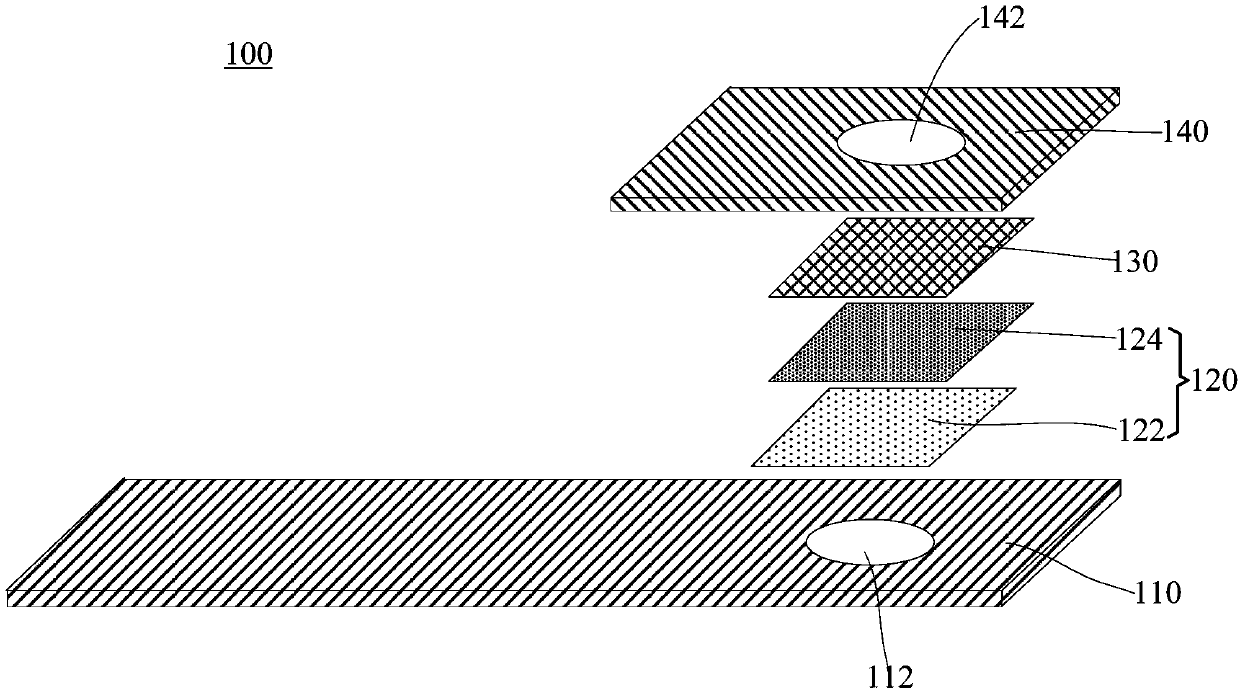
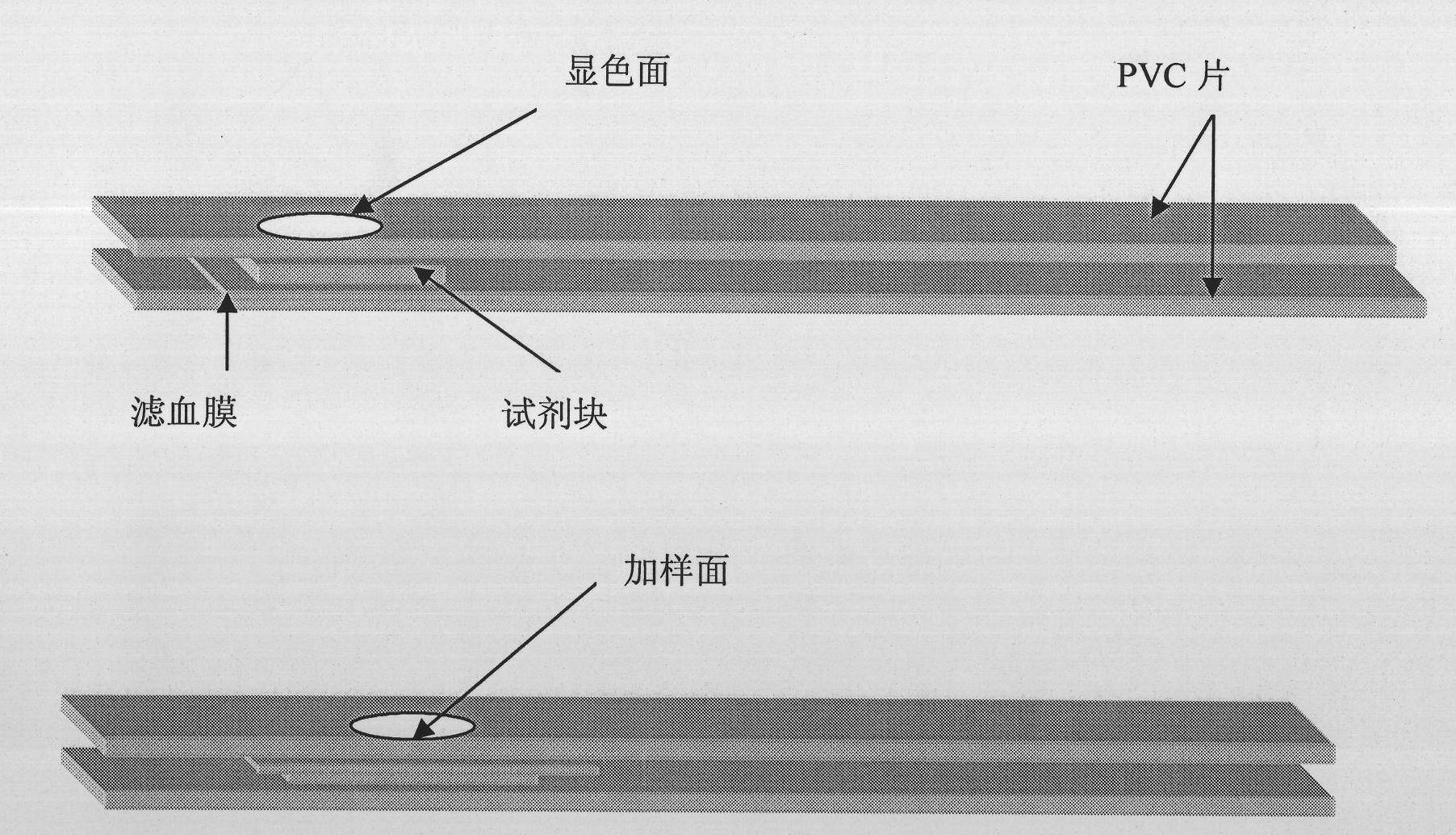
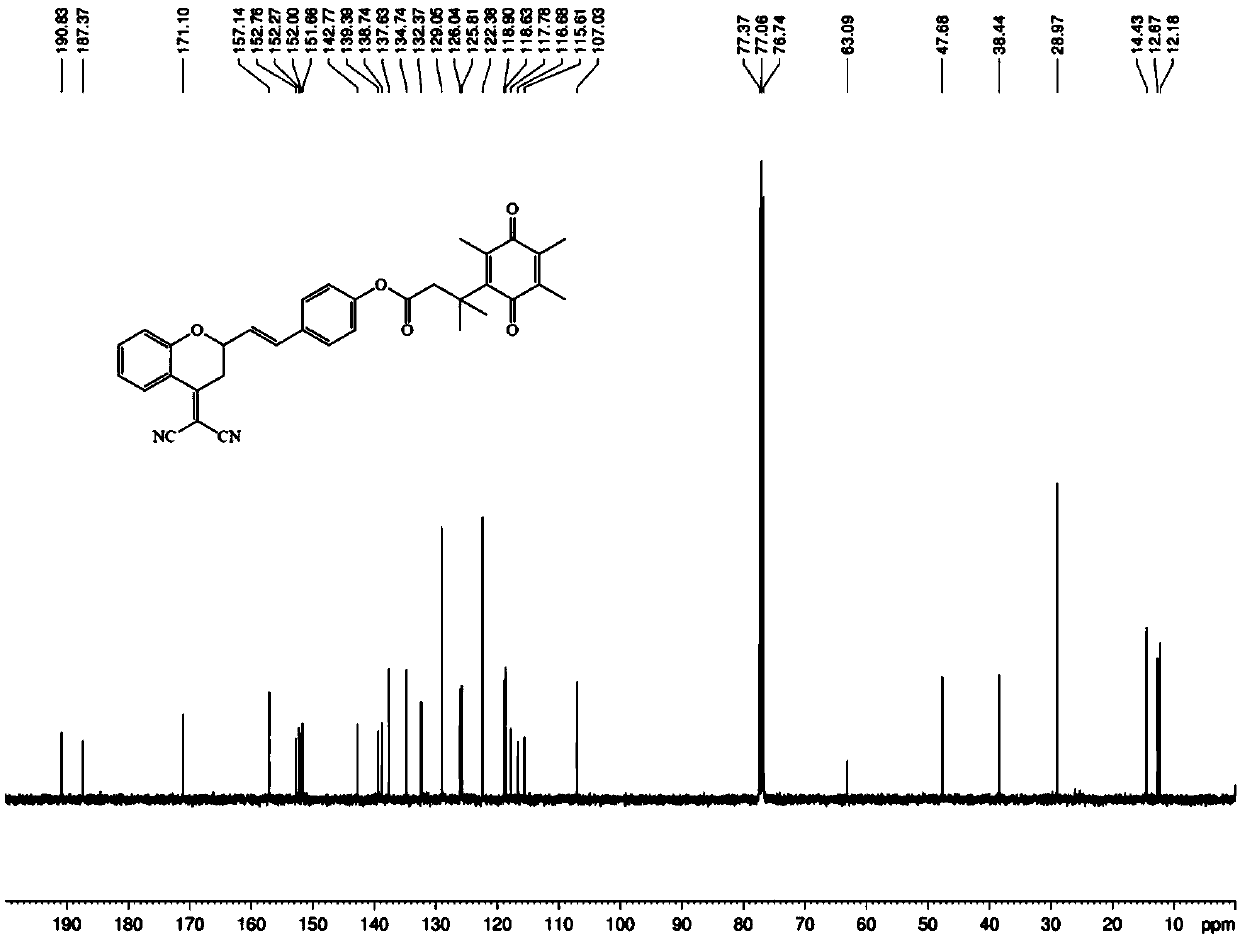
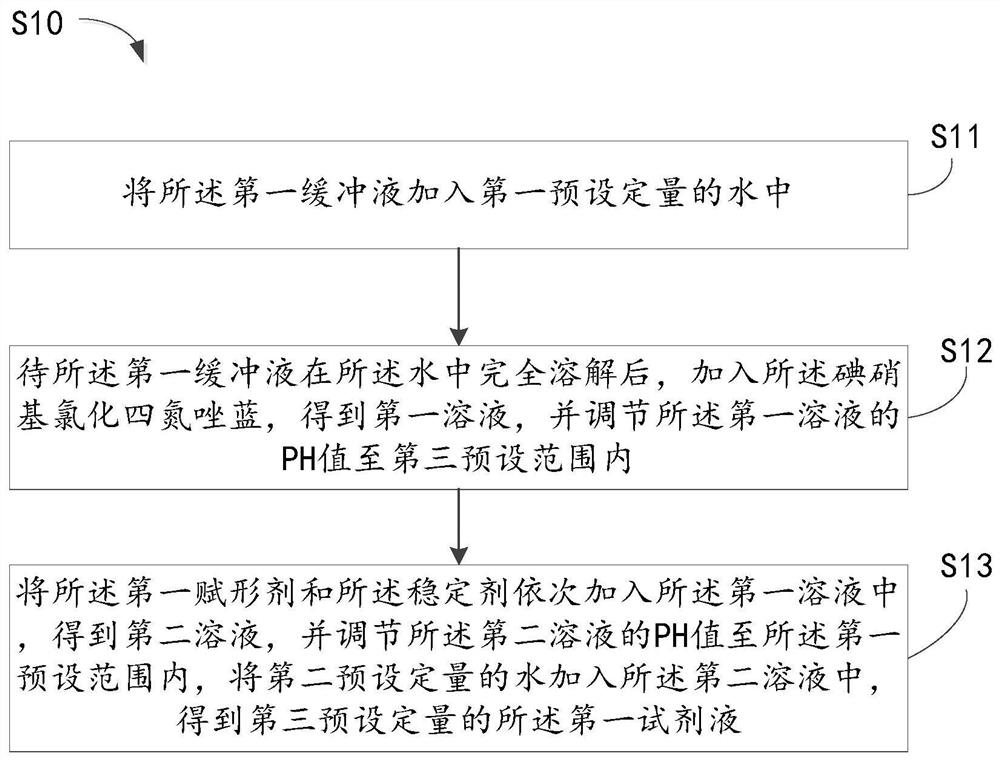
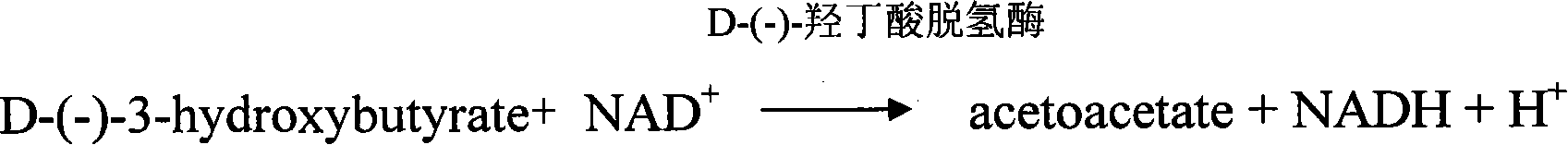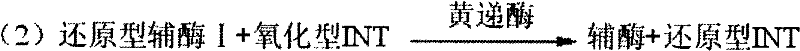Patents
Literature
53 results about "Diaphorase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
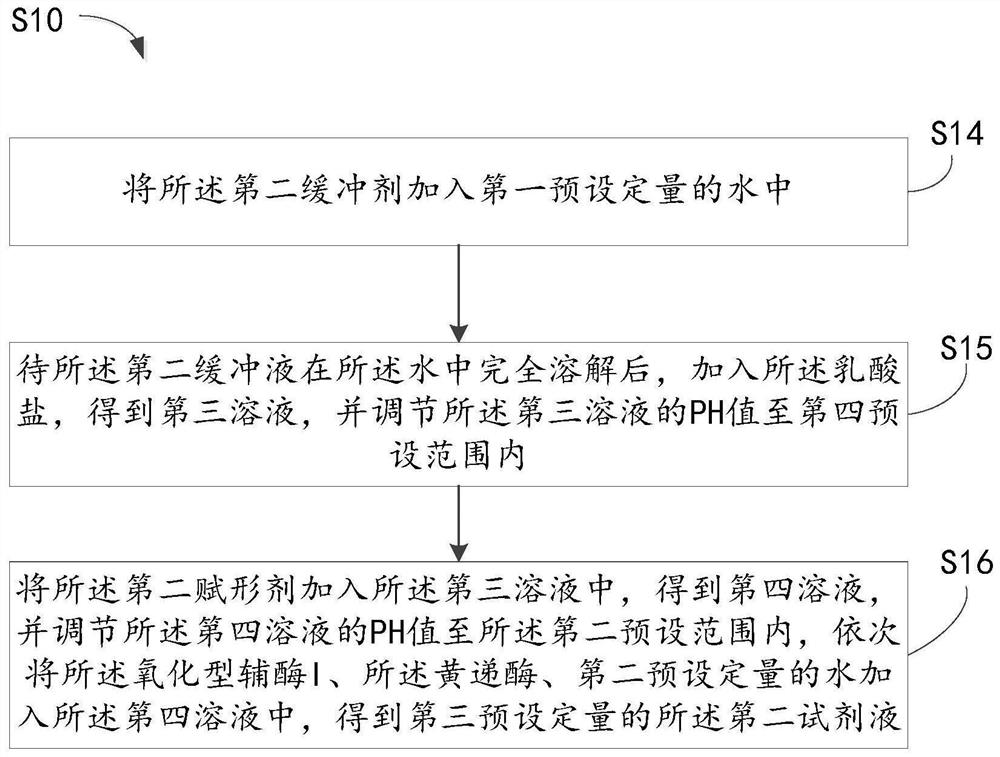
Inventor
Diaphorase may refer to: Cytochrome b5 reductase, an enzyme NADH dehydrogenase, an enzyme NADPH dehydrogenase, an enzyme
Diagnostics based on tetrazolium compounds
InactiveUS6200773B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsOrganic chemistryPyrrolo-Quinoline QuinoneDiaphorase
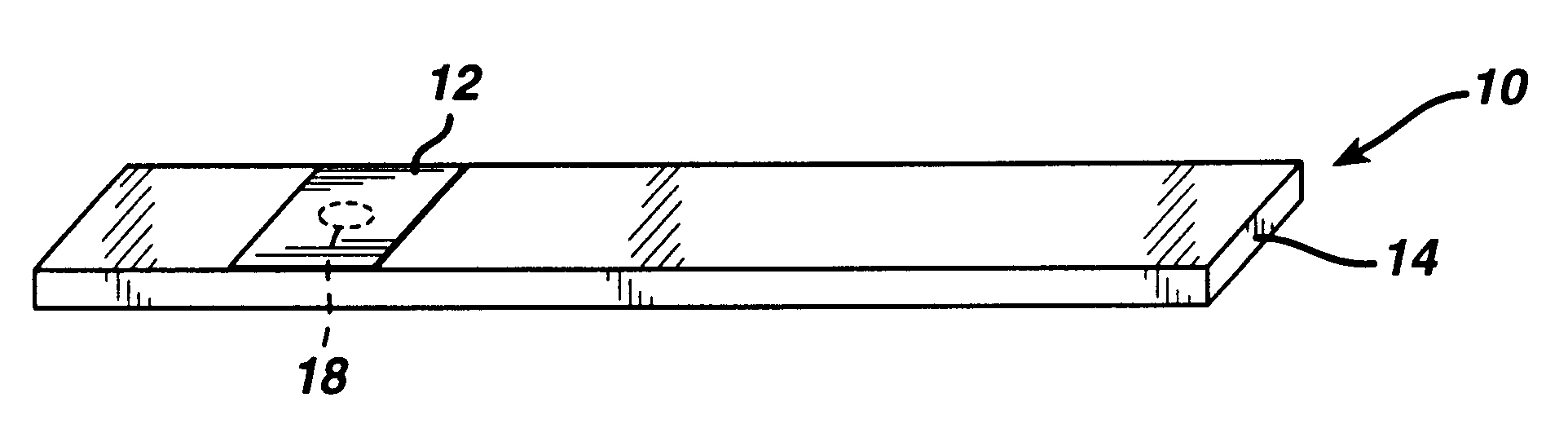
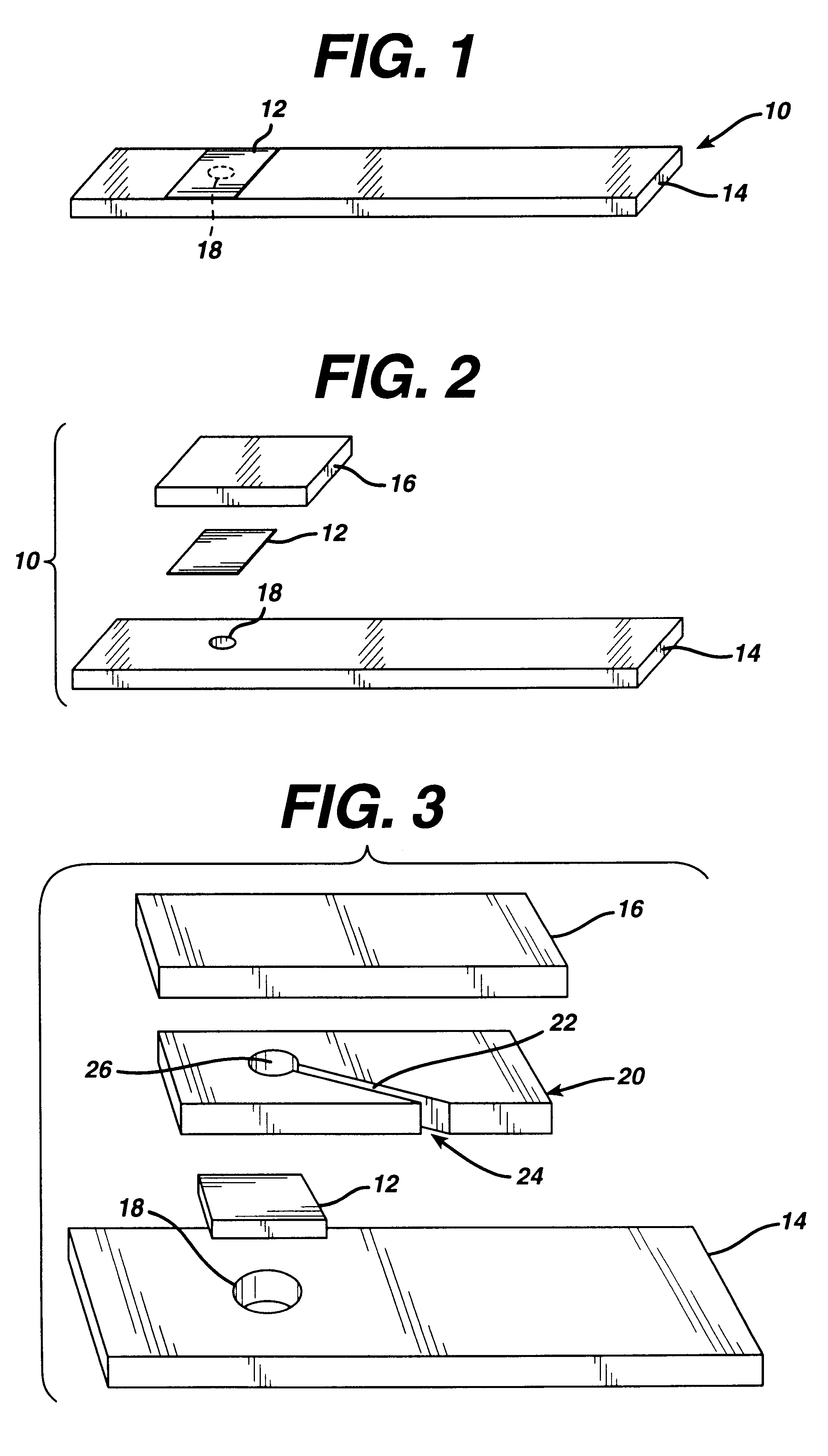
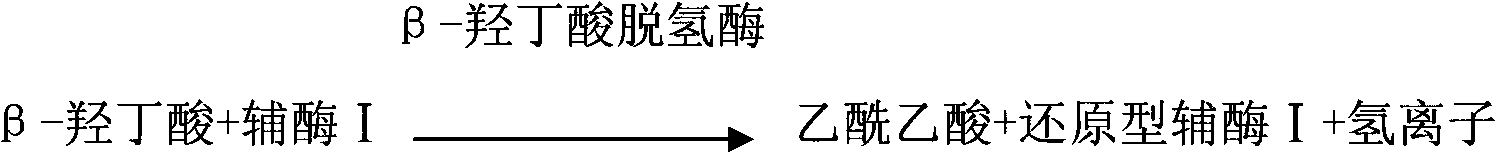
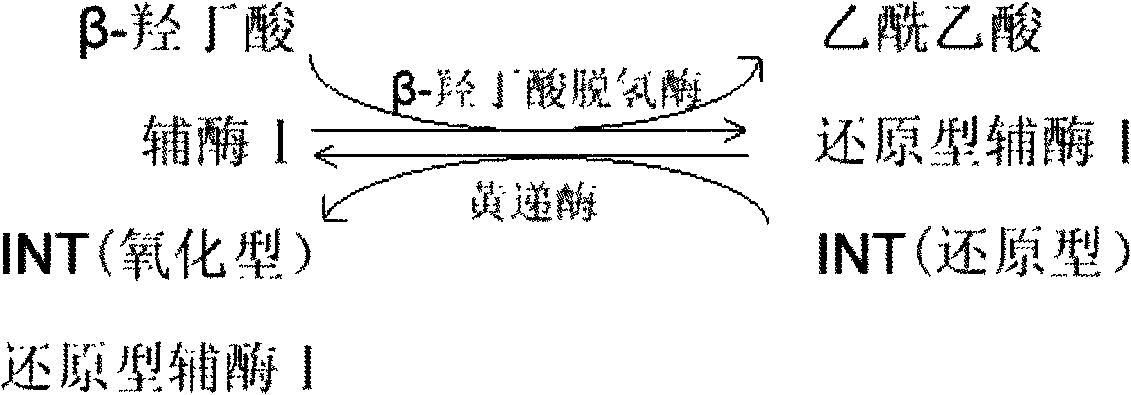
A reagent is suitable for measuring the concentration of an analyte in a hemoglobin-containing biological fluid, such as whole blood. The reagent comprises dehydrogenase enzyme that has specificity for the analyte, NAD, an NAD derivative, pyrrolo-quinoline quinone (PQQ), or a PQQ derivative, a tetrazolium dye precursor, a diaphorase enzyme or an analog thereof, and a nitrite salt. The reagent causes dye formation that is a measure of the analyte concentration. The nitrite salt suppresses interfering dye formation caused non-enzymatically by the hemoglobin. Preferably, the reagent is used in a dry strip for measuring ketone bodies, such as beta-hydroxybutyrate.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
