Nucleic acid aptamer sequence and detection method for quantitative and rapid detection of mercury ions
A nucleic acid aptamer and mercury ion technology, which is applied in the field of nucleic acid sequences for mercury ion detection, can solve the problems of low sensitivity, troublesome and time-consuming operation, and poor specificity, and achieve the effects of low detection cost, convenient operation, and simple structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0027] Example 1: The nucleic acid aptamer sequence used for quantitative and rapid detection of mercury ions contains a stem-loop structure of a specific length of thymine T, and a fluorescent group is connected to the 5' end of the single strand of the stem-loop structure, and a corresponding The fluorescence quenching group forms a self-assembled detection system; when mercury ions exist, the stem-loop structure is closed, and the fluorescence intensity of the reaction system decreases, and the fluorescence intensity is inversely proportional to the concentration of mercury ions.
[0028] The specific structure of the nucleic acid aptamer sequence is: fluorescent group-T (m) -N (n) -T (m) -Fluorescence quenching group; N represents one or more of the nitrogenous bases A, G and C in the nucleic acid, but A and G should be avoided at the same time; wherein m is the number of thymine, and n is the nucleic acid containing The number of nitrogen bases. Nucleic acid aptamers...
example 2
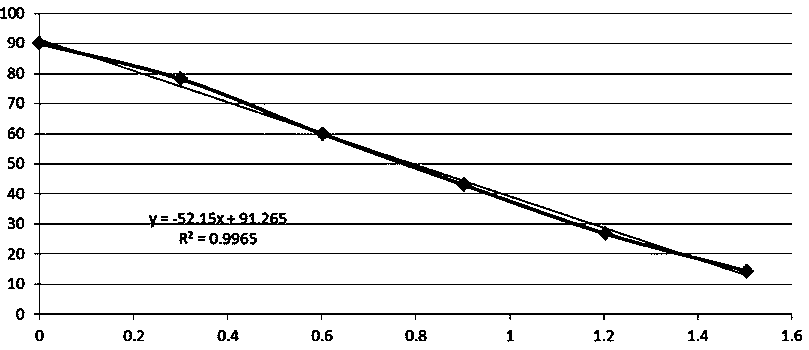
[0032] Example 2: Screening of Standard Curve for Mercury Ion Detection
[0033] (1) According to Example 1, design nucleic acid aptamer sequences of different thymine lengths (see Table 1), couple the FAM fluorescent group to its 5' end, and couple the Dabcyl fluorescence quencher to its 3' end, the sequence Synthesized by a commercial primer company.
[0034] (2) Add mercury ion standard solutions with concentrations of 0, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, and 1024ng / ml to the corresponding microplate (for fluorescence) respectively. In the well, 50 μl / well, each sample was set to repeat at least once;
[0035] (3) Dilute nucleic acid aptamer sequences of different thymine lengths into a 50nM solution with PBS solution, add to the corresponding microwell of the microplate, 50μl per well, and mix well on a shaker, at 37°C Incubate in the dark for 20 minutes;
[0036] (3) Place the microplate plate on a multi-functional microplate reader for reading.
[0037] Experimenta...
example 3
[0043] Example 3: Method for Concentration Detection of Mercury Ions in Water Using Nucleic Aptamers
[0044] (1) Dilute the T6 sequence in Example 2 with PBS solution to form a nucleic acid aptamer solution with a concentration of 50nM; filter the water sample to be tested with filter paper to remove impurities;
[0045] (2) Add the mercury ion standard solution with the concentration of 0, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64ng / ml and the sample to be tested into the corresponding microwells of the microplate (for fluorescence) (50μl / Wells), each sample was set to repeat at least once;
[0046] (3) Add the diluted nucleic acid aptamer solution T6 (50nM) into the corresponding microwell, 50μl / well, mix well on a shaker, and incubate at 37°C in the dark for 20min;
[0047] (4) Place the microplate plate on a multi-functional microplate reader to read the value, and obtain the fluorescence value of the standard substance and the sample to be tested.
[0048] Experimental result processing:...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com