Patents
Literature
460 results about "Thymine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
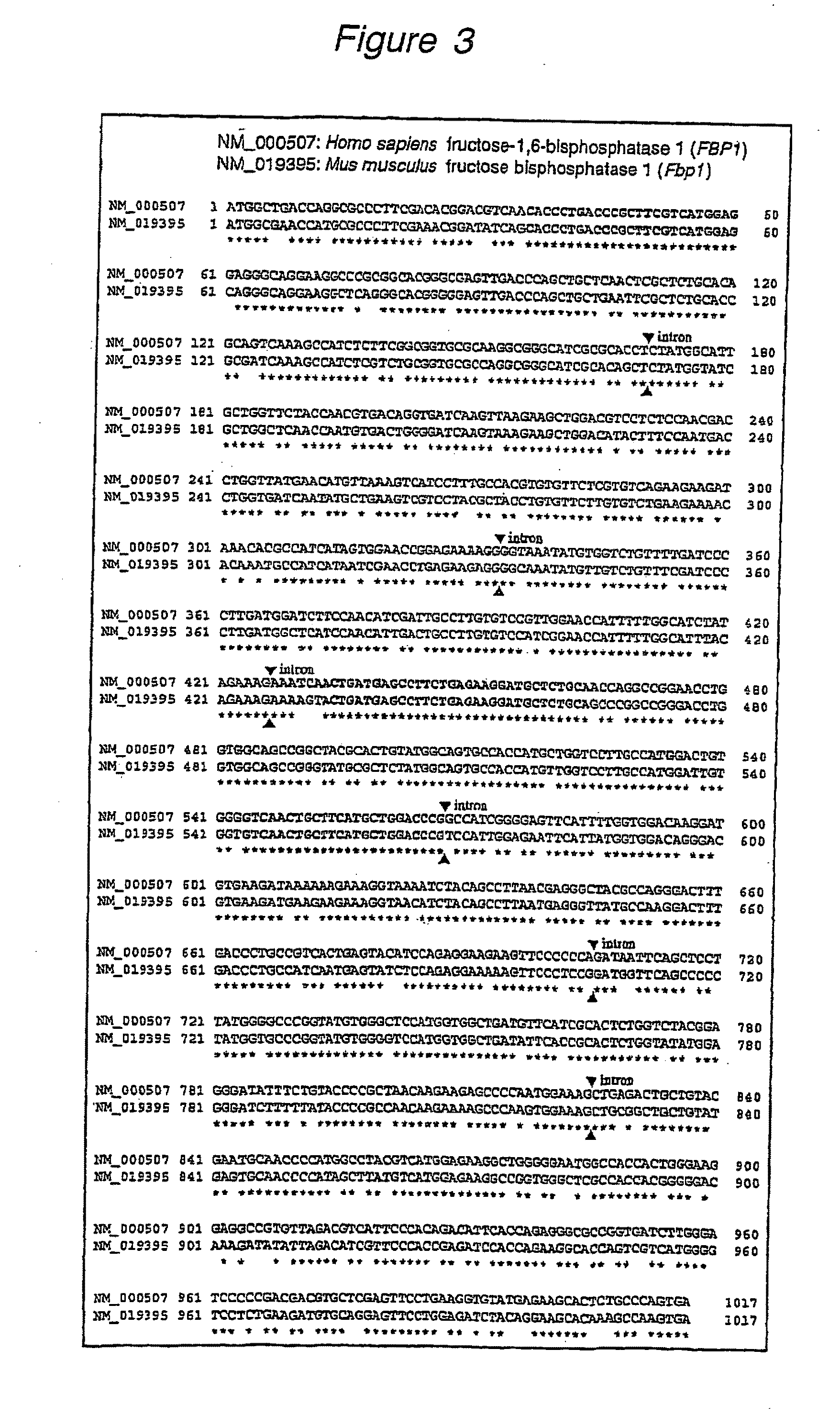
Thymine /ˈθaɪmɪn/ (T, Thy) is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The others are adenine, guanine, and cytosine. Thymine is also known as 5-methyluracil, a pyrimidine nucleobase. In RNA, thymine is replaced by the nucleobase uracil. Thymine was first isolated in 1893 by Albrecht Kossel and Albert Neumann from calves' thymus glands, hence its name.
Polynucleotides for causing RNA interference and method for inhibiting gene expression using the same
InactiveUS20080113351A1High RNA interference effectLittle riskOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderBase JNucleotide
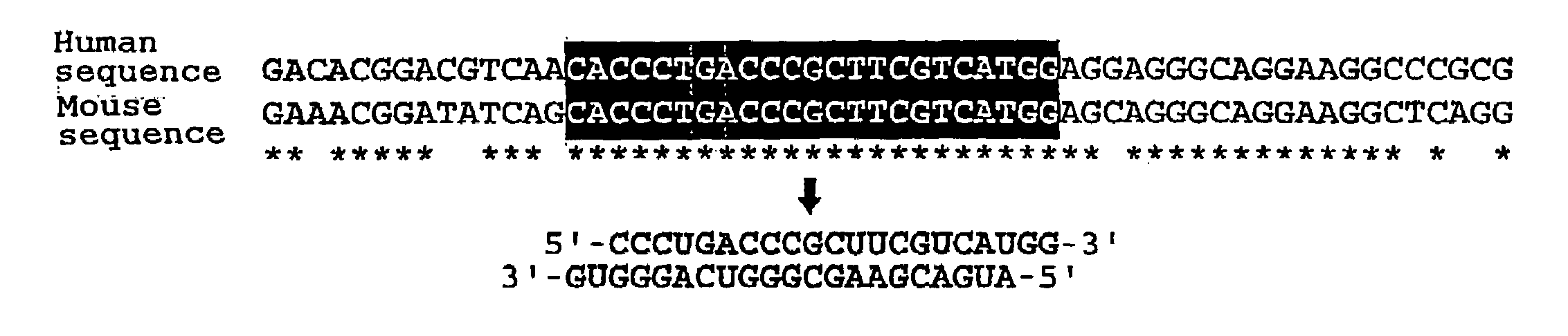
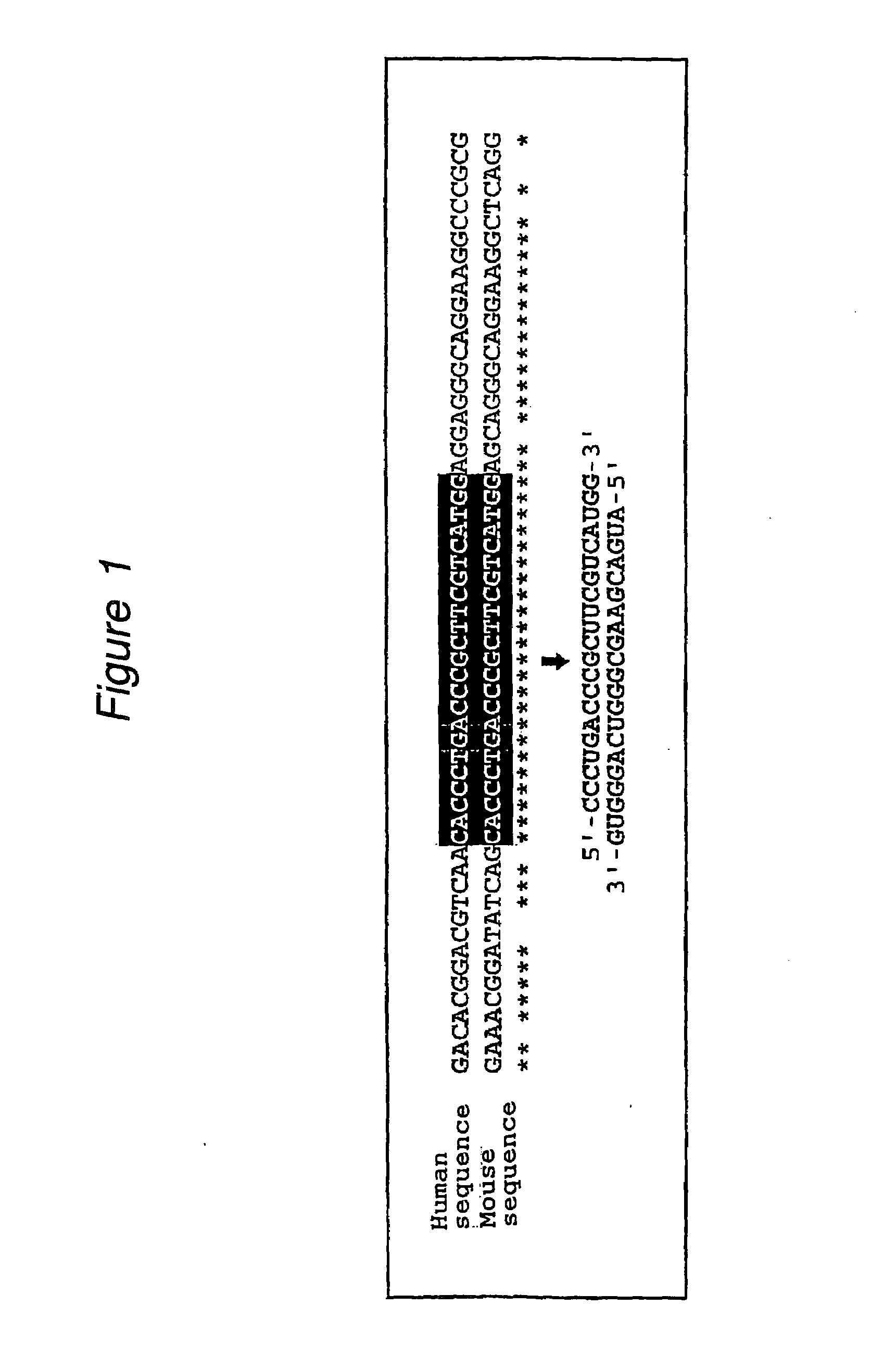
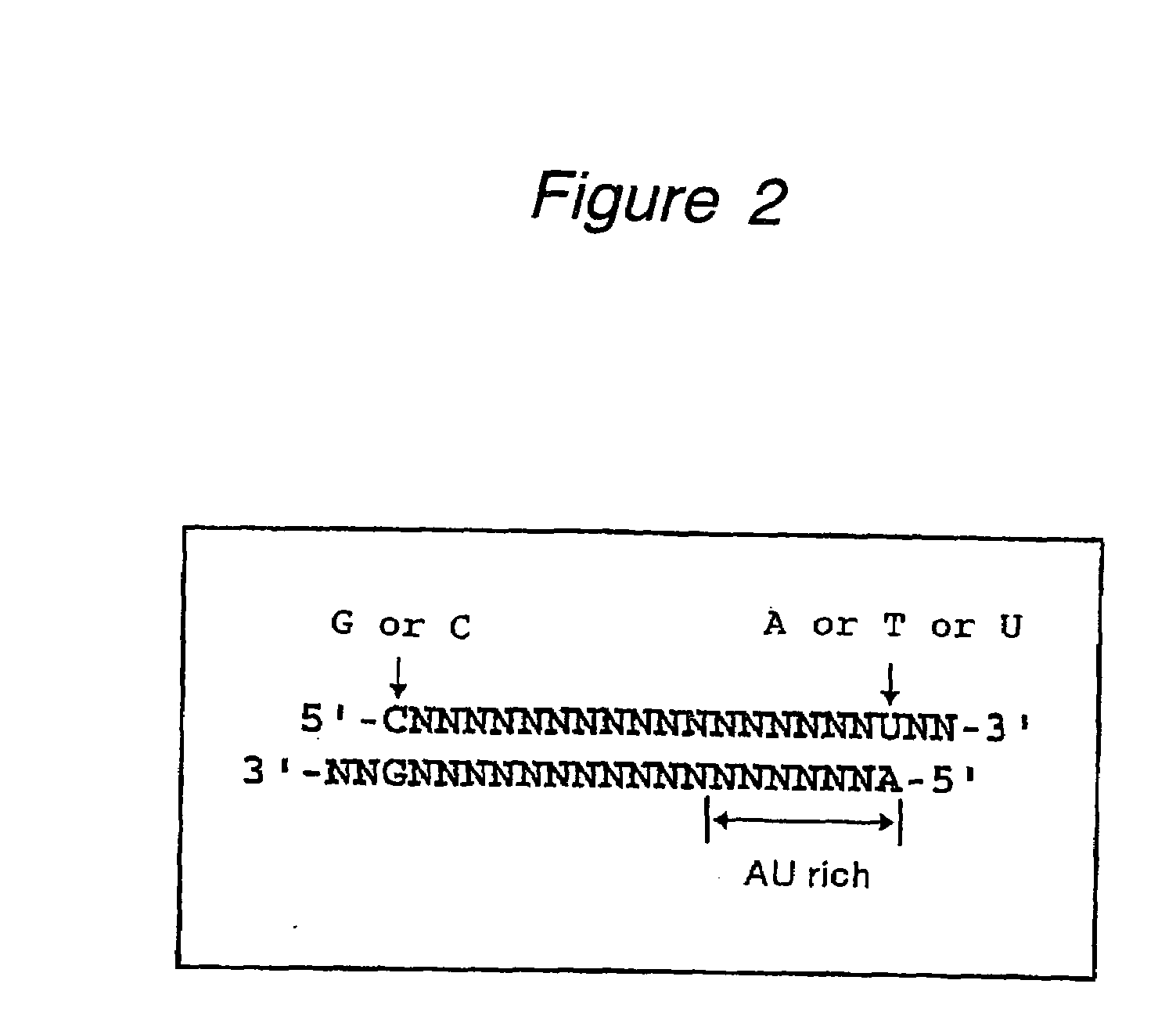
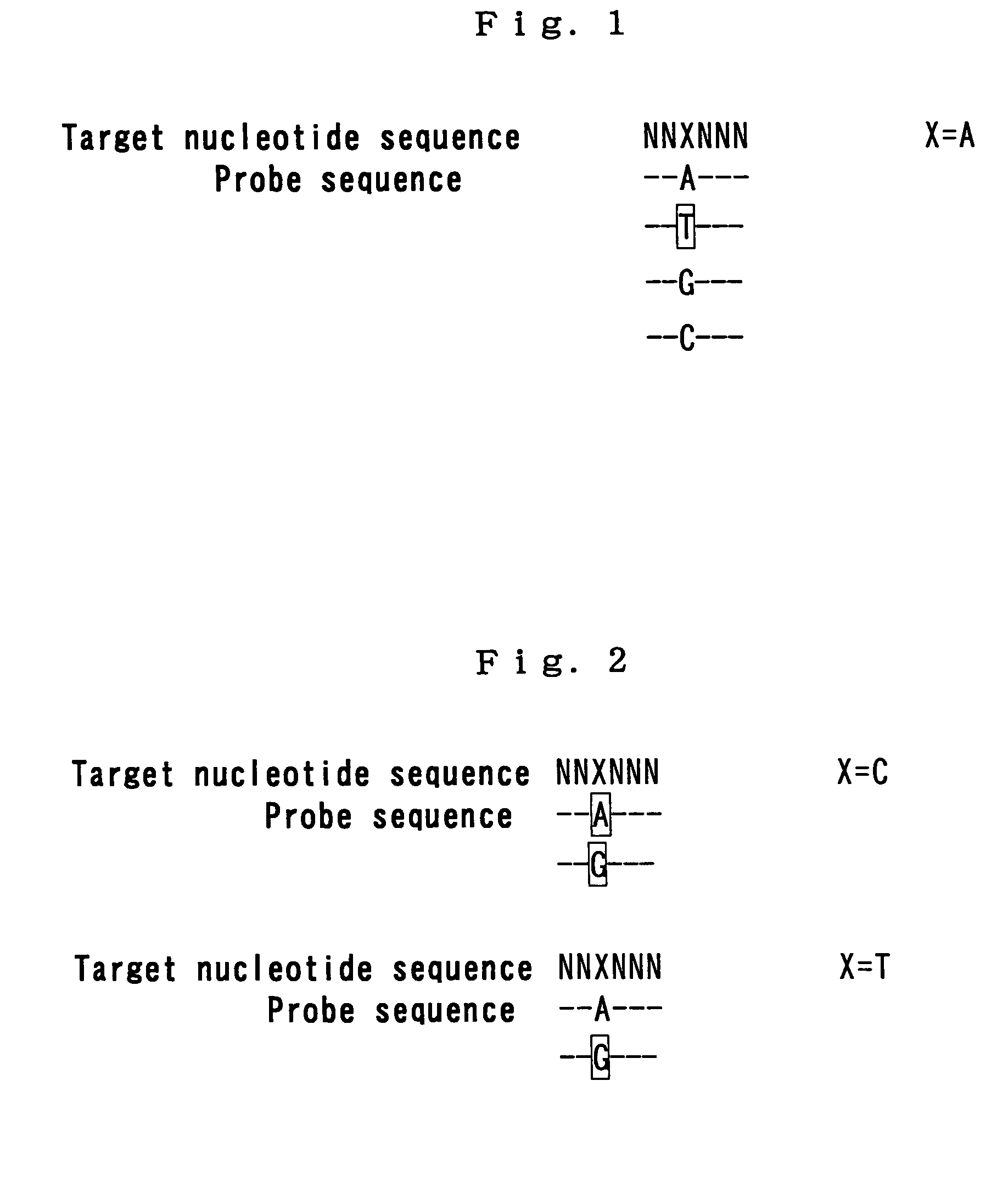
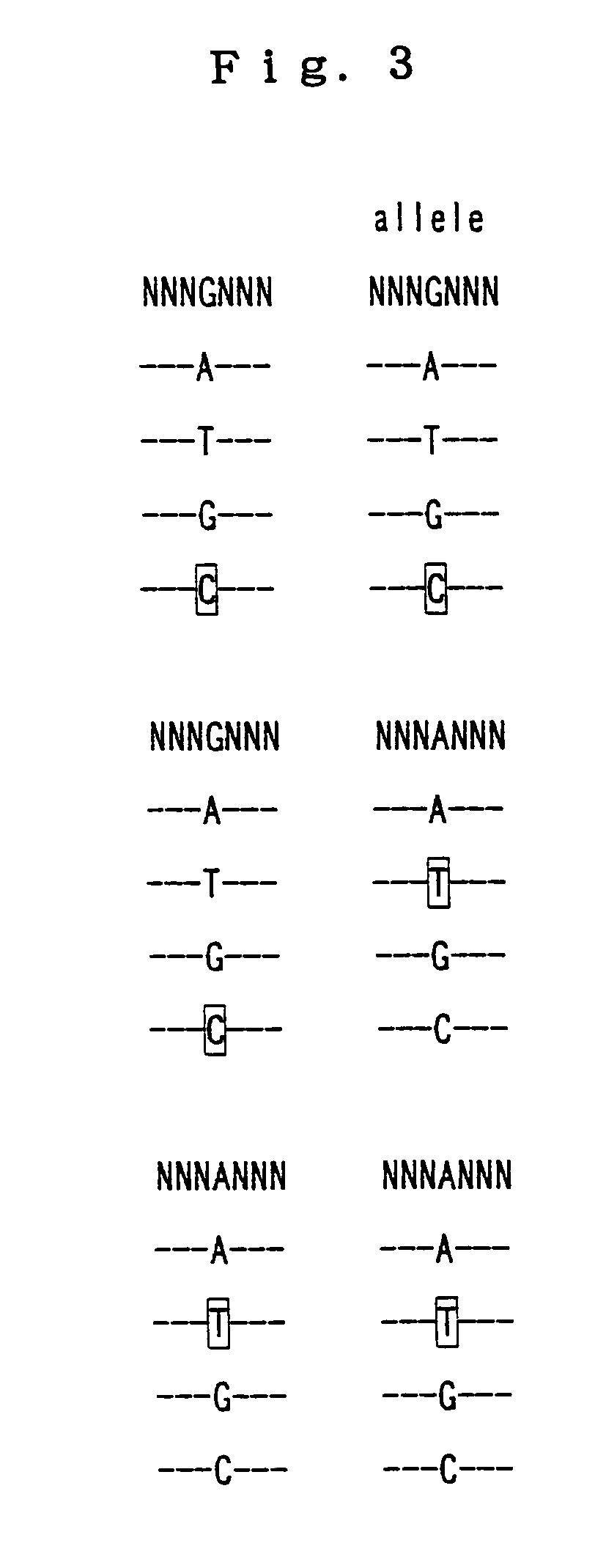
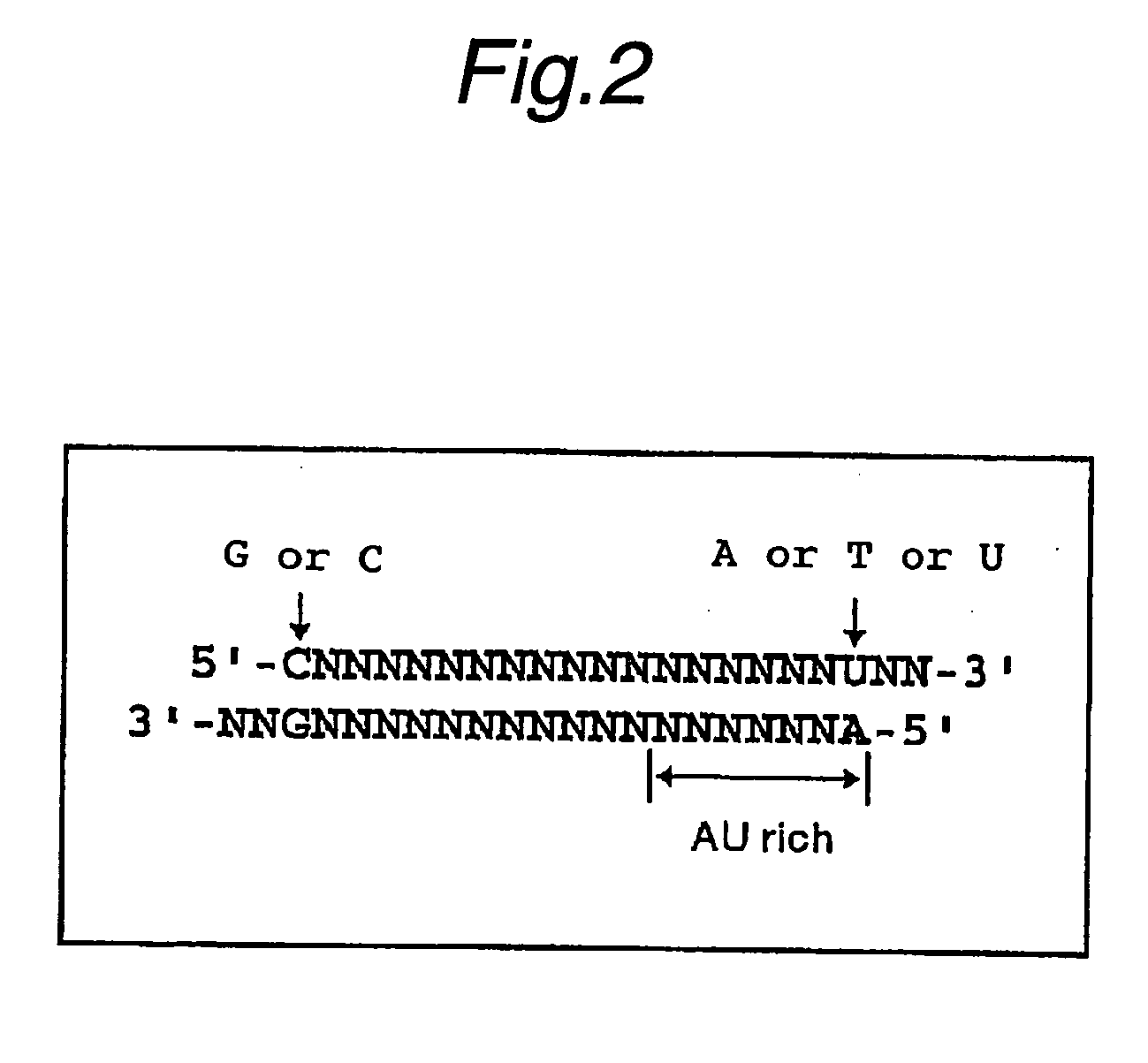
The present invention provides a polynucleotide that not only has a high RNA interference effect on its target gene, but also has a very small risk of causing RNA interference against a gene unrelated to the target gene. A sequence segment conforming to the following rules (a) to (d) is searched from the base sequences of a target gene for RNA interference and, based on the search results, a polynucleotide capable of causing RNAi is designed, synthesized, etc.:(a) The 3′ end base is adenine, thymine, or uracil,(b) The 5′ end base is guanine or cytosine,(c) A 7-base sequence from the 3′ end is rich in one or more types of bases selected from the group consisting of adenine, thymine, and uracil, and(d) The number of bases is within a range that allows RNA interference to occur without causing cytotoxicity.
