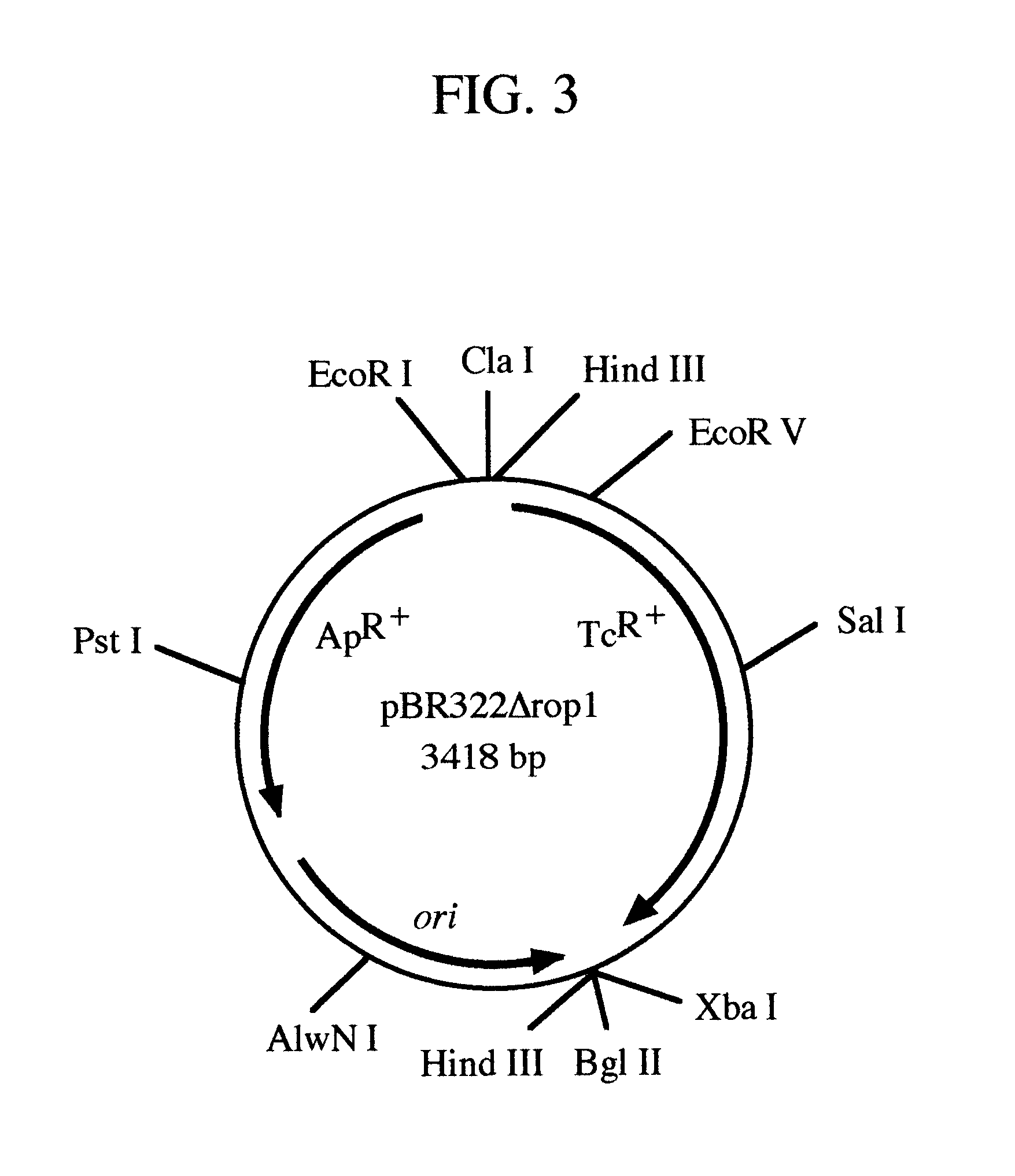
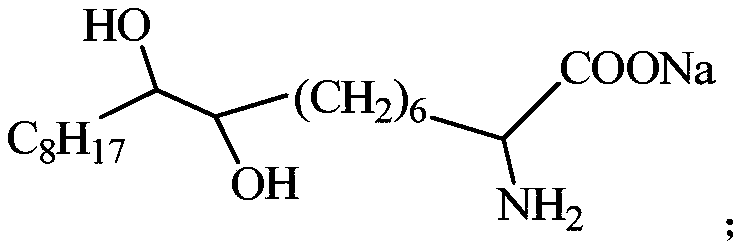Patents
Literature
93 results about "Positive selection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In population genetics, directional selection, or positive selection is a mode of natural selection in which an extreme phenotype is favored over other phenotypes, causing the allele frequency to shift over time in the direction of that phenotype. Under directional selection, the advantageous allele increases as...
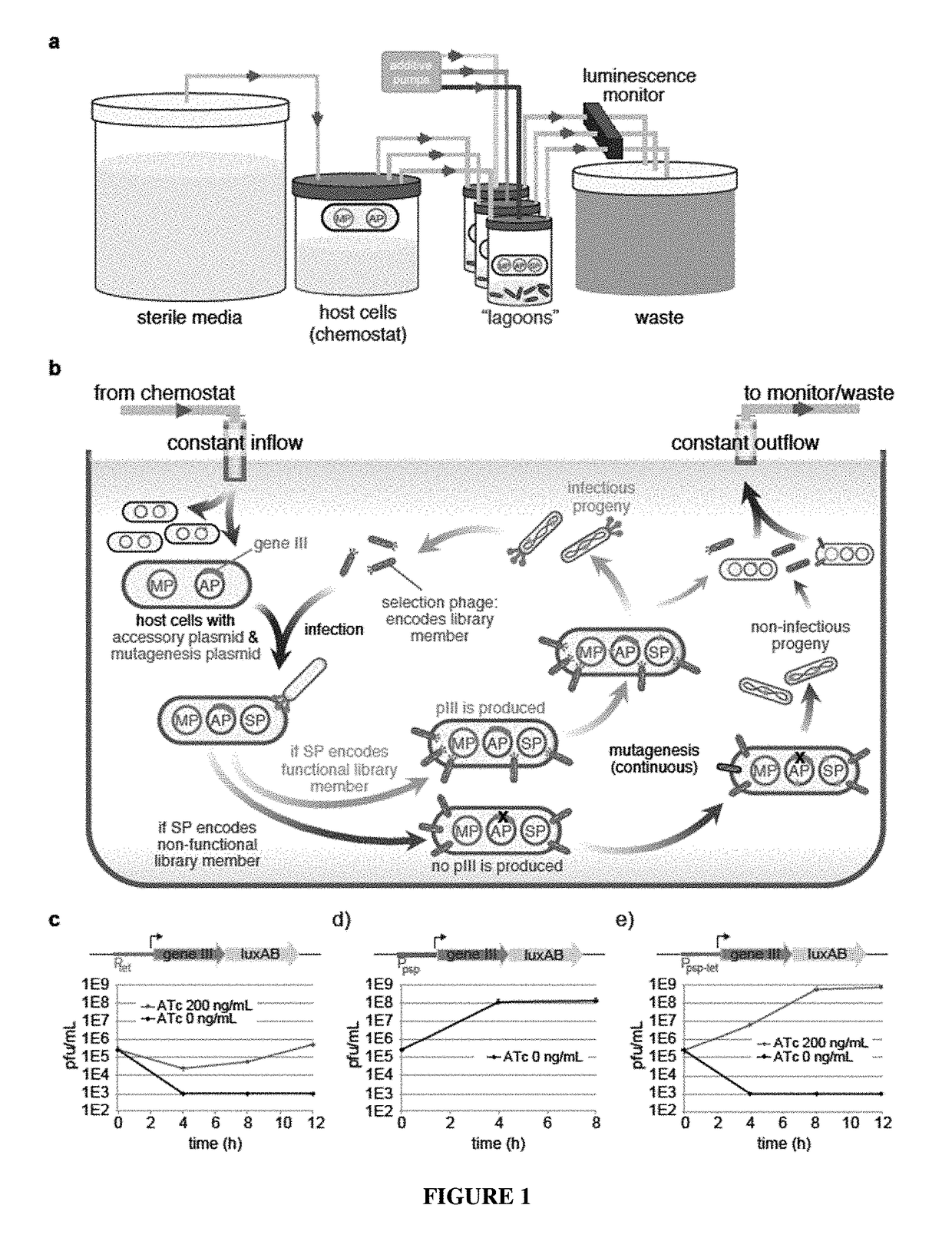
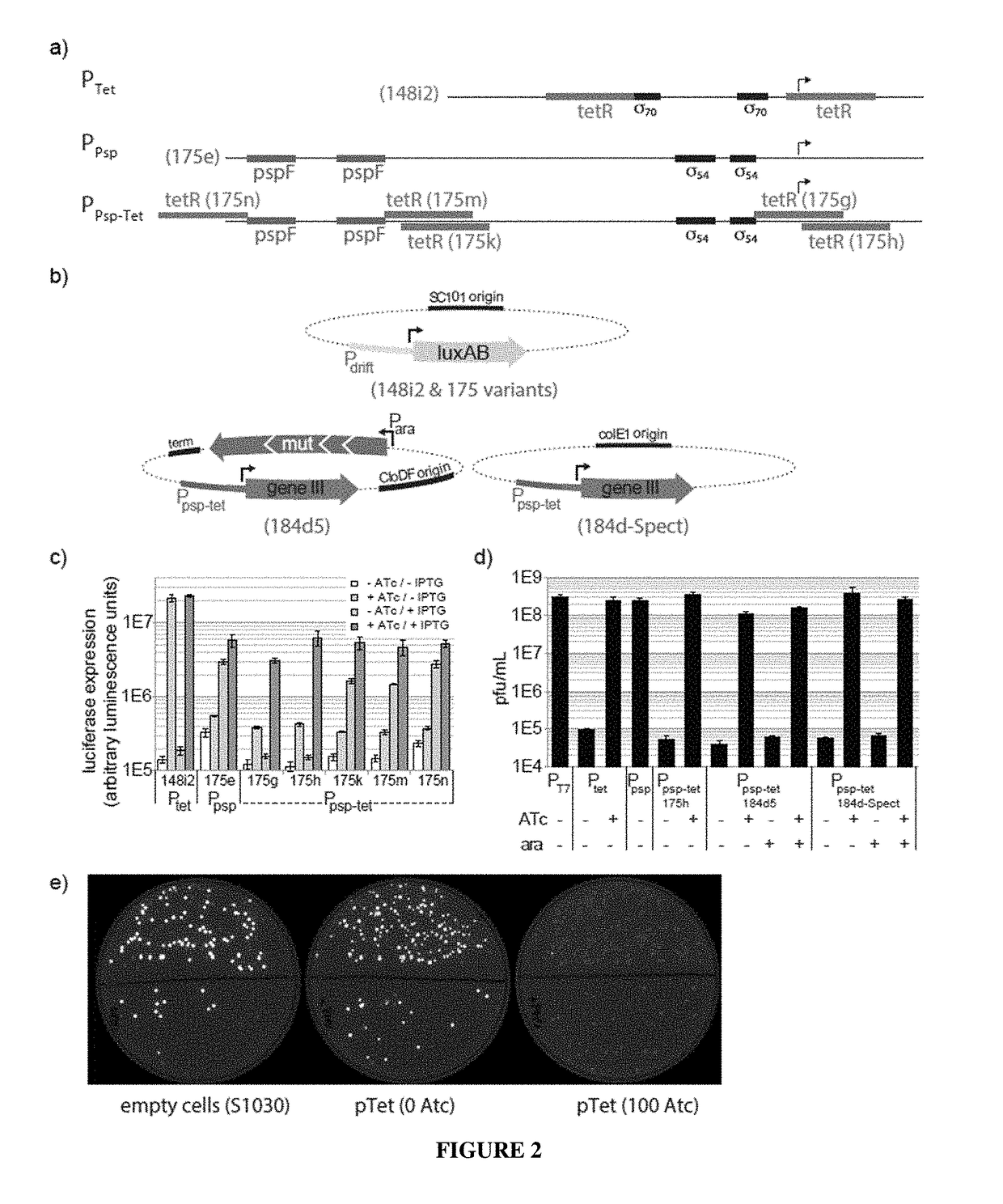
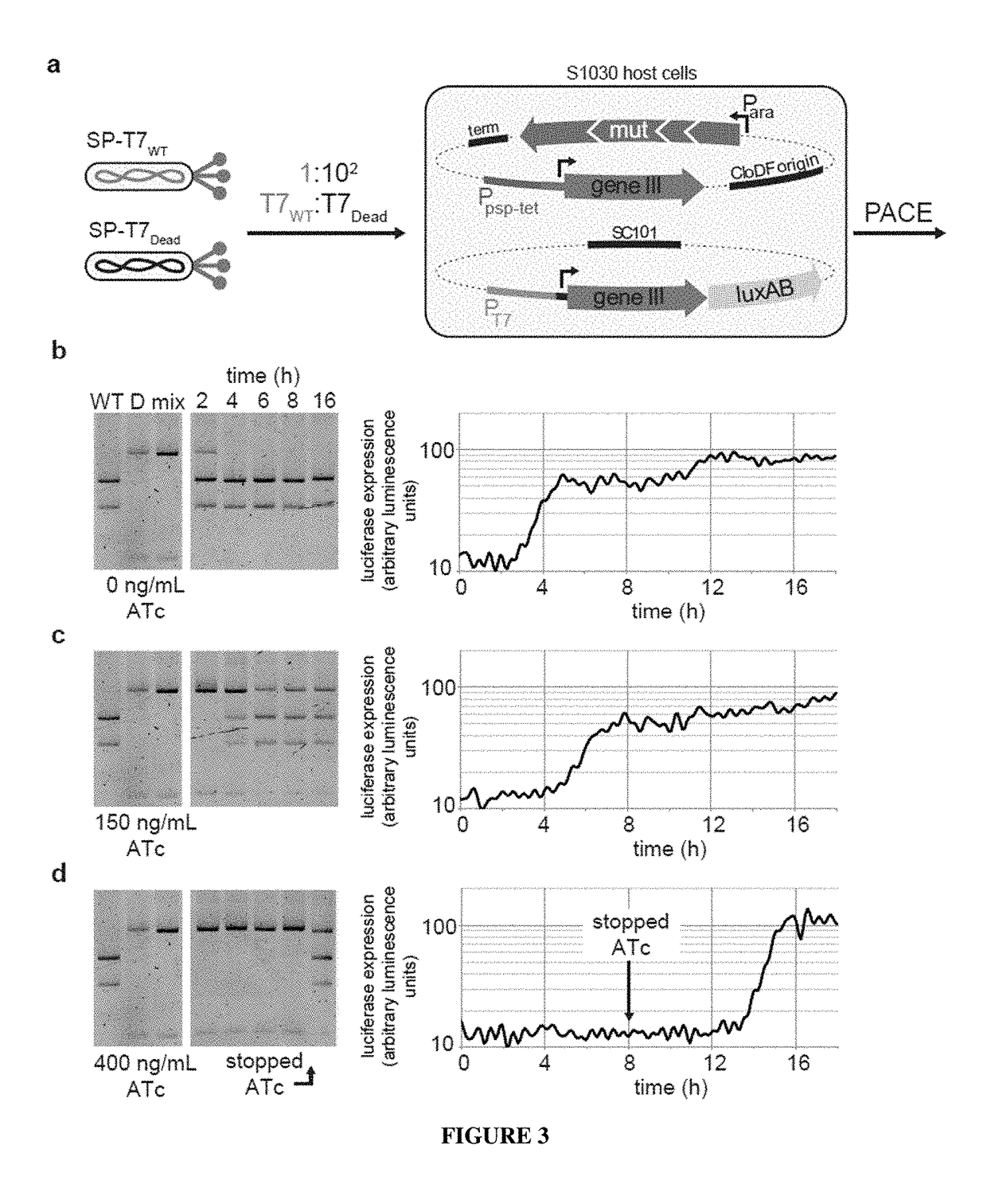
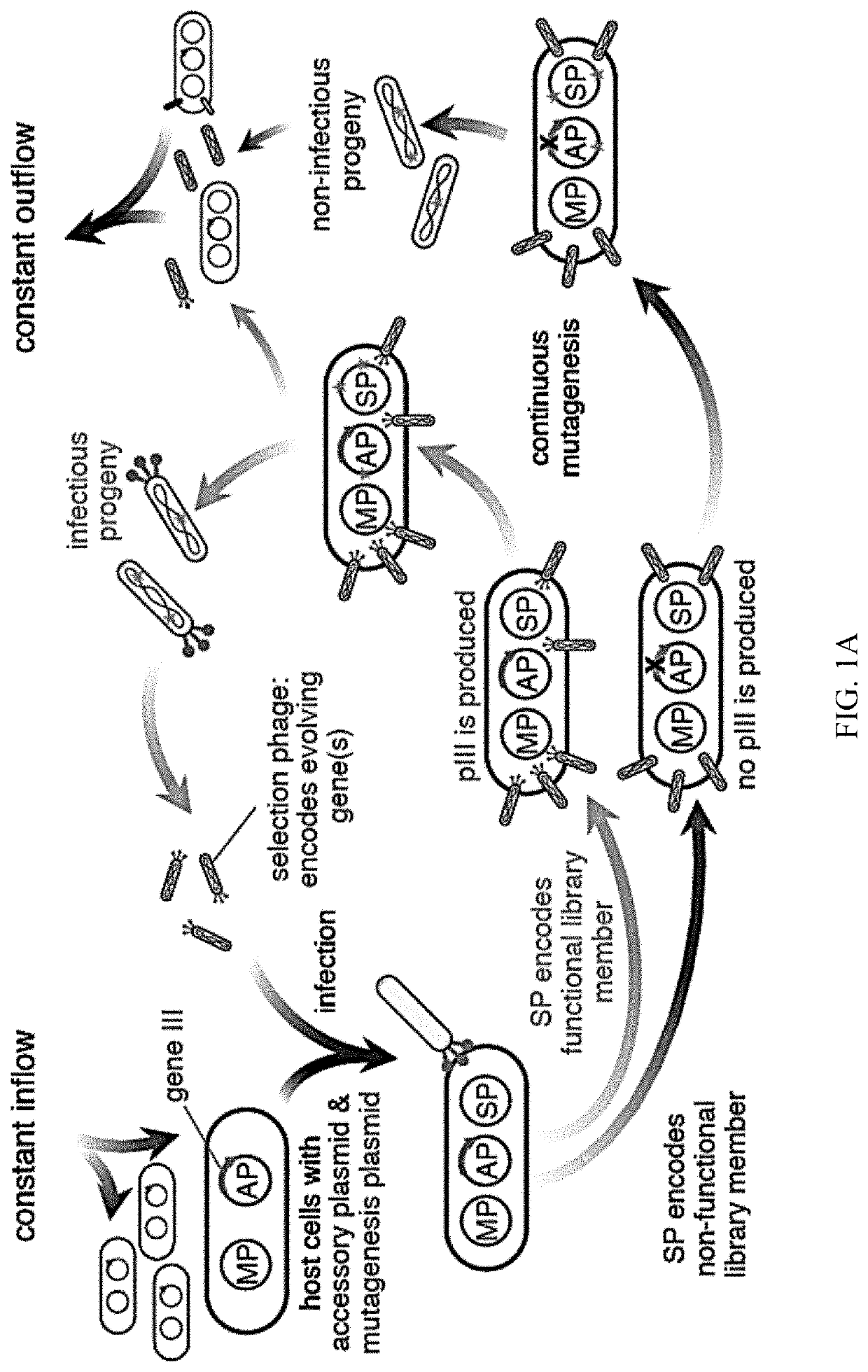
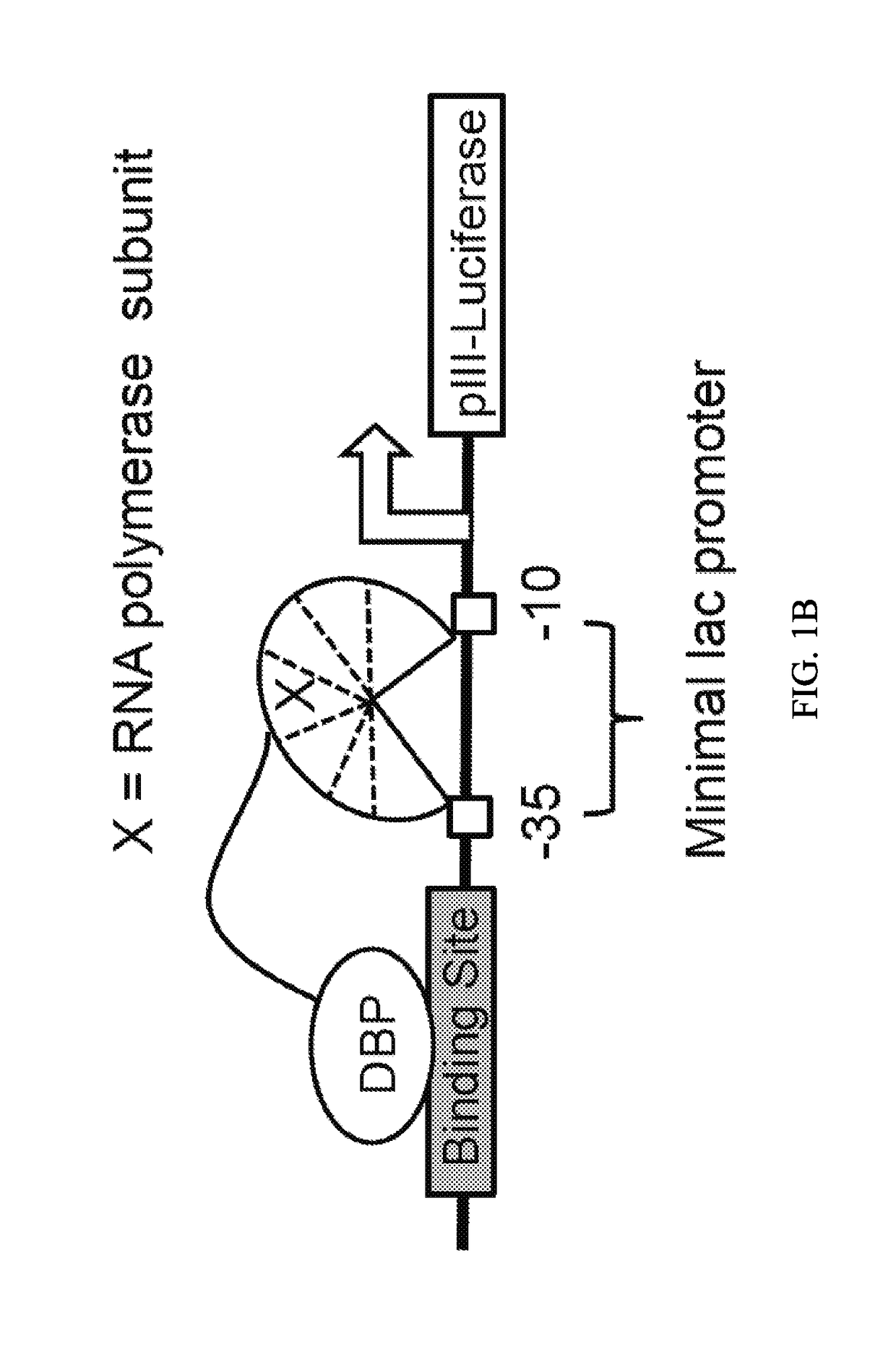
Negative selection and stringency modulation in continuous evolution systems
ActiveUS10179911B2High selectivityStrong specificityFusion with DNA-binding domainAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPositive selectionBiology
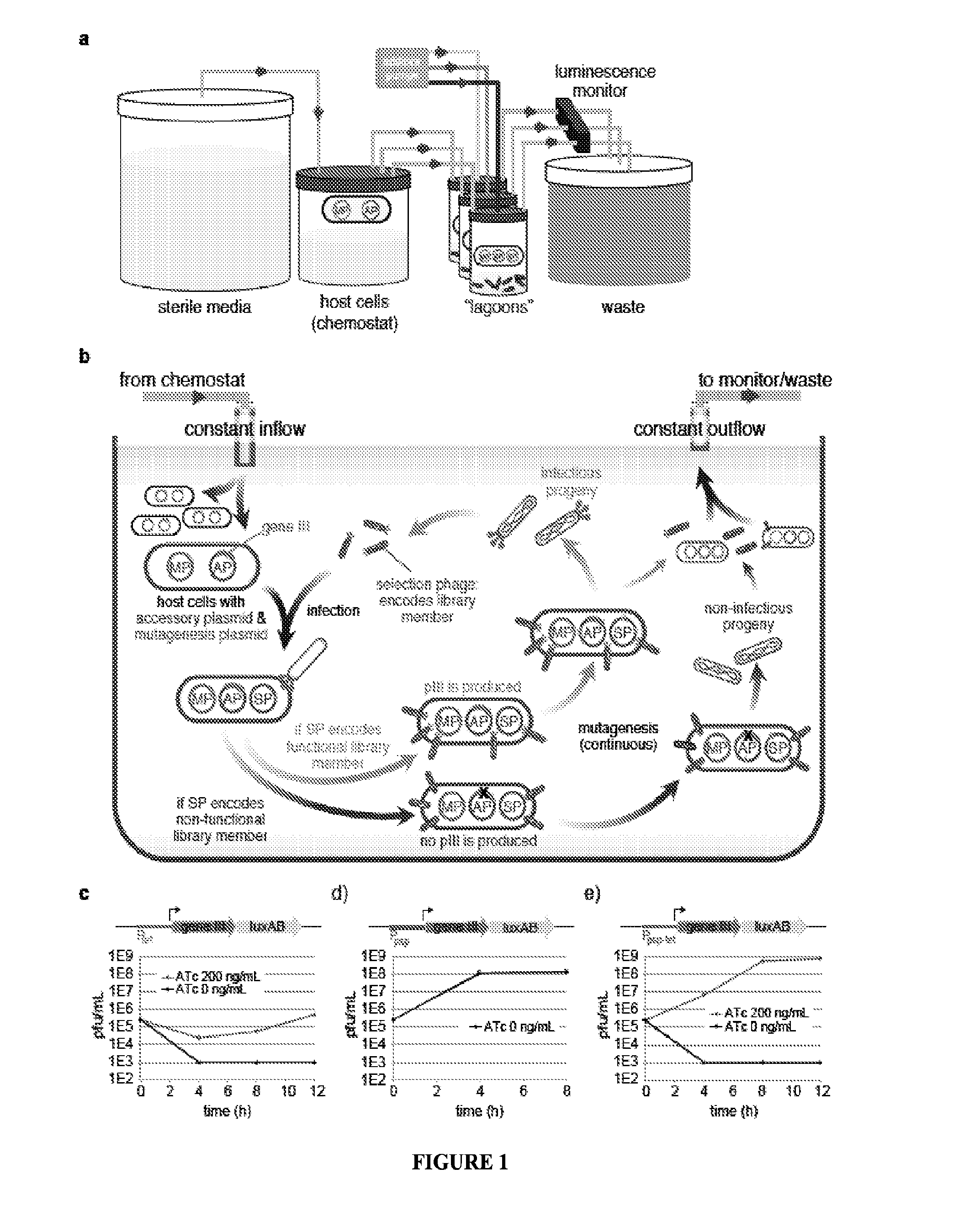
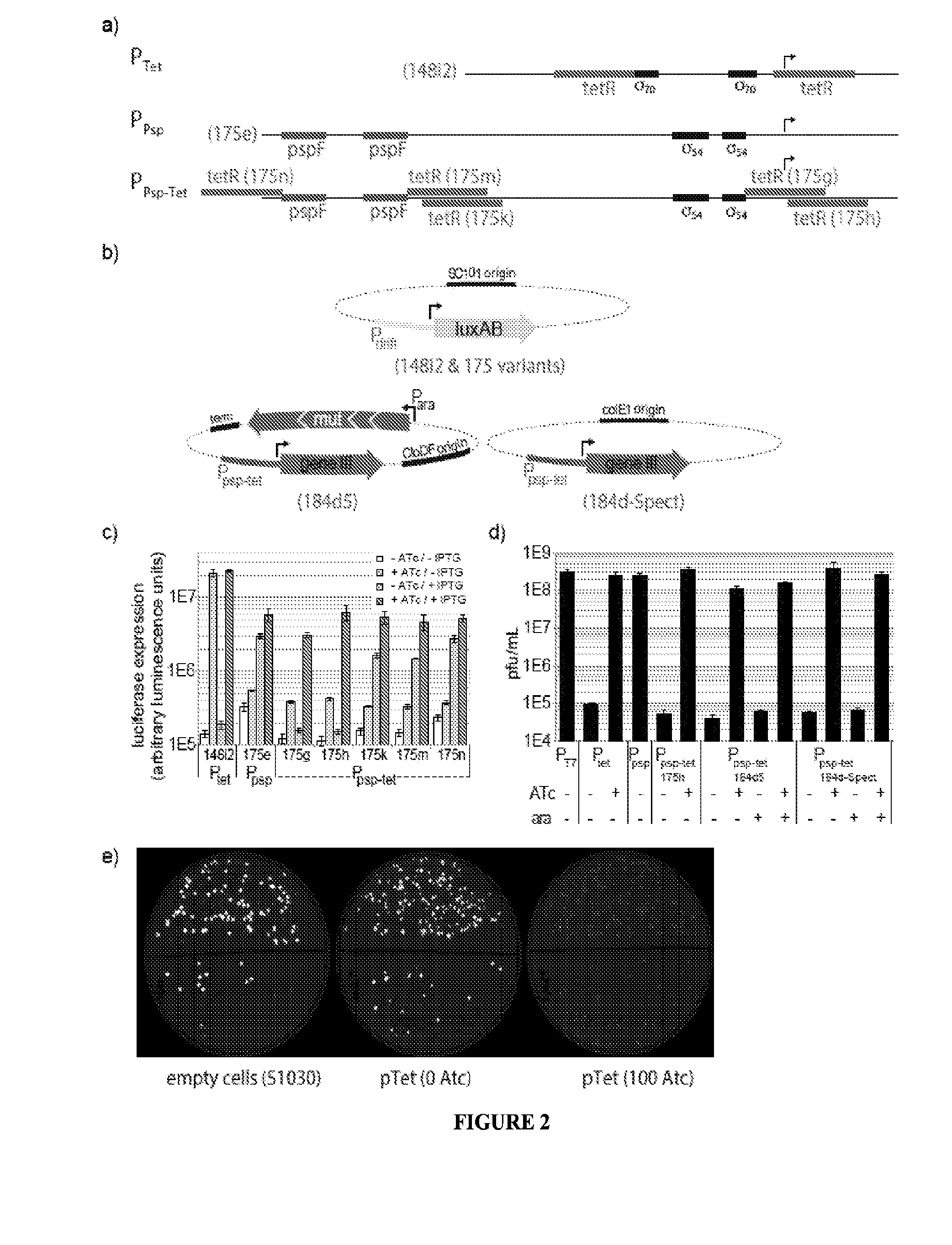
Strategies, systems, methods, reagents, and kits for phage-assisted continuous evolution are provided herein. These include strategies, systems, methods, reagents, and kits allowing for stringency modulation to evolve weakly active or inactive biomolecule variants, negative selection of undesired properties, and / or positive selection of desired properties.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Methods for enhancing segregation of transgenes in plants and compositions thereof
ActiveUS7288694B2Increase nutritionIncrease productionSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesSTATH genePositive selection
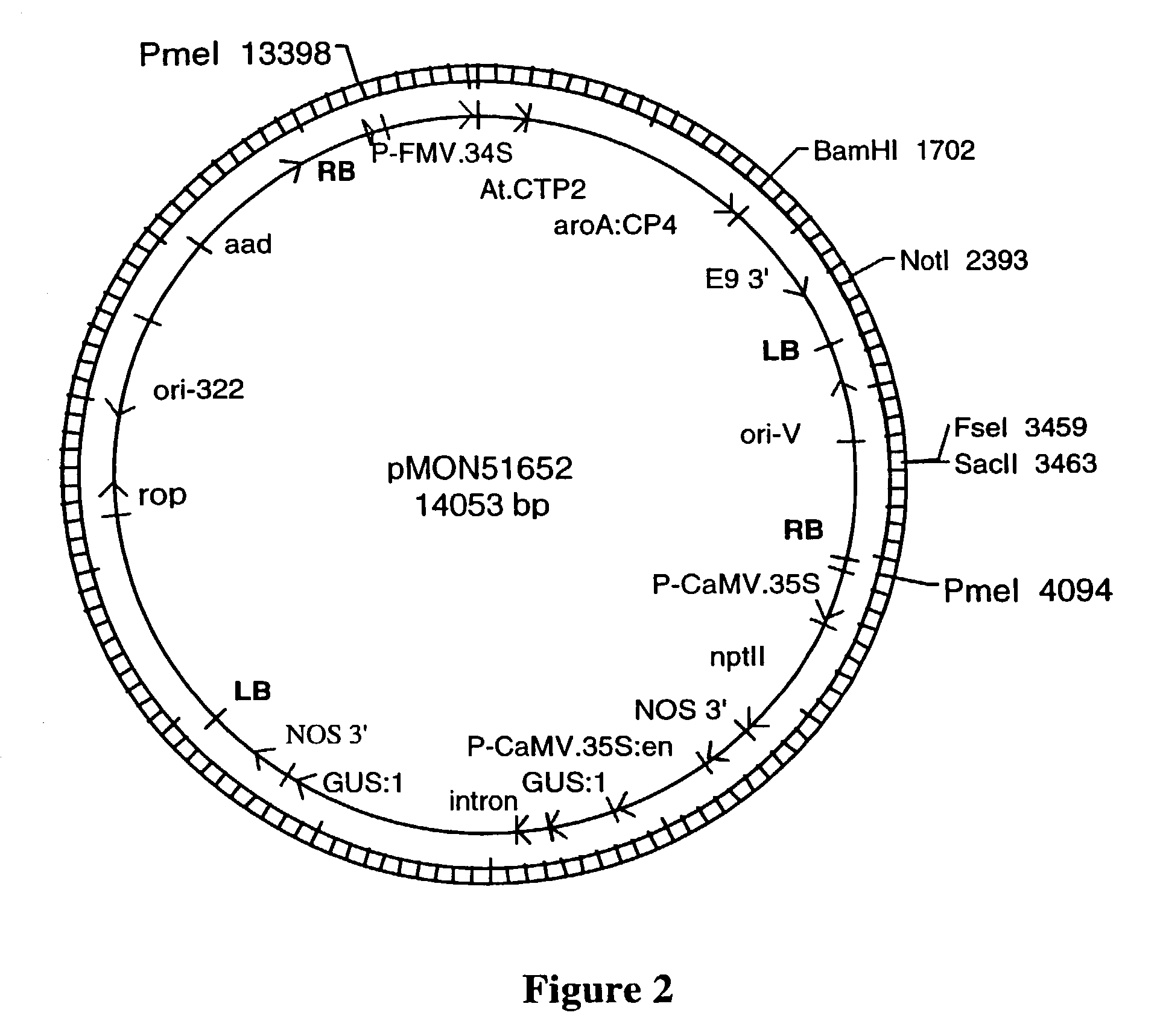
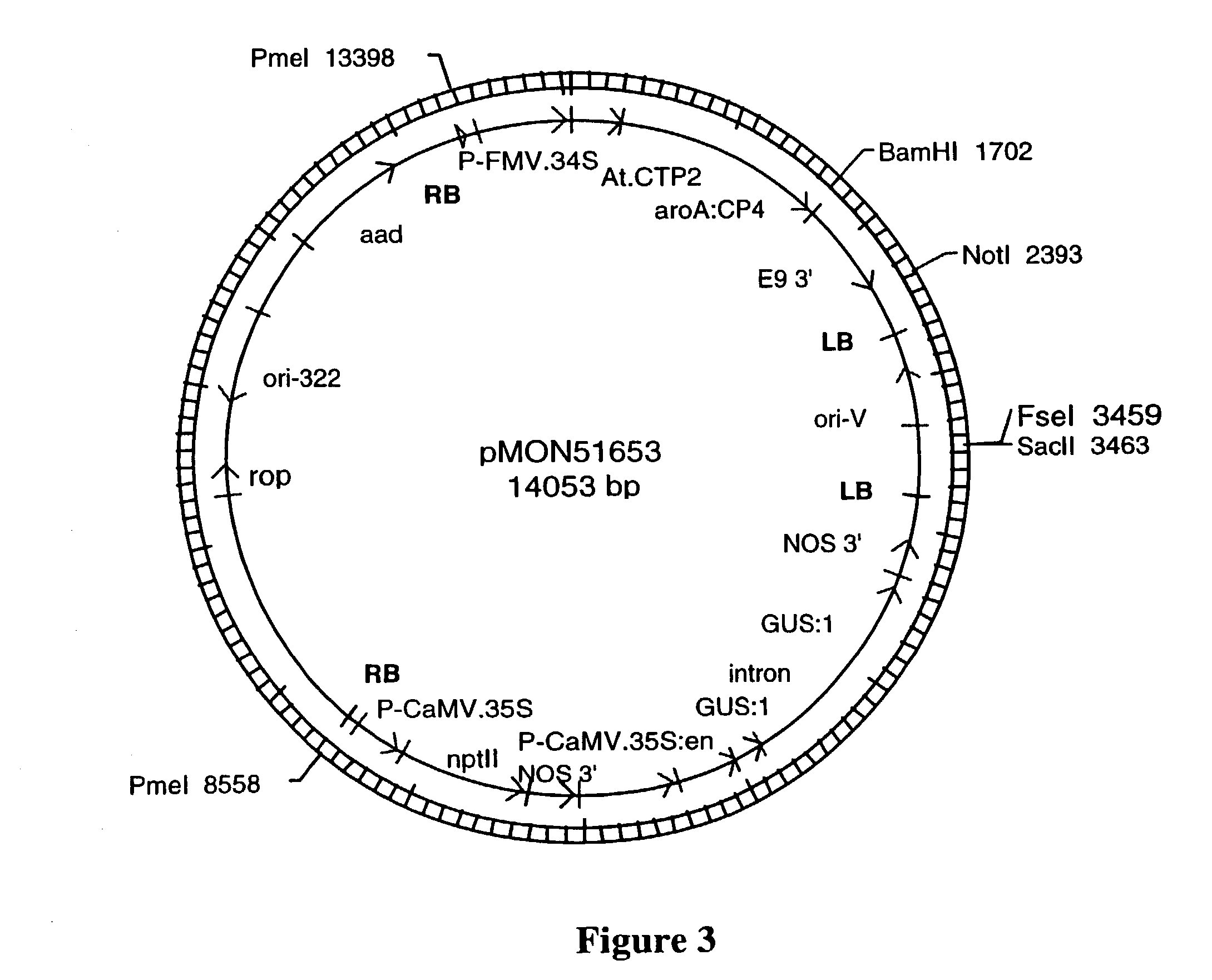
The compositions and methods are provided that enhance the selection of transgenic plants having two T-DNA molecules integrated into a plant genome at different physical and genetic loci. The compositions are DNA constructs that comprise novel arrangements of T-DNA molecules containing genes of interest, positive selectable marker genes, and conditional lethal genes. The methods disclosed herein comprises transforming a plant cell to comprise the DNA constructs of the present invention, regenerating the plant cell into a plant and identifying independant transgene loci, where the selectable marker genes or transgenic elements can be segregated in the progeny.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Negative selection and stringency modulation in continuous evolution systems
ActiveUS20160348096A1High selectivityStrong specificityFusion with DNA-binding domainAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPositive selectionBiology
