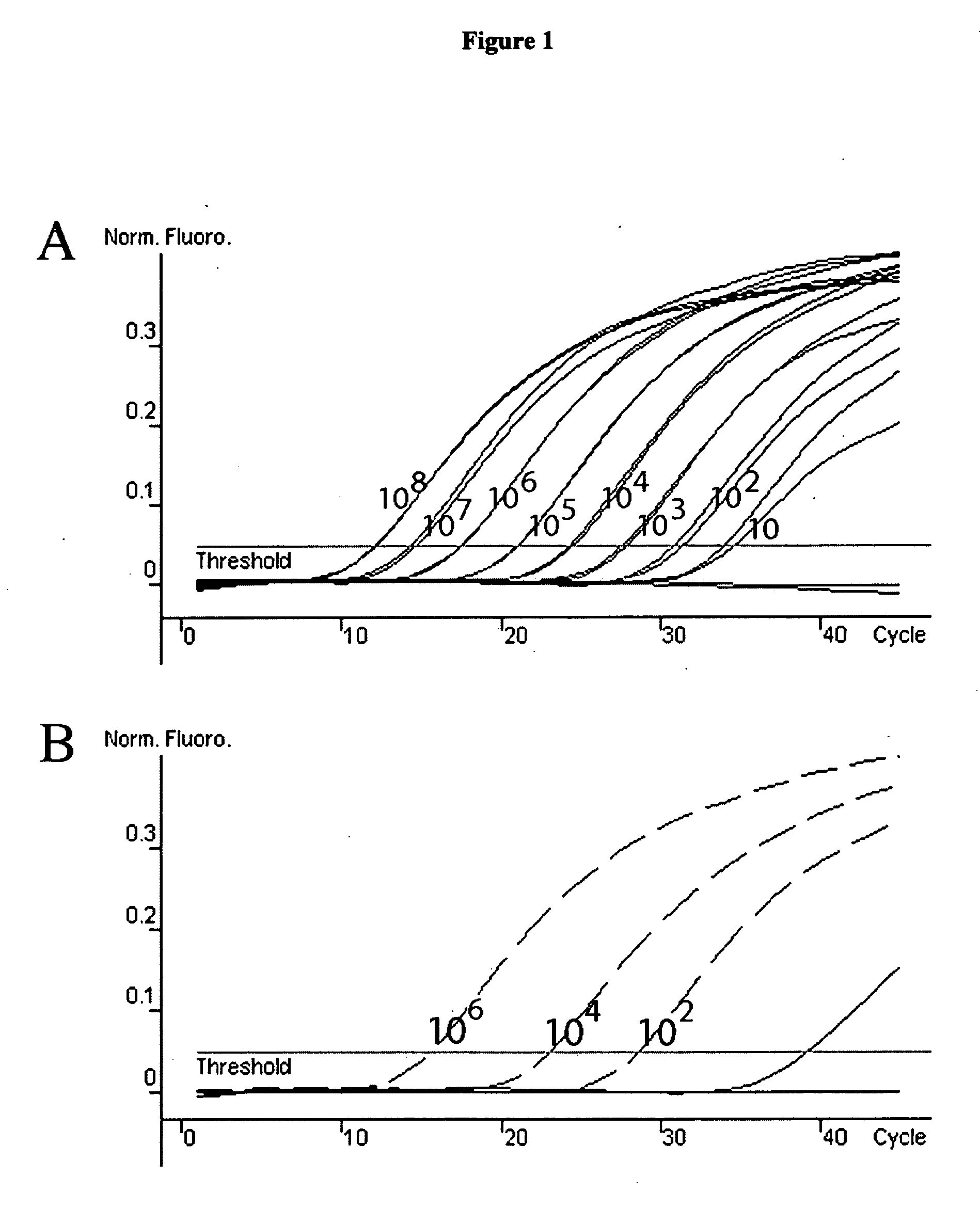
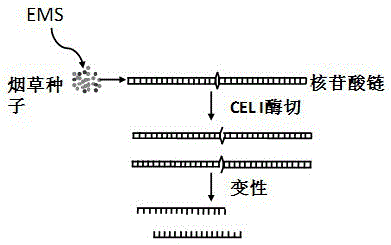
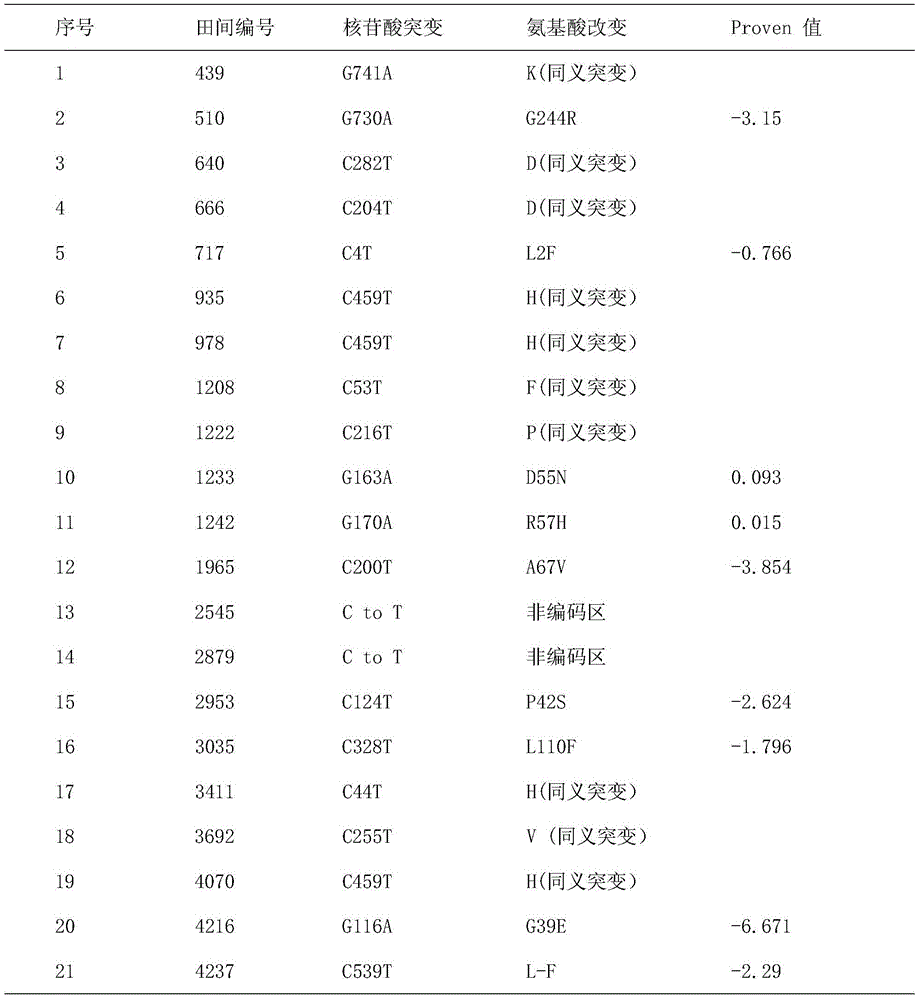
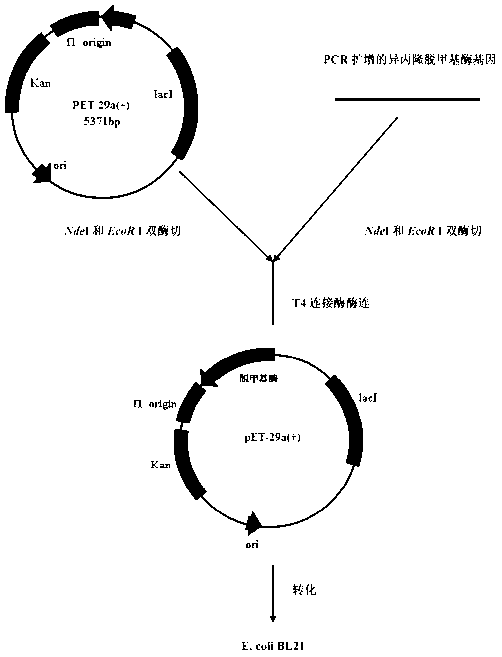
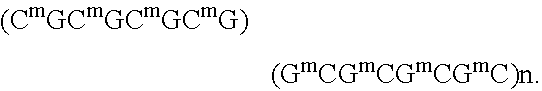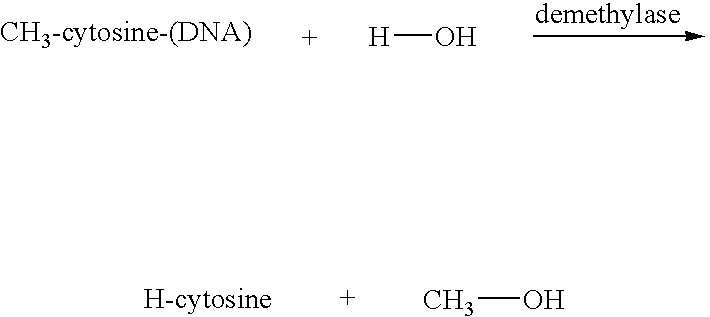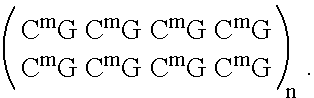Patents
Literature
102 results about "Demethylase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Demethylases are enzymes that remove methyl (CH₃-) groups from nucleic acids, proteins (in particular histones), and other molecules. Demethylase enzymes are important in epigenetic modification mechanisms. The demethylase proteins alter transcriptional regulation of the genome by controlling the methylation levels that occur on DNA and histones and, in turn, regulate the chromatin state at specific gene loci within organisms.
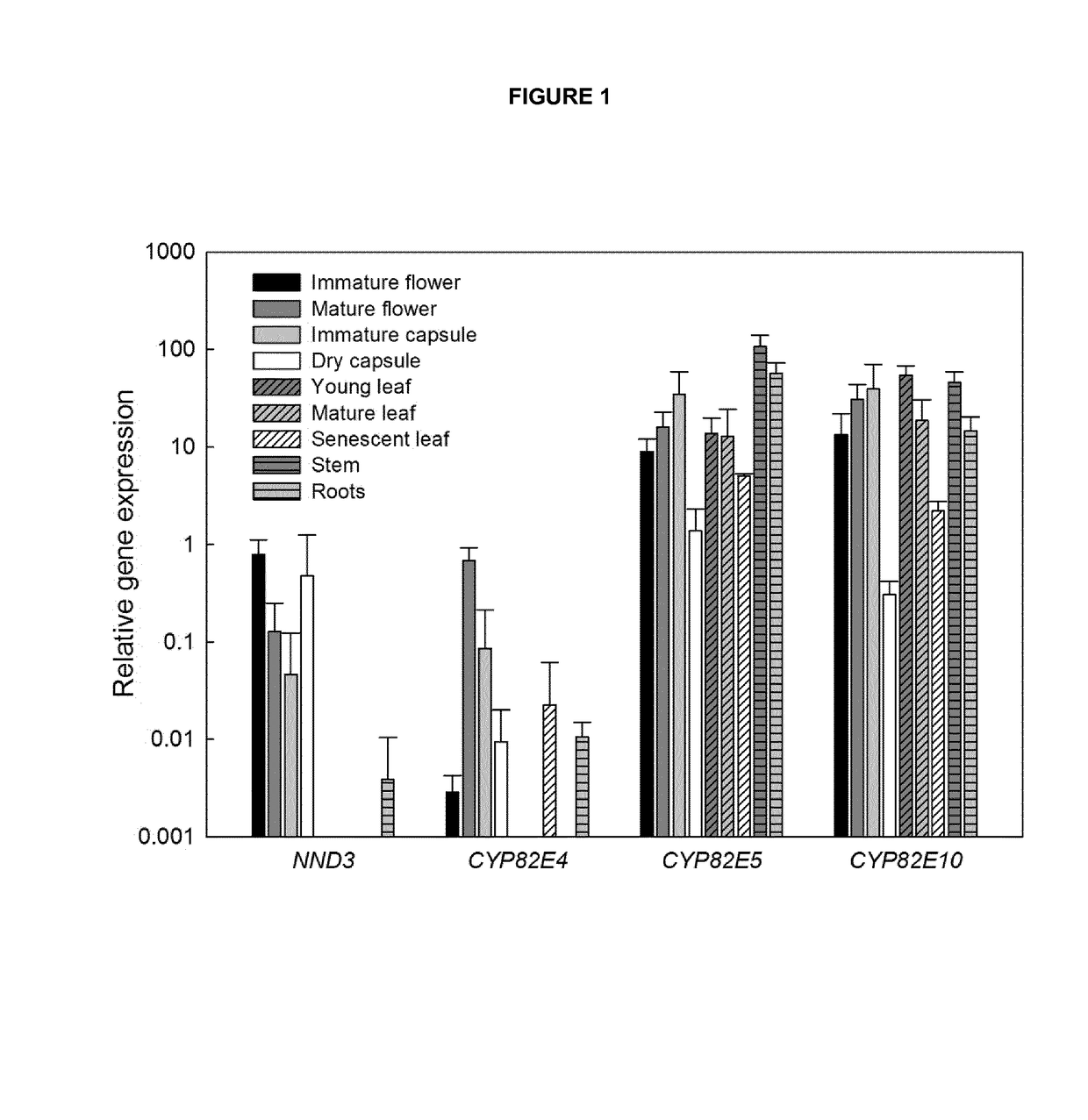
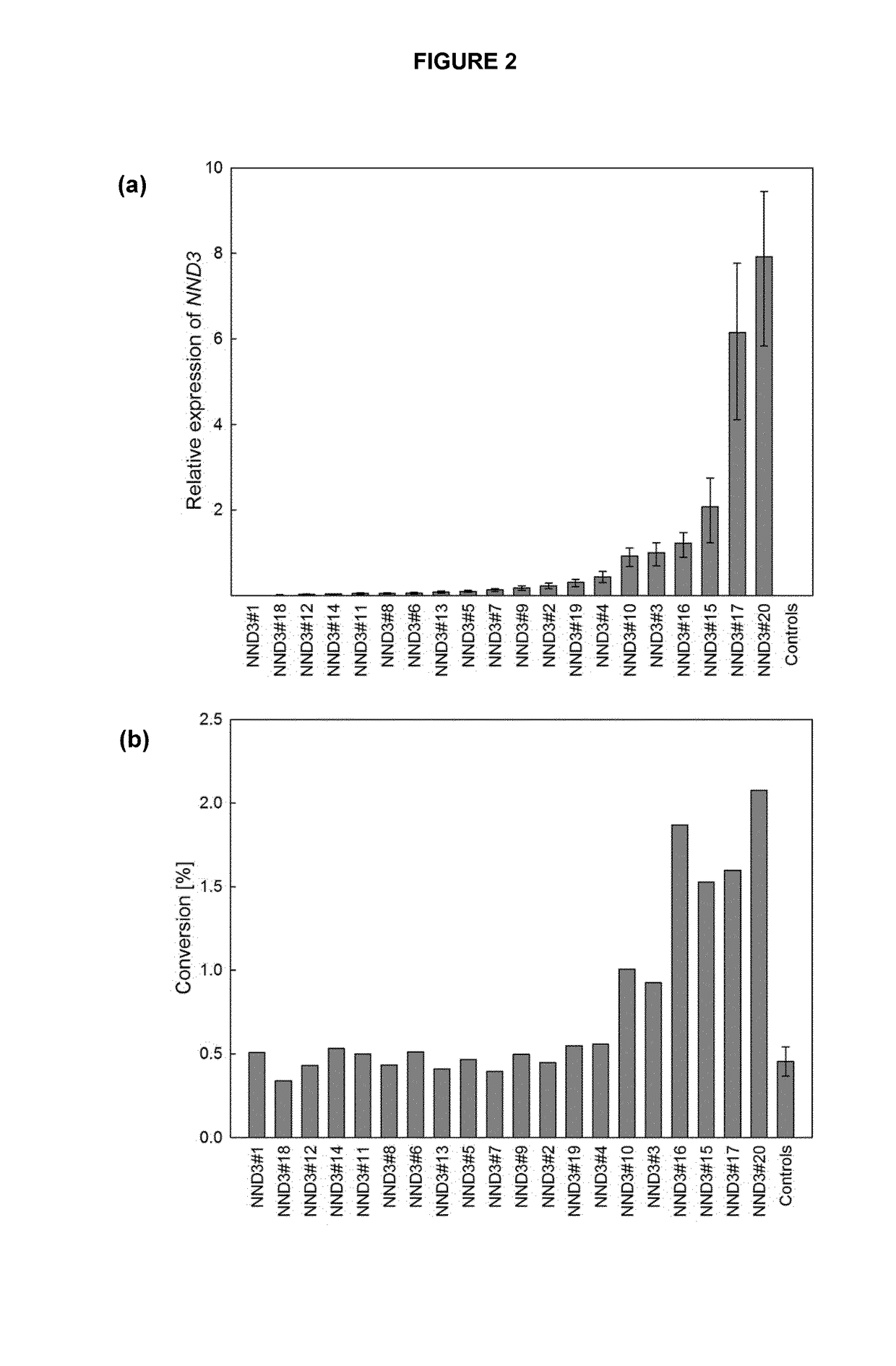
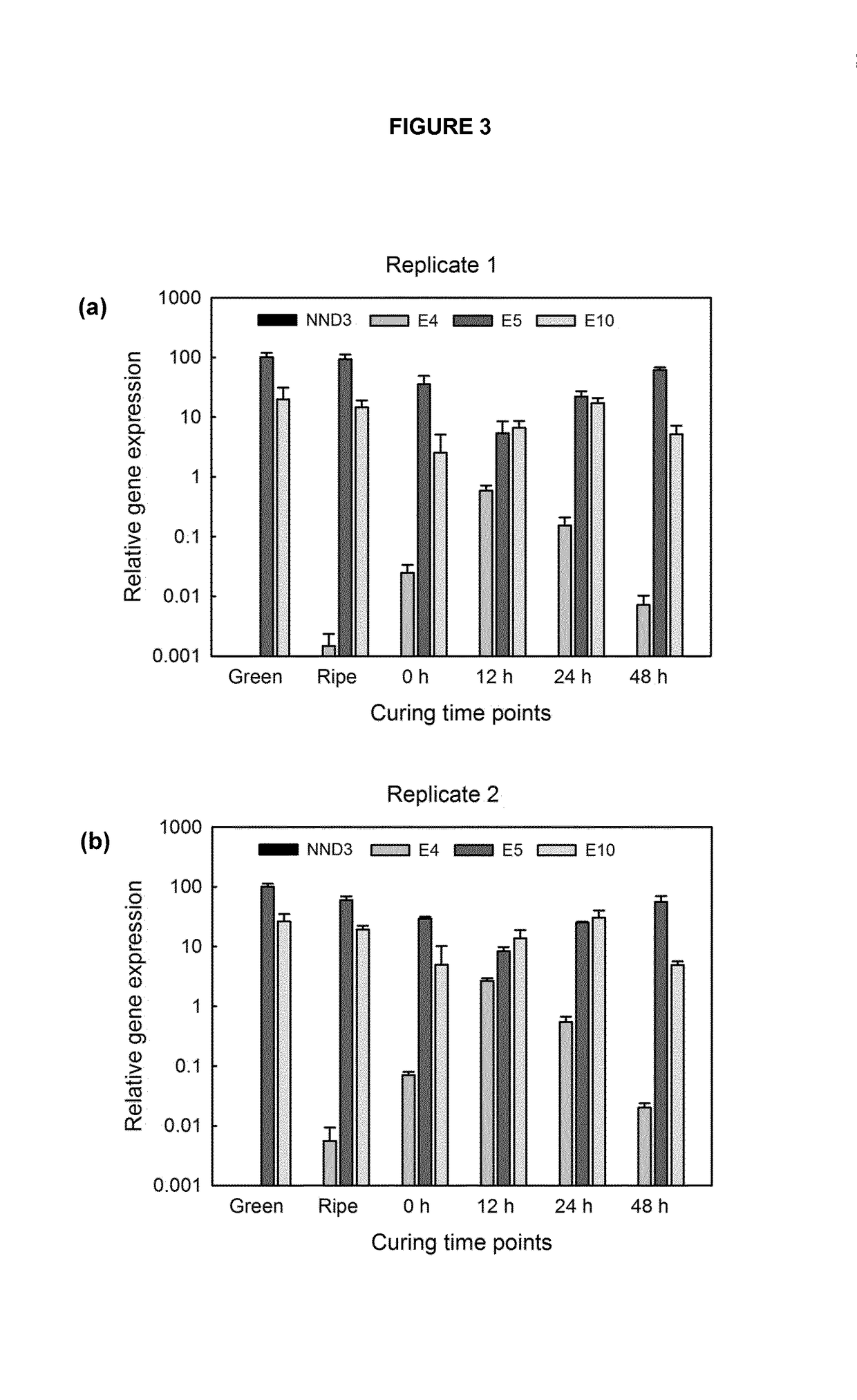
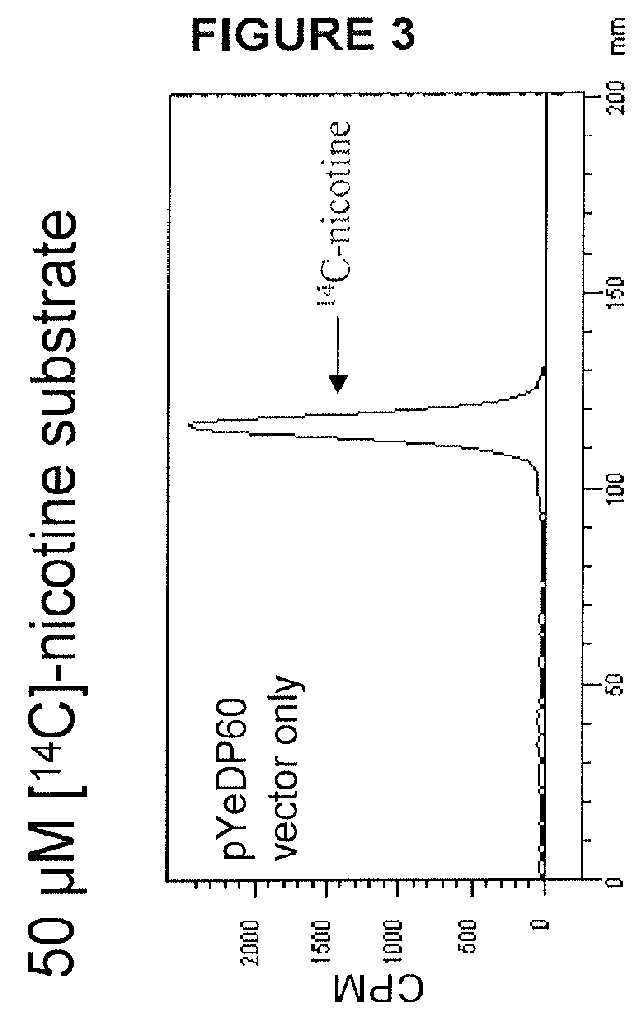
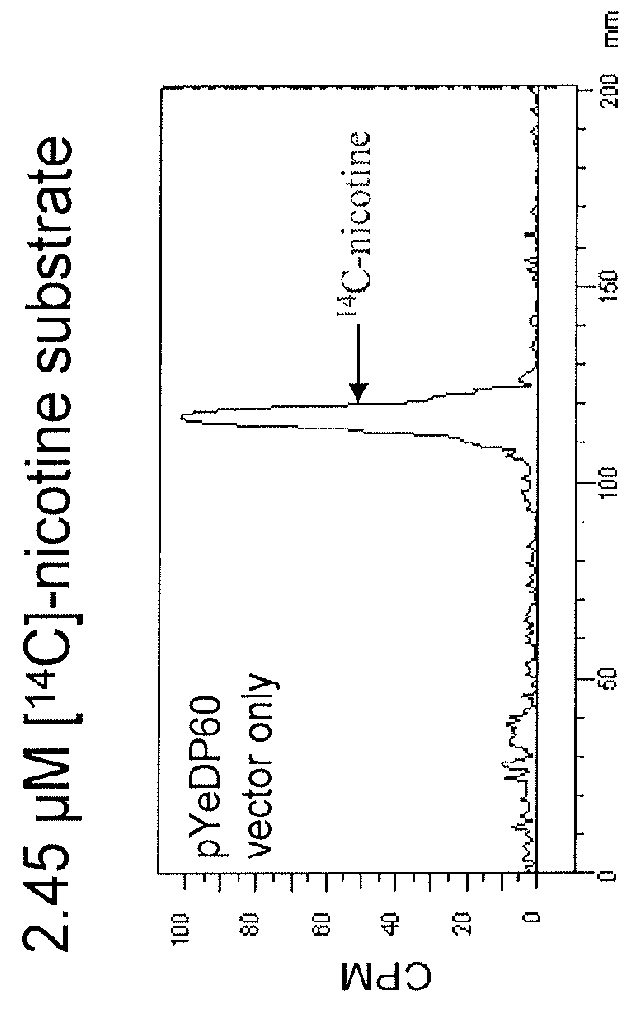
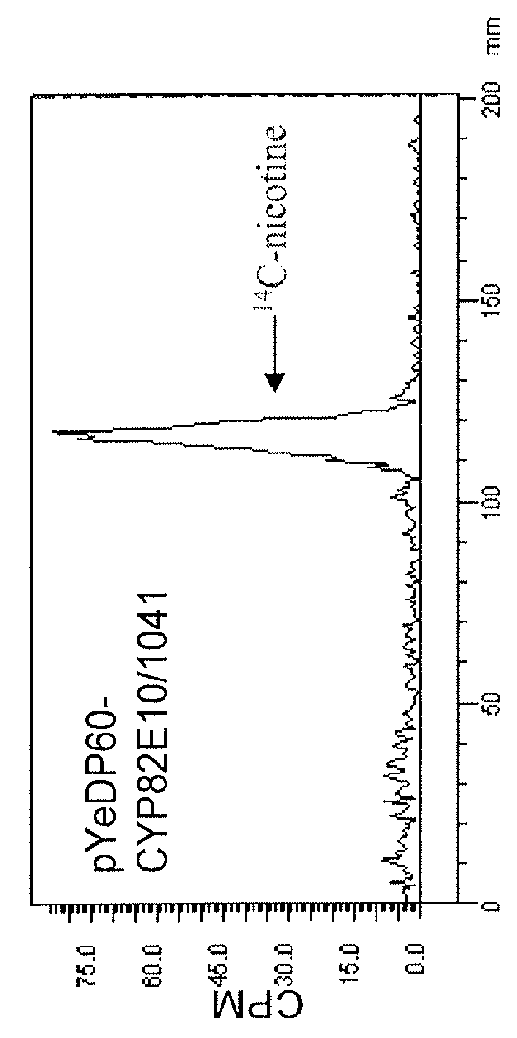
Compositions and methods for minimizing nornicotine synthesis in tobacco
Compositions and methods for reducing the level of nornicotine and N′-nitrosonornicotine (NNN) in tobacco plants and plant parts thereof are provided. The compositions comprise isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides for a root-specific nicotine demethylases, CYP82E10, and variants thereof, that are involved in the metabolic conversion of nicotine to nornicotine in these plants. Compositions of the invention also include tobacco plants, or plant parts thereof, comprising a mutation in a gene encoding a CYP82E10 nicotine demethylase, wherein the mutation results in reduced expression or function of the CYP82E10 nicotine demethylase. Seed of these tobacco plants, or progeny thereof, and tobacco products prepared from the tobacco plants of the invention, or from plant parts or progeny thereof, are also provided. Methods for reducing the level of nornicotine, or reducing the rate of conversion of nicotine to nornicotine, in a tobacco plant, or plant part thereof are also provided. The methods comprise introducing into the genome of a tobacco plant a mutation within at least one allele of each of at least three nicotine demethylase genes, wherein the mutation reduces expression of the nicotine demethylase gene, and wherein a first of these nicotine demethylase genes encodes a root-specific nicotine demethylase involved in the metabolic conversion of nicotine to nornicotine in a tobacco plant or a plant part thereof. The methods find use in the production of tobacco products that have reduced levels of nornicotine and its carcinogenic metabolite, NNN, and thus reduced carcinogenic potential for individuals consuming these tobacco products or exposed to secondary smoke derived from these products.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Lysine demethylase inhibitors for myeloproliferative disorders
ActiveUS20150232436A1Reduce decreaseAvoids side-effectsBiocideOrganic chemistryDiseaseMyeloproliferative disease
The invention relates to methods and compositions for the treatment or prevention of diseases and disorders associated with myeloproliferative disorders. In particular, the invention relates to an LSD 1 inhibitor for use in treating or preventing Philadelphia chromosome negative myeloproliferative disorders.
