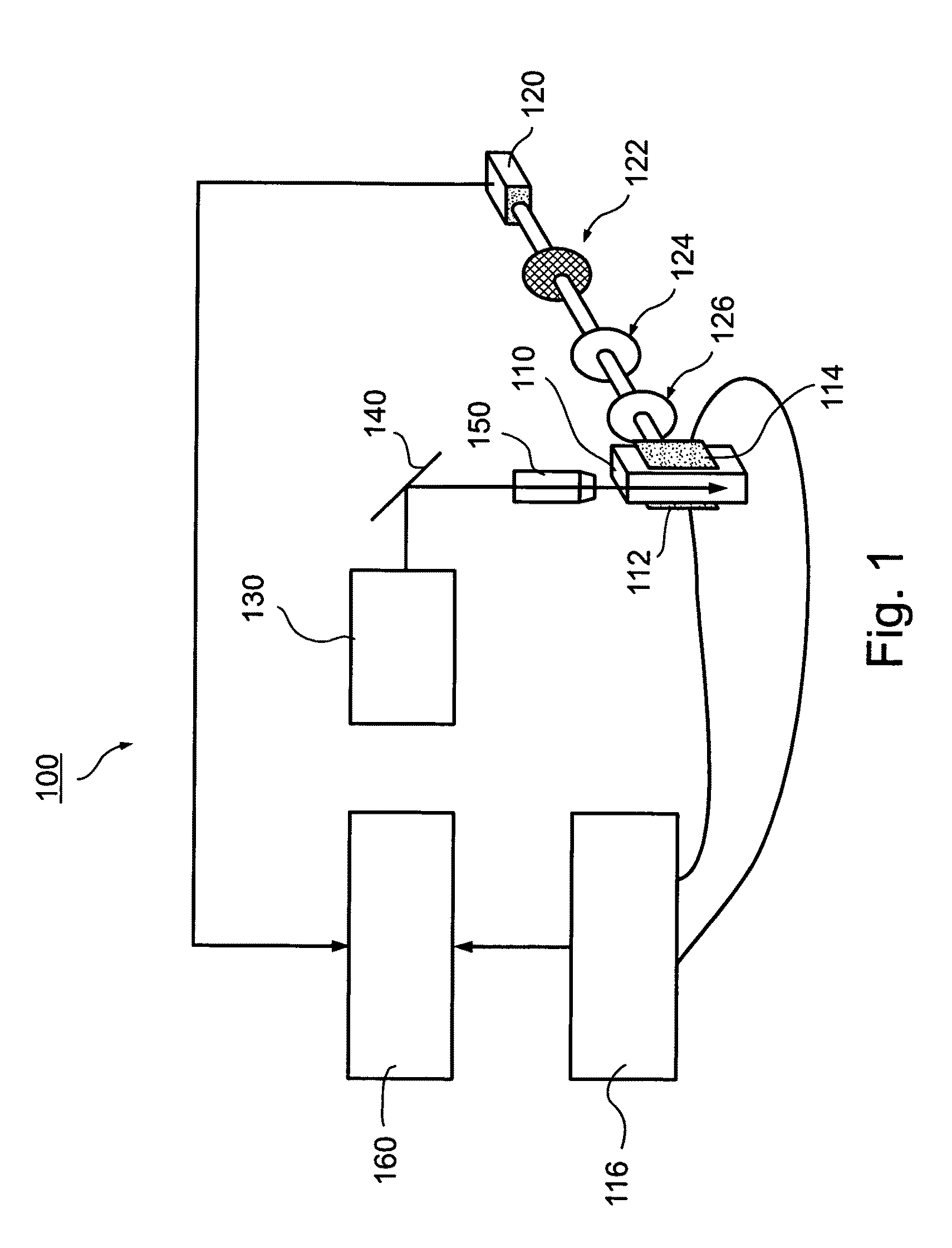
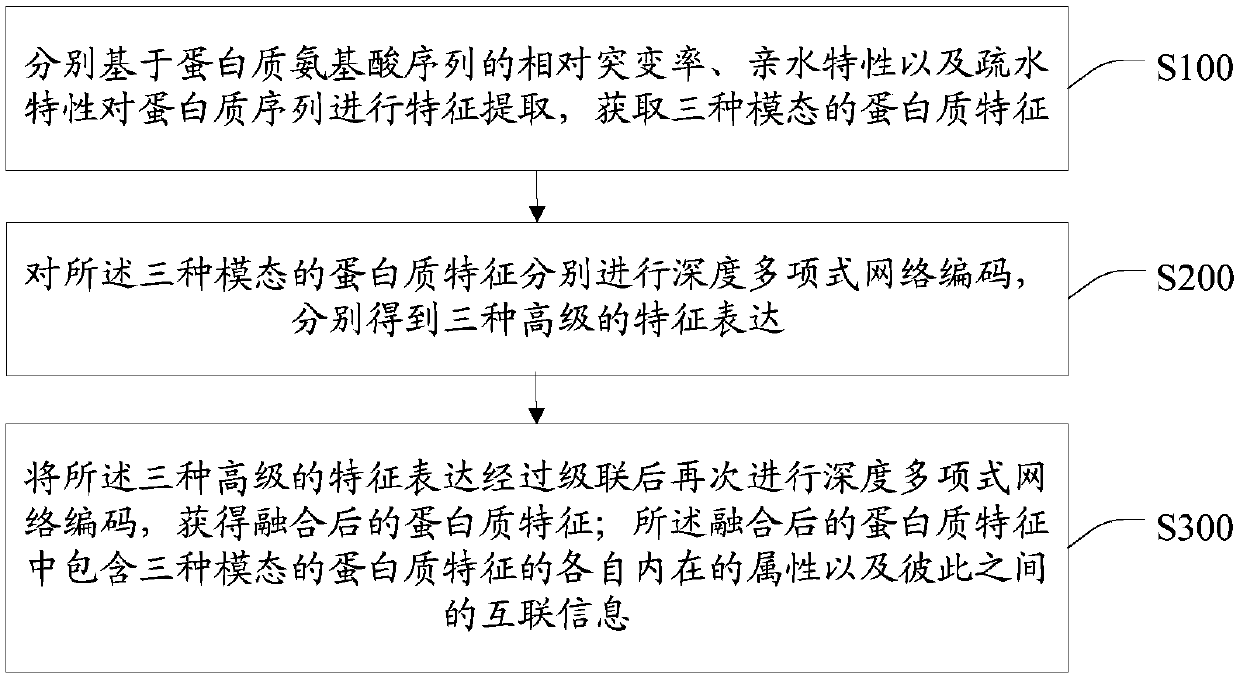
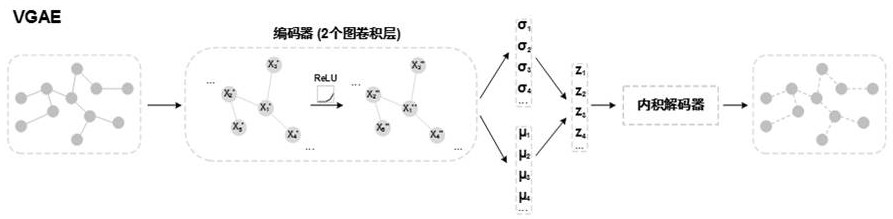
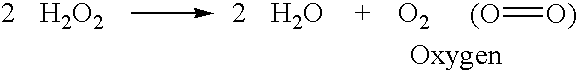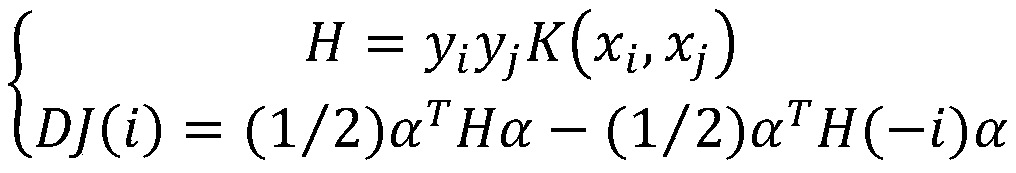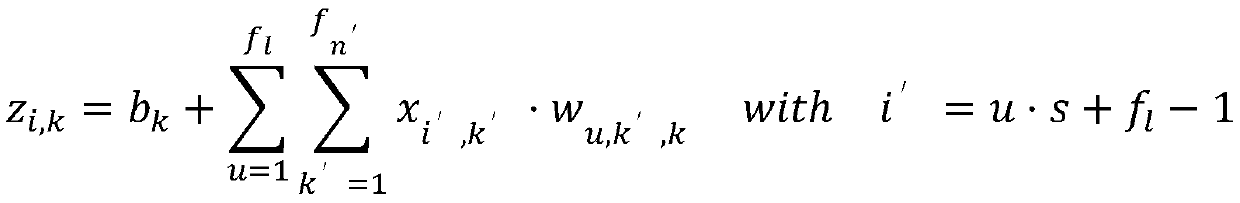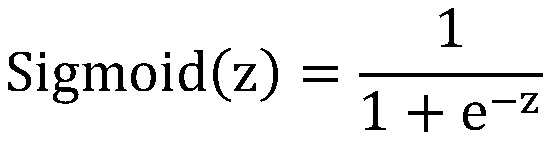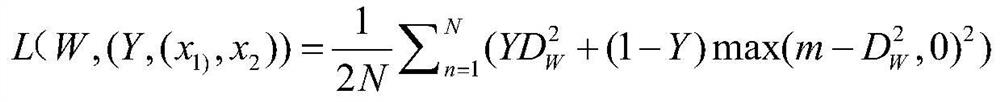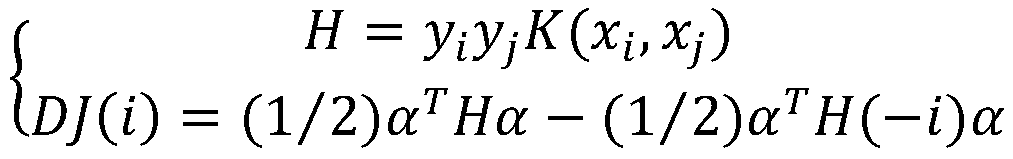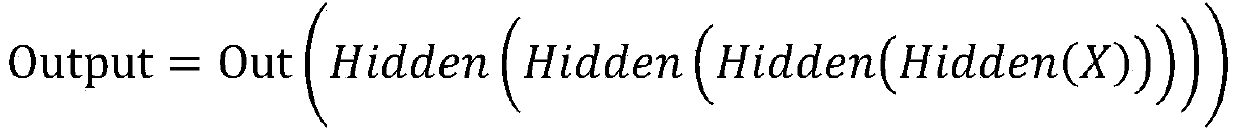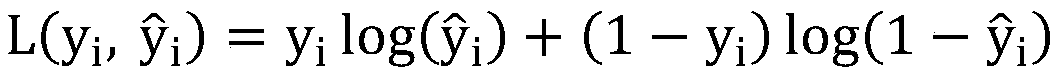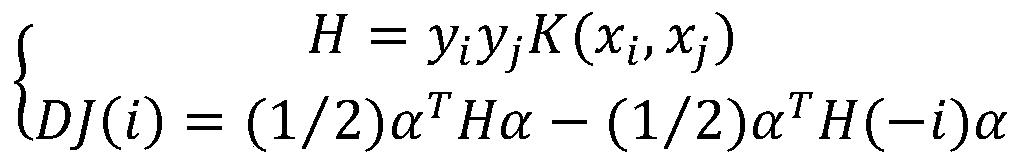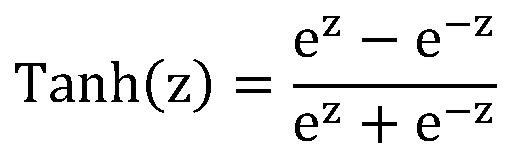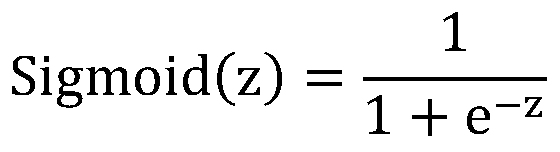Patents
Literature
94 results about "Protein Feature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
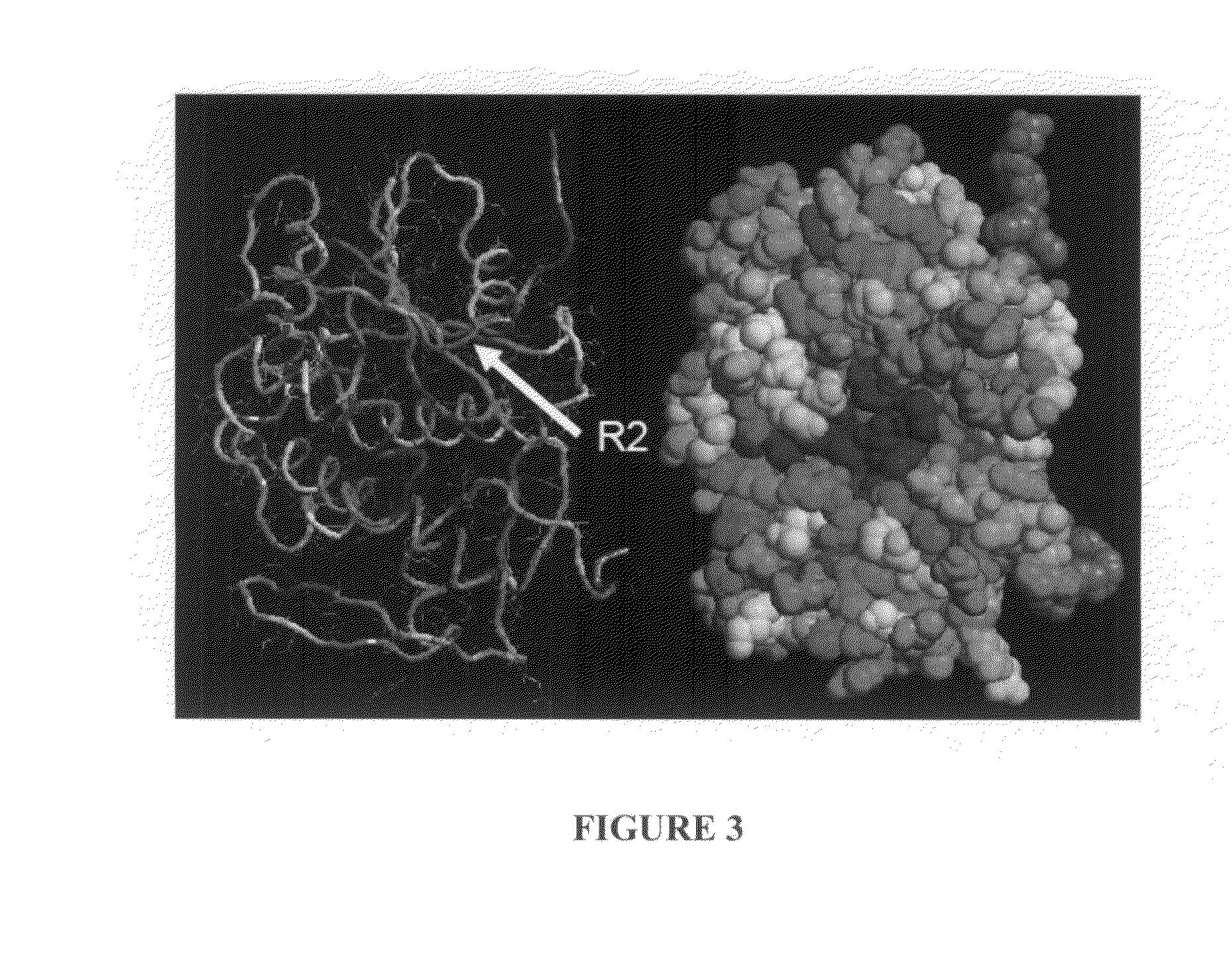
Protein Feature View of PDB entries mapped to a UniProtKB sequence ... Gag-Pol polyprotein may regulate its own translation, by the binding genomic RNA in the 5'-UTR. At low concentration, the polyprotein would promote translation, whereas at high concentration, the polyprotein would encapsidate genomic RNA and then shut off translation.
