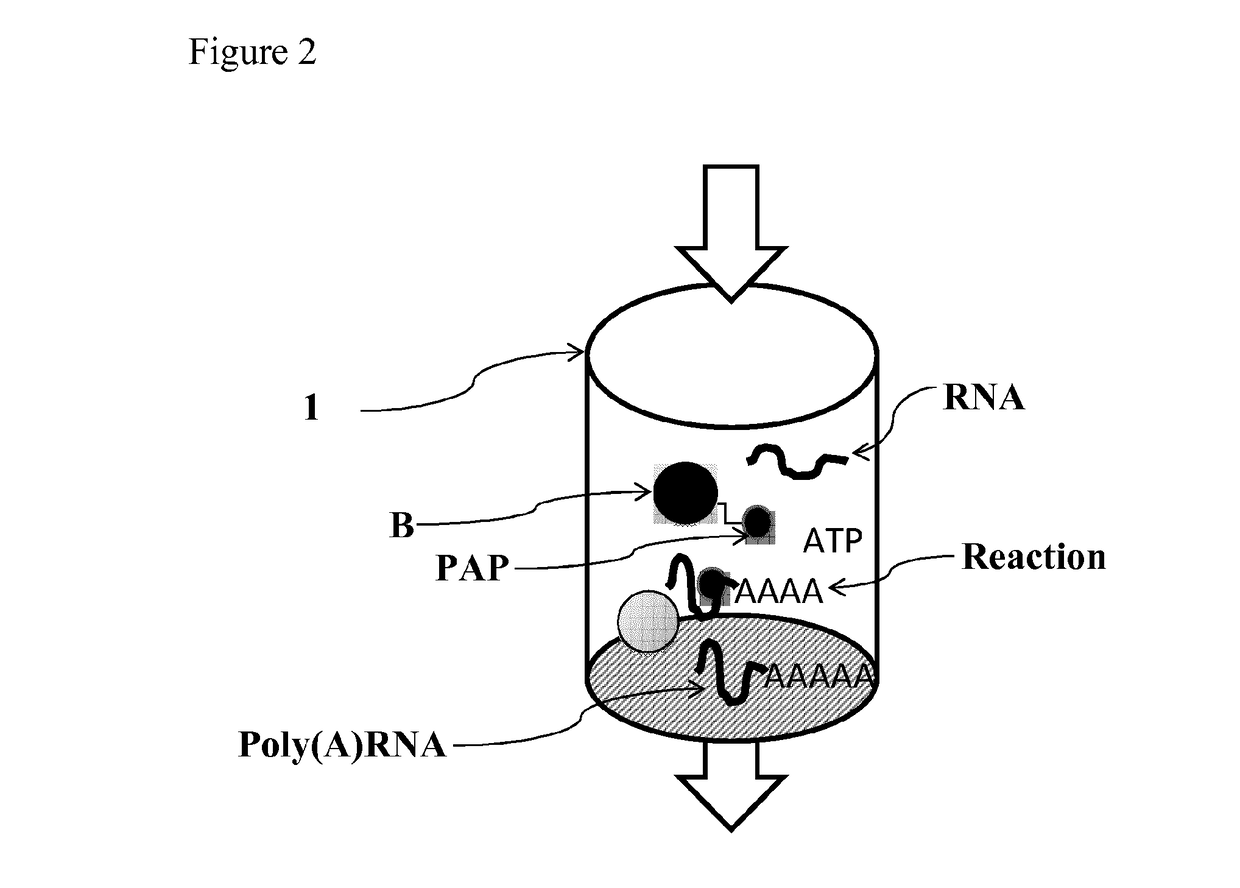
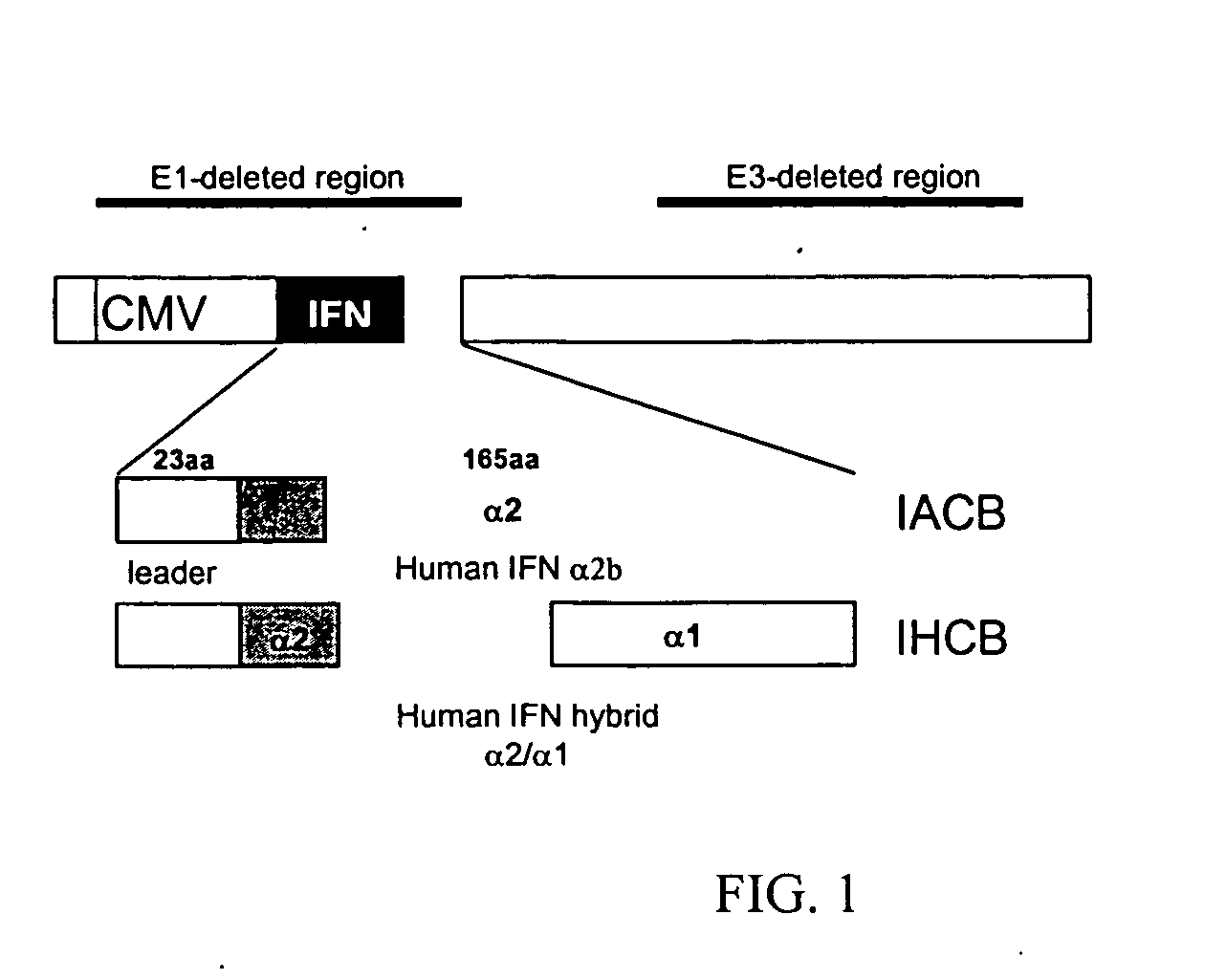
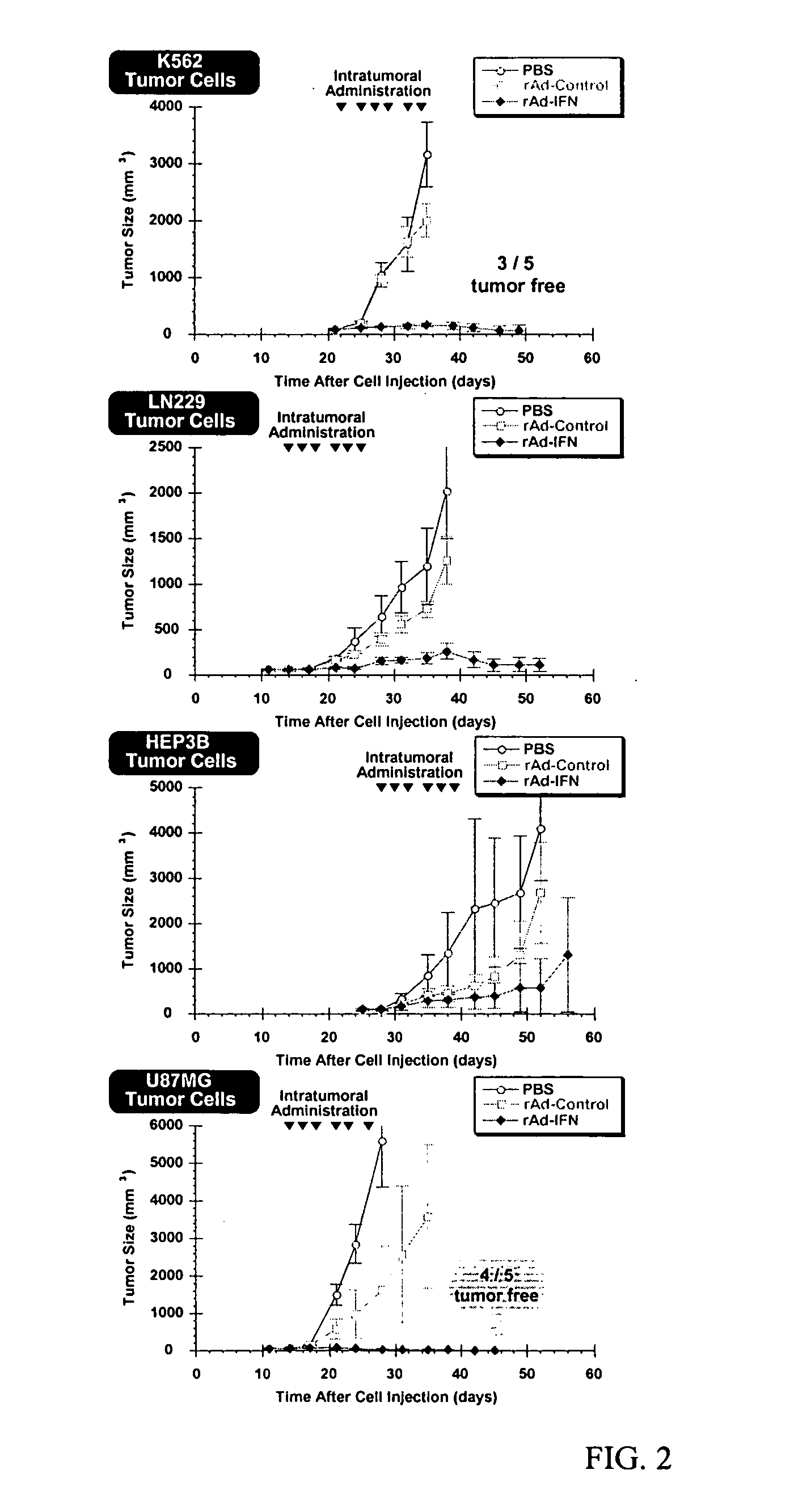
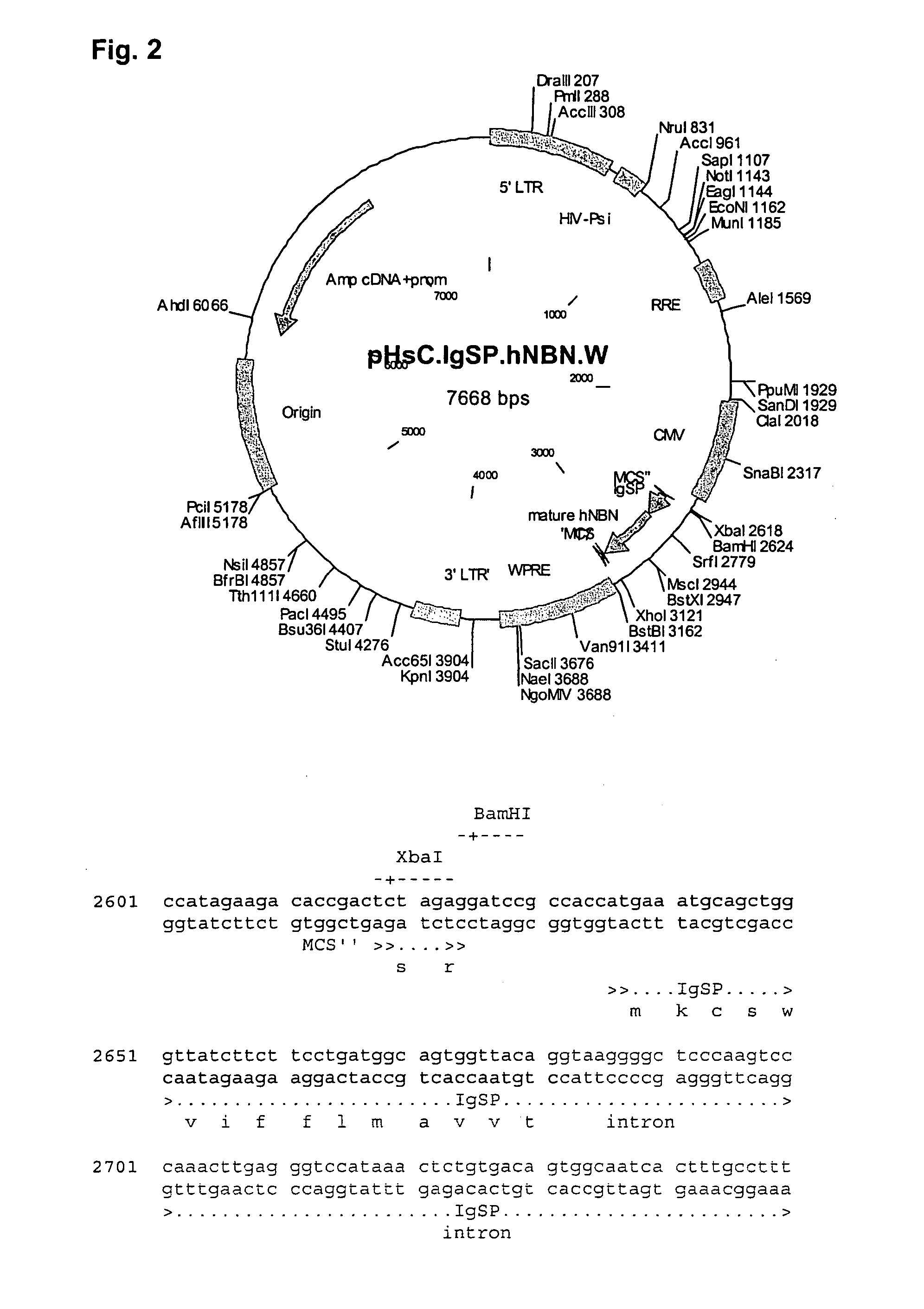
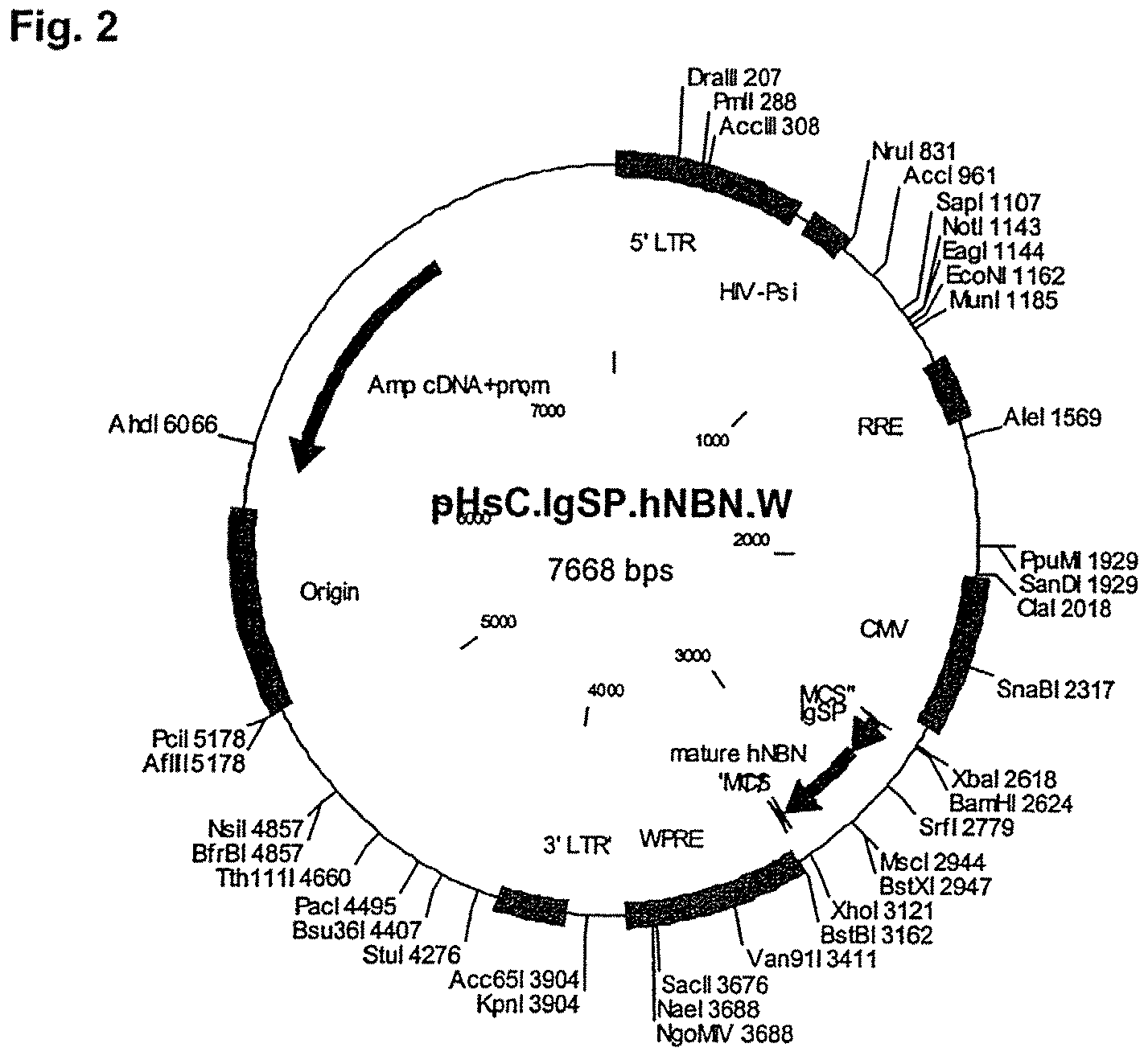
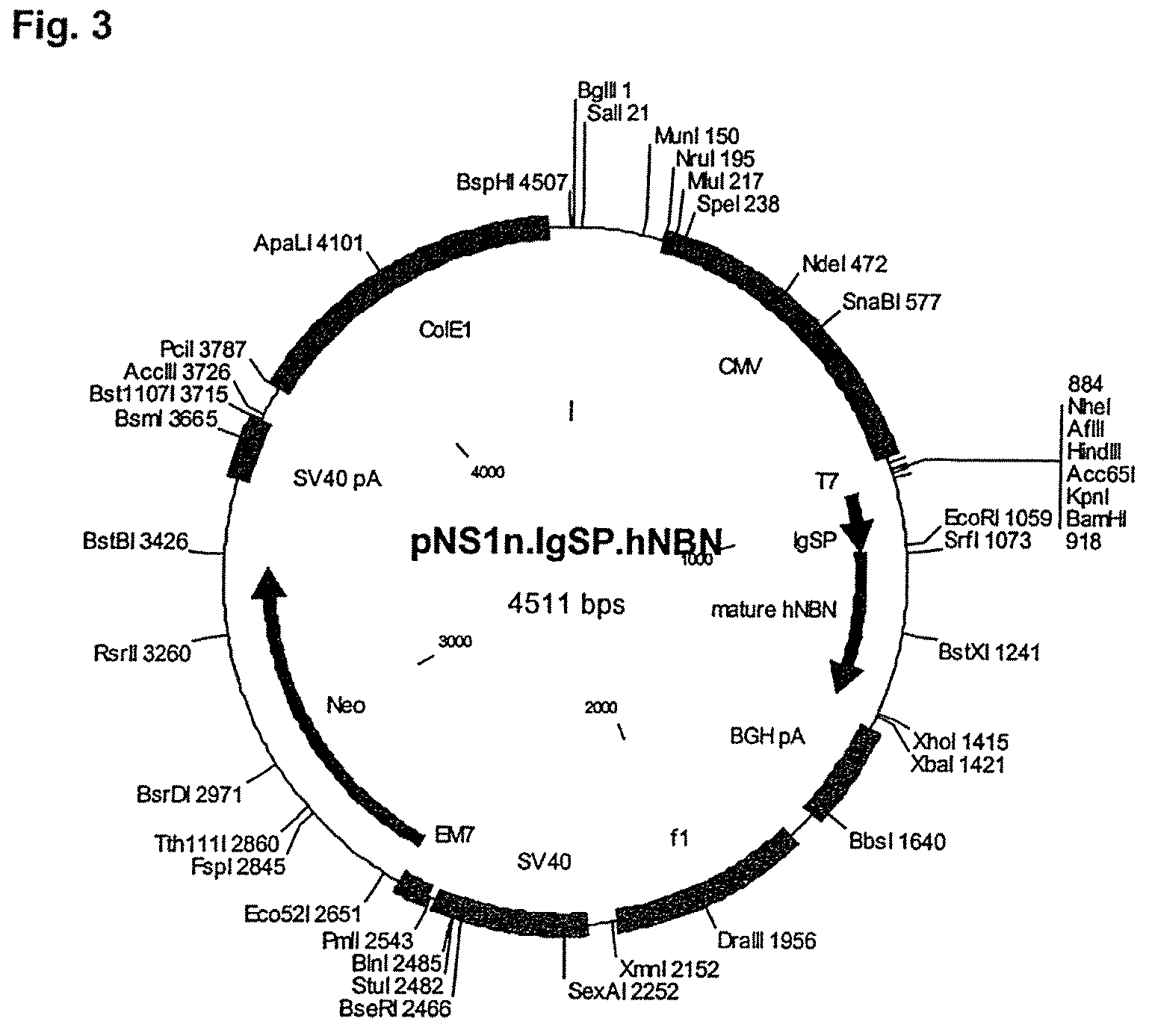
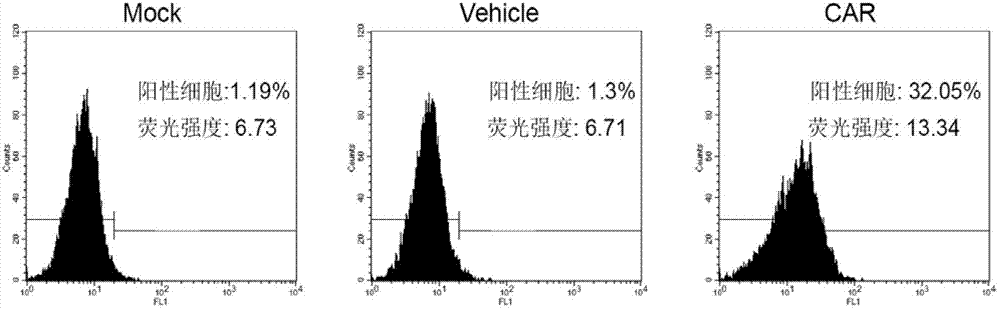
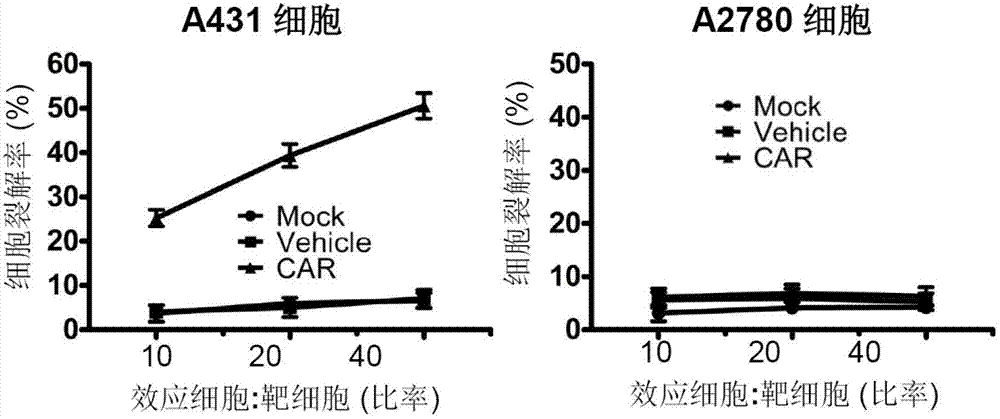
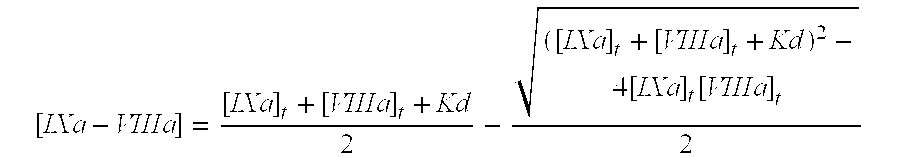Patents
Literature
420 results about "Genetic therapy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gene Therapy. Gene therapy is an experimental technique that aims to treat genetic diseases by altering a disease-causing gene or introducing a healthy copy of a mutated gene to the body. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved the first gene therapy for an inherited disease — a genetic form of blindness — in December 2017.