Owner:ORYZON GENOMICS SA
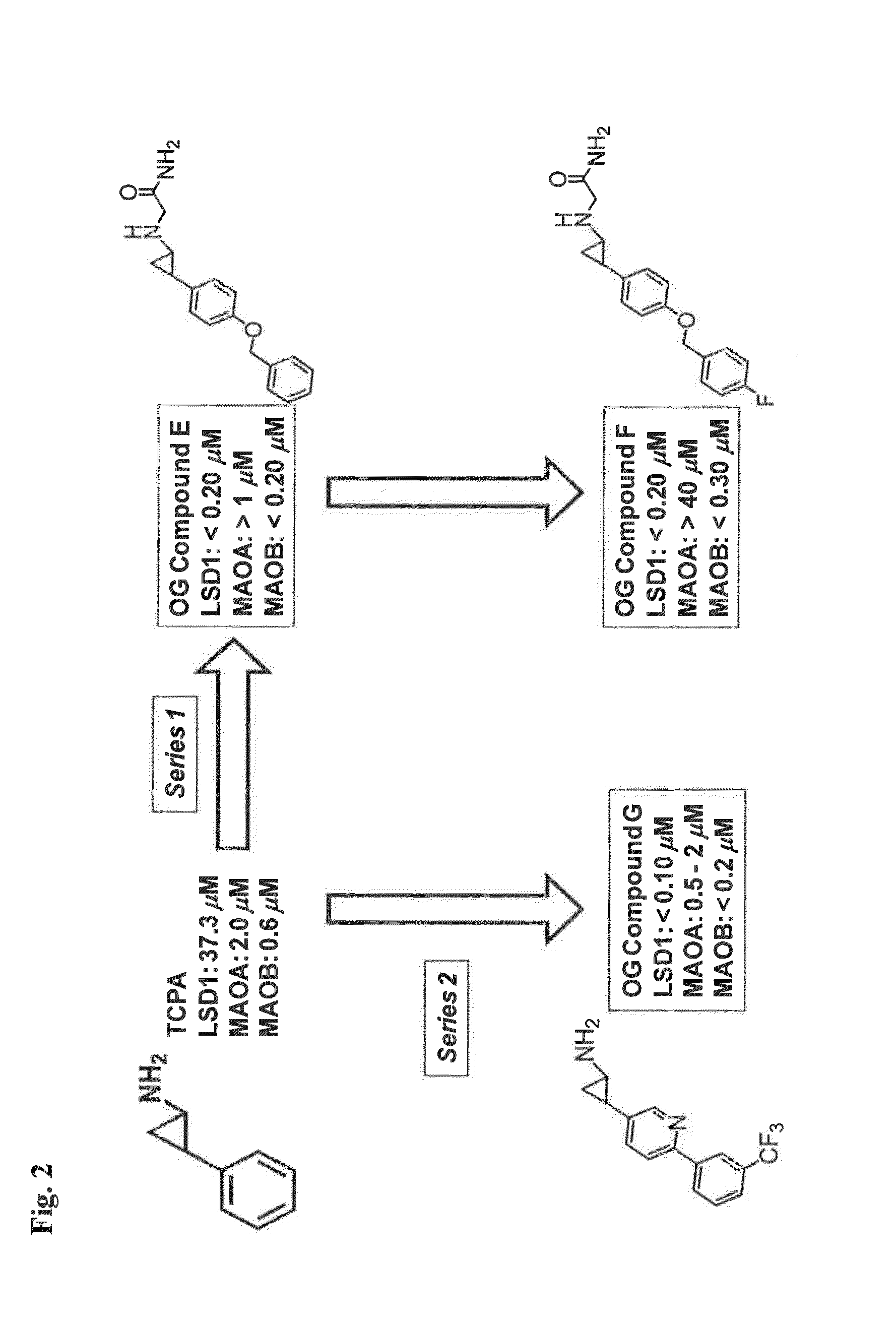
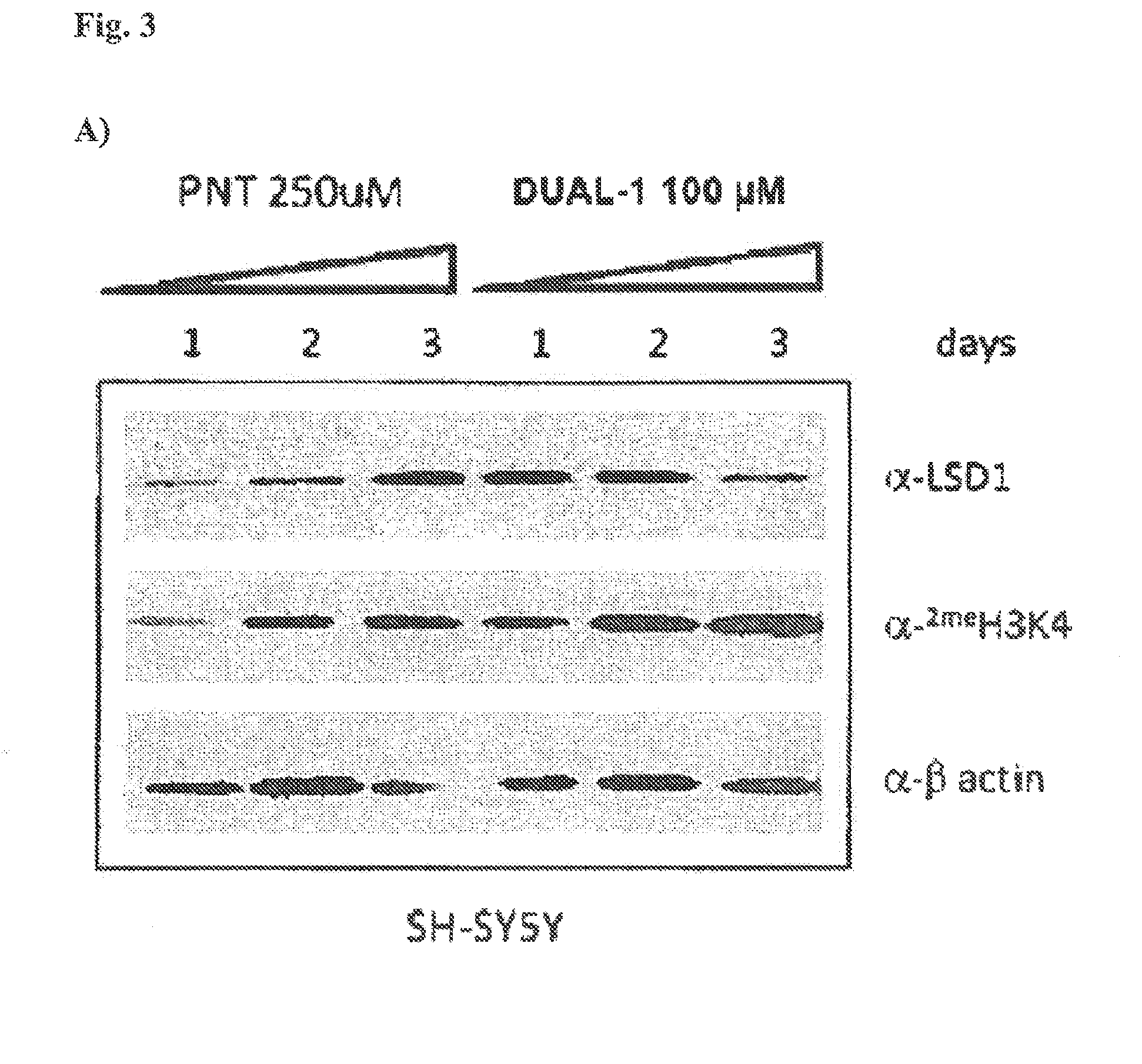
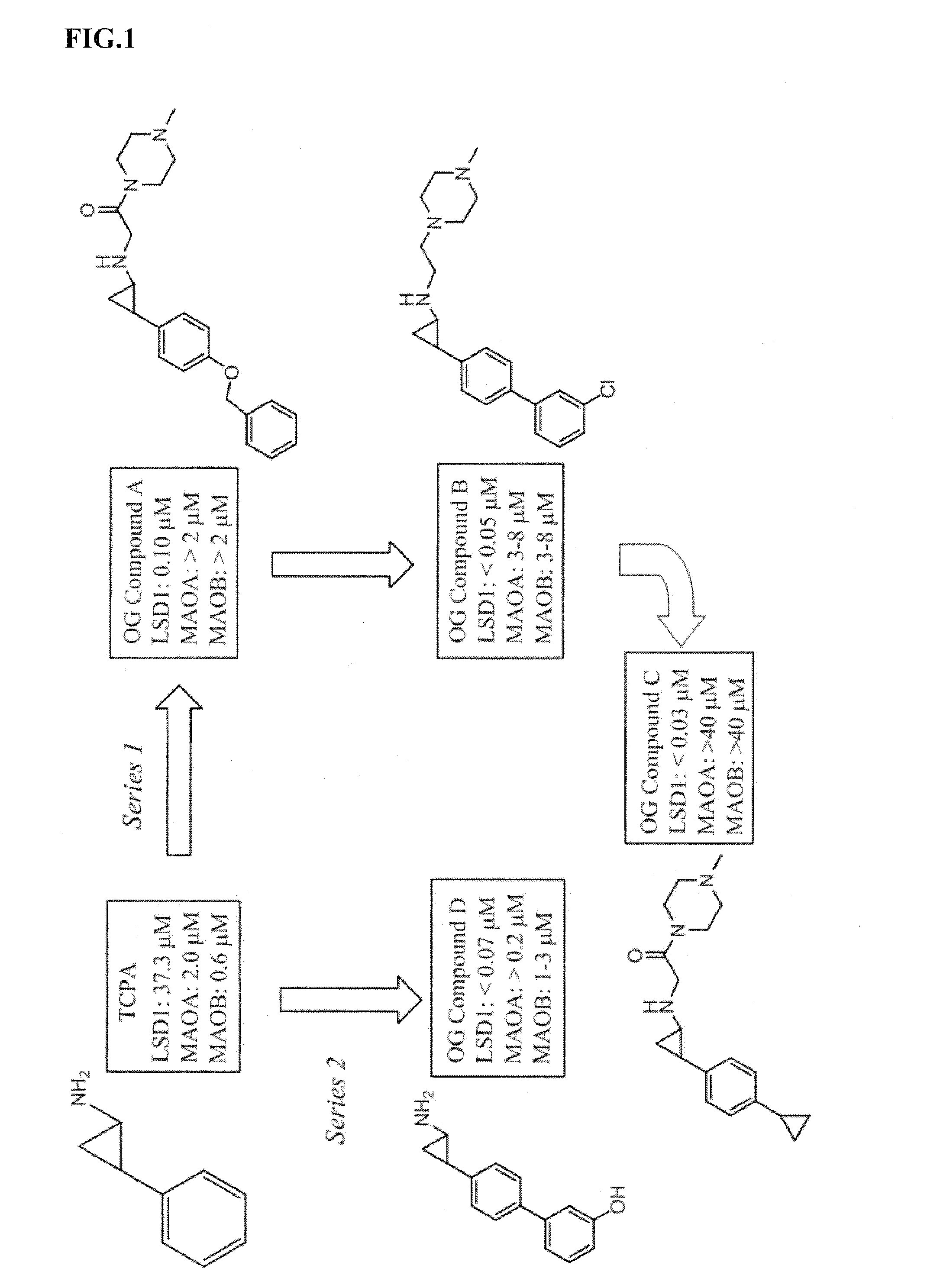
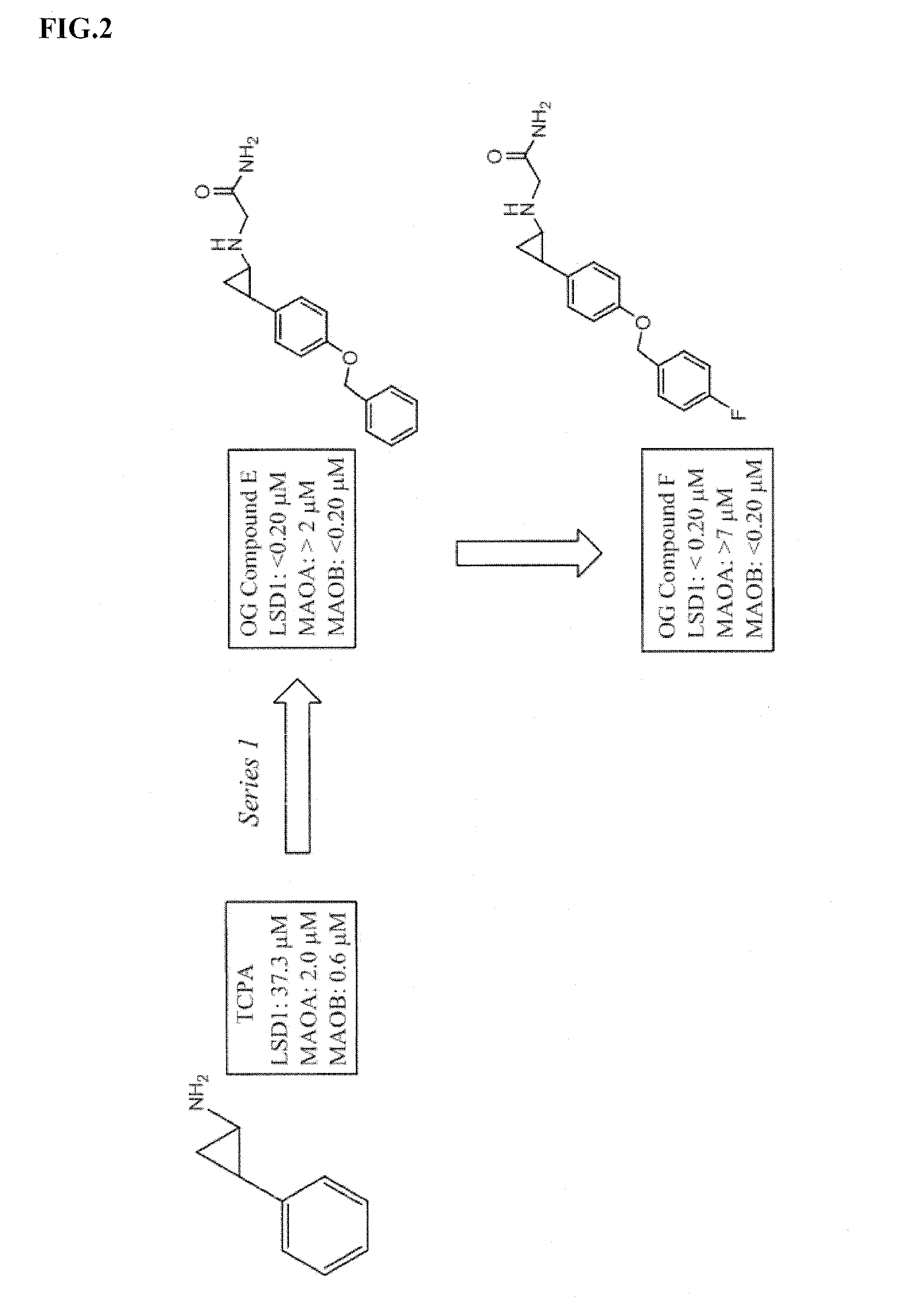
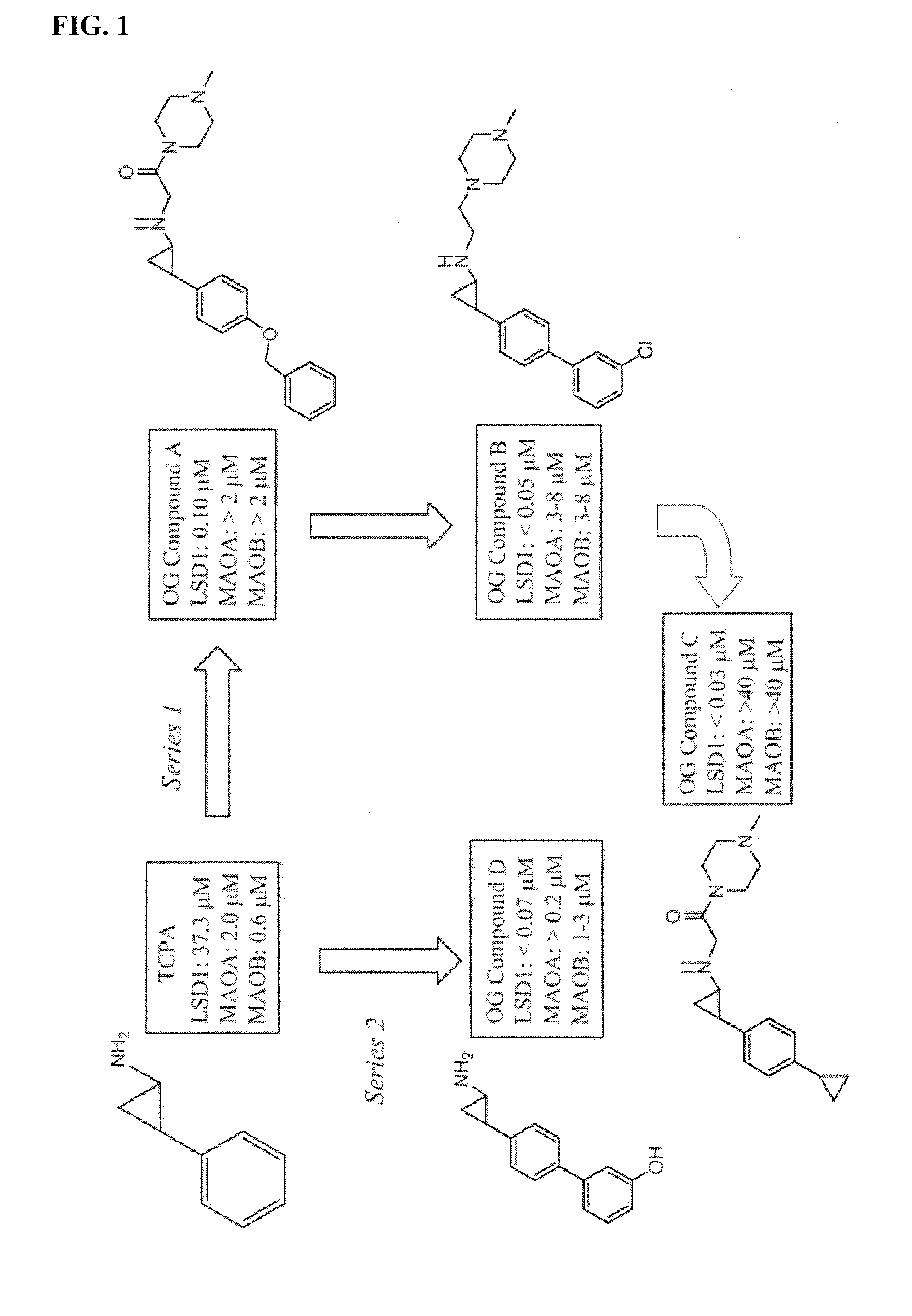
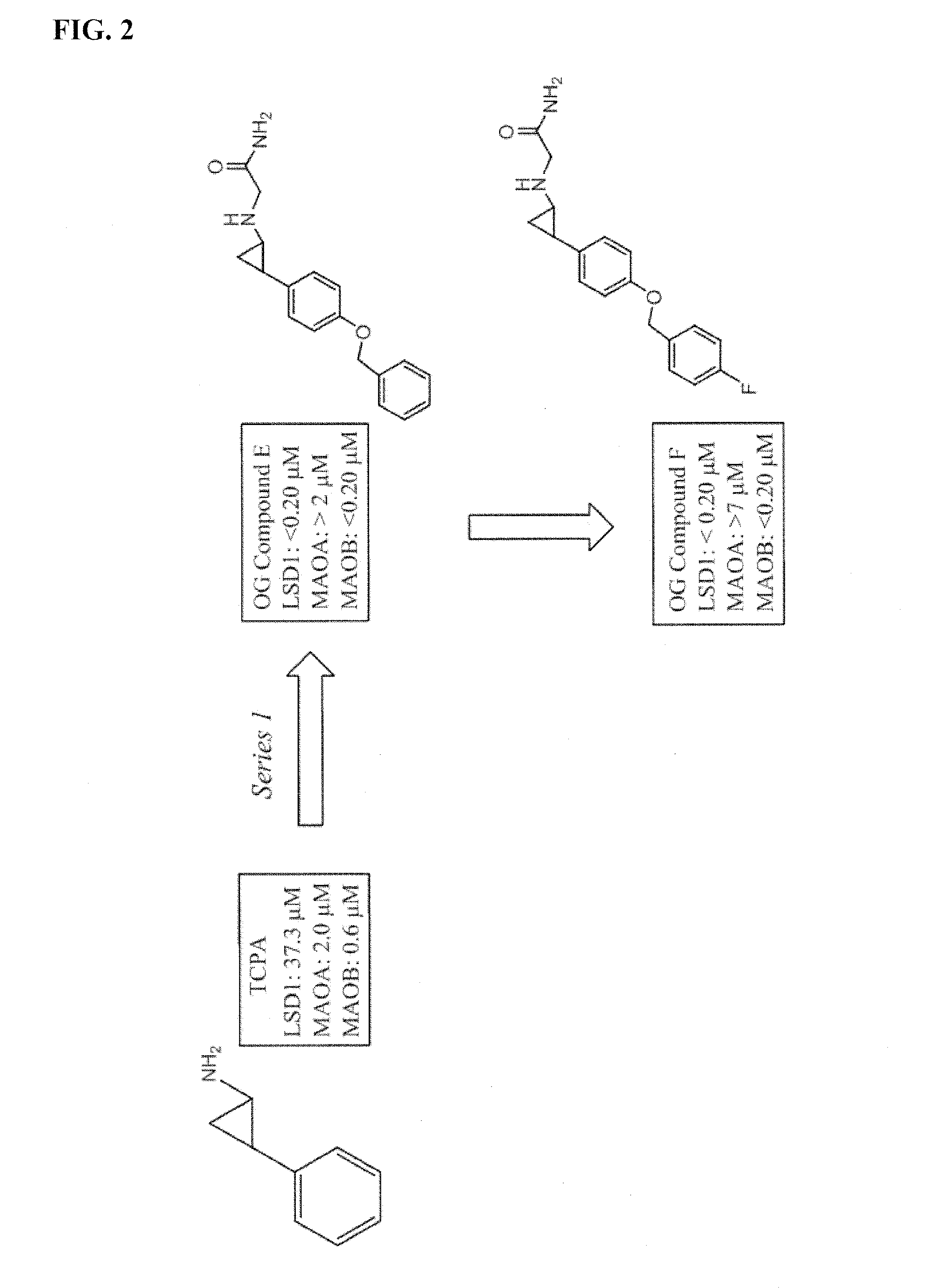
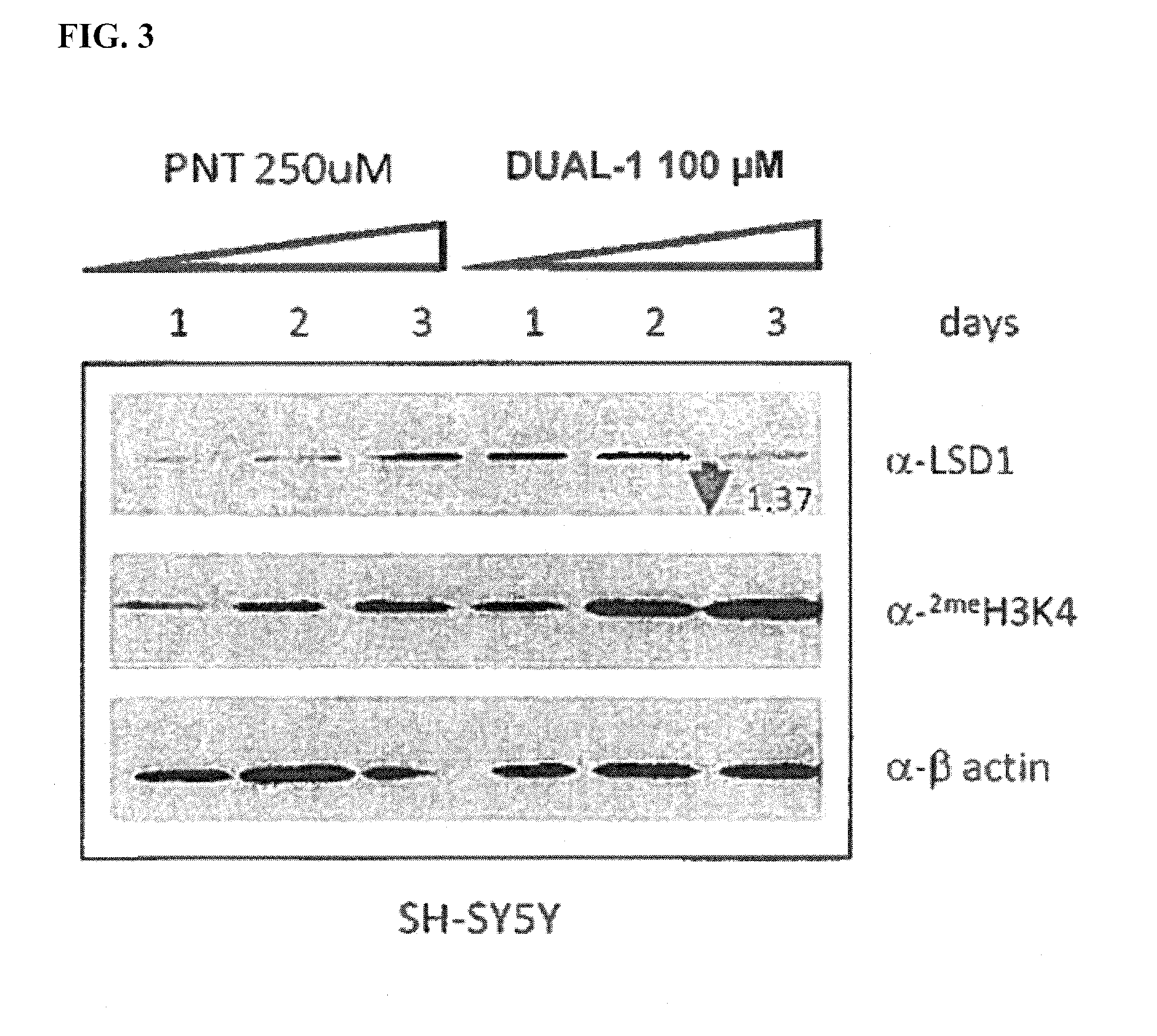
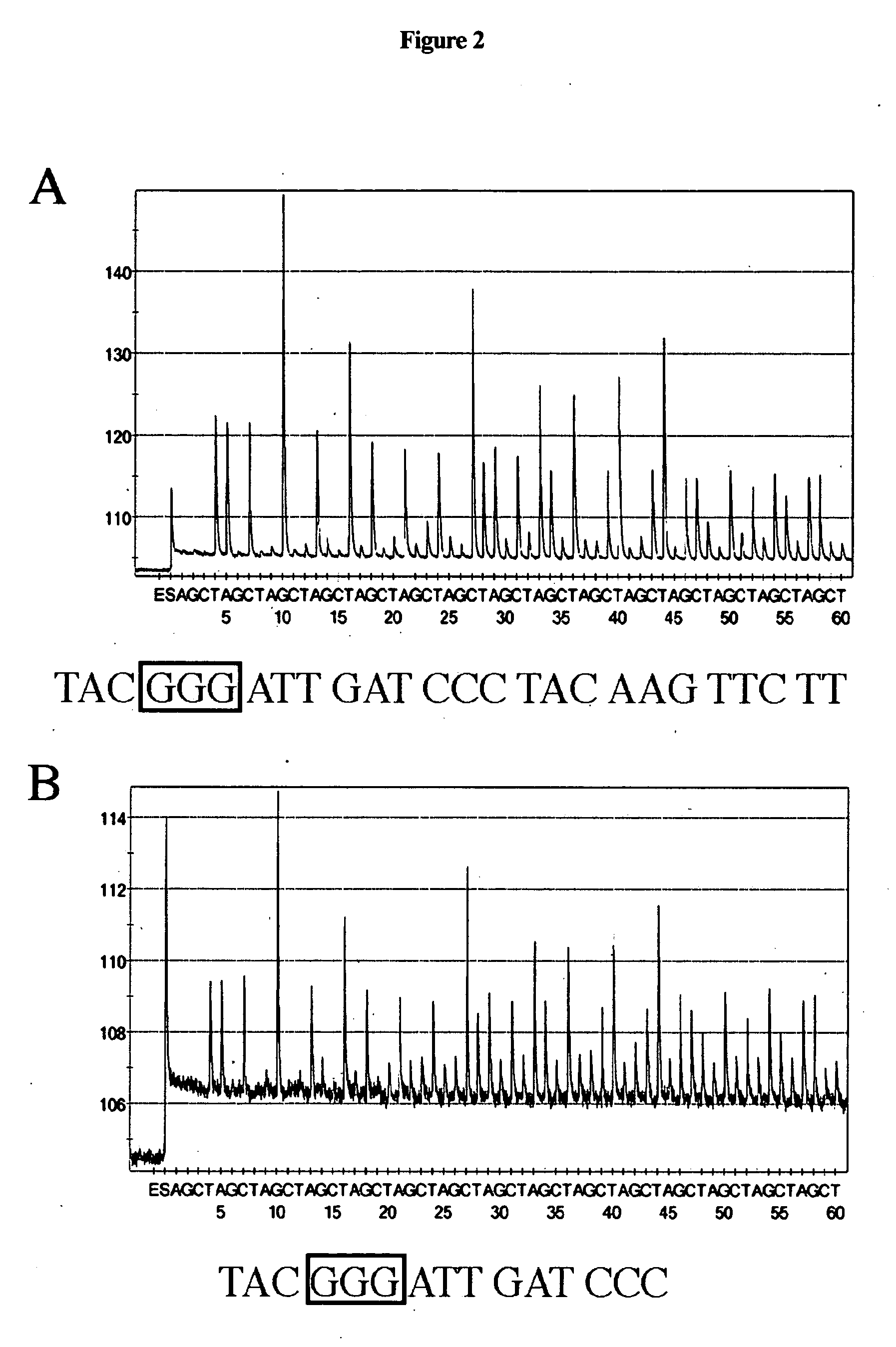
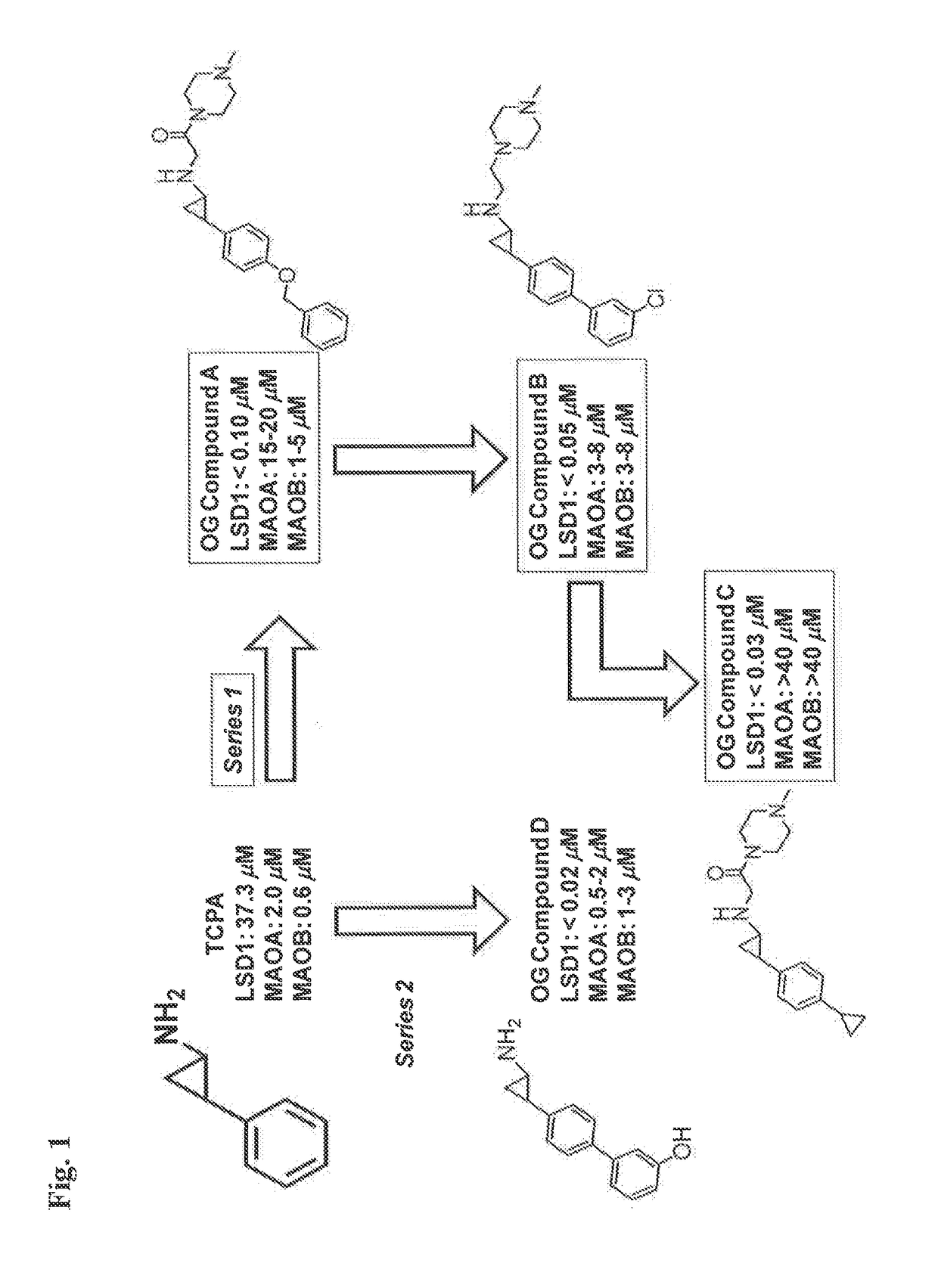
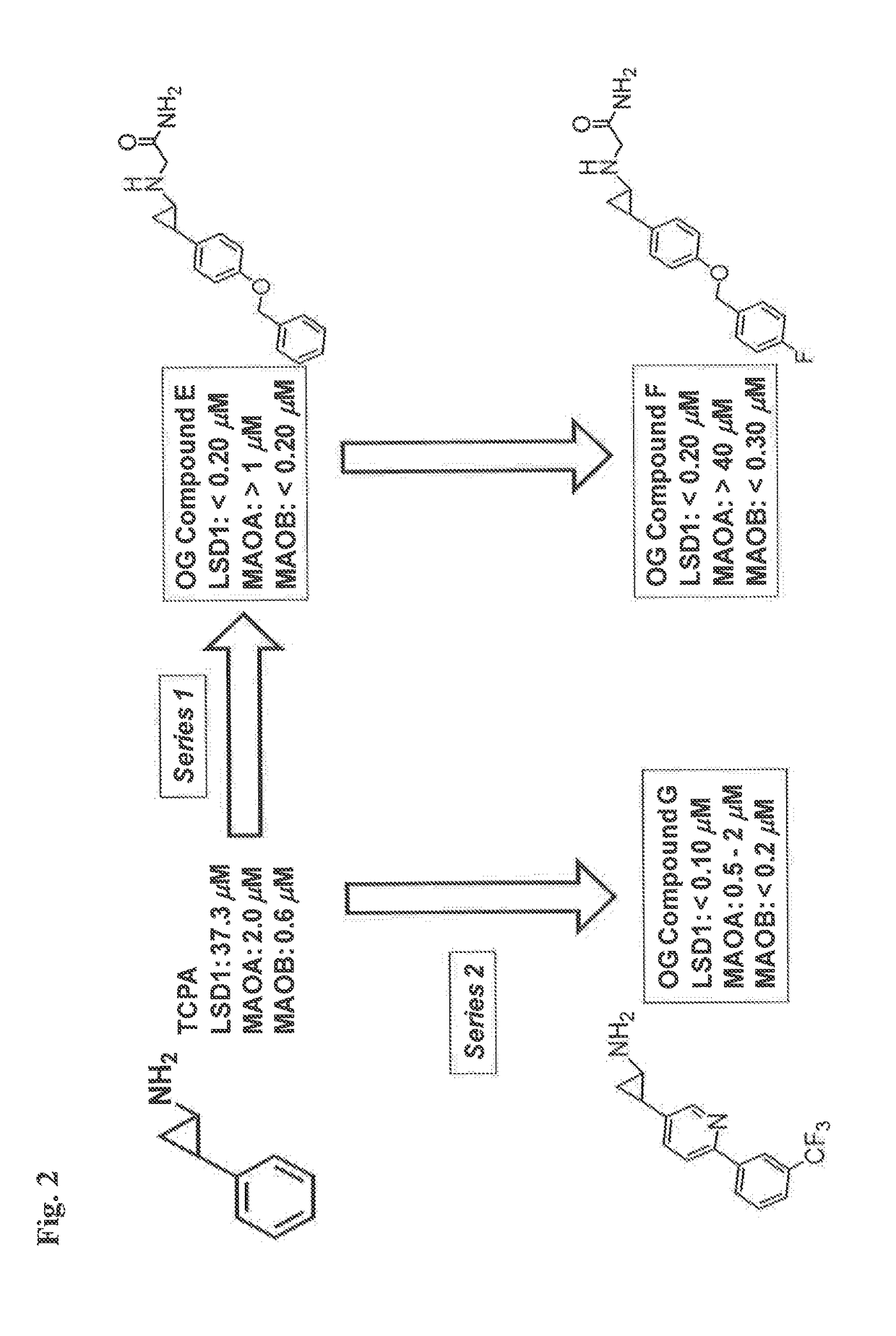
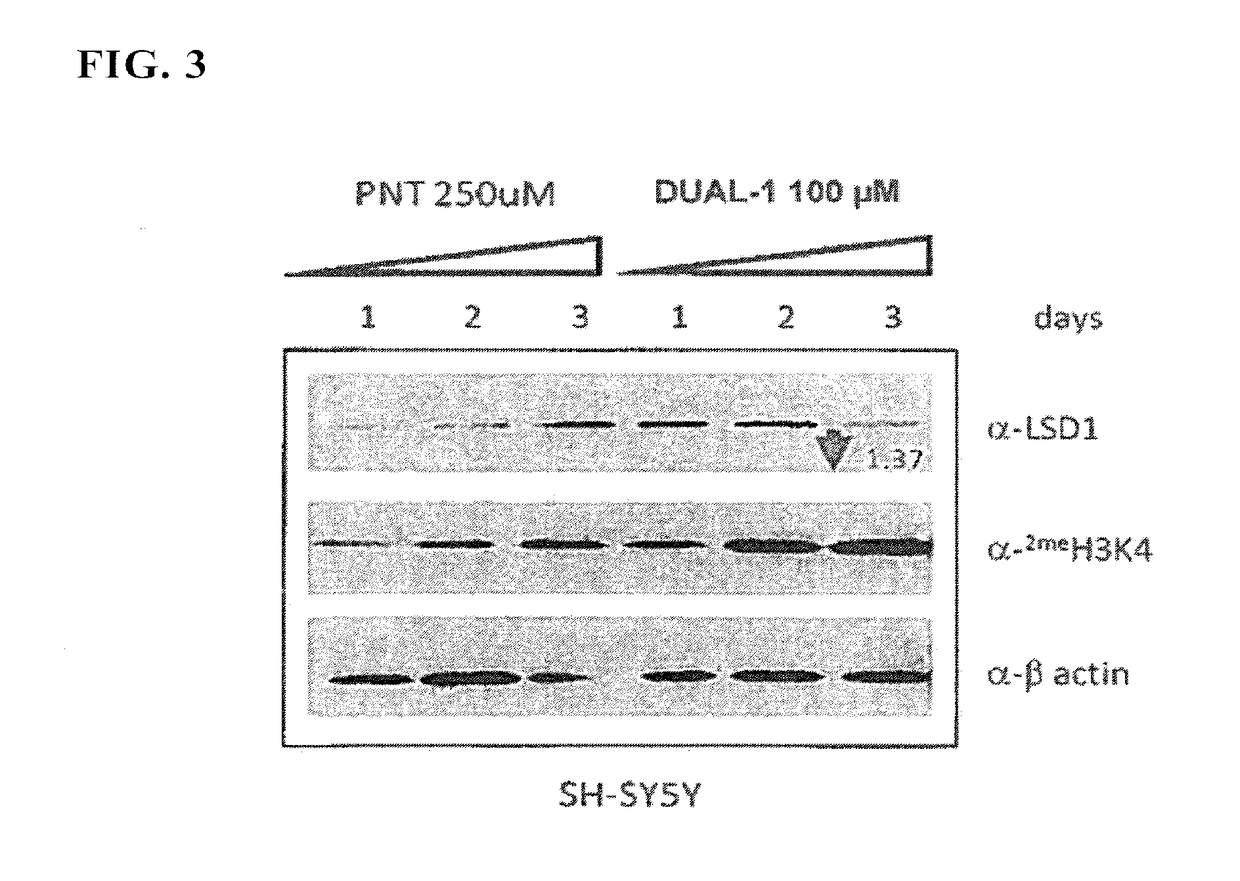
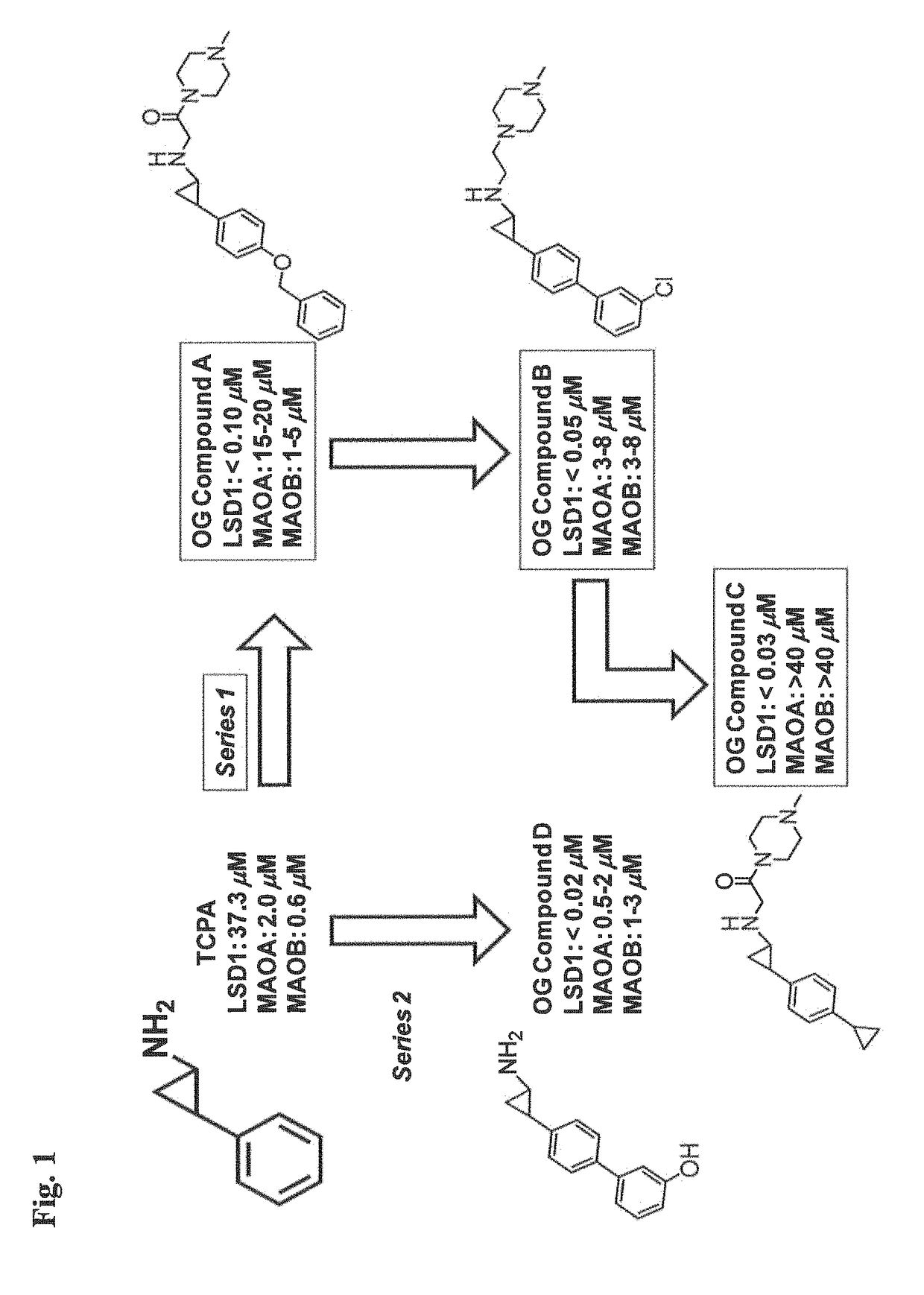
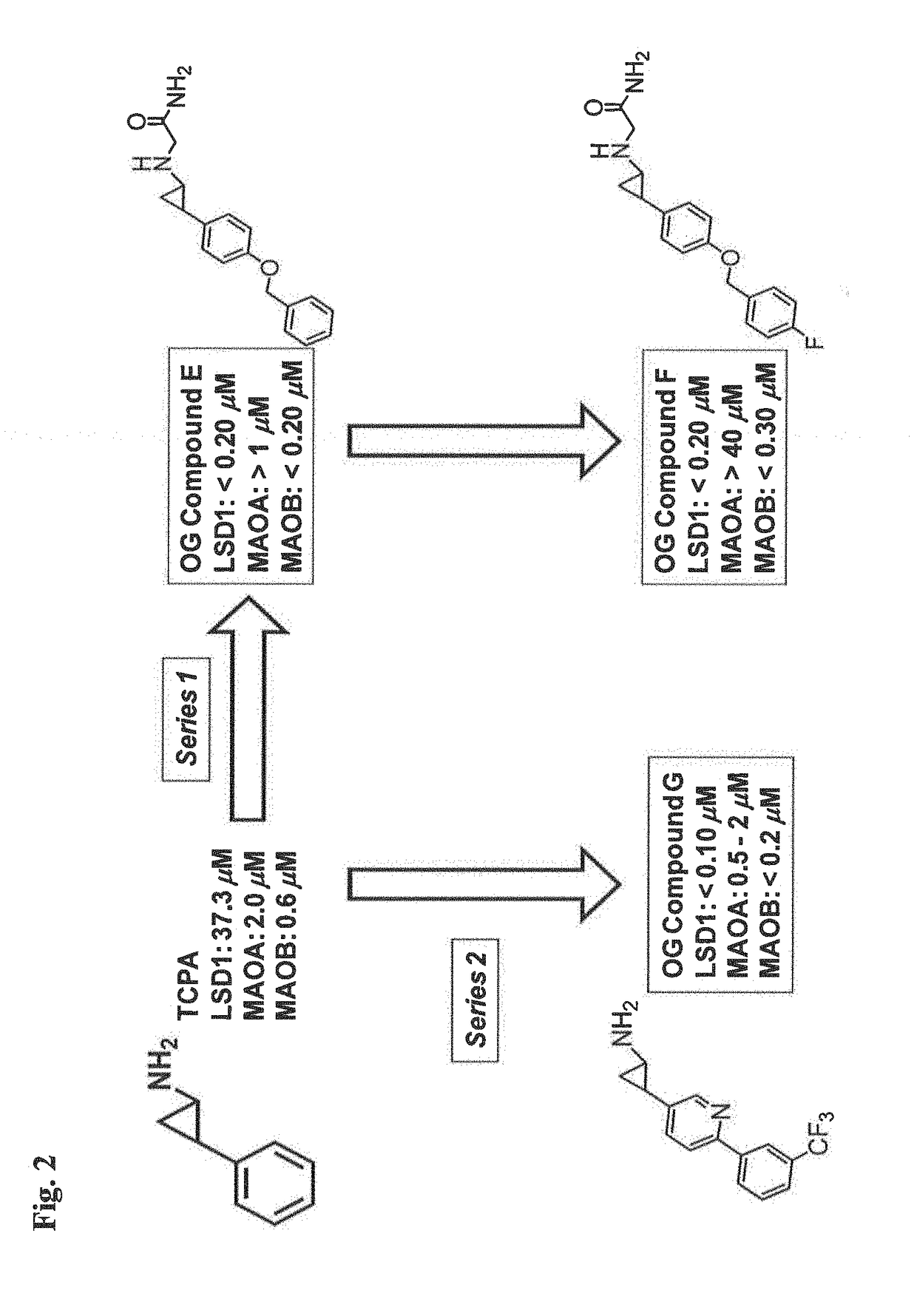
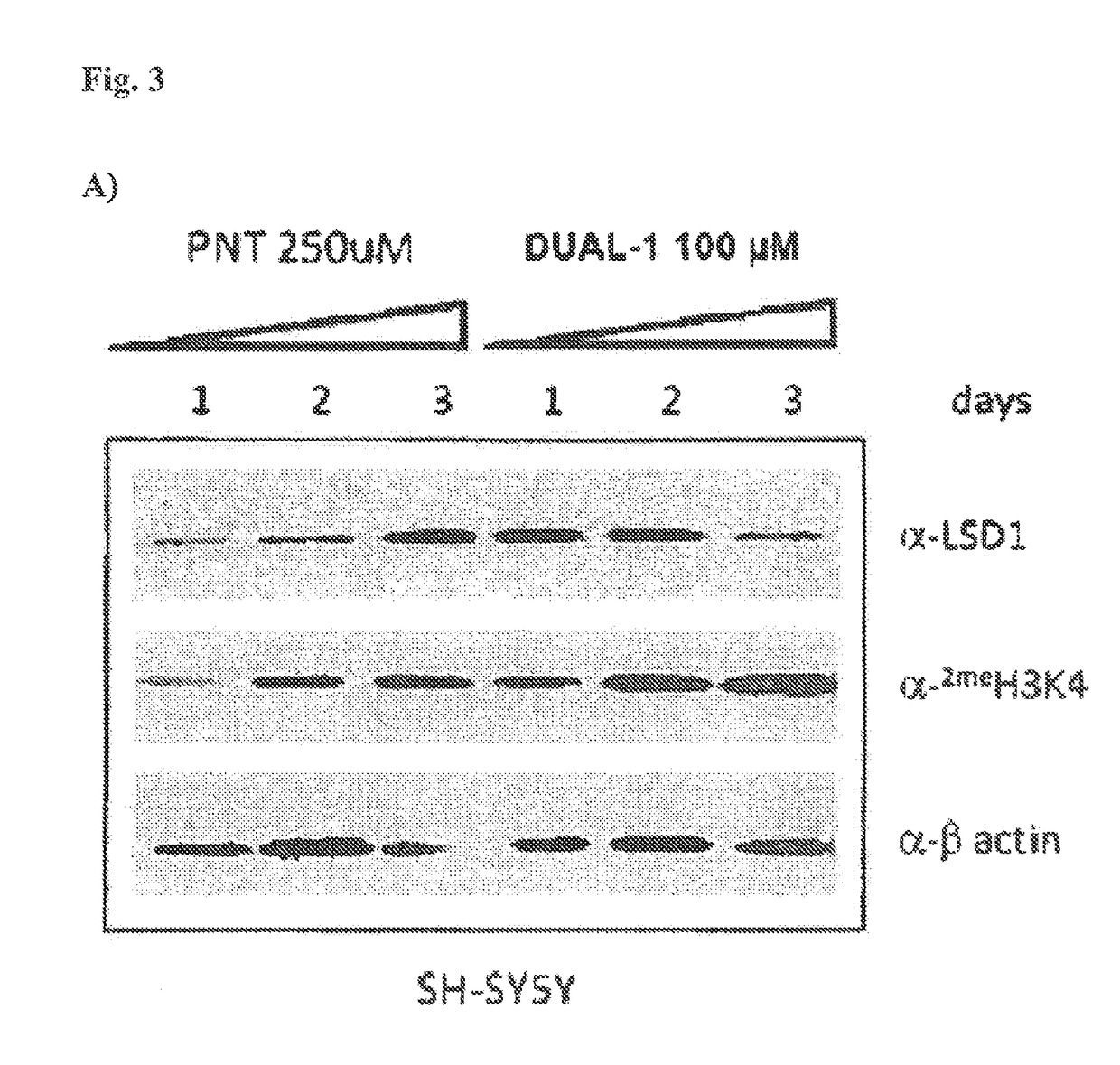
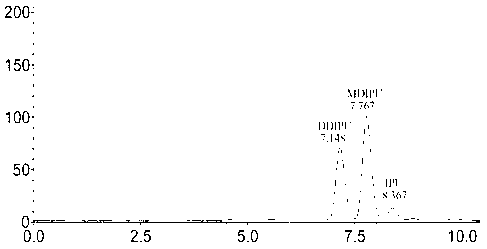
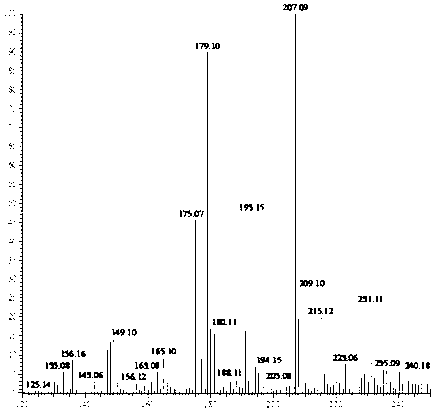
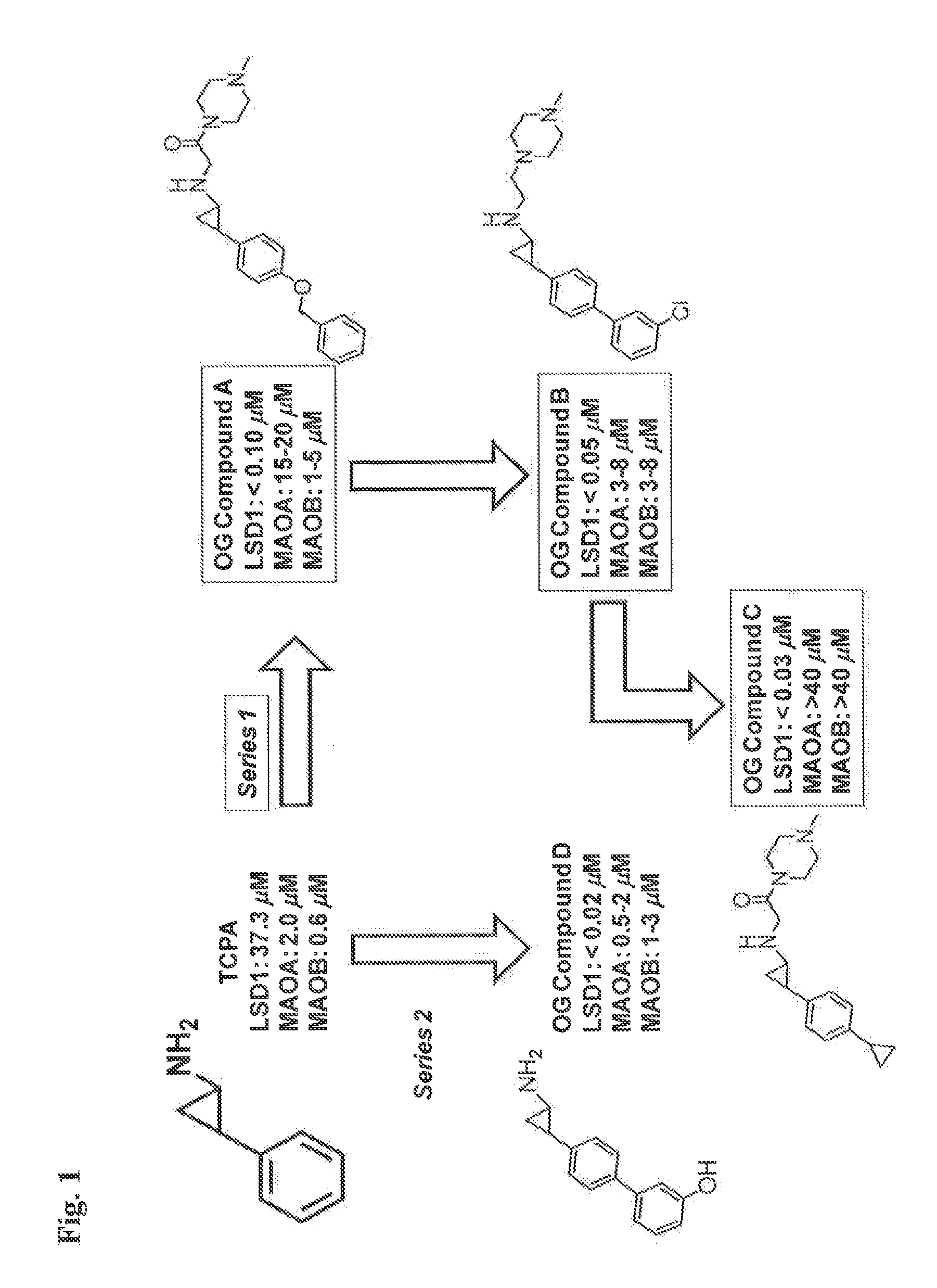
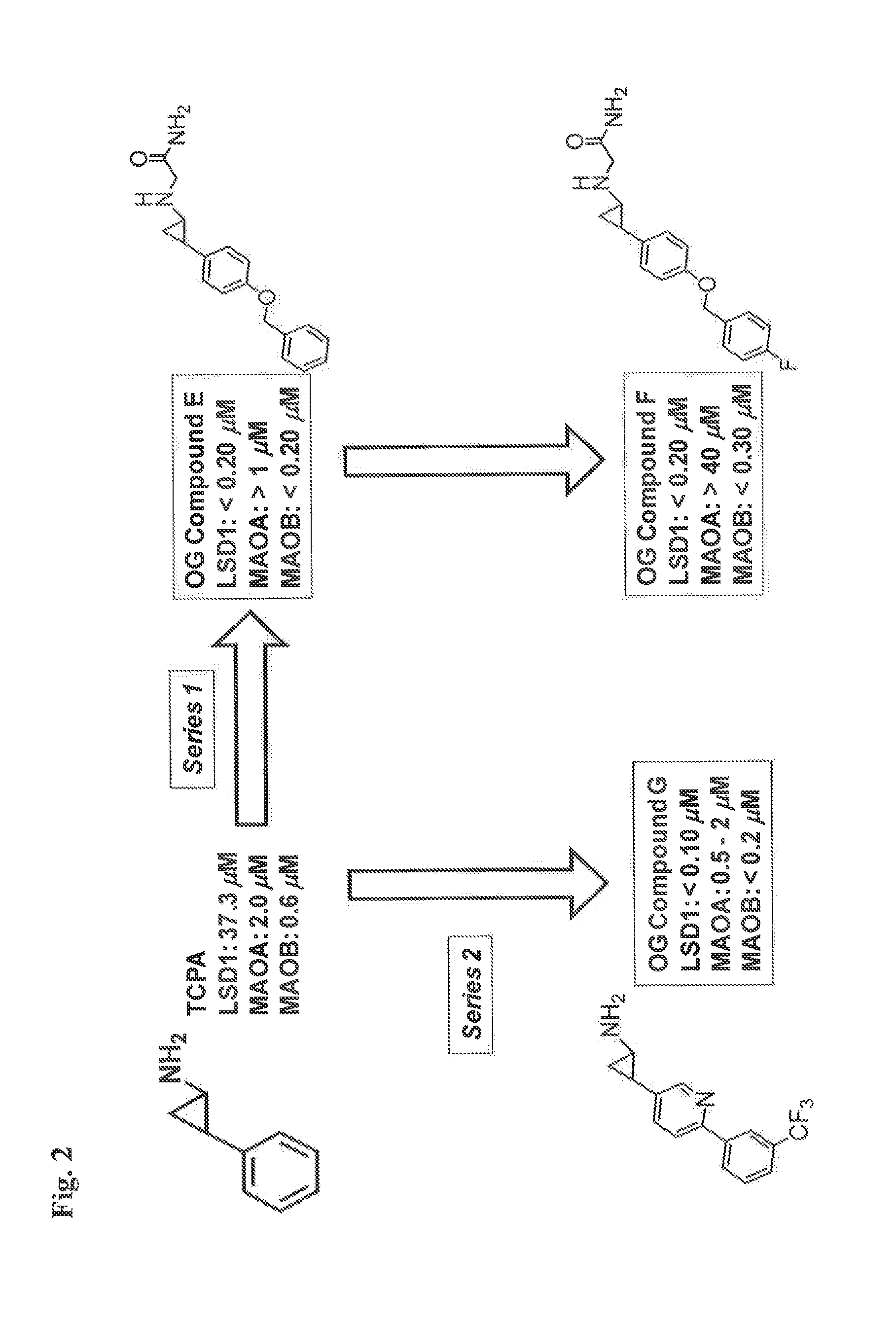
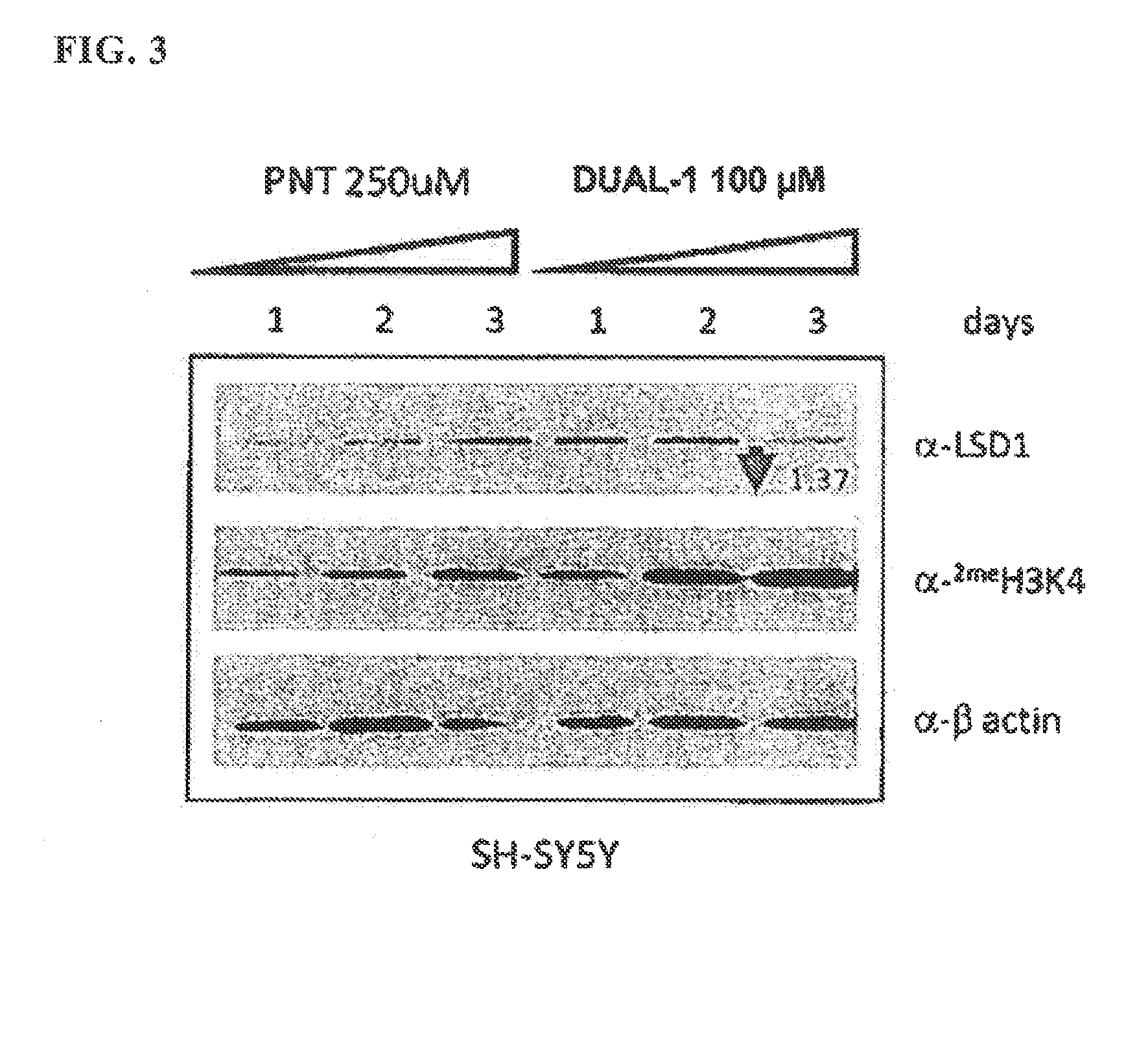
Application of 2-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-2-oxoethyl 4-((3-chloro-4-methylphenyl) amino)-4-oxobutanoate in preparing an LSD1 (lysine-specific demethylase 1) inhibitor medicament
InactiveCN103893163AStrong inhibitory activitySelectiveOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderMedicineMonoamine Oxidase A Gene
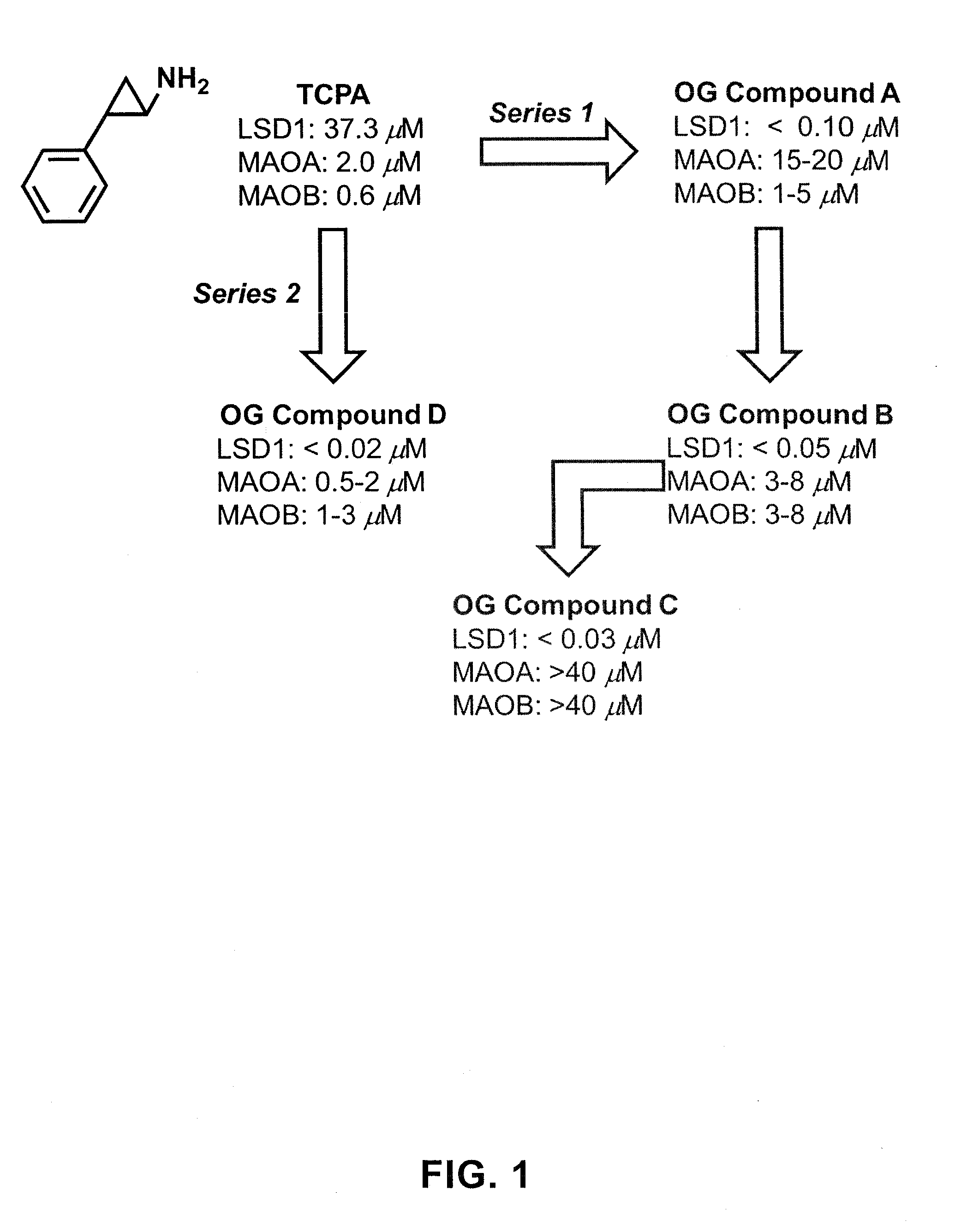