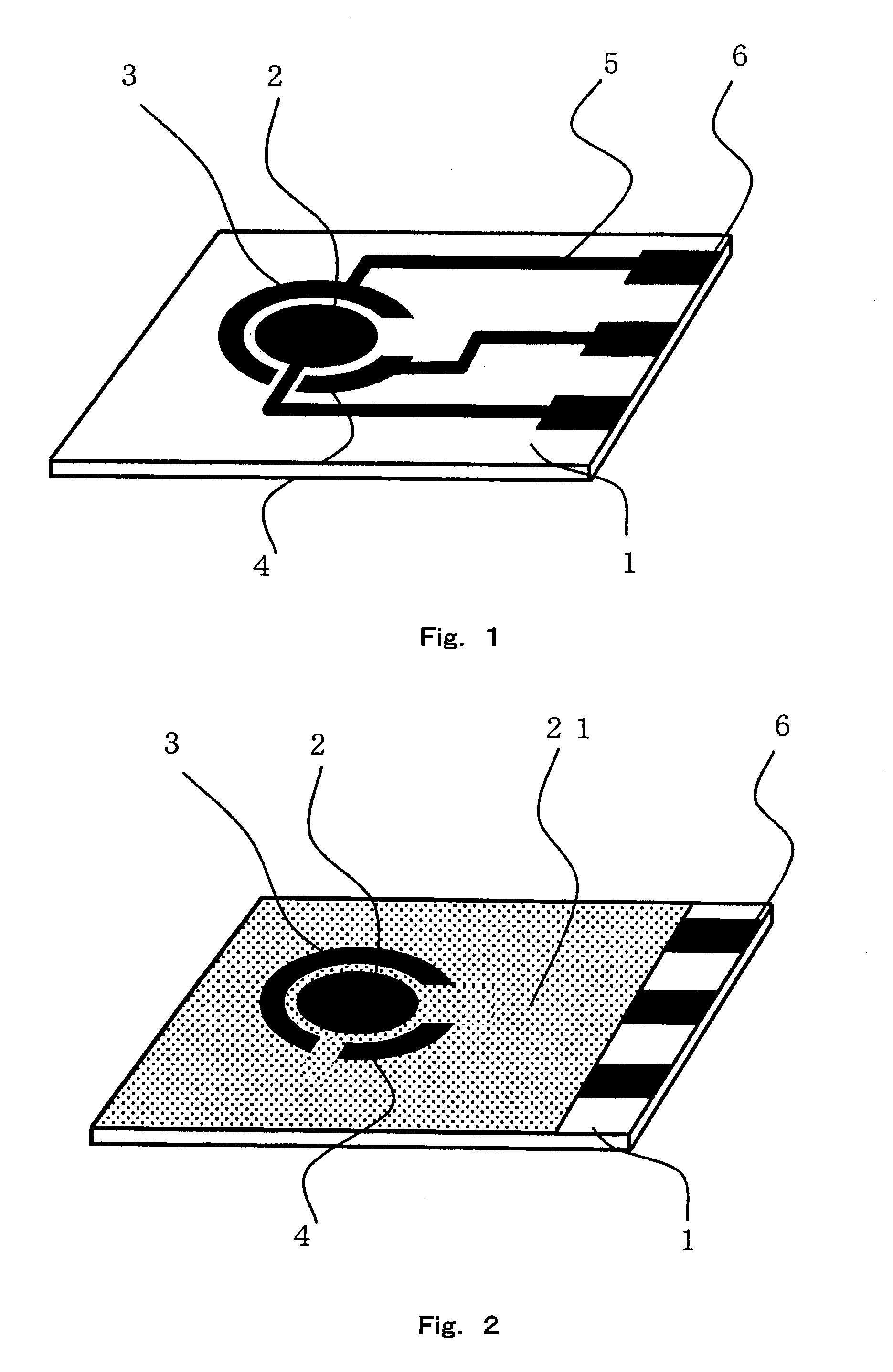
Fuel Cell, Electronic Device, Movable Body, Power Generation System, and Congeneration System
ActiveUS20070218345A1Reduce the amount of wasteEfficient use ofFuel cell auxillariesActive material electrodesDecompositionVitamin K3
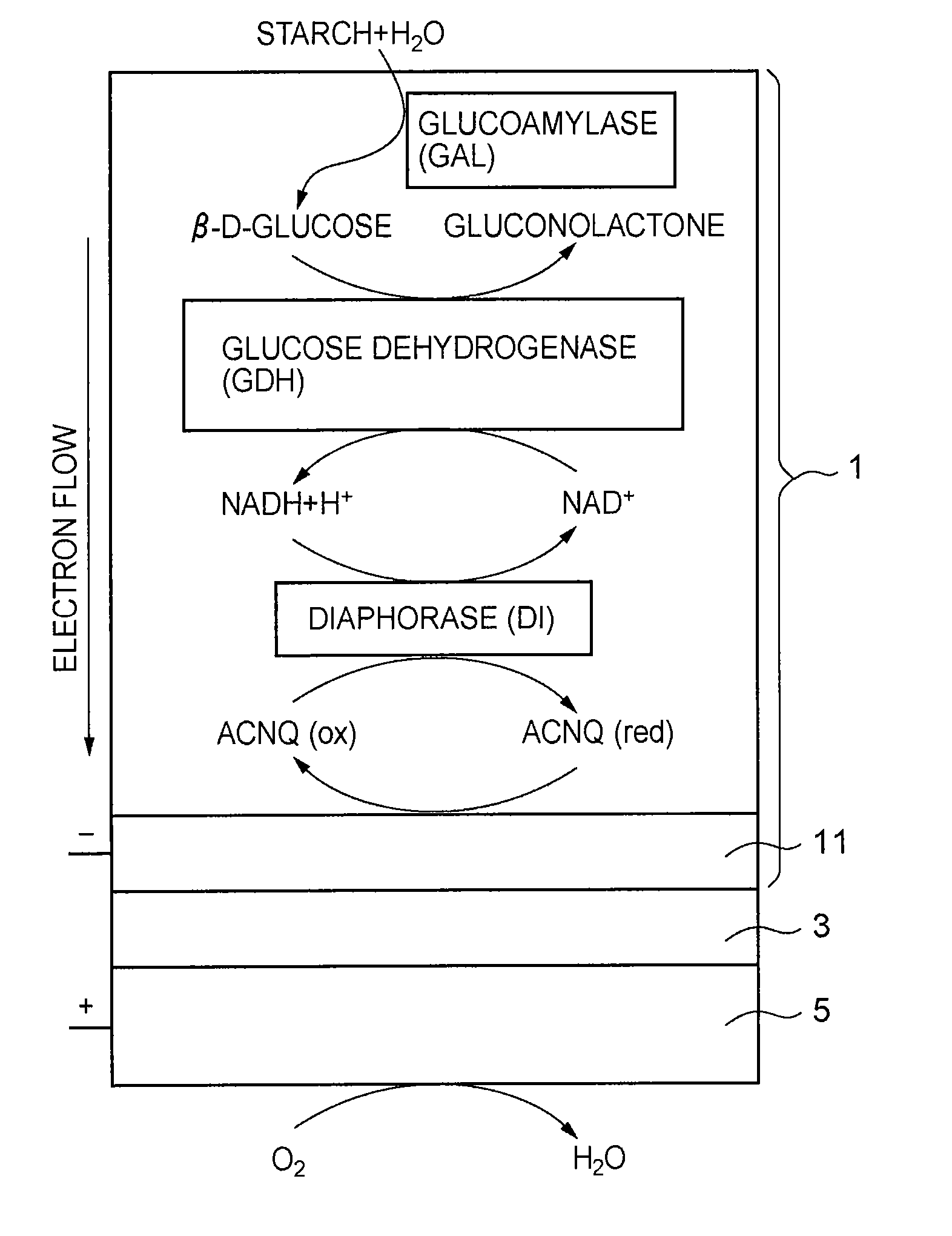
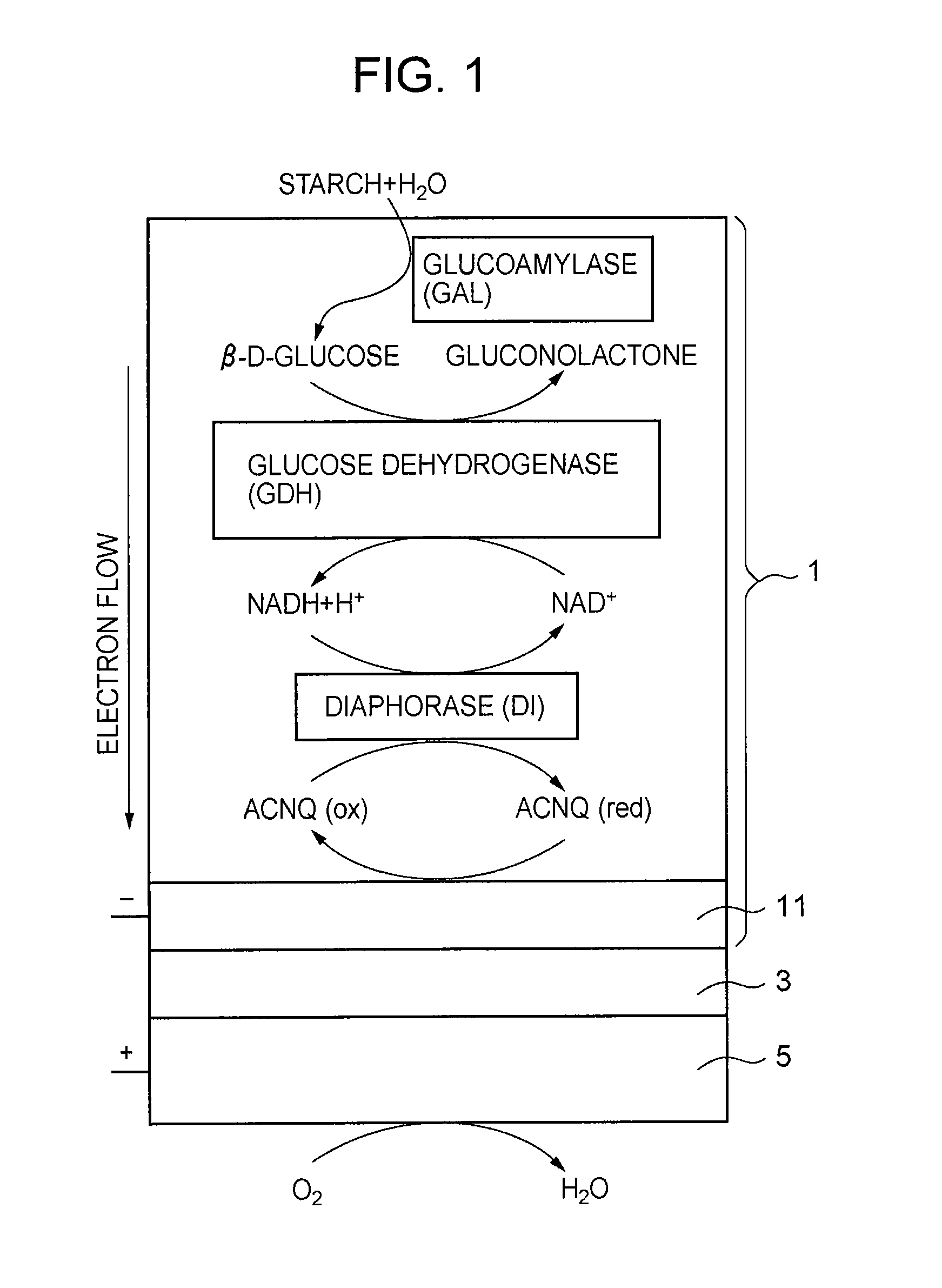
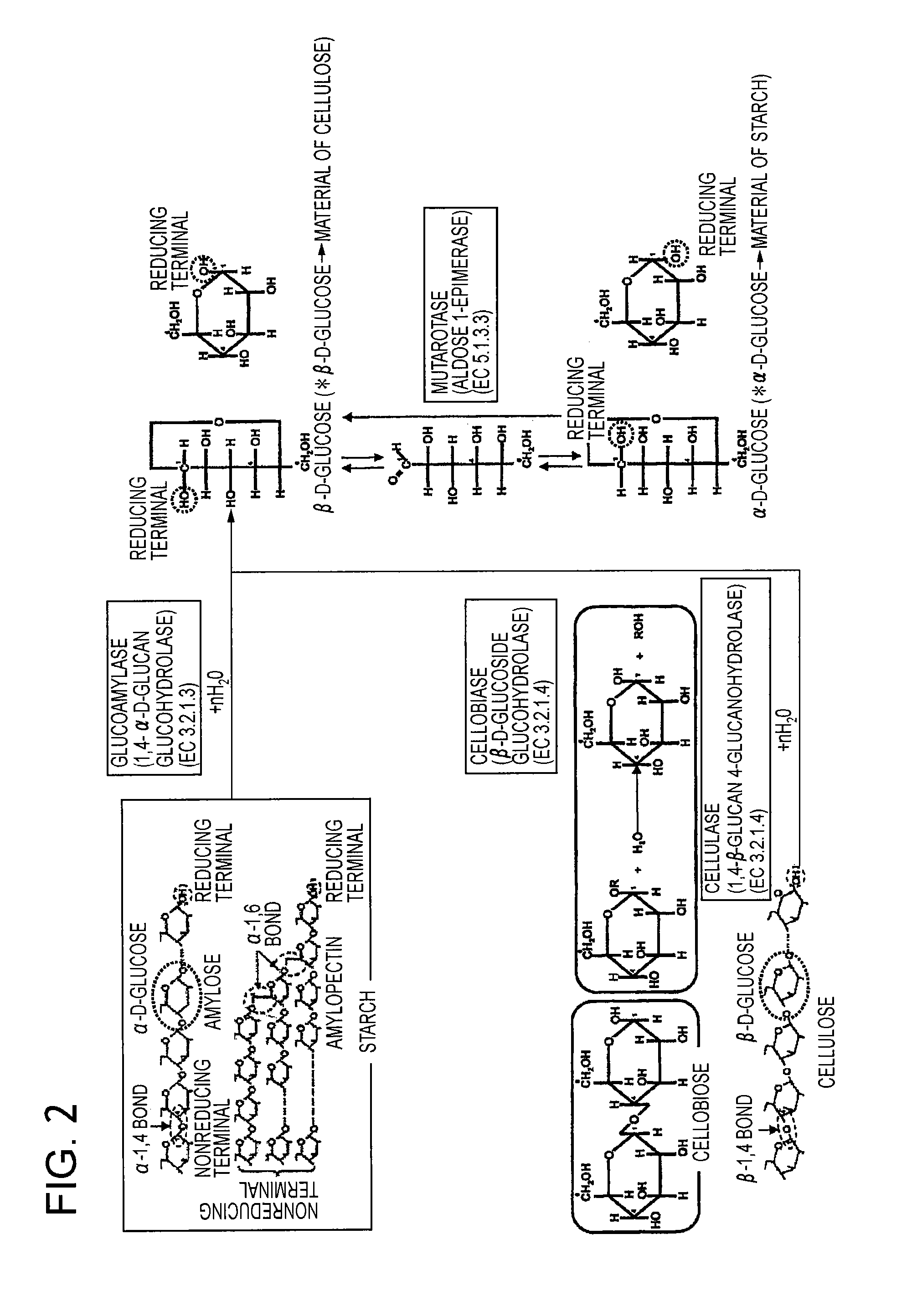
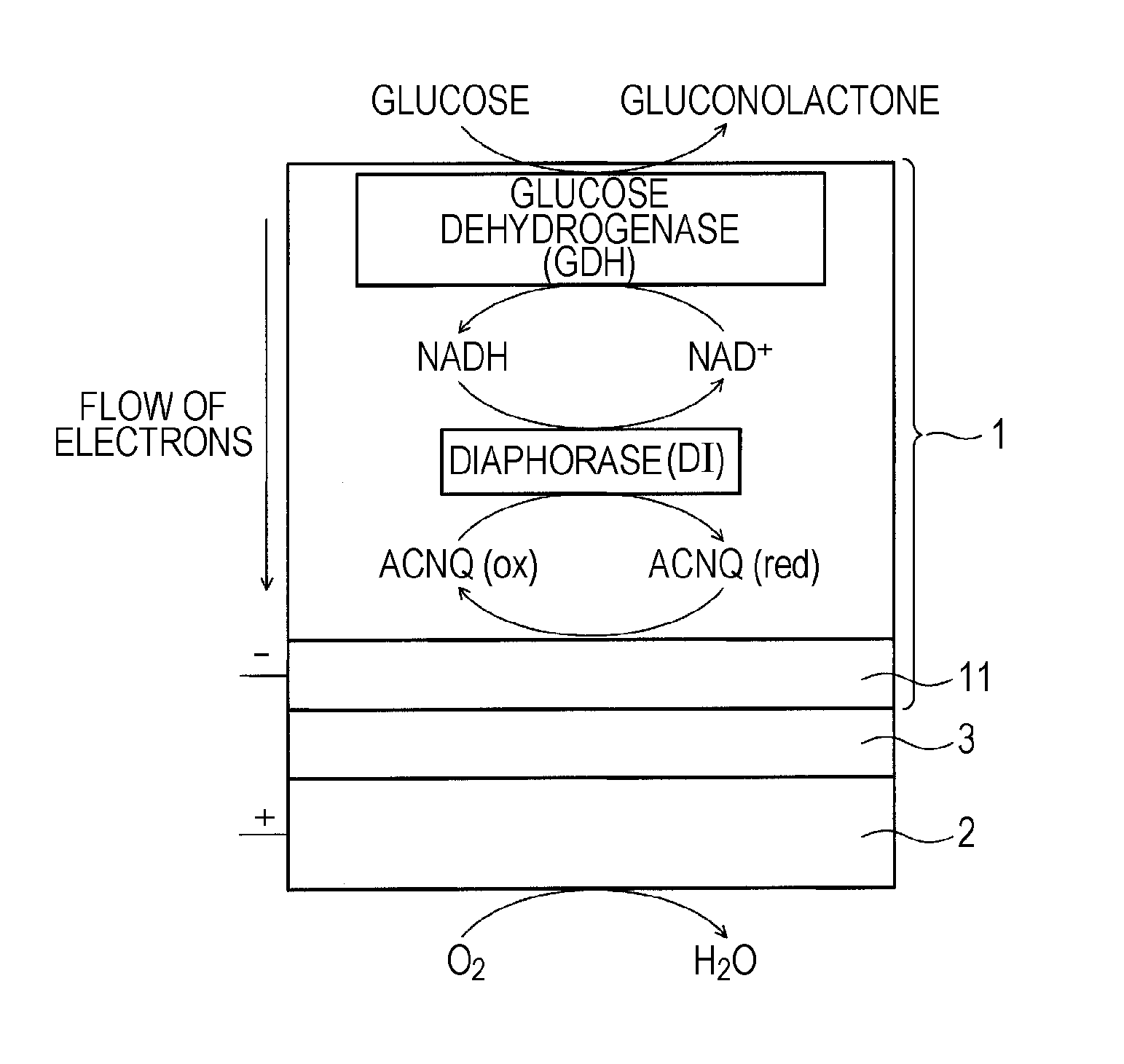
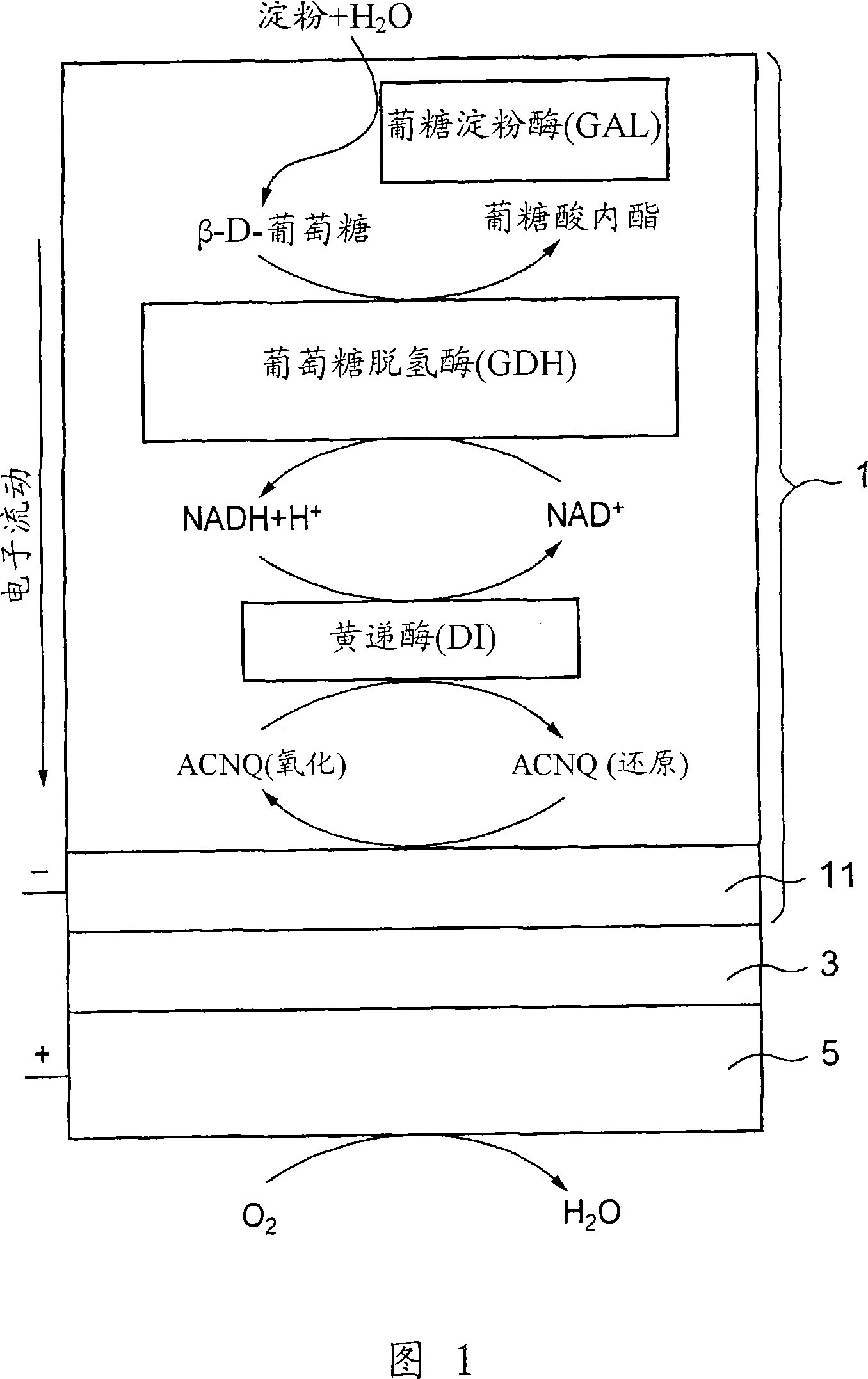
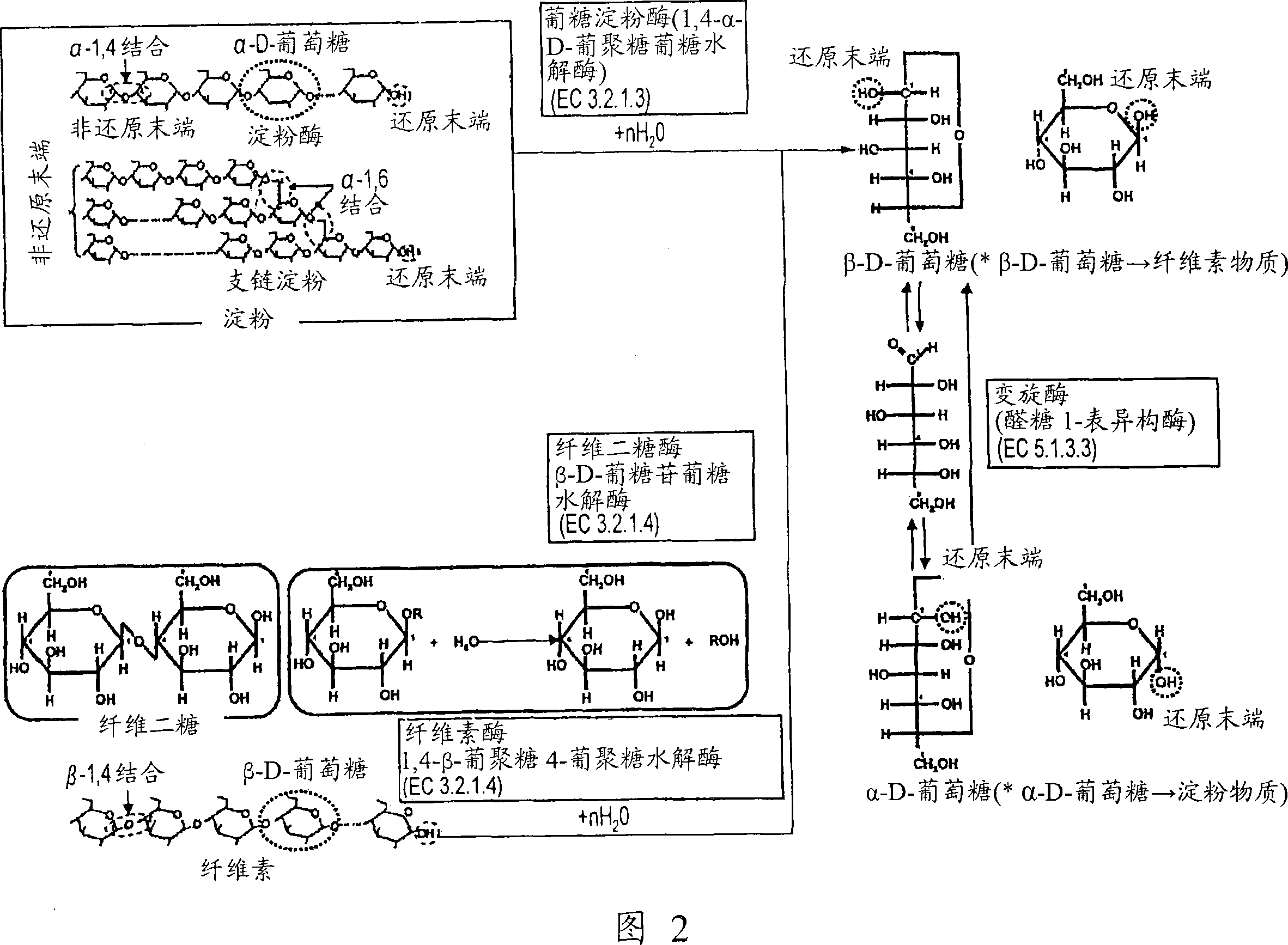
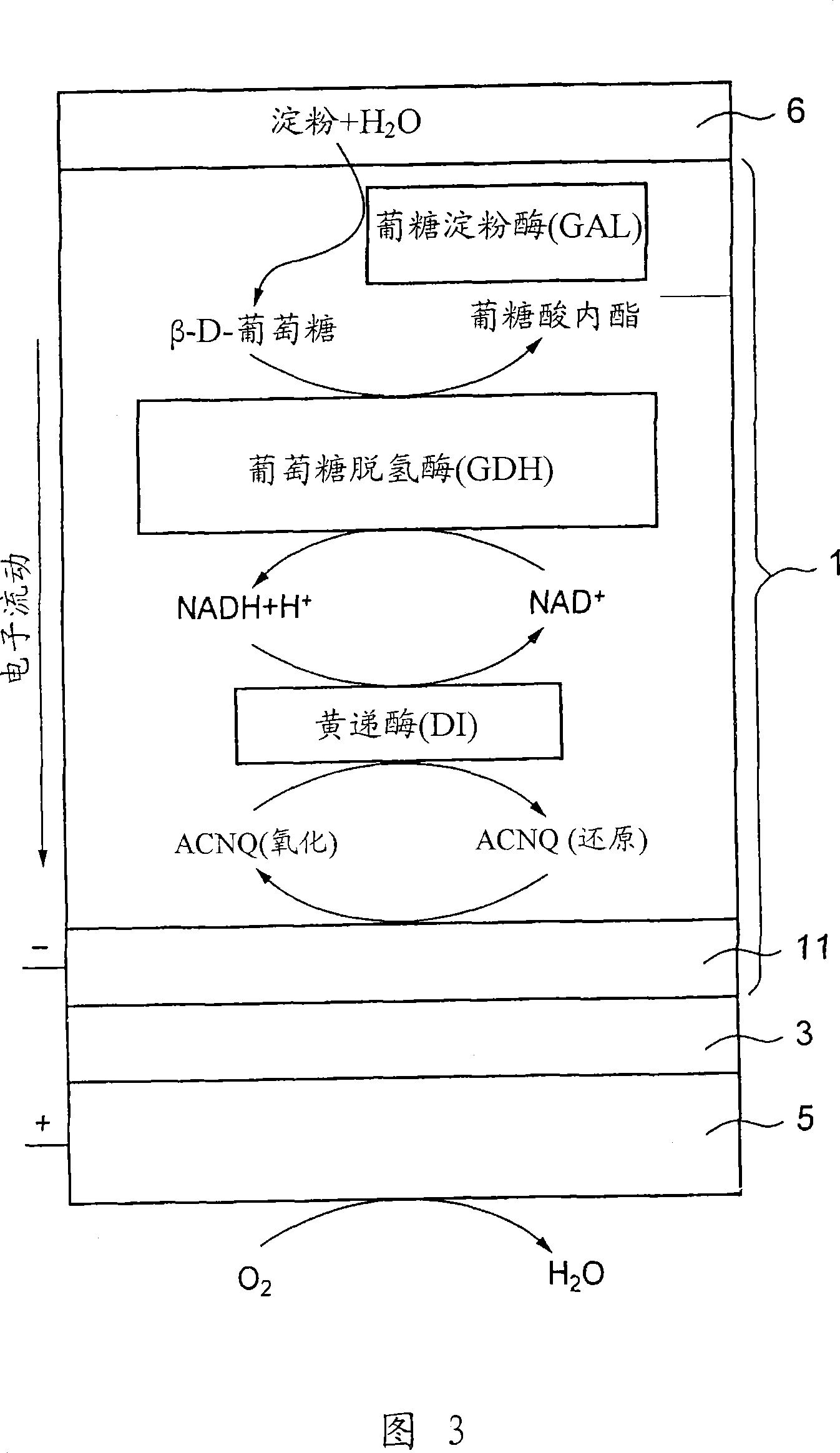
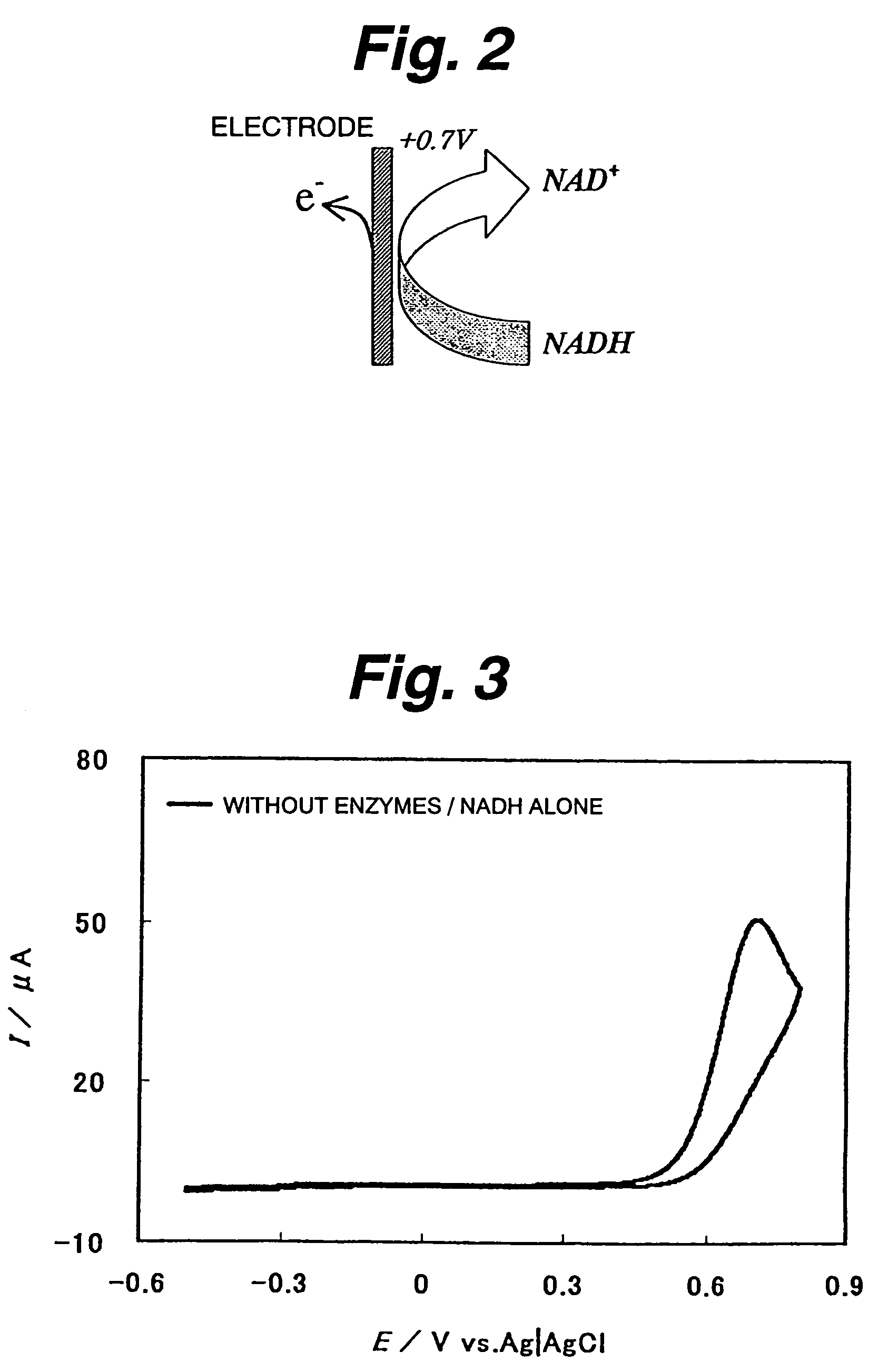
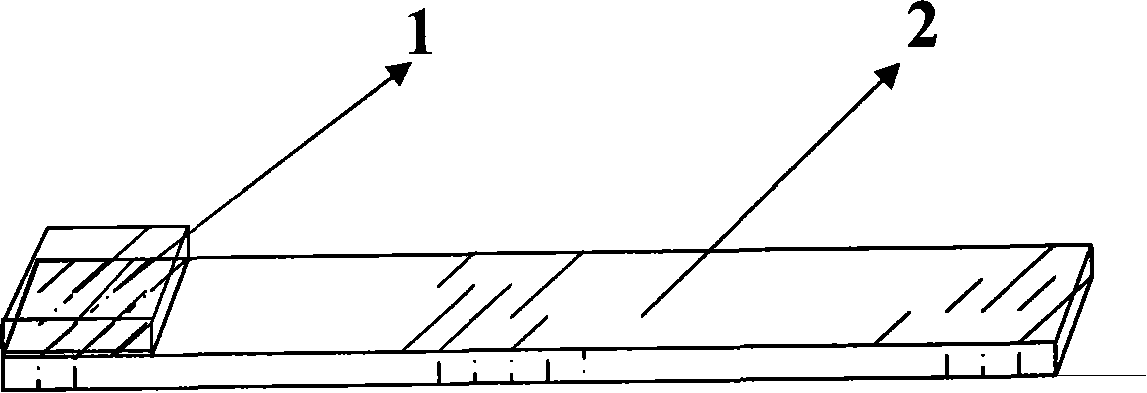
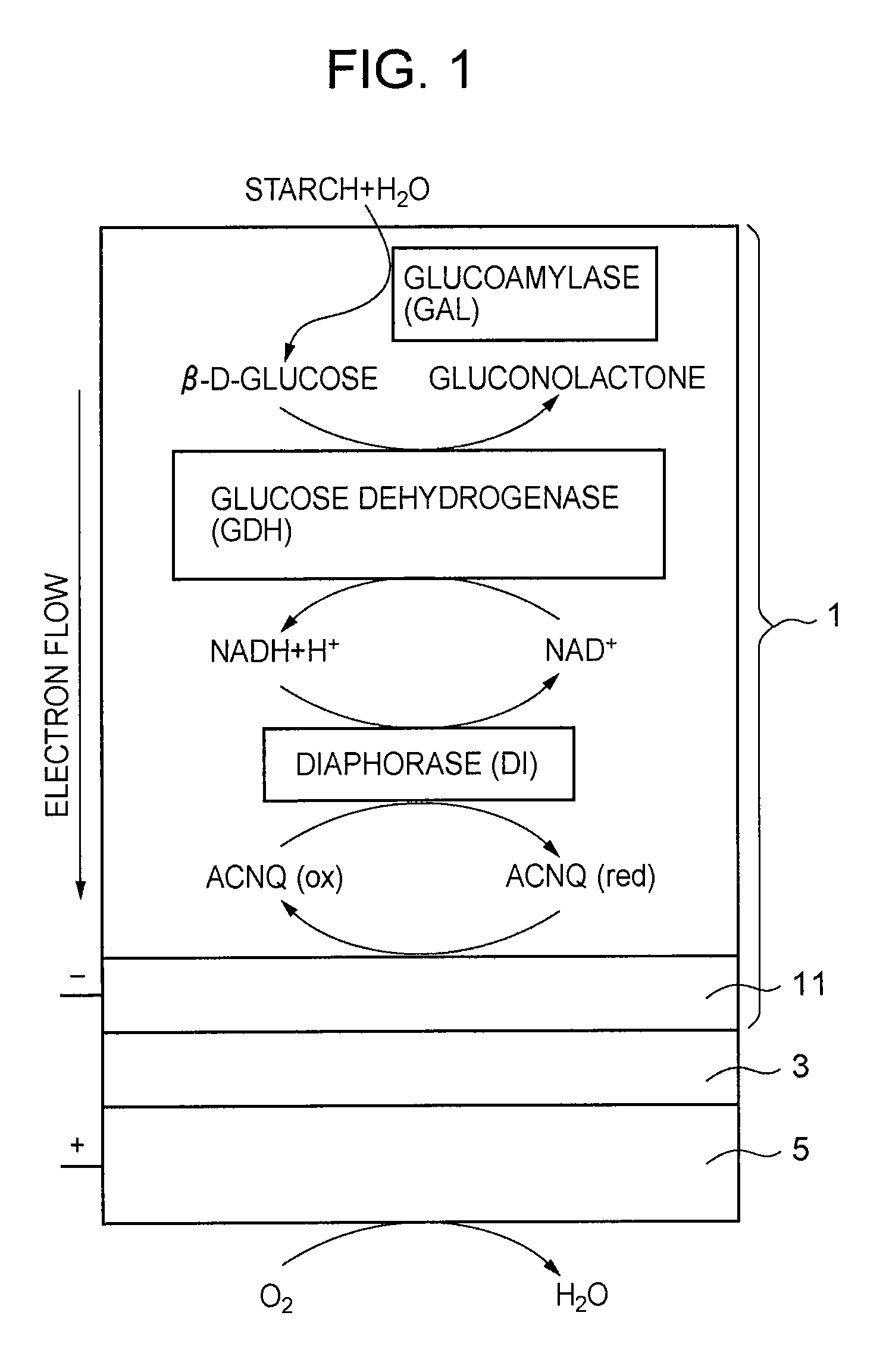
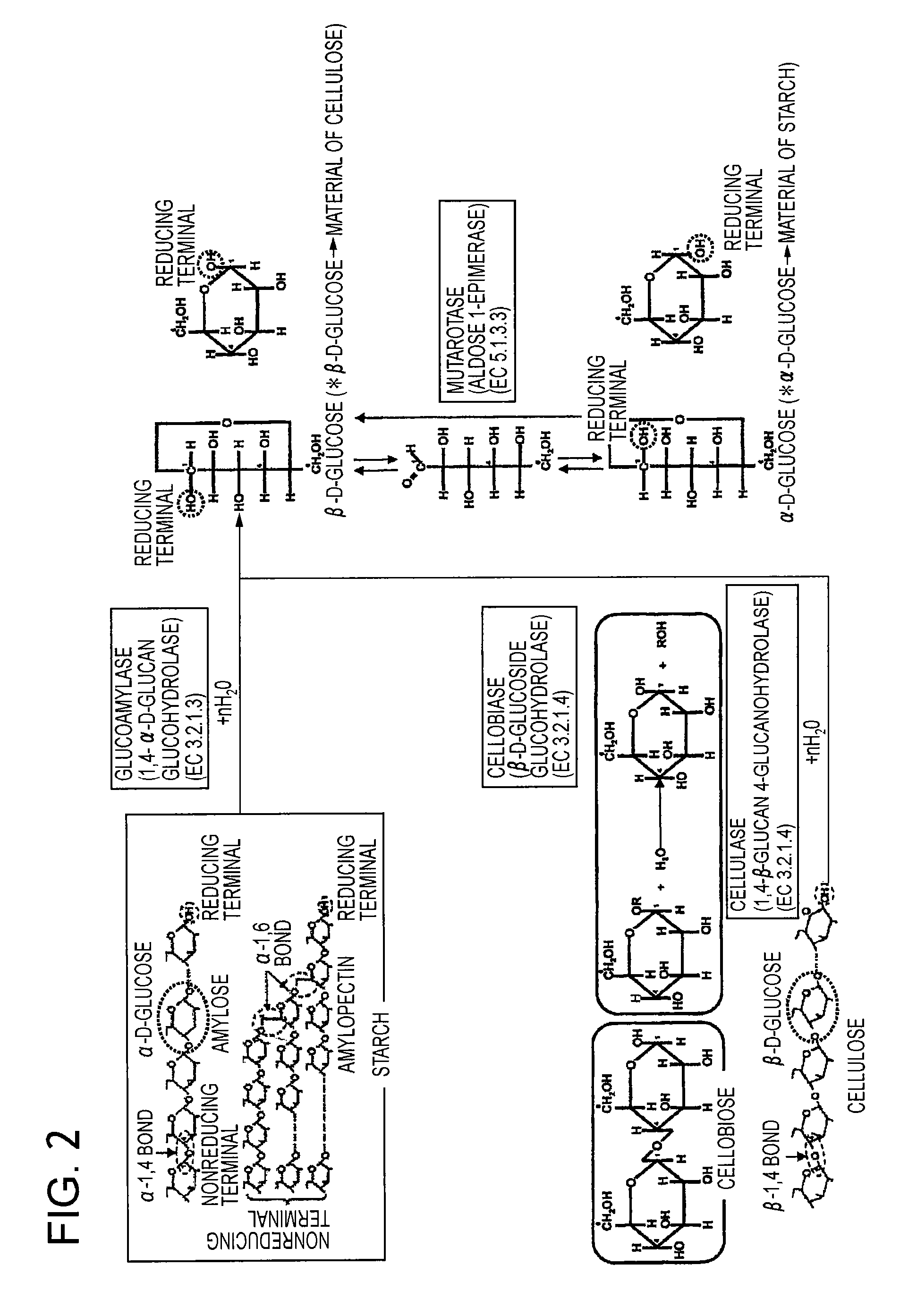
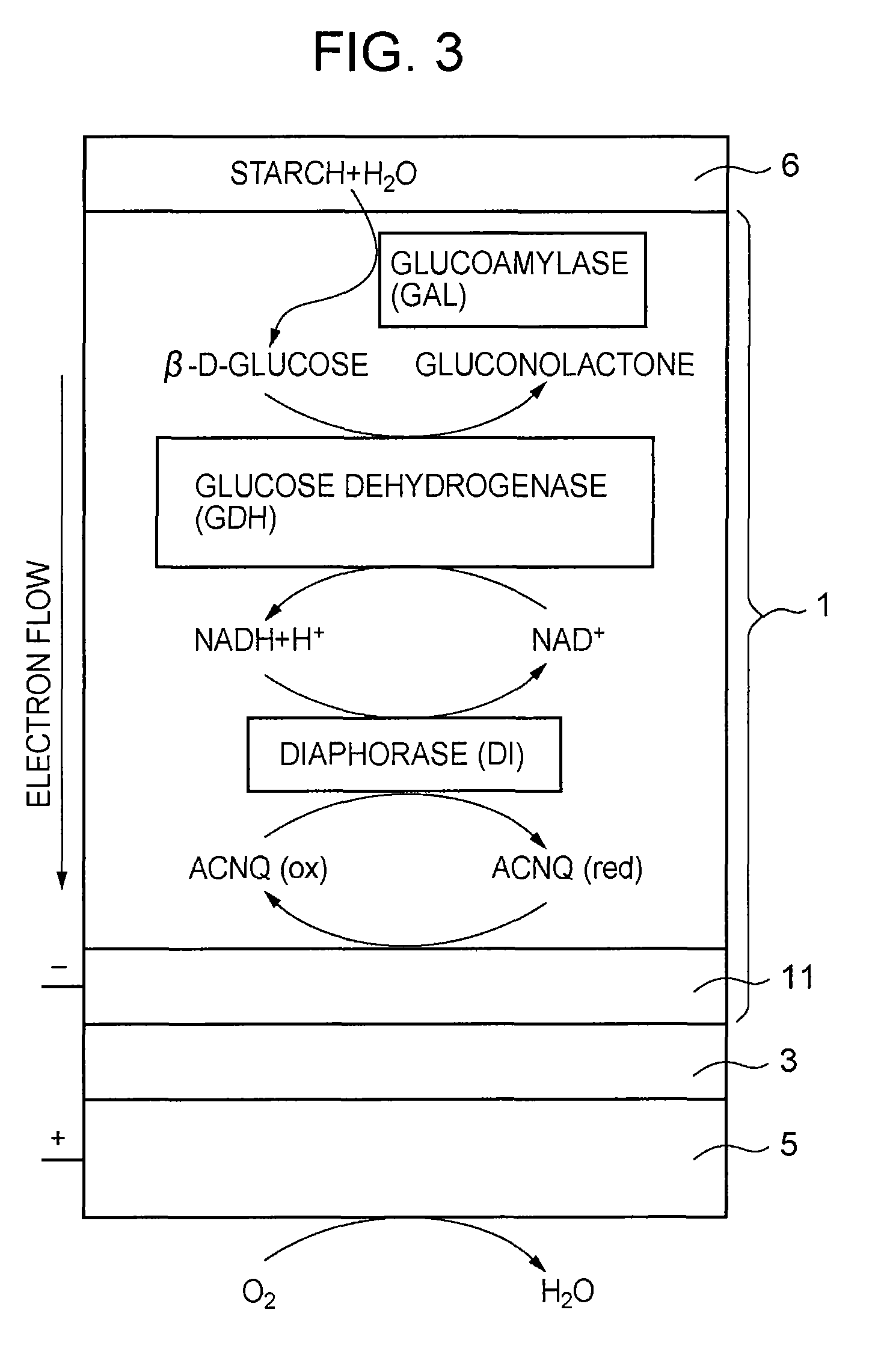
A fuel cell which can directly extract electric power from a polysaccharide, such as starch. A fuel electrode 1 is formed by immobilizing with an immobilizer, on an electrode 11 comprised of, e.g., carbon, an enzyme responsible for decomposing a polysaccharide into monosaccharides, an enzyme responsible for decomposing the monosaccharide formed, a coenzyme (e.g., NAD+ or NADP+) which forms a reductant due to the oxidation reaction in the monosaccharide decomposition process, a coenzyme oxidase (e.g., diaphorase) for oxidizing the reductant of the coenzyme (e.g., NADH