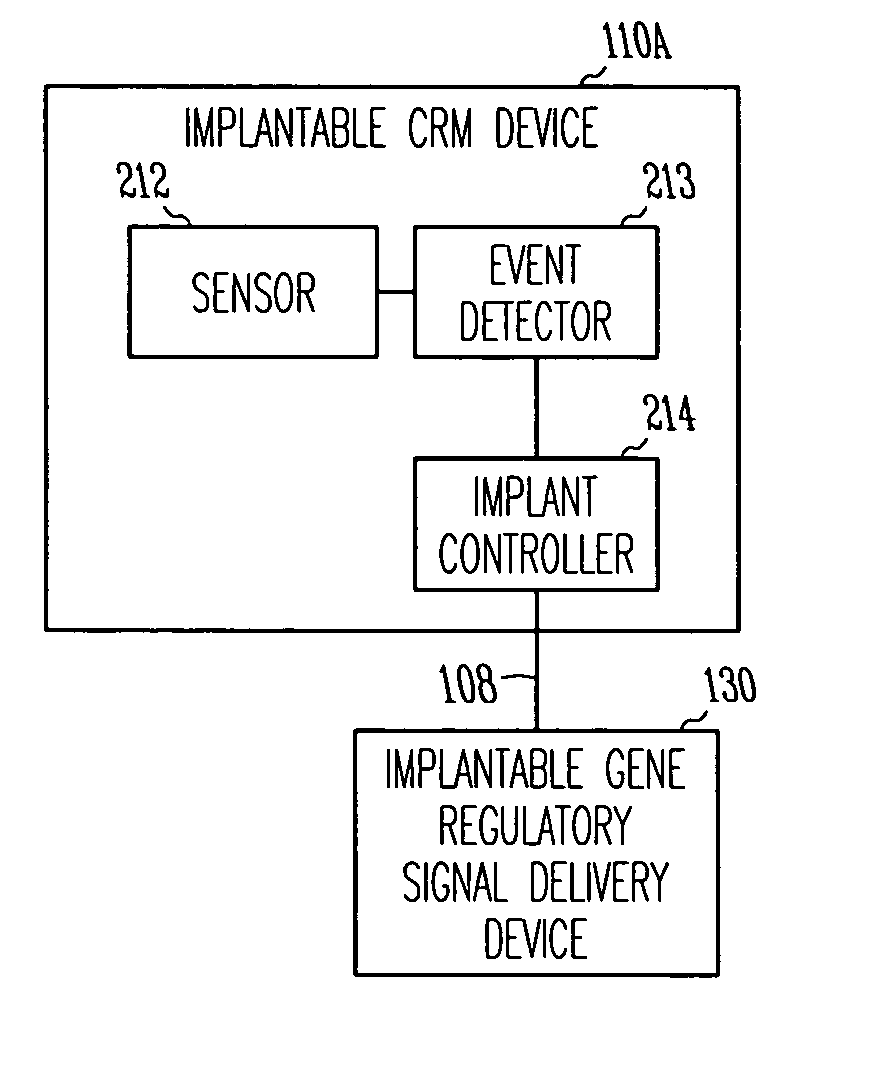
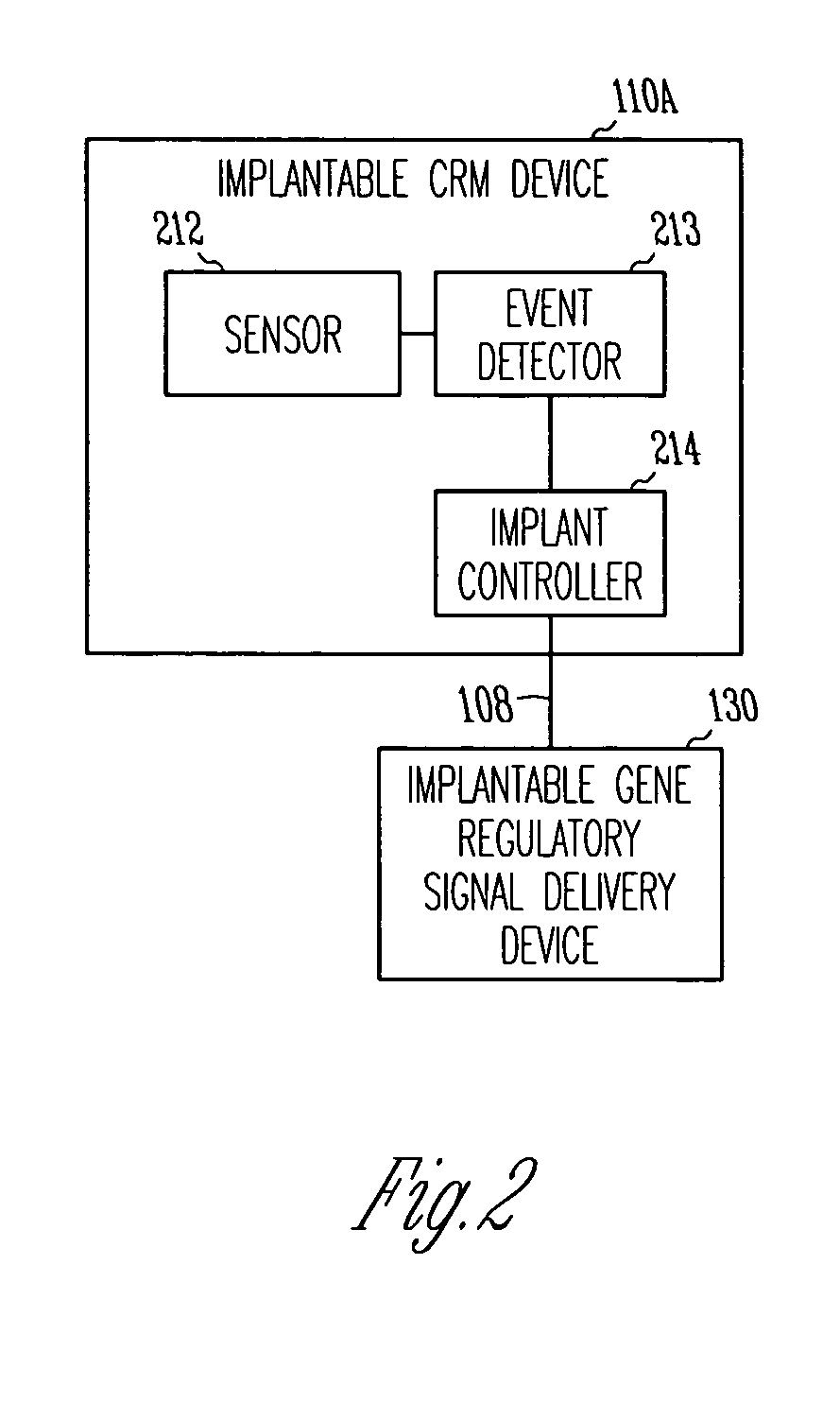
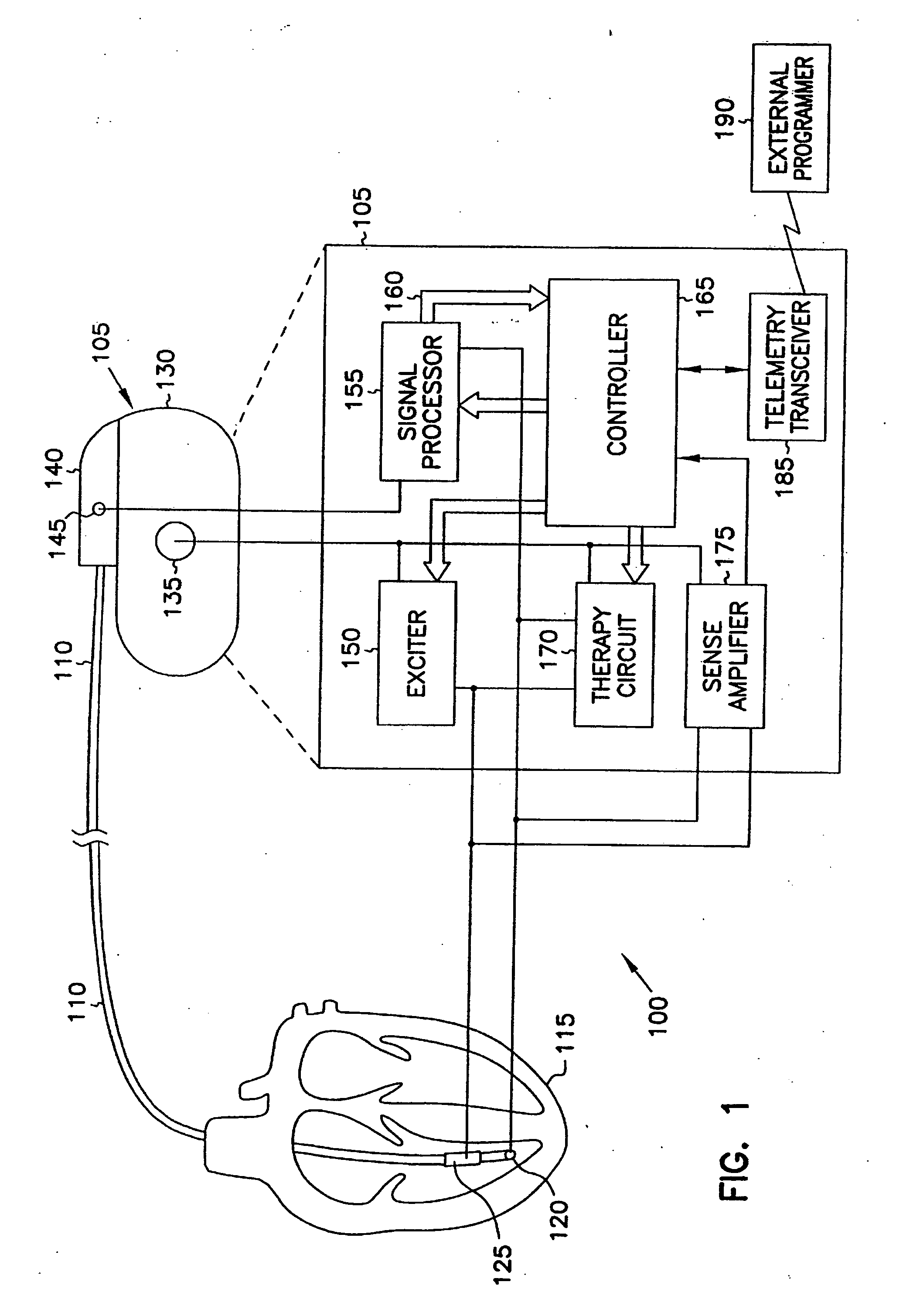
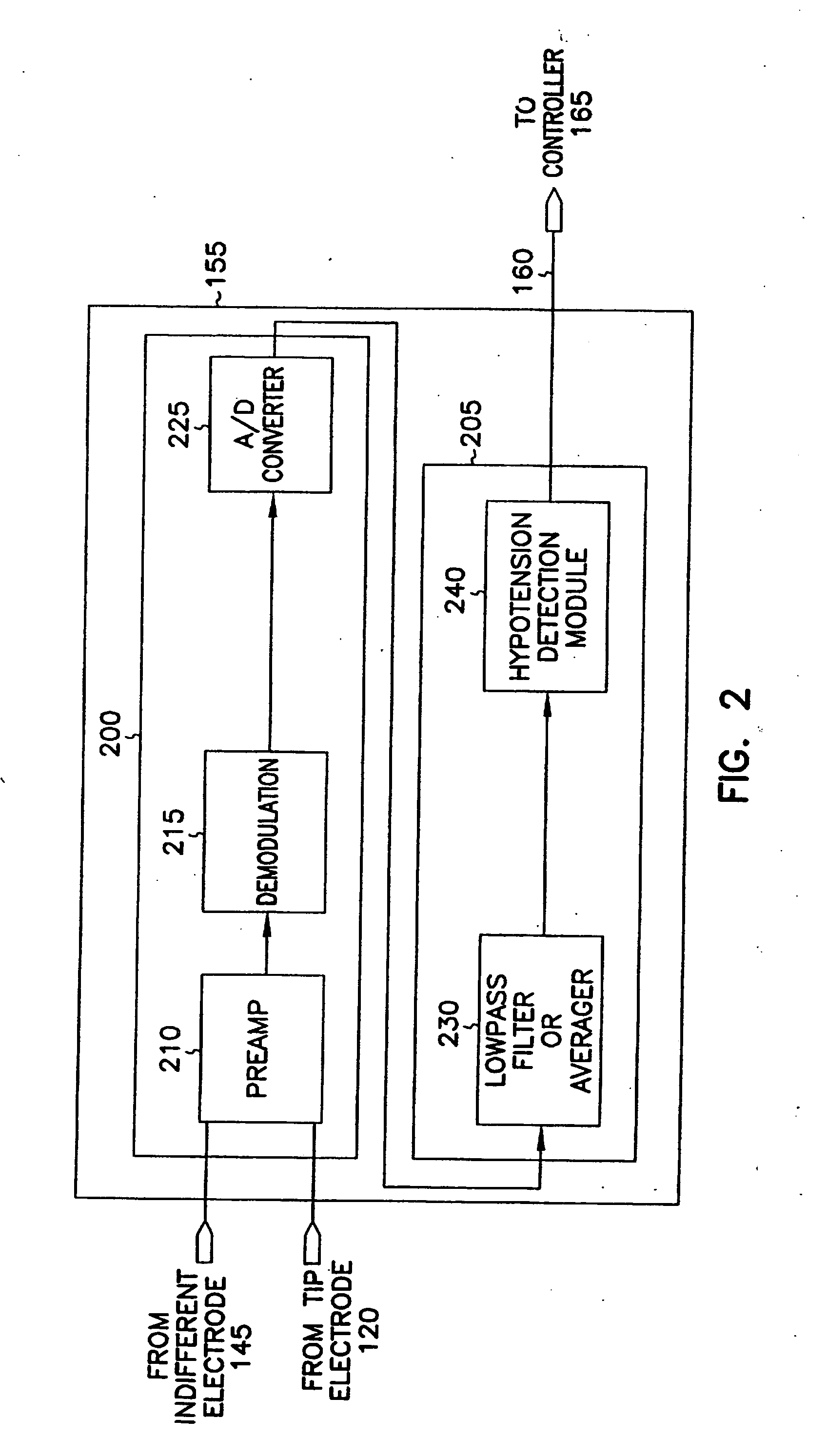
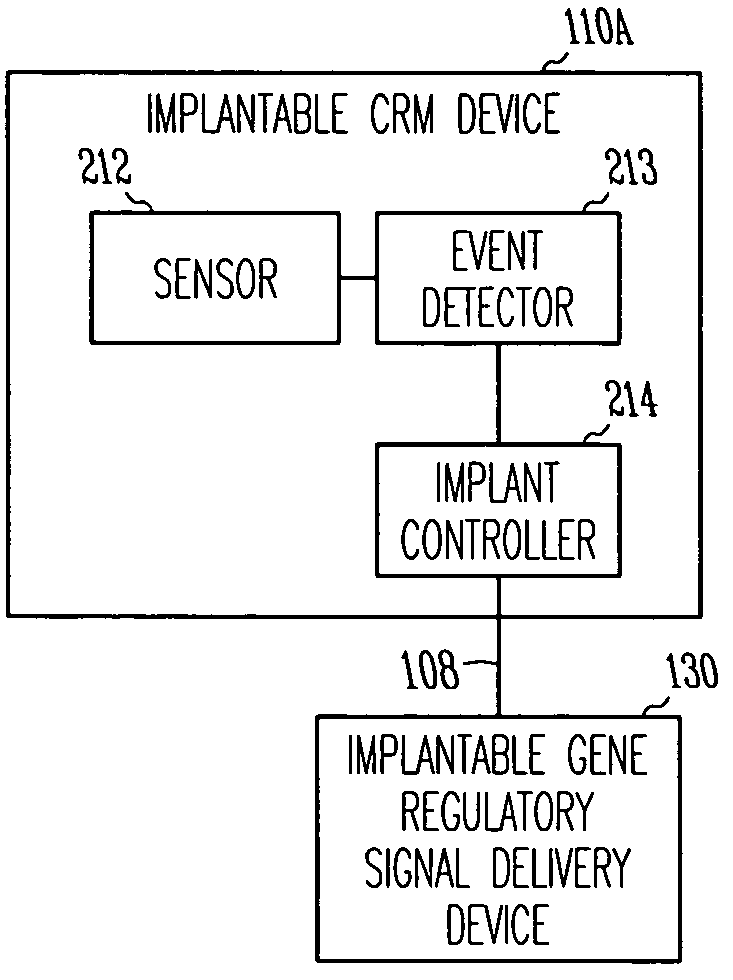
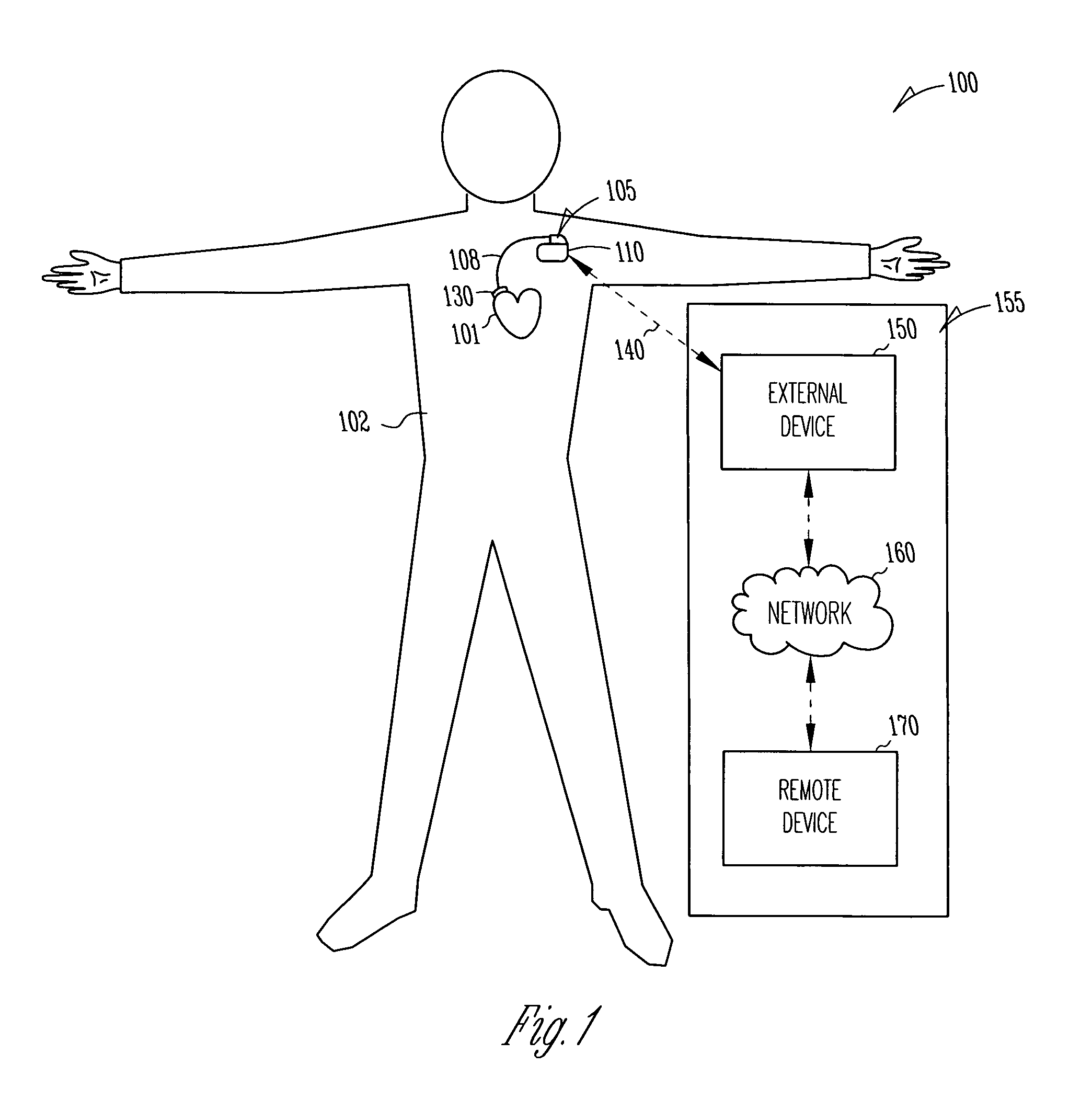
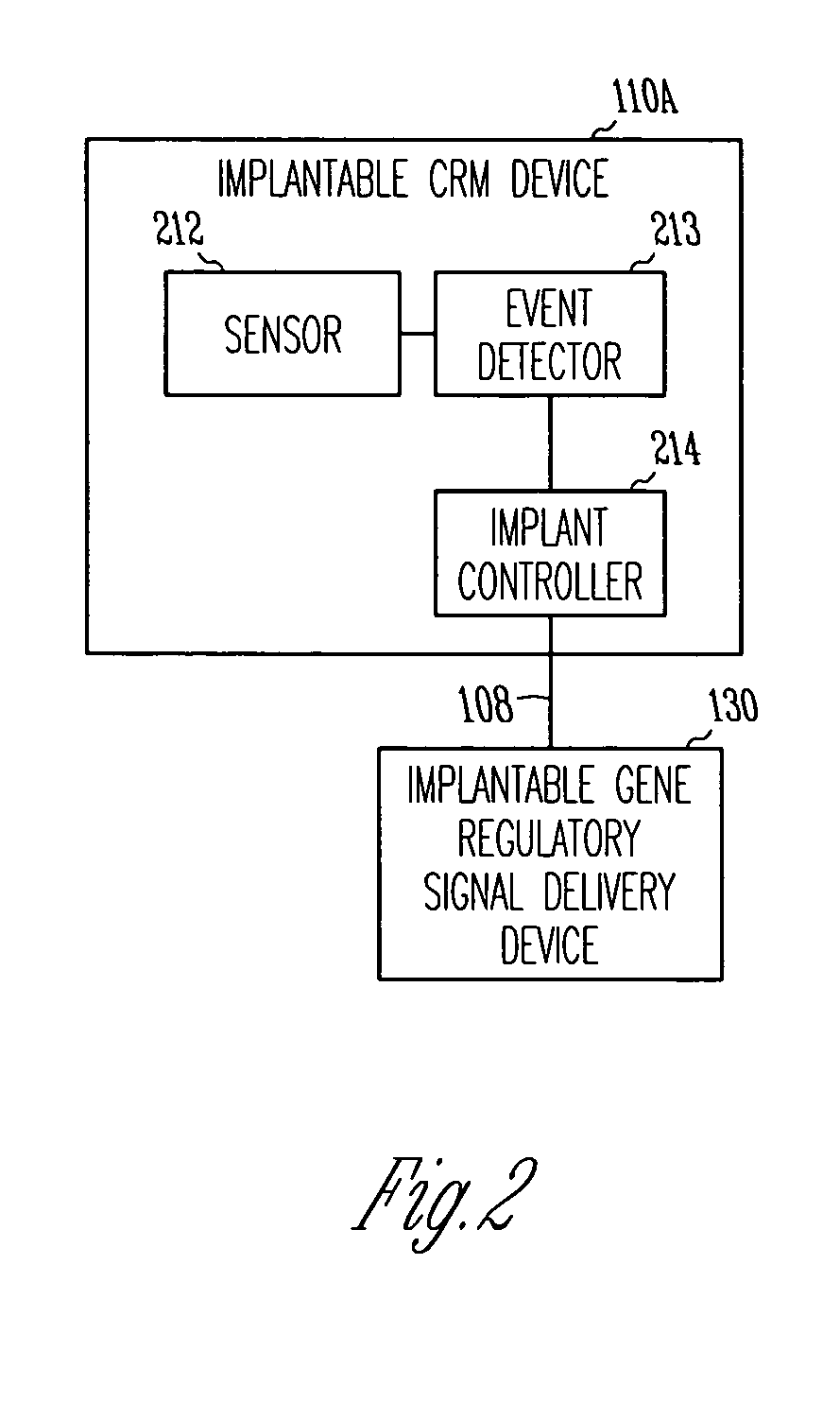
Method and apparatus for device controlled gene expression
InactiveUS20050192637A1Readily be titratedPreventing and inhibiting and cardiac conditionGenetic material ingredientsHeart defibrillatorsForms of energyRegulator gene
A gene regulatory system controls gene therapy by emitting one or more forms of energy that regulate gene expression by triggering promoters. The system includes a sensor to sense a signal indicative of a need for the gene therapy as well as responses to the gene therapy. The regulation of the gene expression is controlled based on the sensed signal and / or a user command. In one embodiment, the system delivers one or more electrical therapies in conjunction with the gene therapy.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Regulation of gene expression
InactiveUS6022863APrevention of fetal rejectionSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsMHC class IDisease
The present invention relates to utrons, RNA molecules which contain promoter regulatory motif(s) and DNA analogs thereof and DNA molecules that can be transcribed to produce the foregoing. In particular, the invention provides gene promoter suppressing nucleic acids which suppress transcription from a promoter of interest. In a preferred embodiment, the invention provides the TSU gene, nucleotide sequences of the TSU gene and RNA, as well as fragments, homologs and derivatives thereof. Methods of isolating TSU genes are also provided. Therapeutic and diagnostic methods and pharmaceutical compositions are also provided. In particular, the invention relates to methods for cell replacement therapy, gene therapy or organ transplantation wherein TSU nucleic acids suppress MHC class I and II gene expression, thus preventing immuno-rejection of non-autologous cells or organs. The invention also provides methods for treatment of diseases or disorders by suppression of MHC class I, MHC class II, ICAM-1, B7-1, B7-2, and / or Fc gamma R expression by provision of TSU function.