Owner:ALPHAGEN
Substituted nucleosides, preparation thereof and use as inhibitors of RNA viral polymerases
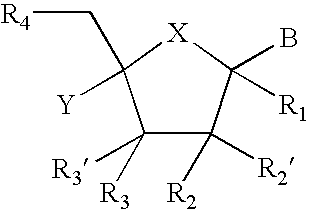
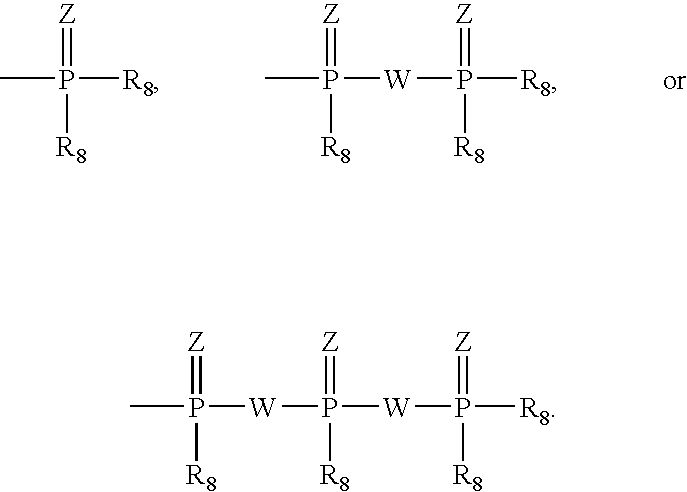
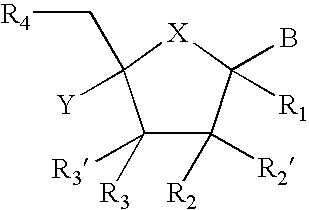
Provided are compounds represented by: X is O, S or NR6, R1 is H or (CH2)mR5, R2, R2', R3 and R3' are independently NO2, N3 or (CH2)mR5, OH R4 is H, OR6, SR6, NR6R6a, CN, C(O)OR6, C(O)NR6R6a, R6, OR7 or (CH2)nR7, R5 is H, halo, OR6, SR6, NR6R6a, CN, C(O)OR6, C(O)NR6R6a, R6, OR7 or (CH2)mR7, R6 and R6a are individually H, alkyl, substituted alkyl, alkenyl, substituted alkenyl, alkynyl, substituted alkynyl, aryl or substituted aryl, R7 is: R8 is H, F, SR9 or OR9, R9 is H, alkyl, alkenyl, alkynyl, aryl or hydroxyprotecting group, Y is H, CH3 or (CH2)mR5, Z is O or S W is CH2, CF2, CHF or O, m is 0-4, B is adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil, thymine, modified purines and pyrimidines substituted pyridines, five membered heterocycles substituted by at least one of amines, substituted amines, amides, substituted amides, esters, halogens, alkyls, ethers; and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof and prodrugs thereof. These ring systems may be substituted.
Owner:BIOCRYST PHARM INC
Polynucleotides for causing RNA interference and method for inhibiting gene expression using the same
InactiveUS20110054005A1High RNA interference effectLittle riskOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderBase JNucleotide
The present invention provides a polynucleotide that not only has a high RNA interference effect on its target gene, but also has a very small risk of causing RNA interference against a gene unrelated to the target gene. A sequence segment conforming to the following rules (a) to (d) is searched from the base sequences of a target gene for RNA interference and, based on the search results, a polynucleotide capable of causing RNAi is designed, synthesized, etc.:(a) The 3′ end base is adenine, thymine, or uracil,(b) The 5′ end base is guanine or cytosine,(c) A 7-base sequence from the 3′ end is rich in one or more types of bases selected from the group consisting of adenine, thymine, and uracil, and(d) The number of bases is within a range that allows RNA interference to occur without causing cytotoxicity.
Owner:BIO THINKTANK
Nucleotide derivative and DNA microarray
ActiveUS7414117B2Easy to prepareSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCytosineDNA microarray
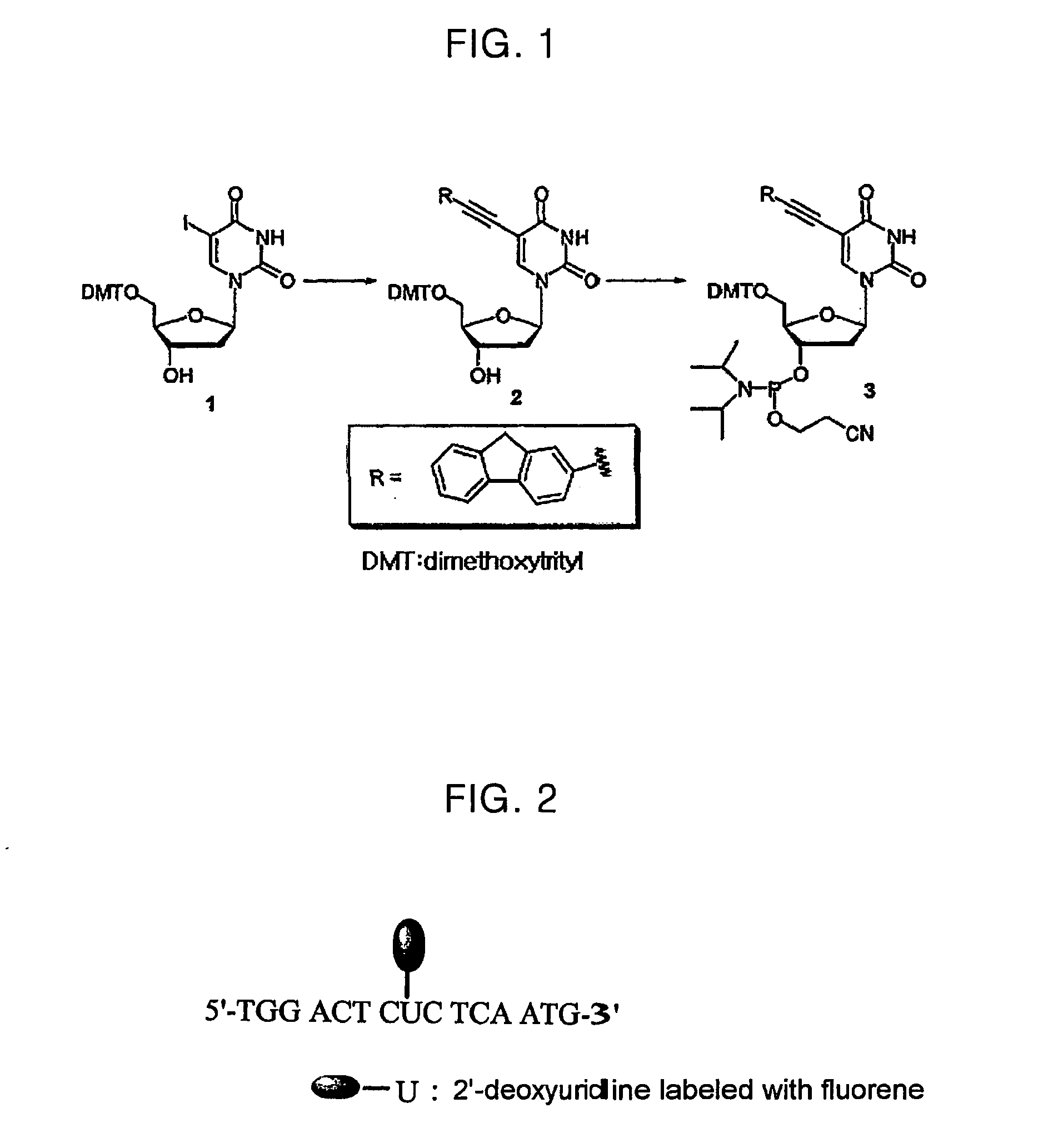
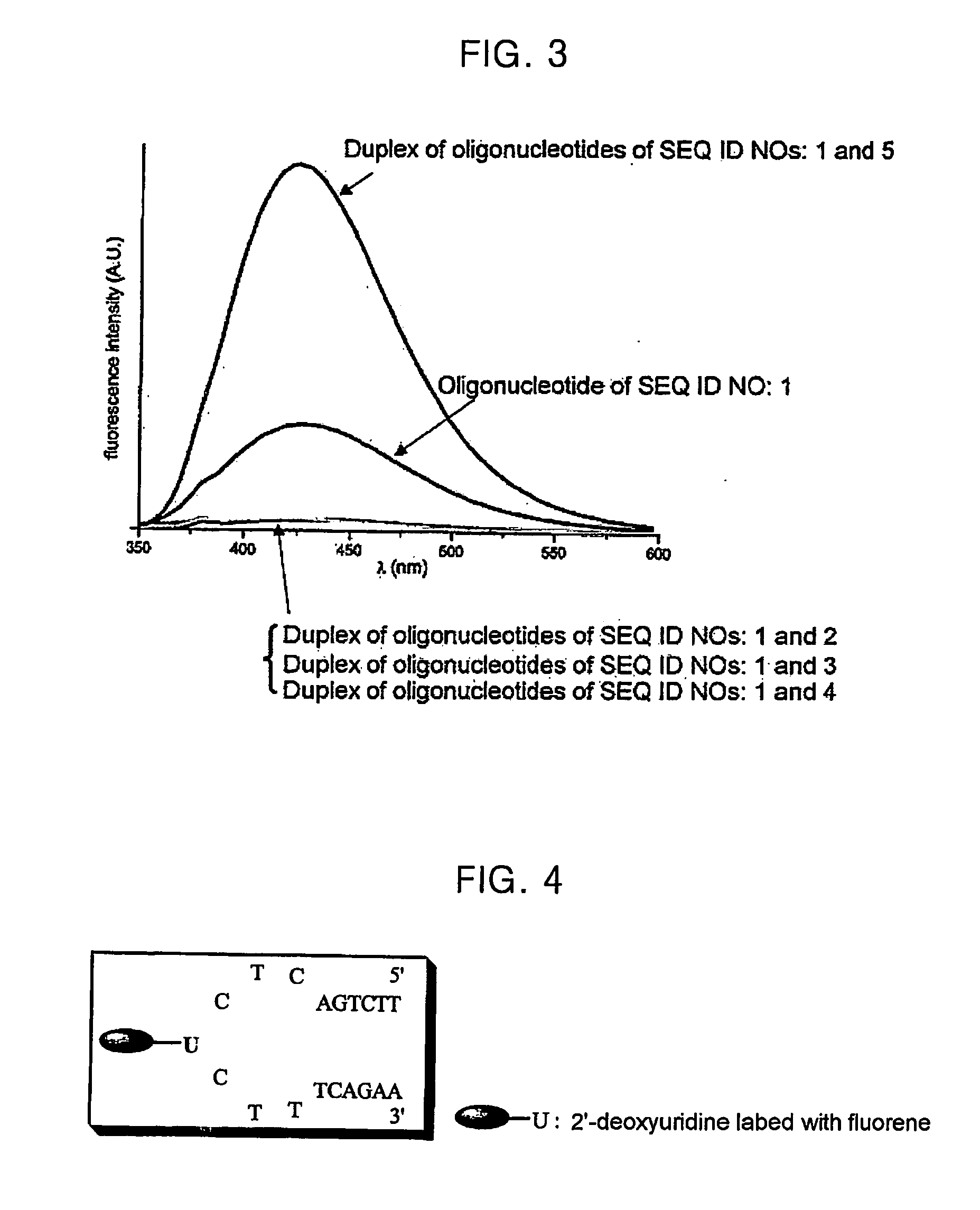
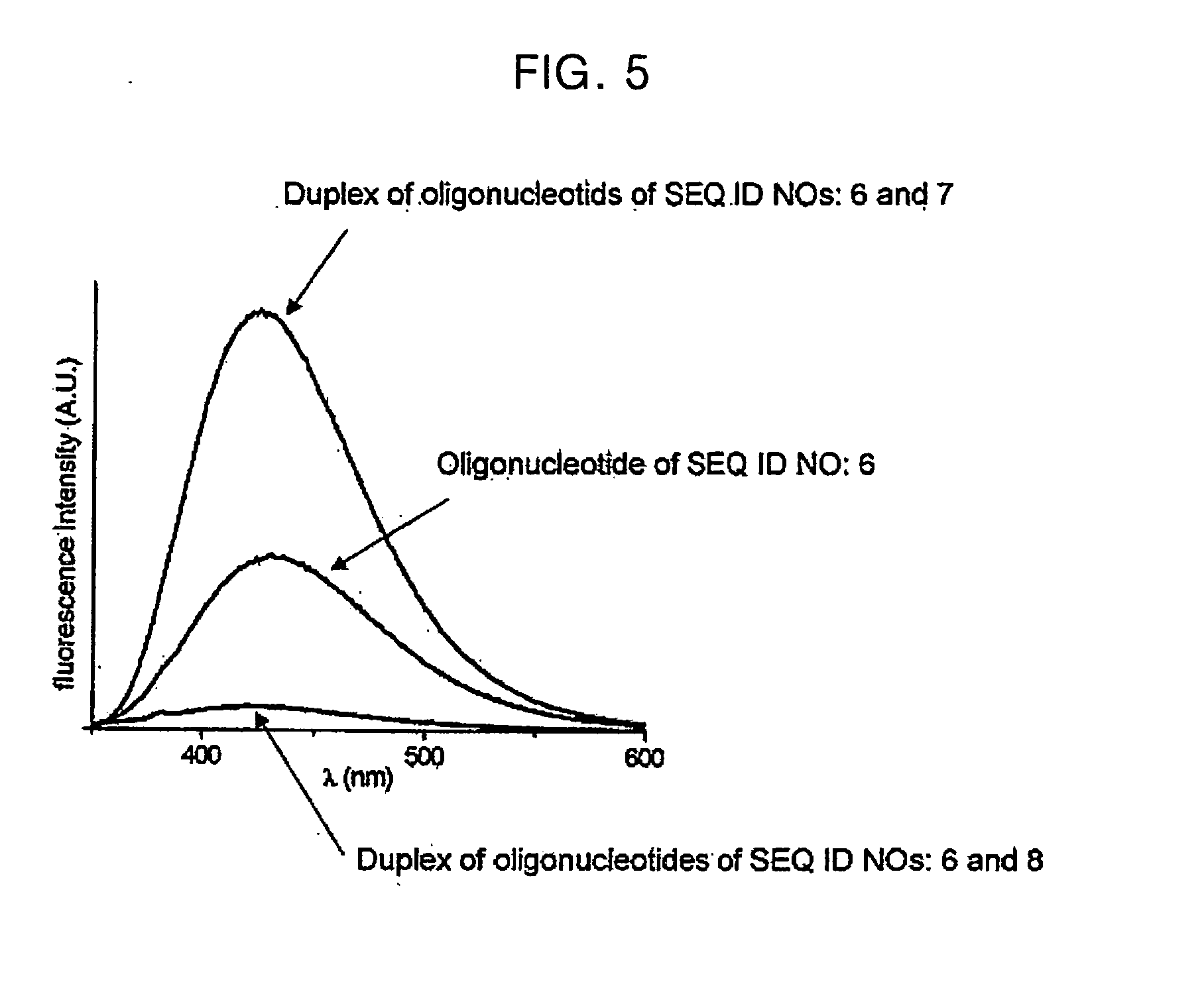
A novel nucleotide derivative, in case of existing as a member of a single-stranded sequence, undergoing a change in the fluorescent signal intendity depending on the corresponding base type in the partner strand with which the single-stranded sequence is hybridized, and which is a thymin / uracil derivative (1) emitting light most intensely when a confronting base in the partner strand with which the single-stranded nucleotide sequence is hybridized is adenine; a cytosine derivative (2) emitting light most intensely when the confronting base is guanine; an adenine derivative (3) emitting light most intensely when the confronting base is cytosine; a guanine derivative (4) emitting light most intensely when the confronting base is cytosine or thymine / uracil; and an adrnine derivative (5) emitting light most intensely when the confronting base is thymine / uracil / .
Owner:SAITO ISAO +1
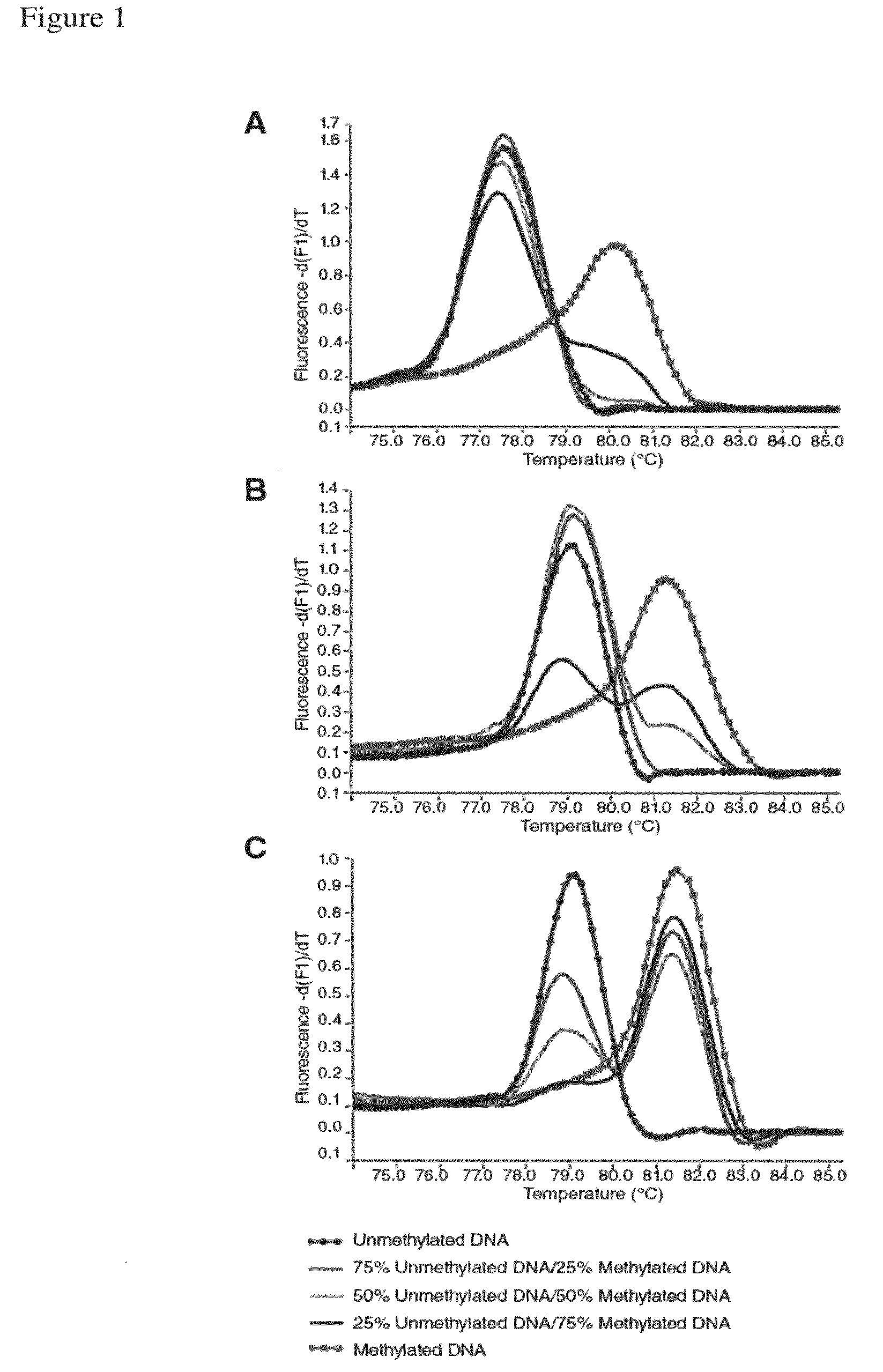
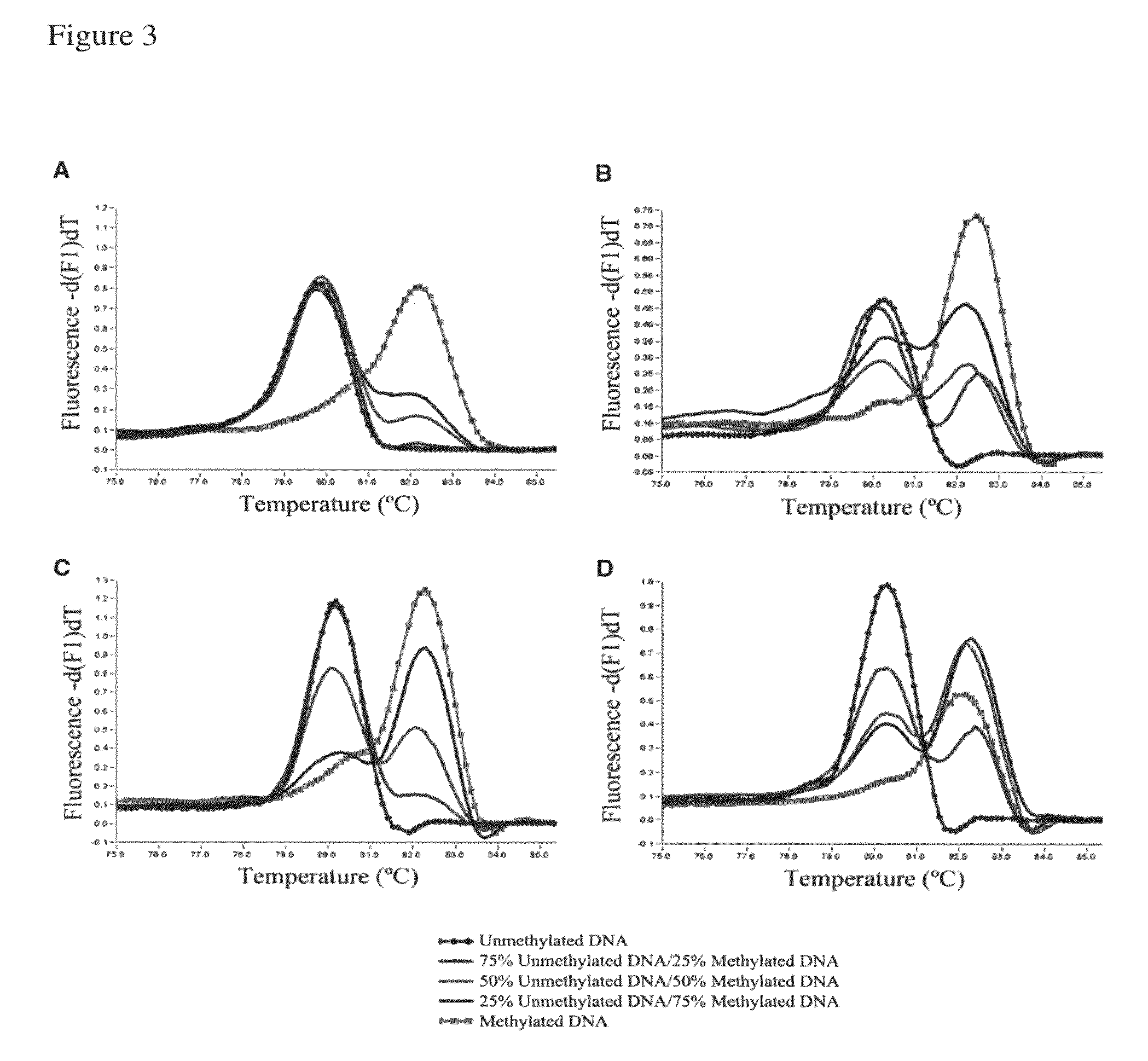
Method for detecting methylation status by using methylation-independent primers
A reliable and highly sensitive method is provided for detecting methylation status of CpG-containing nucleic acids by nucleic acid amplification and melting curve analysis of amplification products. The methods and compositions employs a novel design of primers. CpG-containing methylation-independent oligonucleotide primers, wherein both unmethylated and methylated alleles of a CpG-containing nucleic acid can be detected by use of only one set of primers after the CpG-containing nucleic acid has been subjected to cytosine to thymine conversion of unmethylated Cytosine. The method is useful for detection of methylation status in for example cancer genes and other disease related genes, wherein methylation influences gene expression.
