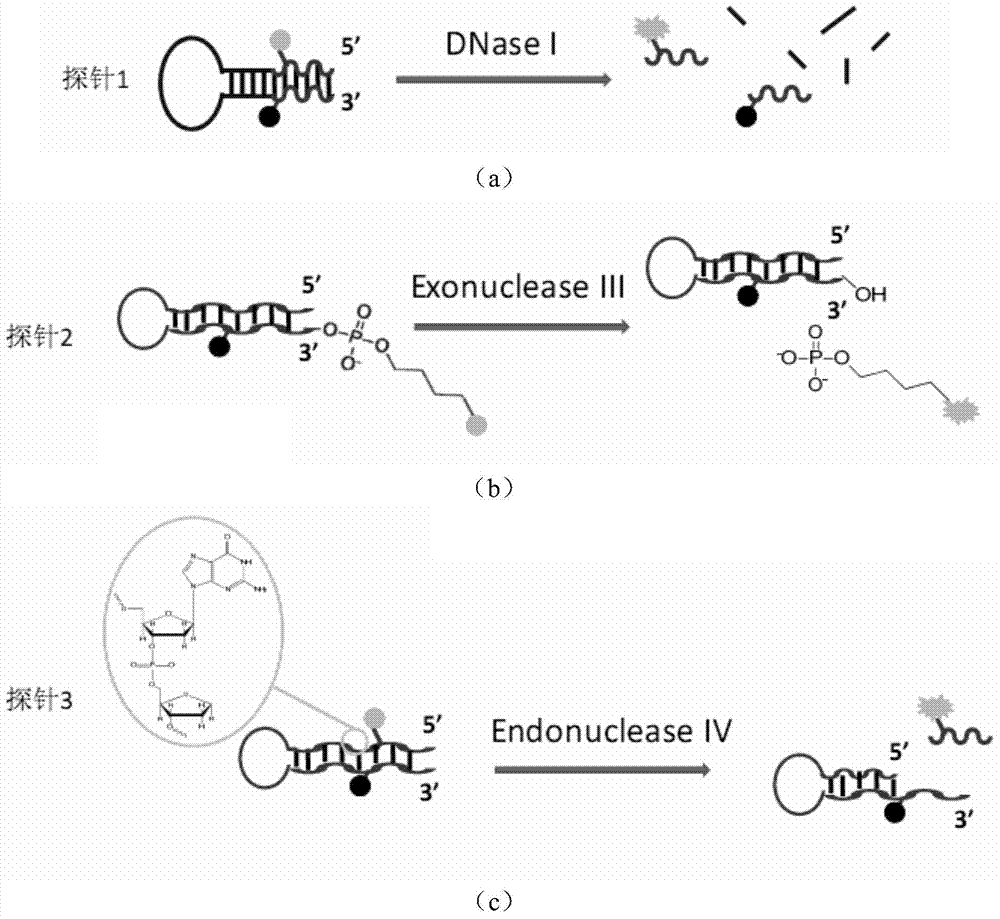
Phosphorthioate-modified oligonucleotide fluorescence probe and application thereof in detection of nuclease
ActiveCN103333888AAccurate analysisHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescenceLyase
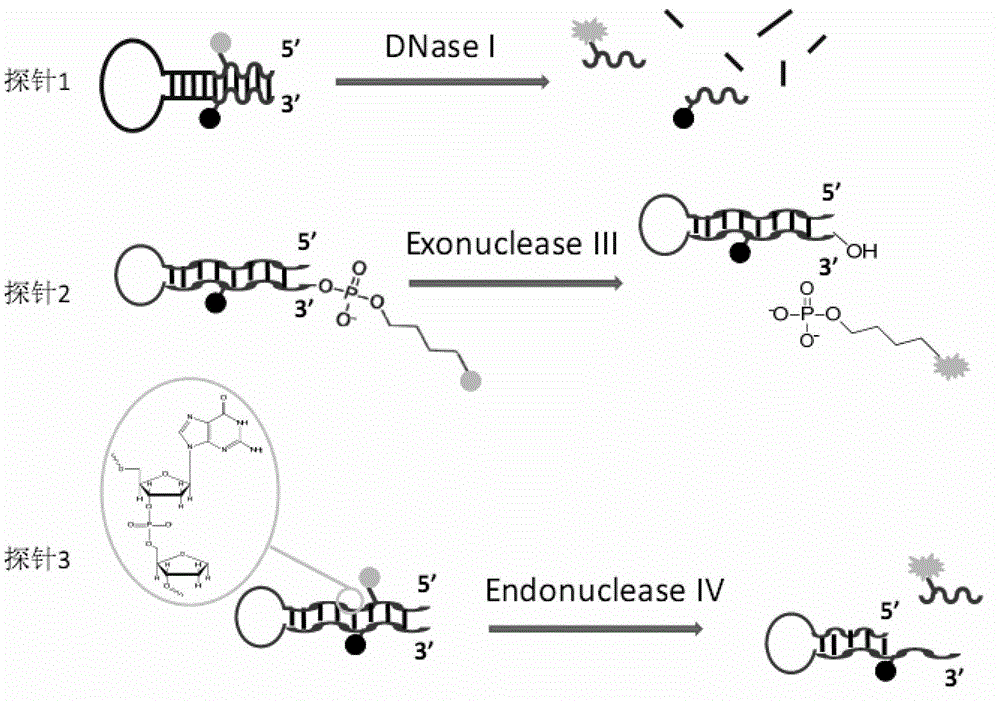
The invention discloses a phosphorthioate-modified oligonucleotide fluorescence probe and an application thereof in the detection of nuclease. The phosphorthioate-modified oligonucleotide fluorescence probe is provided with a stem-and-loop structure, the ring part of the phosphorthioate-modified oligonucleotide fluorescence probe is of a single-stranded structure and comprises 4-8 nucleotide residues, the stem part of the phosphorthioate-modified oligonucleotide fluorescence probe comprises 8-15 pairs of nucleotide residues, O- in part of phosphate diester bond of a probe is replaced by S-, and the probe is divided into a non-restriction endonuclease probe, an exonuclease probes and a depurination / depyrimidination site lyase probes according to the activity function of the nuclease to be detected. The phosphorthioate-modified oligonucleotide fluorescence probe is an accurate and reliable analytic method which can be used for detecting the activity of the nuclease in real time, has strong selectivity and high sensitivity and is fast in speed and low in cost, so that lots of limitations in the prior art are overcome.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Non-dependent ligase gene cloning process based on thio-modification
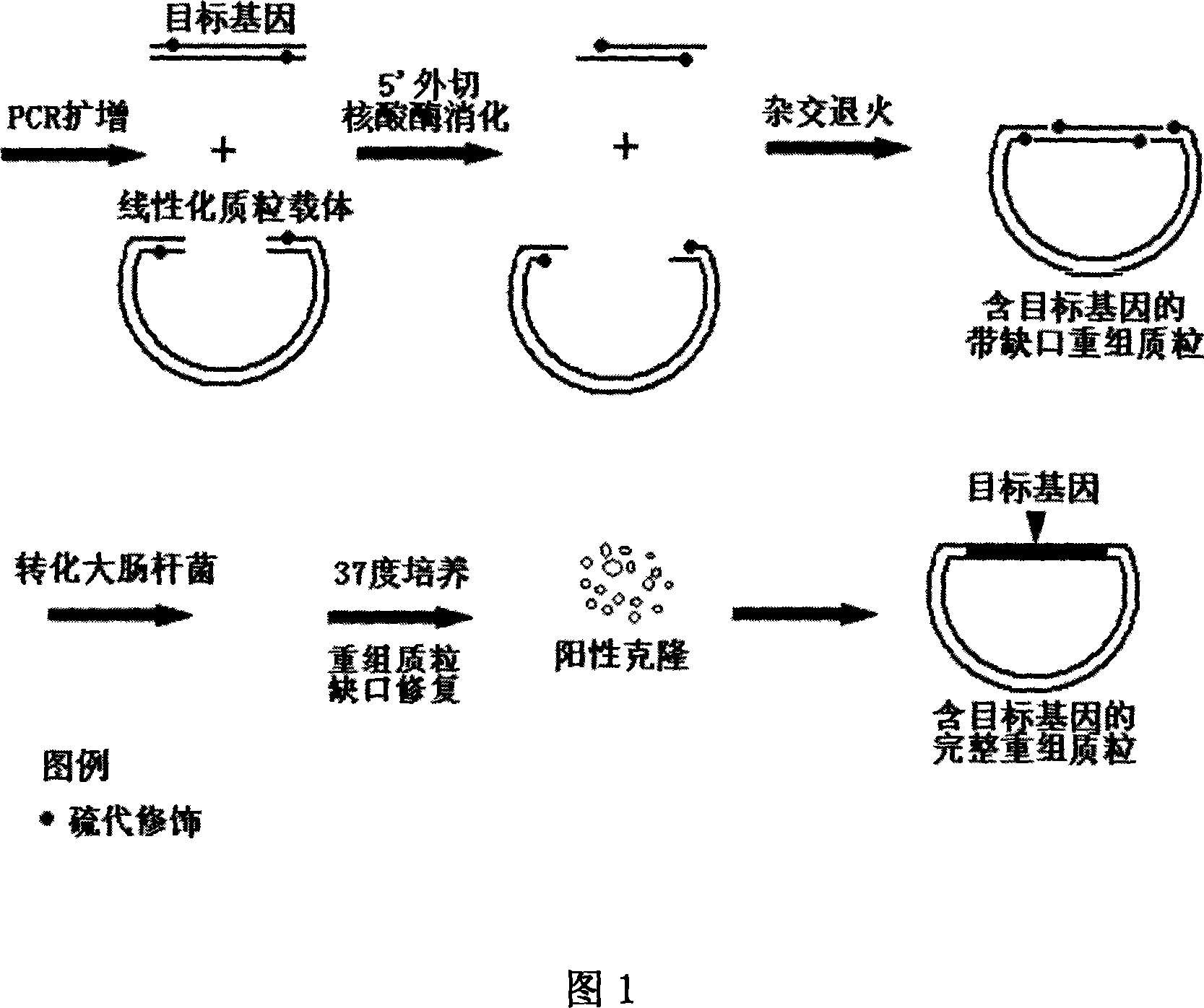
The present invention relates to non-dependent ligase gene cloning process based on thio-modification. Each of the amplified target gene and the primer of the plamid vector has The 5' end thio-modified. The cloning process includes: PCR amplification of target gene and plamid vector and purification of PCR products; degrading DNA chain from the 5' end with 5' exonuclease and thio-modification to create 10-20 of 3' single chain raised ends of nucleoside; and direct transformation to colibacillus. The target gene cloning of the present invention has no dependence on restrictive endonuclease and DNA ligase and great operation flux, and may be used in large scale gene cloning.