Owner:YALE UNIV
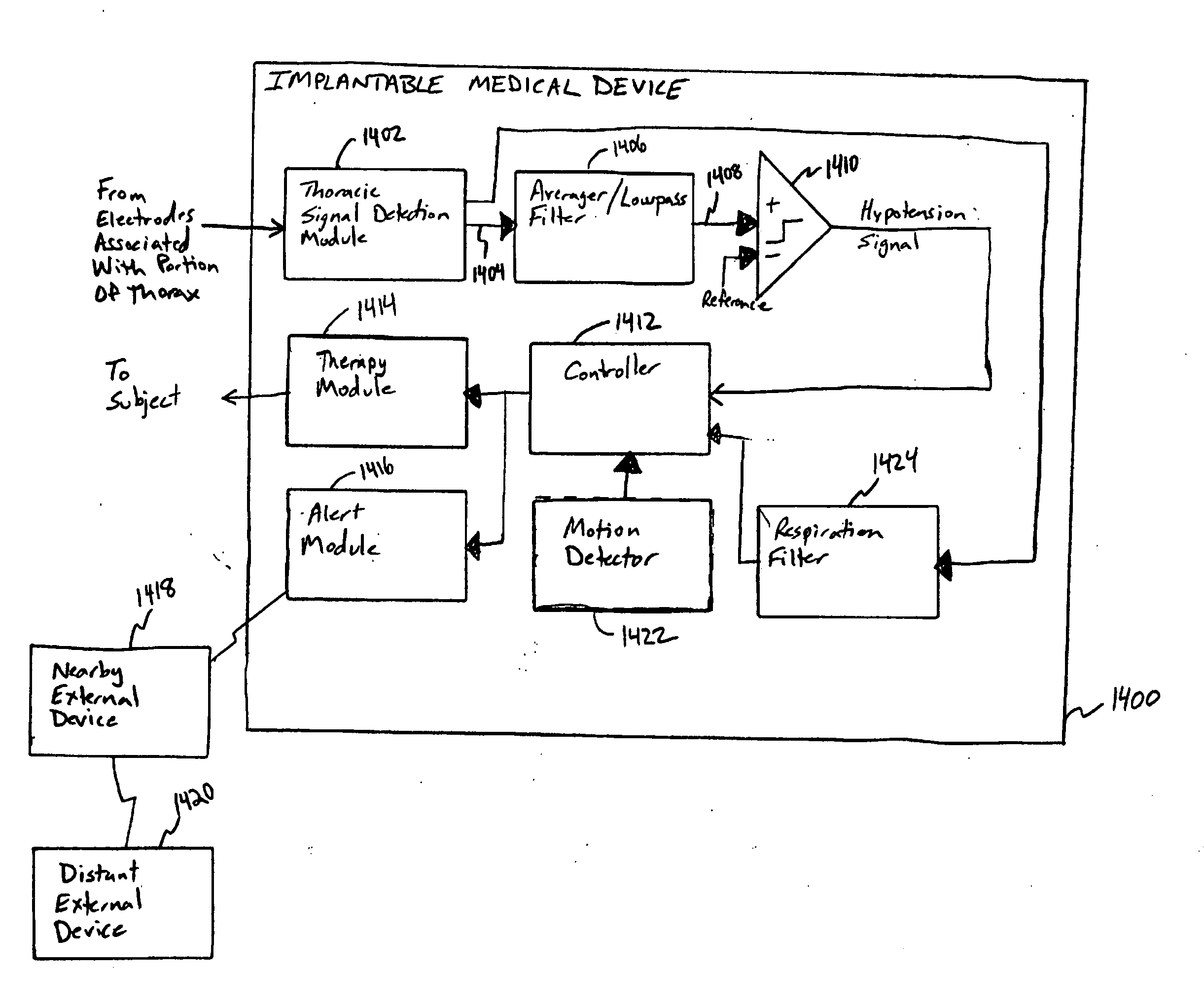
Systems and methods for hypotension
This document discusses, among other things, systems and methods that detect hypotension based on a measurement of thoracic impedance. It also provides an alert, a logging, or a therapy to treat the hypotension. Examples of anti-hypotension therapies include, among other things, pacing therapy, neural stimulation therapy, drug infusion therapy, or gene therapy.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
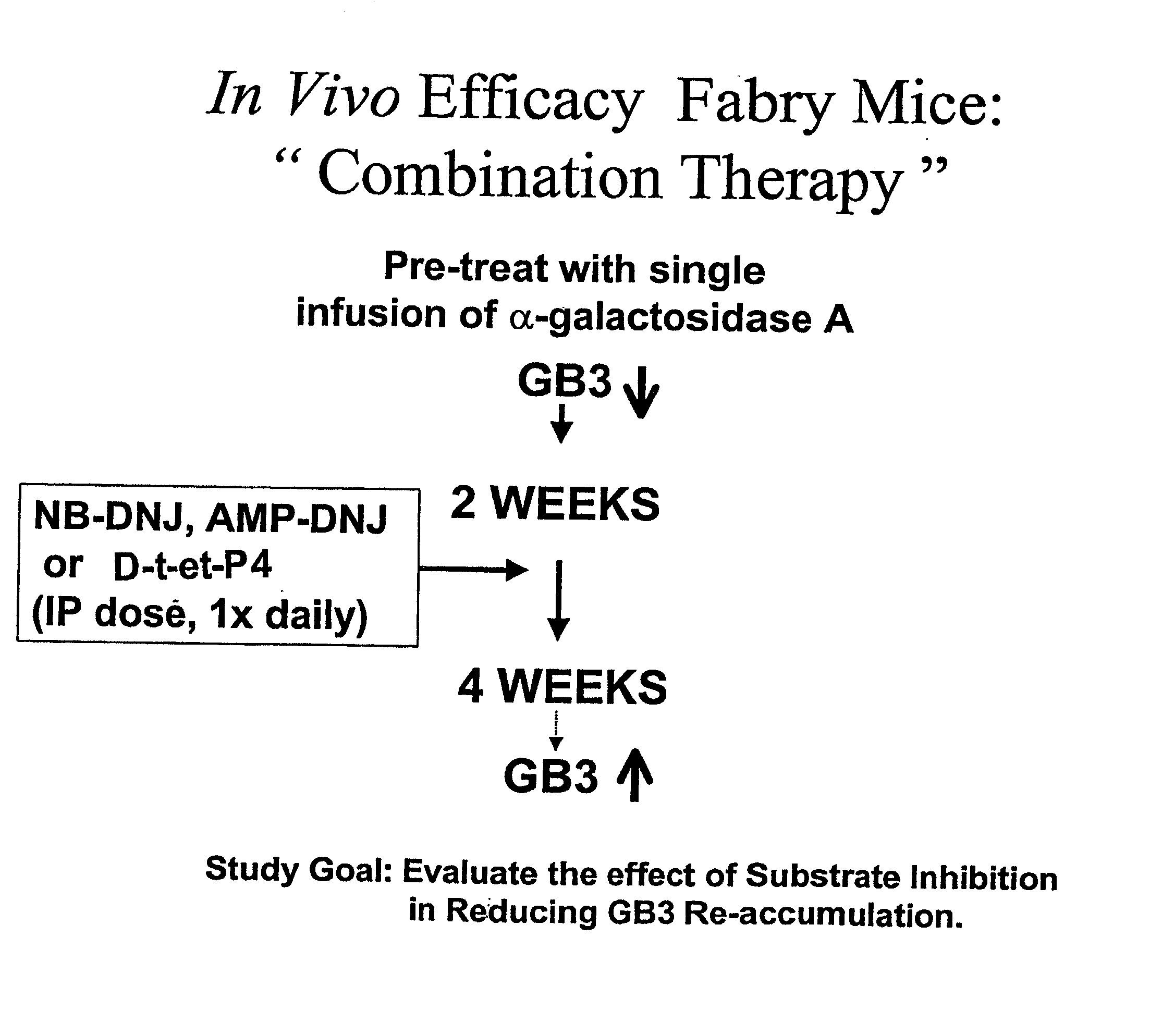
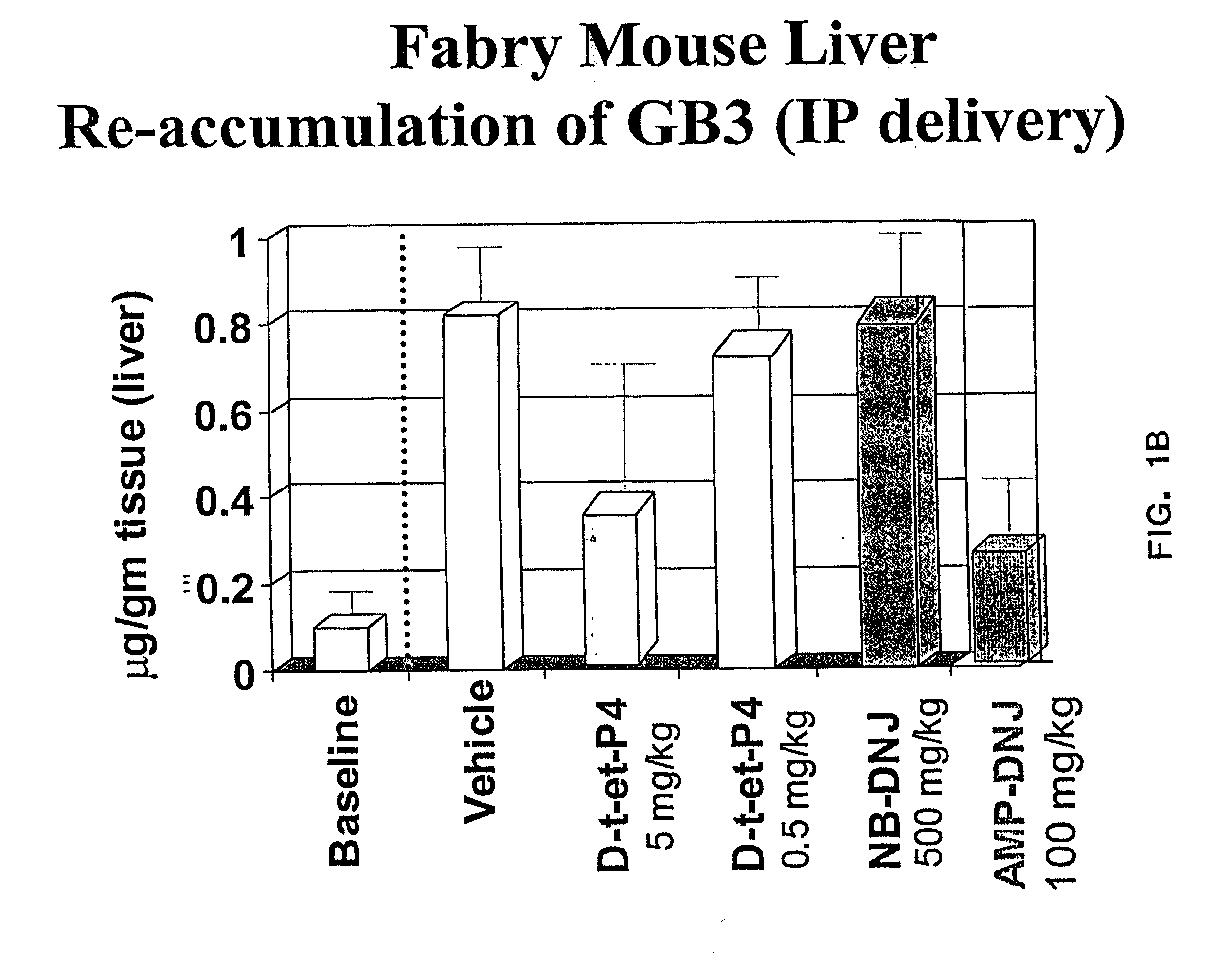
Combination enzyme replacement, gene therapy and small molecule therapy for lysosomal storage diseases
InactiveUS20020095135A1Optimizes clinical benefitReduce disadvantagesPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderLysosomal enzyme defectGene
This invention provides various combinations of enzyme replacement therapy, gene therapy, and small molecule therapy for the treatment of lysosomal storage diseases.
Owner:MEEKER DAVID +1
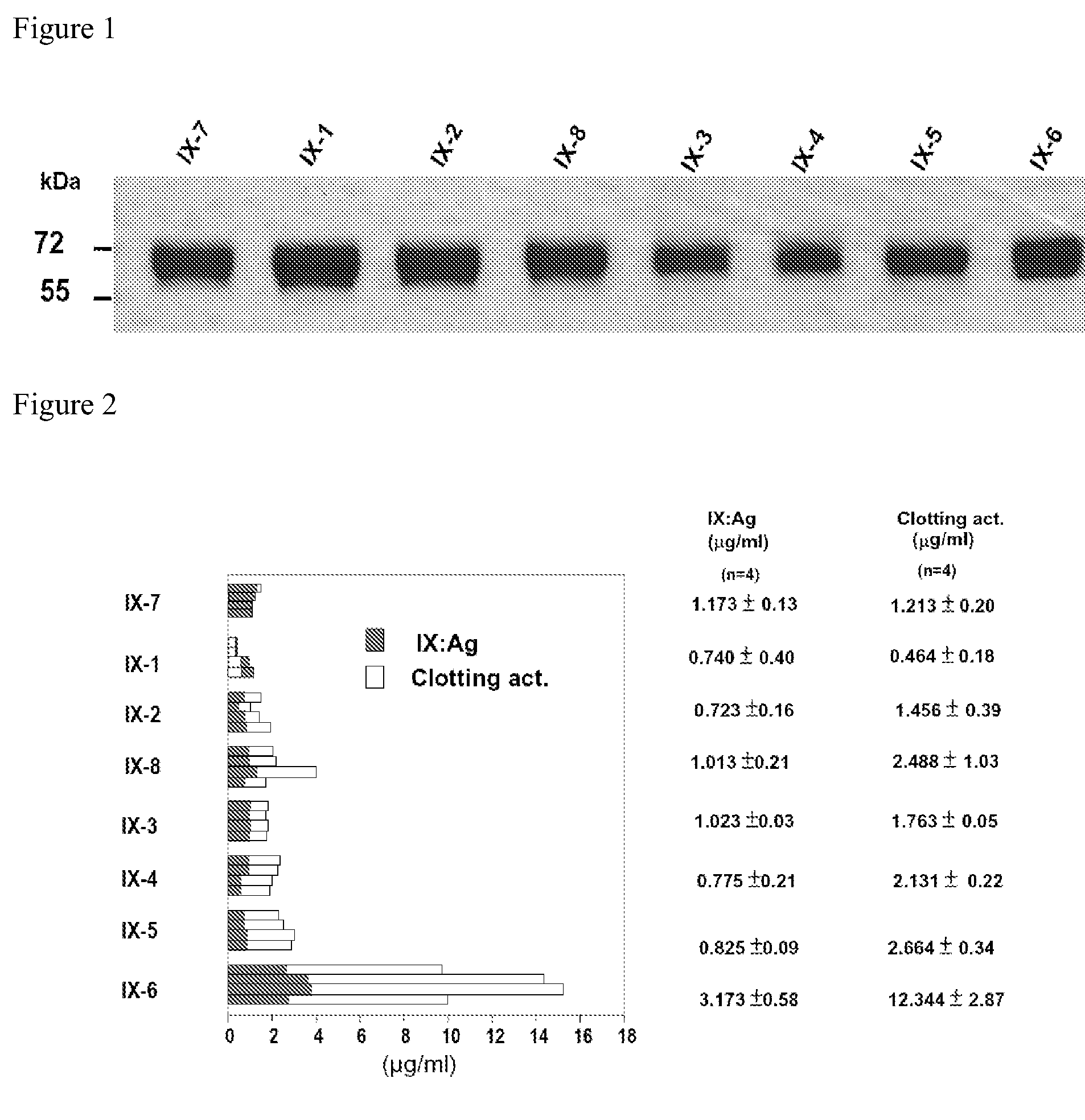
Recombinant human factor ix and use thereof
ActiveUS20080167219A1Easy to adaptPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsWild typeFactor ii
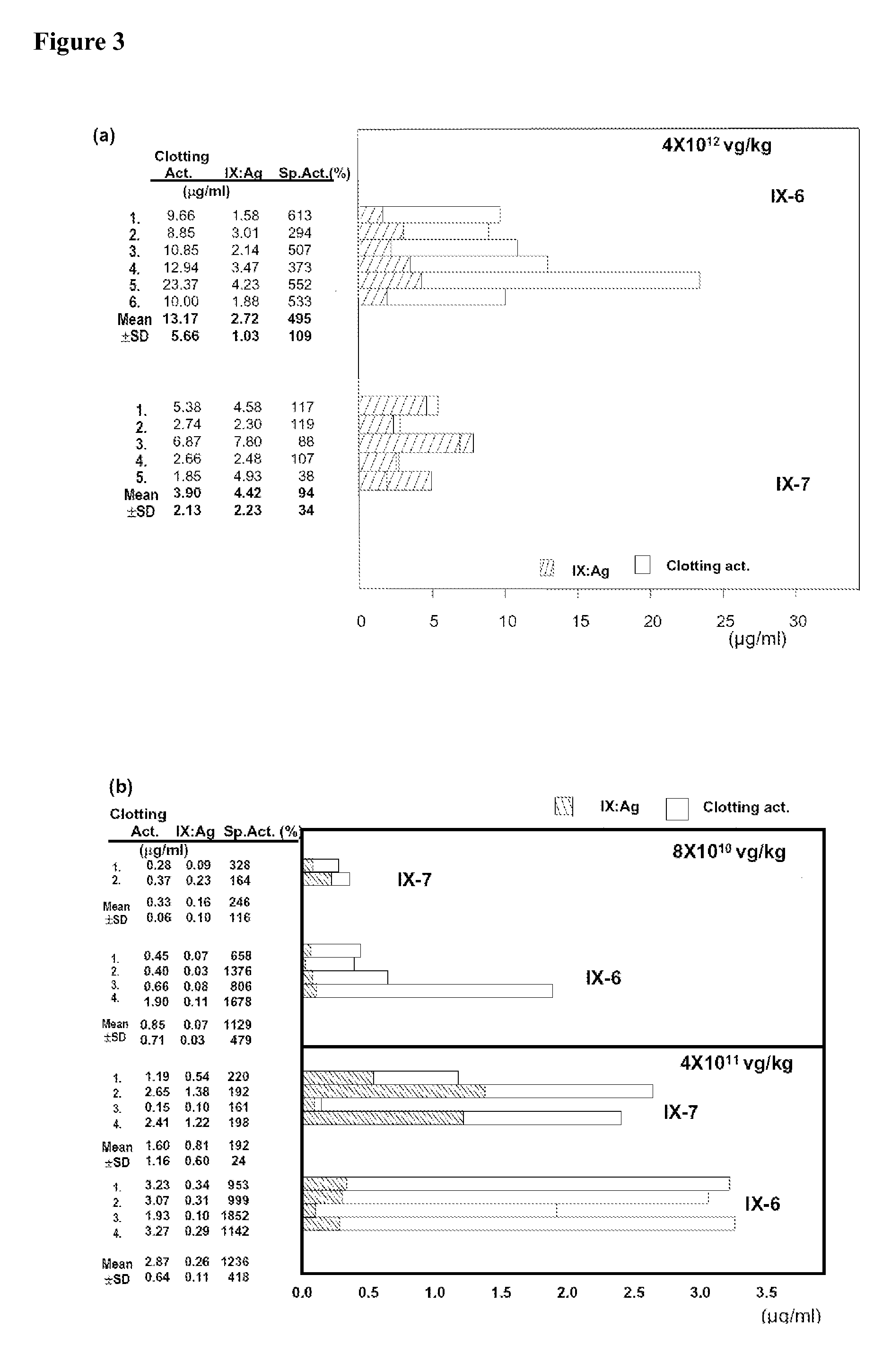
The present invention aims at converting factor IX into a molecule with enhanced activity which provides an alternative for replacement therapy and gene therapy for hemophilia B. Using recombinant techniques, factor IX with replacement at positions 86, 277, and 338 exhibits better clotting activity than recombinant wild type factor IX.