Owner:AARHUS UNIV +1
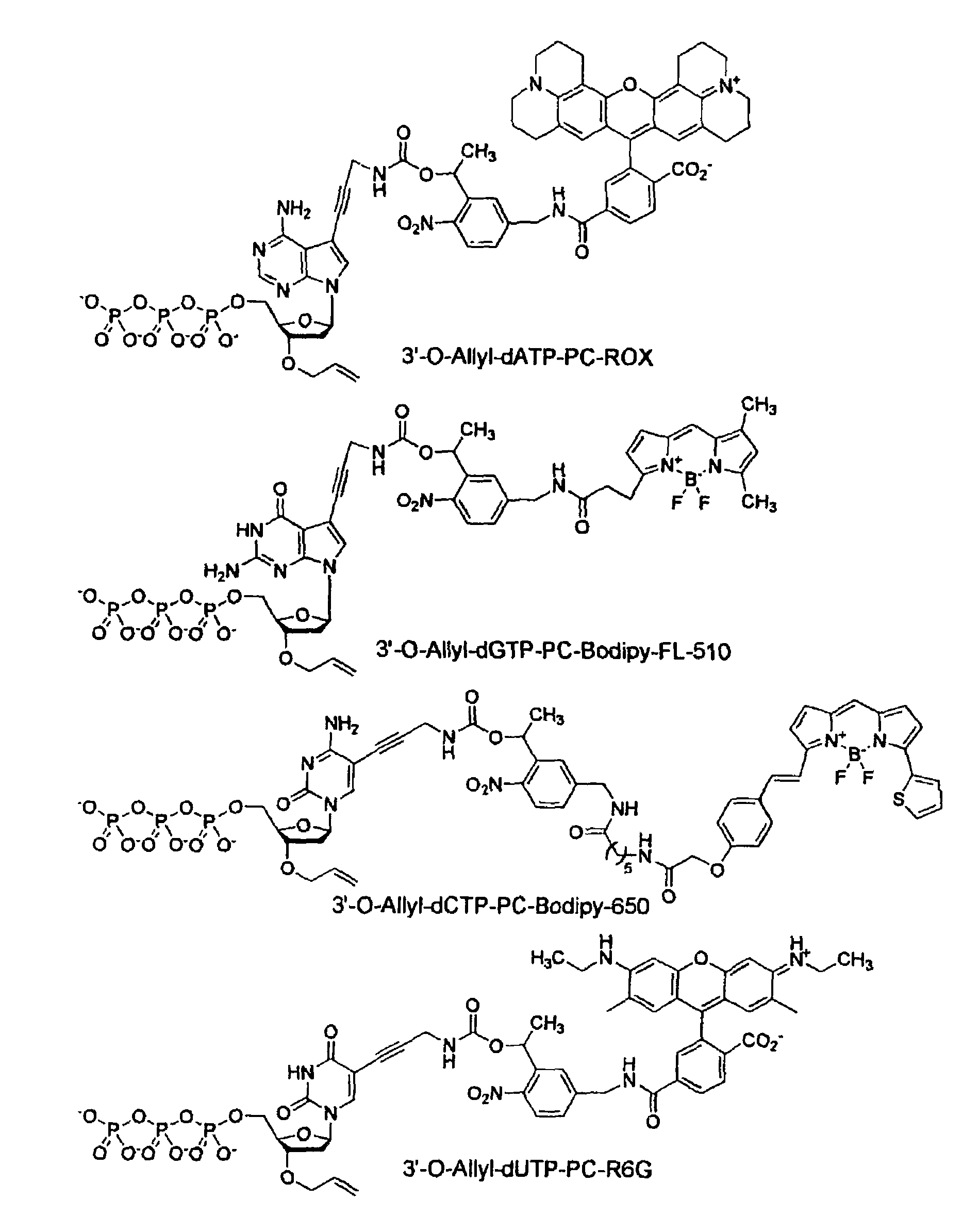
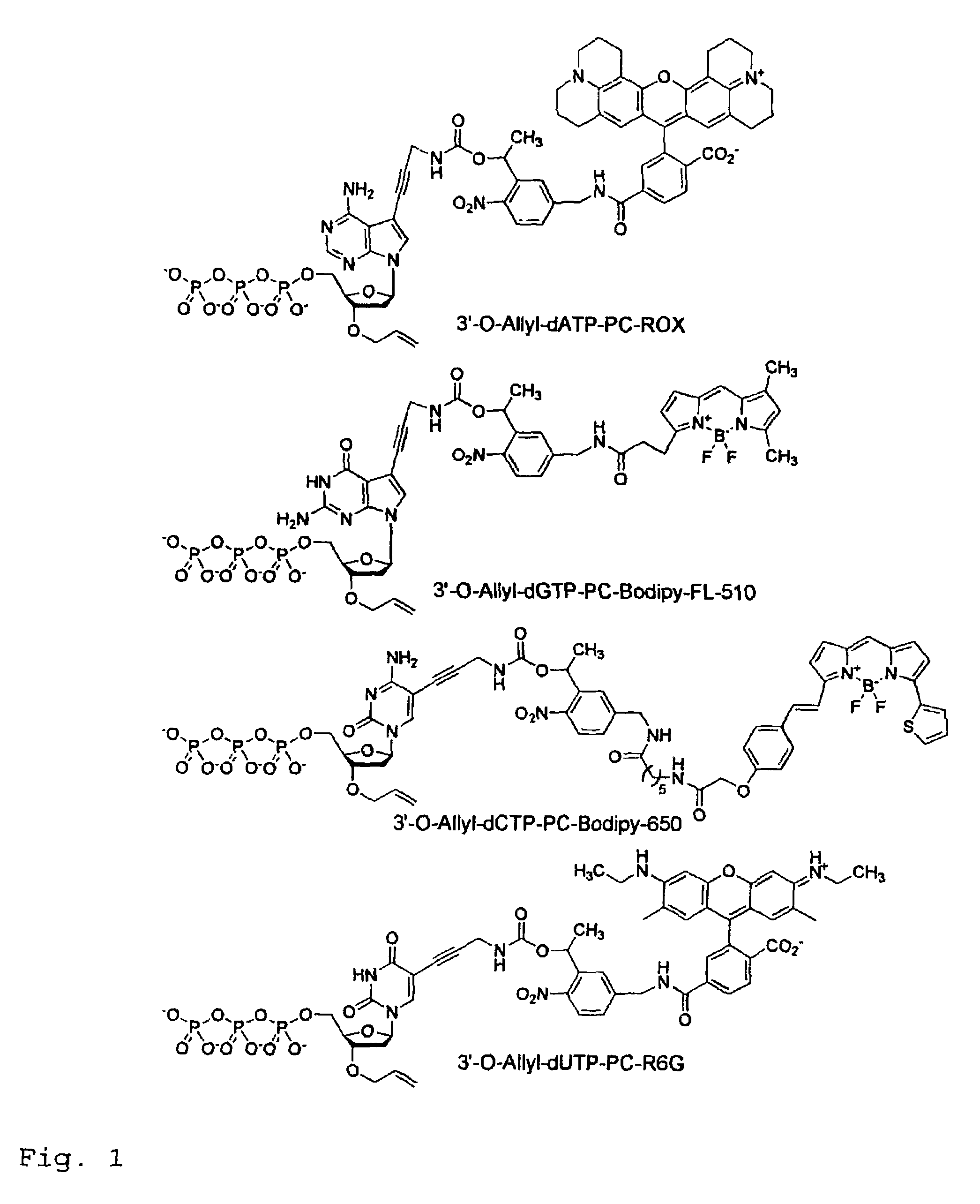
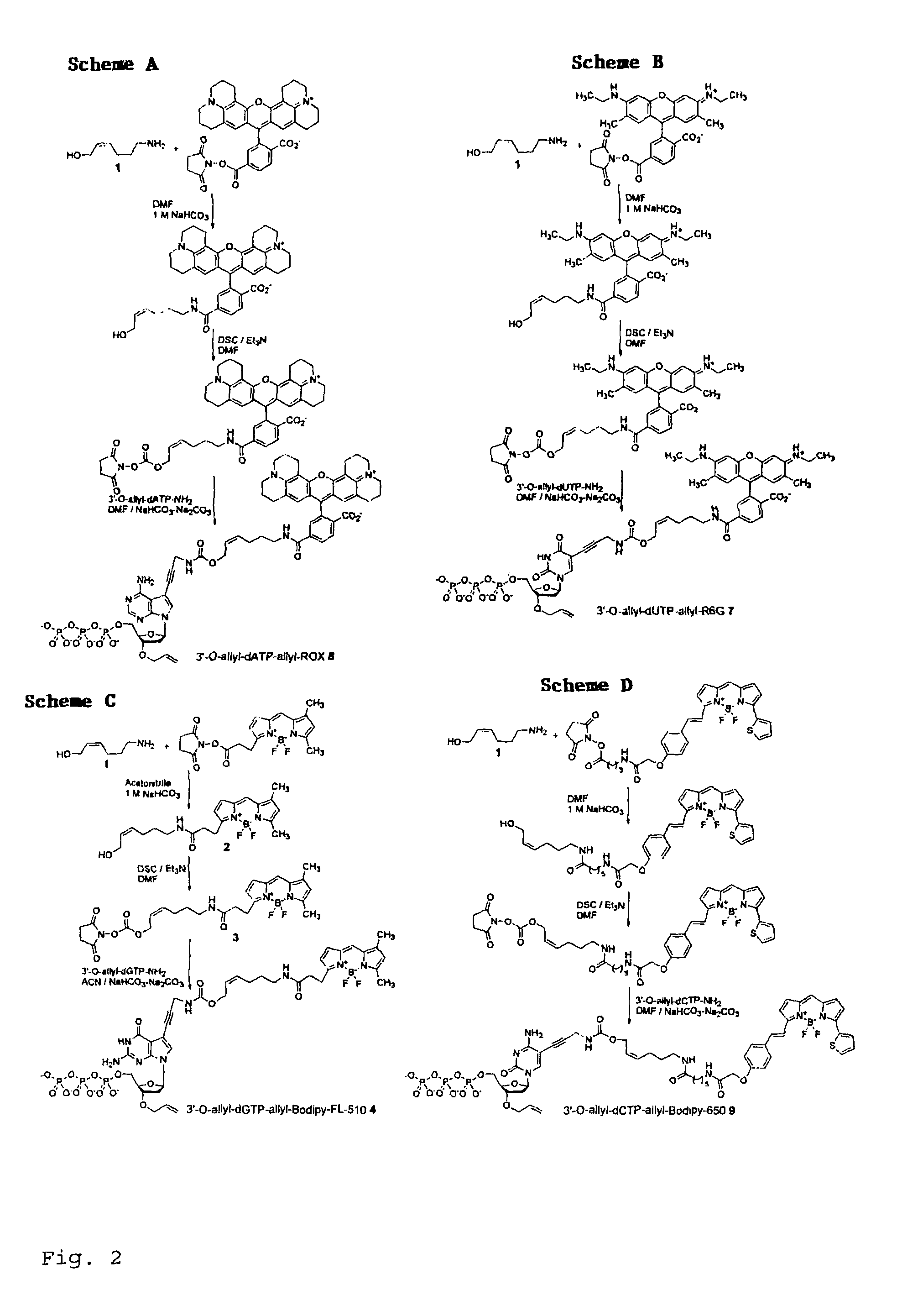
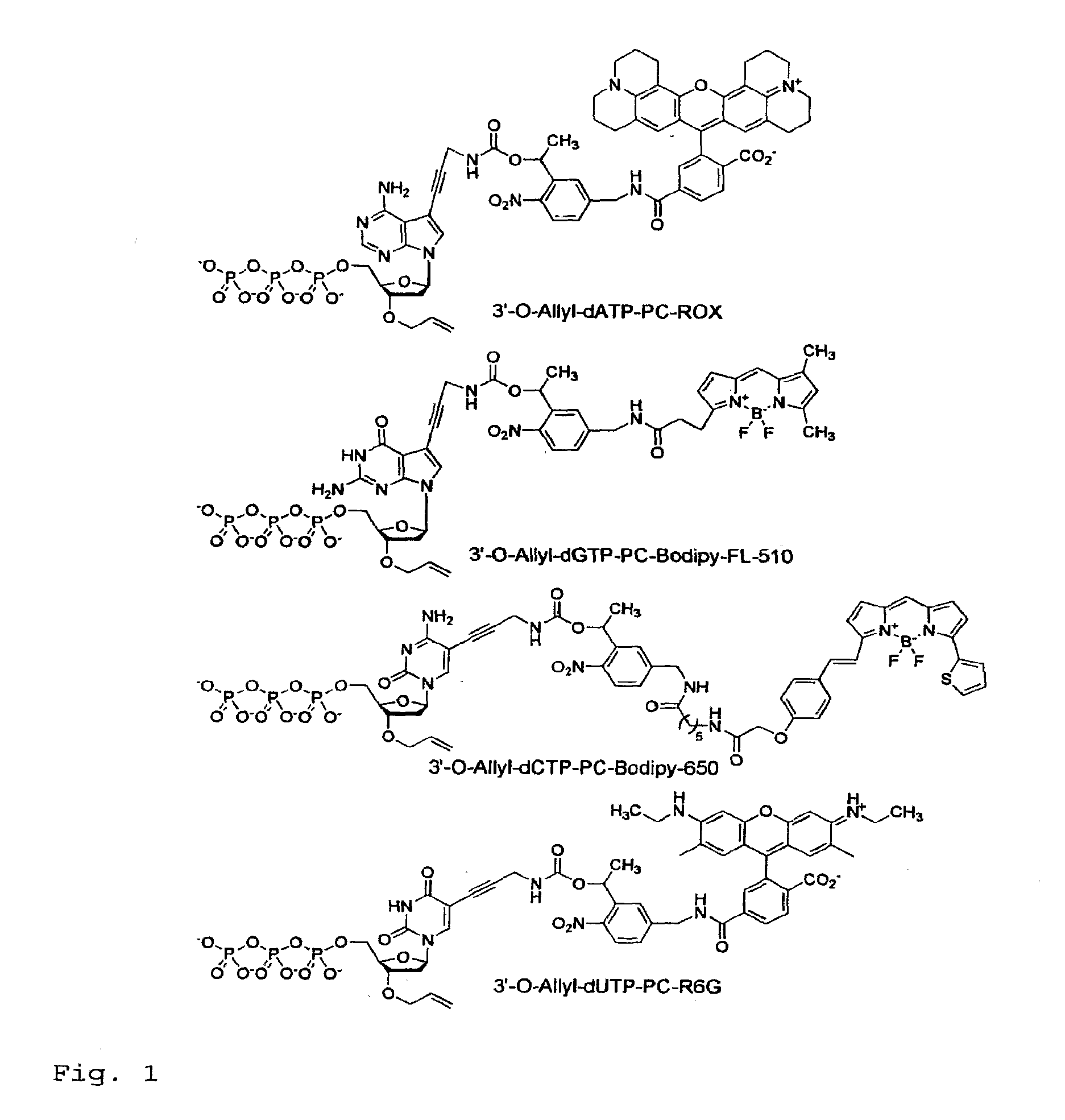
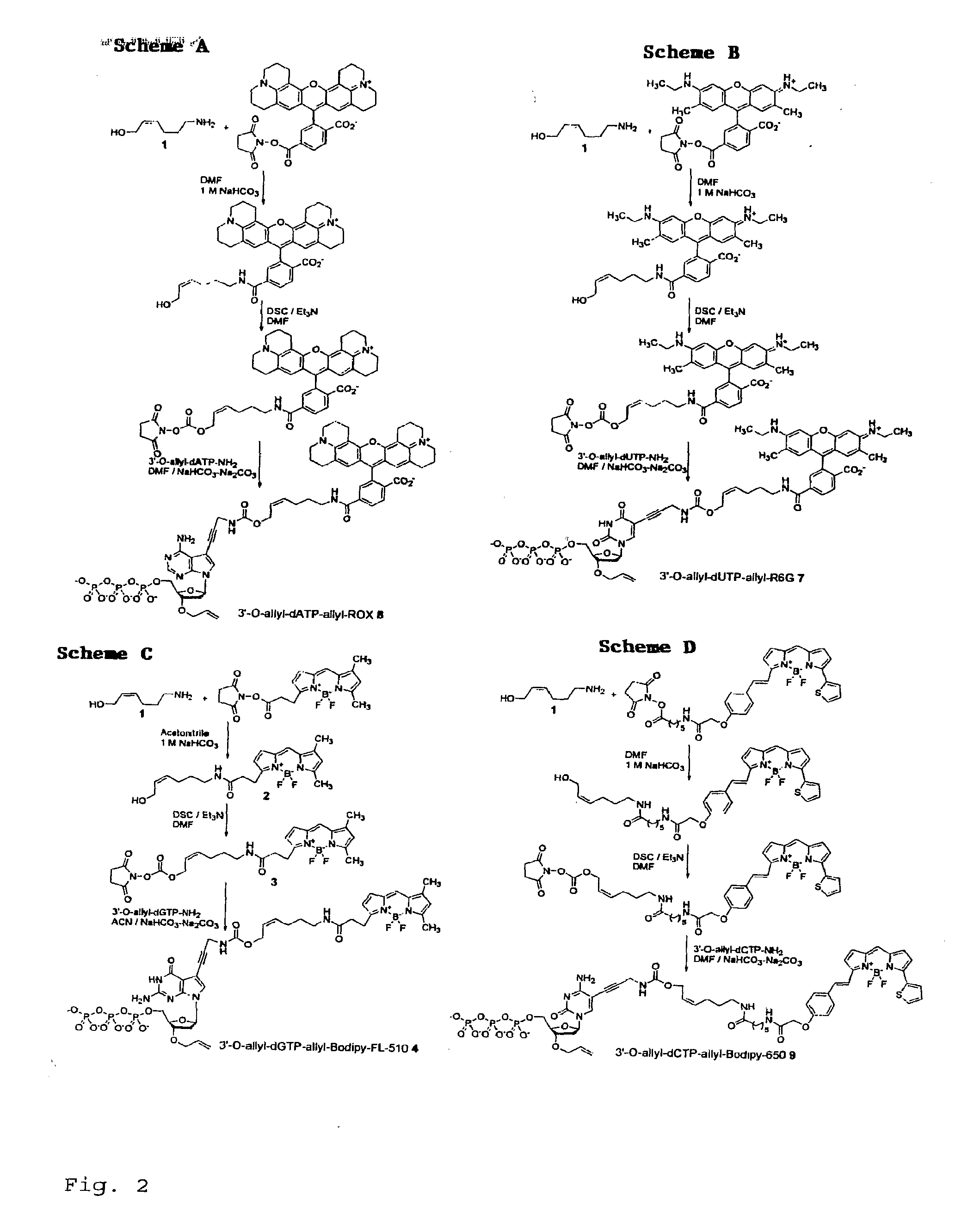
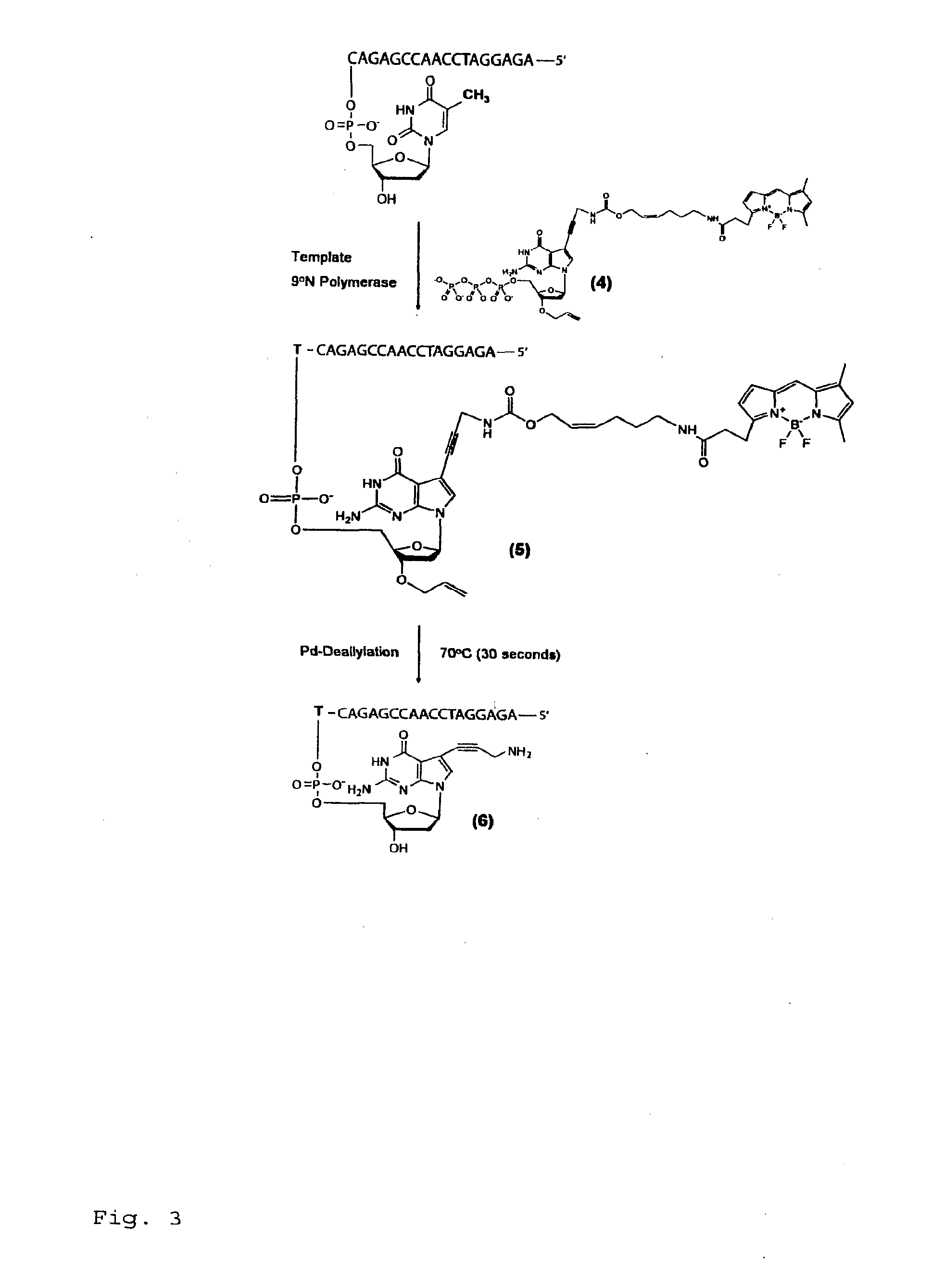
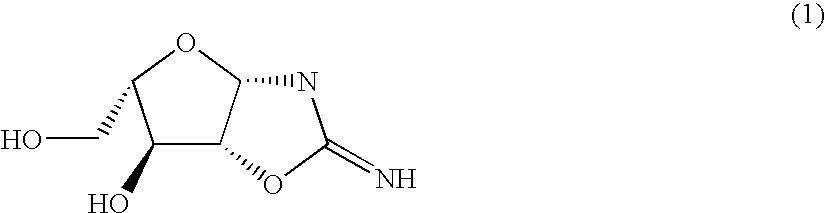
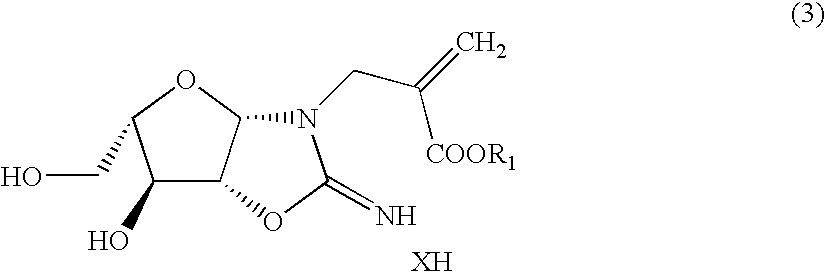
Chemically cleavable 3'-o-allyl-DNTP-allyl-fluorophore fluorescent nucleotide analogues and related methods
This invention provides a nucleotide analogue comprising (i) a base selected from the group consisting of adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine and uracil, (ii) a deoxyribose, (iii) an allyl moiety bound to the 3′-oxygen of the deoxyribose and (iv) a fluorophore bound to the base via an allyl linker, and methods of nucleic acid sequencing employing the nucleotide analogue.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Applications of modified crRNA in CRISPR/Cpf1 gene editing system
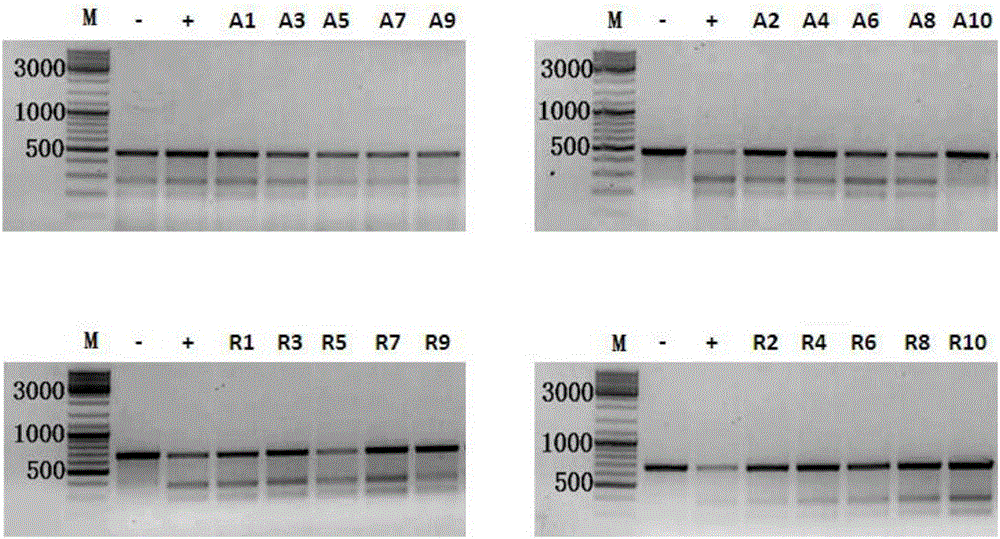
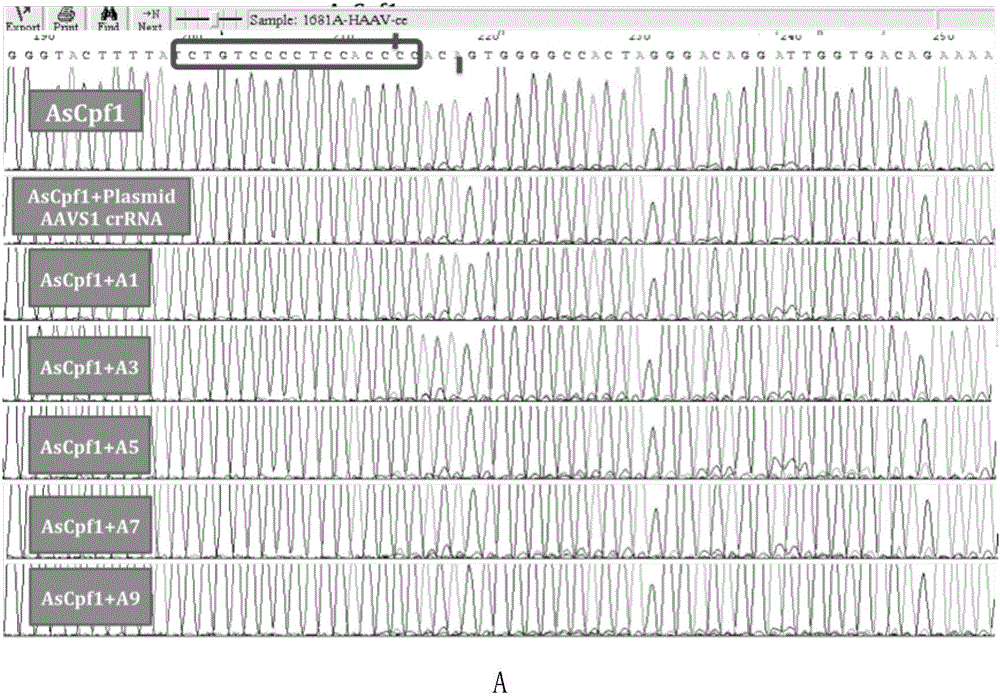
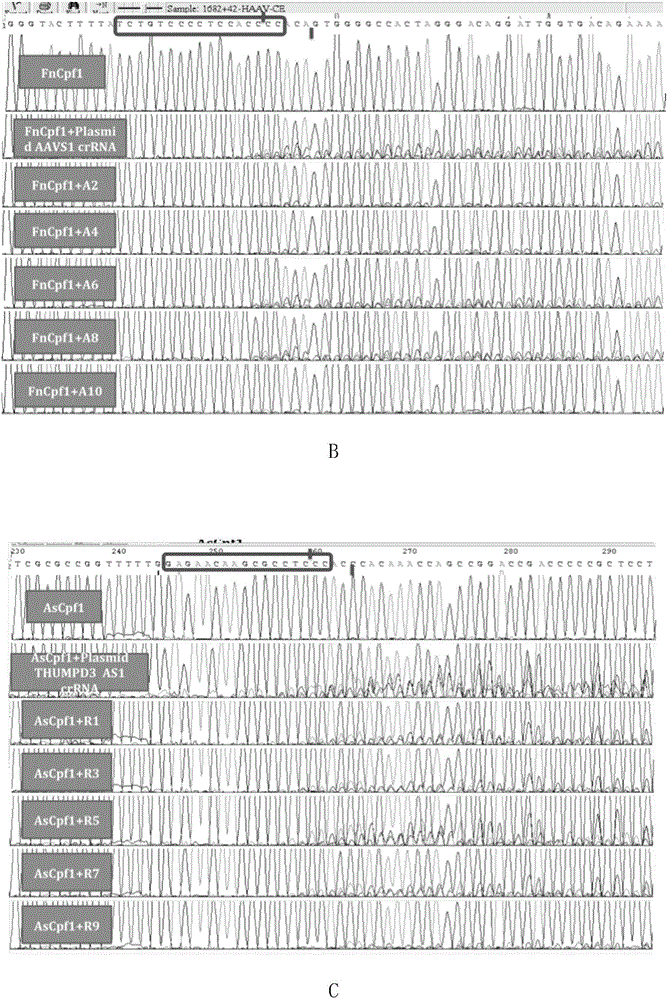
InactiveCN106244591AStrong gene editing abilityNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionChemical synthesisThymine
The invention discloses applications of a CRISPR / Cpf1 system in gene editing. CrRNA in the CRISPR / Cpf1 system is modified crRNA; the modification manner is desoxyribonucleic acid modification; the desoxyribonucleic acid modification method comprises the step of increasing 1-3 desoxyribonucleic acid at the 5' terminal and / or increasing 1-3 desoxyribonucleic acid at the 3' terminal of crRNA; and the desoxyribonucleic acid is deoxythymidine acid. The experiment proves that the crRNA formed through chemical synthesis and having the modification can cause the mutation of an hAAVS1 gene and a THUMPD3-AS1 gene when used for the AsCRISPR / Cpf1 system or the FnCRISPR / Cpf1 system, namely, the modified crRNA has certain gene editing capacity when used for the AsCRISPR / Cpf1 system or the FnCRISPR / Cpf1 system, and therefore, the modified crRNA has a significant application value in gene editing utilizing the CRISPR / Cpf1 system.