Owner:苏州博睐恒生物科技有限公司
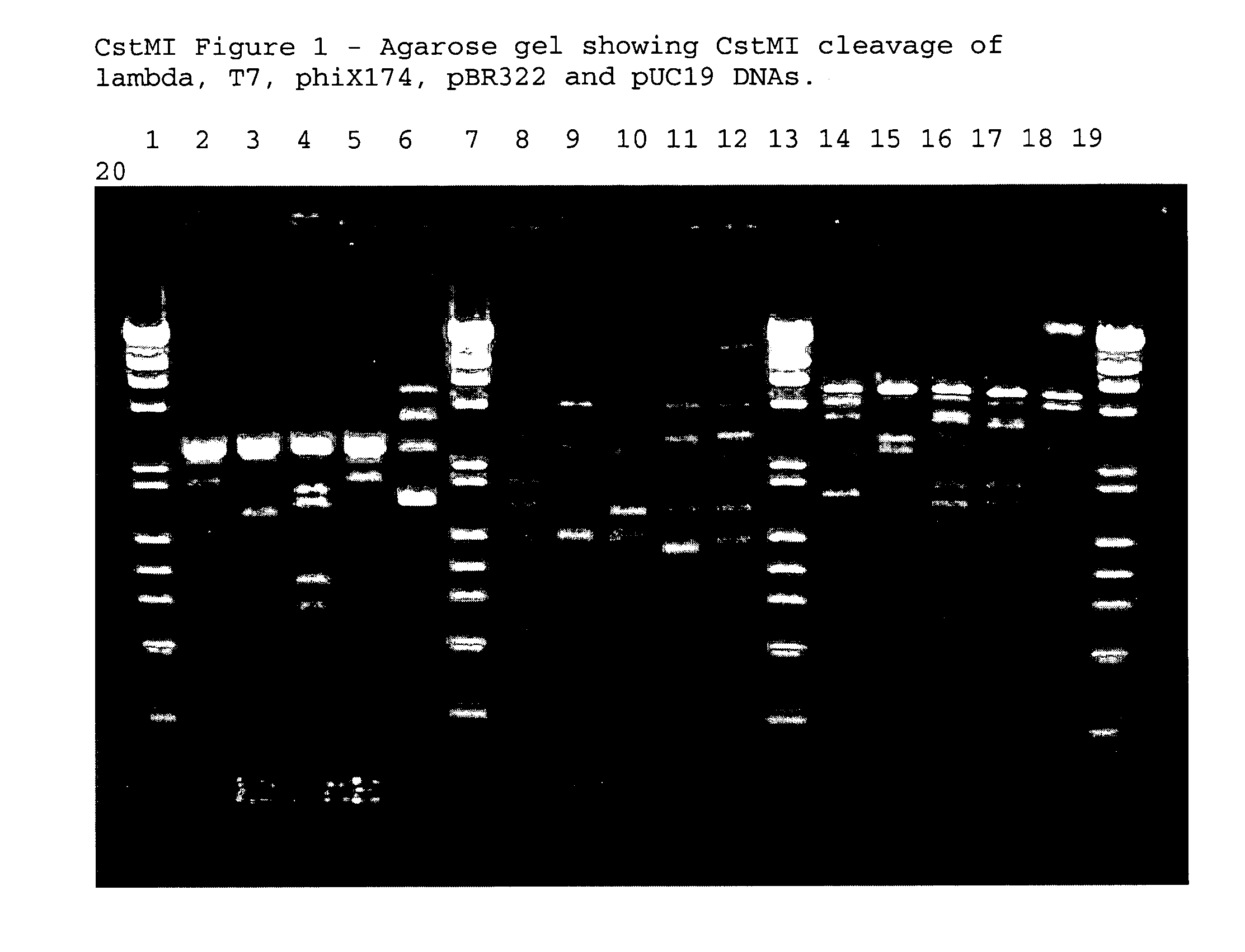
Type II restriction endonuclease, CstMI, obtainable from Corynebacterium striatum M82B and a process for producing the same
In accordance with the present invention, there is provided a novel type II restriction endonuclease, obtainable from Corynebacterium striatum M82B, hereinafter referred to as “CstMI”, which endonuclease:(1) recognizes the nucleotide sequence 5′-AAGGAG-3′ in a double-stranded DNA molecule as shown below,5′-AAGGAGN20↓-3′3′-TTCCTCN18↑-5′(wherein G represents guanine, C represents cytosine, A represents adenine, T represents thymine and N represents either G, C, A, or T);(2) cleaves said sequence at the phosphodiester bonds between the 20th and the 21th nucleotides 3′ to the recognition sequence in the 5′-AAGGAG-3 strand of the DNA, and between the 18th and 19th nucleotides 5′ to the recognition sequence in the complement stand, 5′-CTCCTT-3′, to produce a 2 base 3′extension; and(3) possesses a second enzymatic activity that recognizes the same DNA sequence, 5′-AAGGAG-3′, but modifies this sequence by the addition of a methyl group to prevent cleavage by the CstMI endonuclease activity.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Method of nucleic acid sequence determination
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Methods of synthesizing oligonucleotides using carbonate protecting groups and alpha-effect nucleophile deprotection
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC +1
Artificial endo enzyme containing peptide nucleic acid recognition element, and its preparing method and use
The invention provides the artificial inner cut enzyme which can cut phosphodiester bond in nucleic acid selectivitily. The inner cut enzyme contains recognition and cutting details. The recognition details is single strand of peptide nucleic acid which constitutional unit is 6-200 qae glycine. The cutting details is chelating agent of rare earth metal ion which is chelated with metal ion at the ammonia or carbon terminal of single strand of peptide nucleic acid and which has joint between the chelating agent and single strand. the artificial inner cut enzyme can be used implemental enzyme widely in molecular biology, genetic engineering and medical treatment area.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Iodine dissociation type gene cloning method based on sulfo-modifiers
The invention discloses an iodine dissociation type gene cloning method based on sulfo-modifiers. According to the method, phosphodiester bonds between the positions of 1-15, 16, 17, 18, 19 or 20 of the 5' ends of primers of a target gene and a plasmid vector are amplified into the sulfo-modifiers; a base sequence at the positions of 1-15, 16, 17, 18, 19 or 20 of the 5' ends of forward primers of the target gene and the plasmid vector and a base sequence at the positions of 1-15, 16, 17, 18, 19 or 20 of the 5' ends of reverse primers of the target gene and the plasmid vector are matched in a supplementary mode; after the target gene and the plasmid vector are subjected to PCR amplification, a PCR product is purified; iodine selectively breaks the phosphodiester bonds of the sulfo-modifiers, and under the combined action of existence of the sulfo-modifiers at the positions of 1-15, 16, 17, 18, 19 or 20 of the 5' ends and iodine heat treatment, DNA will generate a 3' single-link protruding end where 20 nucleotides grow. Through the method, cloning of the target gene does not rely on restriction endonuclease, DNA ligase or any other DNA modification enzyme, operation flux is large, and the method can be applied to large-scale gene cloning.
Owner:SUZHOU KUANGSHI JUNCHI BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
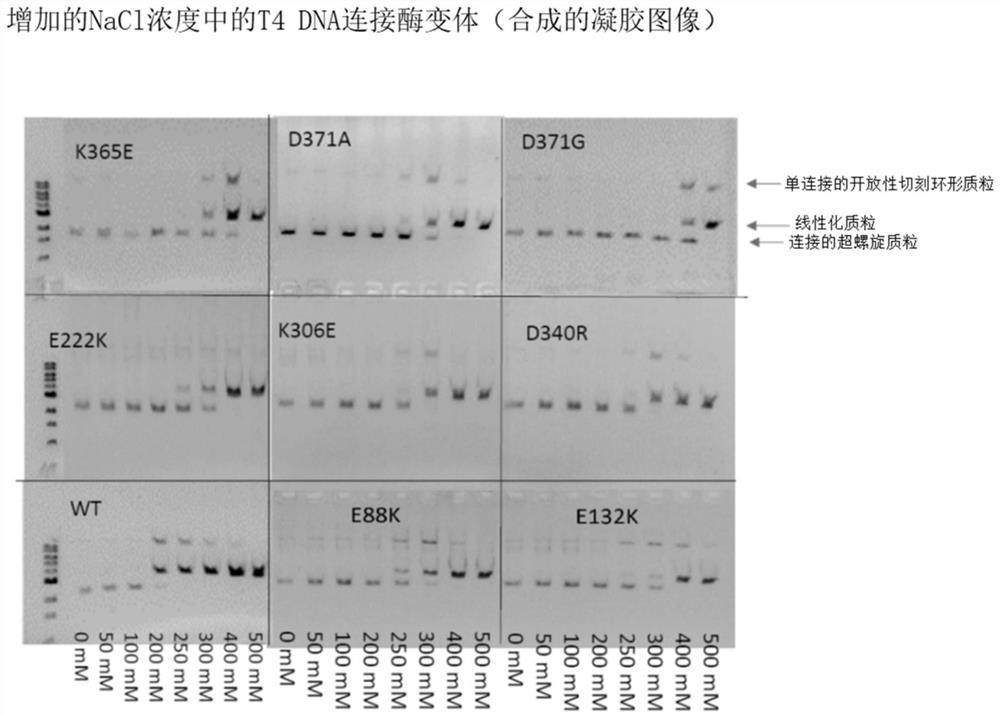
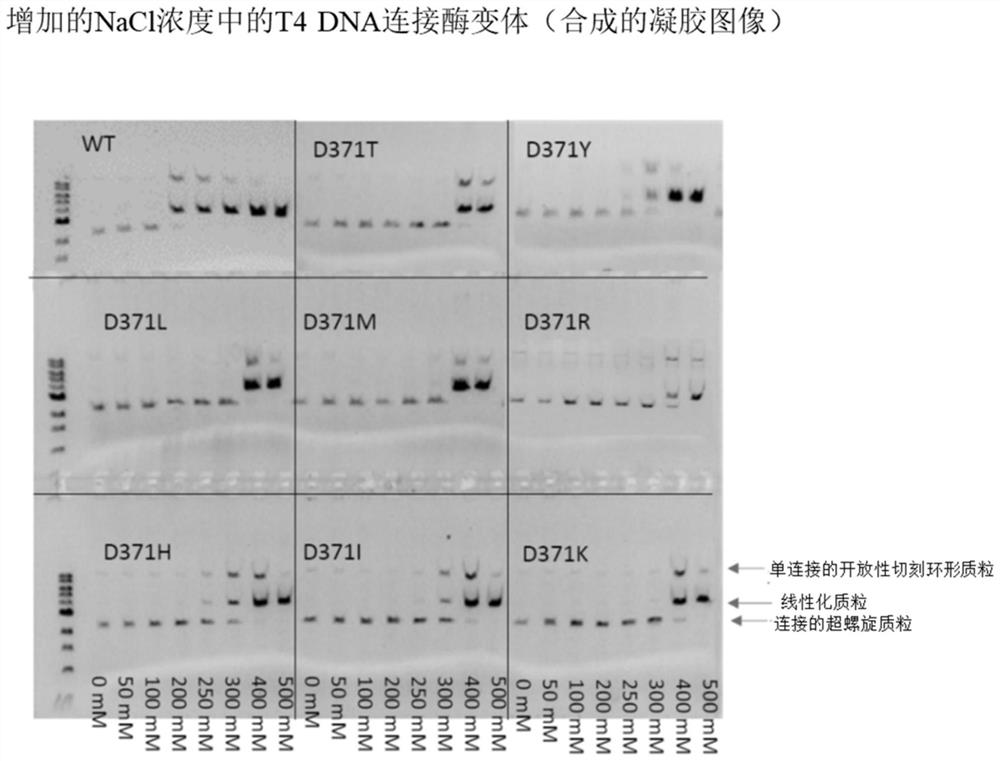
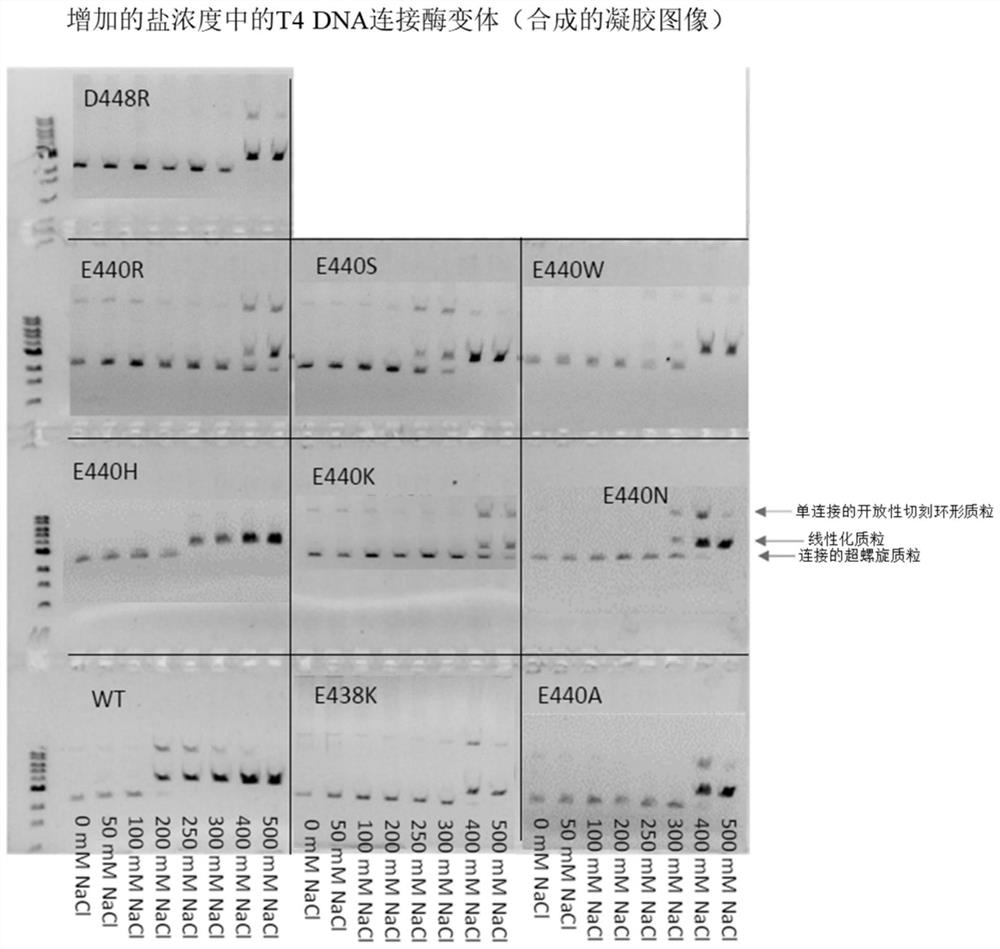
T4 DNA ligase variants with increased salt tolerance
ActiveCN114717209AHigh activityMicrobiological testing/measurementLigasesEnzyme variantEnzyme catalysis
A variety of T4DNA ligase mutants that exhibit enhanced ligation activity at high salt concentrations as compared to wild-type ligases are engineered, characterized and selected via gel electrophoresis of ligation products from standard ligation assays. A ligase catalyzes the formation of a phosphodiester bond between the 5'end and the 3 'end of complementary cohesive or blunt ends of double helix DNA, which process is crucial for many molecular biological processes, including cloning and sequencing.