Owner:LIN SHU WHA
Combination therapy for treating protein deficiencies
InactiveUS7446098B2High biological efficiencyImprove cost efficiencyBiocideMetabolism disorderReactive siteCombined Modality Therapy
This application provides methods of improving gene therapy by combining gene therapy with active site-specific chaperones (ASSCs). The ASSC increases the stability and efficiency of the protein encoded by the recombinant gene that is administered.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
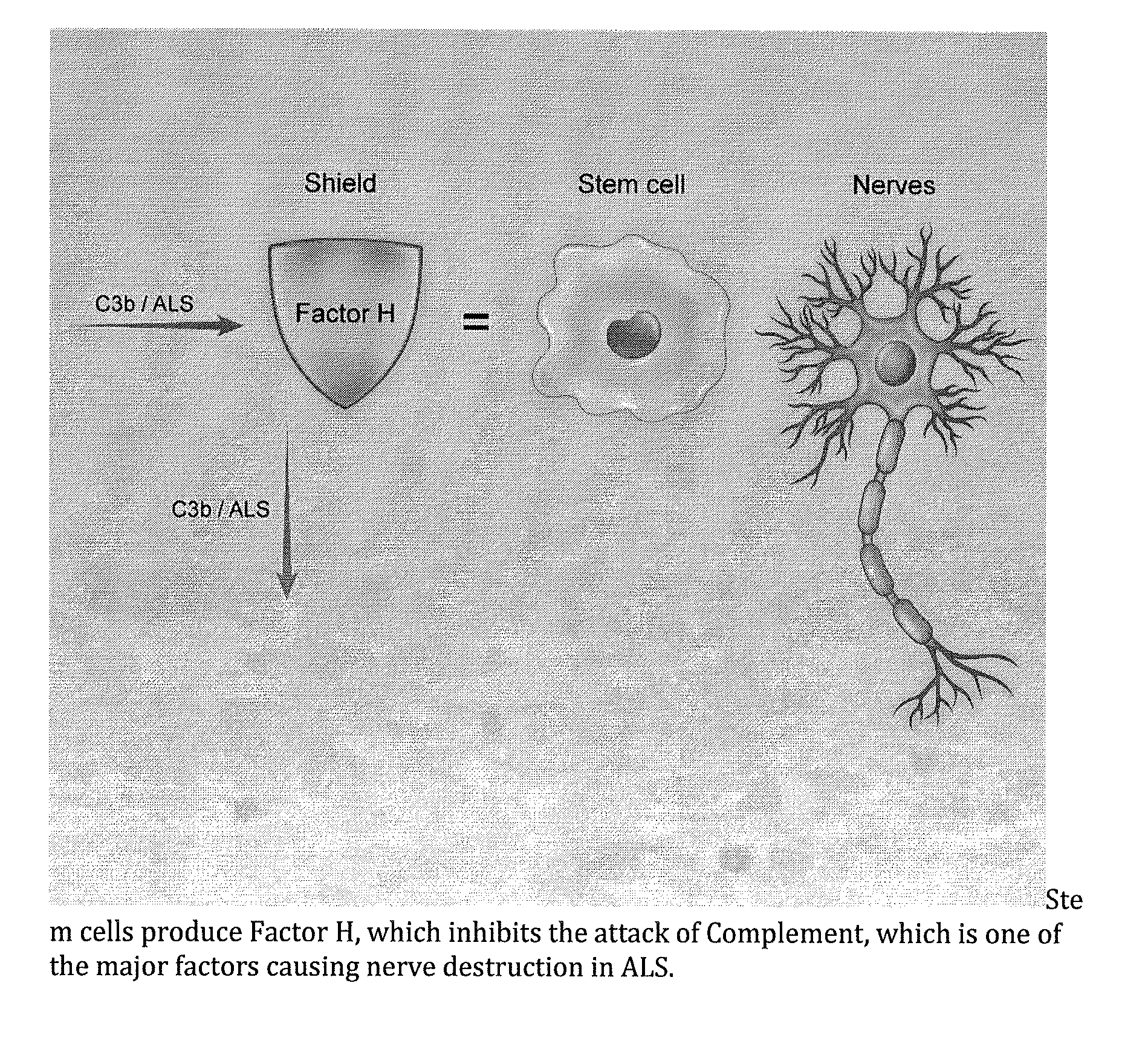
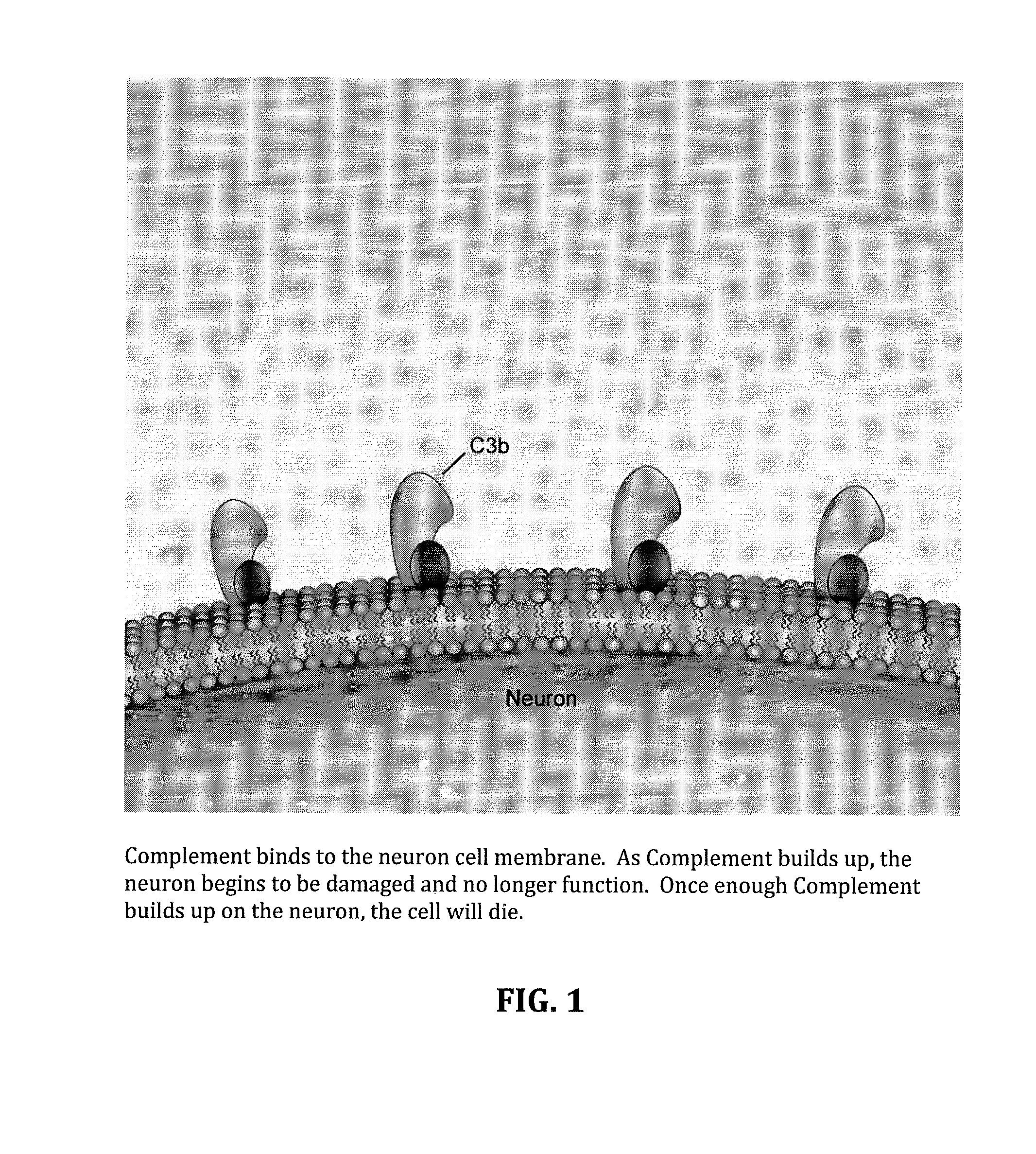
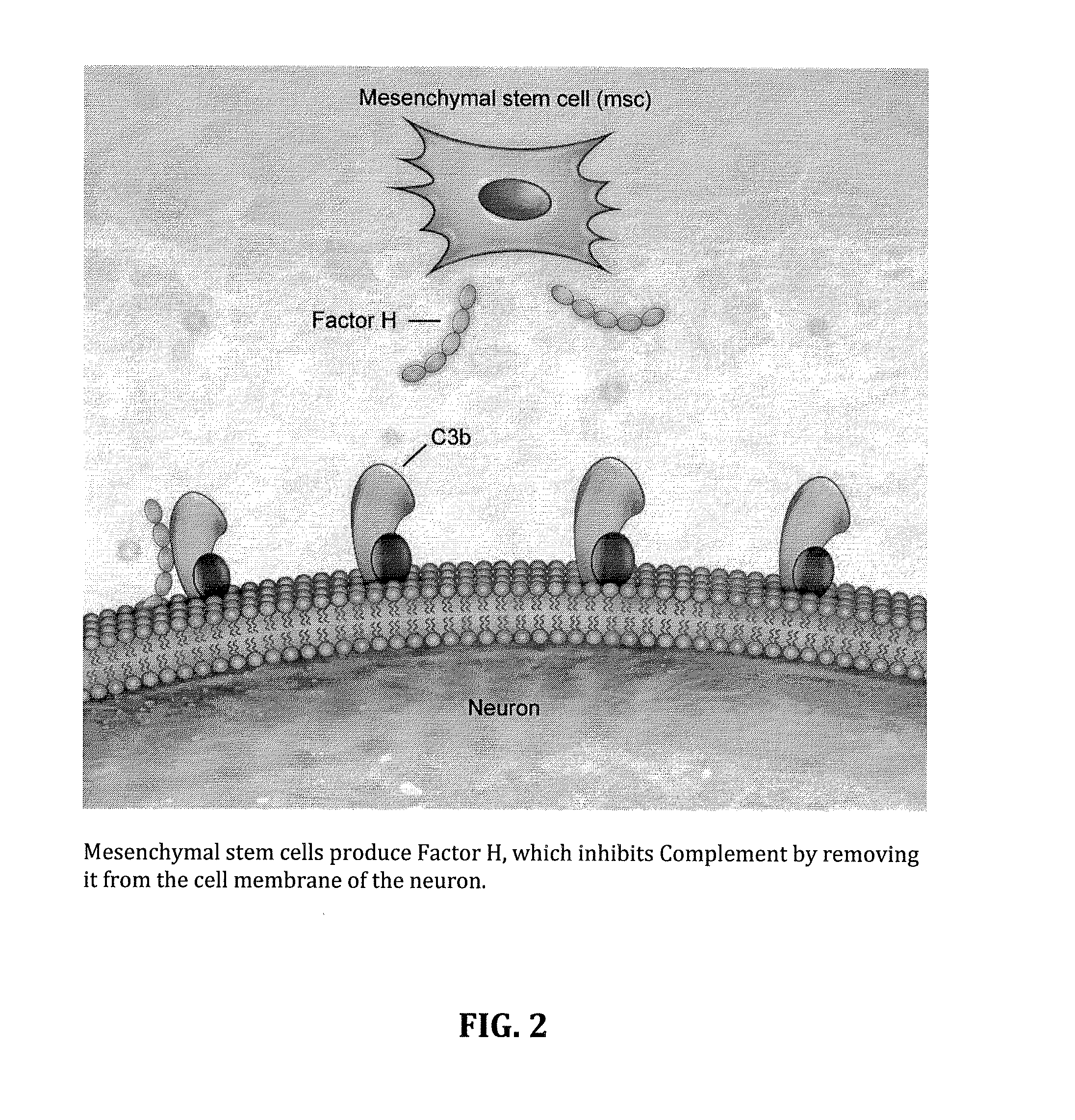
Method for treating ALS via the increased production of factor h
InactiveUS20140234275A1Improve satisfactionInhibition effectBiocideOrganic active ingredientsWhole bodyPrimary motor neuron
Methods and systems for the treatment for ALS incorporating stem cells harvested from the subject to be treated. These stem cells may be genetically altered with the addition of several genes of interest. Then, the patient will receive systemic gene therapy for the muscles and directed specifically at motor neurons. In this multi-pronged treatment approach, the stem cells provide immune regulation and the regeneration of motor neurons. And, the new motor neurons carry the added genes, which are protective against motor neuron death from ALS. The systemic therapy increases the amount of genes, which further reduces the effects of ALS. Additional gene therapy administered in the muscle will be further protective of the axon, while maintaining muscle mass and function.
Owner:BIOVIVA USA
Pluripotent therapeutic compositions and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090274660A1Reduce riskReduce significant riskBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSelf-healingAnticarcinogen
Synthetic Stem Cell-like Tissue Healing and Regeneration Medication with Anti-inflammatory, Protein Synthesis, Enzyme Deficiency Activation and Genetic Therapy, and Anti-cancer Agent derived from a series of inventions that include these products of Biomolecular Engineering, Drug Discovery from a Biologic Periodic Table of Applied Biochemistry and Biophysics. Tissue has a self healing effect promoting tissue healing and tissue regeneration. Not only does it maintain good health but also it has been observed that the patient's blood is withdrawn from the patient and applied to the ulcer has healing qualities. Cartilage placed in a wound promotes and accelerates wound healing. The anabolic biochemical and biophysical equivalent of tissue has been found in these embodiments to have the same pharmacologic qualities, when devoid of genetic DNA mismatch and other catabolic factors including the catabolic effects of microorganism overgrowth that lacks pro-biotic qualities. The healing efficacy of these tissue components gives us further appreciation of the protective action of human tissue over and above and other than the immune protective system or perhaps an integral component part of the immune system.
Owner:IMMUNOPATH PROFILE INC A CORP OF PA
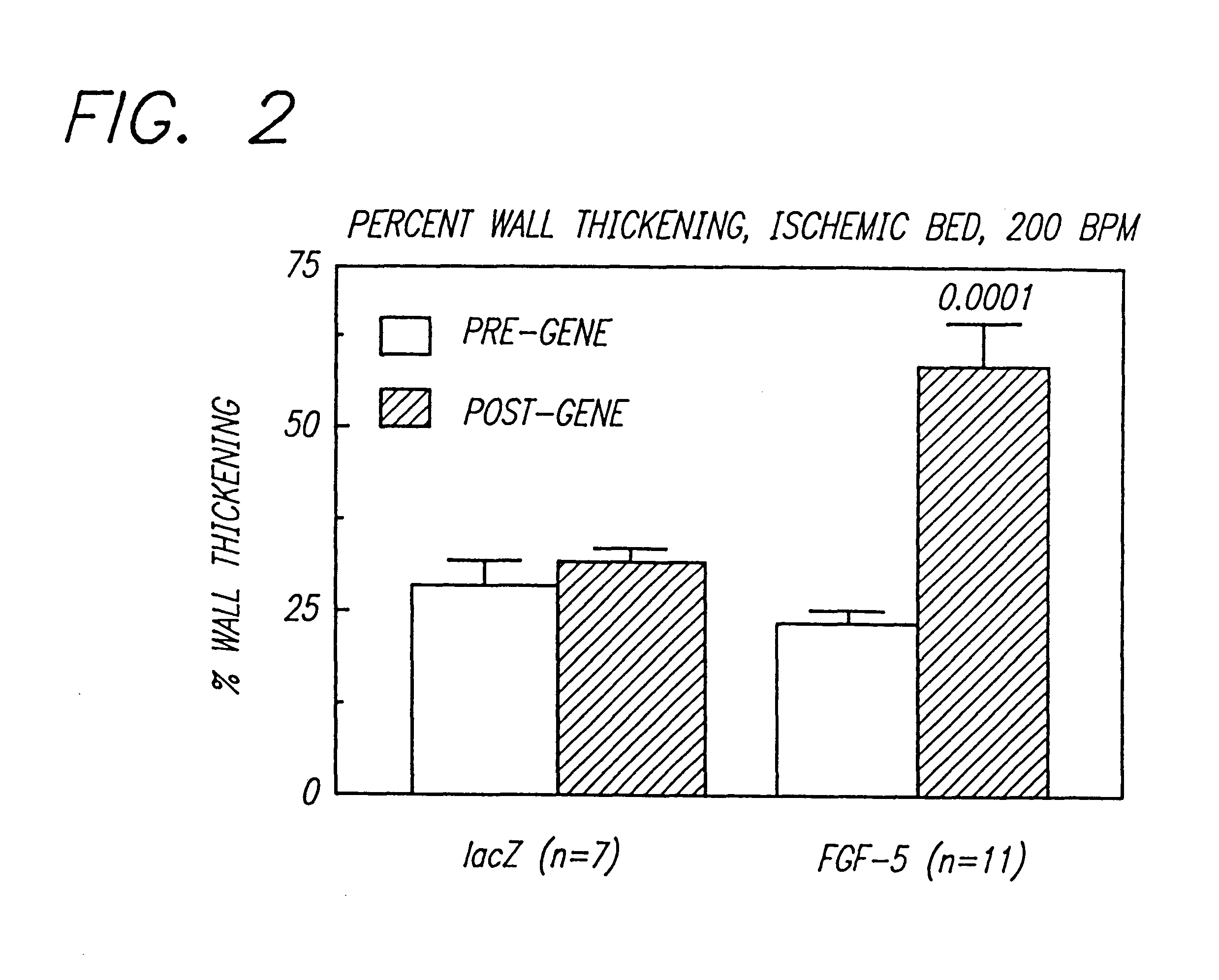
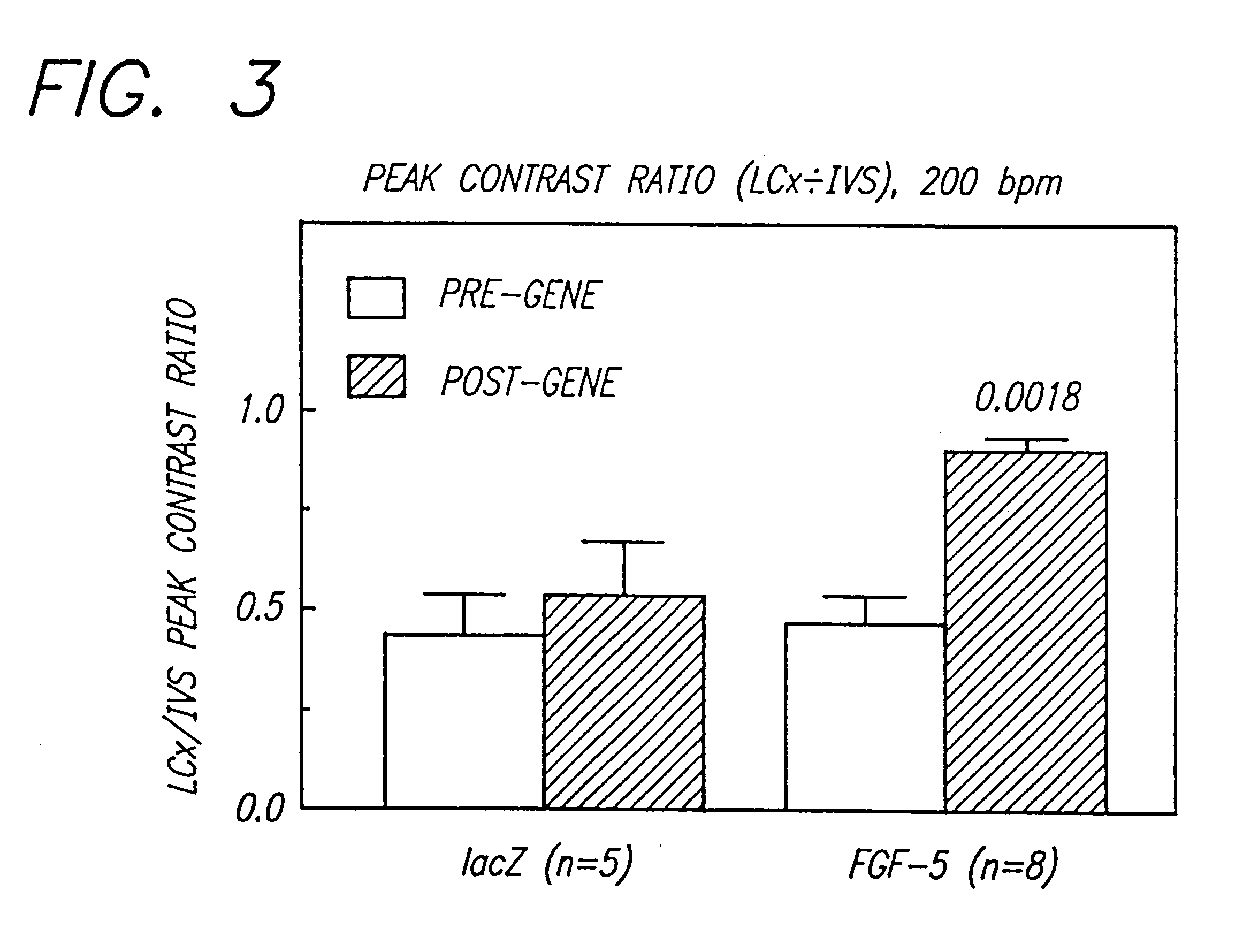
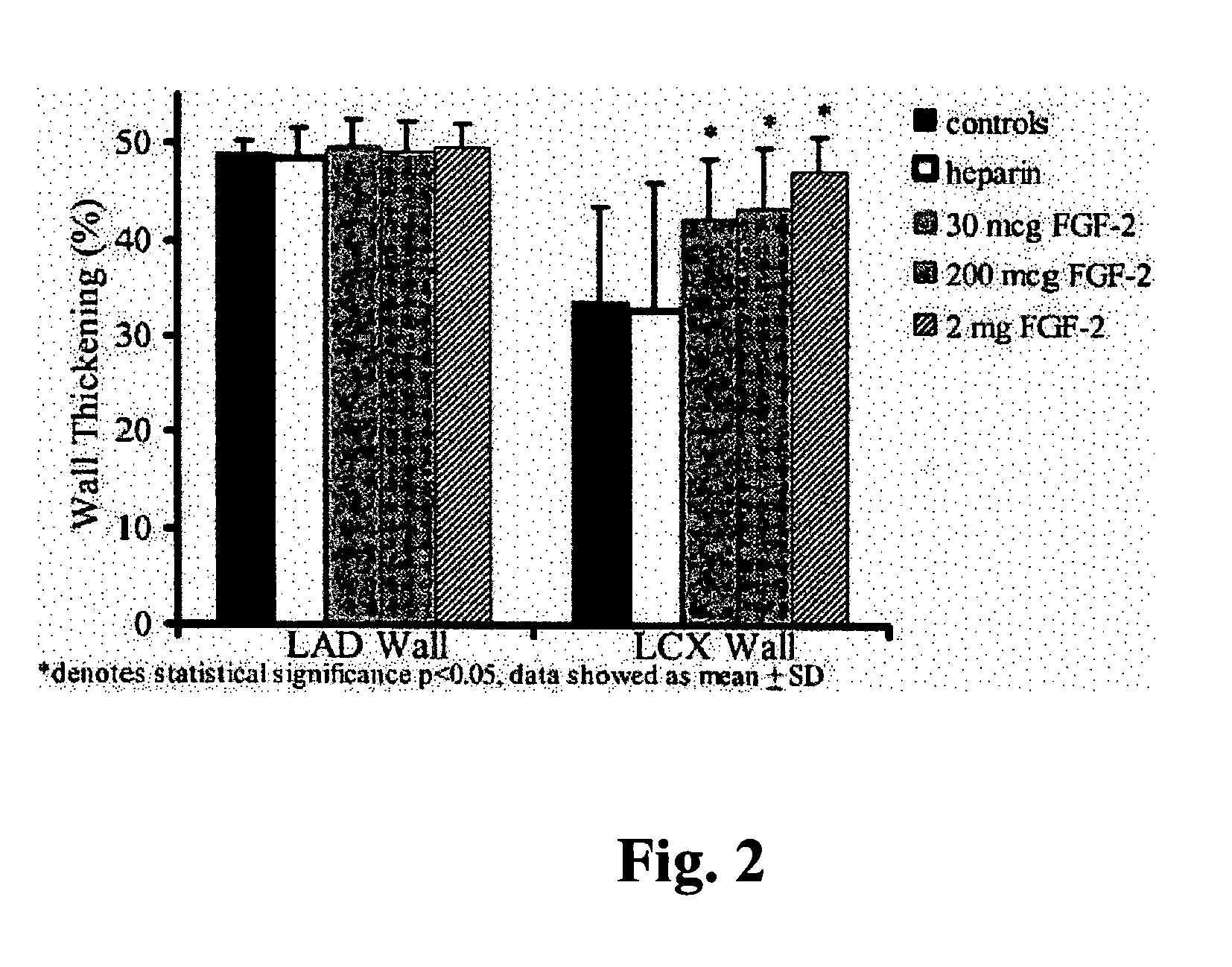
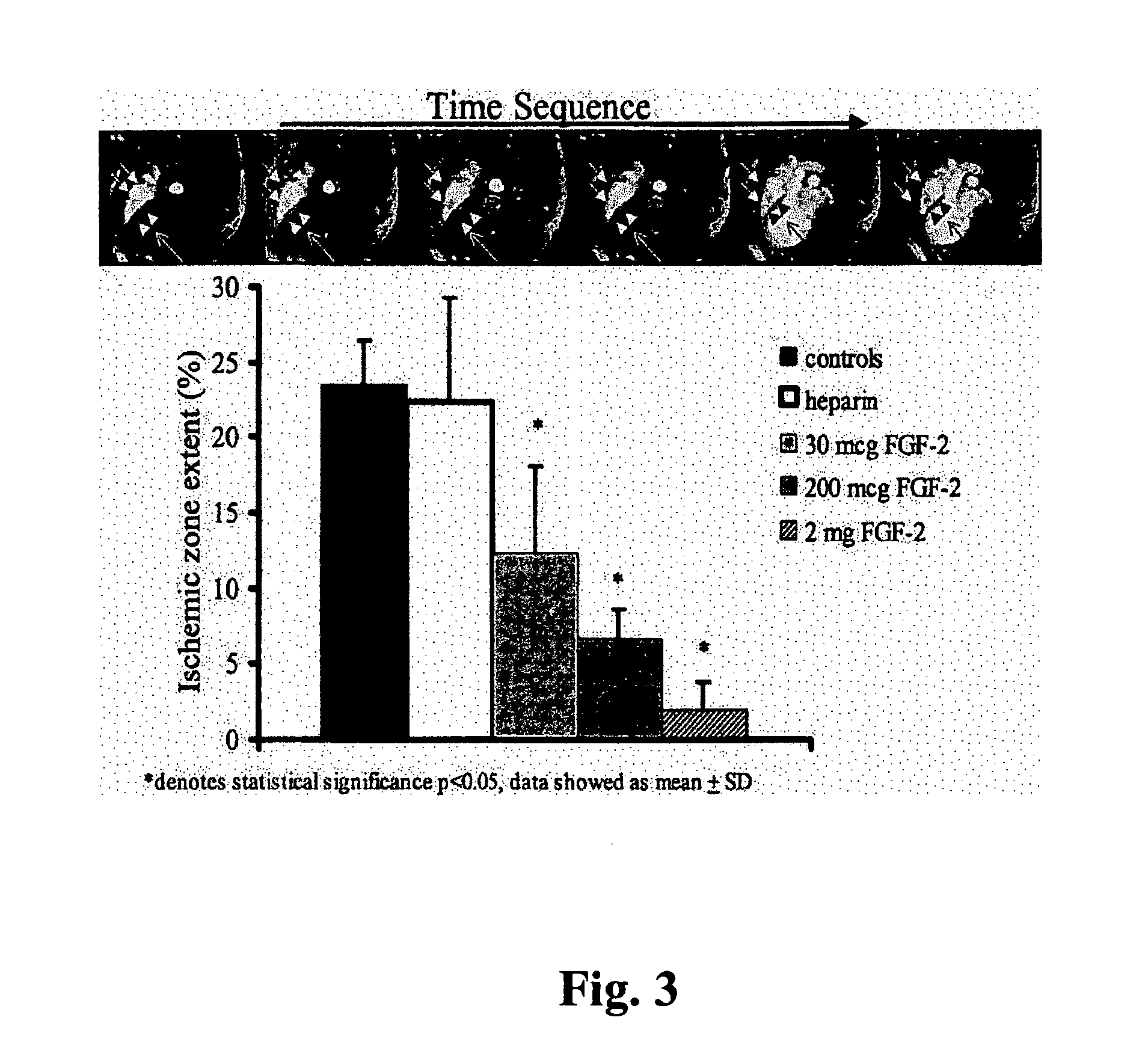
Gene therapies for enhancing cardiac function