or NADPH), and an electron mediator (e.g., ACNQ or vitamin K3) for receiving electrons generated due to the oxidation of the coenzyme from the coenzyme oxidase and delivering the electrons to the electrode 11. The fuel cell comprises the fuel electrode 1 and the air electrode 5 that sandwich an electrolyte layer 3.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Liquid stable kit for measuring beta-hydroxybutyric acid by cyclic enzyme method
ActiveCN102435749AGuaranteed specificityStrong specificityColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingBeta-Hydroxybutyric acidPreservative
The invention discloses a liquid stable kit for measuring beta-hydroxybutyric acid by a cyclic enzyme method. The liquid stable kit consists of a reagent 1 and a reagent 2, wherein 1L of reagent 1 comprises 50 to 500mmol of buffer solution, 1 to 5KU of beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, 1 to 5KU of diaphorase, 0.1 to 100g of surfactant, 1 to 100mmol of stabilizer, 0.1 to 100g of anti-interference agent I, 0.1 to 100g of anti-interference agent II, and 0.1 to 100ml of preservative; and 1L of reagent 2 comprises 50 to 500mmol of buffer solution, 1 to 20mmol of coenzyme I, 0.1 to 10mmol of nitrotetrazolium blue, 1 to 100mmol of stabilizer and 0.1 to 100ml of preservative. The liquid stable kit has the advantages of stability, wide linear range, high measurement accuracy, high antijamming capability and low cost.
