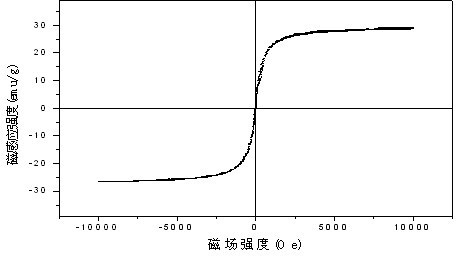
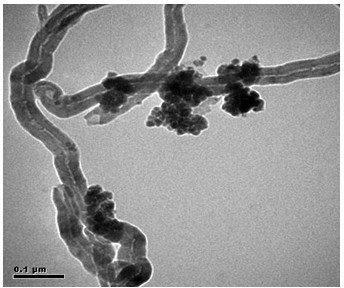
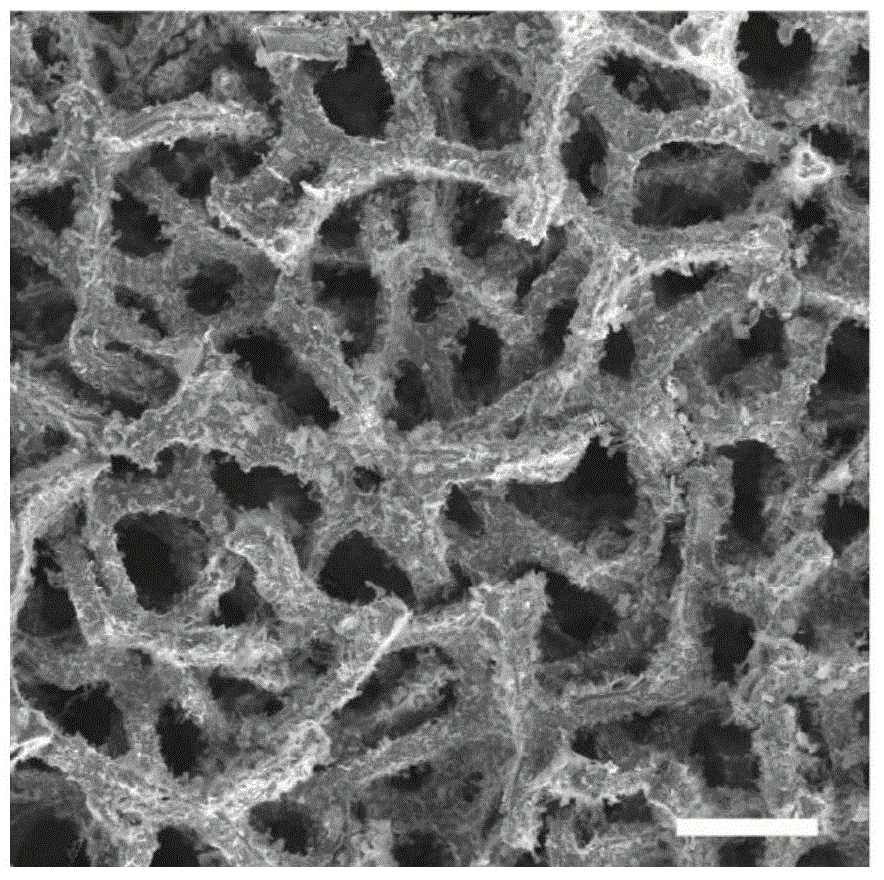
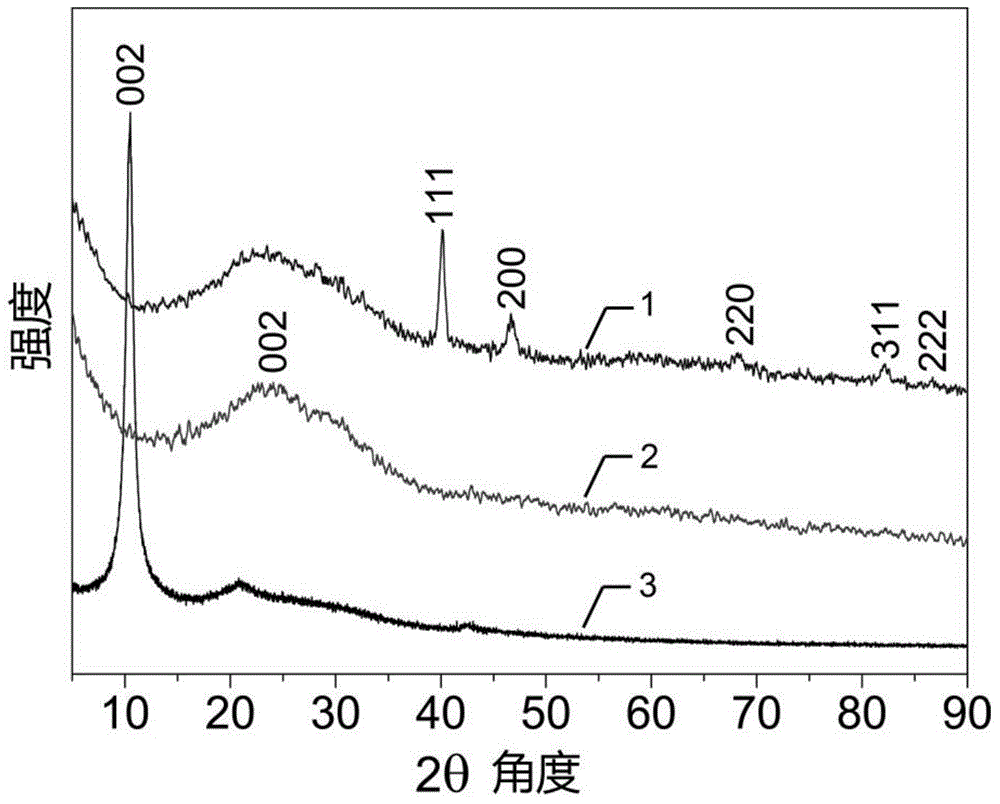
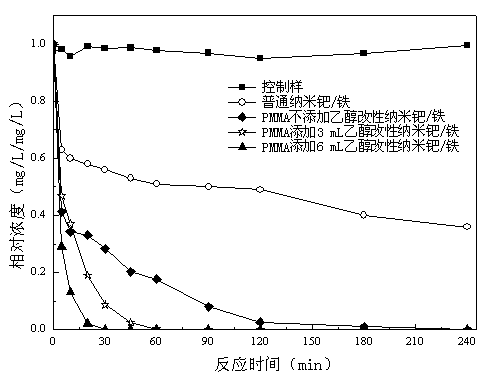
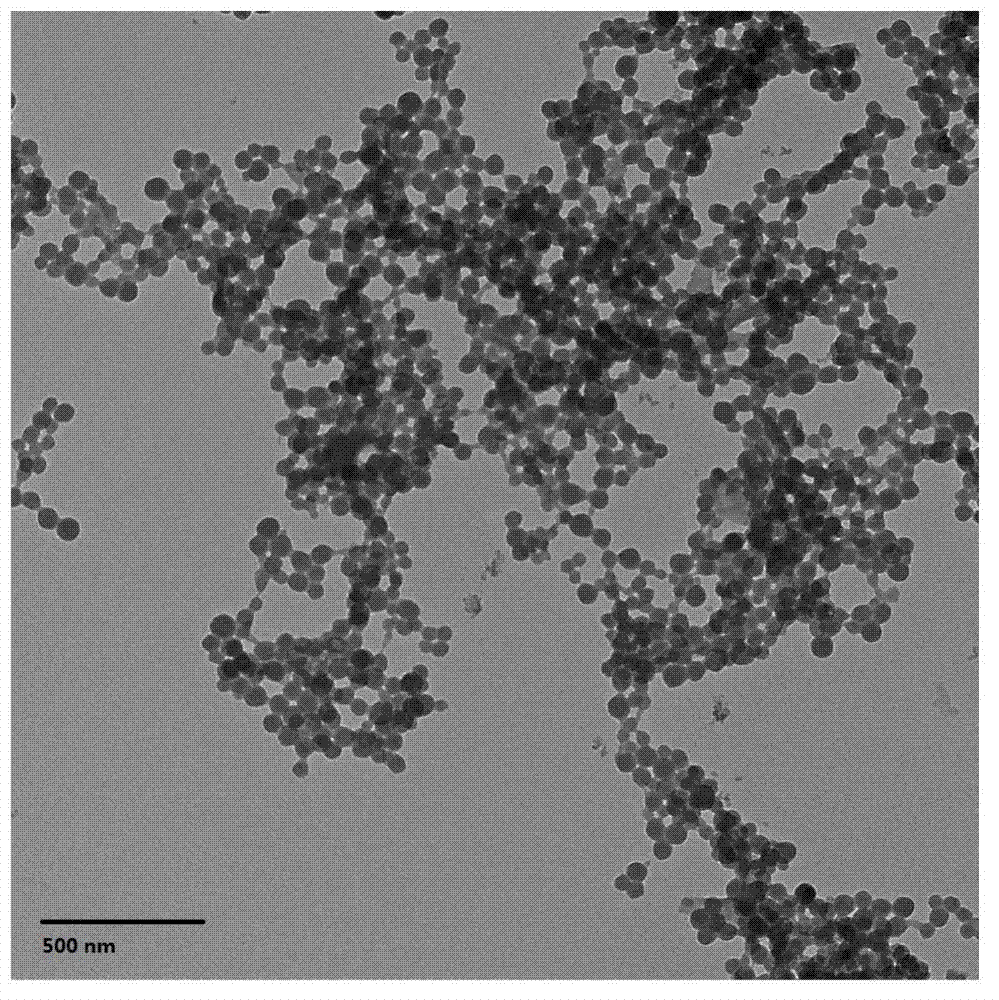
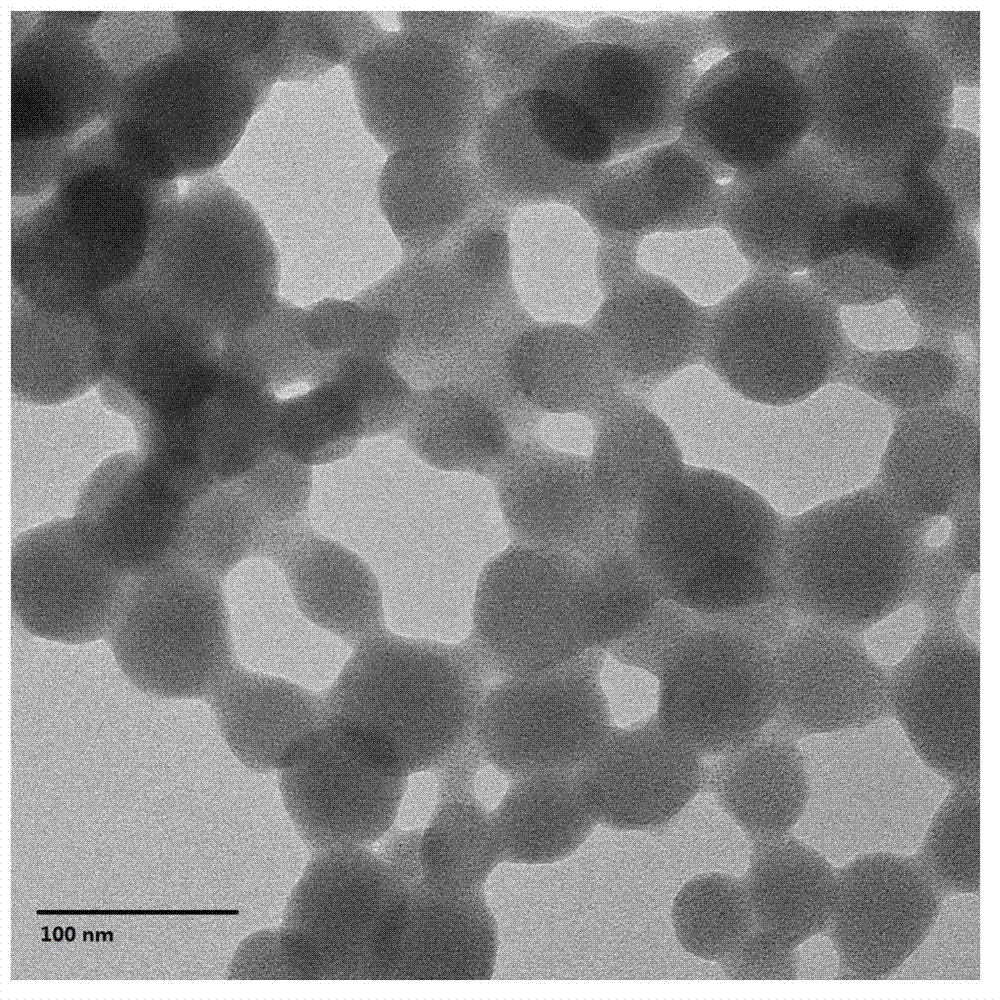
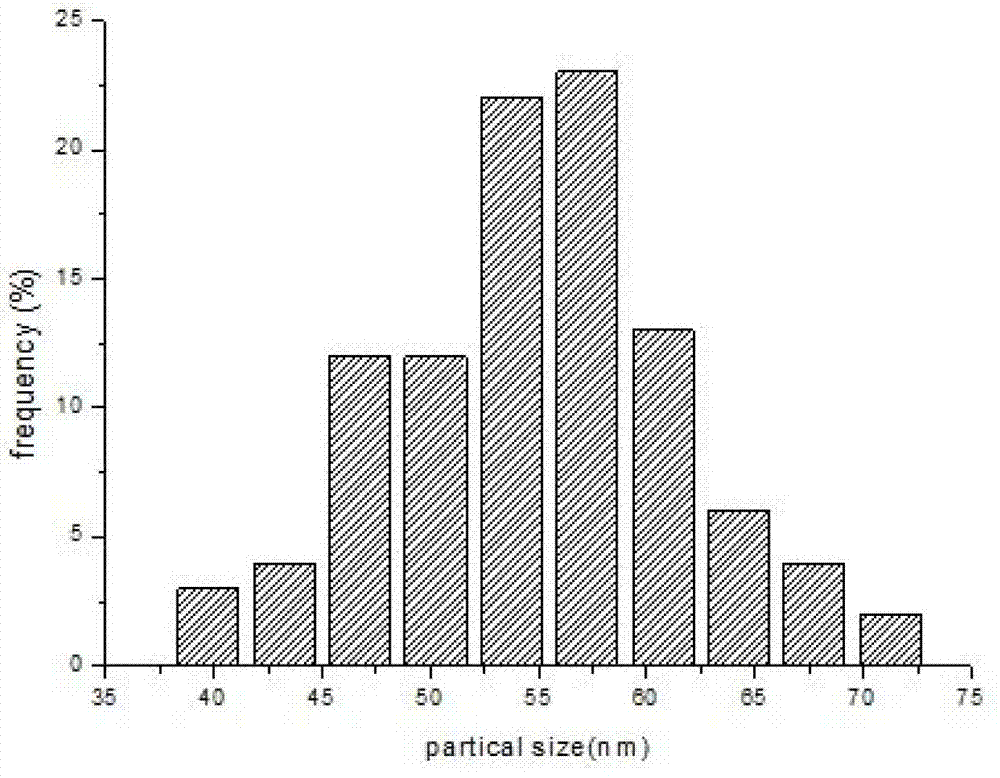
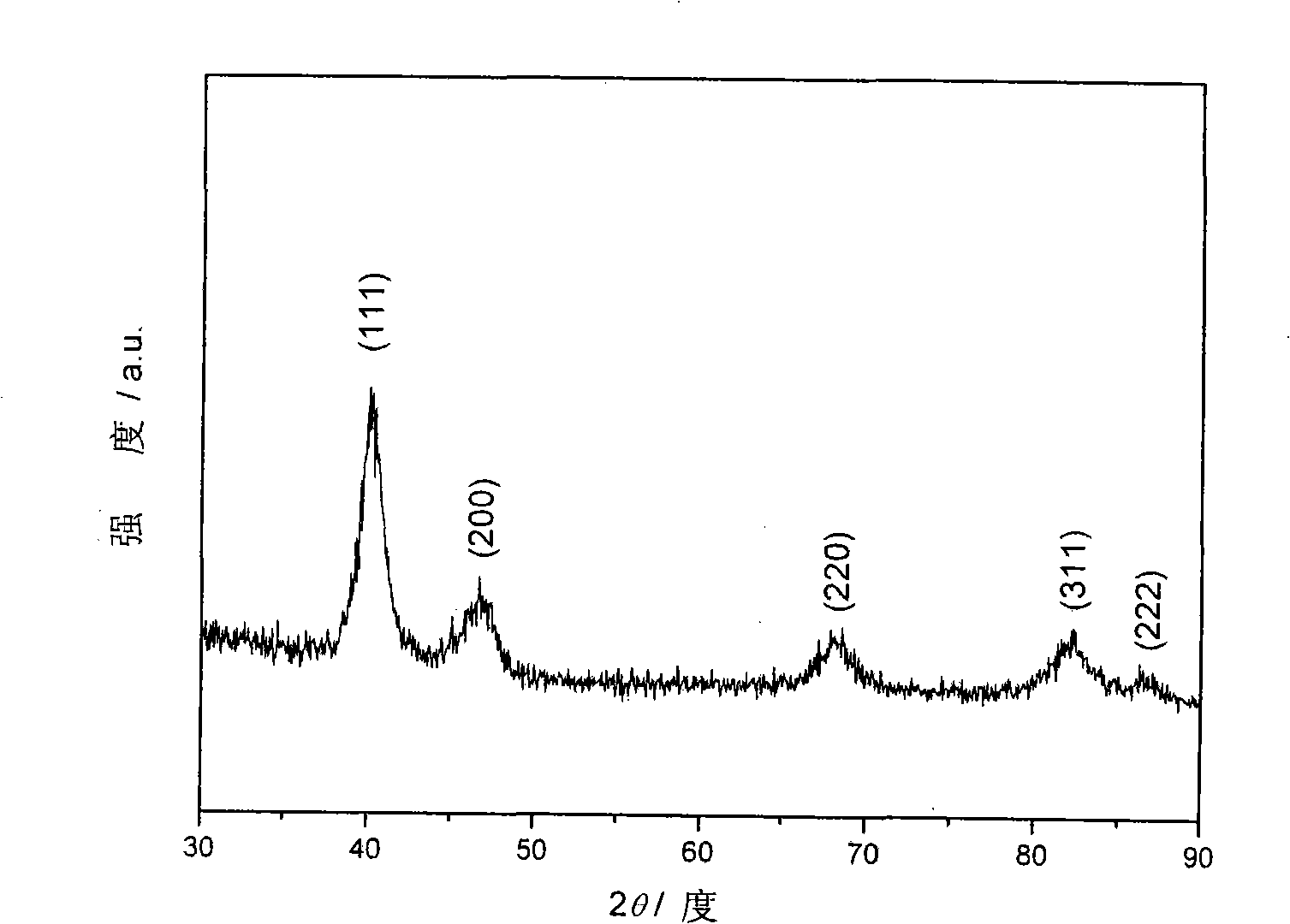
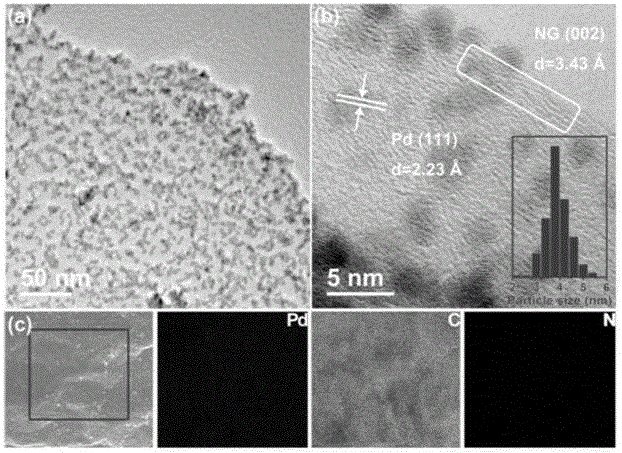
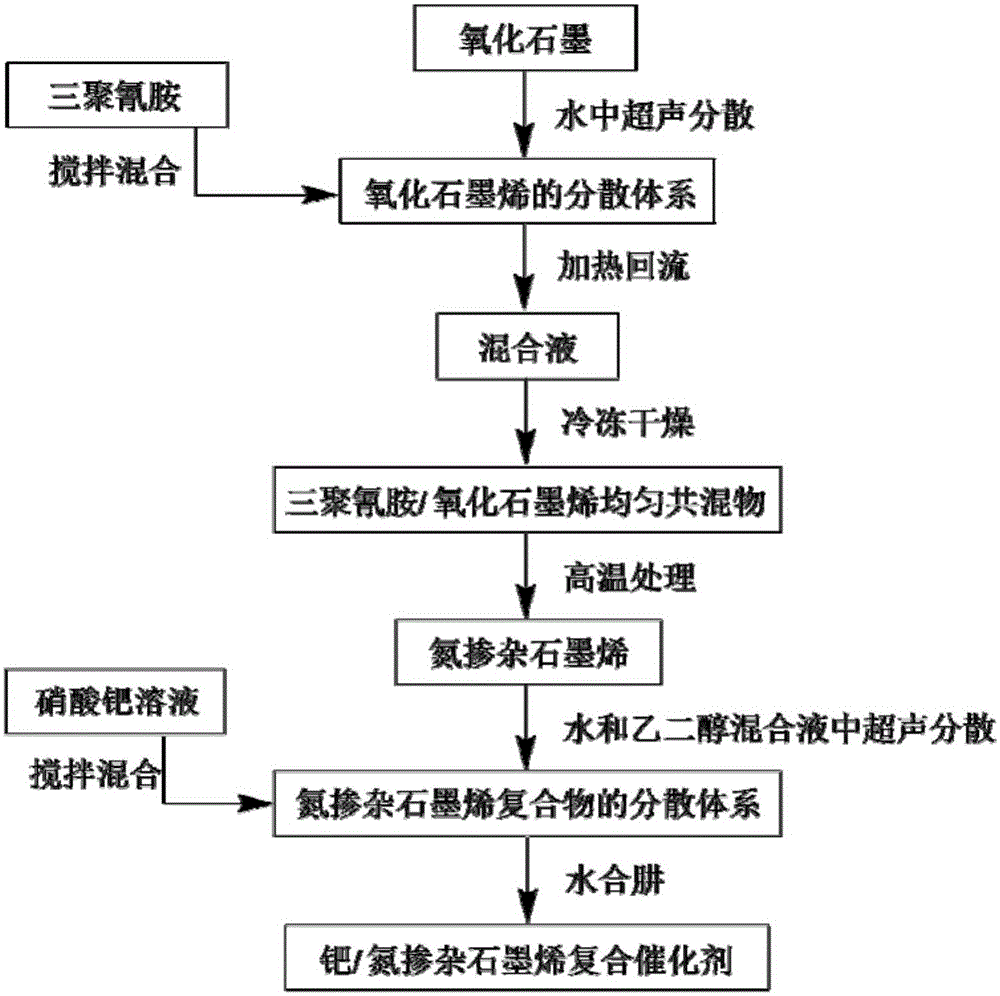
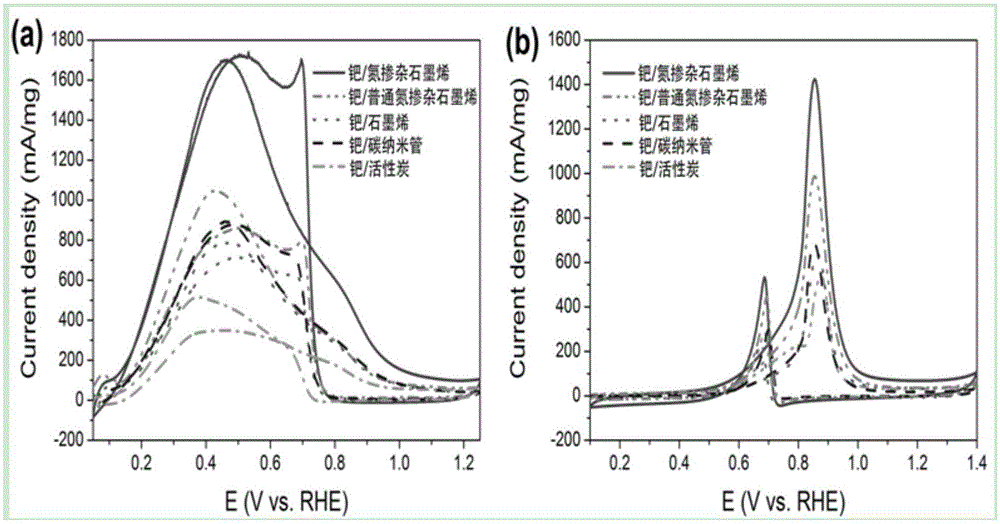
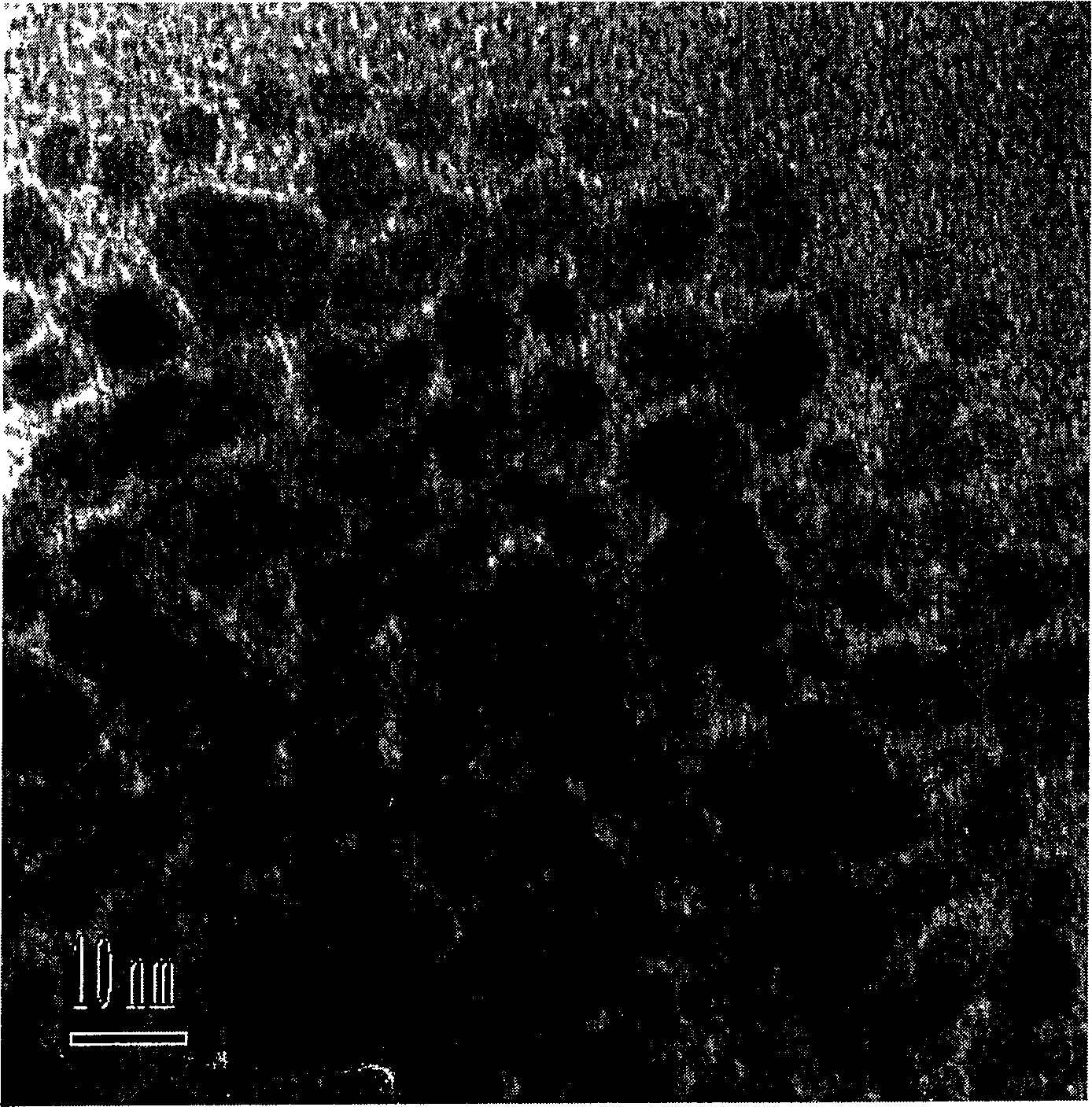Patents
Literature
420 results about "Palladium nanoparticles" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Direct epoxidation catalyst and process
InactiveUS20110152550A1Similar and good olefin selectivityOrganic chemistryMolecular sieve catalystsHydrogenTitanium
A catalyst, useful for the direct epoxidation of olefins, is disclosed. The catalyst comprises palladium nanoparticles, support nanoparticles, and a titanium zeolite having a particle size of 2 microns or greater. The palladium nanoparticles are deposited on the support nanoparticles to form supported palladium nanoparticles, and the supported palladium nanoparticles are deposited on the titanium zeolite; or the supported palladium nanoparticles are deposited on a carrier having a particle size of 2 microns or greater. The invention also includes a process for producing an epoxide comprising reacting an olefin, hydrogen and oxygen in the presence of the catalyst. The catalysts are more active in epoxidation reactions, while demonstrating the same or better selectivity.
Owner:LYONDELL CHEM TECH LP
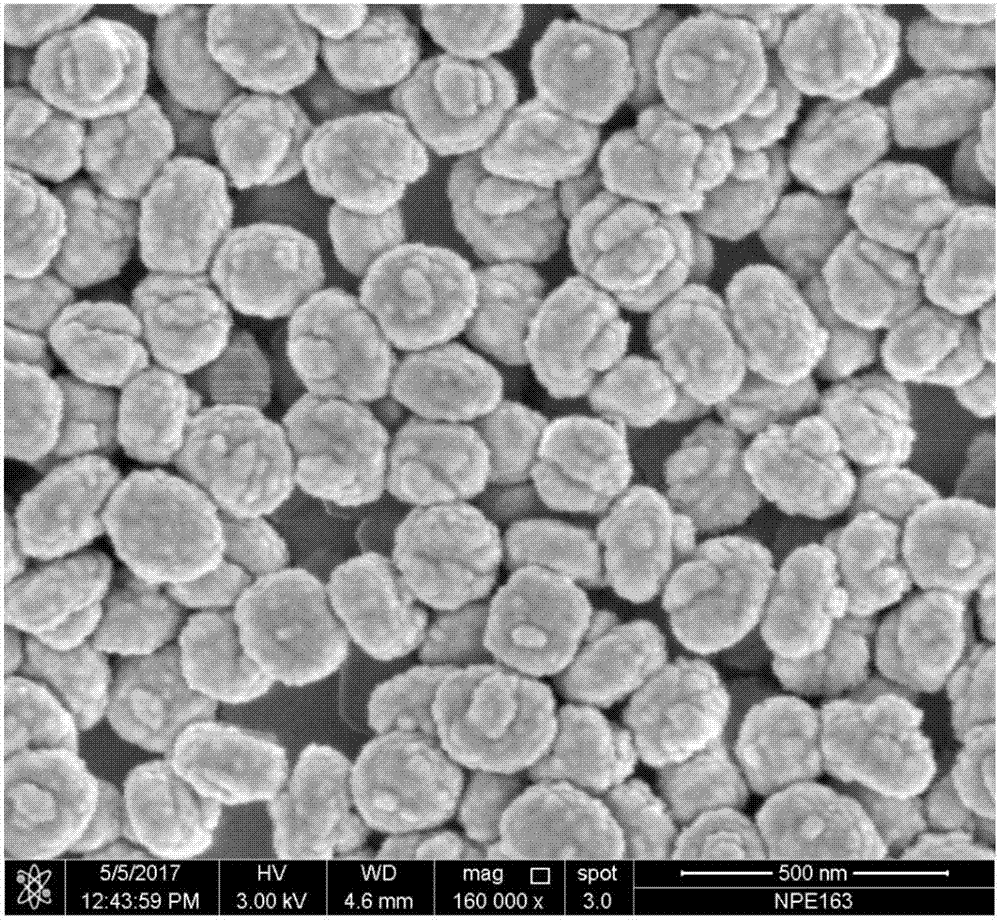
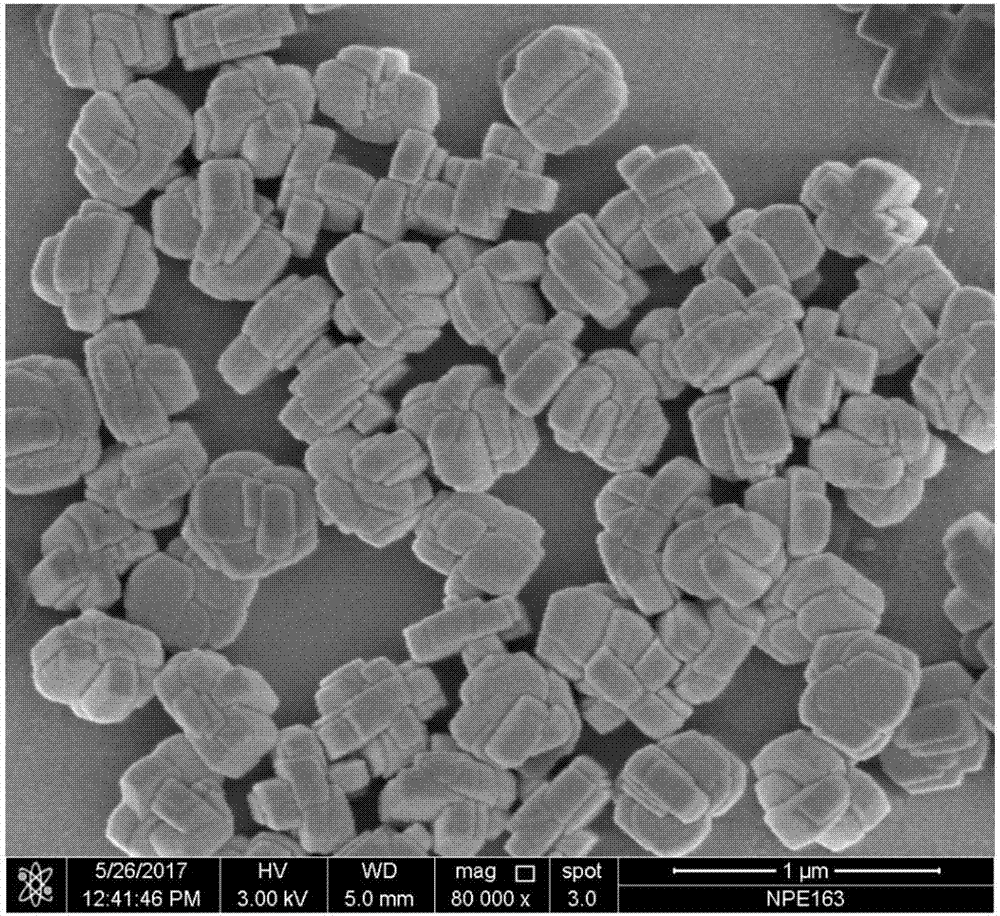
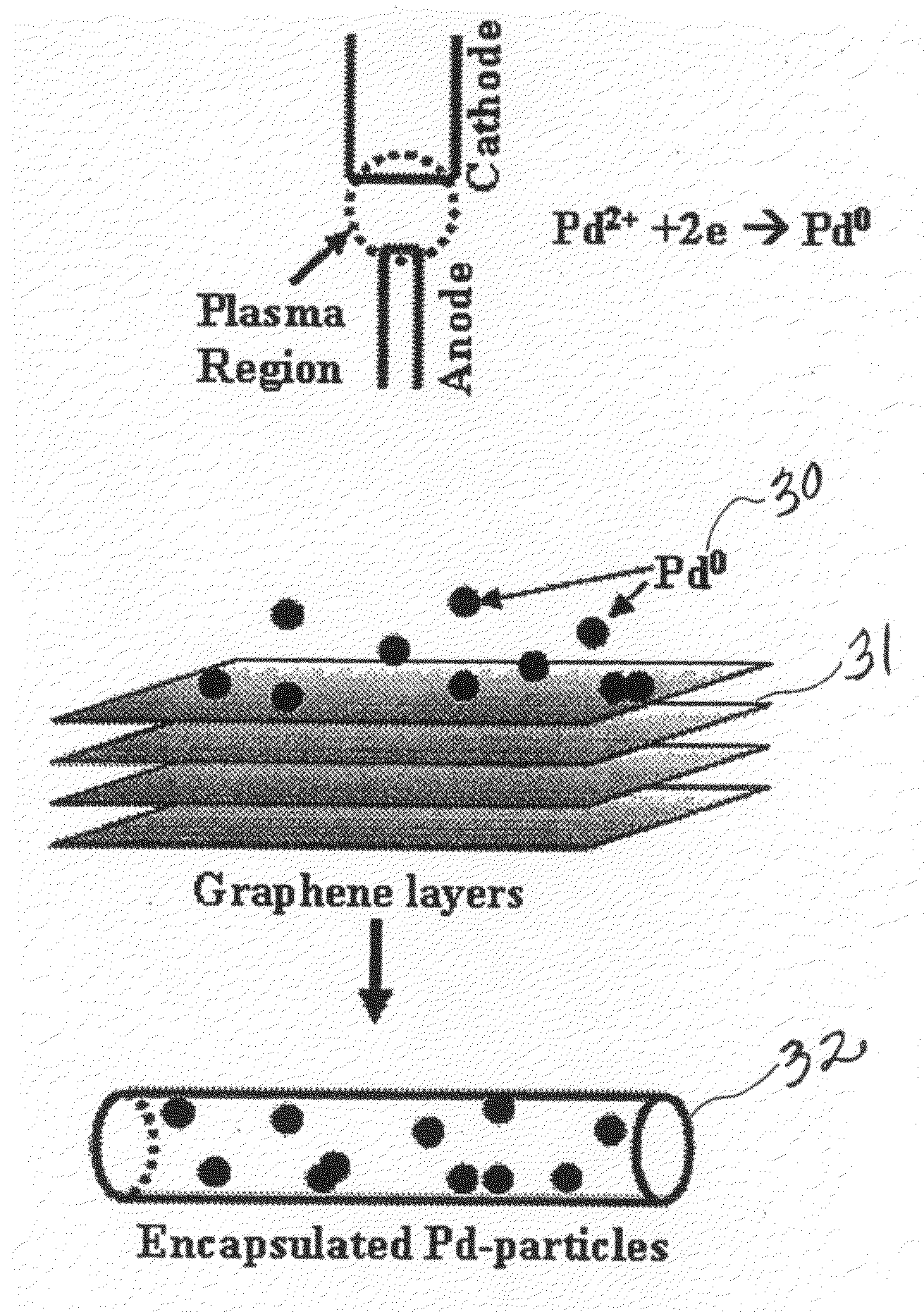
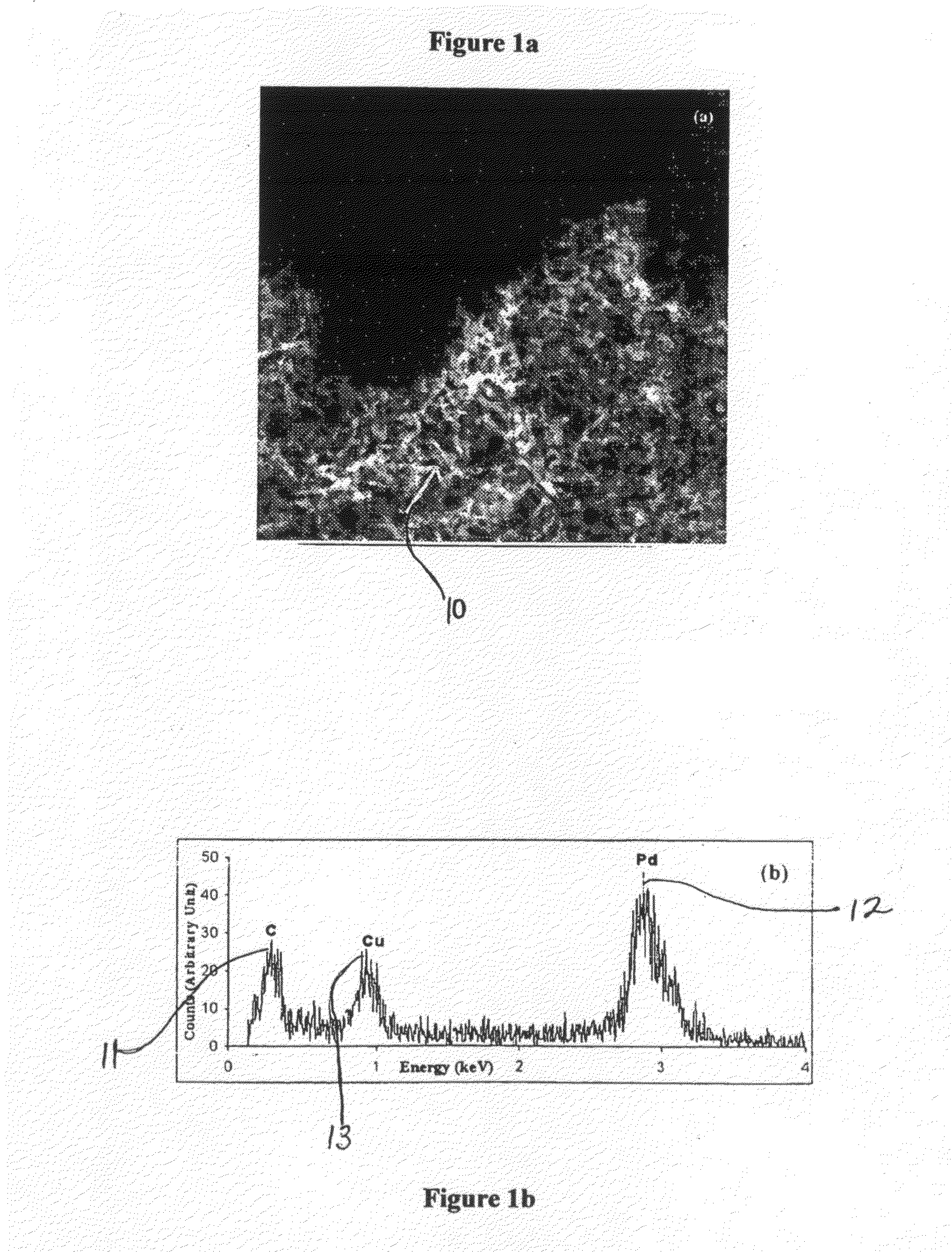
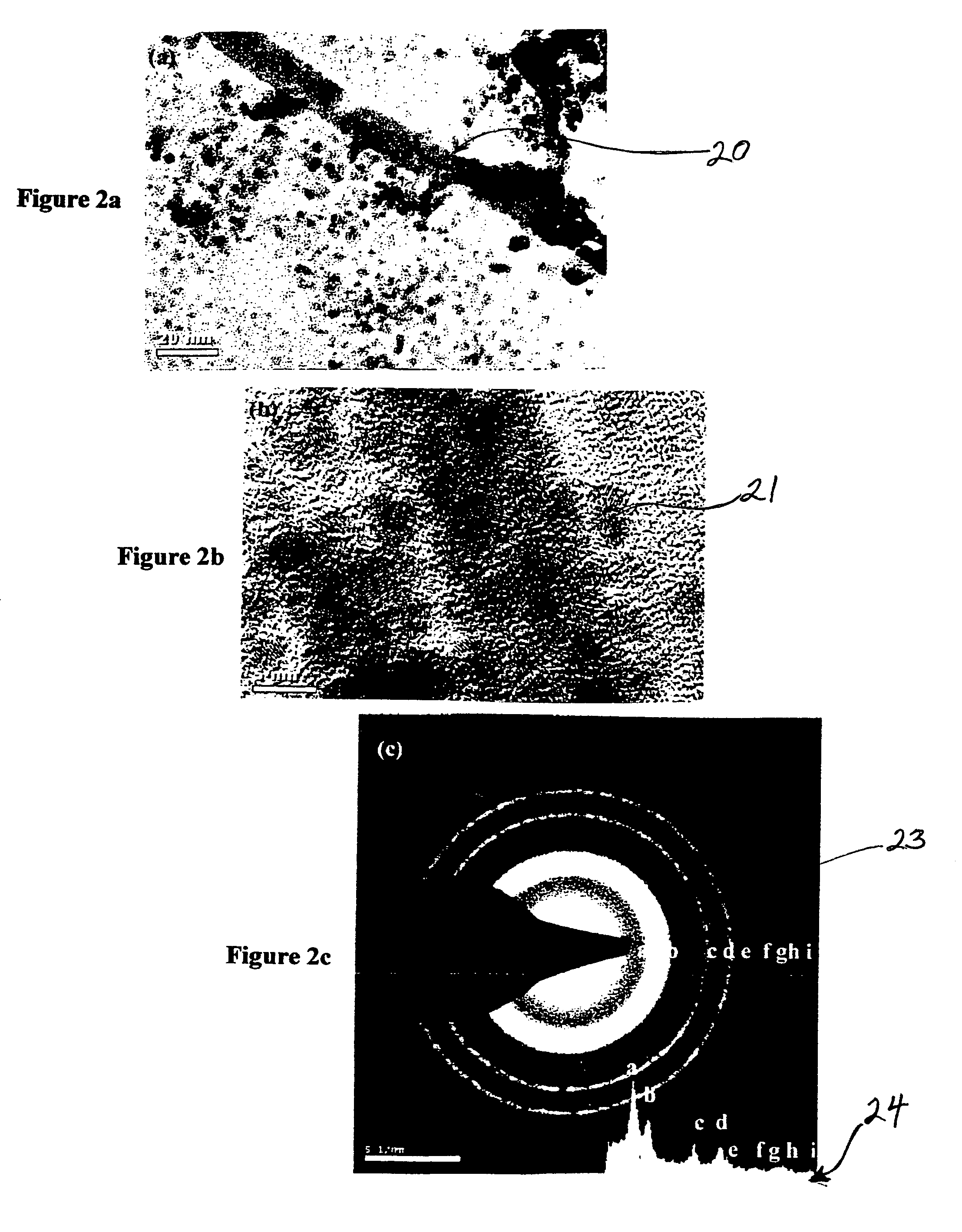
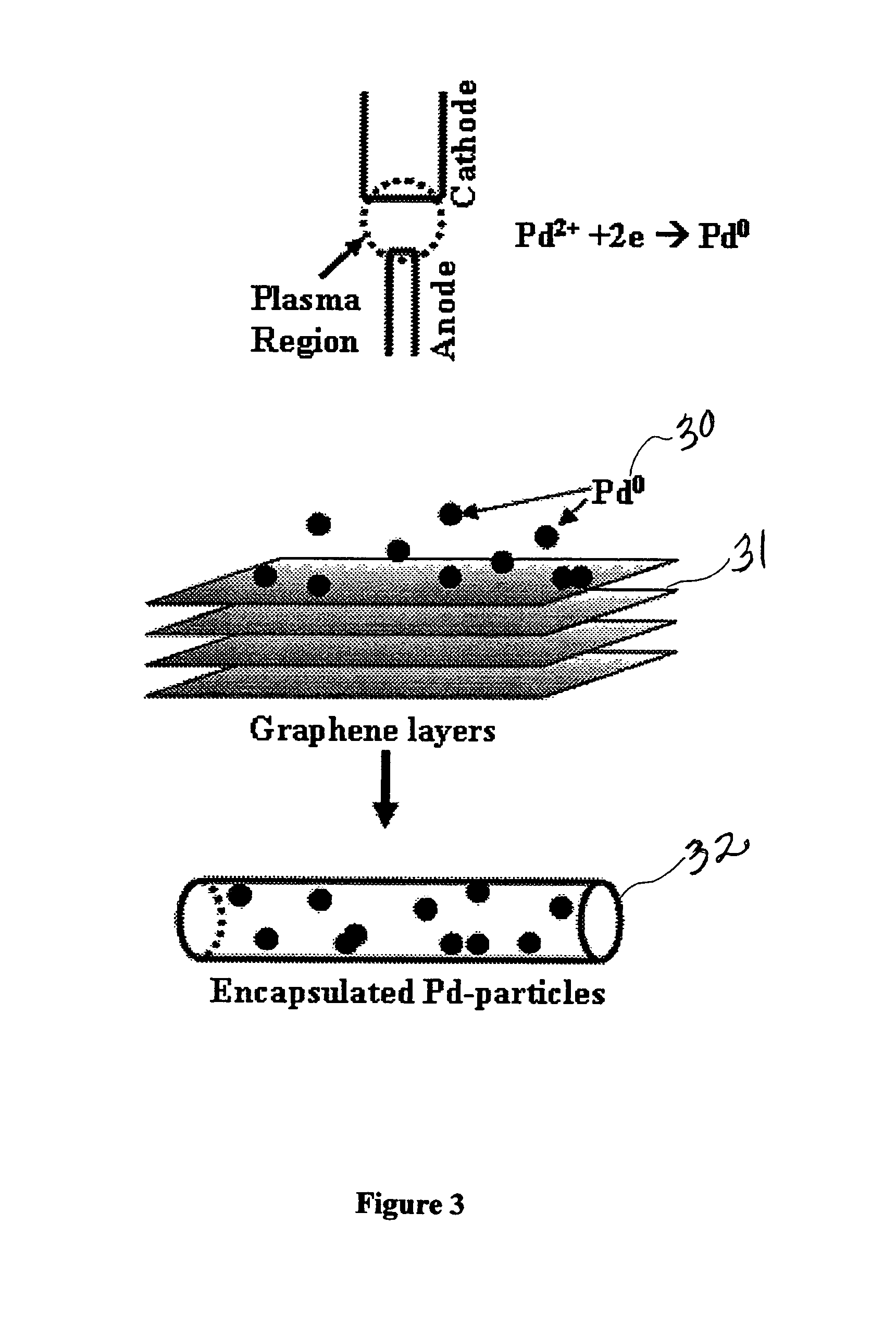
Synthesis of carbon nanotubes filled with palladium nanoparticles using arc discharge in solution
InactiveUS20090072192A1Improve abilitiesMaterial nanotechnologyOther chemical processesNanotubeMaterials science
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
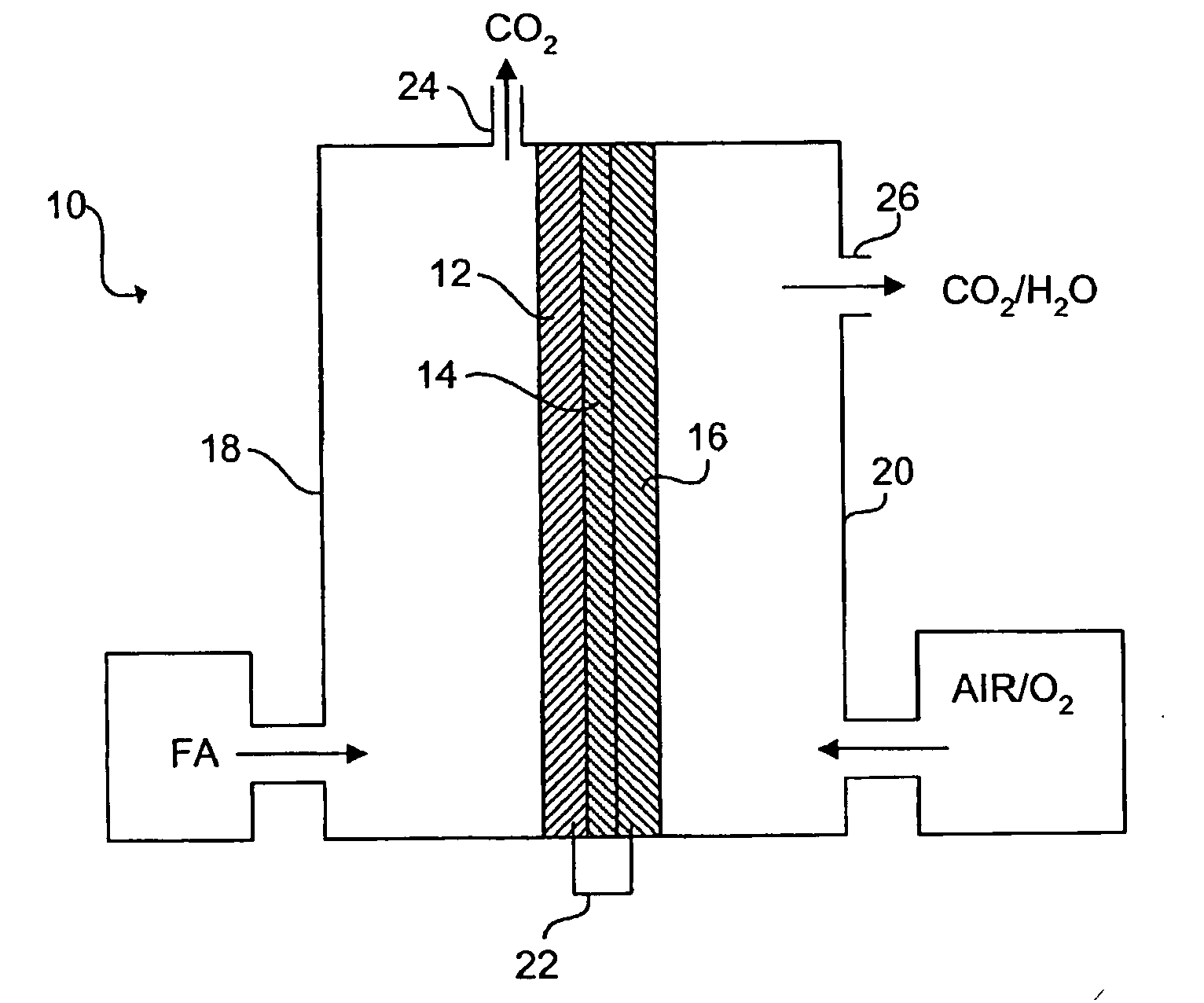
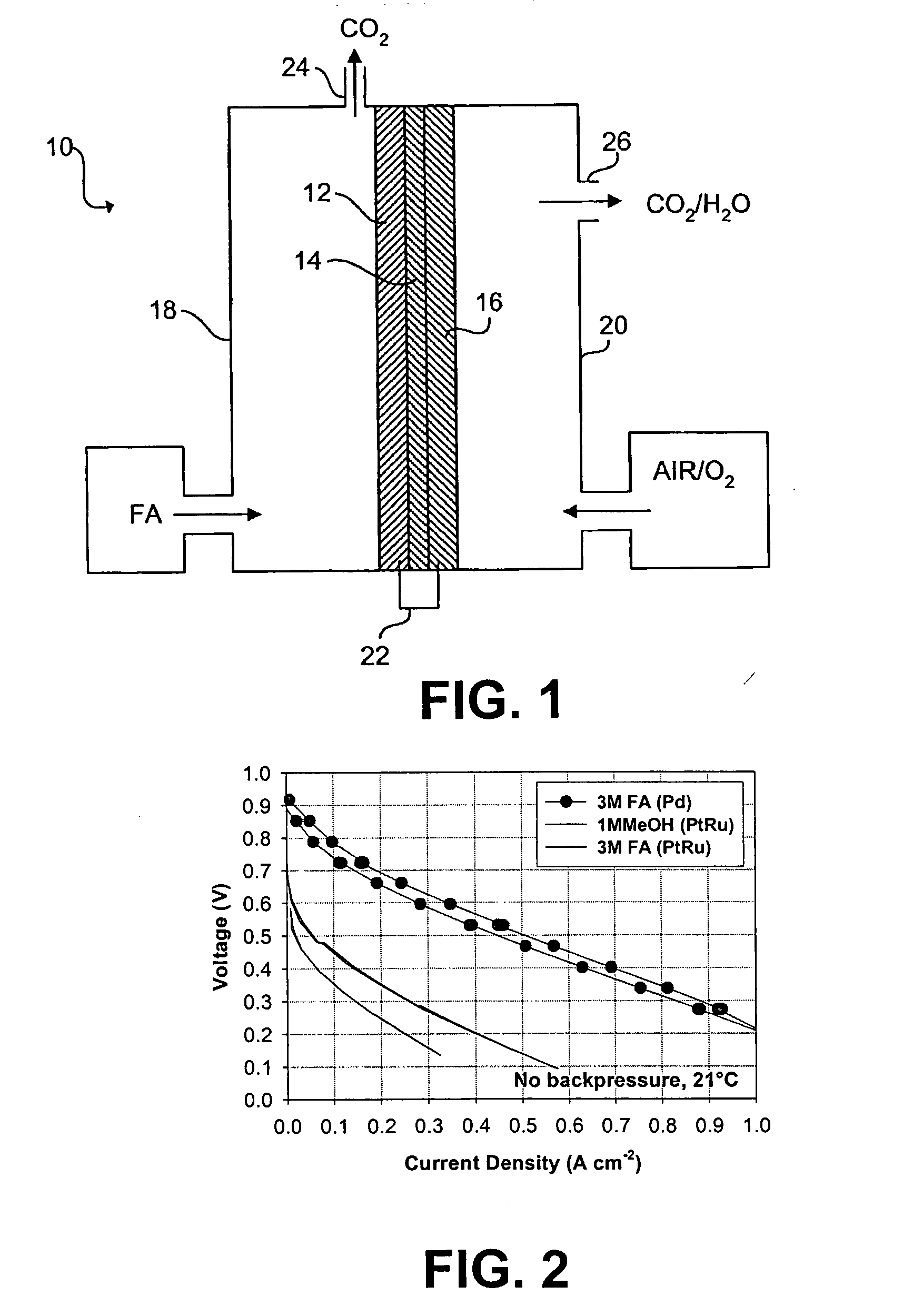
Palladium-based electrocatalysts and fuel cells employing such electrocatalysts