Owner:SUZHOU GENEPHARMA
Gene site-directed mutation vector as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN106834341ANucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionCytosine deaminaseCytosine
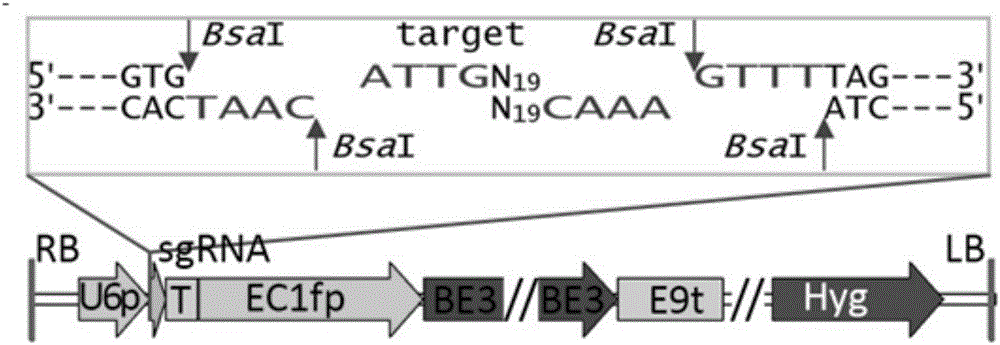
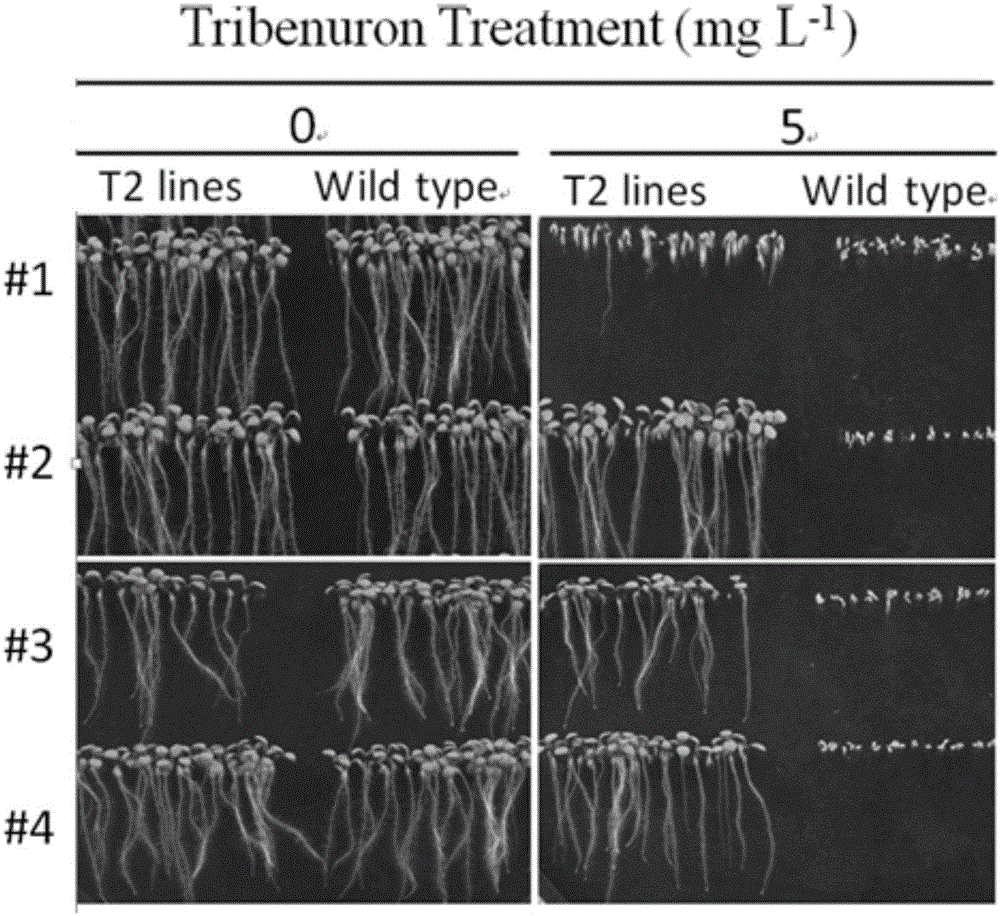
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering and in particular relates to a gene site-directed mutation vector as well as a construction method and application thereof. The invention provides the gene site-directed mutation vector due to lots of optimizations, cytosine deaminase is guided to be close to cytosine through a CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) system, the cytosine is changed into uracil, then uracil is changed into thymine through self-repair in plant cells, and finally, site-specific mutagenesis from C to T is realized in plants so as to generate resistance to herbicides. In addition, point mutation can be produced in a non-sgRNA targeted area, and novel herbicide-resistant great agronomic traits are brought.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Methods and kits for characterizing GC-rich nucleic acid sequences
Methods and kits of characterizing a GC rich region of a nucleic acid of interest are provided. One method is effected by (a) contacting the nucleic acid of interest with an agent that modifies cytosine or guanine residues into residues complementary to adenine or thymine for obtaining a modified nucleic acid in which the cytosine or guanine residues are replaced by the residues complementary to adenine or thymine; (b) amplifying the modified nucleic acid by amplification primers being hybridizable with the modified nucleic acid and being designed for directing amplification of at least a portion of the modified nucleic acid, for obtaining an amplification product corresponding to the GC rich region; and (c) determining the size of the amplification product, thereby characterizing the GC rich region of the nucleic acid of interest.
Owner:GAMIDAGEN
Sequence preserved DNA conversion
InactiveUS20120040869A1Eliminates introductionImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionCytosineThymine
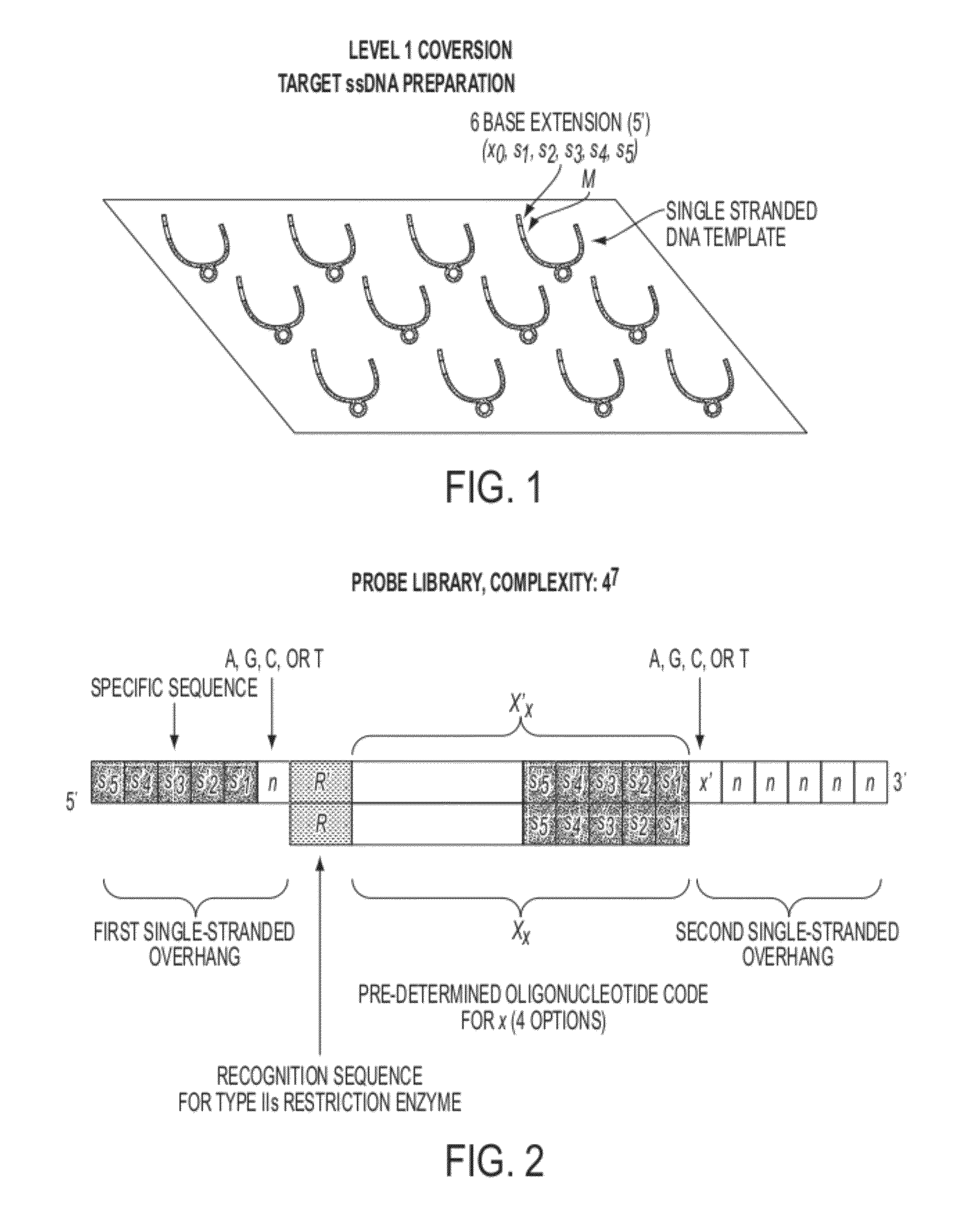
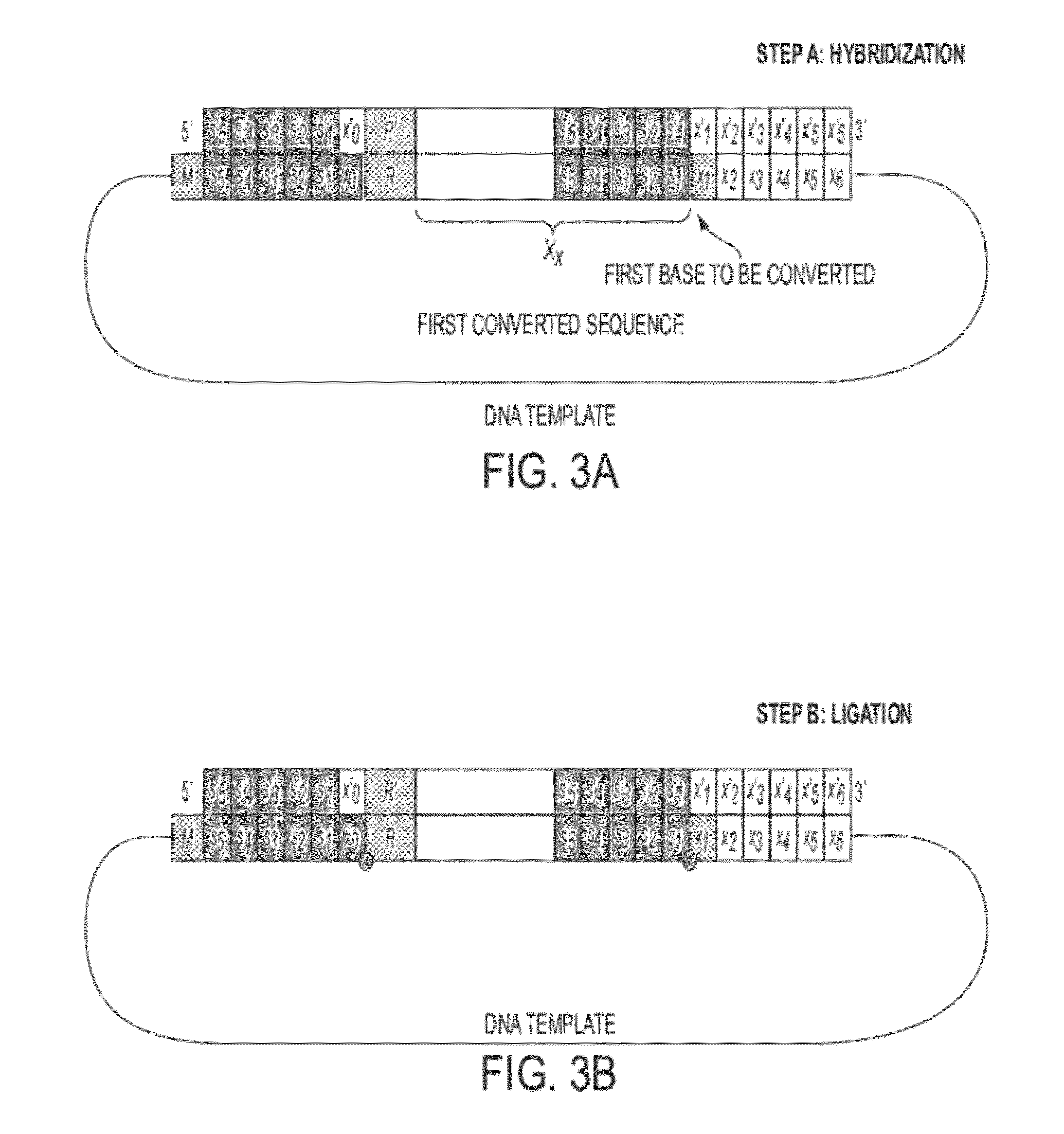
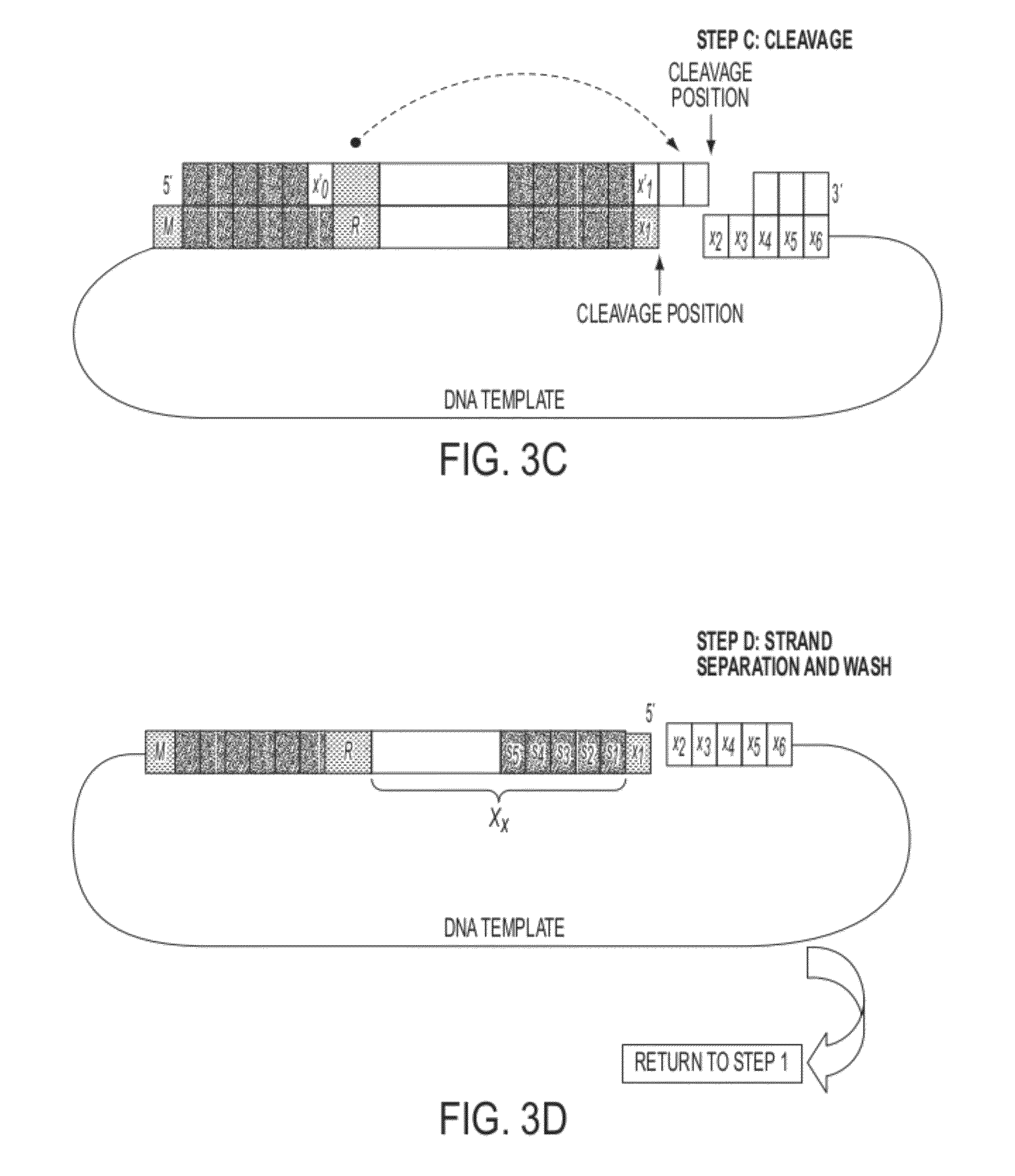
Described herein are inexpensive high throughput methods to convert a target single stranded DNA (ssDNA) such that each nucleotide (or base) adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C) is converted to a pre-determined oligonucleotide code, with the sequential order preserved in the converted ssDNA, or RNA. The method does not require the use of DNA polymerases during the cycles and involves the use of an oligonucleotide probe library with repeated cycles of ligation and cleavage. At each cycle, one or more nucleotides on one end (e.g., either the 5′ end or the 3′ end) of a target, e.g., ssDNA, are cleaved and then ligated with the corresponding oligonucleotide code at the other end of the target ssDNA.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
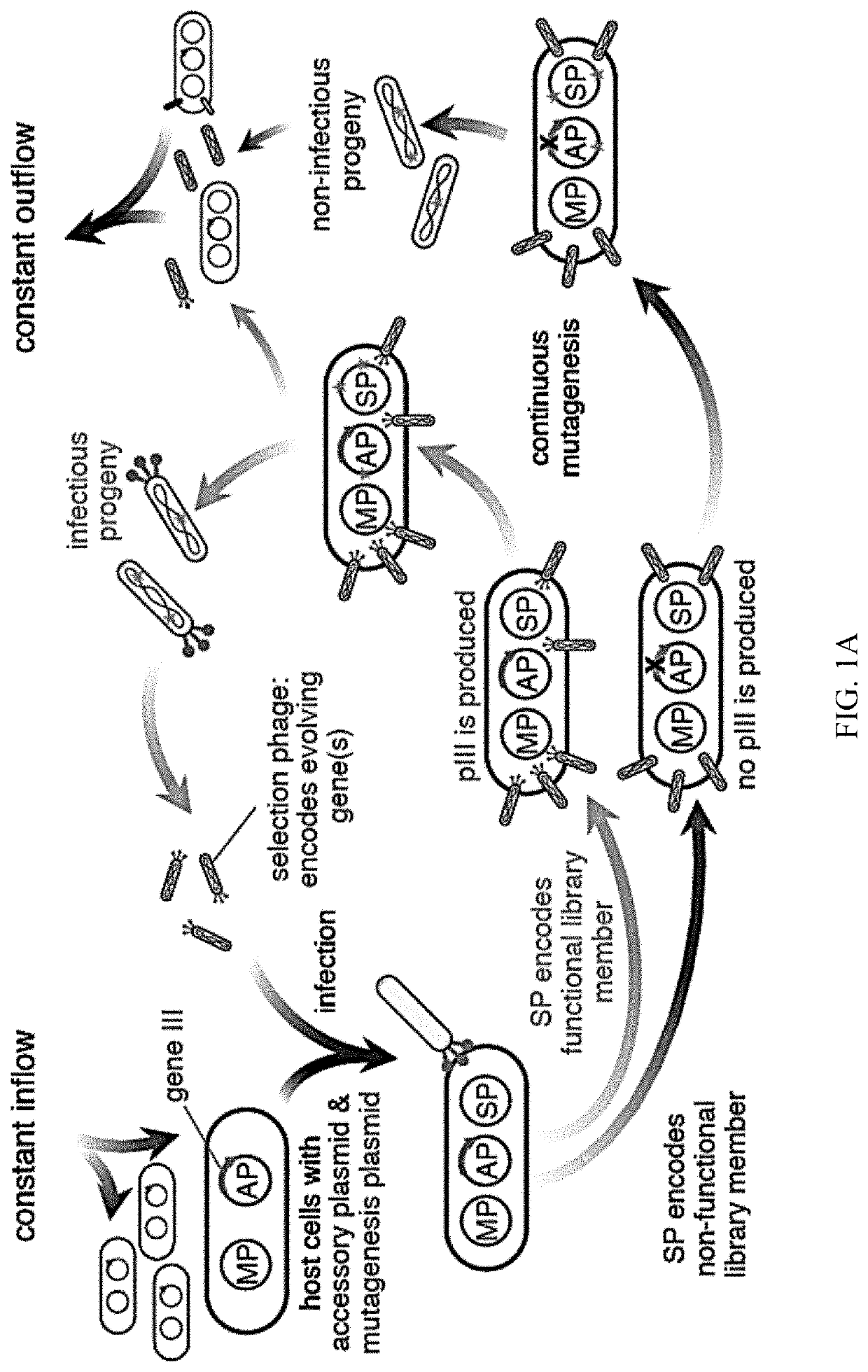
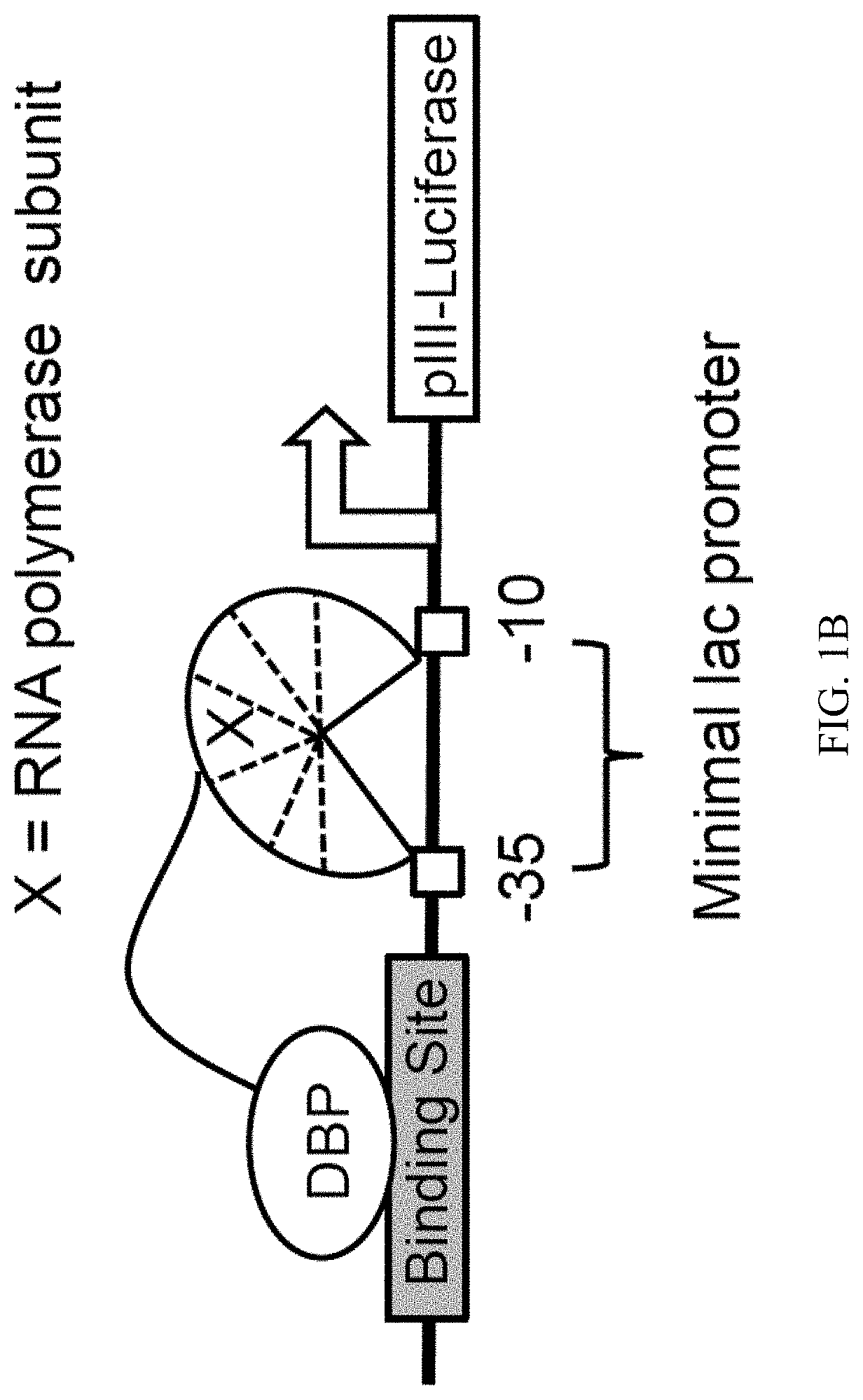
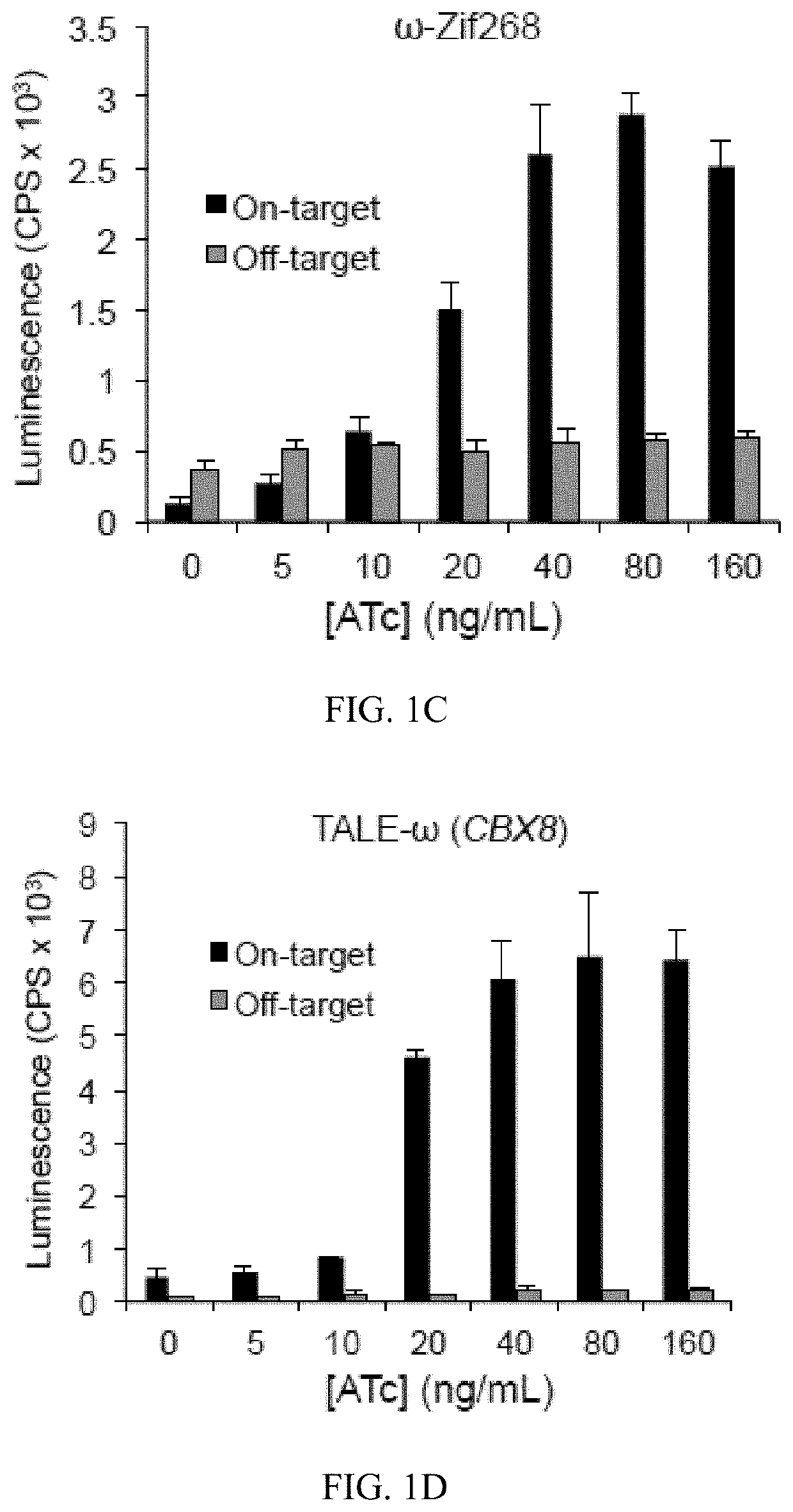
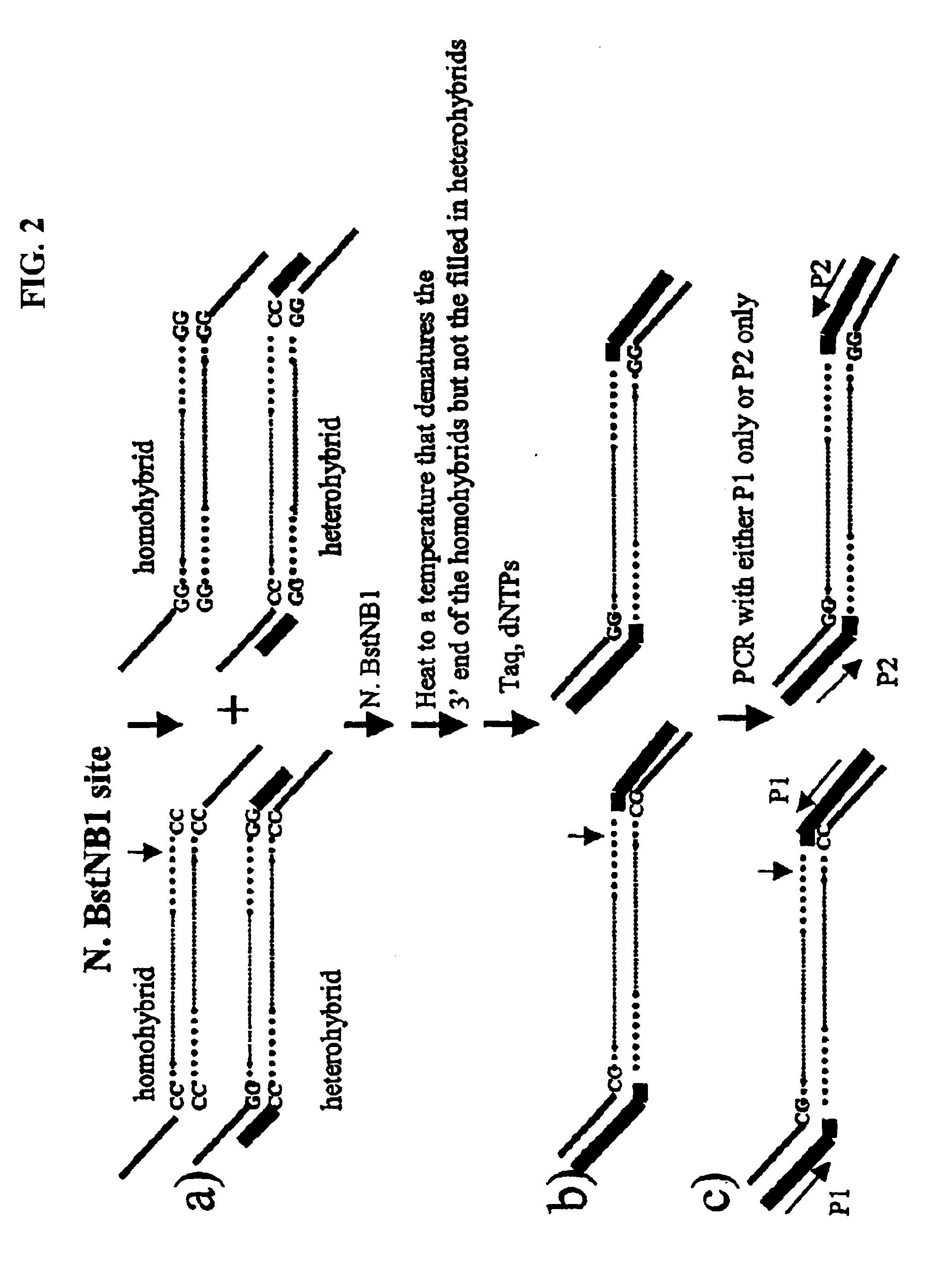
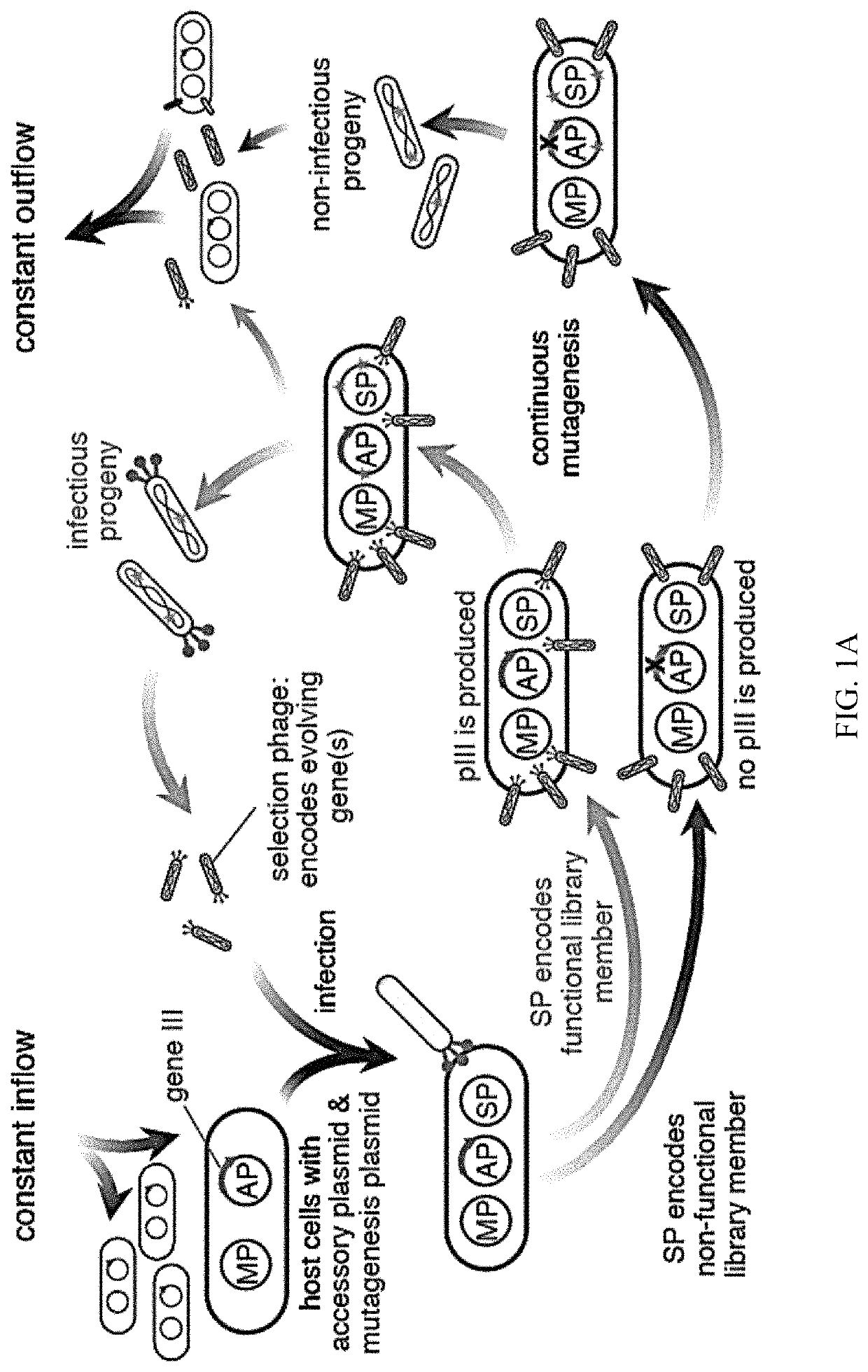
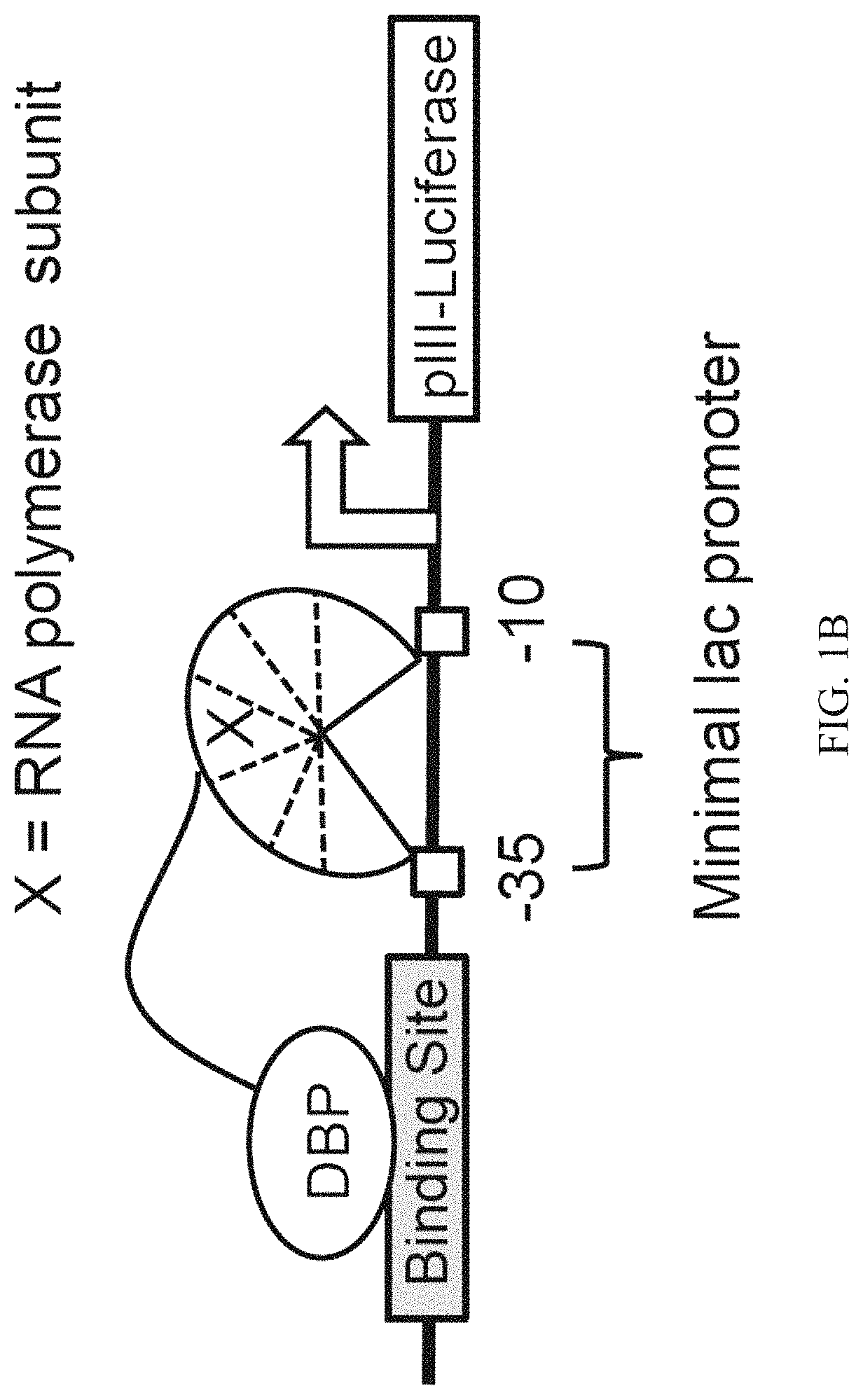
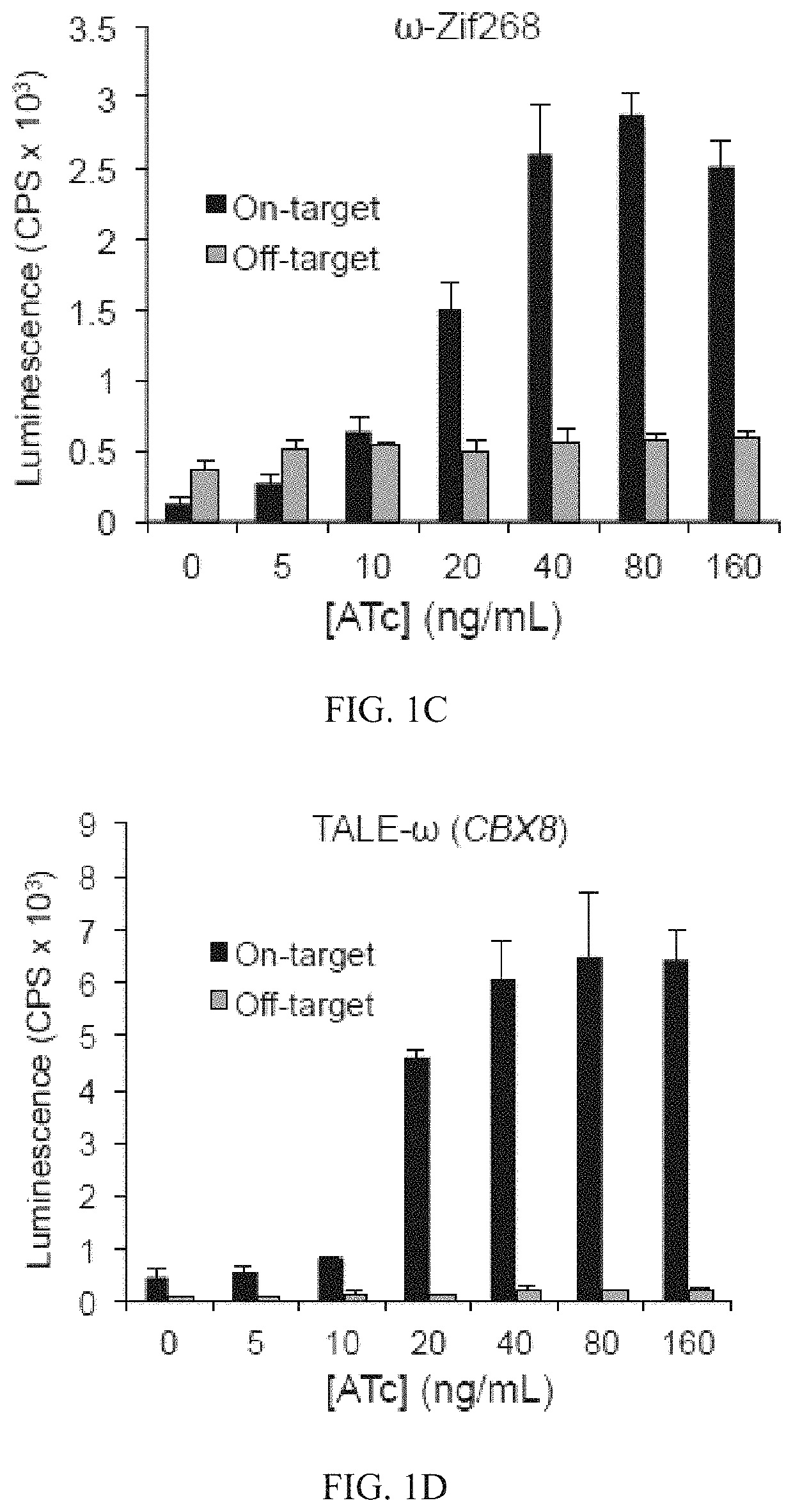
Evolution of talens
ActiveUS20200277587A1Strong specificityHydrolasesGenetic therapy composition manufactureNucleotideEpigenetic Profile
Engineered transcriptional activator-like effectors (TALEs) are versatile tools for genome manipulation with applications in research and clinical contexts. One current drawback of TALEs is that the 5′ nucleotide of the target is specific for thymine (T). TALE domains with alternative 5′ nucleotide specificities could expand the scope of DNA target sequences that can be bound by TALEs. Another drawback of TALEs is their tendency to bind and cleave off-target sequence, which hampers their clinical application and renders applications requiring high-fidelity binding unfeasible. This disclosure provides methods and strategies for the continuous evolution of proteins comprising DNA-binding domains, e.g., TALE domains. In some aspects, this disclosure provides methods and strategies for evolving such proteins under positive selection for a desired DNA-binding activity and / or under negative selection against one or more undesired (e.g., off-target) DNA-binding activities. Some aspects of this disclosure provide engineered TALE domains and TALEs comprising such engineered domains, e.g., TALE nucleases (TALENs), TALE transcriptional activators, TALE transcriptional repressors, and TALE epigenetic modification enzymes, with altered 5′ nucleotide specificities of target sequences. Engineered TALEs that target ATM with greater specificity are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
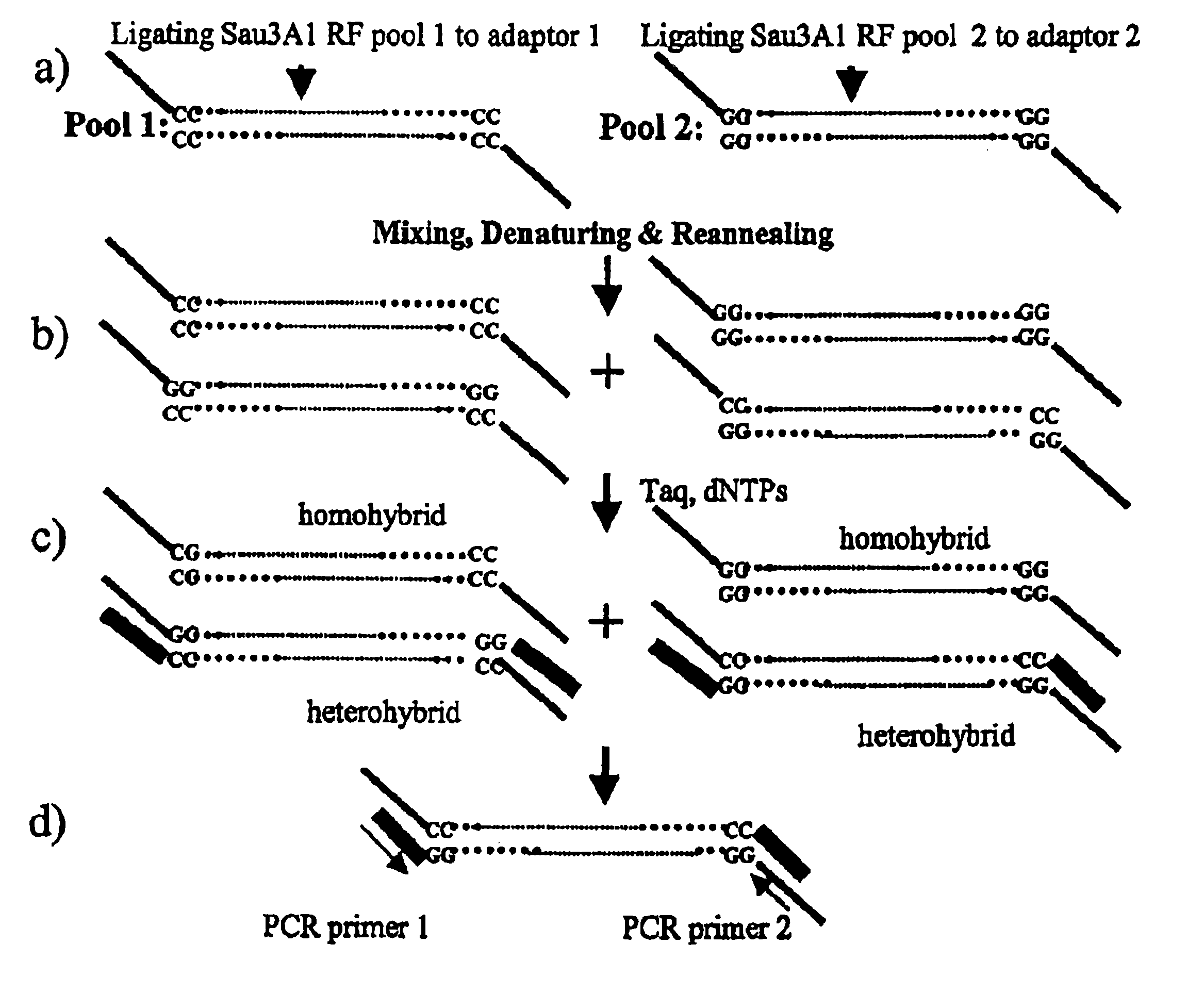
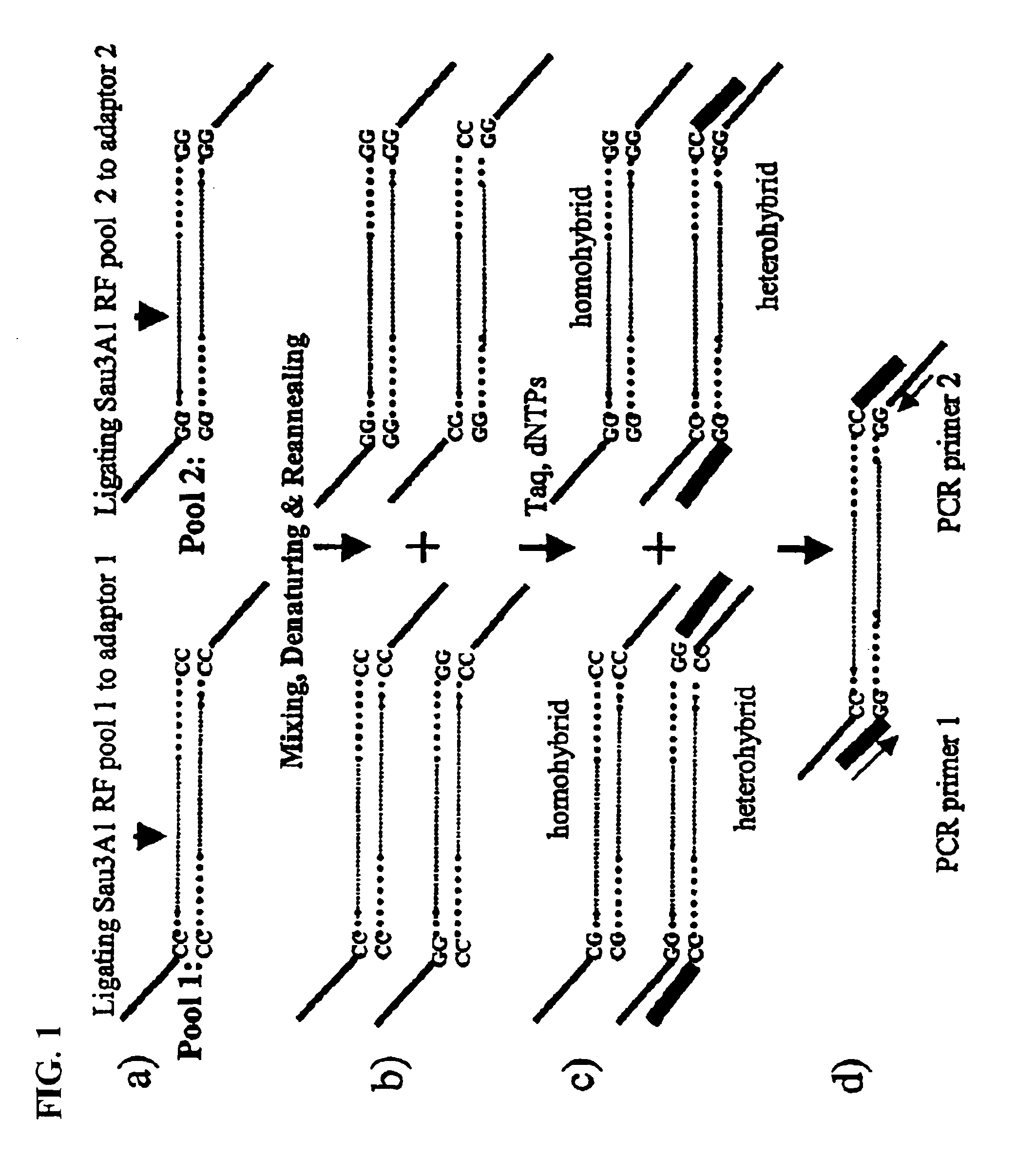
Methods for identifying genes associated with diseases or specific phenotypes
InactiveUS6924104B2Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningHeterologousDNA fragmentation
