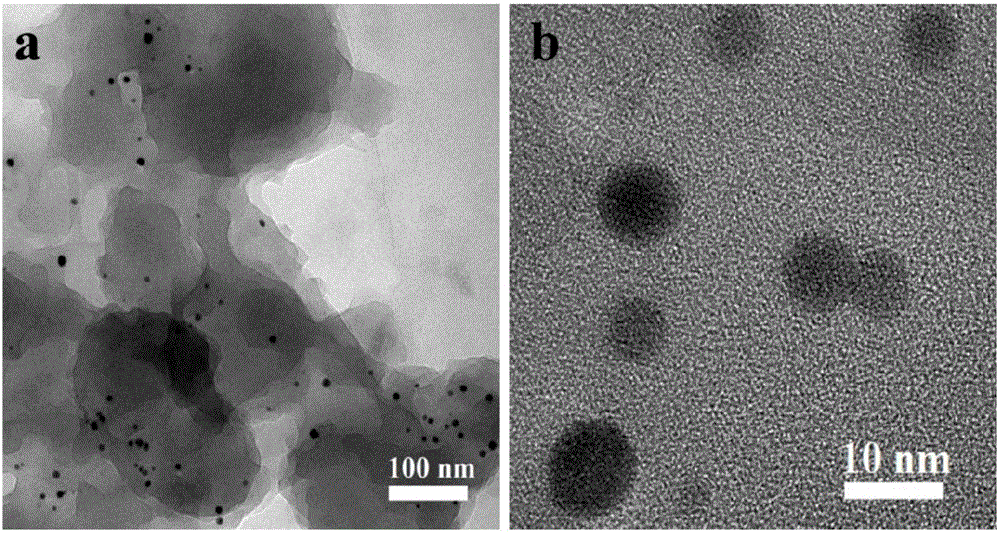
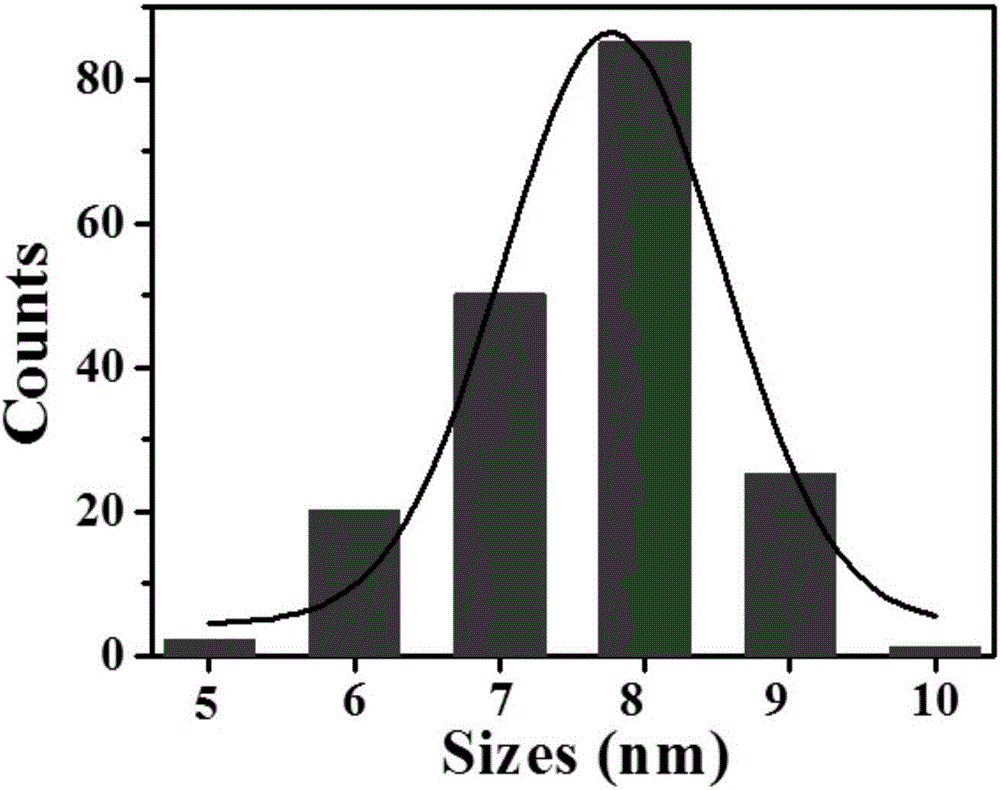
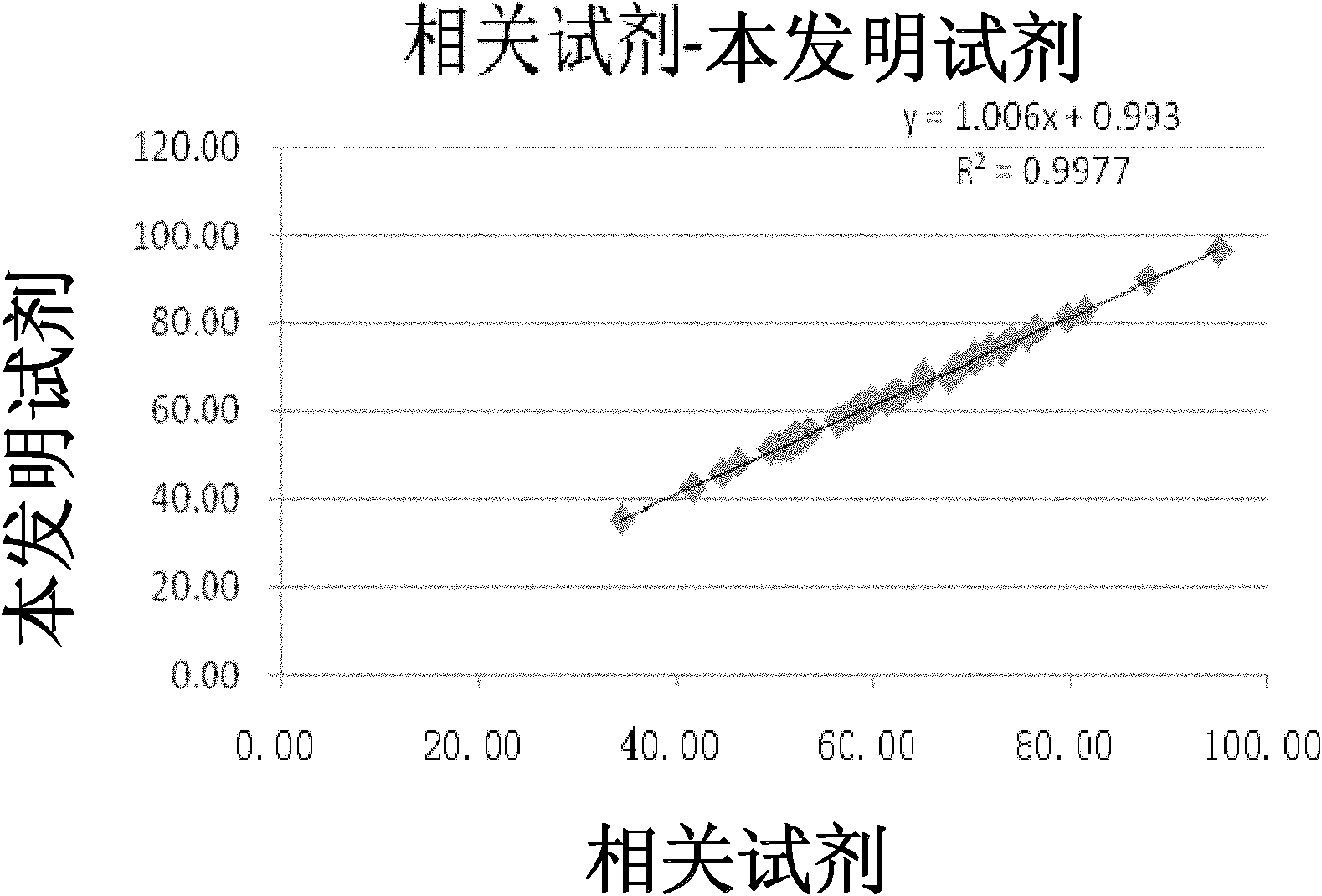
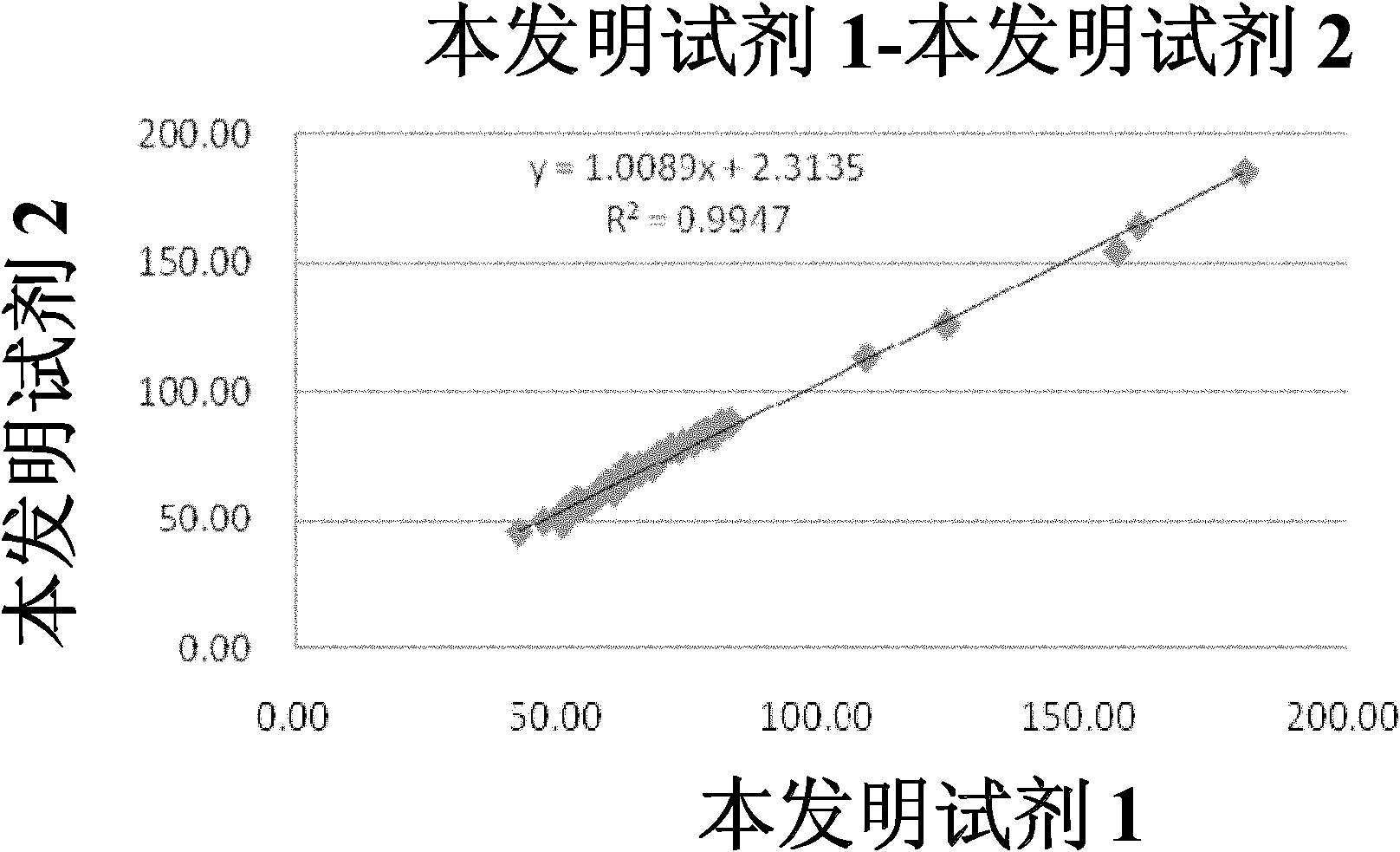
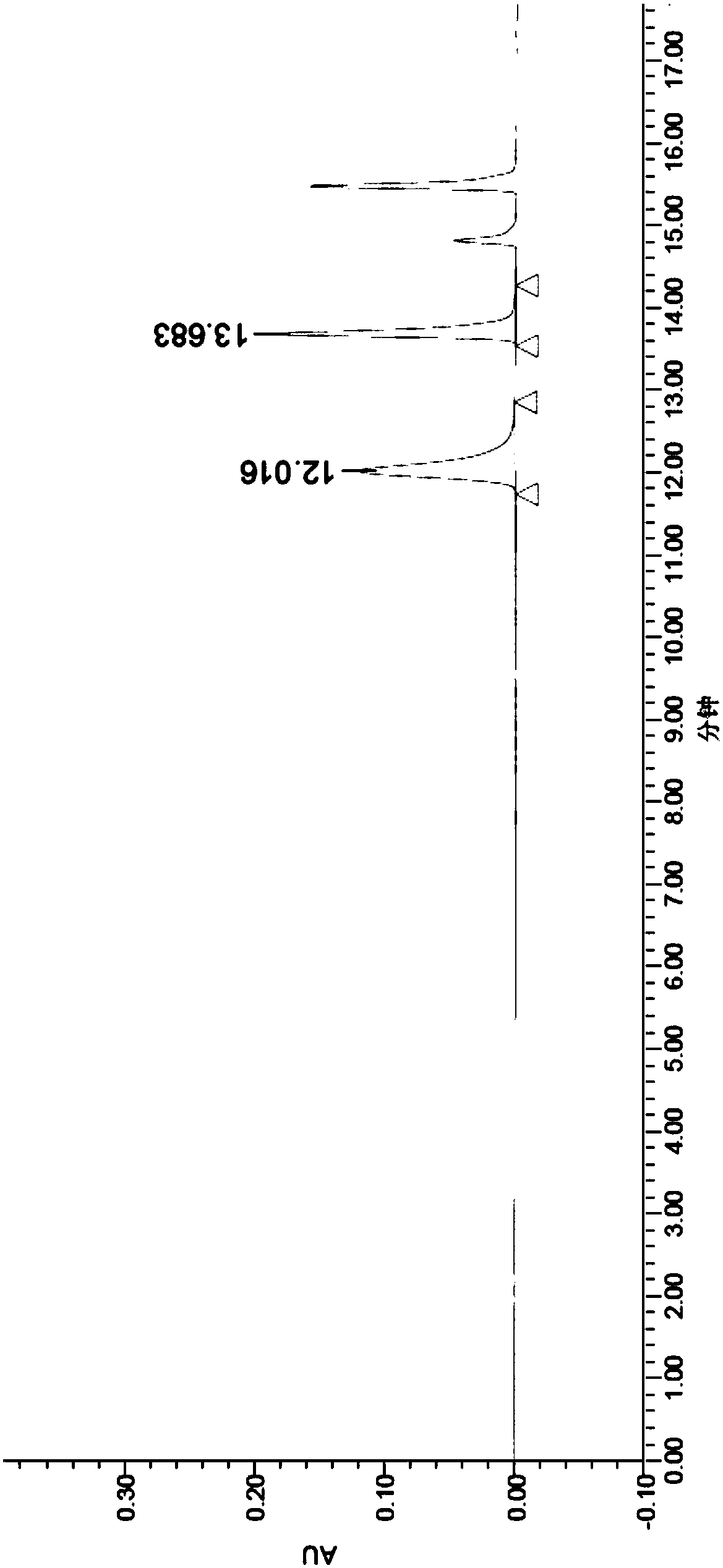
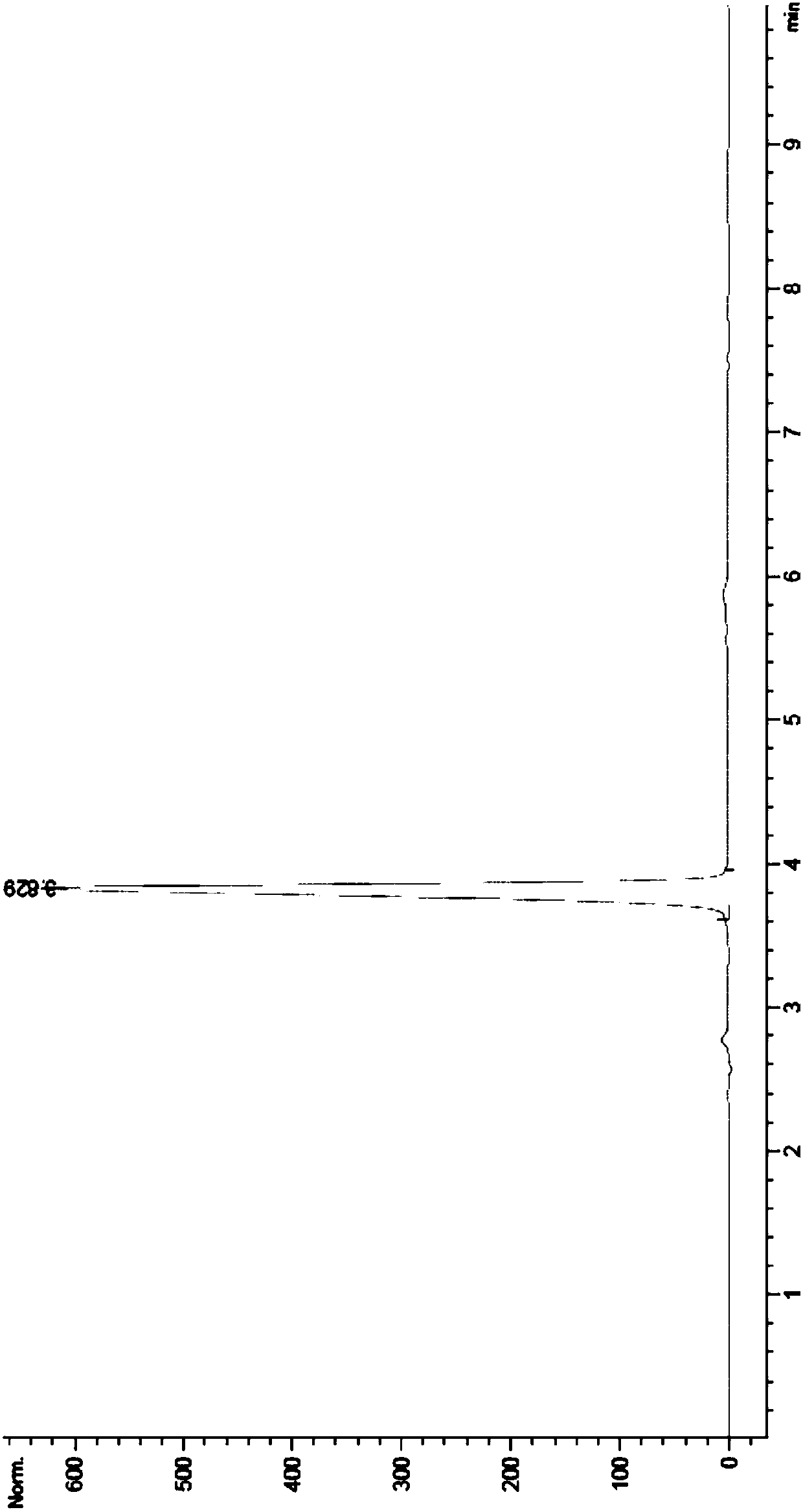
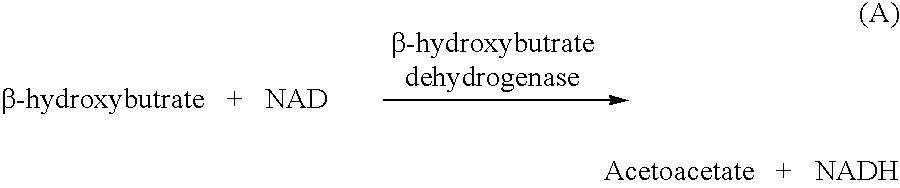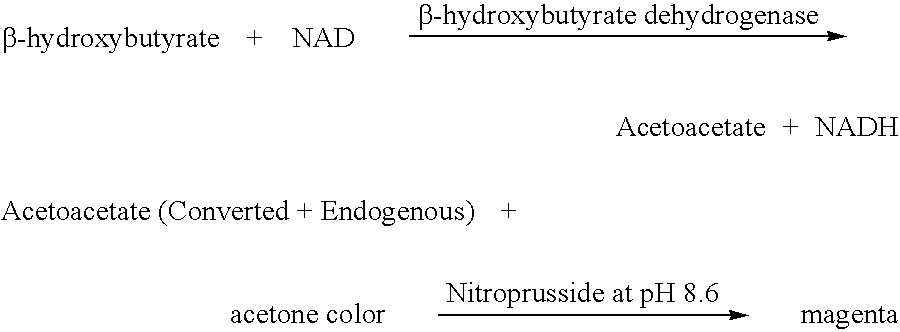Patents
Literature
373 results about "Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
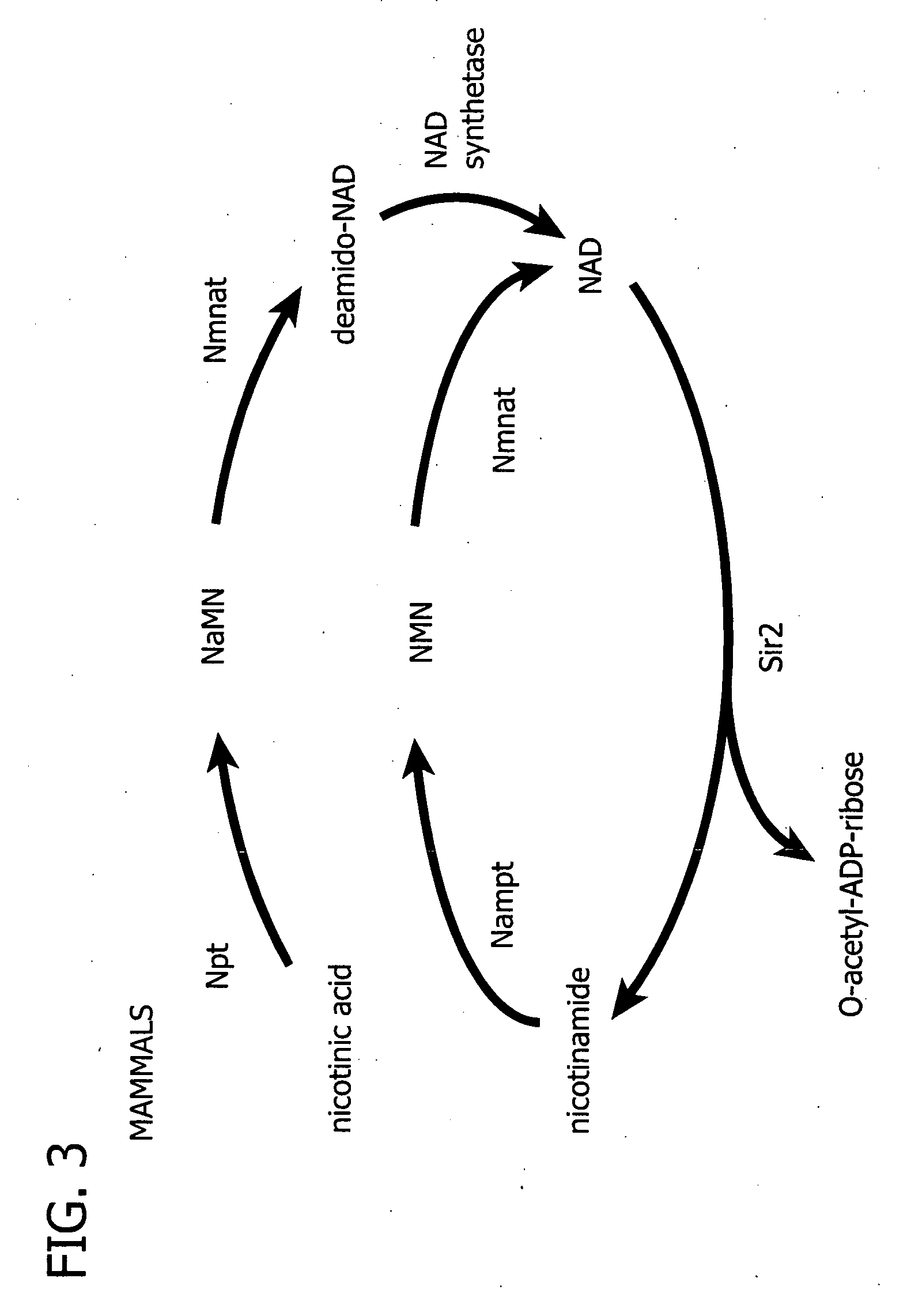
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a cofactor that is central to metabolism. Found in all living cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine nucleobase and the other nicotinamide. NAD exists in two forms: an oxidized and reduced form, abbreviated as NAD⁺ and NADH respectively.
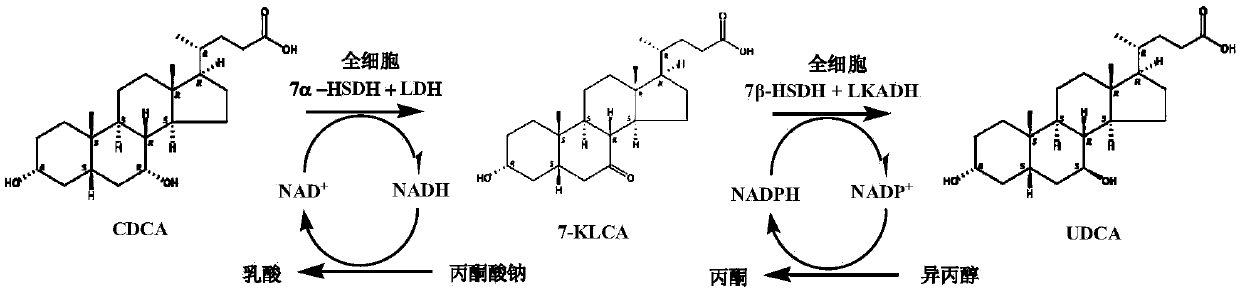
Method for catalyzing chenodeoxycholic acids to compound ursodesoxycholic acids through efficient whole-cells
ActiveCN105368828AFermentation methods are cheap and readily availableSuitable for industrial productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChemical synthesisLactate dehydrogenase
The invention provides a method for catalyzing chenodeoxycholic acids to compound ursodesoxycholic acids through efficient whole-cells. A 7a-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (7a-HSDH) and a lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) for regeneration of coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) are efficiently co-expressed in escherichia coli, escherichia coli whole cells are used to catalyze chenodeoxycholic acids (CDCA) to generate 3 alpha (Alpha)-hydroxyl-7-oxo-5bata (Beta)- cholanic acids (7-KLCA), and a reaction liquid which is obtained by catalyzing the chenodeoxycholic acids through whole cells is adjusted to be 7-KLCA crude products. Reconstitution cells can be easily obtained in low cost through a fermentation process, are better than a chemical synthesis method in production cost and product quality, and are suitable for commercial process.