Owner:WUHAN AIBO TAIKE BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for improving specificity in cutting position of endonuclease V
InactiveCN101693918AAccurate and reliableAccurate cutting positionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA fragmentationA-DNA
The method provides a method for improving the specificity in a cutting position of endonuclease V and relates to a high-throughput method for analyzing DNA sequences, in particular to a high-speed low-cost and high-throughput method for DNA sequencing. Recognition-site deoxyinosine dI containing the endonuclease V and DNA segments of single-chain oligonucleotide at a site where oxygen on one or more phosphodiester bonds in a DNA chain is sulfo-modified are introduced into a DNA probe, and the distance between the recognition site of the endonuclease V and the sulfo-modified site is two or more basic groups. The method can be used for analyzing unknown DNA, namely sequence information of a template DNA to be analyzed. Re-hybridized high-throughput primers are obtained by synthesis and purification by a very mature solid-phase DNA method, and therefore, the method does not have wrongly extended accumulative effect and can maintain the amount of DNA templates and sequencing primers. The determination of the sequence is correct and reliable, having no limitations on sequenced length.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Nucleic acid linker for high-throughput sequencing and library construction method
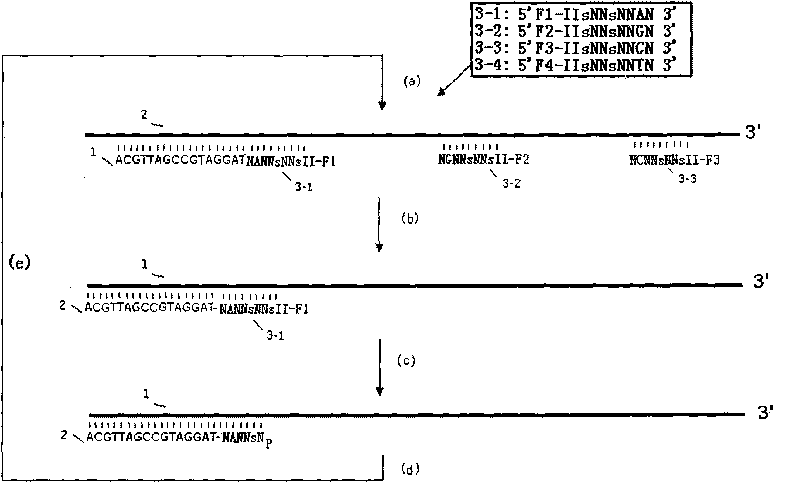
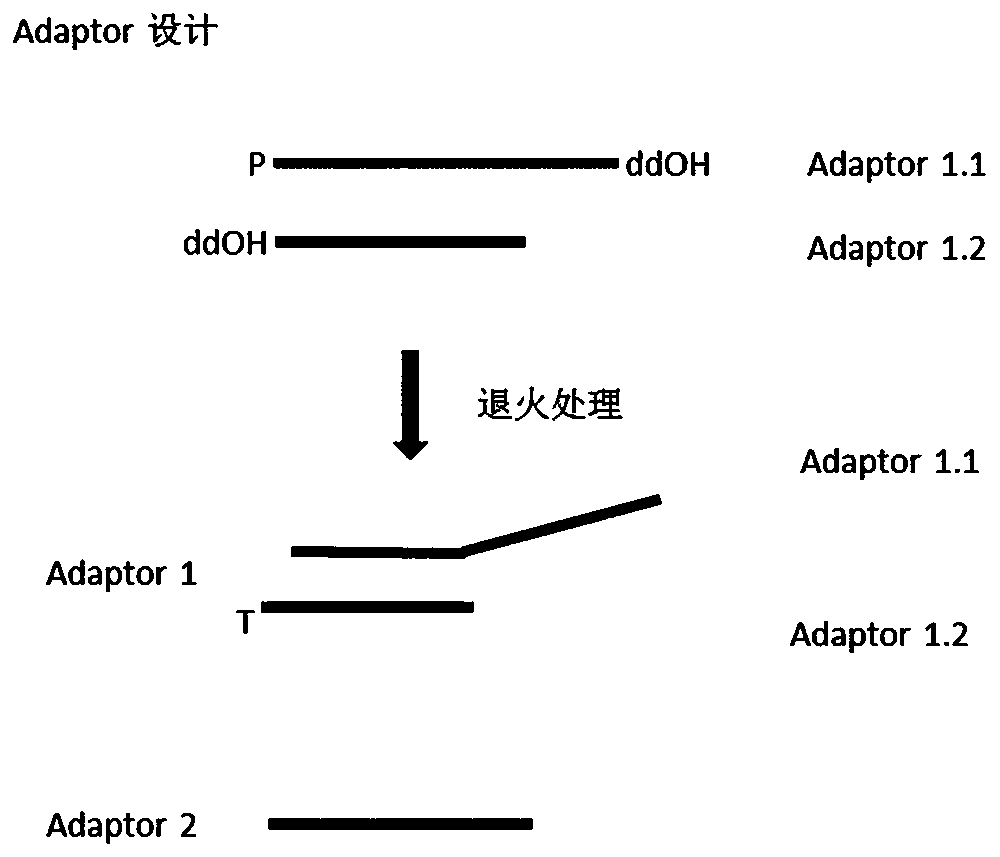
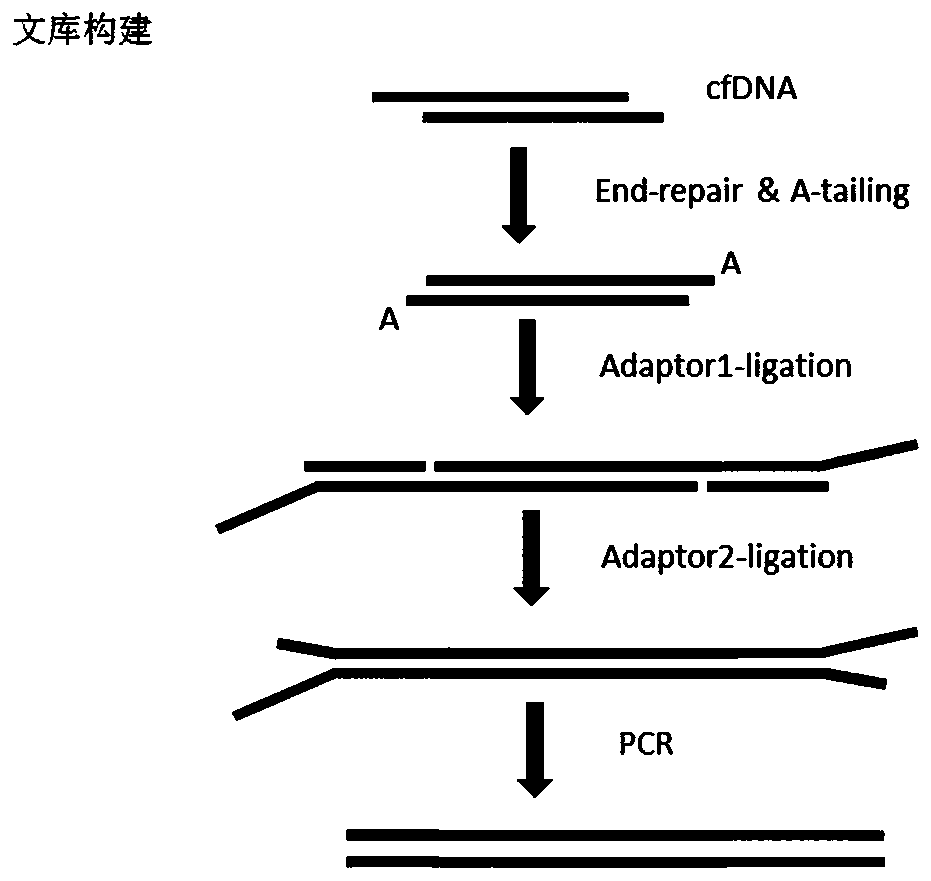
ActiveCN111041026AReduce self-connectionReduce sample lossMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary linkersDimerPhosphorylation
The invention relates to the technical field of high-throughput sequencing, in particular to a nucleic acid linker for high-throughput sequencing and a library construction method. The nucleic acid linker comprises a linker 1 and a linker 2. The linker 1 is double-stranded unequal-length oligonucleotide and comprises a long strand and a short strand, the 5' end of the long strand is phosphorylated, and the 3' end of the long strand and the 3' end of the short strand are modifications capable of blocking formation of a 3' phosphodiester bond. The linker 2 is a single-stranded oligonucleotide. The linker 2 comprises a complementary region to the 5' end of the long strand of the linker 1. According to the linker, linker self-connection can be effectively reduced, PCR amplification can be directly carried out without purification after linker connection, a constructed library has no obvious linker dimer pollution, the loss of DNA samples is effectively reduced, and the efficiency and quality of library construction are improved.
Owner:BEIJING USCI MEDICAL LAB CO LTD
Application of oligonucleotide probe containing dithio nucleotide on detecting DNA sequences
InactiveCN101550448AAccurate and reliableEasy to cutMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideHigh flux
The invention aims at providing an application of oligonucleotide probe containing dithio nucleotide on detecting DNA sequences, namely a nucleotide sequence detecting probe (namely containing dithio) without an enantiomorph structure which uses the degradation of excision enzyme II on the phosphodiester bonds between normal basic groups and the function of not being cut of the excision enzyme on the phosphodiester bonds modified by dithio to remove markers in the sequence detecting reaction and build a new hybridization-enzyme connection-enzyme cutting high flux sequence detecting technology. The nucleotide sequence detecting probe provides a new method for analyzing a genome DNA sequence, builds a quick, accurate and cheap genome sequence detecting technology, and has the advantages of accurate and reliable detecting and easy realization.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method of treating acute myelogenous leukemia