InactiveUS20050136309A1Reduce formationImprove responseSolid electrolytesFuel cell auxillariesFuel cellsNanoparticle
A direct organic fuel cell includes a fluid fuel comprising formic acid, an anode having an electrocatalyst comprising palladium nanoparticles, a fluid oxidant, a cathode electrically connected to the anode, and an electrolyte interposed between the anode and the cathode.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
High-Performance Flexible Hydrogen Sensors
InactiveUS20090084159A1Easy to conformFast recovery timeAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNanotechCarbon nanotubeEvaporation
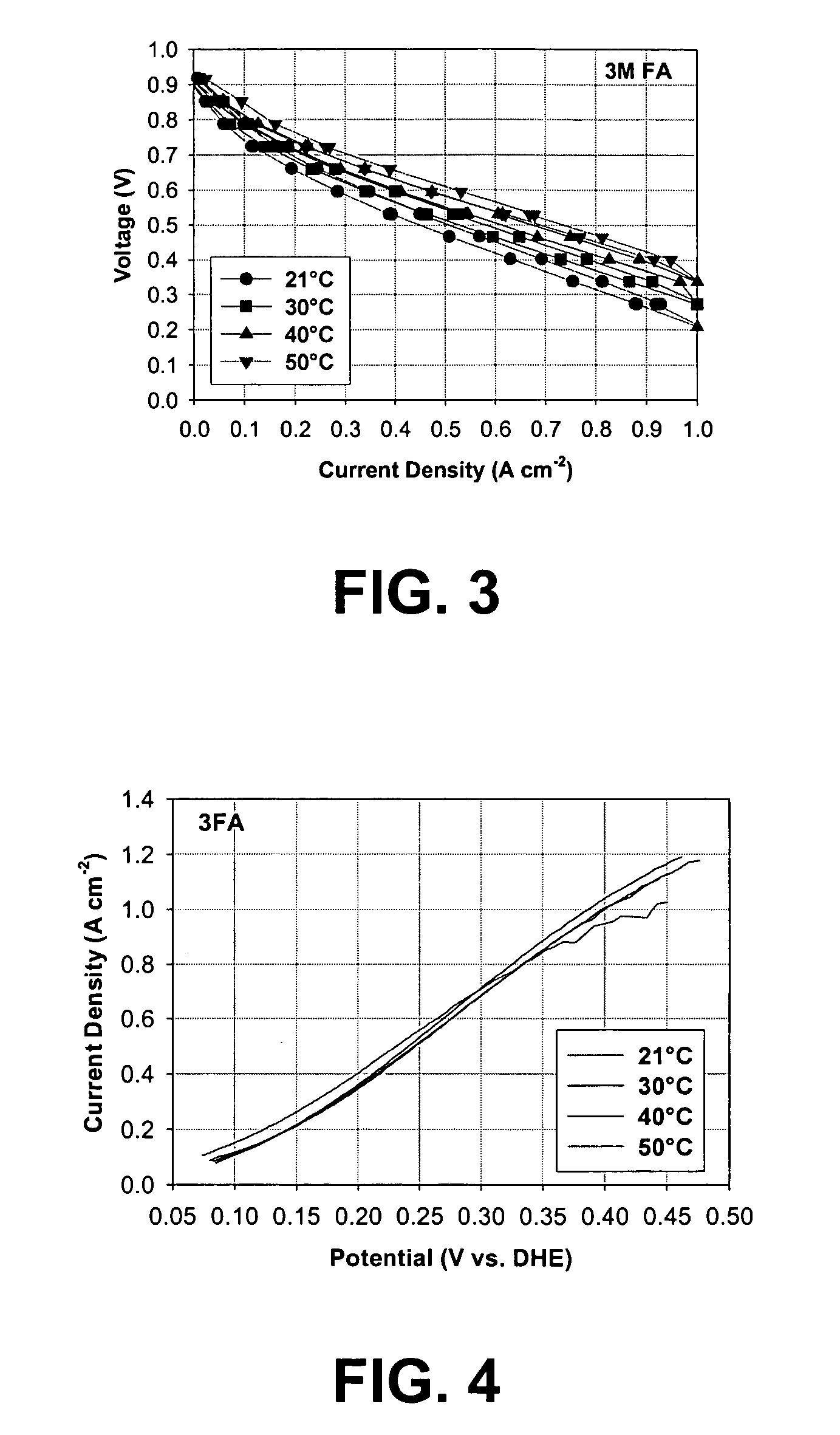
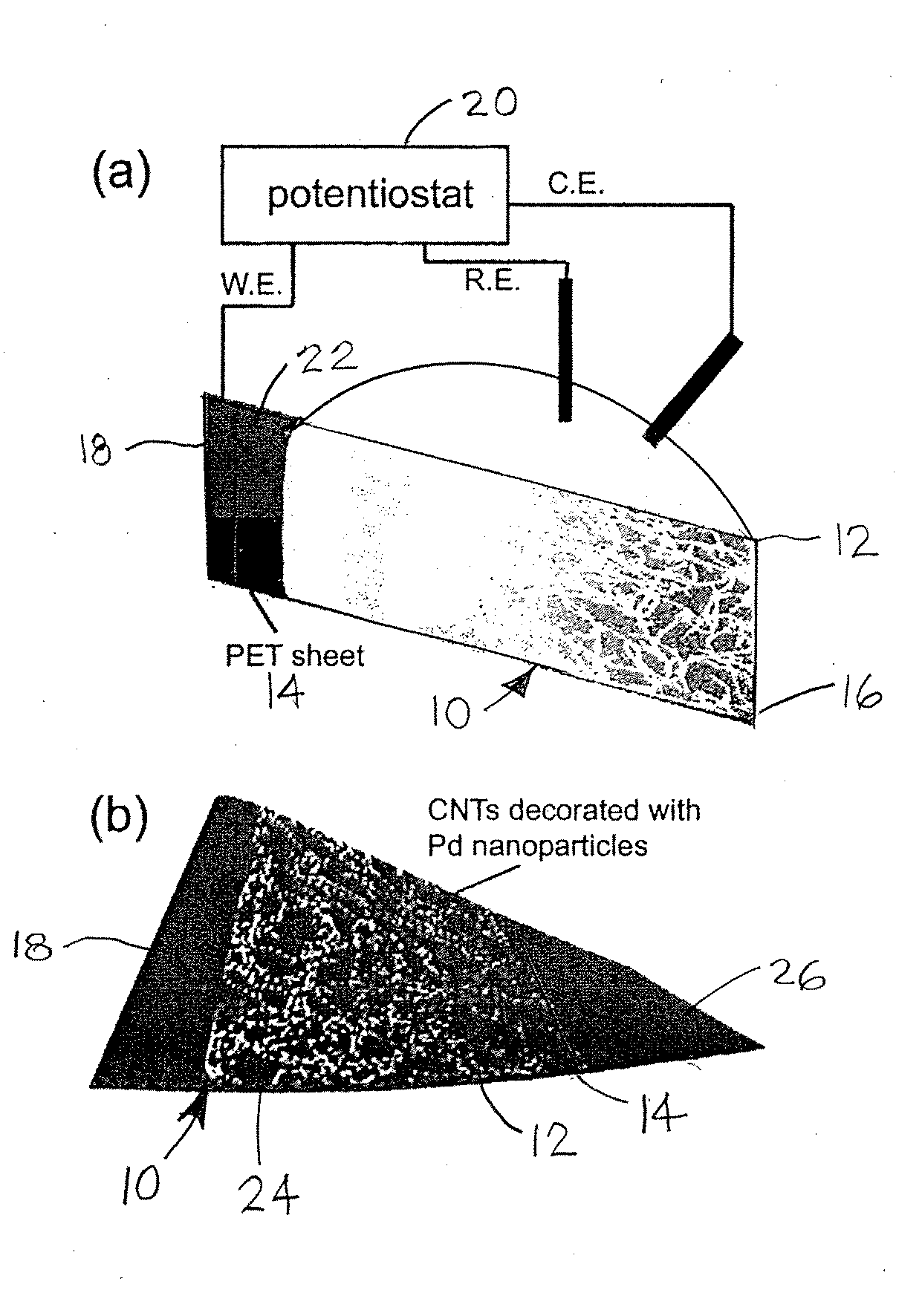
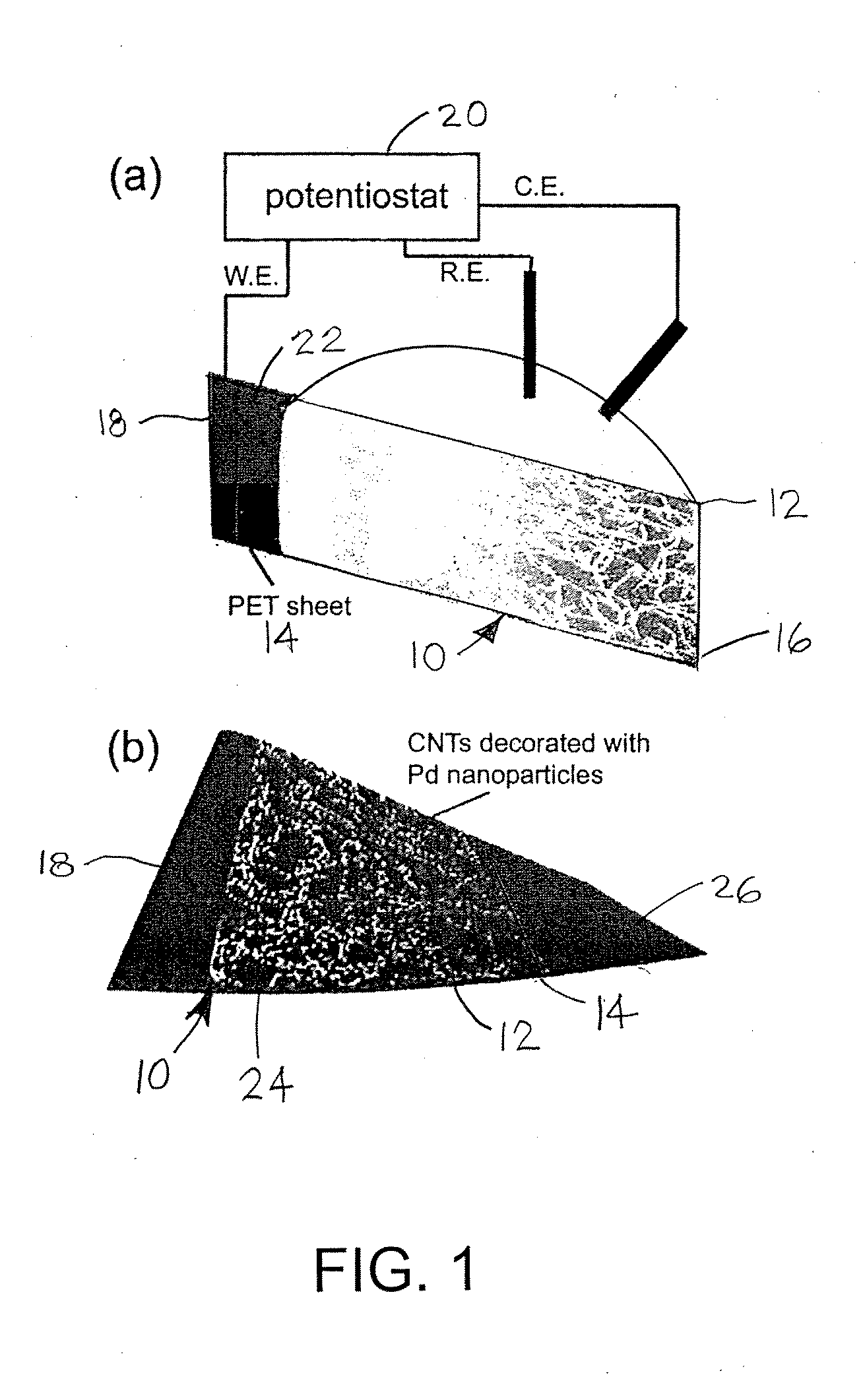
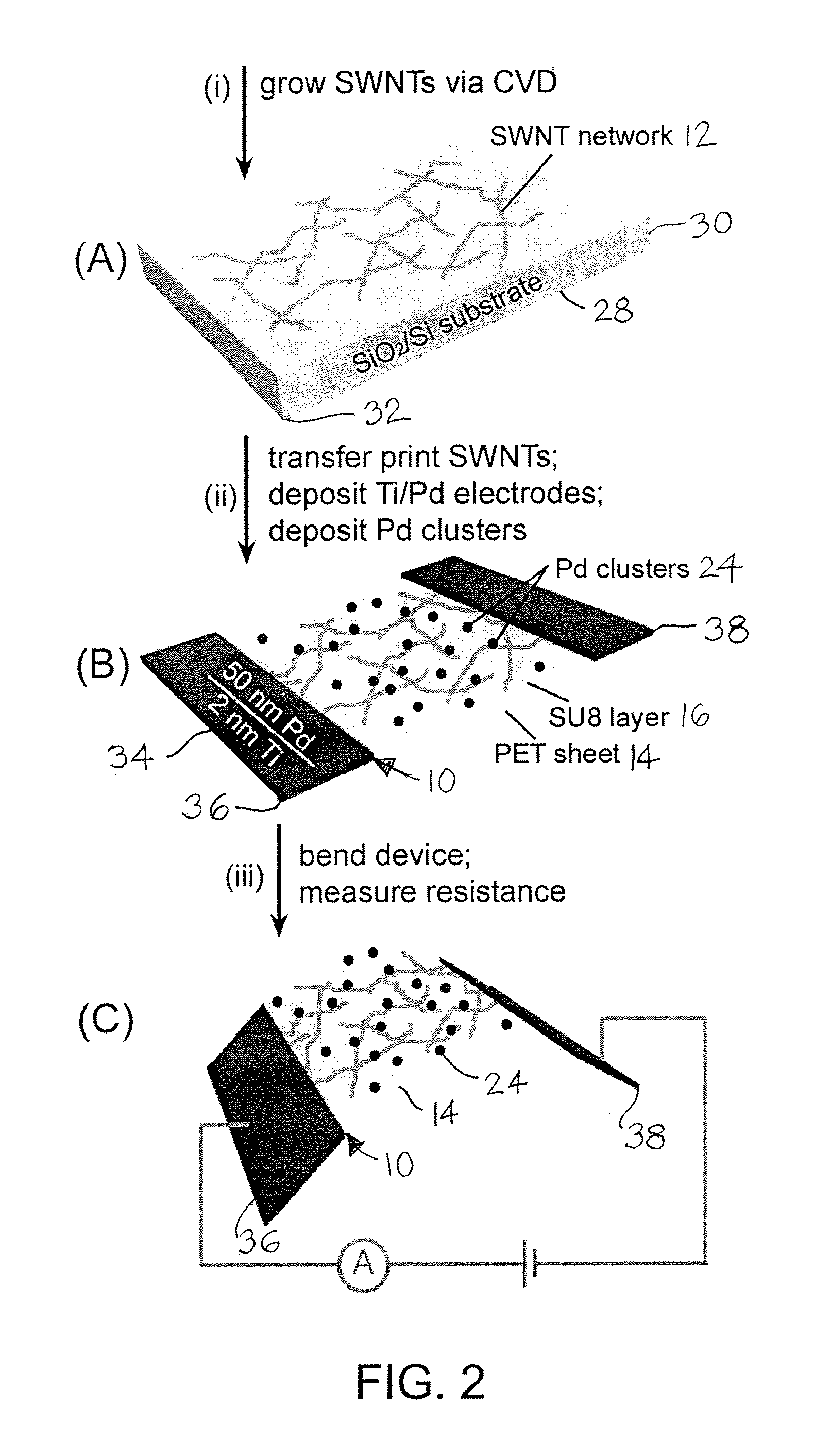
Single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNTs) are decorated with metal nanoparticles to form high-performance flexible hydrogen sensors. The special process to form the high-performance flexible hydrogen sensors can combine a dry transfer printing technique and modification of SWNTs with palladium (Pd) nanoparticles to provide high-performance hydrogen sensors with excellent mechanical flexibility on plastic substrates. Two approaches can be used to decorate the SWNTs. One is physical deposition, such as electron beam evaporation (EBE) and the other is electrochemical deposition which can selectively grow palladium nanoparticles on the surface of the SWNTs, resulting in significantly decreasing the use of palladium. Preferably, the Pd nanoparticles are deposed on the SWNTs in a discontinuous arrangement so that the Pd nanoparticles are spaced away from each other to form individual discontinuous Pd nanoparticles rather a continuous Pd film. Advantageously, the SWNTs are arranged with substantial semiconducting pathways. Desirably, the high-performance flexible hydrogen sensors have an excellent response and recovery time, provide superior sensitivity for detecting hydrogen, and are bendable to conform to the contours of other structures.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Preparation and applications of supported palladium catalyst using MOFs derived carbon-based material as carrier
InactiveCN106902842AEvenly dispersedGood dispersionCatalystsHydrocarbon preparation catalystsMaterials preparationNanoparticle
