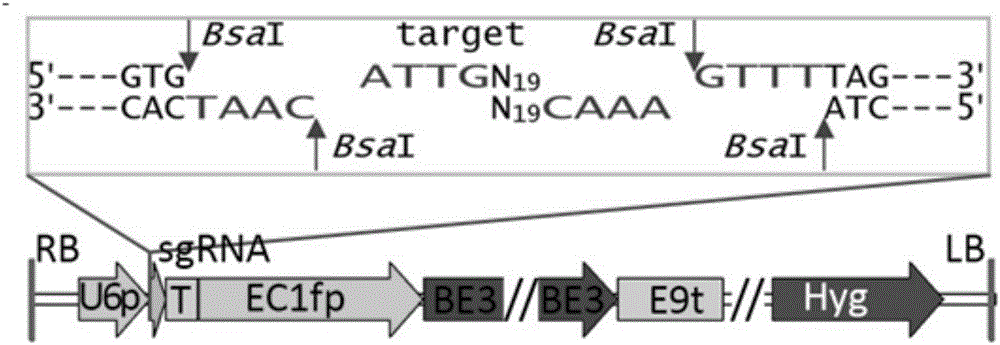
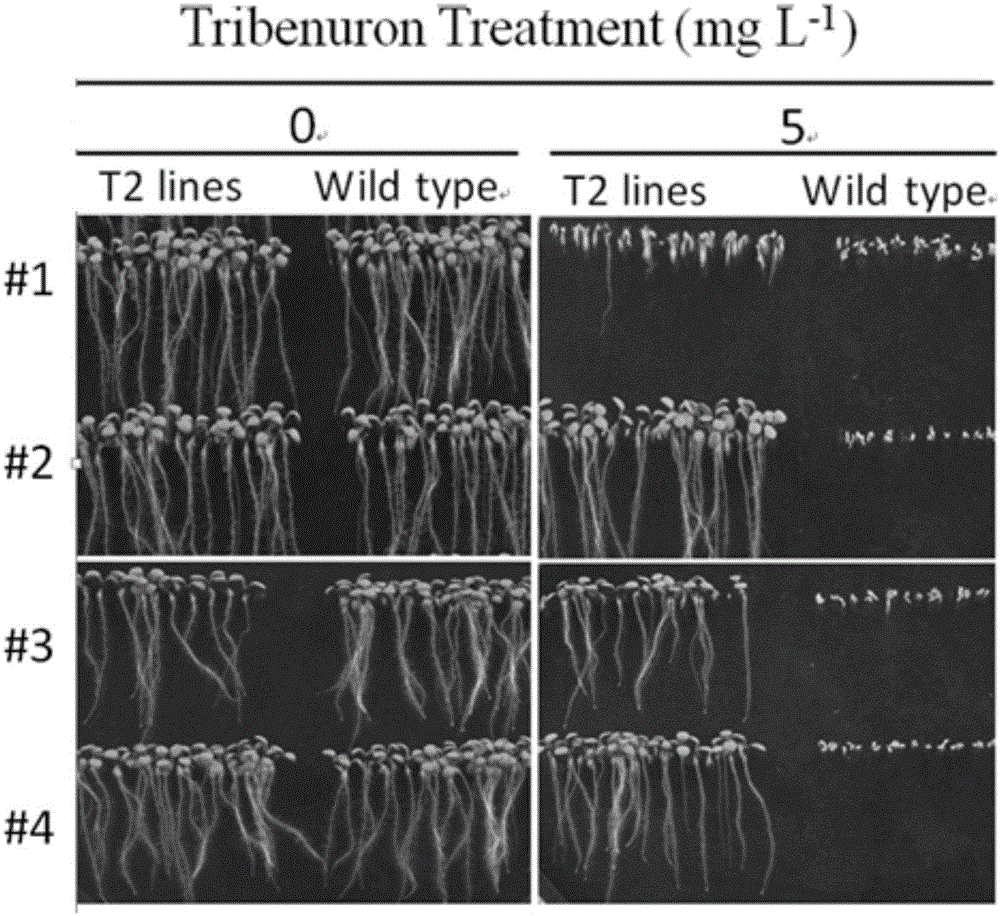
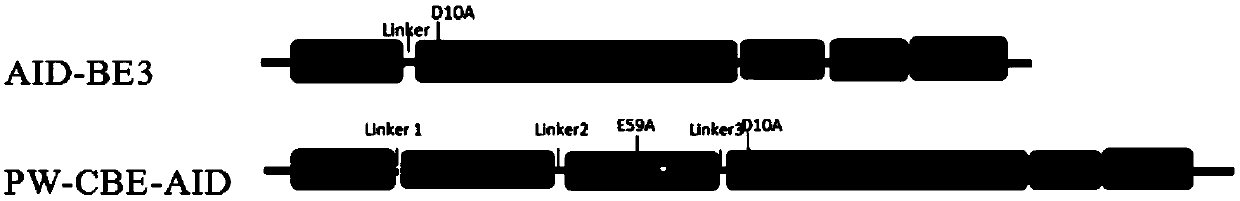
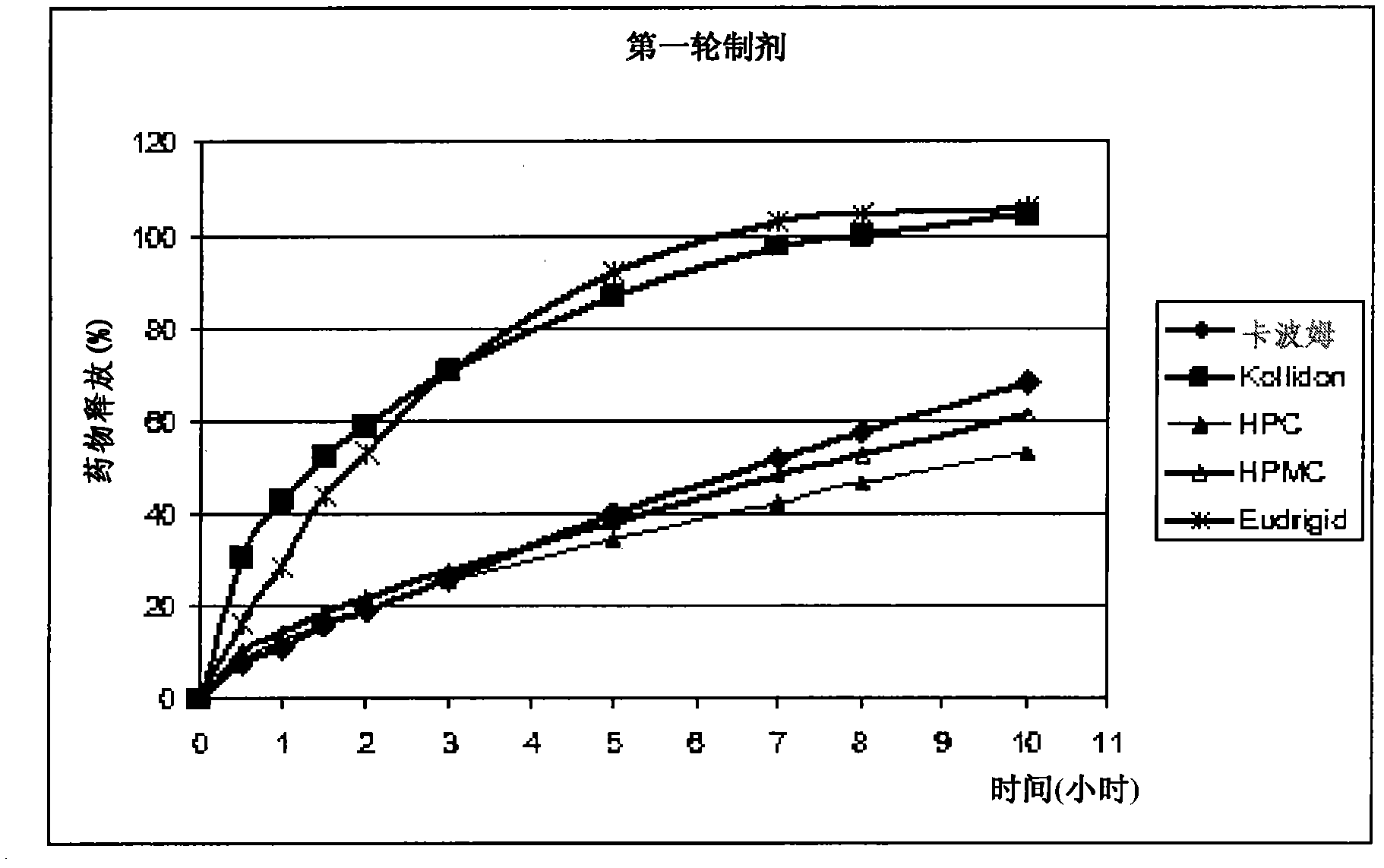
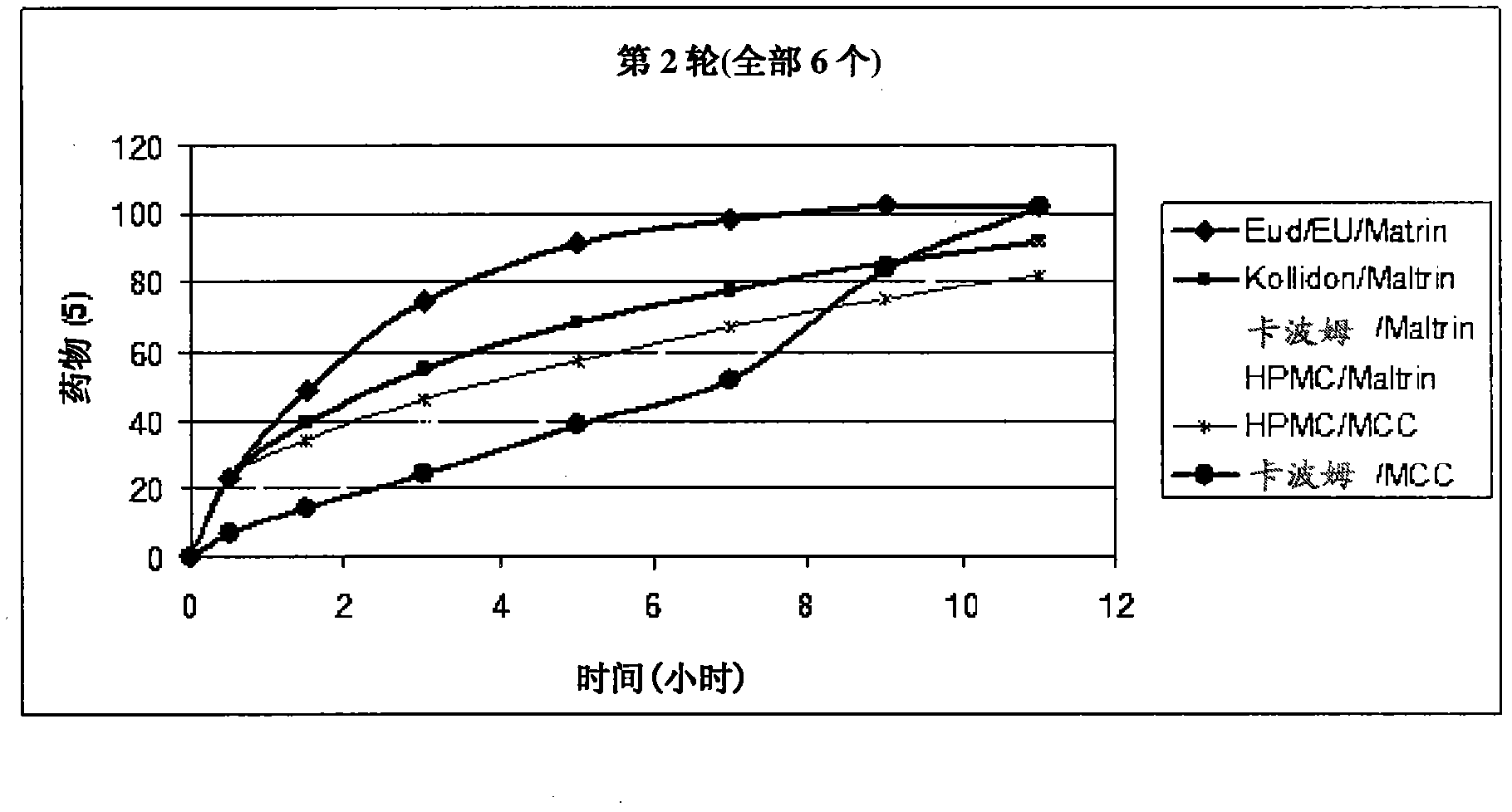
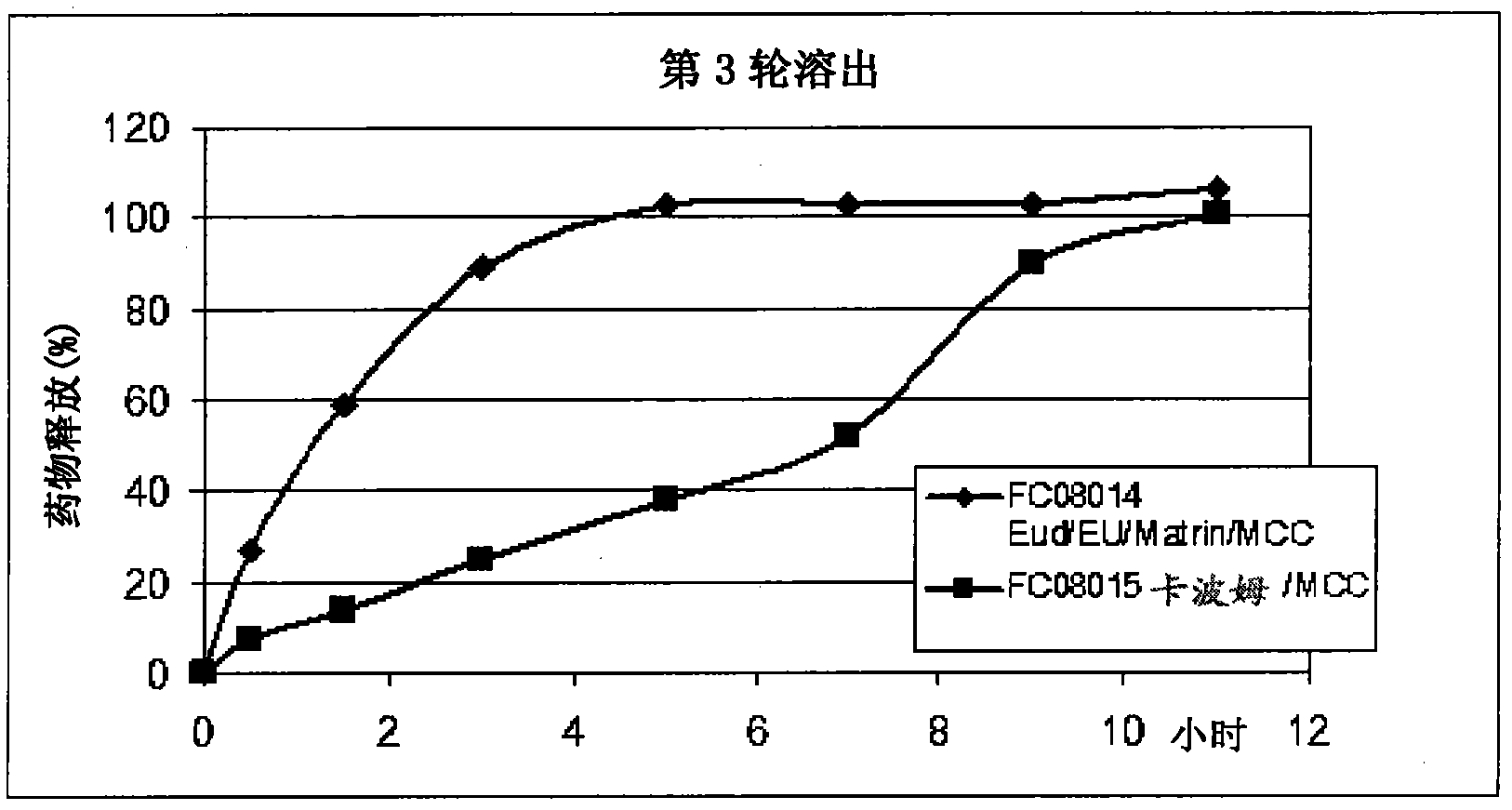
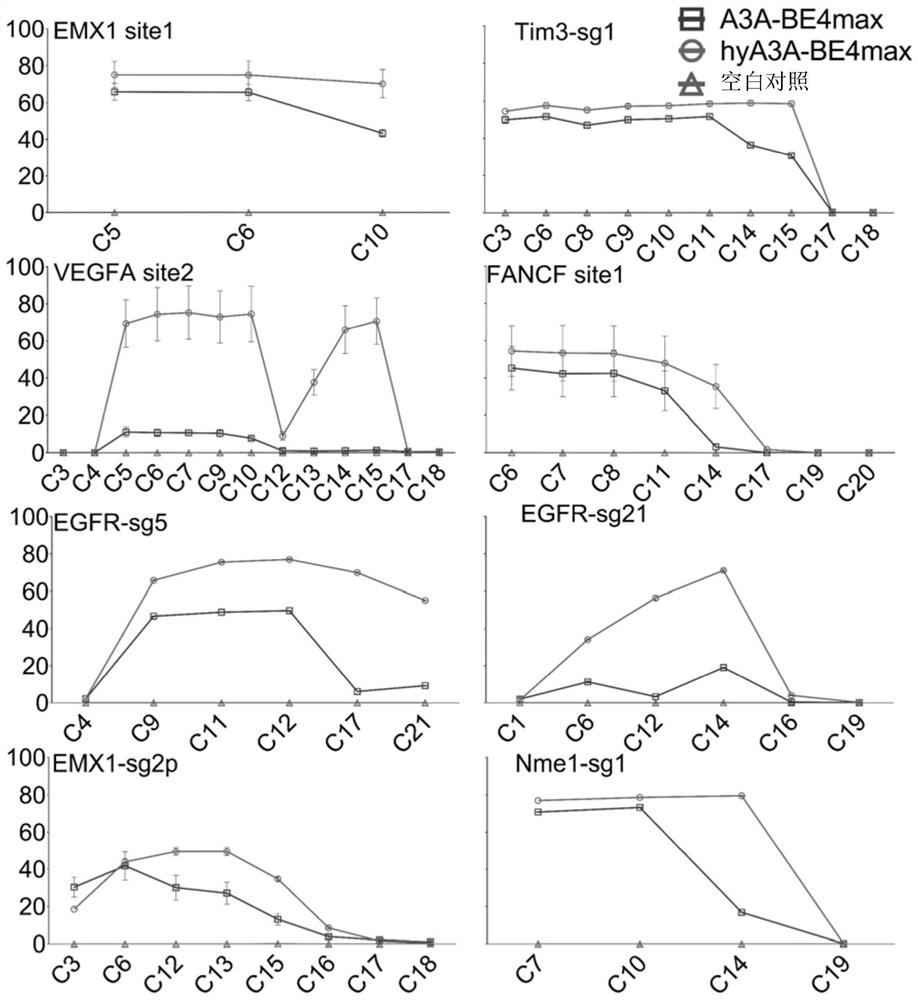
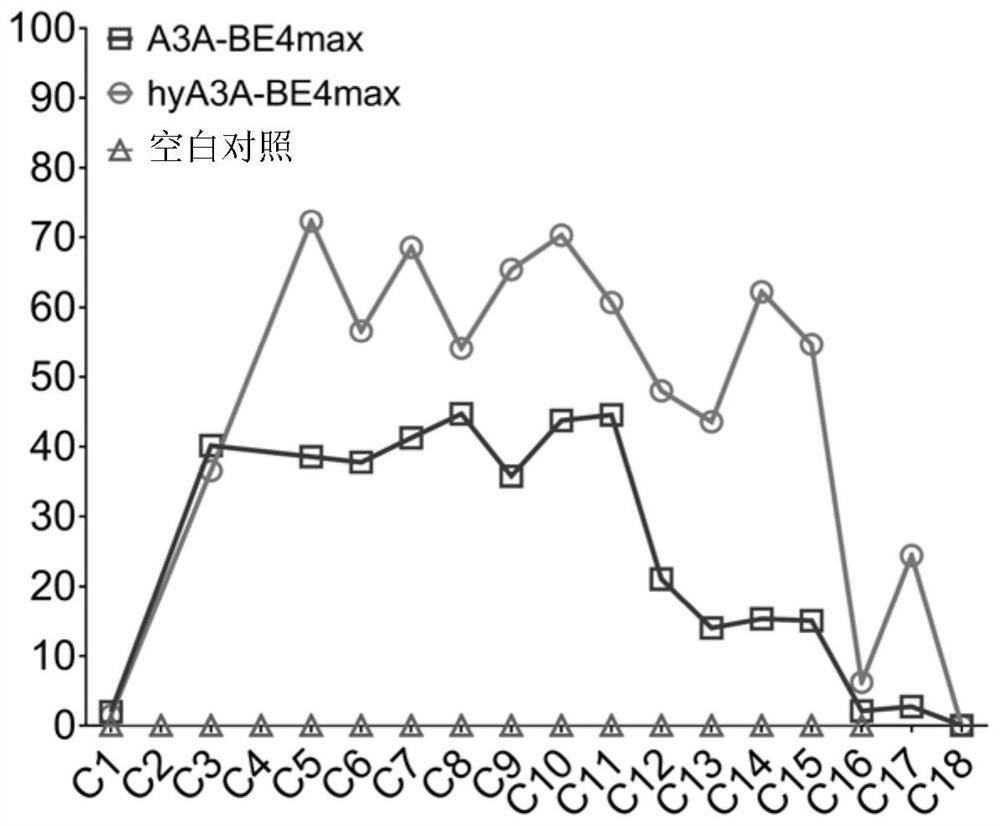
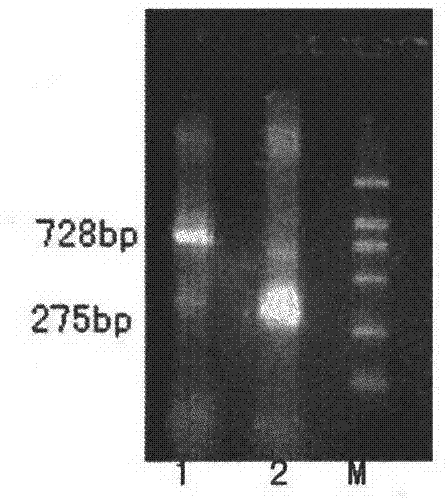
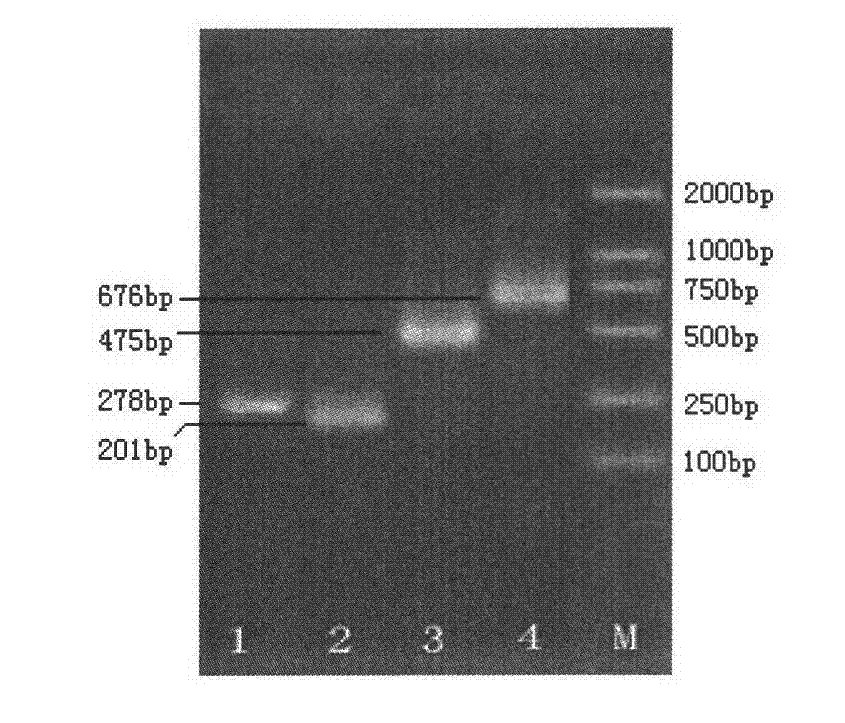
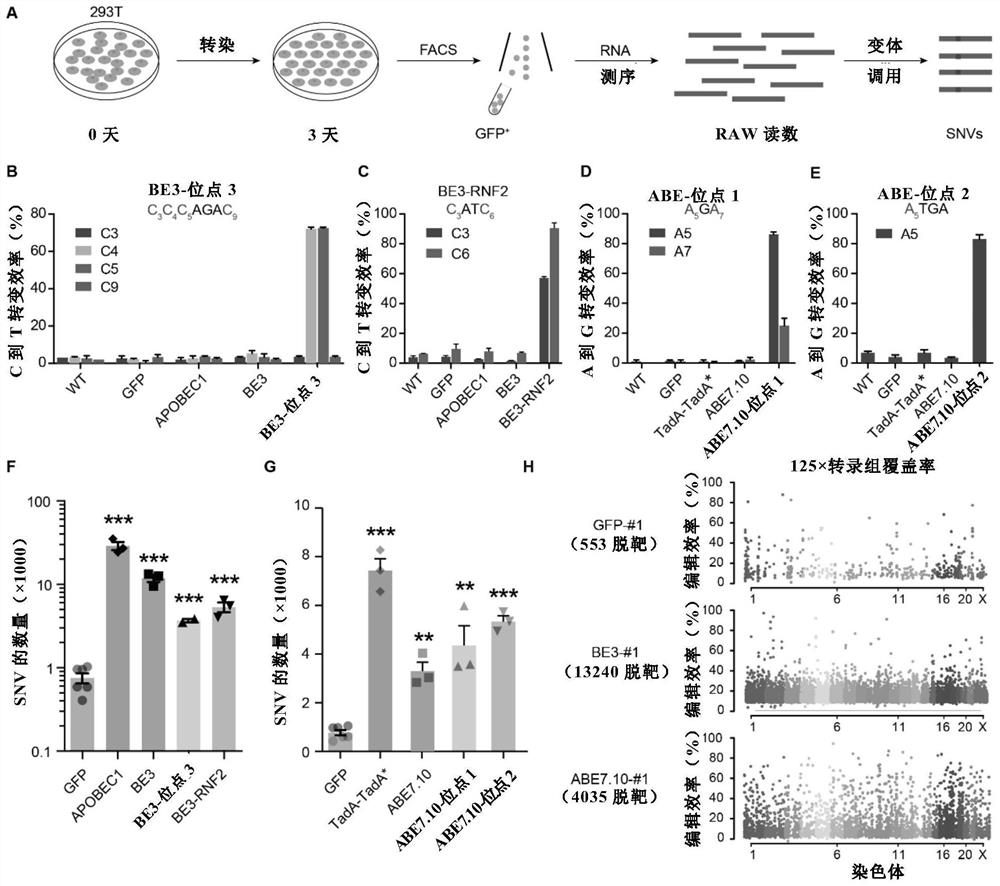
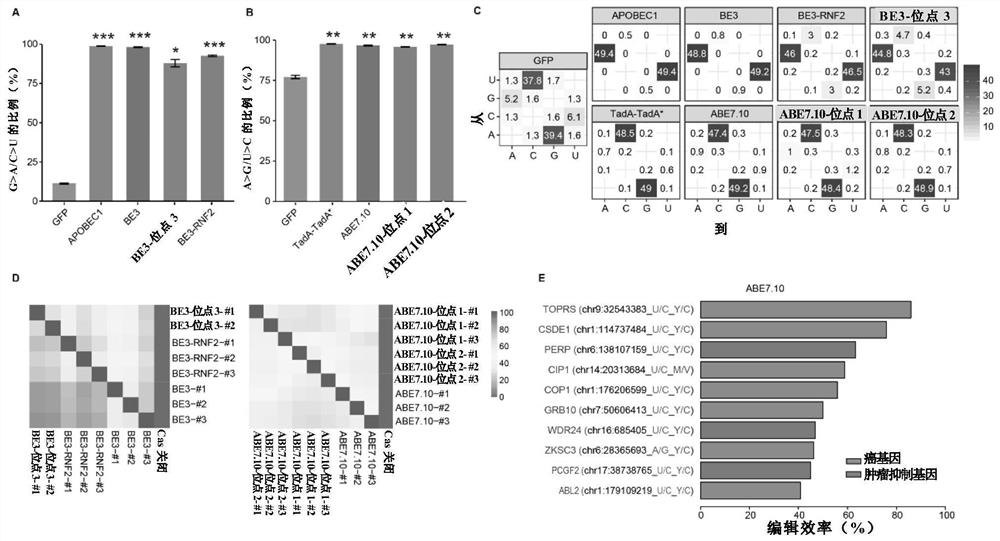
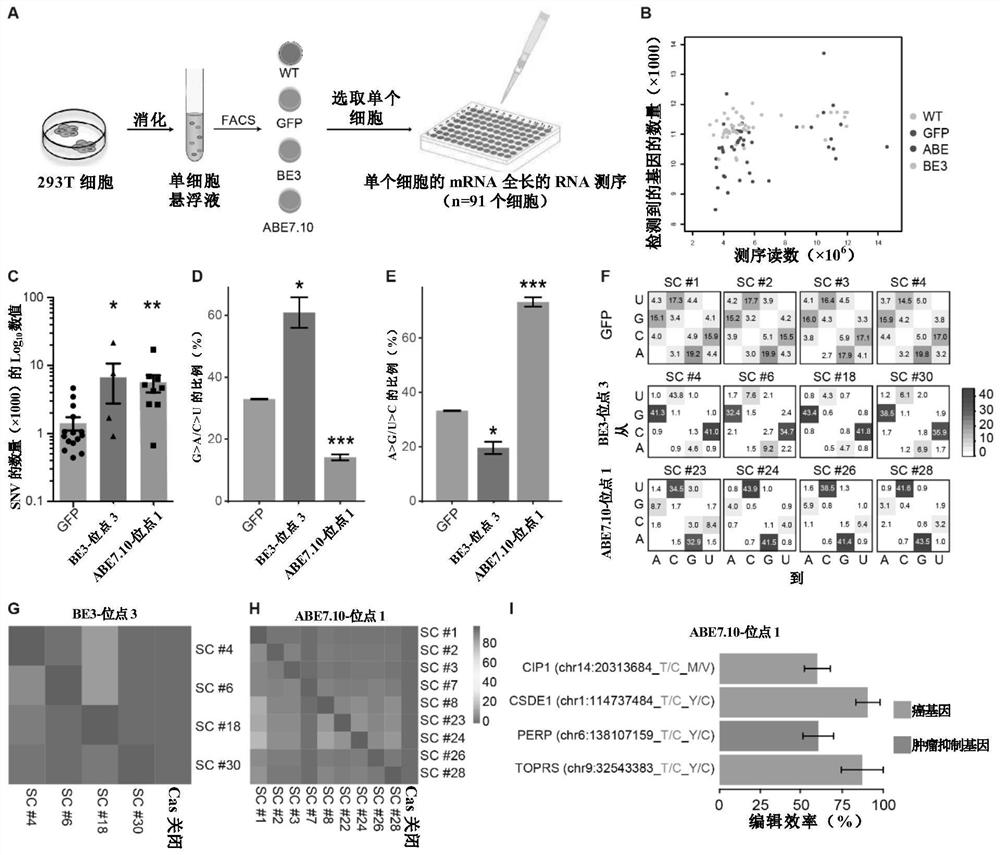
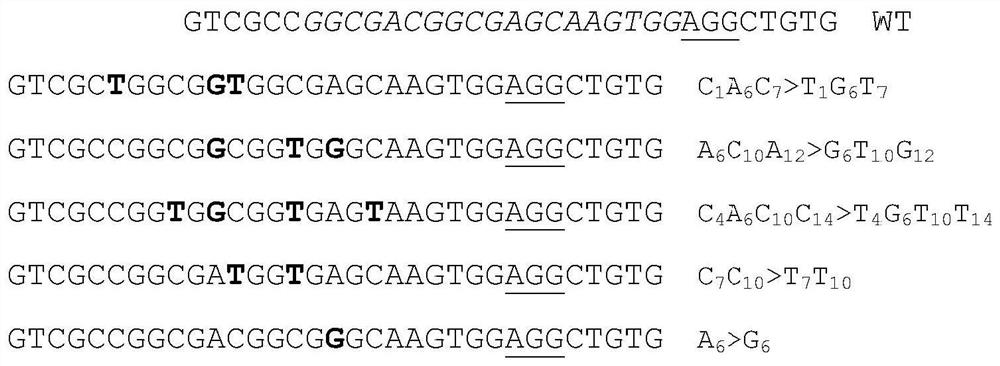Patents
Literature
97 results about "Cytosine deaminase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In enzymology, a cytosine deaminase (EC 3.5.4.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction cytosine + H₂O ⇌ uracil + NH₃ Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are cytosine and H₂O, whereas its two products are uracil and NH₃. This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolases, those acting on carbon-nitrogen bonds other than peptide bonds, specifically in cyclic amidines. The systematic name of this enzyme class is cytosine aminohydrolase.
Gene site-directed mutation vector as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN106834341ANucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionCytosine deaminaseCytosine
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering and in particular relates to a gene site-directed mutation vector as well as a construction method and application thereof. The invention provides the gene site-directed mutation vector due to lots of optimizations, cytosine deaminase is guided to be close to cytosine through a CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) system, the cytosine is changed into uracil, then uracil is changed into thymine through self-repair in plant cells, and finally, site-specific mutagenesis from C to T is realized in plants so as to generate resistance to herbicides. In addition, point mutation can be produced in a non-sgRNA targeted area, and novel herbicide-resistant great agronomic traits are brought.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Composition for modifying nucleotide sequence, method and application
ActiveCN109517841AWide working windowReduce deletionVector-based foreign material introductionDNA preparationCytosine deaminaseNucleotide
