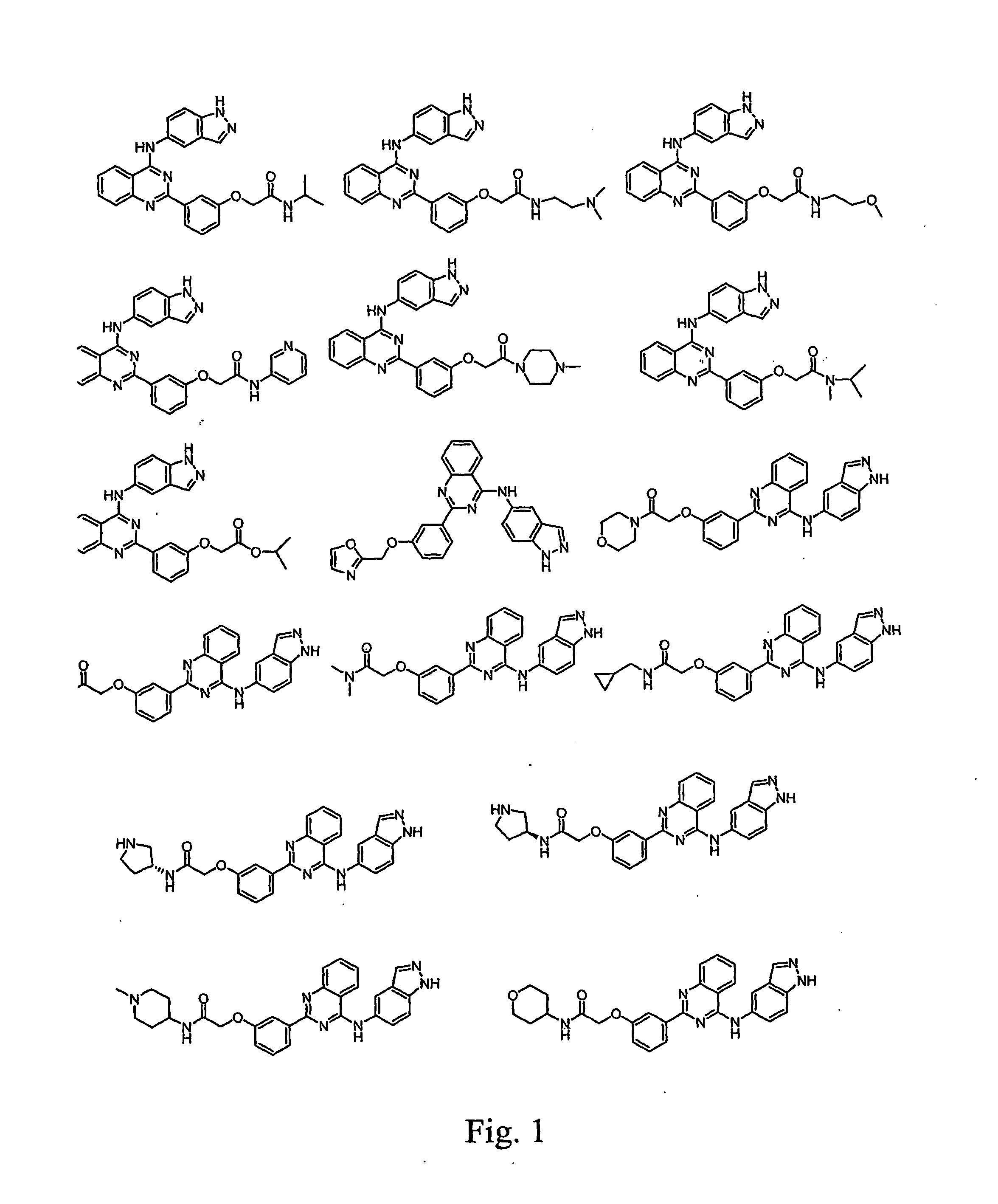Patents
Literature
1098 results about "Pharmacodynamics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of the biochemical and physiologic effects of drugs (especially pharmaceutical drugs). The effects can include those manifested within animals (including humans), microorganisms, or combinations of organisms (for example, infection). Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics are the main branches of pharmacology, being itself a topic of biology interested in the study of the interactions between both endogenous and exogenous chemical substances with living organisms.
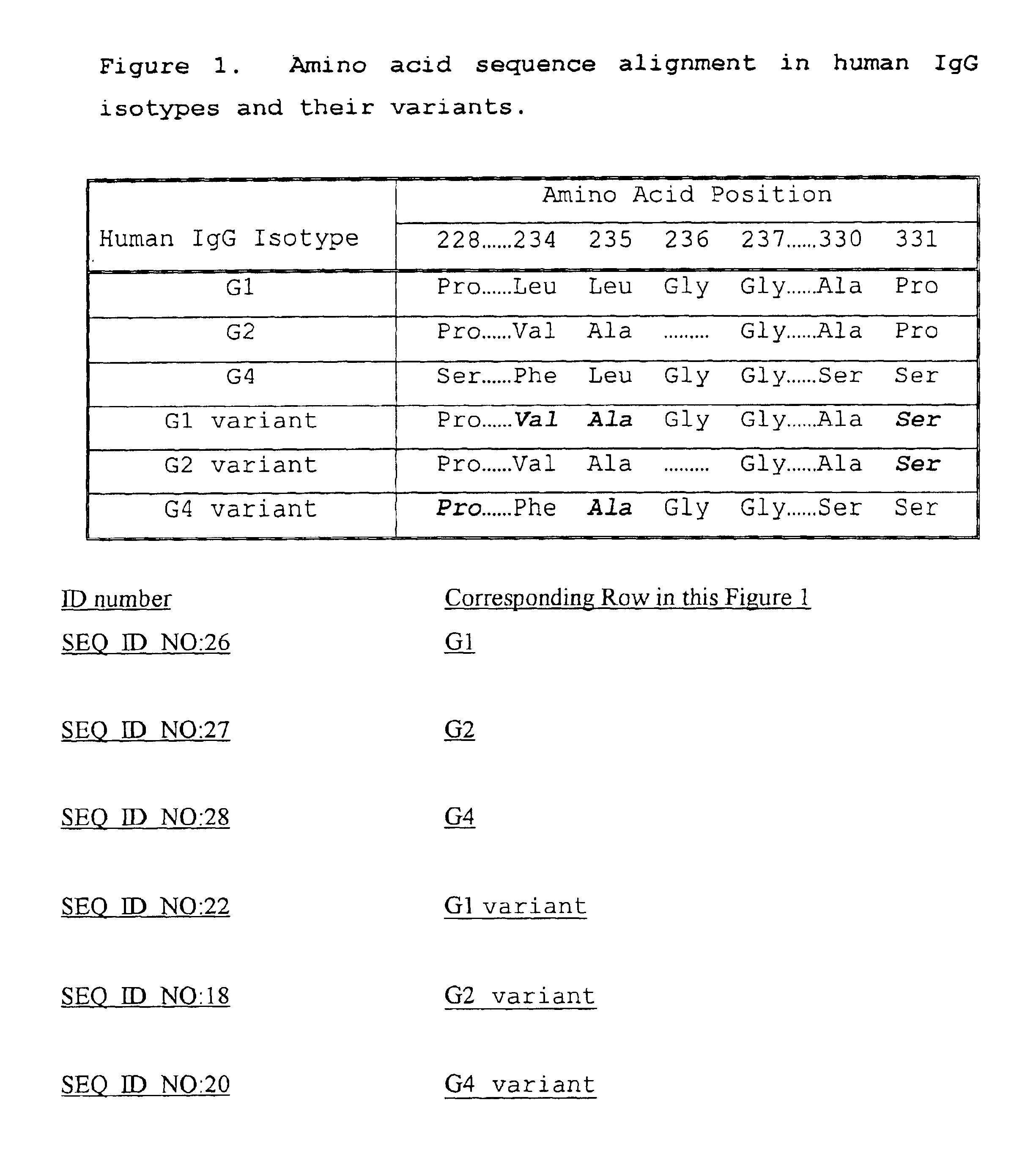
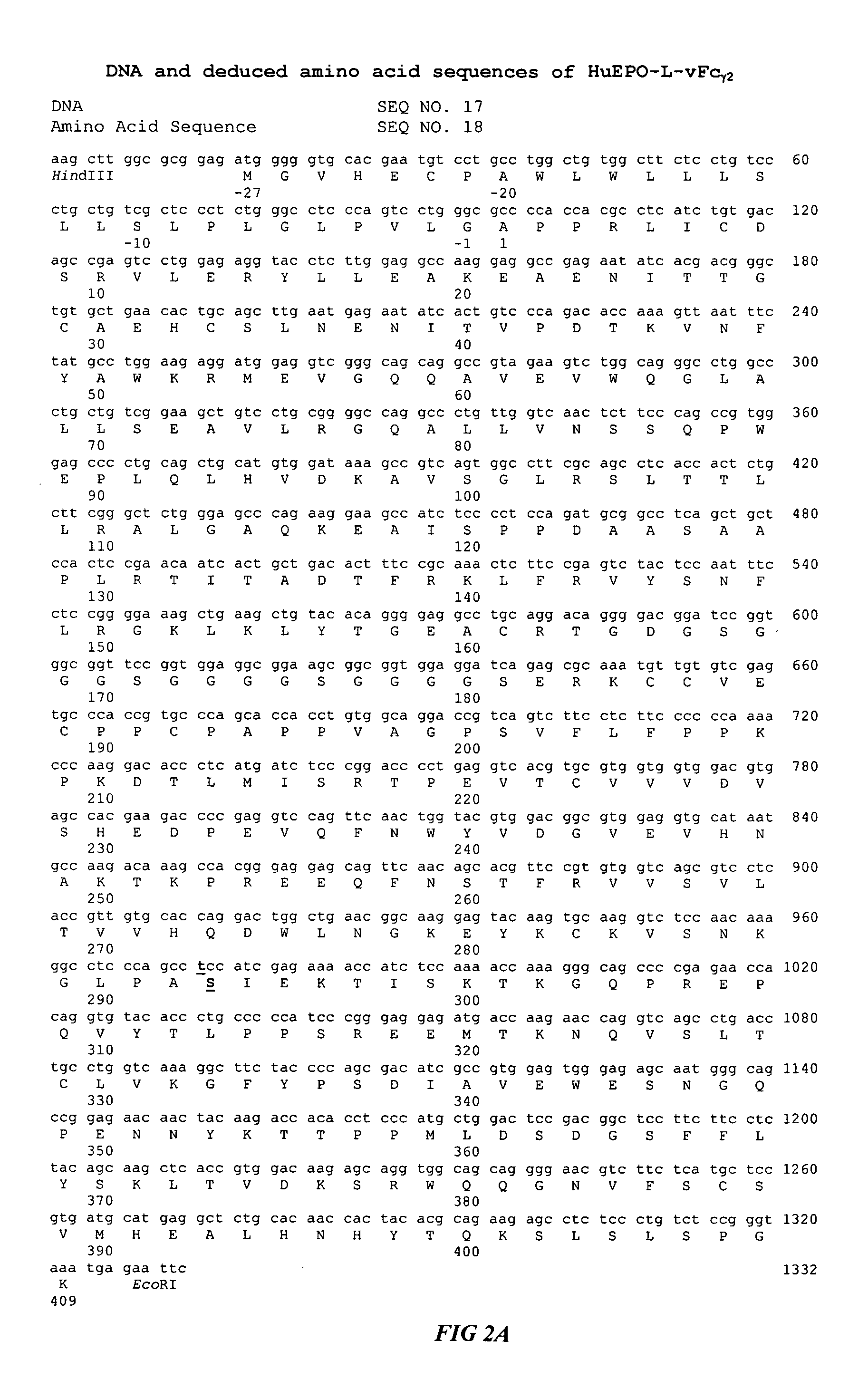
Fc fusion proteins of human erythropoietin with increased biological activities
InactiveUS6900292B2Improve biological activityExtended serumPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSide effectHalf-life
Fc fusion proteins of human EPO with increased biological activities relative to rHuEPO on a molar basis are disclosed. The HuEPO-L-vFc fusion protein comprises HuEPO, a flexible peptide linker of about 20 or fewer amino acids, and a human IgG Fc variant. The Fc variant is of a non-lytic nature and shows minimal undesirable Fc-mediated side effects. A method is also disclosed to make or produce such fusion proteins at high expression levels. Such HuEPO-L-vFc fusion proteins exhibit extended serum half-life and increased biological activities, leading to improved pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, thus fewer injections will be needed within a period of time.
Owner:LONGBIO PHARM (SUZHOU) CO LTD
System and method for integrating and validating genotypic, phenotypic and medical information into a database according to a standardized ontology
InactiveUS20070178501A1Safest and most effective treatmentGood decisionData processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementData validationMedical record
The system described herein enables clinicians and researchers to use aggregated genetic and phenotypic data from clinical trials and medical records to make the safest, most effective treatment decisions for each patient. This involves (i) the creation of a standardized ontology for genetic, phenotypic, clinical, pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic and other data sets, (ii) the creation of a translation engine to integrate heterogeneous data sets into a database using the standardized ontology, and (iii) the development of statistical methods to perform data validation and outcome prediction with the integrated data. The system is designed to interface with patient electronic medical records (EMRs) in hospitals and laboratories to extract a particular patient's relevant data. The system may also be used in the context of generating phenotypic