Strategies, systems, methods, reagents, and kits for phage-assisted continuous evolution are provided herein. These include strategies, systems, methods, reagents, and kits allowing for stringency modulation to evolve weakly active or inactive biomolecule variants, negative selection of undesired properties, and / or positive selection of desired properties.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Negative selection and stringency modulation in continuous evolution systems
PendingUS20190256842A1High selectivityStrong specificityFusion with DNA-binding domainAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPositive selectionBiology
Strategies, systems, methods, reagents, and kits for phage-assisted continuous evolution are provided herein. These include strategies, systems, methods, reagents, and kits allowing for stringency modulation to evolve weakly active or inactive biomolecule variants, negative selection of undesired properties, and / or positive selection of desired properties.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Method for the positive selection of chromosomal mutations in C1 metabolizing bacteria via homologous recombination
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Evolution of talens
ActiveUS20200277587A1Strong specificityHydrolasesGenetic therapy composition manufactureNucleotideEpigenetic Profile
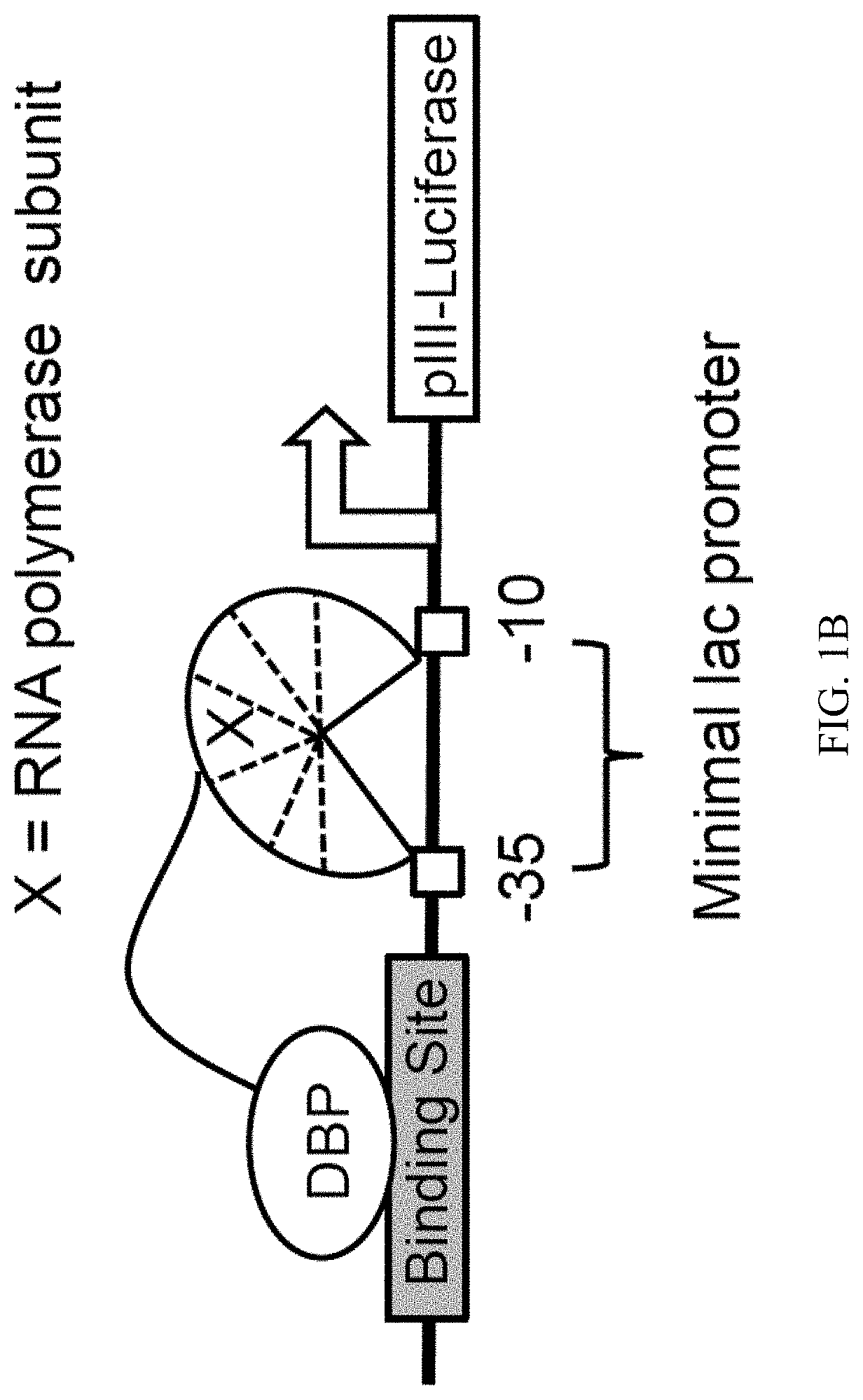
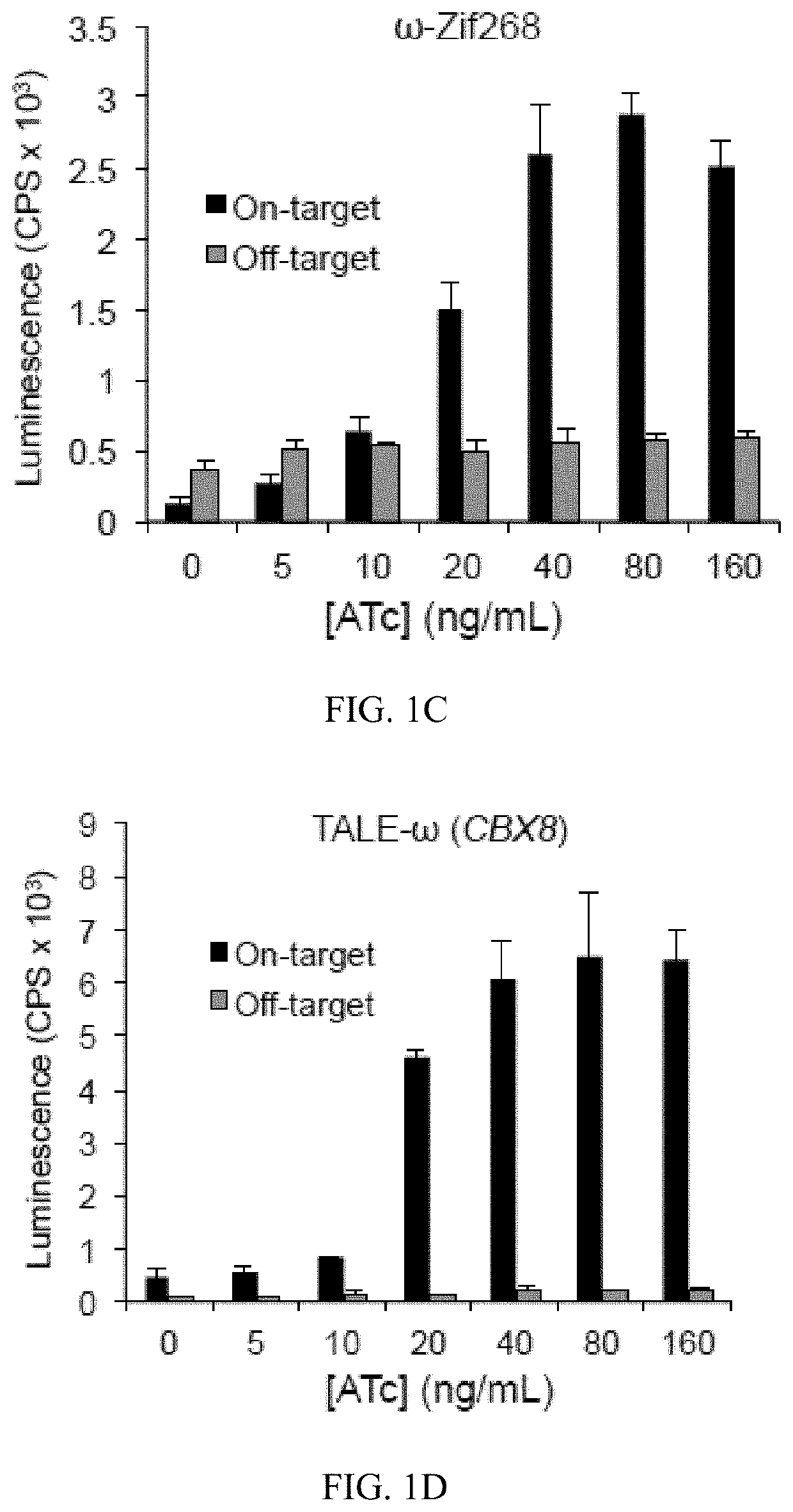
Engineered transcriptional activator-like effectors (TALEs) are versatile tools for genome manipulation with applications in research and clinical contexts. One current drawback of TALEs is that the 5′ nucleotide of the target is specific for thymine (T). TALE domains with alternative 5′ nucleotide specificities could expand the scope of DNA target sequences that can be bound by TALEs. Another drawback of TALEs is their tendency to bind and cleave off-target sequence, which hampers their clinical application and renders applications requiring high-fidelity binding unfeasible. This disclosure provides methods and strategies for the continuous evolution of proteins comprising DNA-binding domains, e.g., TALE domains. In some aspects, this disclosure provides methods and strategies for evolving such proteins under positive selection for a desired DNA-binding activity and / or under negative selection against one or more undesired (e.g., off-target) DNA-binding activities. Some aspects of this disclosure provide engineered TALE domains and TALEs comprising such engineered domains, e.g., TALE nucleases (TALENs), TALE transcriptional activators, TALE transcriptional repressors, and TALE epigenetic modification enzymes, with altered 5′ nucleotide specificities of target sequences. Engineered TALEs that target ATM with greater specificity are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
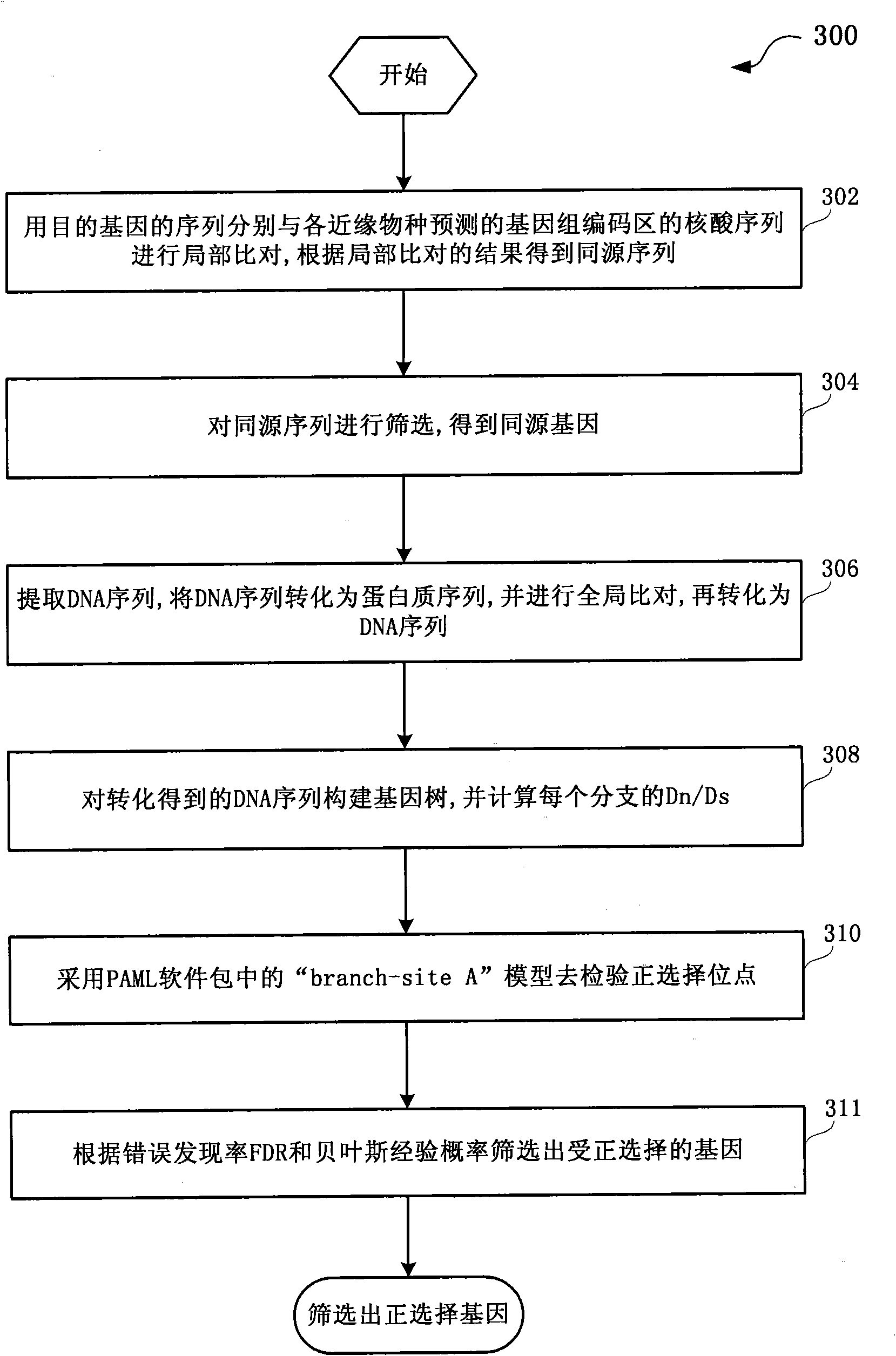
Method and system for detection of phenotype genes and analysis of biological information
ActiveCN101930502AReduce misleadingEasy to handleMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsNucleotideData information
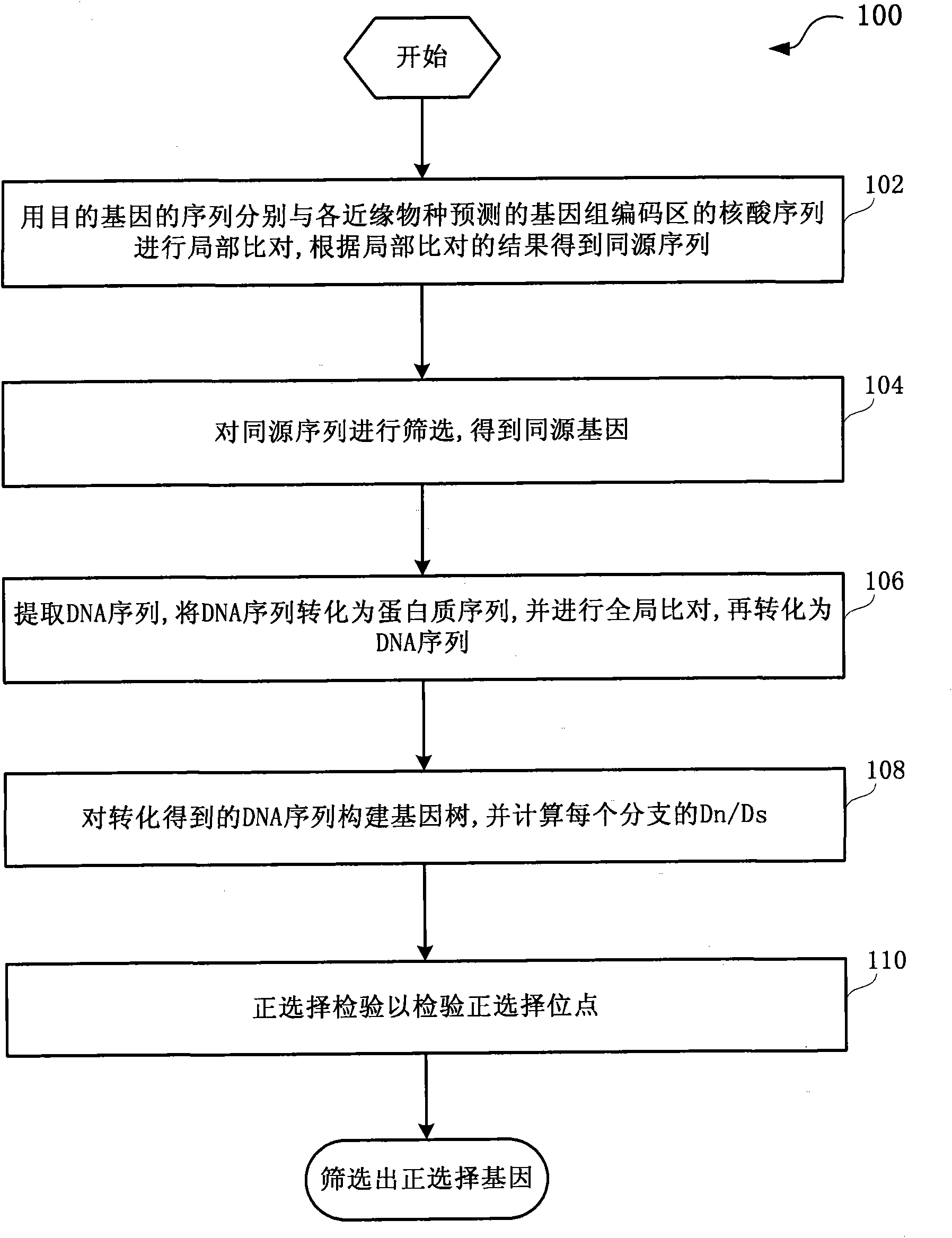