The invention discloses a composition for modifying a nucleotide sequence, a method and application, and relates to the technical field of gene editing. The composition comprises a first vector and asecond vector, wherein the first vector is provided with the following expression elements, such as a cytosine deaminase expression element, an adenine deaminase expression element and a mutant Cas enzyme expression element; the second vector is provided with the following expression elements, such as a gRNA (guide ribonucleic acid) expression element and a uracil glycosidase inhibitor expressionelement. The composition is used for modifying the C bases at the 1st to 16th sites at the upstream of PAM (protospacer adjacent motif) of the target nucleotide sequence, so that the transformation ofC / G to T / A is realized. Compared with the existing gene editing technique, the composition and the method have the advantages that the working window is broader; the DSB (double-strand break) and indels (insertion / deletion mutations) are not introduced, the off-target effect is very low, the safety is higher, and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV +1
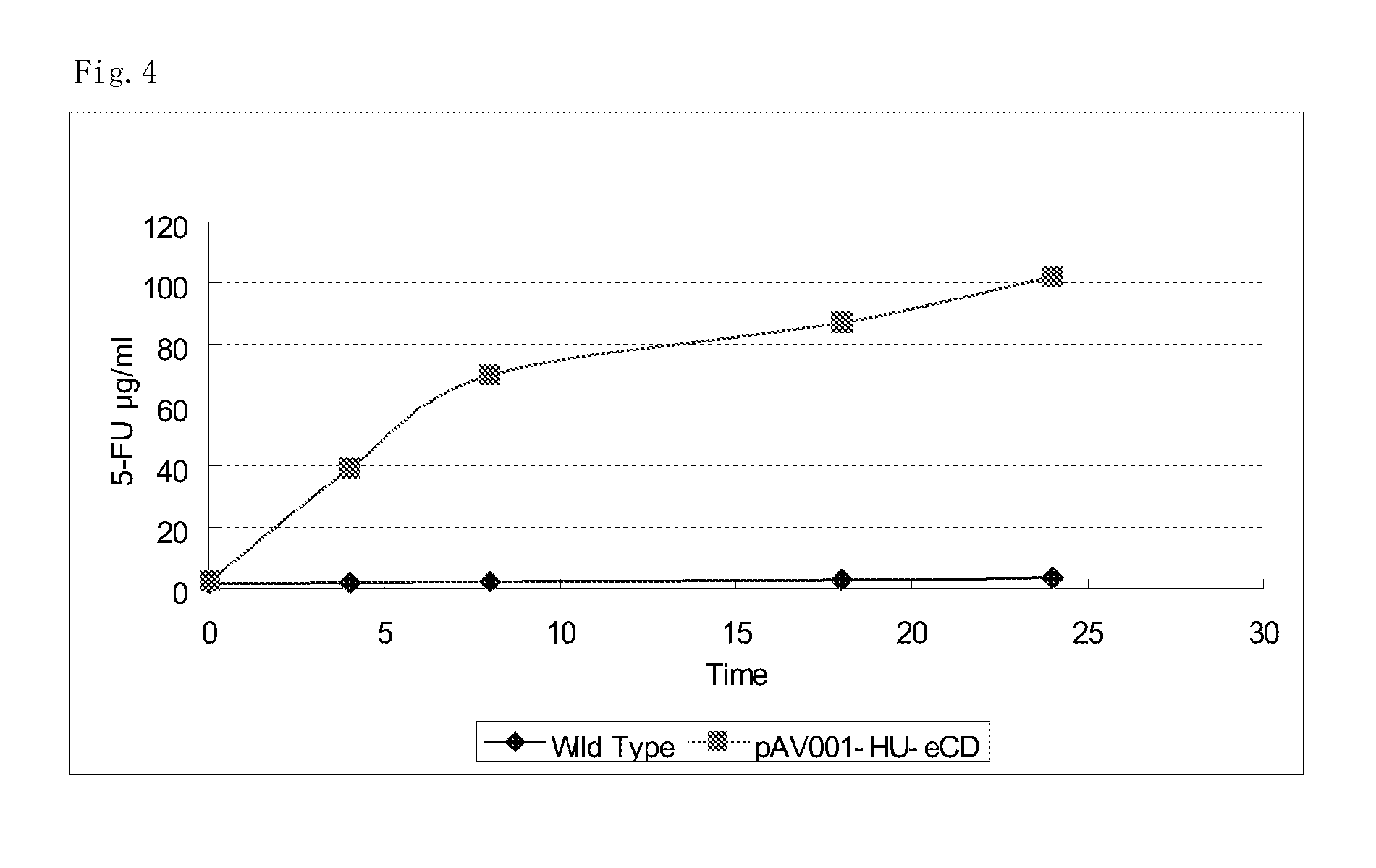
5-fluorouracil-resistant bacteria and method for production thereof
The present invention provides a method for producing a cytosine deaminase (CD)-expressing, 5-fluorouracil (5-FU)-resistant microorganism which can grow in anaerobic tumor tissues, can express CD, and has a resistance to 5-FU at a concentration that is at least effective for antitumor activity. More specifically, the method is a method (A) comprising performing subculture or acclimation culture of a CD-expressing microorganism which can grow in anaerobic tumor tissues, in the presence of 5-fluorocytosine (5-FC), or a method (B) comprising (1) performing subculture or acclimation culture of a microorganism which can grow in anaerobic tumor tissues and does not express CD, in the presence of 5-FU to produce a 5-FU-resistant microorganism and (2) transforming the 5-FU-resistant microorganism by introducing a CD gene. The present invention also provides the CD-expressing, 5-FU-resistant microorganism and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the microorganism.