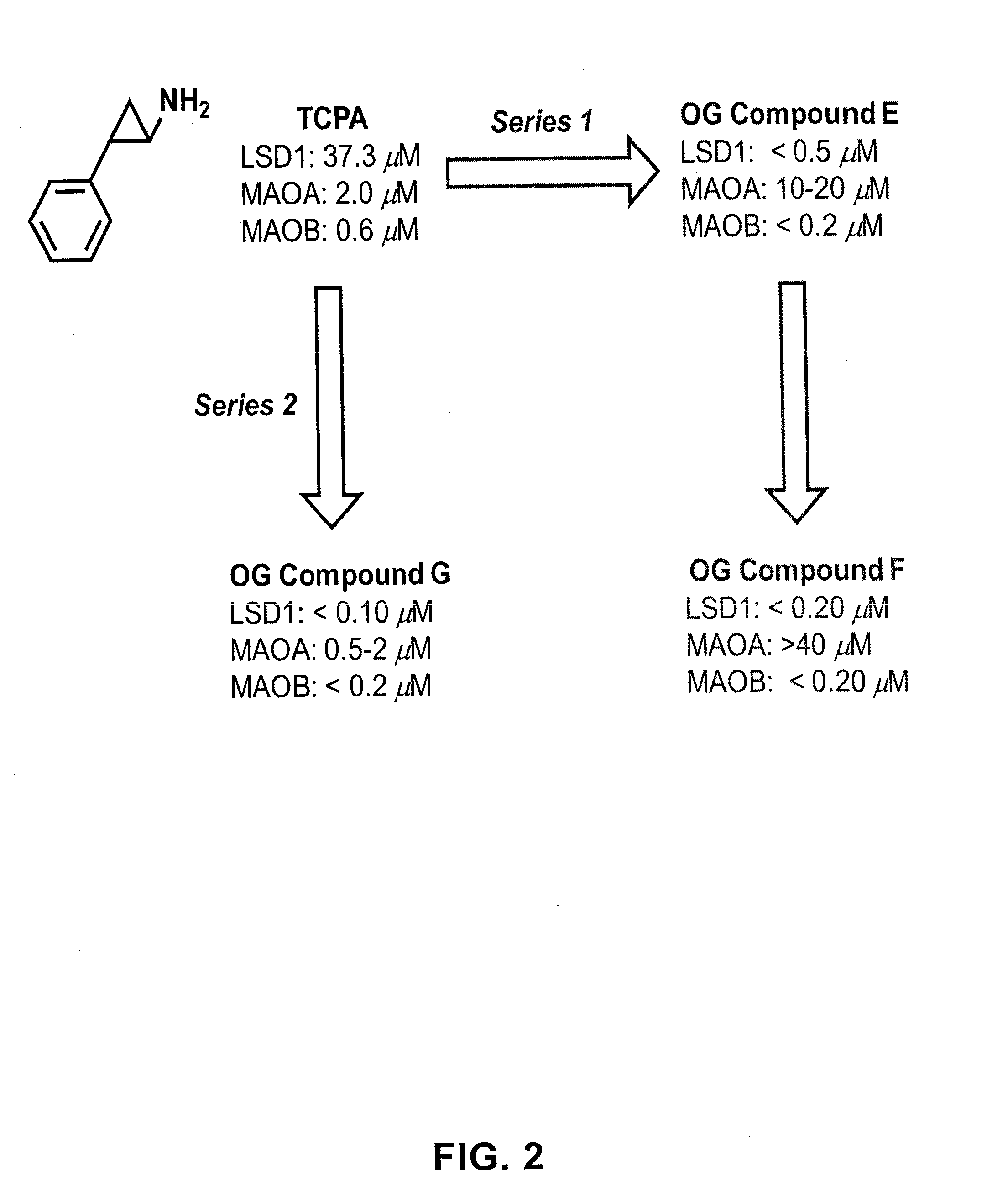
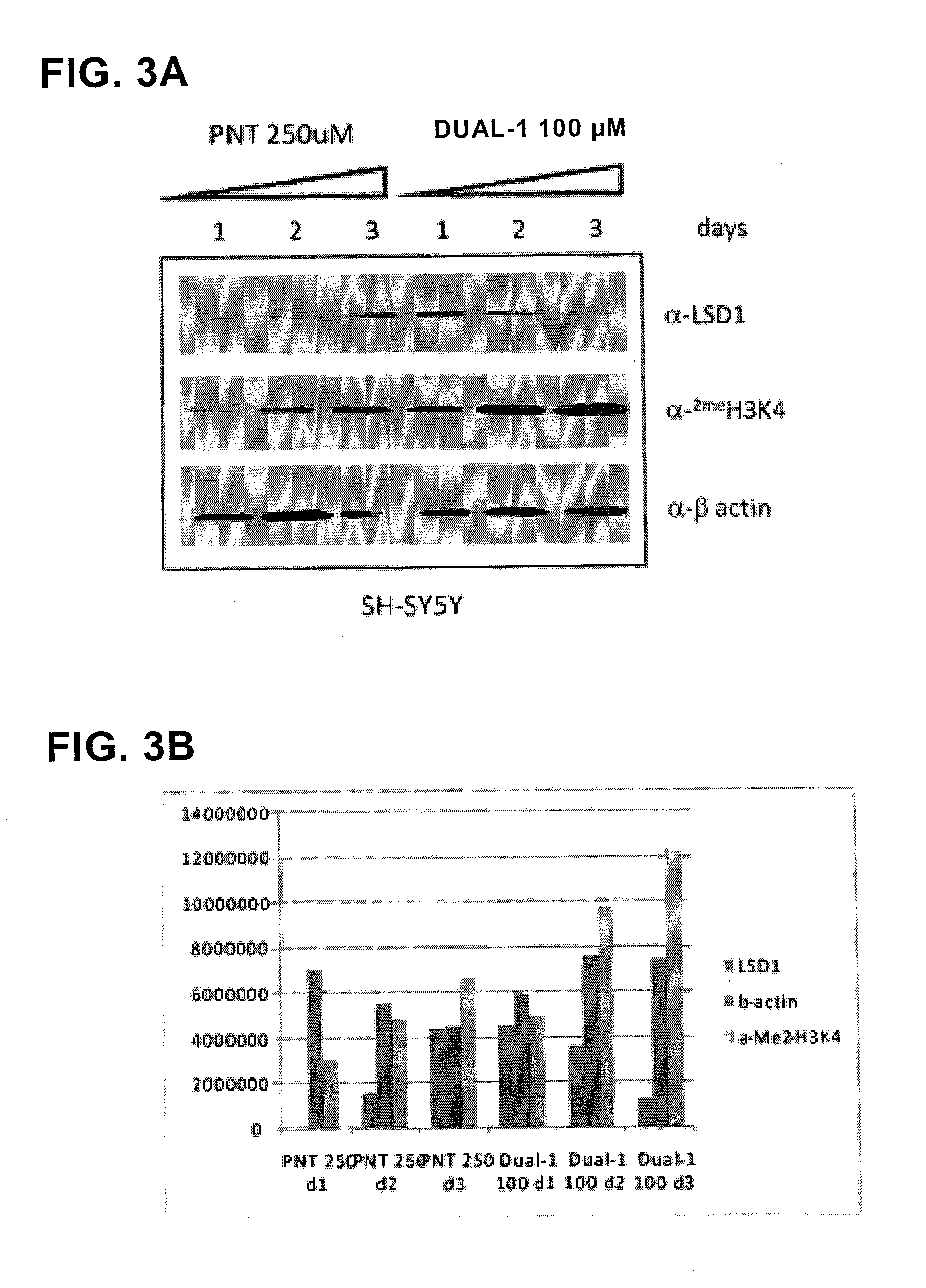
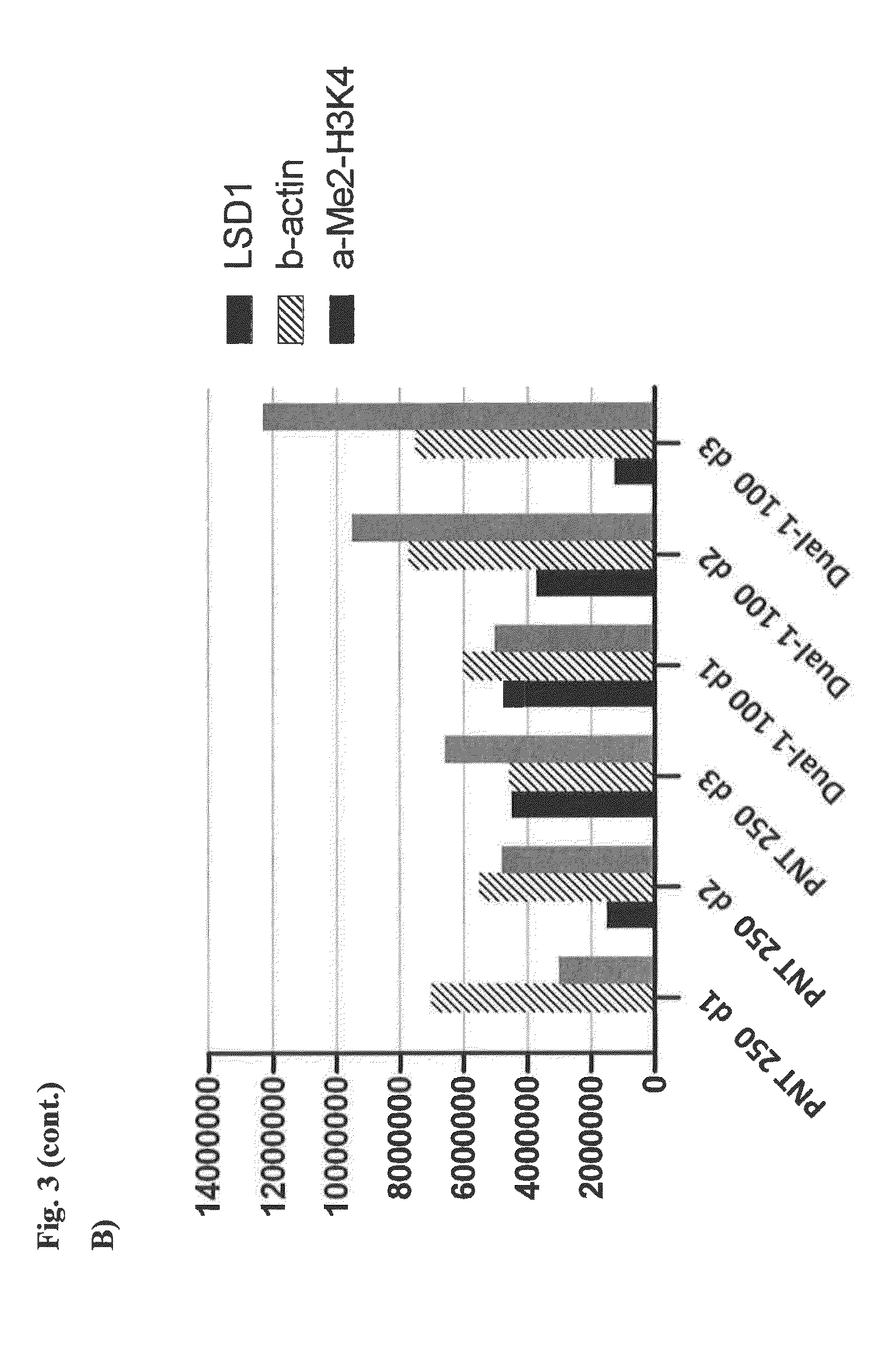
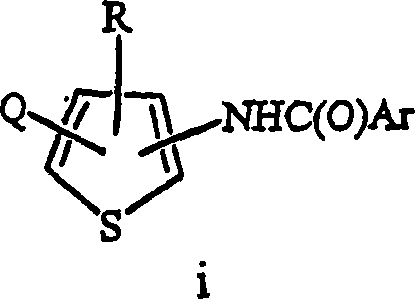
The invention belongs to the field of medicine, and in particular relates to a medical application of 2-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-2-oxoethyl 4-((3-chloro-4-methylphenyl) amino)-4-oxobutanoate in a selective histone lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1) inhibitor, especially the application in anti-tumor medicaments. Pharmacodynamic tests indicate that the 2-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-2-oxoethyl 4-((3-chloro-4-methylphenyl) amino)-4-oxobutanoate has a remarkable LSD1 inhibiting effect, and has selectivity to homologous proteins MAO-A (monoamine oxidase-A) and MAO-B.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Lysine demethylase inhibitors for diseases and disorders associated with hepadnaviridae
ActiveUS20130095067A1Symptoms improvedReduce probabilityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsMammalHepadnavirus