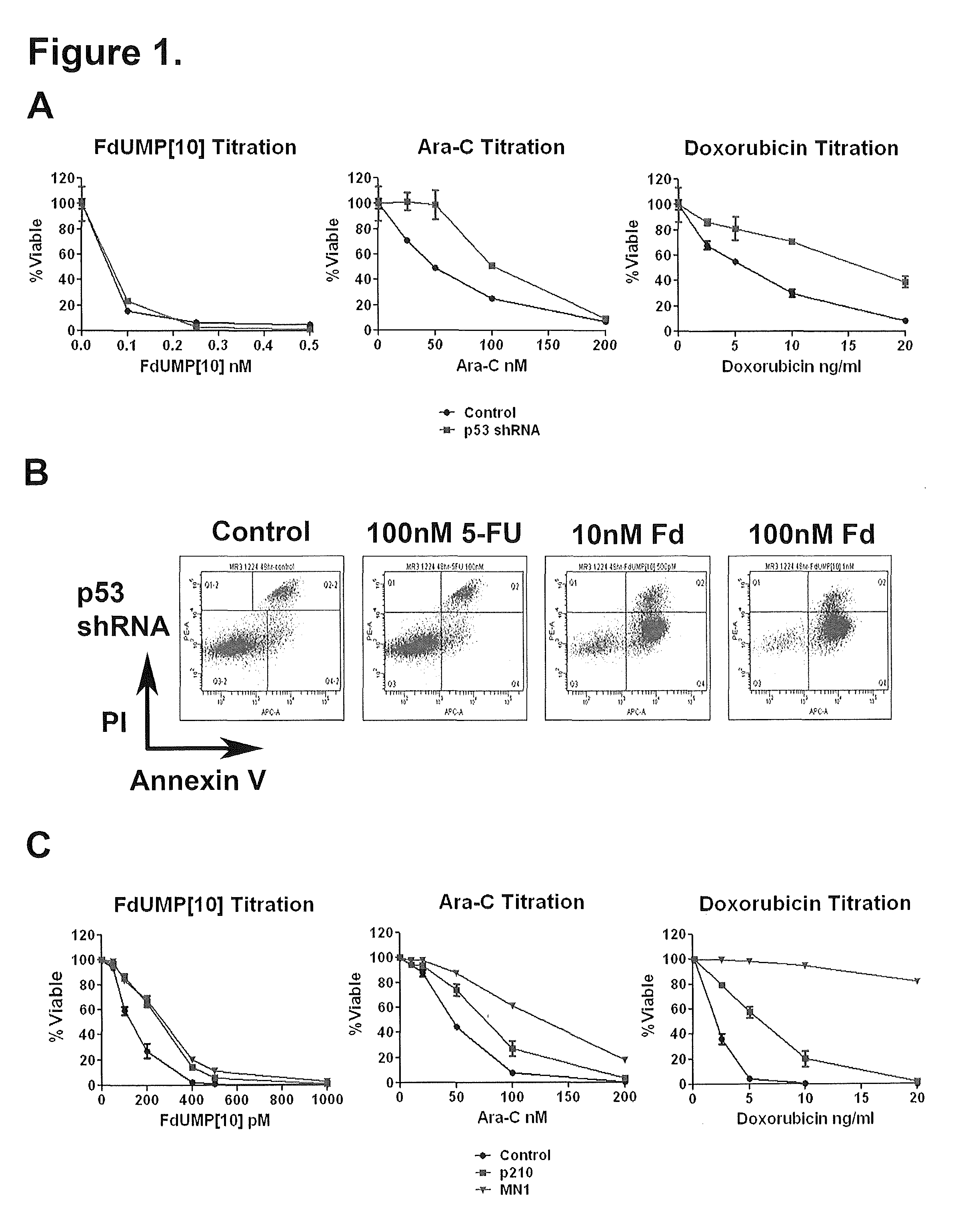
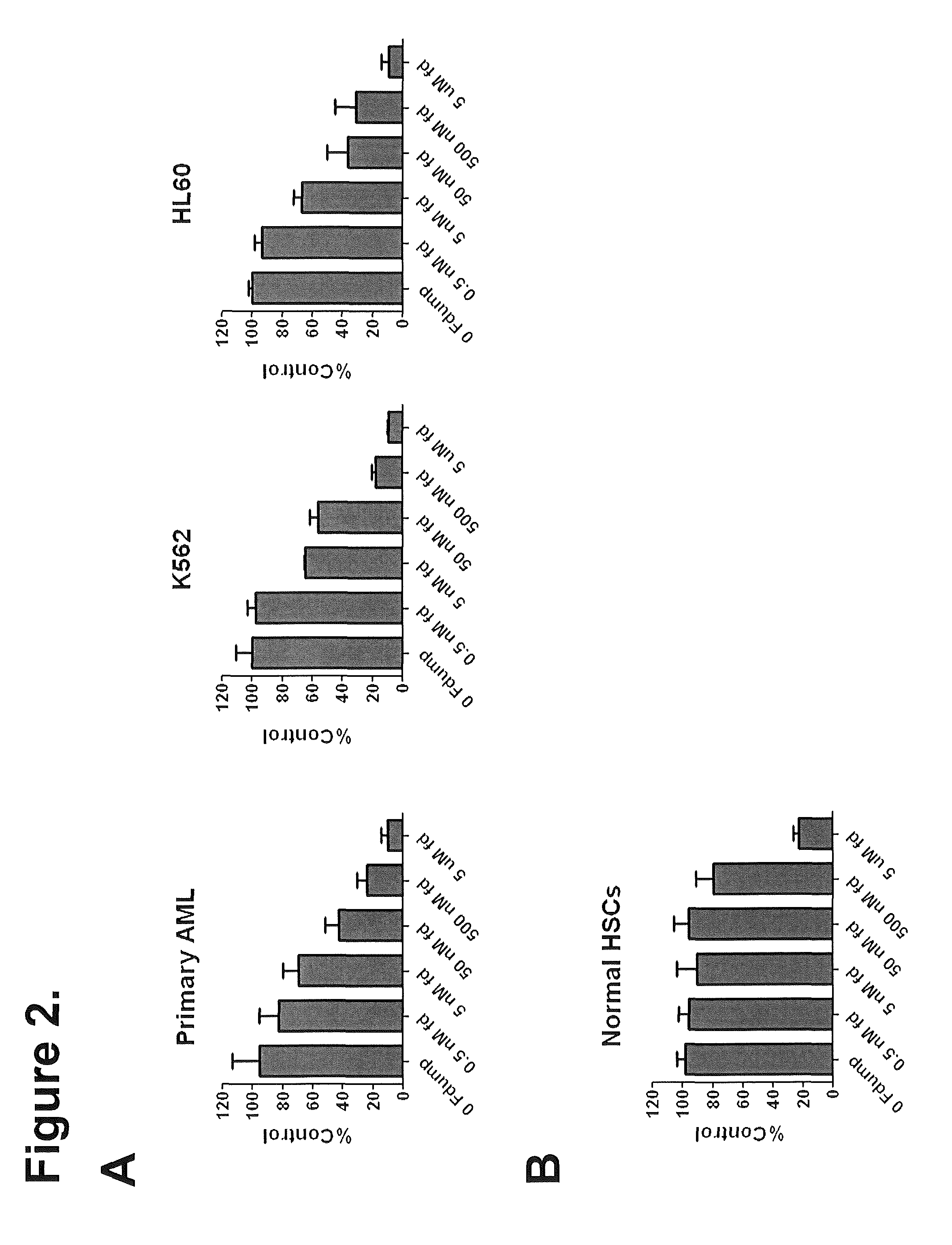
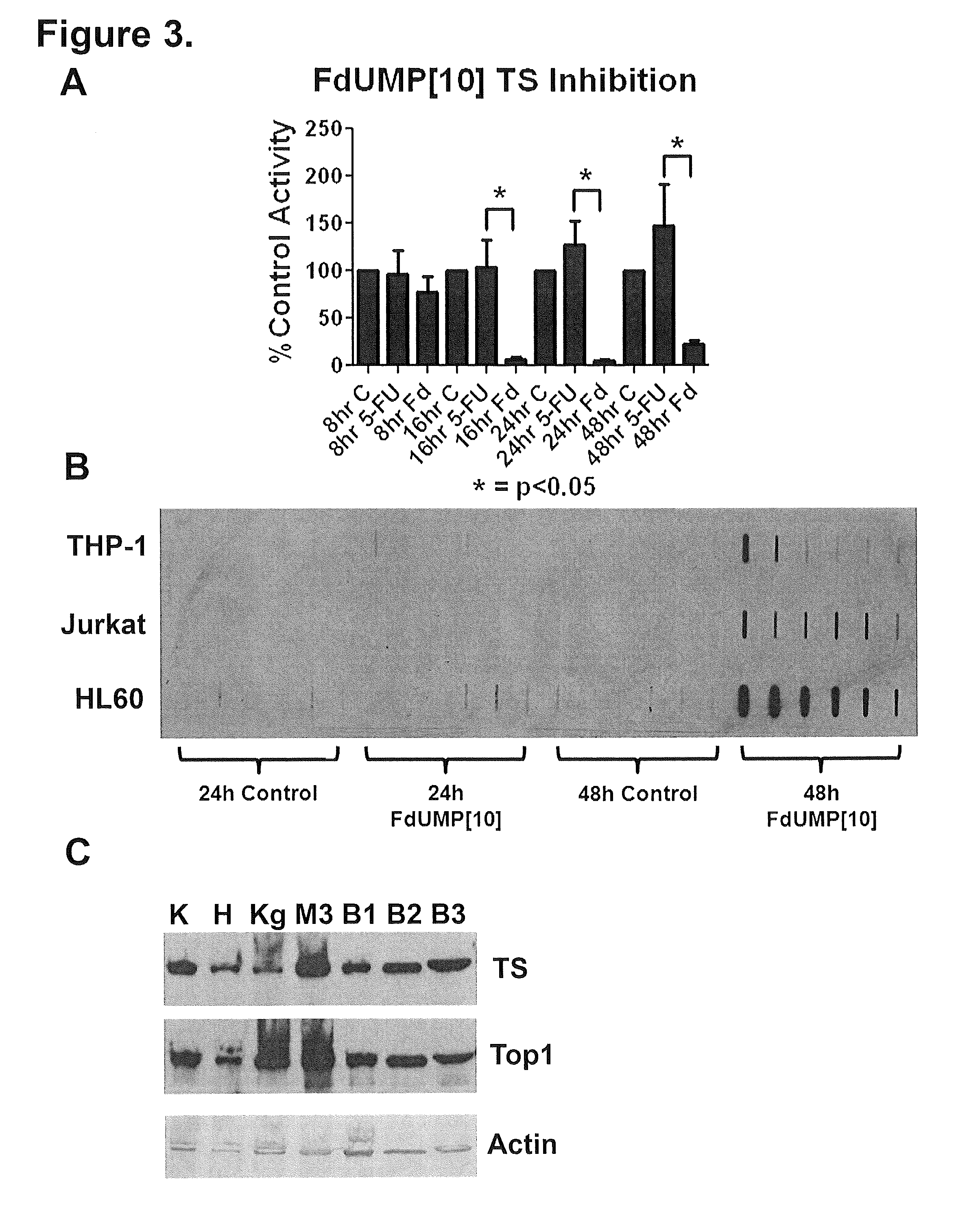
ActiveUS9012422B2Organic active ingredientsSugar derivativesChronic myelogenous leukemiaOligonucleotide
The present invention relates to active compounds for treating acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) in a subject in need thereof and methods of treating AML carried out by administering the subject an active compound in an amount effective to treat the leukemia. The active compound comprises a 10-mer oligonucleotide covalently linked via 3′ to 5′ phosphodiester linkages of 5-fluorodeoxyuridine, FdUMP[10], or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
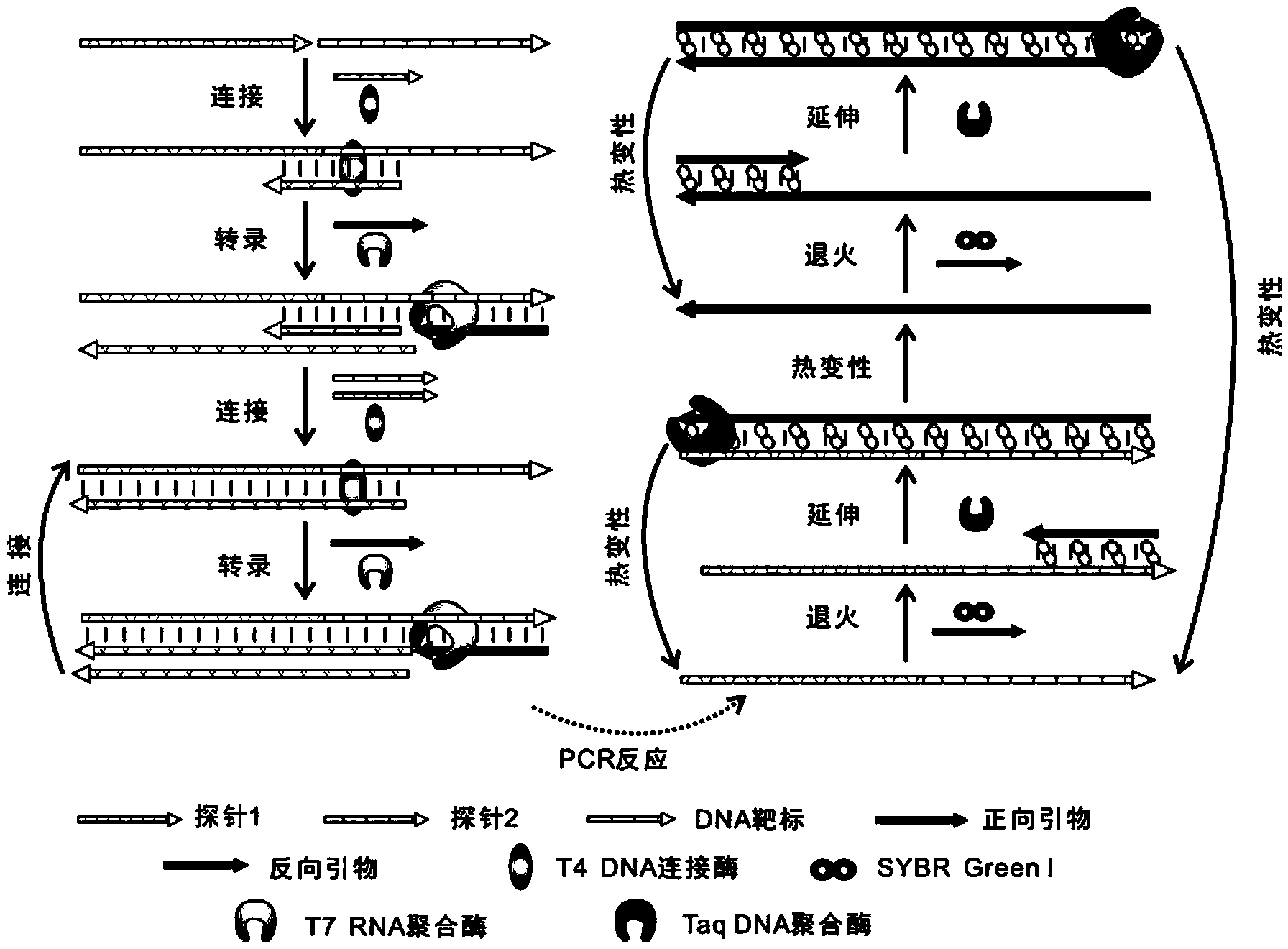
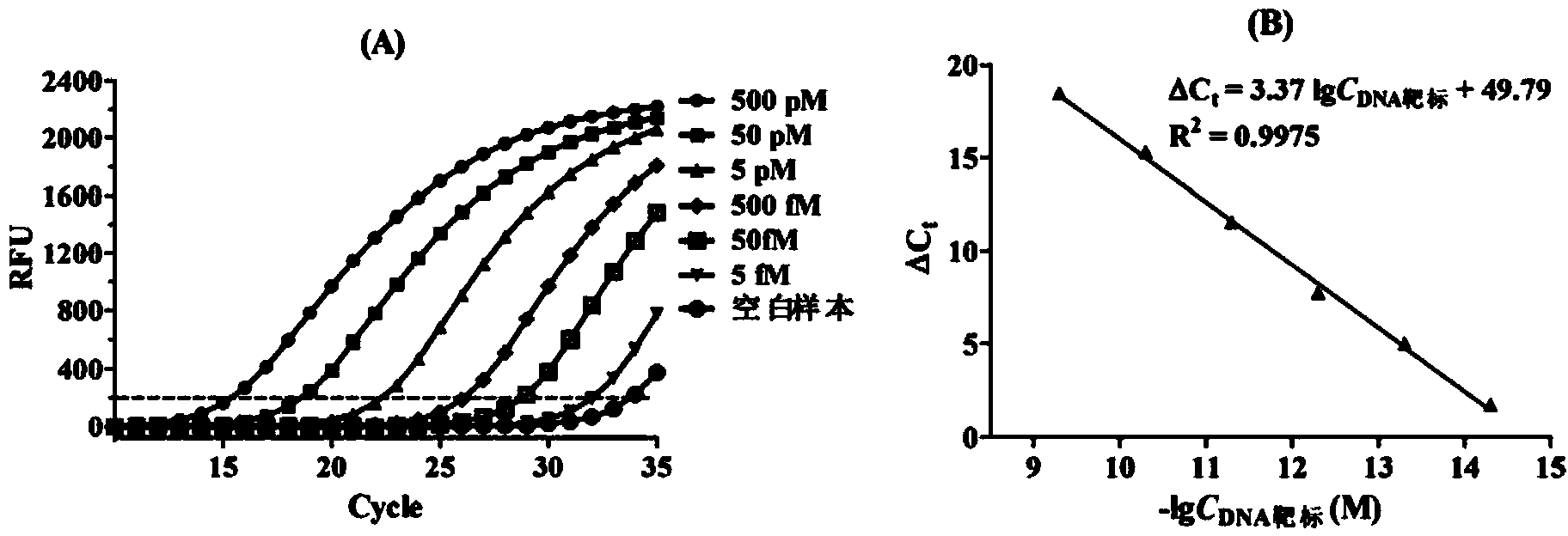
PCR analyzing method for quantitatively detecting nucleic acid through RNA polymerase and ligase coupled reaction medium
InactiveCN104032031AHigh sensitivityHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceOligonucleotide
The invention discloses a PCR analyzing method for quantitatively detecting nucleic acid through RNA polymerase and a ligase coupled reaction medium. The method comprises the following steps that when target nucleic acid exits, 3' end hydroxyl radical and 5' end phosphate group among ligase medium oligonucleotide probes are reacted to form phosphate diester bond, the coupling product has the RNA polymerase promoter sequence, the RNA polymerase is started to synthesize a large number of RNA fragments with the target nucleotide sequence, the RNA fragments can serve as the target nucleic acid to continue to mediate connecting reaction among the oligonucleotide probes, the connecting reaction efficiency is improved through the introduction of the RNA polymerase, more amplification templates are provided for subsequent PCR reaction, the strength of fluorescence signals in a reaction system is measured in real time, and the concentration of the target nucleic acid is worked out through the comparison with a standard work curve. The method has the advantages of being high in sensitivity and specificity, easy to design, short in reaction time, capable of being widely applied to the basic biology study and the nucleic acid detection in the clinical diagnosis.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Methods for tagging dna-encoded libraries
ActiveCN107428795AReservation ConvenienceChemical linkage achievedSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationChemical ligationCyanogen bromide
The present invention relates to methods for producing encoded chemical entities. In particular, the oligonucleotides and methods can include encoded chemical entities having wild-type linkages formed through chemical ligation techniques. One strategy that can be utilized that simultaneously takes advantage of chemical ligation as a means to encode chemical history, while also retaining the ability of polymerases to directly recover tag sequence and association information, is to perform chemical ligation in a manner that generates wildtype phosphodiester linkages. Such methods generally utilize condensing agents such as cyanogen bromide or similar along with 5'-phosphate and 3'-hydroxyl oligonucleotides in a double-stranded or templated context. Similarly cyanogen bromide has also been shown to chemically ligate pairs of substrate oligonucleotides that are 5'-hydroxyl and 3'-phosphate. However, these methods suffer from poor efficiency making them ill-suited for use in an iterative process such as tagging DNA-encoded libraries.