Owner:ANAEROPHARMA SCI
Antiviral protein and uses thereof
InactiveCN101343327ACapable of penetrating membraneLow immunogenicityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsCytosine deaminaseProtein molecules
The invention relates to anti-viral protein. The anti-viral protein is characterized in that the anti-viral protein is fusion protein and comprises a transmembrane peptide structural domain and a tandem body which is formed through at least two cytosine deaminase structural domains originated from an APOBEC family, a transmembrane peptide structural domain and various cytosine deaminase structural domains. The transmembrane peptide structural domain in the anti-viral protein provided by the invention ensures the anti-viral protein to have the transmembrane capability and to freely shuttle among cells and enters the cells in a non-receptor and non-energy dependent way; the cytosine deaminase structural domains originated from the APOBEC family ensures that the anti-viral protein can effectively inhibit the reproduction of human immunodeficiency virus and / or hepatitis B virus after entering cells; because the non-essential sequences in the APOBEC family protein molecules are removed, not only the antiviral activity of the APOBEC family protein molecules is preserved, but also the immunogenicity of the anti-viral protein is reduced, and the transmembrane efficiency of the anti-viral protein is enhanced.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV MEDICAL COLLEGE
Method for increasing editing efficiency of base editing system
InactiveCN109679989AIncrease concentrationImprove editing efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsCytosine deaminaseMutant
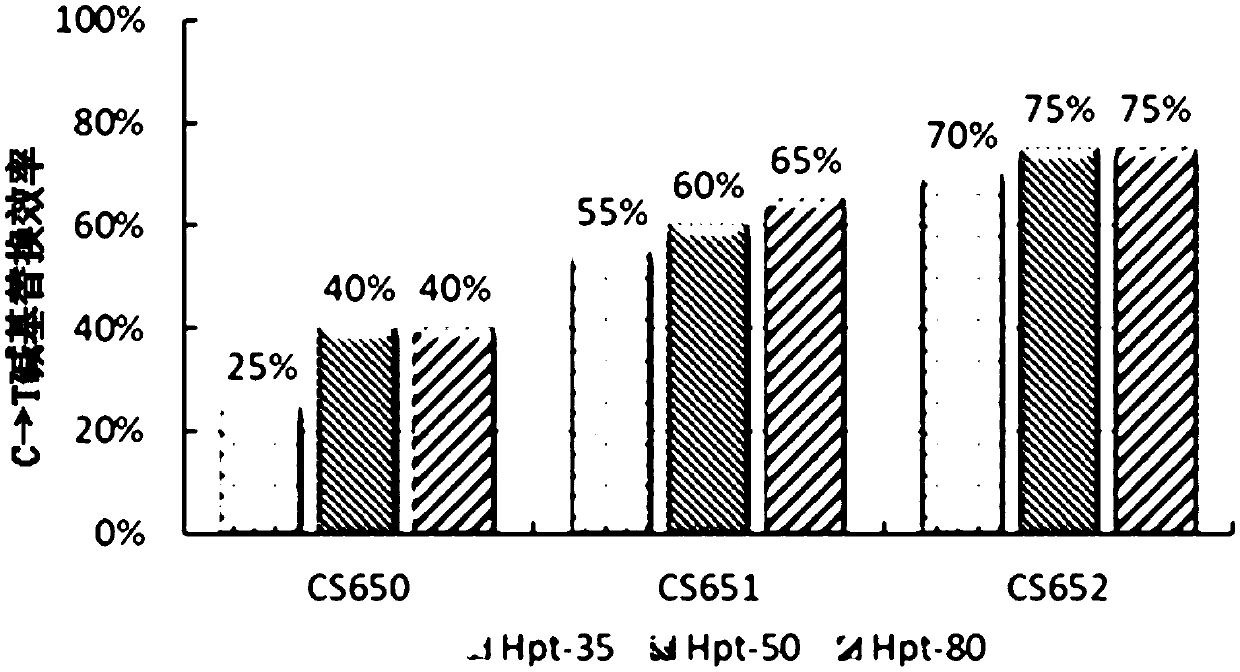
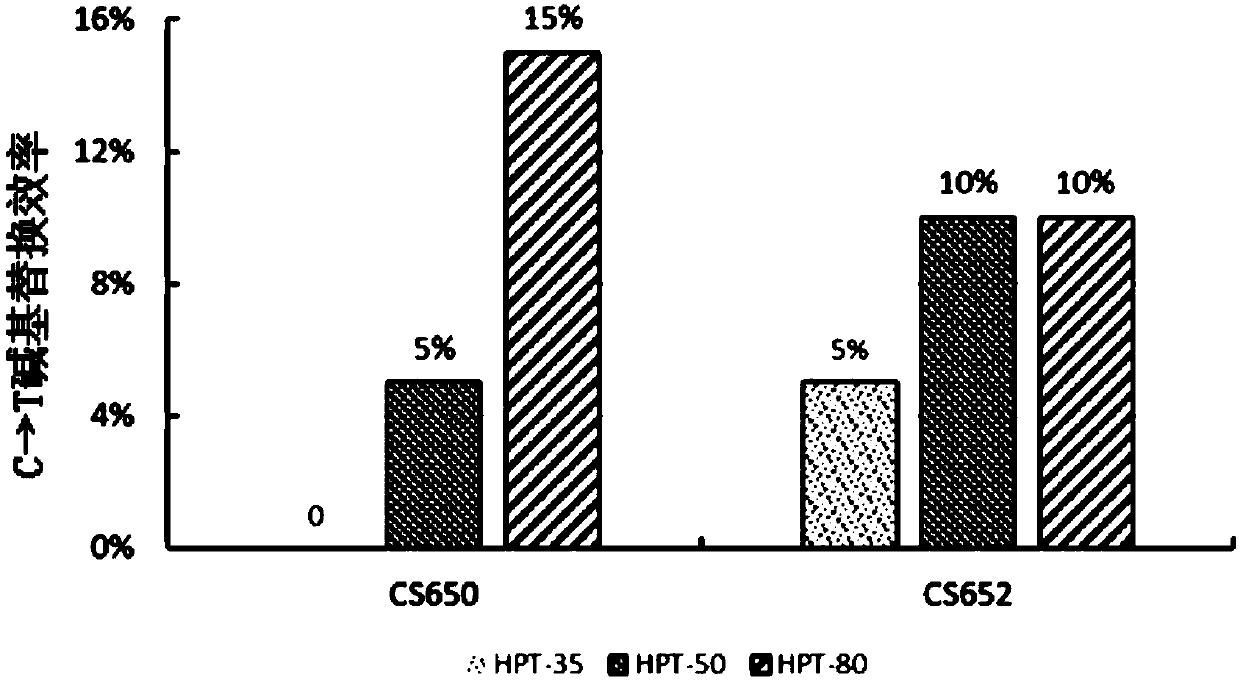
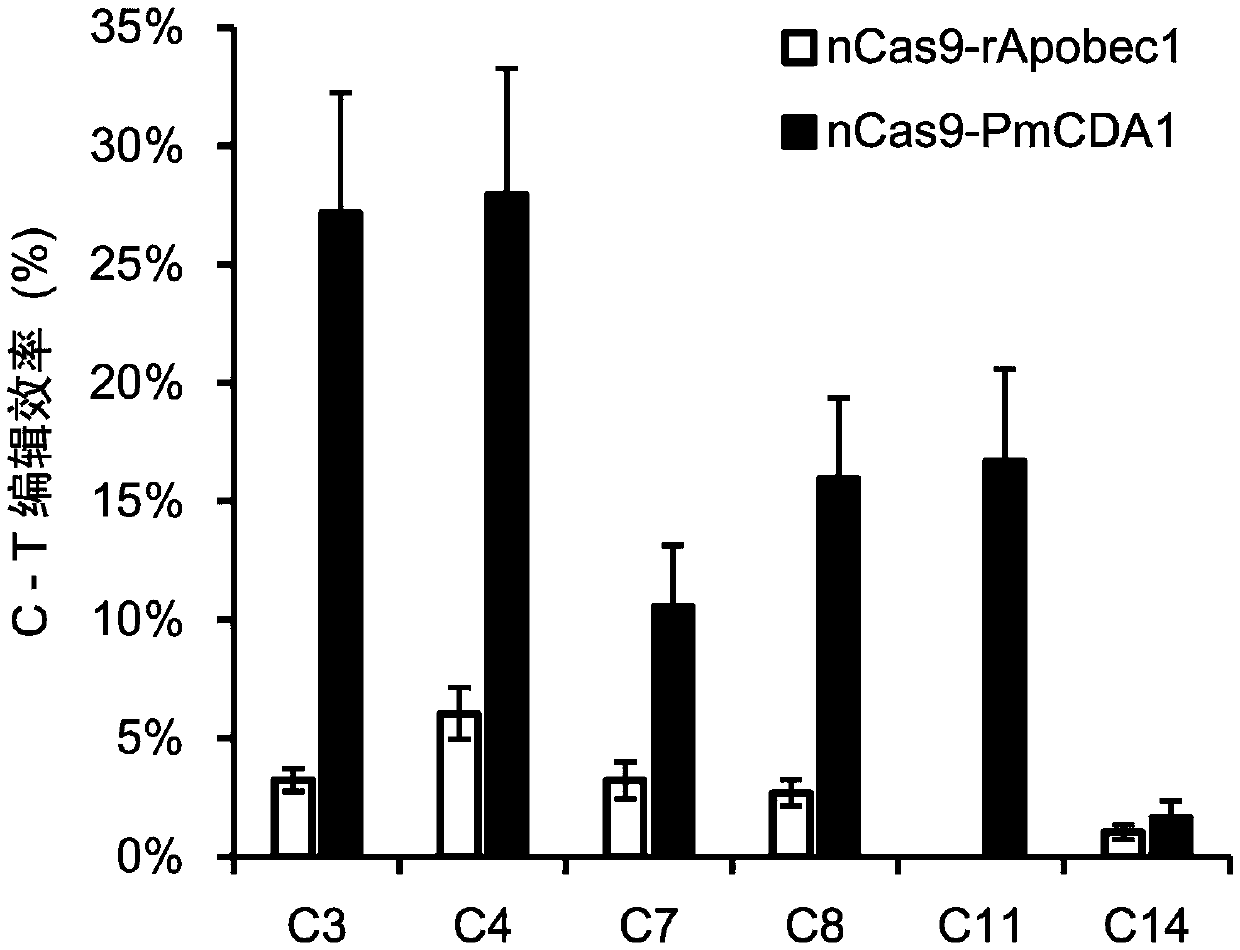
The invention discloses a method for increasing editing efficiency of a base editing system. The method comprises the following steps: expressing sgRNA, anti-hygromycin protein, Cas9 protein, cytosinedeaminase and uracil DNA saccharifying enzyme inhibitor by a receptor, thereby performing base editing on a target gene in a receptor genome, wherein the receptor is a plant callus; taking hygromycinas a screening reagent for screening resistant callus during the process of introducing the plant callus, wherein the concentration of hygromycin is 35-80mg / L. An experiment proves that C arrow T base substitution efficiency of SpCas9n(D10A)&PmCDA1&UGI base editing system and rAPOBEC1&SpCas9n&UGI base editing system can be increased by increasing the concentration of screening reagent hygromycinso as to acquire an efficient mutant. The method has an important application value.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Plant genome directional base editing skeleton vector and application thereof