The present invention provides for the treatment or prevention of Hepadnaviridae infection and disease caused by Hepadnaviridae infection. In particular, the invention provides compositions and methods that affect the ability of Hepadnaviridae to utilize the host's cellular machinery as part of the virus' lifecycle. The invention relates to the discovery that interfering with the normal ability of viruses to utilize the host cell machinery with LSD1 inhibitors reduces HBV replication. Thus, the treatment and prevention of Hepadnaviridae infection and disease caused by Hepadnaviridae according to the invention comprises administering to an individual in need of treatment, a therapeutically effective amount of a LSD1 inhibitor. The individual in need of treatment can be a human or, e.g., another mammal.
Owner:ORYZON GENOMICS SA
Lysine demethylase inhibitors for diseases and disorders associated with flaviviridae
ActiveUS20140256742A1Avoids side-effectsReduce duplicationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsLysineLuetic disease
Owner:ORYZON GENOMICS SA
Lysine demethylase inhibitors for thrombosis and cardiovascular diseases
InactiveUS20140296255A1Reduce plateletAvoids side-effectsBiocideAmide active ingredientsThrombusThrombosis prevention
The invention relates to methods and compositions for the treatment or prevention of thrombosis, thrombus formation, a thrombotic event or complication, or a cardiovascular disease or event. In particular, the invention relates to an LSD inhibitor such as a 2-cyclylcyclopropan-1-amine derivative, a phenelzine derivative and a propargylamine derivative, for use in treating or preventing thrombosis, thrombus formation, a thrombotic event or complication, or a cardiovascular disease or event.
Owner:ORYZON GENOMICS SA
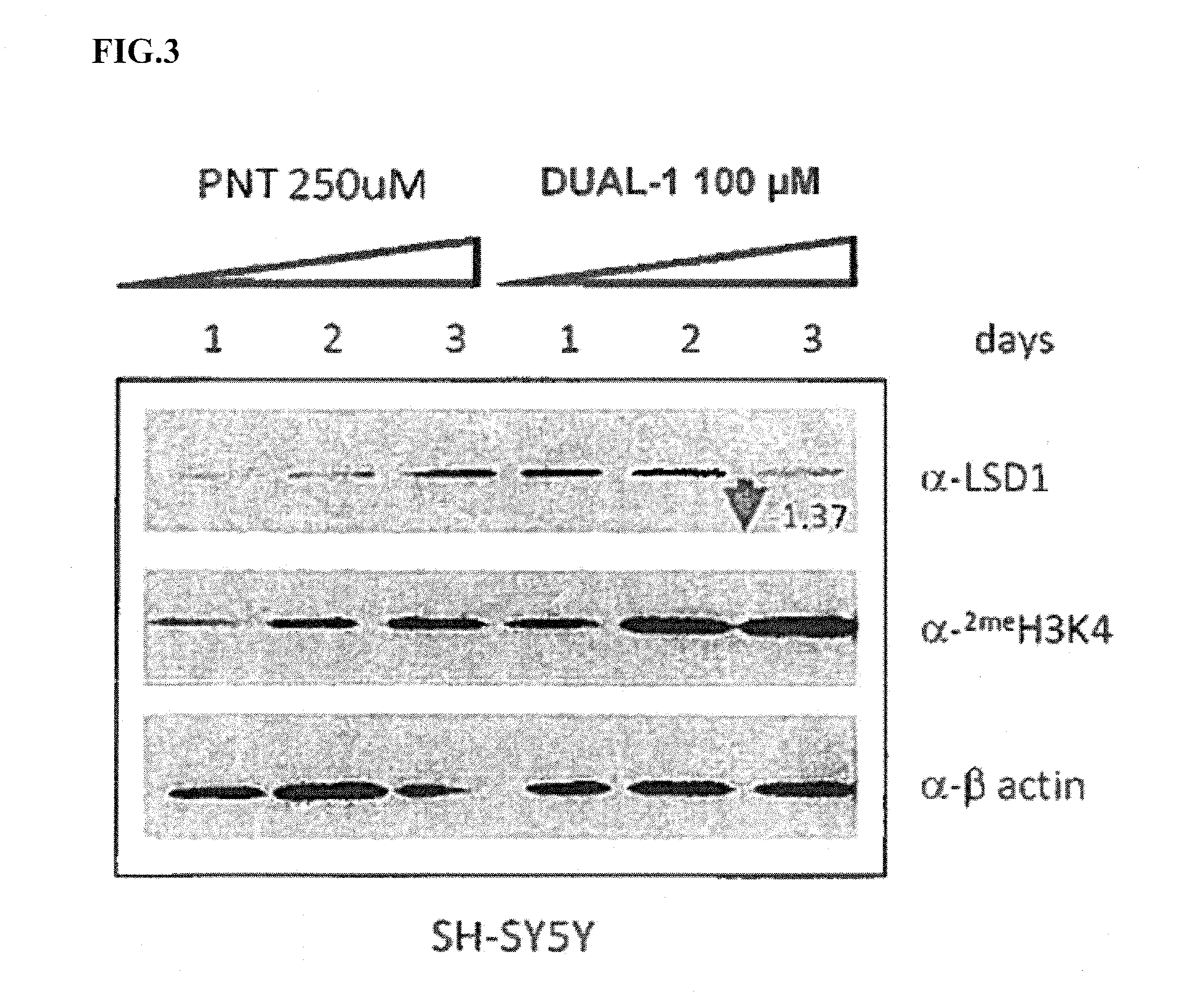
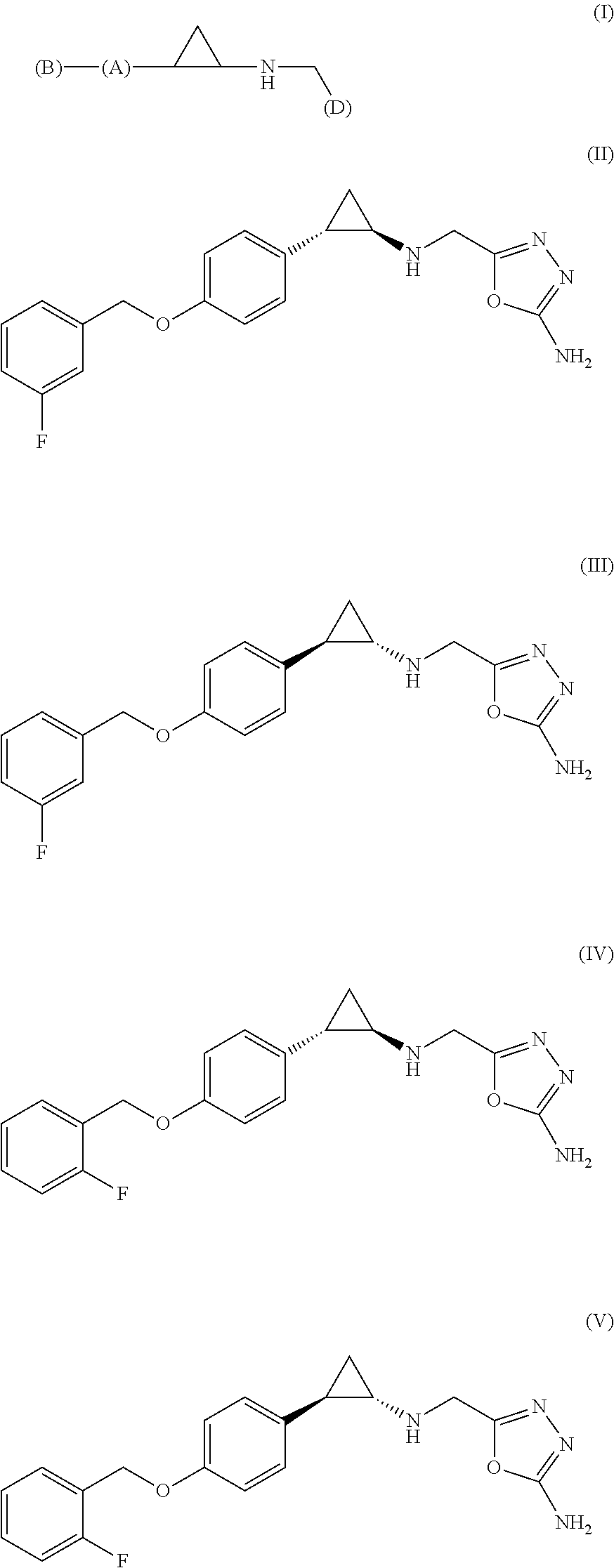
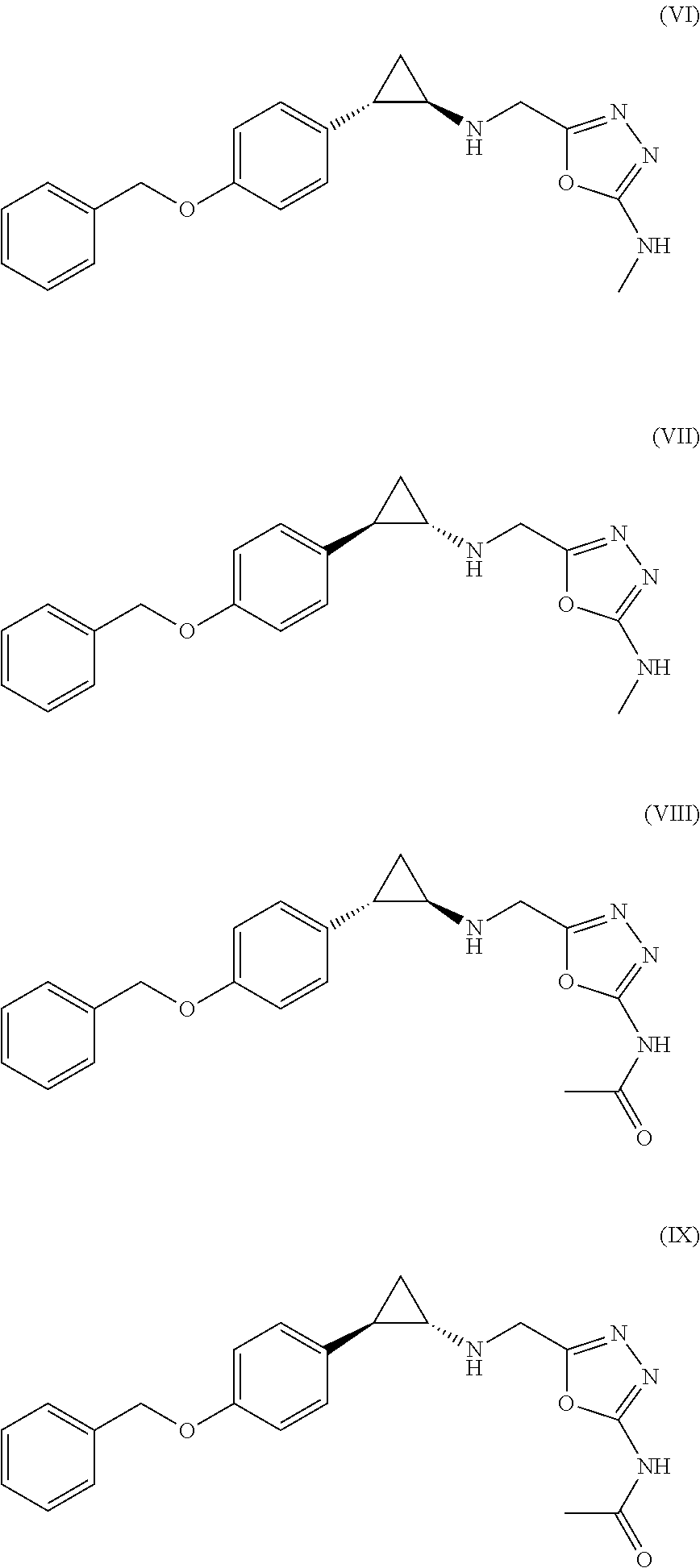
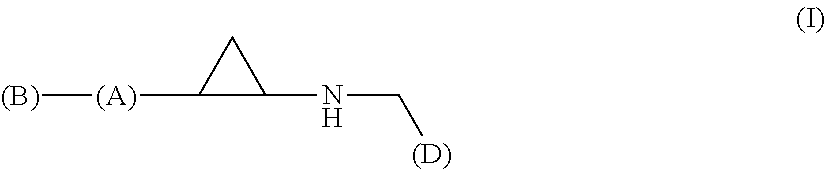
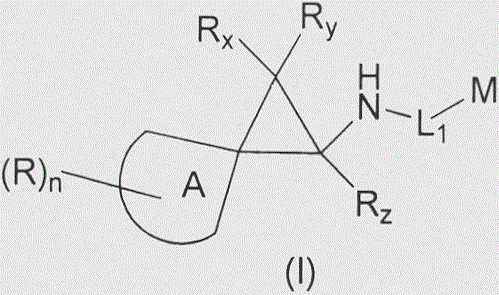
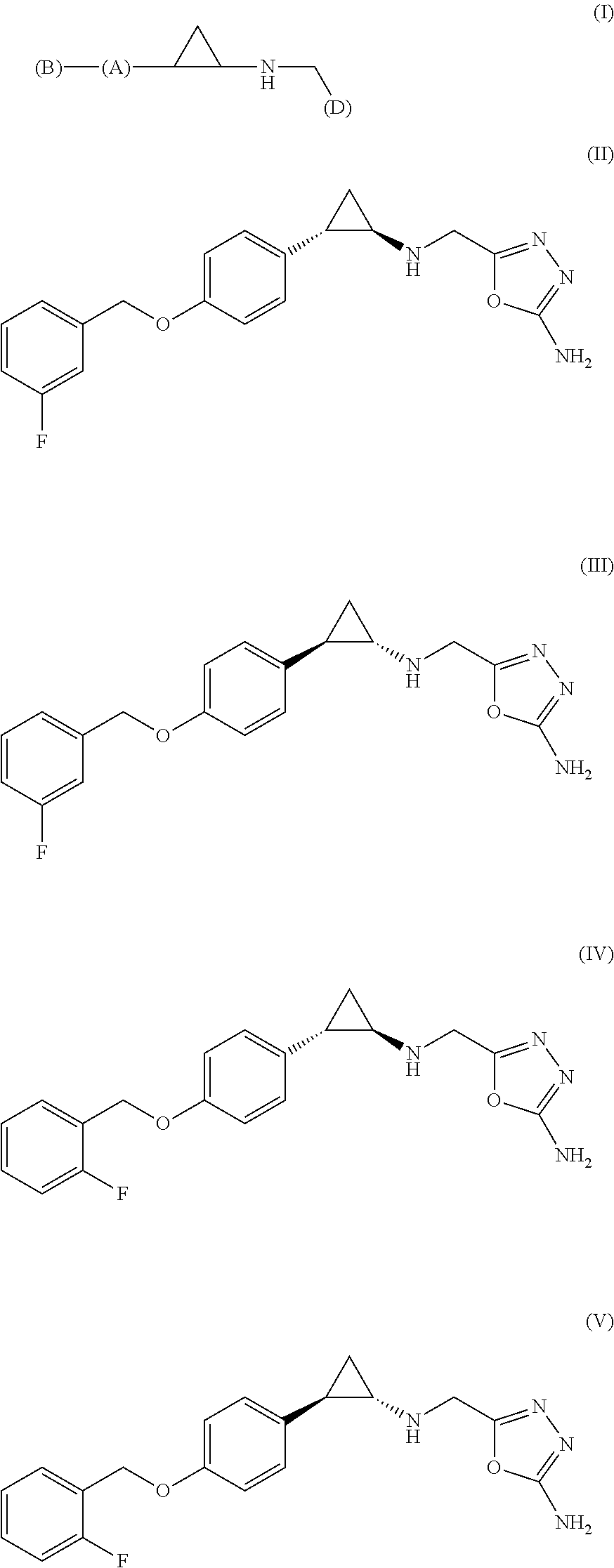
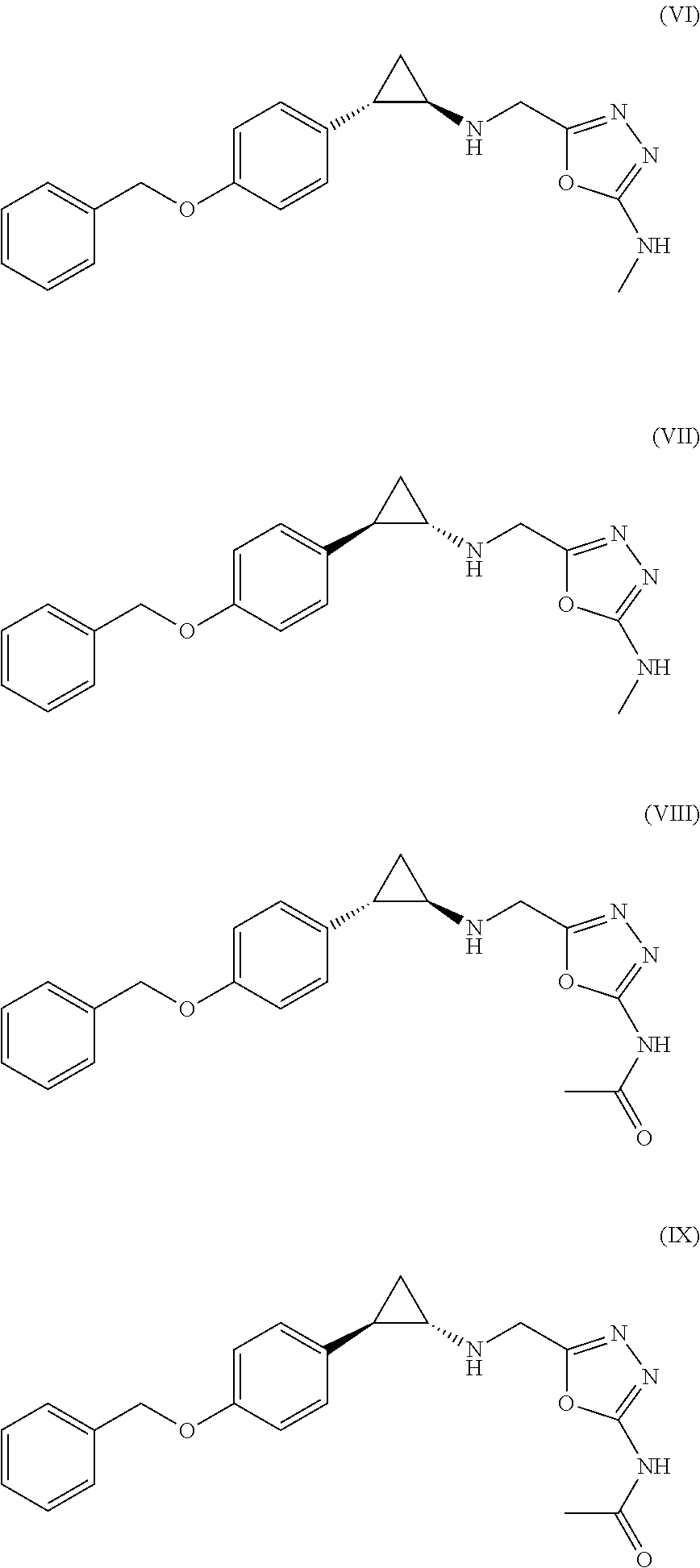
Arylcyclopropylamine based demethylase inhibitors of lsd1 and their medical use
The invention relates to (hetero)aryl cyclopropylamine compounds, including particularly the compounds of formula (I) as described and defined herein, and their use in therapy, including, e.g., in the treatment or prevention of cancer, a neurological disease or condition, or a viral infection. Thus, in one specific aspect the invention relates to formulas (II), (III), (IV), (V), (VI), (VII), (VIII), (IX).