predictions and enhanced medical laboratory reports for treating clinicians. The system may also be used in the context of leveraging the huge amount of data created in medical and pharmaceutical clinical trials. The ontology and validation rules are designed to be flexible so as to accommodate a disparate set of clients. The system is also designed to be flexible so that it can change to accommodate scientific progress and remain optimally configured.
Owner:NATERA
Fc fusion proteins of human erythropoietin with increased biological activities
InactiveUS20050124045A1Improve biological activityExtended serumPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSide effectHalf-life
Fc fusion proteins of human EPO with increased biological activities relative to rHuEPO on a molar basis are disclosed. The HuEPO-L-vFc fusion protein comprises HuEPO, a flexible peptide linker of about 20 or fewer amino acids, and a human IgG Fc variant. The Fc variant is of a non-lytic nature and shows minimal undesirable Fc-mediated side effects. A method is also disclosed to make or produce such fusion proteins at high expression levels. Such HuEPO-L-vFc fusion proteins exhibit extended serum half-life and increased biological activities, leading to improved pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, thus fewer injections will be needed within a period of time.
Owner:SUN LEE HWEI K +2
Compound for detecting and modulating RNA activity and gene expression
InactiveUS6262241B1Tightly boundEfficient executionSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsBond cleavageMinor groove
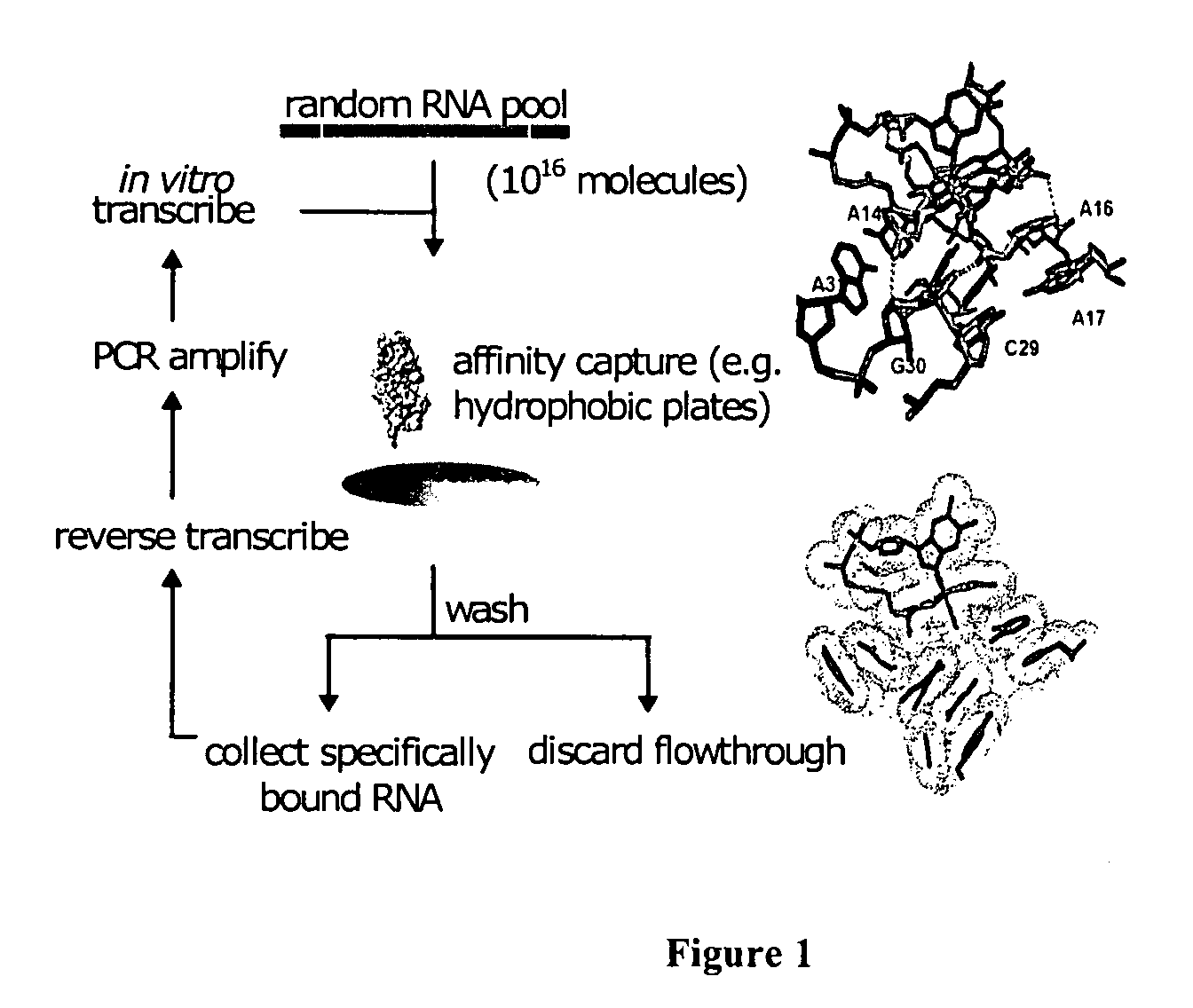
Compositions and methods for modulating the activity of RNA and DNA are disclosed. In accordance with preferred embodiments, antisense compositions are prepared comprising targeting and reactive portions. Reactive portions which act, alternatively, through phosphorodiester bond cleavage, through backbone sugar bond cleavage or through base modification are preferrably employed. Groups which improve the pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties of the oligonucleotides are also useful in accordance with certain embodiments of this invention. Delivery of the reactive or non-reactive functionalities into the minor groove formed by the hybridization of the composition with the target RNA is also preferrably accomplished. Therapeutics, diagnostics and research methods and also disclosed. Synthetic nucleosides and nucleoside fragments are also provided useful for elaboration of oligonucleotides and oligonucleotide analogs for such purposes.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
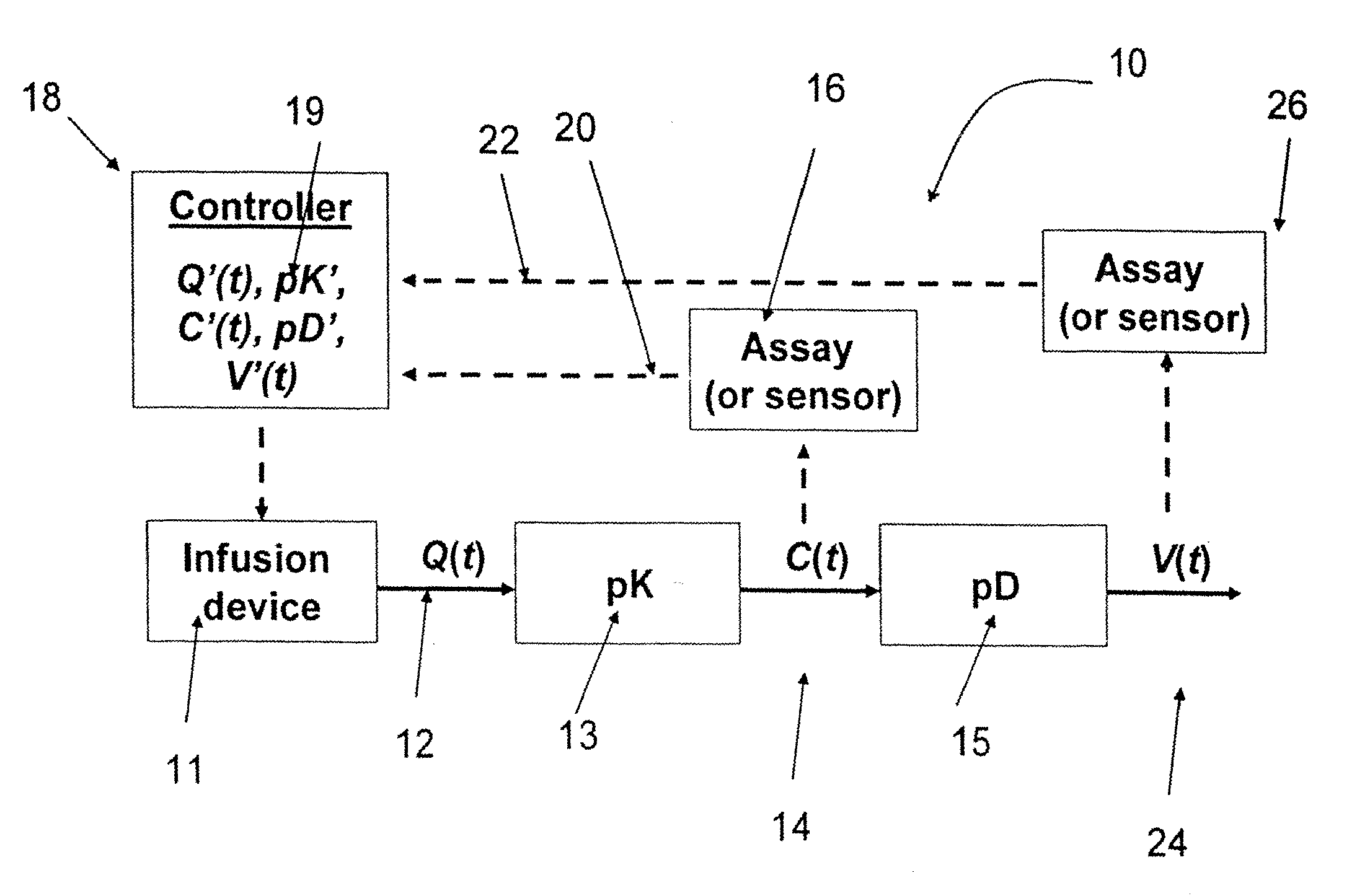
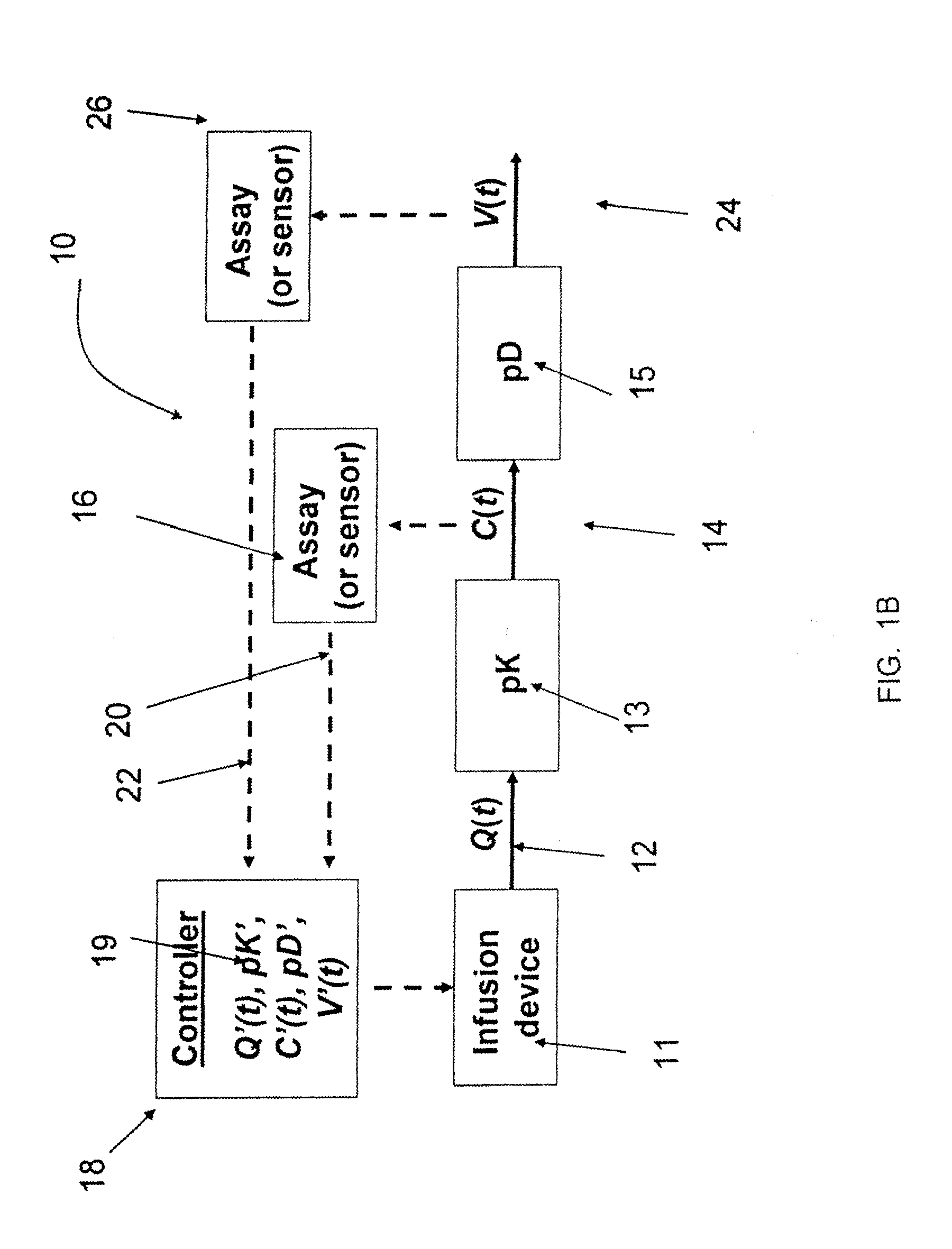
Intelligent Drug and/or Fluid Delivery System to Optimizing Medical Treatment or Therapy Using Pharmacodynamic and/or Pharamacokinetic Data