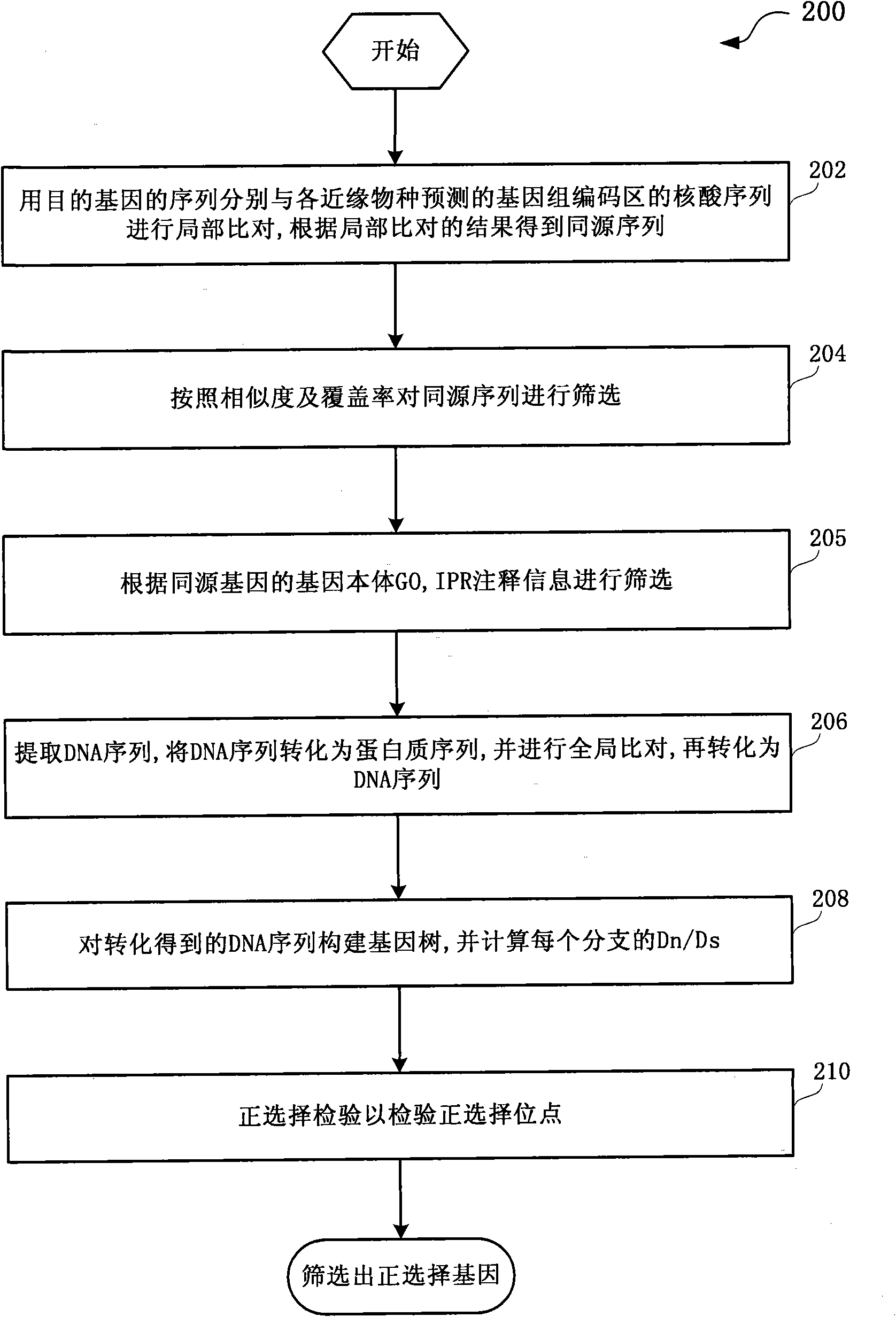
The invention discloses a method and a system for detection of phenotype genes and analysis of biological information. The method comprises the following steps of: performing local comparison between the sequence of target genes and nucleotide sequences of predicted genome coding regions of all allied species respectively, and obtaining a homologous sequence according to the local comparison results; screening the homologous sequence to obtain the homologous genes; extracting a DNA sequence from the homologous genes, converting the DNA sequence into a protein sequence, performing the overall comparison, and then converting the protein sequence into the DNA sequence; constructing a gene tree for the DNA sequence obtained by conversion, and working out Dn / Ds of each branch; and performing positive selection detection and detecting positive selection loci. The method and the system provided by the invention have the advantages of quickly processing a large amount of data information and discovering more accurate information, reducing misguiding of pseudogenes on analysis of biological information and helping to acquire the biological information to explain more biological problems.
Owner:BGI TECH SOLUTIONS
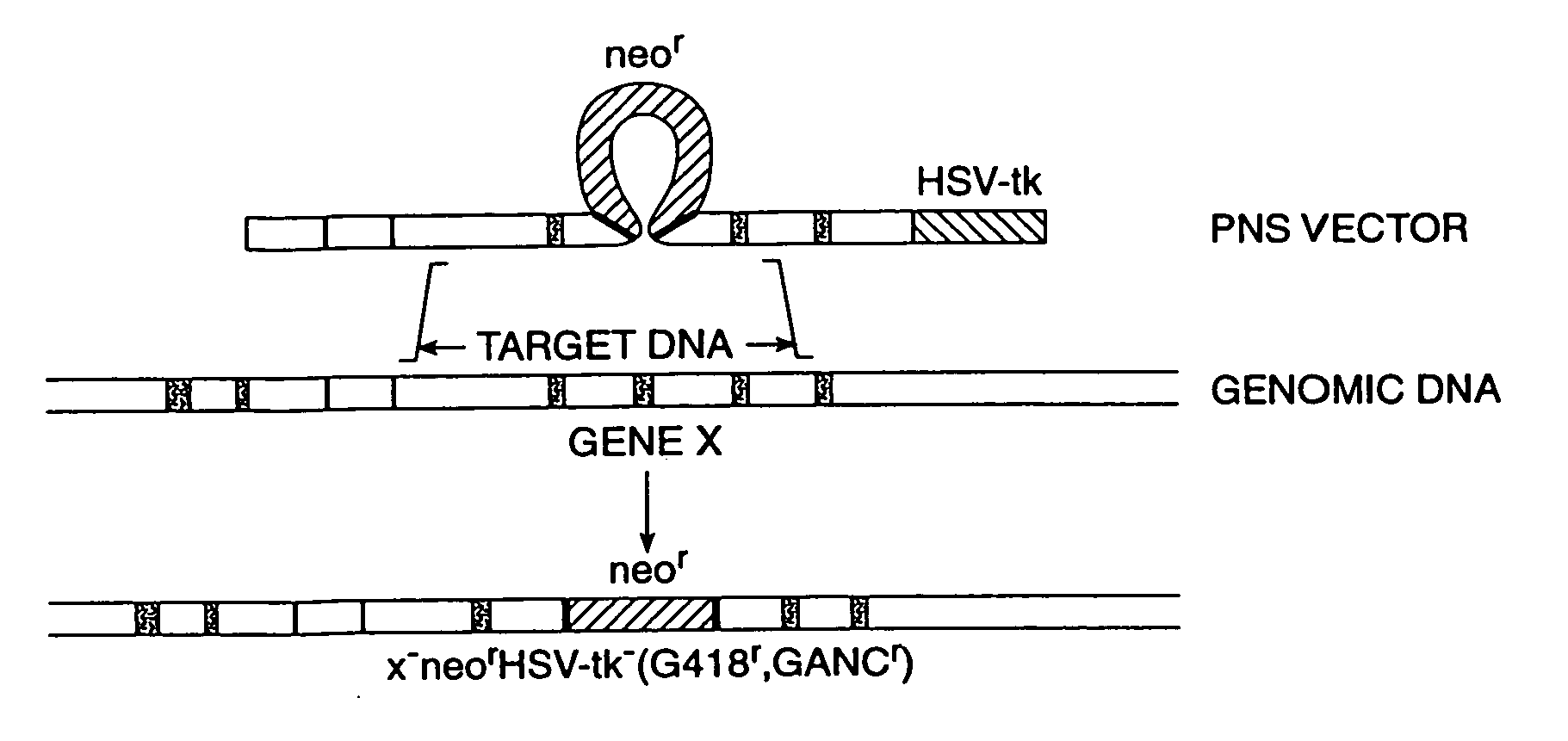
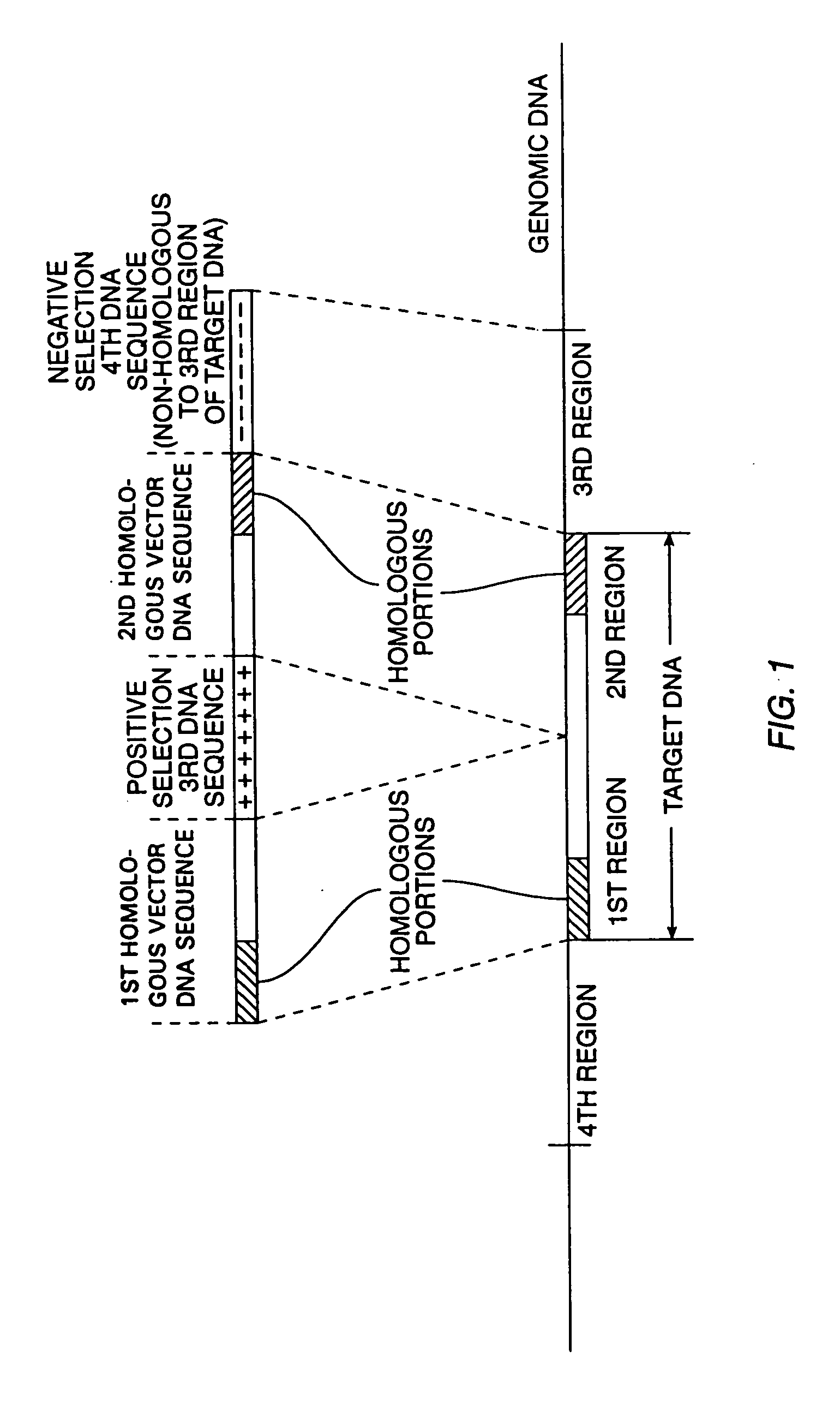
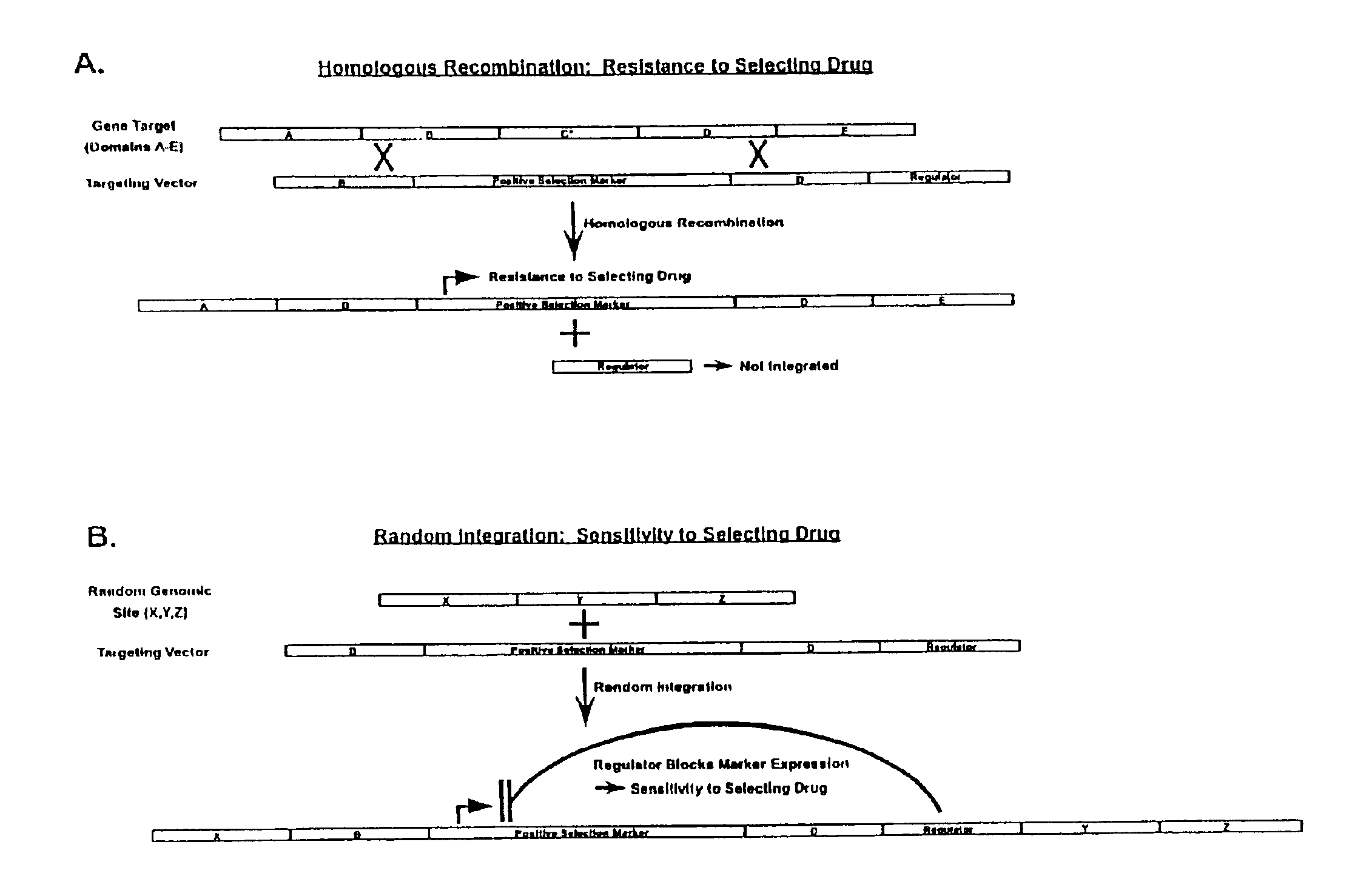
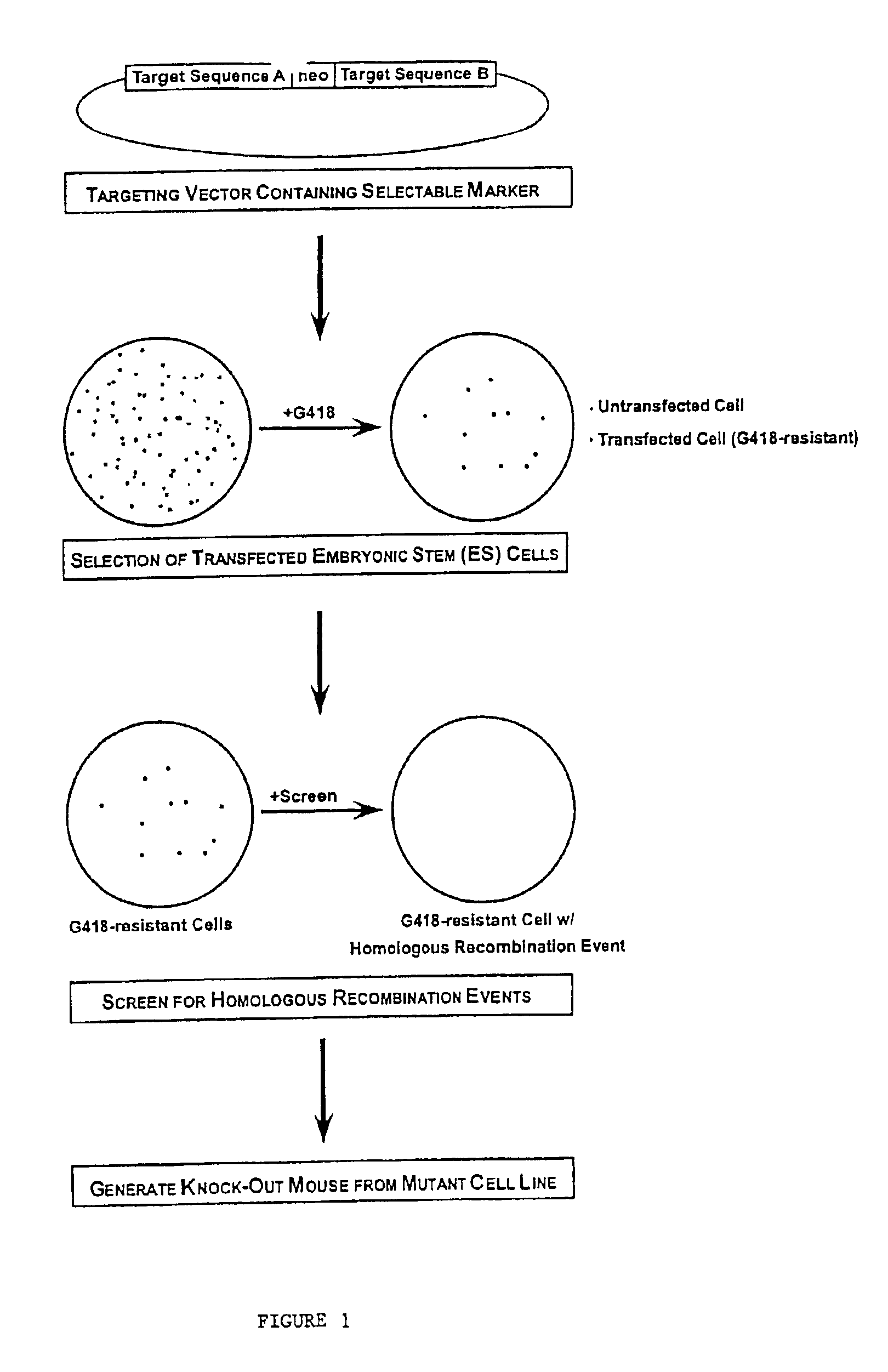
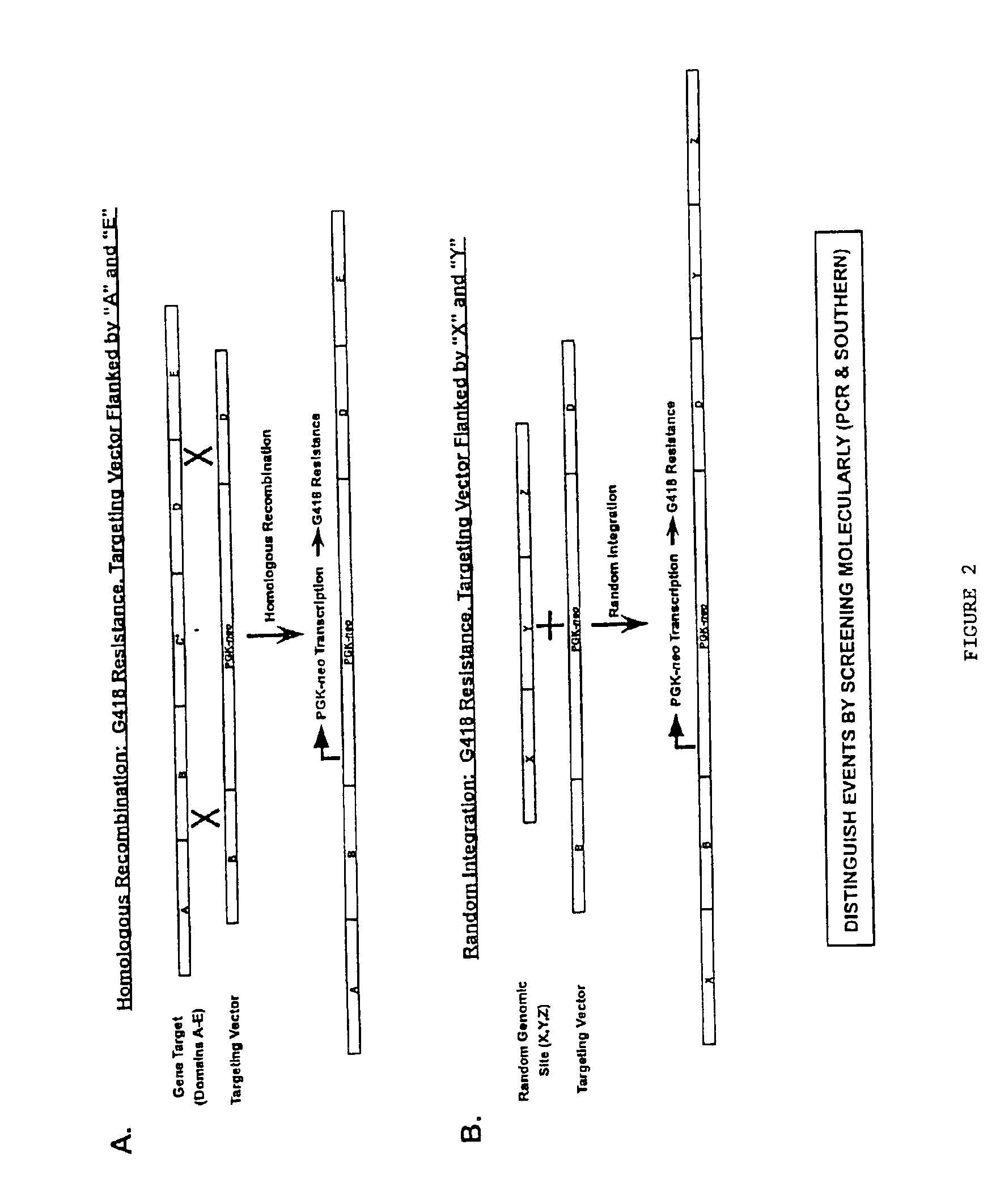
Cells and non-human organisms containing predetermined genomic modifications and positive-negative selection methods and vectors for making same
Positive-negative selector (PNS) vectors are provided for modifying a target DNA sequence contained in the genome of a target cell capable of homologous recombination. The vector comprises a first DNA sequence which contains at least one sequence portion which is substantially homologous to a portion of a first region of a target DNA sequence. The vector also includes a second DNA sequence containing at least one sequence portion which is substantially homologous to another portion of a second region of a target DNA sequence. A third DNA sequence is positioned between the first and second DNA sequences and encodes a positive selection marker which when expressed is functional in the target cell in which the vector is used. A fourth DNA sequence encoding a negative selection marker, also functional in the target cell, is positioned 5′ to the first or 3′ to the second DNA sequence and is substantially incapable of homologous recombination with the target DNA sequence. The invention also includes transformed cells containing at least one predetermined modification of a target DNA sequence contained in the genome of the cell. In addition, the invention includes organisms such as non-human transgenic animals and plants which contain cells having predetermined modifications of a target DNA sequence in the genome of the organism.