Owner:NINGBO MEDICAL SYSTEM BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Fuel cell and method for manufacturing the same, enzyme-immobilized electrode and method for manufacturing the same, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20110039165A1Prevent elutionImprove performanceCell electrodesFinal product manufactureFuel cellsEngineering
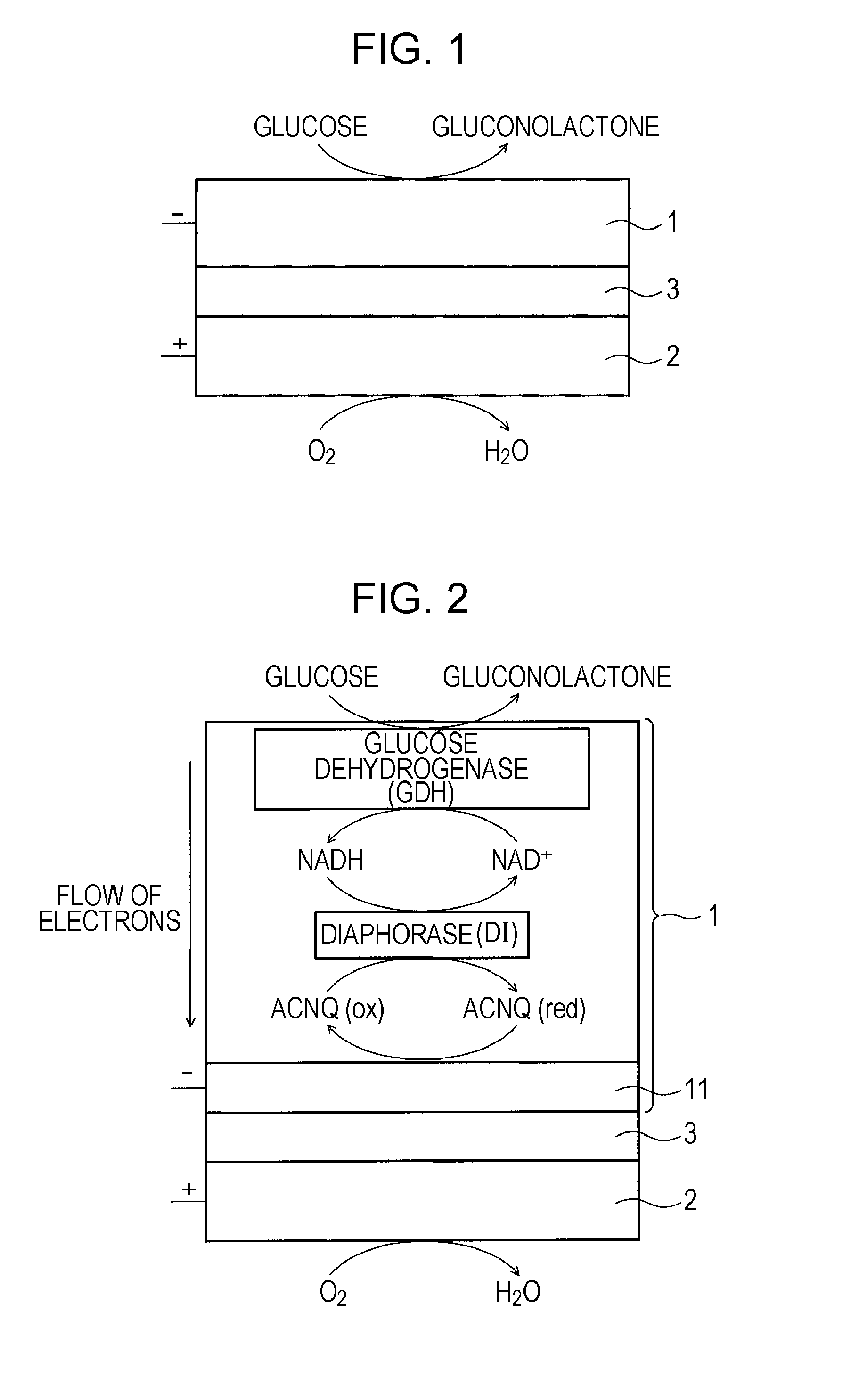
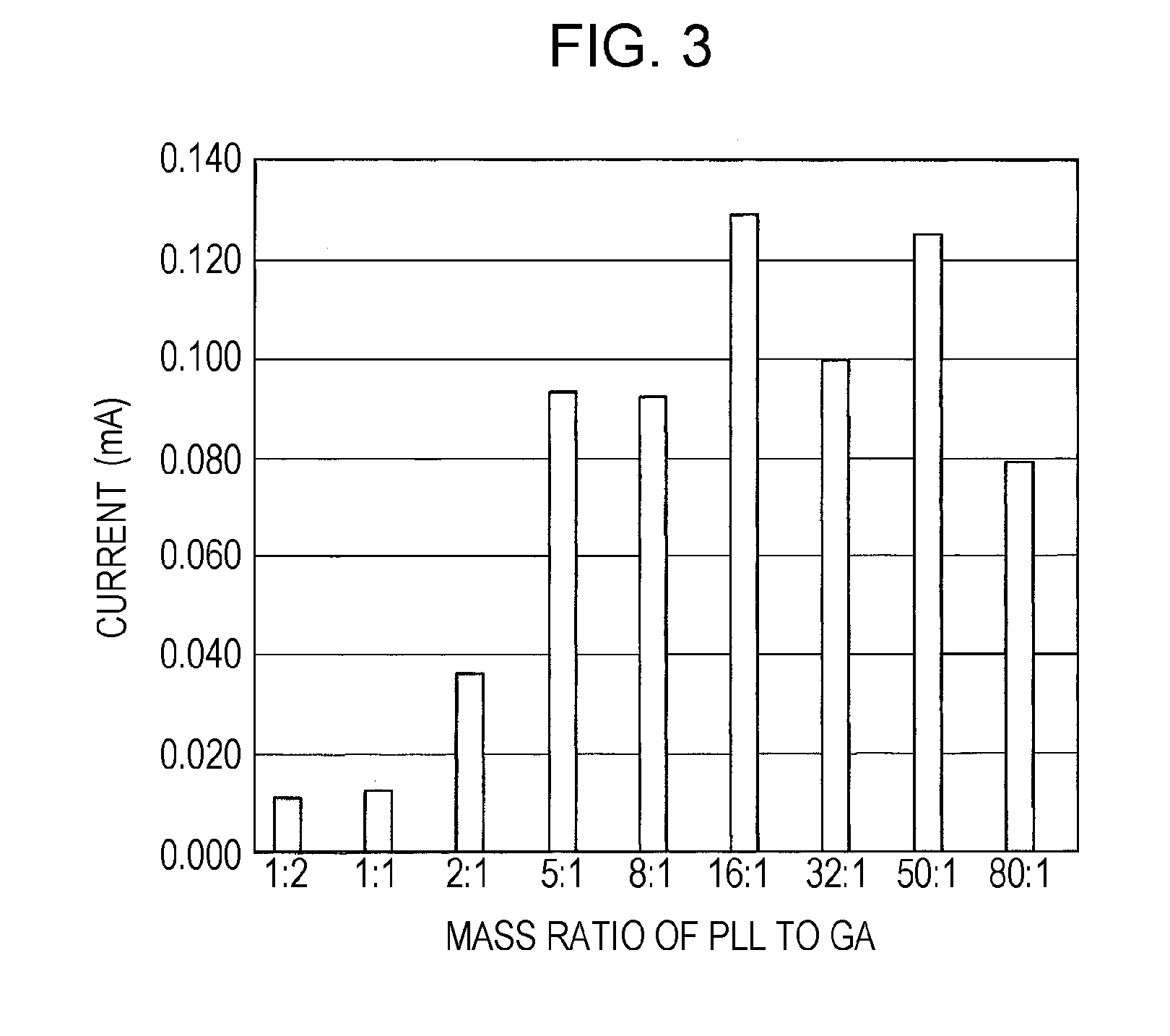
There is provided a fuel cell whose current density and maintenance ratio can be improved when at least glucose dehydrogenase and diaphorase are immobilized on an anode using an immobilizing material composed of poly-L-lysine and glutaraldehyde. The fuel cell has a structure in which a cathode 2 and an anode 1 face each other with an electrolyte layer 3 therebetween, the anode 1 being obtained by immobilizing at least glucose dehydrogenase and diaphorase on an electrode using an immobilizing material composed of poly-L-lysine and glutaraldehyde, wherein the mass ratio of the poly-L-lysine to the glutaraldehyde in an immobilizing material is 5:1 to 80:1, the mass ratio of the glucose dehydrogenase to the diaphorase is 1:3 to 200:1, and the average molecular weight of the poly-L-lysine is 21500 or more.
Owner:SONY CORP
Fuel cell, electronic equipment, movable body, power generation system and cogeneration system
InactiveCN1993855ASimplify the supply systemEfficient use ofCell electrodesBiochemical fuel cellsDecompositionVitamin K3
A fuel cell capable of directly abstracting electric power from polysaccharides, such as starch. Fuel electrode (1) is produced by fixing on electrode of carbon, etc. (11) by means of a fixative an enzyme participating in decomposition of polysaccharides to monosaccharides, an enzyme participating in decomposition of formed monosaccharides, a coenzyme (e.g., NAD<+>, NADP<+>, etc.) whose reduced form is produced in accordance with an oxidation reaction during the process of monosaccharide decomposition, a coenzyme oxidase (e.g., diaphorase) capable of oxidizing the reduced form of coenzyme (e.g., NADH, NADPH, etc.), and an electron mediator (e.g., ACNQ, vitamin K3, etc.) capable of receiving electrons generated by the coenzyme oxidation from the coenzyme oxidase and delivering the same to the electrode (11). The fuel electrode (1) is disposed opposite to air electrode (5) through electrolyte layer (3) to thereby construct a fuel cell.
Owner:SONY CORP
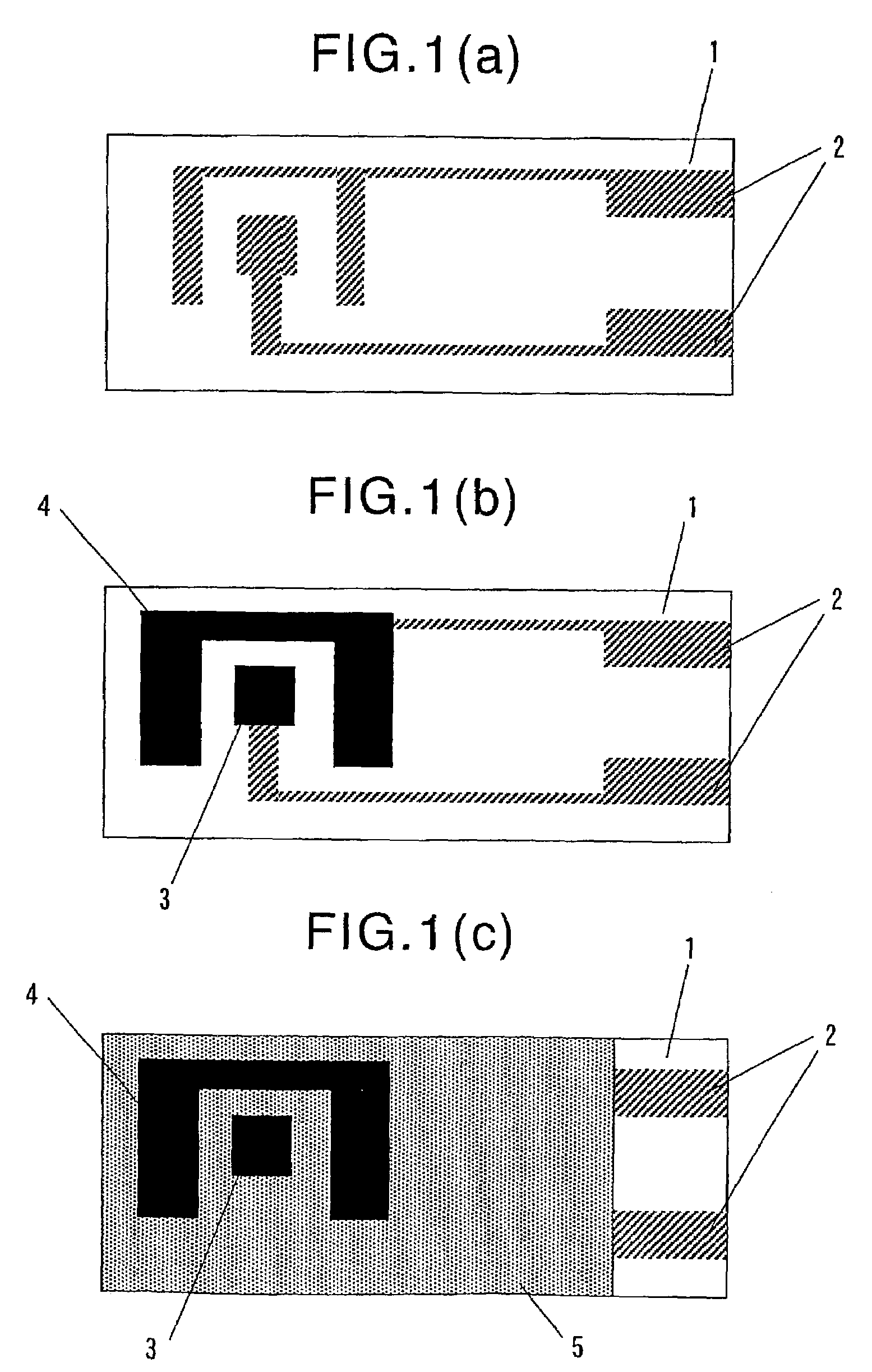
Immobilization support, process for producing the same, electrode, process for producing the same, electrode reaction utilizing apparatus and process for producing the same
ActiveUS7520970B2Easy to useImprove performanceImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNaphthoquinoneDiaphorase
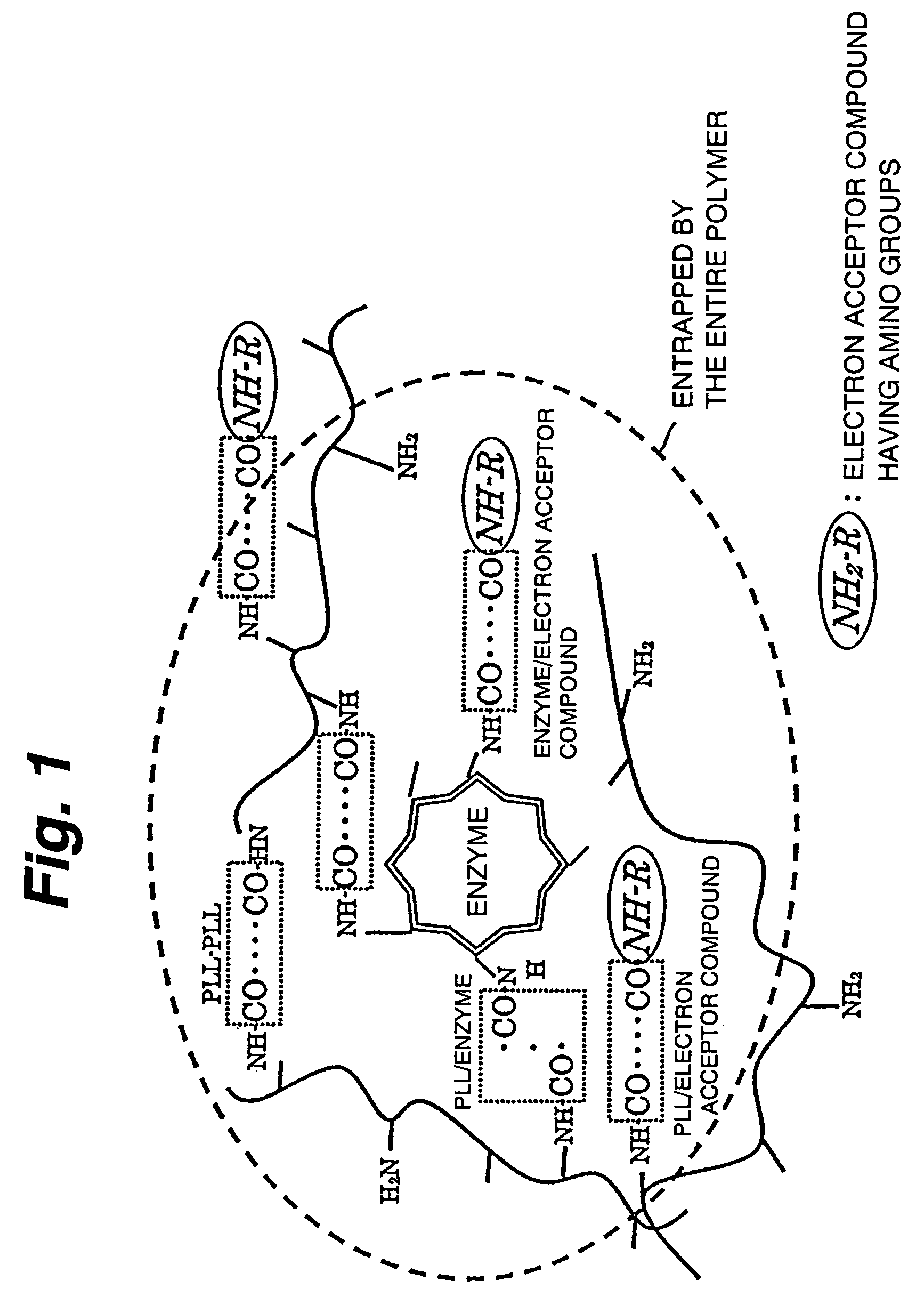
An immobilization carrier containing an electron acceptor compound is used in addition to glutaraldehyde and poly-L-lysine to immobilize an enzyme and an electron acceptor compound simultaneously to an electrode. For example, here are used diaphorase as the enzyme and 2-amino-3-carboxy-1,4-naphthoquinone (ACNQ) as the electron acceptor compound.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Subclinical ketosis of milk cattle diagnose indicator paper
InactiveCN101118237AMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementHeifer calfMilk cow's
The present invention relates to a dairy cow sub-clinical ketosis diagnosis test paper which belongs to the art of the veterinary clinical laboratory science. The present invention comprises a support cushion and a test cushion that is fixed on the support cushion; and the present invention is characterized in that the test cushion of the test paper comprises the following reagents: D-(-)-3-Hydroxybutyrate Dehydrogenase with 2270U / mg and 50mg-100mg; nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide with 300mg-500mg; diaphorase with 35U / mg-45U / mg and 500-1,000mg; NBT with 100mg-200mg; Tris Base with molecular weight 121.14 and 1.21g; oxalic acid with molecular 126 and 126mg; fucose with molecular 383 and 4-6g; and distilled water with 100ml. The dairy cow sub-clinical ketosis diagnosis test paper of the present invention is used conveniently and has the advantages of economic practicality, high sensitivity and specificity, and good stability. The test paper is used to test D-(-)-3-Hydroxybutyrate and D-(-)-3-Hydroxybutyrate sodium in the milk of the milch cow.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Ethanol concentration detection kit and manufacture method thereof
InactiveCN102520198AEasy to carryThe detection process is fastBiological testingReagent stripEthanol dehydrogenase
The invention provides an ethanol concentration detection kit and a manufacture method thereof. The ethanol concentration detection kin is composed of a reagent strip and a standard comparison card, the reagent strip is a filter paper strip with width ranging from 0.5cm to 1cm. Immobilized ethanol dehydrogenase, diaphorase, oxidized iodonitrotetrazolium (INT) and coenzyme are arranged on the filter paper strip. The standard comparison card comprises color developing comparison areas of ethanol with different concentrations. The detection kit is convenient, sanitary, fast and high in sensitivity and stability when being used for detecting ethanol concentration of the drunks, and the detection kit is easy to carry and particularly suitable for on-site detection.