Owner:苏州天绿生物制药有限公司
Stable nad/nadh derivatives
ActiveUS20080213809A1Good chanceEnabling detectionSugar derivativesMicroorganismsEnzyme complexReagent
The present invention provides for stable nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD / NADH) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP / NADPH) derivatives of formula (I), enzyme complexes of these derivatives and their use in biochemical detection methods and reagent kits.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Phasor Method to Fluorescence Lifetime Microscopy to Discriminate Metabolic State of Cells in Living Tissue
ActiveUS20120276578A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPlant Germ CellsPorphyrin
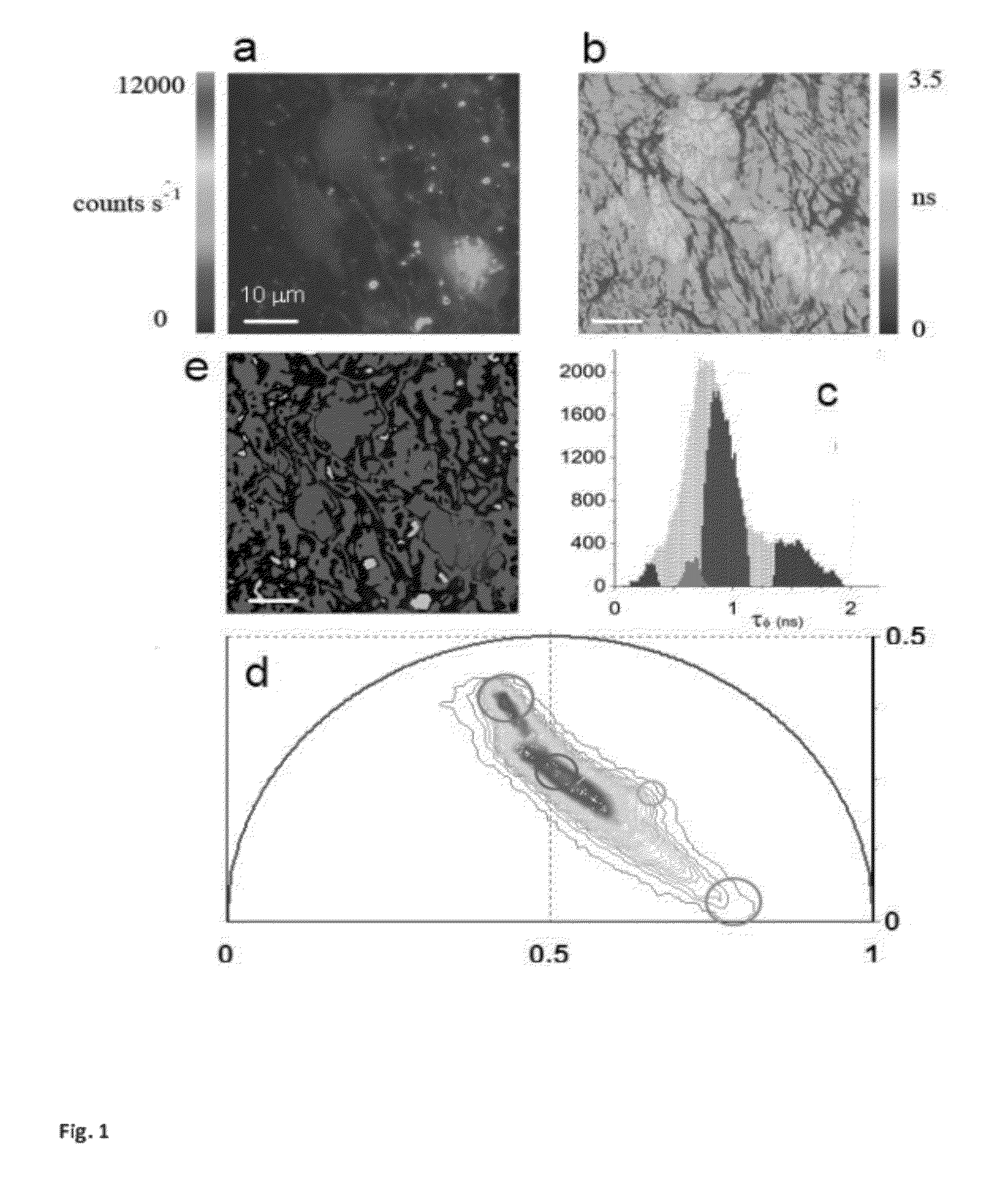
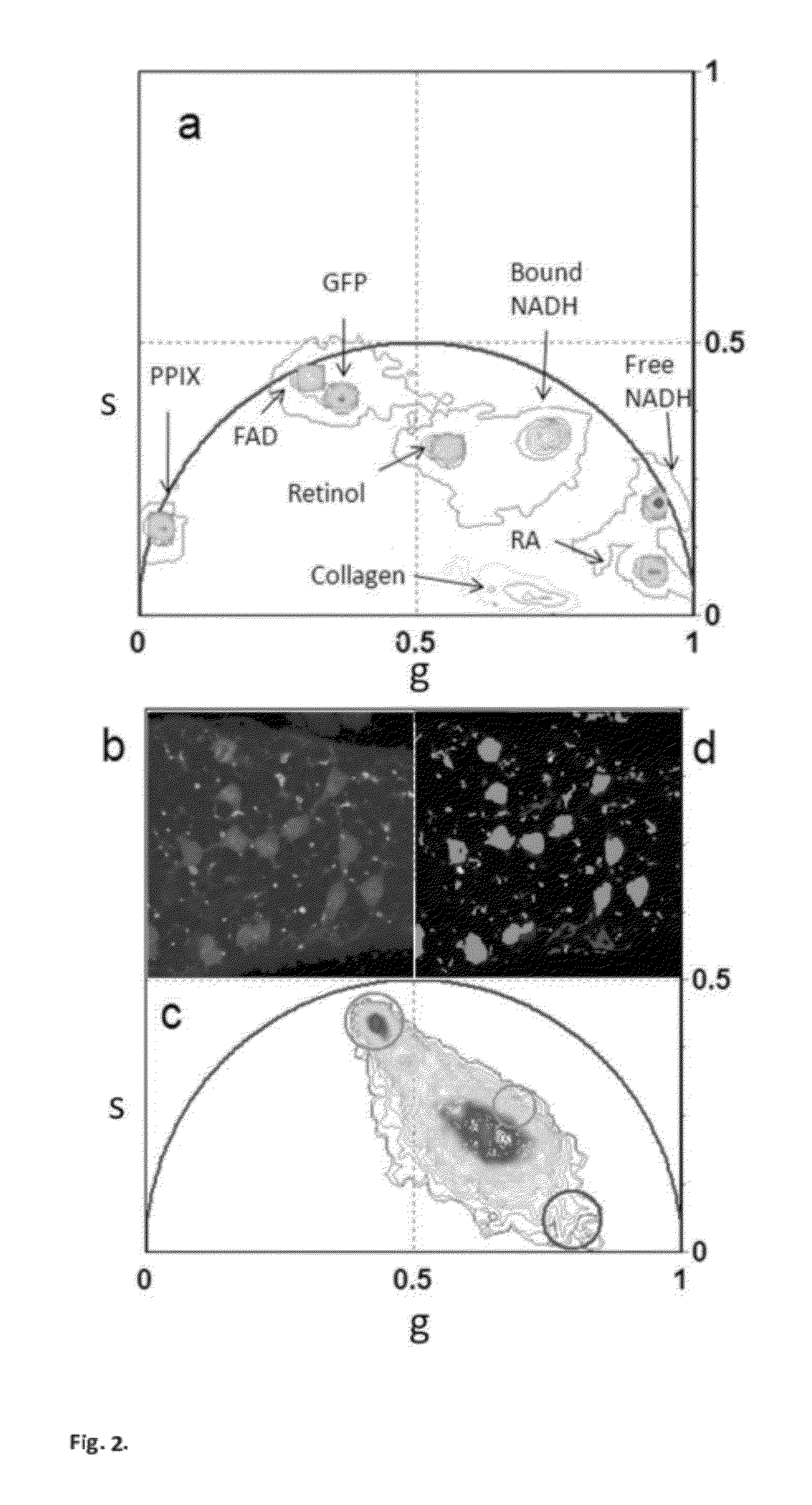
“A label-free imaging method to monitor stem cell metabolism discriminates different states of stem cell as they differentiate in a living tissues. We use intrinsic fluorescence biomarkers and the phasor approach to Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy (FLIM). We identify and map intrinsic fluorophores such as collagen, retinol, retinoic acid, flavins, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) and porphyrin. We measure the phasor values of germ cells in C. Elegans germ line. Their metabolic fingerprint cluster according to their differentiation state, reflecting changes in FAD concentration and NADH binding during the differentiation pathway. The phasor approach to lifetime imaging provides a label-free, fit-free and sensitive method to identify different metabolic state of cells during differentiation, to sense small changes in the redox state of cells and may identify symmetric and asymmetric divisions and predict cell fate.”