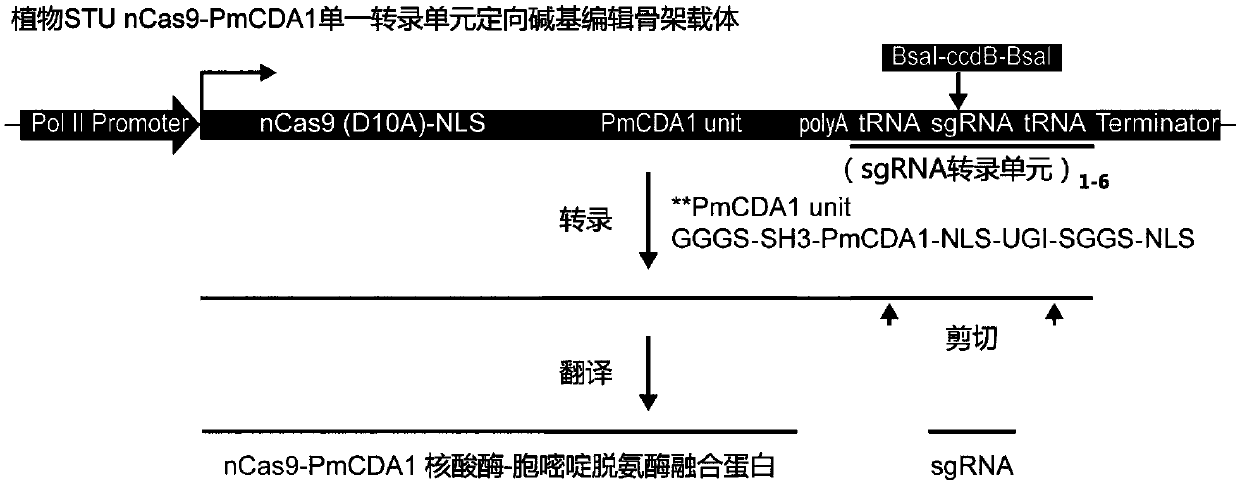
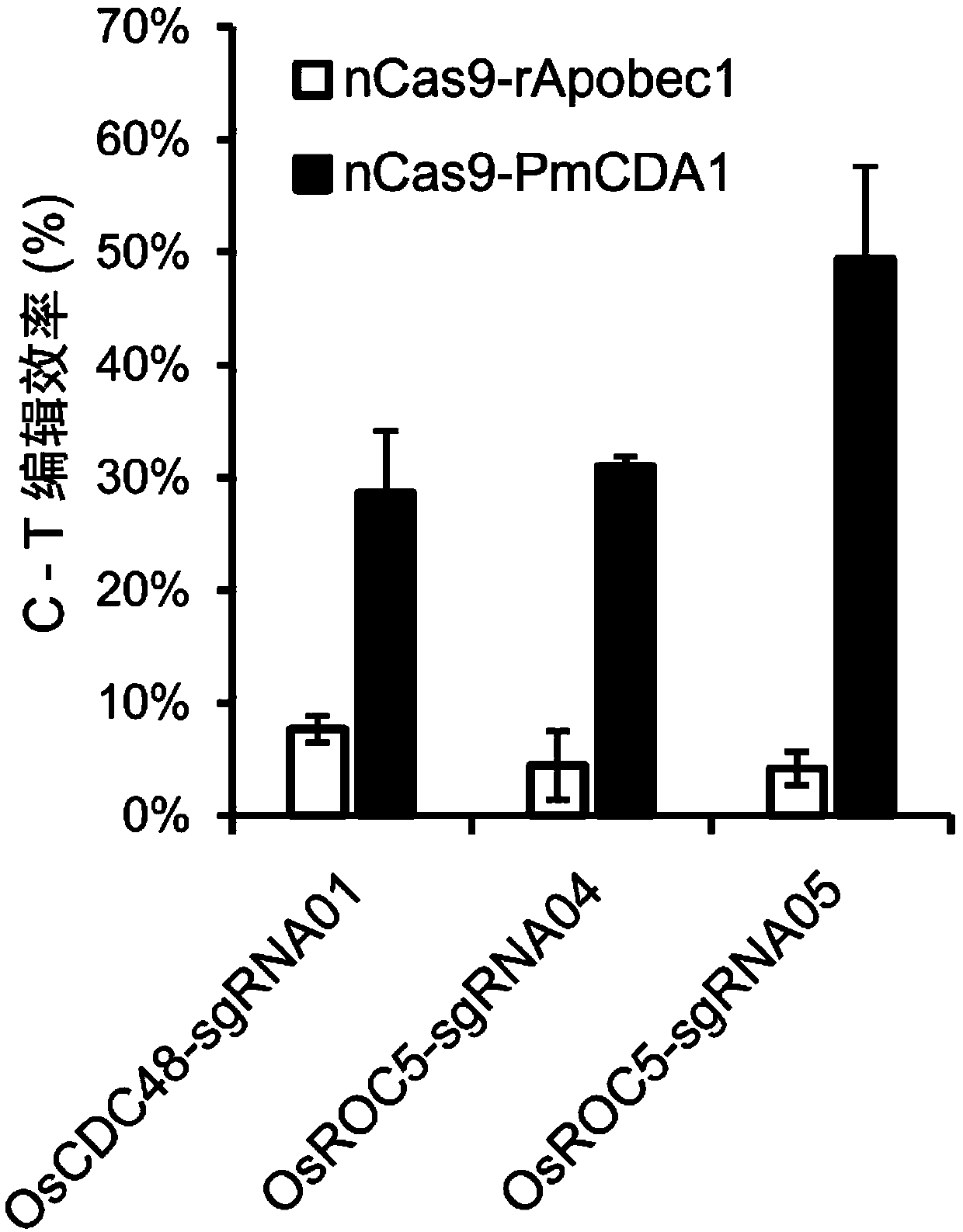
ActiveCN110607320AImprove editing efficiencyGuaranteed effective useVectorsVector-based foreign material introductionFusion Protein ExpressionCytosine deaminase
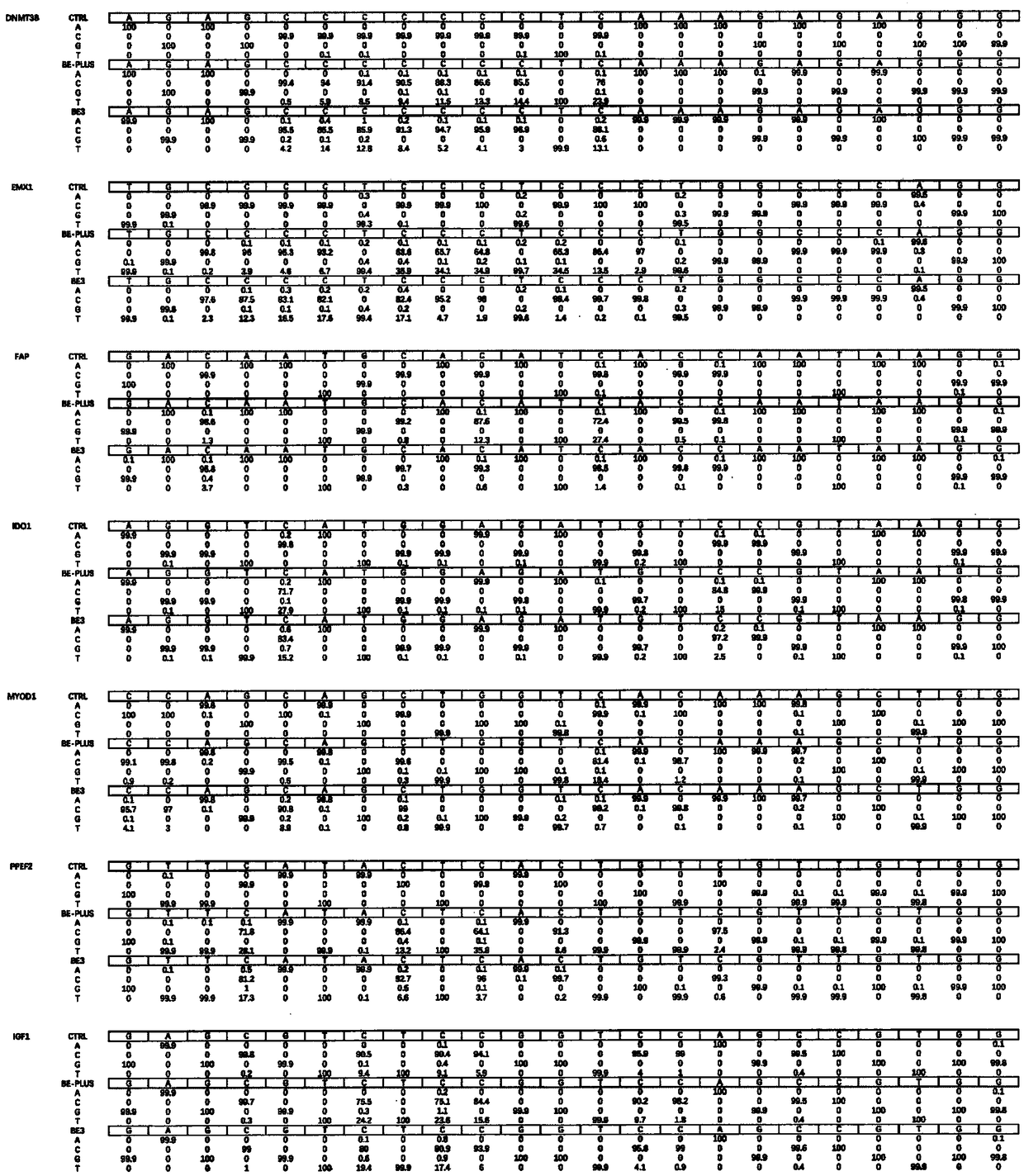
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, and particularly relates to a plant genome directional base editing skeleton vector and an application thereof. The technical problemto be solved by the invention is to improve the directed base editing efficiency of a plant cell genome and expand a base editing window. The technical scheme for solving the technical problem is to provide the plant genome directional base editing skeleton vector. The skeleton vector is characterized in that a PolII type promoter drives transcription of a core unit consisting of two core regions,i.e., an nCas9-PmCDA1 nuclease-cytosine deaminase fusion protein expression unit and a synthetic guide RNA (sgRNA) transcription expression unit. The single transcription unit oriented base editing skeleton vector can effectively realize simple, rapid and efficient oriented editing of converting cytosine bases (C) into thymine bases (T), and is a molecular tool for effectively realizing orientedediting of plant genome bases.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Base editing tool and application thereof
ActiveCN108715861AIncrease windowImprove accuracyVectorsVector-based foreign material introductionCytosine deaminaseSingle-Chain Antibodies
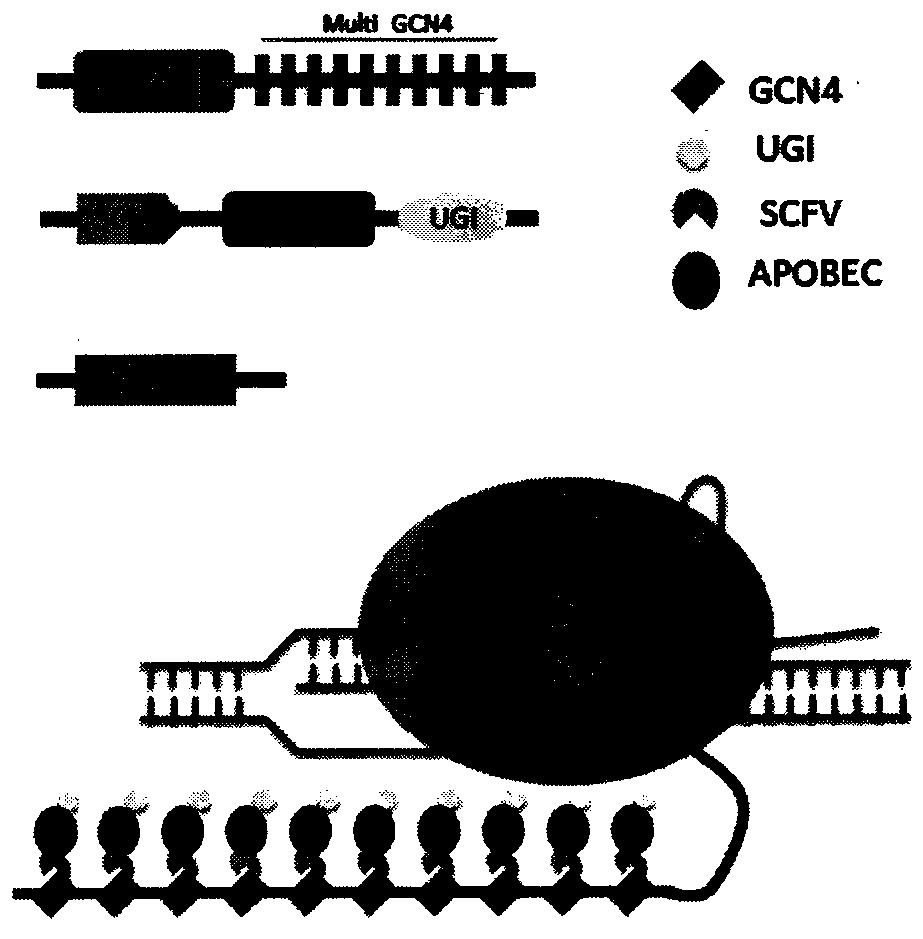
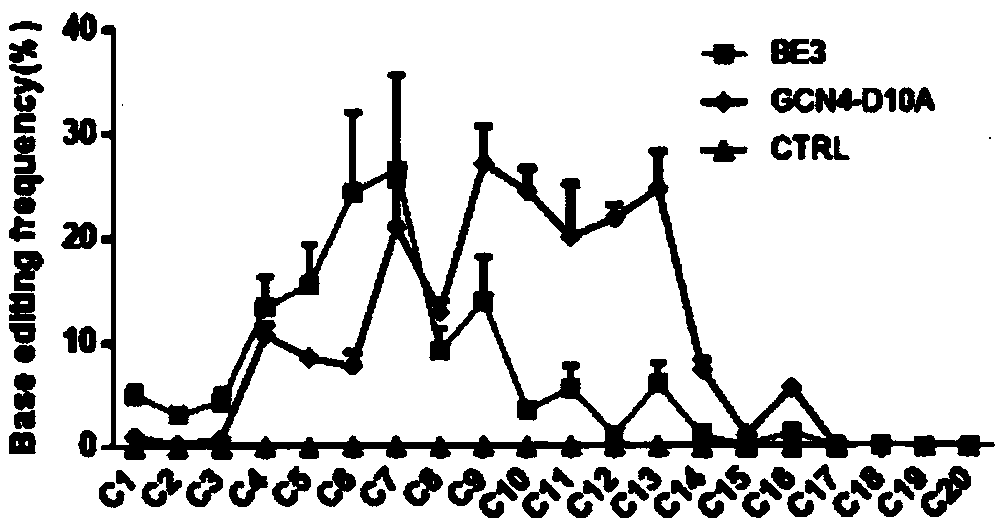
The invention provides a base editing tool and application thereof. The base editing tool is characterized by comprising GCN4-D10A, a scFv-APOBEC-UGI vector or a scFv-APOBEC-UGI-GB1 vector, and sgRNAat target specific sites, wherein the GCN4-D10A is formed by connecting multi-copied GCN4 to D10A-Cas9; the scFv-APOBEC-UGI vector is formed by connecting cytosine deaminase APOBEC and uracil glycosylase inhibitors UGI to a single-chain antibody scFv; the scFv-APOBEC-UGI-GB1 vector is formed by connecting the cytosine deaminase APOBEC and uracil glycosylase inhibitors UGI and a thermal stability domain GB1 for preventing multimerization to the single-chain antibody scFv. Compared with a commonly used base editing tool, the base editing tool disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the base editing windows are obviously increased, and the application range of base editing in genome is further widened.
Owner:SHANGHAI TECH UNIV
Application of novel base conversion editing system on gene therapy
ActiveCN110835632AGuaranteed to workAchieve changeHydrolasesGenetic material ingredientsCytosine deaminaseBase J