The invention discloses preparation and applications of a supported palladium catalyst using a MOFs derived carbon-based material as a carrier, and belongs to the technical field of catalyst material preparation. According to the present invention, ZIF-67 is adopted as a template, reduced palladium nanoparticles are uniformly supported in the pore channels in the ZIF-67 during a ZIF-67 synthesis process, and under a nitrogen protection condition, the carbon-based nanometer material supported palladium catalyst having excellent catalysis performance is constructed through high temperature carbonation; the preparation method of the invention is simple and easy to perform; and the prepared catalyst maintains the high specific surface area and the abundant pore structure characteristics of the precursor ZIF-67 to a large extent, such that the uniform dispersion and the stabilization of the palladium nanoparticles are easily achieved, and the excellent catalytic activity is provided.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Palladium/graphene nano electro-catalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101740785AGood chemical stabilityLarge specific surface areaCell electrodesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsSodium acetatePalladium nanoparticles
The invention discloses a palladium / graphene nano electro-catalyst which takes graphene as a carrier and palladium as an active component, wherein the mass fraction of the palladium in the catalyst is 10 to 40 percent. A preparation method of the palladium / graphene nano electro-catalyst comprises the following steps of: (1) ultrasonically dispersing graphite oxide nano sheets in liquid polyalcohol, then adding a palladium salt solution and a sodium acetate solution, and fully and evenly mixing, wherein the content of the graphene oxide nano sheets in the mixture is 0.48 to 1.3g / L, the concentration of palladium salts is 0.0005 to 0.005mol / L, and the sodium acetate concentration is 0.0033 to 0.012mol / L; and (2) transferring the mixture into a microwave hydro-thermal reaction kettle, carrying out microwave heating and reacting for 5 to 10 minutes, then filtering, washing and drying to obtain the palladium / graphene nano electro-catalyst. The preparation method has the advantages of energy saving, high speed, simple process, and the like; and palladium nanoparticles in the prepared palladium / graphene nano electro-catalyst have even particle sizes. The catalyst has high electro-catalysis activity to formic electrooxidation and has wide application in fuel cells.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