An improved method for screening genomic, cDNA, or any DNA fragments in general is described. Novel adapters are ligated to the ends of DNA fragments from two different individuals or two different pools of individuals. The DNA fragment-adapter complexes are mixed, denatured and reannealed to form homohybrid and heterohybrid DNA duplexes, which are separated based on characteristics of the adapters. Sequence differences between heterohybrids can be revealed as mismatched base pairs in the heterohybrid DNA duplex. Mismatch base pairs are discovered using genome mismatch scanning techniques that use thymine glycosylases and related enzymes that capture DNA containing mismatched base pairs. The perfectly base paired DNA or DNA containing mismatched base pairs can be further separated into homohybrids and heterohybrids using novel adapters that allow physical capture of either heterohybrid or homohybrid DNA.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Evolution of TALENs
ActiveUS10612011B2Strong specificityHydrolasesGenetic therapy composition manufactureNucleotideEpigenetic Profile
Engineered transcriptional activator-like effectors (TALEs) are versatile tools for genome manipulation with applications in research and clinical contexts. One current drawback of TALEs is that the 5′ nucleotide of the target is specific for thymine (T). TALE domains with alternative 5′ nucleotide specificities could expand the scope of DNA target sequences that can be bound by TALEs. This disclosure provides methods and strategies for the continuous evolution of proteins comprising DNA-binding domains, e.g., TALE domains. In some aspects, this disclosure provides methods and strategies for evolving such proteins under positive selection for a desired DNA-binding activity and / or under negative selection against one or more undesired (e.g., off-target) DNA-binding activities. Some aspects of this disclosure provide engineered TALE domains and TALEs comprising such engineered domains, e.g., TALE nucleases (TALENs), TALE transcriptional activators, TALE transcriptional repressors, and TALE epigenetic modification enzymes, with altered 5′ nucleotide specificities of target sequences. Engineered TALEs that target ATM with greater specificity are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Oligonucleotide For Detecting Target Dna Or Rna
An oligonucleotide that can be used for detecting the presence of a target DNA or RNA in a sample, a method for detecting a target DNA or RNA by using the oligonucleotide, and a kit comprising the oligonucleotide are provided. The oligonucleotide comprises a nucleoside labeled with a fluorophore and at least one neighboring nucleoside positioned next to the fluorophore-labeled nucleoside, the nucleobase of the neighboring nucleoside being thymine or cytosine.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
Method of detecting target base sequence of rna interference, method of designing polynucleotide base sequence causing rna interference, method of constructing double-stranded polynucleotide, method of regulating gene expression, base sequence processing apparatus, program for running base sequence processing method on comp
InactiveUS20060275762A1Simplified and efficientBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCytotoxicityPurine
In the present invention, a sequence segment conforming to the following rules (a) to (d) is searched from the base sequences of a target gene of RNA interference and, based on the search results, siRNA capable of causing RNAi is designed, synthesized, etc.: (a) The 3′ end base is adenine, thymine, or uracil, (b) The 5′ end base is guanine or cytosine, (c) A 7-base sequence from the 3′ end is rich in one or more types of bases selected from the group consisting of adenine, thymine, and uracil, and (d) The number of bases is within a range that allows RNA interference to occur without causing cytotoxicity.
Owner:BIO THINK TANK
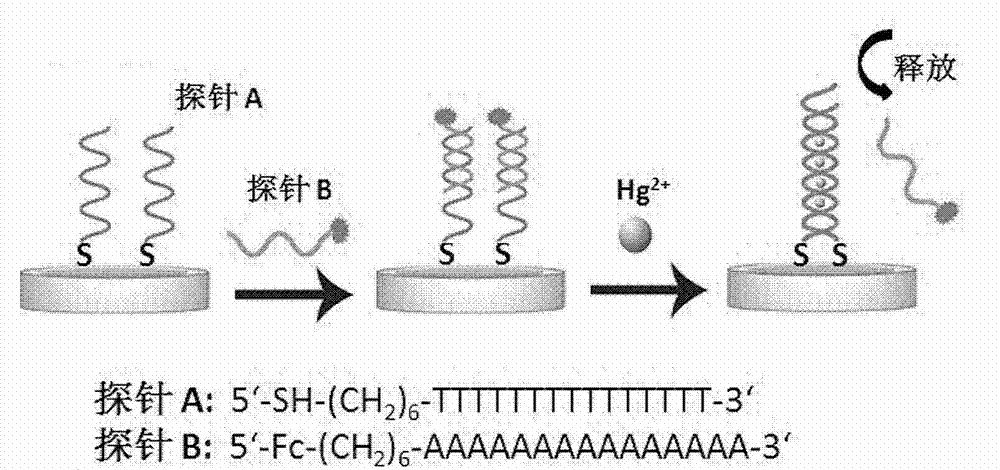
SERS (Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering) sensor for detecting mercury ions as well as preparation method and detection method thereof
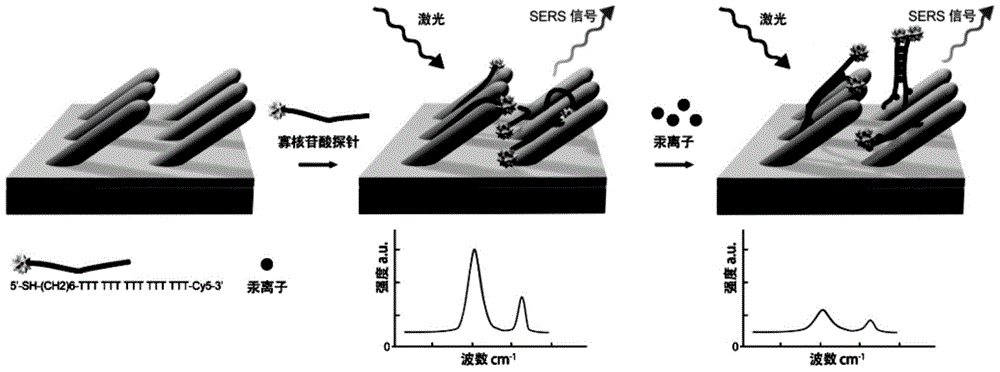
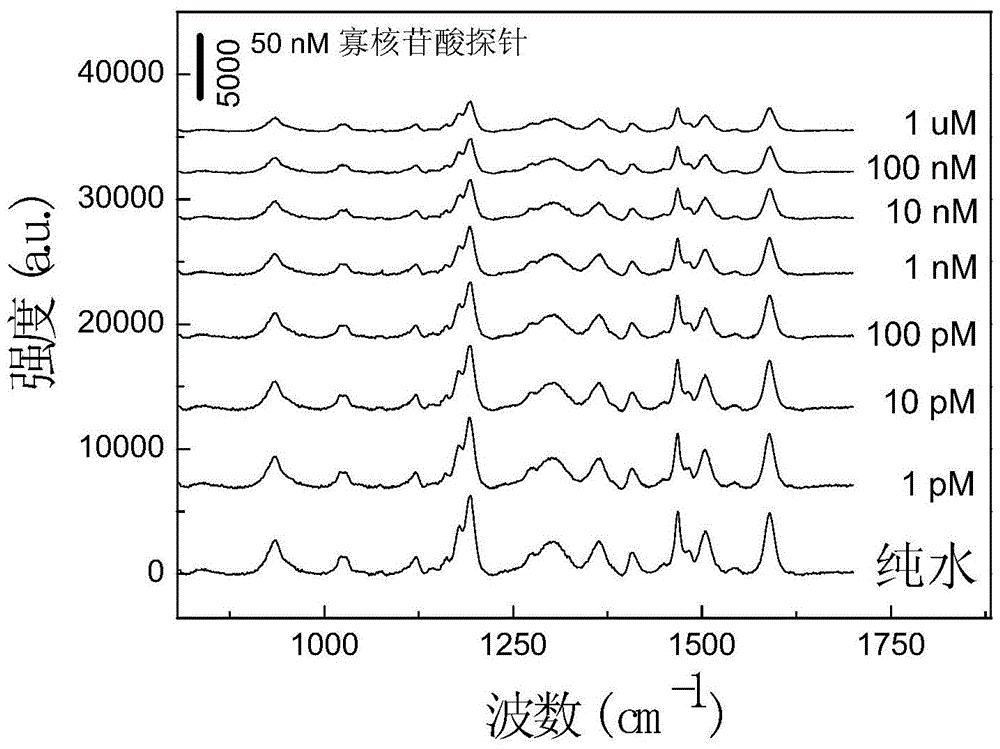
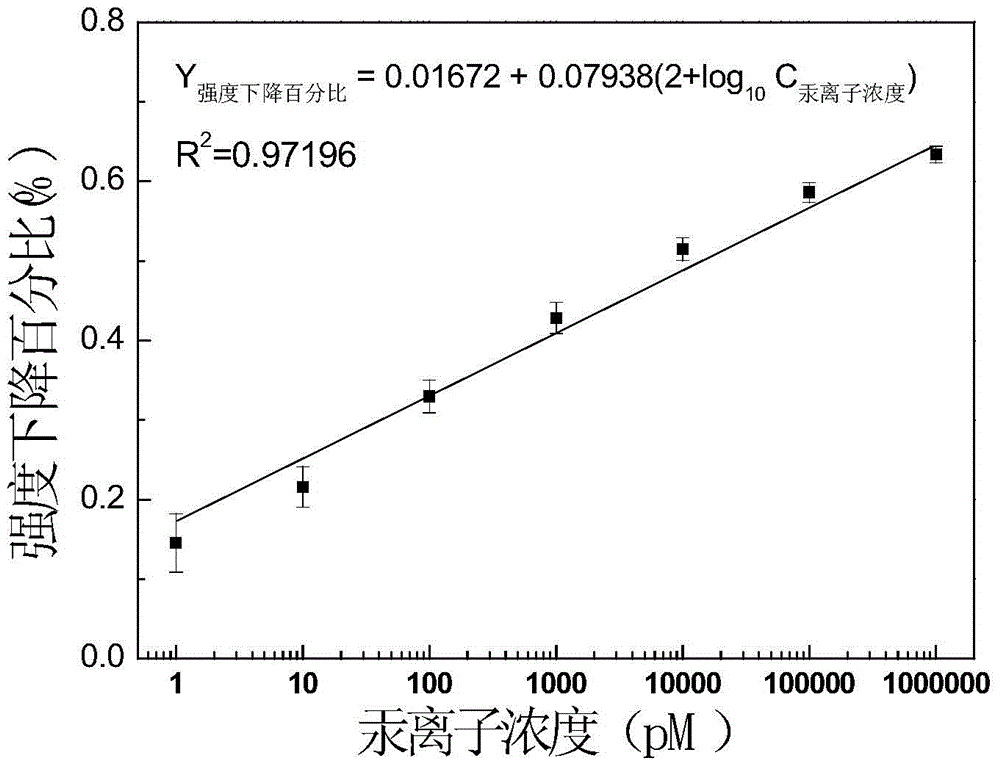
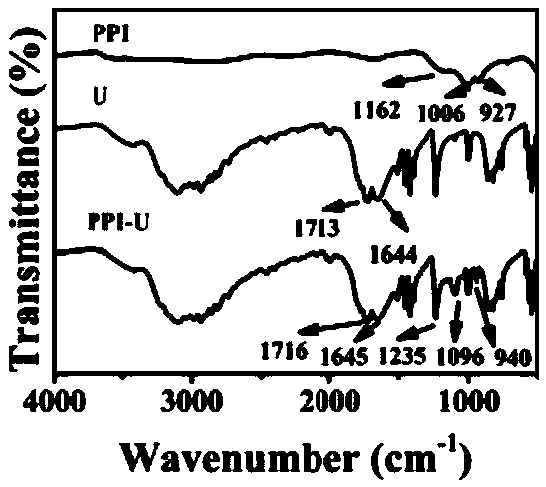
InactiveCN105699355AEasy to separateExcellent uniformityRaman scatteringThymineUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses an SERS (Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering) sensor for detecting mercury ions as well as a preparation method and a detection method thereof. The sensor is obtained by modifying an oligonucleotide probe chain to the surface of a solid SERS substrate, wherein the oligonucleotide probe chain is composed of three parts; and one end of the oligonucleotide probe chain is modified by sulfydryl and is connected with a base, the other end of the oligonucleotide probe chain is modified by Raman dyestuff, and the middle part is composed of 5-25 pure thymine. The oligonucleotide probe chain is 5'-SH-(CH2)6-TTT TTT TTT TTT TTT-Cy5-3'. The solid SERS substrate is a silver nano rod array type SERS substrate. When the SERS sensor is used, the sensor is directly immersed into a solution to be detected; and when the sample contains the mercury ions, the mercury ions can be specifically combined with an oligonucleotide probe, so that the aim that the mercury ions are detected through detecting the intensity change of an SERS signal is realized. The mercury ion SERS sensor is simple and convenient in preparation process, short in preparation time and easy to carry, can realize rapid detection of the mercury ions and has good selectivity; and the sensor has no obvious interference on other metal ions and has high sensitivity, and the detection limit can reach the magnitude order of -0.1pM.