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
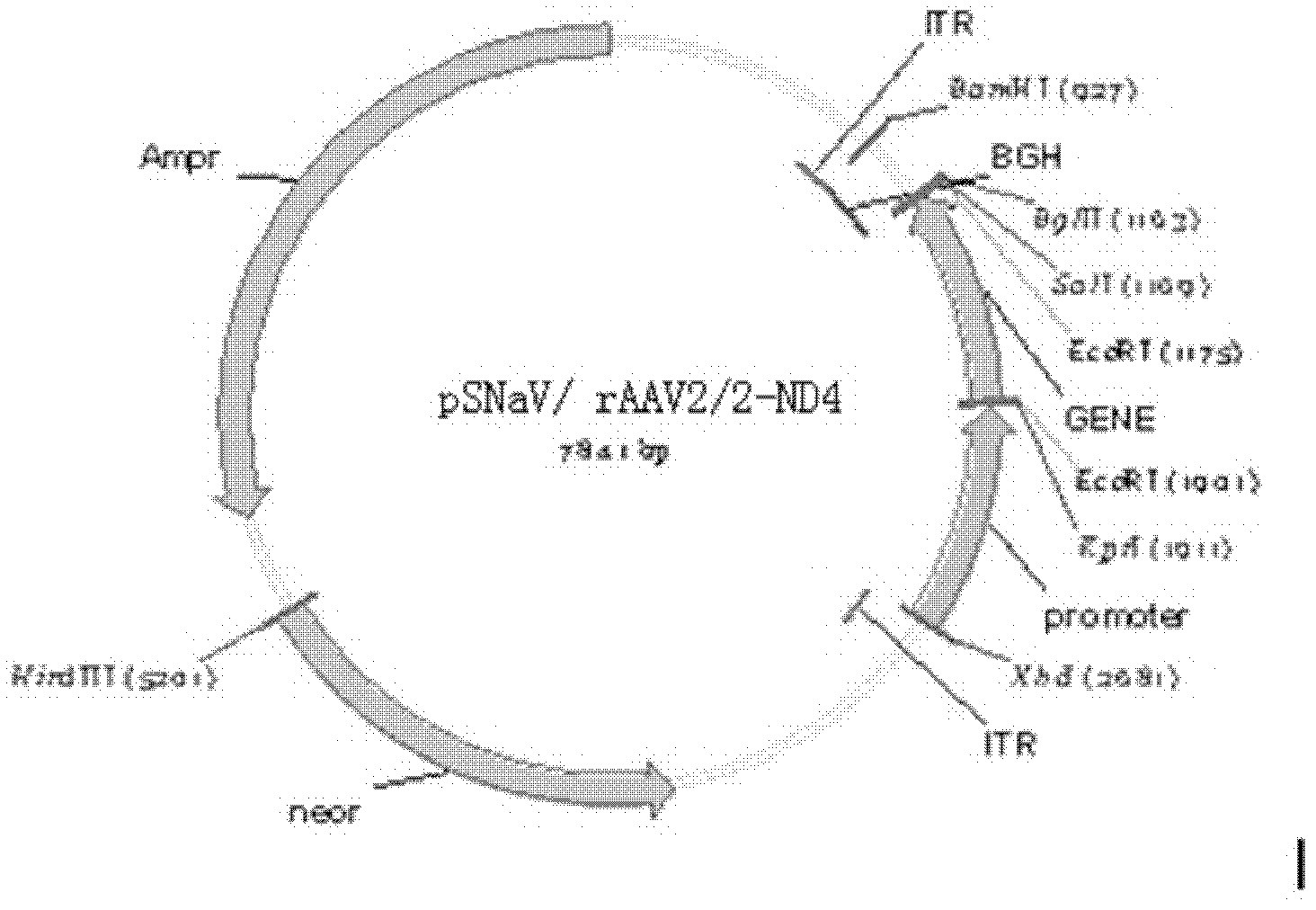
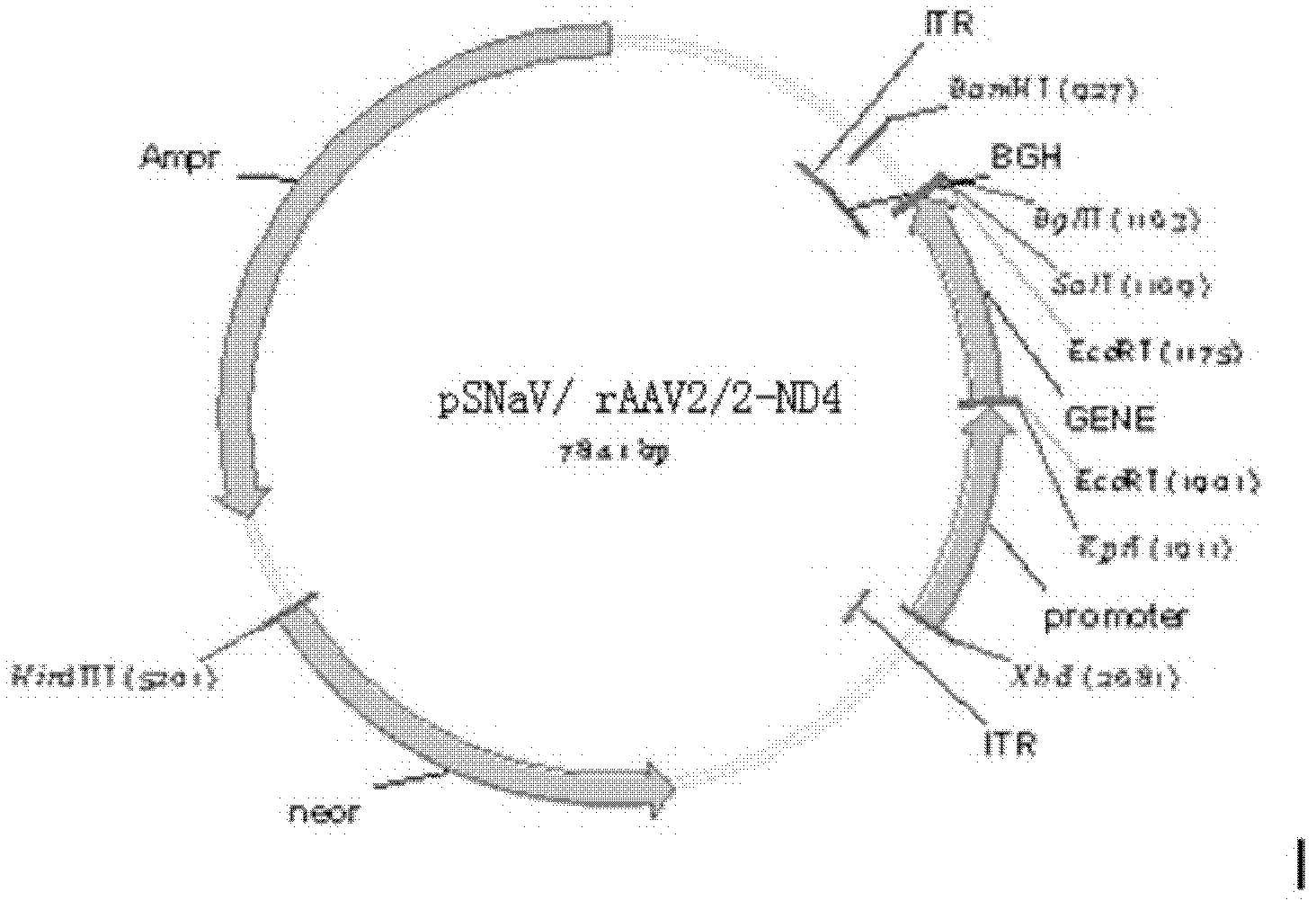
Recombinant human NADH (nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide) dehydrogenase subunit-4 gene and constructing method of expression vector thereof
The invention discloses a recombinant human NADH (nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotid) dehydrogenase subunit-4 gene and a constructing method of an expression vector thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown in SEQ ID NO:1, and the size of the nucleotide sequence is 2889 bp. The constructing steps of adeno-associate virus vectors are as follows: firstly constructing a recombinant adeno-associated virus vector containing the human NADH dehydrogenase subunit-4 gene, and then coating, infecting, purifying, concentrating and identifying the recombinant adeno-associated virus. According to the method, the recombinant adeno-associated virus vector with the recombinant human NADH dehydrogenase subunit-4 gene can be quickly and simply constructed, and is packaged to obtain the adeno-associated virus vector with complex defects. The gene can be used for gene therapy of LHON (leber's hereditary optic neuropathy).
Owner:WUHAN NEUROPHTH BIOTECHNOLOGY LTD CO
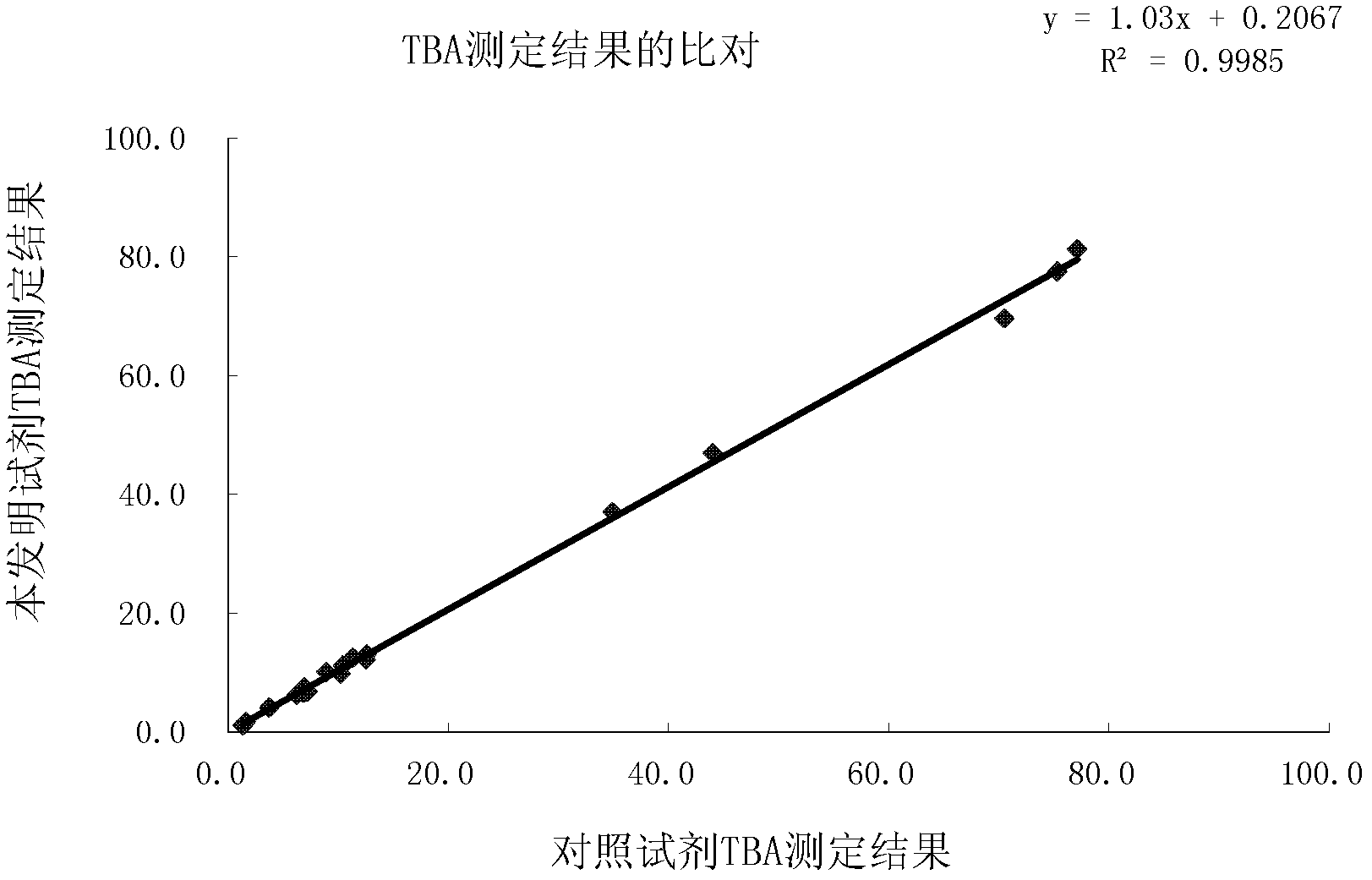
Total bile acid quantitative determination method and determination reagent kit
InactiveCN102539791AColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingSerum samplesQuantitative determination
The invention provides a reagent for quantitatively determining content of total bile acid in a human serum sample through an enzymological method. The reagent is suitable for an automatic biochemical analyzer to automatically and quantitatively determine the total bile acid. The reagent consists of a solution reagent 1 and a reagent 2 which are separately placed, wherein the reagent 1 contains oxidized thio-nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide (Thio-NAD), buffer and stabilizer; and the reagent 2 contains reduced coenzyme I (NADH), hydroxysteroiddehydrogenase (HSD), stabilizer and buffer. The invention additionally provides a reagent kit with the reagent 1 and the reagent 2, and a method for determining the content of total bile acid in the serum. The reagent, the reagent kit and the method provided by the invention have the advantages of high sensitivity, low cost, simplicity, convenience and rapidness in operation and easiness in popularization.
Owner:宁波天康生物科技有限公司
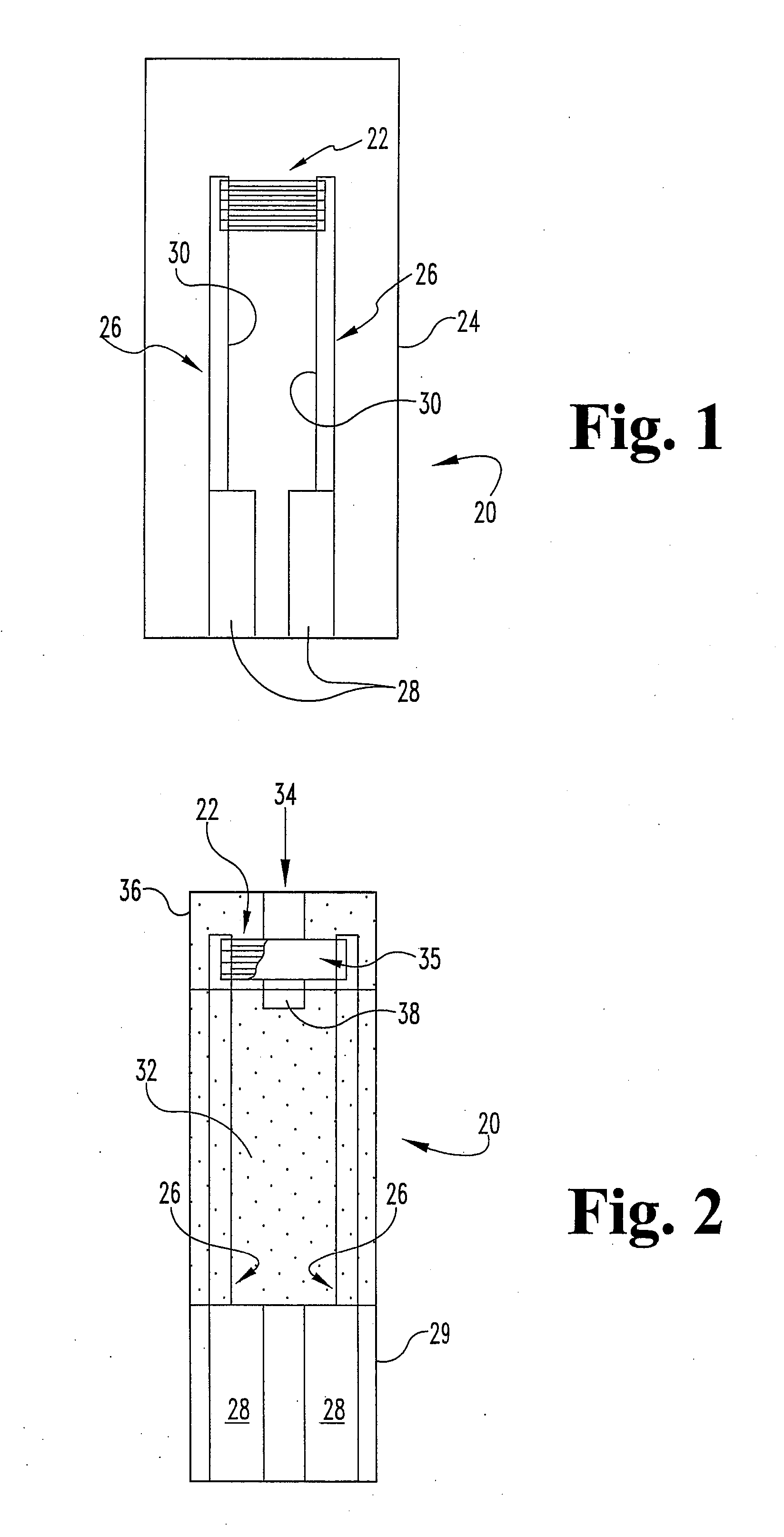
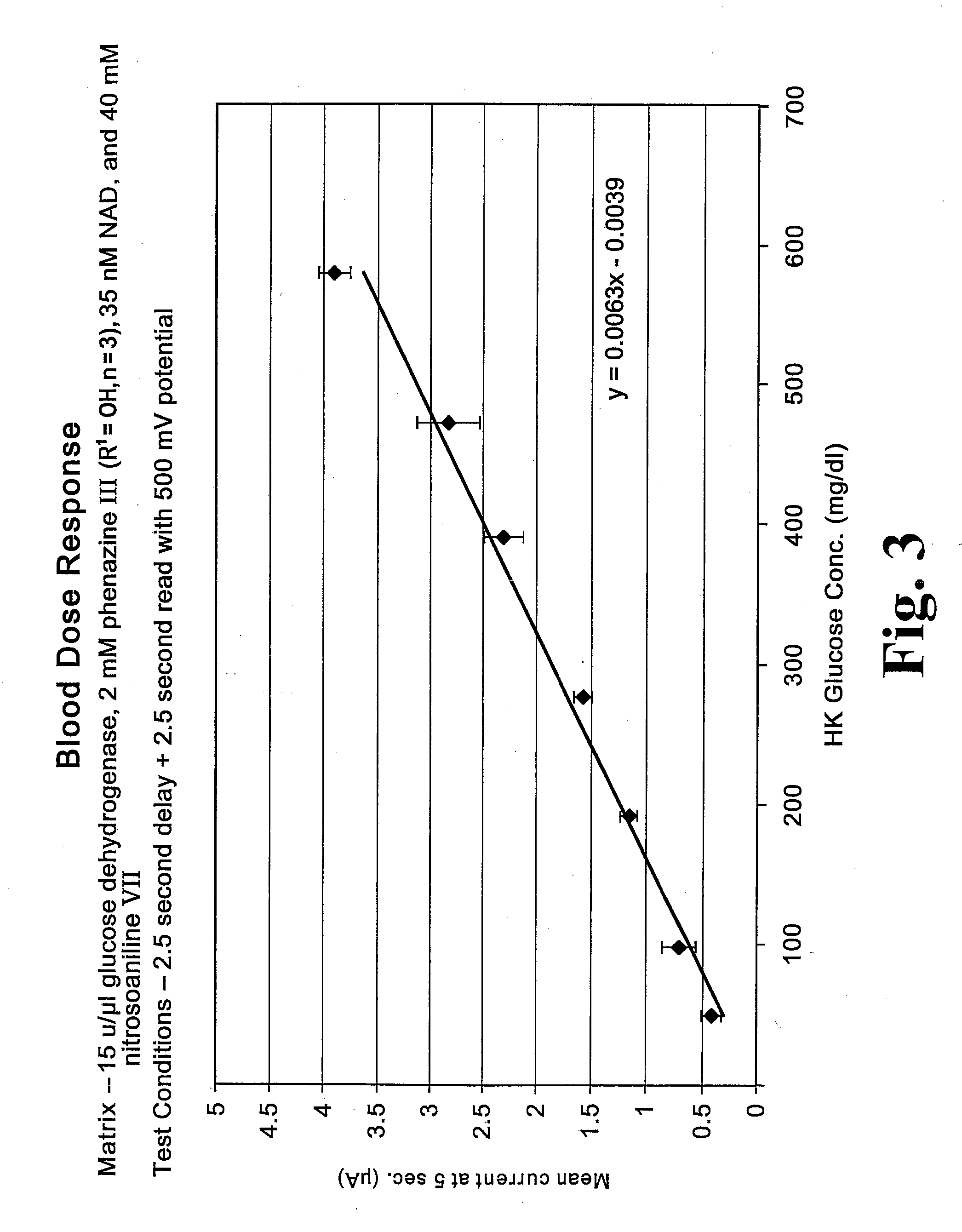
Biosensor with improved analyte specificity
ActiveUS20090246808A1Strong specificityInterference minimizationOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrochemical biosensorAnalyte
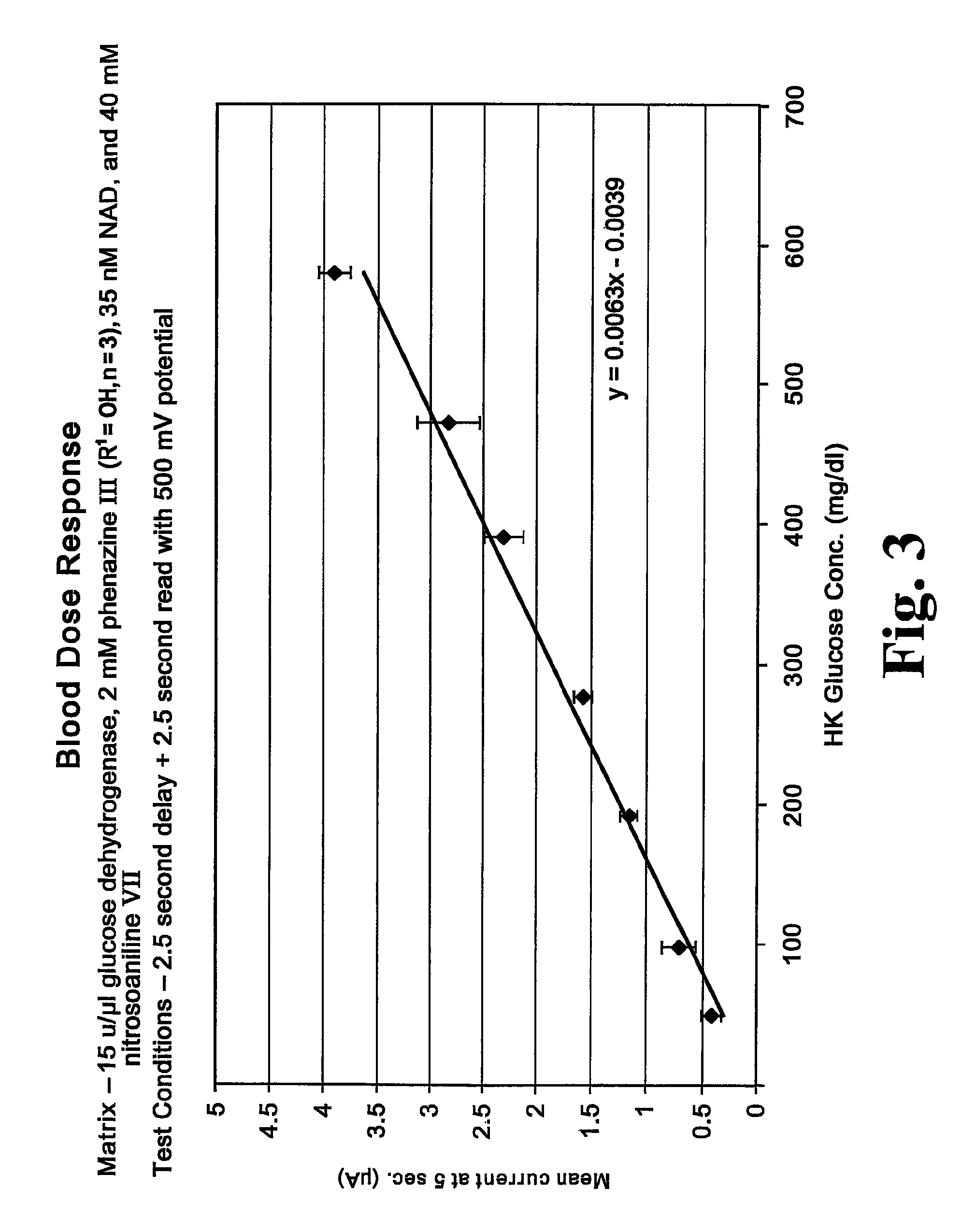
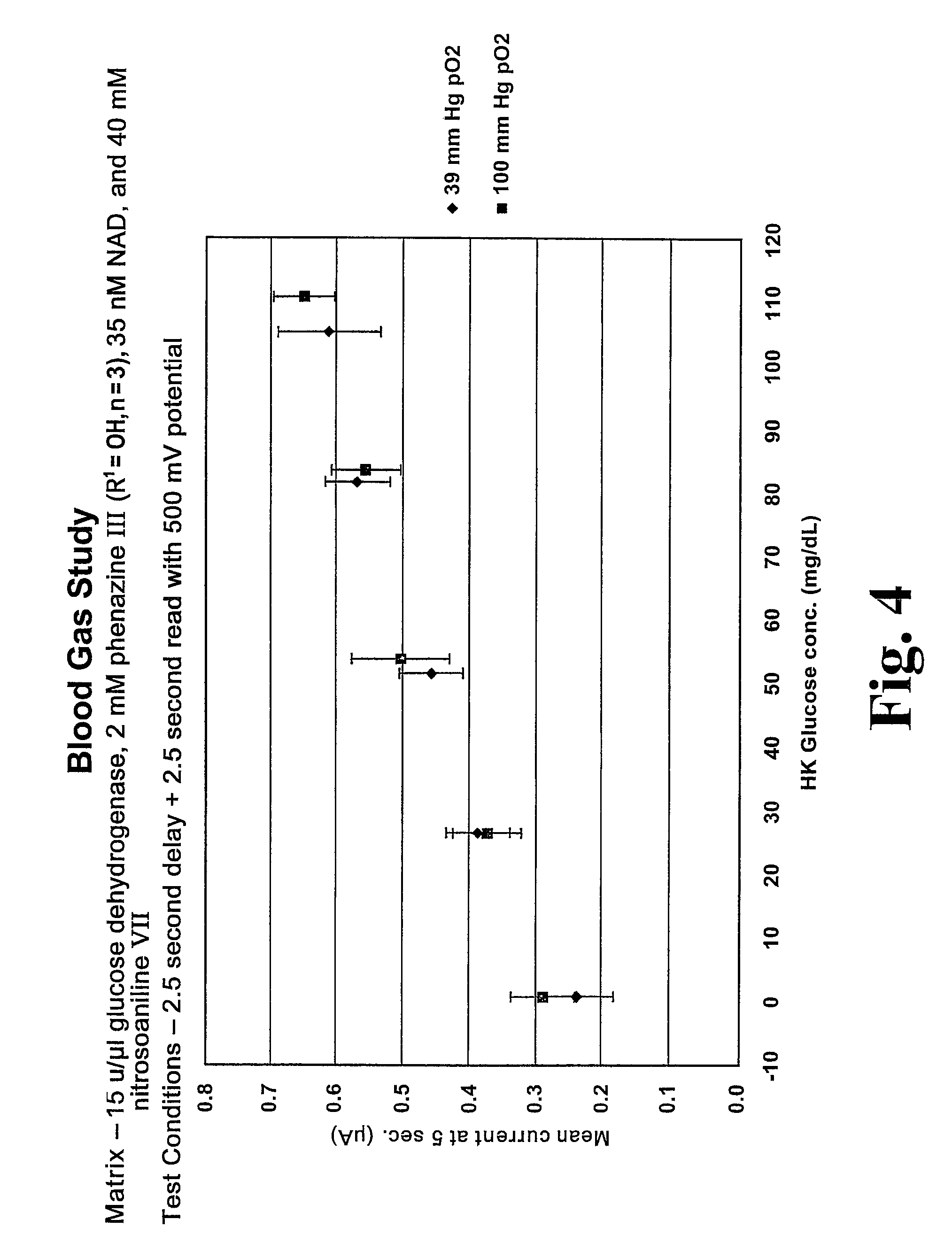
A chemistry matrix for use in determining the concentration of an analyte in a biological fluid includes a glucose dehydrogenase, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, an alkylphenazine quaternary salt, and / or a nitrosoaniline. The chemistry matrix is used with an electrochemical biosensor to determine the concentration of an analyte after a reaction occurs within the biosensor, at which time an analysis is completed to determine the concentration. A method of determining the concentration of an analyte using the chemistry matrix of glucose dehydrogenase, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, an alkylphenazine quaternary salt, and / or a nitrosoaniline is another aspect that is described. The method also further features test times of five seconds or less. Methods utilizing the new chemistry matrix can readily determine an analyte such as blood glucose at concentrations of from about 20-600 mg / dL at a pH of from about 6.5 to about 8.5.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