Methods for the isolation and analysis of cellular protein content
InactiveUS6969614B1Rapid and reliable to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementWithdrawing sample devicesLymphatic SpreadPresent method
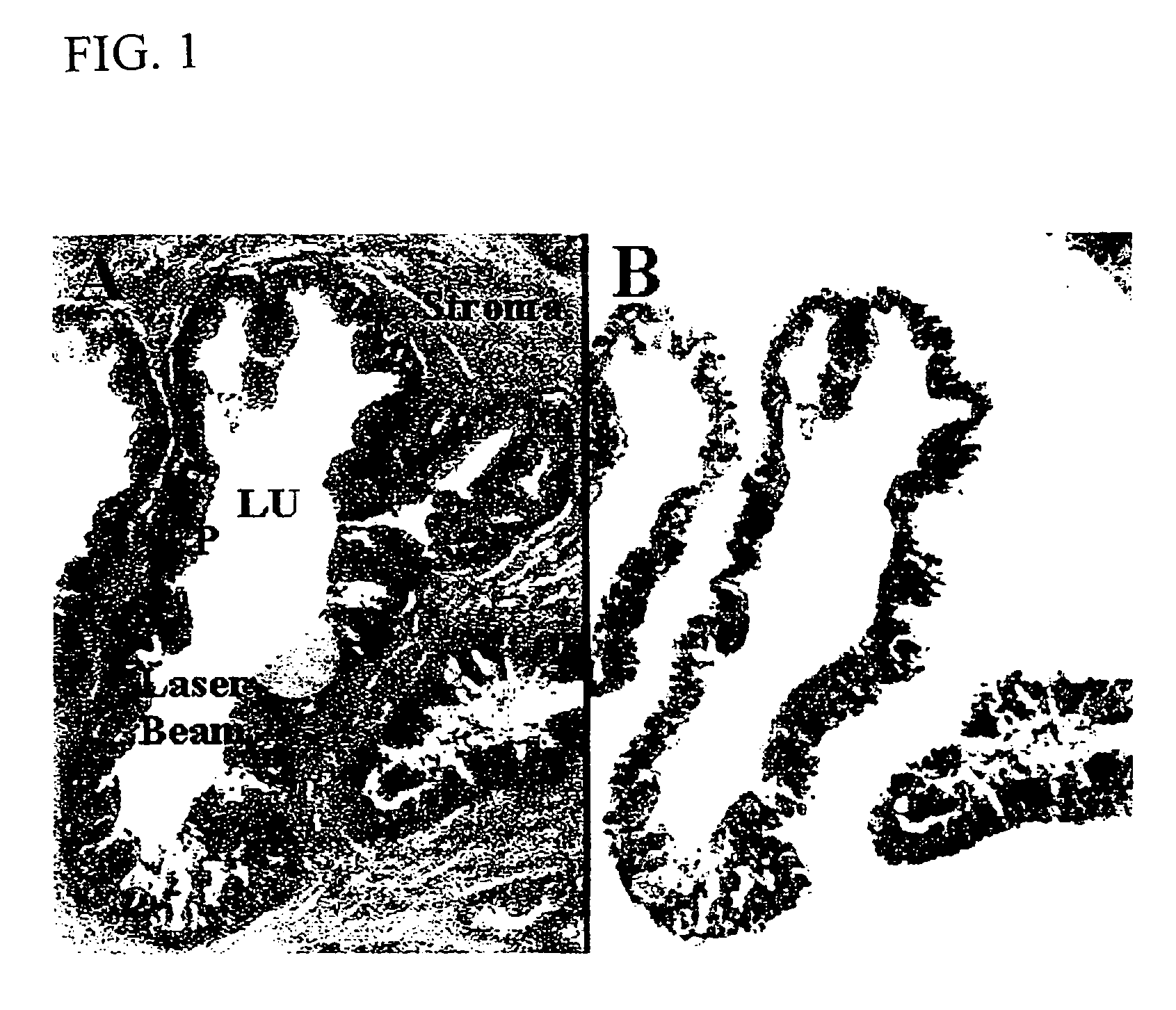
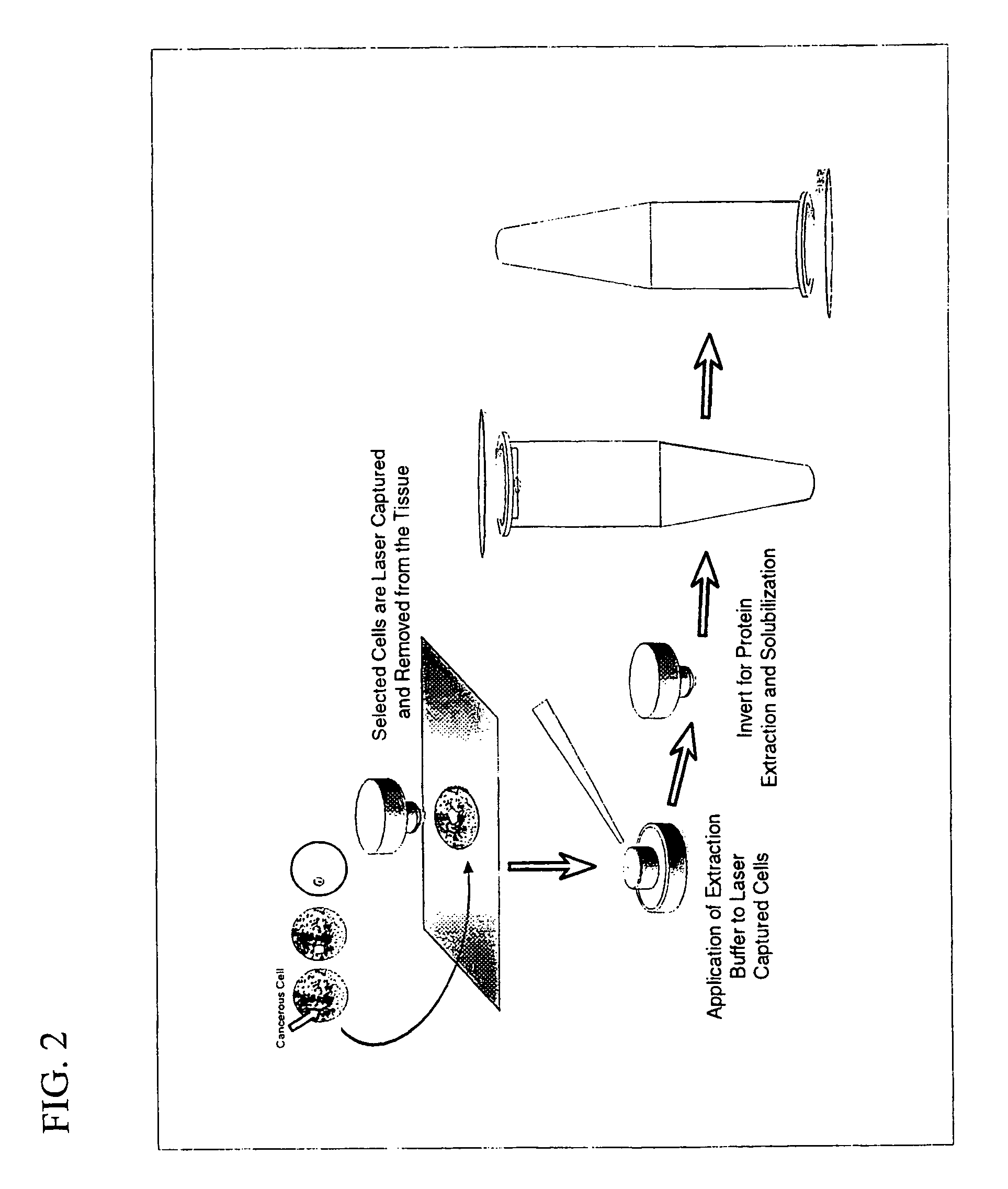
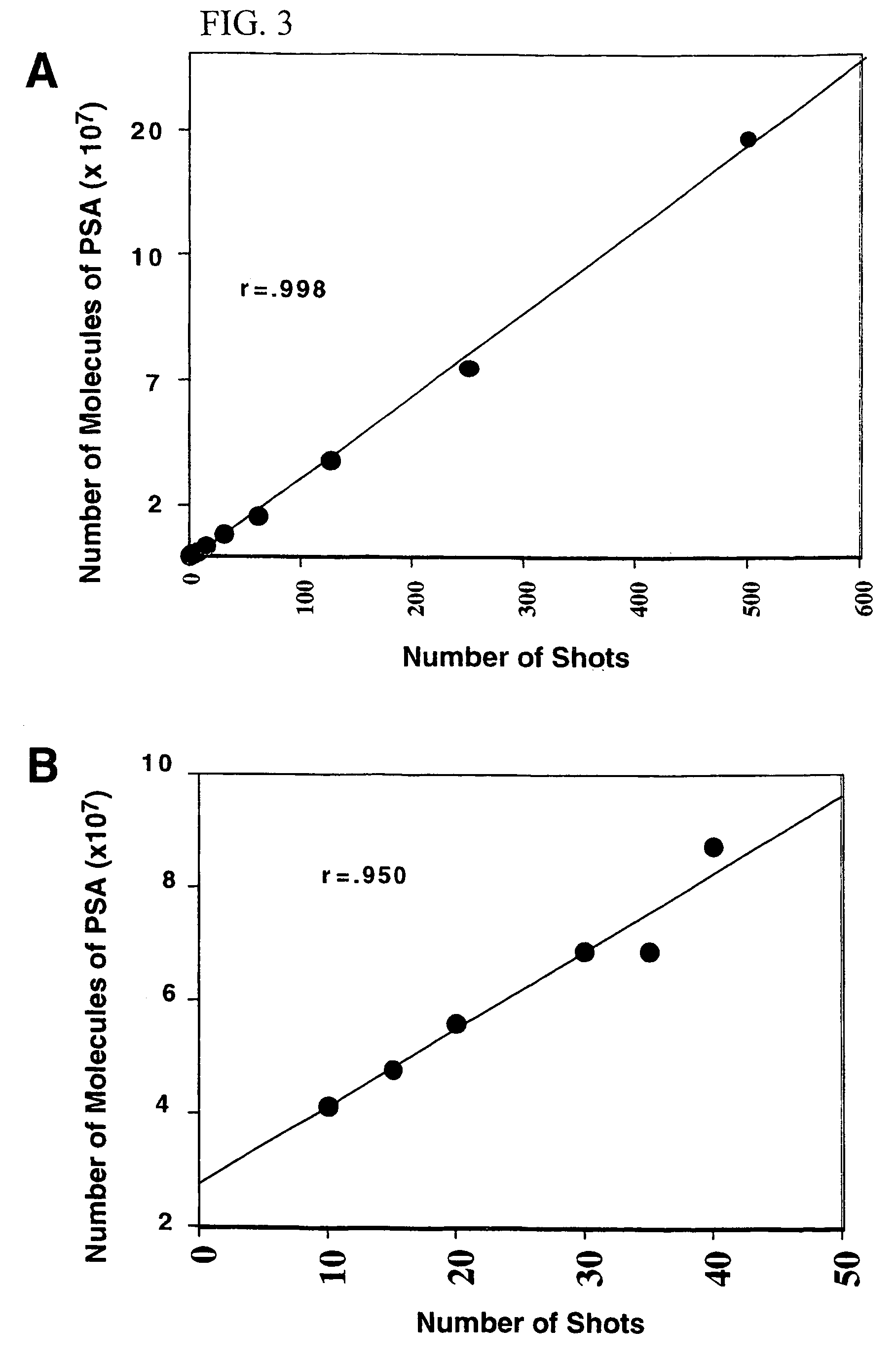
The present invention describes devices and methods for performing protein analysis on laser capture microdissected cells, which permits proteomic analysis on cells of different populations. Particular disclosed examples are analysis of normal versus malignant cells, or a comparison of differential protein expression in cells that are progressing from normal to malignant. The protein content of the microdissected cells may be analyzed using techniques such as immunoassays, 1D and 2D gel electrophoresis characterization, Western blotting, liquid chromatography quadrapole ion trap electrospray (LCQ-MS), Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization / Time of Flight (MALDI / TOF), and Surface Enhanced Laser Desorption Ionization Spectroscopy (SELDI). In addition to permitting direct comparison of qualitative and quantitative protein content of tumor cells and normal cells from the same tissue sample, the methods also allow for investigation of protein characteristics of tumor cells, such as binding ability and amino acid sequence, and differential expression of proteins in particular cell populations in response to drug treatment. The present methods also provide, through the use of protein fingerprinting, a rapid and reliable way to identify the source tissue of a tumor metastasis.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
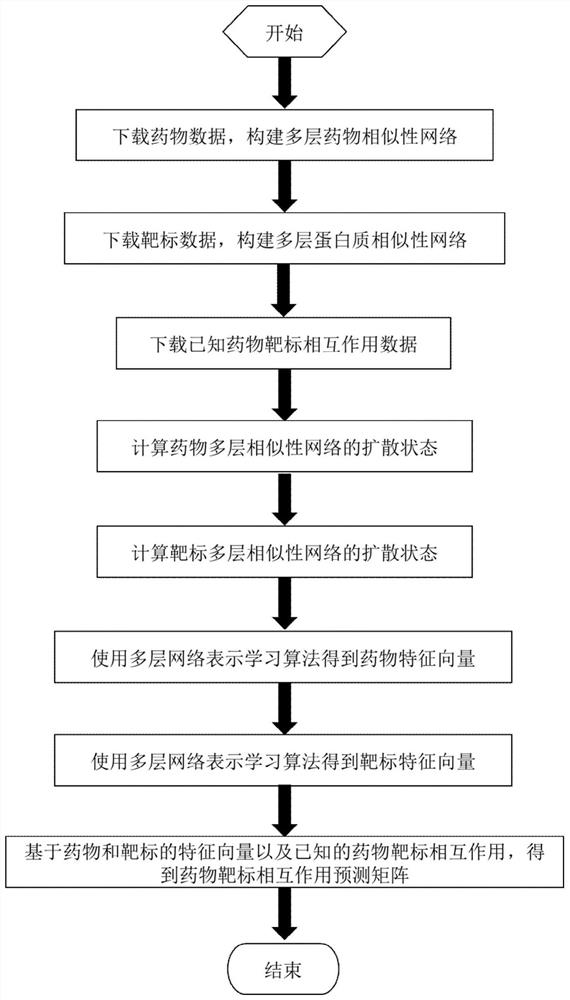
Drug target interaction prediction method based on multilayer network representation learning
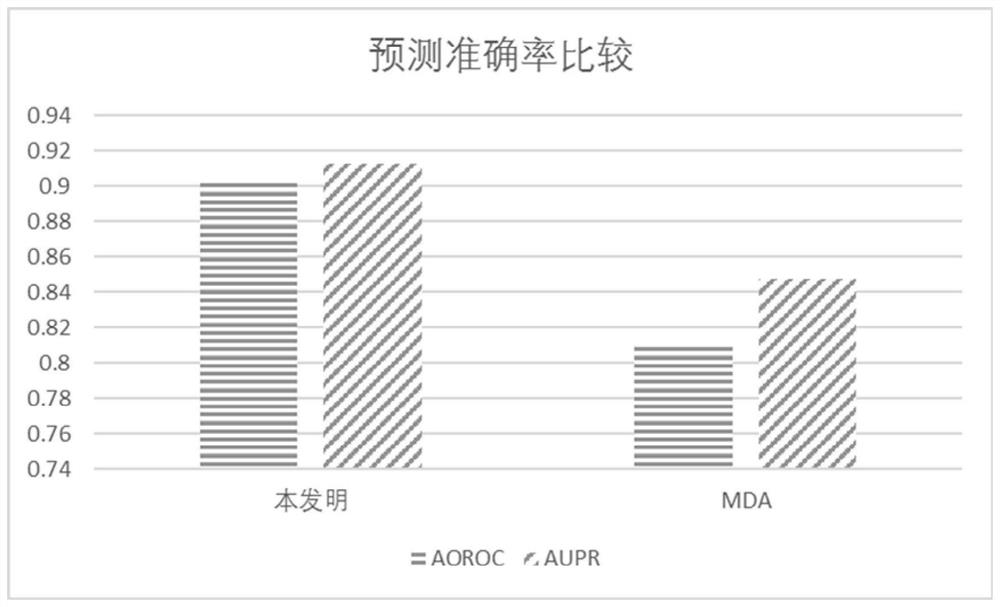
PendingCN111785320AImprove forecast accuracyAvoid the disadvantage of being biasedBiostatisticsInstrumentsPharmaceutical drugProtein Feature
The invention discloses a drug target interaction prediction method based on multilayer network representation learning, and mainly solves the problem of low prediction accuracy in the prior art. Themethod comprises the following steps: downloading data from a drug and protein database, and respectively constructing multilayer similarity networks of drugs and proteins; calculating diffusion states of the two similarity networks respectively, and integrating the diffusion states respectively to obtain feature vectors of drugs and proteins; taking known drug target interaction data as supervision information, putting the drug and protein feature vectors into the same drug target space, and respectively obtaining projection matrixes of the drug and the protein by using a bilinear function; obtaining a prediction score matrix of drug target interaction according to the two projection matrixes and ranking the prediction score matrix; regarding eight top-ranked unknown drug target pairs aspotential drug target interactions. According to the method, the prediction accuracy of drug target interaction is improved, and the method can be used for predicting candidates of drug target pairs.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Secondary protein structureprediction method based on deep neural network
InactiveCN105930686AImprove forecasting efficiencyImprove forecast accuracySpecial data processing applicationsNeural learning methodsNerve networkAlgorithm
The invention discloses a secondary protein structureprediction method based on a deep learning andneural network method, and relates to the technical field of neural networks and secondary protein structureprediction. The method comprises the steps of inputting a protein characteristic sequence, and predicting a space secondary structure of an amino acid residue at each site of the sequence through a designed deep recurrent neural network model. The method provided by the invention realizes automatic predication of the secondary structure based on input characteristics, has better generalization ability, and can train a specific model and realize secondary structure predication with high accuracy according to the different input characteristics.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Biochemical method and apparatus for detecting protein characteristics
InactiveUS20040152129A1Low costCompound screeningSequential/parallel process reactionsProtein FeatureComputer science
There is described a biochemical method for detecting one or more protein characteristics. The method utilizes supports (1), wherein the largest dimension (3) of each support (1) is less than 250 mum and wherein each support (1) incorporates sequential identification means (2). The method is distinguished in that it includes the steps of: attaching an information molecule (7), which is capable of interacting with at least one of said one or more protein characteristic to be detected, to a main surface (11) of a support (1); suspending supports (1) comprising one or more different sequential identifications means (2) and one or more different information molecules (7) in a fluid; adding a sample (8) to be analysed to the fluid; detecting interaction signals from supports (1) in the fluid using signal detecting means (40); and reading the sequential identification means (2) of the supports (1) which have an interaction signal using reading means (3), thereby detecting at least one of said one or more protein characteristic (8). There is also described apparatus susceptible for use in executing the above method.