Owner:NINGBO MEDICAL SYSTEM BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Method for detecting TMAO (trimethylamine oxide) by enzyme method and application thereof
ActiveCN108507984AHigh sensitivityRapid and stable detectionFluorescence/phosphorescenceNad dependent dehydrogenaseFluorescence
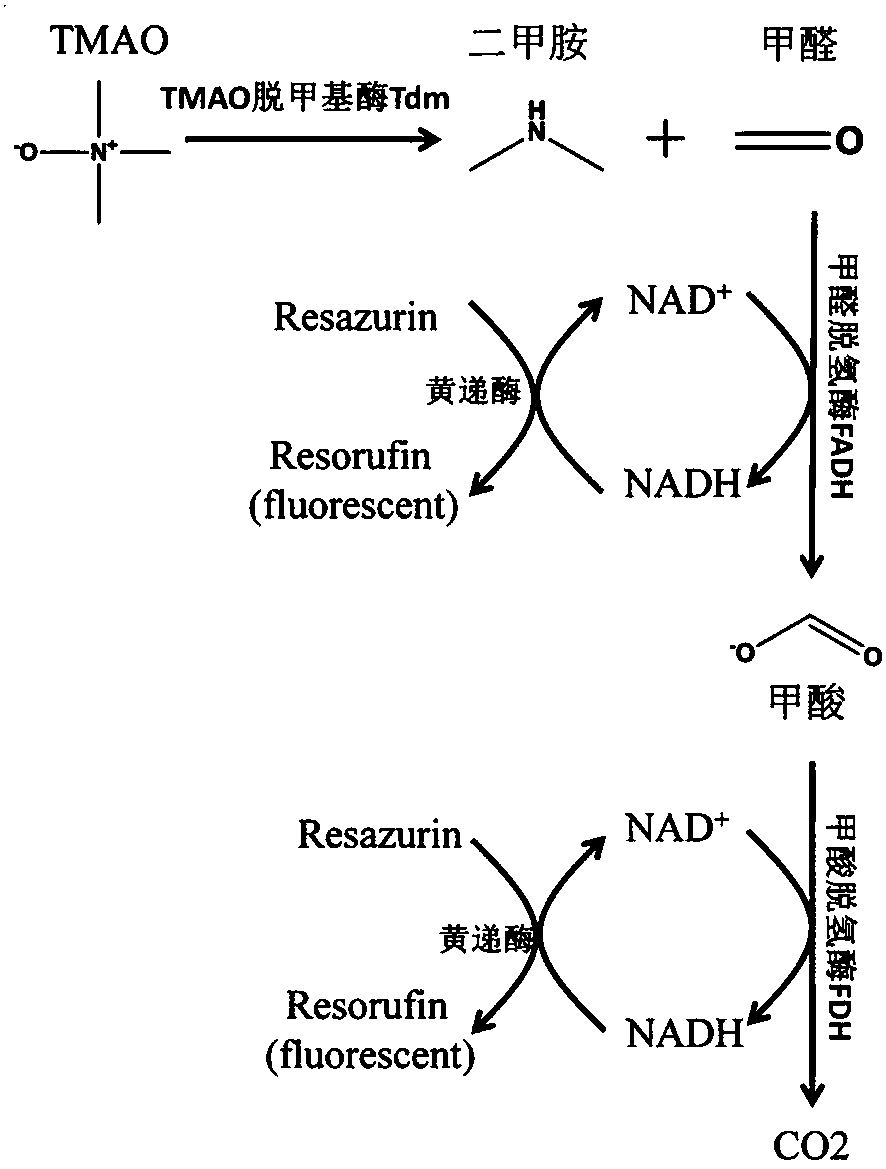
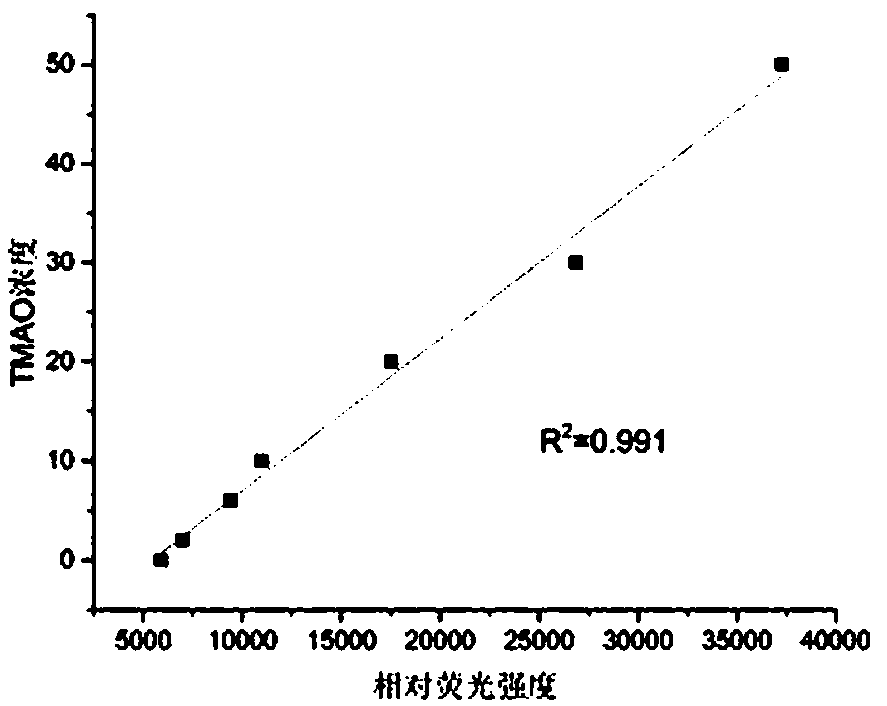
The invention discloses a method for detecting TMAO (trimethylamine oxide) by an enzyme method and application thereof. The detection method utilizes a multi-enzyme combination system containing TMAOTDM (demethylase), FADH (formaldehyde dehydrogenase), FDH (formate dehydrogenase) and diaphorase, so as to perform fluorescence determining on the TMAO; the method can be used for developing a TMAO detection kit. The method for detecting the TMAO by the enzyme method has the advantages that the defect of failure to directly determine based on dehydrogenase and diaphorase coupling because of no participation of NAD dependence dehydrogenase in the metabolism path of the TMAO is overcome; by adopting the multi-enzyme coupling of TDM-FADH-FDH-diaphorase, the system for fluorescence determining ofthe TMAO is constructed, and one TMAO molecule is decomposed into two fluorescence signals; the sensitivity is high, the detection is rapid and stable, the repeatability is good, the operation is simple and convenient, and the cost is lower.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL OF SHANDONG UNIV
Reaction liquid for preparing dry chemical test paper for determination of alpha-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, and dry chemical test paper
PendingCN109612983AEasy to measureReduce pollutionMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorHydroxybutyric acidColor reaction
The invention discloses reaction liquid for preparing dry chemical test paper for determination of alpha-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, and dry chemical test paper. The dry chemical test paper comprises a reaction chromogenic layer containing alpha-hydroxybutyric acid, coenzyme I, diaphorase and a chromogenic reagent capable of generating a chromogenic reaction with NADH under the catalysis of diaphorase. The dry chemical test paper prepared by the reaction liquid can be used in combination with a small instrument to determine the content of alpha-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase in a short period of time only by collecting a small amount of blood, the operation is simple and convenient, no professional operation is required, the intensity of color development is high, the uniformity is good,the pollution is small, the detection process does not rely on a large-scale biochemical analyzer, the market requirements under special conditions can be met, especially emergency treatment, and compared with a traditional method for detecting by adopting a liquid biochemical reagent, the dry chemical test paper can provide a method capable of conveniently and quickly measuring the activity of alpha-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase for the emergency department, primary hospitals, families and small clinics.
Owner:GUANGZHOU WONDFO BIOTECH
Method for measuring beta-hydroxybutyric acid by using enzyme colorimetric reaction, matched kit and application thereof
ActiveCN101726463ASmall sample sizeShort reaction timeMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsBeta-Hydroxybutyric acidAbsorbance
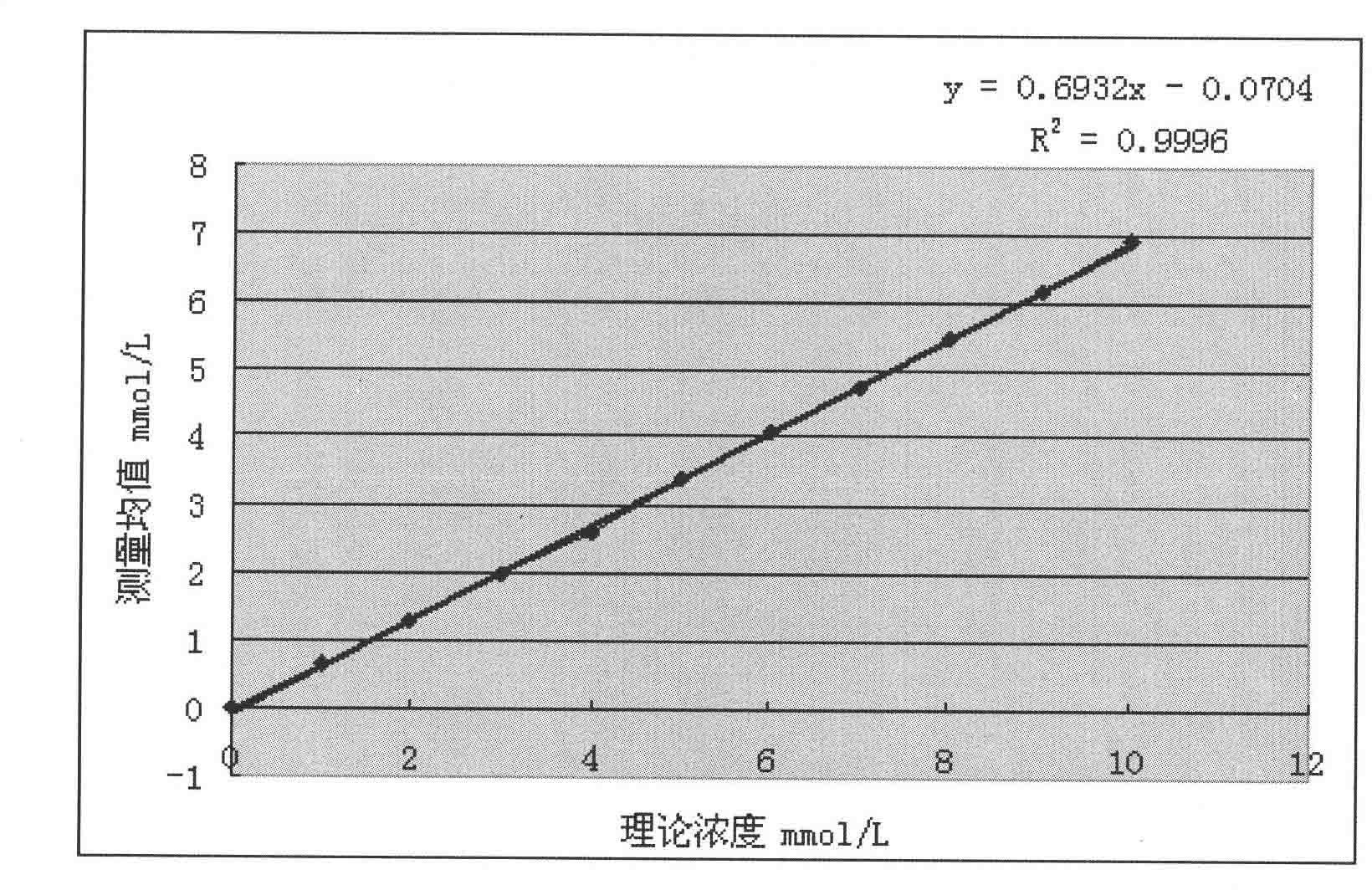
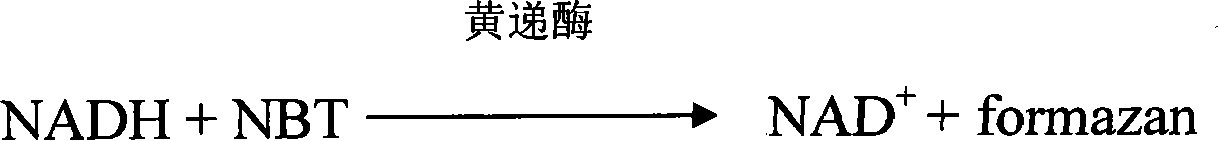
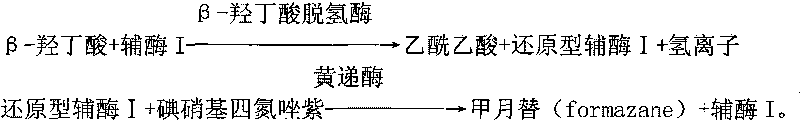
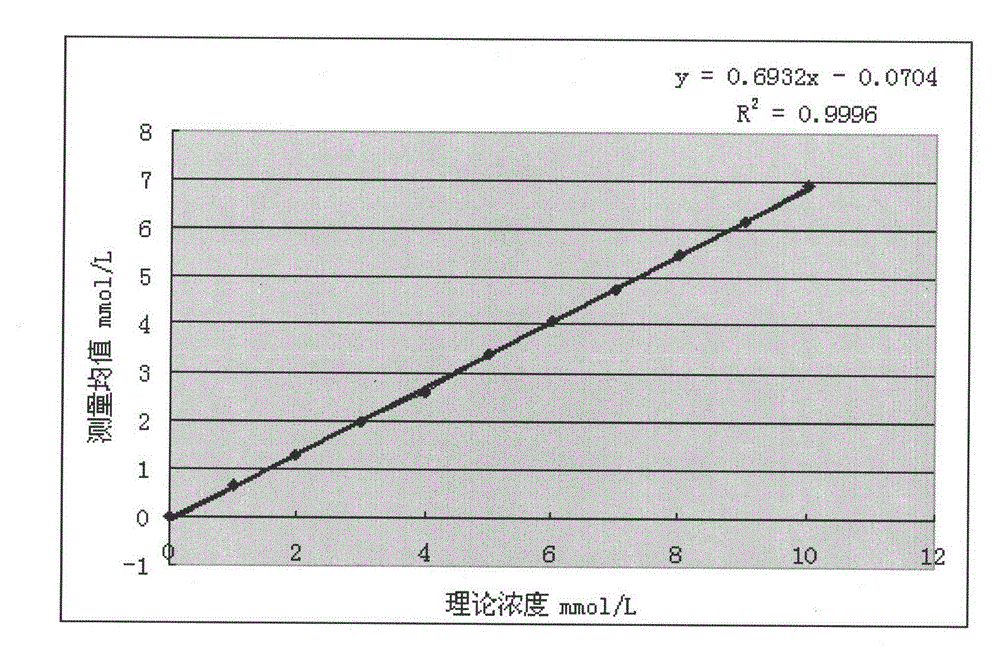
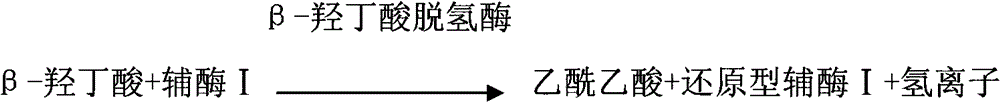
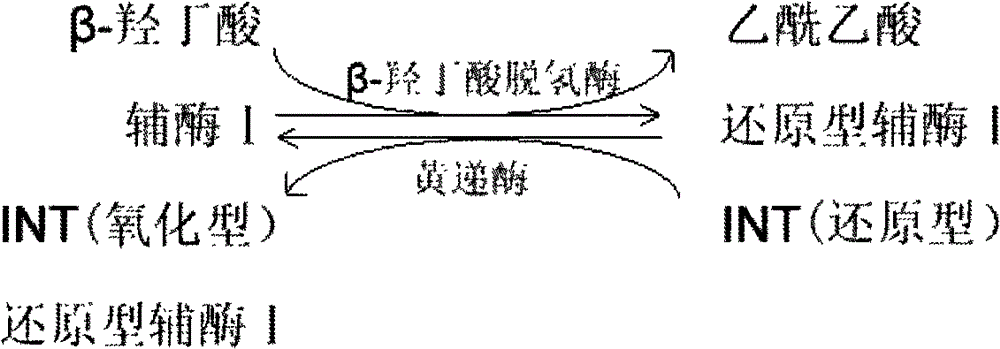
The invention provides a method for measuring beta-hydroxybutyric acid by using enzyme colorimetric reaction, a matched kit and application thereof. Under the system of Tris-HCL buffer solution, serum beta-hydroxybutyric acid and coenzyme I are dehydrogenized under the catalysis of beta-hydroxybutyric acid dehydrogenase to generate acetoacetic acid and reduced coenzyme I, the generated reduced coenzyme I and iodonitrotetrazole chloride are reacted under the catalysis of diaphorase to generate a red substance formazane of which the highest absorbance is 505 nanometers, and then the content of the beta-hydroxybutyric acid in a biological sample is quantified by measuring the change of the absorbance of the red product at the wavelength of 505 nanometers. The method can linearly measure the concentration range (0 to 4.5 mmol / L) of the beta-hydroxybutyric acid in the biological sample, the measurement is used for judging the human ketosis for acid poisoning diagnosis, the reagent used by the method is liquid dual-reagent, and the quantity of the sample required for measuring the beta-hydroxybutyric acid is little; moreover, the reaction time during measuring is short, the operation is simple, and the method is suitable for mass detection.
Owner:NINGBO RUI BIO TECH
Diagnosis test paper for diabetic ketosis and other symptoms of relatively high ketone body
InactiveCN101900734AEasy to operateQuick checkMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiological testingReagent stripBovine serum albumin
The invention relates to diagnosis test paper for diabetic ketosis and other symptoms of relatively high ketone body. The diagnosis test paper comprises the following reagents: (1) first-phase immersion liquid which comprises a stabilizer and a protective agent, bovine serum albumin, oxalic acid, NAD<+>, NADP<+>, diaphorase, 3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase and buffer solution; and (2) second-phase immersion liquid which comprises NBT, PMS and an organic solvent. The diagnosis test paper is prepared by the following steps of: soaking filter paper in the first-phase immersion liquid, sucking redundant immersion liquid and quickly and warmly drying the soaked filter paper at the temperature of between 20 and 50 DEG C; soaking the dried filter paper in the second-phase immersion liquid and drying at the temperature of between 20 and 50 DEG C again to obtain base paper of the diagnosis test paper; and sticking the base paper on a plastic base and cutting into pieces to obtain the diagnosisreagent strips. The diagnosis test paper can be assembled into various detection devices, has the advantages of convenient operation, fast detection, good sensitivity, high accuracy and the like, cansemiquantitatively detect the 3-hydroxybutyric acid content of milk, urine and blood, and has good application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI GAOFENG MEDICAL ELECTRICAL EQUIP
Method for determining alcohol concentration by using enzyme cycling method and alcohol determination kit
InactiveCN102564979AStrong response specificityHigh detection specificityColor/spectral properties measurementsEthanol dehydrogenasePreservative
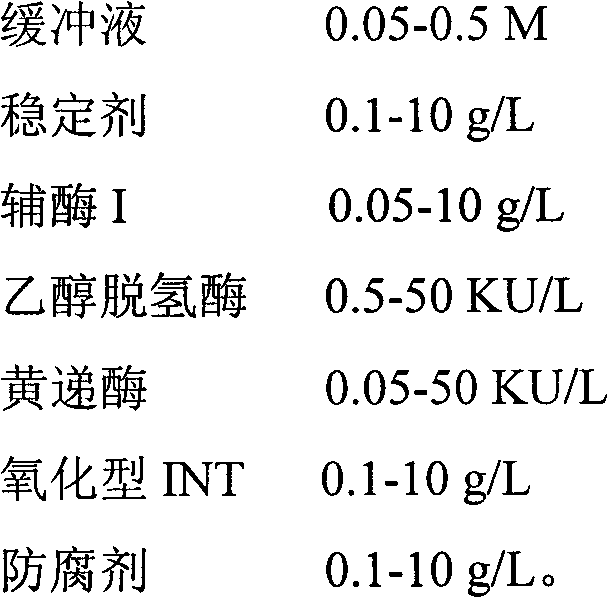
The invention provides a method for determining alcohol concentration by using an enzyme cycling method and an alcohol determination kit. The method comprises the following steps of: generating reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide I by using nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide I and alcohol under the action of alcohol dehydrogenase, reacting the reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide I with oxidized iodonitrotetrazolium (INT) under the action of diaphorase to generate red reduced INT, detecting a change in the absorbance of a final reactant, and then calculating the alcohol concentration of a sample. The kit consists of the following components: 0.05 to 0.5M of a buffer solution, 0.1 to 10g / L of a stabilizer, 0.05 to 10g / L of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide I, 0.5 to 50KU / L of alcohol dehydrogenase, 0.05 to 50KU / L of diaphorase, 0.1 to 10g / L of oxidized INT and 0.1 to 10g / L of a preservative. The method is high in reaction specificity, detection specificity and sensitivity, wide in linear range and low in cost; and the kit is high in stability and accuracy.