The transgene-inserted replication-deficit adenovirus vector is effectively used in in vivo gene therapy for peripheral vascular disease and heart disease, including myocardial ischemia, by a single intra-femoral artery or intracoronary injection directly conducted deeply in the lumen of the one or both femoral or coronary arteries (or graft vessels) in an amount sufficient for transfecting cells in a desired region.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
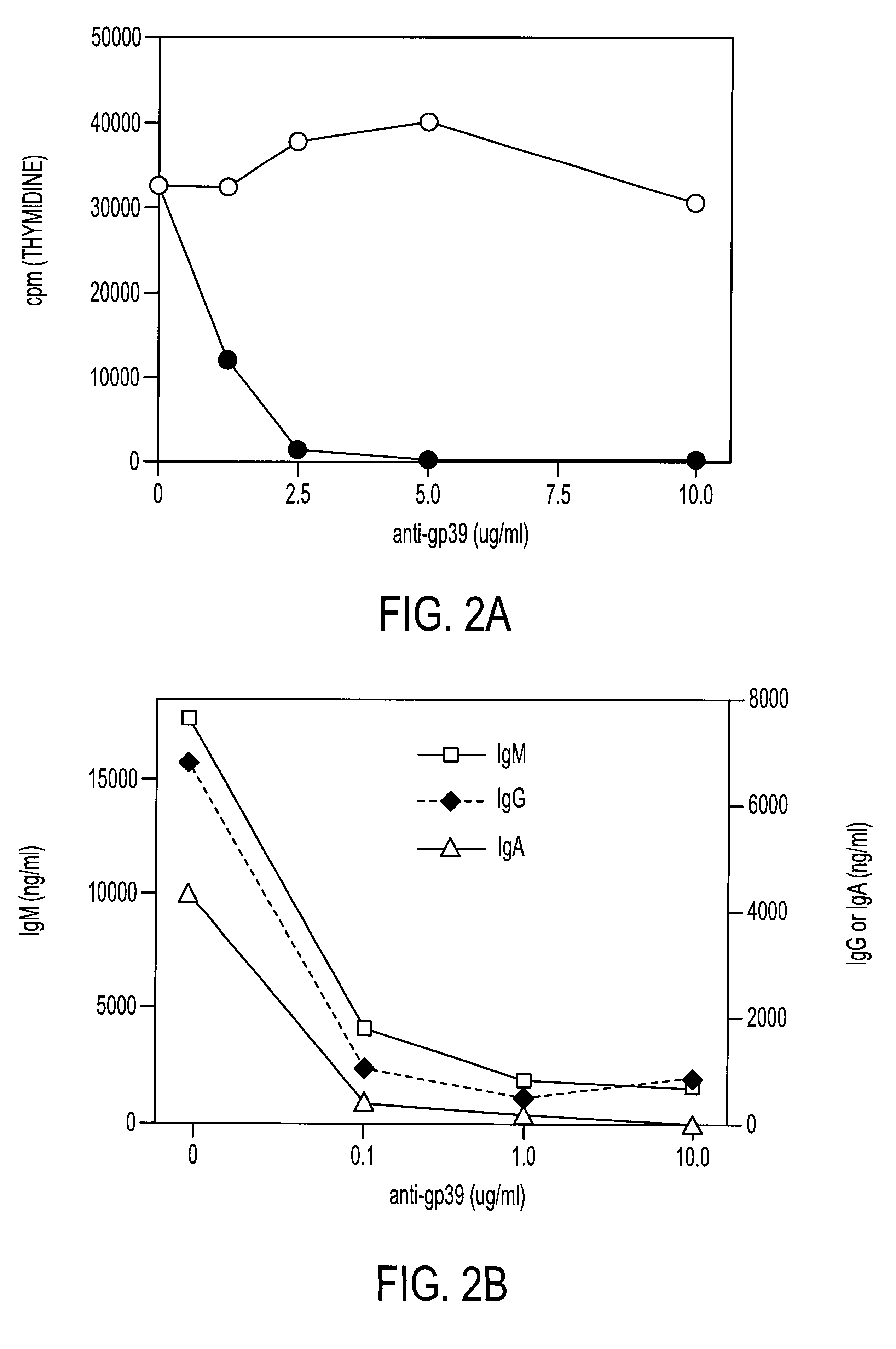
Methods of treating autoimmune diseases with gp39-specific antibodies
InactiveUS6440418B1Prolong half-life in vivoReduced Fc receptor bindingOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDiseaseAutoimmune responses
The present invention is directed to humanized antibodies which bind human gp39 and their use as therapeutic agents. These humanized antibodies are especially useful for treatment of autoimmune diseases; and an immunosuppressant during transplantation of heterologous cells, tissues or organs, cell therapy, and gene therapy.
Owner:BIOGEN INC
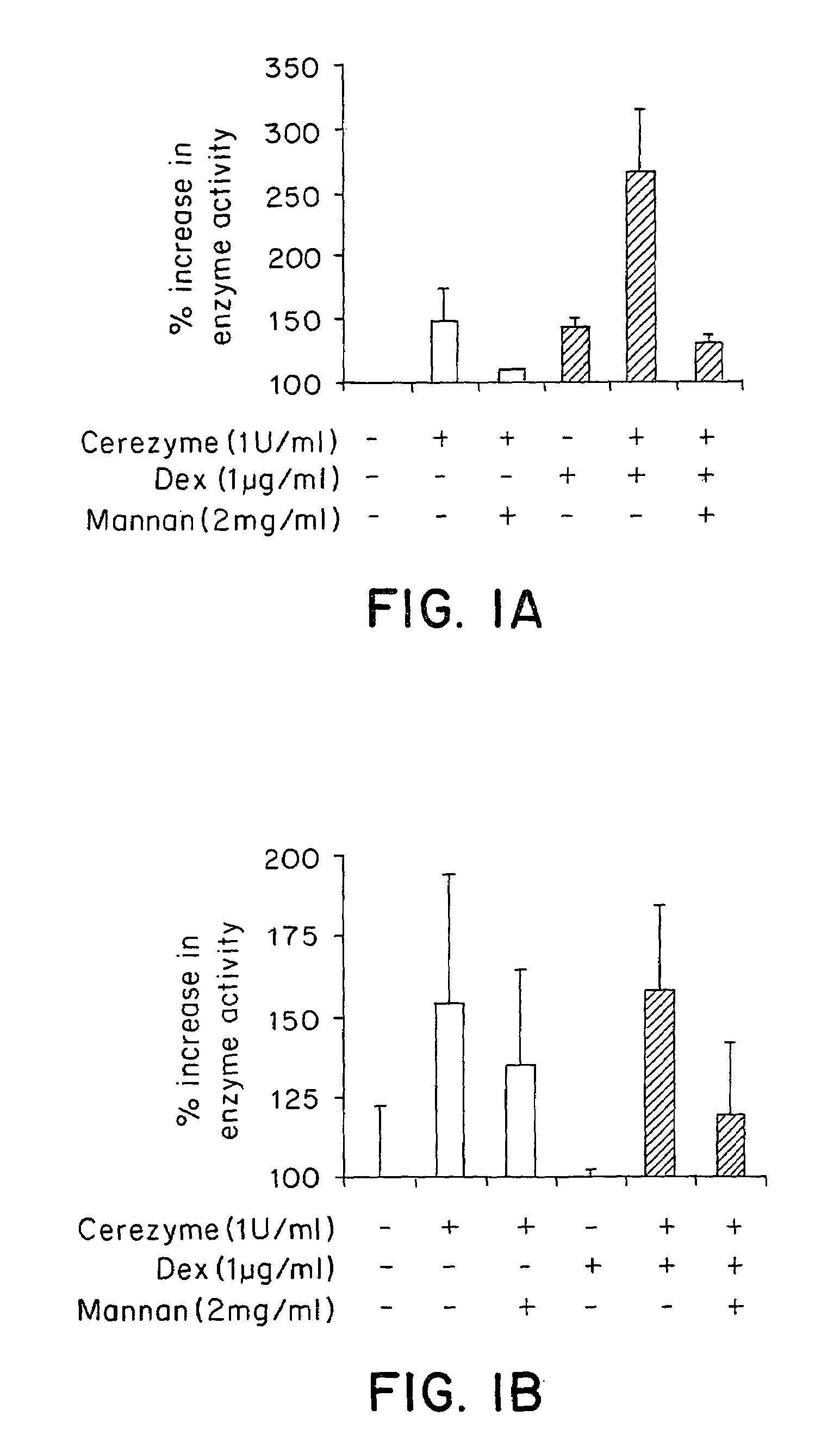
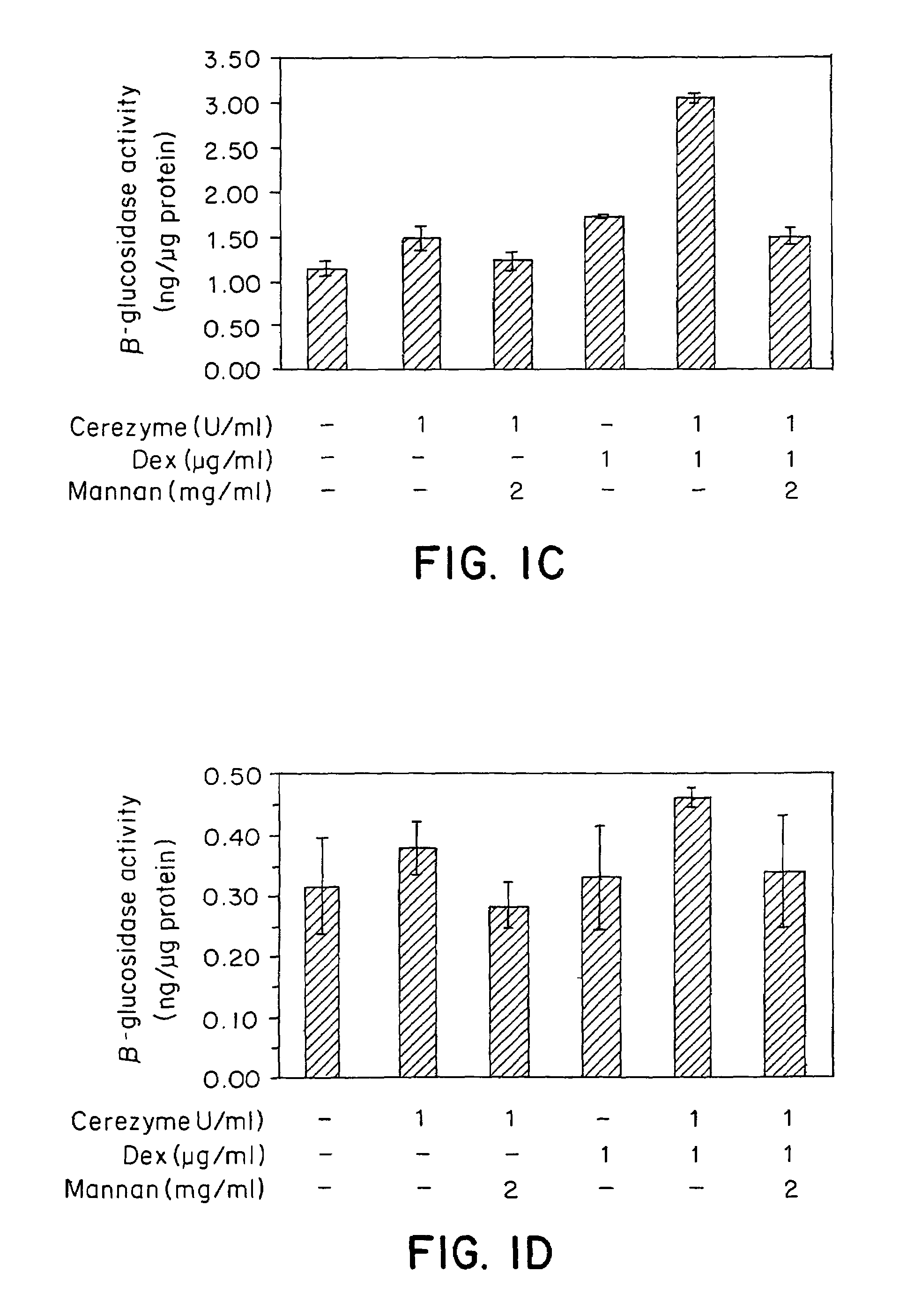
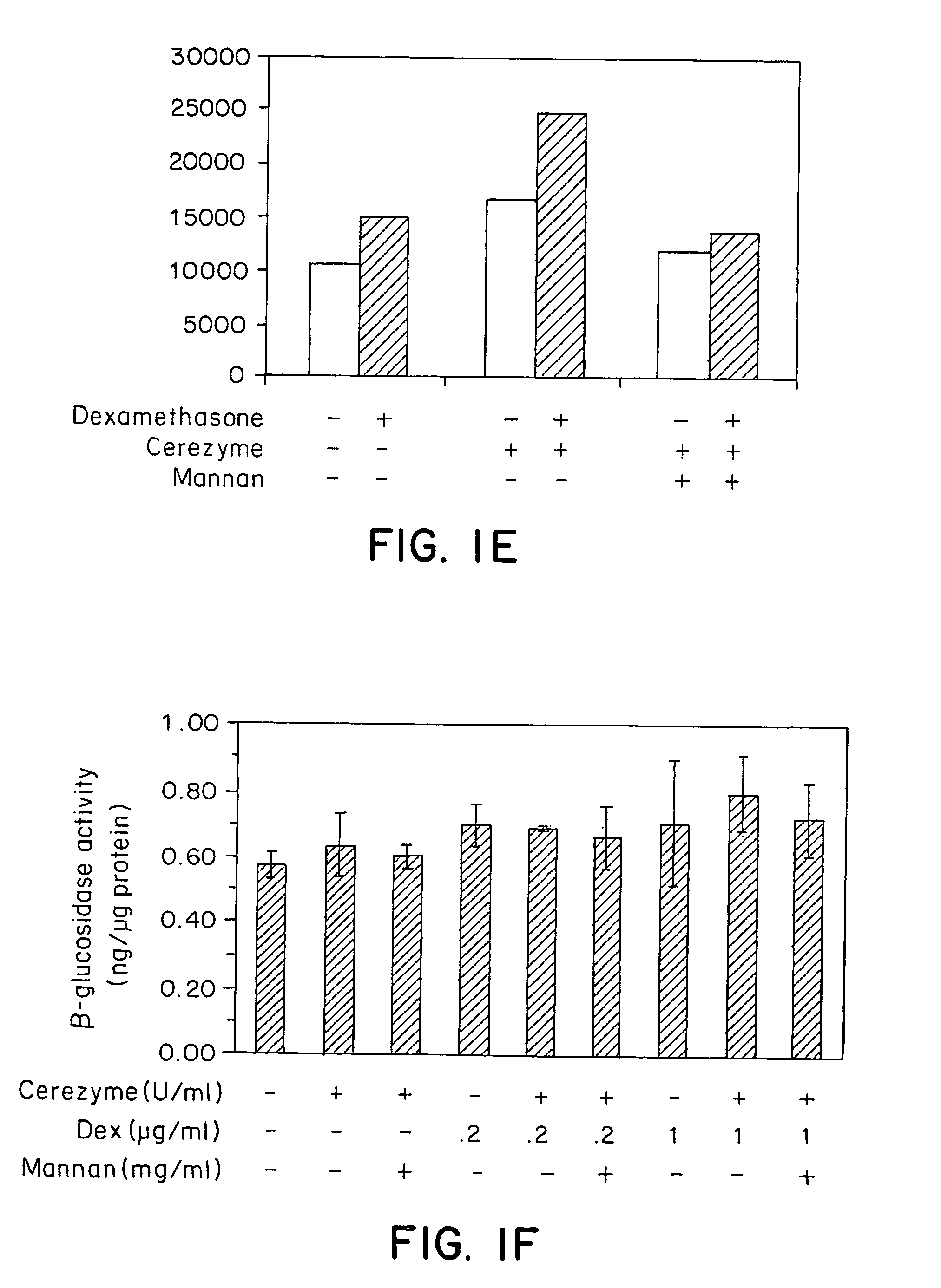
Methods of enhancing lysosomal storage disease therapy by modulation of cell surface receptor density
InactiveUS7658916B2Promote absorptionUptake of extracellular lysosomal enzymes by cells can be increasedBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsLysosomeFabry disease
Methods of modulating uptake of extracellular lysosomal enzymes by administering a pharmaceutical agent and methods of treating a lysosomal storage disease (such as Gaucher disease, Pompe disease, Fabry disease or Niemann-Pick disease) or enhancing enzyme replacement therapy or gene therapy, comprising administering a pharmaceutical agent such as dexamethasone, glucose or insulin, are provided.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Method and apparatus for device controlled gene expression
InactiveUS7840263B2Readily be titratedInhibit expressionGenetic material ingredientsHeart defibrillatorsForms of energyRegulator gene
A gene regulatory system controls gene therapy by emitting one or more forms of energy that regulate gene expression by triggering promoters. The system includes a sensor to sense a signal indicative of a need for the gene therapy as well as responses to the gene therapy. The regulation of the gene expression is controlled based on the sensed signal and / or a user command. In one embodiment, the system delivers one or more electrical therapies in conjunction with the gene therapy.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Combination growth factor therapy and cell therapy for treatment of acute and chronic heart disease
Acute and chronic heart disease is treated using a rational, multi-tier approach. A patient is pretreated with growth factor proteins or gene therapy, followed by the administration of adult stem cells. The progress of treatment is continuously monitored by echo-cardiogram with growth factor treatment and / or stem cell administration adjusted according to the results of the echo-cardiogram or clinical status of the patient. Heart disease is also treated by a method that comprises administration of a therapeutically effective amount of a growth factor protein by oral inhalation therapy.