Owner:ORYZON GENOMICS SA
Lysine demethylase inhibitors for inflammatory diseases or conditions
InactiveUS20140329833A1Reduce plateletAvoids side-effectsBiocideOrganic chemistryAmine derivativesInflammation
The invention relates to methods and compositions for the treatment or prevention of inflammation and inflammatory diseases or conditions. In particular, the invention relates to an LSD1 inhibitor, such as a 2-cyclylcylopropan-1-amine derivative, a phenelzine derivative and a propargylamine derivative, for use in treating or preventing inflammation and inflammatory diseases or conditions.
Owner:ORYZON GENOMICS SA
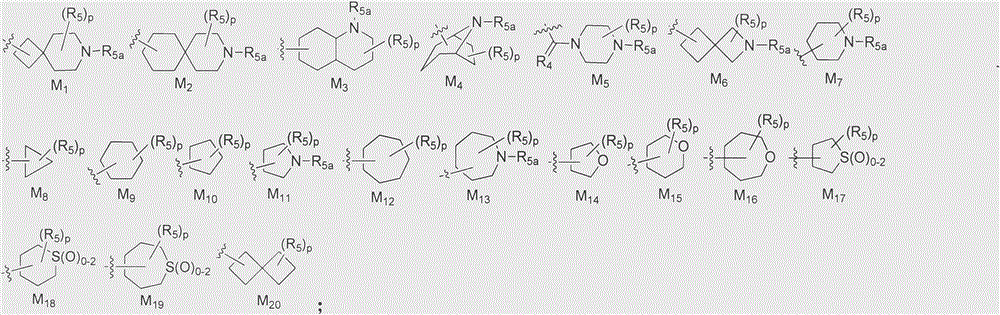
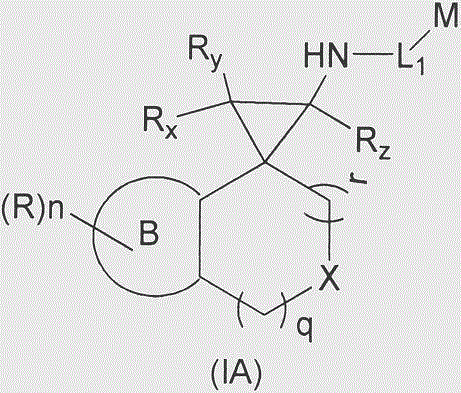
Cyclopropylamine spiro(hetero)cyclic compound, and pharmaceutical composition and application thereof
The invention relates to a preparation method for a cyclopropylamine spiro(hetero)cyclic compound and a composition containing the same, and application of the compound and the composition as an inhibitor for human lysine-specific demethylase (LSD1). The inhibitor is the cyclopropylamine spiro(hetero)cyclic compound as shown in a formula (I) which is described in the specification, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, predrug, solvate, polymorphic crystal or stable isotope derivative thereof. The compound can be used for treating or preventing diseases related to human lysine-specific demethylase, e.g., cancers and nerve diseases.
Owner:SHANGHAI DE NOVO PHARMA
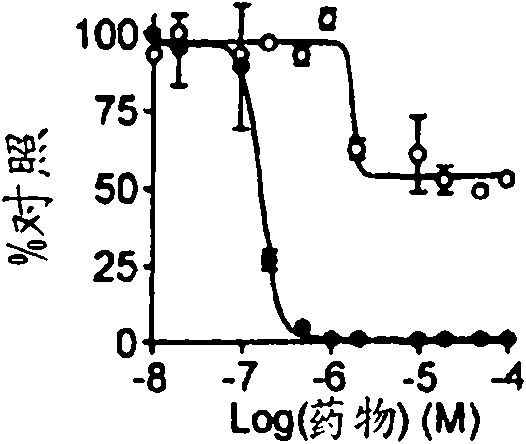
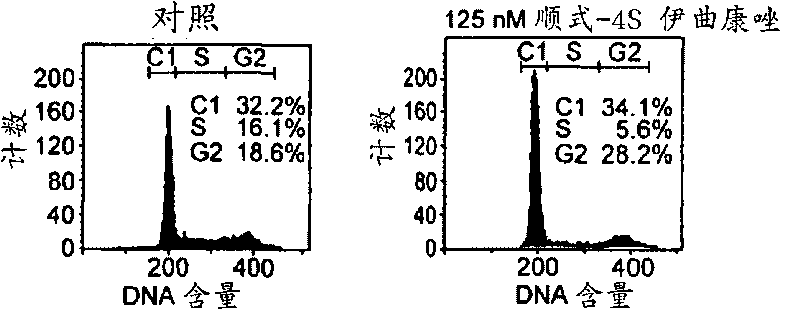
Chirally pure isomers of itraconazole and inhibitors of lanosterol 14A-demethylase for use as angiogenesis inhibitors
Described herein are methods of inhibiting angiogenesis, and treating or preventing a disease or disorder (or symptoms thereof) associated with angiogenesis, wherein an anti-angiogenesis compound is administered to a subject.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
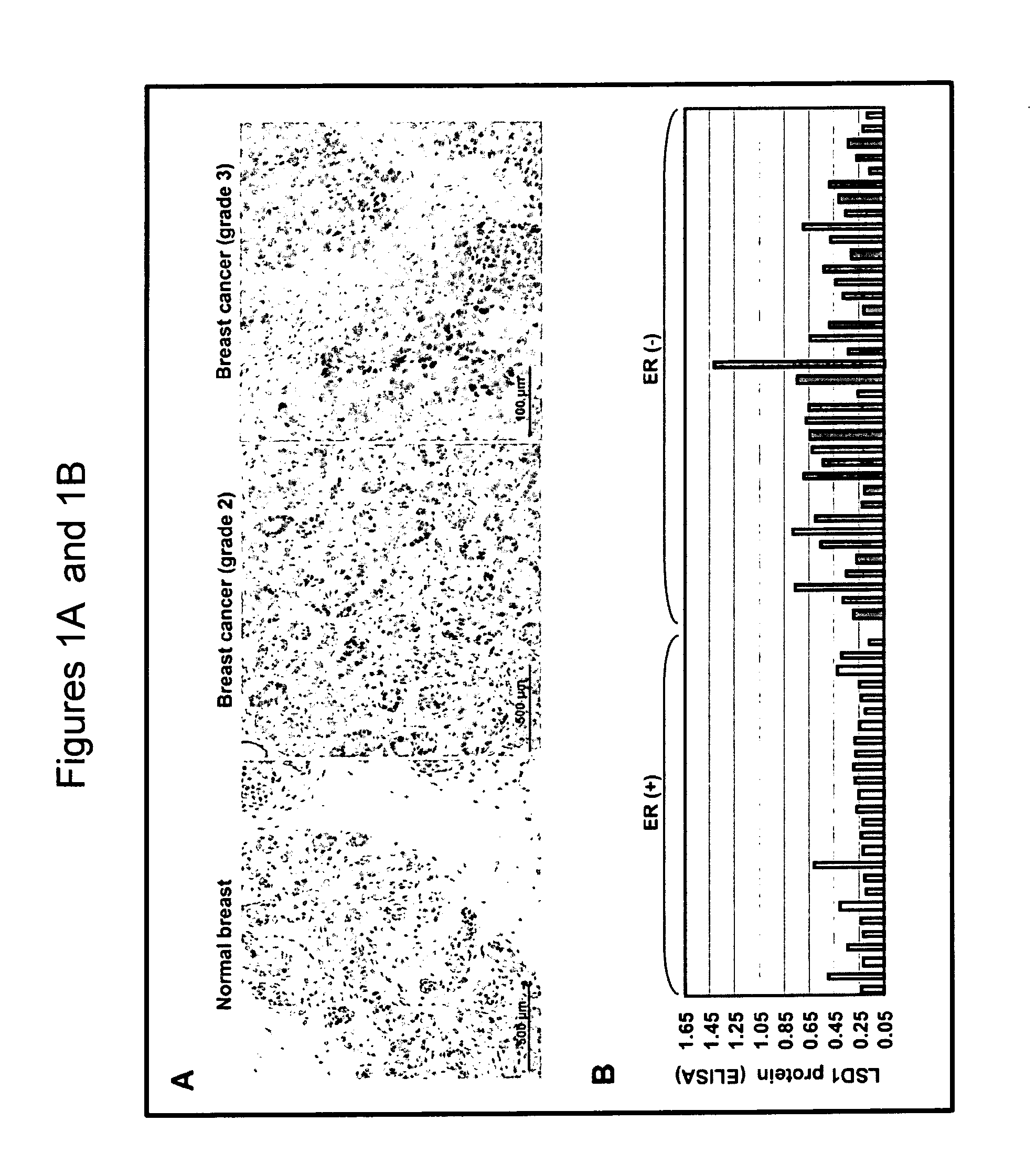
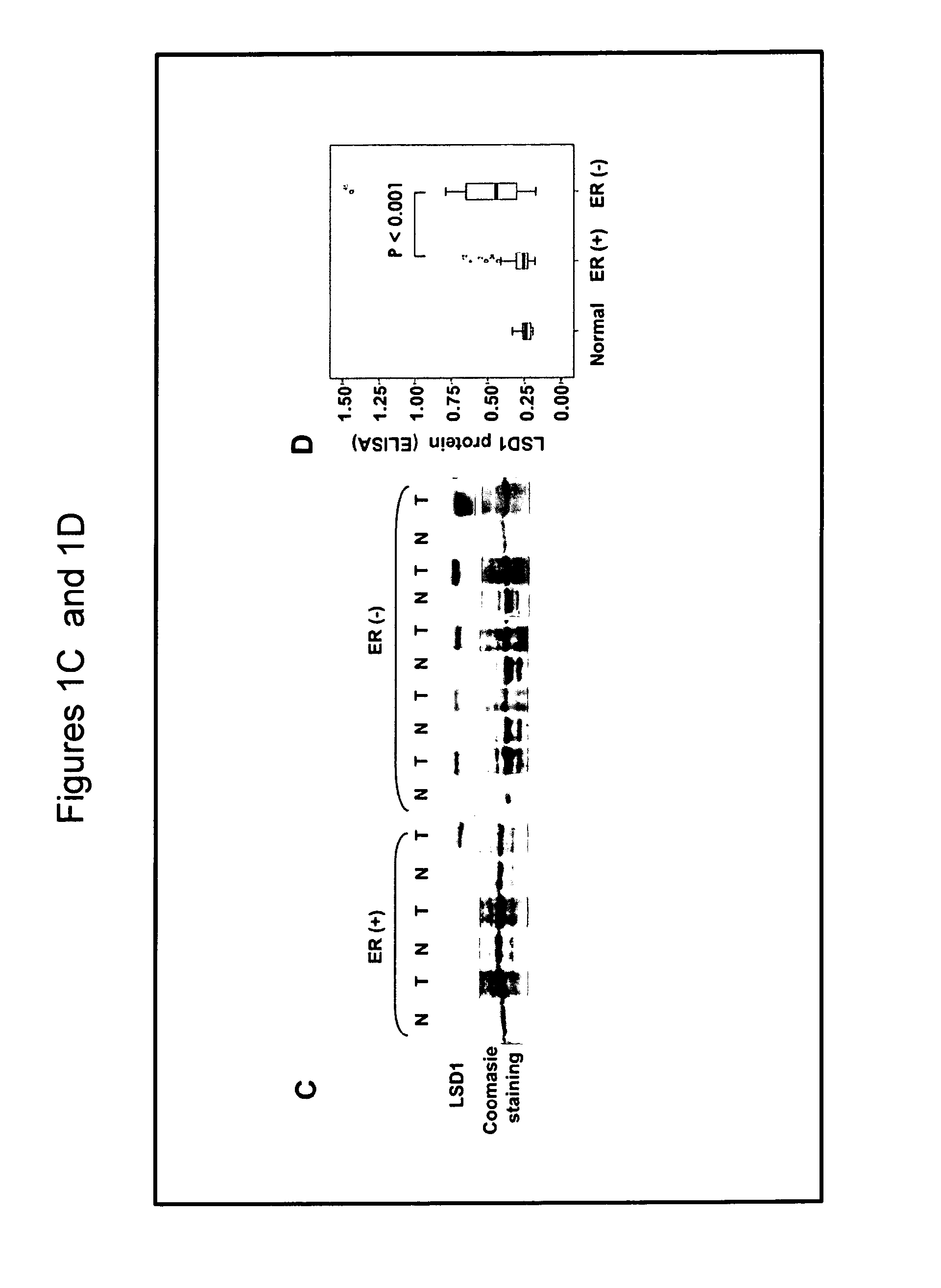
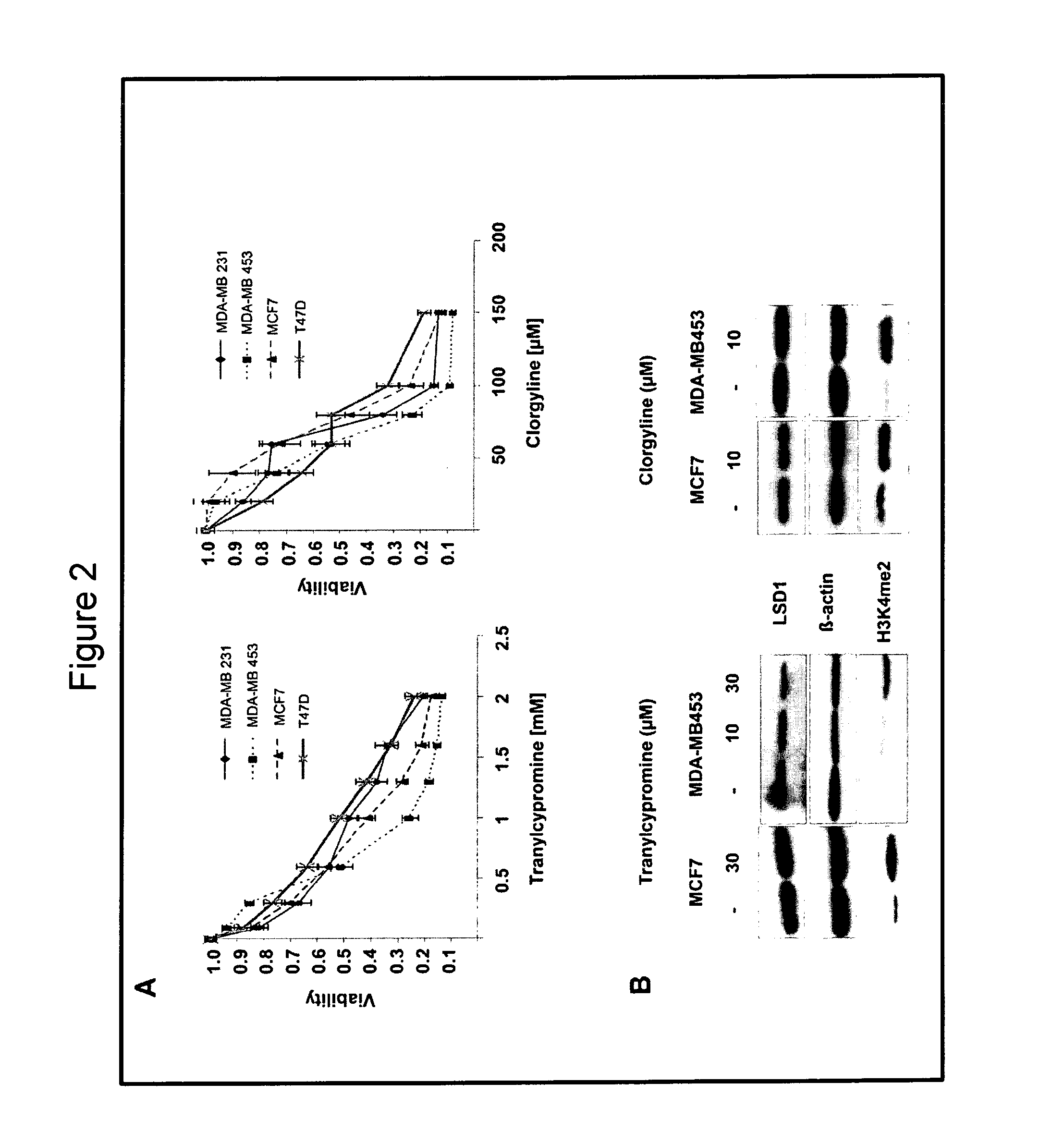
Lysine-specific demethylase 1(LSD1) is a biomarker for breast cancer
The present invention relates to novel biomarker for breast cancer, namely LSD1 and its application in inter alia the diagnosis of breast cancer. Furthermore, the present invention discloses a method of determining the LSD1 protein amount and the effect of LSD1 inhibitors on cancer cells selected from breast cancer, lung carcinoma and sarcoma.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG +1
Arylcyclopropylamine based demethylase inhibitors of LSD1 and their medical use
The invention relates to (hetero)aryl cyclopropylamine compounds, including particularly the compounds of formula (I) as described and defined herein, and their use in therapy, including, e.g., in the treatment or prevention of cancer, a neurological disease or condition, or a viral infection. Thus, in one specific aspect the invention relates to formulas (II), (III), (IV), (V), (VI), (VII), (VIII), (IX).
Owner:ORYZON GENOMICS SA
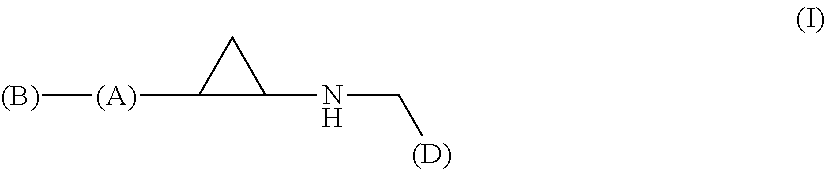
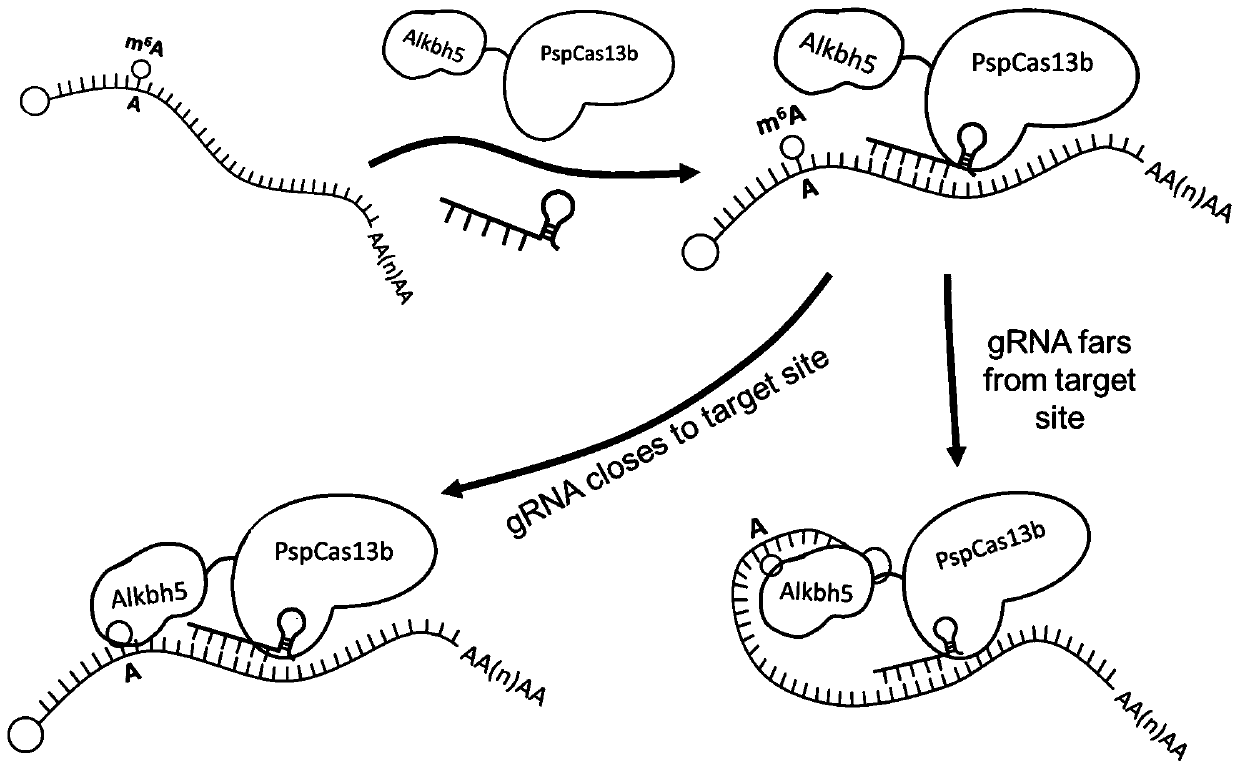
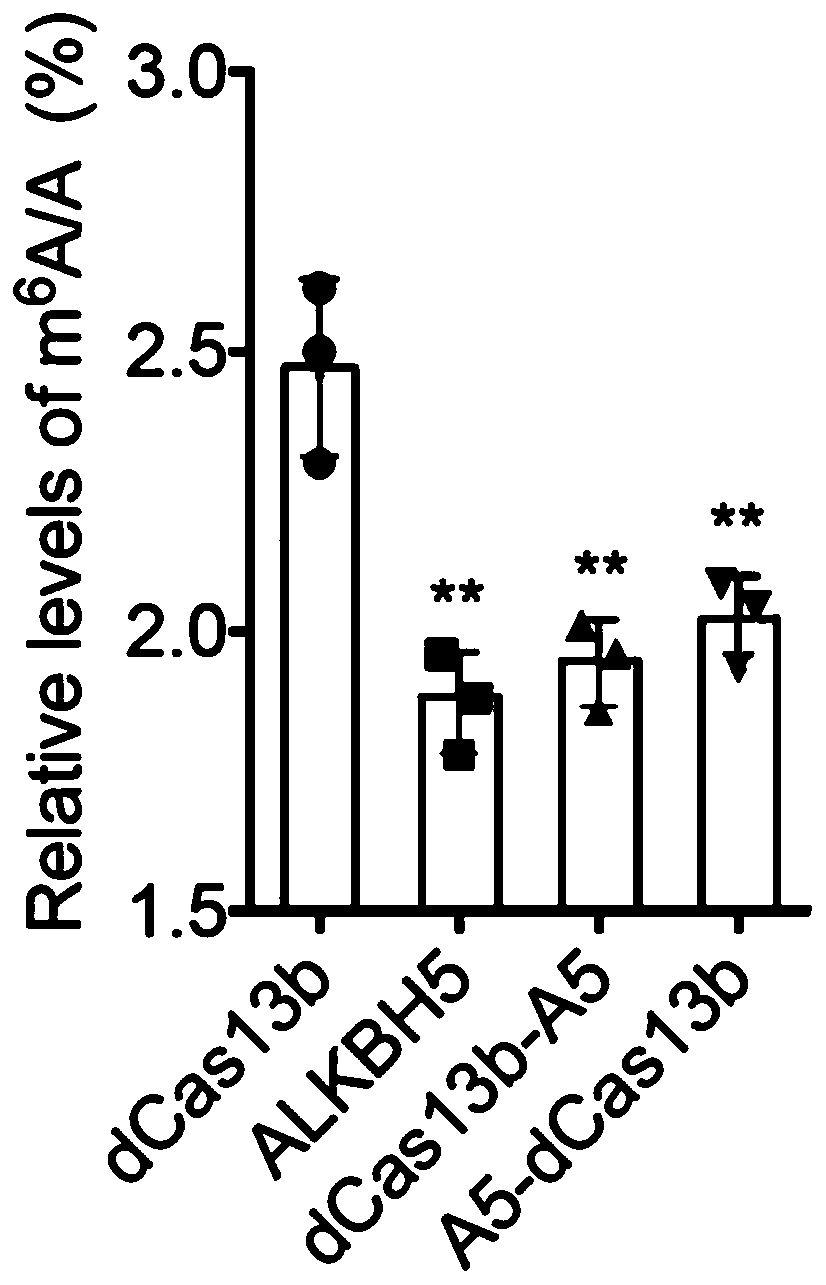
PspCas13b-Alkbh5 single gene specific m6A modification editing method
The invention discloses application of demethylation modification of targeted mRNA by using PspCas13b in combination with m6A demethylase Alkbh5. A study shows that a PspCas13b-Alkbh5 fusion protein can perform demethylation modification by targeting target gene (such as CYB5A and CTNNB1) mRNA through the specific gRNA to further regulate the target gene expression. m6A RNA immunoprecipitation assays and m6A site quantitative PCR results show that the PspCas13b-Alkbh5 fusion protein can effectively reduce the m6A methylation level of the target gene mRNA in the cell, and no off-target phenomenon is found. The PspCas13b is used as a means and combined with the m6A demethylase Alkbh5 to achieve the demethylation modification of the targeted mRNA for the first time and regulate the expressionof the specific purpose and application accordingly. The method breaks through the previous specific protein expression regulation based on previous change of DNA genetic information, provides a newpotential treatment mode and strategy for treatment of various diseases in the future, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Inhibitor of demethylase, antitumorigenic agent, and an in vitro assay for demethylase inhibitors
The present invention relates to a DNA demethylase (dMTase) inhibitor which comprises s-adenosylmethionine, a metabolite of s-adenosylmethionine or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Resveratrol derivative, preparation method thereof and application of resveratrol derivative serving as LSD1 inhibitor
ActiveCN106045881AStrong LSD1 inhibitory activityHigh activityOrganic chemistryAntiviralsDiseaseHalogen
The invention discloses a resveratrol derivative, a synthesizing method thereof and application of the resveratrol derivative serving as a histone lysine specificity demethylase 1 inhibitor and belongs to the field of medicinal chemistry. The formula of the resveratrol derivative is as shown in the specification, wherein R is preferably hydrogen, hydroxyl, methoxy, nitro or halogen, and X represents N atom and C atom. The resveratrol derivative has good inhibitory effect on the histone lysine specificity demethylase 1 and can be used as the candidate for further development or the lead compound to develop medicine for treating diseases such as tumors and AIDS.