ActiveUS20130296823A1Improve securityStrengthen security controlData processing applicationsDrug and medicationsPharmacodynamic StudyDelivery system
Owner:XHALE ASSURANCE INC +1
Conjugated oligomeric compounds and their use in gene modulation
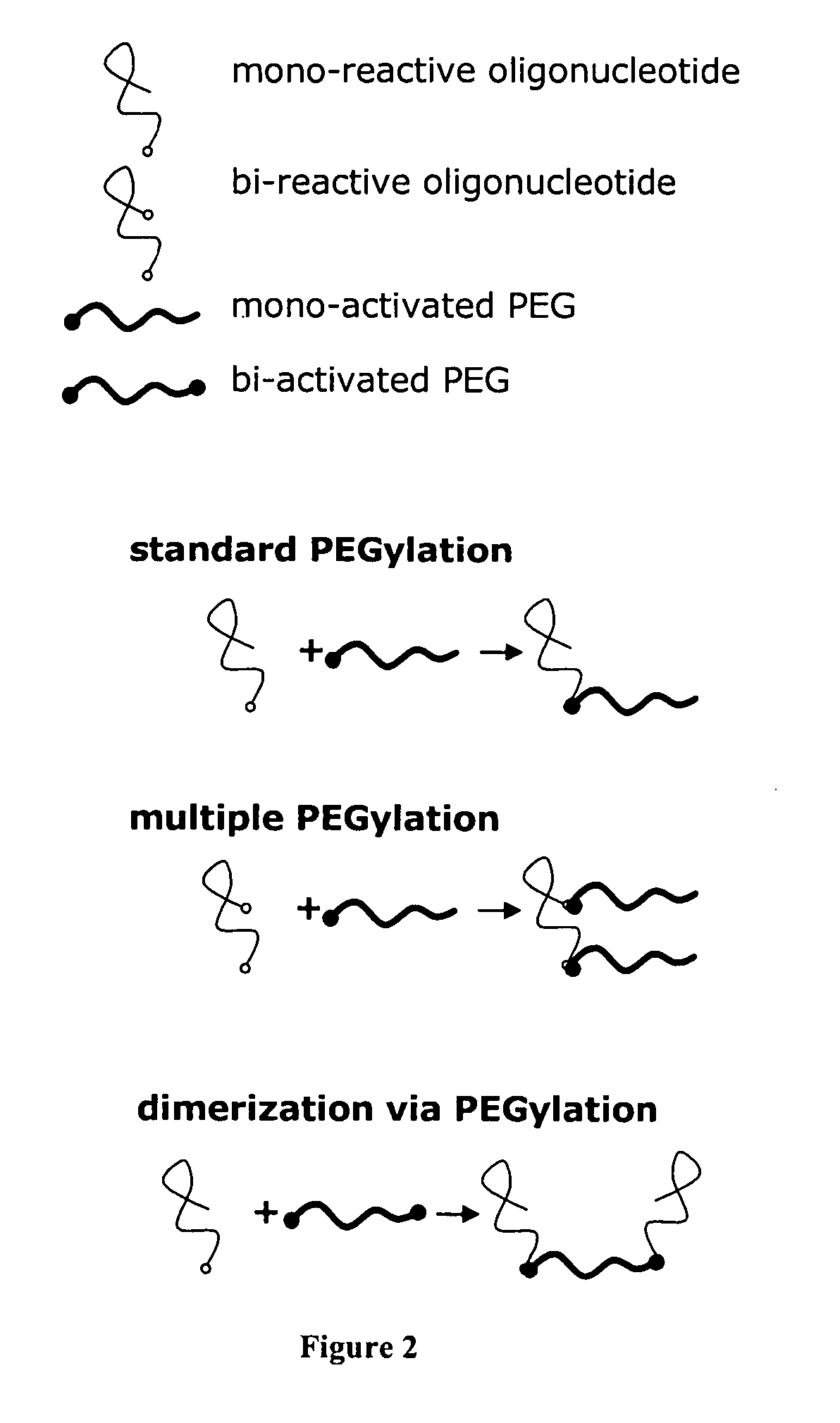
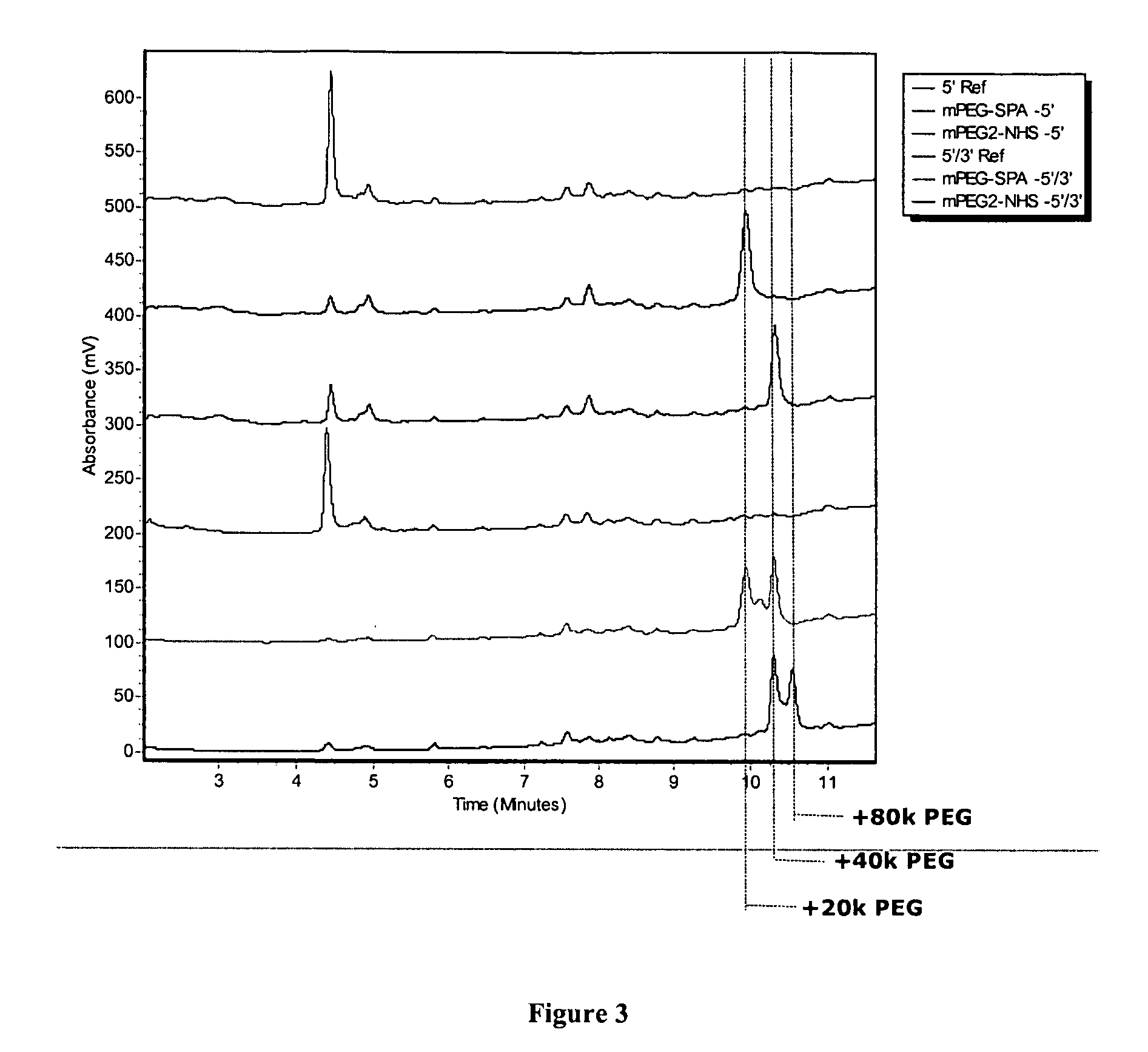
The present invention provides modified oligomeric compounds that modulate gene expression via an RNA interference pathway. The oligomeric compounds of the invention include one or more conjugate moieties that can modify or enhance the pharmacokinetic and phamacodynamic properties of the attached oligomeric compound.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
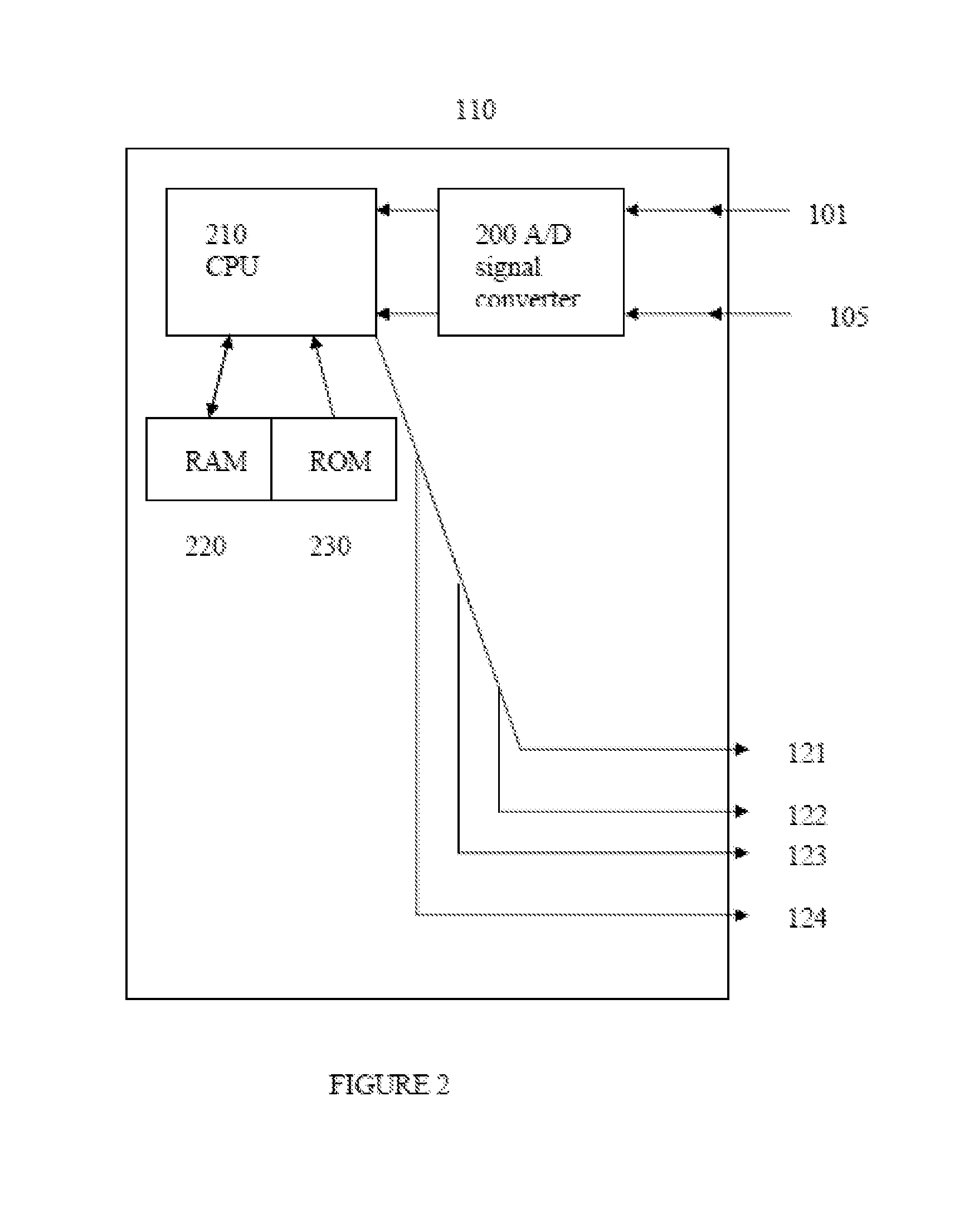
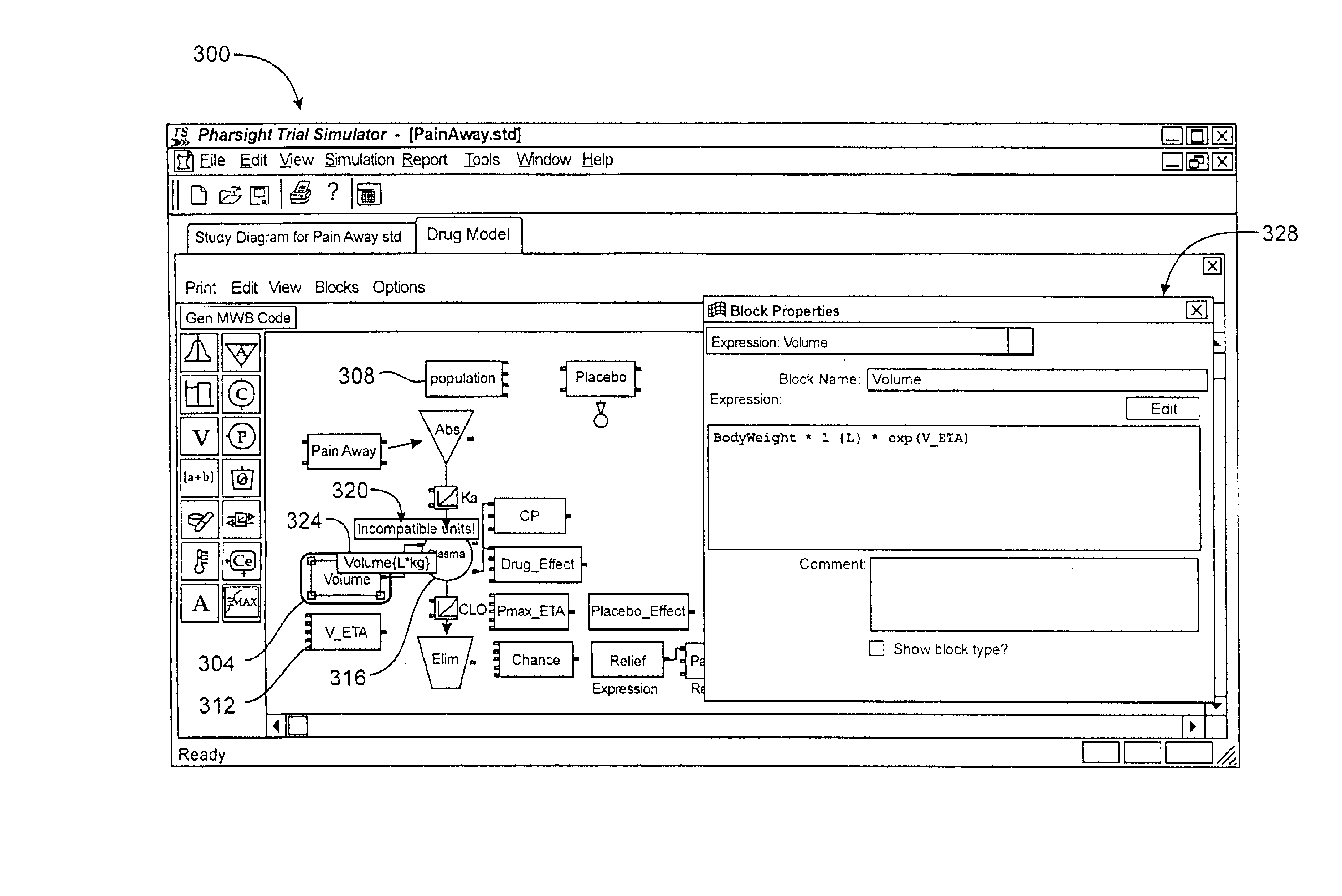
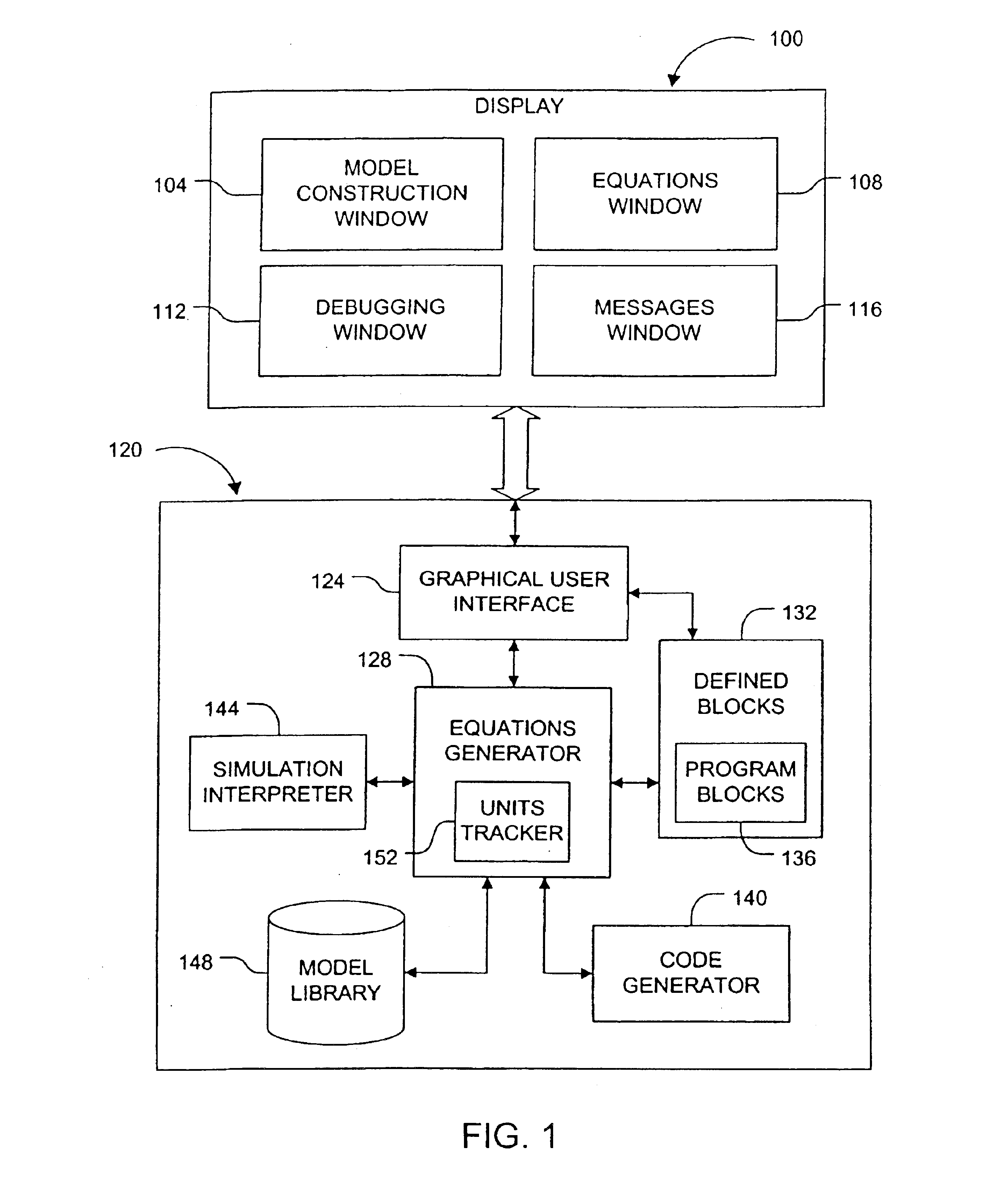
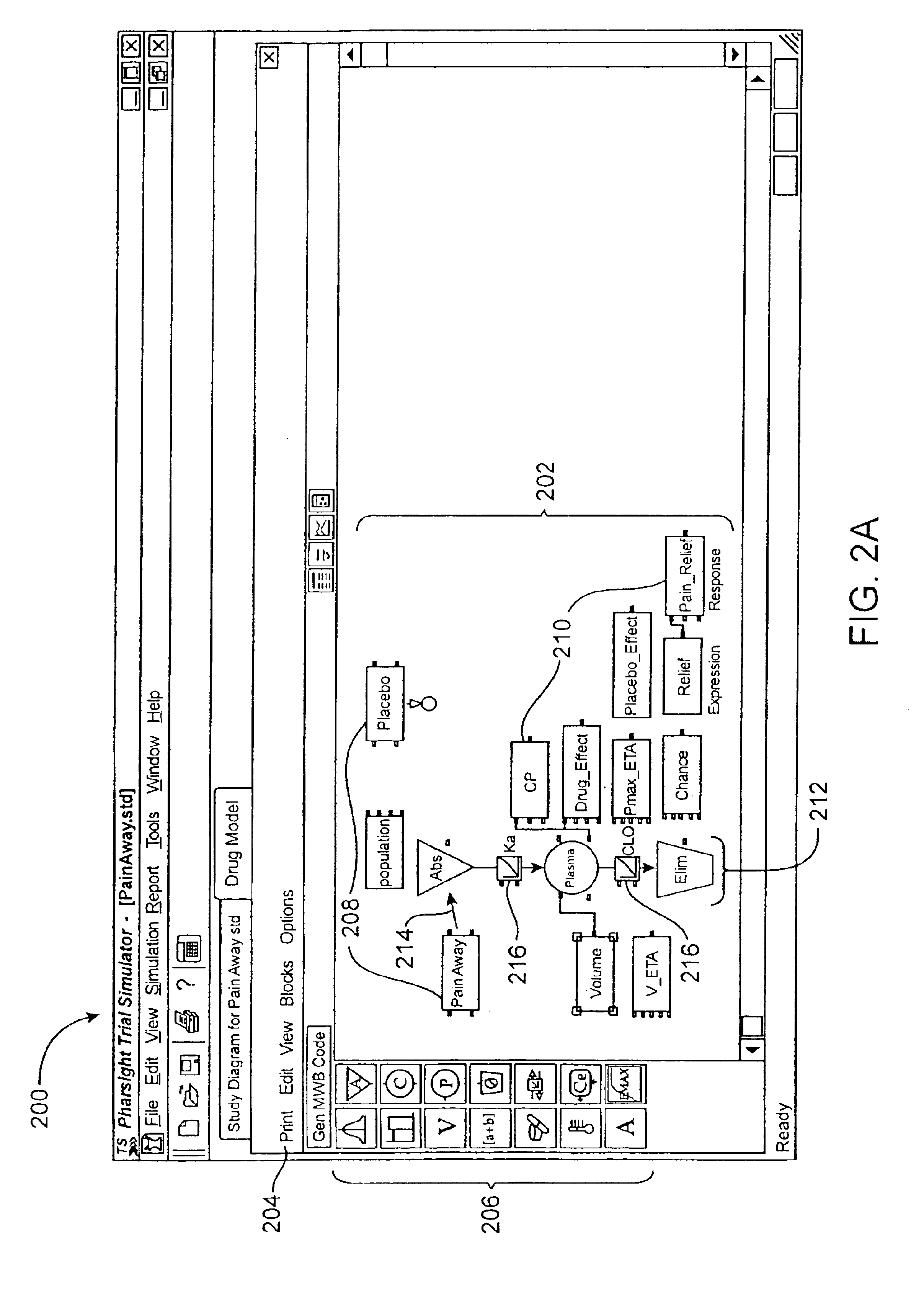
Unit tracking and notification in a graphical drug model editor
InactiveUS6937257B1Accelerating model buildingIncrease the verification processData visualisationAnalogue computers for chemical processesGraphicsGraphical user interface
A method for maintaining consistent unit relationships during graphical pharmacological computational model construction is disclosed. A graphical user interface is presented through which a user may place and connect objects representing pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic elements. The user may specify units definitions for variables and constants using unit expressions. As the objects are converted into an internal format representing the statements of the corresponding computational model, the unit expressions are included in this internal format as multidimensional data type information. This multidimensional data type information is regularly and automatically propagated for each statement in the internal format to identify inconsistent units. When such inconsistent units are identified, a warning message is generated to notify the user, substantially immediately after the inconsistent units are created.
Owner:CERTARA
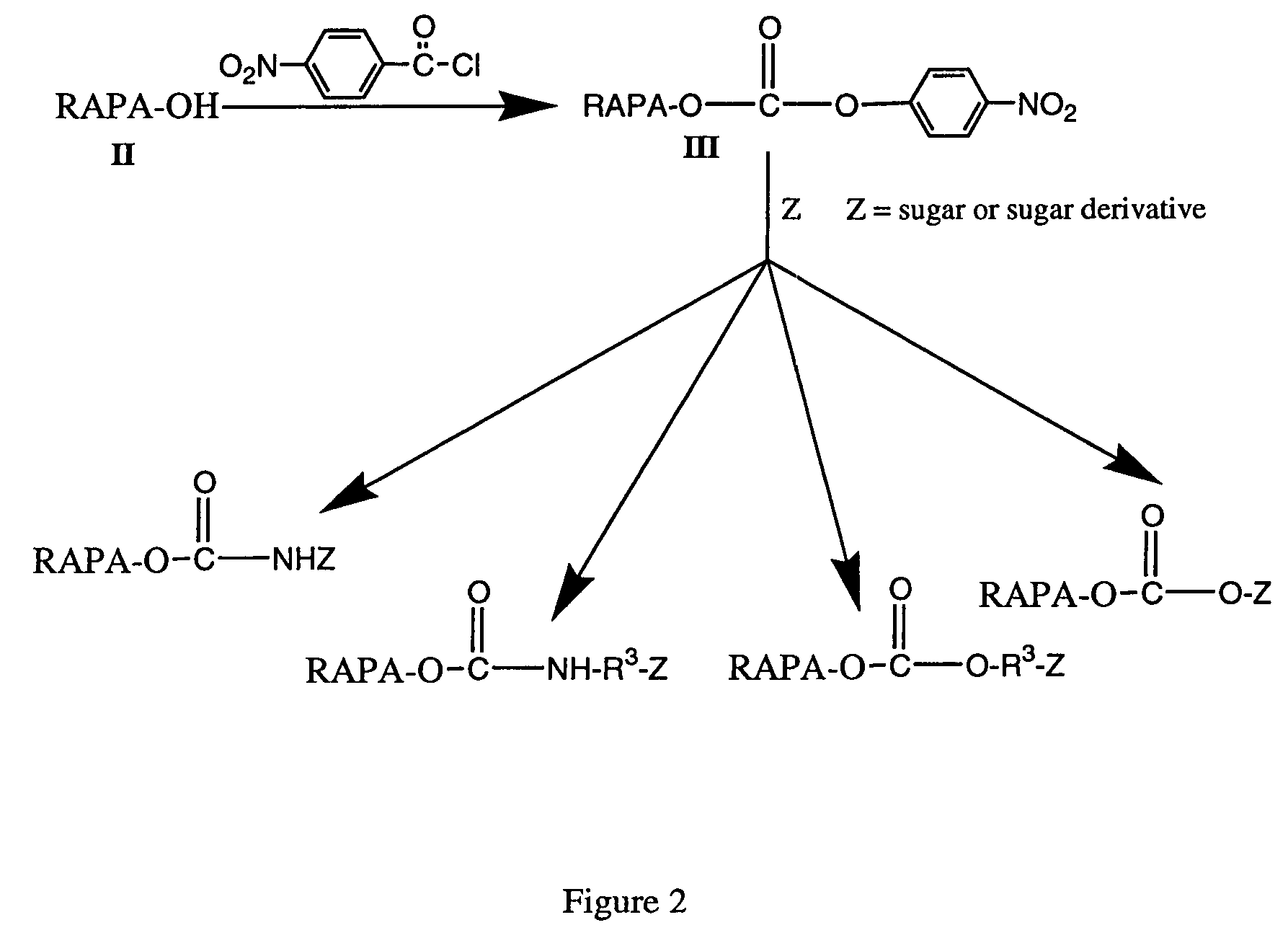
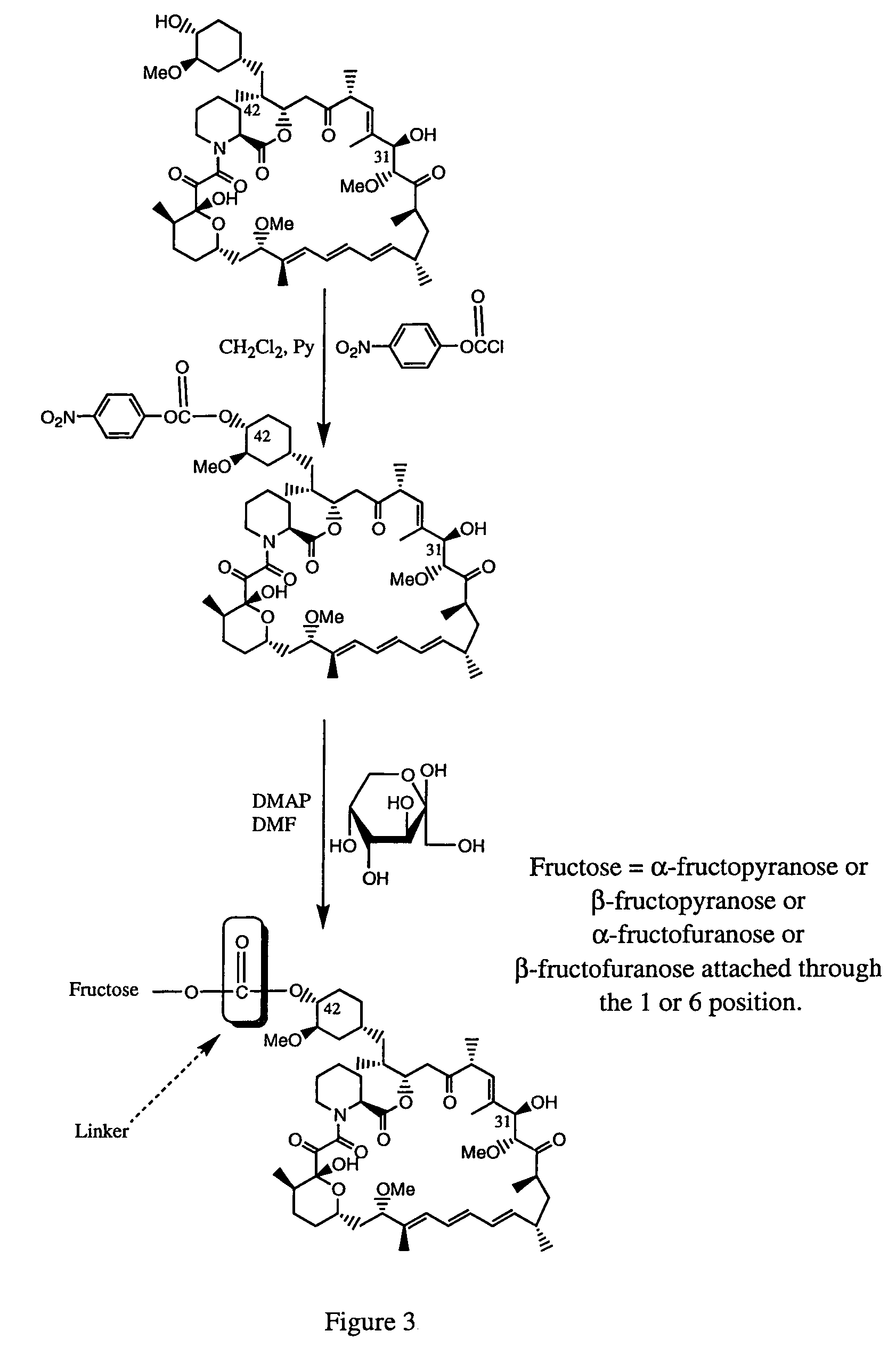
Rapamycin carbohydrate derivatives
InactiveUS7160867B2Low toxicityMore water solubleAntibacterial agentsBiocidePseudosugarsCarbohydrate derivative
This invention provides modified rapamycins that have specific monosaccharide(s), oligosaccharide(s), pseudosugar(s) or derivatives thereof attached through a linker to create rapamycin carbohydrate derivatives having enhanced pharmacokinetic and / or pharmacodynamic profiles. For example, administration of the rapamycin carbohydrate derivative results in altered pharmacokinetic profiles and reduced toxicities. Thus, the present invention provides compounds with characteristics that are distinct from other drugs in its class such as rapamycin.