The invention innovatively provides an application of a novel base conversion editing system on gene therapy for the first time; according to the system, the function of a single-base gene editing system is reserved, which is characterized in that conversion from C / G to T / A of a single base at a specified site is realized, conversion from A / T to G / C is realized, and the conversion from C / G to T / Aand from A / T to G / C can be also realized. The basic group conversion editing system comprises sgRNA, nuclease, cytosine deaminase, adenosine deaminase and uracil glycosidase inhibitors, and the nuclease, the cytosine deaminase, the adenosine deaminase and the uracil glycosidase inhibitors can target and recognize DNA sequences. The invention further provides a pharmaceutical composition containingthe base conversion editing system and the application of the pharmaceutical composition in gene editing, gene therapy, drug screening and model animal construction.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Viral vector driven mutant bacterial cytosine deaminase gene and uses thereof
InactiveUS20070225245A1Low efficiencyGreat fold substrate preferenceVectorsHydrolasesCytosine deaminaseHuman glioma
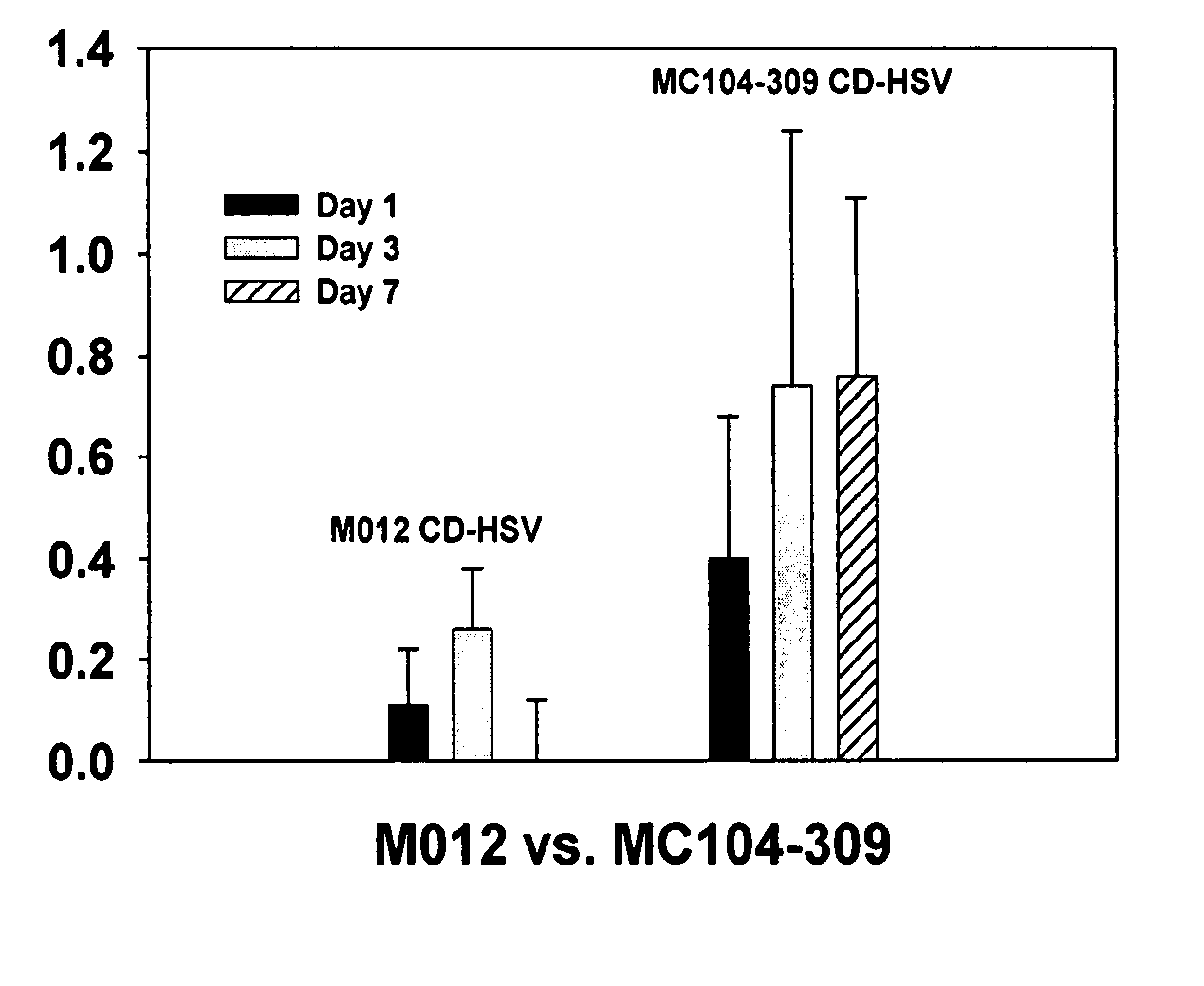
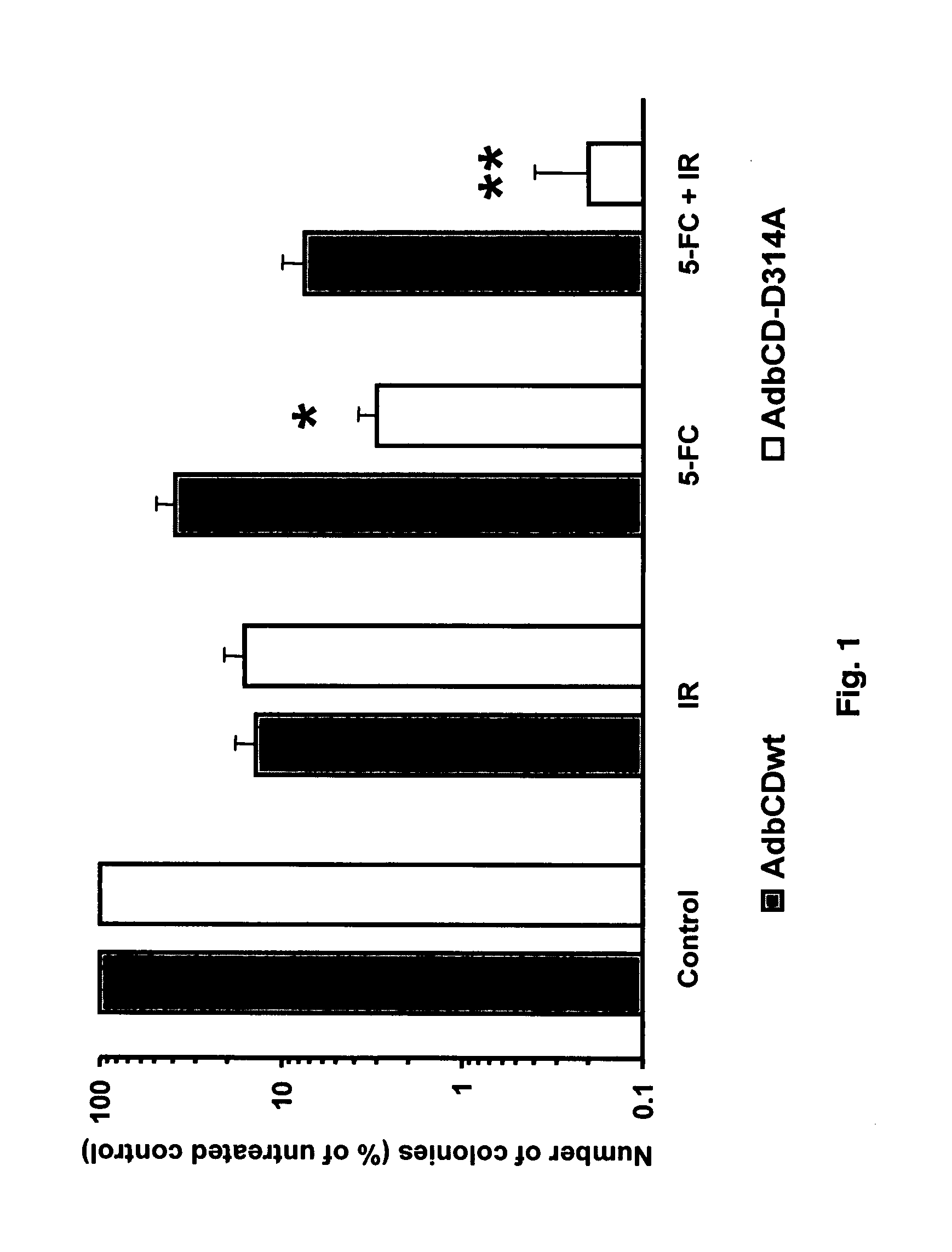
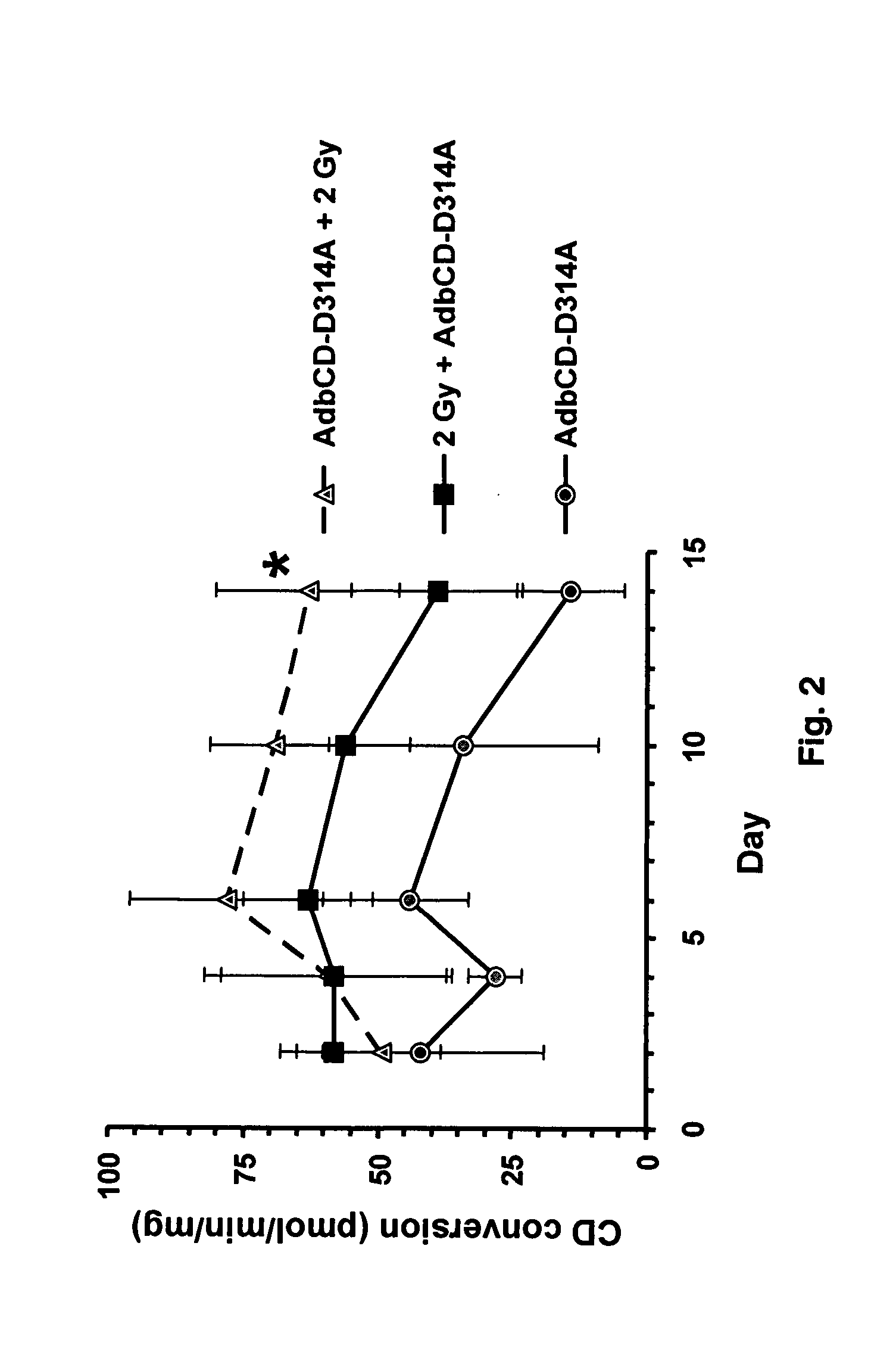
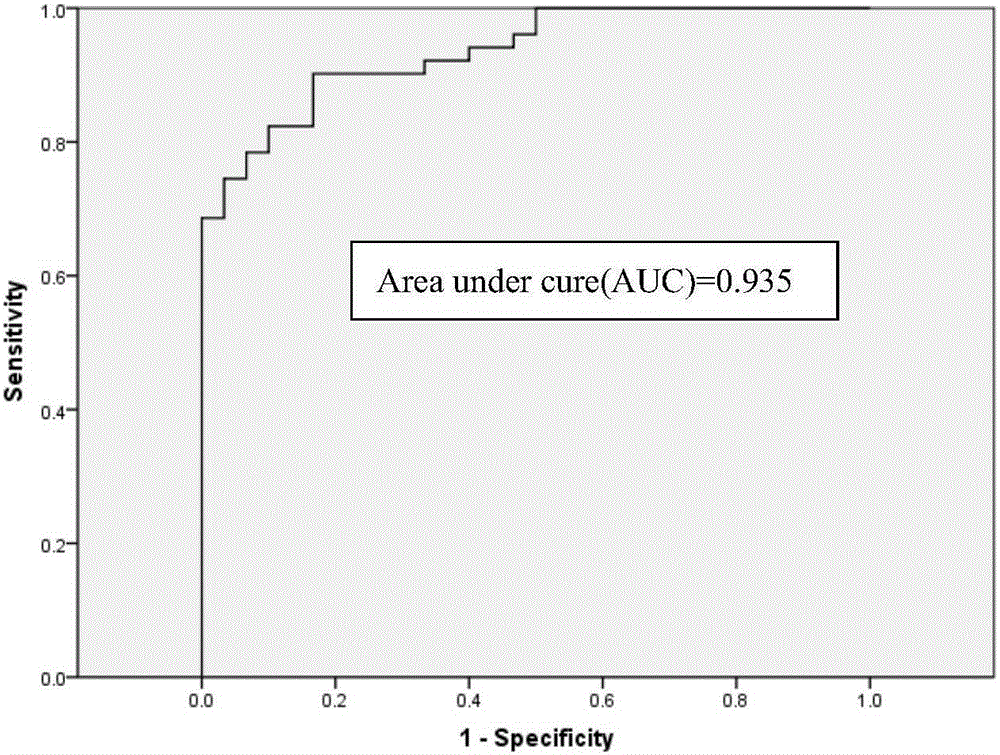
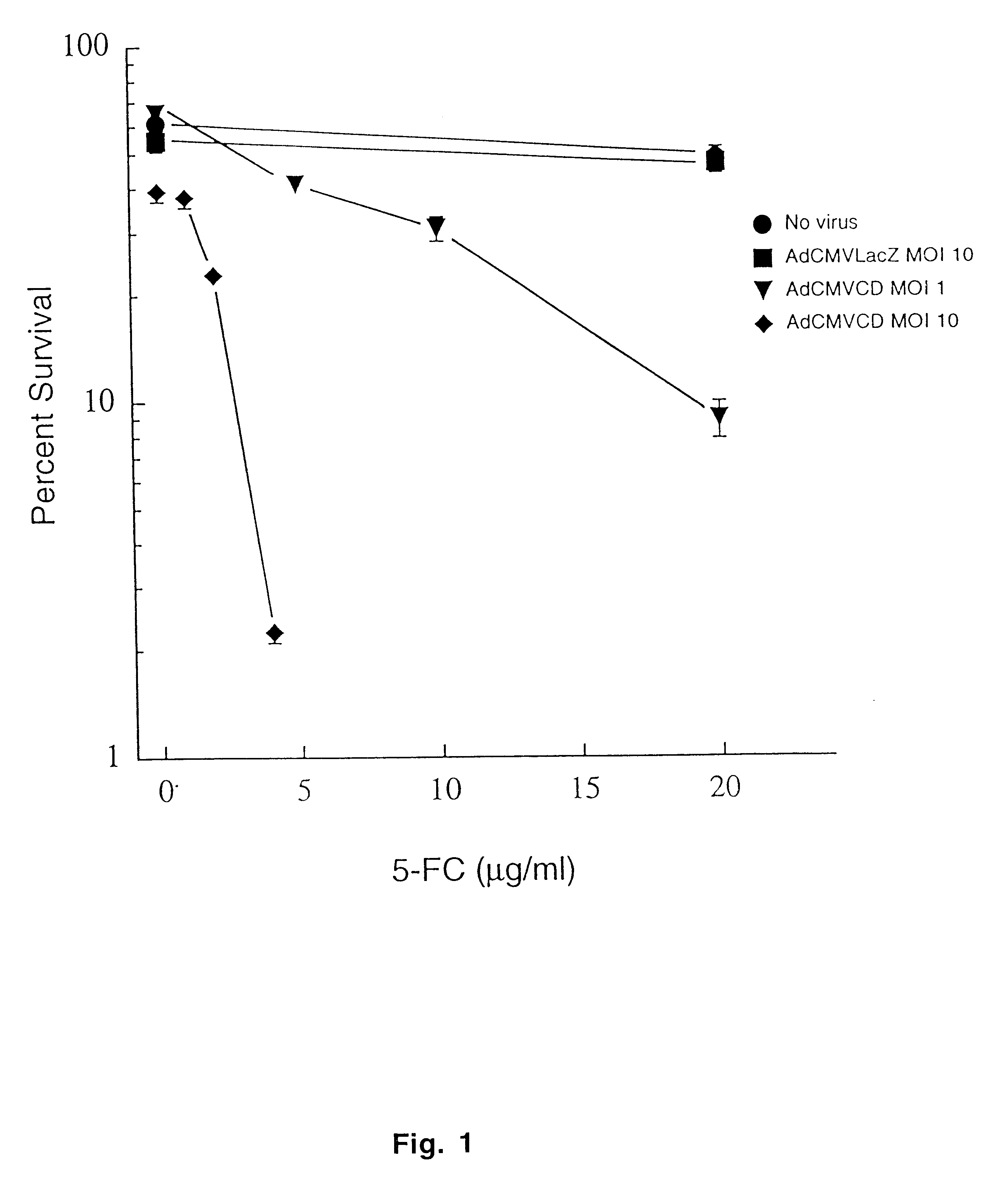
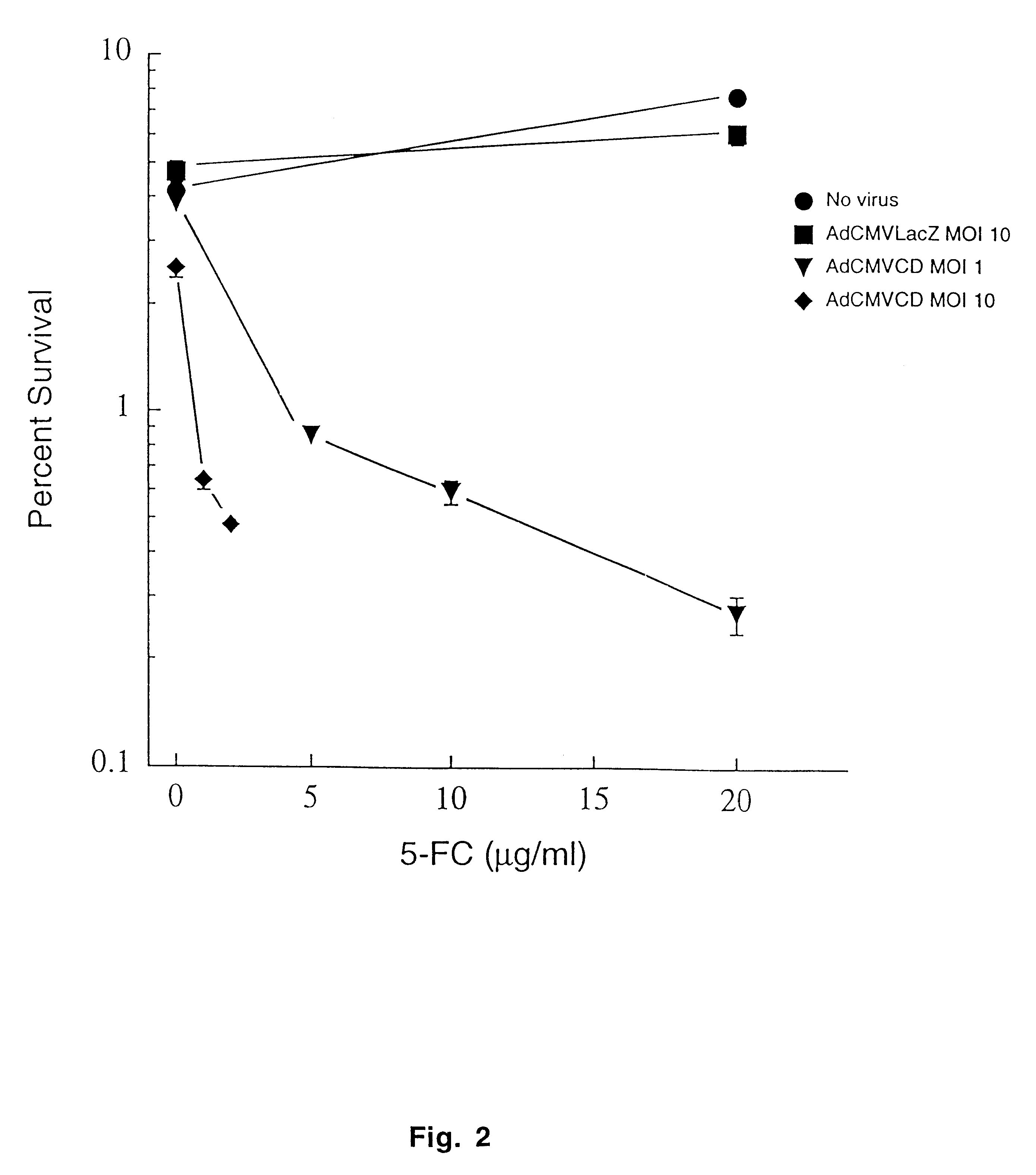
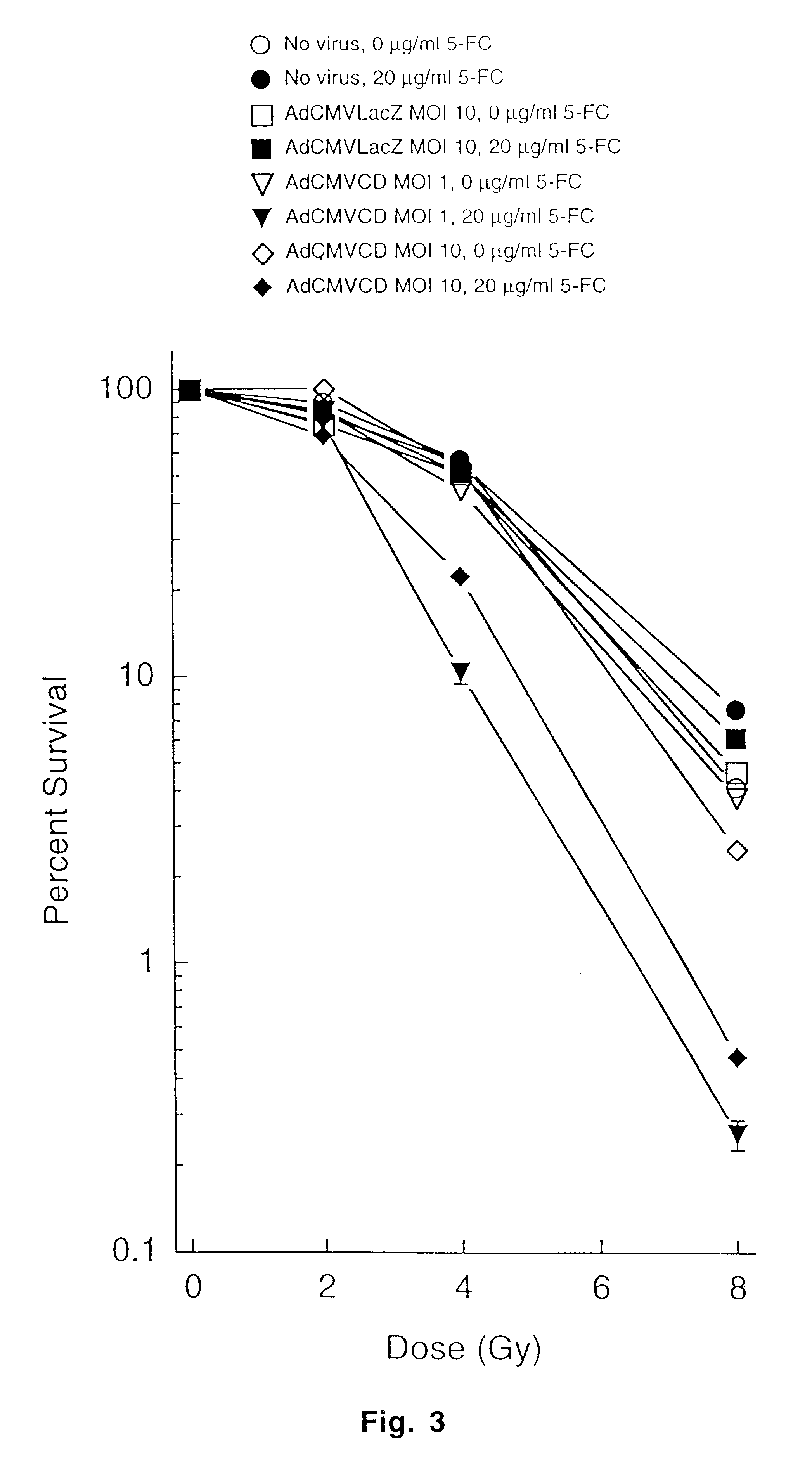
The instant invention has developed viral vectors encoding a mutant bacterial cytosine deaminase (bCD) gene, which have a higher affinity for cytosine than wild type bCD (bCDwt). The purpose of the present invention was to evaluate cytotoxicity in vitro and therapeutic efficacy in vivo of these vectors in combination with the prodrug 5-FC and ionizing radiation against human glioma. The present study demonstrates that infection with the viral vector expressing the mutant cytosine deaminase gene resulted in increased 5-FC-mediated cell killing, compared with vectors expressing the wild-type gene. Furthermore, a significant increase in cytotoxicity following infection with viral vector expressing the mutant cytosine deaminase gene and radiation treatment of glioma cells in vitro was demonstrated as compared to infection with viral vector expressing the wild-type gene. Animal studies showed significant inhibition of subcutaneous or intracranial tumor growth of D54MG glioma xenografts by the combination of AdbCD-D314A / 5-FC with ionizing radiation as compared with either agent alone, and with AdbCDwt / 5-FC plus radiation. These data indicate that combined treatment with this mutant enzyme / prodrug therapy and radiotherapy provides a promising approach for cancer therapy.