Owner:PRONOSTICS LTD
DBN algorithm based drug targeting protein action prediction method
InactiveCN108959841AEffective use of biochemical propertiesGood foundation in biochemical interpretationNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsMedicineDrug development
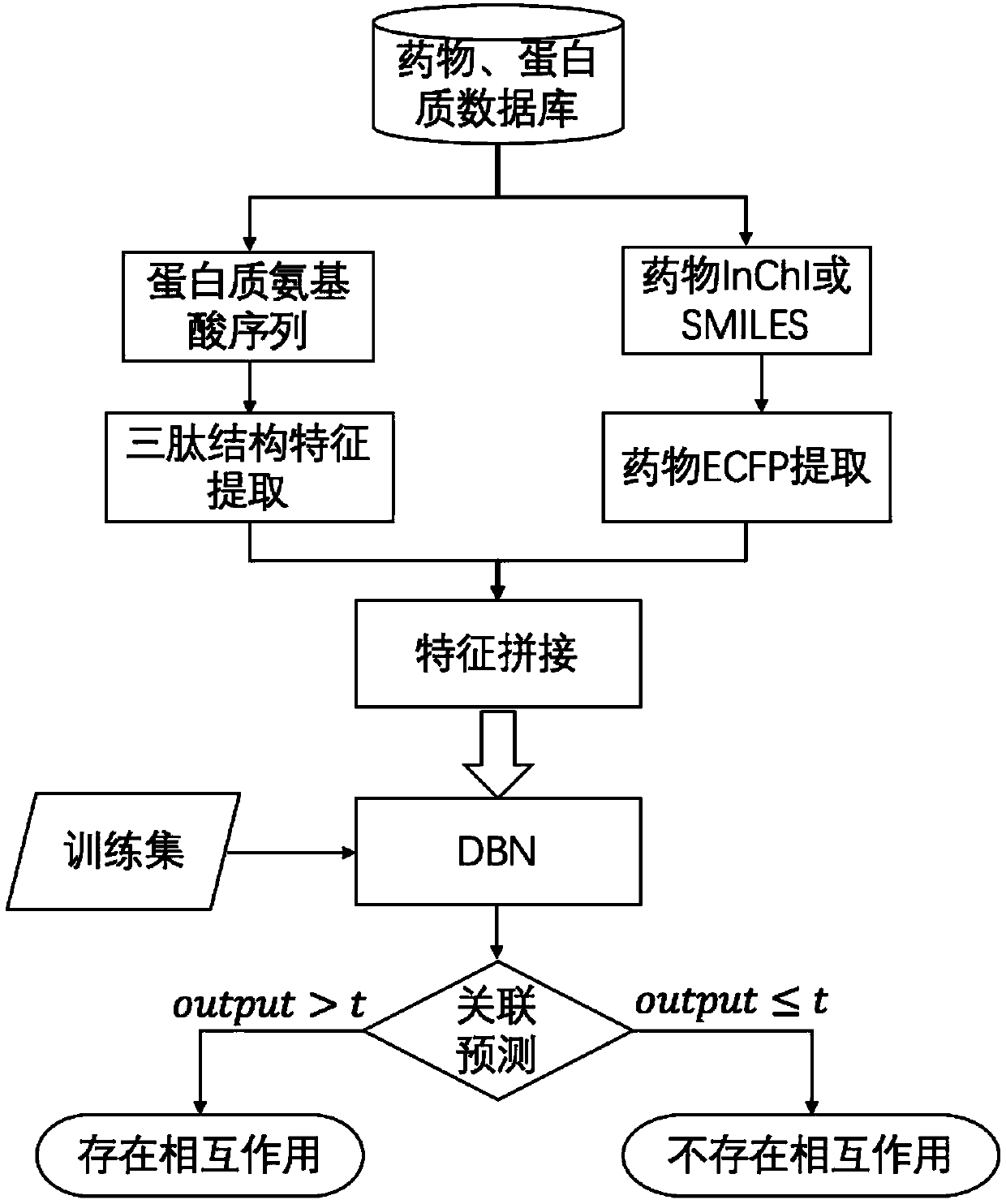
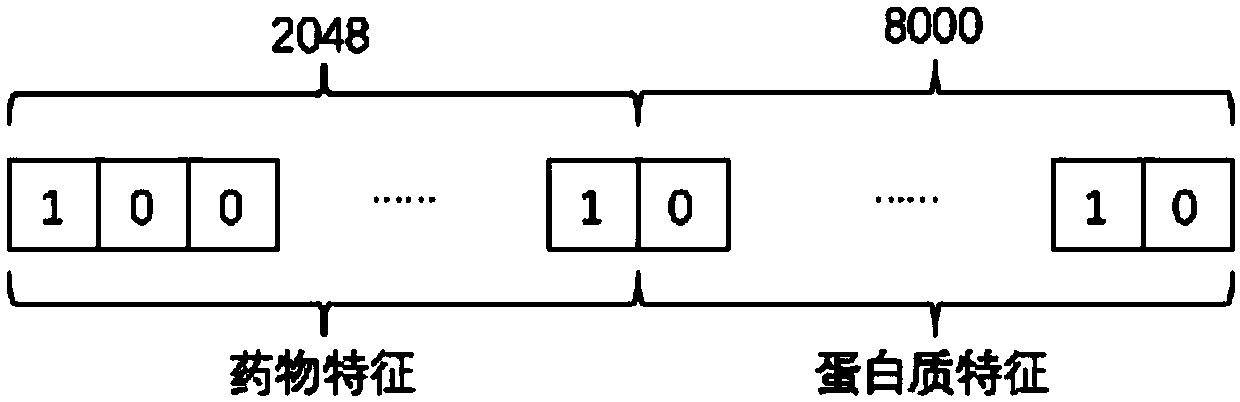
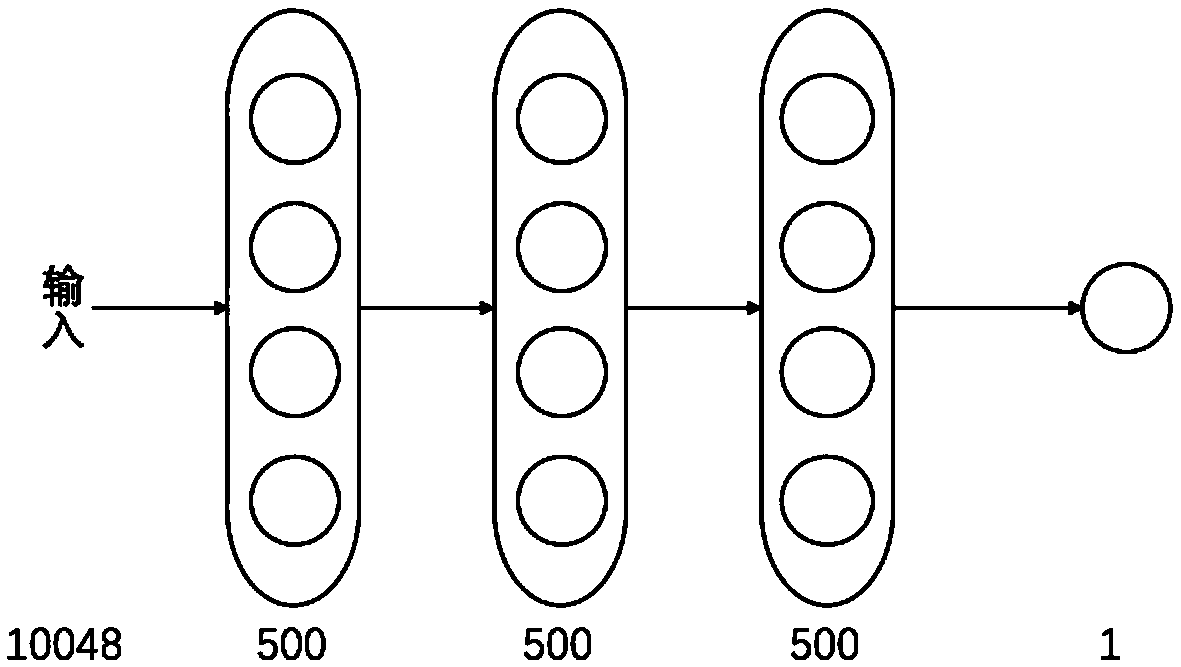
The invention discloses a DBN algorithm based drug targeting protein action prediction method. The method comprises the steps of extracting extended communication fingerprint of the drug by starting with the molecular structure of the drug; extracting tripeptide structural characteristic of the protein by starting with amino acid sequence of the protein, splicing the extended communication fingerprint of the drug and the tripeptide structural characteristic of the protein to compose a drug-protein characteristic vector, then inputting the drug-protein characteristic vector to a depth confidence network, wherein the output of the network is the probability of the drug-protein input by the network for the mutual action, and finally selecting a suitable threshold to judge the pair of the association is set up. The DBN algorithm based drug targeting protein action prediction method can give out possible interaction pair of drug-targeted protein rapidly without manual intervention, can accordingly save drug development and testing costs and speeds up drugging and discovery of new functions of drugs.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for predicting membrane protein beta-barrel transmembrane area based on sparse coding and chain training
ActiveCN104615911AHigh precisionImprove predictive performanceSpecial data processing applicationsData setPosition-Specific Scoring Matrices
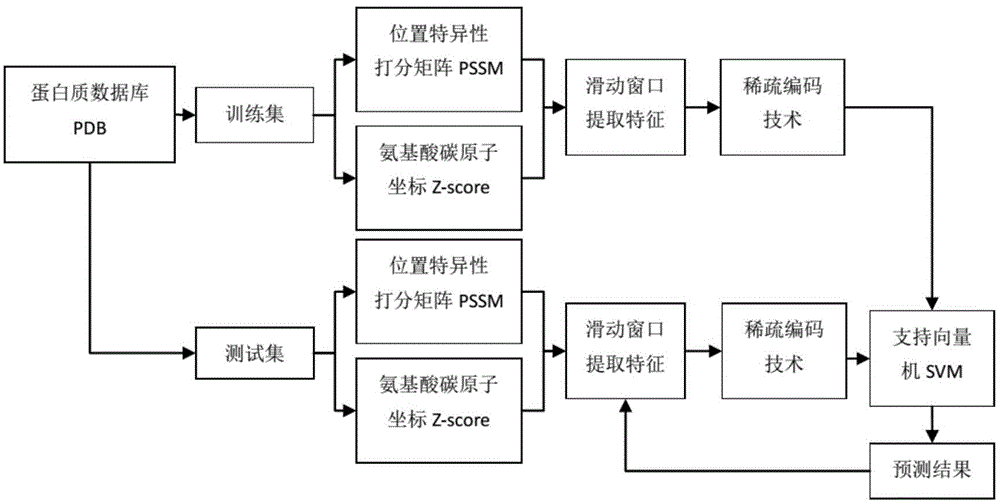
The invention provides a method for predicting a membrane protein beta-barrel transmembrane area based on sparse coding and chain training and relates to a sparse coding technology, a chain learning algorithm and a support vector machine. Structure prediction is conducted on the membrane protein beta-barrel transmembrane area through a computing method, and important information is provided for the research of the structures and functions of proteins. According to the method, the concept of digital image processing is introduced creatively, sparse coding is conducted on a protein feature matrix, and feature dimensionality reduction and denoising are achieved; a membrane protein beta-barrel data set is organized in a protein database PDB, a position-specific scoring matrix and a Z score are extracted and used as features, the position-specific scoring matrix represents amino acid evolution information, the Z score represents the position information of amino acid residues, a feature vector is extracted through a sliding window, multi-feature fusion is achieved, a chain learning algorithm training model based on a SVM classifier is provided, a predication effect is remarkably improved, and a Jakenife cross validation result shows that the precision can reach 92.5%.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
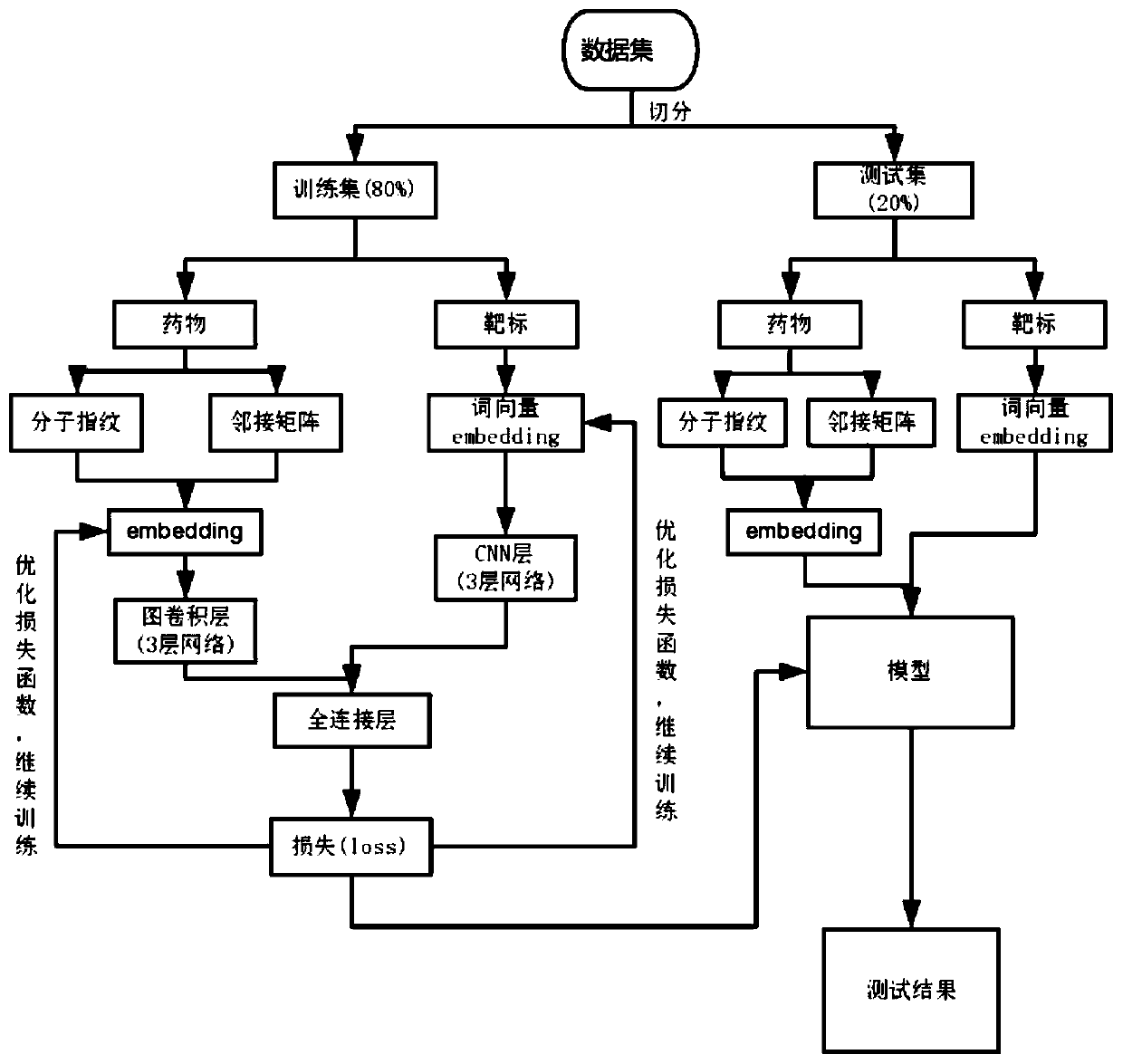
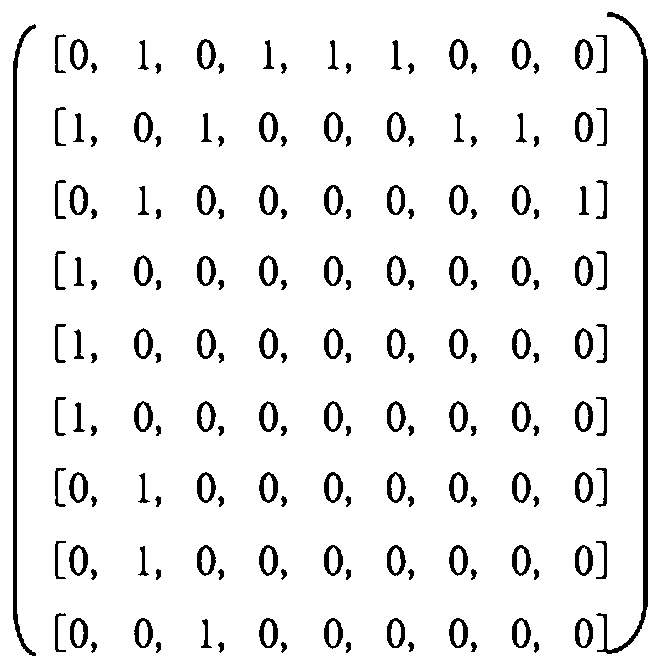
Drug-target interaction prediction method based on graph convolution and word vector
ActiveCN110289050AImprove accuracyShorten the timeMolecular designChemical processes analysis/designAlgorithmProtein molecules
The invention provides a drug-target interaction prediction method based on graph convolution and word vectors. The method comprises the steps of: extracting molecular fingerprint features and adjacency matrix features from the medicine; training the features by utilizing graph convolution, cutting a protein molecular expression into groups, expressing the groups by utilizing a 100-dimensional vector, training word vector characteristics of the target by utilizing the CNN, and finally, combining the trained drug and the target together to carry out final result prediction. The method has the beneficial effects that more characteristics related to the medicine can be provided, so that higher accuracy is achieved; protein features are constructed by utilizing the word vectors, so that the feature construction time is greatly shortened; related information of a drug molecular diagram can be completely stored without losing characteristics; training time can be greatly shortened.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
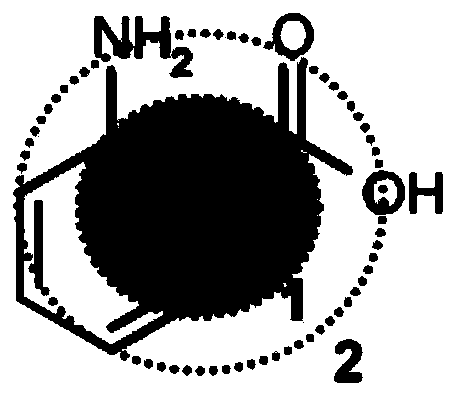
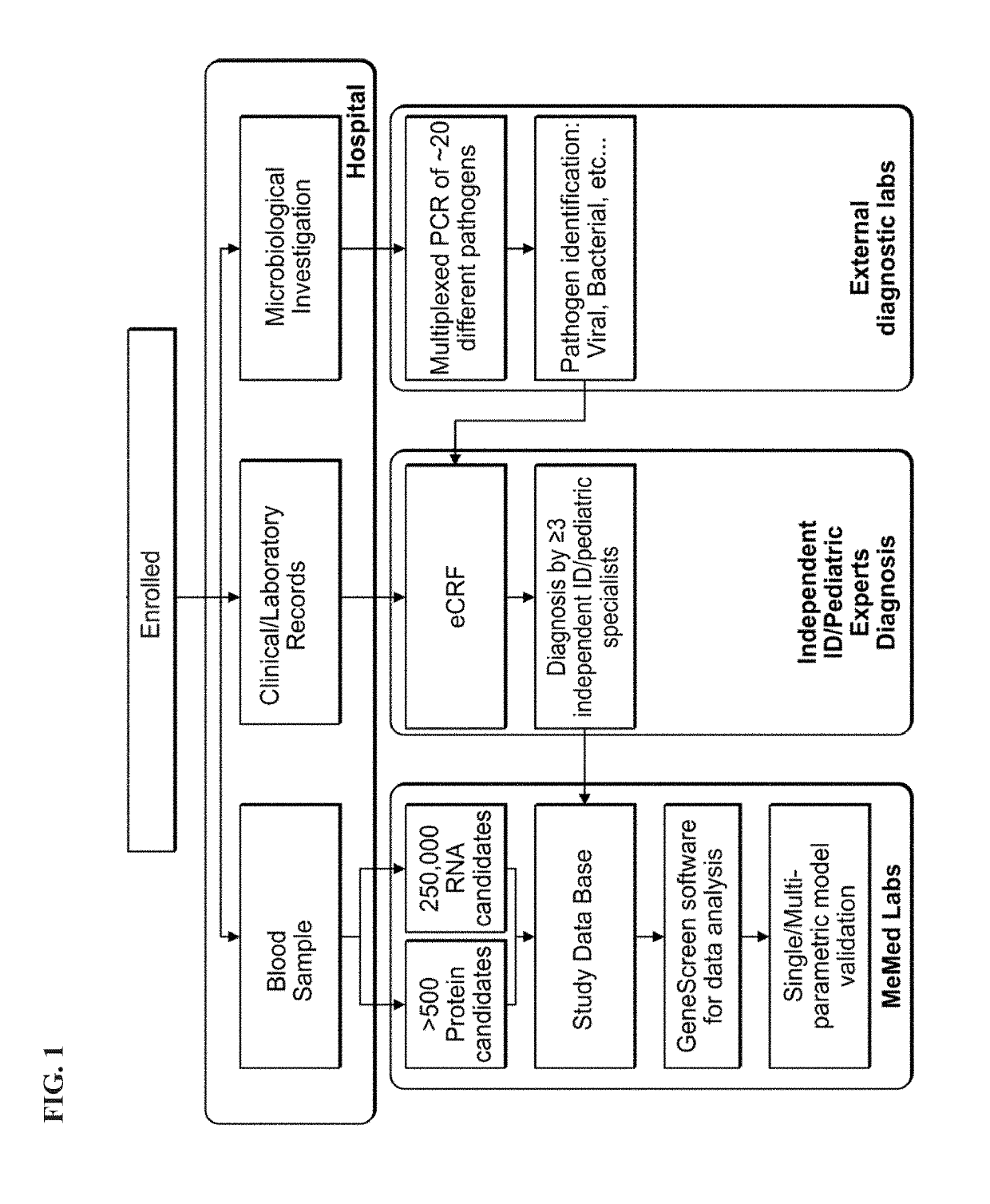
Protein signatures for distinguishing between bacterial and viral infections
ActiveUS20190120837A1Increased mortalityHigh diagnostic sensitivityTumor necrosis factorImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsBacteroidesProtein Feature
Owner:MEMED DIAGNOSTICS
Combinatorial multidomain mesoporous chips and a method for fractionation, stabilization, and storage of biomolecules
ActiveUS20110065207A1High protein recoveryLow protein amountElectrolysis componentsSamplingFractionationTherapeutic effect