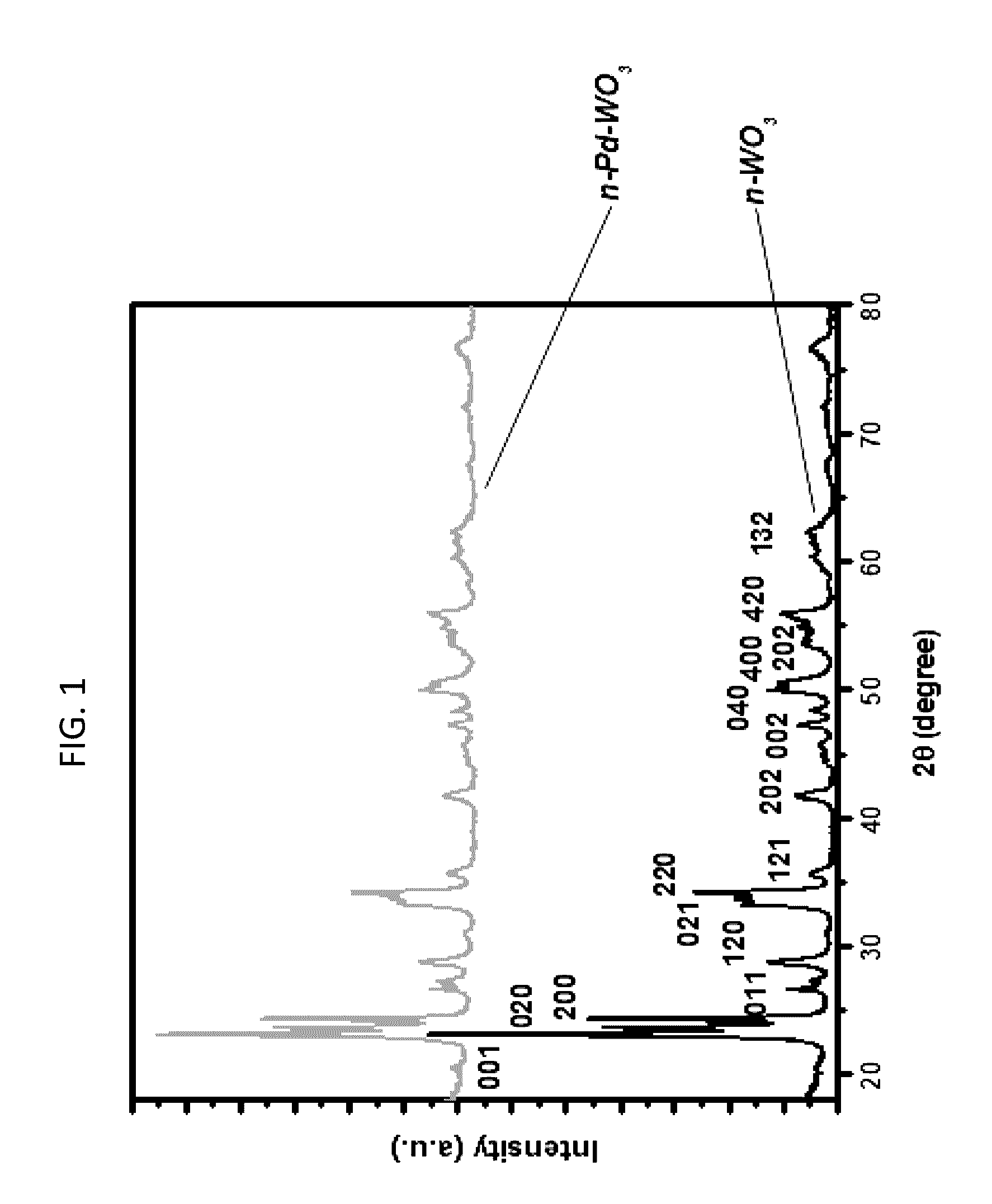
Method for disinfecting a fluid with a palladium-doped tungsten trioxide photo-catalyst
InactiveUS20160355409A1Reduce in quantityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsNanoparticleTungsten trioxide
The present disclosure relates to a method of disinfecting a fluid comprising at least one live microbial organism. The method includes contacting the fluid comprising the at least one microbial organism with an effective amount of a photo-catalyst while exposing the fluid and the photo-catalyst to light from at least one light source with a wavelength of about 300-550 nm to reduce the number of the at least one live microbial organism to a predetermined level. The photo-catalyst comprises tungsten trioxide nanoparticles doped with palladium nanoparticles, and the palladium nanoparticles are present in an amount of about 0.1-5% of the total weight of the tungsten trioxide nanoparticles and the palladium nanoparticles.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
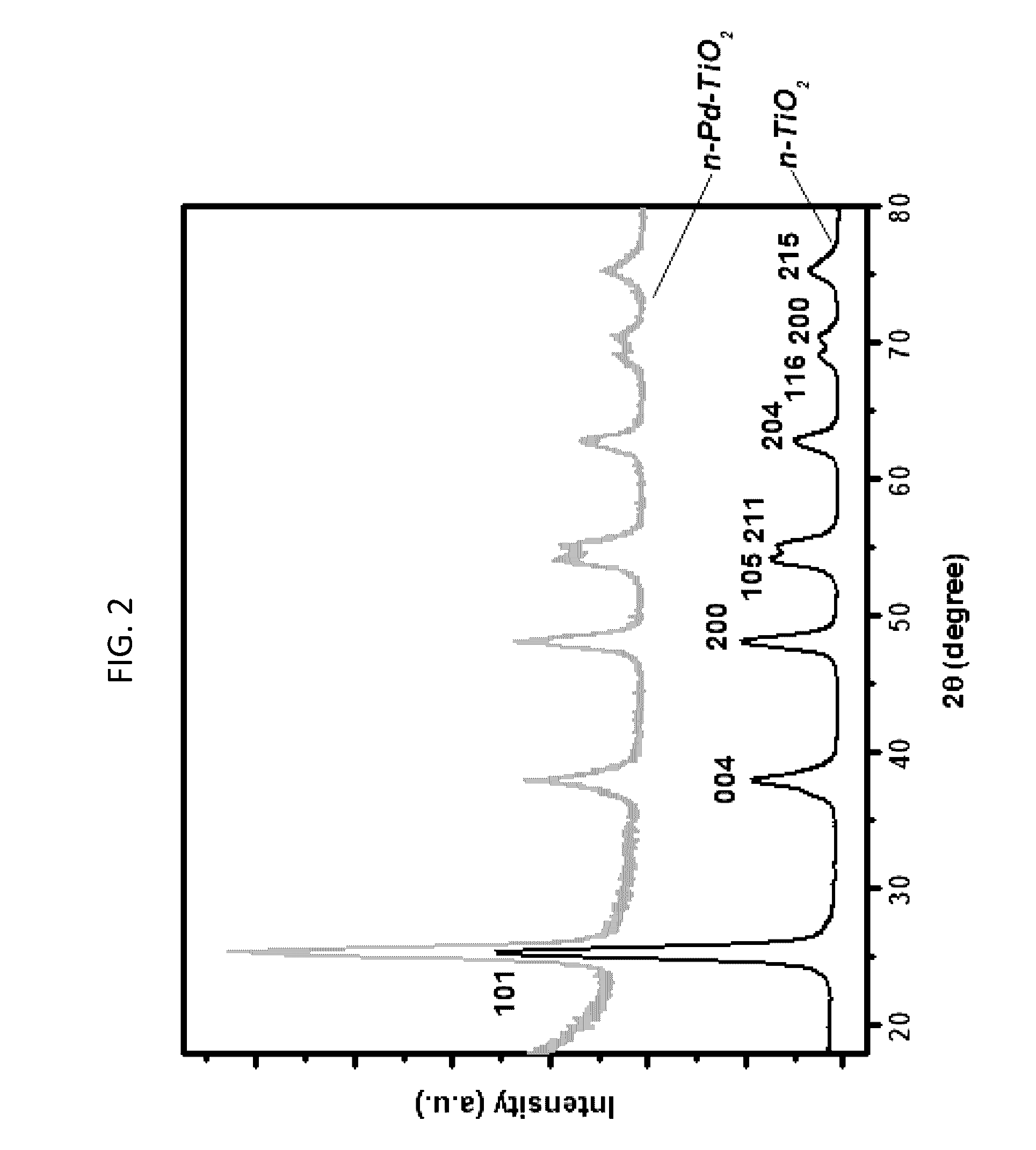
Titanium dioxide nanotube carried palladium nano catalyst and preparation method of same
ActiveCN102698745AGroundbreakingSmall particle sizeCell electrodesCatalyst activation/preparationNano catalystOrganic synthesis
The invention relates to a nano catalyst and a preparation method thereof, in particular to a titanium dioxide nanotube carried palladium nano catalyst and a preparation method. The method comprises the steps as follows: preparing a titanium dioxide nanotube array electrode first, depositing palladium nanoparticle on the titanium dioxide nanotube electrode through chemical deposition, and preparing an electrochemical post-processing solution; adopting a three-electrode electrochemical electrolytic cell system, and adding the electrochemical post-processing solution in an electrolytic cell, wherein the three electrodes include a working electrode, an auxiliary electrode and a reference electrode, the working