Owner:BUCHSBAUM DONALD J +3
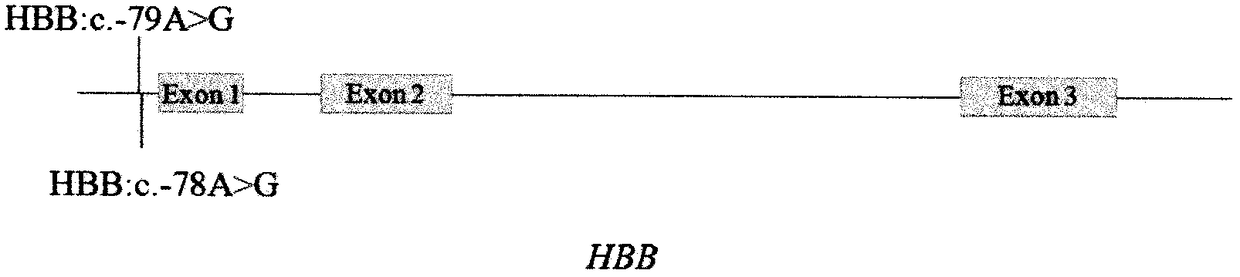
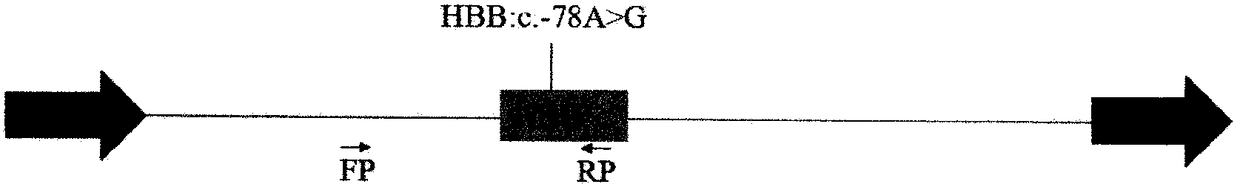
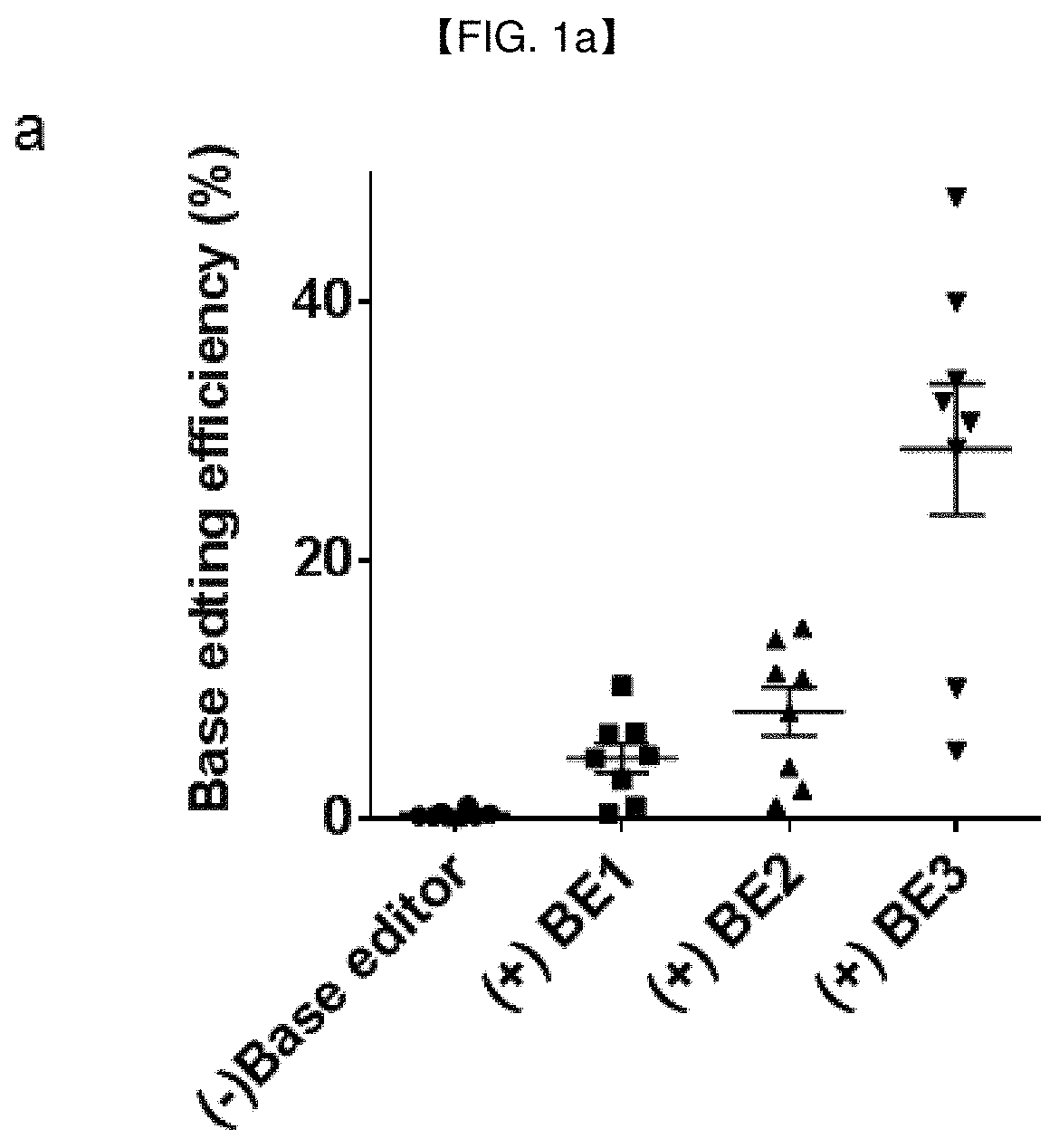
Basic group editing system and method for specifically repairing HBB gene mutation, kit and application of system and method and kit in human genital system
The invention provides a basic group editing method for specifically repairing HBB gene mutation in a human genital system. The method comprises the steps of delivering a basic group editing system used for specifically repairing HBB gene mutation so that the basic group editing system is close to relevant sequences of HBB mutant genes, and obtaining repaired HBB genes, wherein the basic group editing system comprises a basic group editing enzyme and gRNA, the basic group editing enzyme is fusion protein, and the fusion protein includes effect protein structural domains, cytidine deaminase structural domains and uracil DNA glycosylase inhibitor structural domains of a CRISPR / Cas system. The gene editing system is guided into a human germ cell, a human fertilized ovum or a human embryo, A>Gpathogenic mutation can be precisely repaired, and thus beta-mediterranean anemia is cured. The basic group editing method has a wide application prospect in the field of genetic therapy.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for identifying DNA base editing by means of cytosine deaminase
PendingUS20200131536A1Accurate and efficient validationMicrobiological testing/measurementStable introduction of DNACytosine deaminaseBase J
Provided are: a composition for DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), comprising (1) a cytosine deaminase and an inactivated target-specific endonuclease, (2) a guide RNA, and (3) a uracil-specific excision reagent (USER); a method for producing DNA double-strand breaks by means of a cytosine deaminase using the composition; a method for analyzing a DNA nucleic acid sequence to which base editing has been introduced by means of a cytosine deaminase; and a method for identifying (or measuring or detecting) base editing, base editing efficiency at an on-target site, an off-target site, and / or target specificity by means of a cytosine deaminase.
Owner:TOOLGEN INC +2
Kit and primer pair group for detecting expression of cytosine deaminase and molecular genes related to cytosine deaminase in free DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) in peripheral blood
ActiveCN105177141AIncreased sensitivityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCytosine deaminaseTreatment effect
The invention discloses a kit and a primer pair group for detecting expression of cytosine deaminase (Apobec3B / C, Apobec3F / G and AID) and molecular (UNG) genes related to cytosine deaminase in free DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) in peripheral blood. The primer pair group is shown in SEQ ID No:1-SEQ ID No:8 in a sequence table. The kit containing the primer pair group evaluates the risk of cancer incidence and the treatment effects by detecting methylation modification of Apobec3B / C, Apobec3F / G, AID and UNG gene promoters. A detection method has the characteristics of high sensitivity, specificity, directness, real-time property and stability.
Owner:欧浦德生物科技(北京)有限公司
Molecular chemotherapy enhancement of radiotherapy
The present invention provides a new approach for cancer treatment by utilizing gene therapy combined with radiation therapy to enhance cytotoxicity in malignant cells. Specifically, the present invention demonstrates that molecular chemotherapy with the cytosine deaminase gene and 5-fluorocytosine is an effective radiosensitizing strategy which may lead to substantial improvement in tumor control, with less normal tissue toxicity than conventional systemic administration of 5-fluorouracil, that would translate into improved cure rates and better survival. Also provided is a noninvasive method for continuous in vivo monitoring of 5-fluorouracil production via magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
Owner:CDEPT
Cell therapeutic agent for cancer treatment and combination therapy with same
PendingCN107454844AGood tumor suppressor effectMaximize the effect of cancer treatmentOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderCytosine deaminaseProliferative capacity
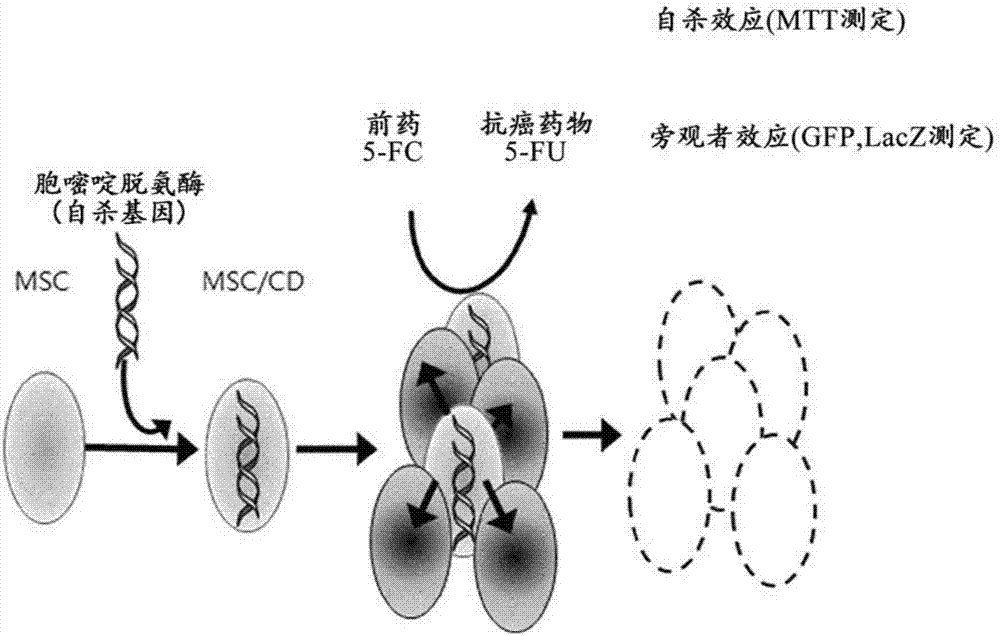
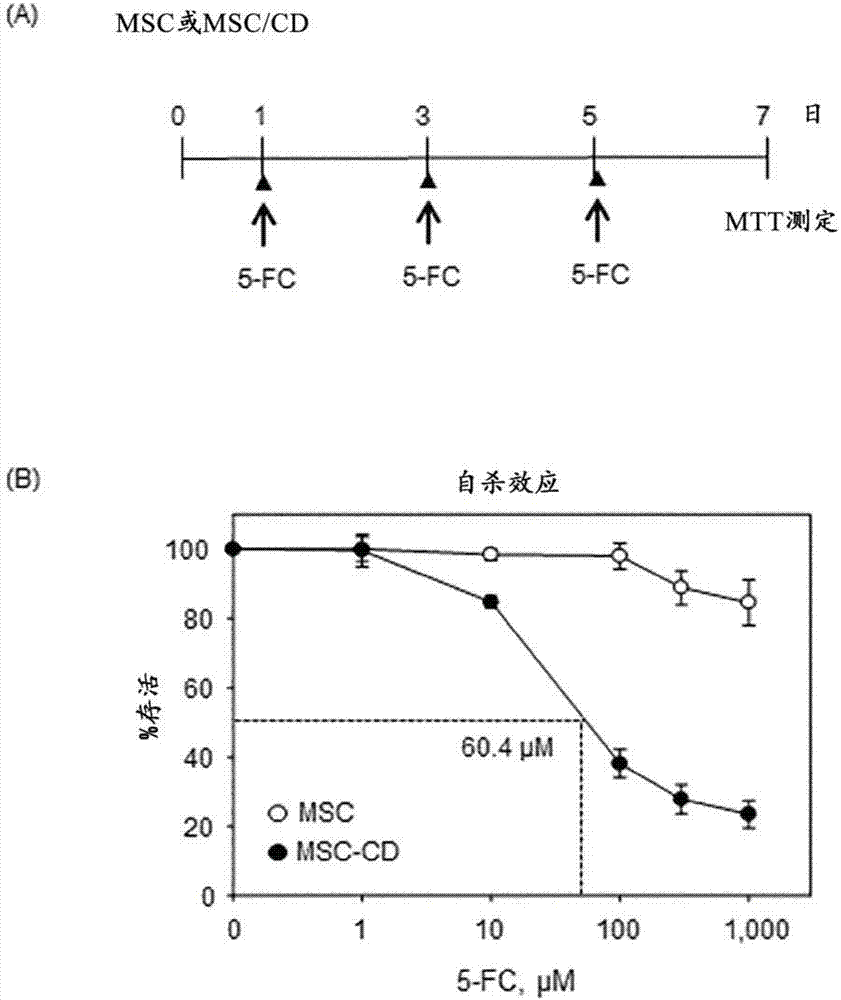
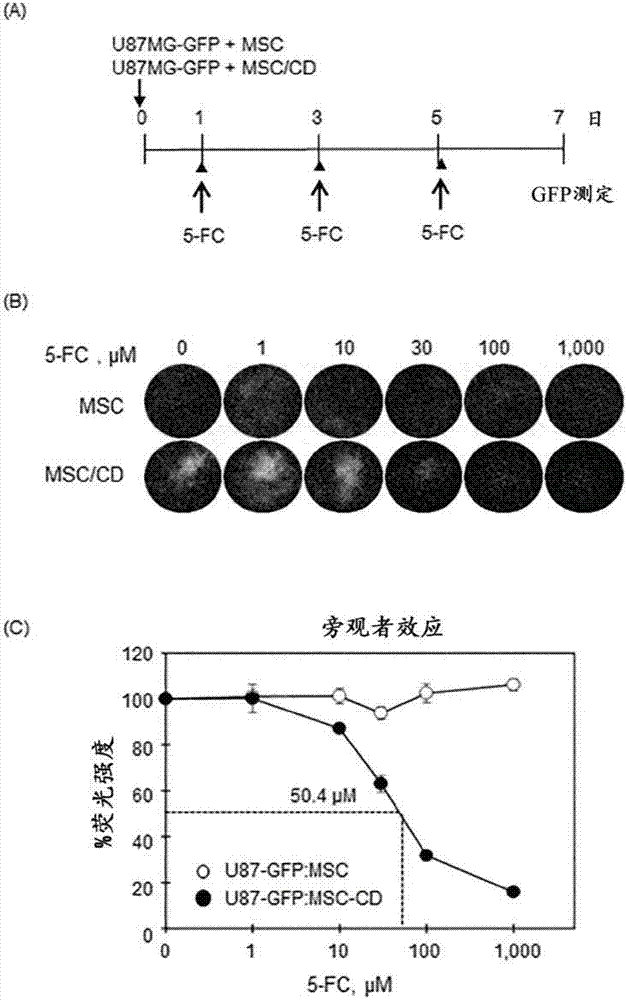
The present invention relates to a method for preparing cells for cancer treatment and a kit for cancer treatment comprising cells prepared by the method. The preparation method of the present invention can provide F cells, which, in spite of having no difference in the proliferative capacity compared with mesenchymal stem cells expressing cytosine deaminase, which are harvested and used immediately after the culture, exhibit a very excellent tumor suppressive effect through the treatment together with 5-FC and induce a remarkable synergistic effect exceeding an effect from combinative treatment with an existing anticancer drug in cases of a combinative treatment with another anticancer drug. Therefore, the present invention can be utilized for a kit for cancer treatment comprising such F cells, and thus can be favorably used to maximize the effect of existing cancer treatments.