Owner:X CHEM
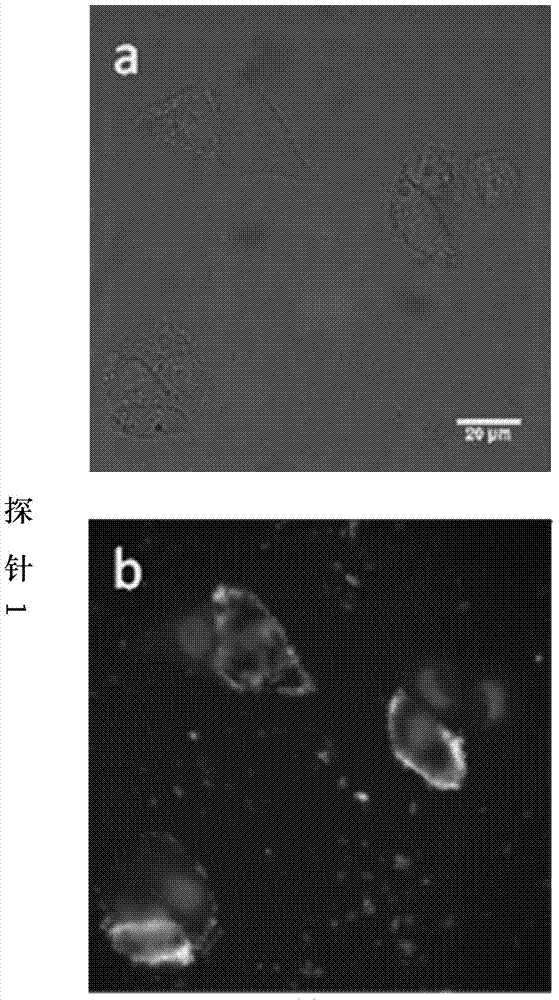
Nucleic acid/polysaccharide complex
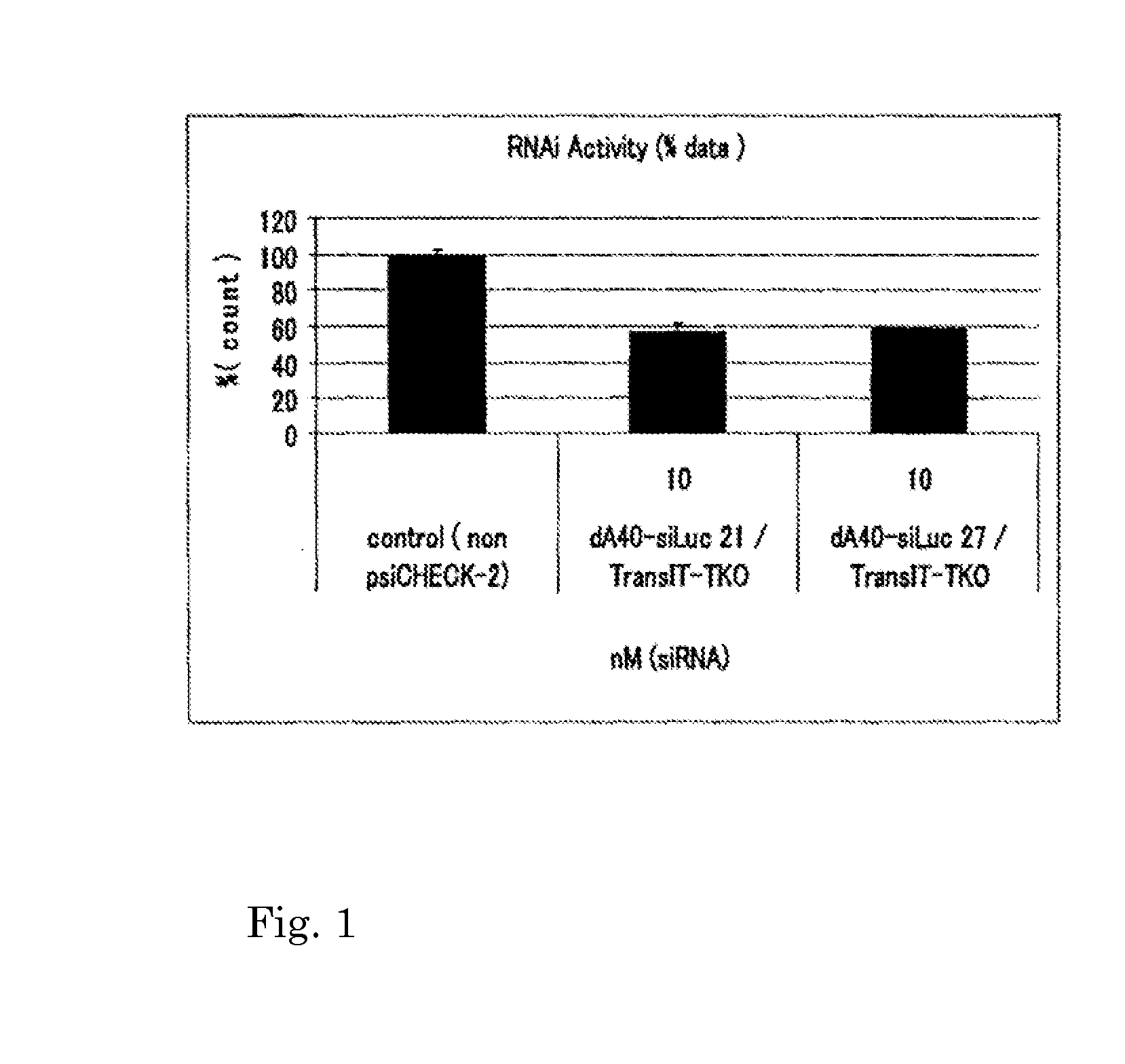
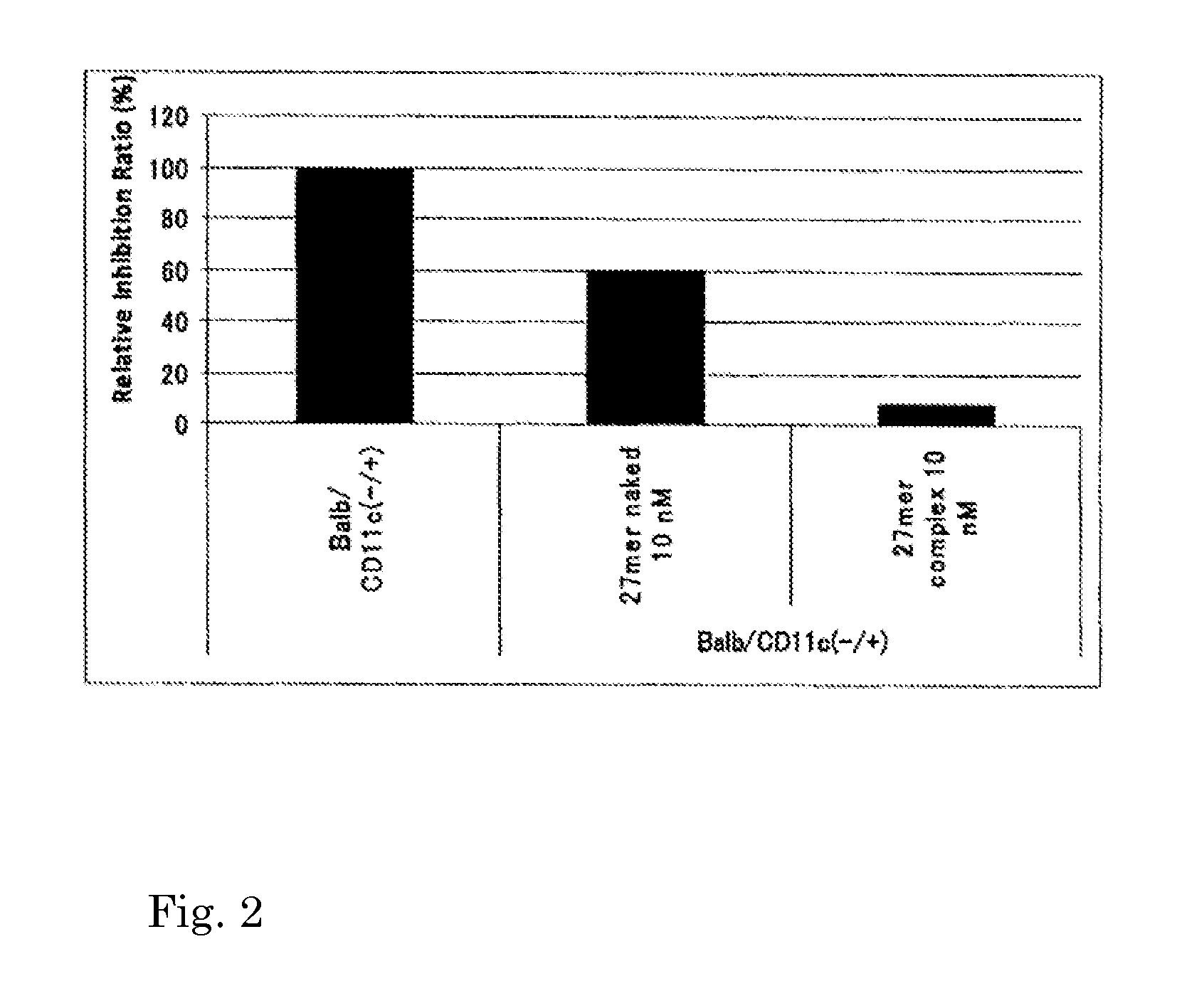
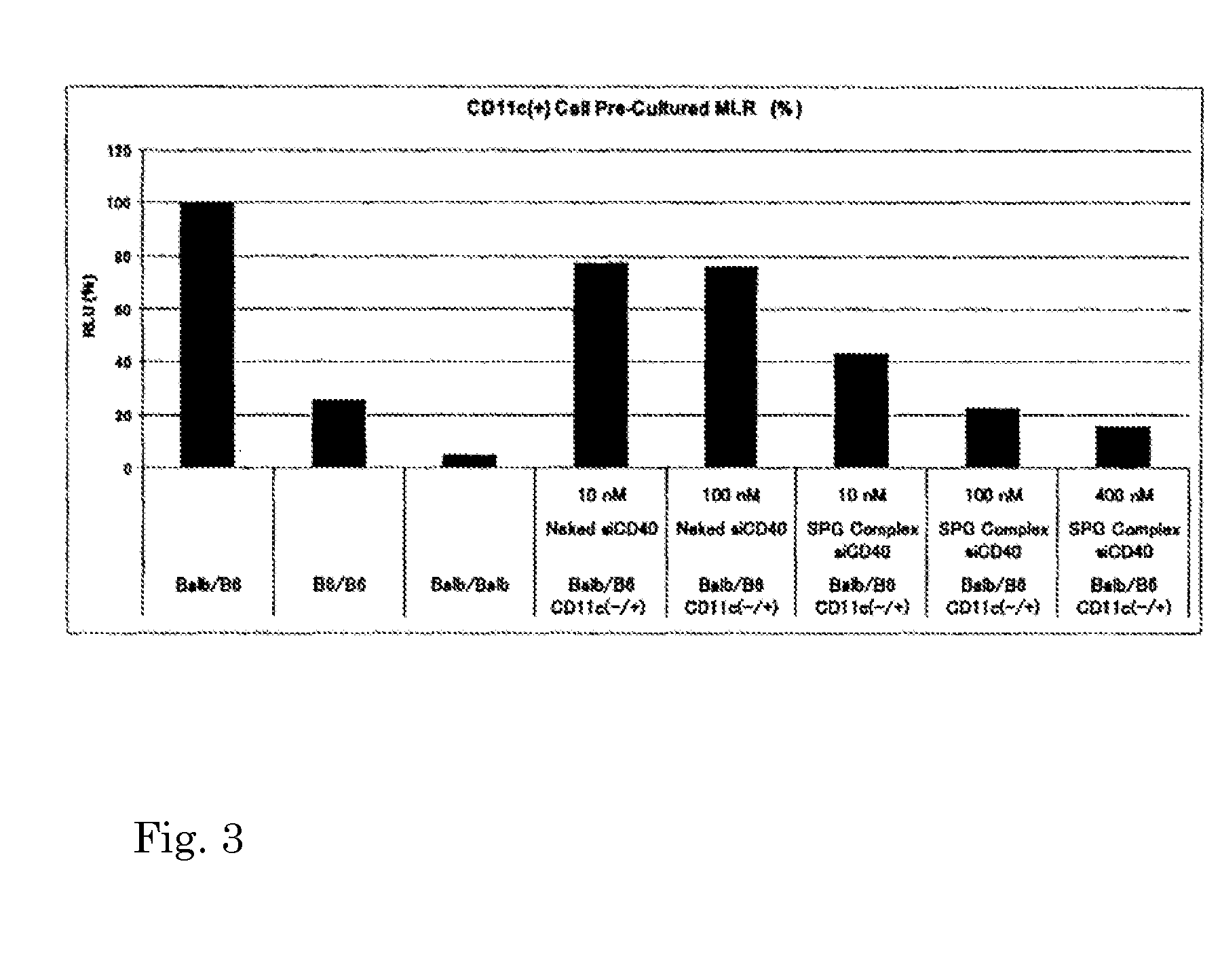
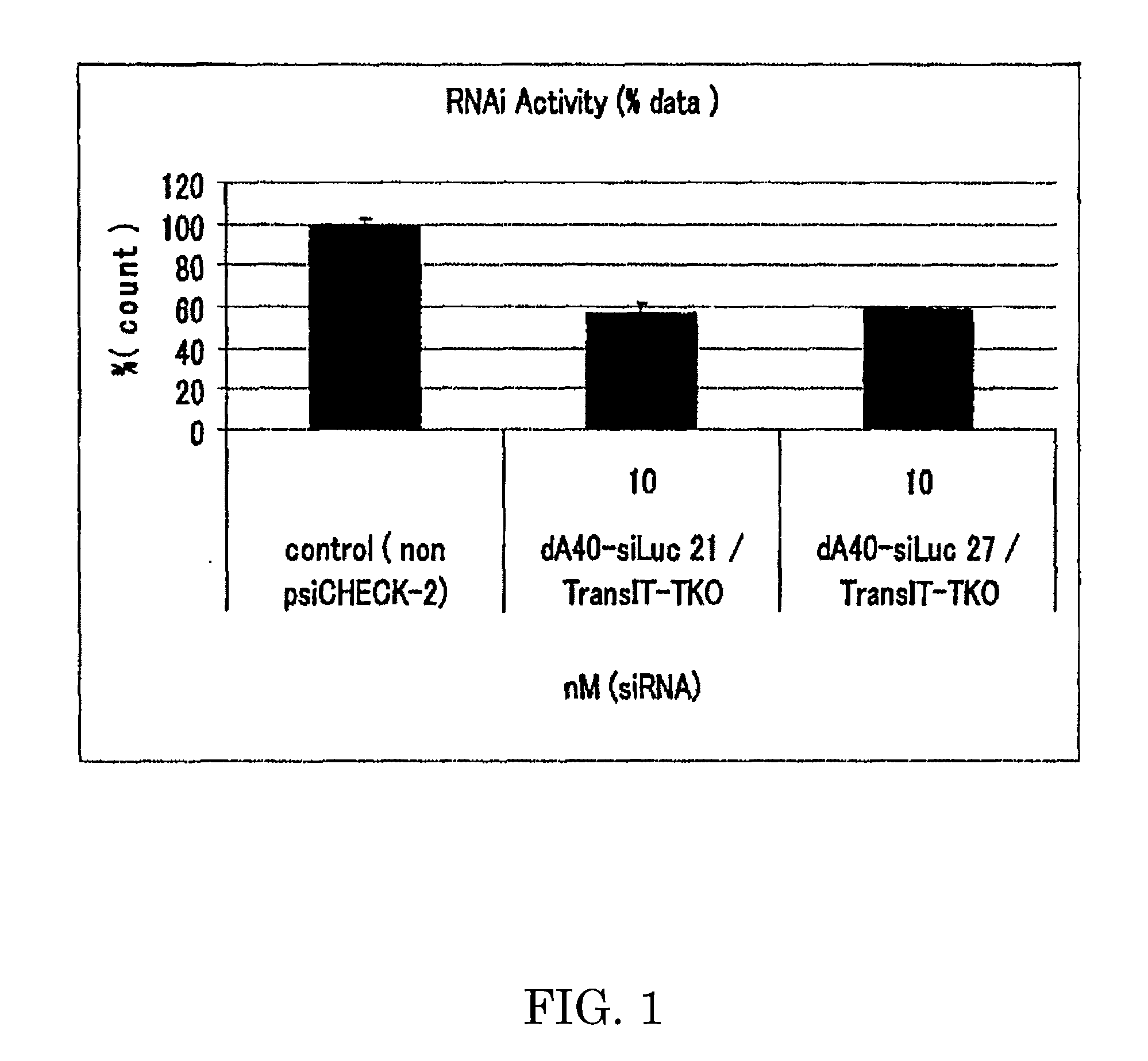
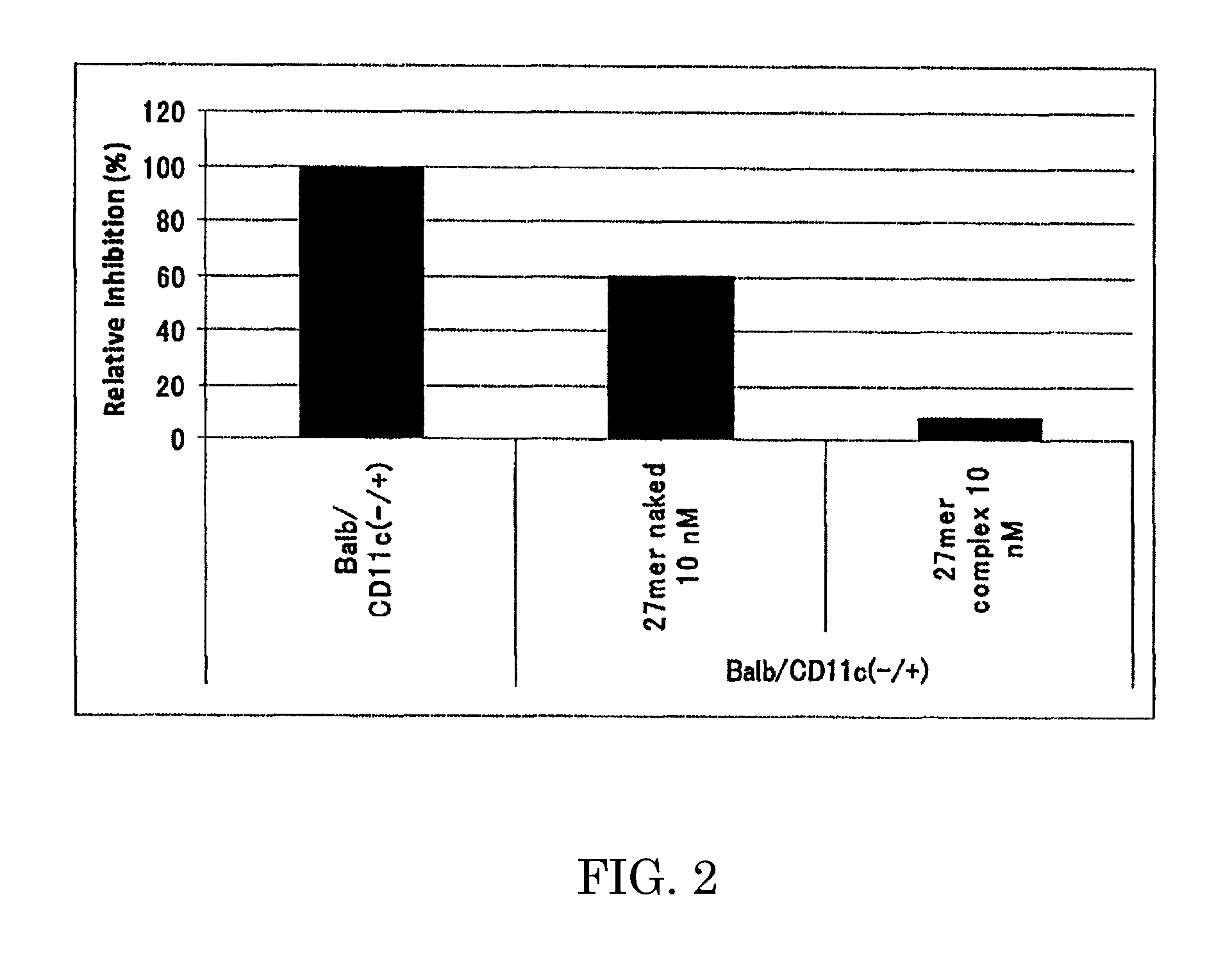
An object of the present invention is to provide a highly stable nucleic acid-polysaccharide complex of an siRNA and schizophyllan. A nucleic acid-polysaccharide complex is formed by adding polydeoxyadenine in which at least part of the phosphodiester link portion is phosphorothioated to an siRNA and allowing the siRNA and schizophyllan to form a complex.