electrode is a titanium dioxide nanotube array carried palladium electrode, and the auxiliary electrode is a palladium sheet; adopting an electrochemical program potential step processing method, wherein the upper limit of potential is 0.5-5.5 volt, the upper limit of time is 10-300 seconds, the lower limit of potential is (-4.5)-(-0.5) volt, the lower limit of time is 10-300 seconds, and the processing time is 0.1-6 hours; and taking out the working electrode, flushing and then obtaining the product. The titanium dioxide nanotube carried palladium nano catalyst can be used for preparation of fuel cells and electric organic synthesis as an electro-catalyst.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for removing mercury ions in water and regeneration method of adsorbent used in same
InactiveCN102432085ANanostructure, large specific surface areaLarge specific surface areaOther chemical processesCombustible gas purificationSorbentModified carbon
The invention relates to a method for removing mercury ions in water and a regeneration method of an adsorbent used in the same. An adsorbent is put in water to be treated to adsorb mercury ions in the water. The adsorbent is a palladium nanoparticle supported / iron oxide magnetic modified carbon nanotube composite material. The carbon nanotube composite material provided by the invention has nanostructure and large specific area; and after the carbon nanotube composite material is oxidized and activated, carboxyl group, hydroxyl group and other active functional groups are formed on the surface of the carbon nanotube composite material, thereby enhancing the hydrophilic property and the adsorptive capacity for positively charged metallic ions. The iron oxide is coated on the surface of the activated carbon nanotube composite material, and therefore, the activated carbon nanotube composite material has strong soft magnet property, and can easily implement solid-liquid separation of the adsorbent and the polluted water body under the action of an external magnetic field. The palladium modification strengthens the affinity of the composite material with mercury ions, and greatly enhances the adsorption capacity and selectivity of the original carbon nanotube composite material for mercury ions (the maximum adsorption capacity is 55.3mg / g).