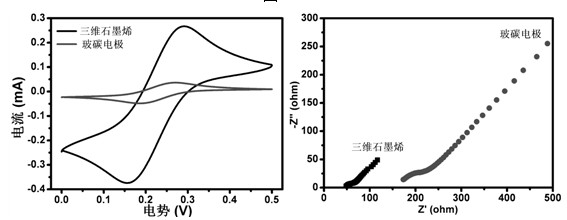
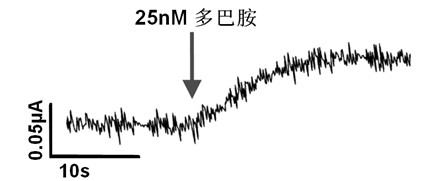
Preparation method and application of three-dimensional graphene electrode for electrochemical biosensor
InactiveCN102621208ASimple preparation processLow priceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrochemical biosensorFunctional modification
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a three-dimensional graphene electrode for an electrochemical biosensor. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: fixing spongy graphene in which industrially produced foam nickel is taken as a substrate and which has a three-dimensional structure and is synthesized through chemical vapor deposition on a glass or quartz sheet; connecting the spongy graphene with the three-dimensional structure and a wire by using a silver conductive adhesive; and coating organic silica gel on a connection point of the metal wire and the graphene for insulation to obtain a spongy graphene electrochemical electrode with the three-dimensional structure. The three-dimensional spongy graphene electrode has the outstanding characteristics of high conductivity, high specific surface area, high electrochemical stability and the like, is easily subjected to surface functional modification, and has high detection sensitivity to dopamine and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; and a highly sensitive electrochemical biosensor for non-enzymatically and selectively detecting glucose can be obtained after the surface of the electrode is modified by Co3O4.
Owner:南京南工维明新材料科技有限公司
Method and test strips for the measurement of fat loss during weight loss programs
InactiveUS20040043376A1Great advantageEasy to manufactureMicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementPhysiologyAcyl CoA dehydrogenase
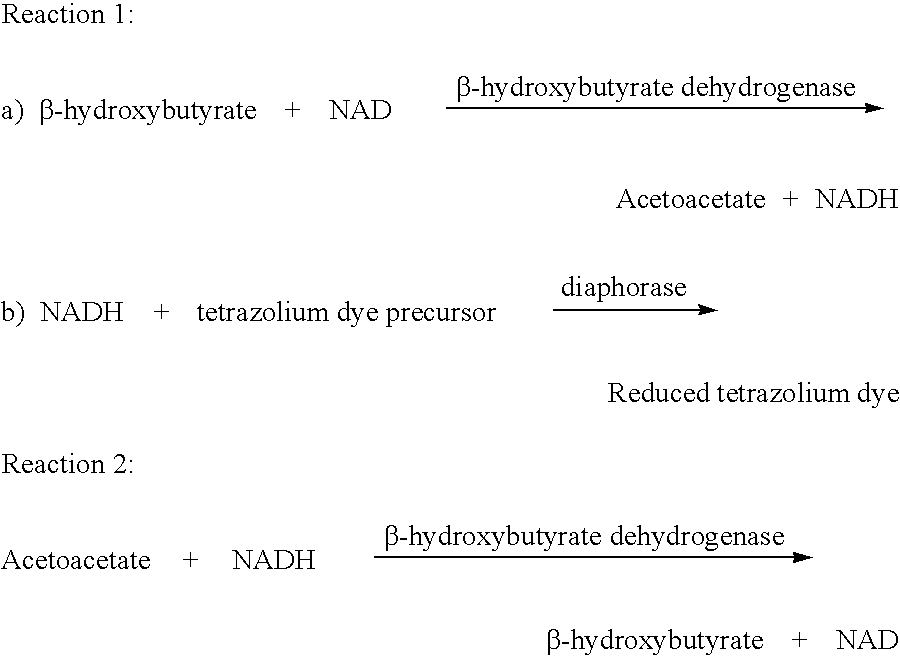
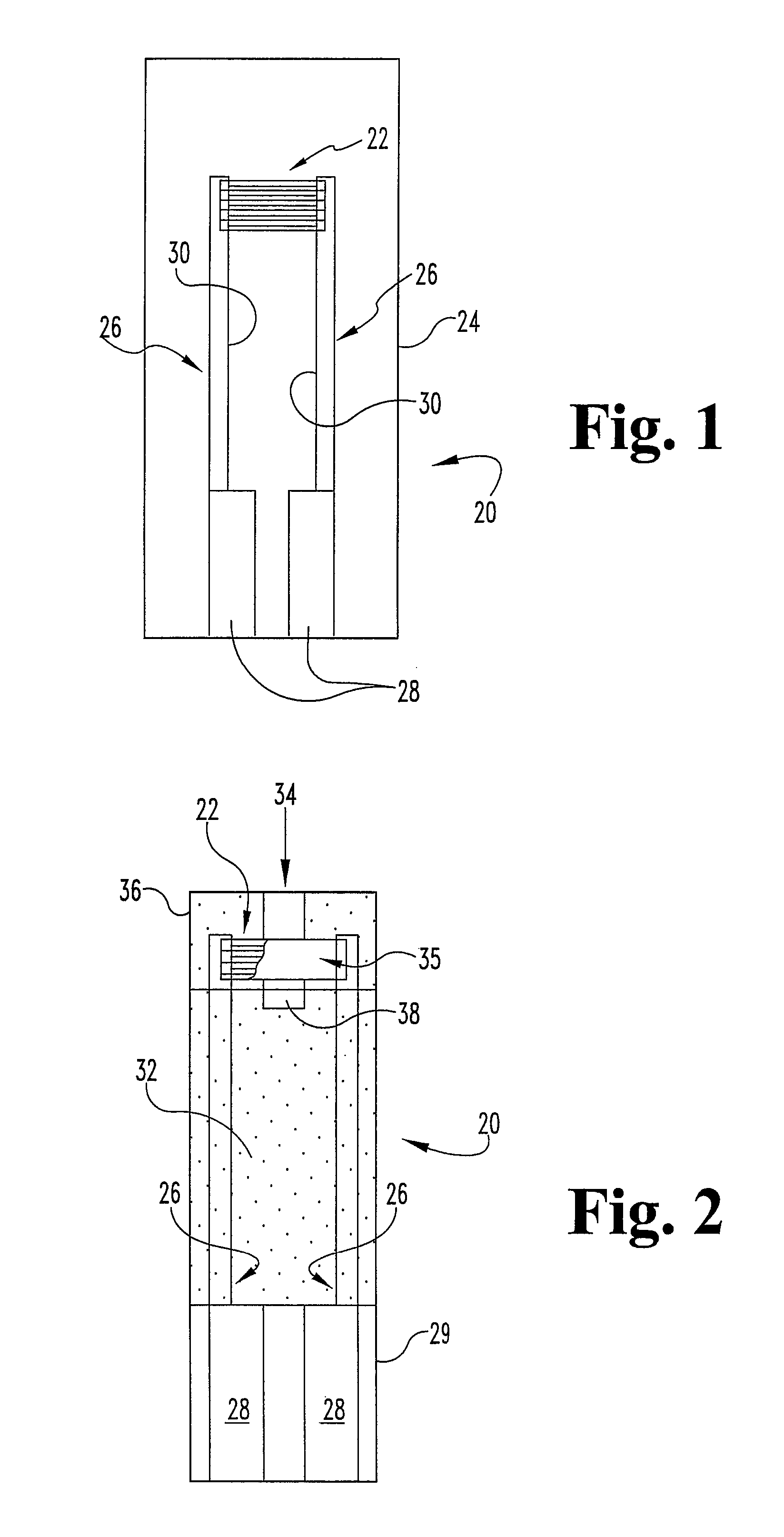
Disposable test strips and a wet chemistry method for measuring each of beta-hydroxybutyrate alone, combined beta-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate or total ketone bodies (i.e., beta-hydroxybutyrate, acetoacetate and acetone) in human bodily fluid samples, including but not limited to urine, saliva or sweat are described. The test strips need only be dipped in the sample and can be used by anyone in almost any milieu. Measurement can be made electrochemically, spectrophotometrically, fluorometrically or by comparision to a color standard. Combined acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate which account for 97-98% of total ketone bodies and may be measured in a cyclic reaction that occurs at pH about 7.0 to about 8.3 with beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, (beta-HBD), nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, a tetrazolium dye precursor and an electron mediator. Using this reaction, false positive results obtained from urine samples taken from patients on sulfhydryl drugs are avoided. beta-HBD from some sources was found to cause false negative results in samples (e.g. urine) containing high chloride content due to chloride inhibition of beta-HBD. Using a simple test for chloride inhibition, it was found that beta-HBD from Alcaligenes is not so inhibited. Using either beta-HBD that is not inhibited by chloride or using 10-20 times the normal concentration of this enzyme eliminates false negatives in samples having substantial chloride content, such as urine, both in the reaction described above and in other reactions disclosed for measuring each of beta-hydroxybutyrate alone, combined beta-hydroxybutyrate and acetoacetate and total ketone bodies, all of which reactions occur in the pH range of about 8.6 to about 9.5.