Owner:NINGBO MEDICAL SYSTEM BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
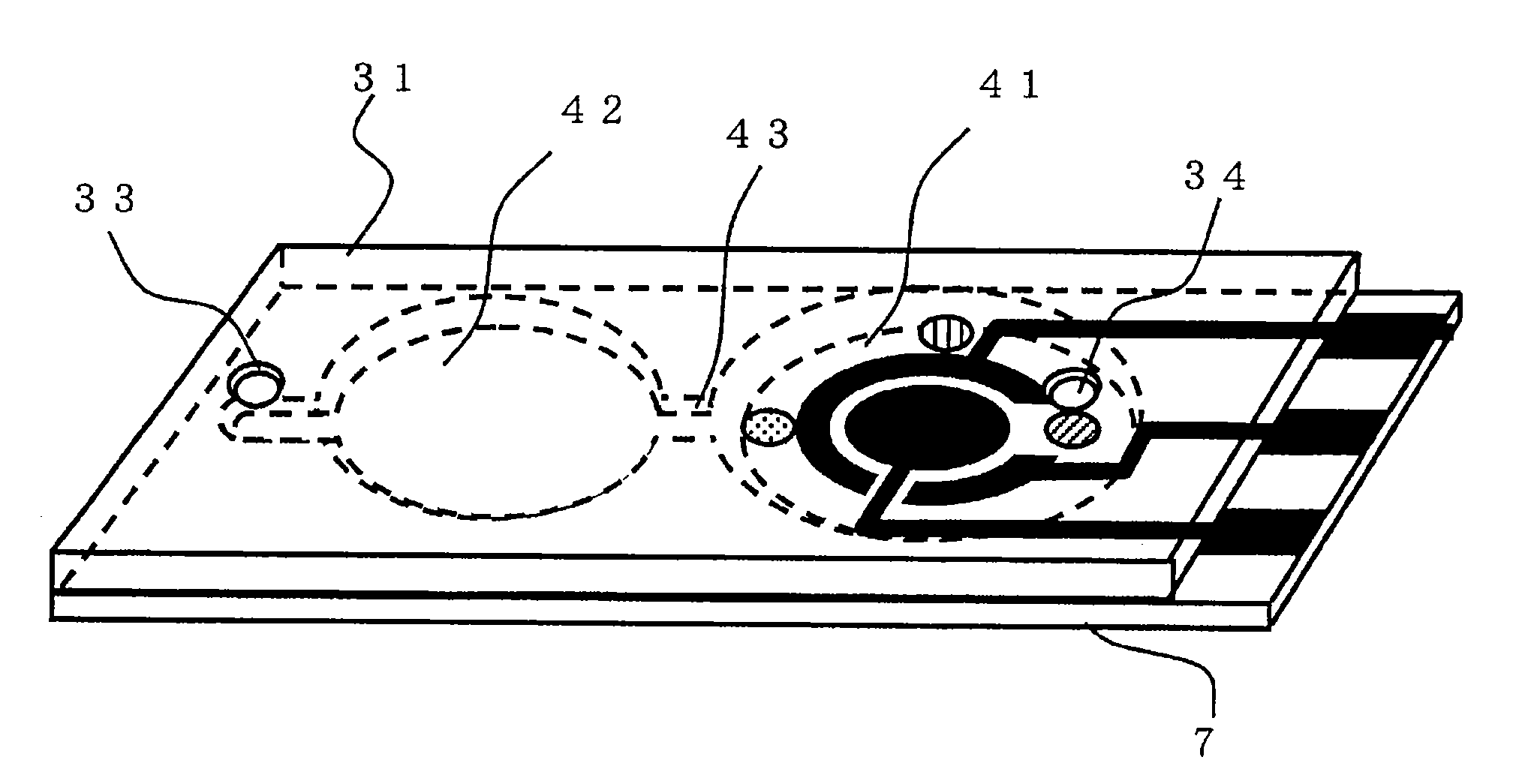
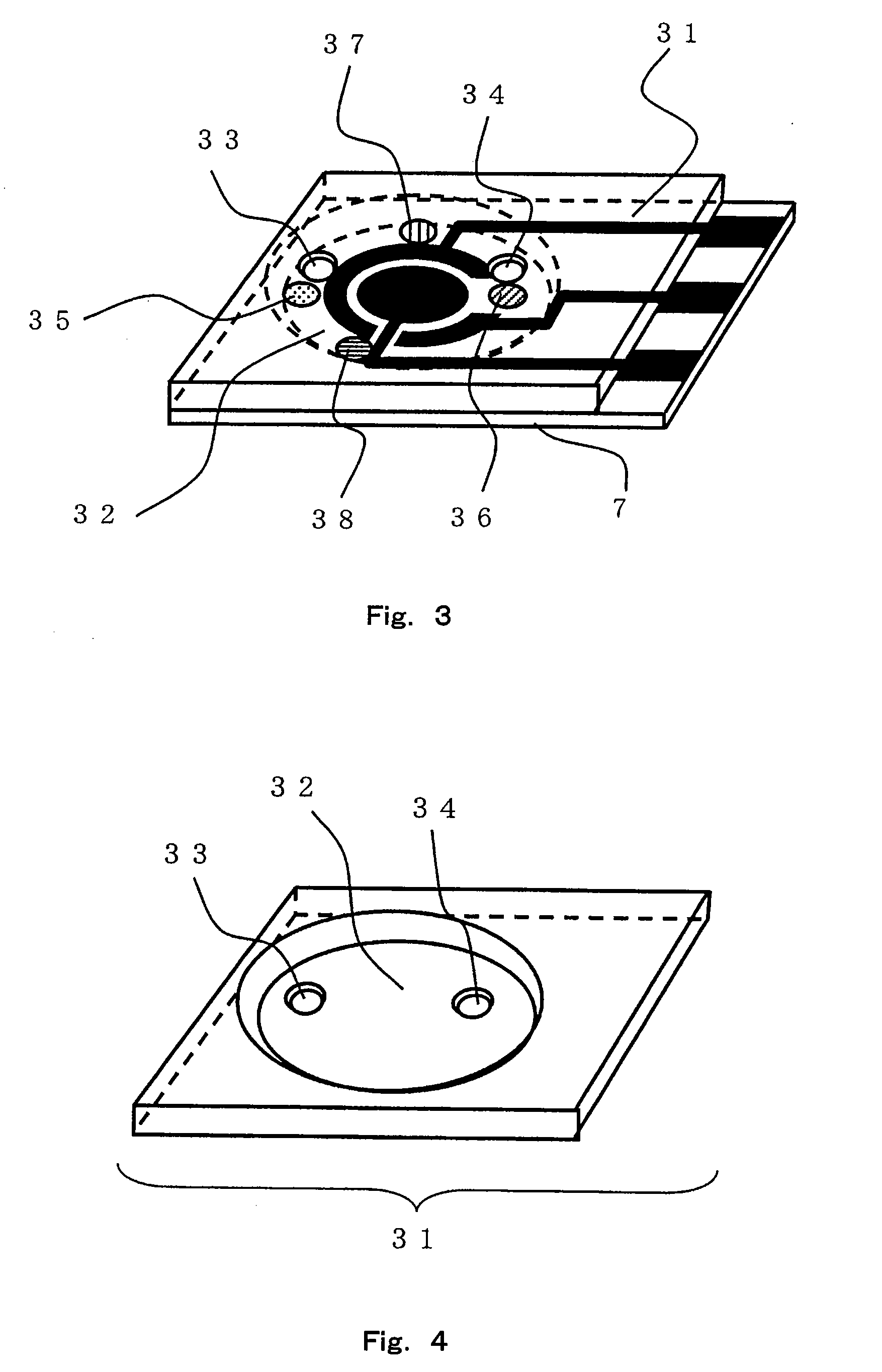
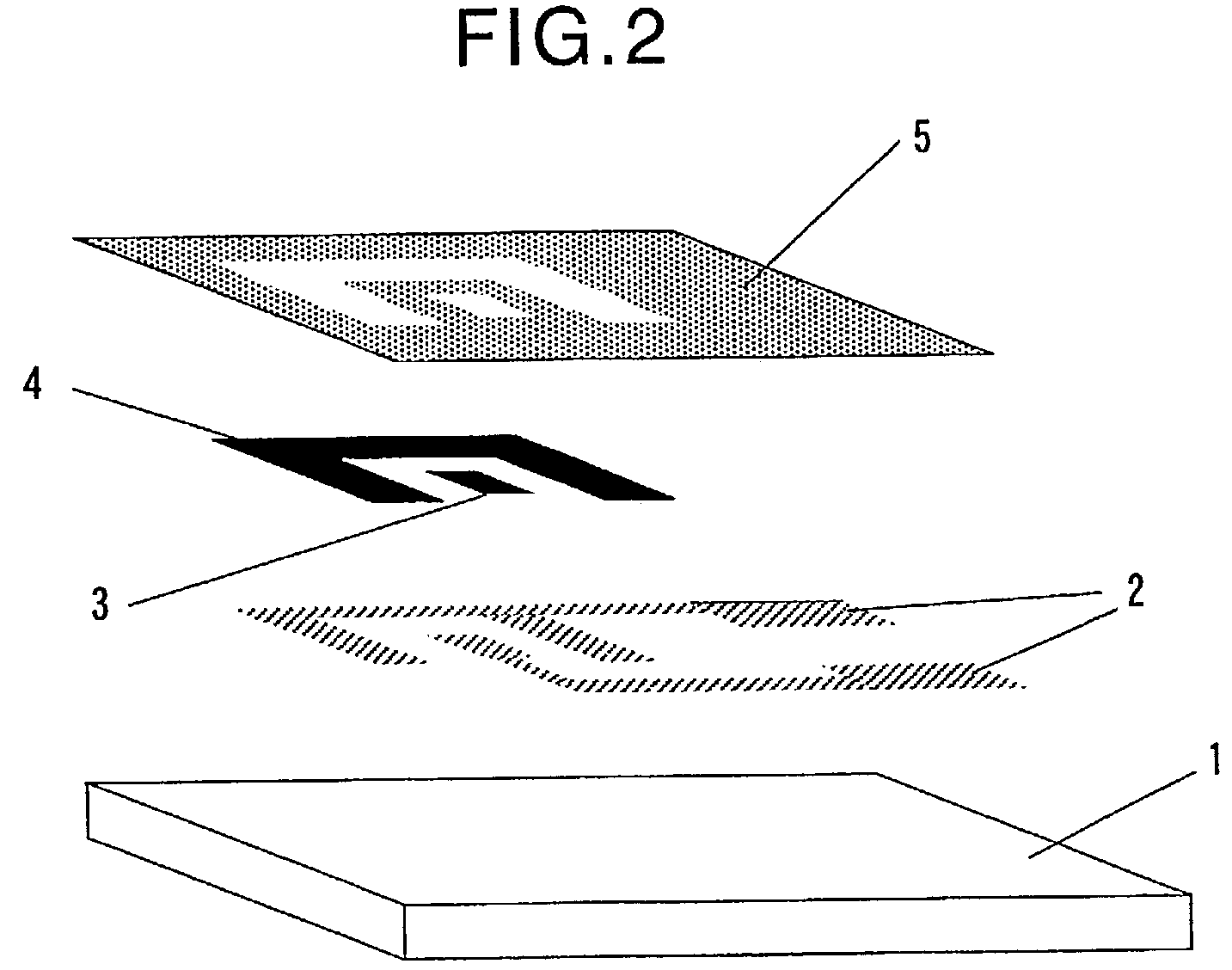
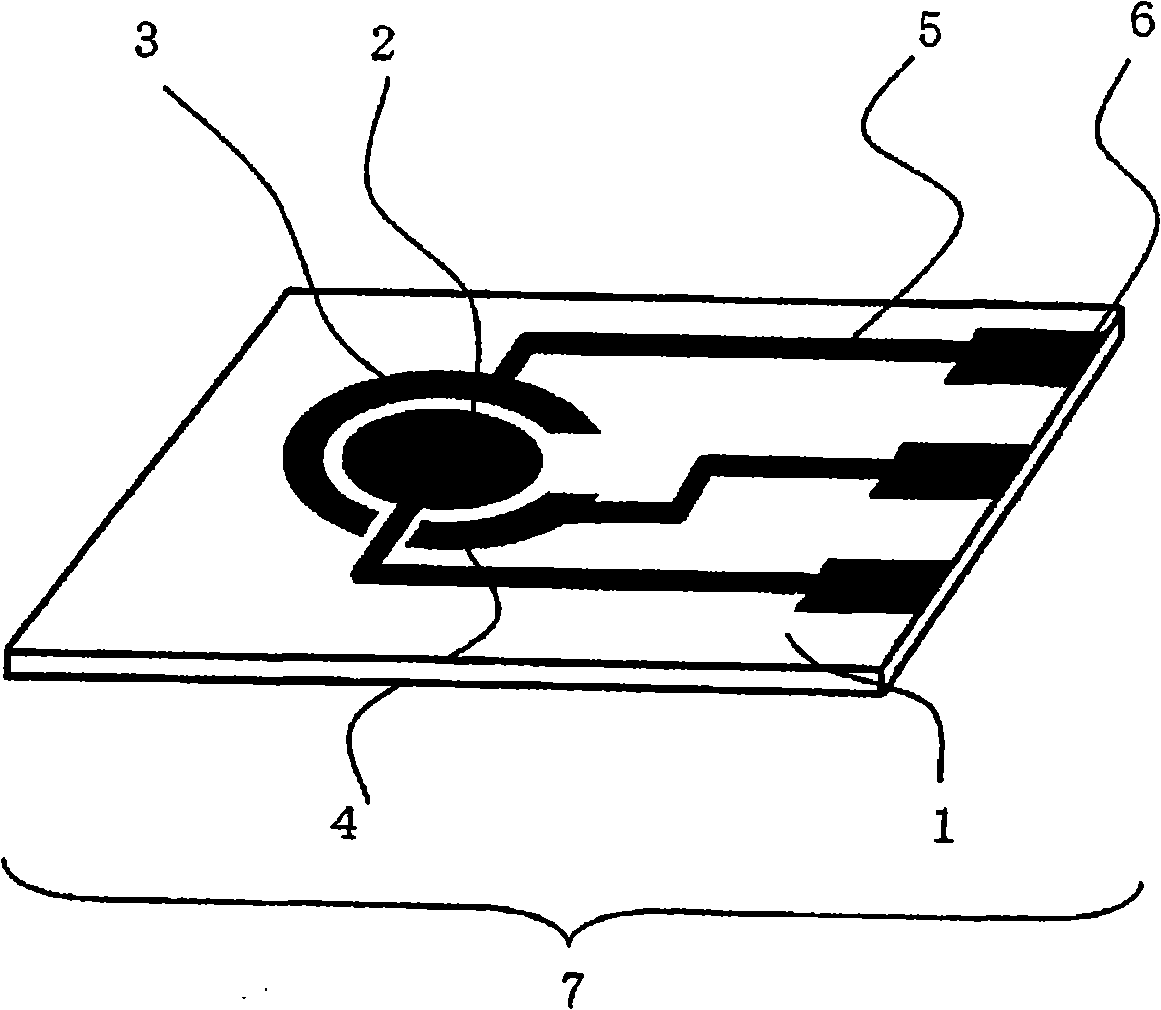
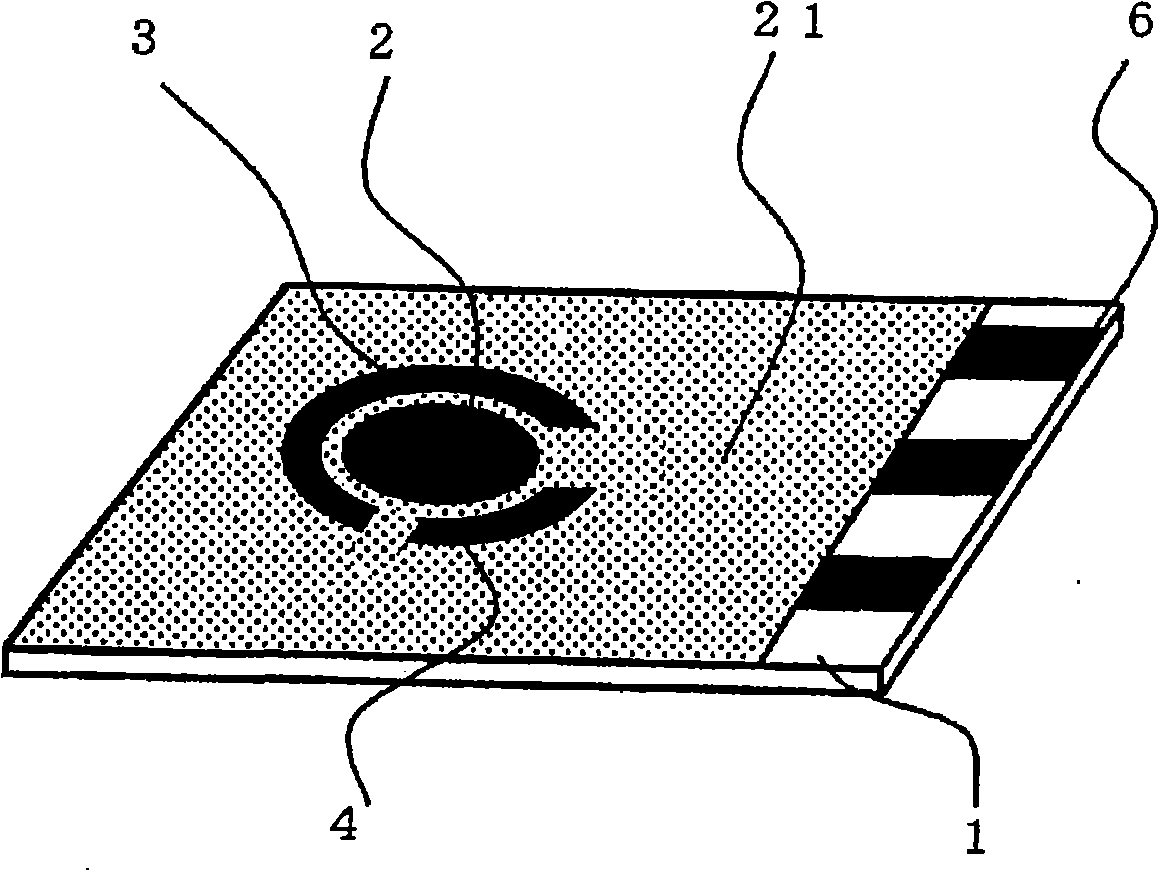
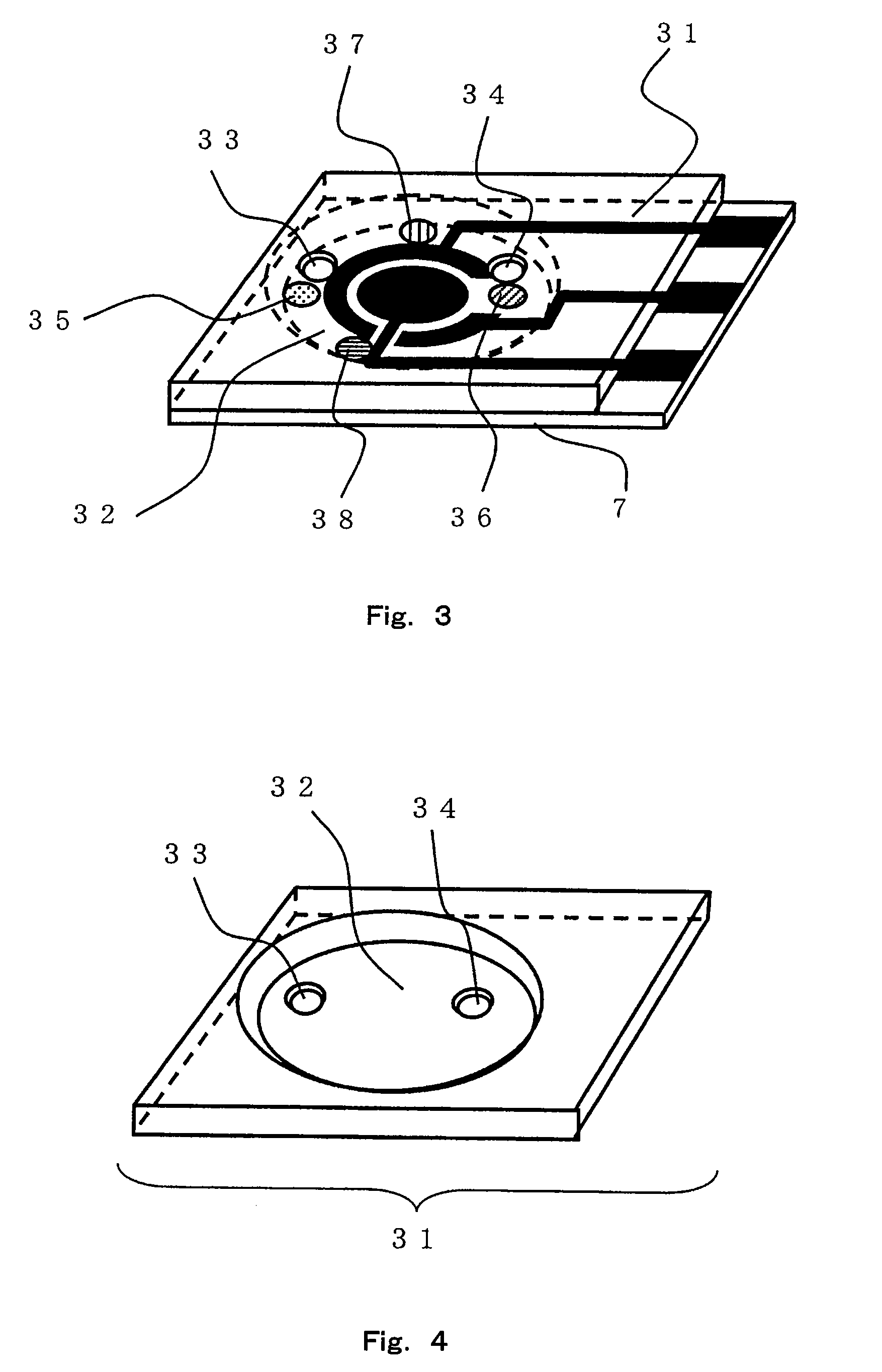
Sensor of pyrophosphate and SNP typing sensor using the same
ActiveUS20080293128A1High sensitivityEasy to measureImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMagnesium saltPhosphoric acid
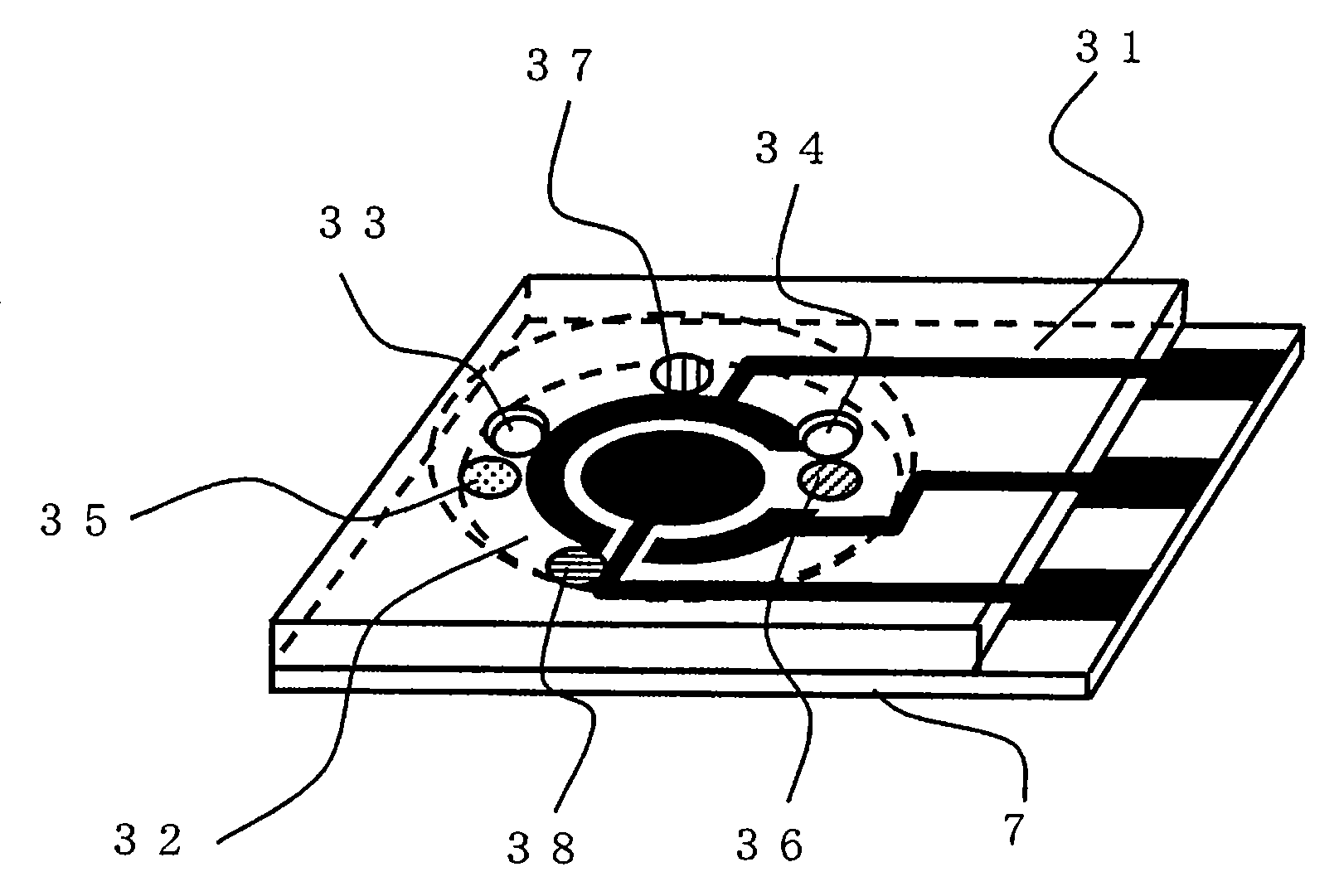
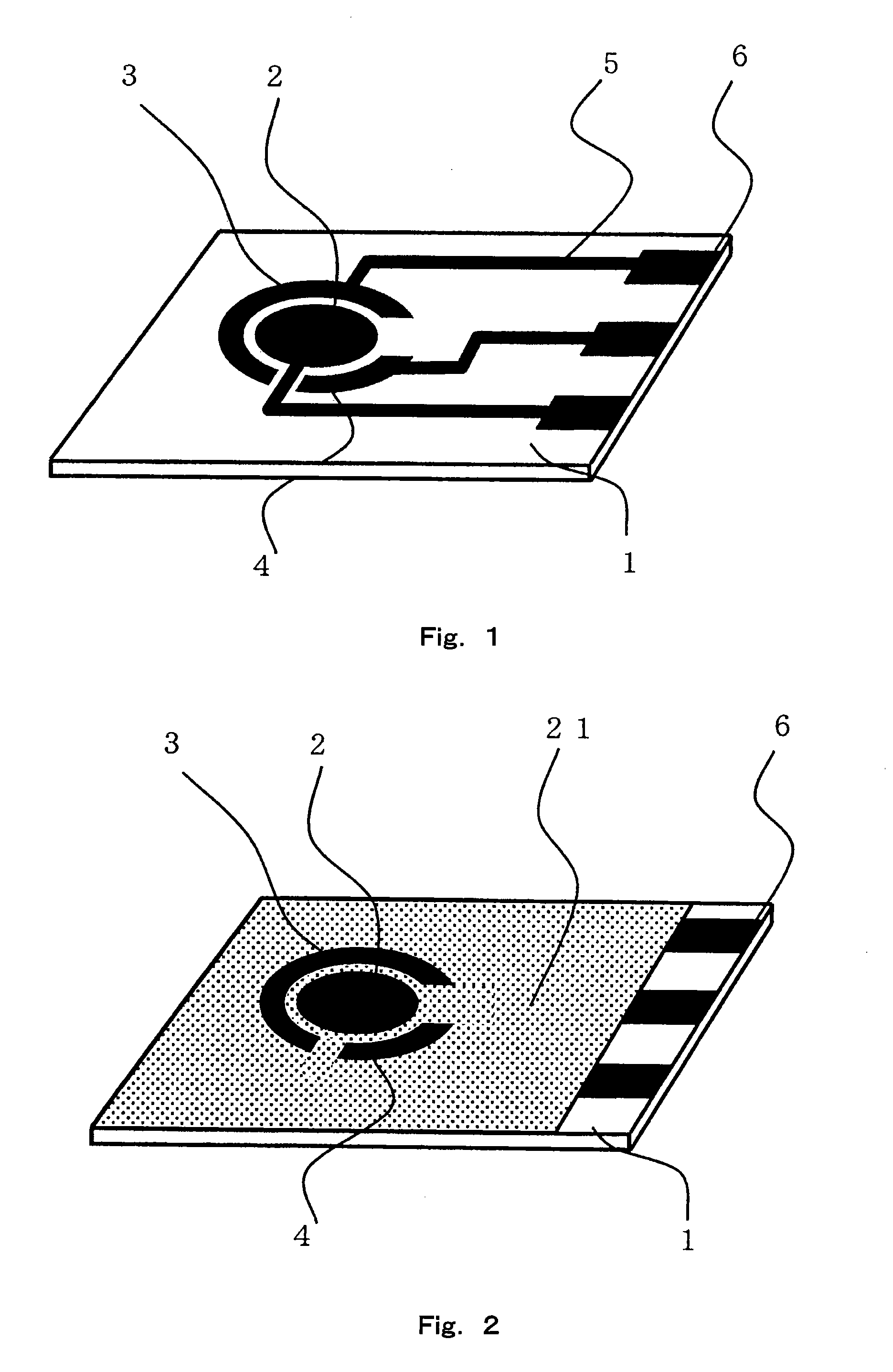
A sensor of pyrophosphate which can detect pyrophosphate conveniently with high sensitivity in a method for measuring pyrophosphate in SNP typing utilizing a primer extension reaction is provided.A sensor of pyrophosphate which is characterized by including: an insulative substrate 1; an electrode system that is formed thereon and has a measurement electrode 2 and a counter electrode 3; and a plurality of reaction reagent layers that are provided on the substrate 1 and include pyrophosphatase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, diaphorase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, oxidized nicotineamide adenine dinucleotide, an electronic mediator, a magnesium salt and a buffer component, reaction reagent layer 36 including the enzyme being separated from reaction reagent layer 35 including the buffer component, and reaction reagent layer 37 including glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate being separated from the reaction reagent layer 35 including the buffer component.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
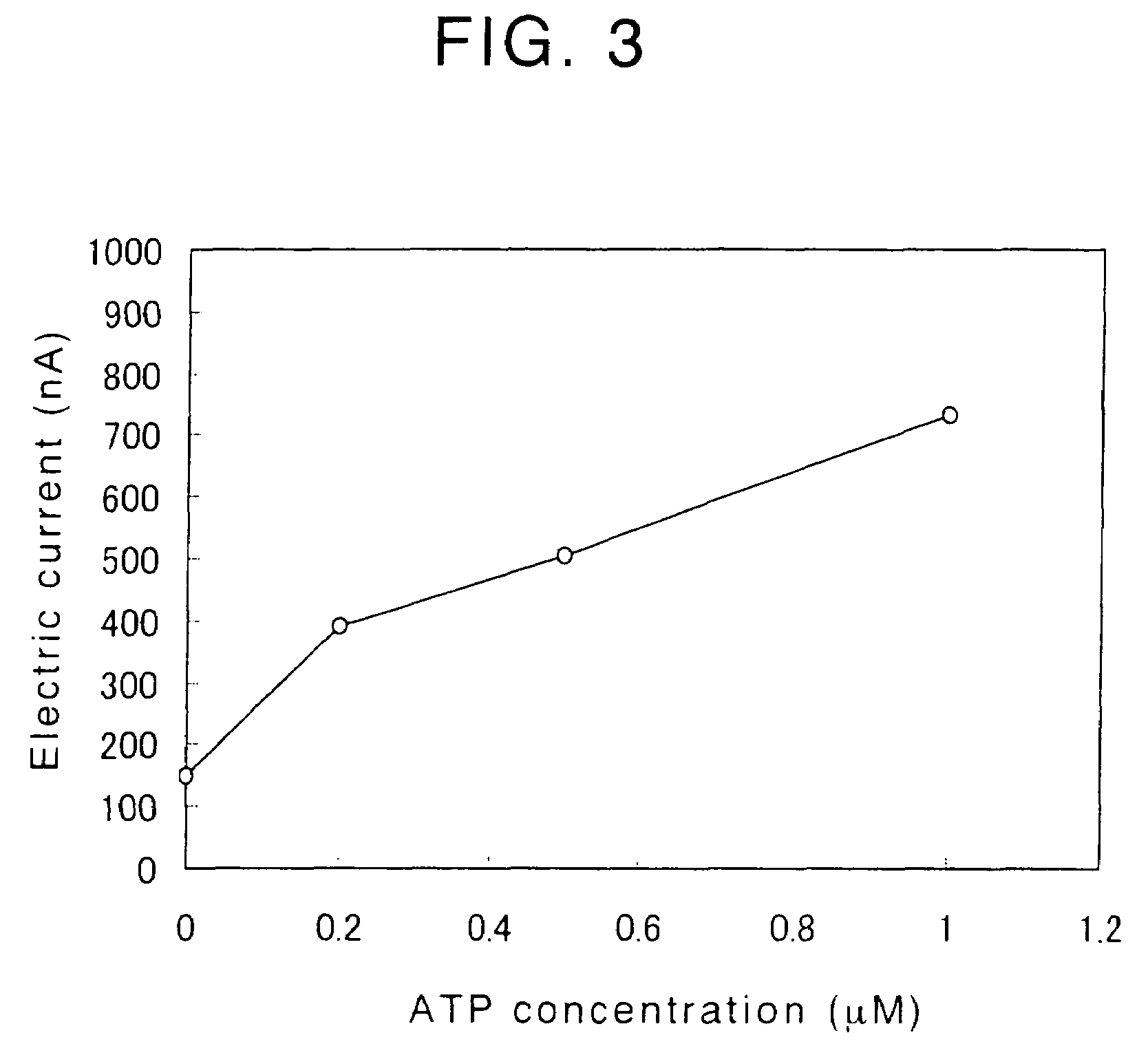
Enzyme electrode
InactiveUS7169273B2Easy and rapid determinationHigh sensitivityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsReaction layerEnzyme electrode
Disclosed is an enzyme electrode comprising an electrode system comprising an insulating substrate having formed thereon a working electrode, a counter electrode and optionally a reference electrode, and a reaction layer formed on the electrode system, wherein the reaction layer comprises diaphorase (DI), 12α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (12α-HSD) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide synthetase (NADS), at least a portion of the reaction layer being superposed on the working electrode, wherein the DI, 12α-HSD and NADS contained in the reaction layer are immobilized on the surface of the working electrode, so that a compound generated in the reaction layer can reach the surface of the working electrode. Also disclosed are a method for and a system for determining the concentration of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in a sample by using the above-mentioned enzyme electrode.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI KK
Fluorescent probe molecule for detecting diaphorase based on benzopyranidonitrile, preparation and application thereof
PendingCN109666012AClear structureGood choiceOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceOrganic chemistry
The invention relates to a fluorescent probe molecule for detecting diaphorase based on benzopyranidonitrile, a preparation method and an application thereof. The molecular structure of the fluorescent probe is shown below. Further disclosed are a preparation method of the fluorescent probe molecule for detecting the diaphorase based on benzopyranidonitrile and the application of detecting the diaphorase in various substances, such as water samples and cells.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
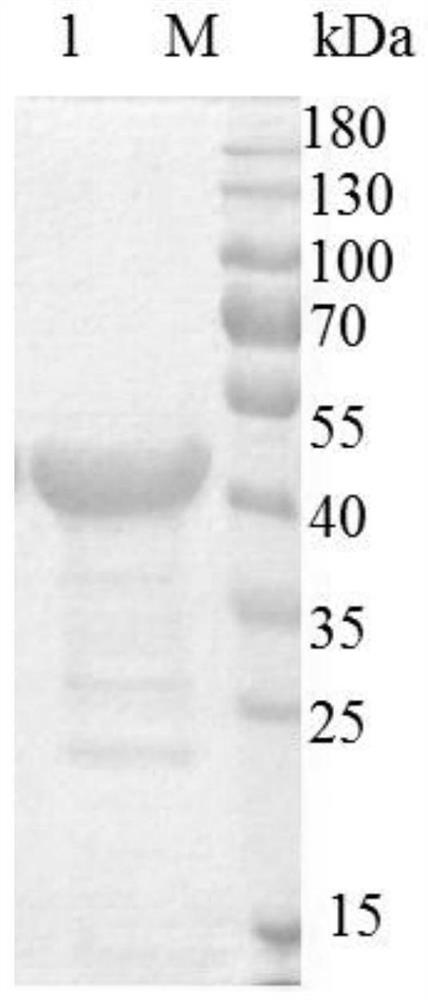
Thermostable diaphorase gene
The present invention provides a gene derived from a thermophilic Bacillus, comprising the nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID No.2 and encoding a thermostable diaphorase comprising the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID No.1, a recombinant vector possessing the gene, a transformant with the recombinant vector and a process for producing the thermostable diaphorase by using the transformant.