Owner:NAPAJEN PHARMA
Thio probe for detecting nuclease with 3'-5' exo activity
ActiveCN104293917AAccurate analysisHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationThio-Phosphate
Owner:PEKING UNIV
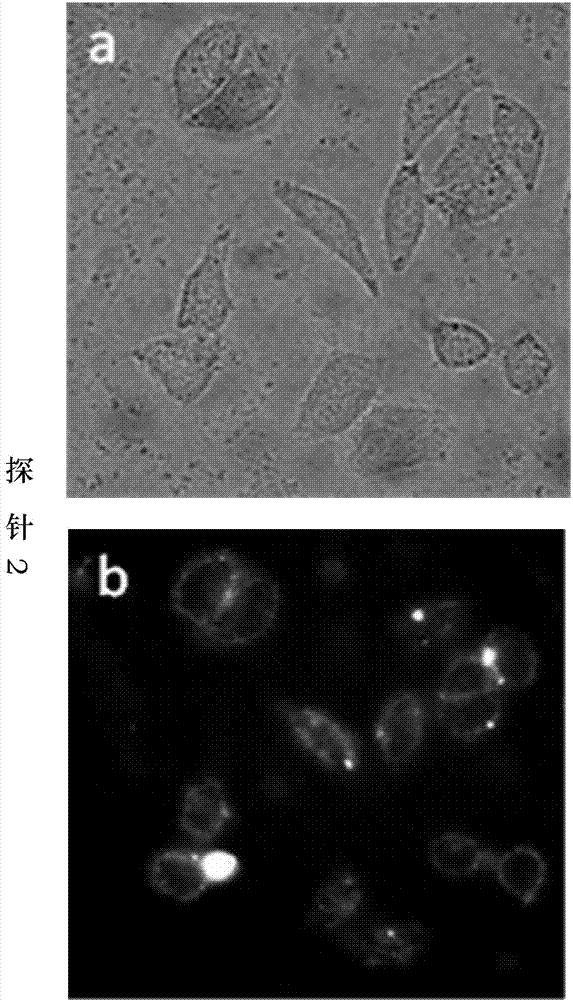
Nucleic acid/ polysaccharide complex
An object of the present invention is to provide a highly stable nucleic acid-polysaccharide complex of an siRNA and schizophyllan. A nucleic acid-polysaccharide complex is formed by adding polydeoxyadenine in which at least part of the phosphodiester link portion is phosphorothioated to an siRNA and allowing the siRNA and schizophyllan to form a complex.