A new fractionation device shows desirable features for exploratory screening and biomarker discovery. The constituent MSCs may be tailored for desired pore sizes and surface properties and for the sequestration and enrichment of extremely low abundant protein and peptides in desired ranges of the mass / charge spectrum. The MSCs are effective in yielding reproducible extracts from complex biological samples as small as 10 μl in a time as short as 30 minutes. They are inexpensive to manufacture, and allow for scaled up production to attain the simultaneous processing of a large number of samples. The MSCs are multiplexed, label-free diagnostic tools with the potential of biological recognition moiety modification for enhanced specificity. The MSCs may store, protect and stabilize biological fluids, enabling the simplified and cost-effective collection and transportation of clinical samples. The MSC-based device may serve as a diagnostic tool to complement histopathology, imaging, and other conventional clinical techniques. The MSCs mediated identification of disease-specific protein signatures may help in the selection of personalized therapeutic combinations, in the real-time assessment of therapeutic efficacy and toxicity, and in the rational modulation of therapy based on the changes in the protein networks associated with the prognosis and the drug resistance of the disease.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method for predicting protein bound with ribonucleic acid
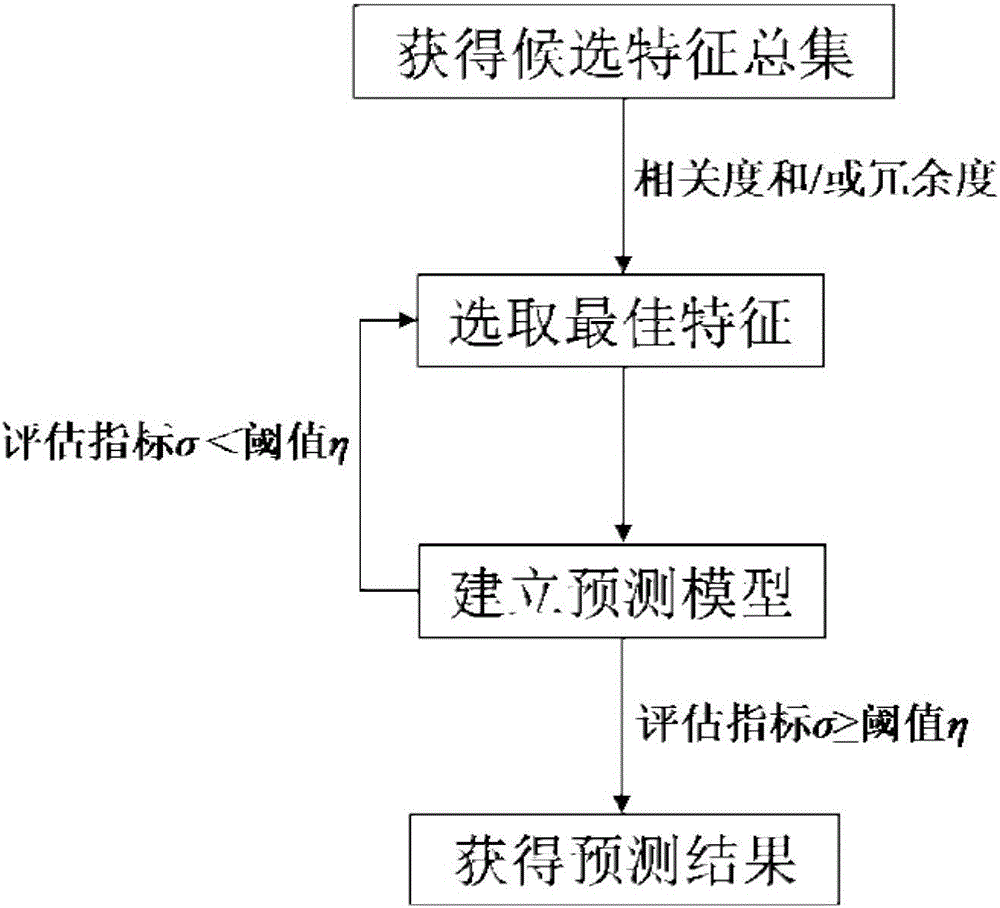
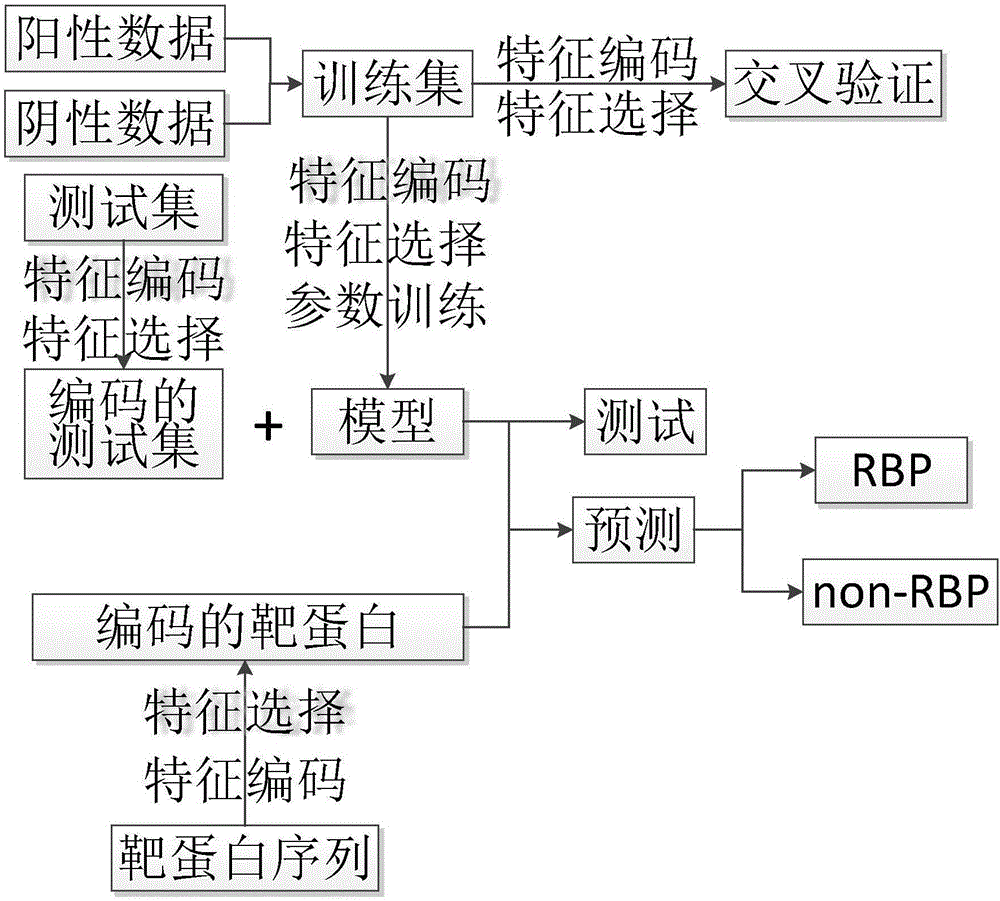
ActiveCN106529207AAccurate predictionSmall amount of calculationProteomicsGenomicsCorrelation coefficientFeature vector
The invention discloses a method for predicting a protein (RBP) bound with ribonucleic acid. The method comprises the steps of firstly, obtaining a total candidate feature set of a sample protein according to characteristics of amino acid; secondly, selecting W optimal features from the total candidate feature set to serve as eigenvectors; thirdly, building a prediction model according to the eigenvectors and protein characteristics of the sample protein; and finally, obtaining a prediction result of protein characteristics of a to-be-predicted protein according to eigenvectors of the to-be-predicted protein. According to the method, the total candidate feature set covers various characteristics of amino acid; various factors influencing the performance of binding the protein to ribonucleic acid are comprehensively considered; and the accuracy exceeds 90% through verification, the accuracy in the prior art is improved by 35%, a Mathew correlation coefficient is 0.788, and the Mathew correlation coefficient in the prior art is increased by two times, so that the prediction is more comprehensive and accurate.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
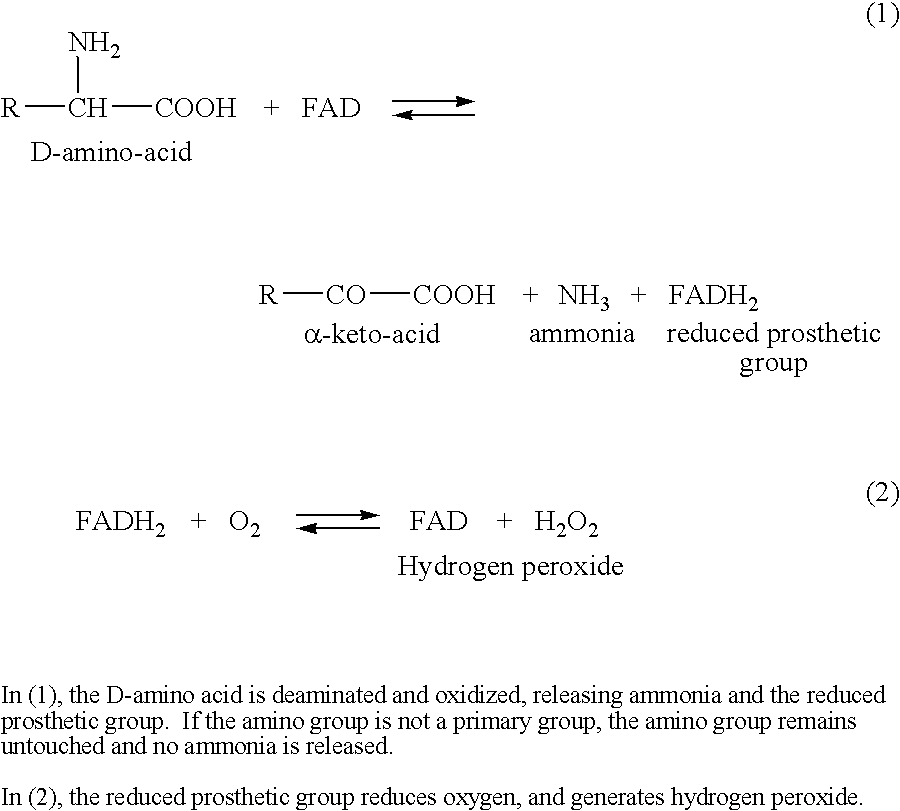
Identification and characterization of racemases, definition of protein signatures, and a test for detecting D-amino acid and for screening molecules capable of inhibiting the activity of racemase, especially proline racemase
InactiveUS20060014162A1Raise the potentialCompound screeningApoptosis detectionImmune complex depositionProline racemase
This invention provides identification and characterization of racemases and definition of protein signatures of these racemases. This invention also provides identification of nucleic acid molecules encoding a peptide consisting of a motif characteristic of the protein signatures, and to the peptides consisting of these motifs. Antibodies specific for the peptides and to immune complexes of these antibodies with the peptides are also provided. Further, the invention relates to methods and kits for detecting racemases using the nucleic acid molecules of the invention, as well as the peptides consisting of the motifs and antibodies to these peptides.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
Prediction method for protein subcellular site formed based on improved-period pseudo amino acid
InactiveCN102819693AProtein data equalizationLess predictable offsetSpecial data processing applicationsProtein FeatureProtein
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Methods and systems for predicting proteins that can be secreted into bodily fluids
The present invention is directed to methods and systems for predicting protein secretion into bodily fluids. In an embodiment, a method uses a feature set comprising secretory properties of collected proteins to train a classifier, based on the feature set, to recognize protein features corresponding to proteins that are likely to be secreted into a biological fluid. Another method determines, using a trained classifier and identified features of a received protein sequence, the probability of the protein sequence being secreted into a biological fluid. In an embodiment, a system predicts the secretion of proteins into a biological fluid. The system comprises components configured to construct a protein feature set comprising properties of collected proteins, train a classifier to predict features of a protein that is likely to be secreted into the biological fluid, receive a protein sequence, and identify the received protein sequence as a secretory protein.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
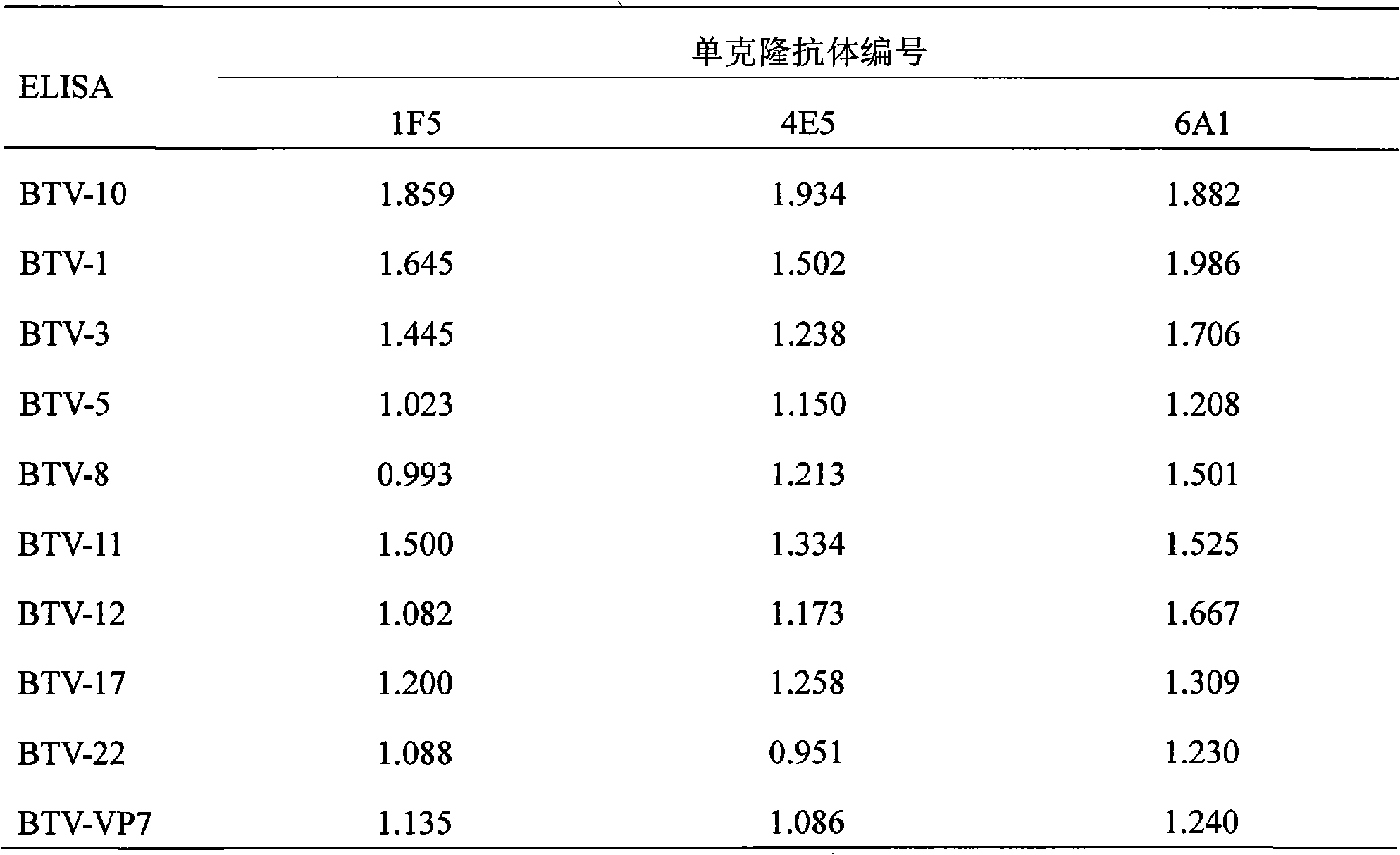