Owner:FRANCO WAYNE P
Immobilized poly(n)polymerase
ActiveUS20180142275A1Improve stabilityMore time-effectiveMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical industryVaccinationRNA - Ribonucleic acid
The present invention relates to an immobilized poly(N)polymerase (PNP), methods of producing said PNP and uses thereof. Further disclosed is an enzyme reactor and kit comprising the PNP for producing polynucleotidylated ribonucleic acid poly(N)RNA)molecules which are useful in gene therapy, immunotherapy, protein replacement therapy and / or vaccination.
Owner:CUREVAC SE
Compositions and Methods for Detection, Prognosis and Treatment of Breast Cancer
InactiveUS20090118175A1Improved prognosisOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDiseasePost translational
The present invention relates to methods of detection, prognosis and treatment of breast cancer using a plurality genes or gene products present in normal and neoplastic cells, tissues and bodily fluids. Gene products relate to compositions comprising the nucleic acids, polypeptides, antibodies, post translational modifications (PTMs), variants, derivatives, agonists and antagonists of the invention and methods for the use of these compositions. Additional uses include identifying, monitoring, staging, imaging and treating cancer and non-cancerous disease states in breast as well as determining the effectiveness of therapies alone or in combination for an individual. Therapies include gene therapy, therapeutic molecules including but not limited to antibodies, small molecules and antisense molecules.
Owner:MACINA ROBERTO A
Methods and compositions for interferon therapy
InactiveUS20050025742A1Long contact timeKeep for a long timePeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsGene deliveryInterferon therapy
Methods and pharmaceutical compositions for administering protein or gene therapy to tissues or organs having an epithelial cell layer are provided. A protein or nucleic acid encoding the protein is administered to the target tissue or organ in combination with treatment with a delivery enhancing agent which increases the delivery of the interferon or nucleic acid to the cells of the target tissues or organs. The methods and combinations are particularly useful in the treatment of cancers and other conditions responsive to interferon therapy. An exemplary method comprises the transurethral intravesical administration to the bladder of a therapeutically effective amount of a pharmaceutical composition comprising an alpha-interferon or a gene delivery system encoding the interferon and SYN3 or a SYN3 homolog or analog. In the urinary bladder, as much as a 10 to 1000 fold increased in interferon levels and activity may be observed with the use of a SYN3 formulation as opposed to a PBS formulation of the same interferon protein or interferon gene delivery system.
Owner:CANJI
Secretion of neublastin
InactiveUS20050089960A1Reduce the possibilityObstruct passageSenses disorderNervous disorderNervous systemPro region
The present invention concerns improved methods and compositions for producing a Neublastin polypeptide as well as local delivery of Neublastin to specific regions of the nervous system including the central nervous system and the eye for example by gene therapy. The invention also concerns Neublastin expression constructs which do not encode a pro-region of a Neublastin polypeptide, which expression construct result in increased secretion of bioactive Neublastin. The invention includes the delivery of Neublastin from transduced or transfected cells encapsulated into a macrocapsule with a semipermeable membrane. The invention further concerns mammalian cells capable of producing Neublastin in increased amounts.
Owner:NSGENE AS
Molecular chemotherapy enhancement of radiotherapy
InactiveUS6552005B1Tumour growth inhibitionCurrent is limitedBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsWhole bodyCytotoxicity
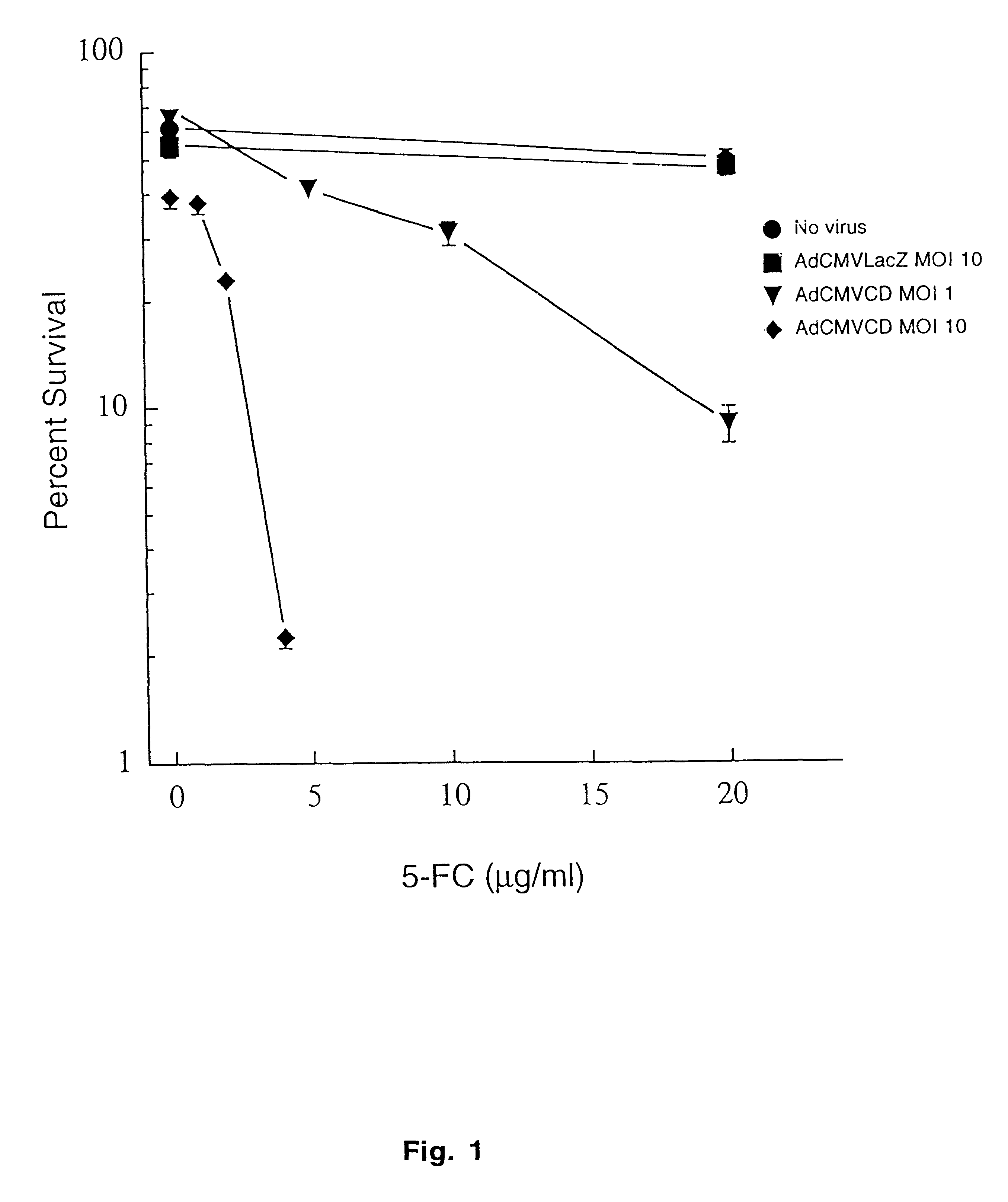
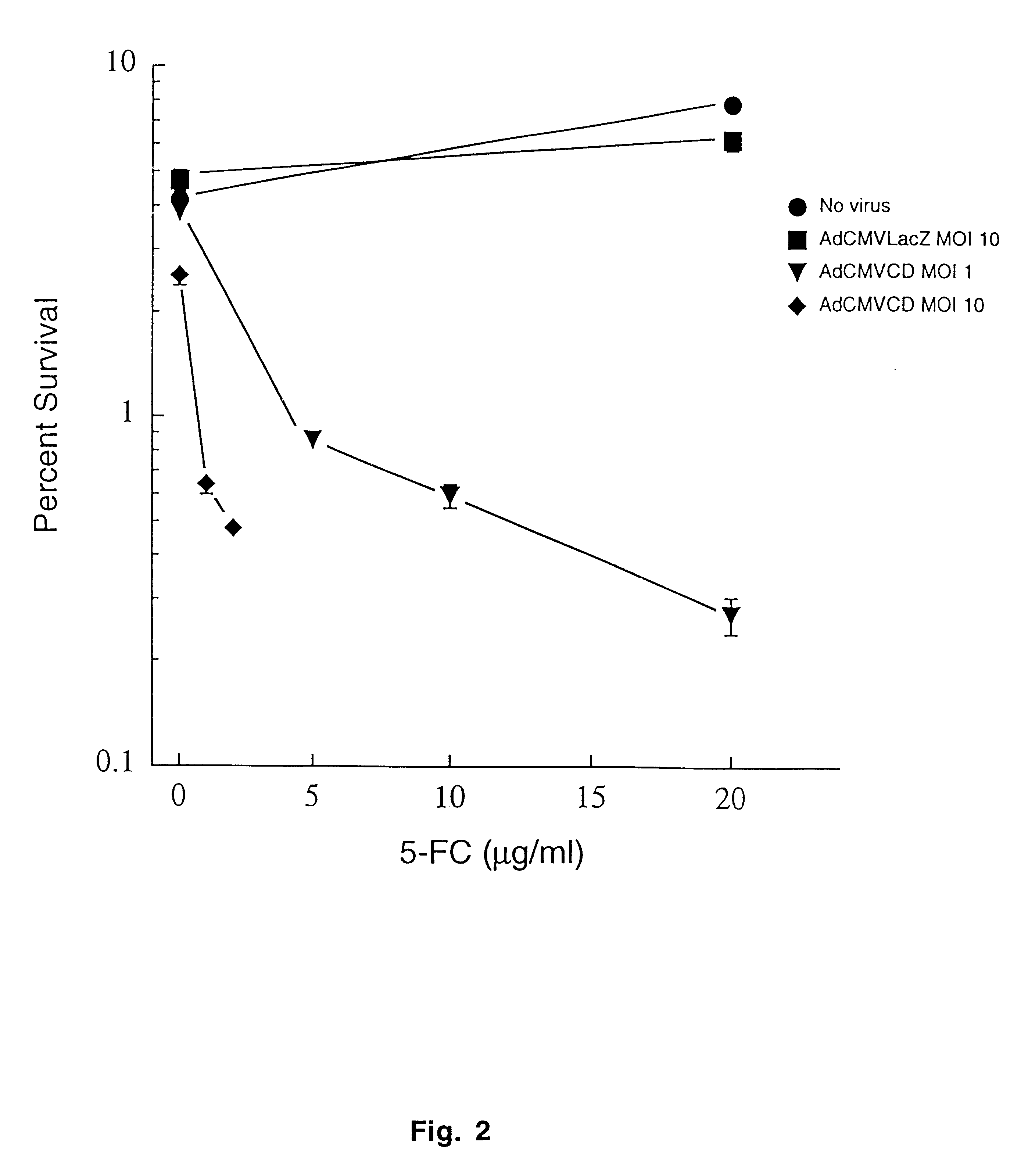
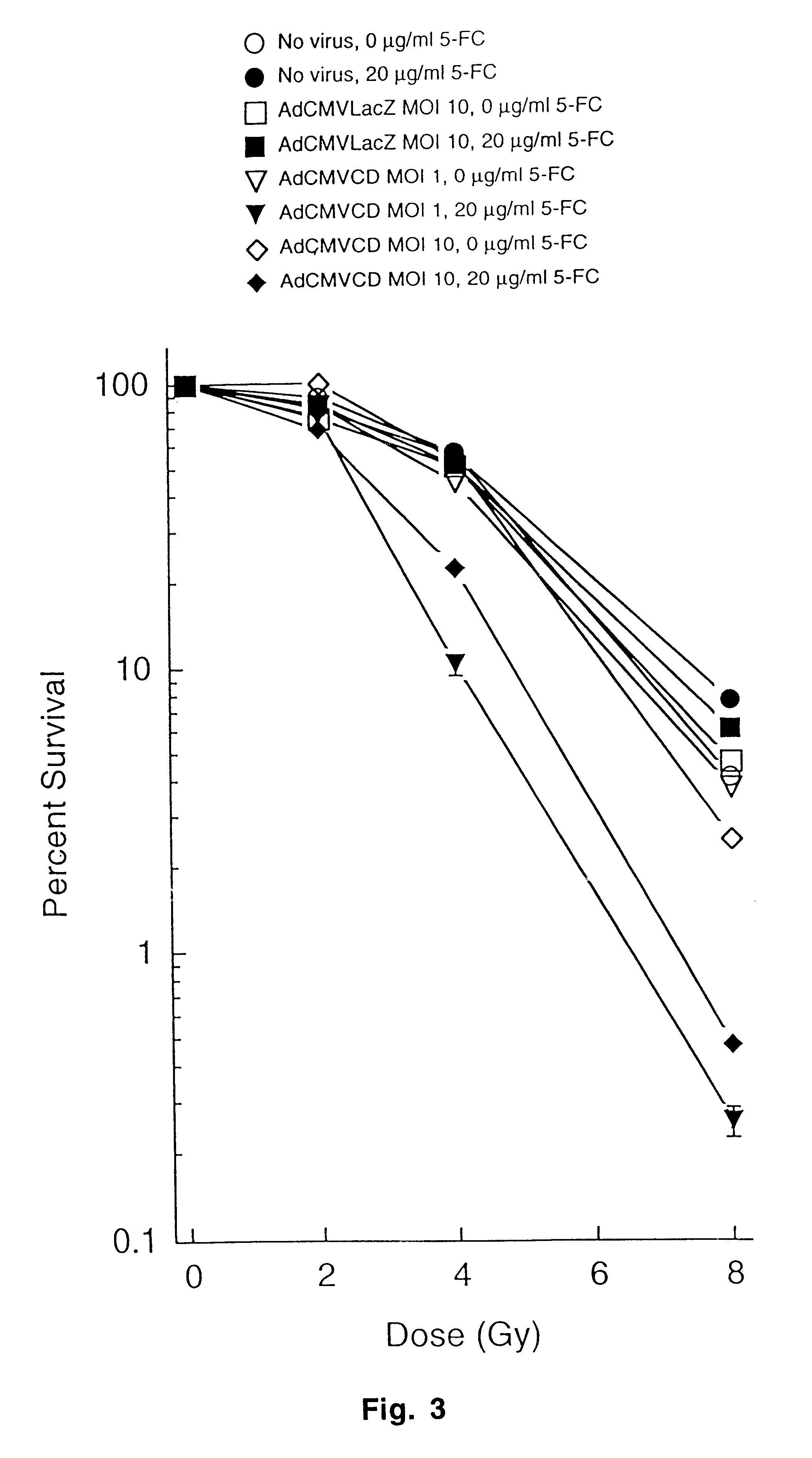
The present invention provides a new approach for cancer treatment by utilizing gene therapy combined with radiation therapy to enhance cytotoxicity in malignant cells. Specifically, the present invention demonstrates that molecular chemotherapy with the cytosine deaminase gene and 5-fluorocytosine is an effective radiosensitizing strategy which may lead to substantial improvement in tumor control, with less normal tissue toxicity than conventional systemic administration of 5-fluorouracil, that would translate into improved cure rates and better survival. A noninvasive method is described for continuous in vivo monitoring of 5-fluorouracil production via magnetic resonance spectroscopy. An adenovirus encoding cytosine deaminase gene which selectively replicates in tumor cells with a defective p53 pathway was constructed. Also provided is an adenovirus which encodes a fusion protein of cytosine deaminase and uracil phosphoribosyltransferase.
Owner:CDEPT
Methods to identify polynucleotide and polypeptide sequences which may be associated with physiological and medical conditions
InactiveUS20090304653A1Extend your lifePositive evolutionarily significant changeBiocideGenetic material ingredientsNucleotideTherapy related
Disclosed are methods to identify an agent which may modulate resistance to HIV-1-mediated disease, comprising contacting at least one agent to be tested with a cell comprising human ICAM-1, and detecting the cell's resistance to HIV-1 viral replication, propagation, or function, wherein an agent is identified by its ability to increase the cell's resistance to HIV-1 viral replication, propagation, or function. Also disclosed are human mutant ICAM-1 polypeptides and methods to treat HIV-1 viral replication, propagation, or function in a human subject by ICAM-1 gene therapy relating to one or more of the following 10 mutations to human ICAM-1: L18Q, K29D, P45G, R49W, E171Q, wherein the mutant ICAM-1 is otherwise identical to human ICAM-1.