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for synthesizing fluorescent copper nanocluster with thymine as template
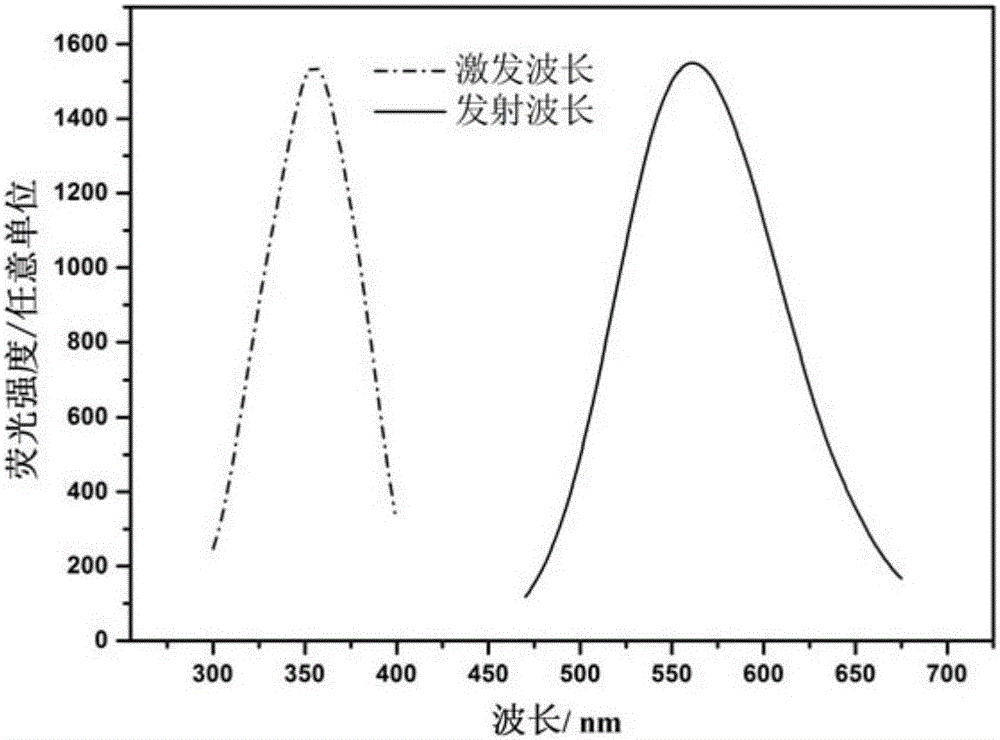
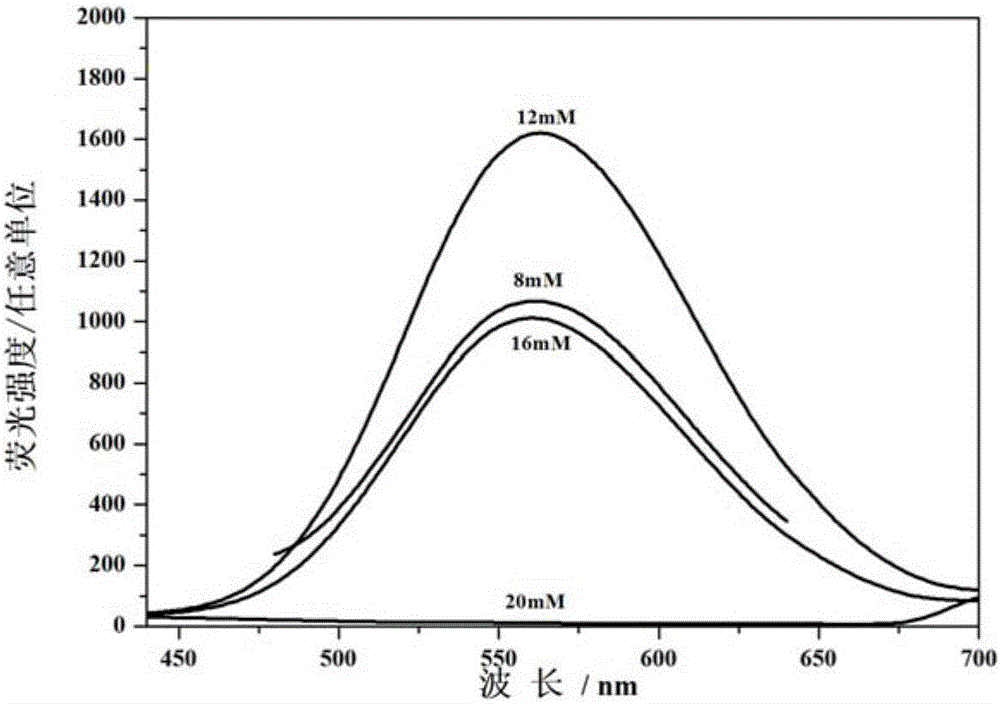
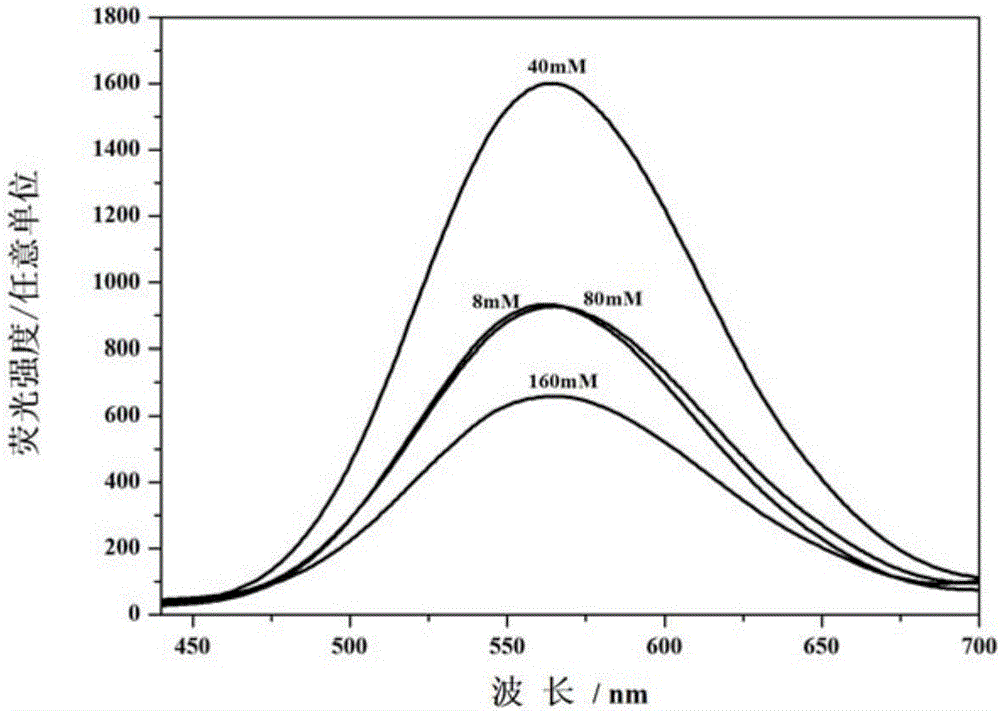
InactiveCN105834444AImprove stabilityHigh fluorescence intensityMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingThymineHydroxylamine Hydrochloride
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing fluorescent copper nanocluster with thymine as a template, and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The method comprises the following steps: (1) thymine solution is uniformly mixed with copper sulfate solution; and the mole ratio of thymine to copper sulfate is 2-5: 2; (2) hydroxylamine hydrochloride solution is added in the product obtained in the step (1) for uniform mixing; and the mole ratio of thymine, copper sulfate and hydroxylamine hydrochloride is 2-5: 2: 2-40; and (3) the product obtained in the step (2) is adjusted pH to 7-12, and is reacted by 1-2 h. The method has the following beneficial effects: thymine is introduced as the template, and hydroxylamine hydrochloride serves as a reducing agent to realize synthesis of the copper nanocluster in a water phase; and compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of high stability and high fluorescence intensity.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Evolution of talens
ActiveUS20180237758A1Strong specificityHydrolasesGenetic therapy composition manufactureDNA-binding domainOff targets
Engineered transcriptional activator-like effectors (TALEs) are versatile tools for genome manipulation with applications in research and clinical contexts. One current drawback of TALEs is that the 5′ nucleotide of the target is specific for thymine (T). TALE domains with alternative 5′ nucleotide specificities could expand the scope of DNA target sequences that can be bound by TALEs. This disclosure provides methods and strategies for the continuous evolution of proteins comprising DNA-binding domains, e.g., TALE domains. In some aspects, this disclosure provides methods and strategies for evolving such proteins under positive selection for a desired DNA-binding activity and / or under negative selection against one or more undesired (e.g., off-target) DNA-binding activities. Some aspects of this disclosure provide engineered TALE domains and TALEs comprising such engineered domains, e.g., TALE nucleases (TALENs), TALE transcriptional activators, TALE transcriptional repressors, and TALE epigenetic modification enzymes, with altered 5′ nucleotide specificities of target sequences. Engineered TALEs that target ATM with greater specificity are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Vectors, cells and processes for pyrimidine deoxyribonucleosides production
Novel DNA constructs and host cells comprising the same are disclosed. DNA constructs comprise a transcription unit (e.g. operon) comprising DNA sequences encoding for ribonucleotide reductase and thioredoxin. In preferred embodiments, constructs further comprise DNA sequences encoding for thymidylate synthase and / or transcription units comprising sequences encoding for uridine kinase preferably together with dCTP deaminase. In particularly preferred embodiments, host cells comprising constructs having all of the above characteristics wherein the host cell displays repressed or no uracil DNA glycosylase activity. This may be achieved by removal of the host cell ung gene. Use of host cells in the manufacture of pyrimidine deoxyribonucleotides e.g. thymidine is also disclosed.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
Self-containing lactobacillus strain
The invention relates to a recombinant Lactobacillus strain, with limited growth and viability in the environment. More particularly, it relates to a recombinant Lactobacillus that can only survive in a medium, where well-defined medium compounds, preferably thymidine or thymine, are present. A preferred embodiment is a Lactobacillus that may only survive in a host organism, where the medium compounds are present, but cannot survive outside the host organism in absence of the medium compounds. Moreover, the Lactobacillus strain can be transformed with prophylactic and / or therapeutic molecules and can, as such, be used to treat diseases such as, but not limited to, inflammatory bowel diseases.