Monoclonal antibody of bluetongue virus (BTV) and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101597334ASame structureUniform compositionImmunoglobulins against virusesFermentationBALB/cHamster
The invention relates to the biotechnology field. A monoclonal antibody against a BTV VP7 protein of a bluetongue virus (BTV) of the invention is prepared by the following steps: adopting the hybridoma cell technology, taking splenocytes of BALB / c mice immunized with purified BTV for fusion with a mouse myeloma cell (SP2 / 0), after culturing the cells with an HAT selective medium, carrying out screening with indirect ELISA coated by a purified BTV antigen, a BTV VP7 protein antigen expressed by a gene engineering and a control antigen of a normal hamster kidney continuous cell (BHK21), carrying out screening and cloning by limiting dilution to obtain a hybridoma cell line which has the capacities of stable continuous culture and secretion of the monoclonal antibody (McAb) against the specific BTV VP7 protein and preparing McAb mouse ascites of the BTV VP7 protein. The monoclonal antibody against the BTV VP7 protein features strong specificity, high ascites titer, high affinity and simple preparation method, can be used in the detection method of the BTV antibody and antigen and provides an important technical means for prevention and control of bluetongue in China.
Owner:花群义
Method and system for detecting a target within a population of molecules
ActiveUS8465989B2Microbiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceProtein Feature
A method (800) of detecting a target within a population of molecules comprising: contacting a plurality of labeled probe molecules with the population of molecules potentially containing a target of the probe molecules (810); acquiring a probe specific signal emitted by said labeled probe molecules that bound to said target together with a background signal (820); modulating said probe specific signal by at least one of modulating said acquisition and modulating an emission of said probe specific signal (830); and detecting said probe specific signal over said background signal using said preferential modulation (840). The target comprises one or more molecule type selected from the group consisting of a nucleic acid sequence, an amino acid sequence, a carbohydrate sequence, an ion and a feature of a protein determined by non-primary structure. The probe specific signal may be a fluorescent signal.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Method and system for detecting a target within a polupation of molecules
ActiveUS20100041166A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalysis by electrical excitationFluorescenceProtein Feature
A method (800) of detecting a target within a population of molecules comprising: contacting a plurality of labeled probe molecules with the population of molecules potentially containing a target of the probe molecules (810); acquiring a probe specific signal emitted by said labeled probe molecules that bound to said target together with a background signal (820); modulating said probe specific signal by at least one of modulating said acquisition and modulating an emission of said probe specific signal (830); and detecting said probe specific signal over said background signal using said preferential modulation (840). The target comprises one or more molecule type selected from the group consisting of a nucleic acid sequence, an amino acid sequence, a carbohydrate sequence, an ion and a feature of a protein determined by non-primary structure. The probe specific signal may be a fluorescent signal.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
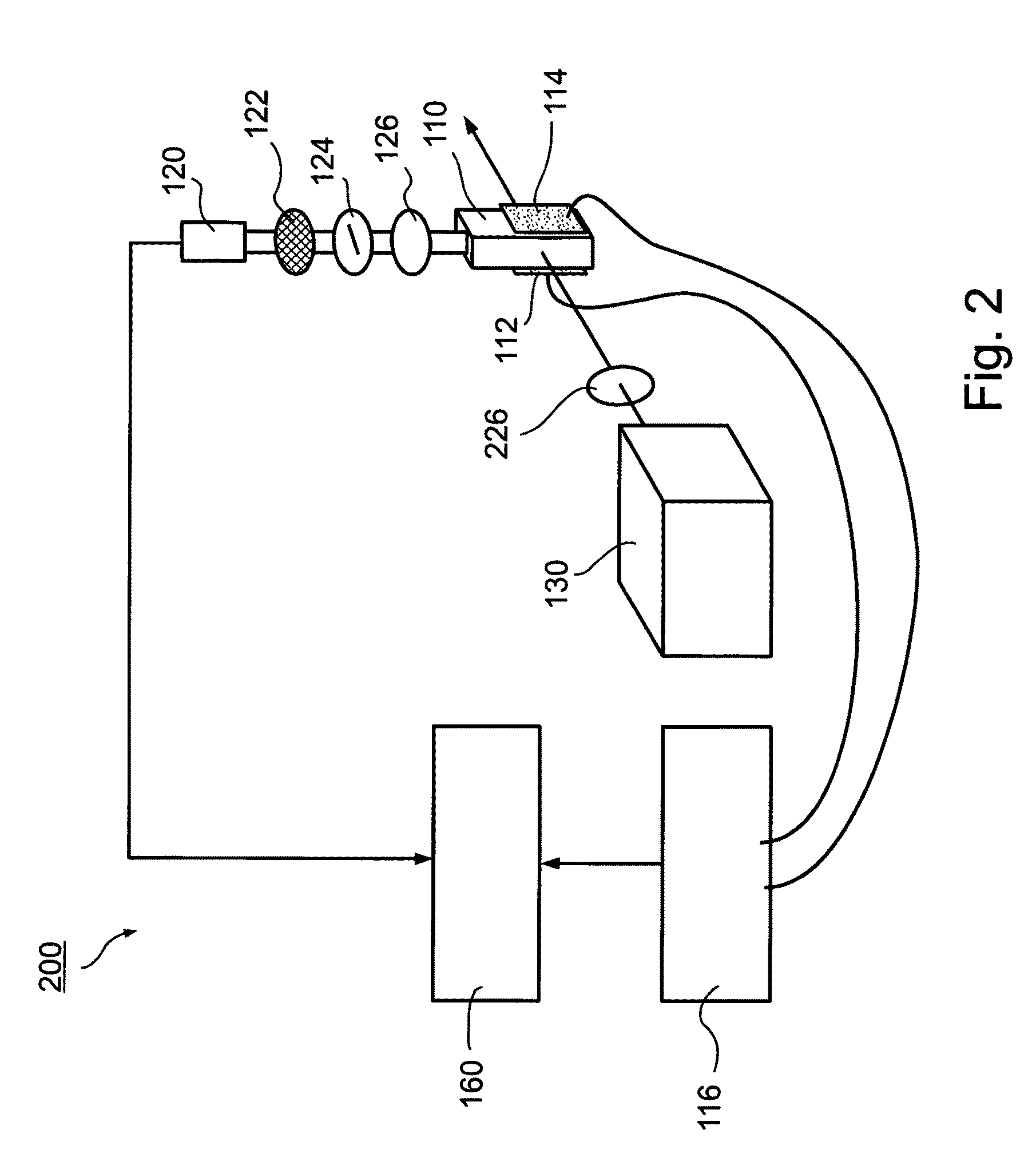
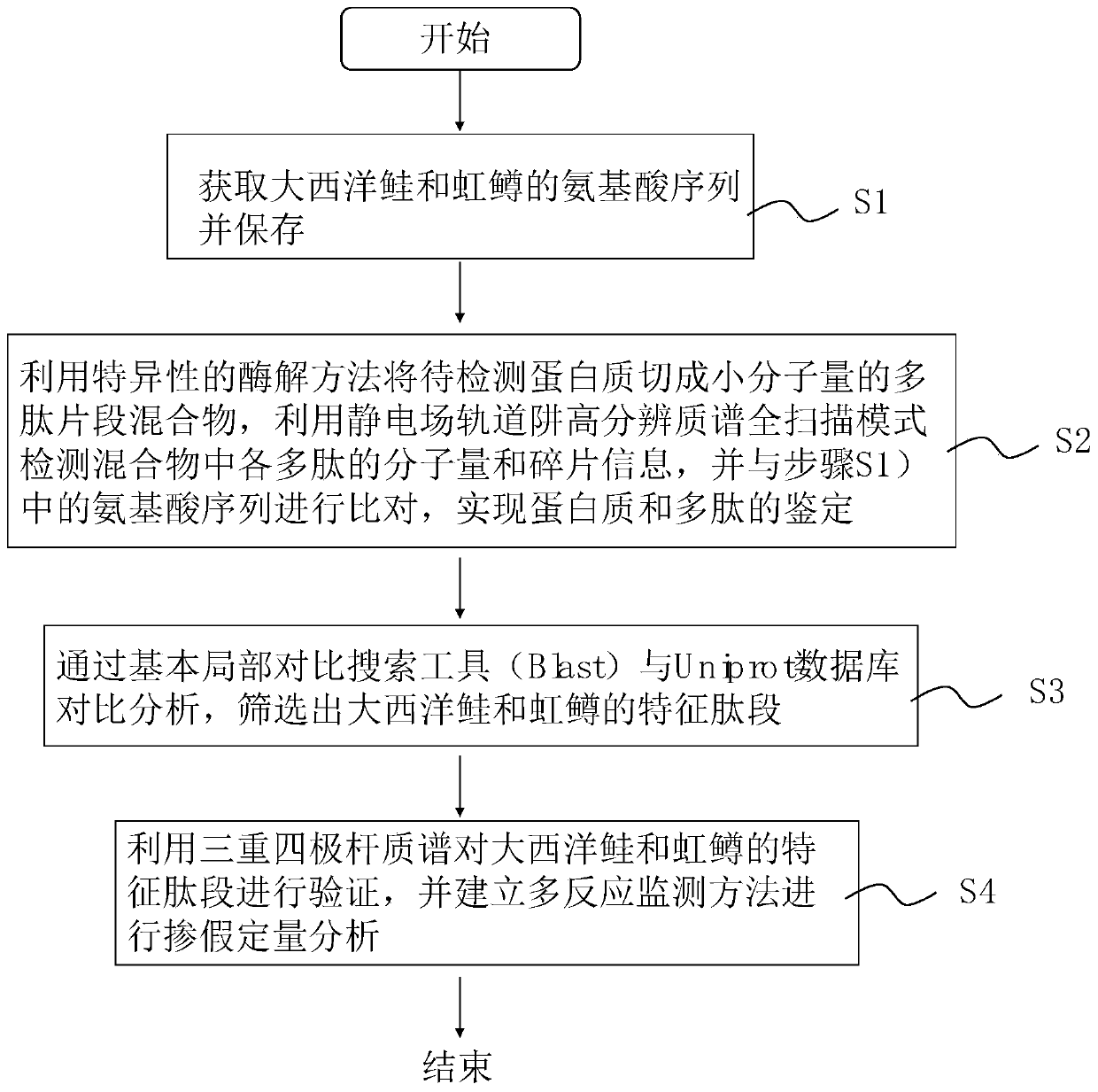
Mass spectrometry identification method for salmo salar and rainbow trout
The invention discloses a mass spectrometry identification method for salmo salar and rainbow trout. The method includes the following steps: a) obtaining the amino acid sequence of salmo salar; b) obtaining the amino acid sequence of rainbow trout; c) utilizing a specific enzymatic method to cut to-be-detected protein into a small molecular weight polypeptide fragment mixture, utilizing an electrostatic field orbitrap high resolution mass spectrometry full scan mode to detect the molecular weight and fragment information of polypeptide in the mixture, performing comparison with an amino acidsequence obtained before, and qualitatively judging whether the characteristic peptide fragments of the salmo salar and rainbow trout exist; and d) selecting the characteristic peptide fragment determined as the salmo salar or the rainbow trout, and utilizing tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry to establish a multi-reaction monitoring method to perform quantitative analysis. Identification can beperformed by utilizing the protein characteristic peptide fragments, so that the qualitative identification and adulteration quantification of the salmo salar and rainbow trout can be simultaneously realized; and minimum detection limit can reach 1%, so that the method is high in sensitivity, high in accuracy and strong in anti-interference ability, and can be widely applied to the identificationof the salmo salar.