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Preparation method of nanometer palladium-graphene three-dimensional porous composite electrocatalyst
ActiveCN104549242AEasy to controlLarge specific surface areaCell electrodesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPorous graphenePotassium
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nanometer palladium-graphene three-dimensional porous composite electrocatalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: cleaning foamed nickel by sequentially adopting glacial acetic acid, acetone, ethanol and deionized water; preparing a graphene oxide water solution with the mass concentration of 0.5-10 mg / mL, then directly soaking the foamed nickel into the graphene oxide water solution, and standing for reaction to form a three-dimensional porous structural foamed nickel-graphene product; directly soaking the foamed nickel-graphene product into a potassium chloropalladate water solution with the molar concentration of 0.05-1 mmol / L; and after the reaction is finished, taking out the foamed nickel-graphene product so as to generate a graphene composite electrocatalyst product which has a three-dimensional porous structure and is loaded with a palladium nanoparticle. By the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the three-dimensional porous graphene foamed product loaded with the palladium nanoparticle can be obtained only through simple two-step soaking operation; and in addition, the three-dimensional porous graphene foamed product is excellent in property and high in stability and can be directly used as the positive pole of an ethanol fuel cell.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
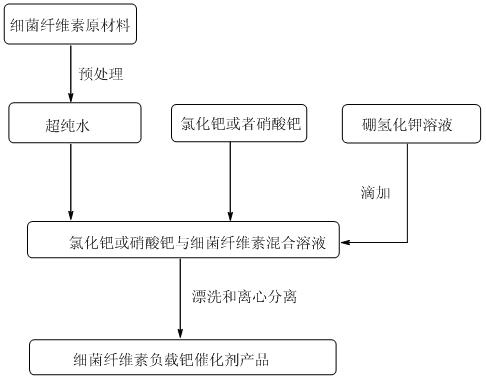
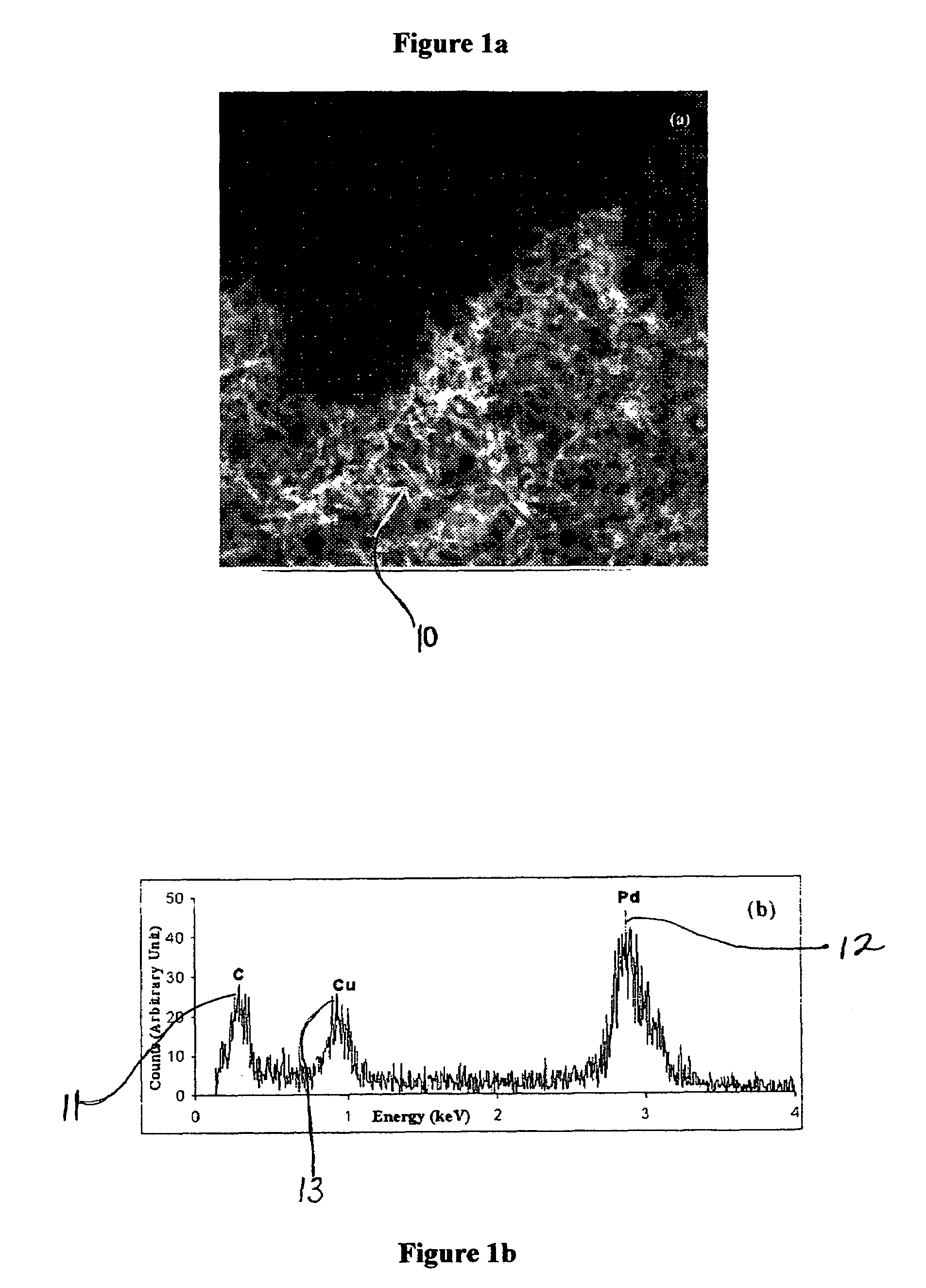
A kind of preparation method of bacterial cellulose supported nanometer palladium catalyst
ActiveCN102274753AEasy to makeImprove thermal stabilityOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPotassium borohydridePtru catalyst
The invention discloses a method for preparing a bacterial cellulose loaded nanometer palladium catalyst. The method comprises the following steps of: pretreating bacterial cellulose, stirring the pretreated bacterial cellulose in ultrapure water, and dispersing; adding palladium chloride or palladium nitrate, dispersing fully, removing oxygen, and heating; adding potassium borohydride solution; and after reaction is finished, blanching and centrifugal separation repeatedly to obtain the bacterial cellulose loaded nanometer palladium catalyst. In the method, divalent potassium ions are reduced by using the potassium borohydride solution under the hydrothermal condition to form the zero-valent palladium catalyst with small grain diameters and uniform distribution; and the preparation process is simple, the prepared catalyst is high in catalytic efficiency, and the method can be applied in the fields of organic synthesis and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Synthesis of carbon nanotubes filled with palladium nanoparticles using arc discharge in solution
InactiveUS7438885B1Improve abilitiesMaterial nanotechnologyFibre chemical featuresNanotubeMaterials science
A novel method for simultaneously forming and filling and decorating carbon nanotubes with palladium nanoparticles is disclosed. Synthesis involves preparing a palladium chloride (PdCl2) solution in a container, having two graphite electrodes, then immersing the graphite electrode assembly, into the PdCl2 solution; connecting the graphite electrodes to a direct current power supply; bringing the electrodes into contact with each other to strike an arc; separating the electrodes to sustain the arc inside the solution; putting the container with electrode assembly in a water-cooled bath; and collecting Pd-nanoparticles encapsulated in carbon nanotubes and carbon nanotubes decorated with Pd-nanoparticles. The temperature at the site of the arc-discharge is greater than 3000° C. At these temperatures, the palladium is ionized into nanoparticles and the graphite electrodes generate layers of graphene (carbon), which roll away from the anode and encapsulate or entrap the Pd-nanoparticles. The unique nanotube structures have significant commercial potential as gas sensors or as a means for hydrogen storage.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Preparation method of nano-palladium or palladium-nickel alloy catalyst having three-dimensional porous structure
InactiveCN102925923AIncrease the specific surface area of electrochemical activityEasy transferPhotography auxillary processesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystMetallurgy
The invention belongs to the technical field of direct methanol fuel cells and discloses a preparation method of a nano-palladium or palladium-nickel alloy catalyst having a three-dimensional porous structure. The preparation method comprises carrying out cathode electrodeposition in a metal salt solution to obtain the nano-palladium or palladium-nickel alloy catalyst having a three-dimensional porous structure, wherein in the cathode electrodeposition, produced hydrogen bubbles are used as dynamic templates. The nano-palladium or palladium-nickel alloy catalyst obtained by the preparation method is a three-dimensional porous Pd or Pd-Ni alloy, has aperture walls composed of nanoscale dendritic crystals, has a large chemically active specific surface area, and has good catalytic activity and stability in electrocatalytic oxidation of methanol. The preparation method has simple processes, obvious effects and a wide application prospect in the field of anode catalysts of direct methanol fuel cells.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Highly dispersed palladium/carbon nanometer tube catalyst for anthraquinone hydrogenation and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103055852AReduce dosageReduce storagePeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsAnthraquinonesSlurry reactor
The invention discloses a highly dispersed palladium / carbon nanometer tube catalyst for anthraquinone hydrogenation and a preparation method thereof, and relates to a catalyst and a preparation method. According to the invention, a carbon nanometer tube industrial product with good conductivity, heat conductivity, high mechanical strength and huge external specific surface is used as a palladium carrier; simultaneously ultrasonic is utilized to further enhance the dispersity and uniformity of palladium and the carbon nanometer tube; and a nanometer palladium catalyst uniformly loaded on the surface of the carbon nanometer tube is prepared in a slurry reactor by adopting a liquid phase reduction method. The catalyst needs no extrusion molding and can be directly suspended in the liquid phase for normal-pressure or pressurized hydrogenation of anthraquinone; the activity of the catalyst is not reduced after the catalyst is used for a plurality of times by filtration and separation; moisture, acid and alkaline do not influence the use effect; the catalytic activity of the new catalyst is 4-8 times higher than that of the traditional Pd / gamma-Al2O3 catalyst, and the amount of the catalyst used can be greatly reduced. The catalyst can be used for replacing the traditional catalyst, the post treatment of the traditional catalyst is simplified, the treatment capability of a device is greatly increased, and the operation cost is lowered.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV +2
Preparation method and use of functional graphene-loaded palladium nanoparticle composite material
InactiveCN103344686AGood dispersionImprove solubilityMaterial electrochemical variablesUltrasonic dispersionSodium salt
The invention discloses a preparation method and a use of a functional graphene-loaded palladium nanoparticle composite material. The preparation method comprises the following steps of carrying out ultrasonic dispersion of graphene in water to obtain a graphene suspension liquid, adding a pyrenetetrasulfonic acid sodium salt aqueous solution into the graphene suspension liquid, carrying out heating stirring for 8-15h, carrying out centrifugal filtration to obtain functional graphene, dispersing the functional graphene in water to obtain a functional graphene suspension liquid, adding a palladium chloride solution into the functional graphene suspension liquid, adding a sodium borohydride solution into the mixed solution, carrying out heating stirring for 8-15h, and carrying out centrifugal filtration to obtain the functional graphene-loaded palladium nanoparticle composite material. Through functionalization of graphene by the pyrenetetrasulfonic acid sodium salt, dispersibility and stability of graphene and palladium nanoparticles are improved. A glassy carbon electrode modified by the functional graphene-loaded palladium nanoparticle composite material has a good nitroaromatic compound catalysis performance, a low nitroaromatic compound detection limit, a wide nitroaromatic compound detection linear range, high nitrobenzene detection sensitivity, a nitrobenzene detection linear range of 170-8ppb, and a nitrobenzene detection limit of 0.62ppb.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing modified nanometer-palladium/iron duplex-metal particles
InactiveCN103100721AGood dispersionImprove antioxidant capacityPolymethyl methacrylateMetal particle
The invention discloses a method for preparing modified nanometer-palladium / iron duplex-metal particles. Macromolecule polymer polymethyl methacrylate is used as a modifying agent, absolute ethyl alcohol is used as cosolvent, and particle surfaces are modified in the process of nanometer-palladium / iron double duplex-metal particle preparation. The preparation method includes that anisole is adopted as solvent of the polymethyl methacrylate, the absolute ethyl alcohol is used as the cosolvent, ferrous saline solution is a precursor solution of zero-valent iron, wherein the zero-valent iron is prepared proportionally through aqueous phase the according to a certain proportion, the precursor solution forms nanometer zero-valent iron particles under the action of reducing agent hydroboration, and then an impregnation method is adopted to conduct palladiumizing to the nanometer zero-valent iron particles, and finally high polymer which is added with the nanometer-palladium / iron duplex-metal particles modified by ethanol is prepared. The nanometer-palladium / iron duplex-metal particles prepared through the method have good dispersity, inoxidizability, and dechlorinating reactivity. The method can be achieved simply in common temperature and common pressure, is simple and convenient to manufacture, and has wide application prospects.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing hammer-shaped palladium nanoparticle by utilizing octreotide acetate as template
InactiveCN103203461AExcellent biological templateSimple molecular structureOctreotide acetateSodium borohydride
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Preparation of Pd nano particle
InactiveCN101279375ABiocompatibleShort reaction timeAqueous sodium hydroxideBiocompatibility Testing
A preparation method of palladium nanoparticles dissolves H2PdCl4 and glucose in water, the amount ratio of the H2PdCl4, glucose and water is that: H2PdCl4: glucose: water is equal to 1mmol: 30 to 100mmol: 50 to 200ml, sodium hydroxide water solution is dropped till the pH value of the reaction solution achieves 7 to 8 under the stirring situation, the color of the reaction system turns red from yellow, thus obtaining the palladium nanoparticles with the pure face-centered cubic phase and the diameter of the particles of 3 to 4 nanometers. The preparation method of the palladium nanoparticles of the invention is carried out under the normal temperature and the normal pressure, which is simple and safe, the reaction time is short, the preparation method almost has no power consumption, the used reagent is environment-friendly and cheap; furthermore, as the invention adopts the glucose as a reducing agent and a stabilizer, the obtained palladium nanoparticles have biocompatibility.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Processes for producing palladium nanoparticle inks
A process for preparing a palladium nanoparticle ink comprises reacting a reaction mixture comprising a palladium salt, a stabilizer, a reducing agent, and an optional solvent to directly form the palladium nanoparticle ink. During the formation of the palladium nanoparticle ink, the palladium nanoparticles are not isolated from the reaction mixture.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Palladium/nitrogen-doped graphene composite electrode catalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105024086AImprove electrochemical performanceGood repeatabilityCell electrodesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsNitrogen doped grapheneHigh pressure
The invention discloses a palladium / nitrogen-doped graphene composite electrode catalyst and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out ultrasonic dispersion on oxidized graphene in water, adding tripolycyanamide, heating and stirring the mixture, freezing and drying the mixed system and carrying out high-temperature heat treatment, so as to obtain nitrogen-doped graphene; carrying out ultrasonic dispersion again on the nitrogen-doped graphene in an ethylene glycol solution, adding a palladium nitrate solution to the ethylene glycol solution and mixing the mixture evenly; reducing palladium nitrate by virtue of a mild reduction method, and depositing palladium nanoparticles in-situ on the surface of the nitrogen-doped graphene; and after reaction is ended, carrying out centrifugal separation to obtain a solid product, and washing and drying the product to obtain the catalyst. By virtue of the mild reduction method, the palladium nanoparticles are deposited in-situ on the surface of the nitrogen-doped graphene; and high temperature or high pressure is not needed, so that the preparation method is simple and controllable, and the repeatability is relatively good. The prepared palladium / nitrogen-doped graphene composite electrode catalyst has excellent electrochemical properties as a direct methanol / formic acid fuel cell cathode material.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Method for preparing nano-sized metal particles on a carbon support
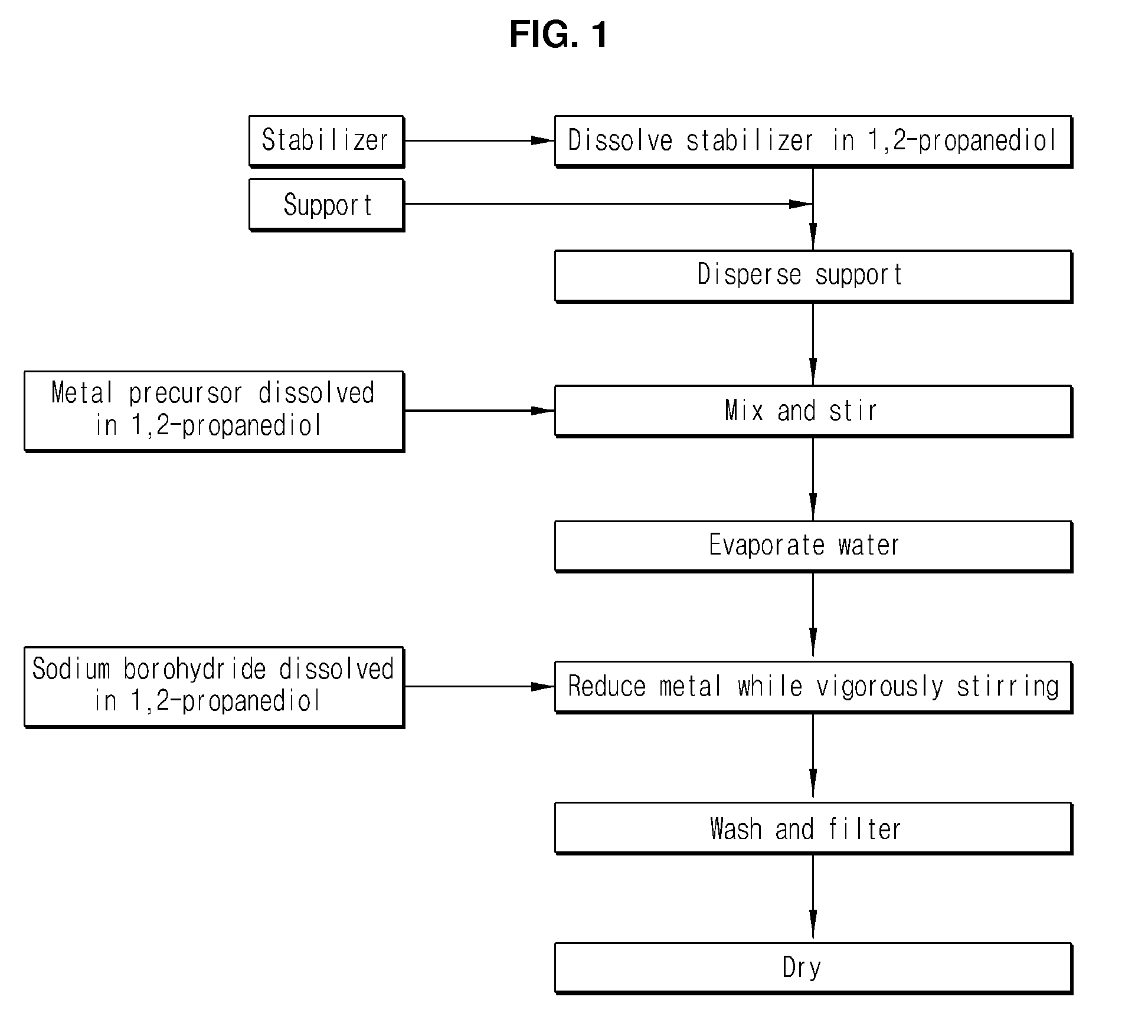
ActiveUS20110123908A1Narrow particle size distributionSimple processNanostructure manufactureActive material electrodesMetal particlePropanediol
Disclosed is a method for preparing nickel or palladium nanoparticles supported on a carbon support. To a mixture solution wherein a stabilizer is dissolved in 1,2-propanediol, a carbon support is added to prepare a dispersion. Then, a precursor solution wherein a nickel or palladium precursor dissolved in 1,2-propanediol is mixed therewith and stirred. Then, nickel or palladium nanoparticles supported on the carbon support are prepared by reduction. The disclosed method for preparing nickel or palladium nanoparticles supported on a carbon support allows preparation of nanoparticles with narrow particle size distribution and good dispersibility through a simple process and the resulting nickel or palladium nanoparticles may be usefully applied, for example, as electrode materials of fuel cells.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Palladium/carbon nanotube catalyst for hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101703930AFine and uniform particle sizeHigh selectivityOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationPalladium catalystCarbon nanotube
The invention discloses a palladium / carbon nanotube catalyst for the hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde and a preparation method thereof. The carrier of the catalyst is carbon nanotubes, and the active ingredient of the catalyst is noble metal palladium nanoparticles with an average particle size of 5 to 6 nanometers. The catalyst contains 0.1 to 5 mass percent of palladium and the balance of the carbon nanotubes. The preparation method of the catalyst comprises: 1) dissolving a palladium salt in deionized water to prepare 0.01 to 0.2 mol / L aqueous solution of the palladium salt, adding the carbon nanotubes into the aqueous solution of the palladium salt and subjecting the solution to ultrasonic dispersion for 0.5 to 1 hour; 2) with magnetic stirring, dripping reducer-containing aqueous solution till the ratio of the reducer and the palladium is 1:1 to 2:1, and continuously stirring for 1 to 2 hours after the dripping is finished; and 3) finally, stirring the solution in an oil bath for 1 to 2 hours, and obtaining the palladium / carbon nanotube catalyst by filtering, washing and drying. Compared with active carbon supported palladium catalyst, the palladium / carbon nanotube catalyst has high selectivity for the preparation of benzenepropana by the hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde.