Owner:GUPTA SURENDRA
Matrix composition with alkylphenazine quaternary salt and a nitrosoaniline
ActiveUS8008037B2Strong specificityInterference minimizationOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrochemical biosensorAnalyte
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Application of alcohol dehydrogenase in catalytic generation of ethyl (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyrate
InactiveCN103160547AHigh yieldHigh optical activityMicroorganism based processesFermentationHydroxybutyric acidPtru catalyst
The invention discloses application of alcohol dehydrogenase with amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO:2 in preparing ethyl (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyrate from ethyl 4-chloroacetoacetate by asymmetric reduction. By using alcohol dehydrogenase with amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO:2 as a catalyst, ethyl 4-chloroacetoacetate as a substrate and NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) as a cofactor, asymmetric reduction is carried out to prepare the ethyl (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyrate. The invention applies the alcohol dehydrogenase with amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO:2 in preparing ethyl (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxy butyrate from ethyl 4-chloroacetoacetate by asymmetric reduction for the first time, and has favorable effect. The enzyme activity is up to 5.6 U / mg, the yield of the substrate is up to 94%, and the enantiomeric excess value of the product is 100%. The yield is high, and the production cost is greatly lowered.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
N-CQDs (nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots) with high fluorescence quantum yield as well as preparation method and application of N-CQDs
InactiveCN105802621AGood biocompatibilitySimple manufacturing methodFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsEthylenediamineQuantum yield
The invention discloses N-CQDs (nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots) with high fluorescence quantum yield and a preparation method of the N-CQDs. Alanine is taken as a carbon source, ethanediamine is taken as a surface passivator, and the N-doped carbon quantum dots with high fluorescence quantum yield is successfully prepared with a simple one-step hydrothermal method. Compared with carbon quantum dots synthesized with other protein or amino acid as a carbon source, the nitrogen content of the prepared N-CQDs can reach 61.1%, the average fluorescence lifetime is 4.43 ns, the highest fluorescence quantum yield can reach 46.2% and approaches the fluorescence quantum yield of the carbon quantum dots prepared with a laser ablation method and an electric arc method, and the N-doped carbon quantum dots have low cytotoxicity and excellent biocompatibility and has wide application value in biosensing and bioimaging. The invention further discloses a high quenching effect of NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) on fluorescence of the N-CQDs. On the basis that NADH has high quenching effect on fluorescence of the N-CQDs, high-sensitivity fluorescence biosensing for detecting NADH is established, the linear detection range is as low as 80 mu M, and the limit of detection is 25.1 nM.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Processes for regulating blood glucose in a mammal and novel polypeptides useful in NAD biosynthesis
ActiveUS20070082373A1Increase blood sugar concentrationDecrease blood glucose concentrationBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementMammalD-Glucose
The present invention relates to processes for regulating the blood glucose concentration of a mammal. A polypeptide useful in nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) biosynthesis is also described.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
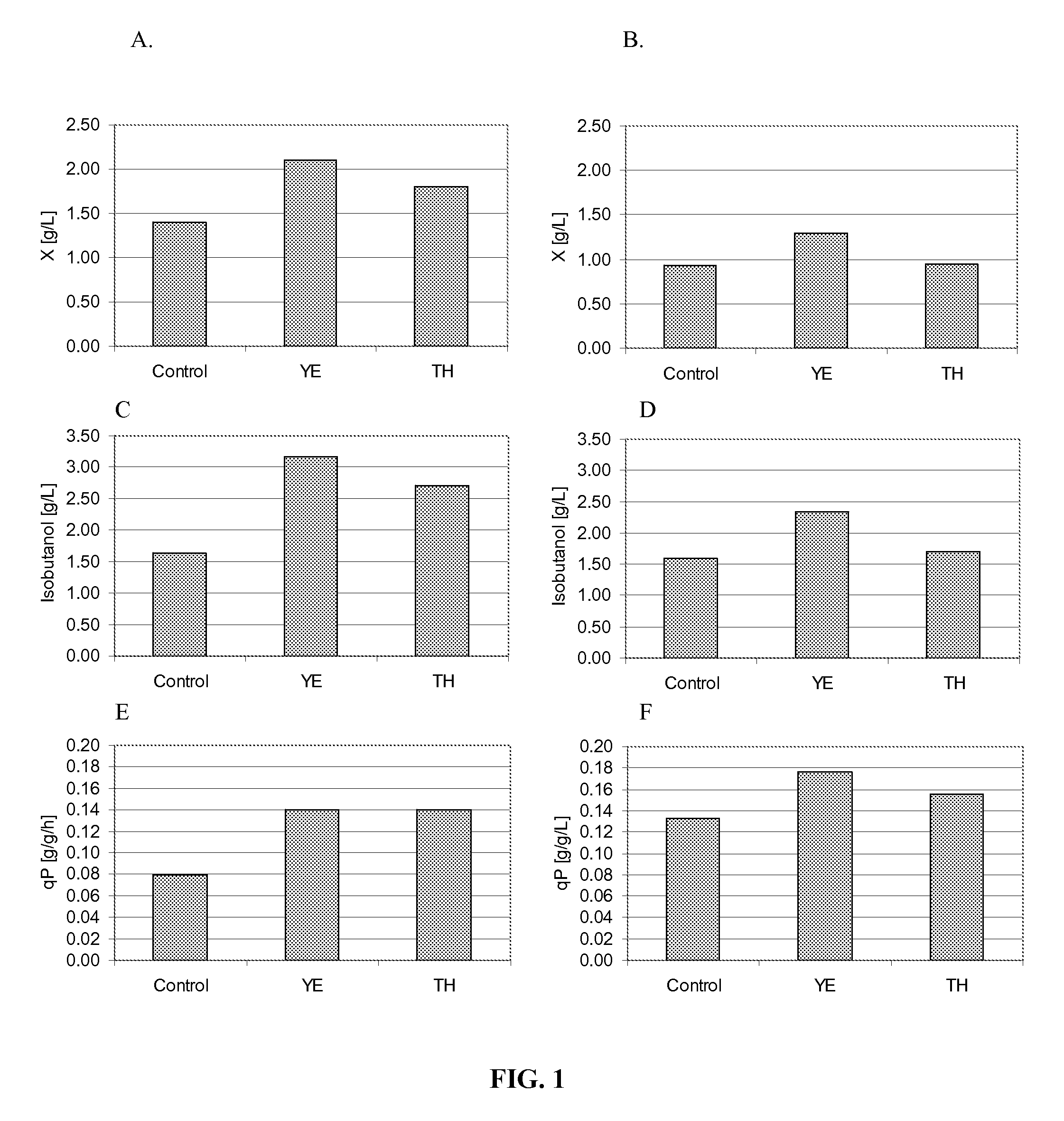
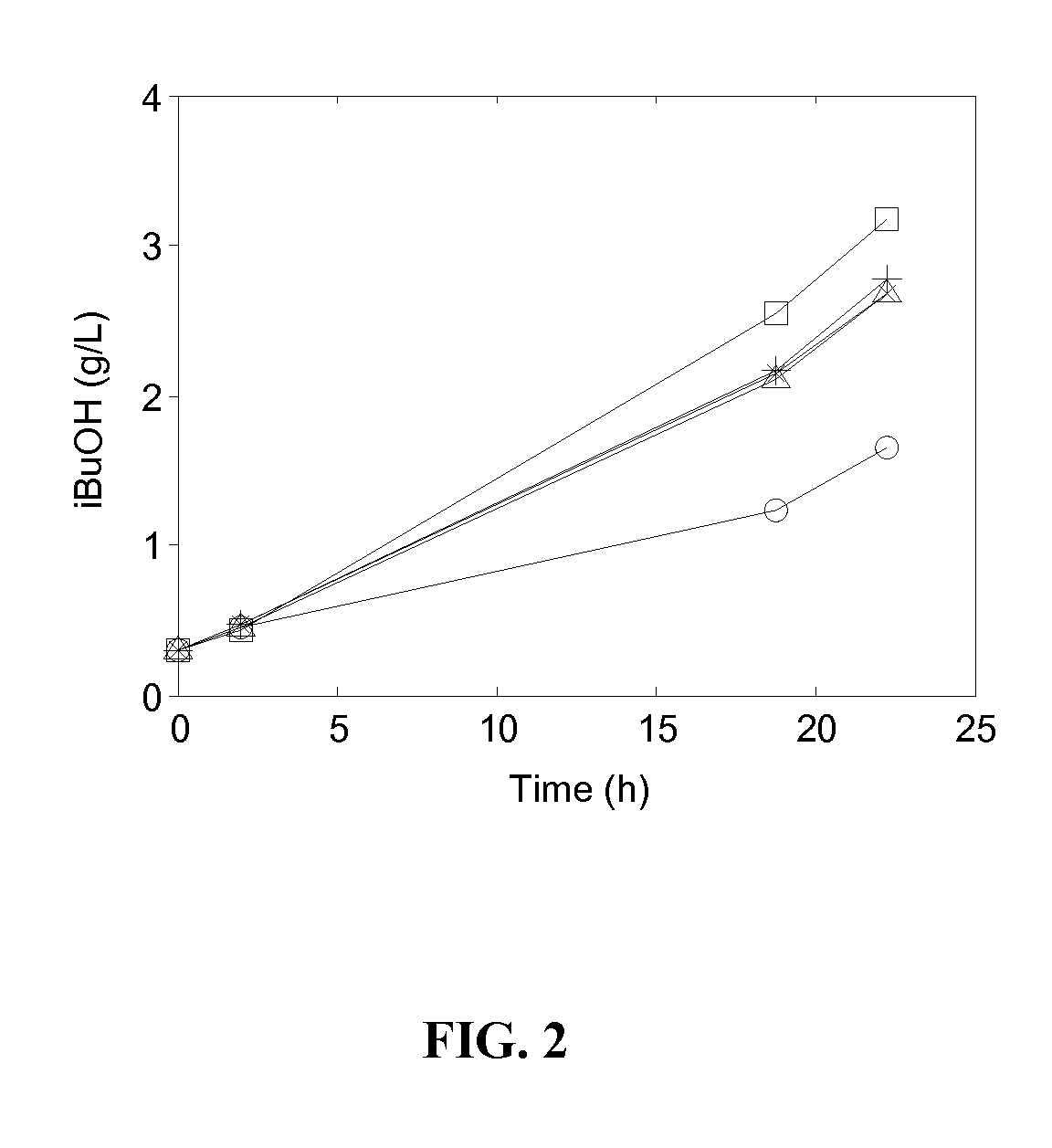
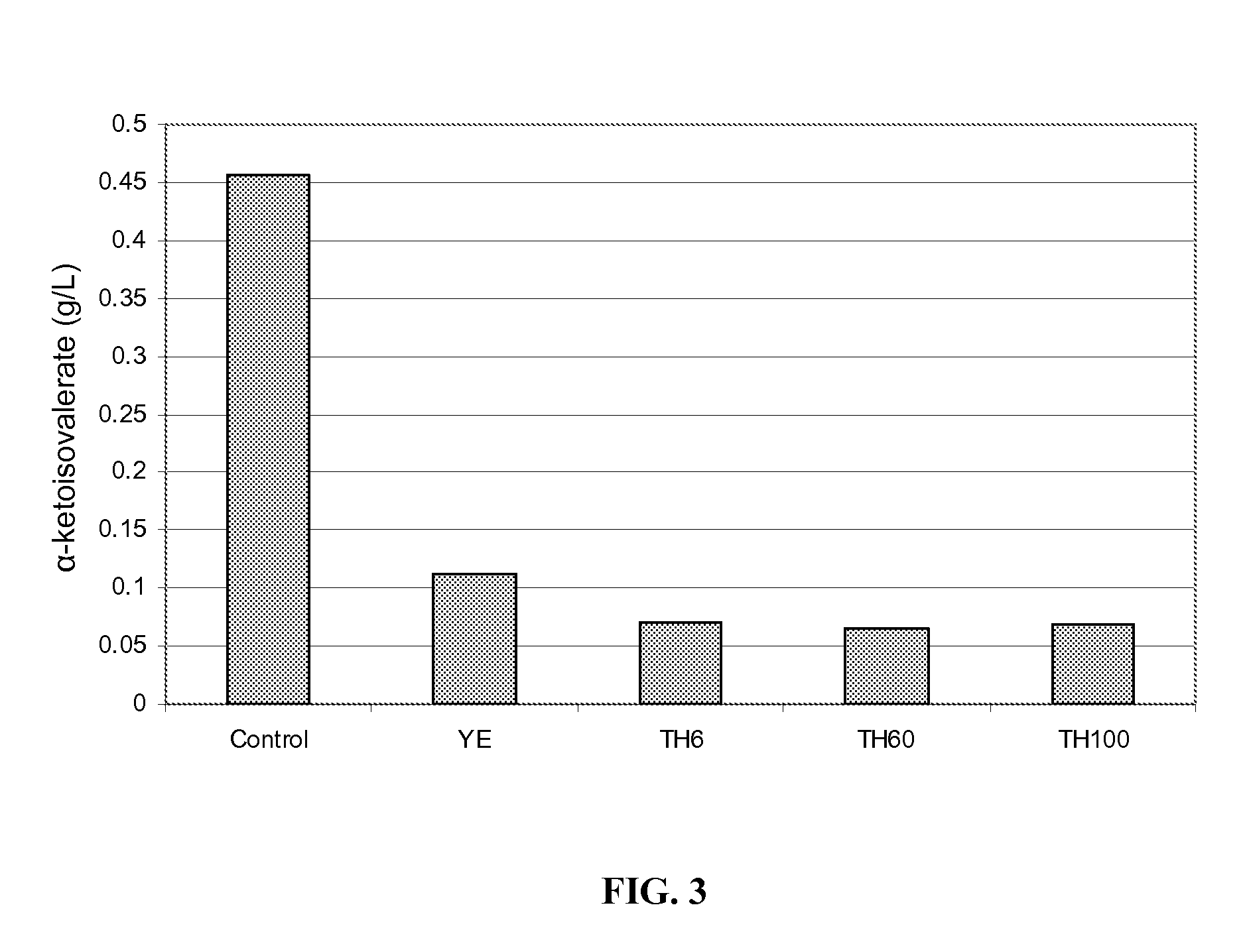
Use of thiamine and nicotine adenine dinucleotide for butanol production
The invention relates generally to the field of industrial microbiology and alcohol production. More specifically, the invention relates to the use of thiamine, biosynthetic precursors of thiamine, nicotinic acid, nicotinamid, nicotinic acid riboside, nicotinamid riboside, or other biosynthetic precursors of nicotine adenine dinucleotide (NAD) to improve butanol production. Butanol production can be improved by providing sufficient amounts of thiamine, biosynthetic precursors of thiamine, nicotinic acid, nicotinamid, nicotinic acid riboside, nicotinamid riboside, or other biosynthetic precursors of nicotine adenine dinucleotide (NAD) in the production media.
Owner:GEVO INC
Recombinant human NADH (nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide) dehydrogenase subunit-4 gene and constructing method of expression vector thereof
Owner:WUHAN NEUROPHTH BIOTECHNOLOGY LTD CO
Reducibility coenzyme composite stabilizer
InactiveCN101140279AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingInorganic saltsOrganic solvent
The present invention provides a reductive coenzyme composite stabilizing agent, which comprises buffering agent, stabilizing agent, organic solvent, chelator, anticorrosive agent and inorganic salt. The present invention has quite high stability for reductive nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) and reductive Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide 2'-phosphate reduced tetrasodium salt (NADPH).
Owner:SHANGHAI FOSUN PHARMA (GROUP) CO LTD +1
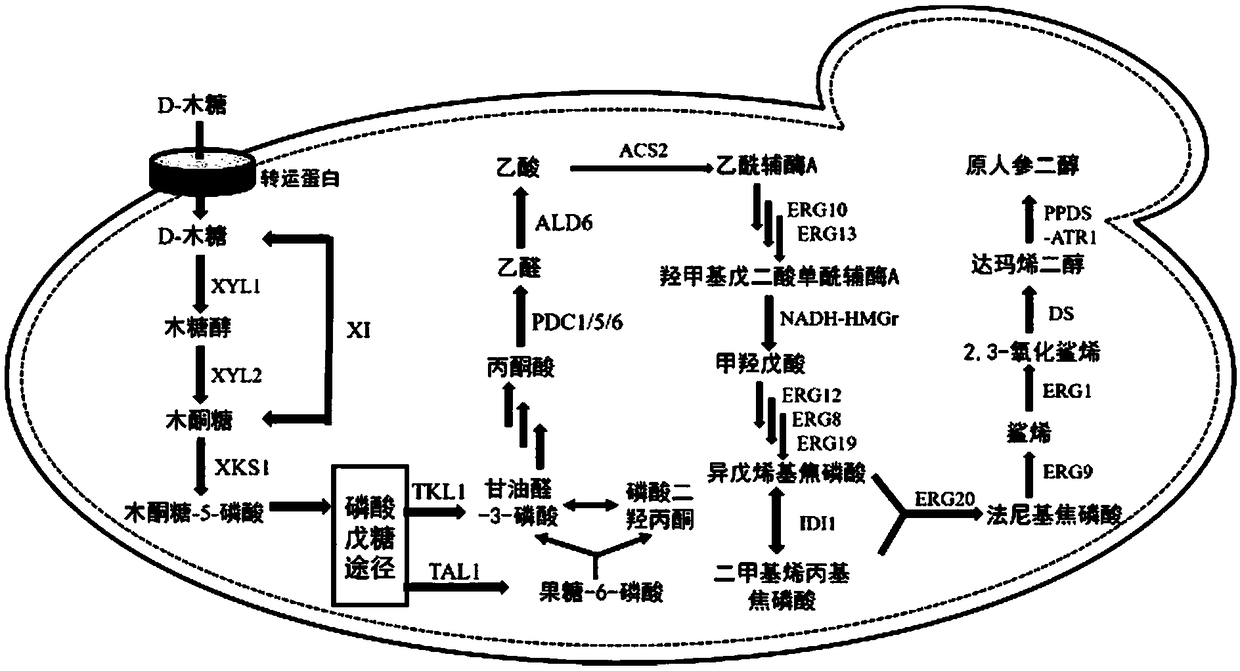
Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing dammarenediol and protopanoxadiol using xylose and construction method
The invention discloses recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing dammarenediol and protopanoxadiol using xylose and a construction method. The construction method comprises the steps of replacing a promoter of a saccharomyces cerevisiae xylulokinase gene XKS1 with a promoter PFBA1 by virtue of a homologous recombination method, introducing xylose reductase XYL1 and a xylitol dehydrogenase XYL2 expression cassette, increasing the activities of transketolase TKL1 and transaldolase TAL1 so as to obtain recombinant bacteria 1, introducing a farnesyl-diphosphate farnesyltransferase gene ERG9, a squalene monooxygenase gene ERG1 and a dammarenediol synthase gene DS into the recombinant bacteria 1 so as to obtain recombinant bacteria 2, and introducing a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene NADH-HMGr, farnesyl diphosphatesynthase ERG20 and a protopanoxadiol synthase-cytochrome P450 reductase fusion protein gene PPDS-ATR1 into the recombinant bacteria 2, so as to obtain recombinant bacteria 3. According to the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae, dammarenediol and protopanoxadiol can be artificially synthesized by virtue of xylose.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for purifying oxidized beta-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
ActiveCN104876993AIncrease productivityReduce manufacturing costSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationFreeze-dryingPhosphoric acid
Owner:BONTAC BIO ENG SHENZHEN
Method and kit for stably detecting sialic acid by enzyme method
The invention relates to a method and a kit for stably detecting sialic acid by an enzyme method. The method comprises the following steps of: generating N-acetylneuraminic acid from bound sialic acid under the catalysis of neuraminic acid aldolase; transforming the N-acetylneuraminic acid into N-acetylmannosamine under the catalysis of neuraminidase; reacting the product with mannosamine dehydrogenase and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) to generate reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH); and measuring the sialic acid content by detecting the amount of the generated NADH. The invention also relates to the kit prepared according to the method. The method and the kit are conveniently and quickly used, the sialic acid is not required to be redissolved by dissolving liquid, is stable for a long time and has small inter-bottle variation, the method and the kit are suitable for various biochemical analyzers, secondary pollution is avoided, and a production process method is simplified.