Owner:CAPECCHI MARIO +1
Phosphopeptide-specific antibodies that are activity specific; methods of production and antibody uses
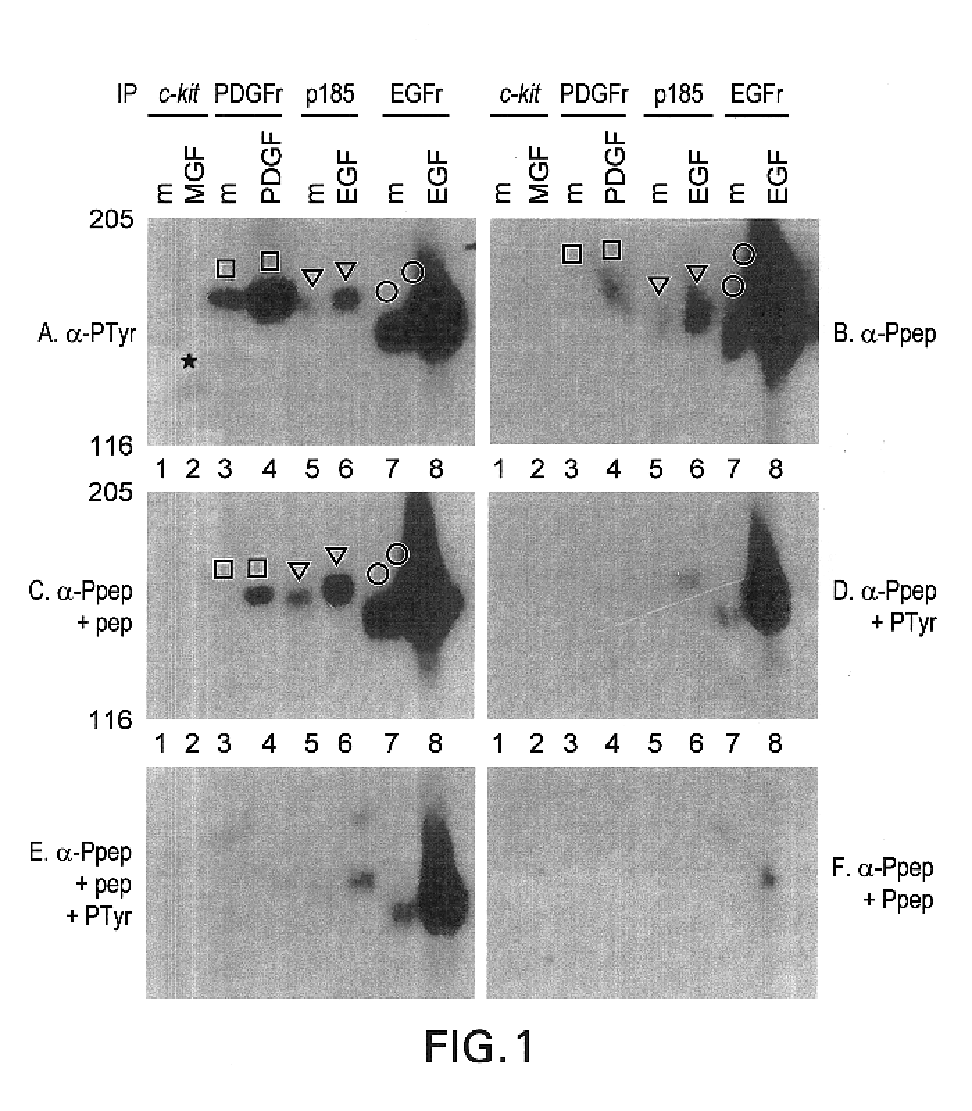
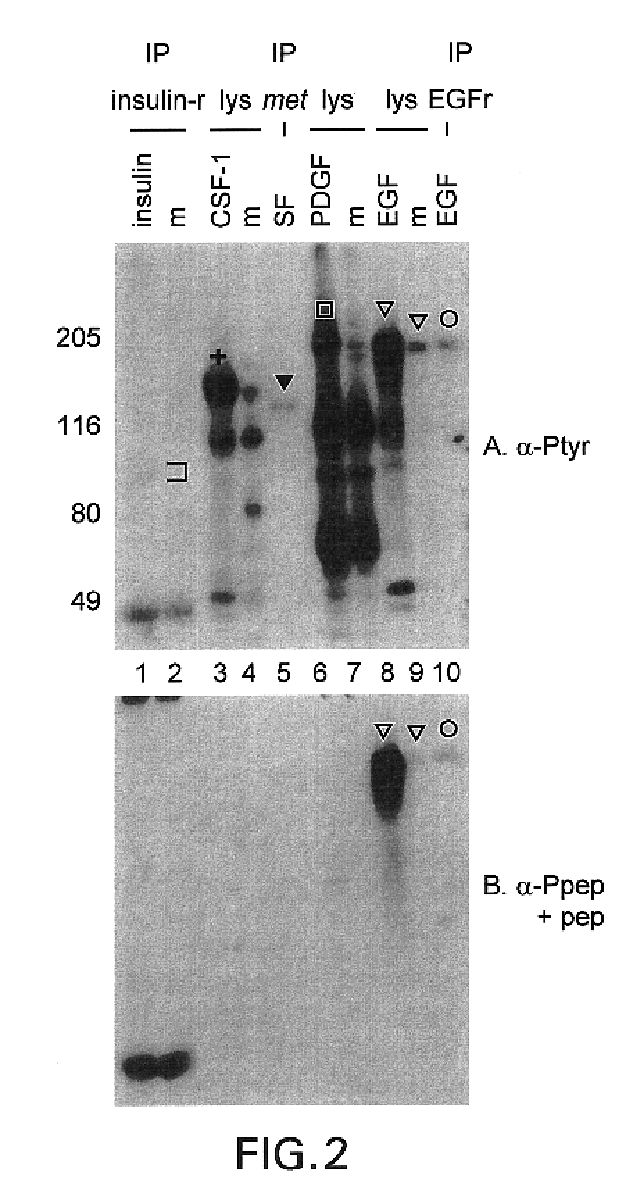
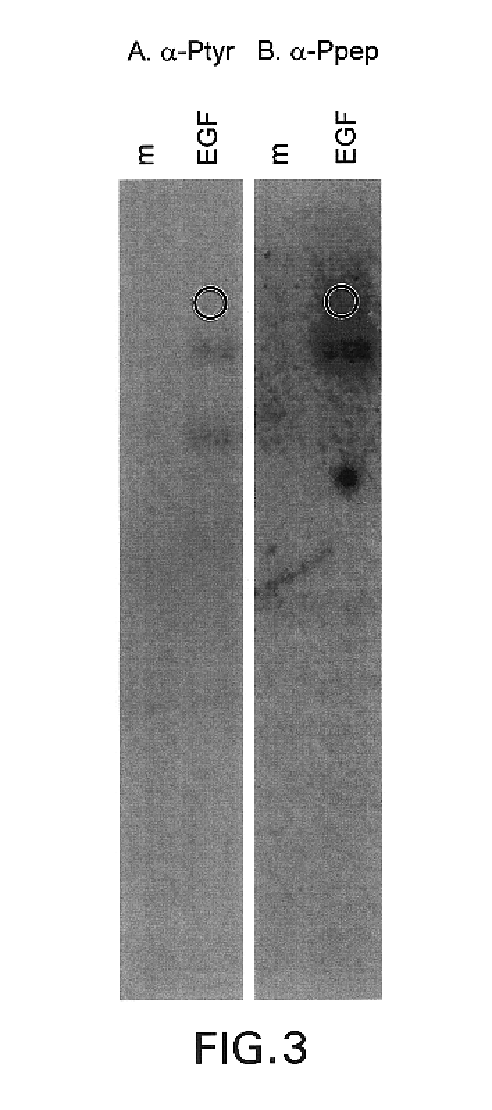
This invention relates to growth regulatory proteins expressed in various disease states, especially receptor tyrosine kinases and similar growth factor receptors. Prior to the Applicants invention, it was not clear that specific antibodies could be generated that recognized peptide epitopes comprising phosphotyrosine in the context of its surrounding amino acid sequence. Applicants generated antibodies to such phosphotyrosine specific peptides, distinct from antibodies that recognize only phosphotyrosine itself. The invention includes methods for producing phosphopeptide specific antibodies by removing contaminating antibody specificities by negative and / or positive selections. Phosphospecific antibodies and their uses in immunodetection, diagnostic or therapeutic applications are also disclosed.
Owner:PHOSPHOPROTEOMICS
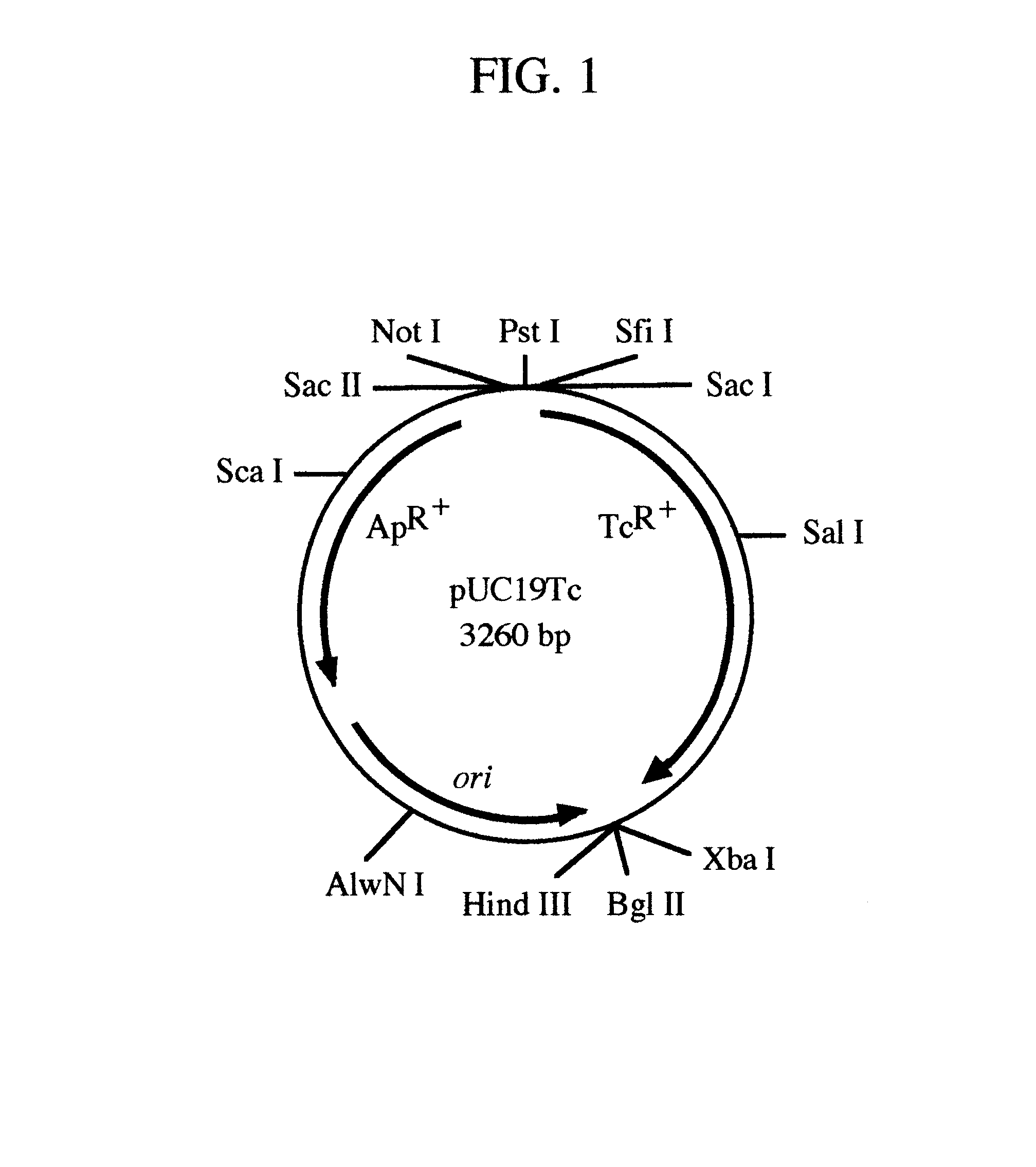
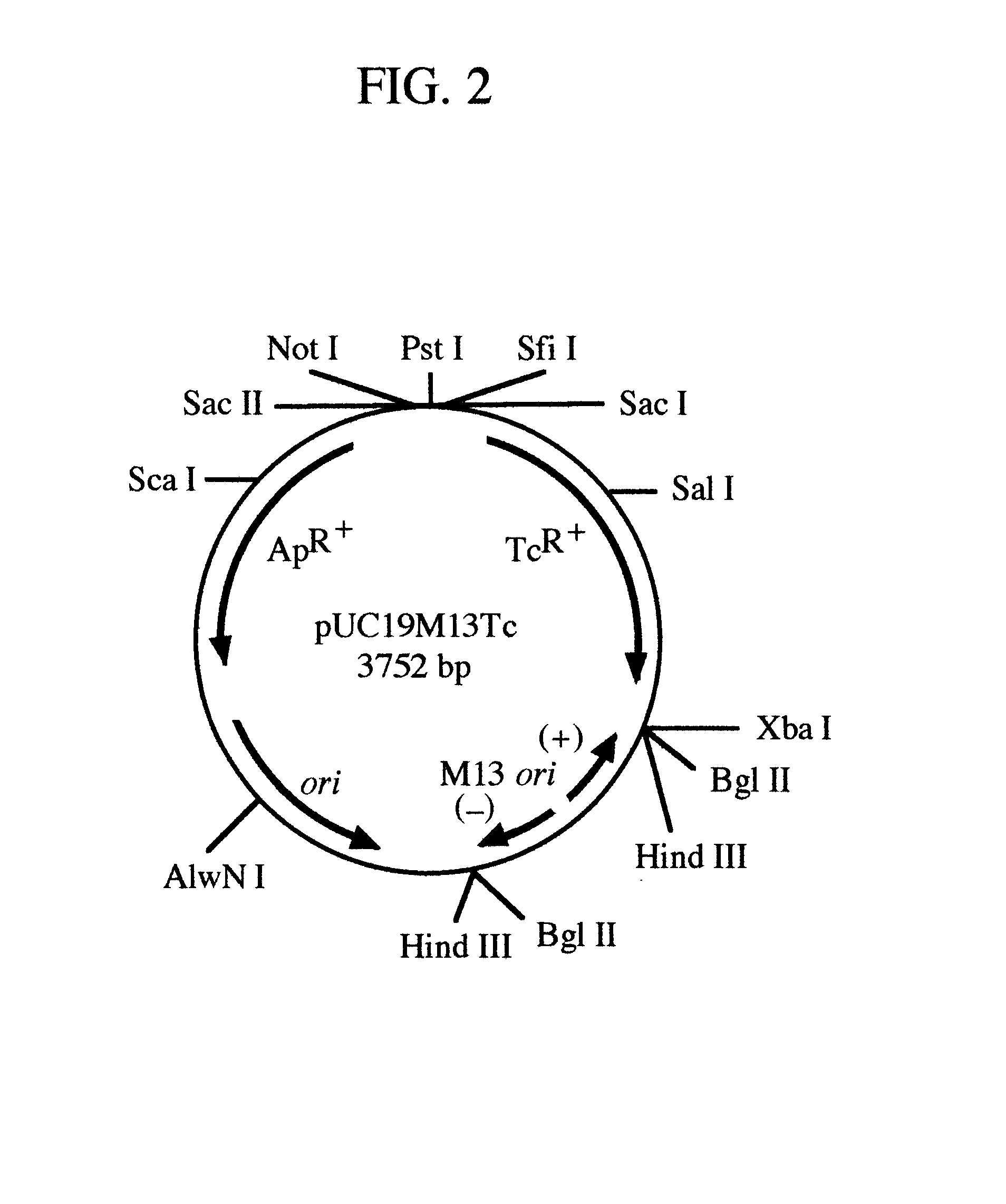
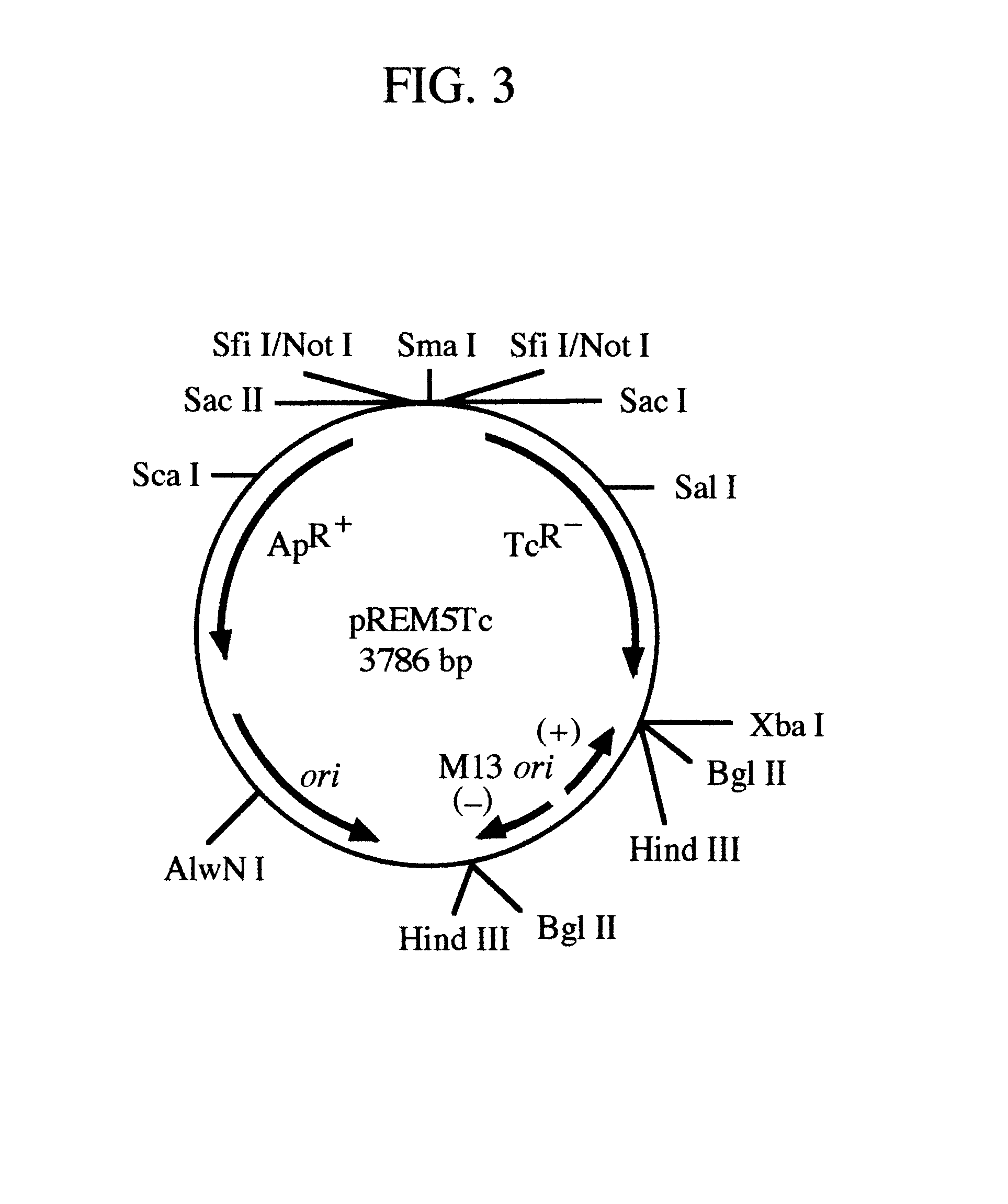
pREM: a positive selection vector system for direct PCR cloning
InactiveUS6544782B1Eliminate and greatly reduce false positive cloneSimple cloningSugar derivativesFermentationEscherichia coliBiology
The present invention describes the development of a positive selection vector based on regulatory element modulation, wherein such modulation is achieved via insertional reconstruction or destruction of a regulatory element controlling transcription, translation, DNA replication and termination. A positive selection cloning vector pREM5Tc has been developed based on insertional reconstruction of a regulatory element of a reporter gene. The vector pREM5Tc carries the tetracycline resistance reporter gene with no functional -35 region of its promoter, a regulatory element, thus resulting in no expression of the tetracycline resistance gene. Hence a host cell carrying the vector pREM5Tc is unable to produce the tetracycline resistance gene protein resulting in inhibition of its growth in presence of tetracycline. An E. coli consensus -35 region is recognized as 5'-TTGACA-3' and a primer used in polymerase chain reaction (PCR) carries at its 5' end the sequence 5'-TGTCAA-3', which is the complementary sequence of 5'-TTGACA-3'. The PCR-amplified DNA fragment is ligated to pREM5Tc thus reconstructing the functional promoter of the tetracycline resistance reporter gene. Subsequent transformation of a host cell with the recombinant vector (carrying an insert DNA) results in production of the tetracycline resistance reporter gene protein that confers resistance to tetracycline thus allowing only the recombinants to grow in presence of tetracycline. The positive selection vector pREM5Tc greatly reduces, if not eliminates, the number of exonuclease-generated false positive clones.
