Method for rapidly determining L-glutamic acid in food
A technology for rapid determination of glutamic acid, applied in the direction of measuring devices, biological testing, material inspection products, etc., can solve the problems of expensive instruments and consumables, failure to achieve high throughput, and non-specificity, etc., to achieve simple operation, The instrument price and detection reagent are low in cost and easy to promote.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0030] 1. Preparation of sample detection solution:
[0031] Solid or semi-solid samples are crushed or minced with a grinder or a meat grinder, and 50 g is put into a homogenizing cup, and 100 mL of 1.0 mol / L dilute perchloric acid solution is added for homogeneous extraction for 5 minutes (Note: the extraction method The resulting L-glutamic acid is free L-glutamic acid, if you want the extract to include L-glutamic acid that constitutes the protein structure, you need to increase the proteolysis step), transfer the mixture to a 50mL centrifuge tube, and centrifuge at 1000g After 5 minutes, carefully remove the floating matter in the upper layer, take the middle clear liquid, and filter it with a medium-speed filter paper (the liquid sample does not need the above pretreatment, just filter it directly), take an appropriate amount of filtrate, and adjust the pH with 2mol / L potassium hydroxide solution to 8.0 to 9.0, and diluted to a certain volume, as a sample detection solut...
Embodiment 1
[0047] 1. Preparation of sample detection solution
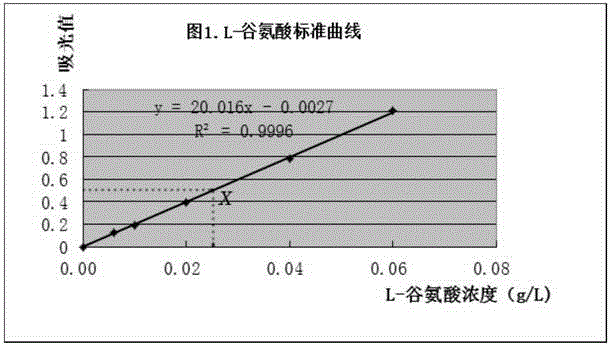
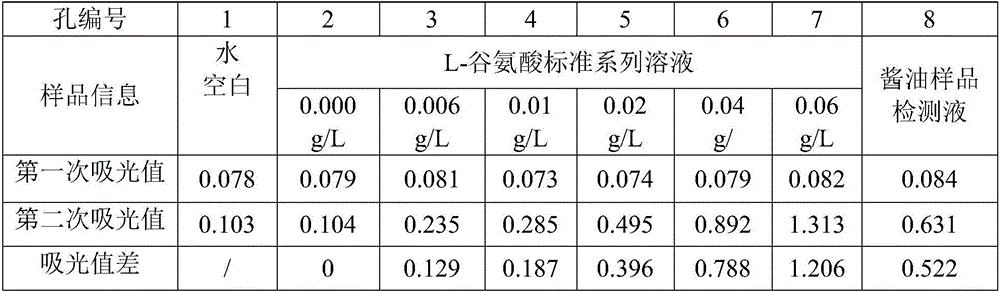
[0048] Weigh 2g of soy sauce sample into a beaker, accurate to 0.01g, dilute with water, adjust the pH to 8.6 with 2.0mol / L potassium hydroxide solution, transfer to a 500mL volumetric flask, and set the volume to the mark, filter to make the soy sauce sample detectable The concentration of liquid L-glutamic acid is controlled within the range of 0.006g / L to 0.06g / L.
[0049] 2. Preparation of Assay Reagents
[0050] Reagent A1: Weigh 1.488g of triethanolamine phosphate, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate (K 2 HPO 4 ) 0.172g, potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH 2 PO 4) 1.4mg, dissolved in water, adjusted the pH to 8.6 with 2mol / L potassium hydroxide solution, added 0.5g of Triton X-100, dilute to 100mL, and made triethanolamine phosphate buffer solution with pH 8.6 . The solution is stored at 2°C to 8°C, and the shelf life is 2 months.
[0051] Reagent A2: Weigh diaphorase freeze-dried powder (enzyme activity unit is 25U / m...
Embodiment 2
[0067] 1. Preparation of sample detection solution
[0068] Cut about 100g of chicken into small pieces, grind it with a meat grinder, weigh 50g, accurate to 0.01g, put it into a homogenizing cup, and add 100mL of 1.0mol / L dilute perchloric acid at 0°C to the homogenizing cup solution, homogenized extraction for 5 minutes (note: the L-glutamic acid obtained by this extraction method is free L-glutamic acid, if you want the extract to include L-glutamic acid that constitutes the protein structure, you need to increase the proteolysis step), Transfer the homogenized mixture to a 50mL centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 2000g for 5 minutes, carefully remove the upper lipid film, take the middle supernatant, and filter.
[0069] Draw 10mL of the filtrate into a beaker, dilute with water, adjust the pH to 8.6 with 2.0mol / L potassium hydroxide solution, transfer it to a 100mL volumetric flask, and set the volume to the mark, so that the chicken sample detection solution L-glutamic acid c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Enzyme activity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com