Owner:ISOTECHNIKA INC
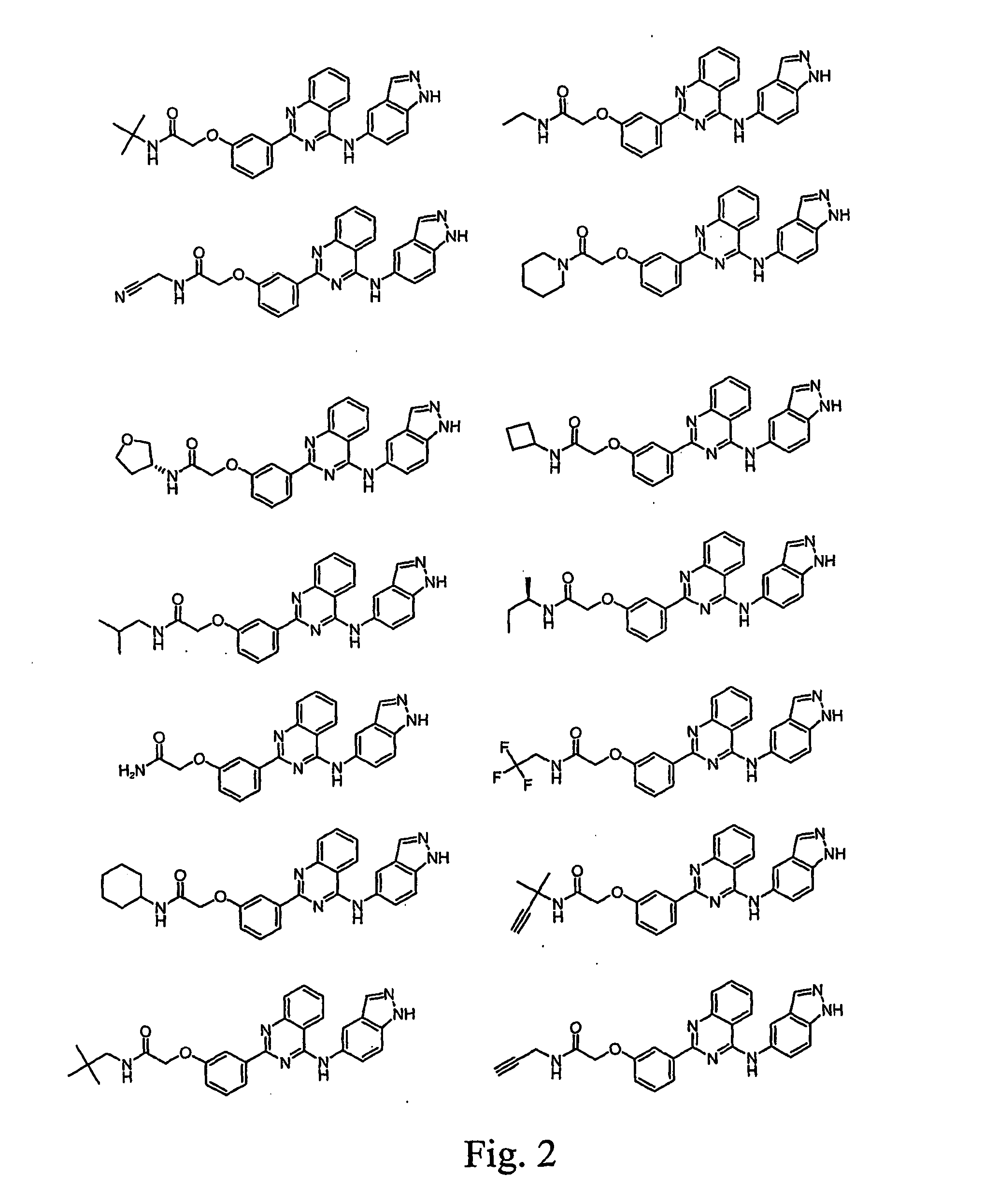
Application of 2-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-2-oxoethyl 4-((3-chloro-4-methylphenyl) amino)-4-oxobutanoate in preparing an LSD1 (lysine-specific demethylase 1) inhibitor medicament
InactiveCN103893163AStrong inhibitory activitySelectiveOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderMedicineMonoamine Oxidase A Gene
The invention belongs to the field of medicine, and in particular relates to a medical application of 2-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-2-oxoethyl 4-((3-chloro-4-methylphenyl) amino)-4-oxobutanoate in a selective histone lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1) inhibitor, especially the application in anti-tumor medicaments. Pharmacodynamic tests indicate that the 2-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-2-oxoethyl 4-((3-chloro-4-methylphenyl) amino)-4-oxobutanoate has a remarkable LSD1 inhibiting effect, and has selectivity to homologous proteins MAO-A (monoamine oxidase-A) and MAO-B.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Modular organ microphysiological system with integrated pumping, leveling, and sensing
ActiveUS20170227525A1Improve reliabilityLow costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSource to sinkMulti organ
Fluidic multiwell bioreactors are provided as a microphysiological platform for in vitro investigation of multi-organ crosstalks for an extended period of time of at least weeks and months. The disclosed platform is featured with one or more improvements over existing bioreactors, including on-board pumping for pneumatically driven fluid flow, a redesigned spillway for self-leveling from source to sink, a non-contact built-in fluid level sensing device, precise control on fluid flow profile and partitioning, and facile reconfigurations such as daisy chaining and multilayer stacking. The platform supports the culture of multiple organs in a microphysiological, interacted systems, suitable for a wide range of biomedical applications including systemic toxicity studies and physiology-based pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic predictions. A process to fabricate the disclosed bioreactors is also provided.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
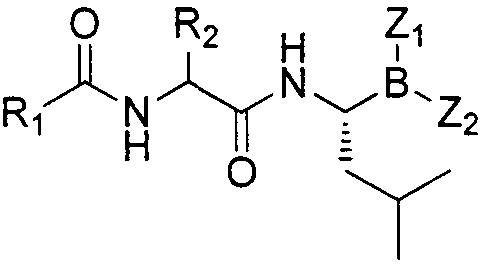
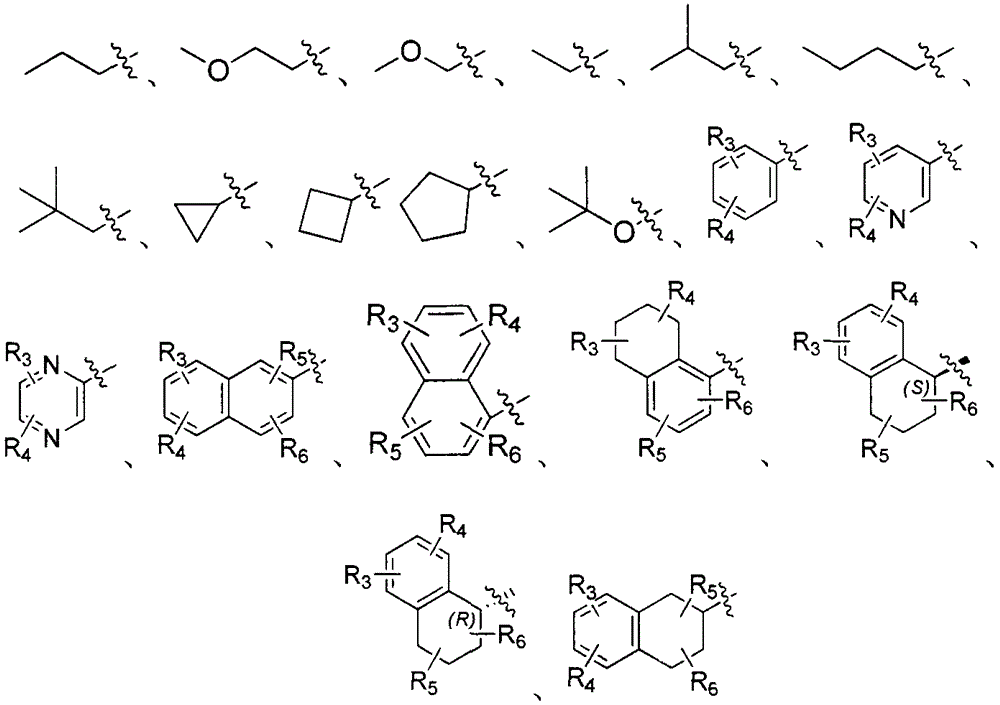
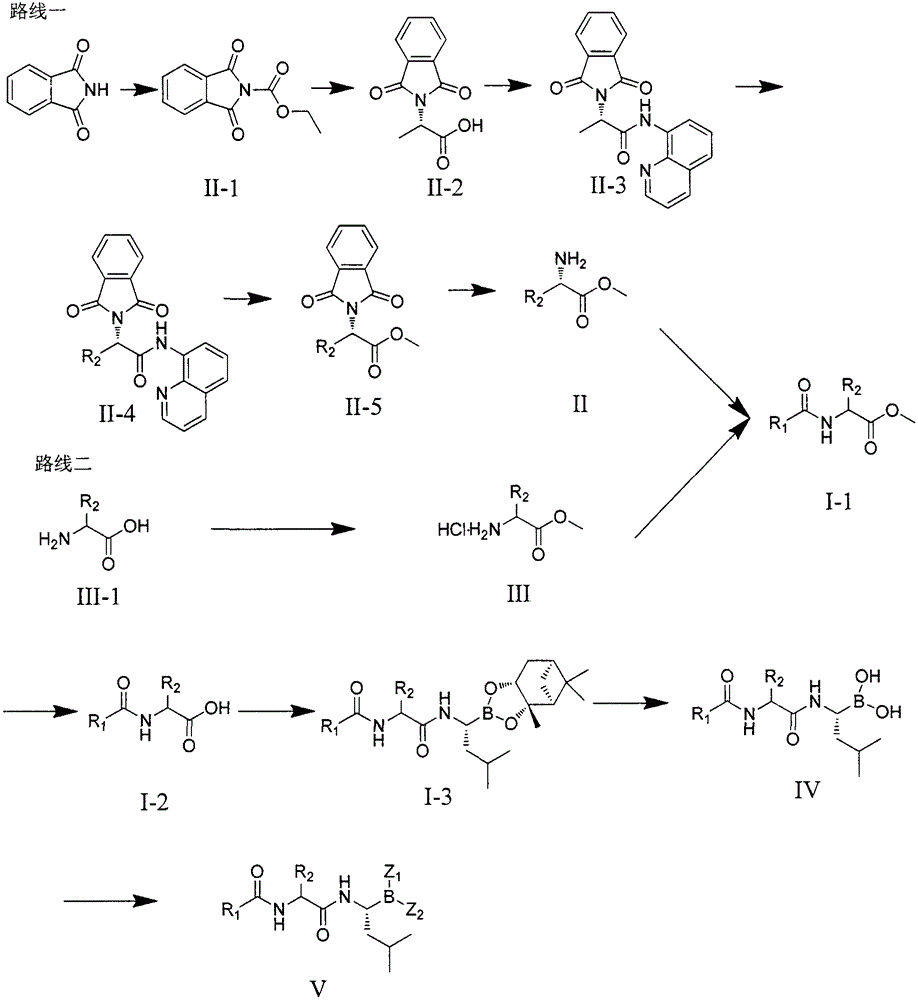
Dipeptide boric acid composed of carboxylic acid and alpha-amino acid as well as ester compound thereof, and preparation method and application of dipeptide boric acid and ester compound thereof
ActiveCN105732683AHigh yieldHigh activityBoron compound active ingredientsGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsProstate cancerProteasome inhibitor
The invention belongs to the field of drug synthesis and in particular relates to a series of novel peptide boric acids as well as an ester compound or pharmaceutical salt thereof, and a preparation method and application of the peptide boric acids as well as the ester compound or pharmaceutical salt thereof in pharmacodynamics. A structure of the peptide boric acid and the ester compound or pharmaceutical salt thereof is shown in a formula I (described in the specification). The compound provided by the invention can be used for preparing a proteasome inhibitor and can further be used for treating solid tumours and blood tumours, wherein the solid tumours are selected from non-small cell lung cancer, small cell lung cancer, lung adenocarcinoma, lung squamous carcinoma, pancreatic cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer, liver cancer, skin cancer, epithelial cell cancer, gastrointestinal stromal tumor, nasopharynx cancer and leukemia; and the blood tumours are selected from multiple myeloma, mantle cell lymphoma and histiocytic lymphoma.
Owner:JIANGSU CHIA TAI FENGHAI PHARMA
Method and system to define patient specific therapeutic regimens by means of pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic tools
Methods for treating Hepatitis infections are provided. In one embodiment, an initial dosage of interferon is administered to a patient, and interferon serum levels and viral load data is collected over time. This data can be used to determine patient-specific pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic parameters and then construct patient-specific interferon delivery profiles. Patient-specific delivery profiles can then be used to design patient-specific therapeutic regimens.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Tolerogenic synthetic nanocarriers and therapeutic macromolecules for reduced or enhanced pharmacodynamic effects
ActiveUS20140328854A1Reduced pharmacodynamically effectiveLow effective dosePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsTolerabilityNanocarriers
Owner:SELECTA BIOSCI
Hydroxy progesterone caproate oral preparation and its use
An orally taken medicine of hyproval-PA in the form of tablet, capsule, soft capsule, instant particles, etc for treating breast cancer and functional metrorrhagia is disclosed. its advantages are high biologic utilization rate and high curative effect.
Owner:北京京卫燕康药物研究所有限公司
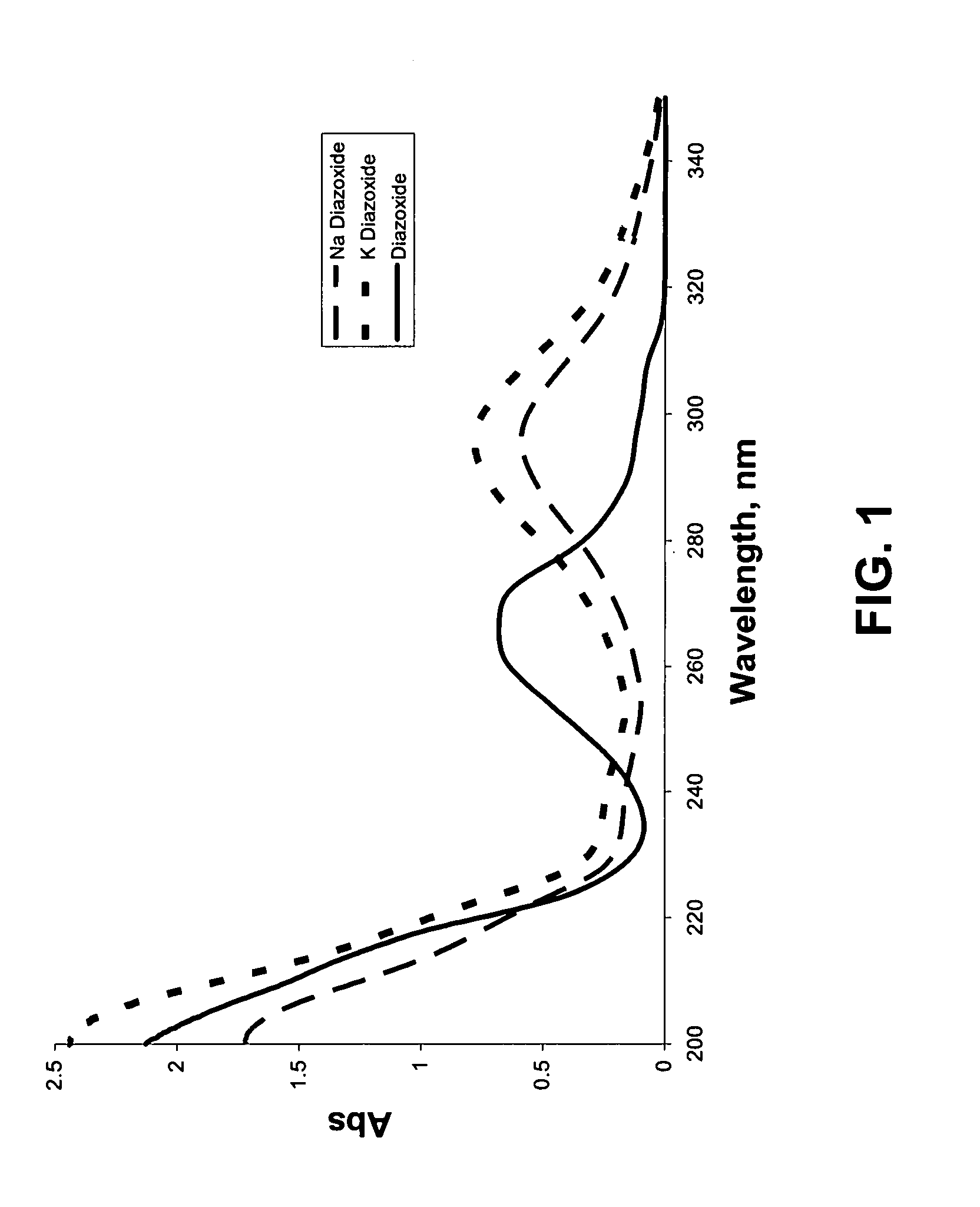
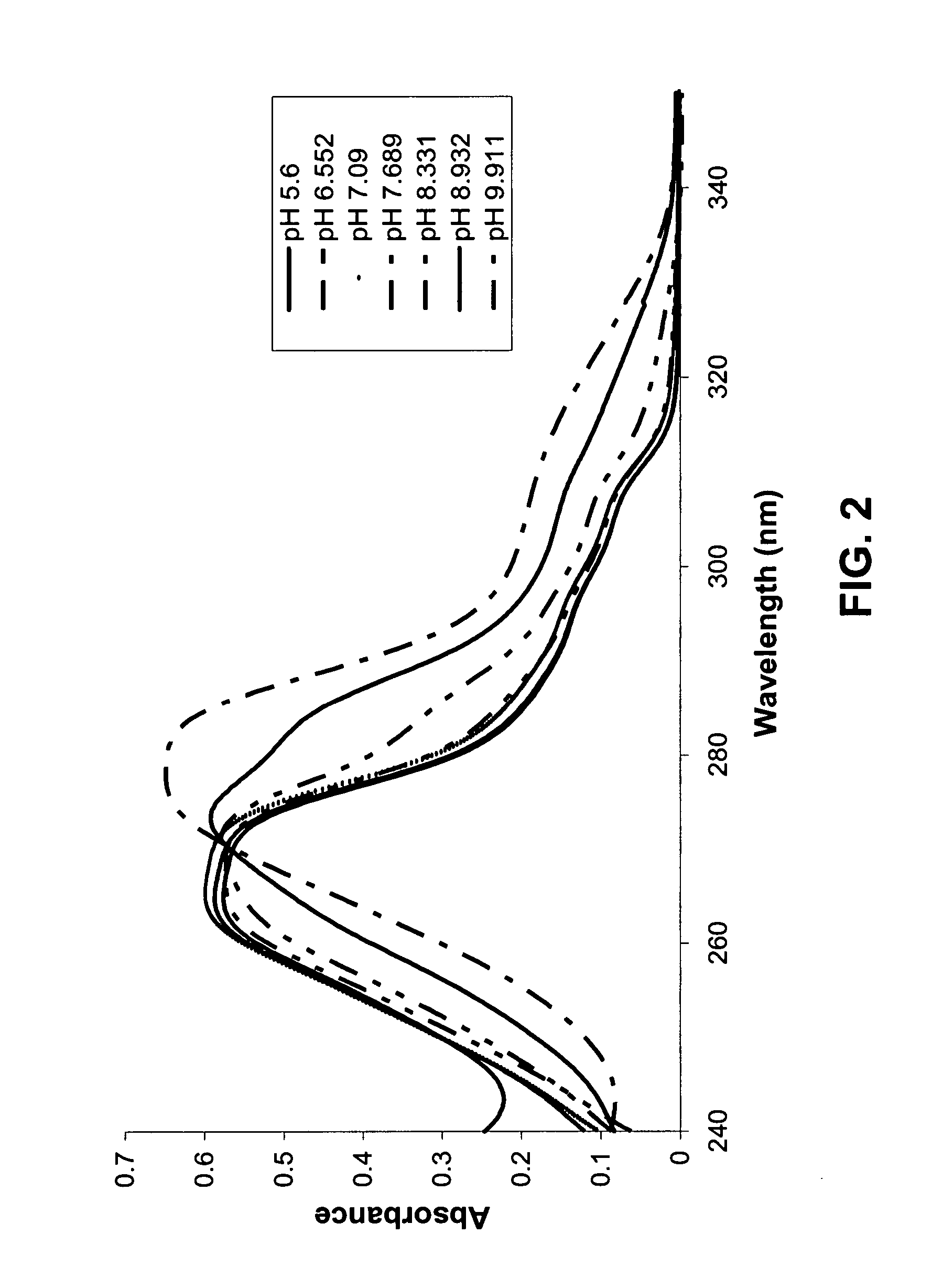
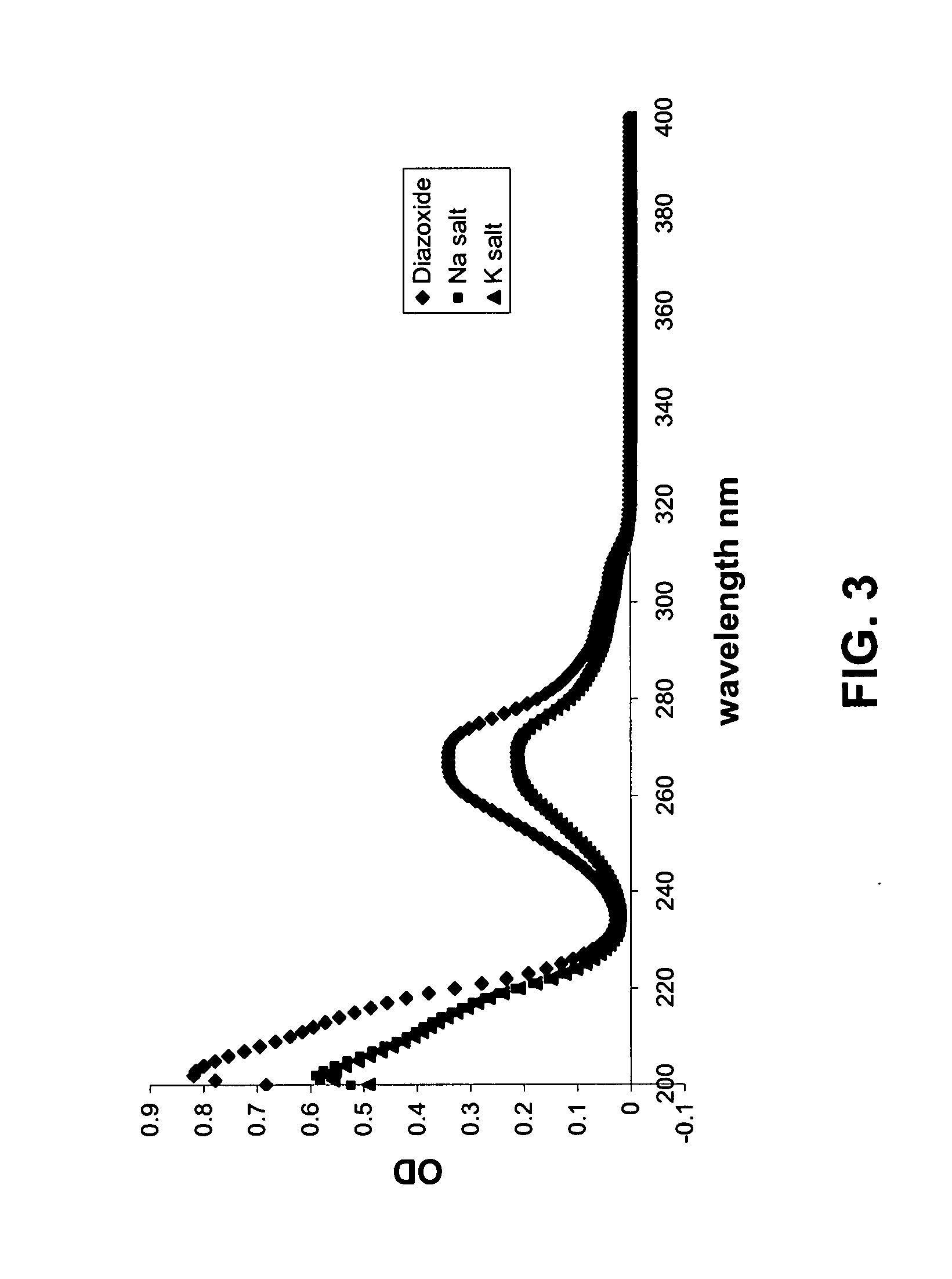
Salts of potassium atp channel openers and uses thereof
ActiveUS20070191351A1Enhanced drug releaseNervous disorderAmino preparation from aminesDiseasePotassium
Provided are immediate or prolonged administration of certain salts of KATP channel openers such as diazoxide to a subject to achieve novel pharmacodynamic, pharmacokinetic, therapeutic, physiological, metabolic and compositional outcomes in the treatment of diseases or conditions involving KATP channels. Also provided are pharmaceutical formulations, methods of administration and dosing of the salts that achieve these outcomes and reduce the incidence of adverse effects in treated individuals. Further provided are method of co-administering the salts with other drugs to treat diseases of humans and animals.