Owner:SYNTHEGEN SYST
Evolution of talens
ActiveUS20180237758A1Strong specificityHydrolasesGenetic therapy composition manufactureDNA-binding domainOff targets
Engineered transcriptional activator-like effectors (TALEs) are versatile tools for genome manipulation with applications in research and clinical contexts. One current drawback of TALEs is that the 5′ nucleotide of the target is specific for thymine (T). TALE domains with alternative 5′ nucleotide specificities could expand the scope of DNA target sequences that can be bound by TALEs. This disclosure provides methods and strategies for the continuous evolution of proteins comprising DNA-binding domains, e.g., TALE domains. In some aspects, this disclosure provides methods and strategies for evolving such proteins under positive selection for a desired DNA-binding activity and / or under negative selection against one or more undesired (e.g., off-target) DNA-binding activities. Some aspects of this disclosure provide engineered TALE domains and TALEs comprising such engineered domains, e.g., TALE nucleases (TALENs), TALE transcriptional activators, TALE transcriptional repressors, and TALE epigenetic modification enzymes, with altered 5′ nucleotide specificities of target sequences. Engineered TALEs that target ATM with greater specificity are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
High fidelity PCR cloning
InactiveUS6566067B2Minimizes number of doublingImprove fidelitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliPolymerase L
The present invention describes a methodology for generating high fidelity PCR products, and also cloning of such high fidelity PCR products in a suitable vector. Generation of polymerase-induced mutant fraction of target sequences during PCR amplification is linearly proportional to the number of doublings of the target sequences. Thus the high fidelity PCR products are generated by minimizing the number of doublings of the target nucleic acid sequences during PCR amplification. Minimization of number of doublings of the target sequences is achieved by reducing the number of cycles of PCR amplification of the target sequences. The high fidelity PCR products thus obtained are then cloned into a suitable vector. As an example, a 960 bp target sequence from E. coli DNA was PCR-amplified only for 3 cycles, and it was then directly cloned into a positive selection cloning vector pRGR2Ap. The functional analysis of the inserts in all clones showed that the clones carried functionally wild-type DNA fragments, and hence the inserts most probably carry no mutation. Cloning of PCR products obtained from 3 cycles of amplification, instead of 30 cycles of amplification, theoretically achieves 10-fold reduction of mutations in the cloned fragments. The invention also contemplates cloning of a target cDNA obtained by primer extension.
Owner:SYNTHEGEN SYST
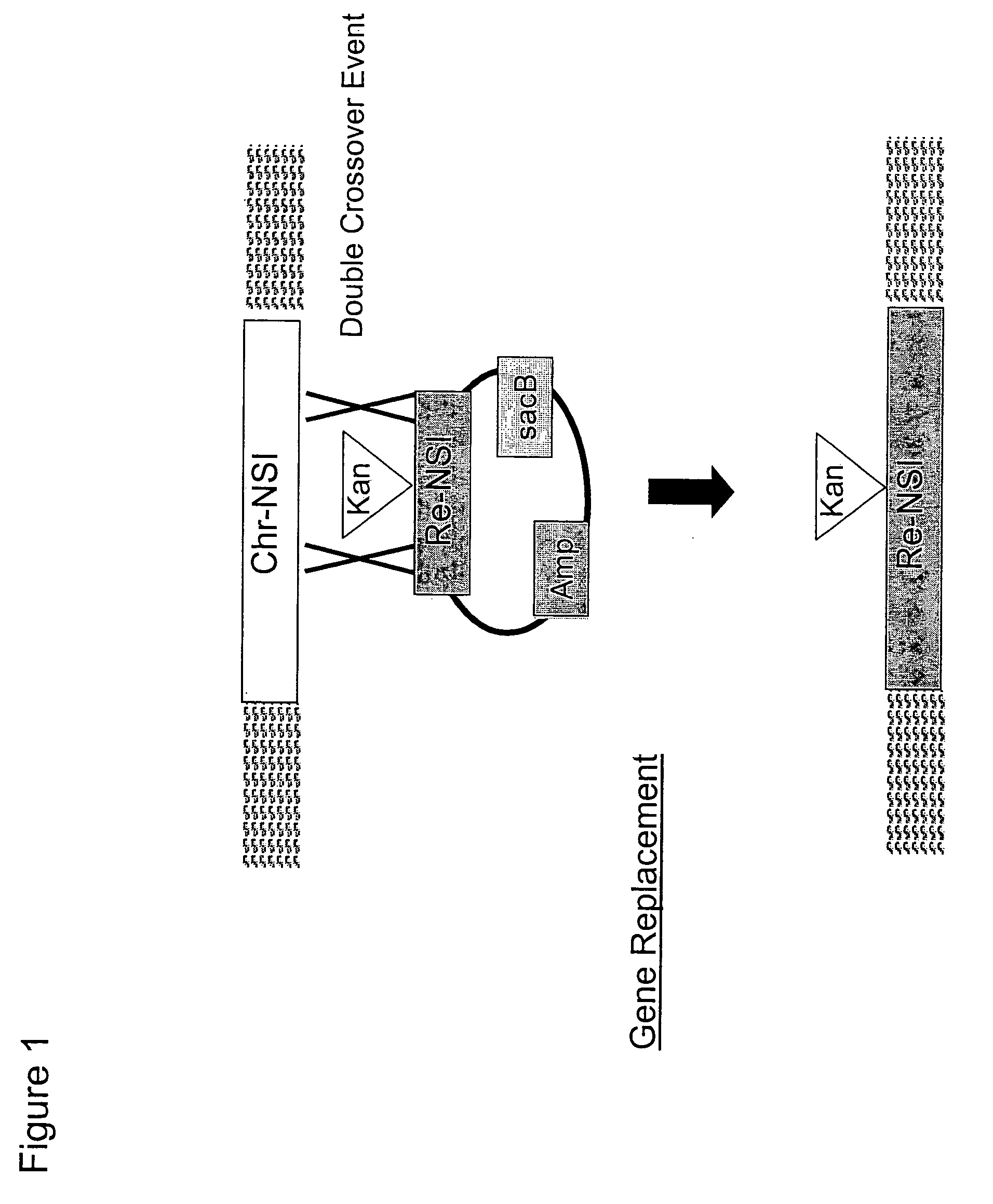
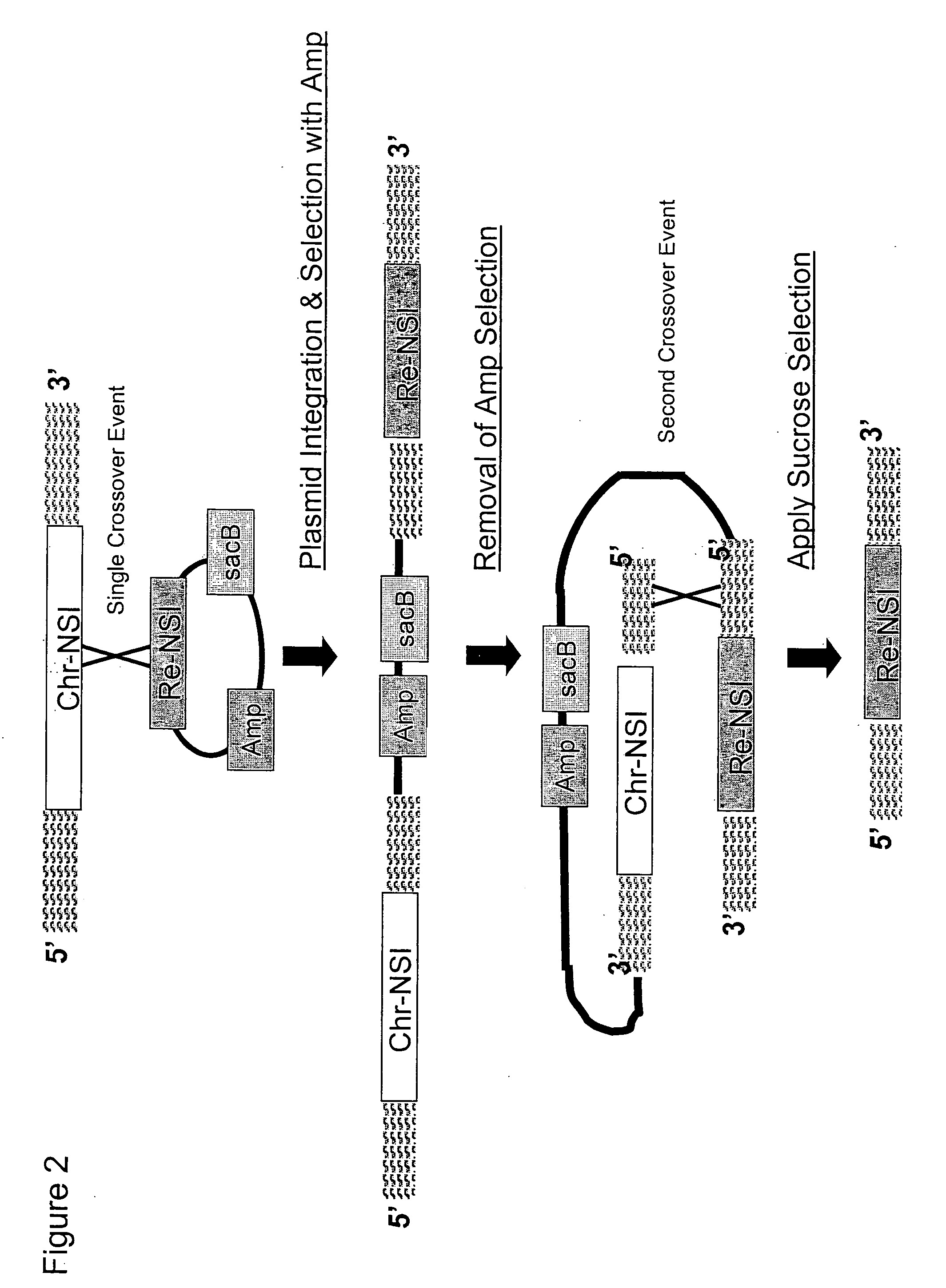
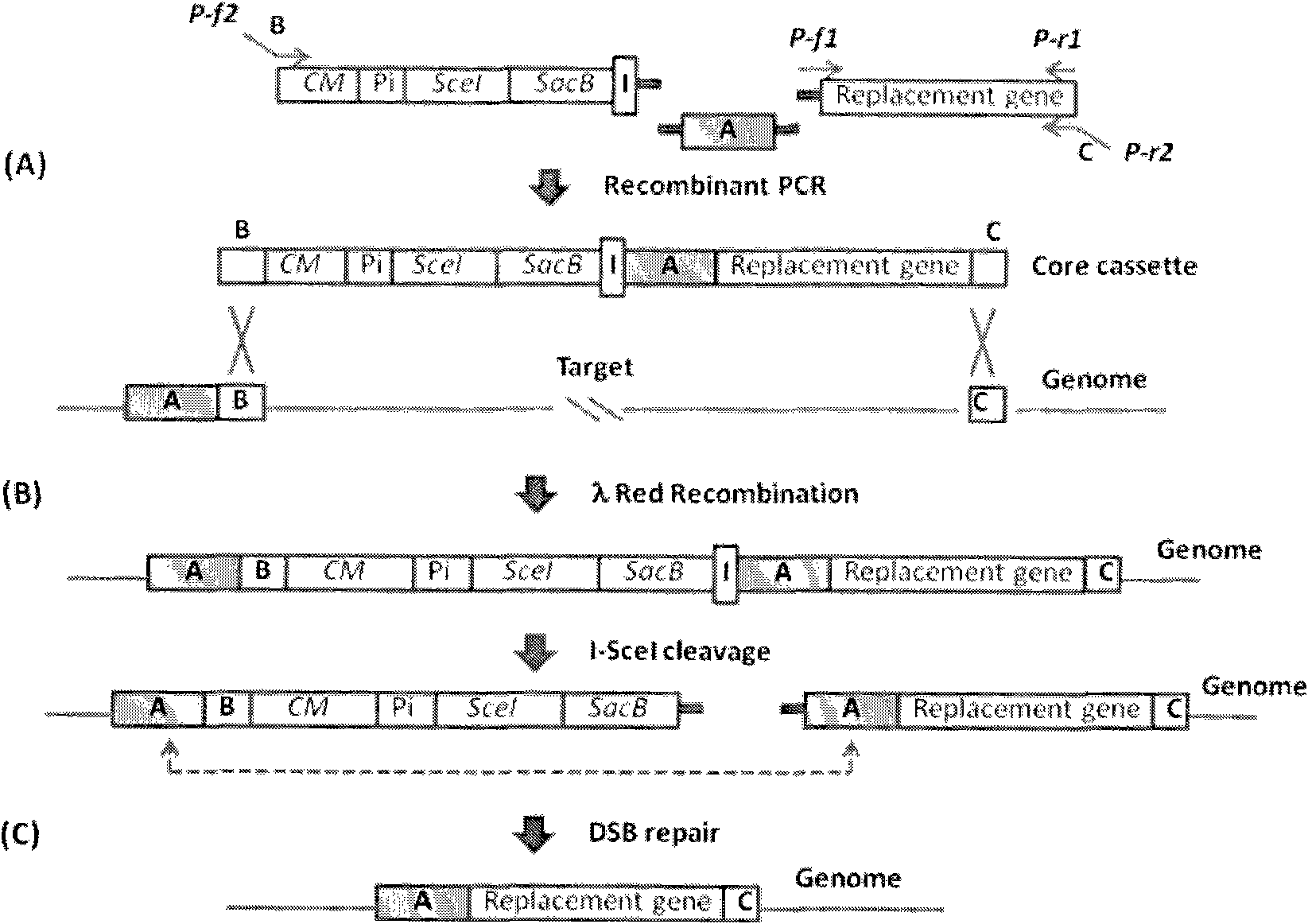
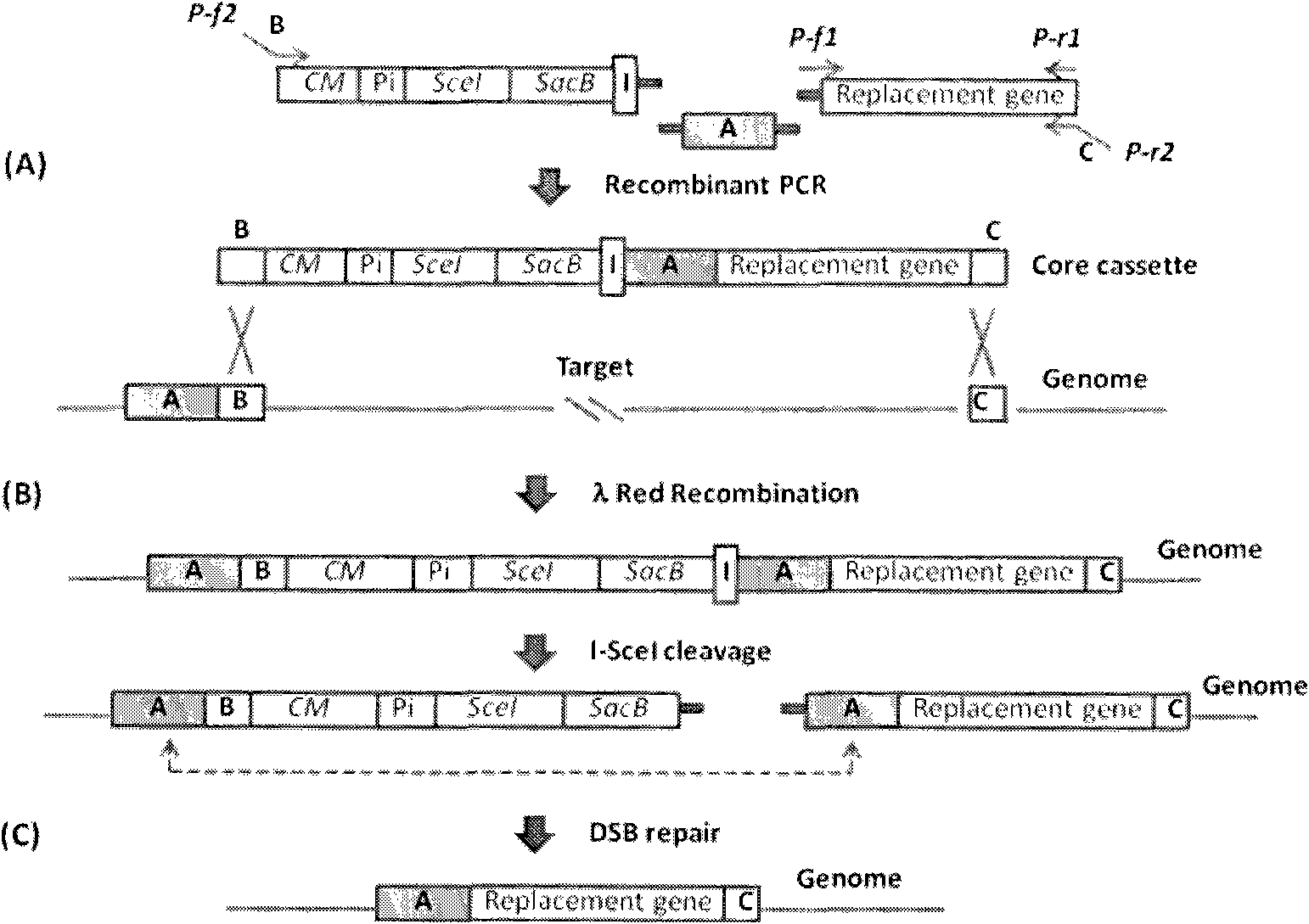
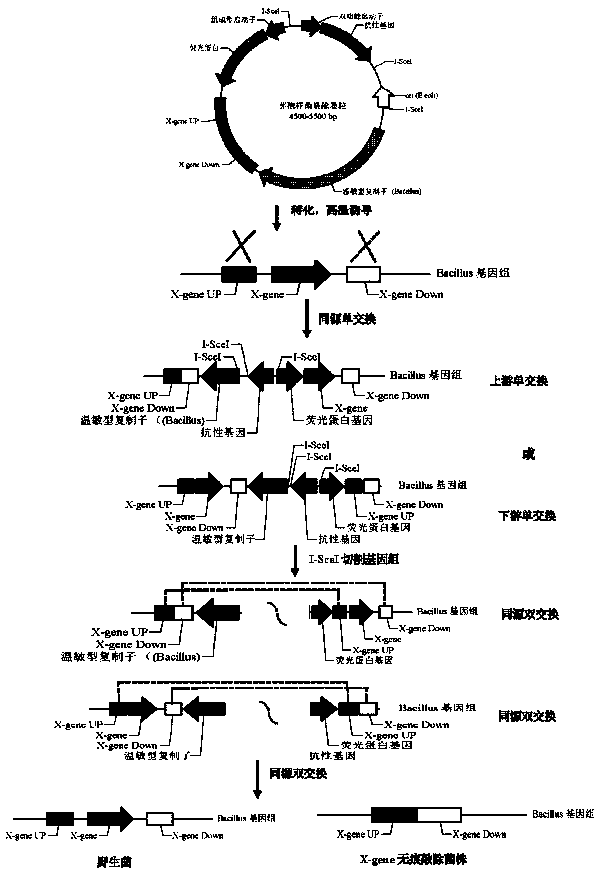
Traceless modification method of chromosome
The invention provides a traceless modification method of a chromosome, comprising the following steps: firstly building a recombinant box composed of a positive selection marker, a counterselection marker, an endonuclease I-SceI, an induced promoter, an I-SceI recognition site and a target nucleic acid displacement sequence which is homologous with a target chromosome nucleic acid sequence; inputting DNA fragments into a host containing recombinant plasmids by electrotransformation; knocking out the following gene sequences from an expected recombinant through a double-strand break repair phenomenon mediated by I-SceI: the positive selection marker, the induced promoter, an I-SceI gene and the counterselection marker; and finally screening the final recombinant from a sucrose medium. The method can help insert, knock out or replace the target gene of the chromosome without any selection markers or exogenous DNA sequences remained, thus being an effective method for traceless modification of the DNA sequence of a host cell.