Owner:BEIJING STRONG BIOTECH INC
Preparation method of L-glufosinate-ammonium
The invention discloses a preparation method of L-glufosinate ammonium. The preparation method comprises the steps: in the presence of L-amino acid dehydrogenase, an inorganic amino donor and a reductive coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, 2-oxo-4-(hydroxymethoxyphosphonyl)butyrate is subjected to ammoniation reaction, and then the prepared L-glufosinate ammonium is subjected to acidification reaction; the L-amino acid dehydrogenase is L-amino acid dehydrogenase derived from bacillus stearophilus and / or L-amino acid dehydrogenase derived from intermediate high temperature actinomycetes. The preparation method of L-glufosinate-ammonium is simple to operate, does not use expensive reductive coenzyme NADPH, adopts a coenzyme NADH, reduces the cost of reaction and is beneficial to industrialized production.
Owner:SHANGHAI QIZHOU ZIYUE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Systems and methods for determining lesion depth by using fluorescence imaging
Systems, catheter and methods for treating Atrial Fibrillation (AF) are provided, which are configured to illuminate a heart tissue having a lesion site; obtain a mitochondrial nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide hydrogen (NADH) fluorescence intensity from the illuminated heart tissue along a first line across the lesion site; create a 2-dimensional (2D) map of the depth of the lesion site along the first line based on the NADH fluorescence intensity; and determine a depth of the lesion site at a selected point along the first line from the 2D map, wherein a lower NADH fluorescence intensity corresponds to a greater depth in the lesion site and a higher NADH fluorescence intensity corresponds to an unablated tissue. The process may be repeated to create a 3 dimensional map of the depth of the lesion.
Owner:GEORGE WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY +1
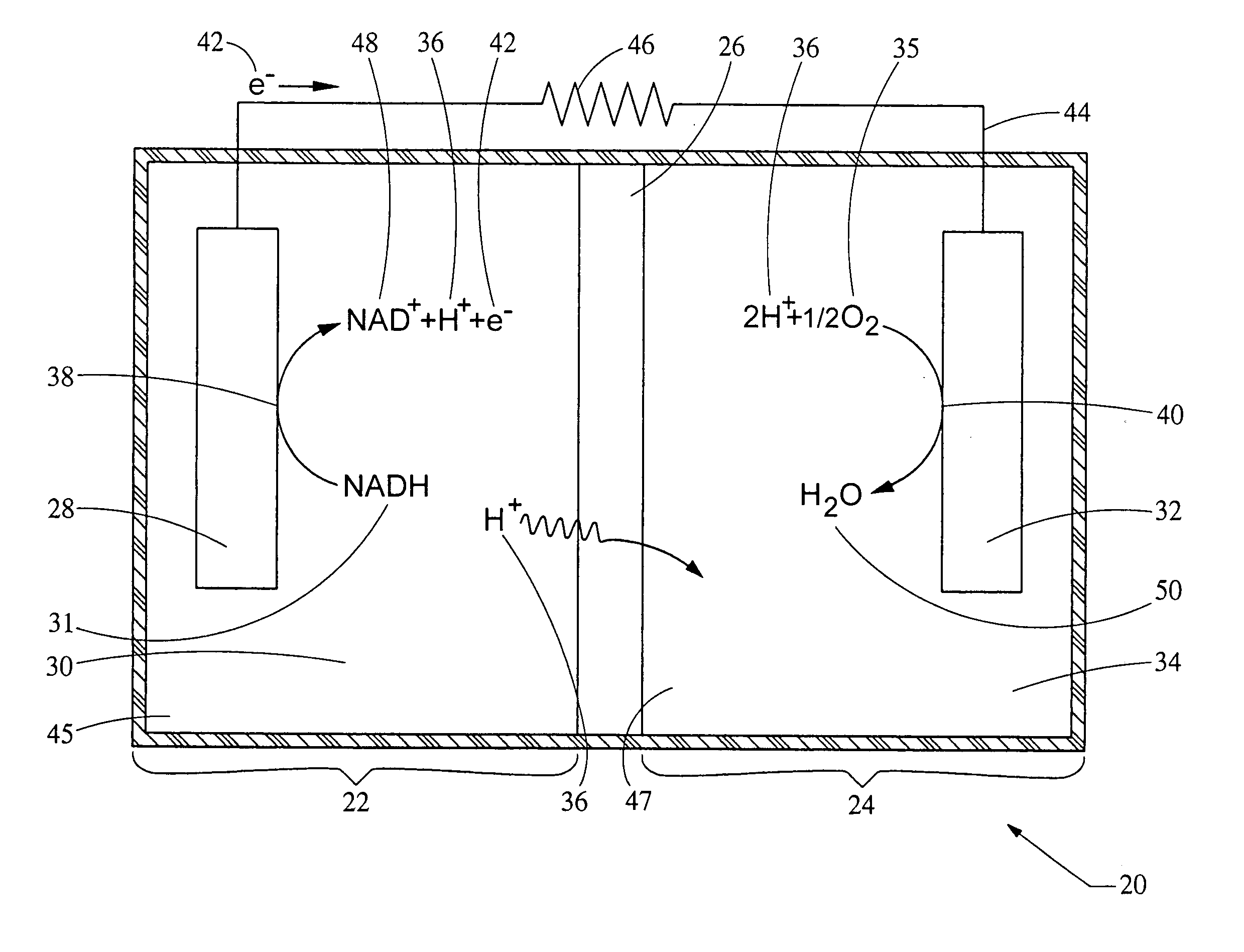
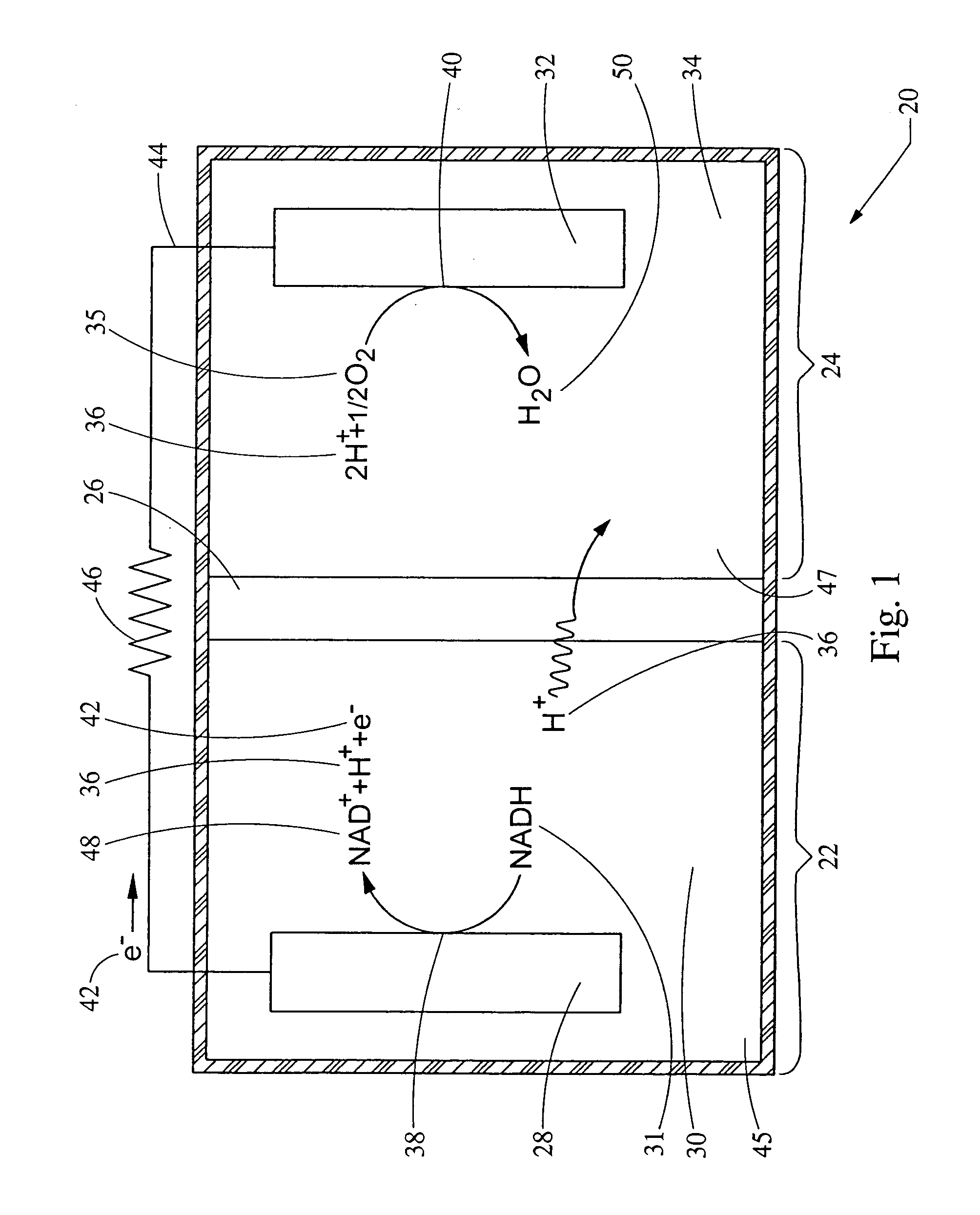
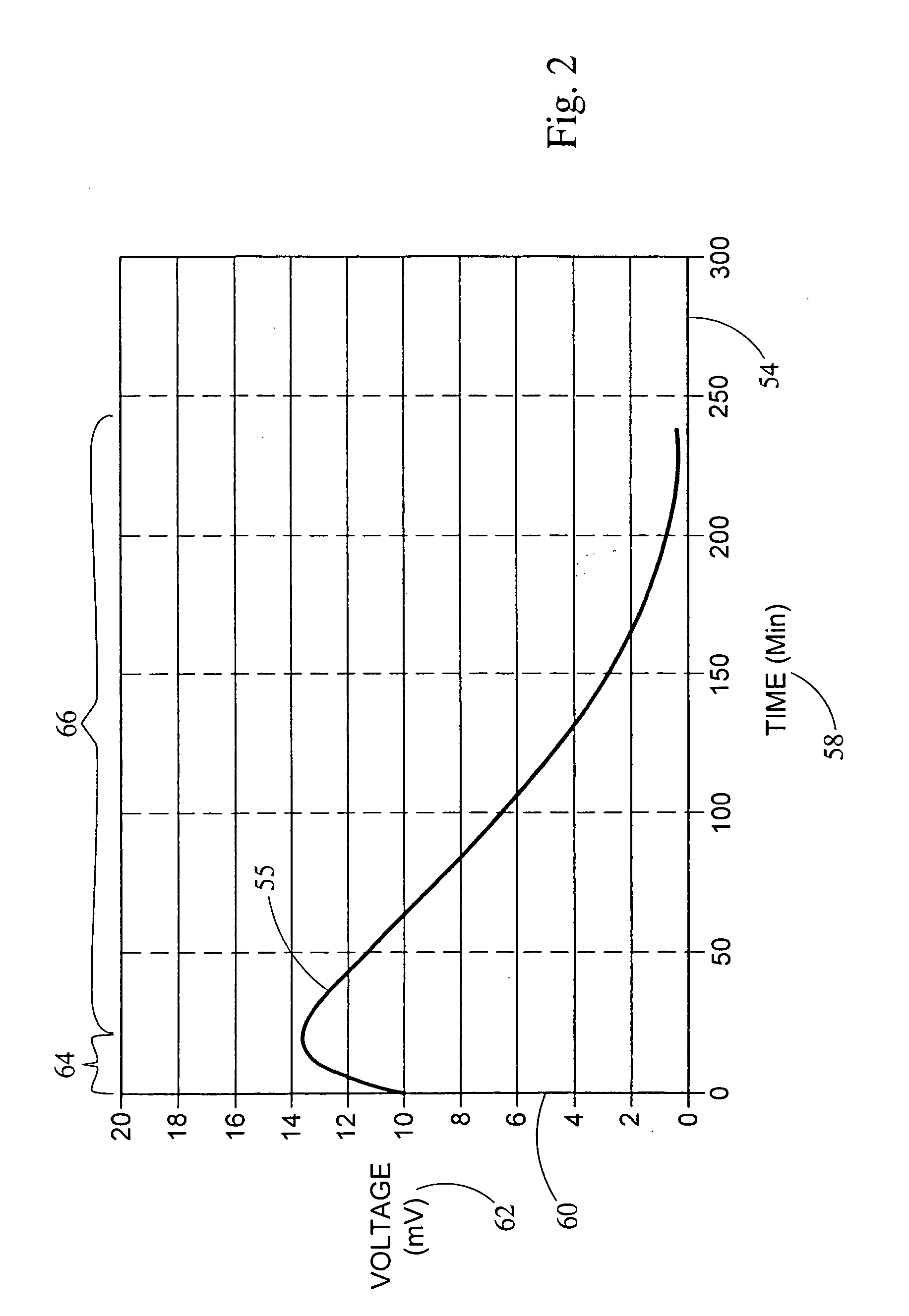
Bio-battery
InactiveUS20050287399A1Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsProtonMembrane configuration
A bio-battery includes a biomolecular energy source, a first electrode and a second electrode. In some configurations, a bio-battery may also include a first cell containing the first electrode and the biomolecular energy source, and a second cell having a reducible substrate and the second electrode. The first cell can be in ionic communication with the second cell, for example by a proton exchange membrane. Various biomolecular energy sources can be used, including proton donor molecules or electrolytically oxidizable molecules. For example, the biomolecular energy source can be selected from the group consisting of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NADH), Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate (NADPH) and 5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase (FADH).
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
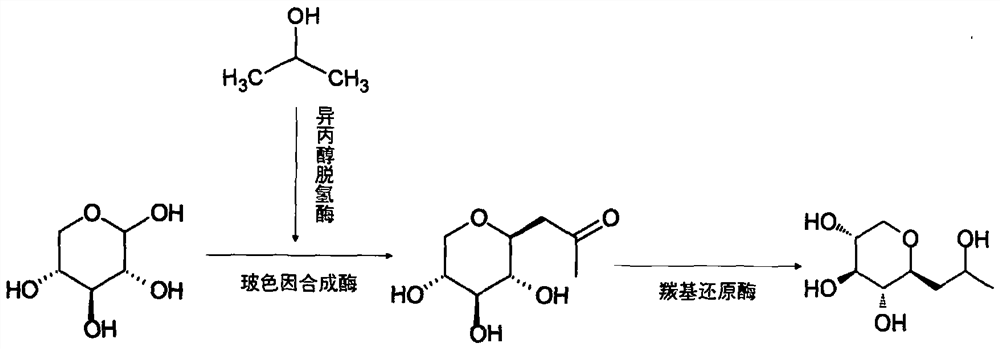
Method for preparing pro-xylane from biological enzyme by one-pot method
PendingCN111876452AThe method is simple, reliable and directLow costOxidoreductasesFermentationNiacinamideNucleotide
The invention discloses a method for preparing pro-xylane from a biological enzyme by a one-pot method. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of taking xylose and isopropanol as substrates, generating the pro-xylane under the catalytic action of isopropanol dehydrogenase, pro-xylane synzyme, carbonyl reductase and coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. The method is simple in process, free of chemical reagents, low in cost, high in yield and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:江苏瑞蓓丽生物科技有限公司
Method for purifying oxidized beta-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
ActiveCN104876994AHigh purityHigh yieldSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationFreeze-dryingGradient elution
The invention discloses a method for purifying oxidized beta-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, which comprises the following steps: carrying out microfiltration and nanofiltration on a reaction solution obtained by enzyme catalysis reaction by using filter membranes, and collecting the concentrated solution for later use; adding acid into the concentrated filtrate to regulate the pH value of the concentrated solution, and carrying out gradient elution purification by using an inversed phase chromatographic column as a stationary phase, a buffer salt solution as a phase A and ethanol as a phase B; and carrying out nanofiltration concentration on the purified solution through a filter membrane, and carrying out freeze-drying with a vacuum freeze drier. By using the inversed phase high performance liquid chromatography to purify the oxidized beta-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, the oxidized beta-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide has high purity and high yield, and achieves the industrialization requirements.
Owner:BONTAC INVITROLIFE BIO TECH SHENZHEN CO LTD
Preparation method of oxidation coenzyme I
ActiveCN102605026AMild reaction conditionsEfficient reaction conditions under mild conditionsFermentationRibonucleosideAdenosine
The invention relates to a preparation method of an oxidation coenzyme I. According to the method, nicotinamide ribonucleoside (NR) and adenosine disodium triphosphate (ATP-Na2) react with each other to obtain the oxidation coenzyme I (NAD+, Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide+) in a buffer solution with the pH of 5.0 to 8.0 at a temperature of 30 DEG C to 40 DEG C under the catalytic action of nicotinamide ribonucleoside kinase (NRK) under the condition of the existence of divalent metal ions. According to the invention, a biocatalysis method is adopted, the oxidation coenzyme is prepared by utilizing an NRK one pot process, the reaction system is simple, the conditions are mild, and the preparation method has wide industrialization application prospect.