Owner:NAPAJEN PHARMA
Immunostimulating oligonucleotide complex
ActiveUS10449212B2Well formedReduce the amount of solutionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesNucleotideGenetics
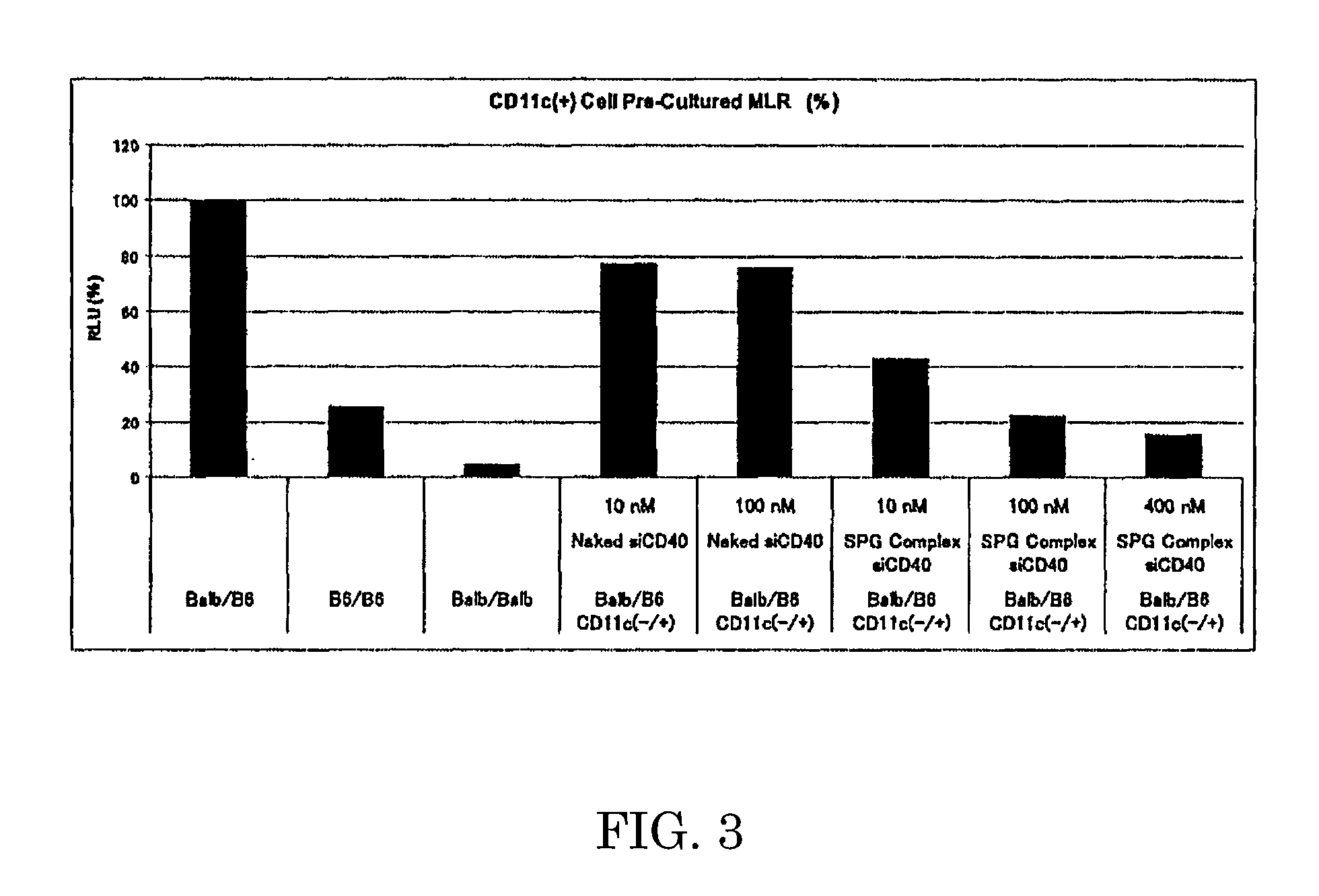
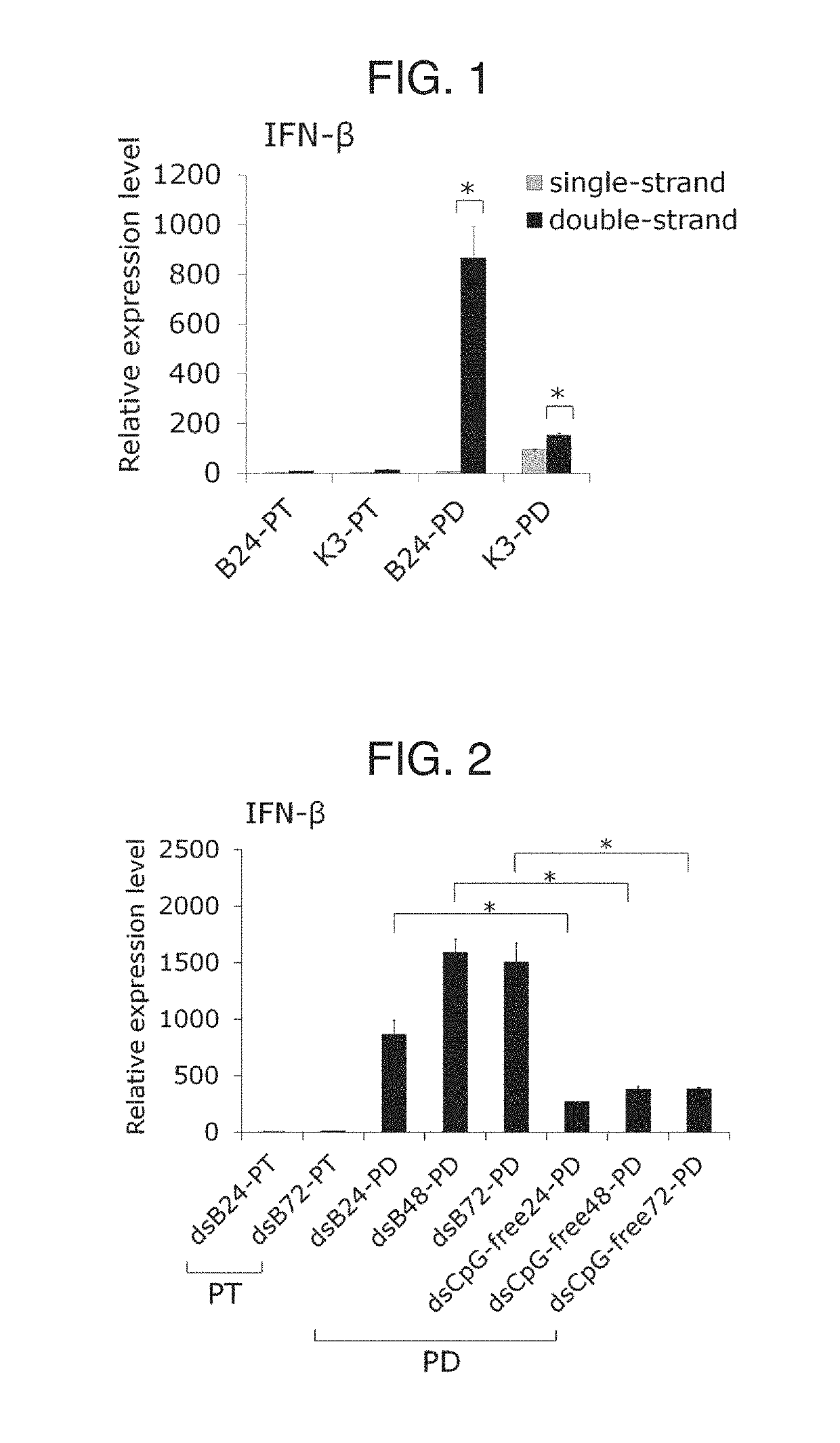
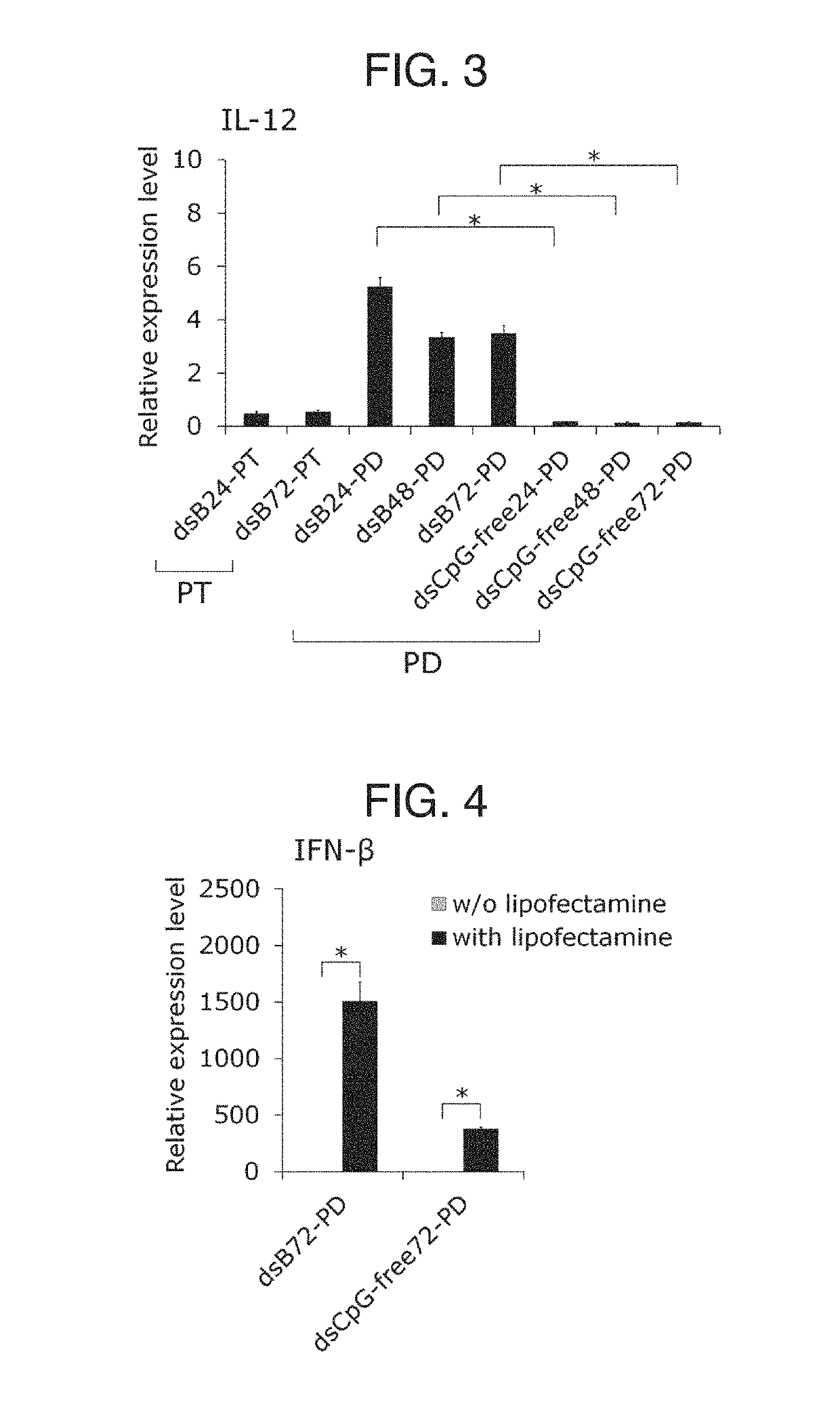
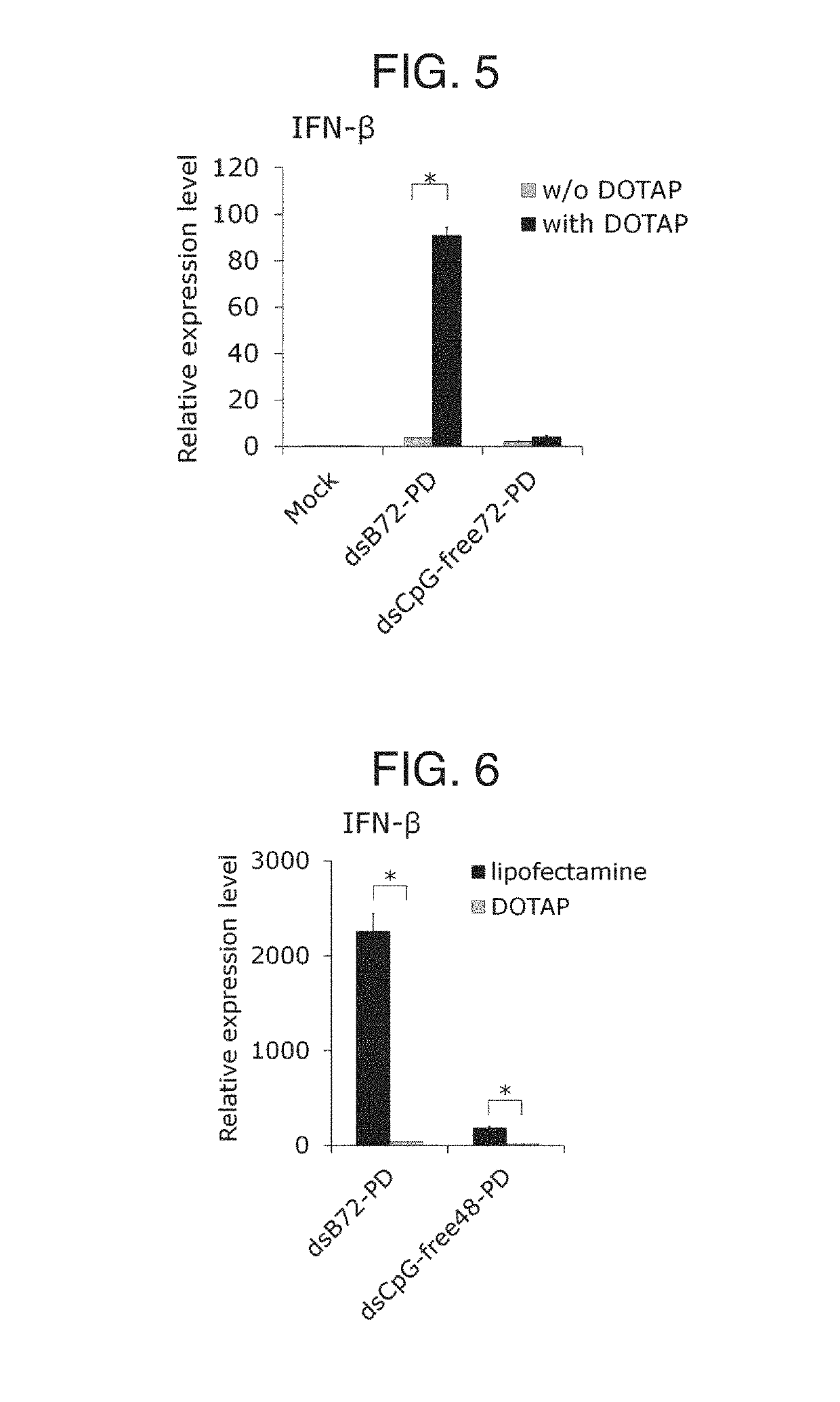
Provided is an immunostimulating oligonucleotide that is suitable for industrial production and has an excellent type-I IFN inducing activity even when not modified to become a phosphorothioate. This linear double-stranded oligonucleotide contains 10-100 base pairs, wherein the single-stranded oligonucleotides constituting the double-stranded oligonucleotide each contain 2-20 phosphodiester-mediated cytosine-guanine (CpG) sequences, and at least 90% of the internucleotide bonds in each single-stranded oligonucleotide are phosphodiester bonds.