Owner:苏州神洲基因有限公司
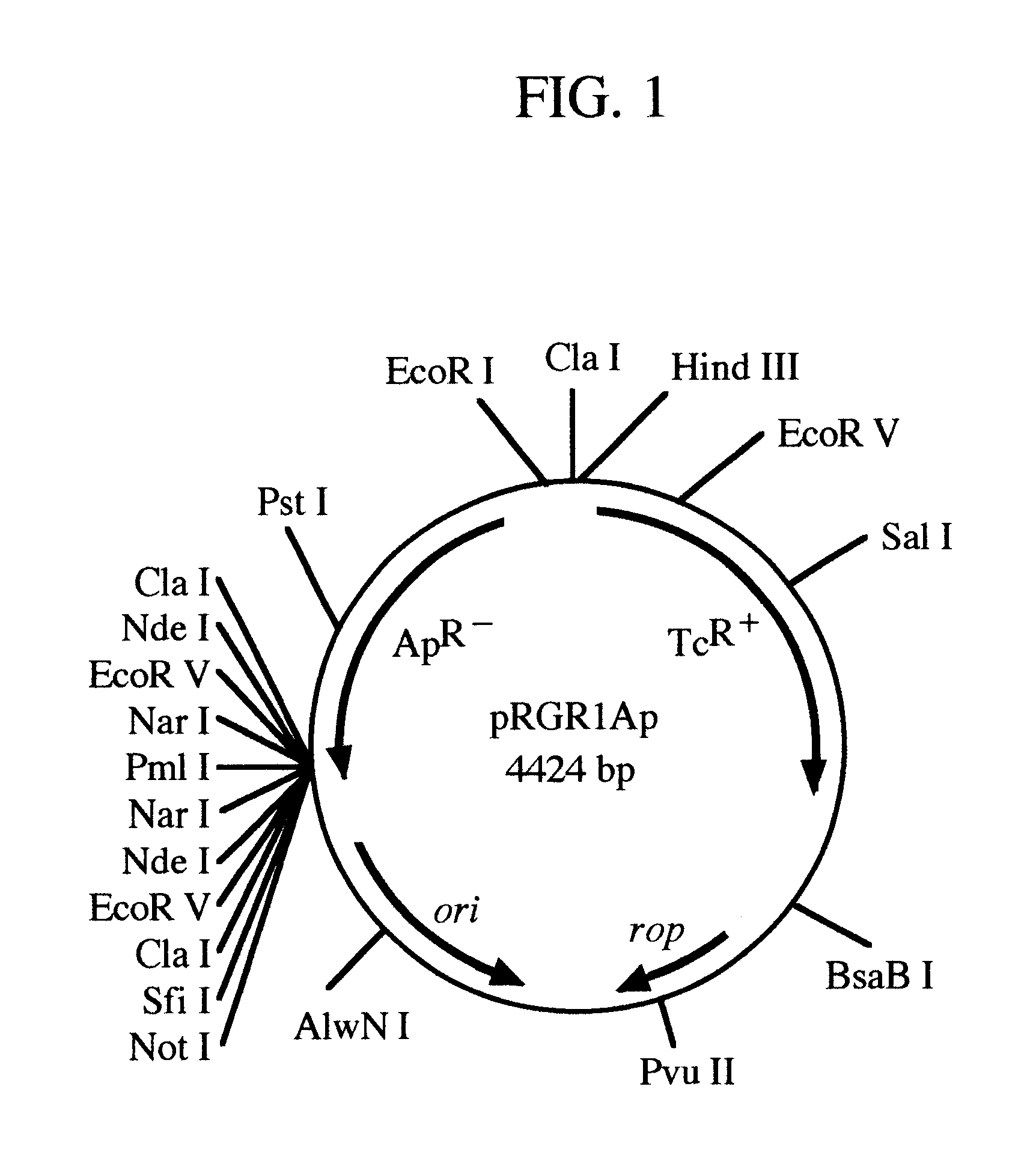
pRGR: a positive selection vector system for direct cloning of PCR amplified DNA fragments
InactiveUS6569678B1Easy extractionEliminate and greatly reduce generationFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionWild typeGene control
The present invention relates to the development of a positive selection vector based on insertional reconstruction of a reporter gene or of a regulatory gene controlling the expression of a reporter gene. The cloning vector carries a reporter gene or a regulatory gene with a mutation rendering the reporter or the regulatory gene protein functionally inactive. A primer carrying a nucleic acid sequence that corrects the mutation is used during PCR amplification of a targeted nucleic acid sequence, and the amplified DNA fragment is then ligated to the said vector thus reconstructing the wild-type reporter or regulatory gene.
Owner:SYNTHEGEN SYST
Allele double knockout targeting vector system and construction method thereof
InactiveCN102094036AHigh target shooting efficiencyShorten experiment timeVector-based foreign material introductionFluorescenceTransgene
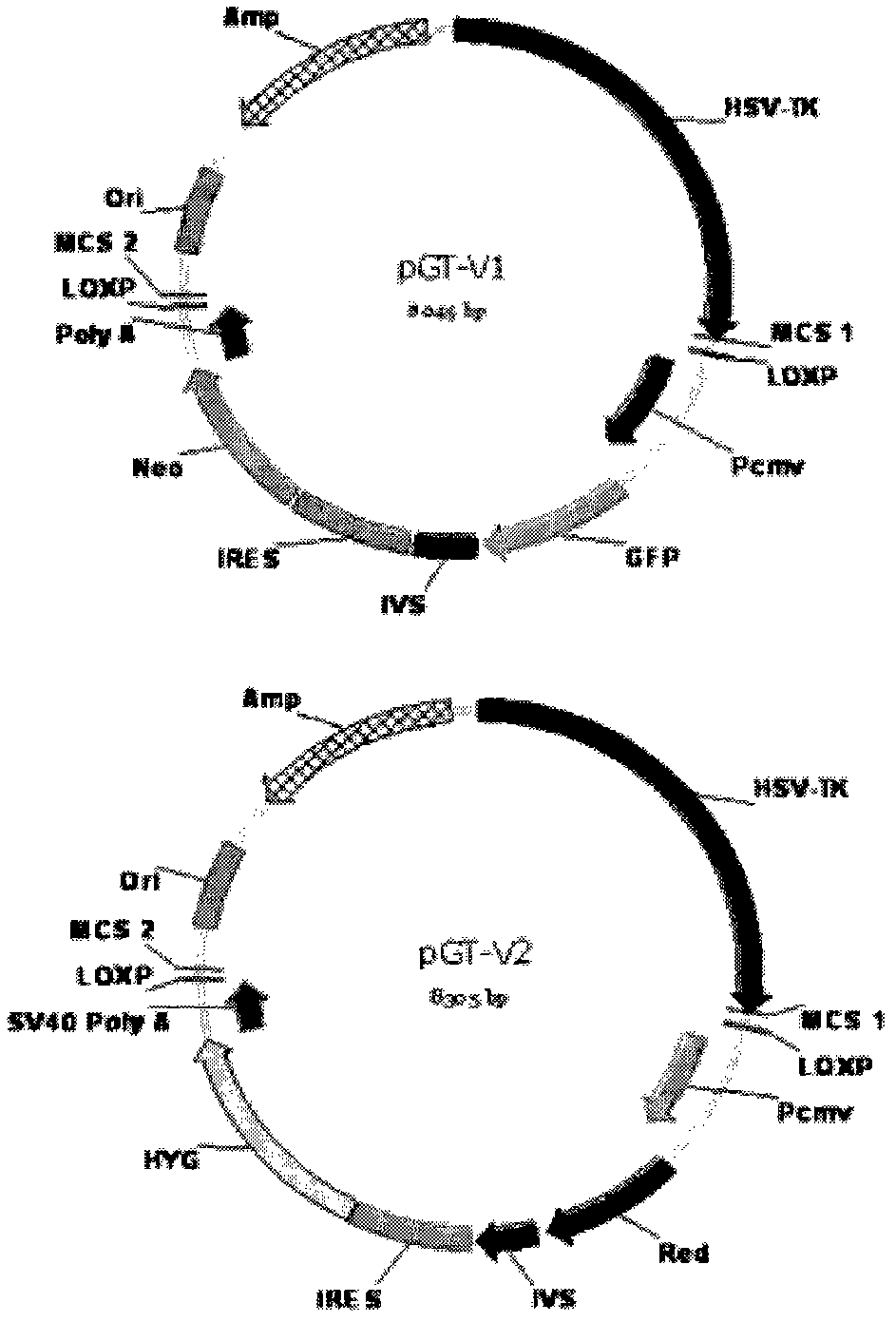
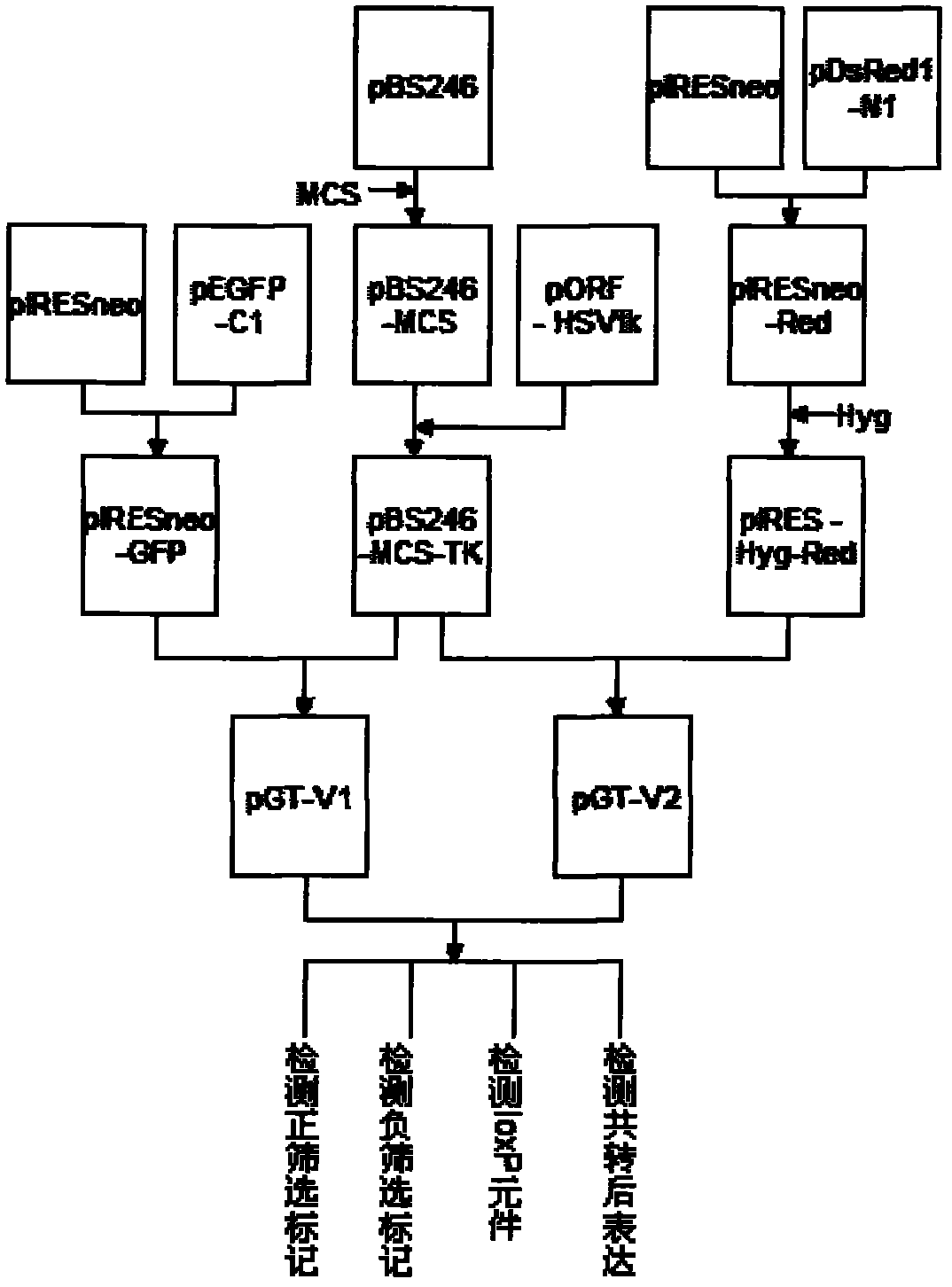
The invention relates to an allele double knockout targeting vector system and a construction method thereof. The system of the invention consists of two complementary vectors, namely pGT-V1 and pGT-V2, wherein each vector contains two in phase LoxP elements which contain a positive selection marker gene Neo / GFP and Hyg / RFP respectively; and the outside of each vector contains a negative selection marker gene TK. Meanwhile, two 8-basic group multiple cloning sites are designed and arranged between the two LoxP elements and the negative selection marker for the insertion of the homology arm. By adopting the constructed targeting vector system of the invention, two complementary targeting vectors are cotransfected into the recipient cell; through the selection of drug and fluorescent double-selection marker, the genetic modification or knockout of the two alleles of the target gene can be realized once; and the interaction of the transfected Cre enzyme and the LoxP elements can be utilized to remove the selection marker gene integrated with the genome, the time of obtaining the homozygous knockout target cell can be shortened, the safety of the transgenic animal can be increased and a valuable technology platform is provided to develop the animal transgenic researches.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Genetic intelligent seed breeding and production system for crossbreeding and production of crops and application thereof
PendingCN113621642ARealize comprehensive utilizationAchieve commercial productionVector-based foreign material introductionPlant protectionBiotechnologyPositive selection
The invention provides a genetic intelligent seed breeding and production system for crossbreeding and production of crops and application thereof. The system contains a GAT system vector, and the vector comprises five functional element expression cassettes: a plant male fertility restoration gene element expression cassette used for restoring male fertility of recessive genic male sterility mutants, a plant pollen abortion gene element expression cassette used for removing pollen containing GAT and keeping a heterozygotic state or a hemizygotic state of a GAT maintainer line, a chemical herbicide positive selection expression cassette used for gene transformation and GAT maintainer line impurity removal and purification, a chemical herbicide negative selection expression cassette used for removing herbicide-sensitive GAT maintainer line pollen and seed escape and removing impurities and purifying a GAT sterile line, and a seed screening element expression cassette used for mechanically sorting seeds. The system can be used for crossbreeding and hybrid seed production of plant recessive genic male sterility materials, so that new varieties of plants with high quality, high yield, wide applicability and high resistance and seeds of the plants are obtained.
Owner:HAINAN BOLIAN RICE GENE TECH CO LTD
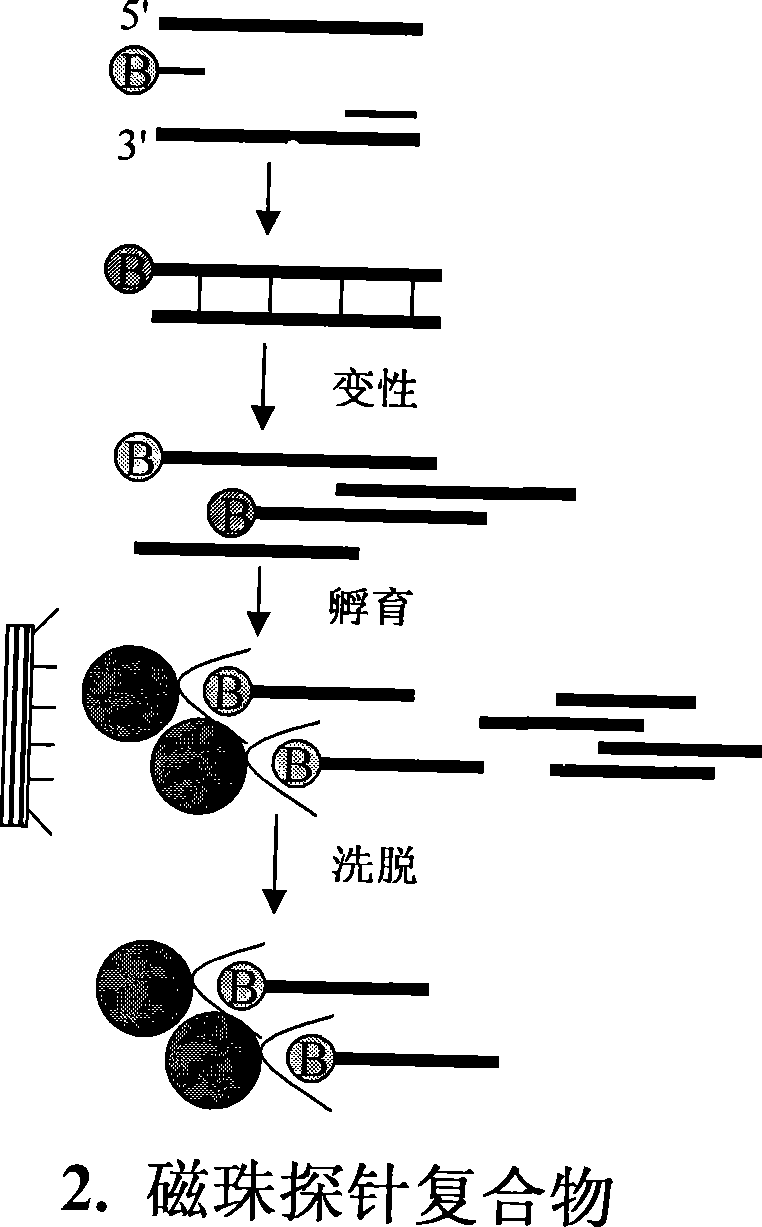
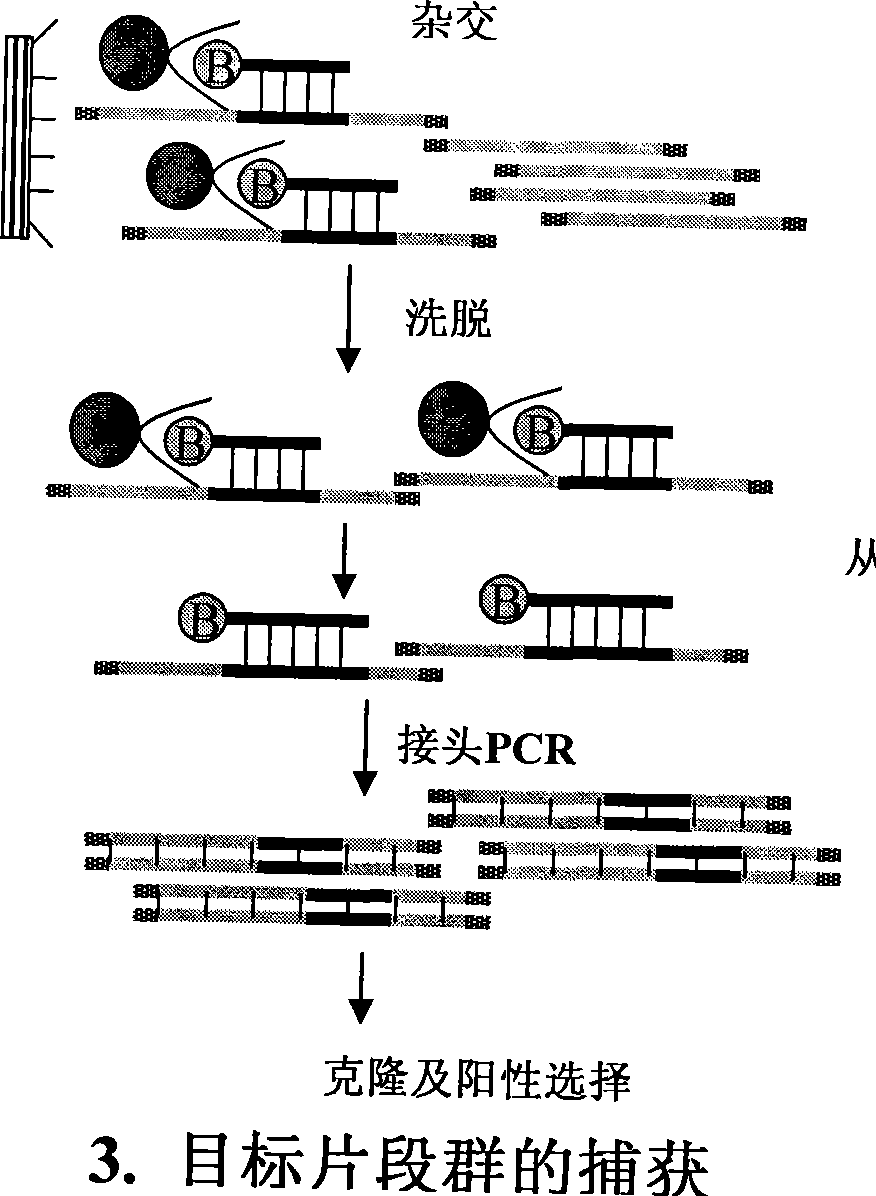
Method for separating short interspersed repeated segments based on magnetic bead probe complexes
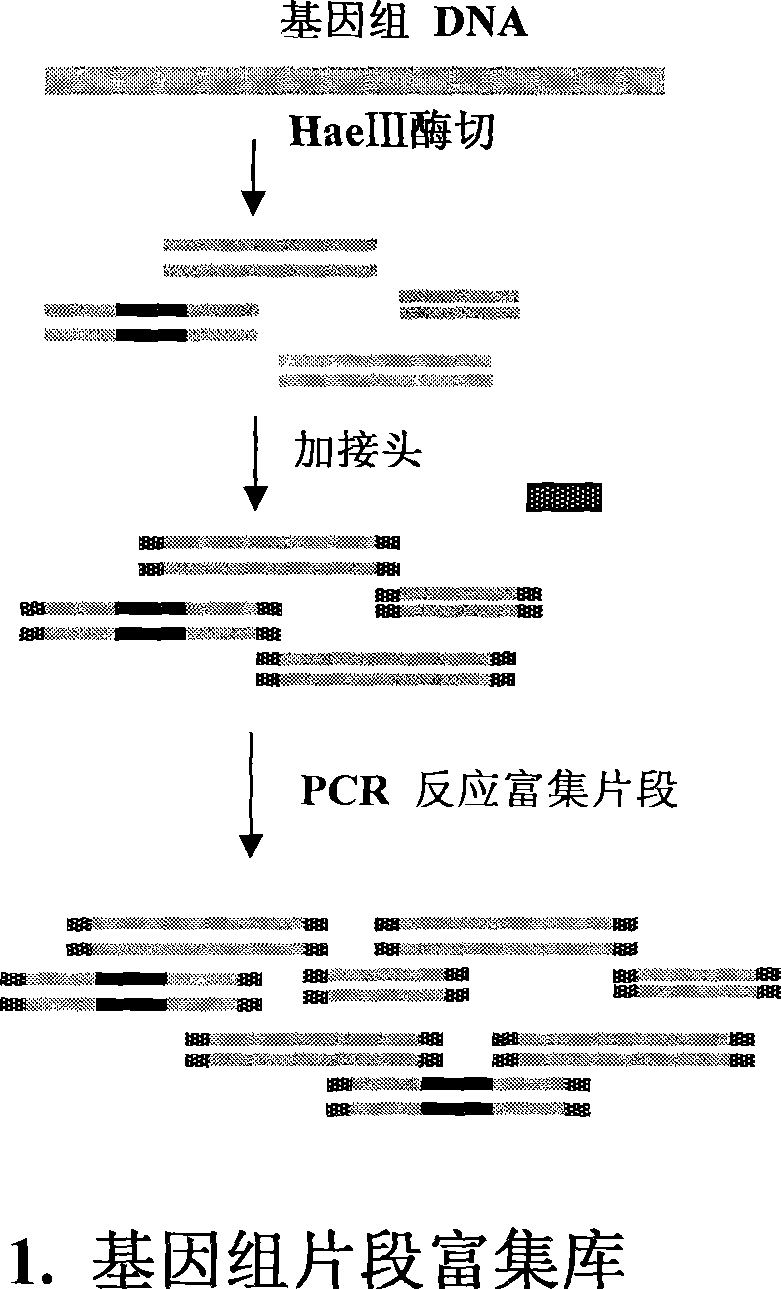
InactiveCN101381724AShort experiment cycleReduce consumption costDNA preparationPositive selectionGenomic Segment
The invention discloses a method for separation, dispersion and sequence repetition of a bead-probe complex. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, the preparation of a genome fragment enriched library, which is to perform restriction enzyme digestion on a genome, to recover fragments with adequate dimensions, to add linkers on T4 ligase, and to perform cyclic amplification of the genome fragment library after restriction enzyme digestion through PCR of a small number of linkers; secondly, the preparation of the bead-probe complex, which is to realize biotin labeled DNA probes by the primer amplification method, and to bind biotin labeled single-chain probes on beads; and thirdly, acquisition of a target fragment group, which is to perform crossover on the bead-probe complex and the genome library, to acquire a target fragment, to separate and clone the target fragment, and to perform positive selection on the target fragment. The method is simple, high-efficiency and quick, shortens the experimental period, reduces the cost consumption, greatly improves the efficiency, and does not require special experimental equipment.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
Floating method of high calcium magnesite
A flotation method of high calcium magnesite, which is carried out according to the following steps: grind the high calcium magnesite and add water to make raw ore pulp; put the raw ore pulp into flotation equipment, add inhibitors and stir; add collector Stirring; adding foaming agent to stir; then reverse flotation roughing, the original concentrate obtained by reverse flotation roughing is subjected to reverse flotation and concentration for 1~2 times; desiliconized pulp is made, and inhibitors are added to stir, and hexadecimal Sodium phosphate is stirred, and RA715 is added to stir, and the positive flotation roughing is carried out, and the obtained desiliconized concentrate is subjected to 1~2 positive flotation concentration, and the magnesite concentrate is obtained. The grade of the ore processed by the method of the invention is low, and the obtained magnesite concentrate can reach the special grade standard of the metallurgical industry, and the flotation effect is good and the cost is low.
Owner:陈淑芳
Method for detecting CTC (circulating tumor cell) surface marker molecule GPC3 (glypican-3)
InactiveCN106645724AHigh sensitivityThe detection method is simpleMaterial analysisSurface markerFluorescence
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology, and particularly discloses a method for detecting a CTC (circulating tumor cell) surface marker molecule GPC3 (glypican-3). The method comprises the following steps: performing erythrocyte splitting on blood, spreading and enriching all of left karyotes (mainly comprising CTCs and lymphocytes) on a nano-substrate for fixation by virtue of a nanotechnology, marking all the cells by virtue of a nucleus fluorescent dye DAPI, performing positive selection by virtue of a tumor immune fluorescent marker, i.e. a cytokeratin antibody anti-CK, and since a CTC surface has a specific expression of the GPC3, incubating all the cells by virtue of a GPC3 primary antibody, performing incubation by virtue of a secondary antibody marked with an FITC fluorescence group, and finally performing scanning by virtue of a high-throughput technology. Compared with the prior art, the detection method has the advantages of convenience, rapidness, economy, high sensitivity and specificity and capability of overcoming the defects of large sample amount requirement and incomplete reaction of GPC3 detection in the prior art.