Owner:EVOLUTIONARY GENOMICS LLC
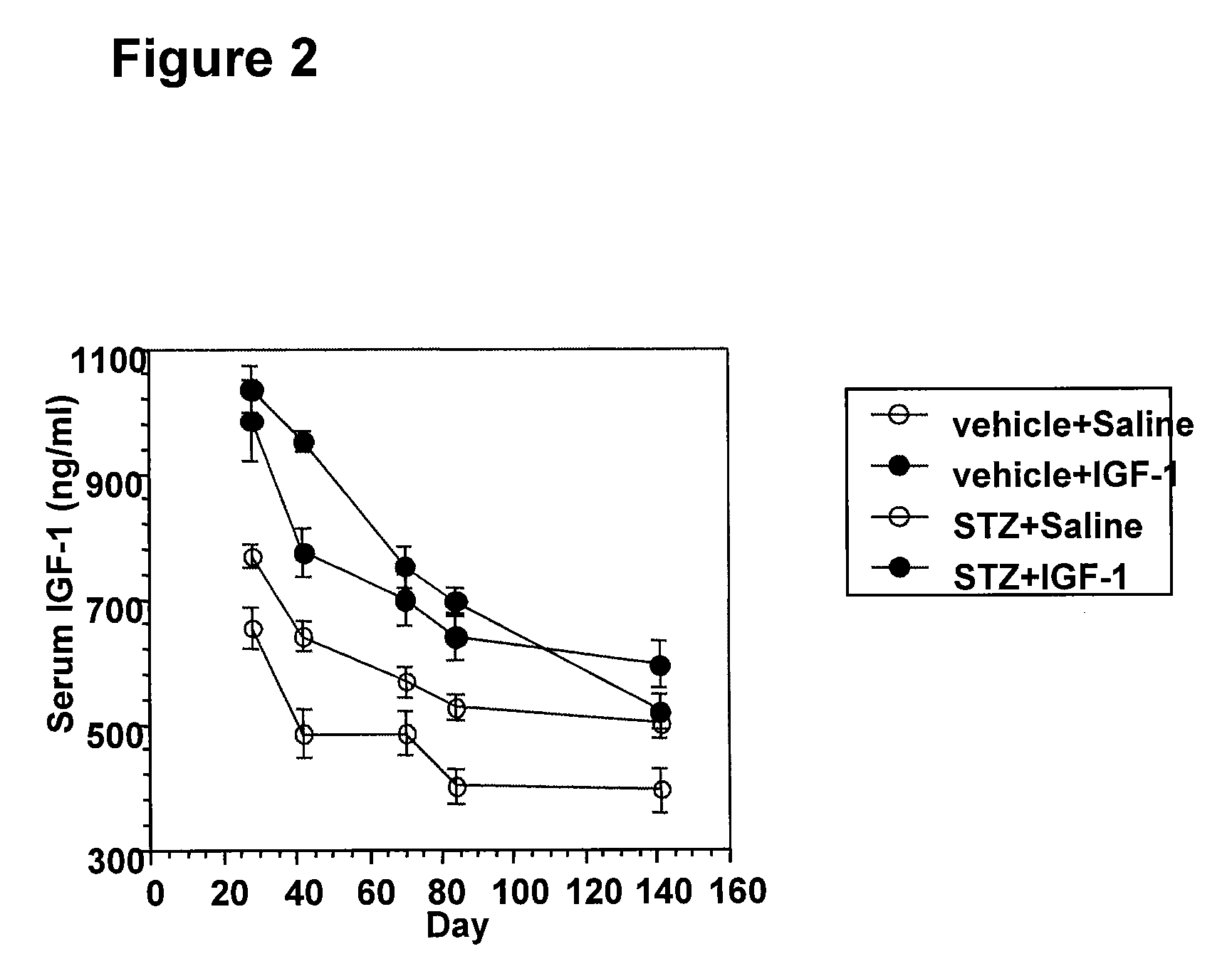
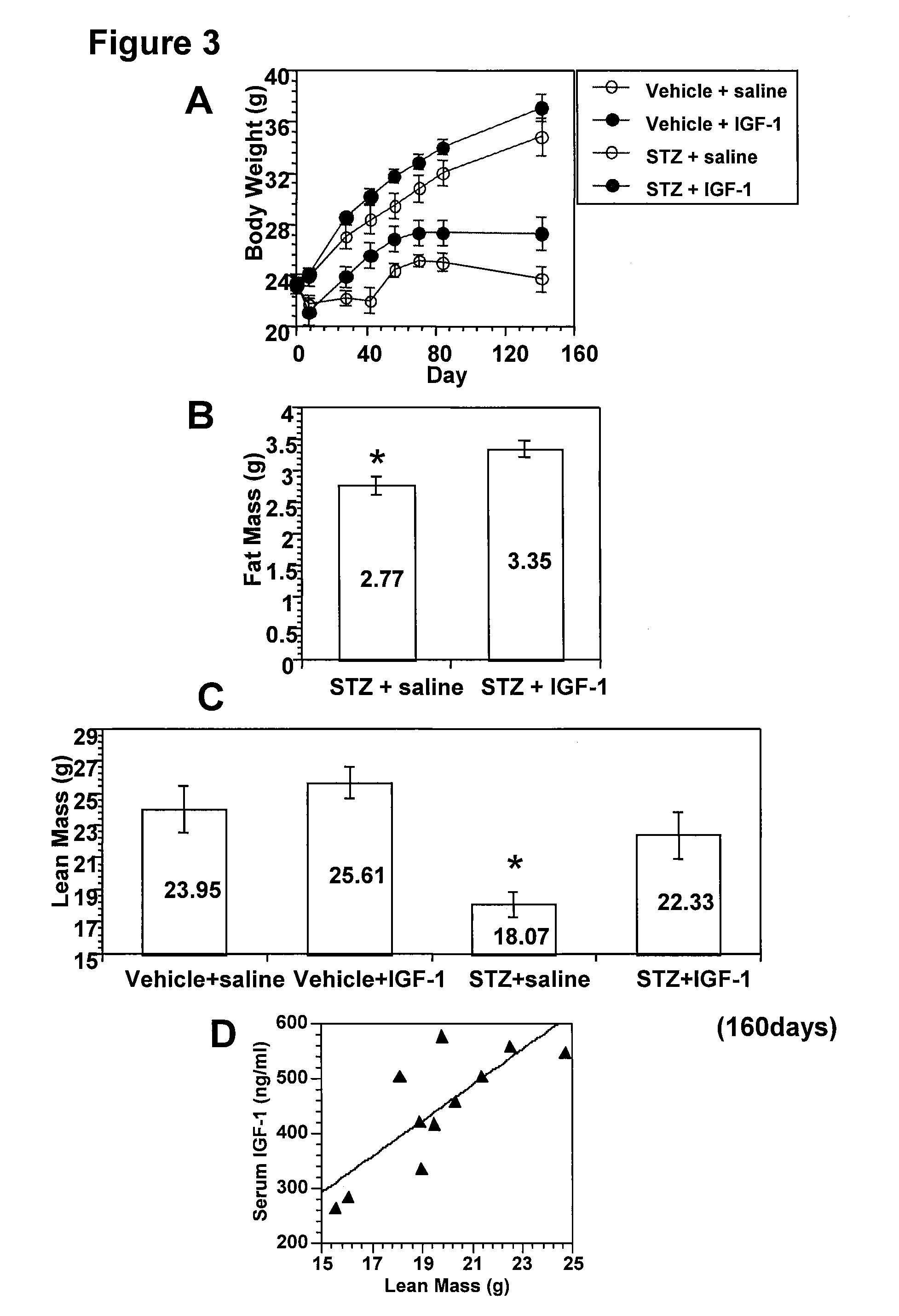
Systemic insulin-like growth factor-1 therapy reduces diabetic peripheral neuropathy and improves renal function in diabetic nephropathy
InactiveUS20100216709A1Prevents subsequent hyposensitivityEasy maintenanceOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderInsulin-like growth factorHyperglycemic disorder
The present invention provides methods of treatment of patients suffering from the complications of blood sugar disorders: diabetic peripheral neuropathy and diabetic nephropathy by administration of IGF-1 via protein therapy or gene therapy. It relates to methods of treating an individual having a diabetic disorder or a hyperglycemic disorder, comprising administering to the individual an effective amount of a DNA vector expressing IGF-1Eb or IGF-1Ec in vivo or an effective amount of at the IGF-1Eb or IGF-1Ec protein in the early hyperalgesia stage or in patients that have advanced to the hyposensitivity stage. Treatment at the early hyperalgesia stage prevents subsequent hyposensitivity with increases or maintenance of sensory nerve function. IGF-1Eb or IGF-1Ec treatment also increases muscle mass and improves overall mobility, which indicates a treatment-related improvement in motor function. Treatment with IGF-1Eb or IGF-1Ec at the hyposensitivity stage reverses hyposensitivity and improves muscle mass and overall health. Systemic IGF-1 provides a therapeutic modality for treating hyposensitivity associated with DPN. In addition, IGF-1Eb or IGF-1Ec provides a therapeutic modality for treating diabetic nephropathy. IGF-1Eb or IGF-1Ec improves renal function as evidenced by a modulation in serum albumin concentration and a reduction in urine volume and protein levels. IGF-1Eb or IGF-1Ec also reduces diabetic glomerulosclerosis.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Method of preparing hydroxyapatite based drug delivery implant for infection and cancer treatment
InactiveUS20070190102A1Sustained releaseLow effective dosePharmaceutical containersPretreated surfacesDiseaseAnticarcinogen
A bioresorbable material is incorporated with bioactive agents to form an implant used for treatment against hard tissue or soft tissue defects and diseases. Antibiotics or anti-cancer agents are incorporated to treat hard or soft tissue infections or cancers. Sustained release of the bioactive agents or drug molecules may be achieved after implantation at the targeted sites. The dosage of the active agents or molecules, the microstructure, morphology, and composition of the bioresorbable material allow control of the release profile. The invented implant may be used for drug delivery, chemotherapy, or gene therapy. Various microstructure and the morphologies of the implants are injectable like putty or shaped with multilayers.
Owner:LUO PING
Compositions and methods for therapeutic use
The present invention is directed to compositions and methods of treating cancer by gene therapy using a therapeutic gene formulated in a buffer comprising a delivery-enhancing agent. The delivery-enhancing agents of the invention can be used to formulate therapeutic or diagnostic agents, such as proteins, nucleic acids, antisense RNA, small molecules, etc., for administration to any tissue or organ having an epithelial membrane. The delivery-enhancing agents include detergents, alcohols, surfactants and other molecules.
Owner:CANJI +1
Enrichment method of virus
InactiveUS20110053250A1Maintaining their infection abilityImprove concentrationBiological material analysisRecovery/purificationEnrichment methodsViral vector
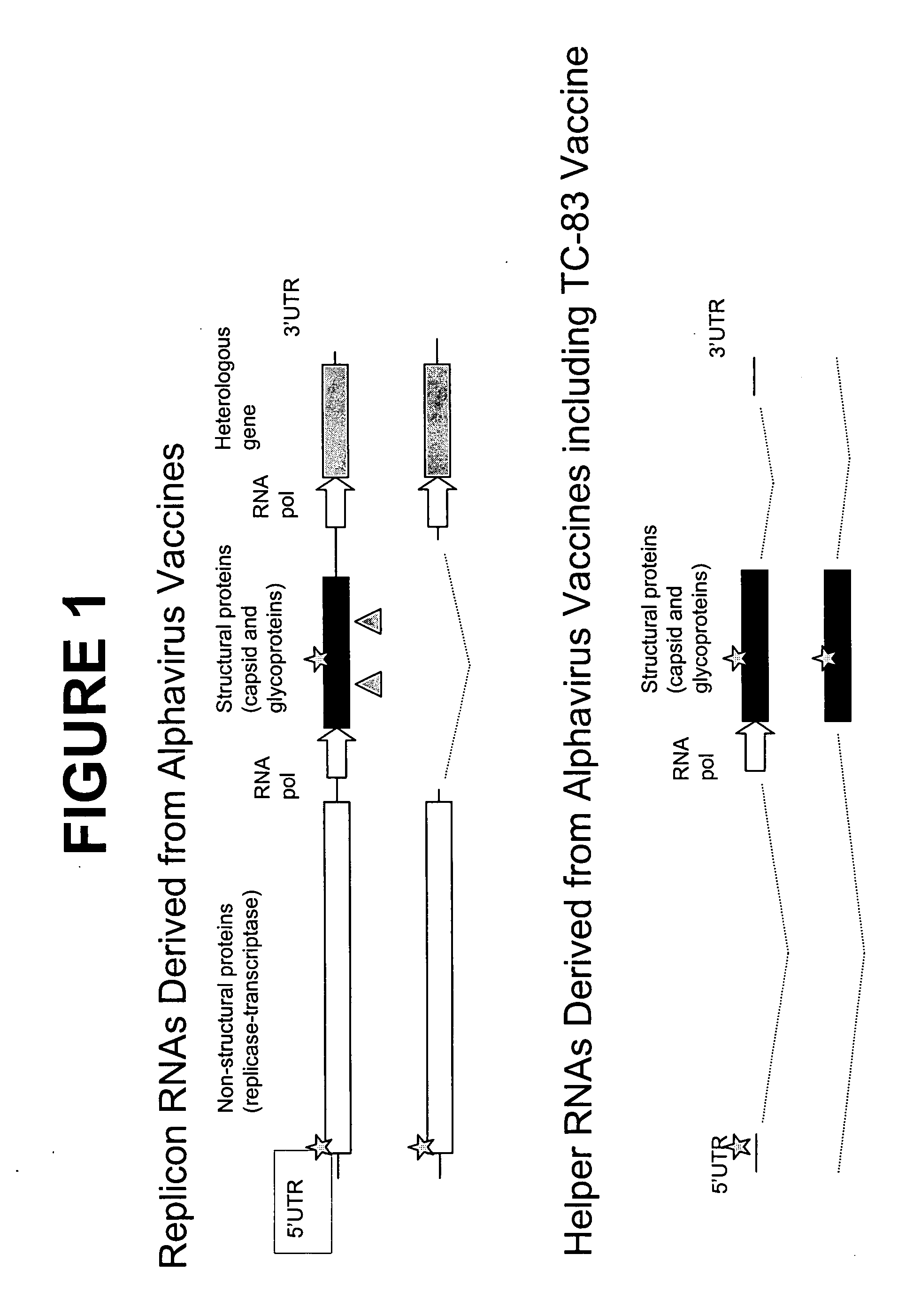
The present invention provides a novel method that can increase readily a virus or viral vector concentration in a solution having a low concentration and a kit for performing the method. Conventional methods require complicated operations, expensive equipment, or highly trained experts for efficiently concentrating viruses from low-concentration virus solutions. The method of the present invention can concentrate viral vectors readily while maintaining infection abilities of the viral vectors, and thus it can be used as a safe and simple technique for concentrating a vector useful in the field of a genetic therapy or a vaccine therapy using a viral vector.
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC +1
Use of the sodium iodine symporter to effect uptake of iodine
The present invention relates to the use of gene therapy to introduce an iodine symporter into cell to increase iodine uptake therein. This approach has particular utility in the treatment of cancers that incapable of removing iodine. In addition, strategies are provided for reducing the export of sodium from cells to improve the efficacy of the iodine symporter gene therapy.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
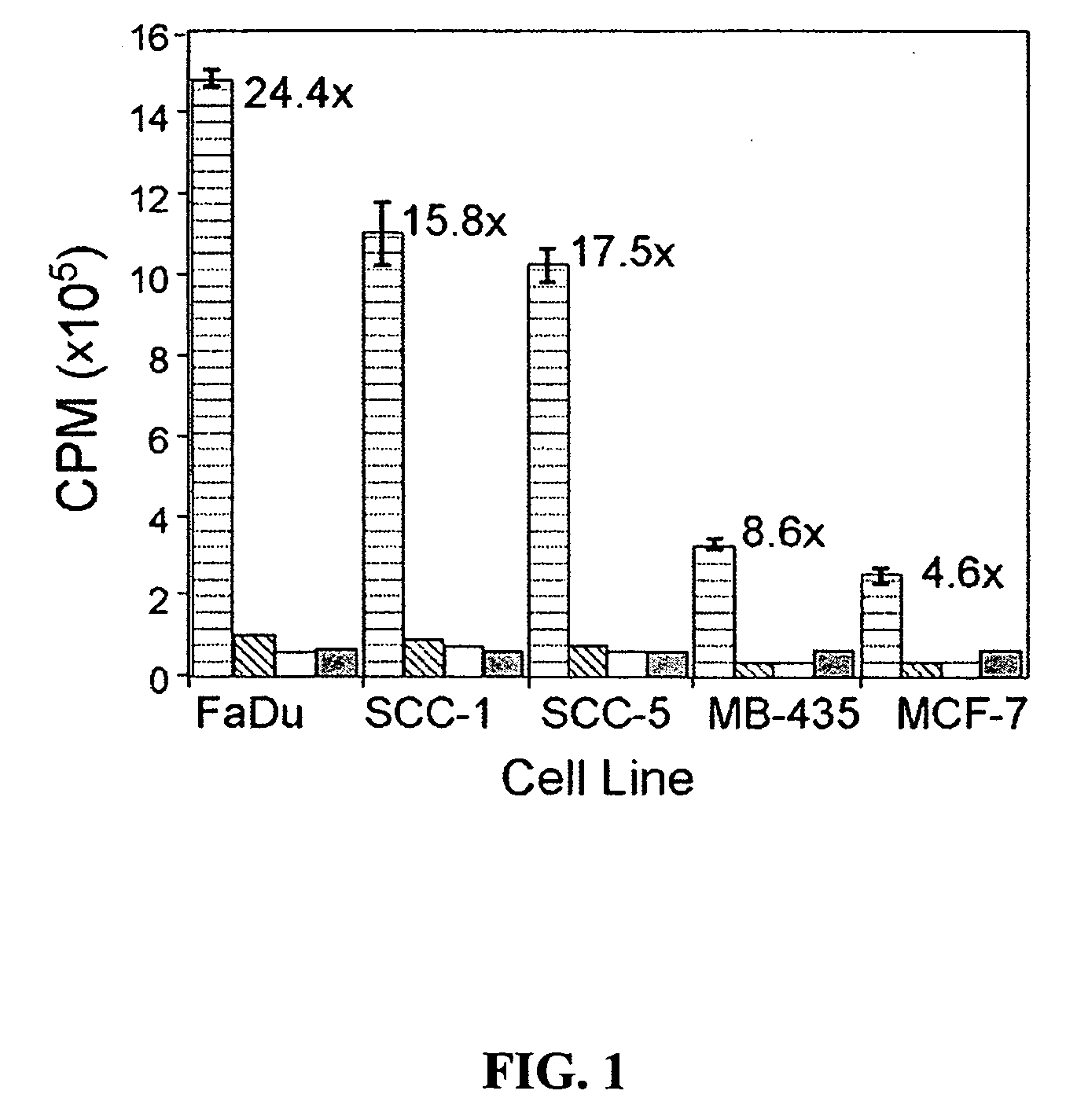
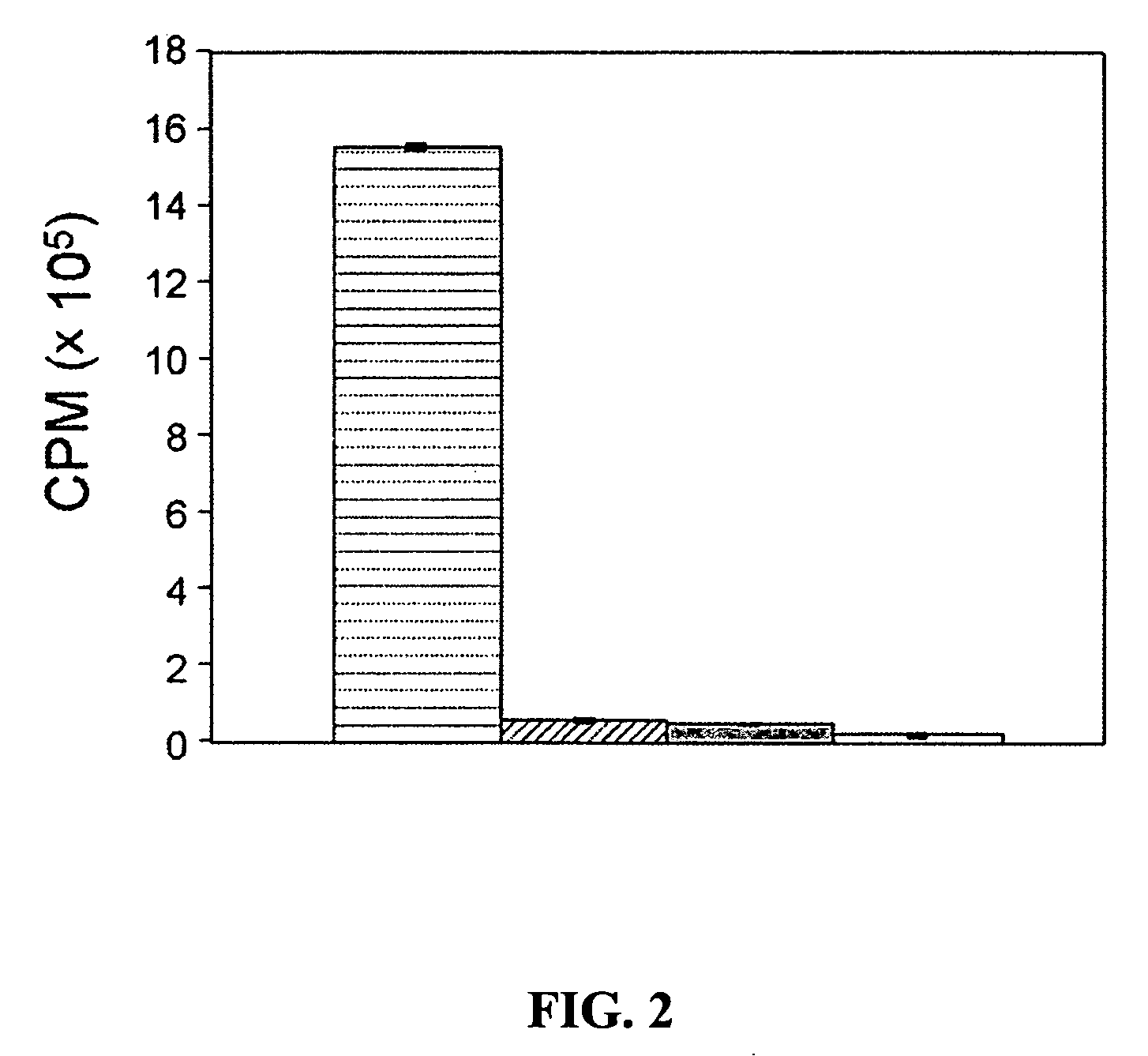
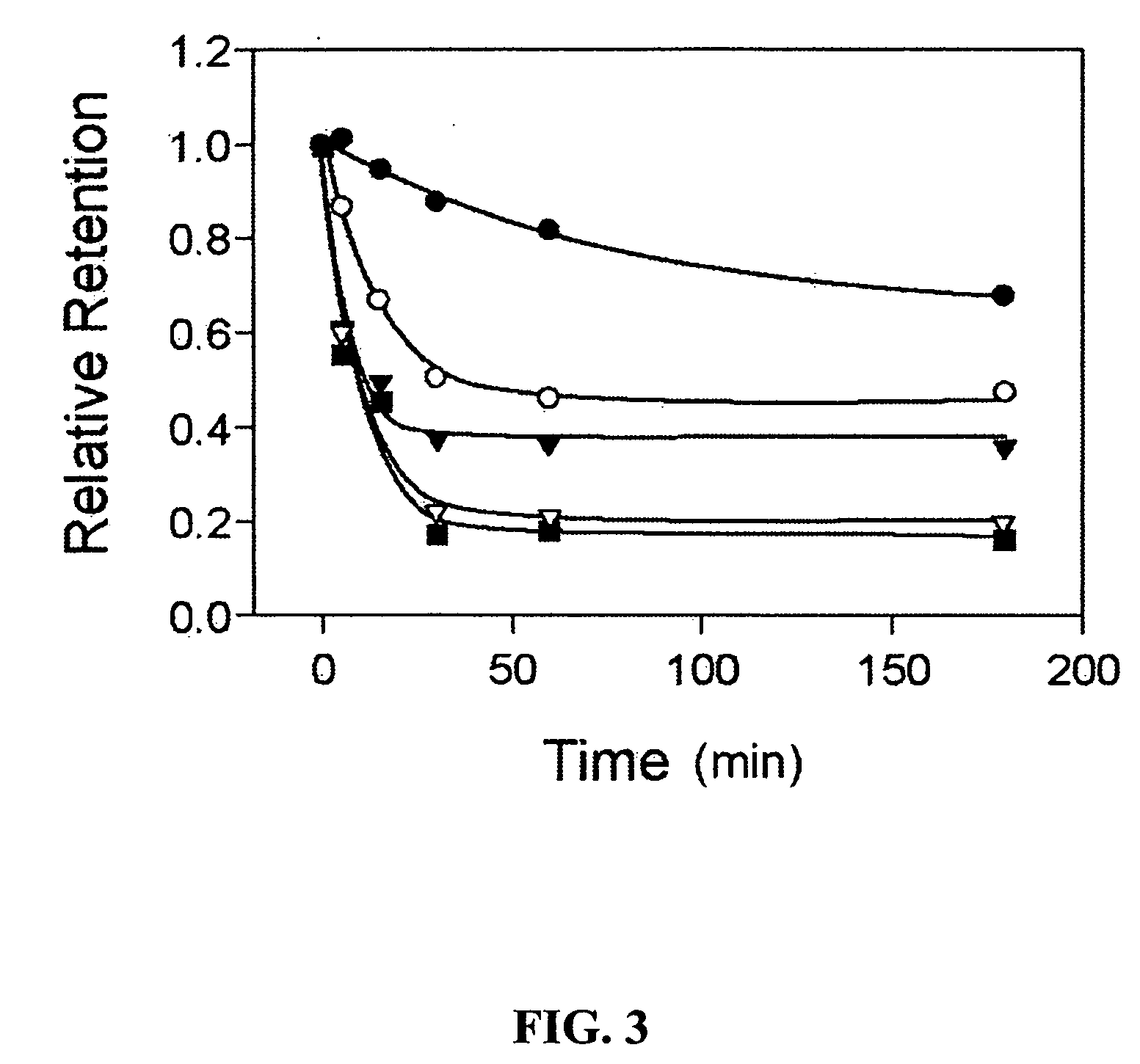
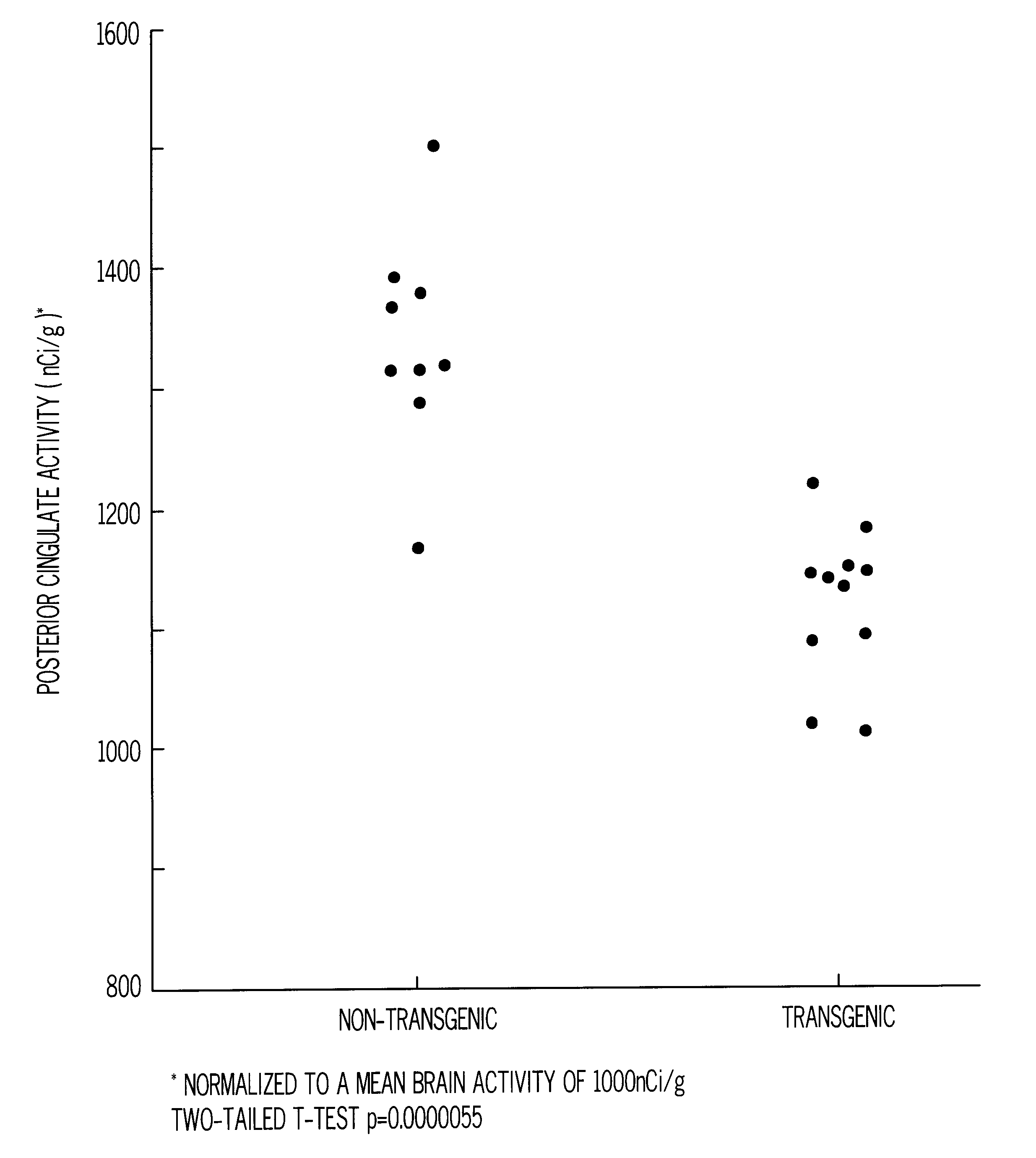
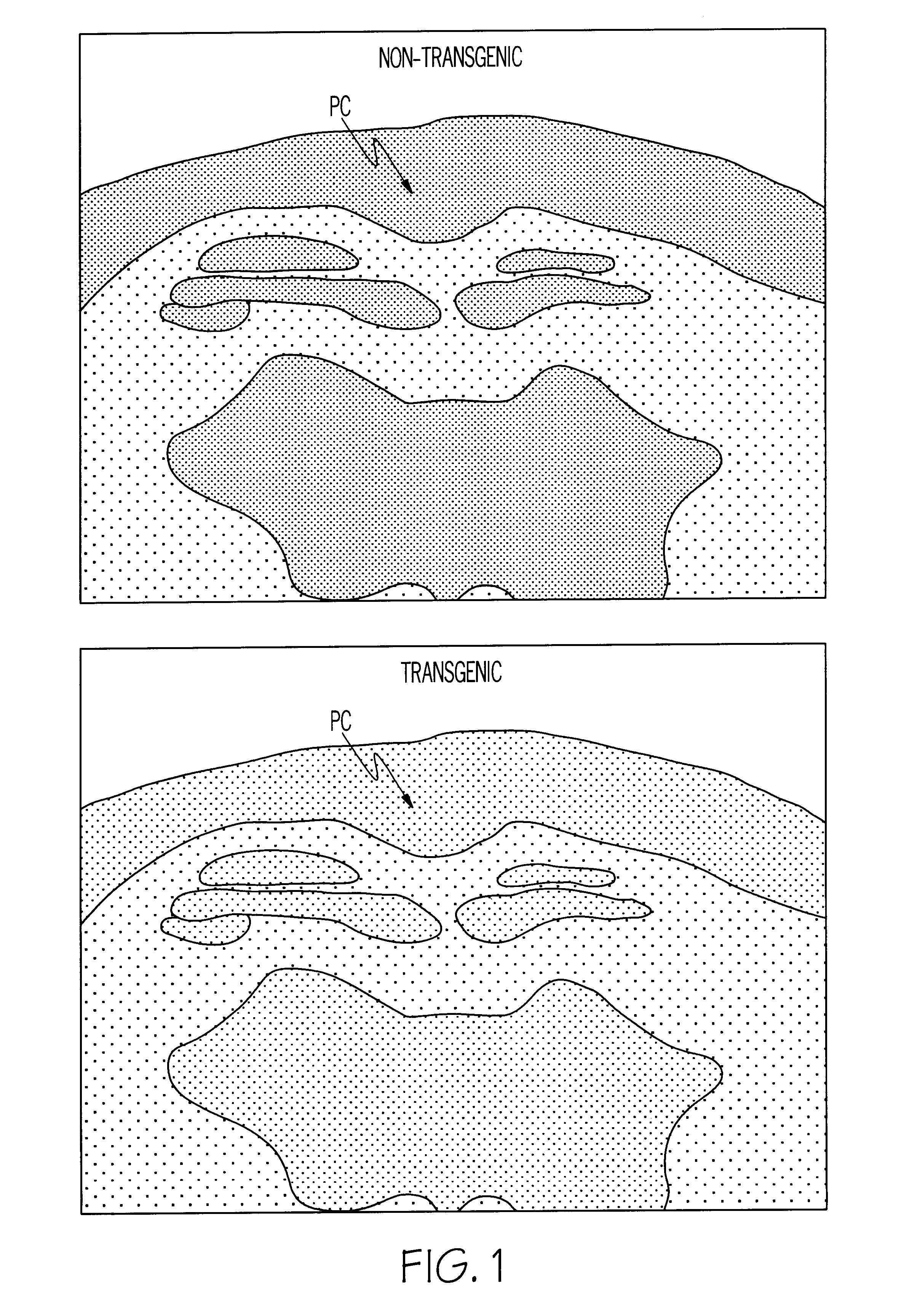
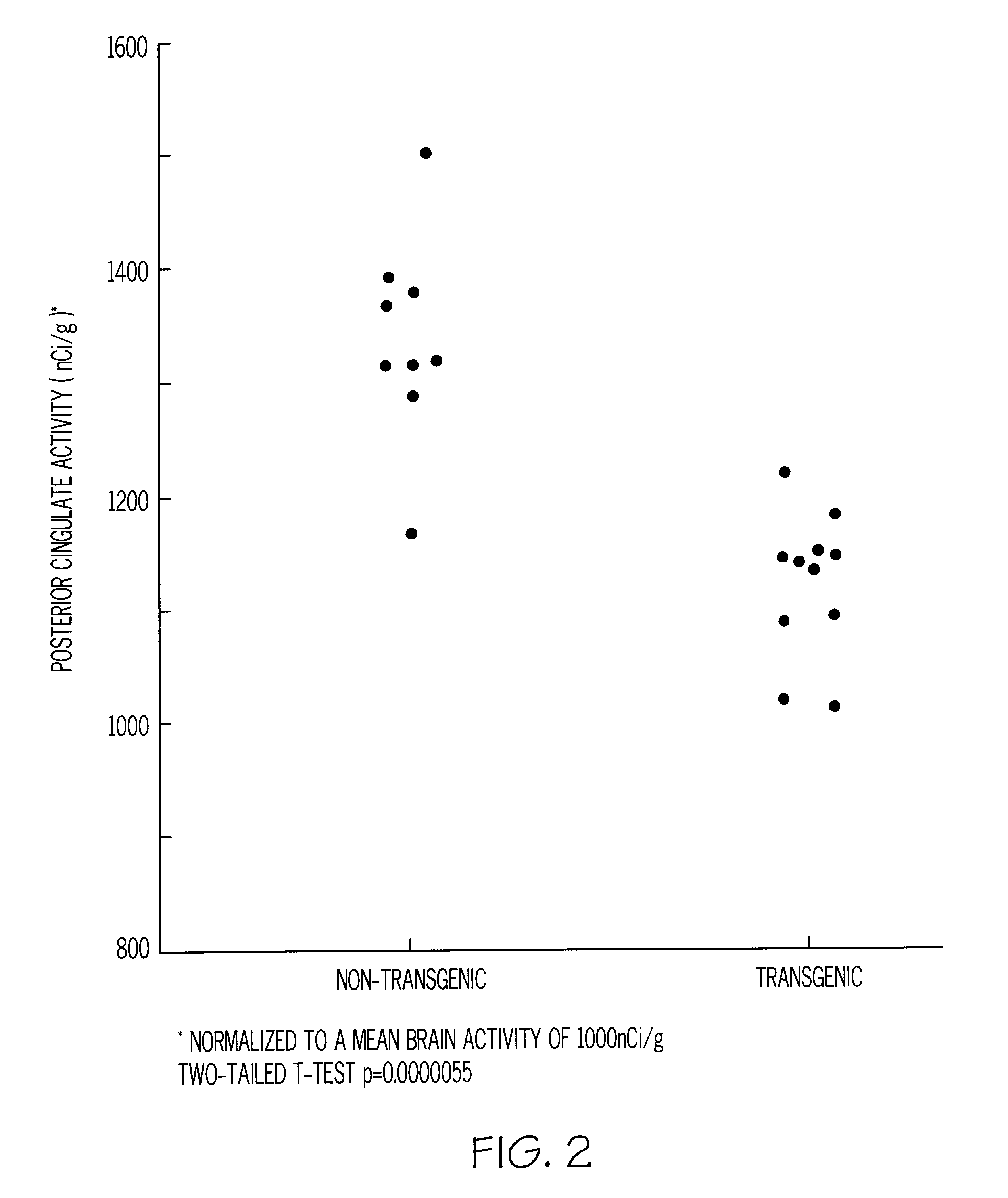
Methods for tracking the progression of Alzheimer's disease identifying treatment using transgenic mice
InactiveUS6374130B1Decrease the declinationDecrease declinationTissue cultureDiagnostic recording/measuringDietary supplementTransgene