Owner:XINXIANG MEDICAL UNIV
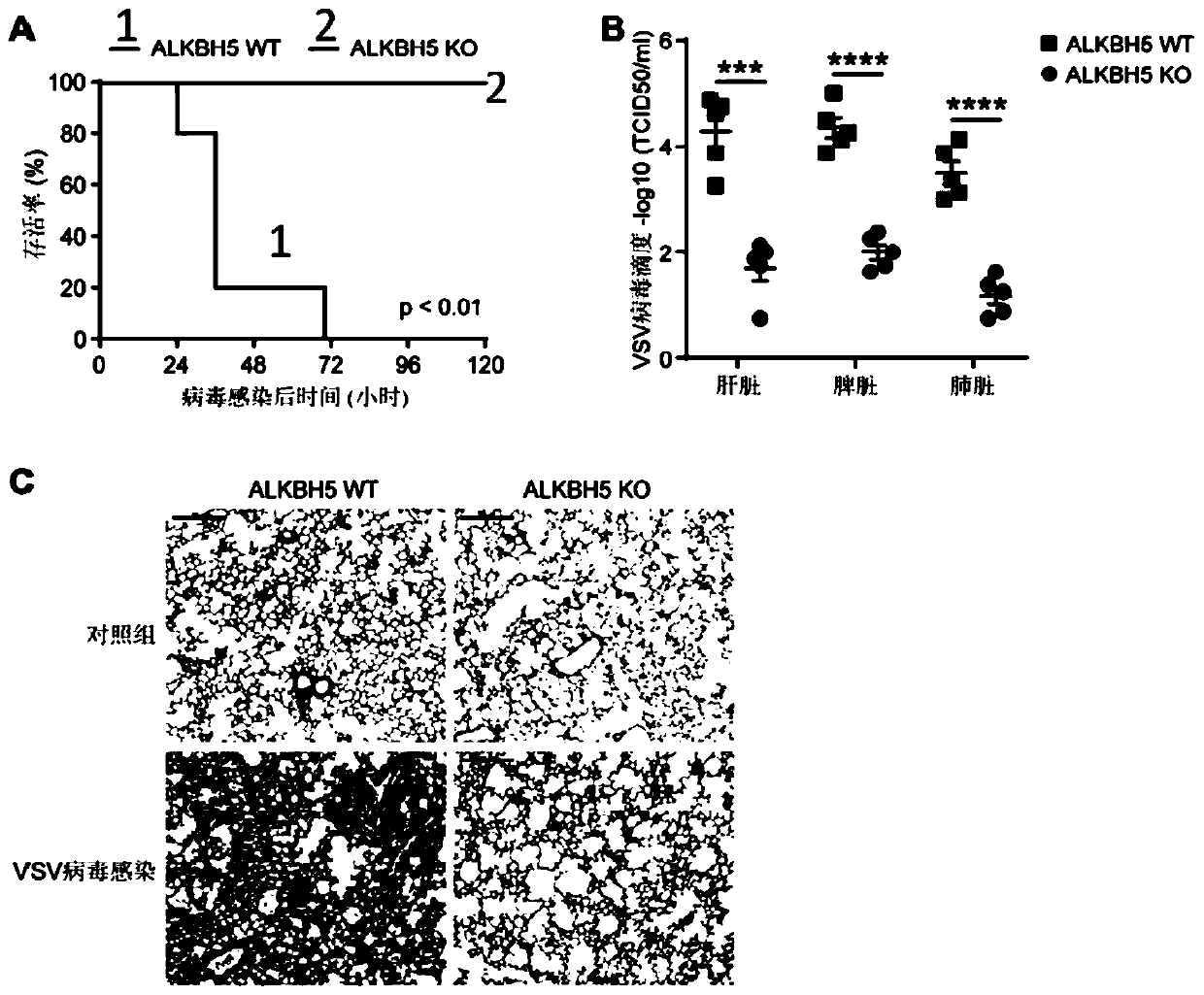
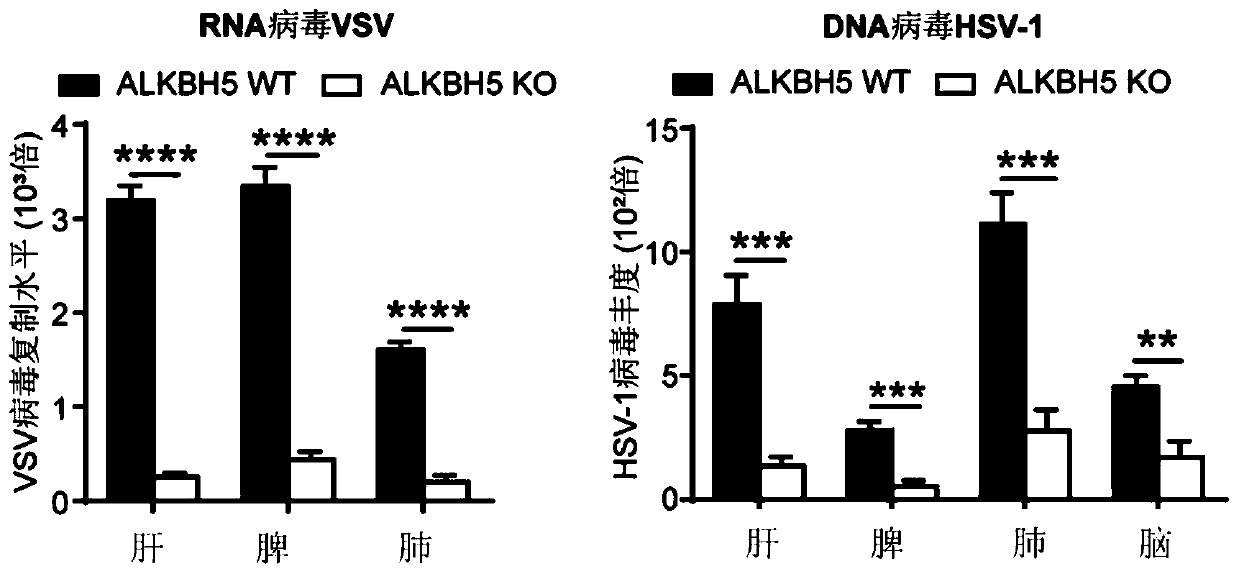
Application of ALKBH5 inhibitor in treatment of virus infectious diseases
ActiveCN110420331APeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementViral infectious diseaseViral infection
The invention relates to application of an AlkB homologous 5 (ALKBH5) inhibitor of demethylase in the treatment of virus infectious diseases. In particular, the invention relates to the use of the ALKBH5 inhibitor in the preparation of products for the treatment of the virus infectious diseases and / or diseases and / or symptoms related to virus infection, and a corresponding pharmaceutical composition or kit of the products. The application can be used for inhibiting and treating the virus infection, especially for objects with abnormal natural immune functions, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:THE INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
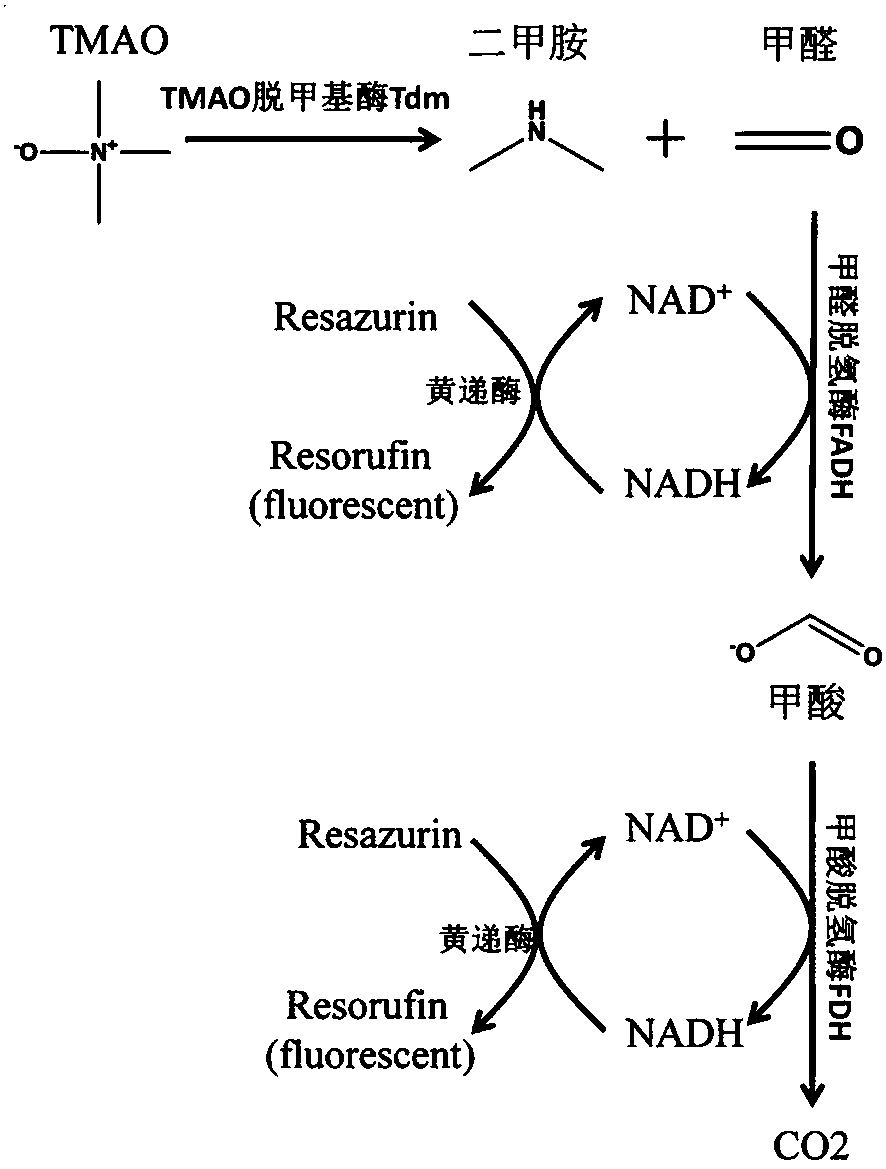
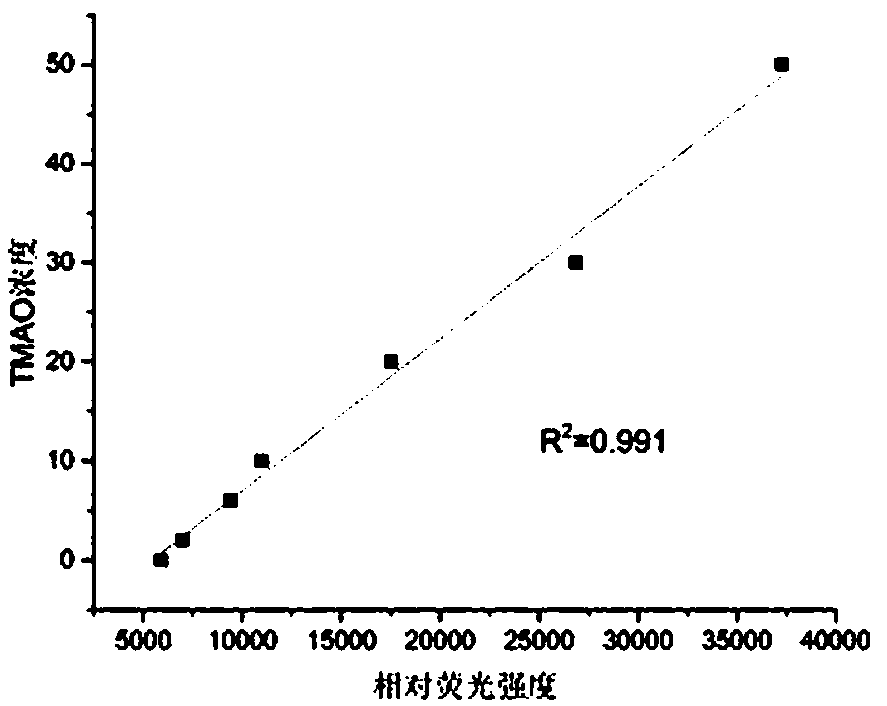
Method for detecting TMAO (trimethylamine oxide) by enzyme method and application thereof
ActiveCN108507984AHigh sensitivityRapid and stable detectionFluorescence/phosphorescenceNad dependent dehydrogenaseFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for detecting TMAO (trimethylamine oxide) by an enzyme method and application thereof. The detection method utilizes a multi-enzyme combination system containing TMAOTDM (demethylase), FADH (formaldehyde dehydrogenase), FDH (formate dehydrogenase) and diaphorase, so as to perform fluorescence determining on the TMAO; the method can be used for developing a TMAO detection kit. The method for detecting the TMAO by the enzyme method has the advantages that the defect of failure to directly determine based on dehydrogenase and diaphorase coupling because of no participation of NAD dependence dehydrogenase in the metabolism path of the TMAO is overcome; by adopting the multi-enzyme coupling of TDM-FADH-FDH-diaphorase, the system for fluorescence determining ofthe TMAO is constructed, and one TMAO molecule is decomposed into two fluorescence signals; the sensitivity is high, the detection is rapid and stable, the repeatability is good, the operation is simple and convenient, and the cost is lower.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL OF SHANDONG UNIV
DNA demethylase, therapeutic and diagnostic uses thereof
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Oligonucleotides useful in methods for detecting and characterizing Aspergillus fumigatus
InactiveUS20060127934A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerPolymerase L
Oligonucleotides and methods for using these oligonucleotides in the detection of Aspergillus fumigatus are disclosed. Aspergillus fumigatus is the causative agent for medical conditions including invasive aspergillosis. The oligonucleotides of the invention have nucleotide sequences derived from the gene encoding the cytochrome P450 14 alpha-sterol demethylase (i.e., the Cyp51A protein) of Aspergillus fumigatus. The oligonucleotides of the invention include forward primers and reverse primers which in combination are capable of priming the synthesis of amplicons specific to cyp51A in polymerase chain reactions using nucleic acids isolated from Aspergillus fumigatus as templates. The oligonucleotides of the invention also include probes capable of detecting these cyp51A-specific amplicons. Thus, a biological sample is tested for the presence of Aspergillus fumigatus by isolating nucleic acid from the sample, conducting a polymerase chain reaction in a mixture containing this nucleic acid and these forward and reverse primers, and then determining, using an oligonucleotide probe, whether an amplicon is produced in the mixture, wherein detection of the amplicon indicates the presence of Aspergillus fumigatus in the sample. The oligonucleotides of the invention also include primers for nucleotide sequencing reactions to determine whether an isolate of Aspergillus fumigatus is more tolerant than wild-type Aspergillus fumigatus to a triazole, which is a compound commonly used as an antifungal drug. Specifically, a strand of a cyp51A-specific amplicon is at least partially sequenced using a nucleotide sequencing primer in a primer extension reaction. Identification of mutations giving rise to amino acid substitutions at positions 54, 138, 220, and 448 of the amino acid sequence of the wild-type Cyp51A protein indicates that the isolate of Aspergillus fumigatus from which the amplicon is derived exhibits decreased susceptibility to at least one triazole.
Owner:MEDICAL DIAGNOSTIC LAB
Lysine demethylase inhibitors for myeloproliferative or lymphoproliferative diseases or disorders
InactiveUS20170209432A1Reduce platelets and other blood cellsReduce impactOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsLymphoproliferative diseaseLymphoid tissue hyperplasia
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for the treatment or prevention of diseases and disorder associated with myeloproliferative and lymphoproliferative disorders. In particular, the invention relates to an LSD1 inhibitor for use in treating or preventing diseases and disorder associated with myeloproliferative and lymphoproliferative disorders.
Owner:ORYZON GENOMICS SA
Reduction of nicotine to nornicotine conversion in plants
ActiveUS20170130239A1Reducing nornicotine levelLower conversion rateMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesNicotiana tabacumNucleotide
The present invention relates to a mutant, non-naturally occurring or transgenic tobacco plant cell comprising: (i) a polynucleotide comprising, consisting or consisting essentially of a sequence encoding a functional nicotine N-demethylase and having at least 95% sequence identity to SEQ ID NO:2; (ii) a polypeptide encoded by the polynucleotide set forth in (i); (iii) a polypeptide comprising, consisting or consisting essentially of a sequence encoding a nicotine N-demethylase and having at least 95% sequence identity to SEQ ID NO:3; or (iv) a construct, vector or expression vector comprising the isolated polynucleotide set forth in (i), and wherein the expression or activity of said nicotine demethylase is reduced as compared to a control tobacco plant cell in which the expression or activity of said nicotine demethylase has not been reduced.
Owner:PHILIP MORRIS PROD SA
Lysine demethylase inhibitors for diseases and disorders associated with Flaviviridae
ActiveUS9790196B2Avoid side effectsReduce duplicationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideLysineLuetic disease
The invention relates to methods and compositions for the treatment or prevention of Flaviviridae infections. In particular, the invention relates to an LSD1 inhibitor for use in treating or preventing Flaviviridae infections, including hepatitis C virus infections.
Owner:ORYZON GENOMICS SA
Biosensing method for DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) demethylase based on nanoparticle aggregation
ActiveCN102586463AEnhanced Raman signalStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsFunctionalized nanoparticlesSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
The invention discloses a biosensing method for DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) demethylase based on nanoparticle aggregation. According to the biosensing method, a nucleic acid functionalized nanoparticle probe is prepared; a specific bucleic sequence contains a cleavage site of restriction enzyme; the cleavage site is subjected to methylation treatment; the methylated DNA is enabled to generate a methylated action by the activated DNA demethylase, thereby simultaneously digesting and degrading the DNA for the methylation-sensitive restriction enzyme and exonuclease, causing the nanoparticle to aggregate, enhancing the coupling and realizing high-sensitivity SERS (Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy) detection. Meanwhile, according to the method, the light absorption property is changed and the detection can be carried out by a colorimetric method. The method has the advantages of simple operation steps, quickness, high sensitivity and strong specificity and can become one of new methods for researching the DNA demethylation within the whole-genome range and apparent genetic rearrangement process and provide a technical means for function research, activity analysis and inhibitor investigation of large biological molecules.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Fungicidal mixtures of thiophene derivative
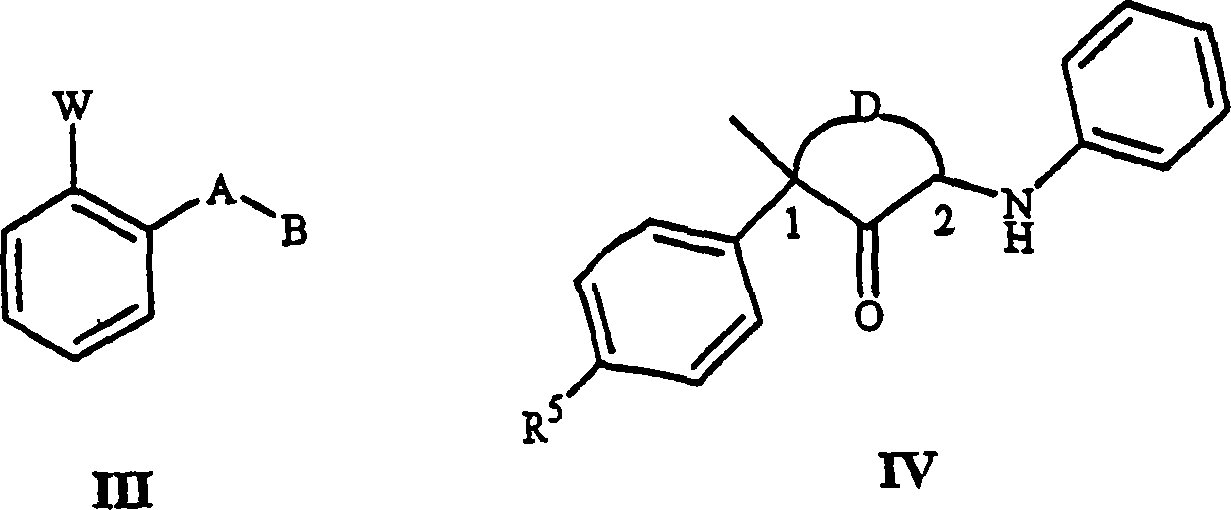
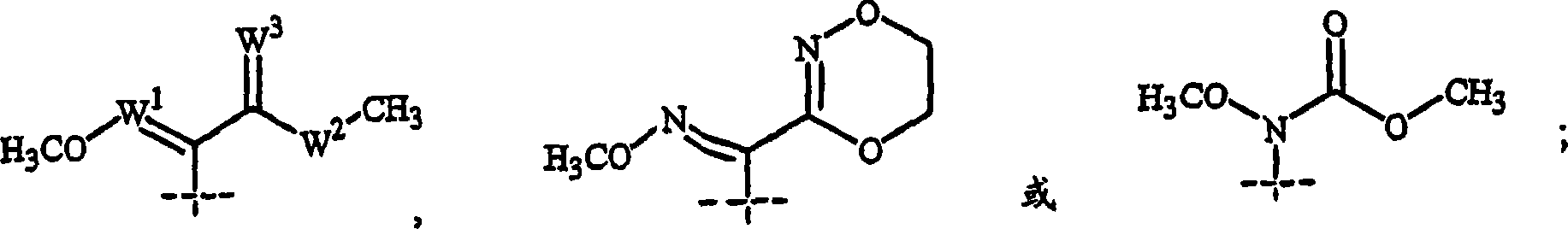
Disclosed are fungicidal mixtures, compositions and methods for controlling plant diseases relating to combinations comprising (a)N-[2-(1,3-dimethyl-butyl)-3-thienyl]-1-methyl-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazole-4-methanamide (comprising all stereo isomers) or agriculture acceptable salt; and (b) at least one compound selected from general formula III or general formula IV, which acts on the bc<1> composition at respiration electron transport position of fungi mitochondrion; wherein W, A, B, D and R<5> are defined in the description, and their agriculture acceptable salt; and optional (c) at least one demethylase compound selected from sterol biosynthesis route and agriculture acceptable salt thereof..