Owner:PLANTS & ANIMALS & FOOD TESTING QUARANTINE TECH CENT SHANGHAI ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Characteristic extraction and coding method and system based on multi-modal protein sequence
ActiveCN108830042AAccurate analysisSpecial data processing applicationsFeature extractionNetwork code
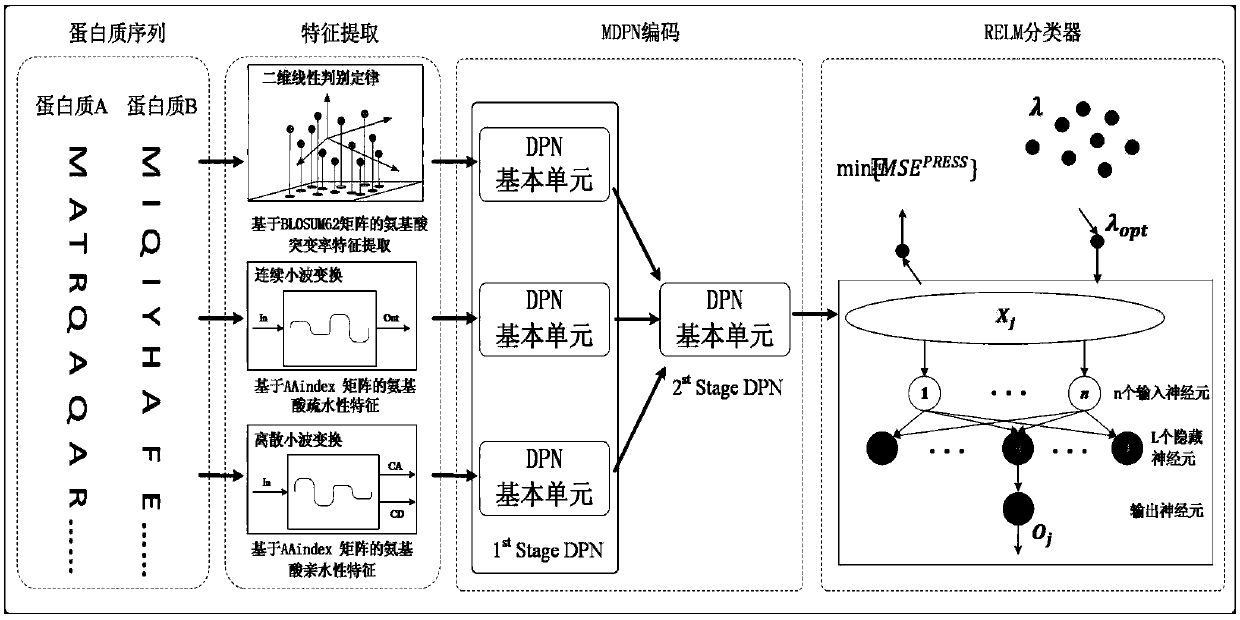
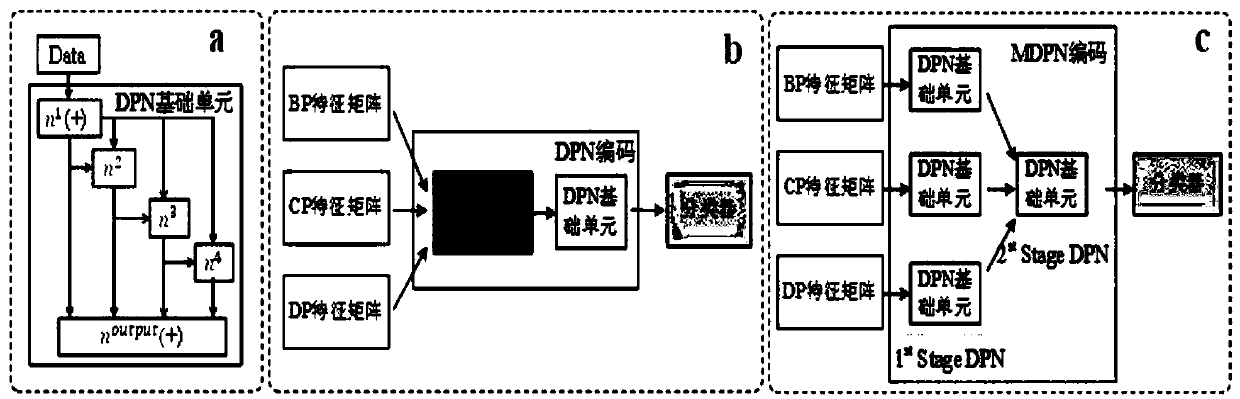
The invention discloses a characteristic extraction and coding method and system based on a multi-modal protein sequence. The method comprises the steps of: performing characteristic extraction on theprotein sequence respectively based on the relative mutation rate, the hydrophilic property and the hydrophobic property of a protein amino acid sequence, and obtaining three-modal protein characteristics; respectively performing depth polynomial network coding on the three-modal protein characteristics, so that three kinds of senior characteristic expression can be respectively obtained; and performing depth polynomial network coding again after cascading the three kinds of senior characteristic expression, so that fused protein characteristics are obtained. Compared with the traditional protein characteristic extraction method, multiple physicochemical properties of the protein amino acid sequence are combined; relatively reliable protein characteristics are extracted; and thus, proteinand protein interaction can be analyzed more accurately.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Semen protein prediction method based on convolutional neural network
The invention discloses a semen protein prediction method based on a convolutional neural network, and belongs to the technical field of big data and artificial intelligence. According to the method,a protein list verified by biological experiments in semen of existing literatures and databases is used as a positive sample for model training; protein family information corresponding to the positive sample is deleted from a Pfam protein family information database, protein families with the number of proteins exceeding 5 in the families are searched for in the remaining protein family information database, and five pieces of protein information are randomly selected from the protein families to serve as negative samples for model training. The method also comprises the steps of dividing the positive sample data and the negative sample data into a training set, a verification set and a test set; carrying out feature selection on protein features, building a model, training the model byusing the training set, carrying out parameter adjustment on the verification set, and carrying out performance evaluation on the test set. The input is a protein feature, and the output is a prediction result, so that the semen prediction accuracy is improved, and finally, semen protein prediction is realized.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
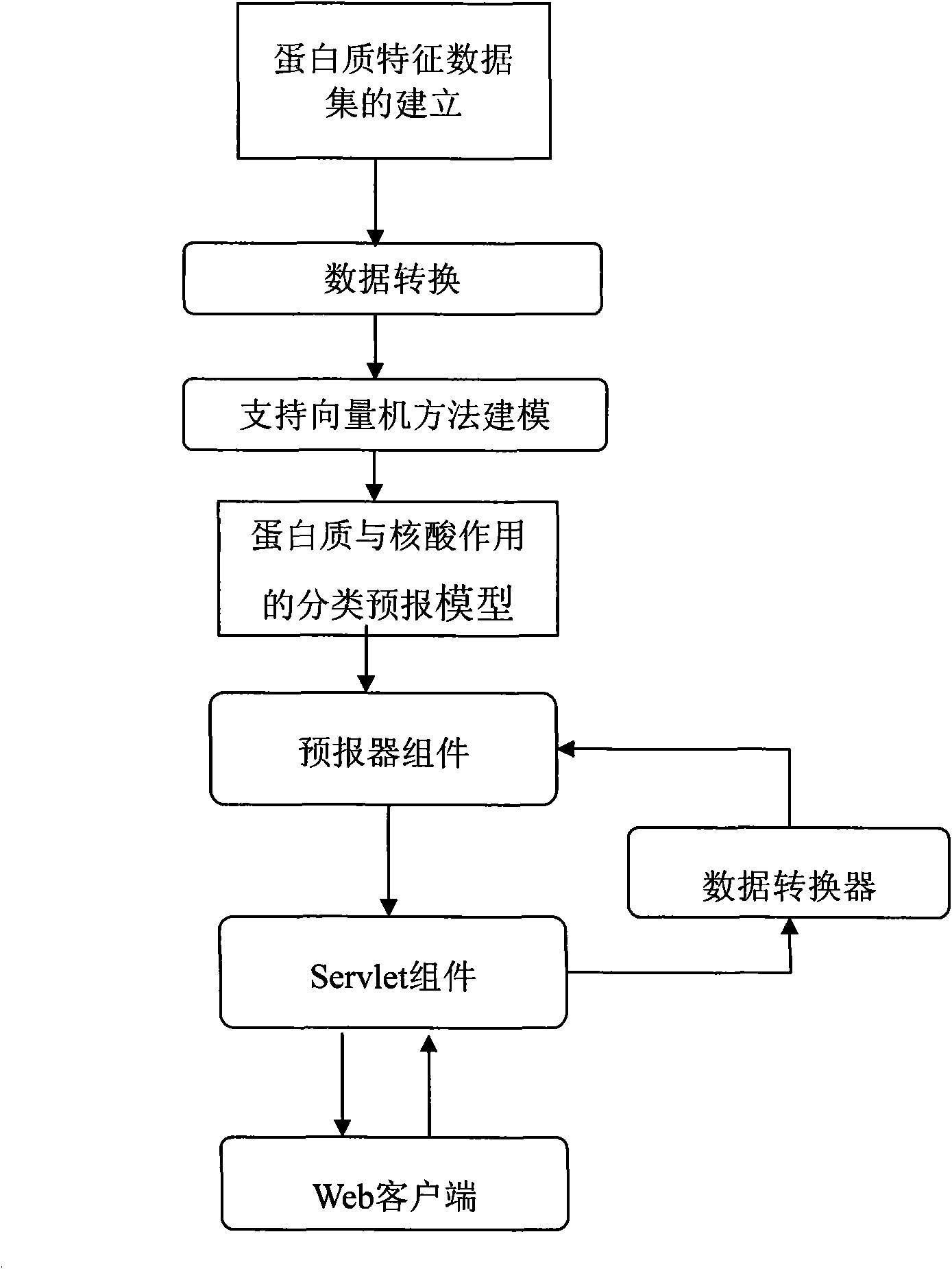
Method based on support vector machine for on-line prediction of interaction of protein and nucleic acid
InactiveCN101630346AImprove accuracyShort forecast timeSpecial data processing applicationsData setProtein insertion
The invention discloses a method based on a support vector machine for the on-line prediction of the interaction of protein and nucleic acid. The method includes the following steps: 1, the establishment of a training sample set of a protein sequence dataset; 2, the conversion of the protein sequence dataset; 3, the training of generated protein feature dataset by the support vector machine; and 4, prediction of the reading and the data conversion of protein sequence and the online prediction of type of the interaction classification of the protein and the nucleic acid. The invention can detect whether the protein acts with the nucleic acid or not under the circumstance that the interaction of the protein and the nucleic acid is not detected; proved by verification results, the accuracy rates of the 10 folded cross validation prediction of the protein which acts with r RNA, RNA and DNA respectively achieve 93.75 percent, 83.41 percent and 81.85 percent; and the accuracy rates of models obtained by verification of an external testing set are respectively 93.8 percent, 84.52 percent and 81.9 percent. During on-line prediction, a user only needs to provide the protein sequence to predict on the interface of a prediction webpage, data of the protein sequence is converted so as to accomplish the training of the support vector machine and the prediction of target types, and the result of prediction is outputted.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Structure-Based Analysis For Identification Of Protein Signatures: CUSCORE
Disclosed are computational methods, and associated hardware and software products for scoring polypeptide residues that combine the use of a structure-based alignment with a method of selecting against confounding proteins. The scores can be used to identify protein signatures of interest that are useful, e.g., as targets in developing highly specific ligands for diagnostic or therapeutic uses.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
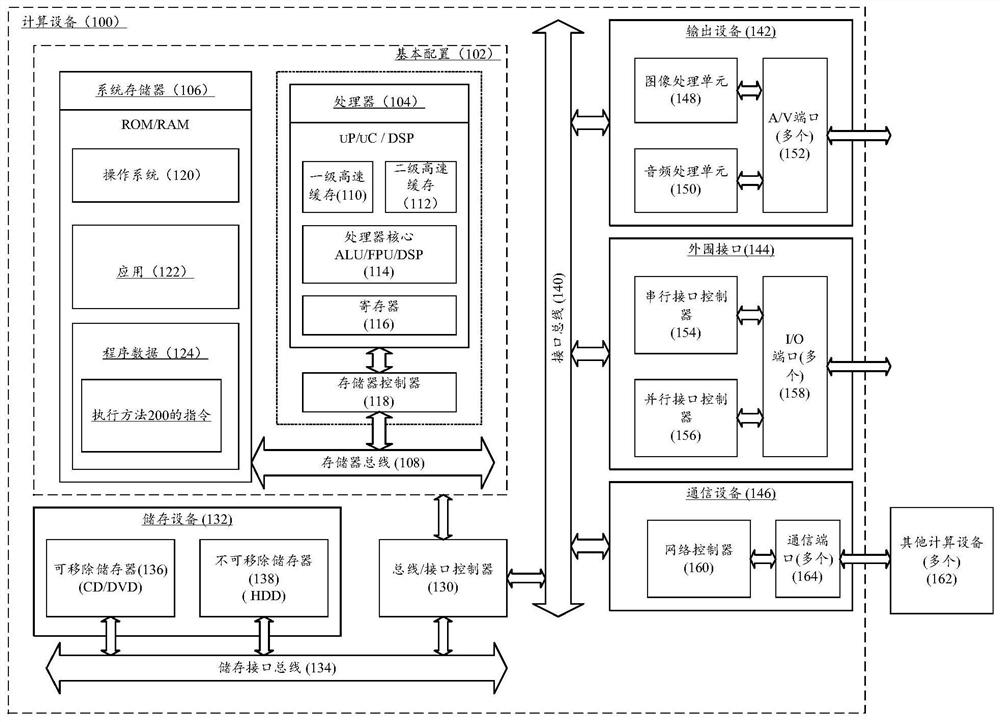
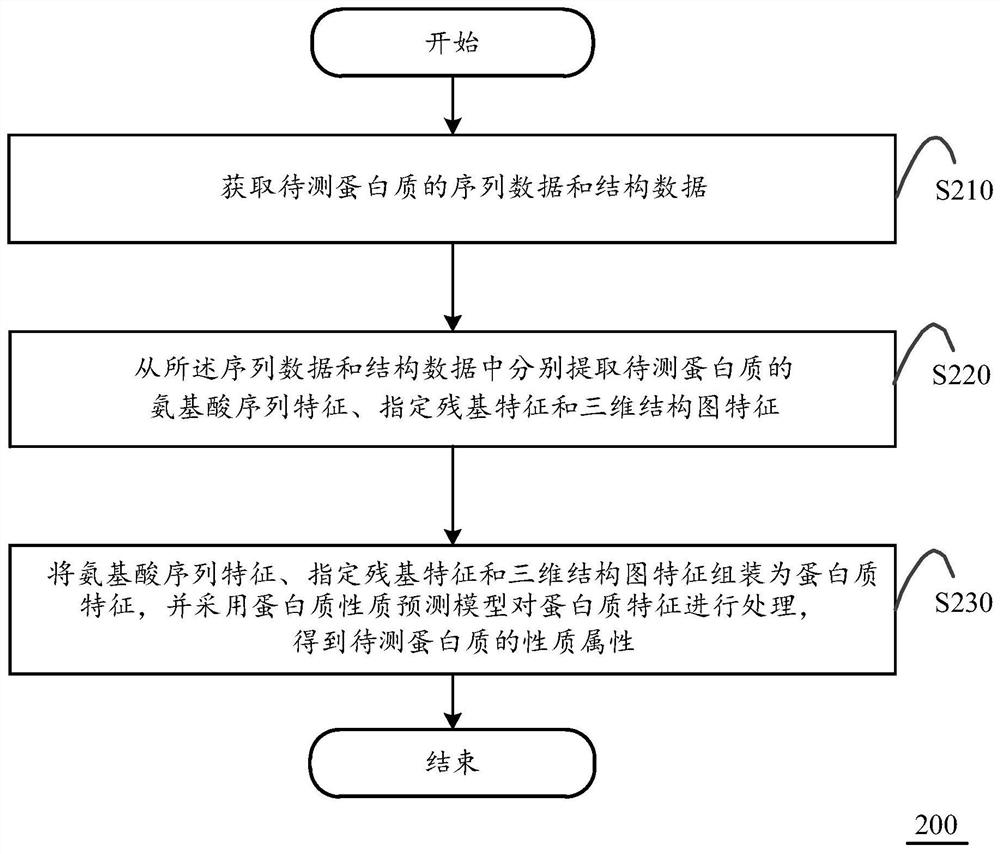
Protein property prediction method and device based on multi-dimensional characteristics and computing equipment
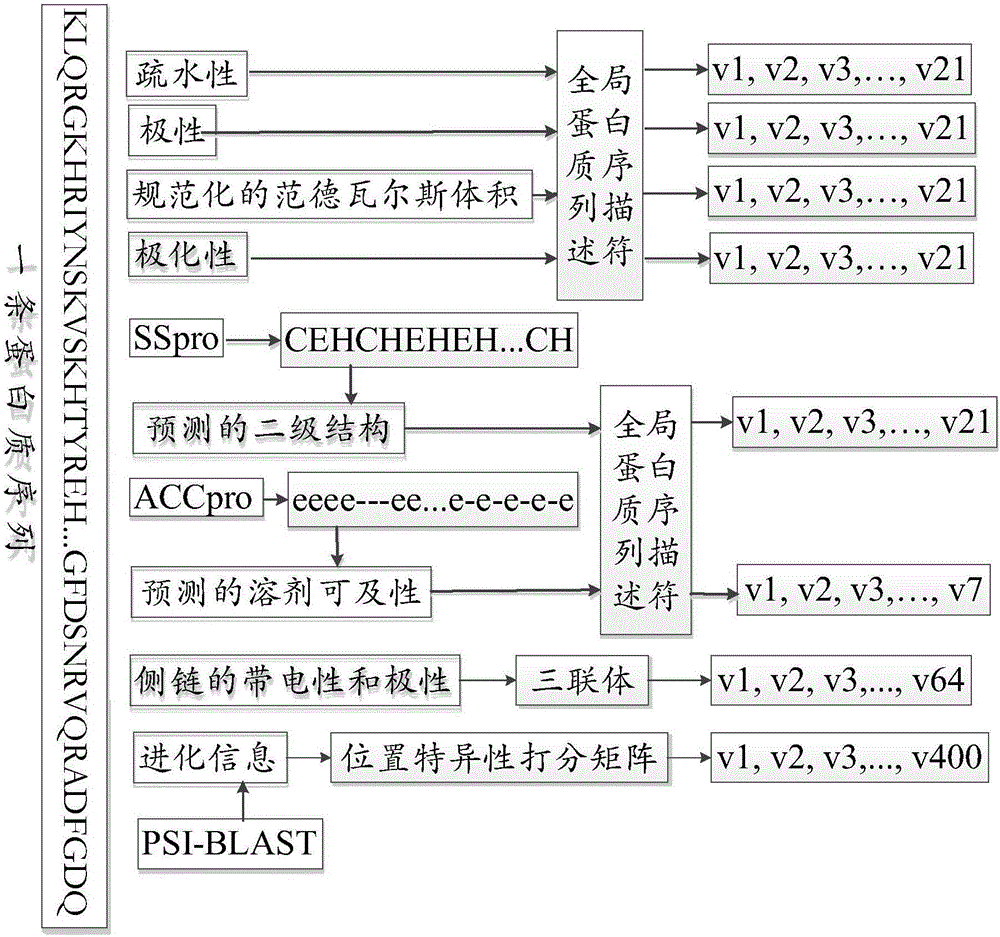
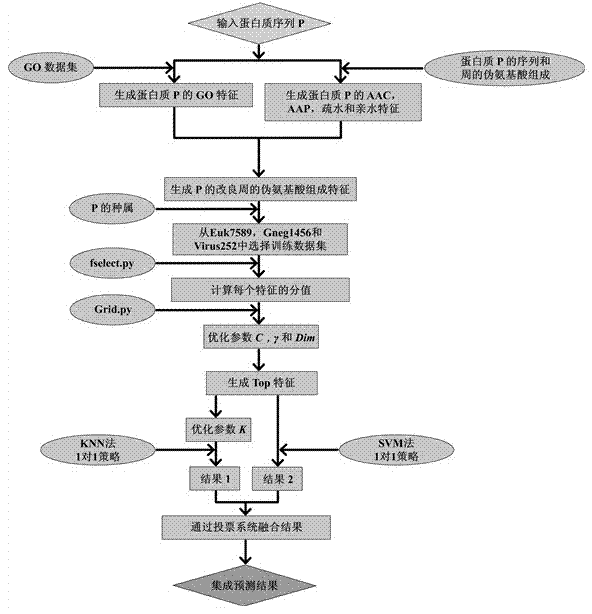
PendingCN111627494APrediction is accurateImprove screening efficiencyProteomicsGenomicsEngineeringProtein Feature