Owner:ENZYMEWORKS
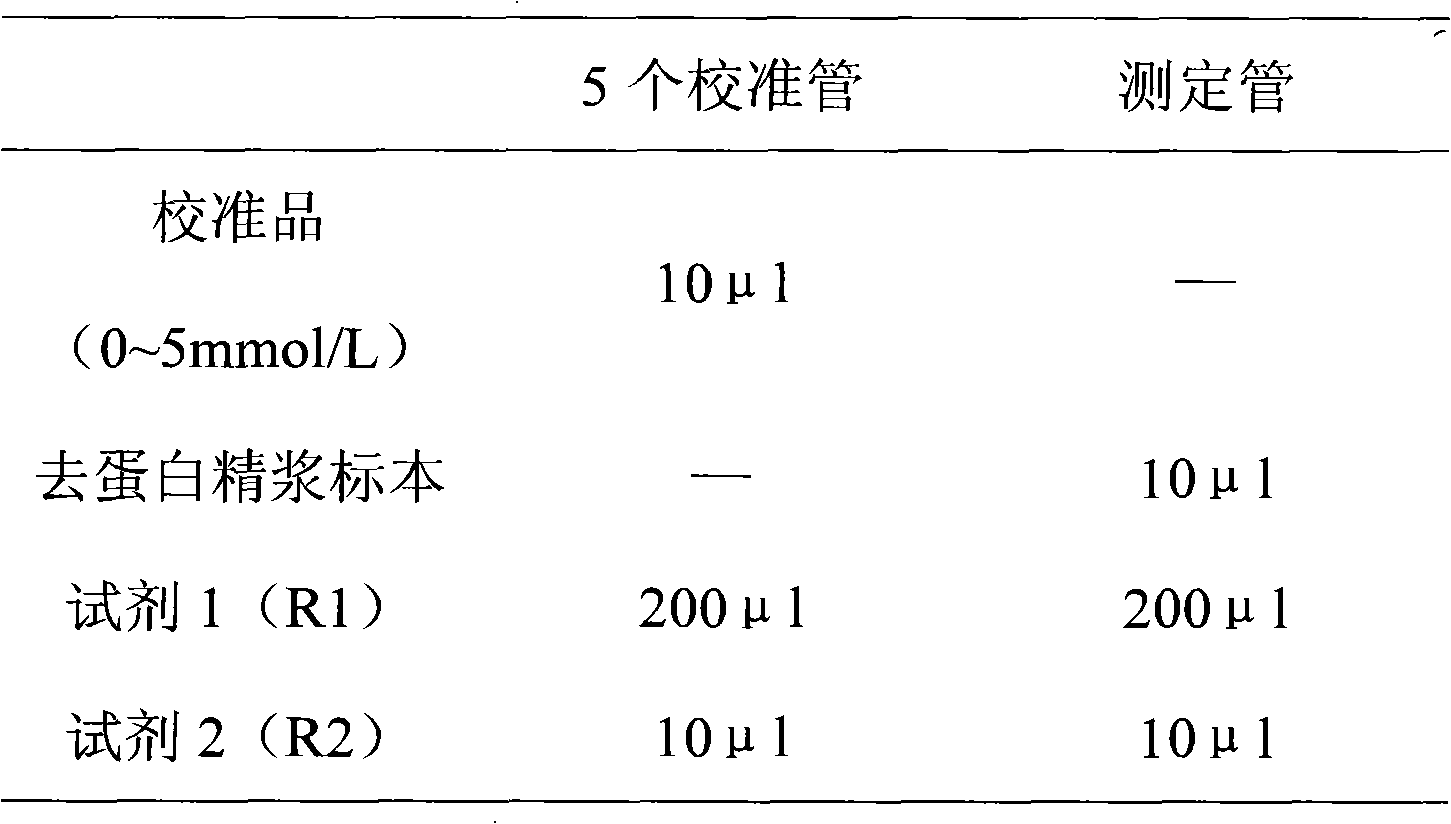
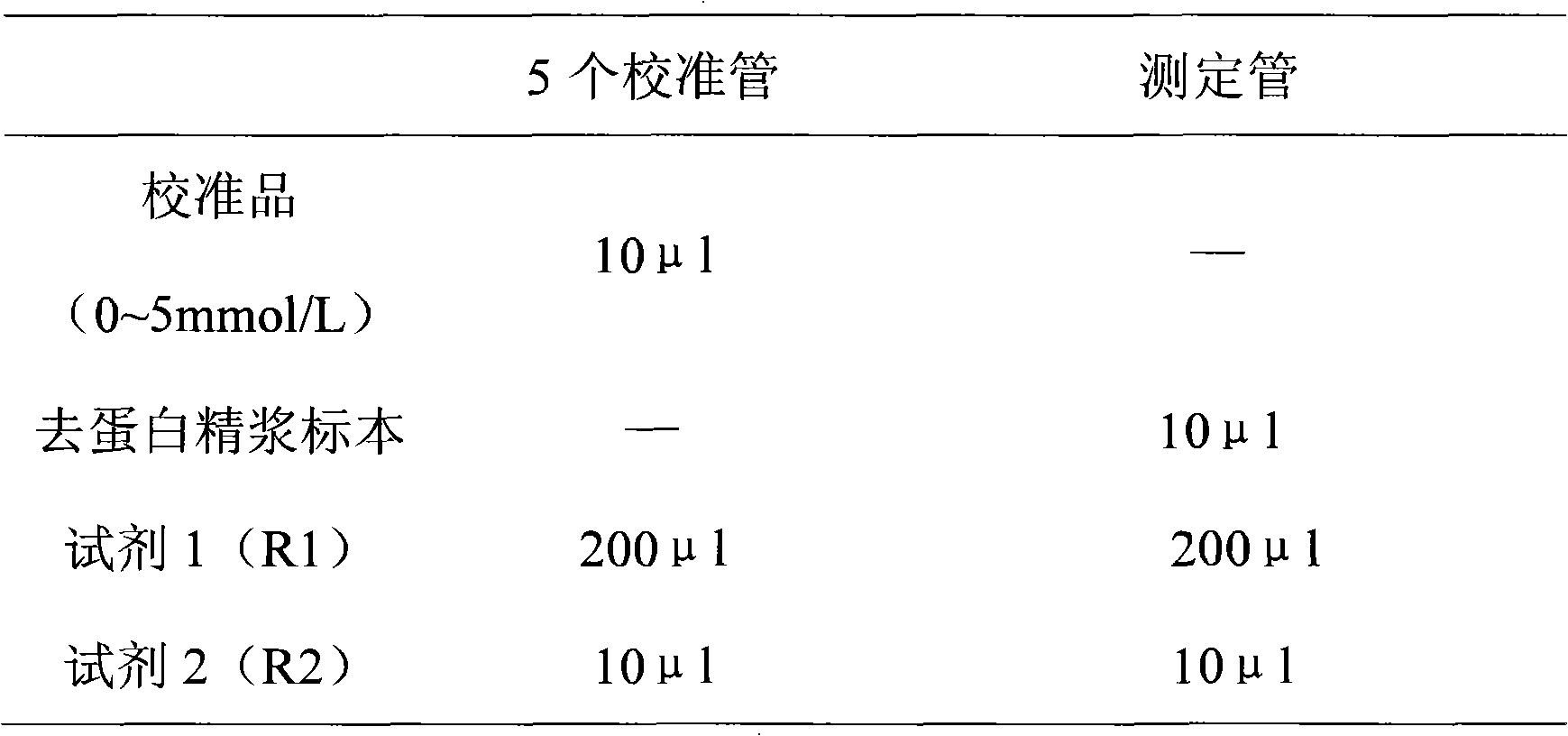
Quantitative fructose assay kit and application thereof as well as quantitative seminal plasma fructose assay method
InactiveCN102061332AEco-friendly formulaEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationPhosphateHexokinase
The invention discloses a quantitative fructose assay kit which comprises inorganic acid deproteinized extract A, inorganic base deproteinized extract B, fructose calibration solution, a reagent 1 containing 0.001-0.1mol / L adenosine triphosphate sodium salt, a reagent 2 containing 1-100KU / L hexokinase and 1-100KU / L glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, and a reagent 3 containing 0.001-0.1mol / L nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. The seminal plasma fructose assay method comprises the following steps: respectively adding the reagent 1 and the reagent 2 to deproteinized seminal plasma and the fructose calibration solution, and mixing uniformly; reacting at the temperature of 10-40 DEG C for 5-120 minutes, then reading the absorbance respectively at the wavelength of 280-400nm; adding the reagent 3 respectively, and mixing uniformly; reacting under the same conditions and reading the absorbance; and calculating the difference between the absorbance read at the first time and the absorbance read at the second time, and comparing or calculating the absorbance of a seminal plasma specimen and the fructose calibration solution to obtain the concentration of the seminal plasma fructose. The kit and the method can be used for quantitative determination of fructose in sera, plasma, body fluid, food and solid extracting solution, the methodology is special, unique, clean and environment-friendly, manual operation and automatic batch assay can be realized, and the kit and the method are easy to popularize and apply clinically.
Owner:BRED LIFE SCI TECH
Lactic dehydrogenase detection kit and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102766677AAvoid interferenceReduce distractionsMicrobiological testing/measurementPreservativeTurbidity
The invention discloses a lactic dehydrogenase detection kit and a preparation method of the kit. The kit disclosed by the invention consists of a reagent I and a reagent II which are independent each other, wherein the components of the reagent I comprise a biobuffer, a metal ion complex, a lactic dehydrogenase reactive substrate, a surfactant, a lactic dehydrogenase activity activating agent, a preservative and water; and the components of the reagent II comprise a biobuffer, a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide oxidation state, a surfactant, a preservative and water. The detection kit disclosed by the invention adopts a dual reagent mode to effectively avoid the interference of the nonspecific reaction and synchronously furthest reduce the interference of the sample turbidity, thereby guaranteeing the stable and reliable measurement result; and the detection kit has the advantages of good stability, high precision, wide linear testing range, good repeatability, and strong anti-interference performance and the like. In addition, the detection kit disclosed by the invention does not need to pre-dilute the sample in the detecting process, thereby being convenient for clinical use, simple and fast to operate, and suitable for an automatic biochemical analyzer.
Owner:WUHAN LIFE ORIGIN BIOTECH LTD
Process for preparing dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors and intermediates therefor
InactiveUS20050260712A1Procedure of process can be improvedReduce processing timeSugar derivativesBacteriaPhenylalanine dehydrogenaseDipeptidyl peptidase
A process for production of cyclopropyl-fused pyrrolidine-based inhibitors of dipeptidyl peptidase IV is provided which employs a BOC-protected amine of the structure prepared by subjecting an acid of the structure to reduce amination by treating the acid with ammonium formate, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, dithiothreitol and partially purified phenylalanine dehydrogenase / formate dehydrogenase enzyme concentrate (PDH / FDH) and without isolating treating the resulting amine of the structure 2 with di-tert-butyl dicarbonate to form the BOC-protected amine.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