Owner:NIPRO CORP
Diaphorase mutant with high thermal stability, diaphorase mutant gene with high thermal stability and preparation method of diaphorase mutant
ActiveCN111662888AAchieve prokaryotic expressionImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementGlycineWild type
The invention provides a diaphorase mutant with high thermal stability, a diaphorase mutant gene with high thermal stability and a preparation method of the diaphorase mutant. The diaphorase mutant isobtained through mutation of the 122nd position amino acid in the amino acid sequence of wild-type diaphorase from glycine to aspartic acid, and the amino acid sequence of the diaphorase mutant is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The enzymatic properties of the diaphorase mutant are the same as the enzymatic properties of the wild-type diaphorase, the thermal stability of the diaphorase mutant is significantly higher than that of the wild-type diaphorase, and the stable range of the pH value is wide; an engineering means is adopted by the preparation method of the diaphorase mutant, genes of the diaphorase mutant are cloned into an expression vector, prokaryotic expression is achieved through transformation of host cells, and a large number of highly stable diaphorase mutants can be obtained; and alot of raw materials are provided for development of clinical diagnostic reagents, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:北京达成生物科技有限公司
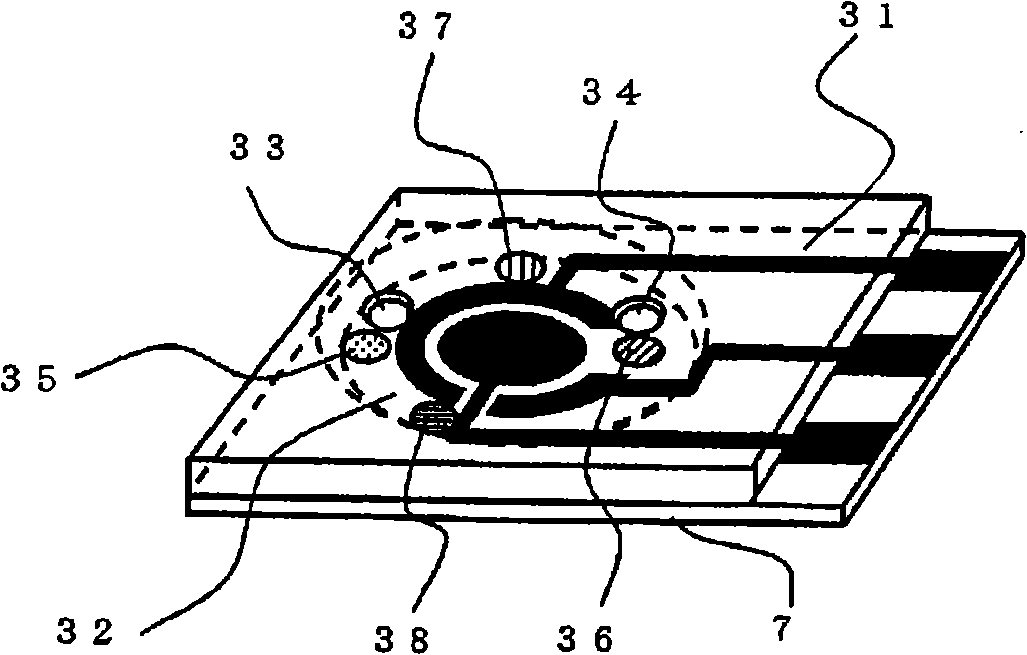
Pyrophosphoric acid sensor and snp typing sensor utilizing the same
ActiveCN101360993ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMagnesium saltGlyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
A pyrophosphoric acid sensor that in the method of measuring pyrophosphoric acid in SNP typing making use of primer extension reaction, realizes convenient detection of pyrophosphoric acid with high sensitivity. There is provided a pyrophosphoric acid sensor composed of insulating substrate (1); formed thereon, an electrode group consisting of measuring electrode (2) and counter electrode (3); and superimposed on the substrate (1), multiple reaction reagent layers consisting of pyrophosphatase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, diaphorase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, oxidized nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, electron mediator, magnesium salt and buffer solution components wherein reaction reagent layer (35) containing buffer solution components is separated from enzyme-containing reaction reagent layer (36), characterized in that reaction reagent layer (37) containing glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is separated from the reaction reagent layer (35) containing buffer solution components.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Enzyme immobilized electrode, fuel cell, electronic equipment, enzyme reaction utilization apparatus, and enzyme immobilized base
InactiveCN101641821ACell electrodesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansFuel cellsPorous carbon
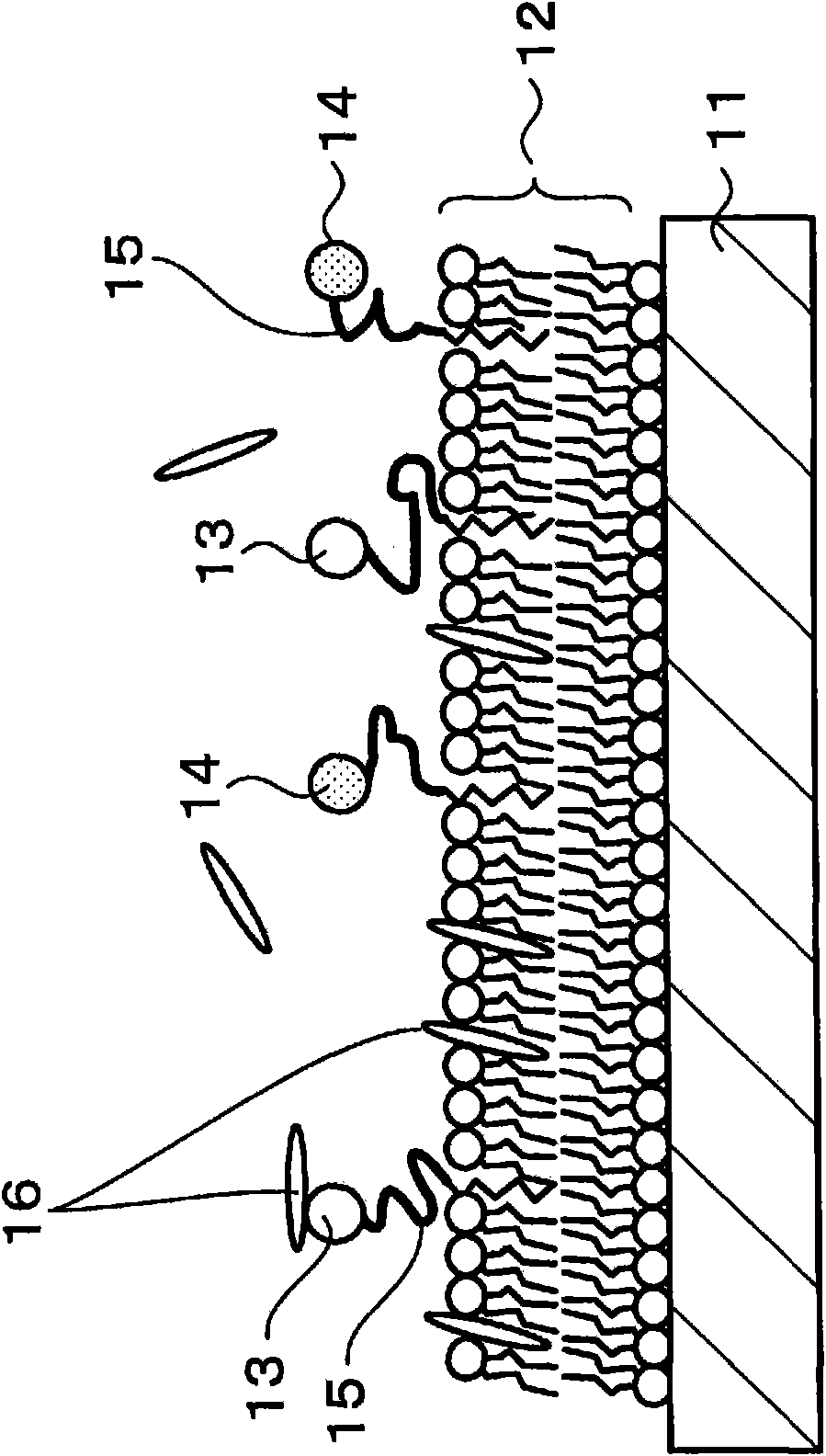
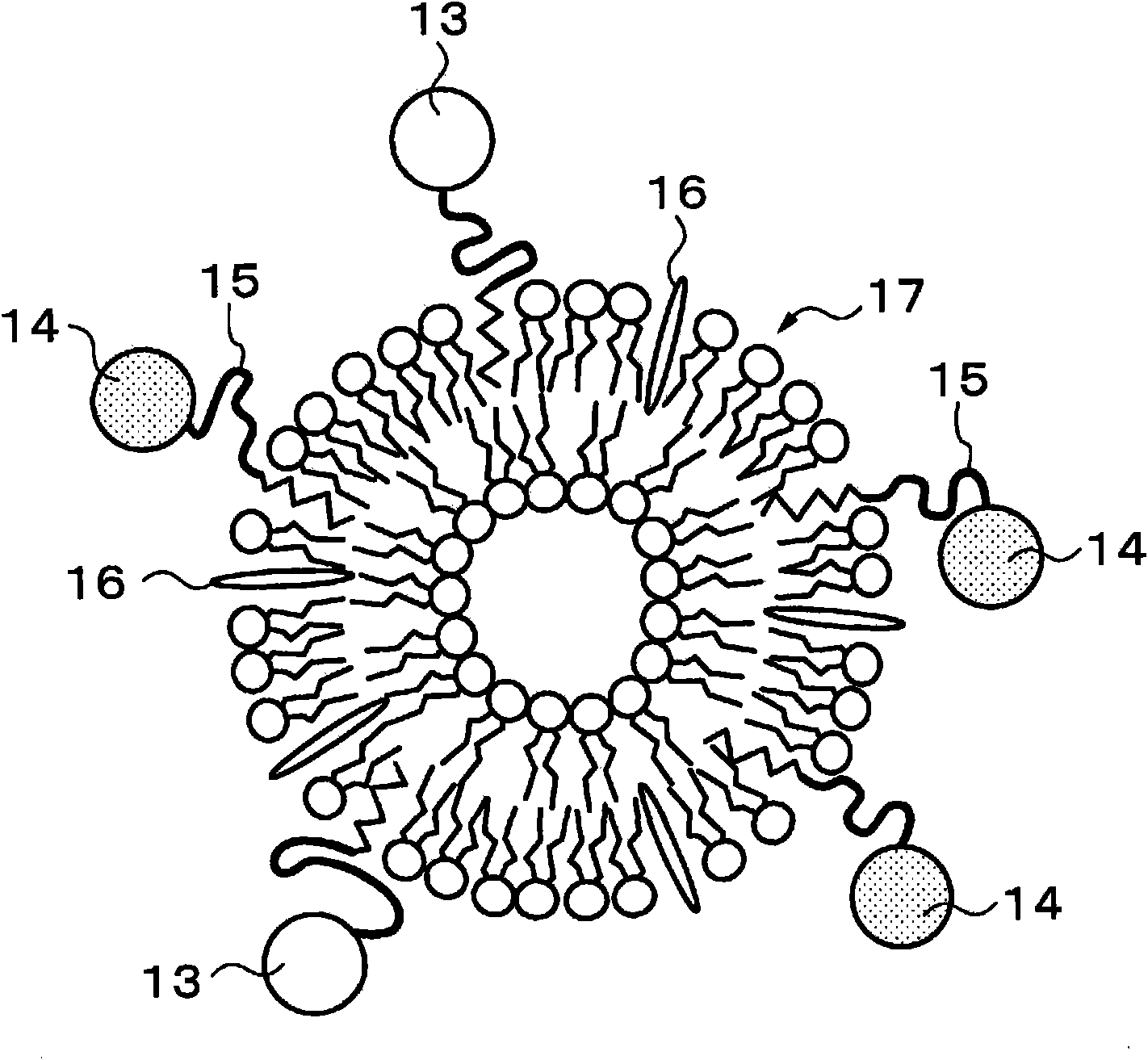
An enzyme-immobilized electrode is provided and includes an electrode composed of porous carbon or the like, a phospholipid layer on the electrode (11), and enzymes immobilized onto the phospholipid layer. The enzymes are, for example, diaphorase and glucose dehydrogenase. An intermediate layer composed of a protein or the like may be provided between the electrode and the phospholipid layer. By using the enzyme-immobilized electrode as a negative electrode or a positive electrode in a fuel cell using an enzyme, one or a plurality of types of enzymes can be immobilized at optimal positions onthe electrode, and thus, there are provided a highly efficient enzyme-immobilized electrode and a highly efficient fuel cell using the enzyme-immobilized electrode.