Owner:葛昌华 +3
Method for preparing nano palladium metal catalyst
InactiveCN103657643ARaw materials are cheap and easy to getHigh activityMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic compound preparationNanoparticlePalladium nanoparticles
The invention discloses a method for preparing a nano palladium metal catalyst. The method for preparing the nano palladium metal catalyst comprises the steps of performing functional grafting pretreatment on a carrier, dipping a palladium salt solution, reducing the palladium salt solution to obtain nano metal particles, and finally coating the nano metal particles separately by using an embedding agent to obtain a final solid-supported nano palladium metal catalyst. The method is characterized by comprising functionally grafting the carrier and separately coating a nano metal catalyst; the effect of the method is shown in a grafting effect of a functional additive, so that forming and dispersing of the nano palladium metal particles are facilitated; through the embedding agent, the stability of the catalyst is improved in the process of using a palladium nanoparticle catalyst; the recycling of the catalyst is facilitated, and the catalyst can be reused. The preparation method of the catalyst is simple and convenient, cheap and easily available in raw materials and applicable to industrial production.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Nano Pd catalyst and its preparation and application
InactiveCN1883793AHigh activityReduce dosageCatalyst activation/preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsAlcoholOrganic base
Disclosed is a nano-palladium catalyst which is polymer loading nano-palladium catalyst produced by water-soluble inorganic palladium salt and water-soluble macromolecule in low-carbon alcohol at 60-90 DEG C. The preparation process is simple, activity of the catalyst is high and the catalyst can be used repeatedly. When using the catalyst to preparation biphenyl, solvent can be water, organic base can be replaced by inorganic base, the process is simplified and avoids more waste gas, liquid and solid, dosage of catalyst is few, purity of product is not less than 99.5 % and yield is not less than 95 %.
Owner:淮北煤炭师范学院
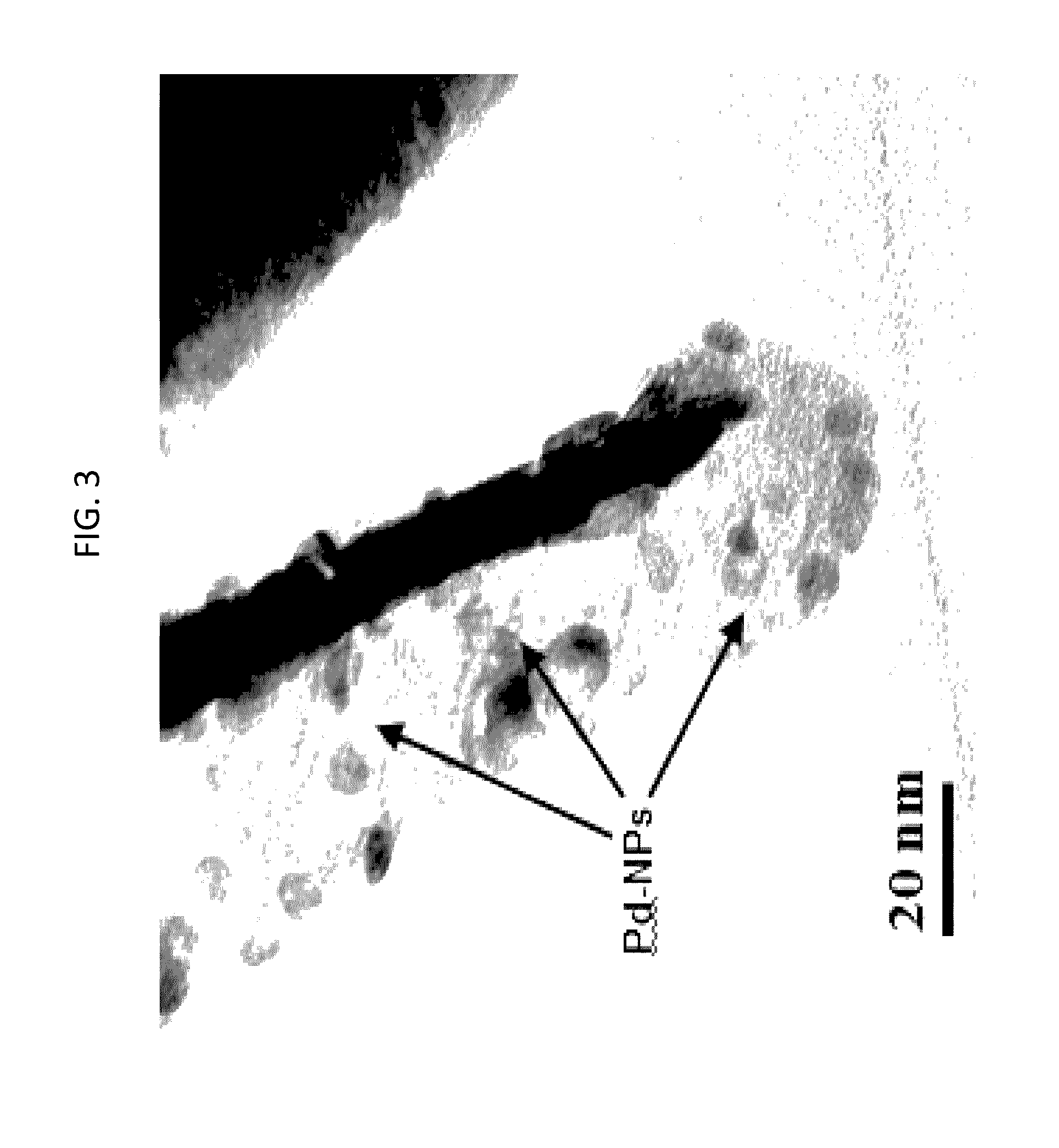
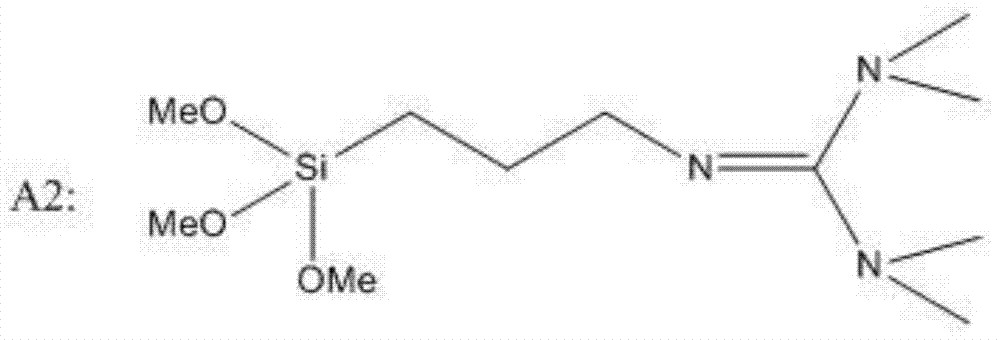
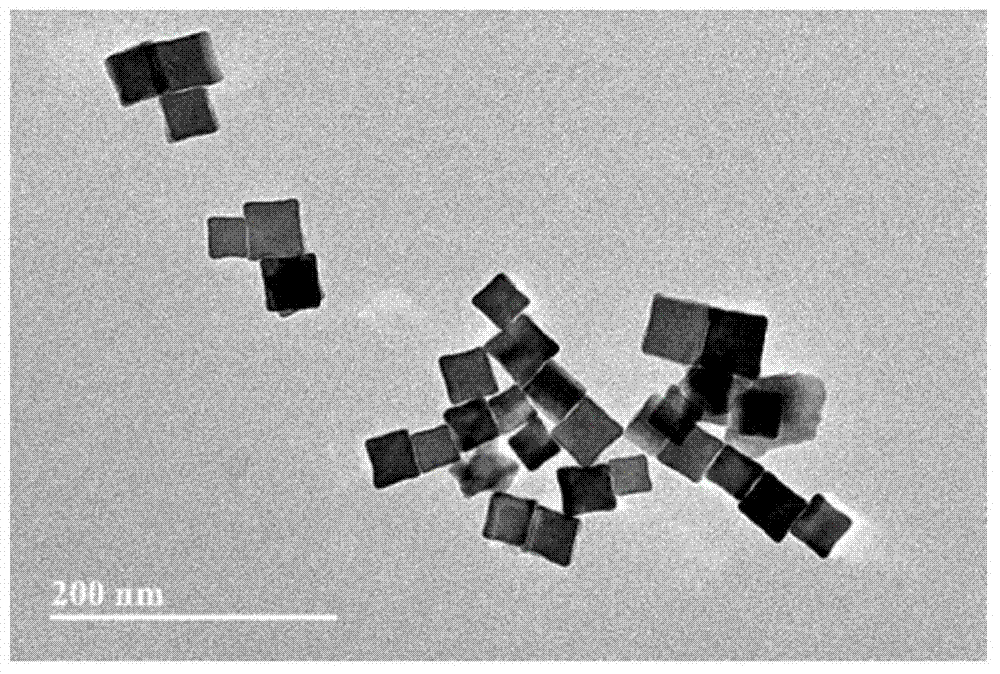
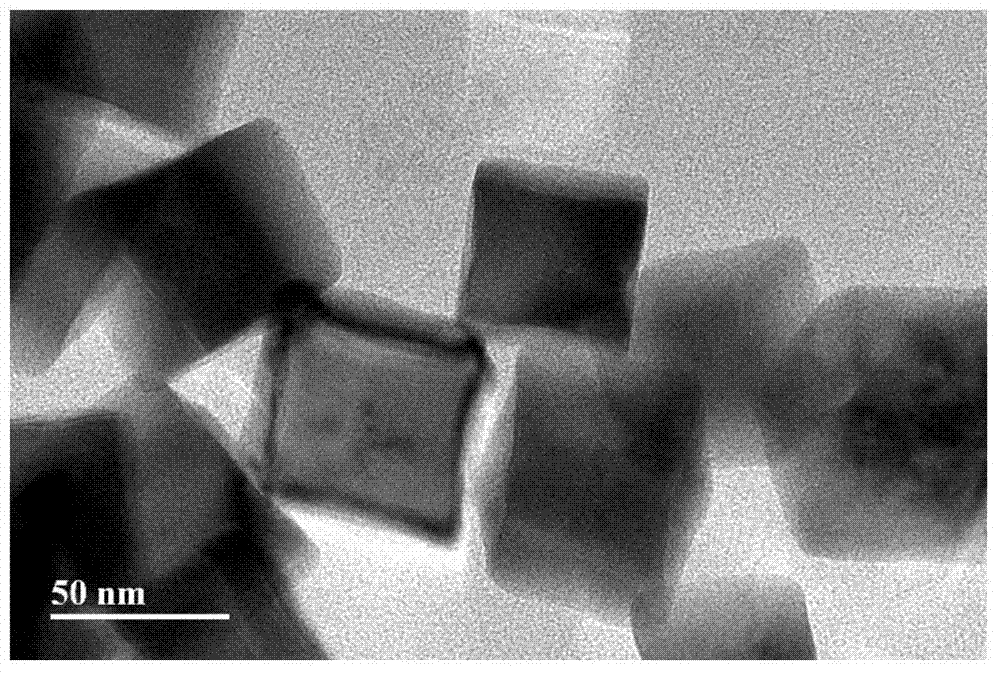
Palladium nanoparticles and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses palladium nanoparticles which are in the shape of concave cubes, wherein the surfaces of the concave cubes consist of high-index crystal surfaces. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the palladium nanoparticles. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing palladium salt with a surfactant, adding a reducer aqueous solution while stirring to obtain a mixed solution, and performing stirring reaction on the mixed solution at 10-90 DEG C for 1-12 hours, wherein the mixed solution contains Br-ions and the molar ratio of the surfactant to the palladium salt is 2 to 1; after the reaction is finished, performing centrifuging, and washing to obtain the palladium nanoparticles. The palladium nanoparticles are prepared by a seed-free one-step method; the preparation process is simple, environment-friendly and mild in reaction condition; the prepared palladium nanoparticles are controllable in shape and relatively good in dispersity.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method and catalytic application of Silicalite-1 single crystal-coated nanopalladium-loaded core-shell catalyst
ActiveCN107442155AMetal loss resistanceWith high temperature aggregationMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon by hydrogenationMolecular sieveSingle crystal
The invention discloses a preparation method and catalytic application of a Silicalite-1 single crystal-coated nanopalladium-loaded core-shell catalyst, and belongs to the field of novel catalytic materials. The preparation method comprises the following steps: under the hydroxyl action between 3-aminopropyl triethoxysilane and the surfaces of Silicalite-1 molecular sieve nanocrystals, modifying amino groups onto the surfaces of the molecular sieve nanocrystals; then, through coordination and complexation actions between the Pd<2+> and the amino groups modified on the outer surfaces of the Silicalite-1, uniformly and fixedly loading the Pd<2+> onto the surface of a nanocrystal molecular sieve to form the palladium-loaded nanocrystals Pd / Silicalite-1; finally, adding the Pd / Silicalite-1 nanocrystals into a synthesis solution of Silicalite-1 molecular sieve single crystals, and synthesizing the Pd@Silicalie-1 single crystal-coated core-shell catalyst via induced growth. By the preparation method, preparation is simple and high in efficiency, and the defects that the conventional catalyst is poor in monodispersity, is required to be roasted for multiple times and takes a long time for crystallizing or posttreating a sample are overcome. Compared with the traditional homogeneous catalyst, the core-shell catalyst has the characteristics of excellent shape selectivity, metal loss resistance, high temperature aggregation resistance and the like, so that the core-shell catalyst has a wide application prospect.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Palladium nanoparticle/carbon nanofiber compound, preparation method and application thereof in electrocatalysis
ActiveCN101665232AGood dispersionImprove stabilityIndividual molecule manipulationMaterial electrochemical variablesCarbon nanofiberPalladium nanoparticles