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW +1
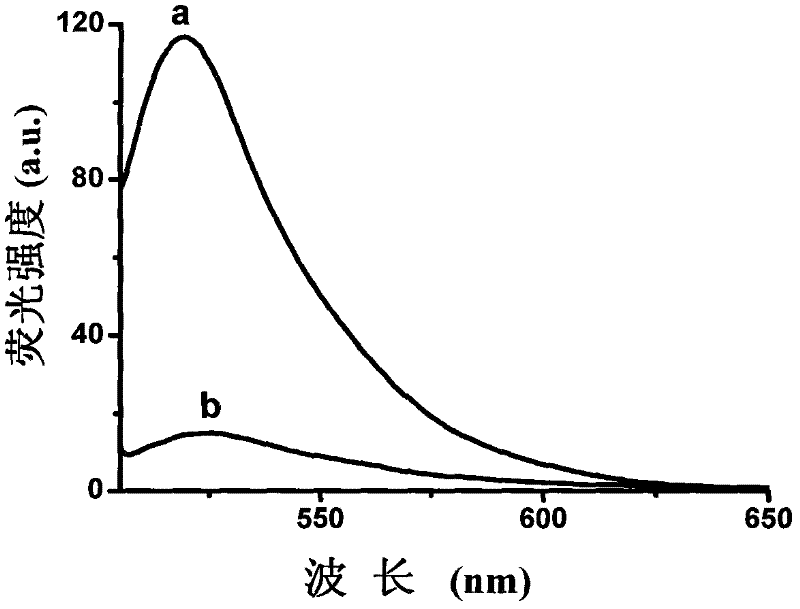
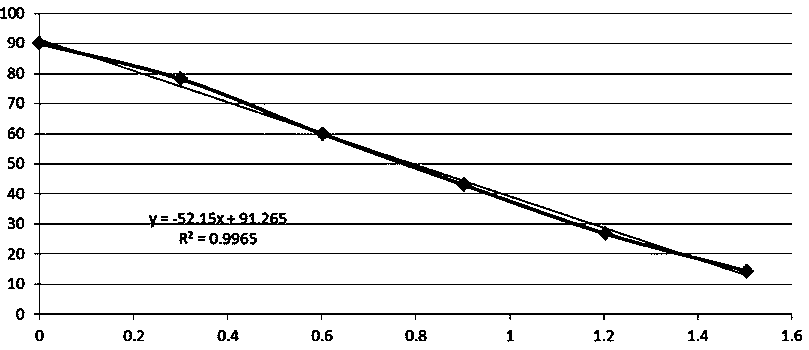
Fluorescence detection method of cysteine
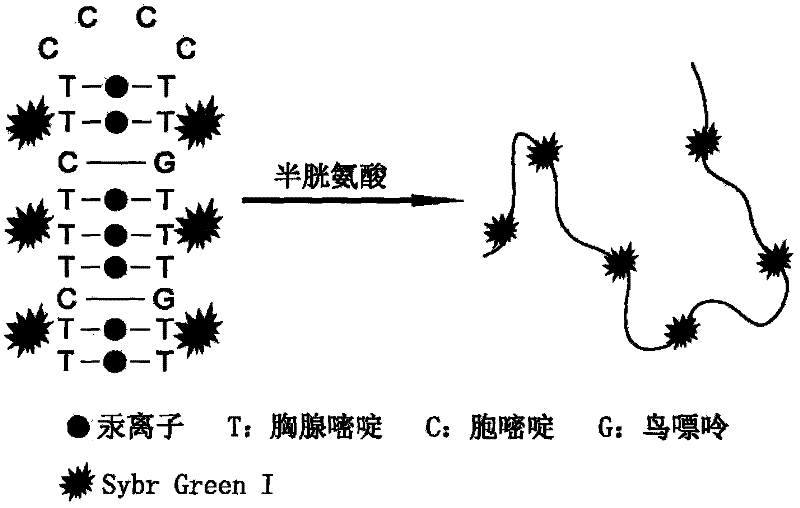
InactiveCN102183495AEasy to operateShorten detection timeFluorescence/phosphorescenceTrue positive rateThymine
The invention discloses a fluorescence detection method of cysteine. In the method, mercury ion specific DNA (mismatching of 7 pieces of thymine-thymine) is in a random curled state without the presence of mercury ions; after the mercury ions are added, a thymine-Hg2<+>-thymine (T-Hg2<+>-T) complex is formed, so that the mercury ion specific DNA has a hairpin-shaped structure; fluorescent dye Sybr Green I, which can be combined with double-chain DNA to emit light and has high fluorescence intensity, is added; and amino acids to be tested are added, when the cysteine is detected, the cysteine and the mercury ions can form a more stable complex, so that the mercury ions can be extracted from the T-Hg2<+>-T complex, the hairpin-shaped structure unwinds, the fluorescence intensity is reduced, and other amino acids cannot cause the change of the fluorescence intensity. The method is high in sensitivity and specificity, simple and quick; and the whole process can be finished within 5 minutes.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Nucleic acid aptamer sequence and detection method for quantitative and rapid detection of mercury ions
InactiveCN104212803AHigh selectivityHigh sensitivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceDNA/RNA fragmentationThyminePyrimidine
The invention relates to a nucleic acid aptamer sequence and detection method for quantitative and rapid detection of mercury ions. The nucleic acid aptamer sequence contains a stem-loop structure of thymine T with a specific length, a fluorophore is connected to a 5' terminal of a single strand, and a corresponding fluorescence quenching group is connected to a 3' terminal of the single strand, thus a self-assembling detection system is formed; when mercury ions exist, the stem-loop structure is closed, the fluorescence intensity of a reaction system is reduced, and the fluorescence intensity and the concentration of the mercury ions are in an inverse proportion. The nucleic acid aptamer sequence disclosed by the invention can be applied to the detection of the mercury ions, is relatively high in sensitivity and selectivity, and is relatively low in detection cost; a to-be-tested sample is directly added in the reaction system during detection, no other reagents need to be added in the whole detection process, and a detection result can be obtained in one step only; and the detection method is high in detection speed and is simple and convenient to operate.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
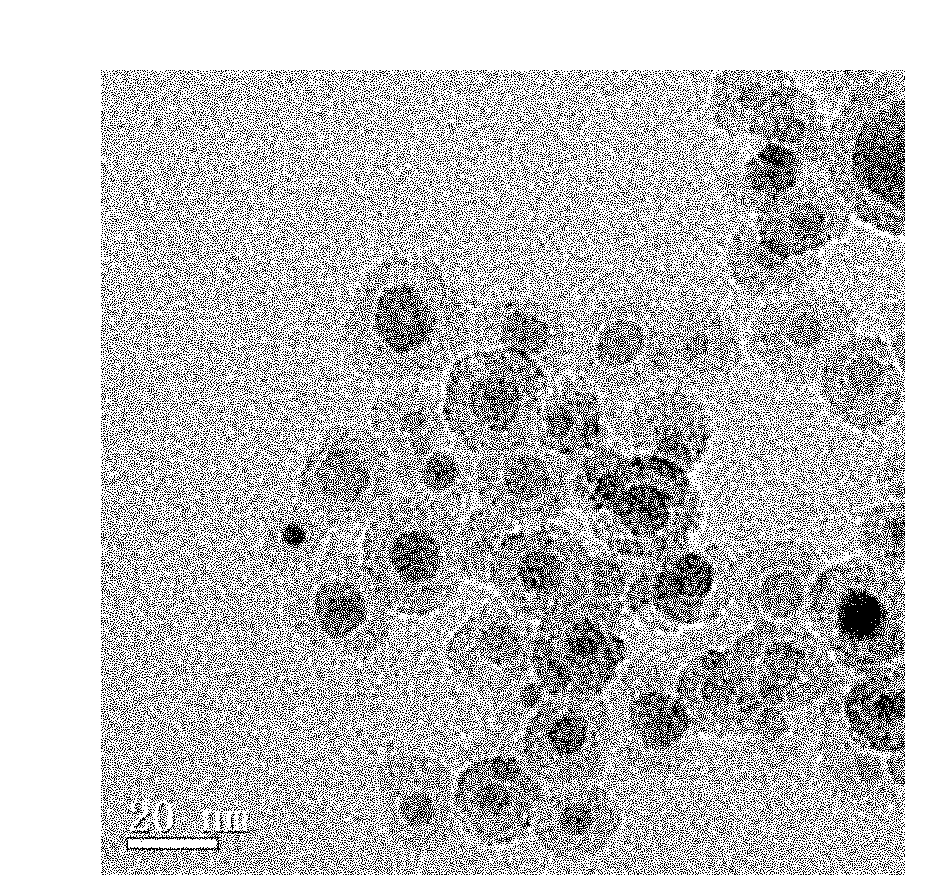
Ferroferric oxide-silicon dioxide-thymine nanoparticles and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102085381AShort reaction timeRaw materials are easy to getNMR/MRI constrast preparationsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceSolubilityNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention relates to the field of magnetic resonance contrast agents and nuclear magnetic resonance sensors and discloses ferroferric oxide-silicon dioxide-thymine nanoparticles which have water solubility, good monodispersity and superparamagnetism, and the average particle size is 10-20nm. The preparation method comprises the steps of preparing the Fe3O4 nanoparticles by high-temperature pyrolysis, wrapping silicon dioxide, connecting with amino groups, and further connecting with thymine. The nanoparticles can be used for preparing the magnetic resonance contrast agents and preparing the nuclear magnetic resonance sensors for detecting mercury ions.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Chemically cleavable 3'-o-allyl-dntp-allyl-fluorophore fluorescent nucleotide analogues and related methods
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
L-nucleic acid derivatives and process for the synthesis thereof
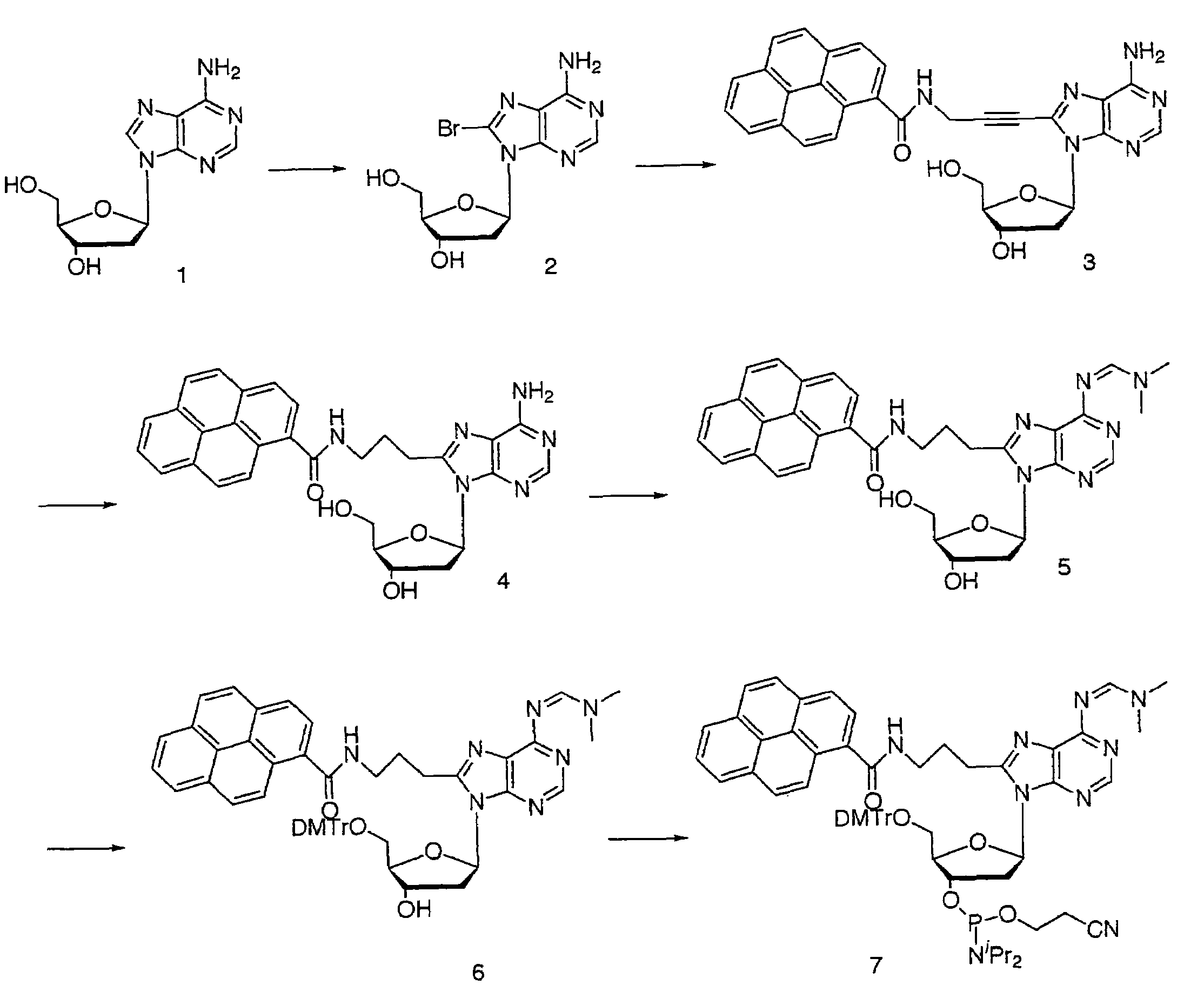
InactiveUS7125983B2Product can be usedOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesCombinatorial chemistryThymine
A novel method has been found to produce 2,2′-anhydro-1-(β-L-arabinofuranosyl)thymine as a novel useful intermediate compound. A novel method has been further found to produce thymidine from 2,2′-anhydro-1-(β-L-arabinofuranosyl)thymine. A novel method has been further found to L-2′-deoxyribose derivatives as a useful synthetic intermediate through L-2,2′-anhydro-5,6-dihydrocyclouridine derivative. According to these methods, synthesis of various L-nucleic acid derivatives, synthesis of which has been difficult till now.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
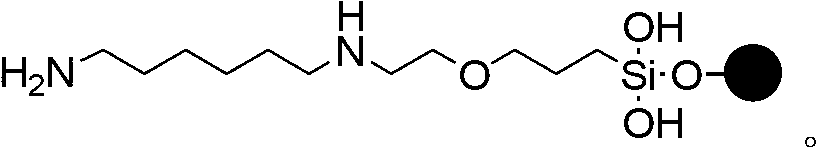
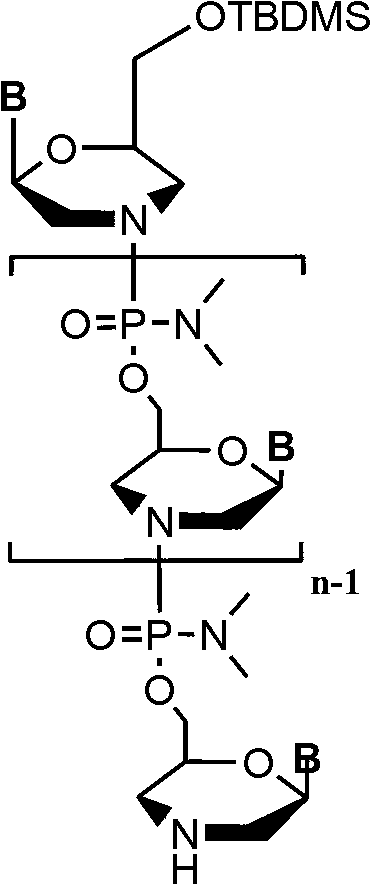
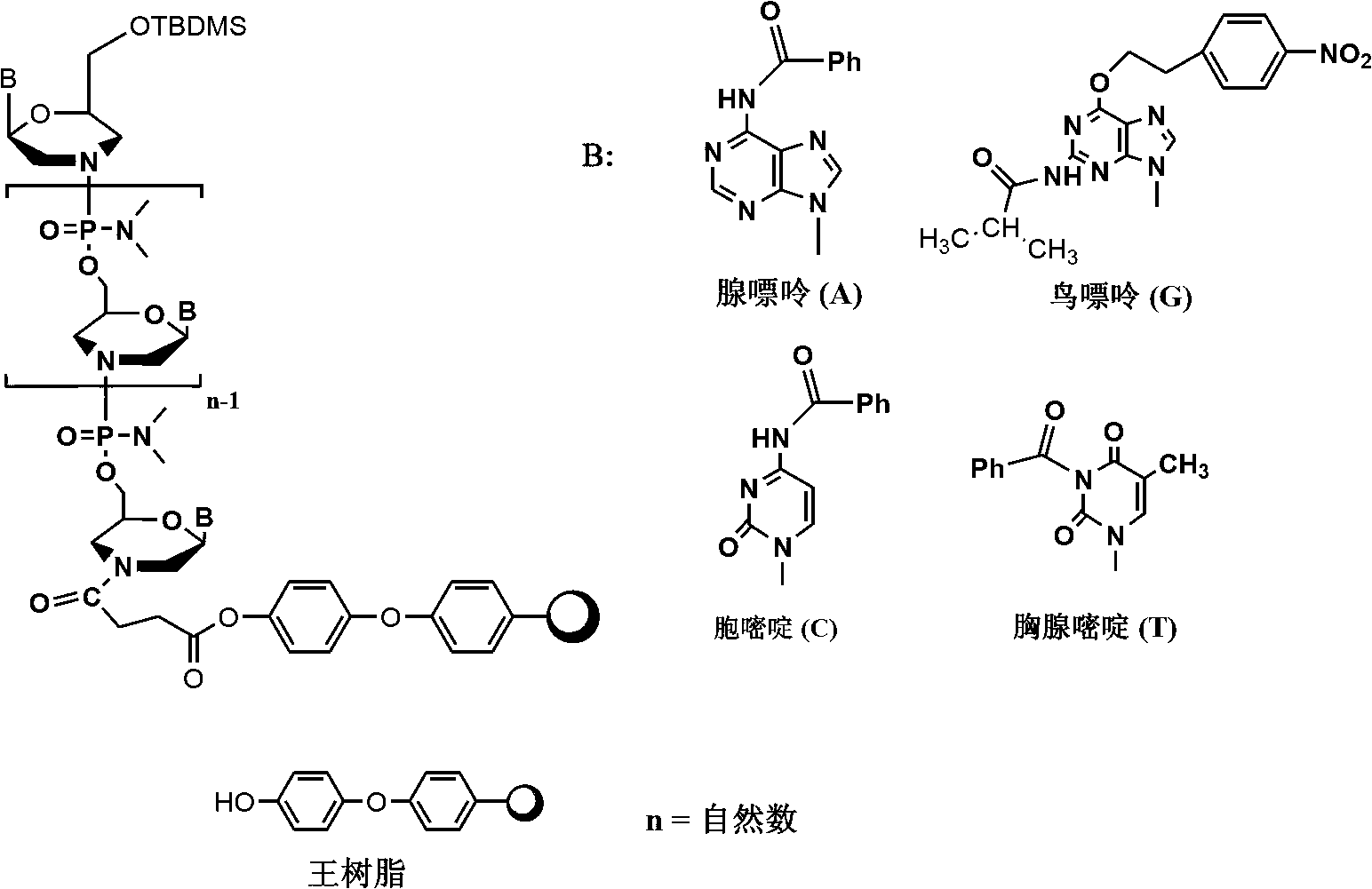
Phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer synthetized by solid phase and method thereof
The invention relates to a method for synthetizing phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer by solid phase. A cheap resin is utilized; Wang resin is as a solid phase carrier; the phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer (PMO) structure of which terminal hydroxyl is protected by tert-butyl dimethyl silicon is shown in the description, wherein a structure of basic group B is any one of adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and thymine (T). Compared with the existing solid phase synthetic technology, the method provided by the invention can greatly reduce synthetic cost, and can be suitable for mass production of phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer.