Owner:SONY CORP
Sensor of pyrophosphate and SNP typing sensor using the same
ActiveUS7632392B2High sensitivityEasy to measureImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMagnesium saltPhosphoric acid
A sensor of pyrophosphate which can detect pyrophosphate conveniently with high sensitivity in a method for measuring pyrophosphate in SNP typing utilizing a primer extension reaction is provided.A sensor of pyrophosphate which is characterized by including: an insulative substrate 1; an electrode system that is formed thereon and has a measurement electrode 2 and a counter electrode 3; and a plurality of reaction reagent layers that are provided on the substrate 1 and include pyrophosphatase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, diaphorase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, oxidized nicotineamide adenine dinucleotide, an electronic mediator, a magnesium salt and a buffer component, reaction reagent layer 36 including the enzyme being separated from reaction reagent layer 35 including the buffer component, and reaction reagent layer 37 including glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate being separated from the reaction reagent layer 35 including the buffer component.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Liquid stable kit for measuring beta-hydroxybutyric acid by cyclic enzyme method
ActiveCN102435749BGuaranteed specificityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementBeta-Hydroxybutyric acidBeta hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase
The invention discloses a liquid stable kit for measuring beta-hydroxybutyric acid by a cyclic enzyme method. The liquid stable kit consists of a reagent 1 and a reagent 2, wherein 1L of reagent 1 comprises 50 to 500mmol of buffer solution, 1 to 5KU of beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, 1 to 5KU of diaphorase, 0.1 to 100g of surfactant, 1 to 100mmol of stabilizer, 0.1 to 100g of anti-interference agent I, 0.1 to 100g of anti-interference agent II, and 0.1 to 100ml of preservative; and 1L of reagent 2 comprises 50 to 500mmol of buffer solution, 1 to 20mmol of coenzyme I, 0.1 to 10mmol of nitrotetrazolium blue, 1 to 100mmol of stabilizer and 0.1 to 100ml of preservative. The liquid stable kit has the advantages of stability, wide linear range, high measurement accuracy, high antijamming capability and low cost.
Owner:NINGBO MEDICAL SYSTEM BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Fuel cell, electronic device, movable body, power generation system, and congeneration system
ActiveUS7955741B2Reduce the amount of wasteEfficient use ofFuel cell auxillariesActive material electrodesDecompositionVitamin K3
A fuel cell which can directly extract electric power from a polysaccharide, such as starch, is provided. A fuel electrode is formed by immobilizing with an immobilizer, on an electrode comprised of, e.g., carbon, an enzyme responsible for decomposing a polysaccharide into monosaccharides, an enzyme responsible for decomposing the monosaccharide formed, a coenzyme (e.g., NAD+ or NADP+) which forms a reductant due to the oxidation reaction in the monosaccharide decomposition process, a coenzyme oxidase (e.g., diaphorase) for oxidizing the reductant of the coenzyme (e.g., NADH or NADPH), and an electron mediator (e.g., ACNQ or vitamin K3) for receiving electrons generated due to the oxidation of the coenzyme from the coenzyme oxidase and delivering the electrons to the electrode. The fuel cell comprises the fuel electrode and the air electrode that sandwich an electrolyte layer.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Detection reagent and test paper for beta-hydroxybutyrate
InactiveCN106706608AQuick checkAccurate detectionMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSiphonReaction layer
The invention discloses a detection reagent and test paper for beta-hydroxybutyrate. The detection reagent contains 3-5 KU / L of diaphorase, 9-13 KU / L of beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, 1.2-2.5 KU / L of NAD and 0.6-1.0 KU / L of NBT. The detection reagent contains various specific enzymes for specific proportioning, thereby being capable of realizing rapid detection and more accurate detection. The test paper comprises a reaction base layer, a reaction layer, a blood filter layer and a hydrophilic layer which are stacked to form a siphon system, and rapid detection and more accurate detection are further guaranteed.
Owner:复星诊断科技(长沙)有限公司
Sensor used for detecting lactic dehydrogenase
InactiveCN105987938AWide range of applicationsJudging the test resultsMaterial electrochemical variablesPotassium ferricyanideDiaphorase
A sensor for detecting lactate dehydrogenase, used for detecting a lactate dehydrogenase content of a biological sample, comprising a substrate, an electrode group, a hydrophobic insulating layer, a cover and a reaction drug membrane. The electrode group includes a working electrode and a reference electrode and is located on the substrate, the hydrophobic insulating layer is arranged on the substrate and includes a gap, the cover covers the gap and is connected to the substrate A sample channel is formed between them to accommodate the reaction drug film, the reaction drug film is selected from the group consisting of lactic acid, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, diaphorase and potassium ferricyanide. The reaction drug film is in contact with the lactate dehydrogenase in the biological sample to generate a bioelectrochemical reaction, so that the electrode group undergoes an electrical signal change reflecting the content of the lactate dehydrogenase.
Owner:EUMED BIOTECH
Lactate dehydrogenase detector
InactiveUS20160265024A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisLactate dehydrogenaseInsulation layer
A lactate dehydrogenase detector, which is used to detect a content of lactate dehydrogenase in a biological sample, comprises a substrate, an electrode assembly, a hydrophobic insulation layer, a cover and a reagent-containing membrane. The electrode assembly is disposed on the substrate and including a working electrode and a reference electrode. The hydrophobic insulation layer is arranged over the substrate and has a notch. The cover hoods the notch and cooperates with the substrate to form a sample channel accommodating the reagent-containing membrane. The reagent-containing membrane is made of materials selected from a group consisting of a lactic acid, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD), diaphorase, and potassium ferricyanide. A bioelectrochemical reaction between the reagent-containing membrane and the lactate dehydrogenase induces an electrical signal variation in the electrode assembly, which indicates the content of the lactate dehydrogenase.
Owner:EUMED BIOTECH
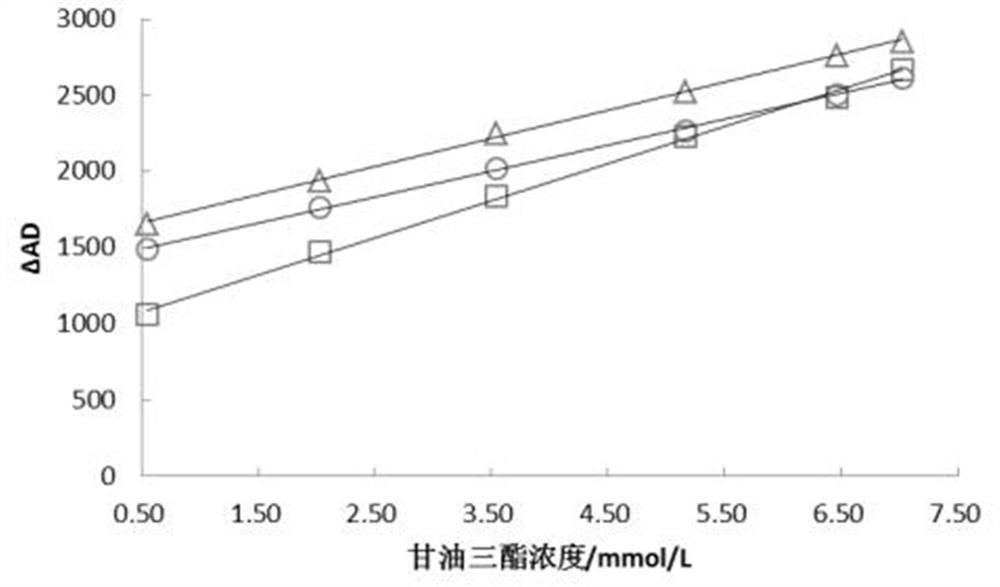
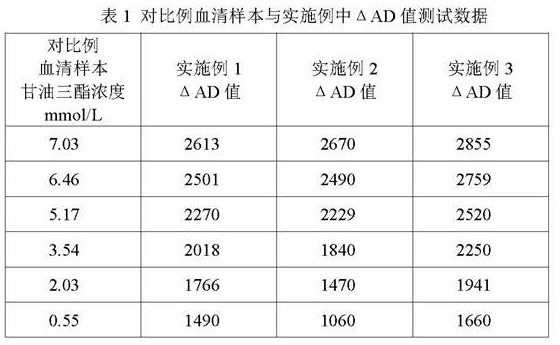
Triglyceride detection reagent, detection test paper and test paper preparation method
InactiveCN111735811AStable detectionReduce the impact of interferenceMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorTetrazoleA lipoprotein
The invention relates to a triglyceride detection reagent, detection test paper and a test paper preparation method. The detection reagent is prepared from 0.5 to 1.5 KU / ml of lipoprotein lipase, 0.3to 0.5 KU / ml of diaphorase, 0.32 to 0.94 KU / ml of glycerol dehydrogenase, 5 to 15mmol / L of coenzyme I and 2 to 6mmol / L of a chromogenic substance, and further comprises a TritonX-100 solution with themass fraction being 0.2%-1.0% and a buffer solution with the concentration being 0.01 mol / L to 0.1 mol / L; wherein the chromogenic substance is one of nitro tetrazole blue chloride, dimethyl thiazolediphenyl tetrazole bromine blue, sodium dichlorophenol indophenolate, TNBT and iodonitrotrtrazolium chloride, the detection test paper comprises a reaction bottom layer, a reaction layer, a blood filtering layer, a capillary sample introduction layer and a hydrophilic layer, and the detection reagent is located on the upper surface of the reaction layer. The interference influence of other substances on the test result is small, and the reagent detection is more stable.
Owner:民康医疗科技(天津)有限公司
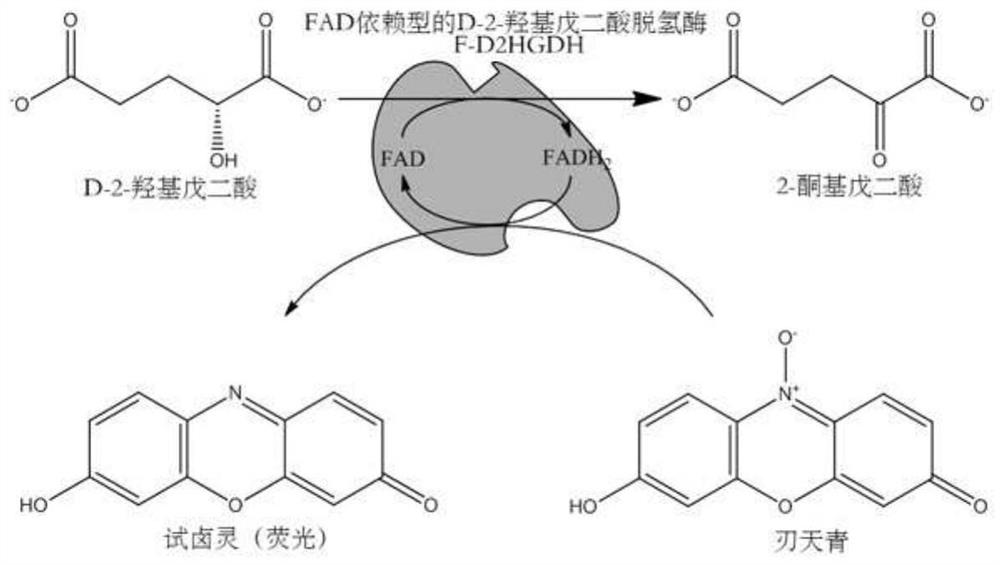
Method for detecting D-2-hydroxyglutarate by using FAD dependent D-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase and resazurin
ActiveCN112592958ALow costSimple compositionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisResazurinDiaphorase
The invention discloses a method for detecting D-2-hydroxyglutarate by using FAD dependent D-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase and resazurin, and relates to the technical field of enzymatic detection.The method uses FAD dependent D-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase, resazurin and a PBS buffer solution to realize detection of D-2-hydroxyglutarate; and the FAD dependent D-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase is an AX-F-D2HGDH protein or a P-D2HGDH protein. The method is simpler in composition, lower in cost and simpler and more convenient to operate. Since no cofactor, coenzyme or diaphorase needs tobe added, introduced interference is less, sensitivity is higher, only one enzyme needs to be prepared, no exogenous cofactor NAD and the like need to be added, and meanwhile, the buffer solution canbe a PBS buffer solution which is lower in cost and easy to obtain, so that cost is lower.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL OF SHANDONG UNIV
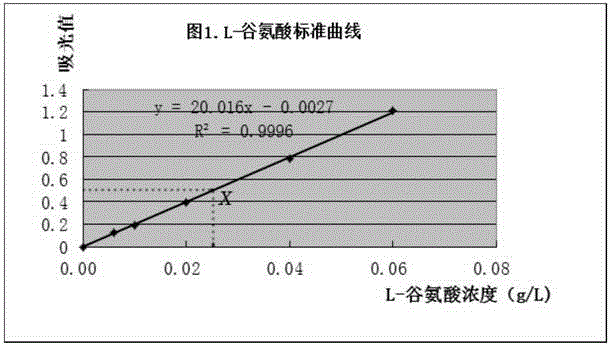
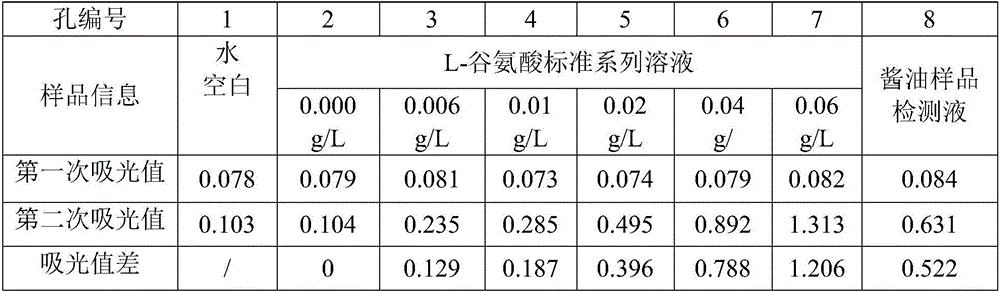
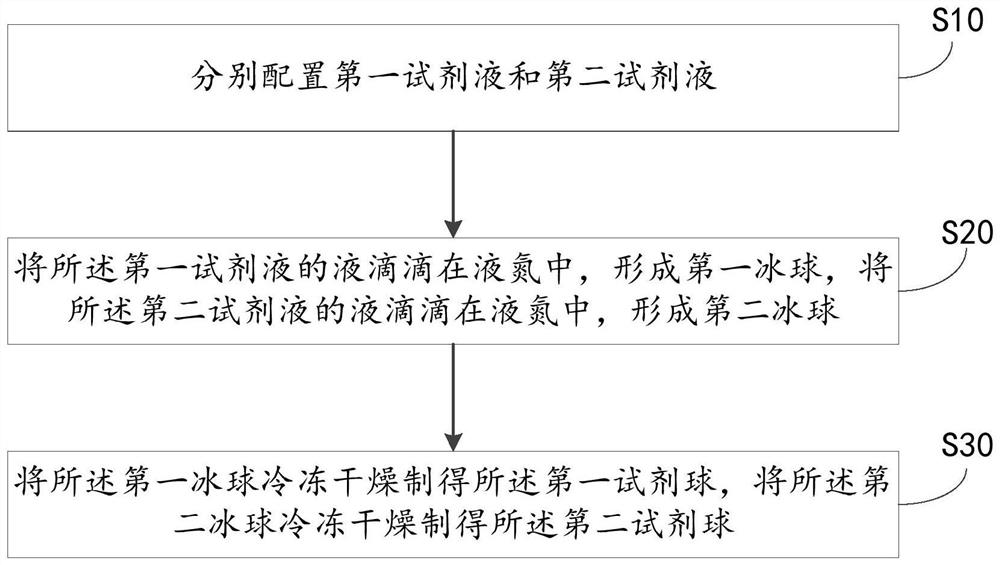
Method for rapidly determining L-glutamic acid in food
The present invention relates to a method for rapidly determining the L-glutamic acid in food. The method comprises: grinding or mincing a solid or semi-solid sample by using a suitable tool, weighing a proper amount of the grinded or minced sample, adding an appropriate solvent, homogenizing, carrying out centrifuged separation, and filtering to obtain a free L-glutamic acid extraction liquid, or carrying out protein hydrolysis to obtain the L-glutamic acid extraction liquid constituting the protein structure (the liquid sample is directly filtered without the pretreatment); properly diluting the sample extraction liquid, and adjusting the pH value to 8.6; reducing nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD<+>) into nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) in the presence of glutamate dehydrogenase(GIDH) through the L-glutamic acid of the sample detection liquid, and carrying out a reaction on the NADH and iodonitrotrtrazolium chloride (INT) under the effect of diaphorase to generate formazan; and determining the absorption peak of the formazan at 490 nm by using a light-absorption microplate reader, and calculating the L-glutamic acid content in the sample according to the absorption value of the formazan by using an external standard method. According to the present invention, the detection method has characteristics of simple operation, good accuracy, fastness, high throughput, easy popularization, and the like.
Owner:CENT TESTING INT GRP CO LTD
Preparation method of lactic dehydrogenase determination reagent spheres, reagent spheres and microfluidic chip
ActiveCN113278675AEasy to shapeImprove solubilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisFormazanLactate dehydrogenase measurement
The embodiment of the invention relates to the technical field of medical detection, and particularly relates to a preparation method of lactic dehydrogenase determination reagent spheres, the reagent spheres and a microfluidic chip. The lactic dehydrogenase determination reagent spheres comprise a first reagent sphere and a second reagent sphere, wherein a first reagent solution forming the first reagent sphere comprises 40-200mmol / L of a first buffer solution, 0.1-10g / L of iodonitrochlorotetrazolium blue, 10-100g / L of a first excipient and 0.1-10 g / L of a stabilizer; and a second reagent solution forming the second reagent sphere comprises 40-200mmol / L of a second buffer solution, 10-100g / L of lactate, 10-50g / L of oxidized coenzyme I, 20-100U / L of diaphorase and 10-100g / L of a second excipient. During detection, the generated reduced coenzyme I (NADH) is further reacted to generate colored stable formazan, so that the concentration of lactic dehydrogenase can be quantified by detecting the absorbance at the wavelength of 490nm, and the sensitivity is greatly improved; and in addition, the first excipient and the second excipient in the dosage range can ensure that the first reagent sphere and the second reagent sphere have good morphology and re-melting solubility respectively, and have high stability and precision.
Owner:GENRUI BIOTECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com