Owner:CELL & BRAIN CO LTD
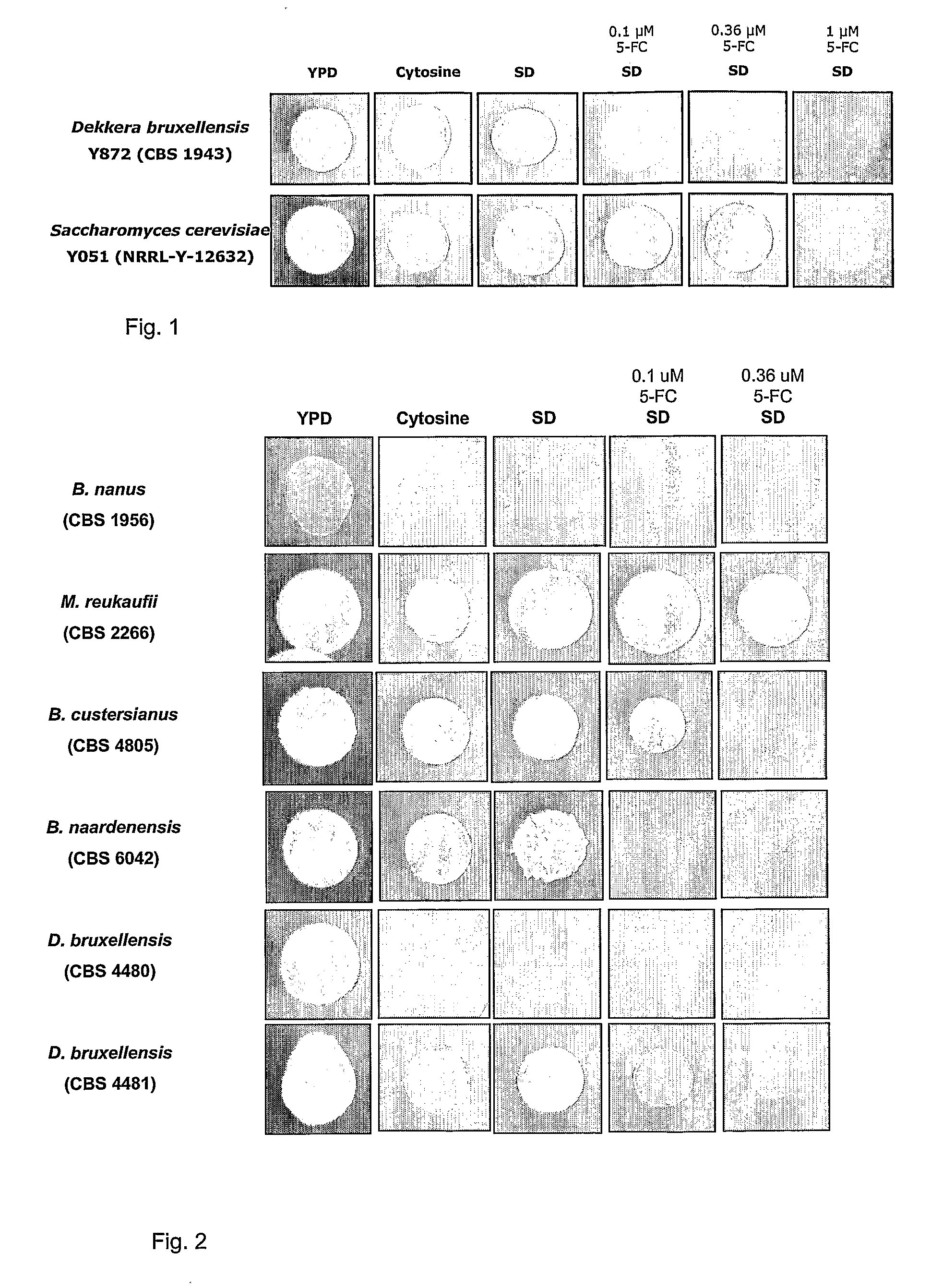
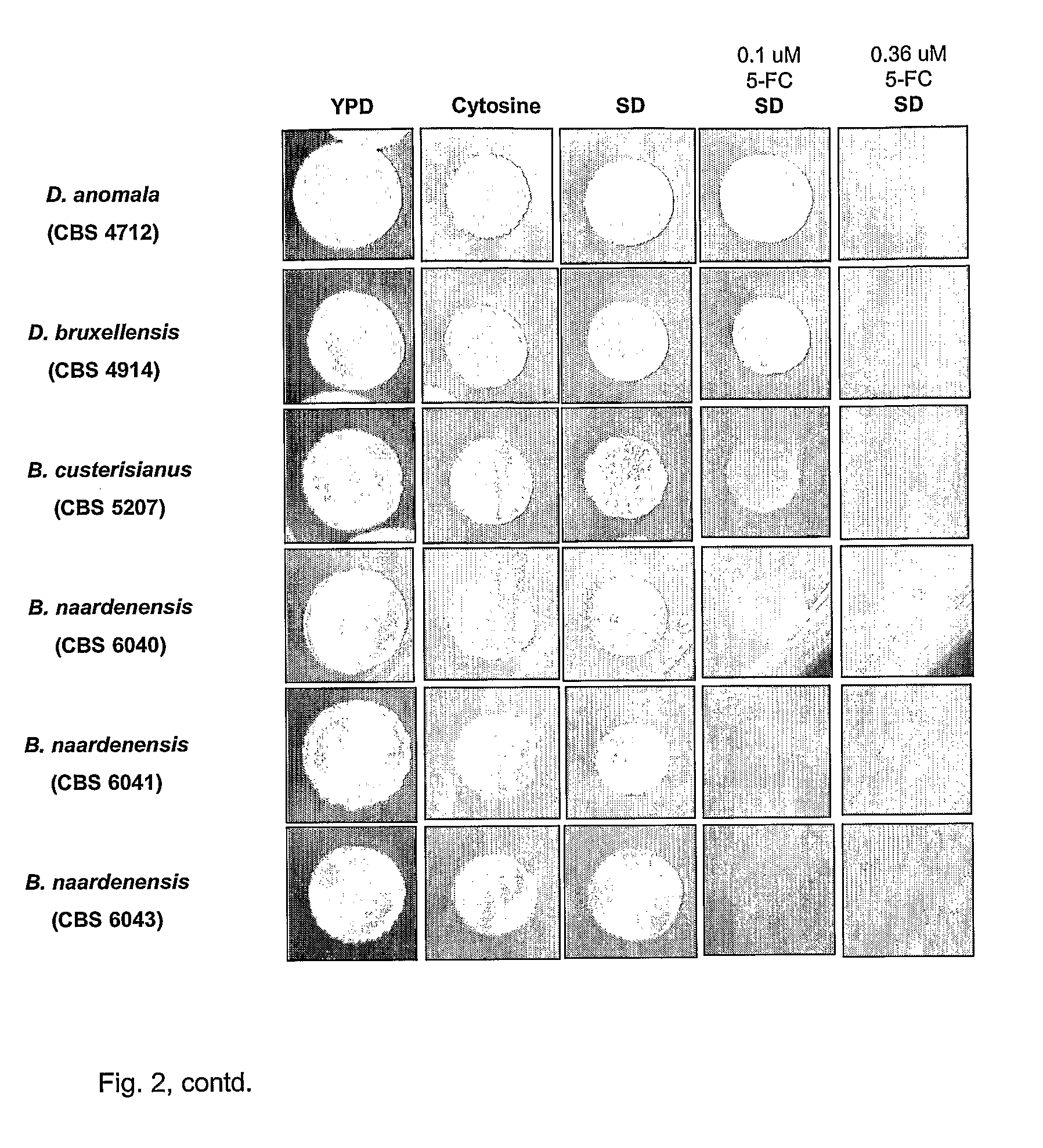
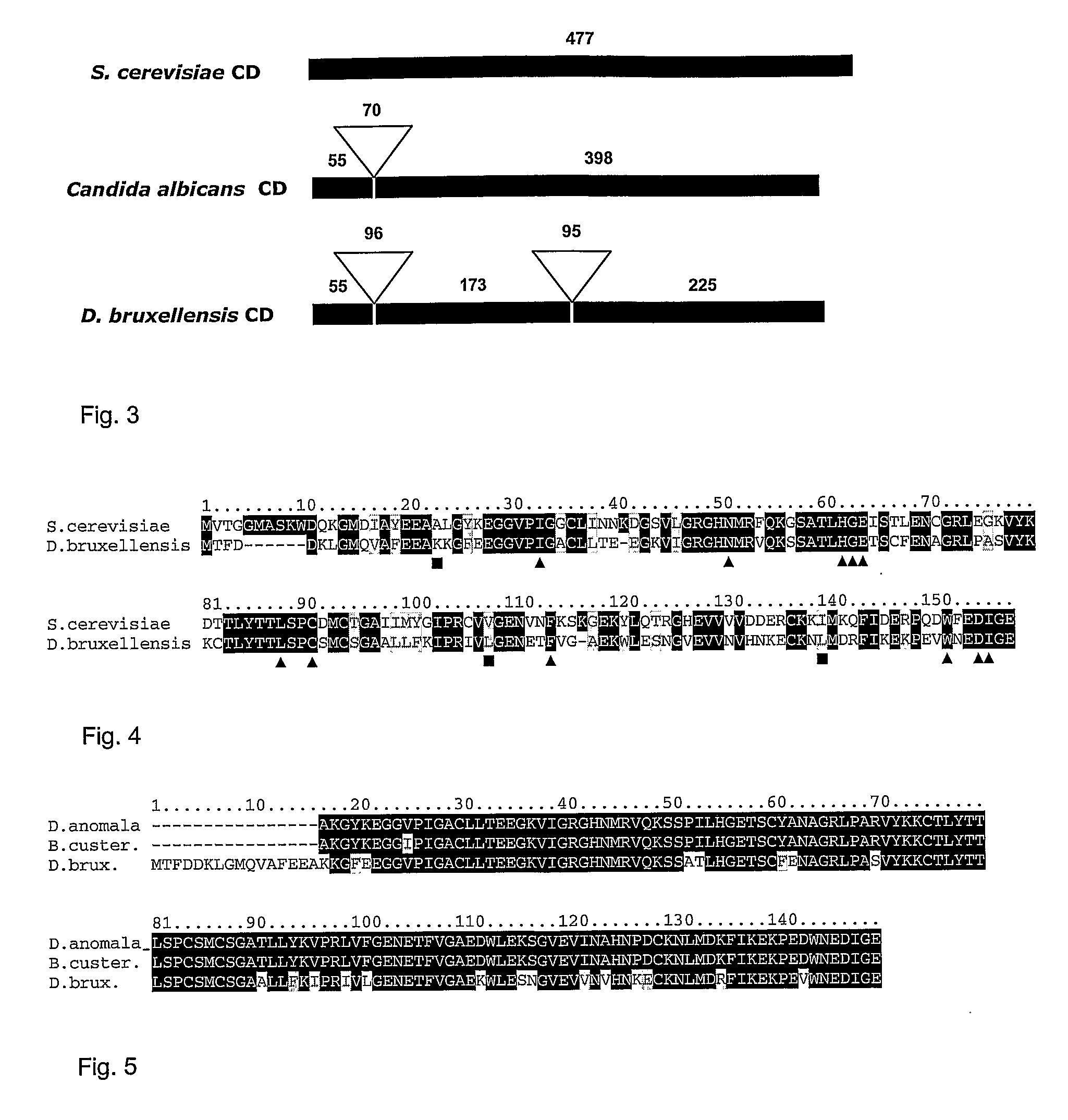
Dekkera/Brettanomyces Cytosine Deaminases And Their Use
The present invention relates to cytosine deaminase protein and cDNA from various species of the yeast genus Dekkera / Brettanomyces. Compared to yeast cytosine deaminase the novel cytosine deaminases are more efficient and have a higher stability. The invention also relates to the field of suicide gene therapy based on activation of a non-toxic prodrug, 5-fluorocytosine to a toxic drug 5-fluorouracil based on the enzymatic activity of novel cytosine deaminses. Finally the invention provides use of 5-fluorocytosine for controlling the growth of Dekkera / Brettanomyces yeast.
Owner:ZGENE
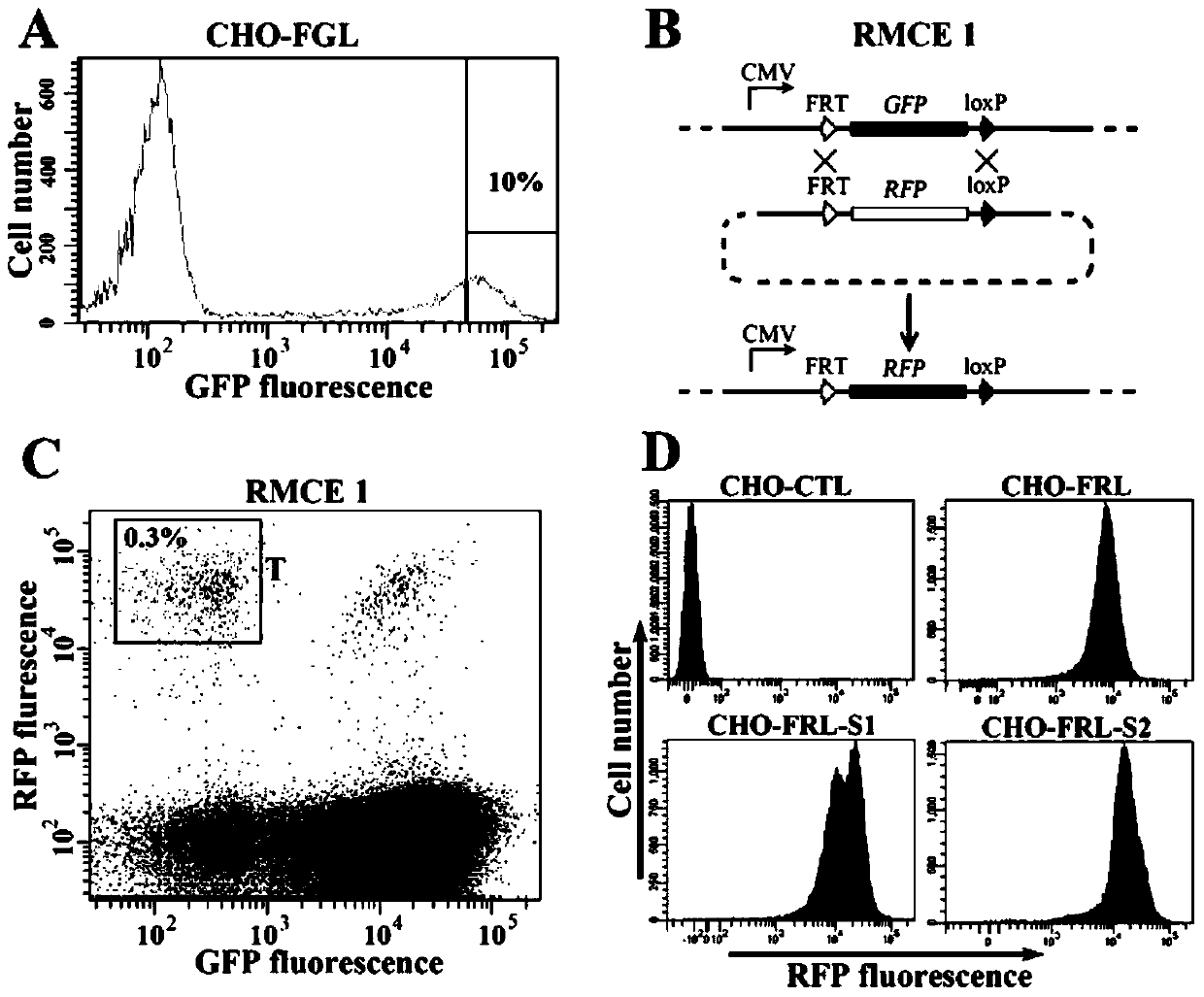
Cell line for antibody affinity maturation screening and method of use thereof
ActiveCN104531623BVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsCytosine deaminaseActivation-induced (cytidine) deaminase
The invention relates to a cell strain for screening affinity maturation of an antibody and a use method thereof. The cell strain is stable in expression of a target antibody by virtue of a RMCE technology. Combined with a somatic hypermutation technology of activation-induced cytidine deaminase, the cell strain for screening affinity maturation of the antibody is relatively high in efficiency and the affinity of the antibody can be improved to a great extent within a relatively short time and screening turns.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
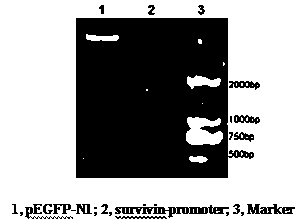
Construction of recombinant adenovirus vector for regulating and controlling cytosine deaminase (CD) gene by Survivin promoter and application thereof
ActiveCN103484462ASelective killingGenetic material ingredientsFermentationCytosine deaminaseCytosine
The invention provides a recombinant adenovirus. The recombinant adenovirus comprises a cytosine deaminase gene (CD gene), wherein the CD gene is controlled by the survivin promoter designed by the invention. More particularly, the invention further discloses a preparation method of the recombinant adenovirus, and a drug in which the recombinant adenovirus is applied to treatment of a cancer. The recombinant adenovirus provided by the invention has excellent specificity on tumour cells; the survival of normal cells is not affected while the suicide program of the tumour cells is started.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
Gene of encoded cytosine deaminease for preventing and controlling crop disease
The invention discloses a phathopoiesis related gene (cytosine deaminase gene) from Xanthomonas causing cabbage black rot. The cytosine deaminase gene provided by the invention contains one of the following nucleotide sequence: 1) DNA sequence shown in SEQ ID No.1, 2) DNA sequence containing over 80% homology with DNA sequence shown in SEQ ID No. 1. The invention also involves the application of the genes in plant disease prevention and cure, as well as the application for drug target in plant disease prevention and cure.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Method for regulating RNA splicing by inducing splice site base mutation or polypyrimidine region base substitution
PendingCN109295053APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifOrganic active ingredientsCytosine deaminaseIntein
A method of regulating RNA splicing by inducing splice site base mutation or polypyrimidine region base substitution is disclosed, the method comprises expressing targeted cytidine deaminase in cellsto induce AG to AA mutation of 3' splicing site of intron of interested of gene of interested in the cells, or GT to AT mutation of 5' splicing site of the intron of interested of the gene of interested in the cells, or respective mutation of multiple C in a polypyrimidine region of the intron of interested of the gene of interested to T. The method can specifically block the exon recognition process, regulates the alternative splicing process of endogenous mRNA, induces exon skipping, activates alternative splicing sites, induces mutual exclusive exon conversion, induces intron retention andenhances exon retention.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
5-fluorouracil-resistant bacteria and method for production thereof
ActiveUS20090280091A1Good for survivalImprove the immunityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideCytosine deaminaseResistant bacteria
The present invention provides a method for producing a cytosine deaminase (CD)-expressing, 5-fluorouracil (5-FU)-resistant microorganism which can grow in anaerobic tumor tissues, can express CD, and has a resistance to 5-FU at a concentration that is at least effective for antitumor activity. More specifically, the method is a method (A) comprising performing subculture or acclimation culture of a CD-expressing microorganism which can grow in anaerobic tumor tissues, in the presence of 5-fluorocytosine (5-FC), or a method (B) comprising (1) performing subculture or acclimation culture of a microorganism which can grow in anaerobic tumor tissues and does not express CD, in the presence of 5-FU to produce a 5-FU-resistant microorganism and (2) transforming the 5-FU-resistant microorganism by introducing a CD gene. The present invention also provides the CD-expressing, 5-FU-resistant microorganism and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the microorganism.