Owner:ESSENTIALIS INC
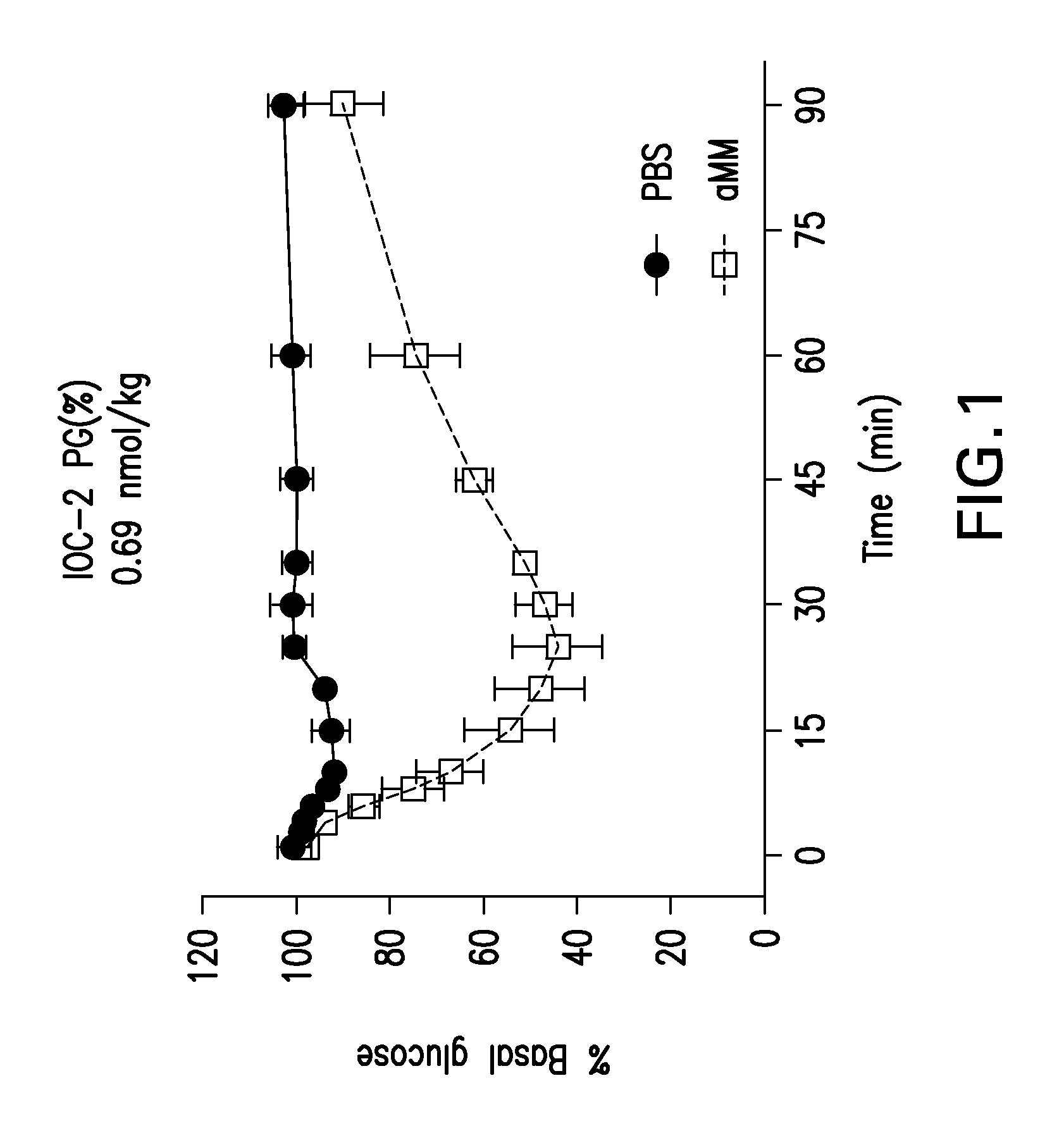
Glucose-responsive insulin conjugates
Insulin conjugates comprising an insulin molecule covalently attached to at least one bi-dentate linker having two arms, each arm independently attached to a ligand comprising a saccharide and wherein the saccharide for at least one ligand of the linker is fucose are disclosed. The insulin conjugates display a pharmacokinetic (PK) and / or pharmacodynamic (PD) profile that is responsive to the systemic concentrations of a saccharide such as glucose or alpha-methylmannose even when administered to a subject in need thereof in the absence of an exogenous multivalent saccharide-binding molecule such as Con A.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
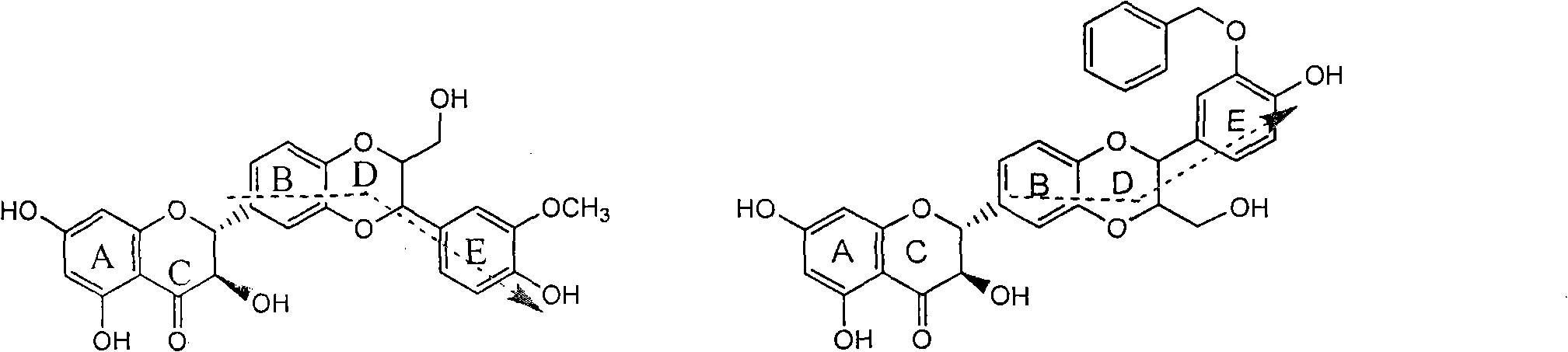
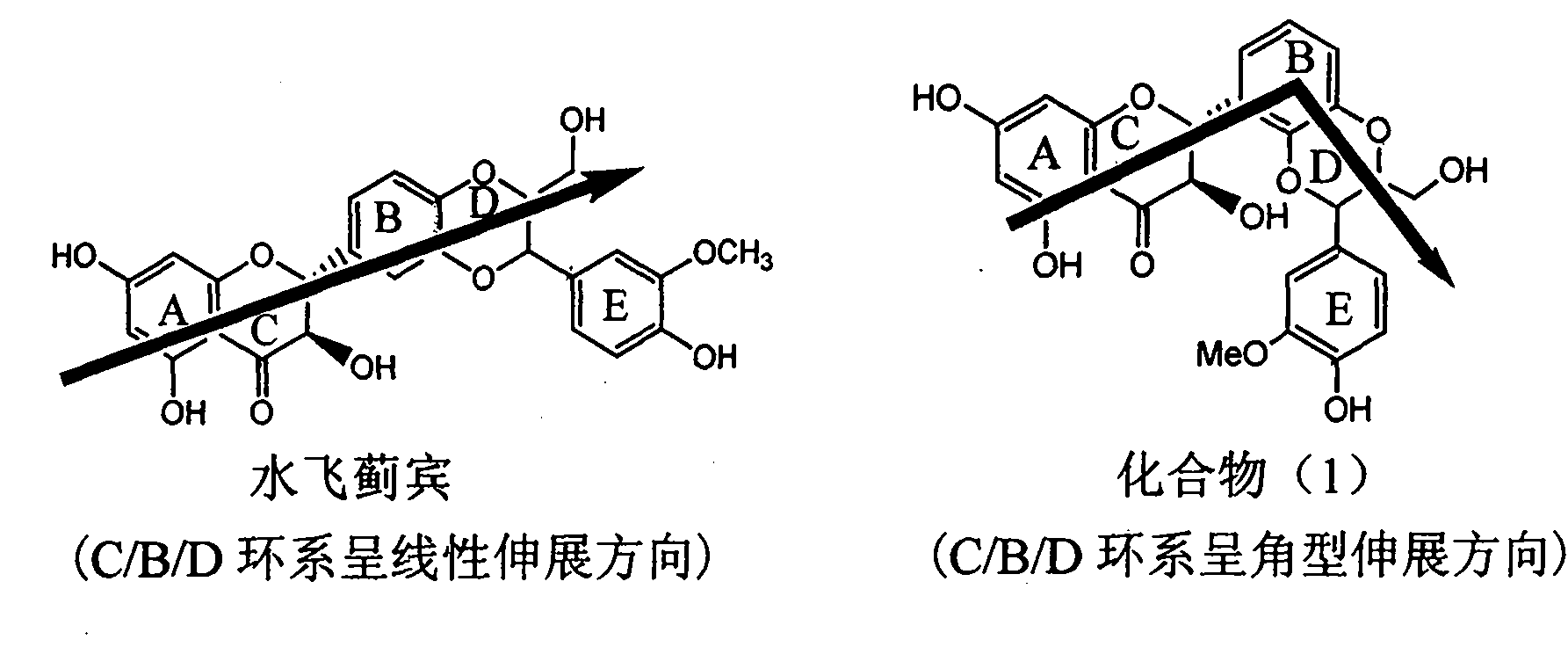
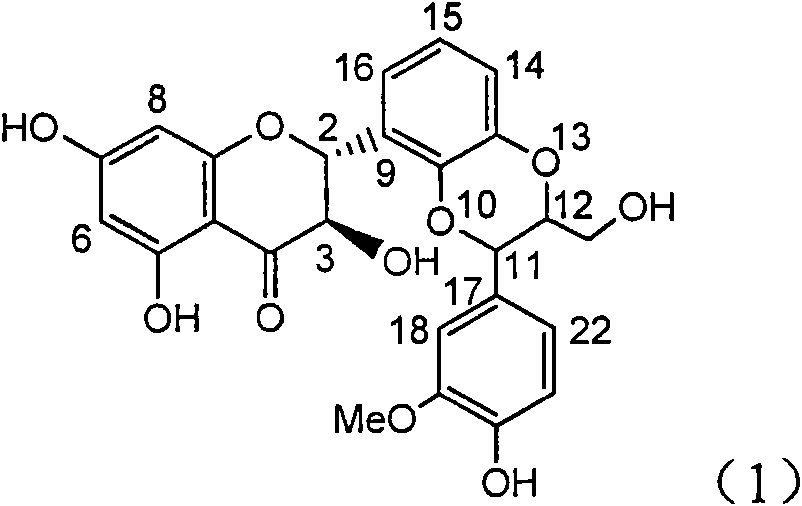
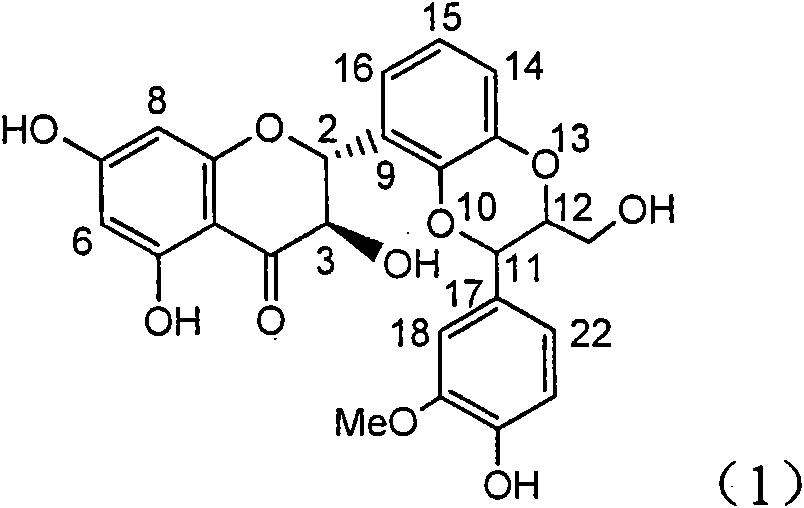
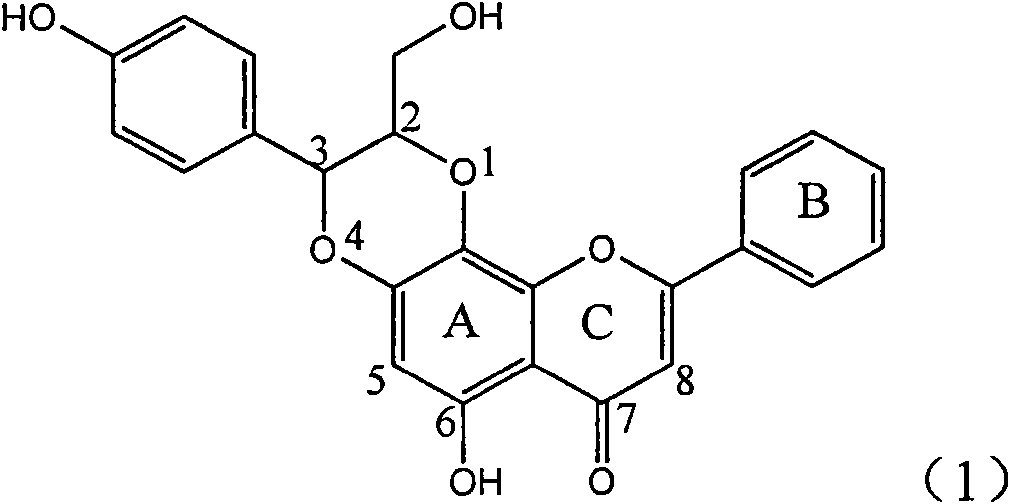
Application of substituted isosilybin in preparing medicament for treating virus hepatitis B
InactiveCN101829098AConvenient sourceThe source is easy to getOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsDiseasePositive control
The invention relates to application of substituted isosilybin in preparing a medicament for treating virus hepatitis B, in particular to application of E-ring substituted isosilybin or medicinal salt thereof in preparing a medicament for clearing hepatitis B e antigen, inhibiting HBV DNA replication and treating hepatitis B virus infected diseases. The E-ring substituted isosilybin has strong effect of inhibiting HBeAg activity, and the strength of the E-ring substituted isosilybin at the concentration of 100 micrograms per milliliter for clearing the HBeAg is 3.5 times that of a positive control front-line medicament (10,000 units per milliliter of alpha-interferon); and moreover, the compound at the concentration of 100 micrograms per milliliter has strong inhibiting rate (97.7 percent) on the HBV DNA. Pharmacodynamical results show that the E-ring substituted isosilybin or the medicinal salt thereof can be expected to be used for preparing the medicament for treating the hepatitis B virus infected diseases.
Owner:DALI UNIV
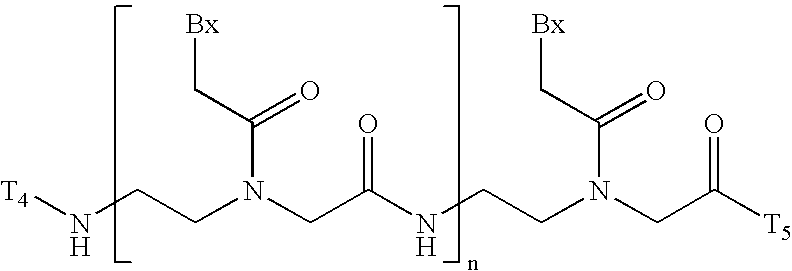
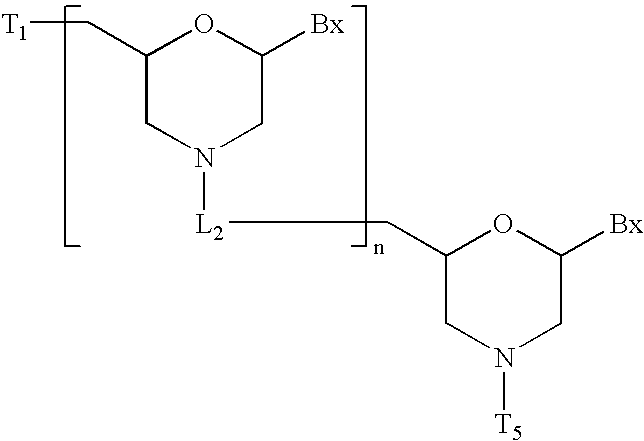
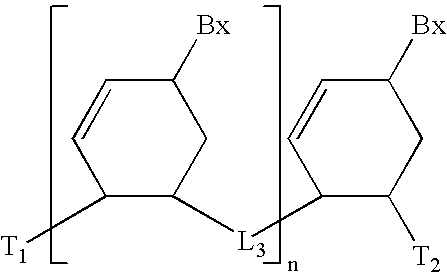
Multivalent aptamer therapeutics with improved pharmacodynamic properties and methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS20070009476A1Improve pharmacological and pharmacodynamic propertyImproved pharmacological and pharmacodynamic propertySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsBiologyDisease
Owner:WILSON CHARLES +3
Application of angle flavonoids lignan to preparation of medicaments for treating viral hepatitis B
InactiveCN101953828AInhibition of replicationConvenient sourceOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsLignanInterferon alpha
The invention relates to application of an angle flavonoids lignan to preparation of medicaments for treating viral hepatitis B, in particular to application of the angle flavonoids lignan or medicinal salts thereof to preparation of medicaments for inhibiting hepatisis B virus (HBV) DNA replication and treating HBV infection diseases. The flavonoids lignan can exactly inhibit HBV DNA activity; the inhibition activity of the flavonoids lignan with high dosage (20 microgram / ml) to the HBV DNA replication is 189 percent higher than that of alpha-interferon with the maximum concentration of 10,000 unit / ml; and the flavonoids lignan belongs to a strong-effect non-nucleosides inhibition HBV natural product. The pharmacological results show that the angle flavonoids lignan or the medicinal salts thereof can be expected to be used for preparing the medicaments for inhibiting hepatisis B virus (HBV) DNA replication and treating the HBV infection diseases.
Owner:DALI UNIV
Application of ring A dioxane flavonolignan in preparing medicaments for resisting hepatitis B viruses (HBV)
InactiveCN101829085AConvenient sourceThe source is easy to getOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsDiseasePositive control
The invention relates to application of ring A dioxane flavonolignan in preparing medicaments for resisting hepatitis B viruses (HBV), in particular to application of ring A dioxane coupling type flavone lignan or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof in preparing medicaments for clearing away hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg), suppressing the HBV DNA replication and treating HBV infection diseases. The flavonolignan has certain activity on resisting the HBeAg, and the intensity of the flavonolignan for clearing away the HBeAg is higher than that of Lamivudine which is a positive control and close to that of 10,000 units / milliliter of alpha-interferon. Meanwhile, the suppression ratio of the compound to the HBV DNA replication is higher than 80 percent in the presence of a concentration of 100 micrograms / milliliter. The pharmacodynamical results indicate that the flavonolignan or the pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof can be expected to be used for preparing the medicaments for clearing away the HBeAg, suppressing the HBV DNA replication and treating the HBV infection diseases.
Owner:DALI UNIV
Application of ring A substituted silybin ester in preparing medicaments for treating viral hepatitis B
InactiveCN101829101AConvenient sourceThe source is easy to getOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemDiseasePositive control
The invention relates to application of ring A substituted silybin ester in preparing medicaments for treating viral hepatitis B, in particular to application of silybin ester flavonolignan substituted by ethoxycarbonyl methyl on the ring A or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof for preparing medicaments for reducing the hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HBsAg), suppressing the HBV (Hepatitis B Virus) DNA replication and treating HBV infection diseases. The flavonolignan has quite obvious activity on suppressing the HBsAg, and in the presence of a concentration of 100 micrograms / milliliter, the intensity of the flavonolignan for clearing away the HBsAG exceeds that of alpha-interferon which is a positive control medicament by 3.3 times. Meanwhile, in the presence of a concentration of 20 micrograms / milliliter, suppression ratio of the compound to the HBV DNA is close to 60 percent. The pharmacodynamical results indicate that the flavonolignan or the pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof can be expected to be used for preparing the medicaments for treating the HBV infection diseases.