Owner:天津特安化学科技有限公司
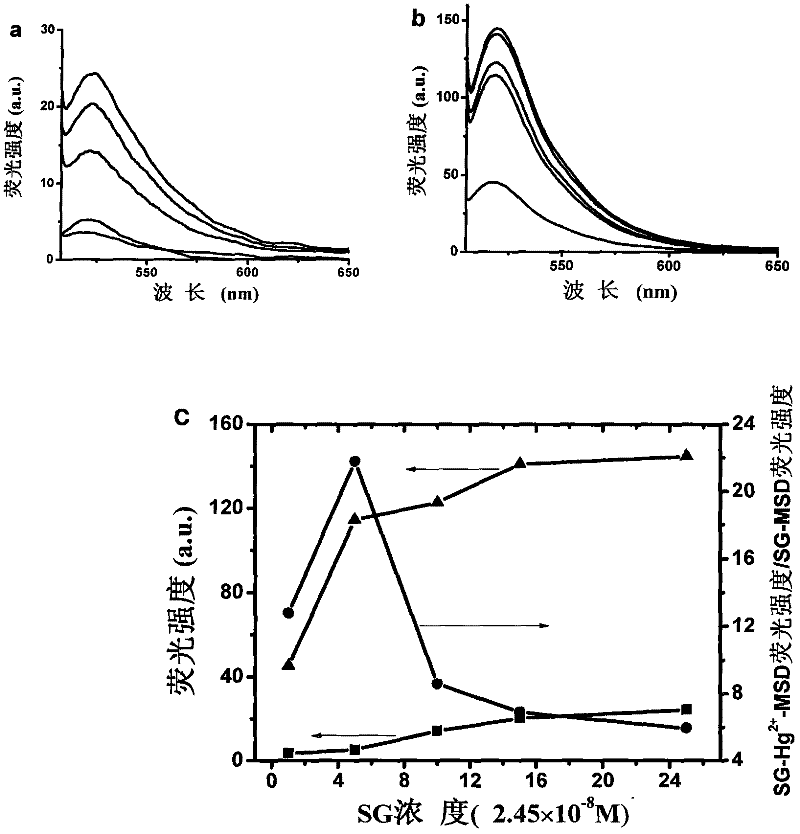
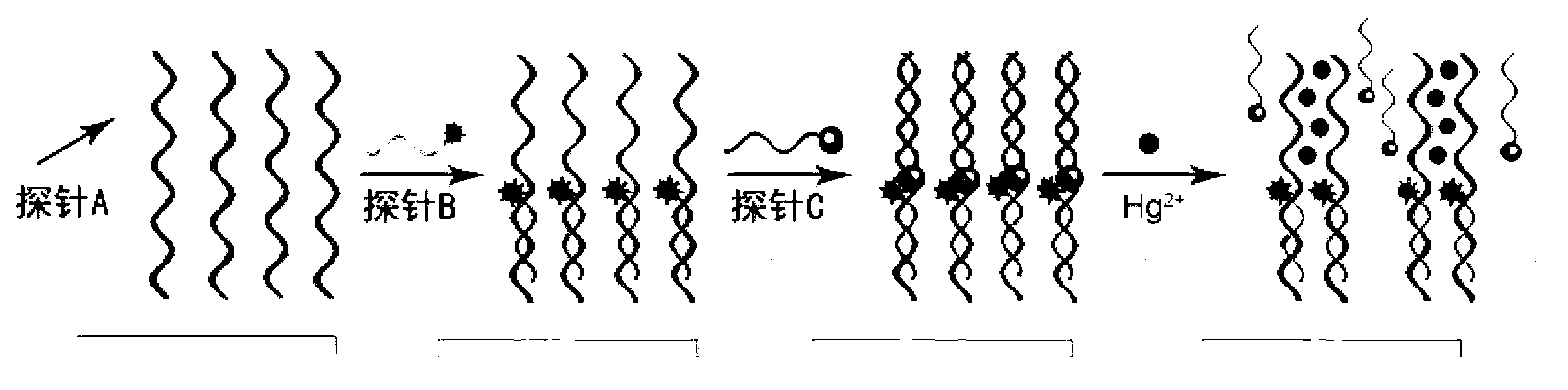
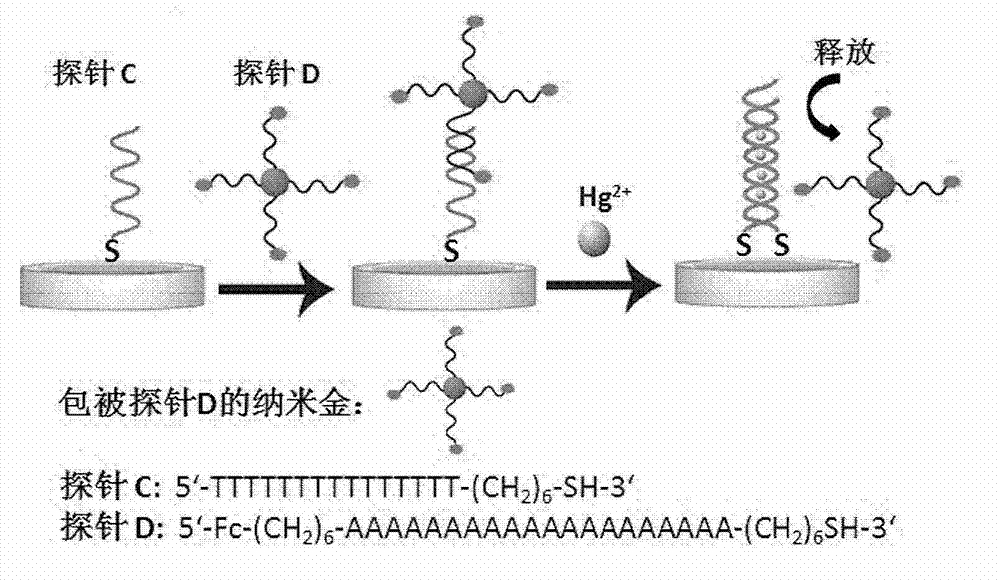
Fluorescence-enhanced Hg<2+> detection chip based on oligonucleotide chains and method thereof
InactiveCN102912011ASimple manufacturing methodHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceThymineChemical modification
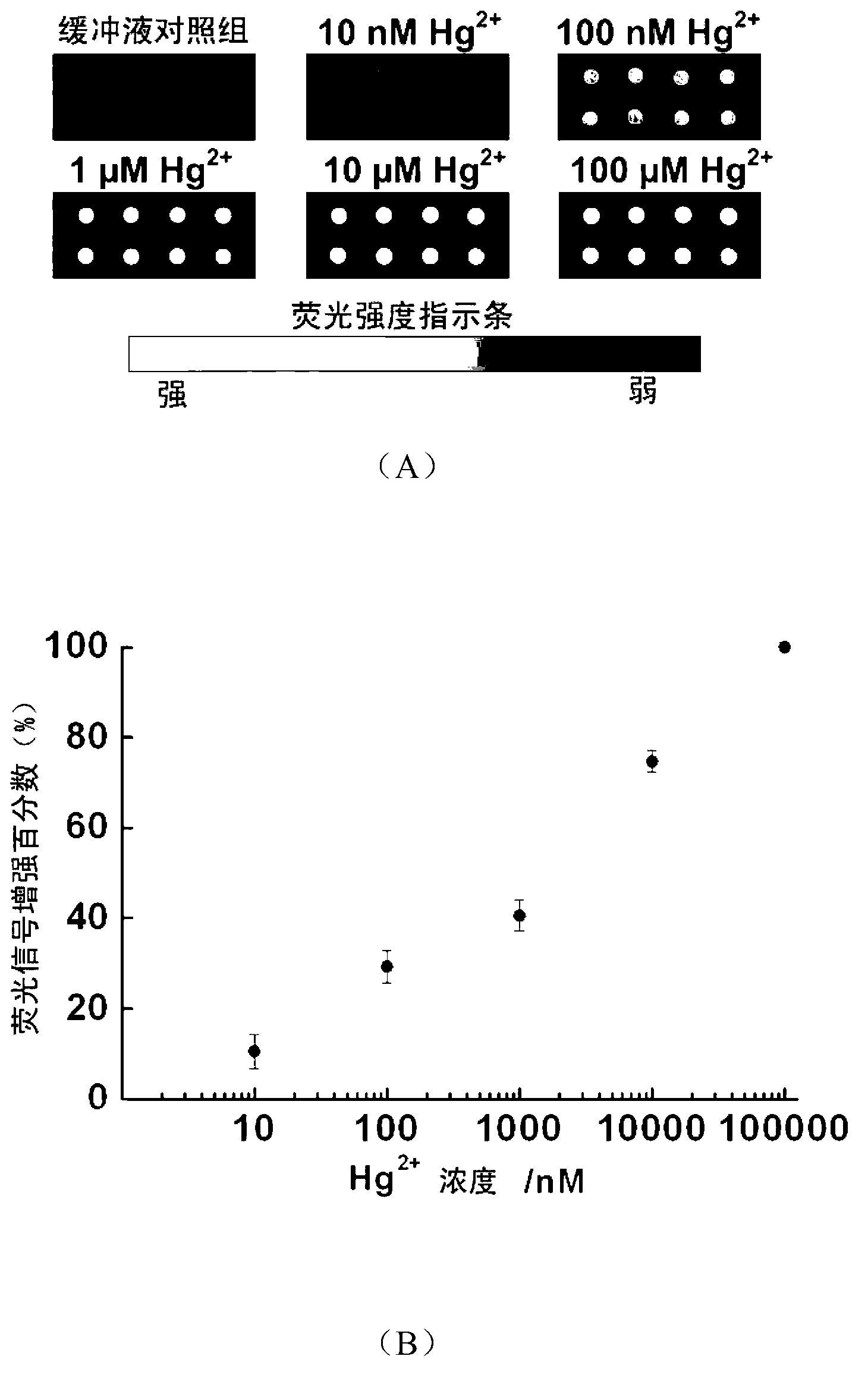
The invention relates to a fluorescence-enhanced Hg<2+> detection chip based on oligonucleotide chains and a method thereof. The invention is characterized in that Hg<2+> can specifically realize the covalent binding with T basic groups on two adjacent full thymine (T) oligonucleotide chains to form a stable intermolecular T-Hg<2+>-T structure, thus inducing the release of complementary chains hybridized with the full T oligonucleotide chains. The preparation method comprises the following steps: fixing a detection probe onto a chemically modified glass slide, and then respectively hybridizing with the fluorescence-labeled and quencher-labeled complementary chains. When the chip is in use, only a sample to be detected needs to be added onto the chip and kept for a time period, the chip is rinsed and then scanned by a fluorescence chip signal analysis system, and the change of a fluorescence signal is analyzed to realize Hg<2+> detection. The higher the Hg<2+> concentration in a sample is, the more the fluorescence signal is enhanced. The concentration range of the detected Hg<2+> is 10 nM-100 muM. The invention has favorable ionic selectivity.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Alkaloid phosphate flame retardant and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an alkaloid phosphate flame retardant and a preparation method thereof. Alkaloid phosphate is formed from alkaloid monomer X and phosphoric acid monomers Y through reaction, and is subjected to surface coating modification treatment by epoxy resin or polyurethane, and the alkaloid phosphate flame retardant is obtained. Water resistance and compatibility of the flame retardant with polymers are improved. The alkaloid monomer X is one or more of cytosine (C), uracil (U), adenine (A), guanine (G) and thymine (T). The phosphoric acid monomers Y are pyrophosphoric acid, perphosphoric acid, polyphosphoric acid, phenylphosphonic acid and phytic acid. A series of phosphorus-containing base salts are prepared from bases of bio-based compounds as a raw material, and the phosphorus-containing base salts can be used as a flame retardant additive and have higher flame retardant efficiency. Therefore, a feasible embodiment is provided for improving the flame retardant efficiency of the bio-based flame retardant additive.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
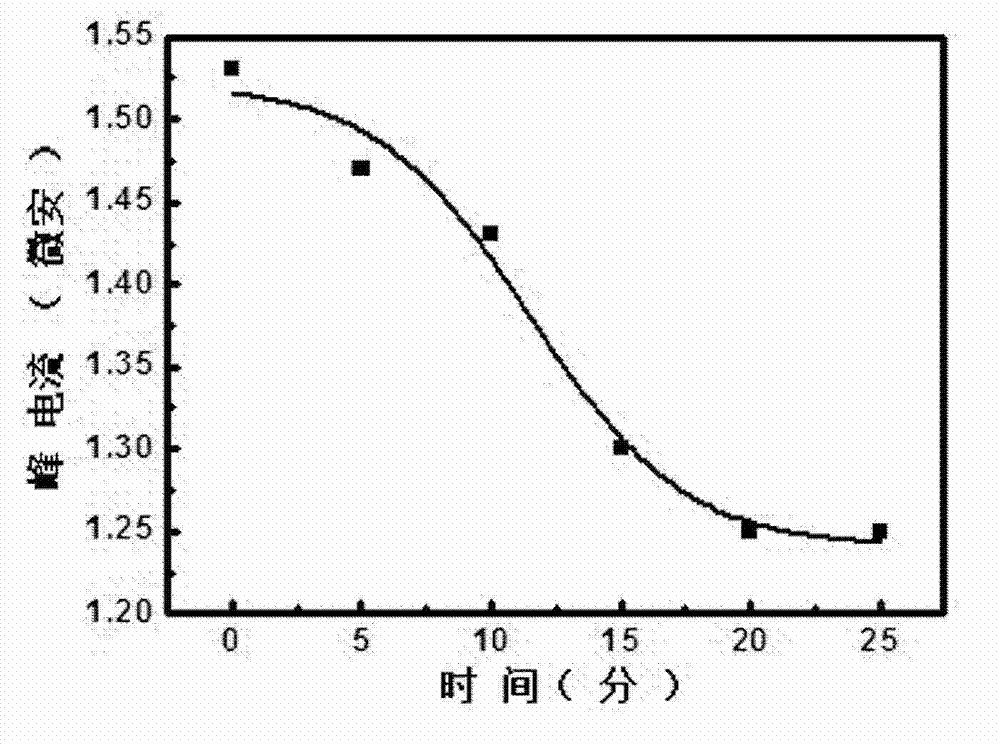
Electrochemical transducer for mercury ion detection and manufacturing method and detection method thereof
ActiveCN102778492AEasy to prepareSimple manufacturing methodMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansTransducerThymine
The invention relates to a mercury ion electrochemical transducer based on oligonucleotide chains and a manufacturing method and a detection method thereof and belongs to the technical field of bioanalysis. The method for manufacturing the sensor comprises the following steps of: fixing a full thymine (T) oligonucleotide chain subjected to chemical modification to a gold electrode; and soaking the gold electrode fixed with the full thymine (T) oligonucleotide chain into hybridization solution of full adenine (A) oligonucleotide complementary chain. The Hg2<+> can be specifically covalently bound with T bases on two adjacent full thymine (T) oligonucleotide chains, a stable intermolecular T-Hg2<+>-T structure is formed, and release of the full adenine (A) oligonucleotide complementary chain which is hybridized with the full thymine (T) oligonucleotide chain is induced. The complementary chain is released through mercury ions, so that the electrochemical signal is reduced, and the electrochemical detection of the mercury ions is realized. The detection sensitivity is greatly improved, and the electrochemical transducer has high ion selectivity.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
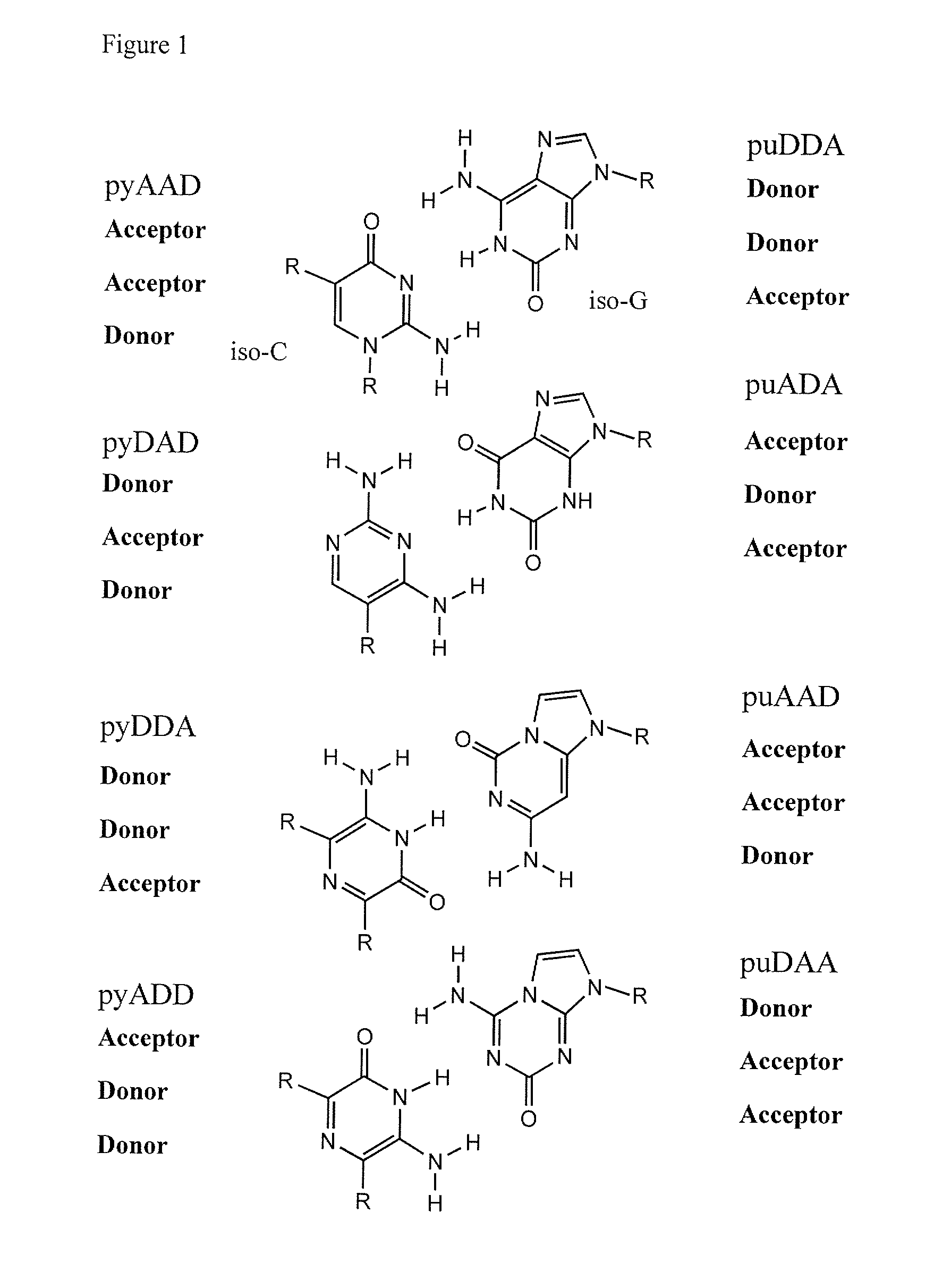
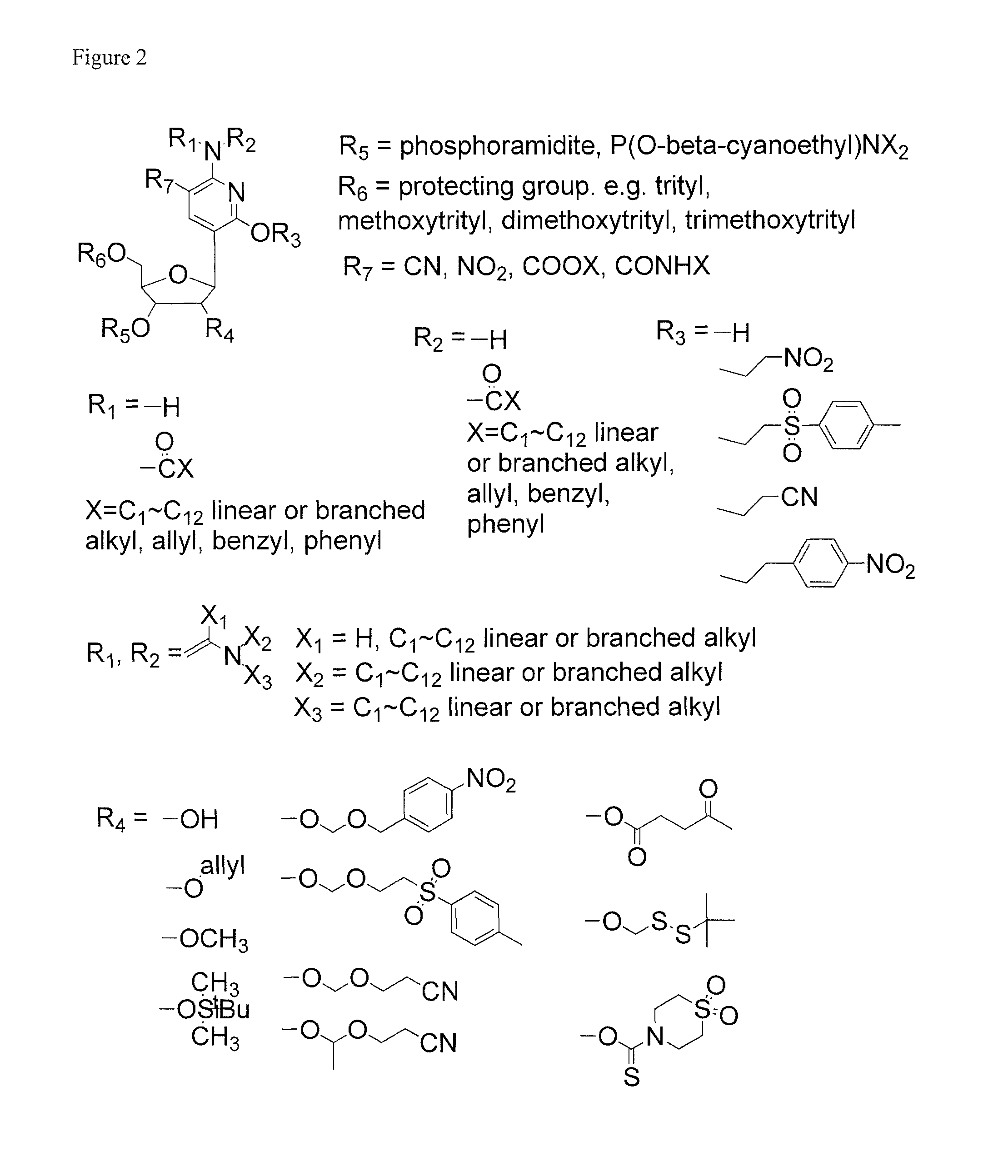
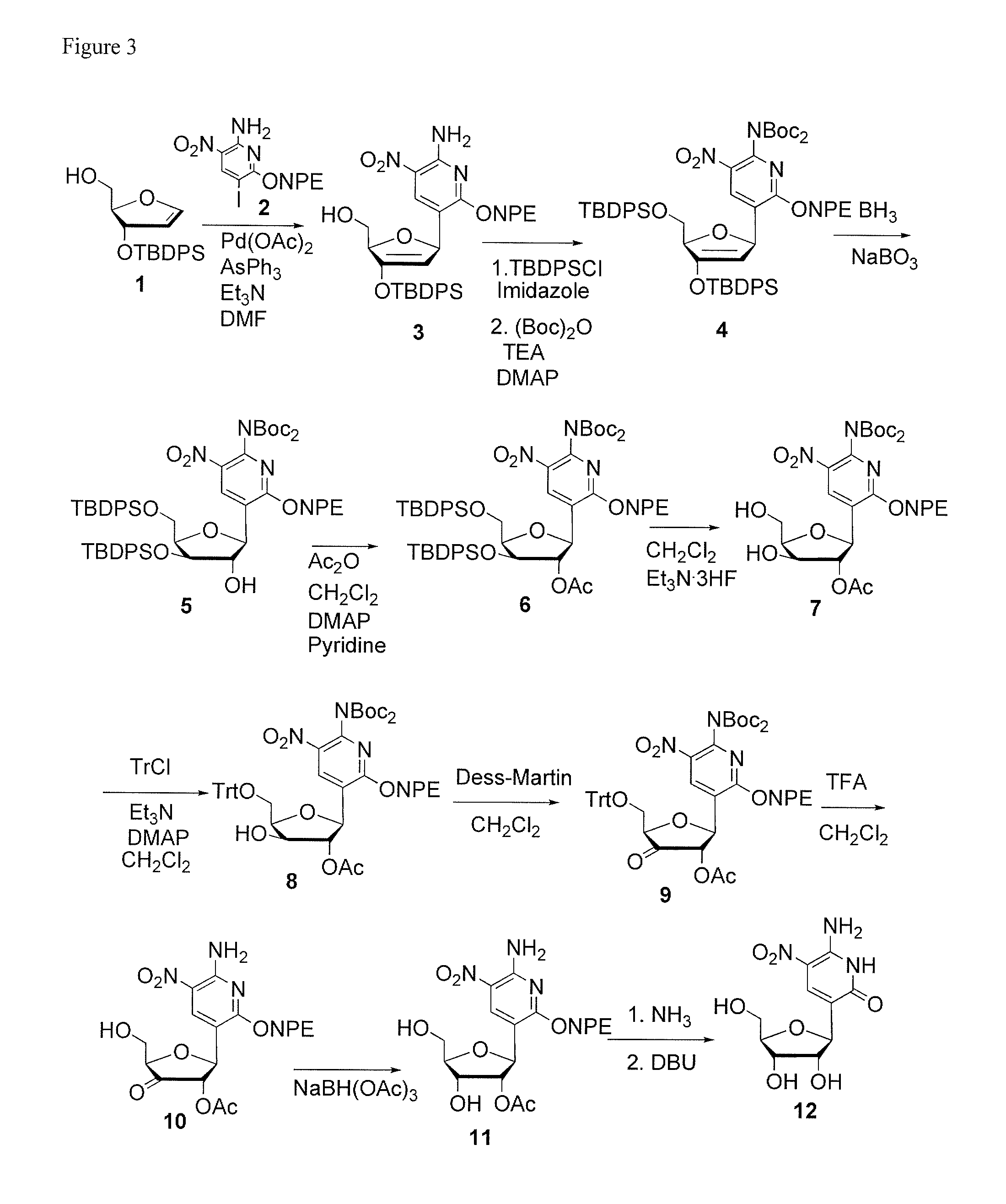
Ribonucleoside analogs with novel hydrogen bonding patterns
This invention relates to nucleoside, nucleotide, and oligonucleotide analogs that incorporate non-standard nucleobase analogs, defined to be those that present a pattern of hydrogen bonds to a paired nucleobase analog in a complementary strand that is different from the pattern presented by adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. The invention is specifically concerned with nucleotide analogs that present the donor-donor-acceptor, hydrogen bonding patterns on pyrimidine analogs, and especially those that are analogs of ribonucleotides, including protected ribonucleotides suitable for phosphoramidite-based synthesis of RNA. The heterocycles on these nucleoside analogs are aminopyridones that have electron withdrawing groups attached to the position analogous to the 5-position of the ring in standard pyrimidines, including nitro, cyano, and carboxylic acid derivatives.
Owner:BENNER STEVEN A +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com