A method of screening pharmaceutical drugs, gene therapies, vaccines, dietary supplements, behavioral and environmental therapies and other clinical treatments for potential efficacy in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease in humans. The method includes selecting transgenic mice that are genetically altered for Alzheimer's disease and using measurement and / or imaging techniques to determine the activity level of the posterior cingulate region of the brains of the mice after treatment. Based on these measurements and comparisons to a control group, the effectiveness of the treatment in arresting or reversing Alzheimer's disease in mice can be determined, and the treatment can be identified as a promising candidate for human trials.
Owner:REIMAN ERIC M
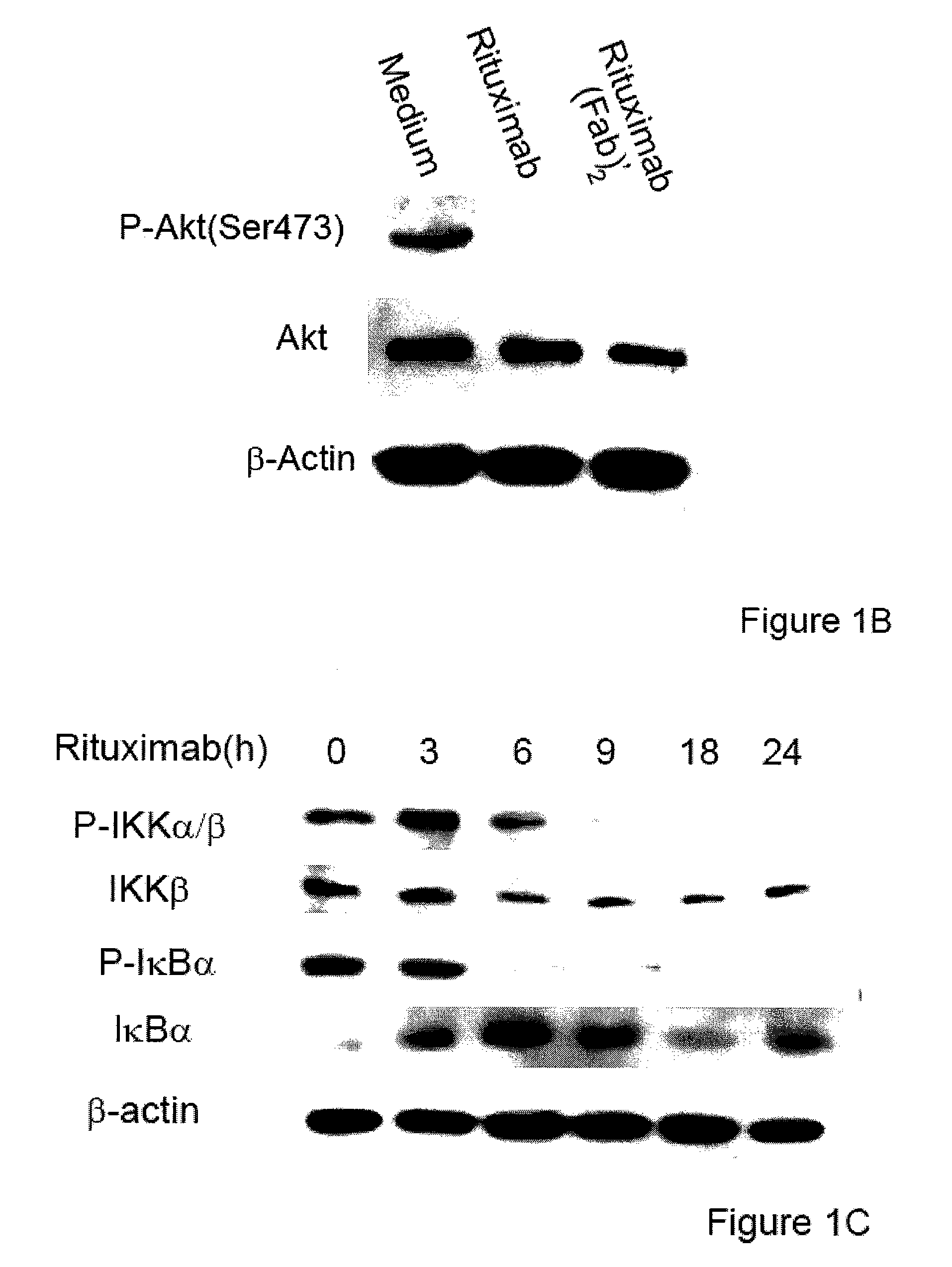
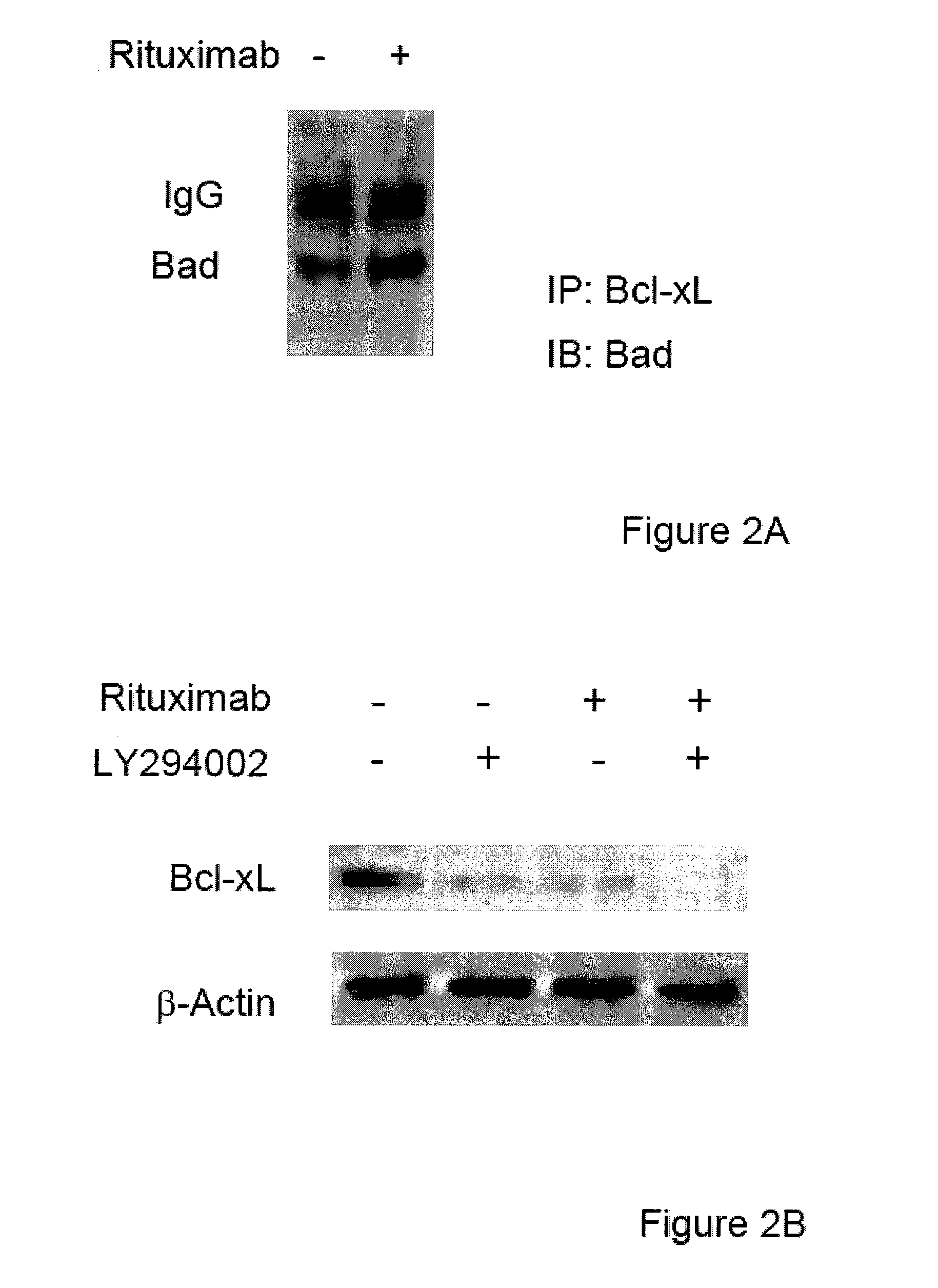
Molecular signaling pathways triggered by rituximab: prognostic, diagnostic, and therapeutic uses
InactiveUS20070172847A1RegulateRegulate the cancer cells' sensitivity to immunotherapyMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisAutoimmune conditionCancer cell
The present invention provides markers associated with activated molecular signaling pathways (example: p38 MAKP, NF-κB, ERK1 / 2, YY-1 and AKT) inhibited by rituximab in cancer cells as well as pathways activated by rituximab (such as death receptors, RKIP, PTEN) all of which are associated with the regulation of chemo and immunoresistance. The present invention provides methods of prognosis and providing a prognosis for cancer such as lymphoma, leukemia, and autoimmune disease, as well as, methods of drug discovery. These markers are also therapeutic targets for treatment of cancer resistant to conventional and experimental cancer therapeutics. Inhibition or activation of expression and / or activity of targeted gene products sensitizes resistant tumor cells to subtoxic doses of cytotoxic treatment including chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or immunotherapy and gene therapy, and the cytotoxic molecules.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Secretion of neublastin
InactiveUS7601518B2Increase secretionReduce the possibilitySenses disorderNervous disorderPro regionNervous system
The present invention concerns improved methods and compositions for producing a Neublastin polypeptide as well as local delivery of Neublastin to specific regions of the nervous system including the central nervous system and the eye for example by gene therapy. The invention also concerns Neublastin expression constructs which do not encode a pro-region of a Neublastin polypeptide, which expression construct result in increased secretion of bioactive Neublastin. The invention includes the delivery of Neublastin from transduced or transfected cells encapsulated into a macrocapsule with a semipermeable membrane. The invention further concerns mammalian cells capable of producing Neublastin in increased amounts.
Owner:NSGENE AS
Antiviral therapy on the basis of RNA interference
InactiveUS20050182010A1Inhibition of replicationGenetic material ingredientsViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsDouble strandBiology
The invention concerns a gene therapy for treatment of animals and humans which suffer from an infection with a chronic virus such as HIV or HCV. It can also be used prophylactically to prevent chronic infection. The therapy makes use of a nucleotide construct stably integrated in the genome of the target cells of the virus, which is able to produce a single transcript or multiple transcripts capable of forming a double-stranded RNA which inhibits replication of the virus in situ.
Owner:VIRUVATION BV
Genetically engineered lymphocyte targeting Human EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor), preparation method and application of genetically engineered lymphocyte
ActiveCN103113470AGood effectInhibit tumor formationGenetic material ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsSingle-Chain AntibodiesTumor antigen
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering, and in particular relates to an anti-EGFR ((Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor) chimeric antigen receptor, and a lymphocyte for expressing the antigen receptor. The technical solution of the invention provides a new effective selection for the anti-tumor technical field. The technical scheme is that a single-chain antibody targeting the EGFR is provided. The single-chain antibody is further designed to be constructed into the chimeric antigen receptor by means of a genetic engineering technology, and the structure of the gained chimeric antigen receptor is anti-EGFR (scFv)-IgG2 (Fc)-CD28-CD3 Zeta. According to the genetically engineered lymphocyte targeting the human EGFR, the chimeric antigen receptor is transfected into the lymphocyte by the nucleofaction technology, and thus the nonspecific lymphocyte can be endowed with the capacity of specifically distinguishing the EGFR tumor antigen and targeting and killing the EGFR over-expression tumor cells. According to the technical scheme, the adoptive cell therapy and the genetic therapy are organically combined, so that remarkable effect of killing the tumor is gained, and a novel effective selection is provided for the field.
Owner:WEST VAC BIOPHARMA CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com