Owner:DALI UNIV
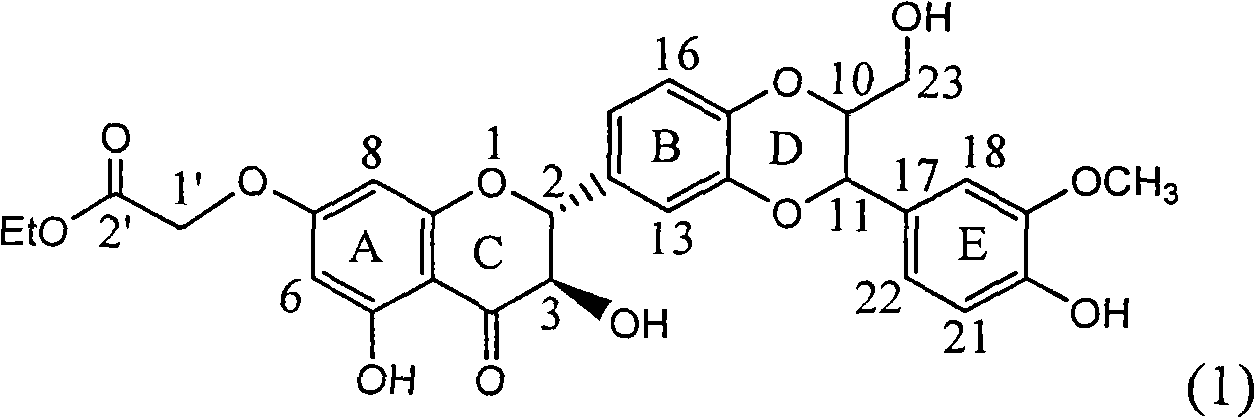
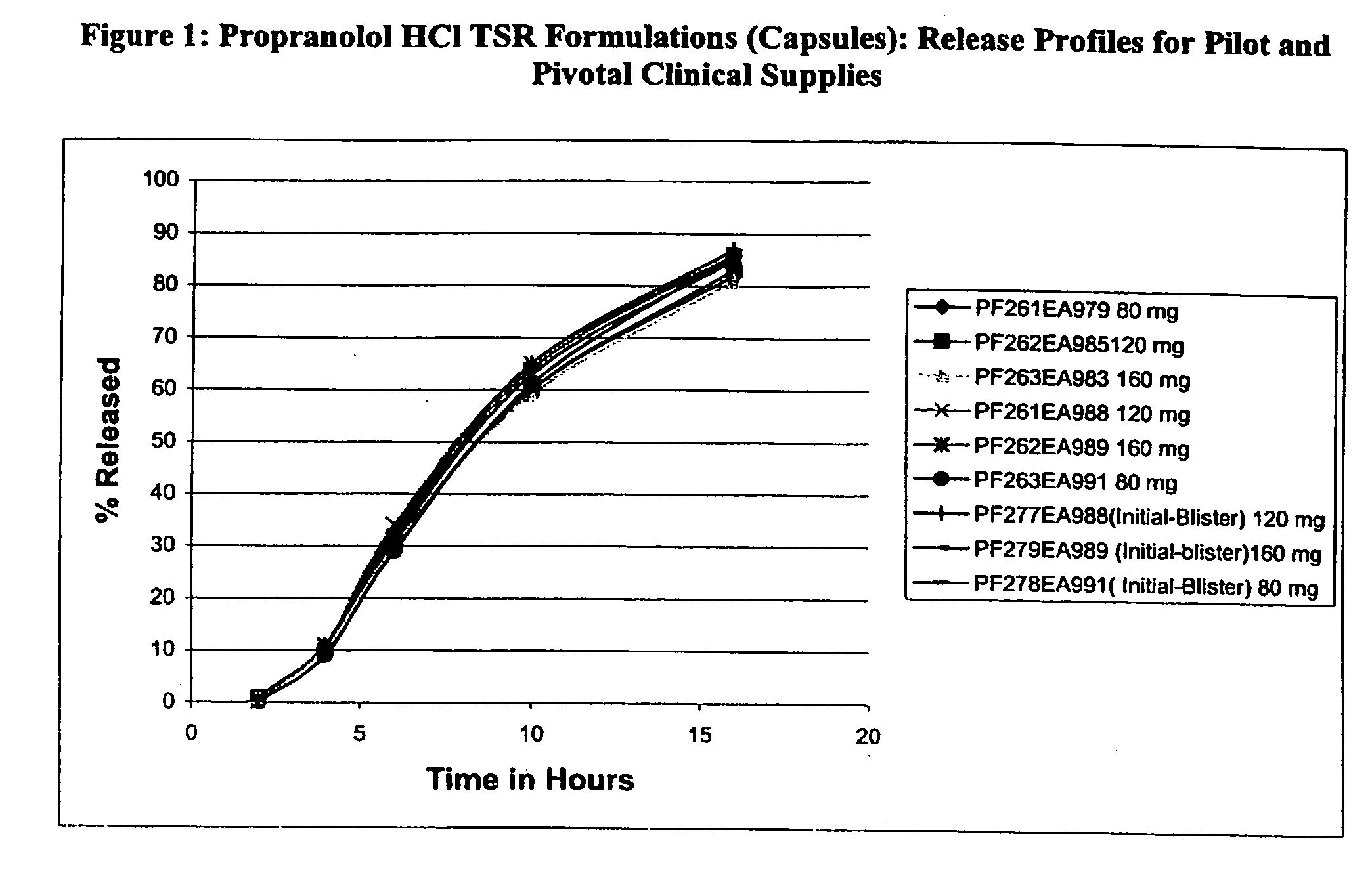
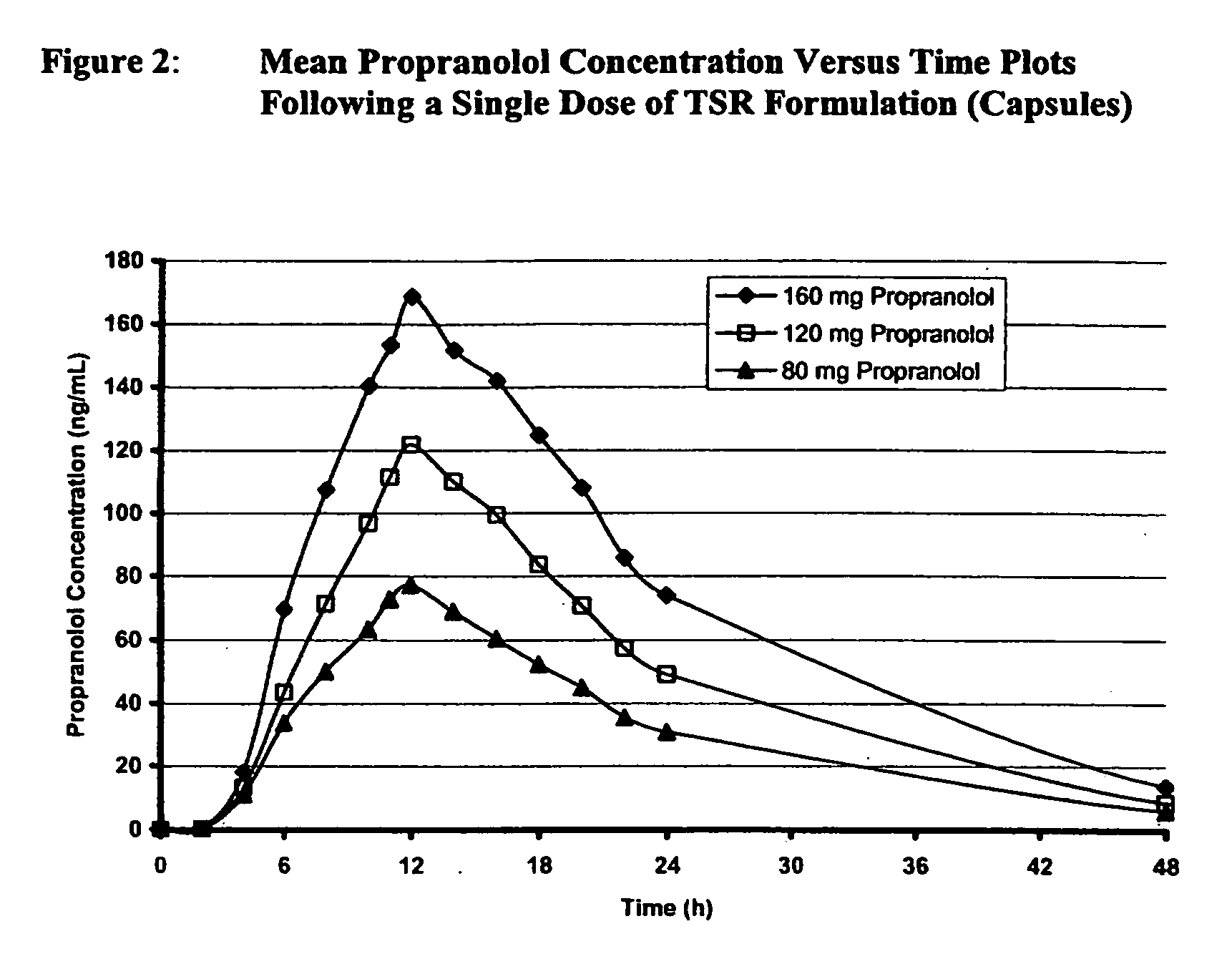
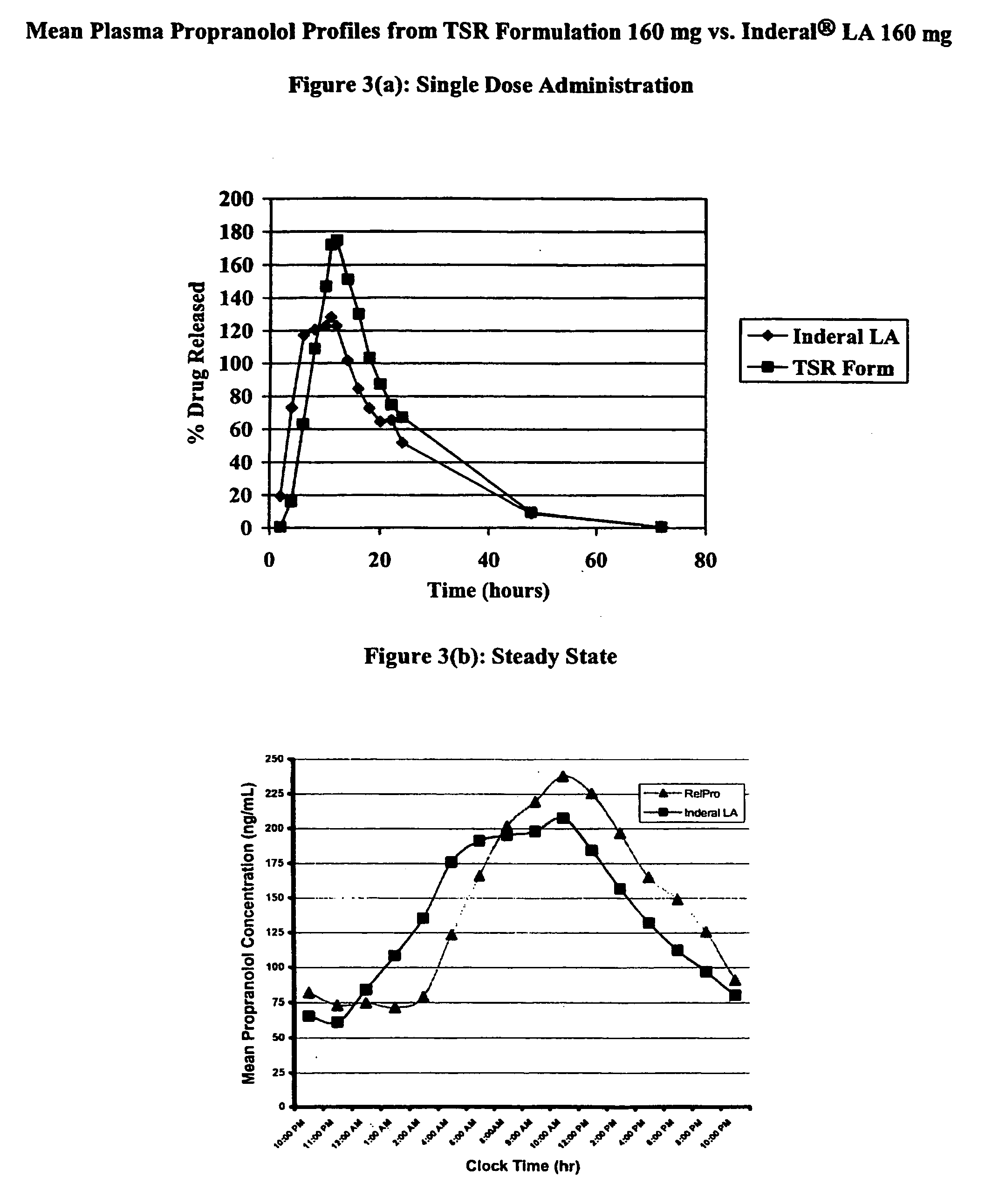
Timed, sustained release systems for propranolol
InactiveUS20060269607A1Lower blood pressureImprove protectionOrganic active ingredientsPill deliveryTime profileBlood plasma
A unit dosage form, such as a capsule or the like for delivering drugs into the body in a circadian release fashion, is comprising of one or more populations of propranolol-containing particles (beads, pellets, granules, etc.). Each bead population exhibits a pre-designed rapid or sustained release profile with or without a predetermined lag time of 3 to 5 hours. Such a circadian rhythm release cardiovascular drug delivery system is designed to provide a plasma concentration-time profile, which varies according to physiological need during the day, i.e., mimicking the circadian rhythm and severity / manifestation of a cardiovascular disease, predicted based on pharmaco-kinetic and pharmaco-dynamic considerations and in vitro / in vivo correlations.
Owner:ADARE PHARM INC
New application of patchouli alcohol
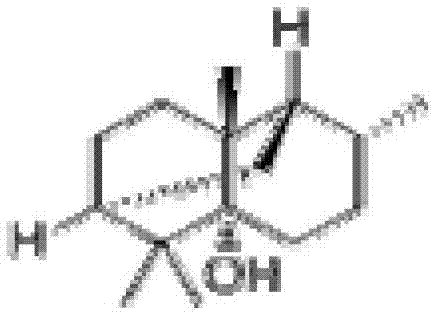
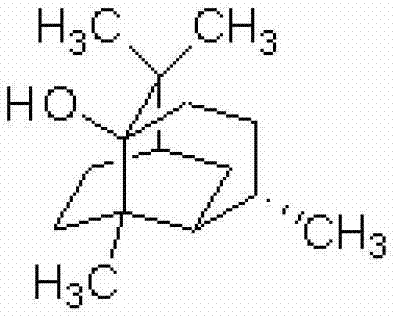
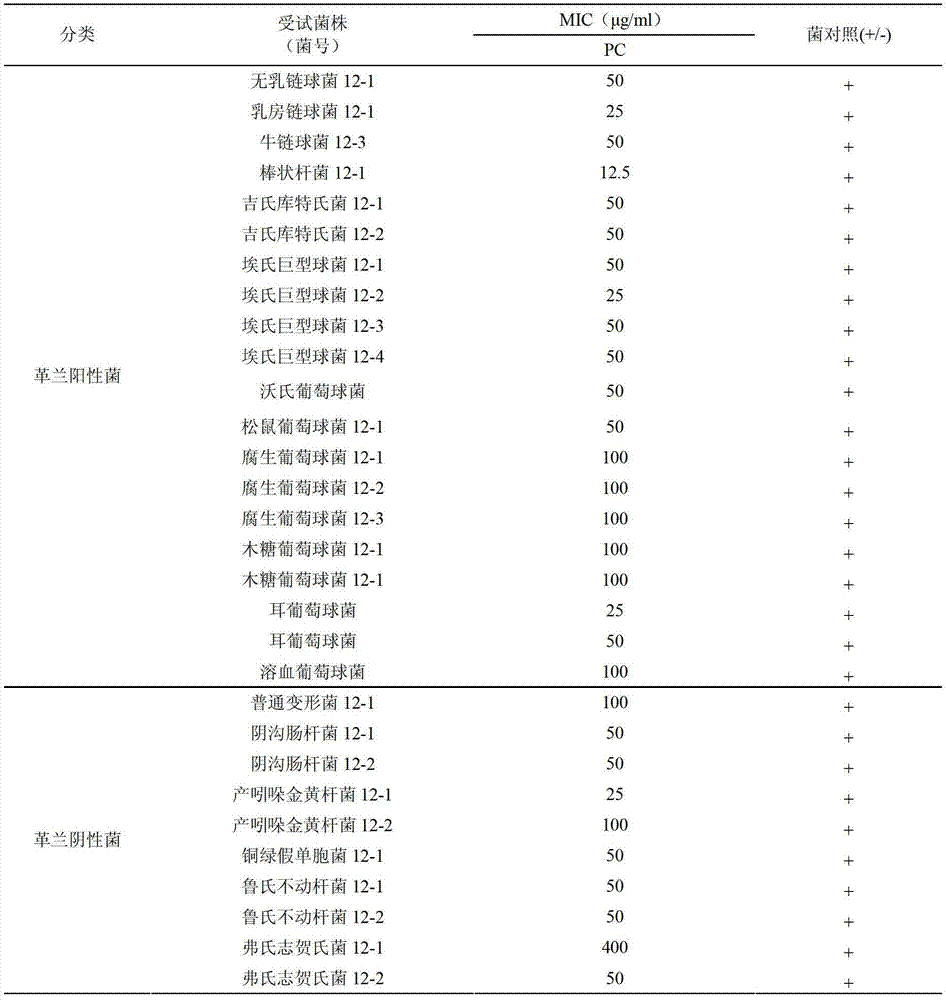
ActiveCN103156826AStrong inhibitory activityEffective treatmentAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsBiotechnologyAntibacterial activity
The invention relates to an application of patchouli alcohol in preparation of antibacterial drugs, healthcare food, food, cosmetics, disinfectors or daily chemical articles. The invention also provides the antibacterial drugs, healthcare food, food, cosmetics, disinfectors or daily chemical articles. The patchouli alcohol has good antibacterial activity on pathogenic bacteria or conditional pathogen, can be used for effectively treating bacterium infectious diseases and simultaneously can also effectively antagonize methicillin-resistant staphylococcus epidermidis drug-resistance bacteria; and the pharmacodynamics activity of the patchouli alcohol is even equivalent to that of vancomycin, thus the possibility is provided for slowing down or avoiding the occurrence of the drug-resistance bacteria.
Owner:CHENGDU HUASUN GRP INC LTD +1
Intelligent drug and/or fluid delivery system to optimizing medical treatment or therapy using pharmacodynamic and/or pharamacokinetic data
ActiveUS9950112B2Safe deliveryDanger is reduced and eliminatedData processing applicationsDrug and medicationsEfficacyPharmaceutical drug
Owner:XHALE ASSURANCE INC +1
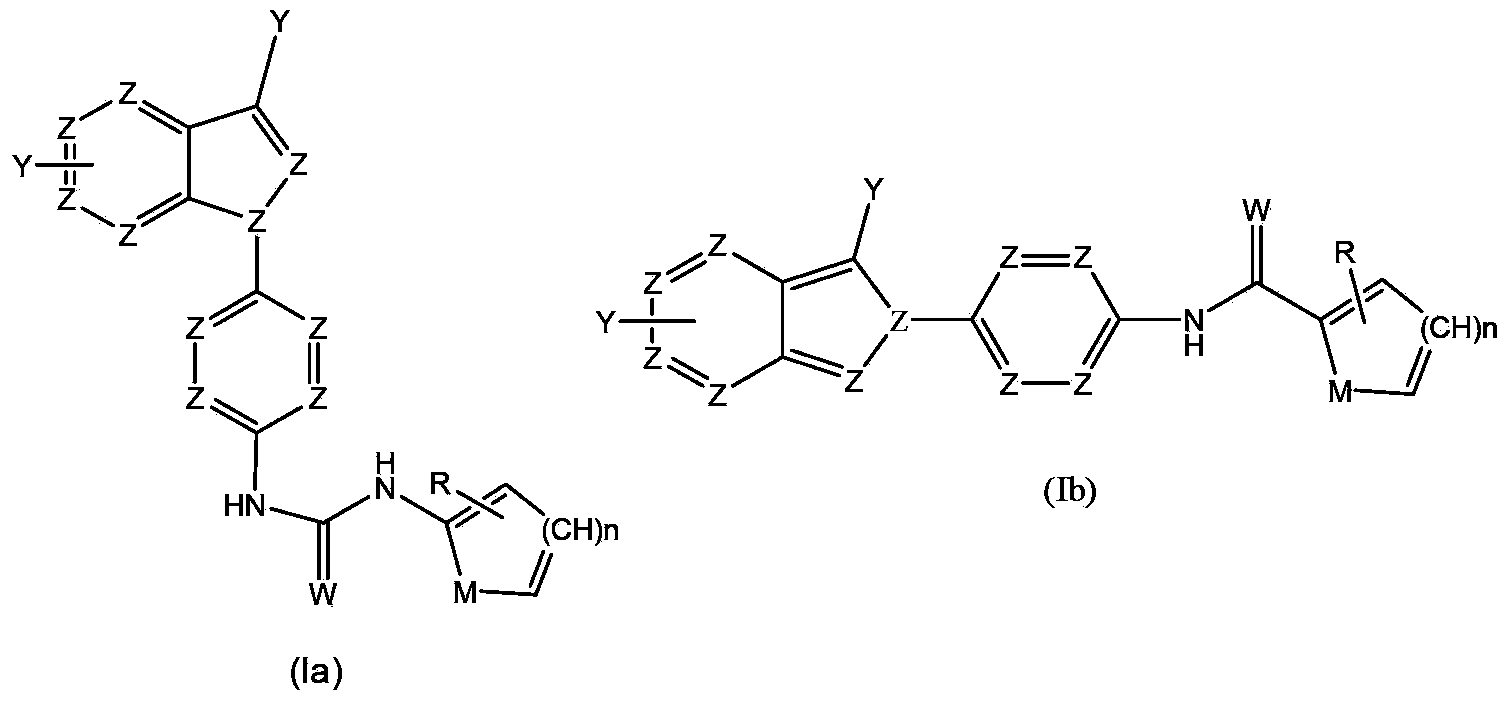
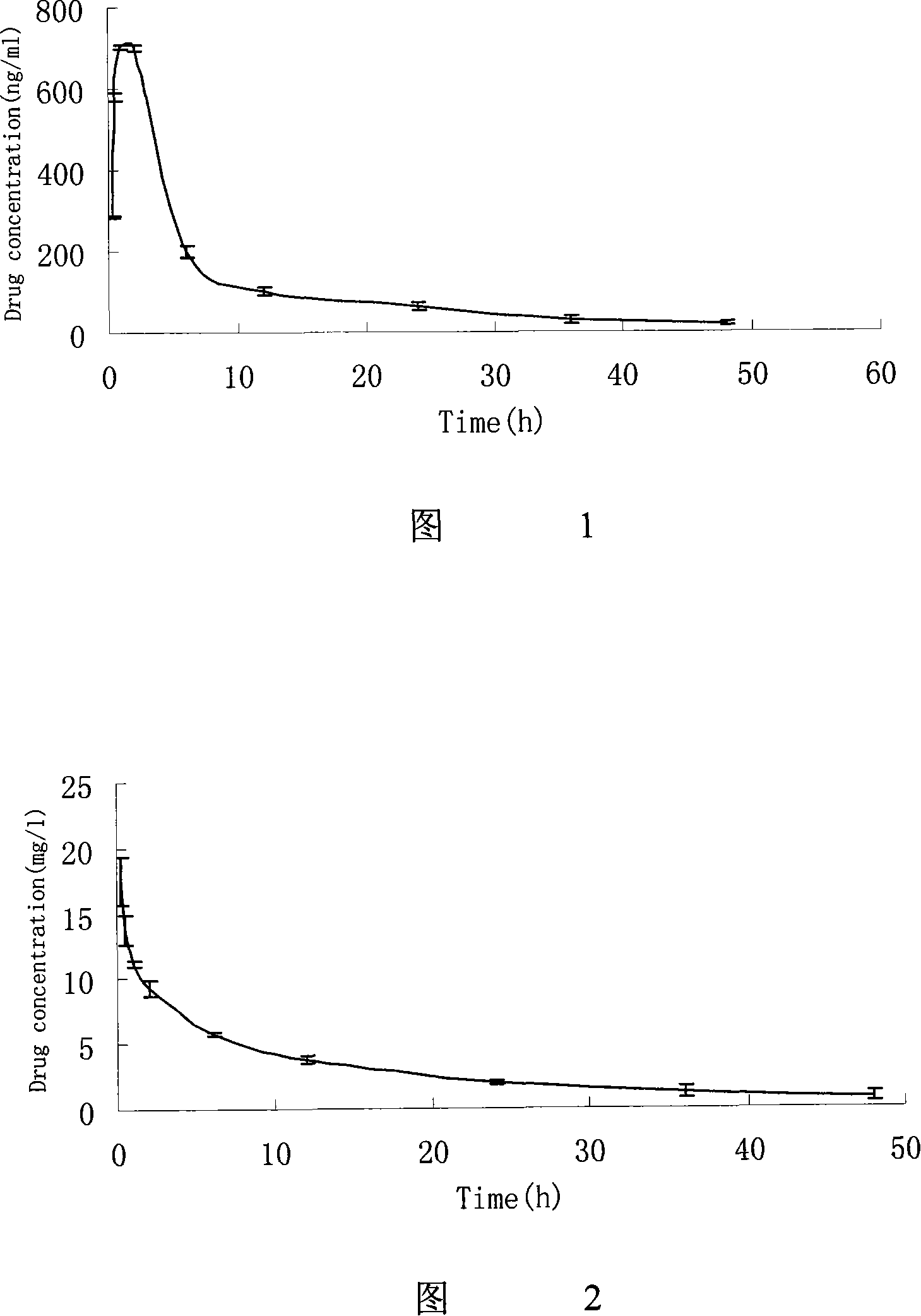
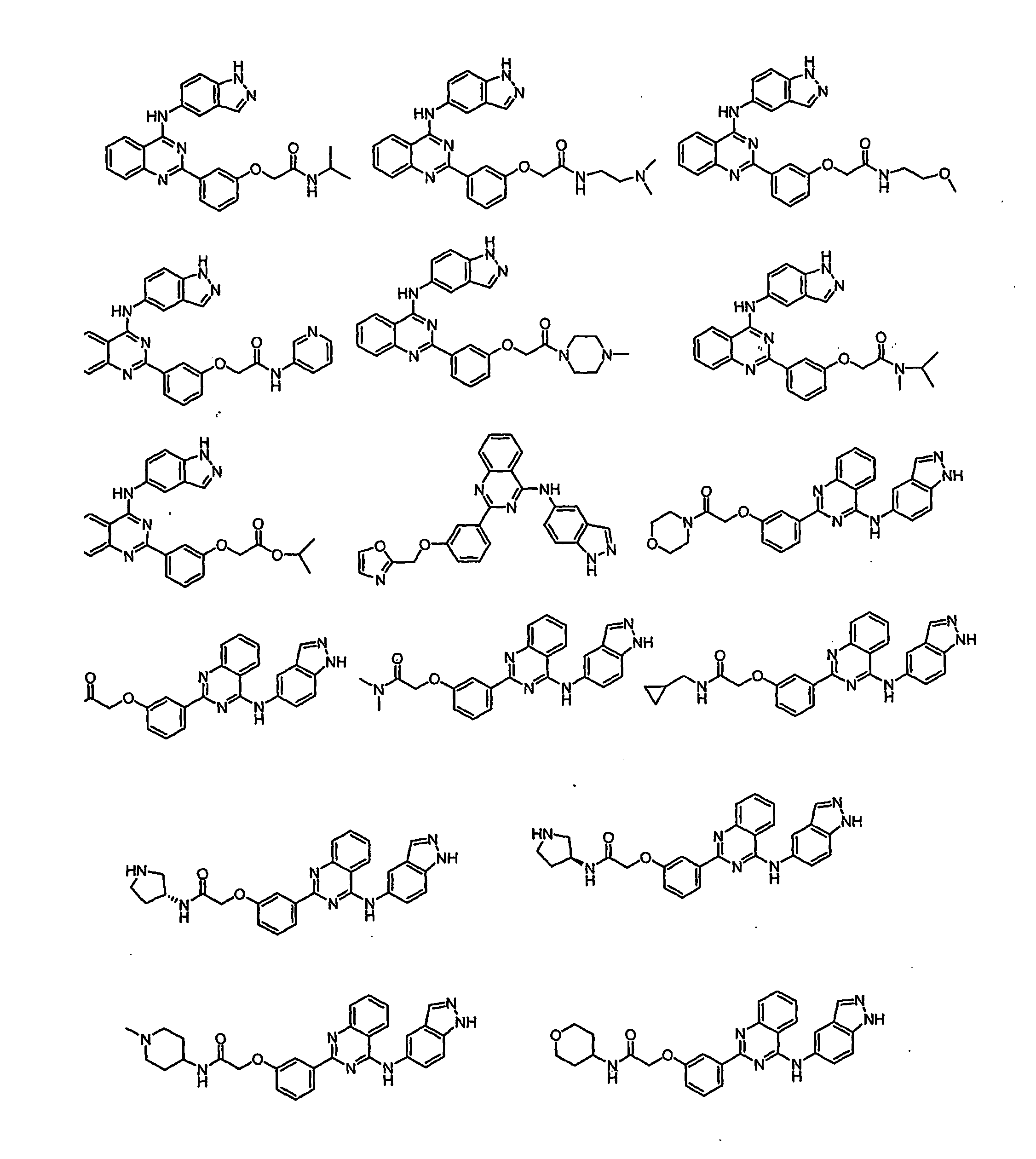
Anti-tumor medicine in double-aryl urea structure based on indazole, indole, azaindazole or azaindole
The invention belongs to the field of medicines, relates to anti-tumor medicines, and in particular relates to anti-tumor medicines in double-aryl urea structures based on indazole, indole, azaindazole or azaindole. The structural formulae of the anti-tumor medicines are shown in formula (Ia) and formula (Ib), wherein Z is N atom or C atom; W is O; M is O, S, N or CH; n is 1 or 2; Y and R are halogen atoms, H, R1, CF3, OCF3, OH, OR2, OCOR3, NH2, NHR4, NR52, NHCOR6, carboxyl group, ester group, cyano group, mercapto group, alkyl sulphanyl, sulfuryl, sulfoxide, sulfonic group, sulfamate, sulfonamide, ketonic group, aldehyde group, nitro group or nitroso group. Pharmacodynamic experiments prove that the medicines have good anti-tumor effects on human lung cancer, human kidney cancer, human colon cancer, human liver cancer, human gastric cancer, human breast cancer, melanoma and the like.