The invention relates to a palladium nanoparticle / carbon nanofiber compound, a preparation method and an application thereof in electrocatalysis. The compound is directly prepared by a one-step electrospinning method. An electrode modified by the compound is used for direct eectrochemical detection on hydrogen peroxide, beta-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, dopamine, ascorbic acid and lithic acid. The electrode modified by the compound has the linear range from 0.2 micrometer to 20 millimetres and the detection limit of 0.2 micrometer when being used for the detection on the hydrogen peroxide and has the linear range of 0.2-716.6 micrometers and the detection limit of 0.2 micrometer when being used for the detection on the beta- nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; and the peak-peak potential differences between the ascorbic acid and the dopamine, the dopamine and the lithic acid as well as the ascorbic acid and the lithic acid are respectively 244mV, 148 mV and 392 mV, thereby showingthat the modified electrode can be used for simultaneous eectrochemical detection of three substances. The compound can be used in the fields of catalysis, fuel cells and sensing.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
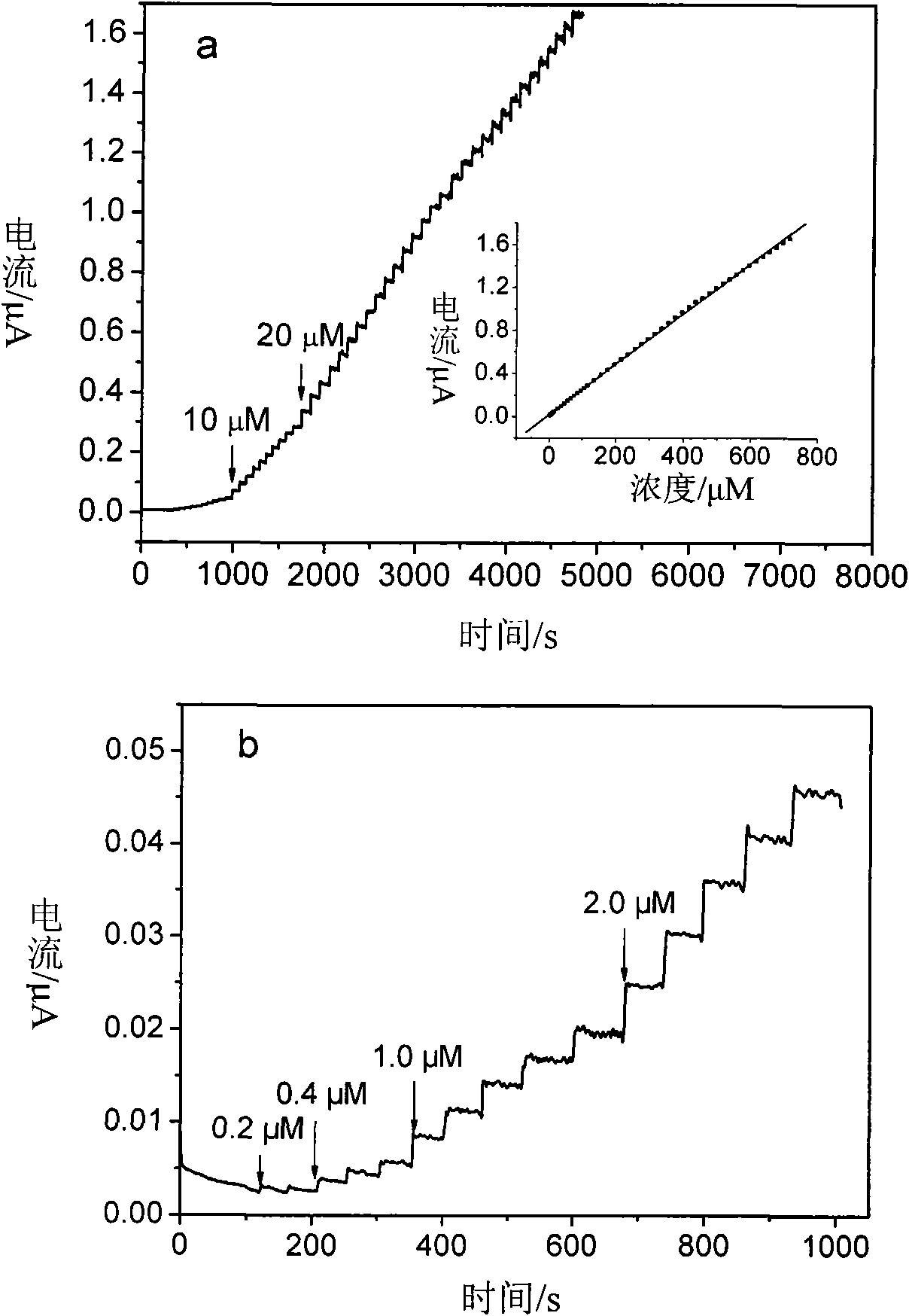
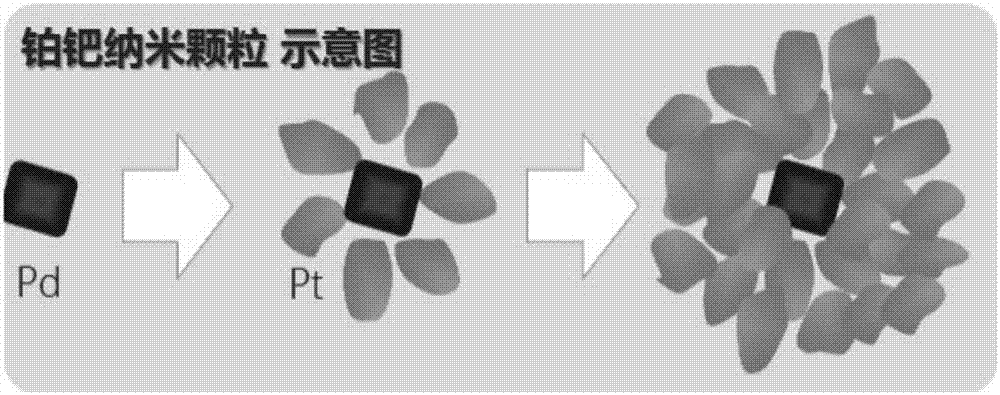
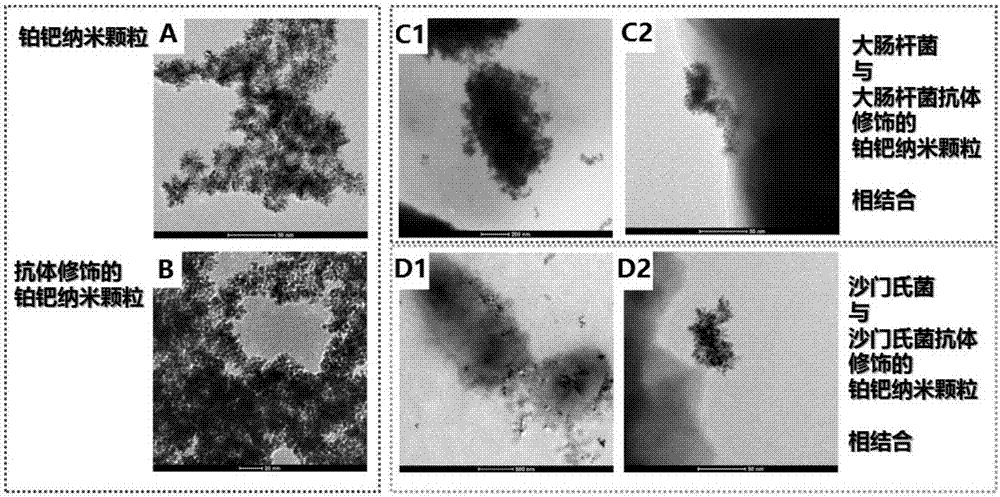
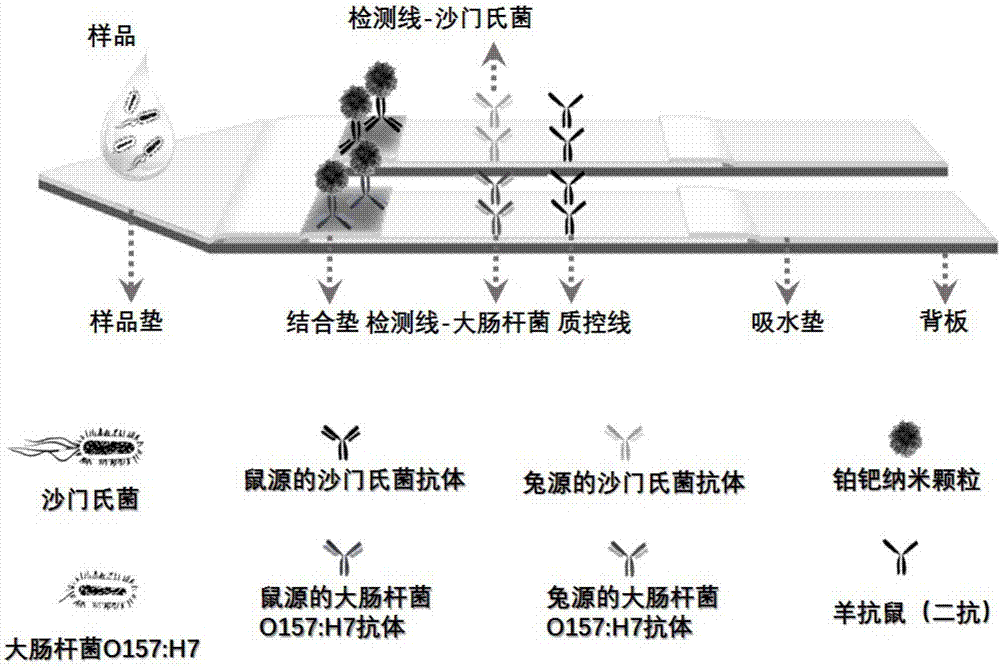
Escherichia coli O157:H7 and salmonella typhimurium co-testing paper, preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to escherichia coli O157:H7 and salmonella typhimurium co-testing paper which comprises a base plate, a sample pad and two absorbing strips, wherein the sample pad is attached to the base plate; the absorbing strips are parallelly arranged on the base plate and are not in contact with each other; a sheep-derived salmonella typhimurium monoclonal antibody and a sheep-derived escherichia coli O157:H7 monoclonal antibody are respectively used as test lines; a goat-anti-rat IgG antibody is a quality control line; and a platinum palladium nanoparticle-salmonella typhimurium monoclonal antibody compound and a platinum palladium nanoparticle- escherichia coli O157:H7 monoclonal antibody compound are coated on a combined pad. According to the invention, the platinum palladium nanoparticle is used for replacing the traditional colloidal gold and is used as a signal element so as to increase the sensitivity, the parallel double-channel design is used for replacing the single multi-detection line design so as to promote the specificity and the co-testing paper can be used for simultaneously detecting escherichia coli O157:H7 and salmonella typhimurium.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
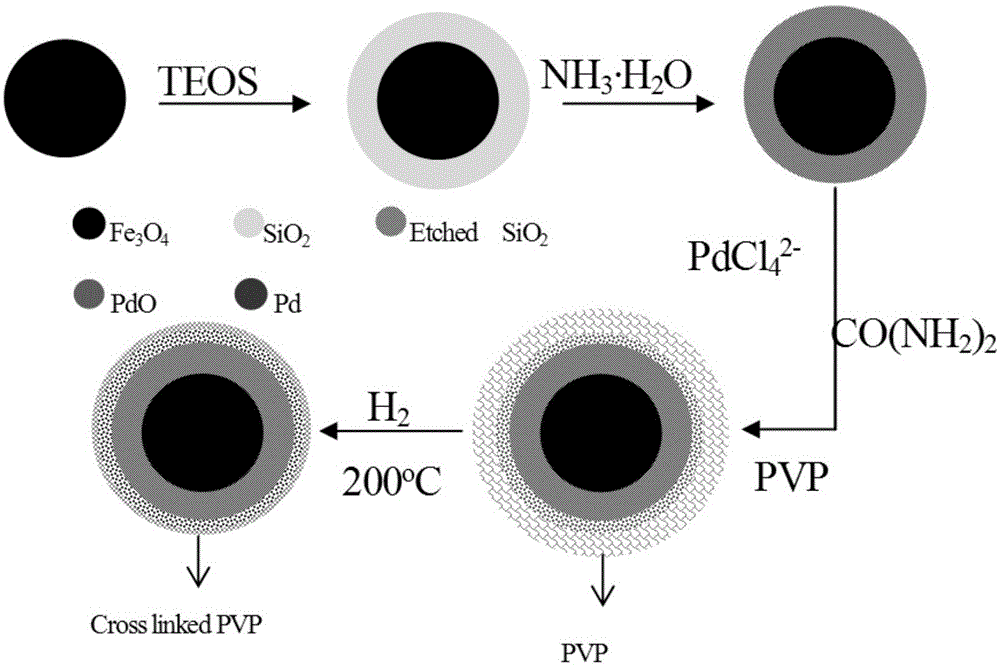
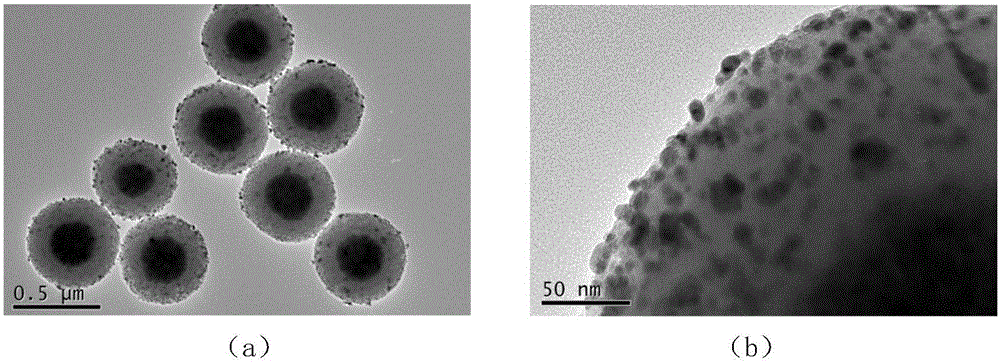
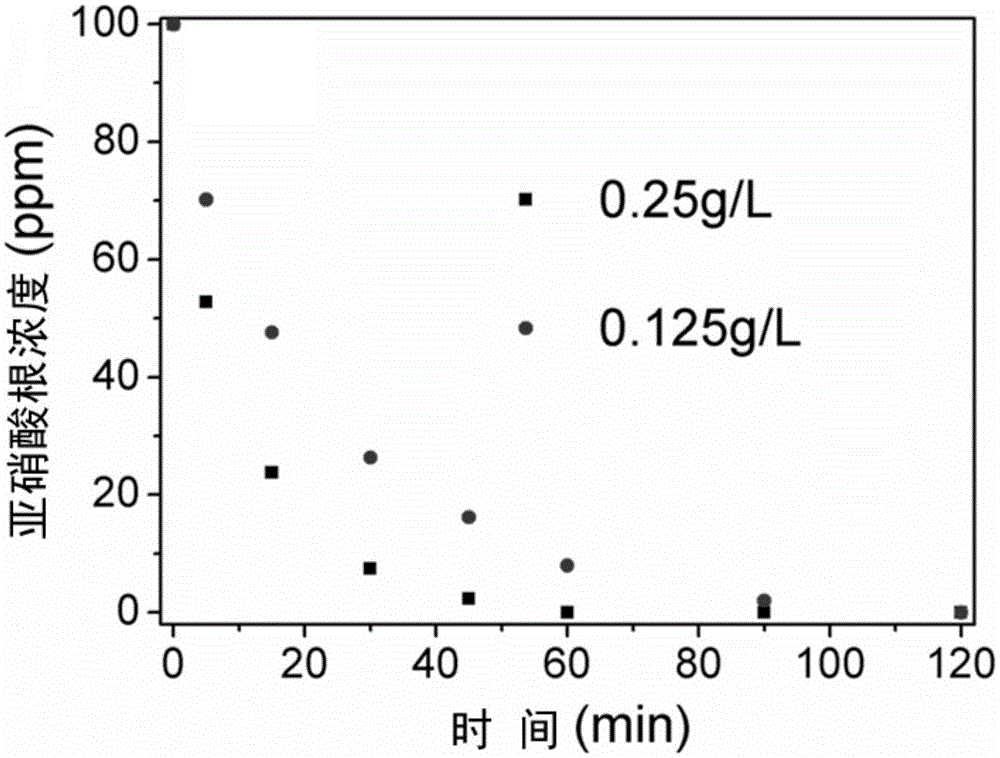
Supported magnetic nano-palladium/gold catalyst and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106466612AAvoid secondary pollutionEasy to manufactureWater contaminantsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsSuperparamagnetismSilicon oxide
The invention discloses a supported magnetic nano-palladium / gold catalyst and a preparation method and an application thereof, which belong to the field of a nano-material and an environment restoration material. The catalyst takes a ferriferrous oxide / silicon oxide core-shell structure as a carrier, the palladium / gold nano particles are supported on the surface; a surface etching method is used for processing the surface of the carrier, a ferriferrous oxide / silicon oxide carrier with the rough surface is constructed; then a homogeneous precipitation method is used for precipitating a palladium oxide which is a precursor of palladium on the surface of a silicon oxide shell layer, finally hydrogen is used for reduction, and crosslinking of polyvinylpyrrolidone is used for fixing the palladium nano particles on the silicon oxide shell layer. The catalyst has good monodispersion performance, the catalytic activity component palladium / gold can be distributed on the surface of the catalyst, so that the utilization is fully realized. The catalyst can be used for catalytic reduction of pollutants such as nitrite, azos dye and hexavalent chromium in water, has superparamagnetism, is easy to separat and reuse, and has high stability.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing nano-palladium electro-catalyst by ethanol reduction
InactiveCN102872861AGuaranteed SolubilityHigh yieldCatalyst activation/preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystAqueous ethanol
The invention relates to a method for preparing a nano-palladium electro-catalyst by ethanol reduction. The method reduces PdCl2 (palladium chloride) to metal Pd (palladium) nano-particles by the aid of ethanol reduction and action of cosolvent, and includes the steps: firstly, preparing ethanol water; secondly, adding PdCl2 powder and protective agents into the ethanol water, feeding shielding gas, heating and stirring to enable palladium positive ions to generate reduction reaction so that the Pd nano-particles are obtained; and thirdly, performing centrifugal separation after reaction is finished to obtain black precipitates, and washing by ethanol and acetone prior to drying so that the nano-palladium electro-catalyst is obtained. The nano-palladium electro-catalyst is synthesized in one step in a normal-temperature environment by using the ethanol water as a solvent and utilizing the reduction action and the solvent effect of the ethanol without additionally adding chemical reduction agents such as ascorbic acid and by means of magnetic stirring and water-bath heating to guarantee solubility of the PdCl2. The method is low in cost, environment-friendly and simple and feasible in operation process, and the prepared nano-palladium electro-catalyst is high in yield and centralized in particle size distribution and has good application prospect.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com