Owner:SHANGHAI PERMED BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
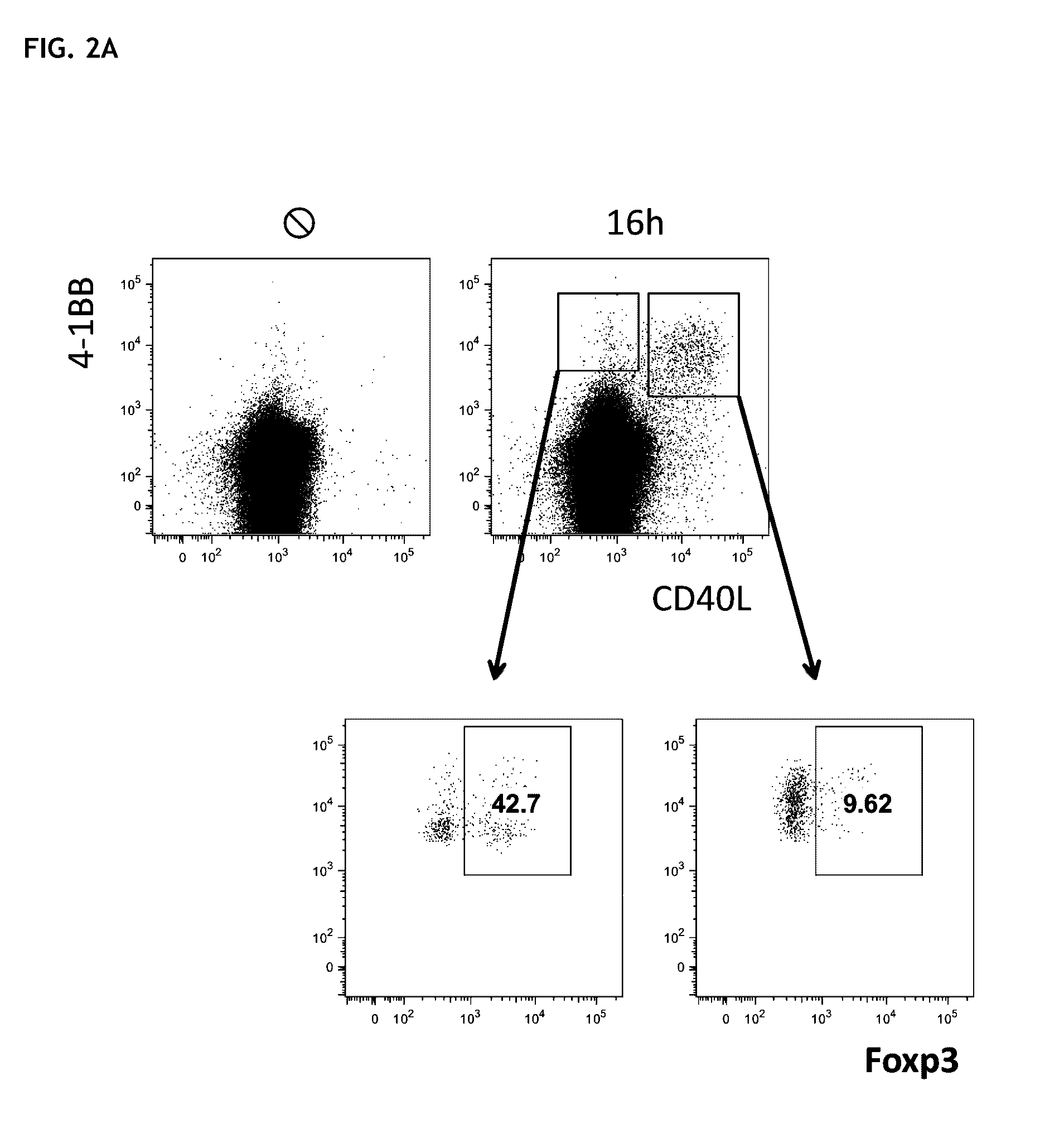
Method for the identification and separation of non-regulatory T-cells from a mixture of regulatory T-cells
The present invention relates to a method of identifying and separating non-regulatory T-cells (conventional T-cells) from a mixture comprising regulatory T-cells by using of the CD154 molecule (CD40 ligand) through depletion of CD154+ T-cells from the mixture or in combination with additional positive selection of Treg using markers that are specific for regulatory T-cells, such as for example, CD25, GITR, CTLA4 or markers which are specific for activated regulatory T-cells, such as, for example, CD137, “latent TGF-beta (LAP)”, GARP (LRRC32), CD121a / b, thereby generating a cell composition of activated Treg cells. The invention relates also to a kit comprising an antibody for detecting CD154 and at least one additional antibody for detecting markers for activated or non-activated regulatory T-cells. The antibodies can be coupled to a fluorescent dye or magnetic microparticles.
Owner:MILTENYI BIOTEC B V & CO KG
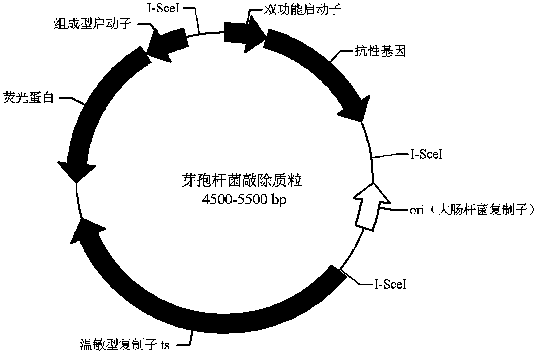
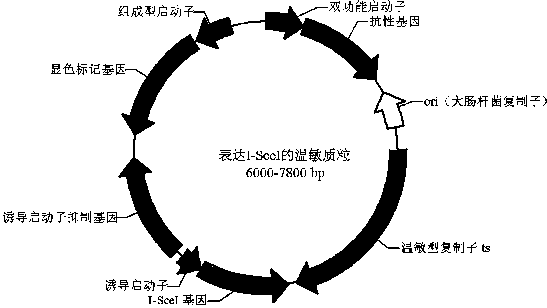
Bacillus gene traceless knockout/knockin plasmid and method, and kit
ActiveCN105505975AEasy to filterImprove efficiencyNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliPromoter
The invention discloses a bacillus gene traceless knockout / knockin plasmid and method, and a kit. The genome of the bacillus gene traceless knockout / knockin plasmid contains only one kind of resistance gene marked with a positive selection marker, a replicon capable of being duplicated in escherichia coli, a thermo-sensitive type replicon capable of being duplicated in bacillus, at least one I-Scel enzyme cutting site and only one kind of chromogenic protein gene, wherein promoters in front of the resistance gene and the chromogenic protein gene are both constitutive promoters in bacillus. The invention further provides a helper plasmid used for improving the knockout / knockin efficiency of the bacillus gene traceless knockout / knockin plasmid, and resistance gene and chromogenic protein gene in the genome of the helper plasmid are different from those of the knockout / knockin plasmid. By the adoption of the two plasmids, one or more target DNA sequences in the genome of bacillus can be modified continuously or iteratively, and the plasmids can be applied to multiple fields including bacillus genetic modification, metabolic process researching, functional genome researching and industrial application researching.
Owner:WUHAN KANGFUDE BIOTECH CO LTD
Selective technique for rapid identification of proteins and genes and uses thereof
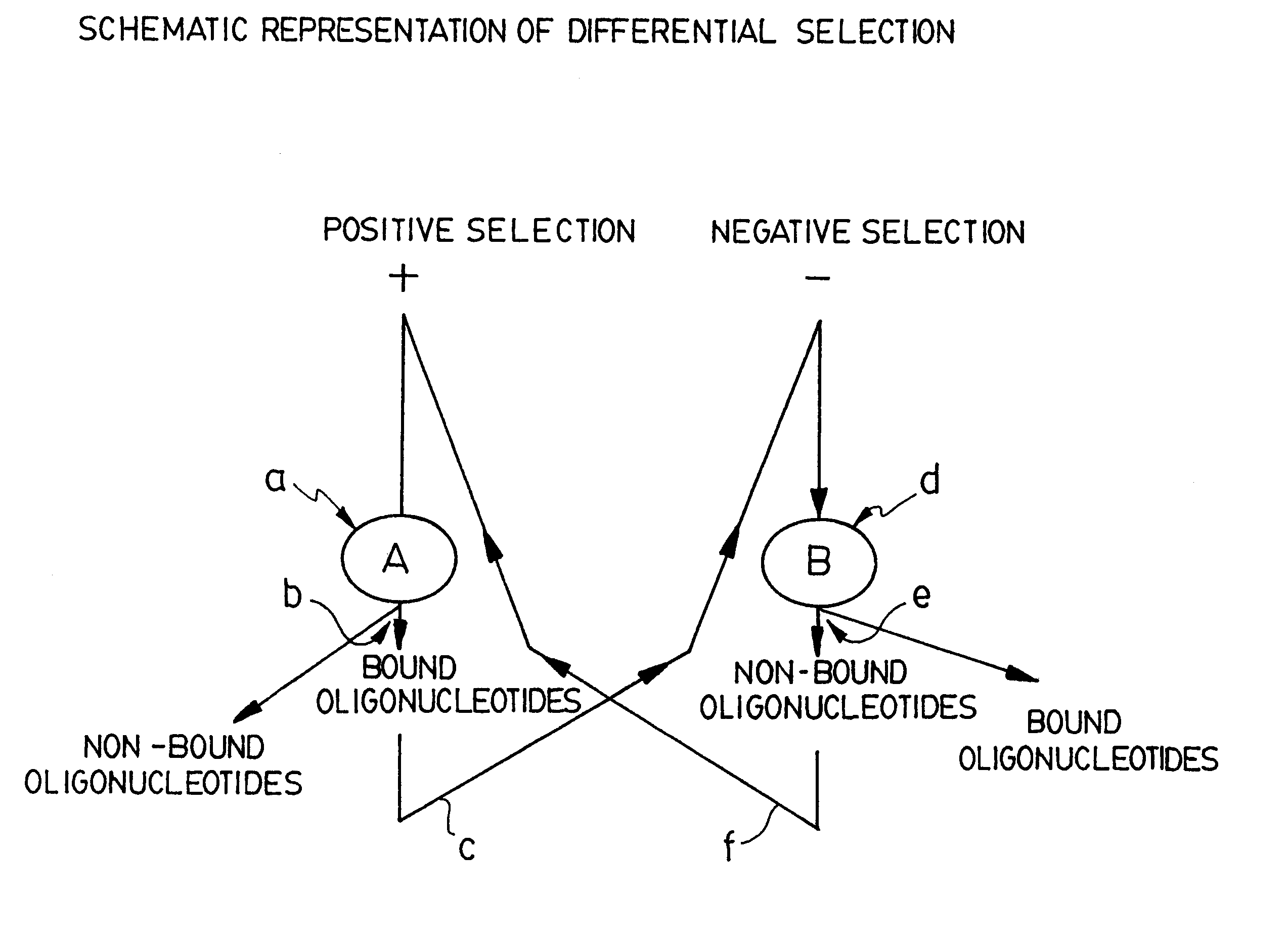
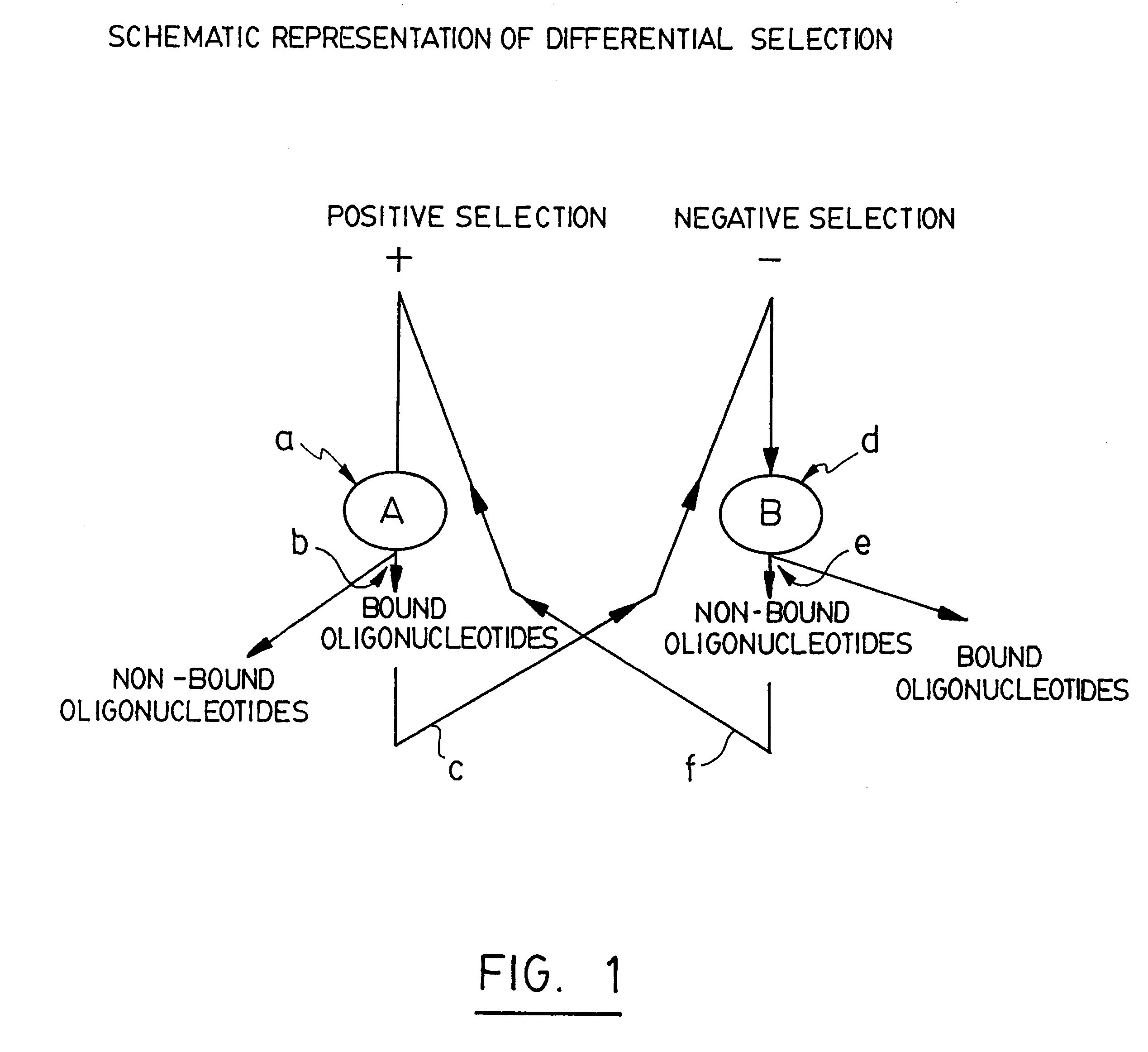
The current invention relates to a method for selecting oligonucleotides able of identifying differences at the molecular level between a plurality of biological systems. This method has been named "STRIPGEN" for "Selective Technique for Rapid Identification of Proteins and GENes". The STRIPGEN method involves selection of oligonucleotides having a higher affinity and specificity for target molecules of a first biological system and a lower affinity for binding target molecules of a second biological system. STRIPGEN is based on a sheme of positive selection over a first biological system and negative selection over a second biological system, and uses step-wise iterations of binding, separation and amplification. This method is very powerful since it can discriminate very subtle differences between biological systems of the same type such as between normal and abnormal cell types.
Owner:POLYGENE INC
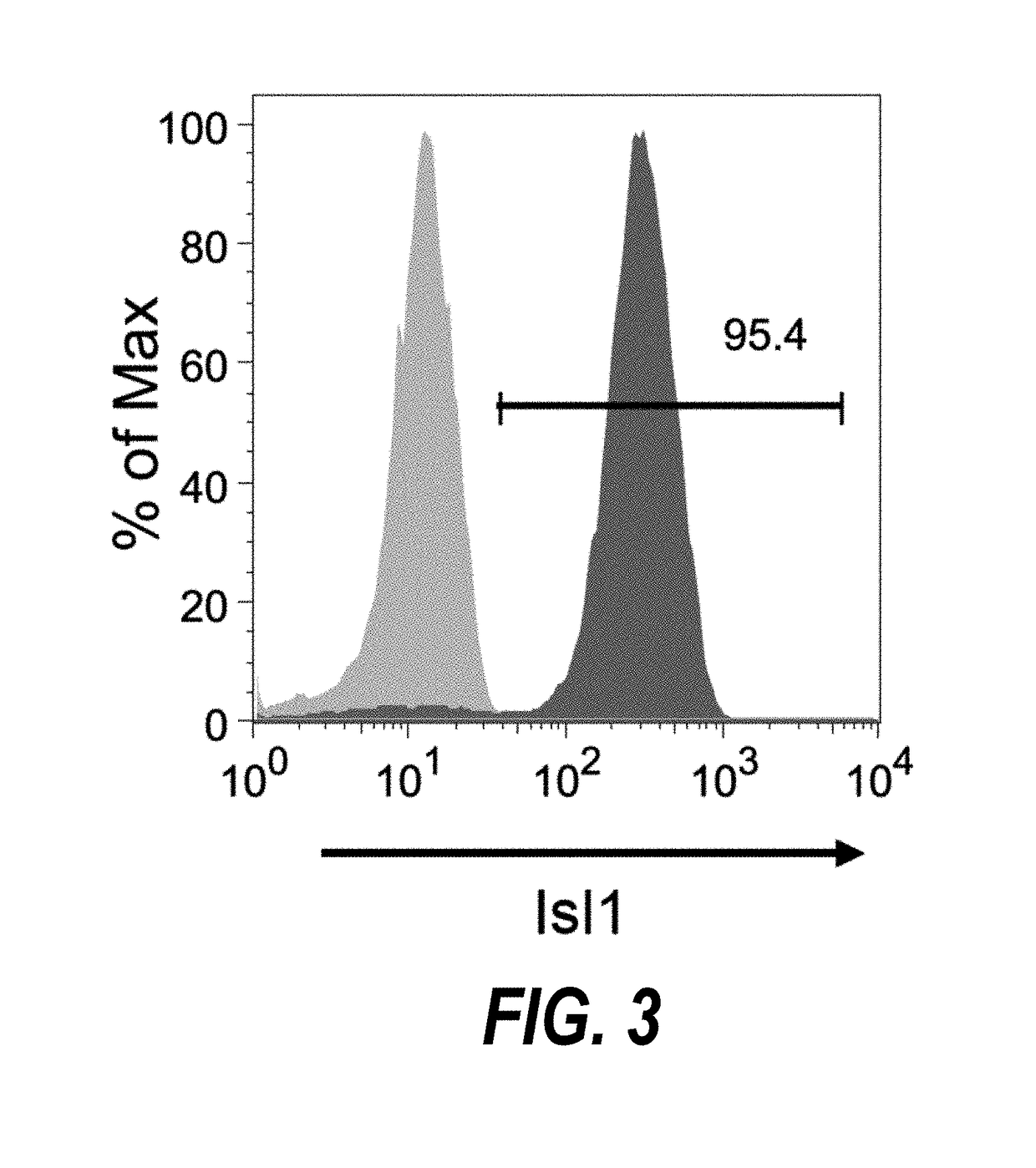
Methods for isolating human cardiac ventricular progenitor cells
ActiveUS20180148691A1Potential variationSkeletal/connective tissue cellsUnknown materialsProgenitorPositive selection
The present invention provides methods for isolating human cardiac ventricular progenitor cells (HVPs), wherein cultures of day 5-7 cardiac progenitor cells are negatively selected for one or more first markers expressed on human pluripotent stem cells, such as TRA-1-60, to thereby isolate HVPs. The methods can further include positive selection for expression of a second marker selected from the group consisting of JAG1, FZD4, LIFR, FGFR3 and TNFSF9. Large populations, including clonal populations, of isolated HVPs that are first marker negative / second marker positive are also provided. Methods of in vivo use of the HVPs for cardiac repair or to improve cardiac function are also provided. Methods of using the HVPs for cardiac toxicity screening of test compounds are also provided.
Owner:PROCELLA THERAPEUTICS AB
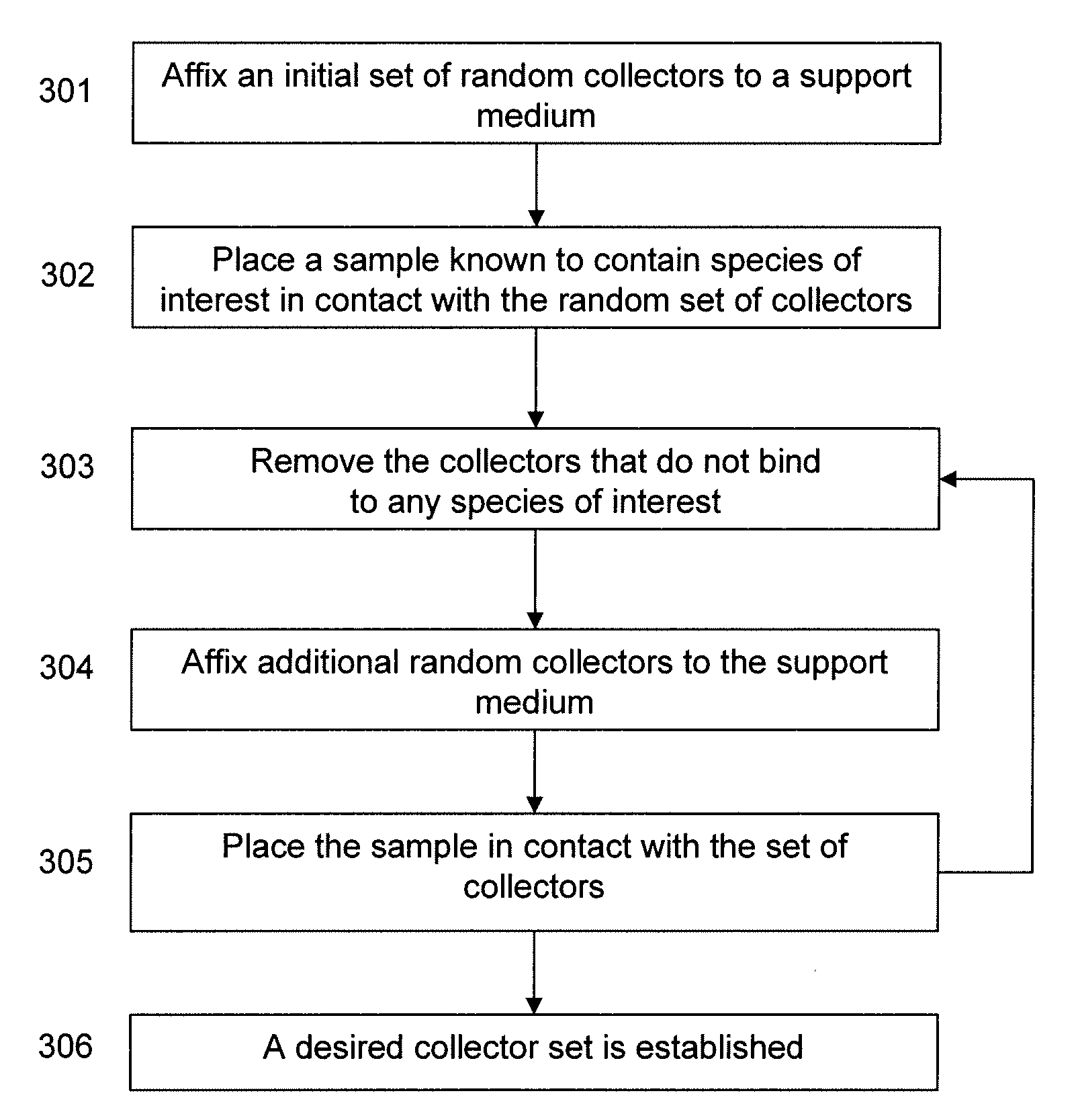
Positive selection of serum proteins for proteomic analysis
ActiveUS20100055697A1Other chemical processesMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein FeatureOrganism
This invention relates to methods and kits for positive selection of species of interest based on peptide / protein sequence from a biological sample. The species of interest may be proteins and / or peptides of interest which may be placed through a mass spectrometer to obtain a blood peptide / protein signature. The blood peptide / protein signature may be used in proteomic analysis. The techniques include but are not limited to the use of collectors comprising nucleic acid molecules to extract a composition that has a lower concentration of a high abundance species of interest from a sample. This limits the level of influence that any collectors species may have on the results of a mass spectra.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT +1
Method for creating non-wrapround rice two-line sterile line with CRISPR/Cas9 technology
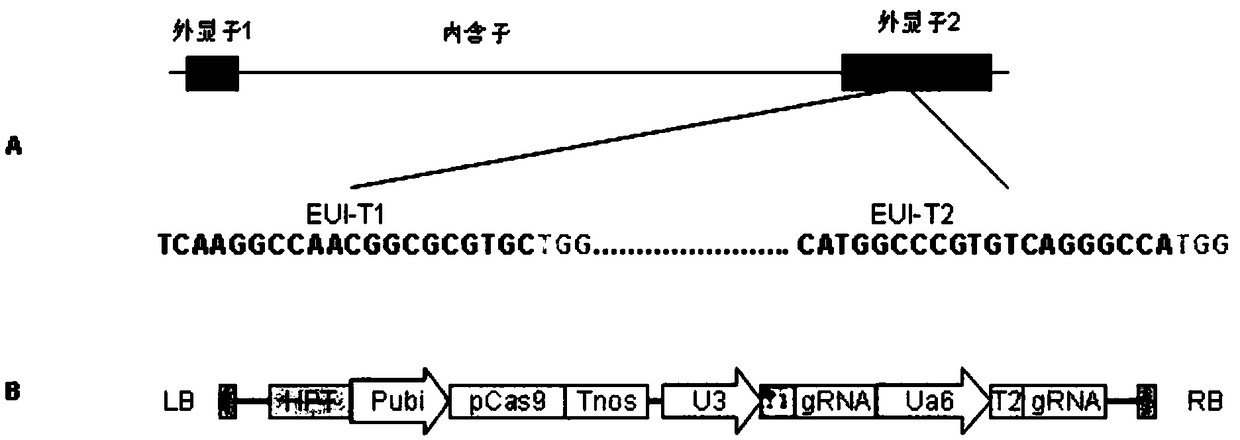
PendingCN109306358AImprovement of Circumcision Genetic DisorderOvercoming the phenomenon of ear wrapping that cannot fully stretch out the sheath of the sword leafHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionSequence analysisPositive selection
The invention provides a method for breeding non-wrapround rice sterile line rice with a CRISPR / Cas9 technology. The method comprises the following steps: designing a target sequence according to an EUI (Elongated Uppermost Internode) gene coding sequence in rice, and constructing a pCRISPR / Cas9-EUI-gRNA recombinant vector containing a target sequence fragment; transforming rice callus tissue through agrobacterium to obtain a transgenic seedling; performing positive selection, sequencing analysis and transgenic element detection on the transgenic seedling to obtain a function deletion mutant free from a transgenic component. By adopting the method, an EUI gene is subjected to site-directed mutation by using the CRISPR / Cas9 technology to realize oriented creation of the non-wrapround rice two-line sterile line free from the transgenic component. The method has the advantages of high targeting efficiency, short breeding period, low cost and high practicability.