The invention discloses a protein property prediction method based on multi-dimensional characteristics, which is executed in computing equipment. The computing equipment includes a protein property prediction model having an input of assembled protein characteristics and an output of predicted protein properties. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining sequence data and structure dataof the to-be-detected protein; respectively extracting amino acid sequence characteristics, specified residue characteristics and three-dimensional structure chart characteristics of the protein to be detected, wherein the amino acid sequence characteristics represent amino acid composition and physicochemical properties, the specified residue characteristics include self attributes and environment attributes of specified residues, and the three-dimensional structure diagram characteristics include residue node attributes and edge attributes; and assembling the extracted three features into protein features, and processing the protein features by adopting a protein property prediction model to obtain the prediction property of the protein to be detected. The invention further discloses acorresponding protein property prediction device based on the multi-dimensional characteristics and computing equipment.
Owner:北京晶泰科技有限公司
Protein folding identification method based on deep metric learning
ActiveCN112116950AImprove recognition accuracyHigh precisionNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsAlgorithmProtein Feature
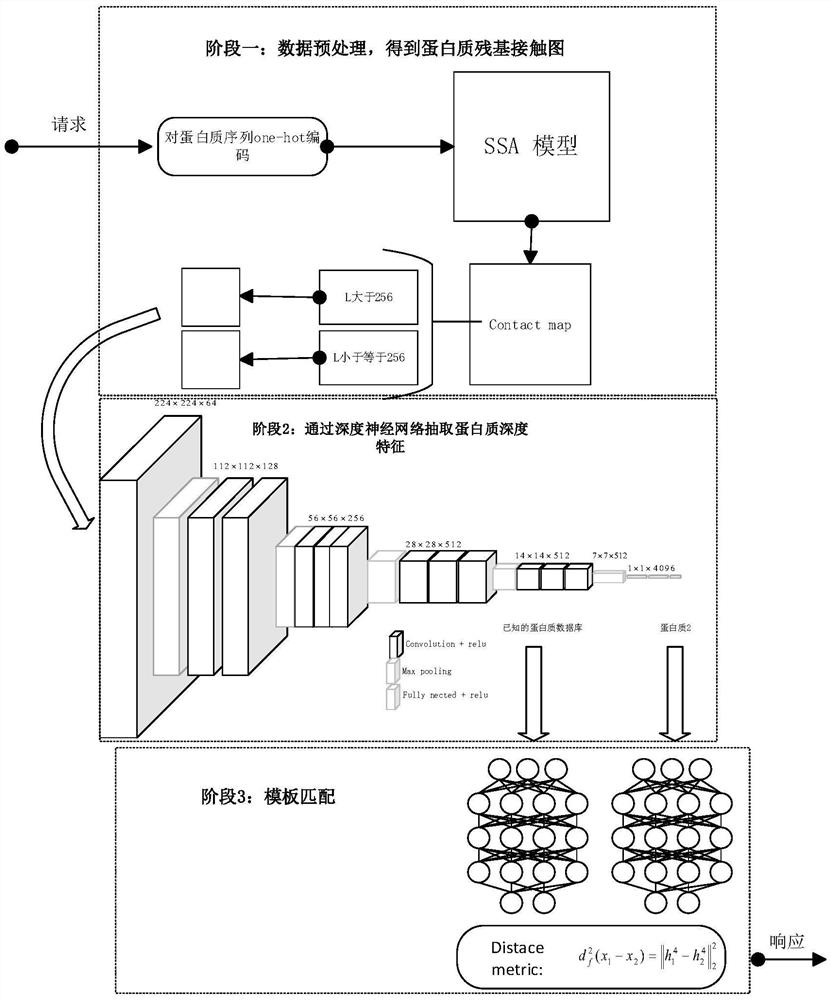
The invention discloses a protein folding identification method based on deep metric learning. The method comprises the following steps of encoding protein to obtain digital expression of a protein sequence, inputting the digital expression of the protein sequence into an SSA model to obtain a potential relational graph of protein residues, and fixing the relational graph to a set size, inputtingthe relational graph into a trained convolutional neural network, and obtaining the output of the previous layer of the classification layer as a depth feature, inputting the depth features into a trained twin network to obtain final protein features, and calculating the Euclidean distance between the query protein and the template protein based on the protein characteristics, and allocating the folding type of the template protein closest to the query protein to the query protein. A twin network is used, so that the distance between protein pairs of the same folding type is closer, and the distance between protein pairs of different folding types is farther.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Cerebrospinal fluid protein prediction method based on deep neural network
InactiveCN110797084AImprove accuracyBiostatisticsHybridisationCerebrospinal fluid proteinsProtein Feature
The invention discloses a cerebrospinal fluid protein prediction method based on a deep neural network, which belongs to the technical field of artificial intelligence and big data. The method comprises the following steps of: taking a protein list which is verified by a biological experiment in cerebrospinal fluid of the existing literature and database as a positive sample for model training, deleting protein family information corresponding to the positive sample from a Pfam protein family information database, searching protein families with more than 10 proteins in the families from the remaining protein family information database, and randomly selecting 10 pieces of protein information from the protein families as negative samples for model training. The positive sample data and thenegative sample data are divided into a training set, a verification set and a test set; and feature selection is carried out on protein features, a model is built, the model is trained by using thetraining set, parameter adjustment is carried out on the verification set, and performance evaluation is carried out on the test set. The input is protein characteristics, and the output is a prediction result. The accuracy of cerebrospinal fluid prediction is improved, and finally cerebrospinal fluid protein prediction is achieved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for protein analysis
ActiveUS20160320377A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingProtein targetProtein insertion
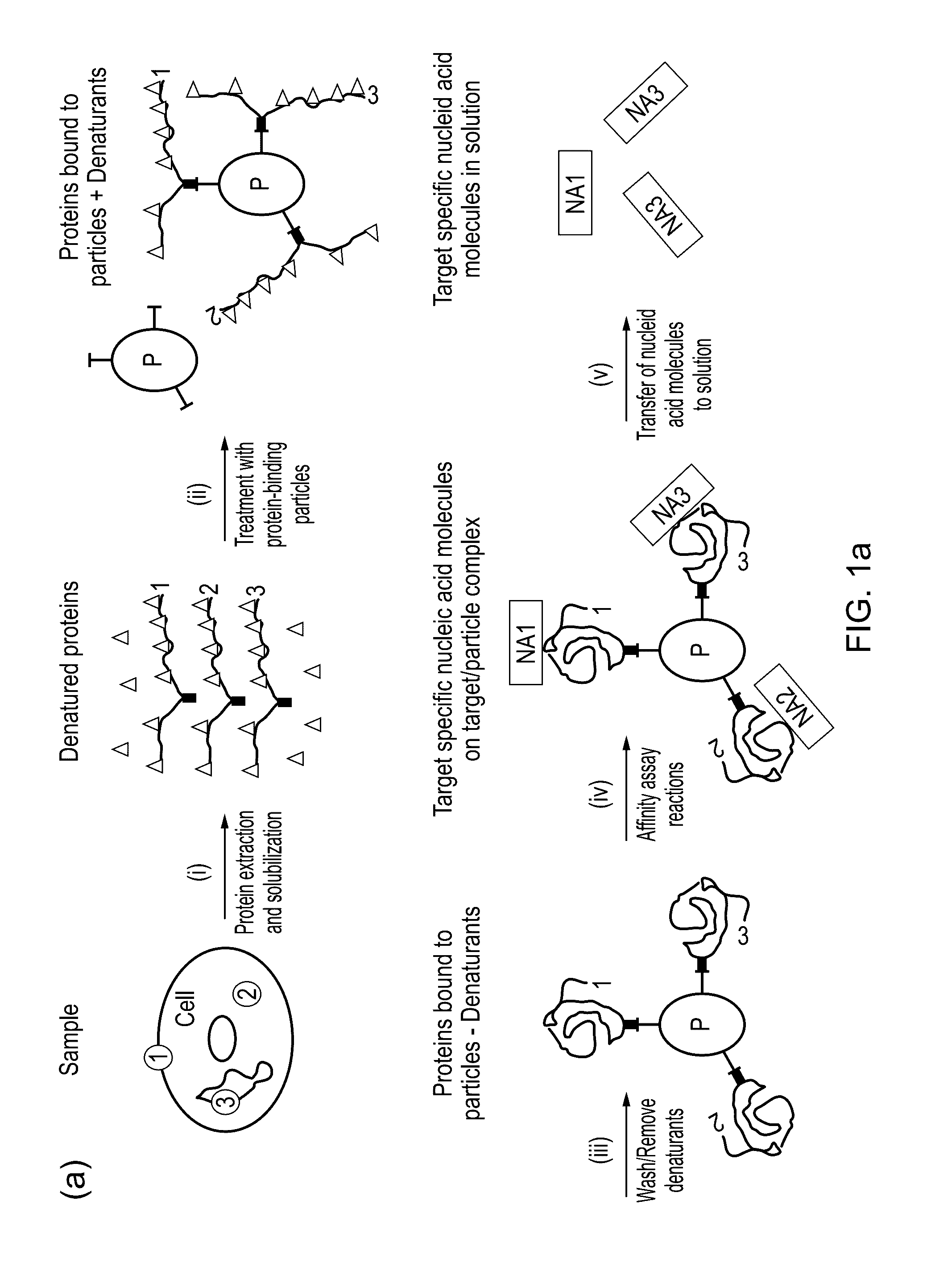
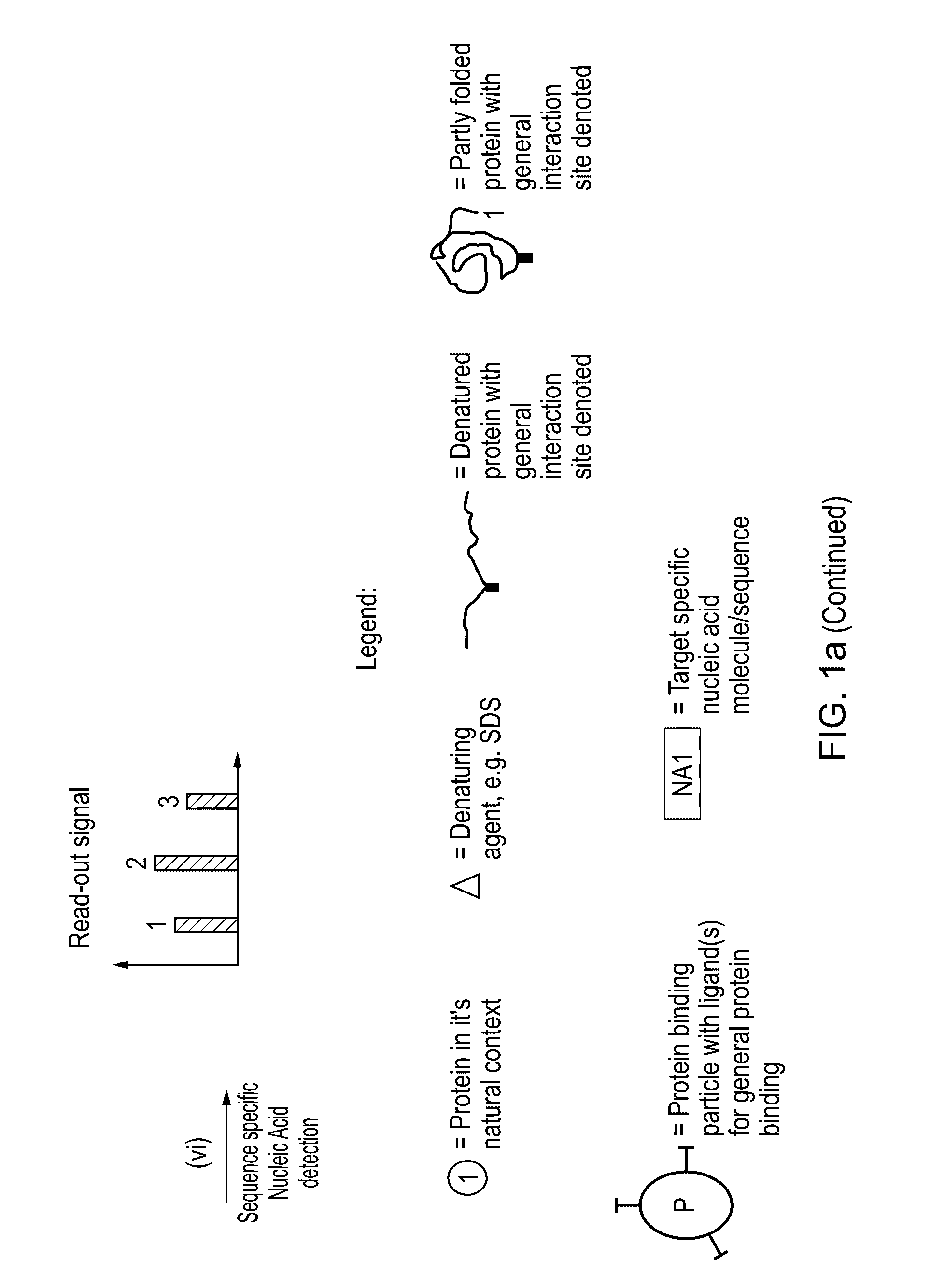
The present invention relates to a method for protein analysis in which the proteins to be analyzed are displayed on a population of discrete and dispersible structures, such as beads or other particles, for subsequent affinity reactions and analysis / detection. More closely the invention relates to a method for protein analysis comprising providing a denatured protein sample in the presence of a denaturing agent, the method comprising the following steps;a) contacting said protein sample with a population of discrete and dispersible protein-binding structures to capture a plurality of different proteins on said structures,b) removal of denaturing agent to display protein- and protein-feature specific epitopes from said sample on said structures;c) performing affinity probing targeted to a sub-group of said protein or protein feature specific epitopes requiring two or more specificity building events per targeted protein or protein feature generating a target specific nucleic acid molecule or sequence for each of the targeted proteins or protein-features;d) liberating said protein- or protein-feature specific nucleic acid sequences or their complements from said structures;e) optionally amplifying said nucleic acid sequences;f) analysing the generated nucleic acid molecules by a quantitative and sequence specific nucleic acid detection method; andg) determining therefrom the quantity or presence of targeted proteins or protein features in said sample.