Owner:JINAN HAILE MEDICAL TECH DEV
Sirolimus lipidosome freeze-dried acanthopanax powder and technique of preparing the same
InactiveCN101129361AGood curative effectExtension of timeOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryDiffusion methodsFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a xiluomosi liposome freeze dried and making technique, which comprises the following steps: selecting liposome component, buffer, organic solvent, antioxidant and freeze-drying protective as raw material; adopting film diffusion method to make the liposome turbid liquor with xiluomosi through high-pressure or hypersonic dispersing method evenly; drying the liposome to improve the storage stability obviously; dispersing the freeze dried at random proportion in the water evenly without any sediment and impurity; making the packing rate of liposome at 96% with the grain size at 50-250nm; improving the drug effect greatly in comparison with oral agent; lengthening the circulating time in the blood; elevating the biological utility of drug.
Owner:山东华诺生物科技有限公司
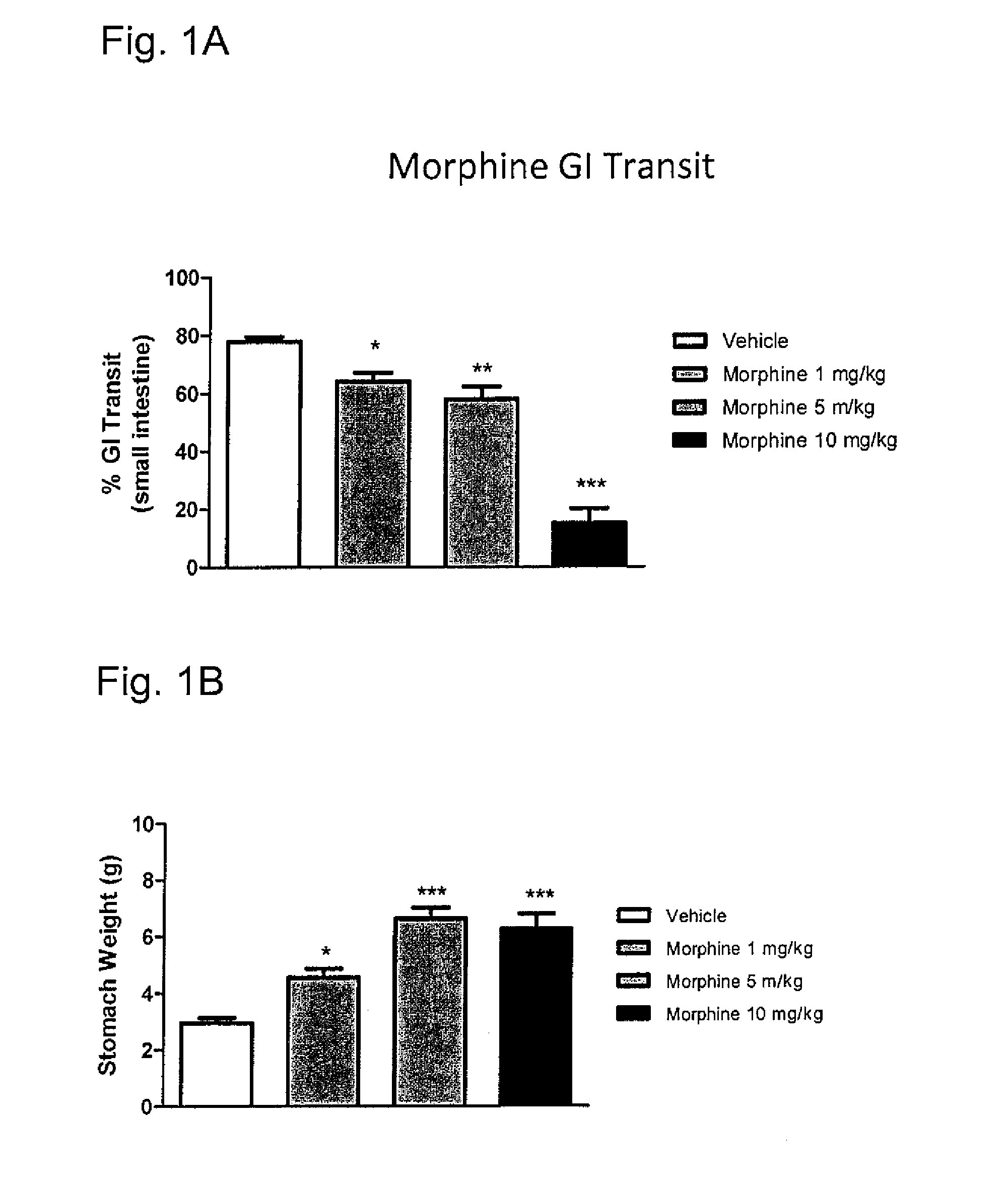
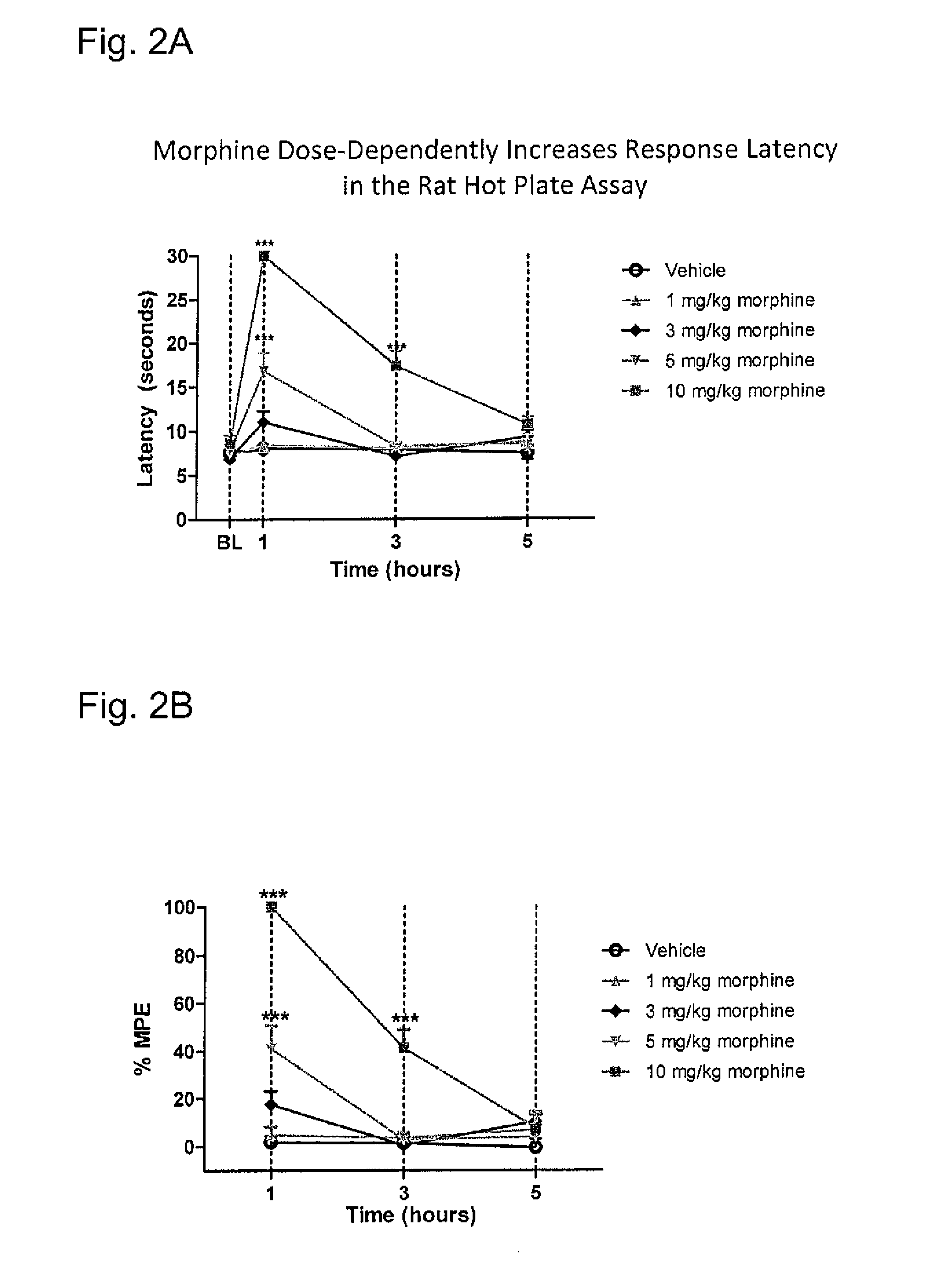
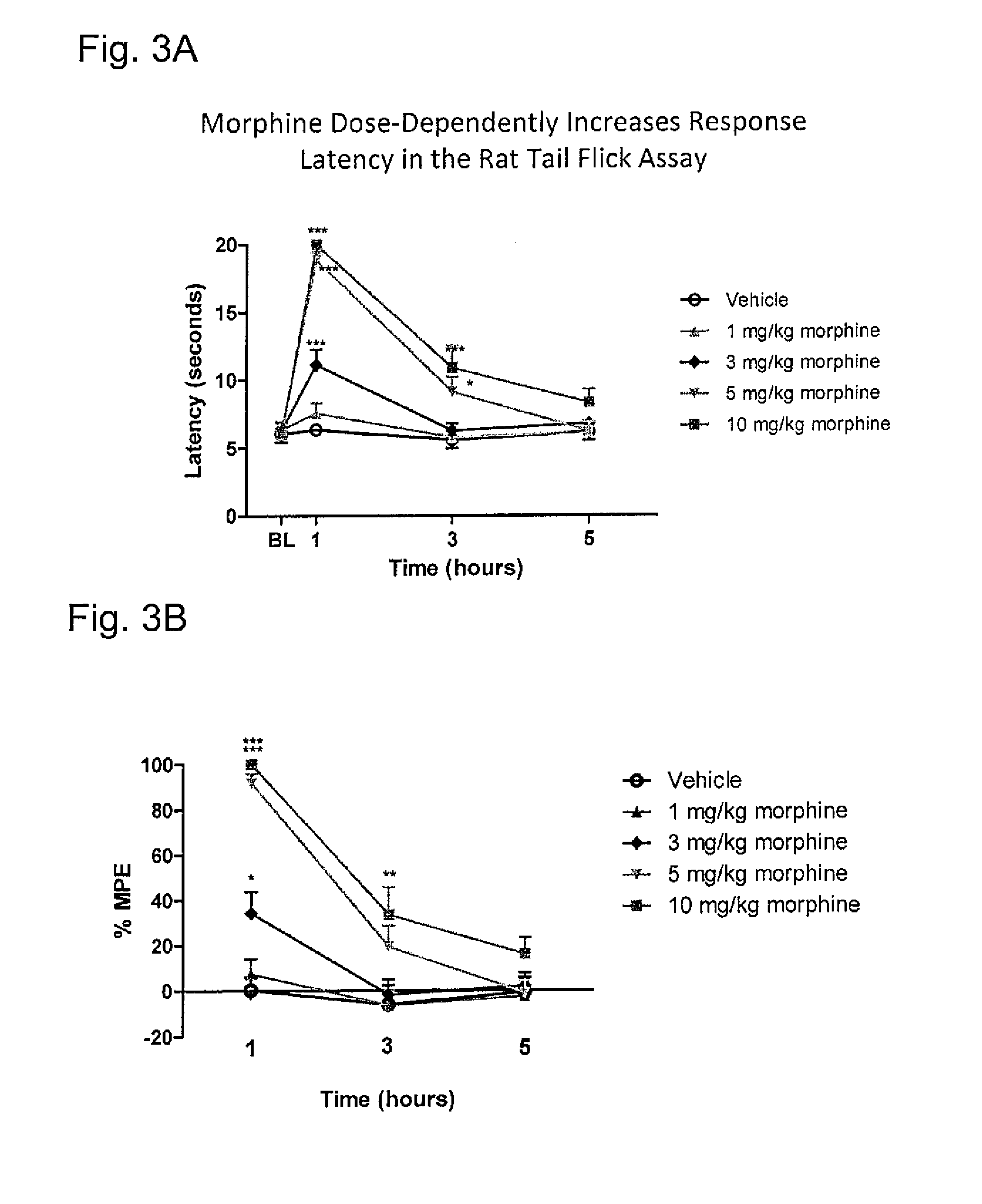
Systems and methods for treating an opioid-induced adverse pharmacodynamic response
Owner:PURDUE PHARMA LP
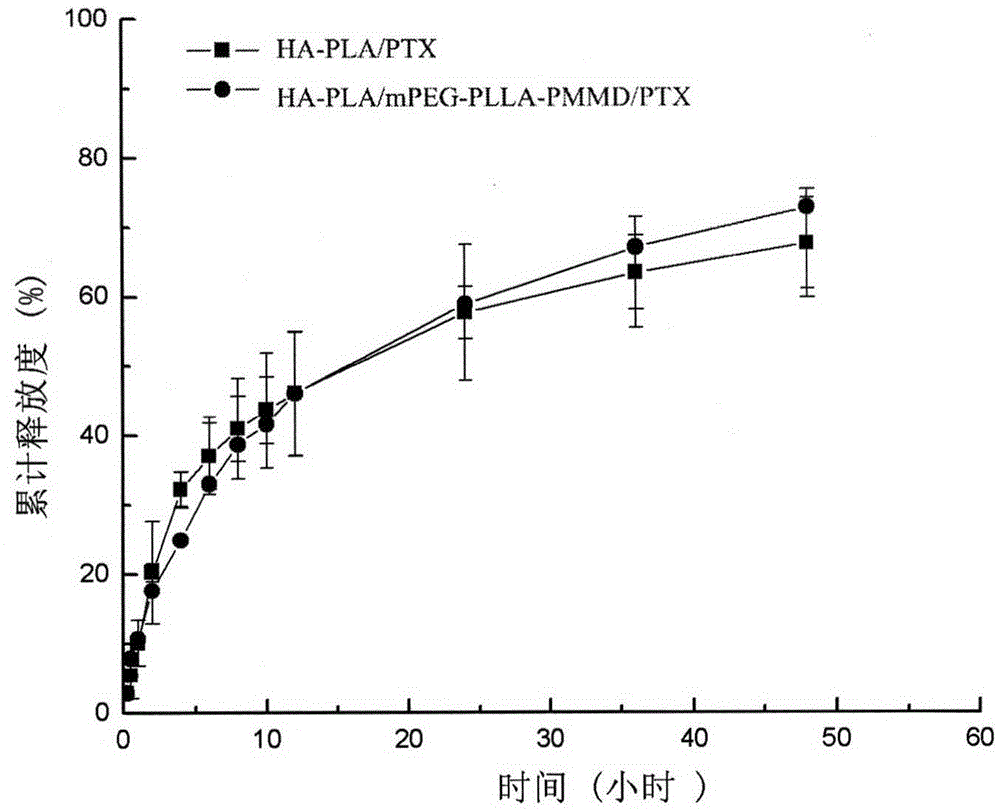
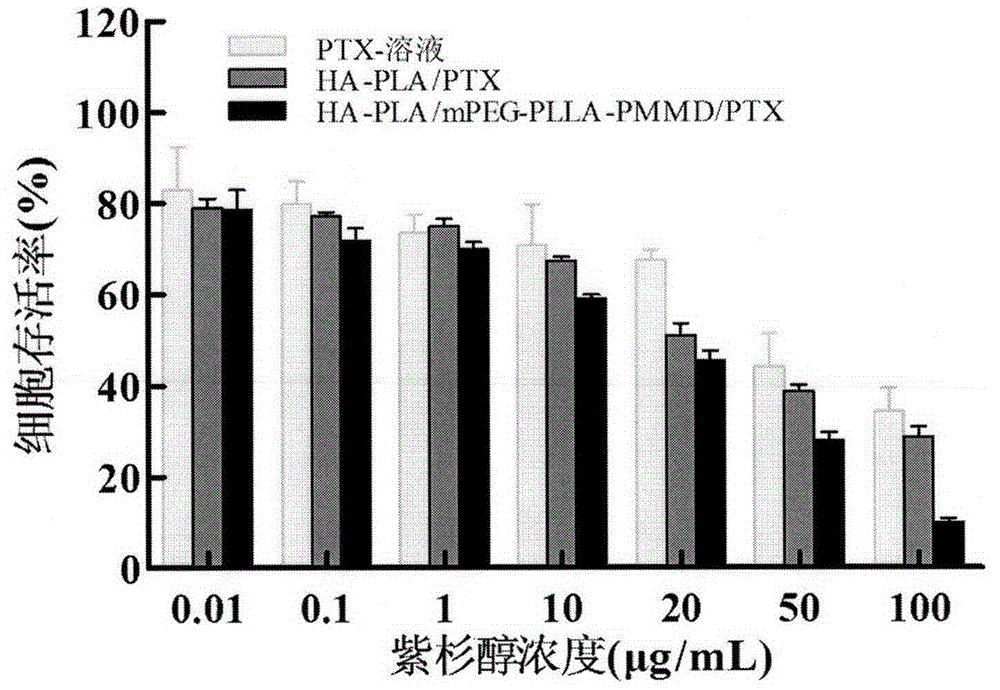
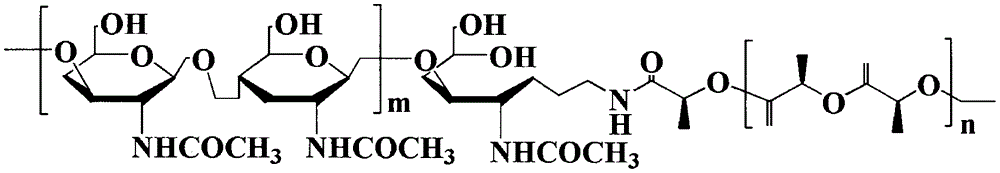
Method for synthesizing multifunctional active targeted hyaluronic acid-polylactic acid carrier and preparing anti-tumor medicinal micelle of multifunctional active targeted hyaluronic acid-polylactic acid carrier
ActiveCN104056275AExtend cycle timeSmall toxicityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsEmulsion deliverySolubilityPolyester
The invention belongs to the fields of polymer chemistry and medicinal preparations, and particularly relates to a method for synthesizing an active targeted hyaluronic acid-polylactic acid carrier, a method for preparing an anti-tumor medicinal micelle of the active targeted hyaluronic acid-polylactic acid carrier and an application thereof. By adopting a novel self-assembly technology, amphipathic PEG (polyethylene glycol) block polyester copolymer and tumor targeted ligand hyaluronic acid-polylactic acid copolymer are self-assembled by means of the electrostatic interaction to form a multifunctional composite micelle; the solubility of insoluble tumor medicaments and the drug loading capacity and encapsulation efficiency of water-soluble anti-tumor medicines can be remarkably improved by virtue of the anti-cancer drug-loaded micelle and composite micelle composition, the medicines can be biodegraded in a body, phagocytosis of a reticuloendothelial system (RES) and excretion of a kidney can be avoided. The active targeted hyaluronic acid-polylactic acid carrier has a long-circulating effect, the multifunctional composition has a prominent advantage of tumor active targeting effect, and parameters of pharmacodynamics in vitro and in vivo of the micelle are remarkably superior to those of common anti-tumor injections. Clinically acceptable administration means of the micelle includes injection administration or mucosal administration, and preparations of the micelle can be injection, transfusion, injection lyophilized powder injections or dry powder inhalation.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
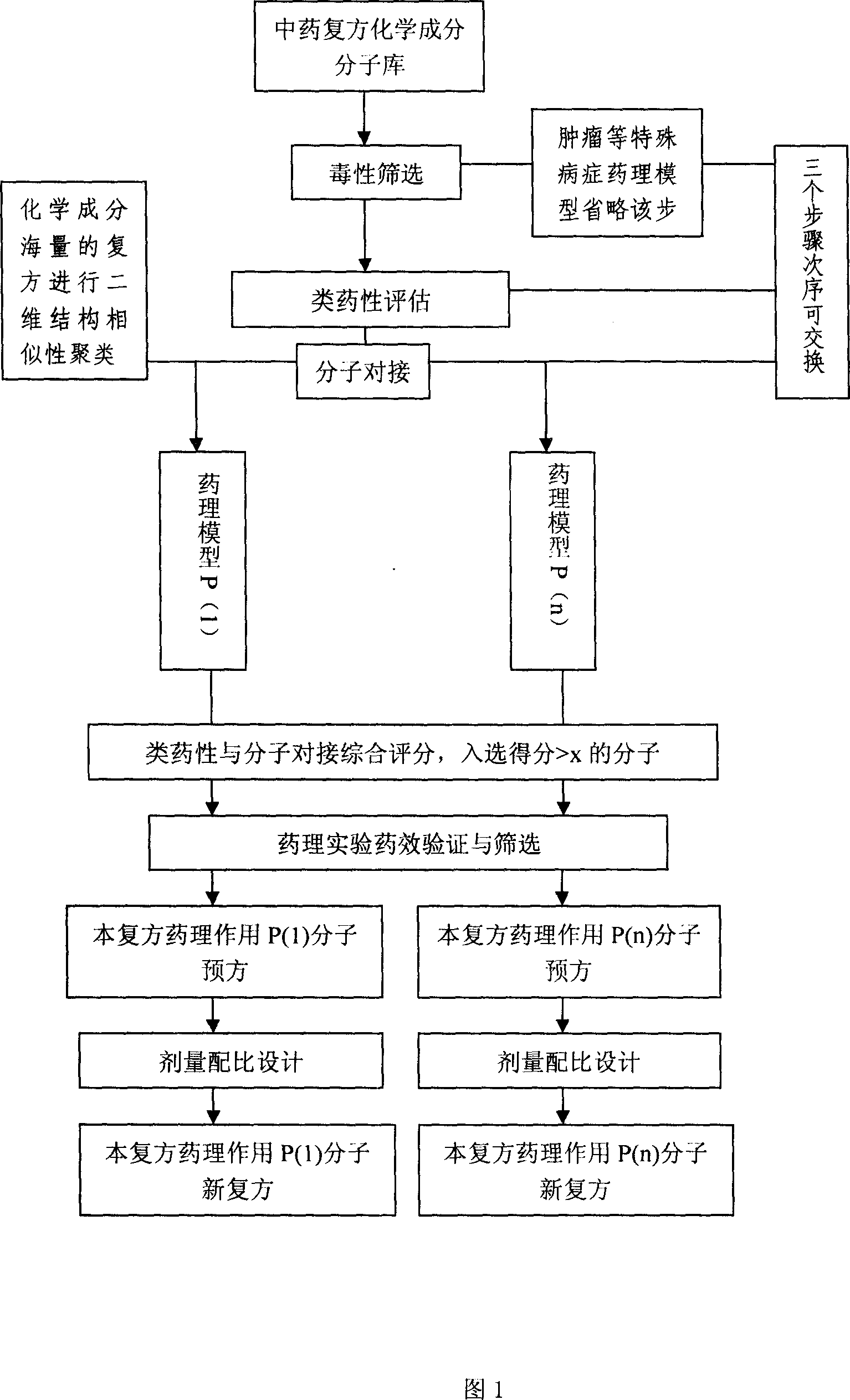
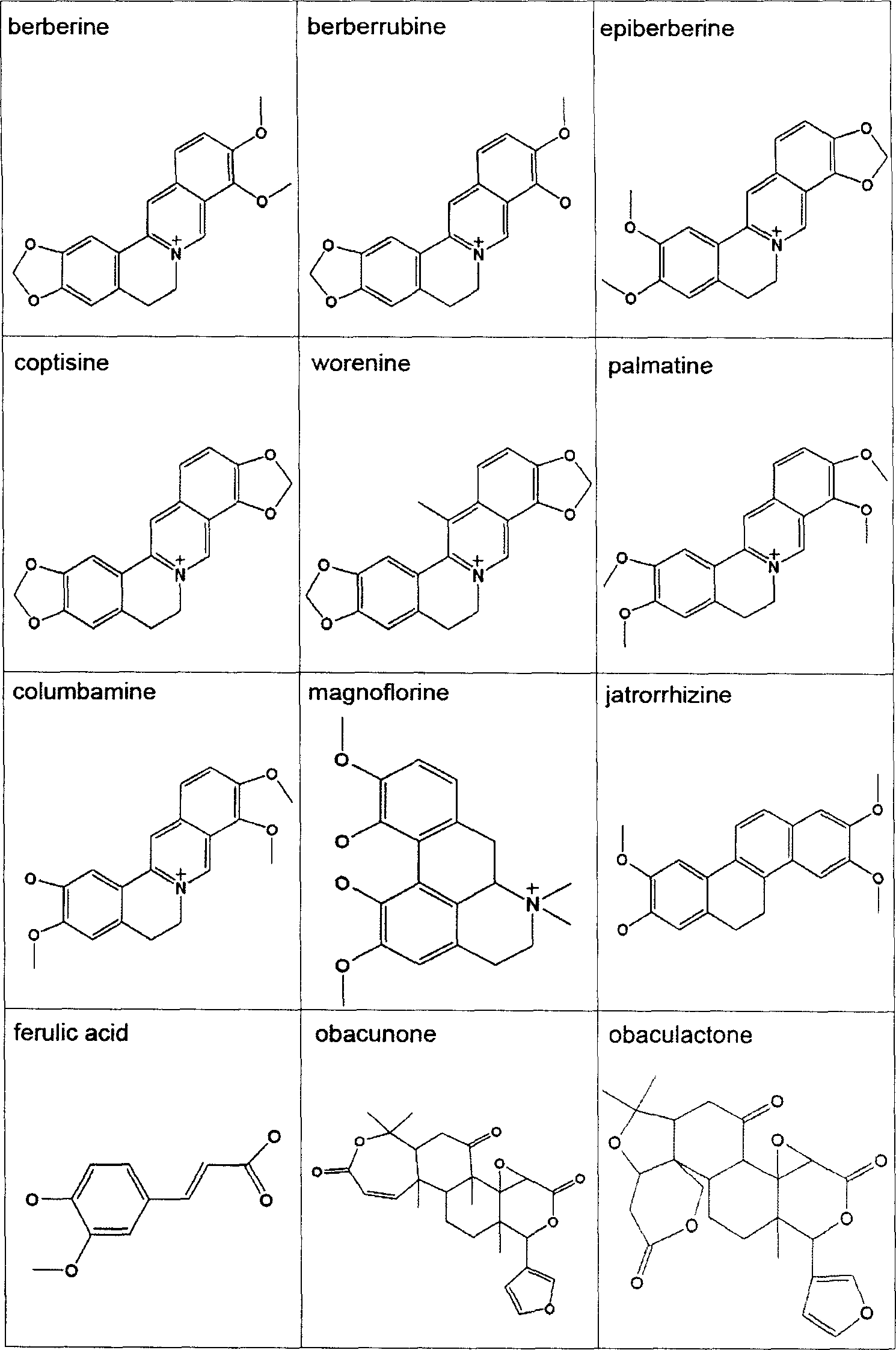