Owner:DENKA CO LTD
Determination method for activity of phospholipase D alpha
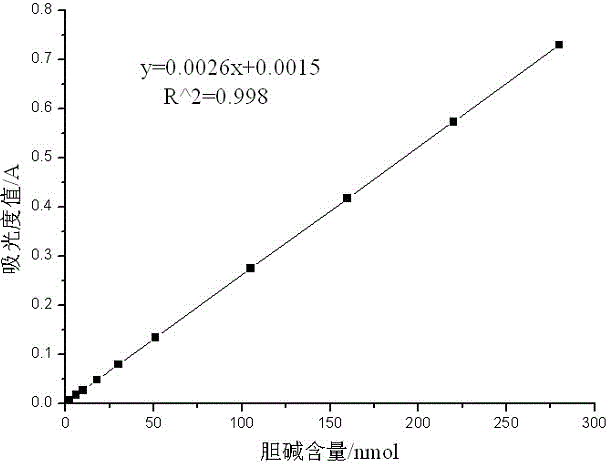
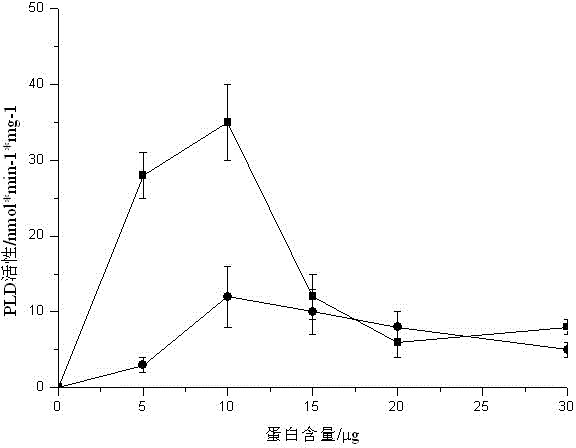
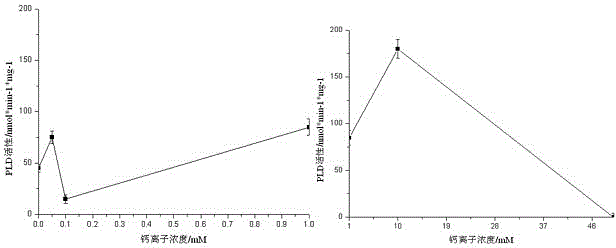
InactiveCN104155291ALower requirementFast wayMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsPhospholipaseBetaine
The invention provides a determination method for the activity of phospholipase D alpha. The determination method for the activity of the phospholipase D alpha is a method for determining the activity of the phospholipase D alpha by using an enzyme-linked colorimetry. The technical scheme is that the determination method comprises the following steps: performing catalyzed hydrolysis on a phosphodiester bond at the tail end of phosphatidylcholine serving as a substrate by the phospholipase D alpha to generate phosphatidic acid and choline; enabling the choline to react to generate betaine and H2O2 under catalytic action of a choline oxidase; oxidizing 4-aminoantipyrine aspirin and redistilled phenol into a pink substance by the generated H2O2 under the catalytic action of peroxidase, determining the absorbance value of the pink substance, determining the corresponding choline content according to a choline standard curve which is prepared in advance, and deducing the activity of the phospholipase D alpha according to the choline content. In a reaction system with 200 microliters of the phospholipase D alpha, the protein content and the Ca<2+> concentration are preferably 10 microgramme and 10mM. The determination method is high in efficiency, convenient, quick, high in sensitivity, low in hazard and stable in results, and is suitable for simultaneously determining the activities of the phospholipase D alpha of a large number of samples.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
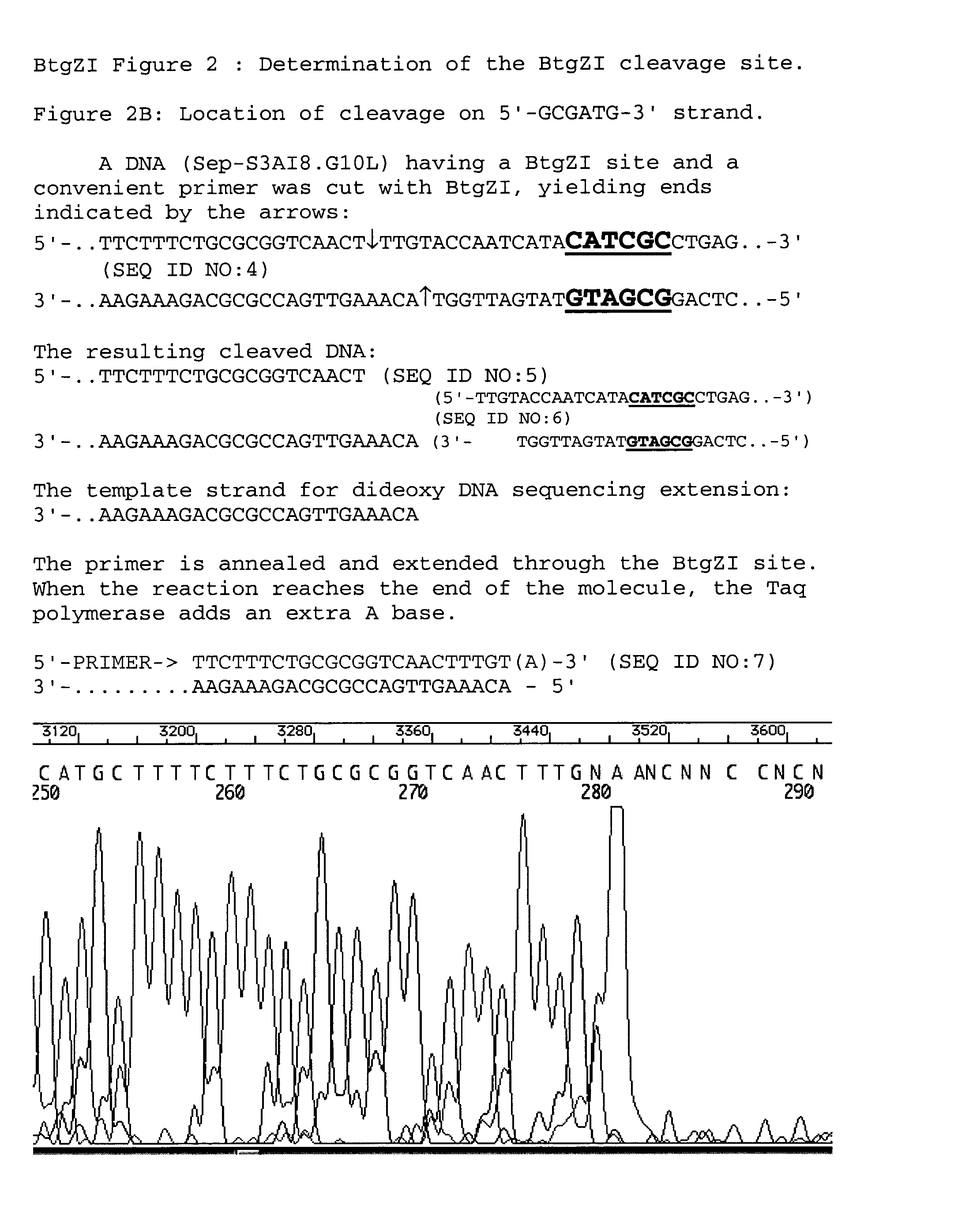
Novel type II restriction endonuclease, BtgZI, obtainable from bacillus thermoglucosidasius 36A and a process for producing the same
In accordance with the present invention, there is provided a novel restriction endonuclease obtainable from Bacillus thermoglucosidasius 36A (NEB#1384), hereinafter referred to as “BtgZI”, which endonuclease: (1) recognizes the nucleotide sequence 5′-GCGATG-3′ in a double-stranded DNA molecule as shown below, 5′-GCGATGNNNNNNNNNN↓-3′(SEQ ID NO:9)3′-CGCTACNNNNNNNNNNNNNN↑-5′ (wherein G represents guanine, C represents cytosine, A represents adenine, T represents thymine and N represents either G, C, A, or T); (2) cleaves said sequence in the phosphodiester bonds between the 10th and the 11th nucleotides 3′ to the recognition sequence in the 5′-GCGATG-3 strand of the DNA, and between the 14th and 15th nucleotides 5′ to the recognition sequence in the complement stand, 5′-CATCGC-3′, to produce a 4 base 5′ extension; and (3) cleaves double-stranded pBR322 DNA to produce 3 fragments of 2892, 1181 and 288 base pairs.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Prodrug with anti-tumor activity and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN110179991AImprove efficacyHigh selectivityOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsHalf-lifeMonomer
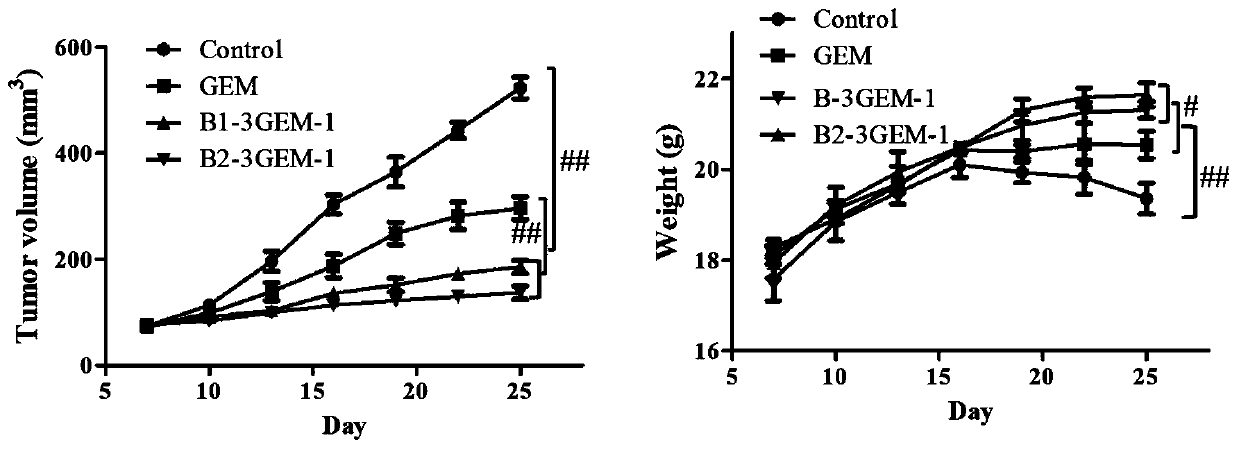
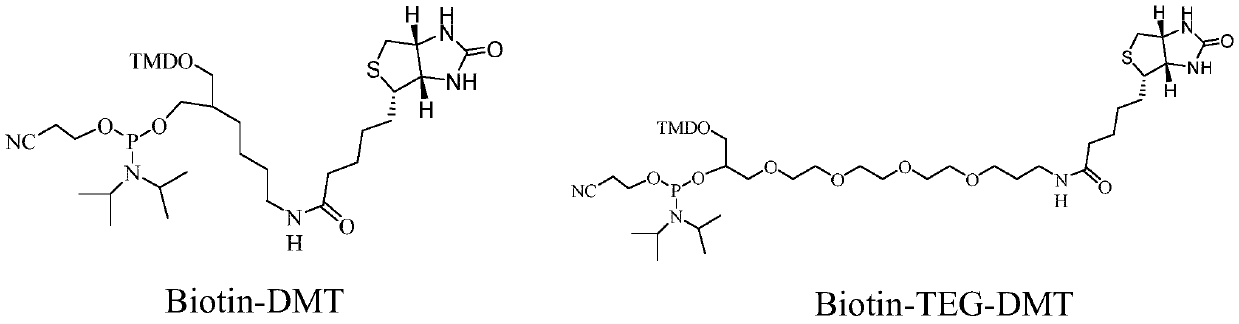
The invention belongs to the field of target drug design and preparation, and particularly relates to a prodrug with anti-tumor activity and preparation and application thereof. The prodrug is obtained by constructing biotin and a phosphoramidite monomer of gemcitabine on 10-100 base nucleic acid skeletons through a 3',5'-phosphodiester linkage, or by cross-linking biotin on a multi-carbon chain which has NH2 and is extended from 10-100 base nucleic acid skeletons containing gemcitabine through an amido linkage. The drug has better inhibition effect on tumor cells and has lower toxicity, and the in vitro cell transport of the prodrug does not depend on the expression of nucleic acid transport vector protein, thereby being beneficial to reducing the drug resistance of GEM; and the drug canmaintain higher drug concentration and half-life period in an organism, overcomes the problems of low anticancer target selectivity, easy deamination passivation and easy drug resistance of GEM, and achieves the effect of clearing cancer cells through target antagonism tumor metabolic pathways.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com