Owner:CYTIVA SWEDEN AB
Amniotic fluid protein prediction method based on recurrent neural network
InactiveCN110827922AImprove accuracyBiostatisticsCharacter and pattern recognitionProtein FeatureTest set
The invention discloses an amniotic fluid protein prediction method based on a recurrent neural network, and belongs to the technical field of big data and artificial intelligence. According to the method, a protein list verified by biological experiments in amniotic fluid of existing literatures and databases is used as a positive sample for model training; protein family information corresponding to the positive sample is deleted from a Pfam protein family information database, protein families with the number of proteins exceeding 5 in the families are searched for in the remaining proteinfamily information database, and five pieces of protein information are randomly selected from the protein families to serve as negative samples for model training. The method further comprises the steps of: dividing the positive sample data and the negative sample data into a training set, a verification set and a test set; and carrying out feature selection on protein features, building a model,training the model by using the training set, carrying out parameter adjustment on the verification set, and carrying out performance evaluation on the test set. The input is a protein feature and the output is a prediction result. The accuracy of amniotic fluid prediction is improved, and finally amniotic fluid protein prediction is achieved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
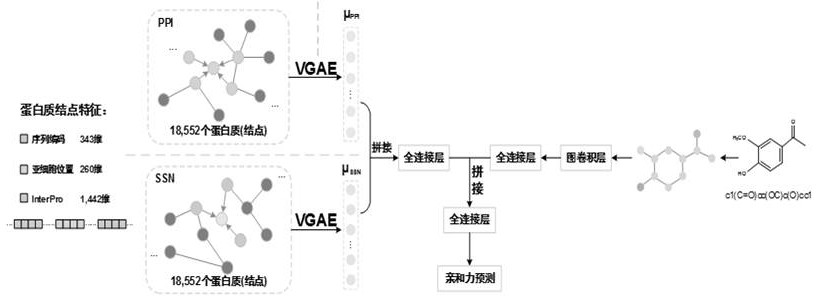
Protein multi-source feature fusion drug-target affinity prediction method
PendingCN114724623AImprove the accuracy of affinity predictionChemical property predictionBiostatisticsProtein targetProtein structure
The invention discloses a method for predicting drug-target affinity based on protein multi-source feature fusion, which comprises the following steps: firstly, constructing a PPI network and an SSN network, extracting protein features from the networks, and then collecting protein features such as subcellular positions, sequence codes, functional sites and structural domains for protein characterization; and fusing multi-source features by using a variational graph auto-encoder, and finally, inputting the multi-source features into a full-connection layer in combination with drug branches to carry out affinity prediction. According to the invention, a PPI network and an SSN network are constructed, so that biological priori knowledge between a target protein and other proteins is learned in addition to focusing on the characteristics of the target protein; according to the method, the protein characteristics are extracted and fused from the aspects of protein interaction, sequence similarity and protein subcellular positions for the first time, so that the drug-target affinity is predicted, and the prediction accuracy is improved; in addition, the characteristic source of the protein does not comprise a protein structure, so that the dependence on the protein structure is abandoned.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Drug molecule recommendation system for regulating and controlling disease targets based on a deep learning, computer equipment and storage medium
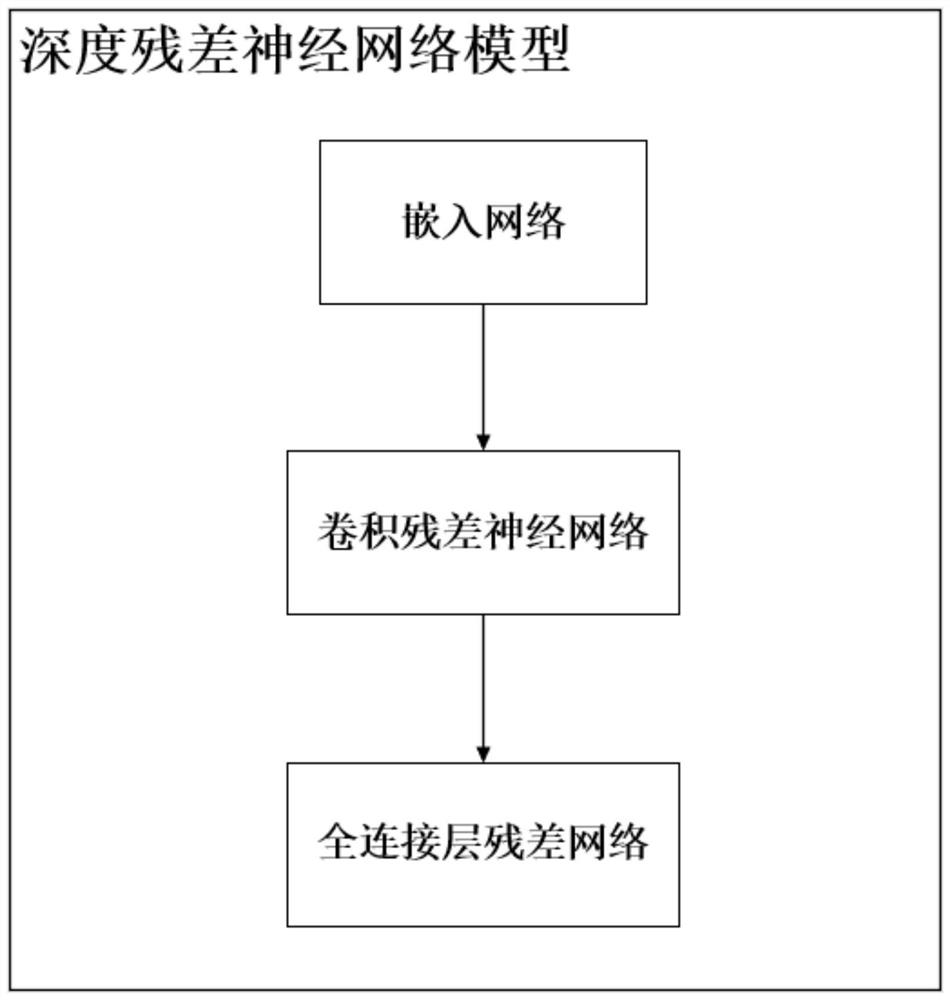
InactiveCN112562790AShorten the R&D processProcessing speedBiostatisticsNeural architecturesDiseaseResidual neural network
The invention discloses a drug molecule recommendation system for regulating and controlling disease targets based on a deep learning method, and belongs to the technical field of drug relocation, convolutional neural networks and residual networks. The system comprises a deep residual error network model, and the deep residual error network model comprises an embedded network, a convolution residual error neural network and a full connection layer residual error network. The embedded network converts a drug molecule SMILES sequence or a protein amino acid sequence into a binary matrix. The convolution residual neural network comprises three convolutional layers, an addition layer and a maximum pooling layer, and is a network represented by a 'learning' drug molecule SMILES sequence or protein amino acid sequence feature, the input of the network is a binary matrix representing a drug molecule or protein, and the output of the network is a feature representation vector of the drug molecule or protein. The full connection layer residual network comprises three full-connection layers, two dropout layers and an addition layer, the input is a splicing vector expressed by drug moleculeand protein characteristics and an actual binding affinity value of the drug molecule and the protein characteristics, and the output is a binding affinity prediction value of the drug molecule and the protein.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Positive selection of serum proteins for proteomic analysis
ActiveUS20100055697A1Other chemical processesMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein FeatureOrganism
This invention relates to methods and kits for positive selection of species of interest based on peptide / protein sequence from a biological sample. The species of interest may be proteins and / or peptides of interest which may be placed through a mass spectrometer to obtain a blood peptide / protein signature. The blood peptide / protein signature may be used in proteomic analysis. The techniques include but are not limited to the use of collectors comprising nucleic acid molecules to extract a composition that has a lower concentration of a high abundance species of interest from a sample. This limits the level of influence that any collectors species may have on the results of a mass spectra.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT +1
Process for producing fiber from peanut protein
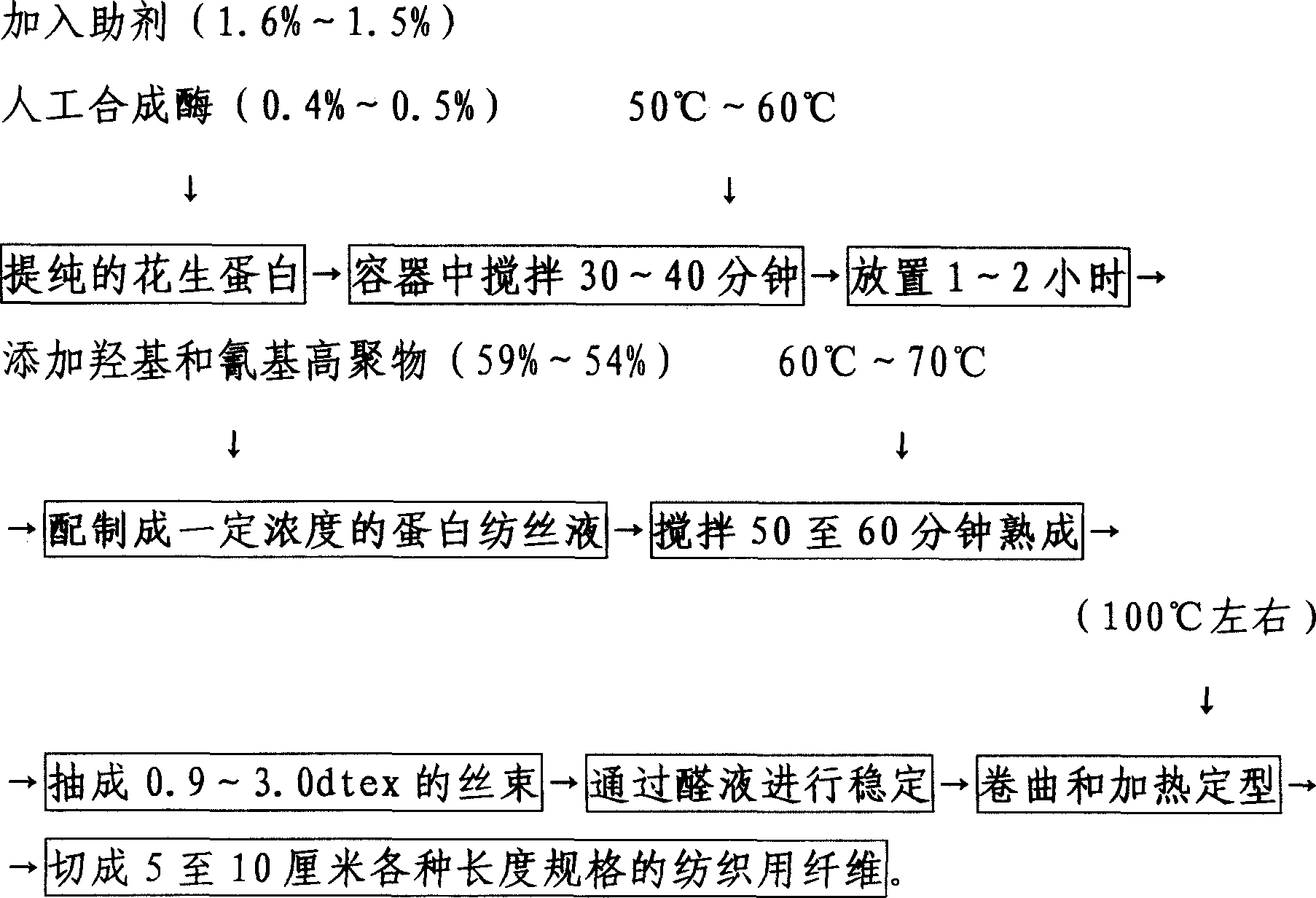
InactiveCN1683615AImprove insulation effectMold resistantMonocomponent globulin artificial filamentFiberResource utilization
The process of producing fiber with peanut protein features the material comprising peanut globulin 39-44 wt%, polymer 54-59 wt%, artificial synthetase 0.4-0.5 wt%, and assistant 1.5-1.6 wt%. The present invention provides new way of utilizing peanut protein, raises the peanut resource utilization and is suitable for peanut globulin producing industry.
Owner:青岛润德粮油制品有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com