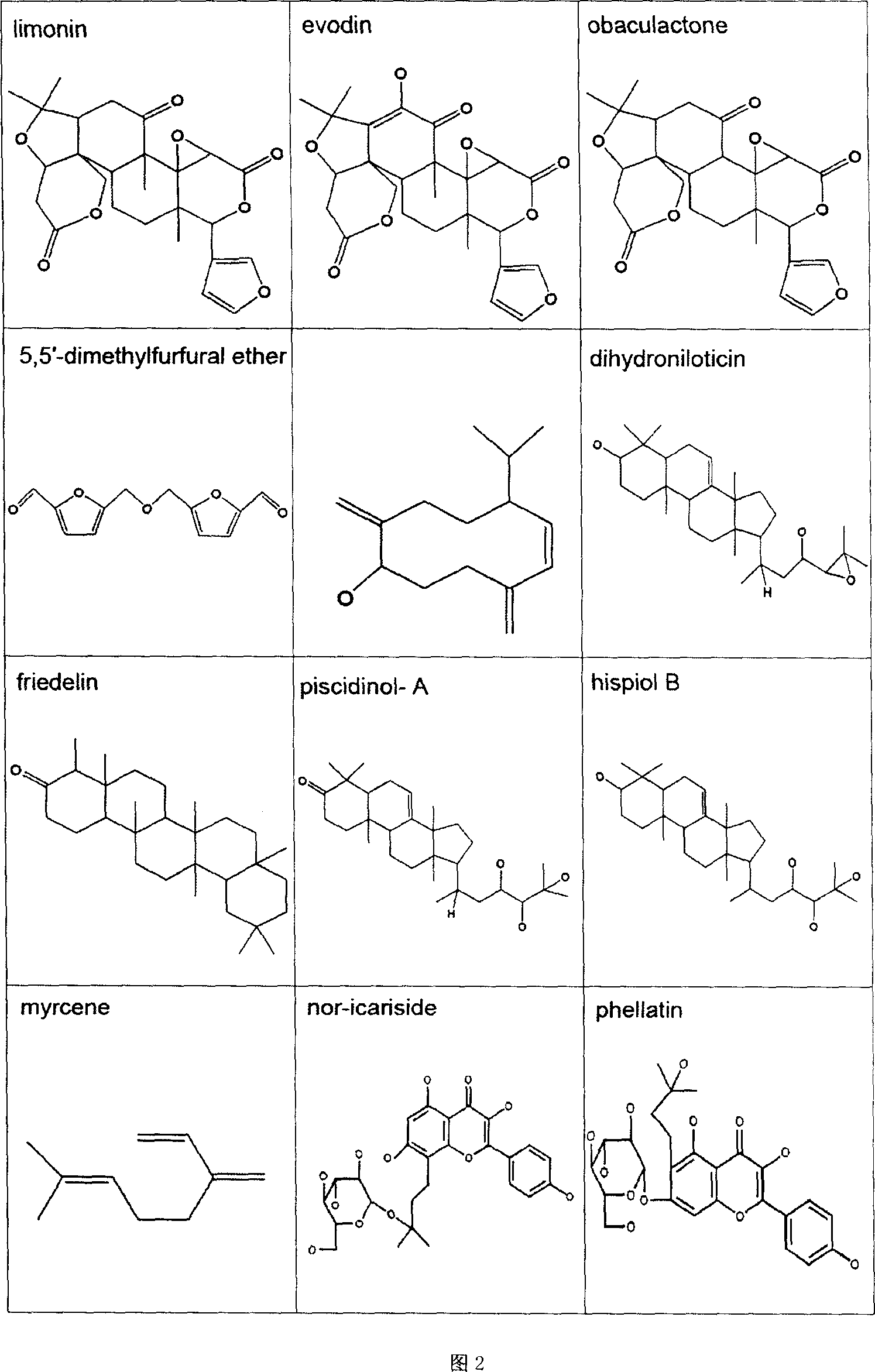
Virtual screening method for compound pesticide effect matter base of traditional chinese medicine
InactiveCN101089245AEconomic noveltyAbandon the shortcomings that are not conducive to poor compliance of preparationsLibrary screeningResearch ObjectAdditive ingredient
In this invention, first It is set that an object of study of a compound traditional Chinese medicine with its chemical compositions being clear about. The molecules of chemical constitutions of each ingredient of the Chinese medicine prescription are collected and reorganized, and setting a data base for chemical constitutions molecules of said Chinese medicine prescription. For the aim of pharmacodynamics effects of main therapeutical functions of the traditional Chinese medicine prescription with their clear therapeutical effects, clear mechanism and definited target spots, we search or set up the corresponding molecular target spots. Three procedures (without odor of priority) are: poisonousness sieving, analogous medicine properties estimation and molecular abutment decision to these molecular data base of the set pharmacodynamics models respectively. Finally we estimating all the molecules in the molecular data base, selecting-out the molecules with higher grading, to obtain the pharmacodynamics effect P(i) molecular pre-prescription, and then producing novel prescriptions.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Pharmacokinetically improved compounds
The present invention relates to inhibitors of ROCK1 and ROCK2 and methods of modulating the pharmacokinetic and / or pharmacodynamic properties of such compounds. Also provided are methods of inhibiting ROCK1 and or ROCK2 that are useful for the treatment of disease.
Owner:SURFACE LOGIX INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
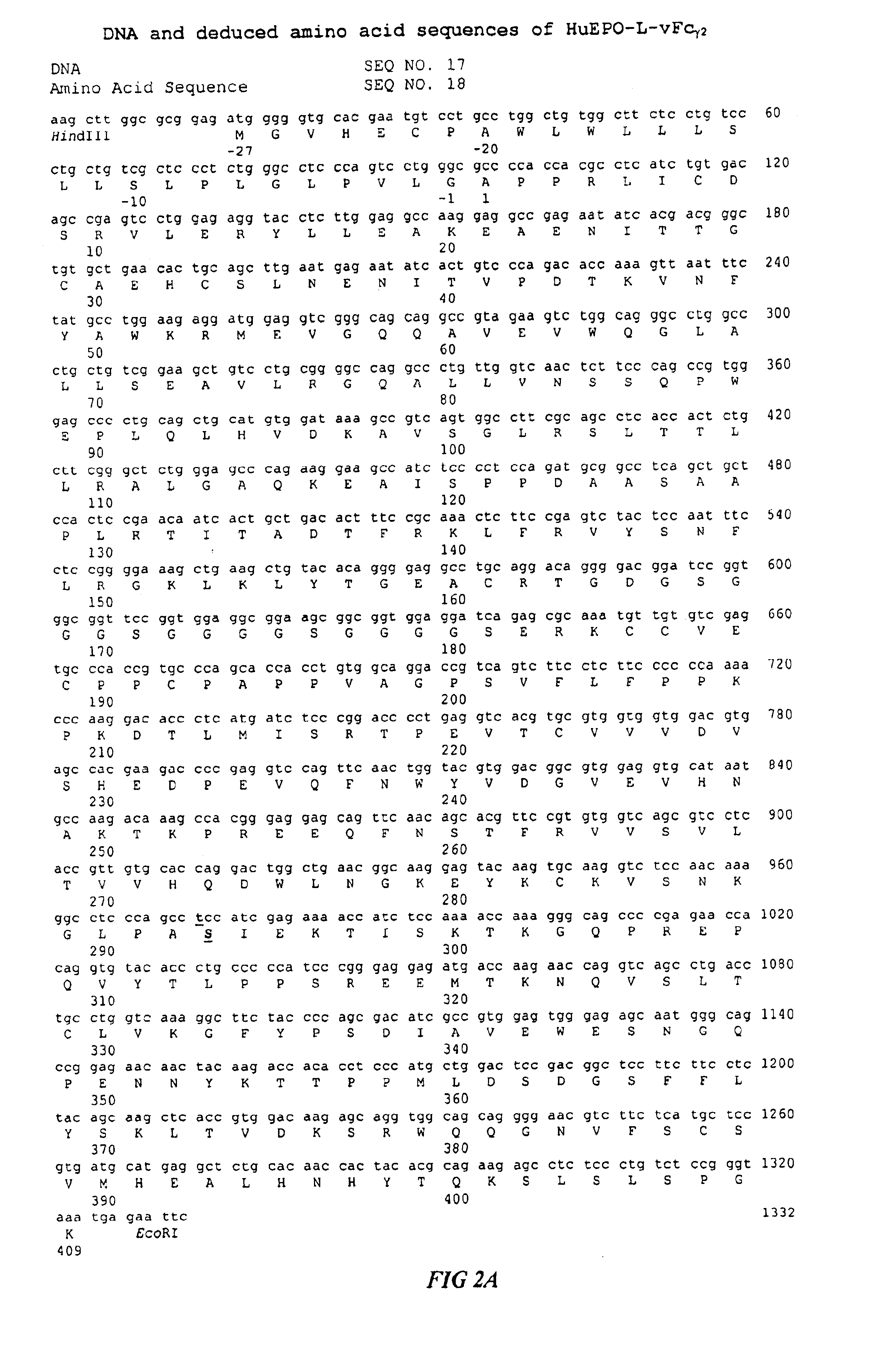




![Application of 2-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-2-oxoethyl 4-((3-chloro-4-methylphenyl) amino)-4-oxobutanoate in preparing an LSD1 (lysine-specific demethylase 1) inhibitor medicament Application of 2-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-2-oxoethyl 4-((3-chloro-4-methylphenyl) amino)-4-oxobutanoate in preparing an LSD1 (lysine-specific demethylase 1) inhibitor medicament](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/7e706329-04e4-4b5b-b8c9-1a182cd2dbef/HSA0000102396500000011.PNG)
![Application of 2-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-2-oxoethyl 4-((3-chloro-4-methylphenyl) amino)-4-oxobutanoate in preparing an LSD1 (lysine-specific demethylase 1) inhibitor medicament Application of 2-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-2-oxoethyl 4-((3-chloro-4-methylphenyl) amino)-4-oxobutanoate in preparing an LSD1 (lysine-specific demethylase 1) inhibitor medicament](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/7e706329-04e4-4b5b-b8c9-1a182cd2dbef/HSA0000102396500000012.PNG)
![Application of 2-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-2-oxoethyl 4-((3-chloro-4-methylphenyl) amino)-4-oxobutanoate in preparing an LSD1 (lysine-specific demethylase 1) inhibitor medicament Application of 2-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-2-oxoethyl 4-((3-chloro-4-methylphenyl) amino)-4-oxobutanoate in preparing an LSD1 (lysine-specific demethylase 1) inhibitor medicament](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/7e706329-04e4-4b5b-b8c9-1a182cd2dbef/HSA0000102396500000013.PNG)