Owner:ANAEROPHARMA SCI
Formulations of 5-fluorocytosine and uses thereof
The disclosure provides an extended release formulation of 5- f luorocytosine. In another aspect, a method of treating a fungal disease is provided. The method comprises administering to a subject in need thereof a fungus-treating effective amount of a composition comprising 5-f luorocytosine. In yet another aspect, a method of treating a cancer is provided. The method comprises administering to a subject in need thereof a sufficient amount of an expression vector to induce expression of cytosine deaminase which is capable of converting 5-f luorocytosine to 5-f luorourcail in cells of the cancer and a cancer-treating effective amount of a composition comprising 5-f luorocytosine.
Owner:TOCAGEN
Construction method of disease animal model and fusion protein
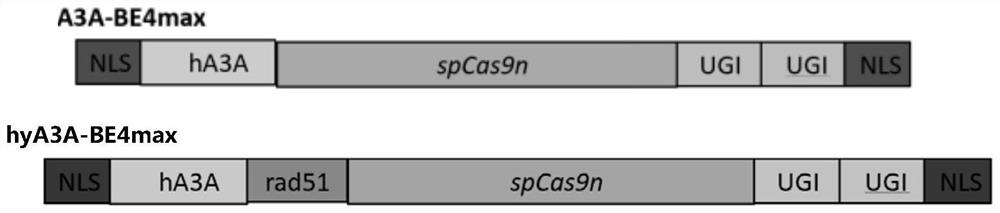
ActiveCN112979822AImprove editing efficiencyThe production is effectiveFusion with DNA-binding domainHydrolasesBiotechnologyRAD51
The invention discloses a construction method of a disease animal model and a fusion protein. The fusion protein comprises a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) binding structural domain of the Rad51, cytosine deaminase APOBEC3A and nuclease. The method comprises the following steps: introducing the fusion protein and sgRNA into animal cells, and carrying out gene editing on a target gene. The invention provides a novel platform for efficiently generating the disease animal model, and the manufacturing process of different animal models is greatly promoted.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV +1
Liver cancer suicide gene therapy medicine based on aminated silicon dioxide nanoparticle-CD/TK (cytosine deaminase-thymidine kinase) fused gene compound
InactiveCN103357024AEfficient killingGenetic material ingredientsDigestive systemTelomeraseCytosine deaminase
The invention provides a liver cancer suicide gene therapy medicine based on an aminated silicon dioxide nanoparticle-CD / TK (cytosine deaminase-thymidine kinase) fused gene compound. A preparation method for the liver cancer suicide gene therapy medicine comprises the following steps of: (1) amplifying CD genes and TK genes via PCR (polymerase chain reaction), and constructing a fused gene, cloning the fused gene into a conventional plasmid vector, promoting the expression of the fused gene by a human-source telomerase promoter in the vector, and enhancing the transcription of the fused gene by a CMV (cytomegalovirus) enhancer; (2) mixing the constructed plasmids with aminated silicon dioxide nanoparticles, so as to form a stable nano-DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) compound; and (3) taking the nano-DNA compound for therapy for liver cancer as a gene therapy medicine, wherein the medicine is capable of transfecting liver cancer cells in vivo or in vitro, and Cd / TK is capable of being highly expressed in the liver cancer cells, and capable of converting a pro-medicine 5-Fc to a toxic medicine 5-Fu, thus having obvious toxic and killing effects on the liver cancer cells.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CELLPRO BIOTECH
Novel single-base editing technology and application thereof
The invention provides a novel single-base editing technology and application thereof. Specifically, the invention provides a gene editing enzyme which is characterized in that the structure of the gene editing enzyme is shown as a formula I of Z1-L1-Z2-L2-Z3-Z4 (I), wherein Z1 is an amino acid sequence of cytosine deaminase APOBEC3A; Z2 is an amino acid sequence of spCas9 (n); and Z1 has a mutation A corresponding to the 128th R residue of the sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1; Z3 is a coding sequence of a uracil DNA glycosylase inhibitor (UGI); L1 and L2 are each independently an optional linker peptide sequence; Z4 is a none or nuclear localization signal element (NLS); And each '-' is independently a peptide bond. The invention also provides a gene single-base fixed-point editing method. The method provided by the invention is high in DNA editing precision, and can significantly reduce the RNA off-target effect.
Owner:HUIGENE THERAPEUTICS CO LTD
Method for mutating base C into base T in plant genome
PendingCN114317590AImprove replacement efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyCytosine
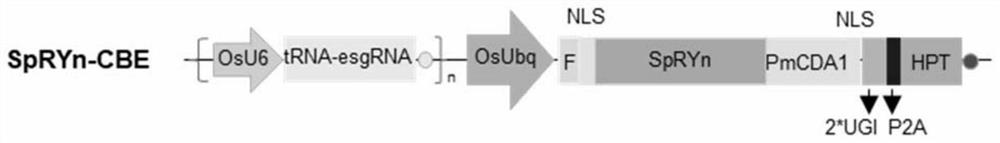
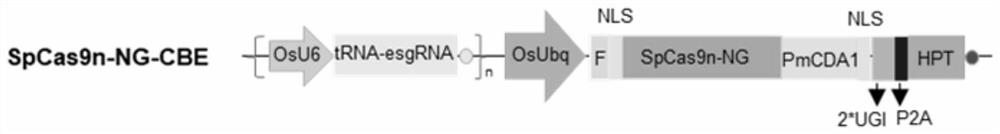
The invention discloses a method for mutating a basic group C into a basic group T in a plant genome. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: introducing SpRYn, cytosine deaminase, sgRNA and UGI into a plant body to realize mutation of C in a plant genome target sequence into T. Experiments prove that the method disclosed by the invention can be used for editing the base C in the target spot sequence of which the PAM sequence is NGN on the plant genome, so that the replacement from the base C to the base T is realized, and the base replacement efficiency is also improved while the range of editable C is expanded.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
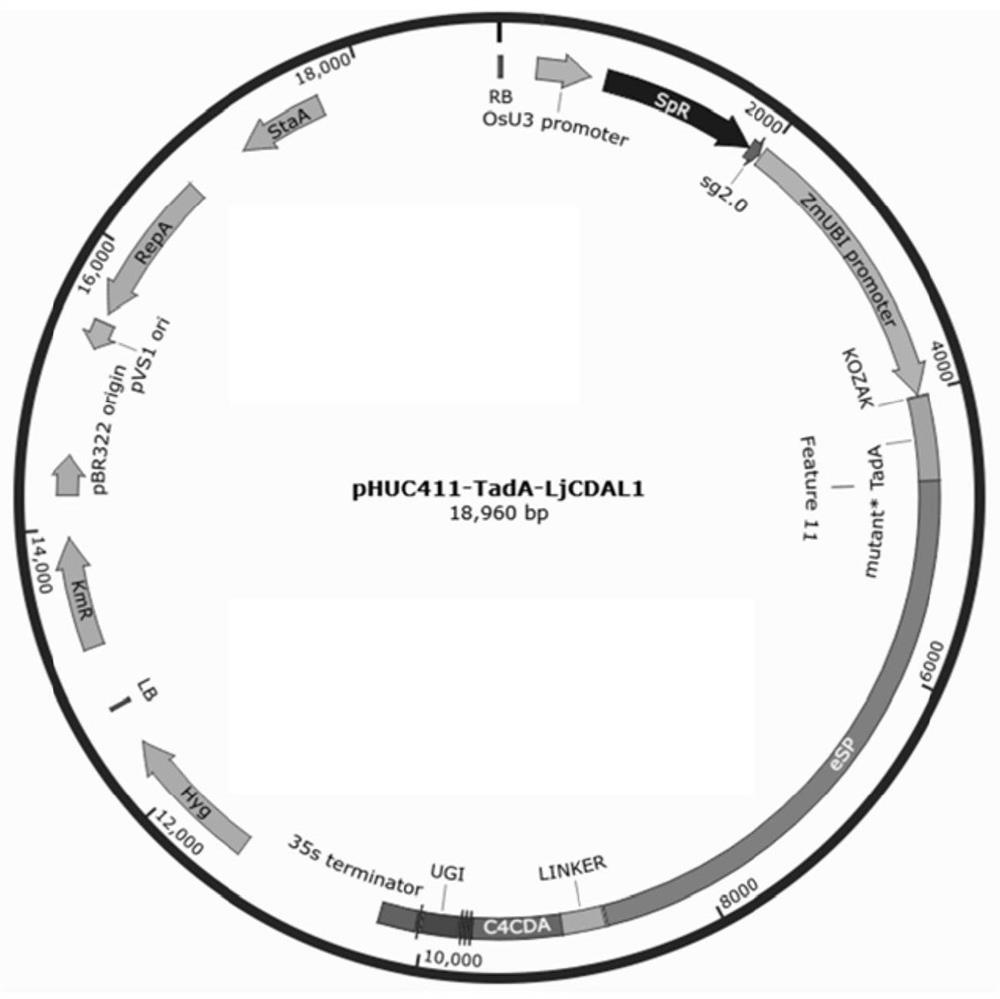
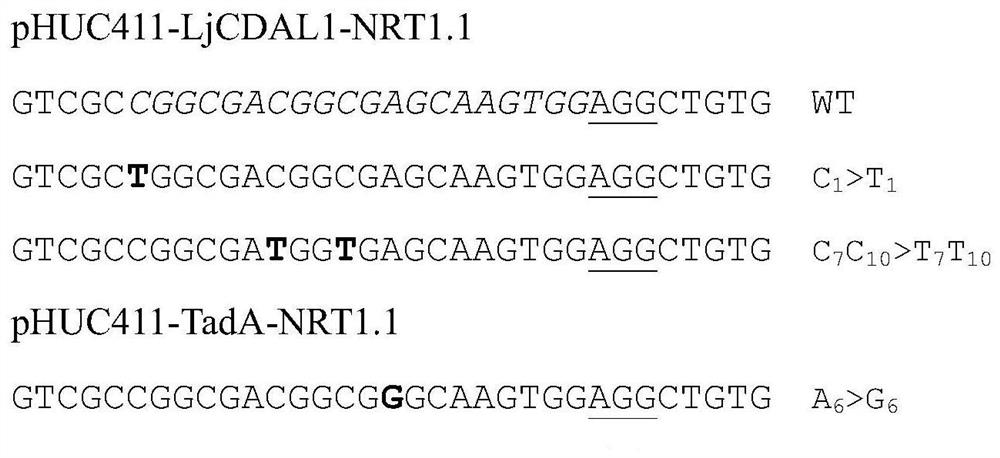
Co-transcription unit gene ABE-CBE system for bidirectional single base editing of rice and application thereof
The invention provides a co-transcription unit gene ABE-CBE system for the bidirectional single base editing of rice, a vector and application thereof. A co-transcription unit gene ABE-CBE comprises an adenine deaminase coding gene TadA and a cytosine deaminase coding gene CDA, and the coding sequences of co-transcription unit genes mutant TadA and LjCDAL1 are constructed in the same expression vector. An expression vector containing a cytosine base editor and an adenine base editor is fused, so that the nucleotide replacement of specific sites of a genome is caused. Experiments prove that a designed fusion editing tool is used for constructing a plant expression vector, and then a rice targeting editing vector is constructed, so that after the gene is introduced into rice cells, the efficiency of the mutual replacement of A:T to G:C on DNA of a rice specific gene locus is improved, the simultaneous replacement of C to T and A to G can be realized at the specific locus of the gene, theapplication range is expanded, and meanwhile, off-target generation is reduced. Therefore, a fused A-C base editing system is enabled to have a wider application prospect.
Owner:RICE RES ISTITUTE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
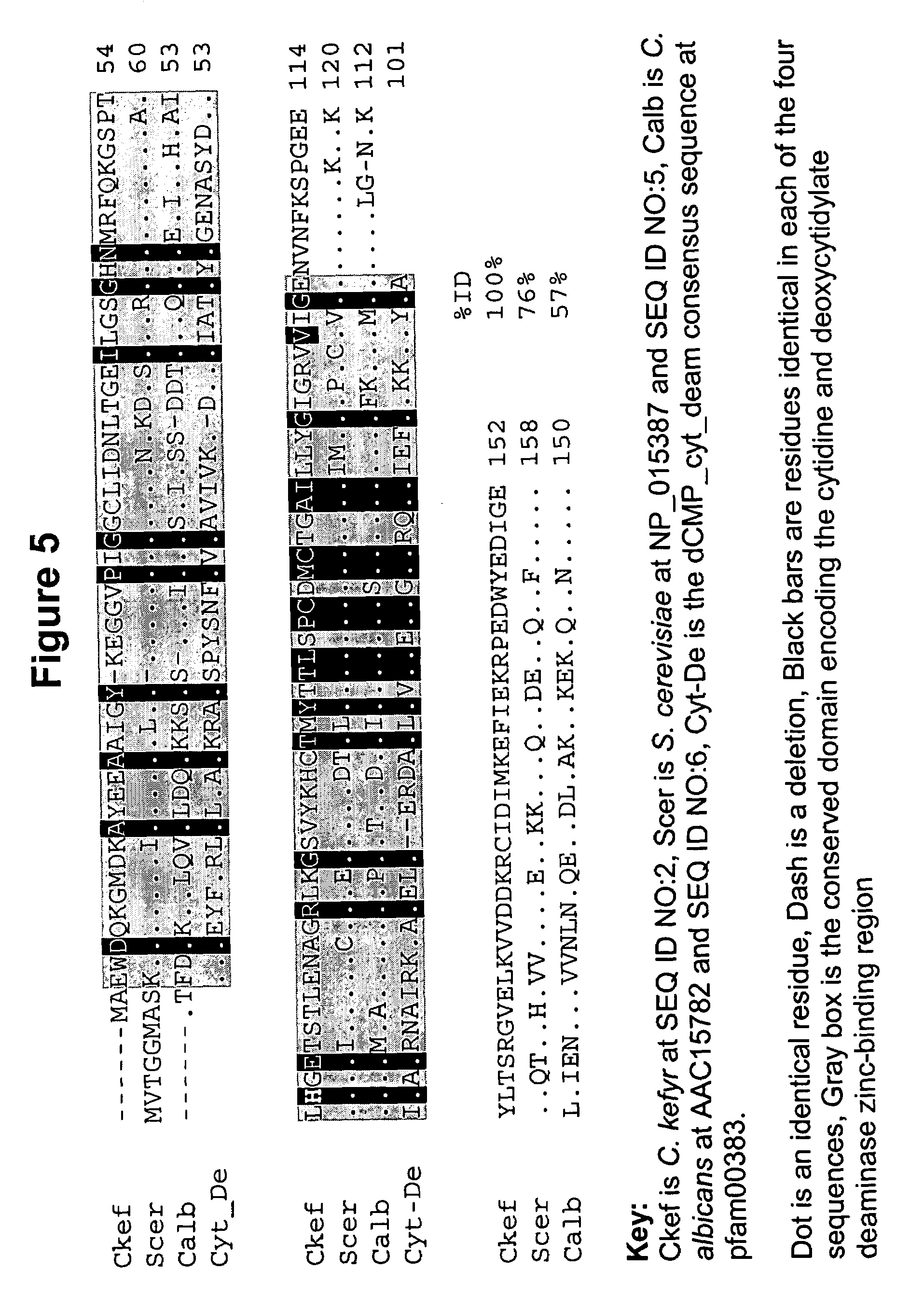
Candida kefyr cytosine deaminase
InactiveUS7141404B2Reduce the amount requiredImprove abilitiesBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliCytosine deaminase
Owner:ONYX PHARMA INC
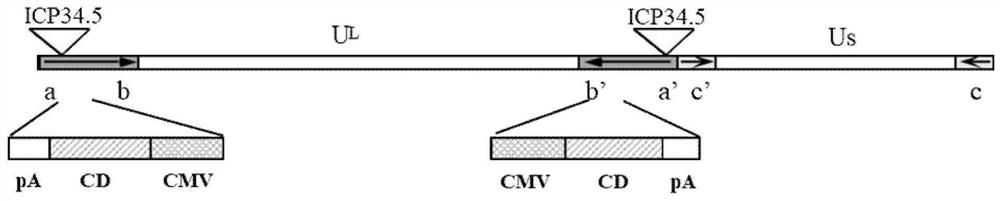
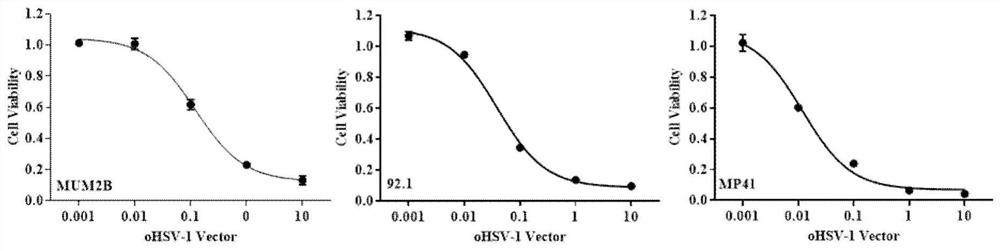
Application of oncolytic virus in treatment on uveal melanoma, marker of treatment effect and detection reagent thereof
ActiveCN111850126AEnhanced cell killingIncrease lethalityOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCytosine deaminaseCD44
The invention discloses a preparation for treating, preventing and / or slowing down uveal melanoma, the preparation comprises oncolytic herpes simplex virus type 1 capable of expressing cytosine deaminase genes and 5-fluorocytosine, and the oncolytic herpes simplex virus type 1 and the 5-fluorocytosine are combined to significantly reduce the volume of the uveal melanoma and improve the lifetime ofa subject. The invention further discloses a marker for evaluating the treatment effect of uveal melanoma through the preparation, and the marker is selected from markers capable of representing theepithelial-mesenchymal transition degree and mainly comprises IL-6, DPD, TWIST1, ZEB1, CD44 and CDH1.
Owner:BEIJING NEUROSURGICAL INST
Plant-derived cytosine deaminases and application thereof to base editing system
The invention discloses plant-derived cytosine deaminases and a method and application thereof to a base editing system. Experiments prove that the plant-derived cytosine deaminase can successfully perform base editing on receptor genes, and has important value for application of gene editing to plants.
Owner:CROPEDIT BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
TAA/ecdCD40L oncolytic virus
InactiveUS10130667B1Maximize tumor cell killMaximize the tumor cell killOrganic active ingredientsHydrolasesCytosine deaminaseL plastin
The present invention relates to a vaccine comprising the insertion of three genes, the TAA / ecdCD40L EA1 and CDA, driven by promoters L-plastin / cytosinedeaminase and CMV as a three gene, three transcription unit oncolytic virus as a conditionally replication competent adenoviral vector which replicates only in tumor cells. In these transcription units, the E1A gene of the adenoviral vector as well as the cytosine deaminase gene are under the control of the L-plastin promoter, while the TAA / ecdCD40L transcription unit is under control of a the CMV promoter.
Owner:MICROVAX
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com