Owner:HUNAN HYBRID RICE RES CENT
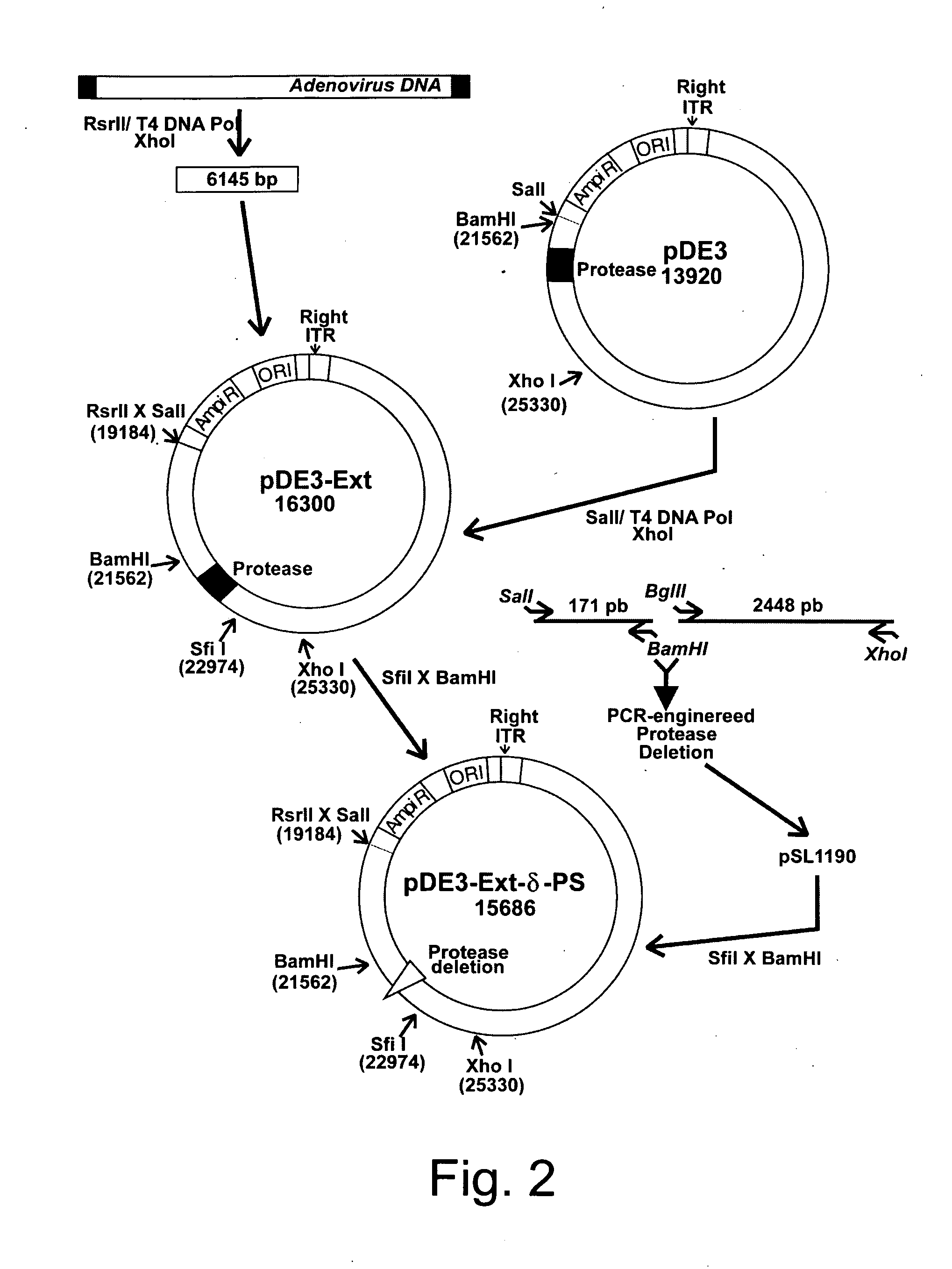
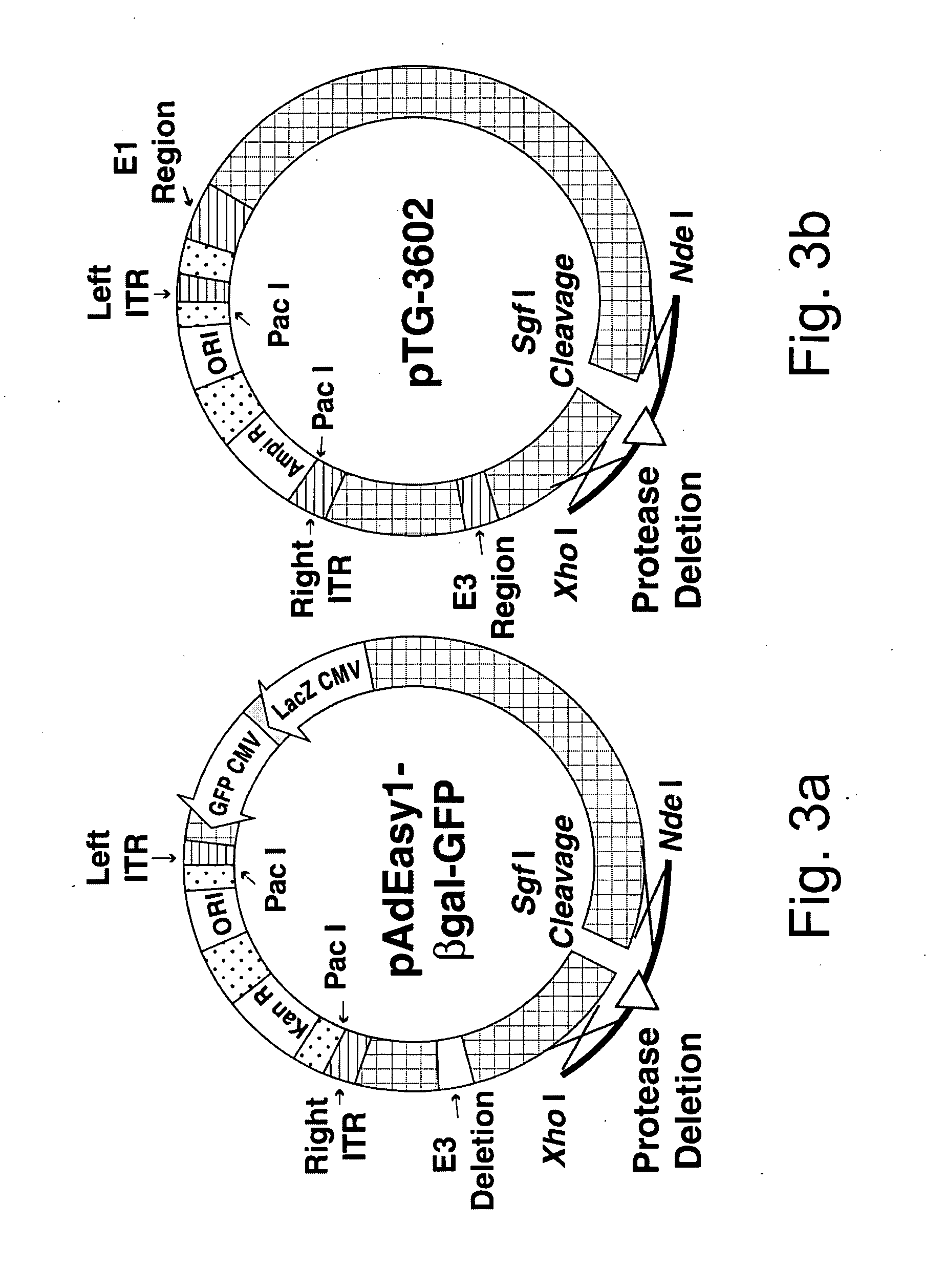
Efficient generation of adenovirus-based libraries by positive selection of adenoviral recombinants through ectopic expression of the adenovirus protease
InactiveUS20060210965A1Improve securityImprove suitabilityVectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementExpression LibraryShuttle vector
Disclosed is a new system for generating recombinant adenovirus vectors and adenovirus-based expression libraries, by positive selection of recombinants deleted for the endogenous protease gene, which gene is expressibly cloned into another region of the adenoviral genome. In a preferred embodiment, the invention allows positive selection of E1-deleted, protease-deleted recombinant adenovirus vectors comprising an exogenous gene or an expressible piece of exogenous DNA, by providing an expression cassette comprising the protease gene and the exogenous DNA inserted in place of E1 region in a shuttle vector. In vivo recombination of the shuttle vector with a protease-deleted adenoviral genome in suitable non-complementing cells generates viable recombinants only when rescuing the protease cloned in E1 region. Non-recombinant viral genomes are not able to grow due to the deletion of the protease gene, ensuring that only recombinant viral plaques are generated. This positive selection can be used for the generation of a large number of high purity recombinant adenovirus vectors and allows generation of adenovirus-based libraries with diversity exceeding 106 clones.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Positive selection of serum proteins for proteomic analysis
This invention relates to methods and kits for positive selection of species of interest based on peptide / protein sequence from a biological sample. The species of interest may be proteins and / or peptides of interest which may be placed through a mass spectrometer to obtain a blood peptide / protein signature. The blood peptide / protein signature may be used in proteomic analysis. The techniques include but are not limited to the use of collectors comprising nucleic acid molecules to extract a composition that has a lower concentration of a high abundance species of interest from a sample. This limits the level of influence that any collectors species may have on the results of a mass spectra.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT +1
Immunomagnetic bead for peripheral blood lymphocyte separation and preparation and application thereof
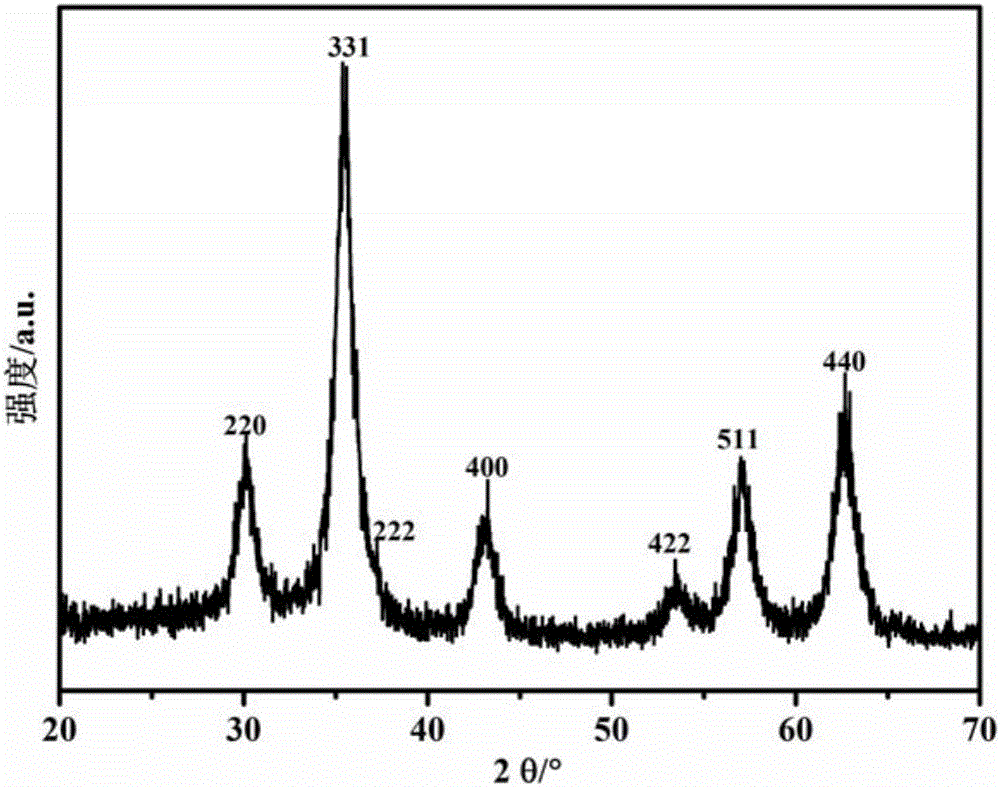
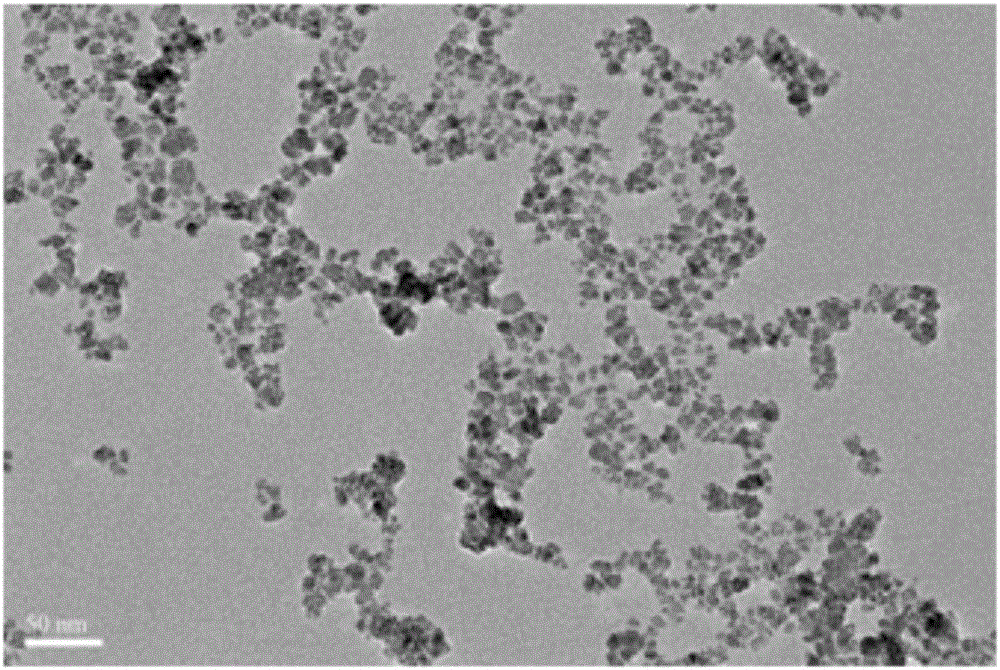
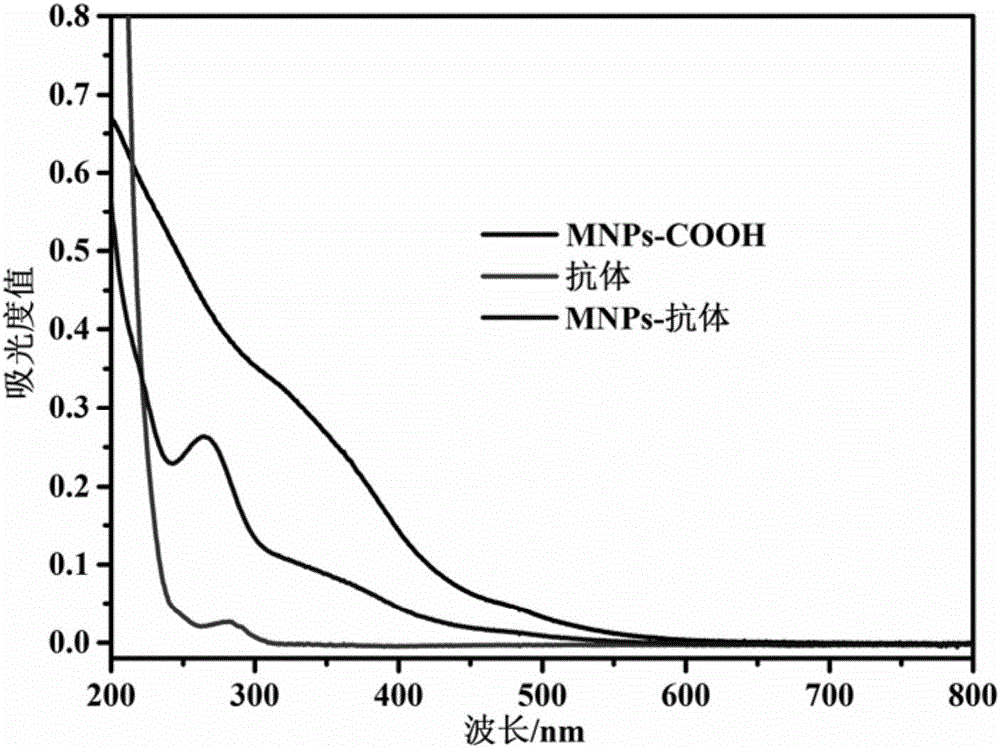
InactiveCN106366194AEasy to makeMake fastMaterial nanotechnologyCell dissociation methodsSolubilityMagnetite Nanoparticles
The invention relates to an immunomagnetic bead for peripheral blood lymphocyte separation. The immunomagnetic bead comprises carboxylic ferroferric oxide magnetic nanoparticles and a specific antibody, wherein the mass ratio of the carboxylic ferroferric oxide magnetic nanoparticles to the specific antibody is (2-5) to (0.1-0.5), a specific antibody is selected from one or more of CD8, CD3E, IL2RA and CD4. The immunomagnetic bead is obtained by preparing the carboxylic ferroferric oxide magnetic nanoparticles uniform in particle size distribution, good in water solubility and excellent in magnetic property through a hydrothermal method and then coupling the nanoparticles with the specific antibody. Compared with the prior art, the immunomagnetic bead has the advantages that the bead is simple in preparation process and good in stability, a matched separation column is large in sample amount, high in positive selection rate, low in cost and the like, sufficient high-activity lymphocytes can be obtained, and the lymphocytes can be preserved for revival, culture and re-delivery at a proper time.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
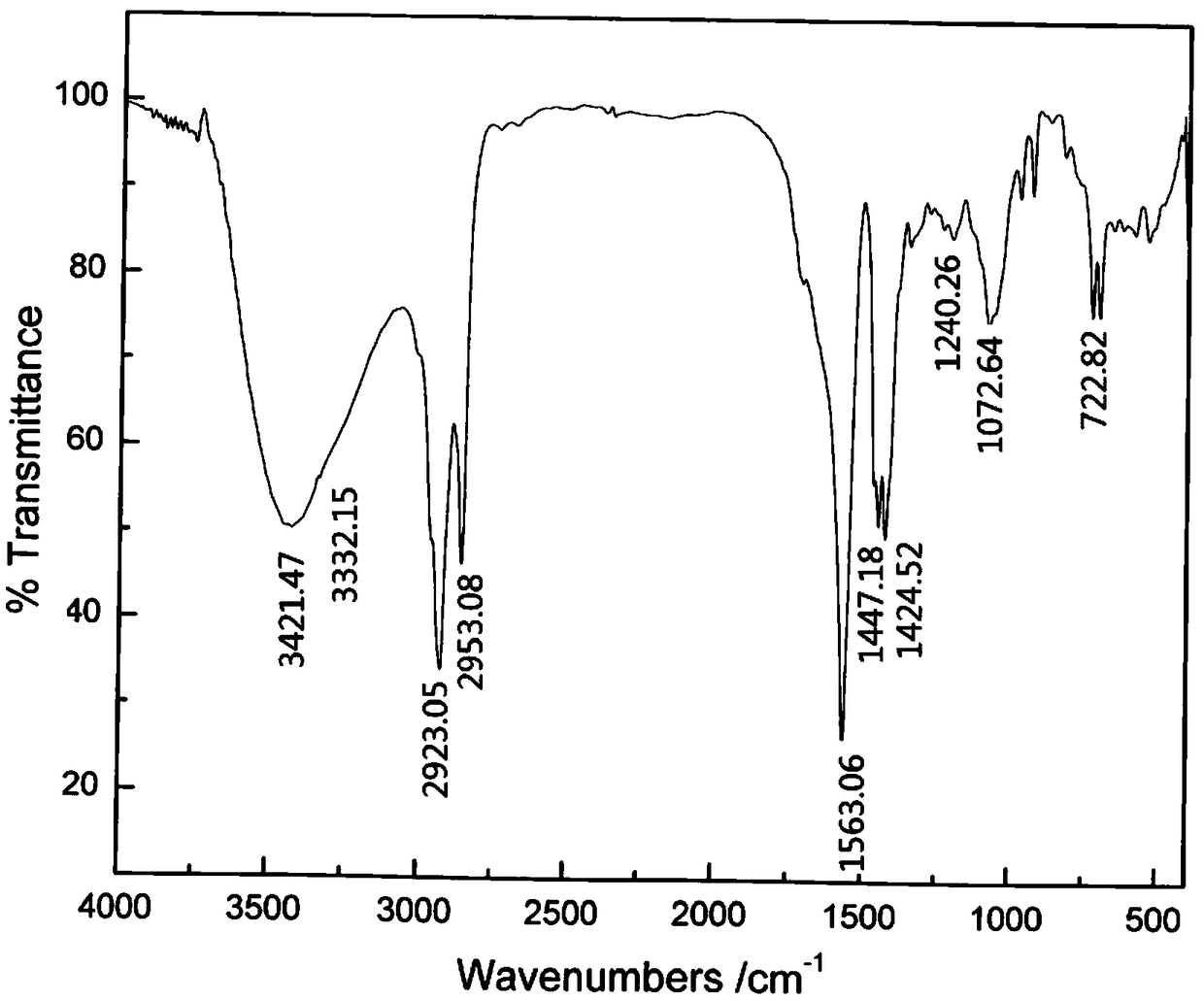
Alpha-aminodihydroxy fatting acid soap collector as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108816523AEnhanced harvesting capacityImprove conductivityFlotationPositive selectionPhosphorite
The invention relates to an alpha-aminodihydroxy fatting acid soap collector as well as a preparation method and application thereof. A structural formula of the alpha-aminodihydroxy fatting acid soapcollector is shown in the following description, wherein C8H17 is a linear-chain octacarbon alkyl group. The collector provided by the invention has efficient selectivity to dolomite, is strong in ore carrying ability, small in dosage of a reagent and good in foam flowability, can be used for desilicication with positive selection and also magnesium removal with reversed selection, has better sorting feature to Ca2+ ions and Mg2+ ions, has good collecting performance, has the mineral processing comprehensive efficiency of 82.91-84.64 percent, is available in raw material and low in mineral processing cost, can perform low-temperature flotation at about 10 DEG C and is suitable for the field of collophanite flotation.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Gene targeting vectors comprising conditional positive selection markers
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions useful in producing cells and animals having a disruption or modification of a target gene. Vectors useful in producing these cells and animals are described. In addition, methods of screening and enriching cells comprising a targeted gene modification are provided.
Owner:DELTAGEN INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com