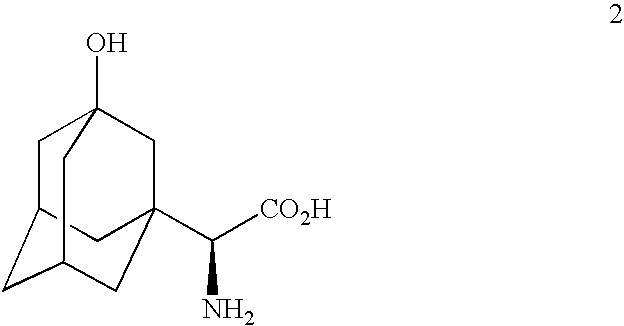
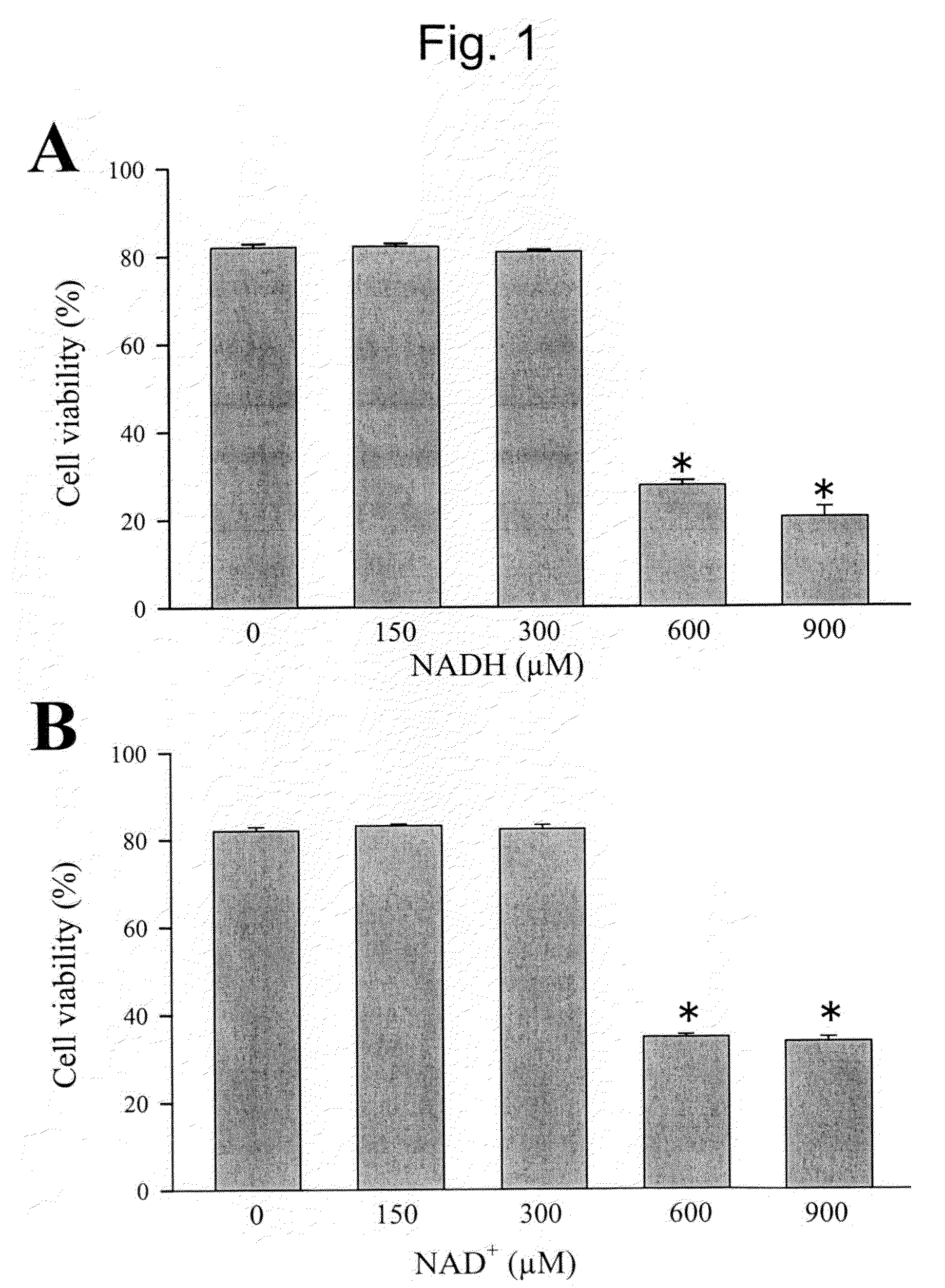
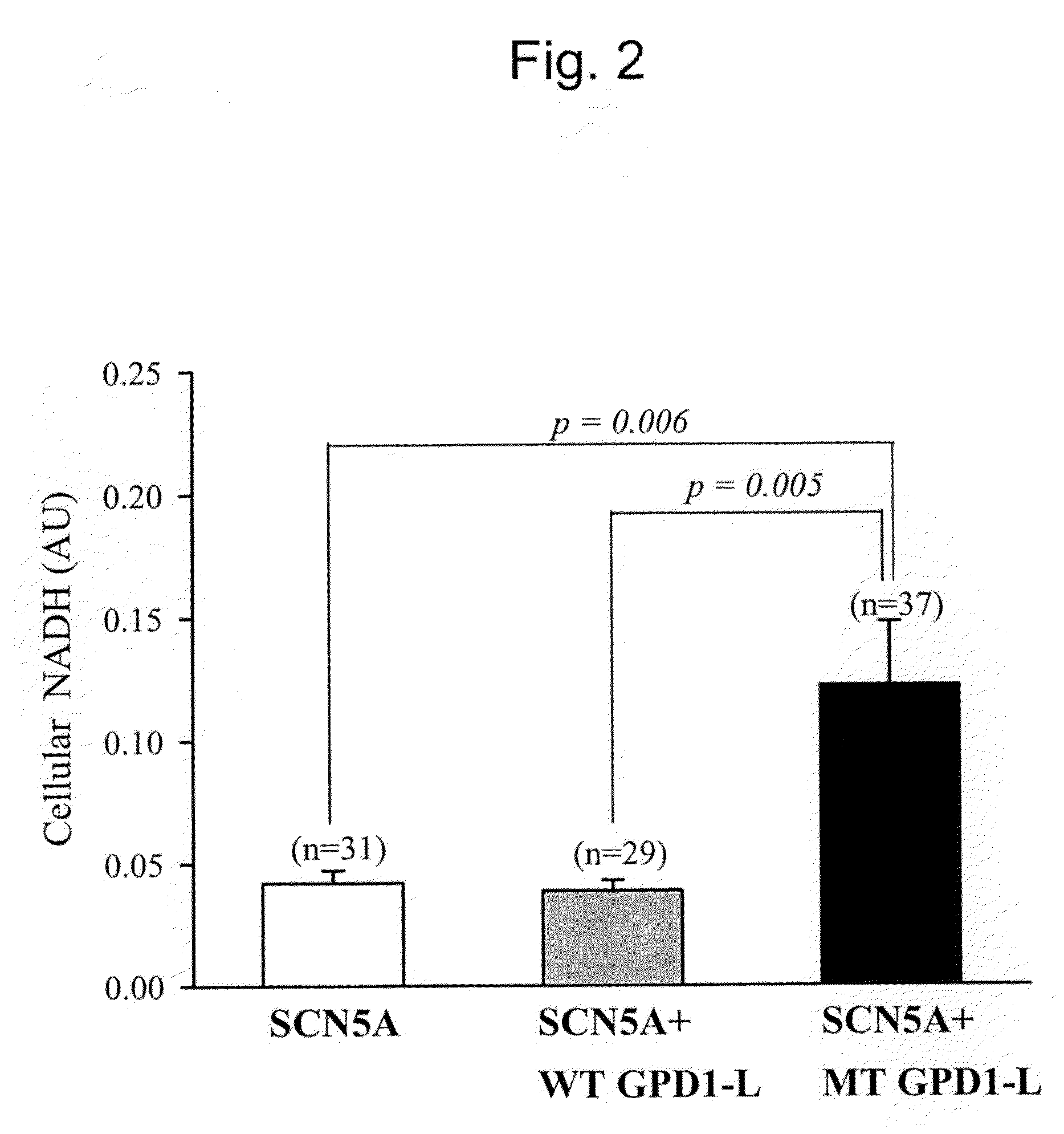
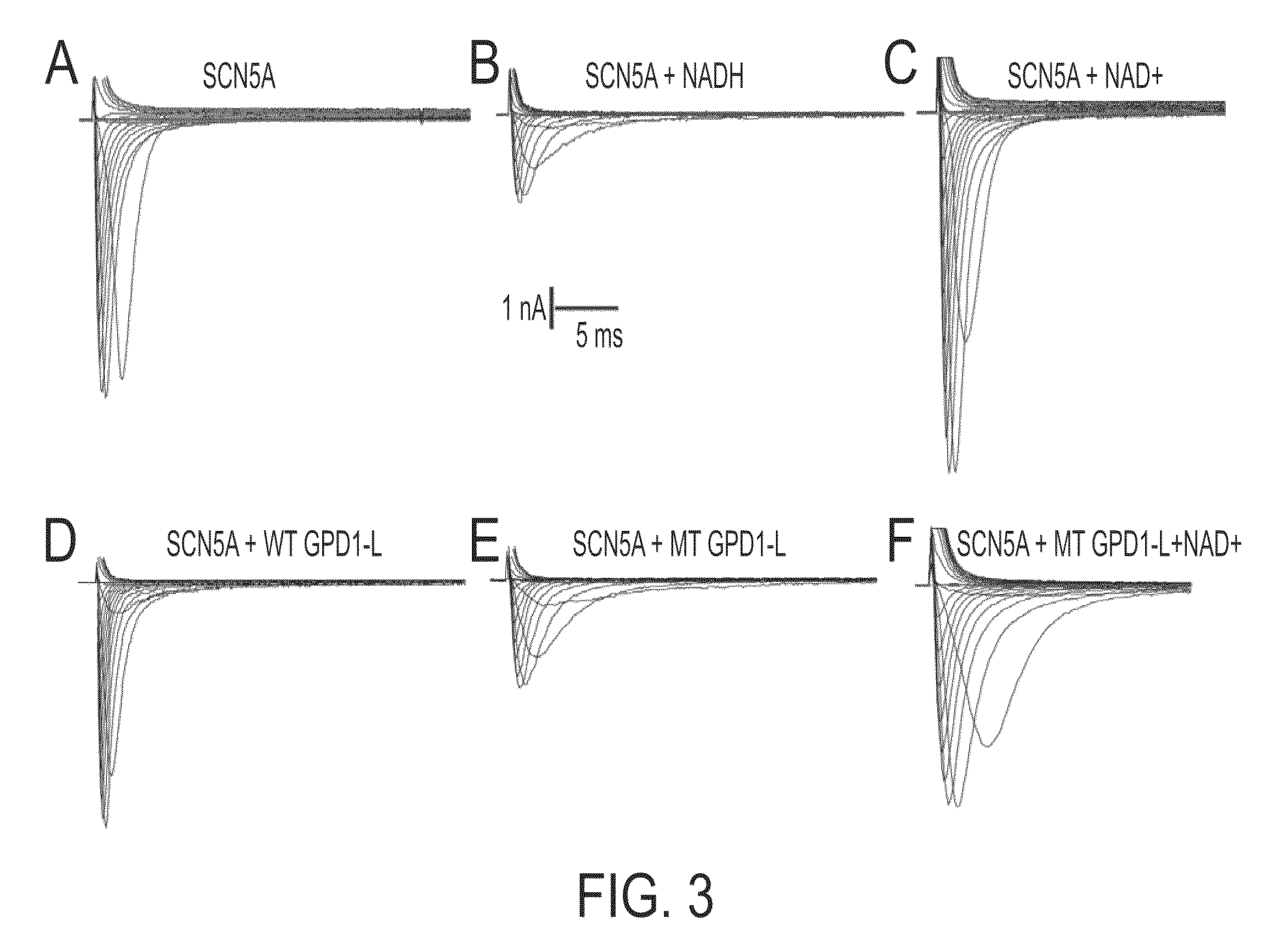
Modulation of sodium channels by nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
InactiveUS8003324B2Lower average currentIncrease currentBiocideSugar derivativesDecreased sodiumNicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
The present invention relates to the use of oxidized nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) or of its reduced form, NADH, as sodium channel modulators. The present invention also relates to the use of compositions containing NAD+ or NADH to treat conditions associated with sodium channel current, such as arrhythmia. NAD+ is found to increase sodium channel current, while NADH is found to decrease sodium channel current. Thus, conditions that are associated with decreased sodium channel current can be treated with NAD+, while conditions that is associated with increased sodium channel current can be treated with NADH.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS +1
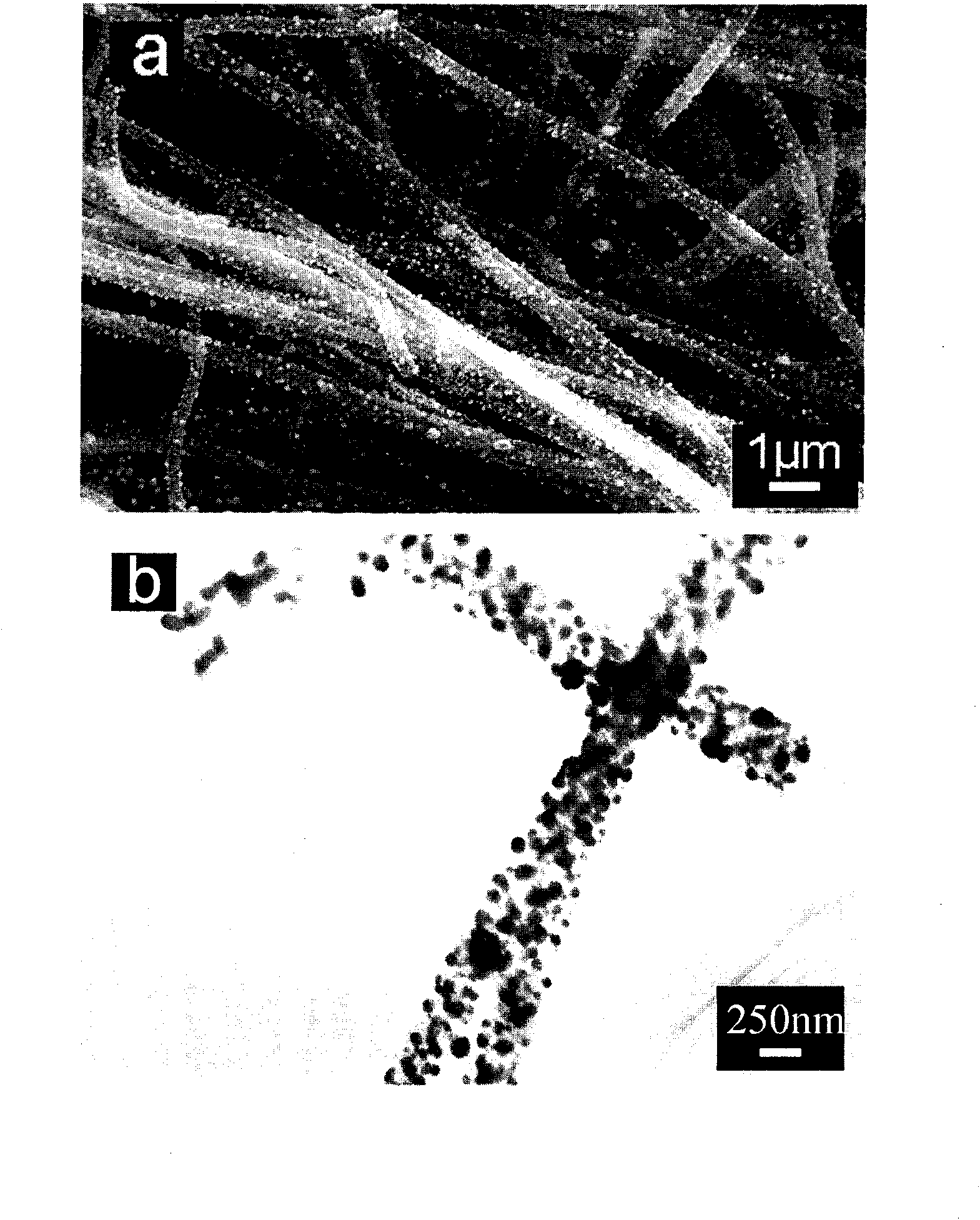
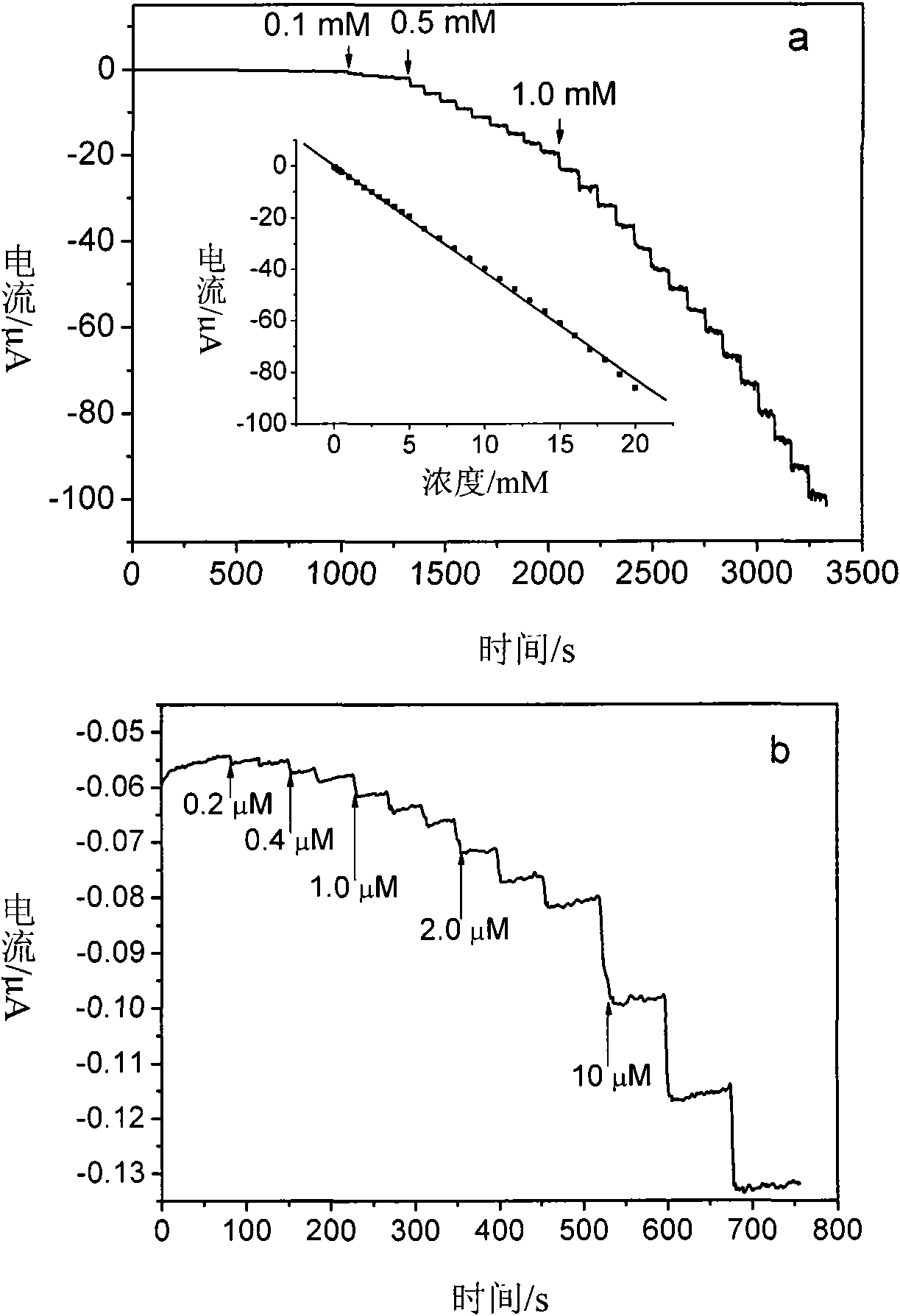
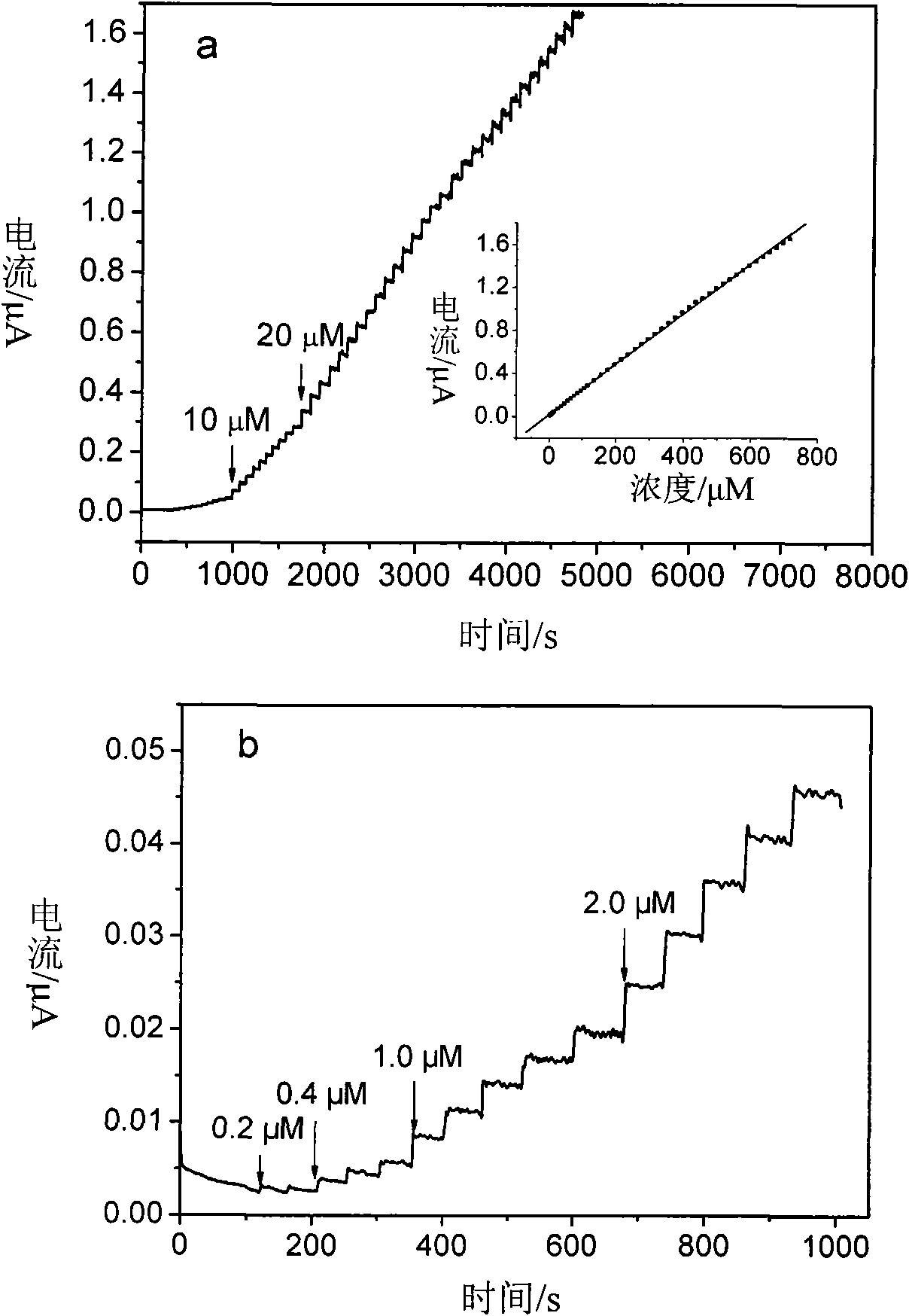
Palladium nanoparticle/carbon nanofiber compound, preparation method and application thereof in electrocatalysis
ActiveCN101665232AGood dispersionImprove stabilityIndividual molecule manipulationMaterial electrochemical variablesCarbon nanofiberPalladium nanoparticles
The invention relates to a palladium nanoparticle / carbon nanofiber compound, a preparation method and an application thereof in electrocatalysis. The compound is directly prepared by a one-step electrospinning method. An electrode modified by the compound is used for direct eectrochemical detection on hydrogen peroxide, beta-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, dopamine, ascorbic acid and lithic acid. The electrode modified by the compound has the linear range from 0.2 micrometer to 20 millimetres and the detection limit of 0.2 micrometer when being used for the detection on the hydrogen peroxide and has the linear range of 0.2-716.6 micrometers and the detection limit of 0.2 micrometer when being used for the detection on the beta- nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; and the peak-peak potential differences between the ascorbic acid and the dopamine, the dopamine and the lithic acid as well as the ascorbic acid and the lithic acid are respectively 244mV, 148 mV and 392 mV, thereby showingthat the modified electrode can be used for simultaneous eectrochemical detection of three substances. The compound can be used in the fields of catalysis, fuel cells and sensing.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
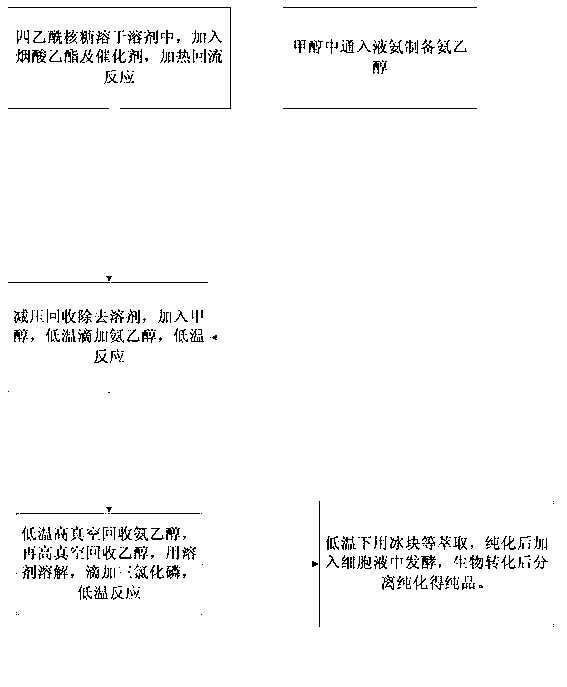
Chemical and biological synthesis method for large-scale preparation of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
ActiveCN103233051ALow costReduce the difficulty of productionFermentationSynthesis methodsEthyl ester
The invention relates to a chemical and biological synthesis method for large-scale preparation of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD). According to the invention, ribofuranose tetraacetate and ethyl nicotinate are adopted as initial raw materials, and the following steps are carried out that: (1) a refluxing reaction is carried out; (2) ammonia ethanol is dropped under a low temperature, such that a reaction is carried out; (3) phosphorus trichloride is dropped under a low temperature, such that a reaction is carried out; and (4) extraction, separation, and purification are carried out, and the material is added into cell fluid and is biologically converted into nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; and a pure product is obtained by purification and drying.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JIAHUA CHEM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com