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Pyrimidine derivative with anticancer effect
InactiveCN111249283AGood antitumor effectEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryAnticarcinogenic EffectCancer prevention
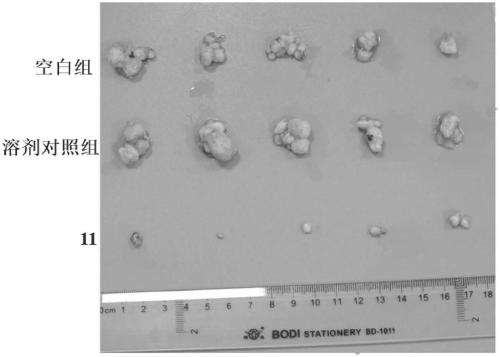
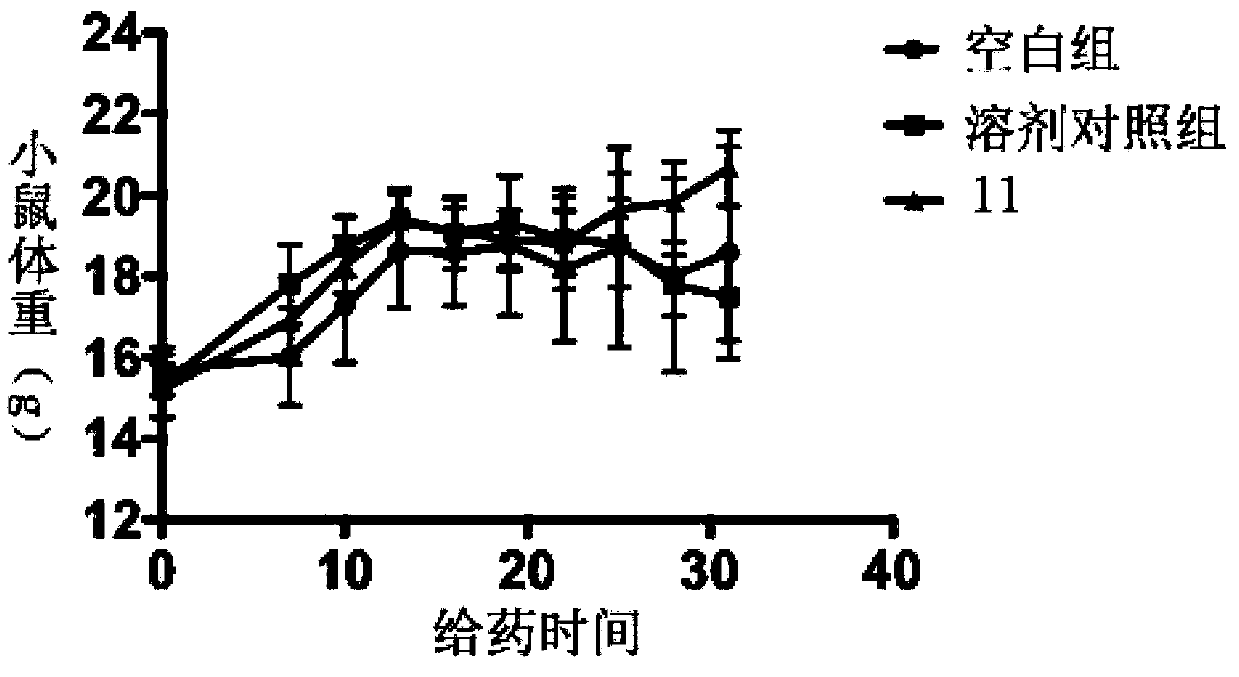
The invention relates to a pyrimidine derivative with an anticancer effect, belonging to the field of chemical medicines. The invention provides an application of a compound as shown in a formula I which is described in the specification or pharmaceutically acceptable salt of the compound in preparation of drugs used for treatment and / or prevention of cancers. Biological experiment results show that the series of compounds show good inhibition effect on histone arginine demethylase, wherein the IC50 of part of the compounds is at a micromolar level and show good inhibition effect on a varietyof clinically common tumor cell strains; and the IC50 of all the compounds is smaller than 1 [mu]M. The compound provided by the invention also shows good effect in vivo, and can significantly inhibittumor growth in mice. In conclusion, the pyrimidine derivative provided by the invention provides a new effective choice for developing a new generation of targeting drugs for tumor treatment, and has good application prospect.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Mutant flue-cured tobacco CYP82E4 gene, and applications thereof
ActiveCN105602961AReduce expressionReduce functionMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a mutant flue-cured tobacco CYP82E4 gene. The nucleotide sequence is represented by SEQ ID NO.2; and when the mutant flue-cured tobacco CYP82E4 gene is compared with wild type CYP82E4 gene, nucleotide G at the 116th site is changed into A via mutation. The invention also discloses a protein encoded by the mutant flue-cured tobacco CYP82E4 gene, and the amino acid sequence of the protein is represented by SEQ ID NO.4. It is shown by research that the mutant flue-cured tobacco CYP82E4 gene is capable of reducing expression or functions of nicotine N-demethylase, inhibiting the activity of nicotine N-demethylase in mature leaves, and reducing nornicotine content of tobacco plants containing the mutant flue-cured tobacco CYP82E4 gene obviously. The mutant flue-cured tobacco CYP82E4 gene can be used in breeding and seed selection of tobacco varieties with reduced nornicotine content; and tobacco varieties with low nornicotine content can be obtained via selfing of tobacco plants containing the mutant flue-cured tobacco CYP82E4 gene, or conventional selection hybridization with other flue-cured tobacco.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD
Compositions and methods for minimizing nornicotine synthesis in tobacco
ActiveUS20130037040A1Reducing nornicotine levelLower conversion rateTobacco preparationTobacco treatmentMetaboliteNornicotine
Compositions and methods for reducing the level of nornicotine and N′-nitrosonornicotine (NNN) in tobacco plants and plant parts thereof are provided. The compositions comprise isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides for a root-specific nicotine demethylases, CYP82E10, and variants thereof, that are involved in the metabolic conversion of nicotine to nornicotine in these plants. Compositions of the invention also include tobacco plants, or plant parts thereof, comprising a mutation in a gene encoding a CYP82E10 nicotine demethylase, wherein the mutation results in reduced expression or function of the CYP82E10 nicotine demethylase. Seed of these tobacco plants, or progeny thereof, and tobacco products prepared from the tobacco plants of the invention, or from plant parts or progeny thereof, are also provided. Methods for reducing the level of nornicotine, or reducing the rate of conversion of nicotine to nornicotine, in a tobacco plant, or plant part thereof are also provided. The methods comprise introducing into the genome of a tobacco plant a mutation within at least one allele of each of at least three nicotine demethylase genes, wherein the mutation reduces expression of the nicotine demethylase gene, and wherein a first of these nicotine demethylase genes encodes a root-specific nicotine demethylase involved in the metabolic conversion of nicotine to nornicotine in a tobacco plant or a plant part thereof. The methods find use in the production of tobacco products that have reduced levels of nornicotine and its carcinogenic metabolite, NNN, and thus reduced carcinogenic potential for individuals consuming these tobacco products or exposed to secondary smoke derived from these products.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Phenylurea herbicide N-demethylase gene pudmA and application thereof
InactiveCN103266117AEfficient degradationBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses a phenylurea herbicide N-demethylase gene pudmA and an application thereof. A nucleotide sequence of the phenylurea herbicide N-demethylase gene pudmA is shown in SEQ ID NO.1; the overall length is 1907bp; the content of G+C is 55.37%; a large subunit code includes 459 amino acids; a small subunit code includes 176 amino acids; and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The phenylurea herbicide N-demethylase gene pudmA provided by the invention can remove N-methyl of phenylurea herbicides such as isoproturon and chlortoluron, so that the herbicidal activity is removed. Therefore, the phenylurea herbicide N-demethylase gene pudmA can be used for building genetically modified crops of an anti-phenyl urea herbicide. In addition, the phenylurea herbicide N-demethylase gene pudmA and encoded protein PudmA also can be used for removing residual phenylurea herbicide in the environment.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Methods and Kits for Quantitative Methyltransferase and Demethylase Measurements
InactiveUS20120142040A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisPeptide substrateMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The invention provides methods and kits for characterizing the activity of a methyltransferase or demethylase. The method involves enzymatically methylating or demethylating in vitro a substrate that is a peptide fragment of a full-length polypeptide, and then non-enzymatically methylating the peptide substrate with methyl groups that differ in molecular weight from the enzymatically added or removed methyl groups. Typically, deuterated or 13C formaldehyde is used to non-enzymatically methylate the substrate. The fully methylated substrate is then characterized by mass spectrometry to determine the ratio of enzymatically produced nonmethyl, monomethyl, and dimethyl residues on the peptide.
Owner:BIOVENTURES LLC
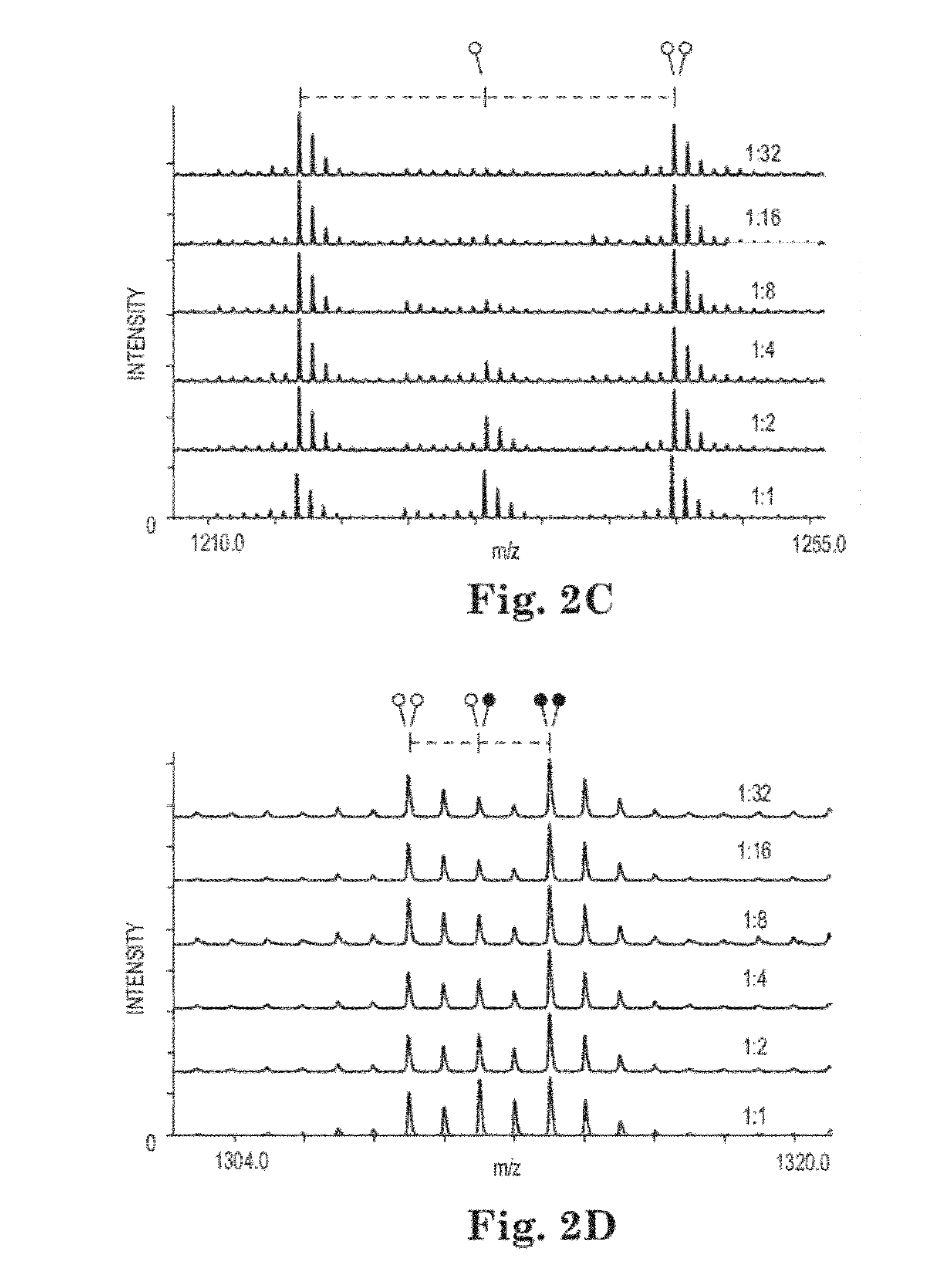
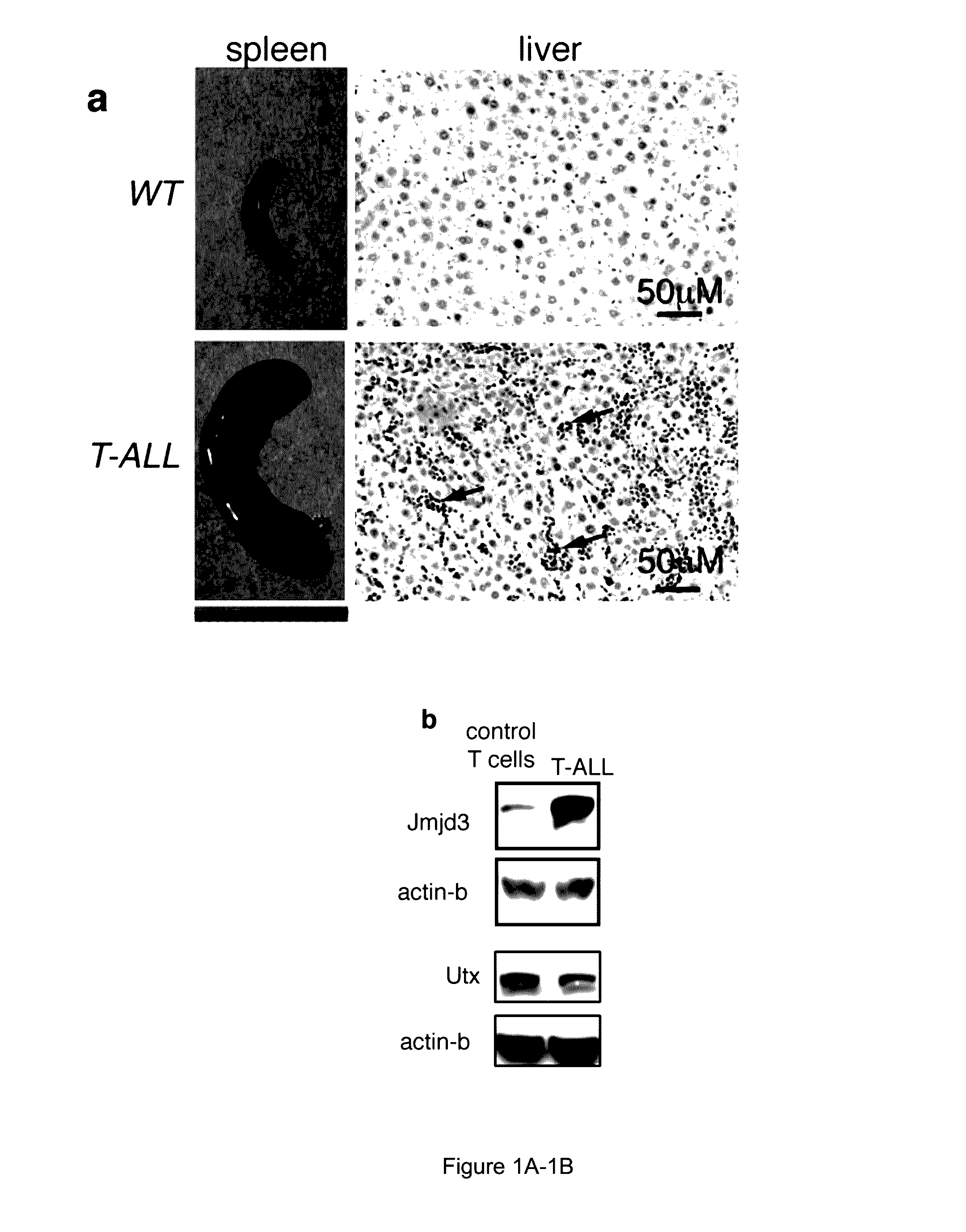
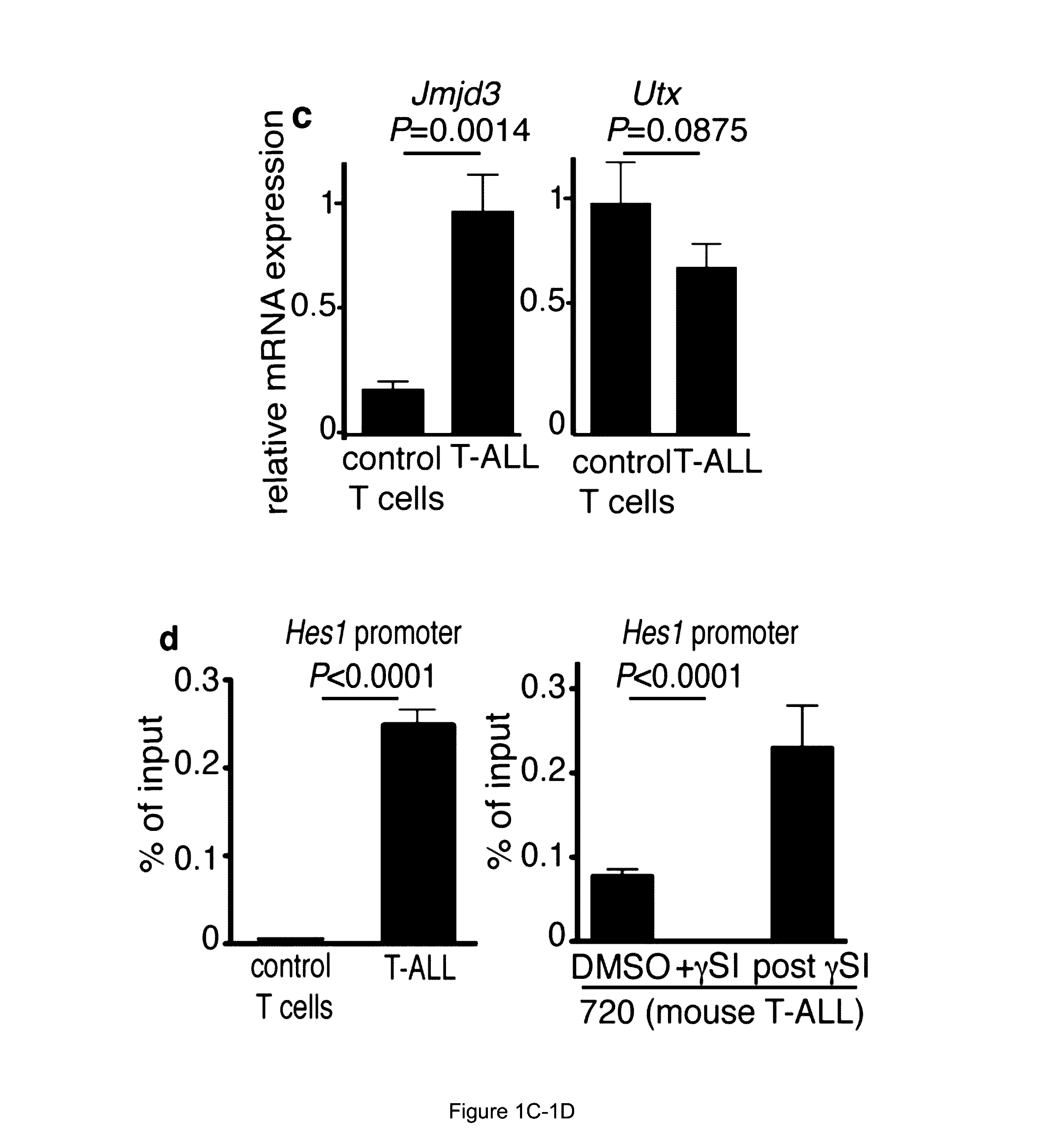
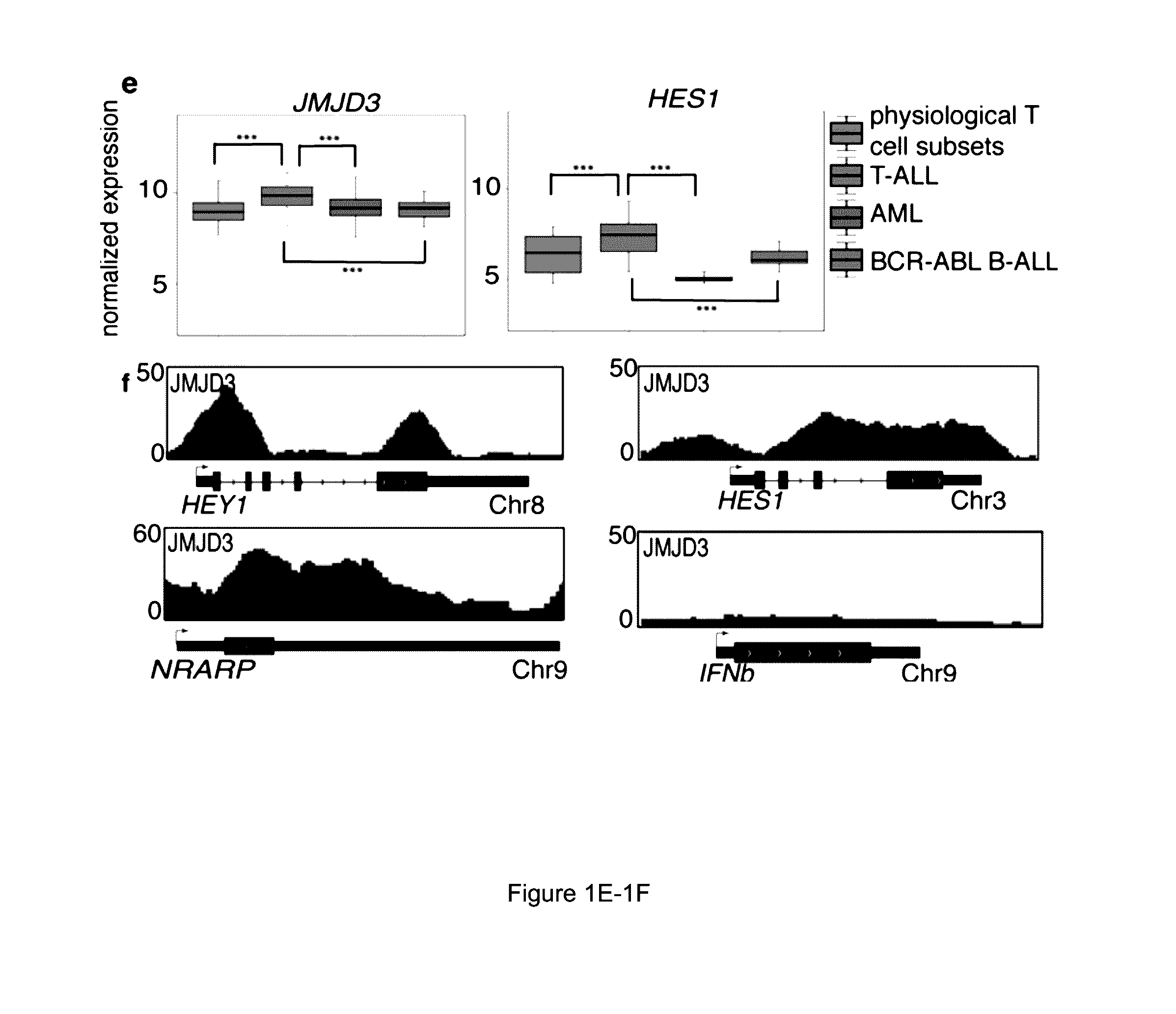
Methods for treating t-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
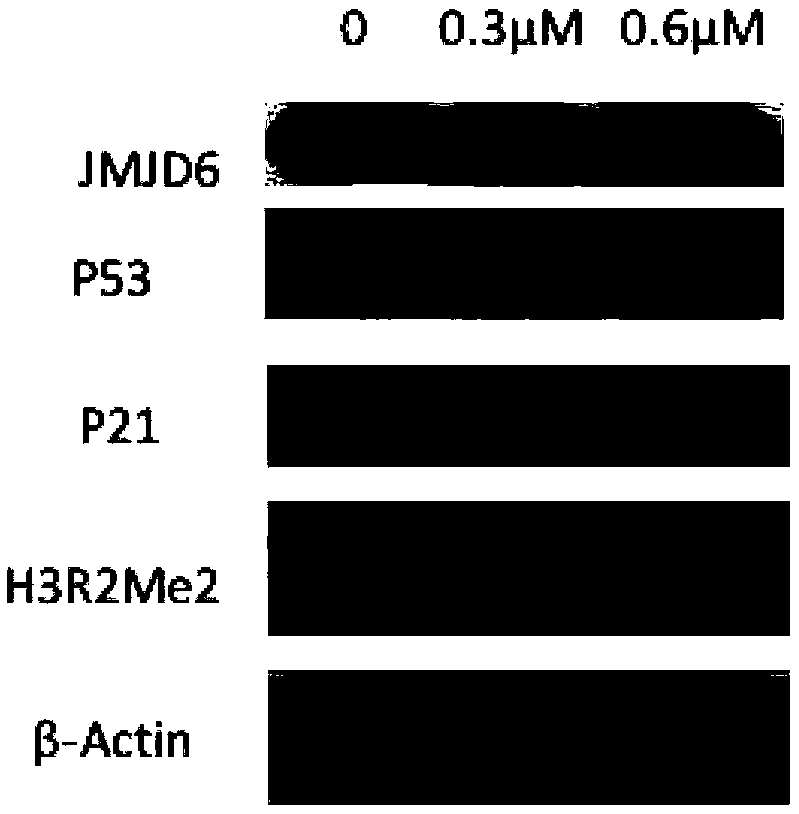
The present invention is directed to methods of treating T-ALL that involve administering an inhibitor of jumonji D3 (JMJD3) demethylase. Another embodiment of the invention relates to methods inhibiting T-ALL cell proliferation and / or survival that involves administering an inhibitor of jumonji D3 (JMJD3) demethylase to a population of T-ALL cells.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![Application of 2-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-2-oxoethyl 4-((3-chloro-4-methylphenyl) amino)-4-oxobutanoate in preparing an LSD1 (lysine-specific demethylase 1) inhibitor medicament Application of 2-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-2-oxoethyl 4-((3-chloro-4-methylphenyl) amino)-4-oxobutanoate in preparing an LSD1 (lysine-specific demethylase 1) inhibitor medicament](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/7e706329-04e4-4b5b-b8c9-1a182cd2dbef/HSA0000102396500000011.PNG)
![Application of 2-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-2-oxoethyl 4-((3-chloro-4-methylphenyl) amino)-4-oxobutanoate in preparing an LSD1 (lysine-specific demethylase 1) inhibitor medicament Application of 2-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-2-oxoethyl 4-((3-chloro-4-methylphenyl) amino)-4-oxobutanoate in preparing an LSD1 (lysine-specific demethylase 1) inhibitor medicament](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/7e706329-04e4-4b5b-b8c9-1a182cd2dbef/HSA0000102396500000012.PNG)
![Application of 2-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-2-oxoethyl 4-((3-chloro-4-methylphenyl) amino)-4-oxobutanoate in preparing an LSD1 (lysine-specific demethylase 1) inhibitor medicament Application of 2-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-2-oxoethyl 4-((3-chloro-4-methylphenyl) amino)-4-oxobutanoate in preparing an LSD1 (lysine-specific demethylase 1) inhibitor medicament](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/7e706329-04e4-4b5b-b8c9-1a182cd2dbef/HSA0000102396500000013.PNG)