Patents
Literature
61 results about "Dry transfer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
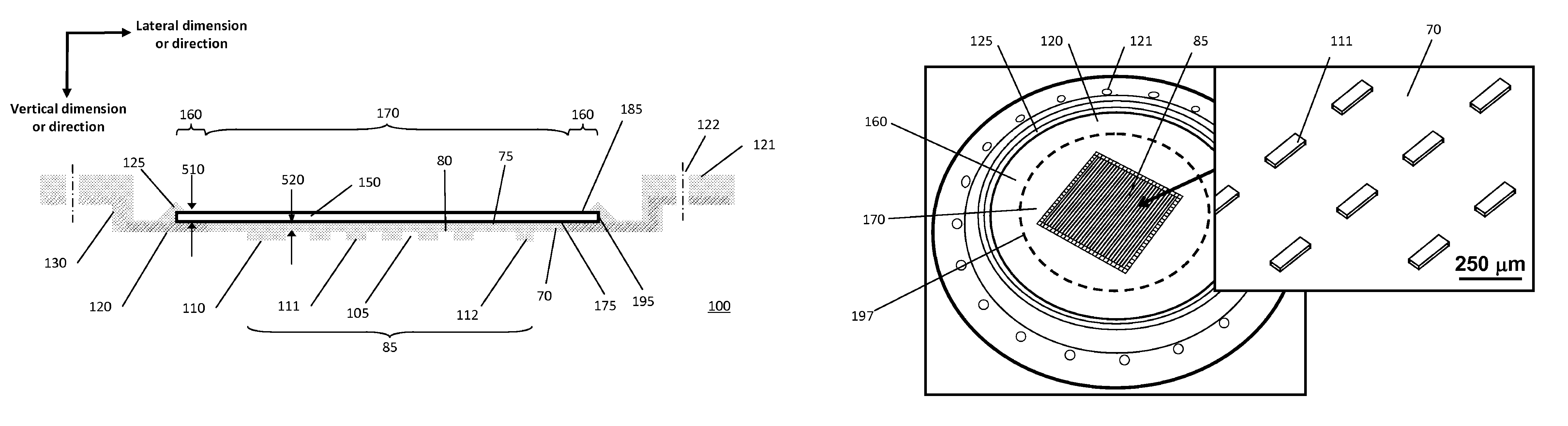
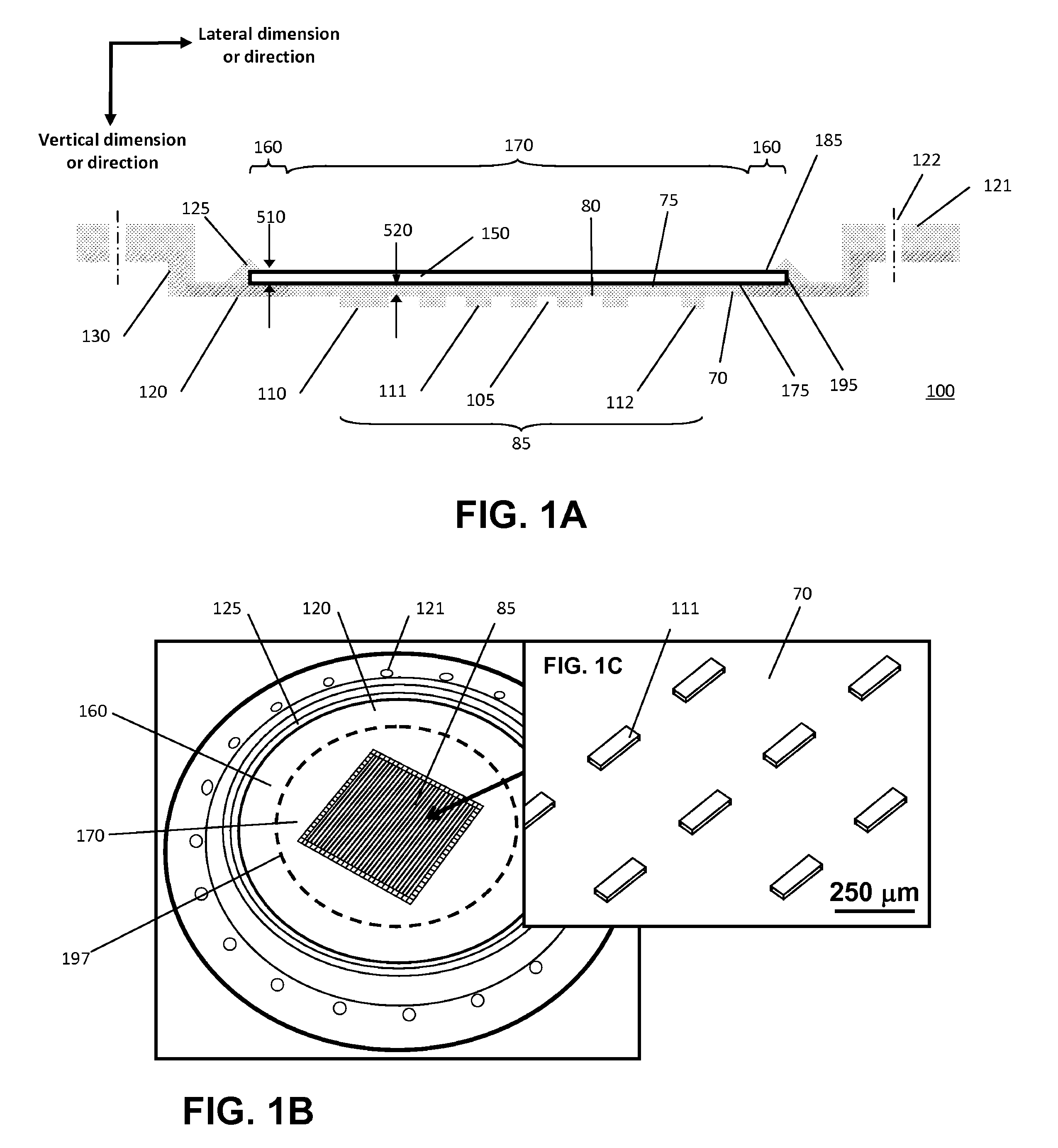
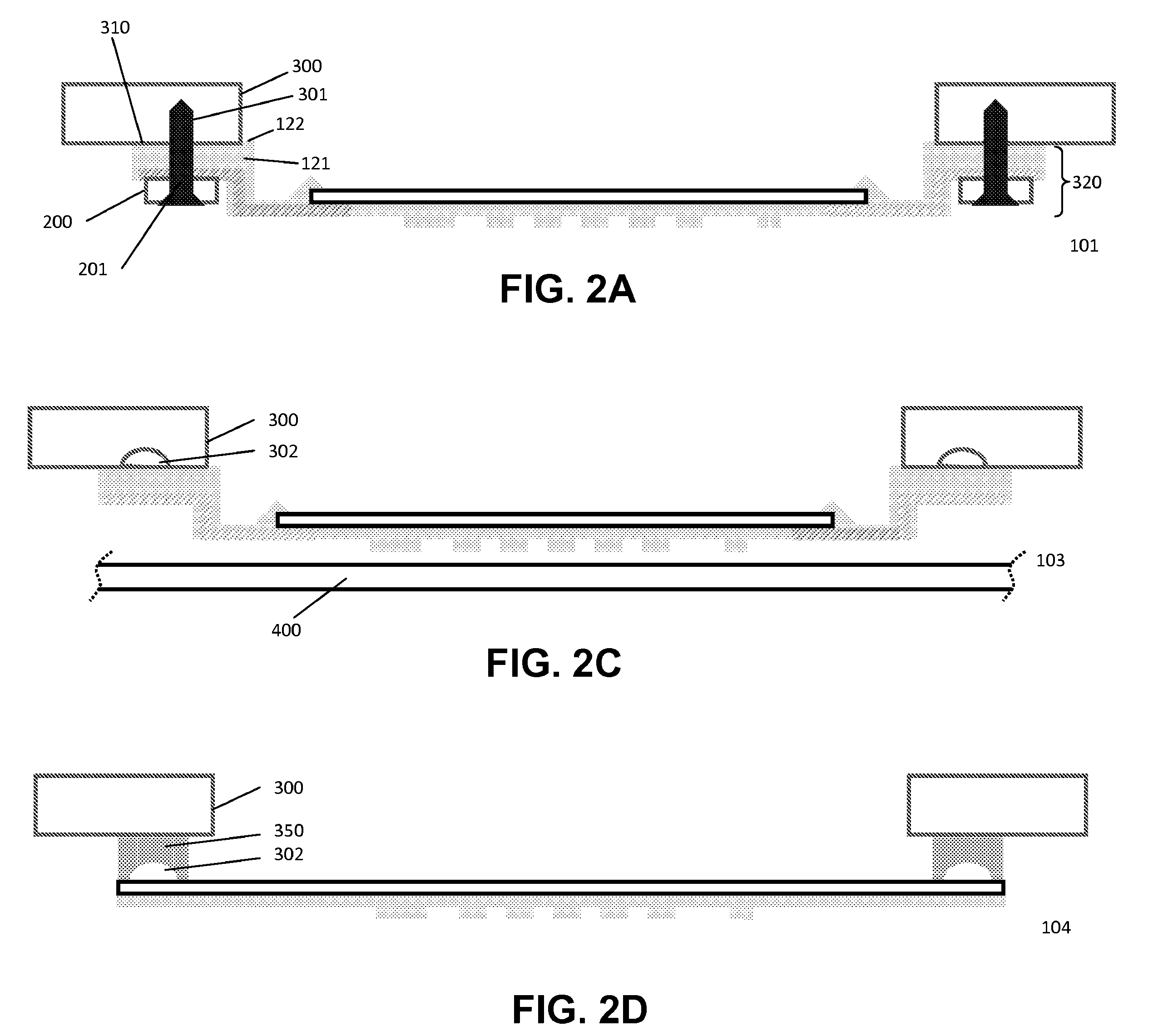
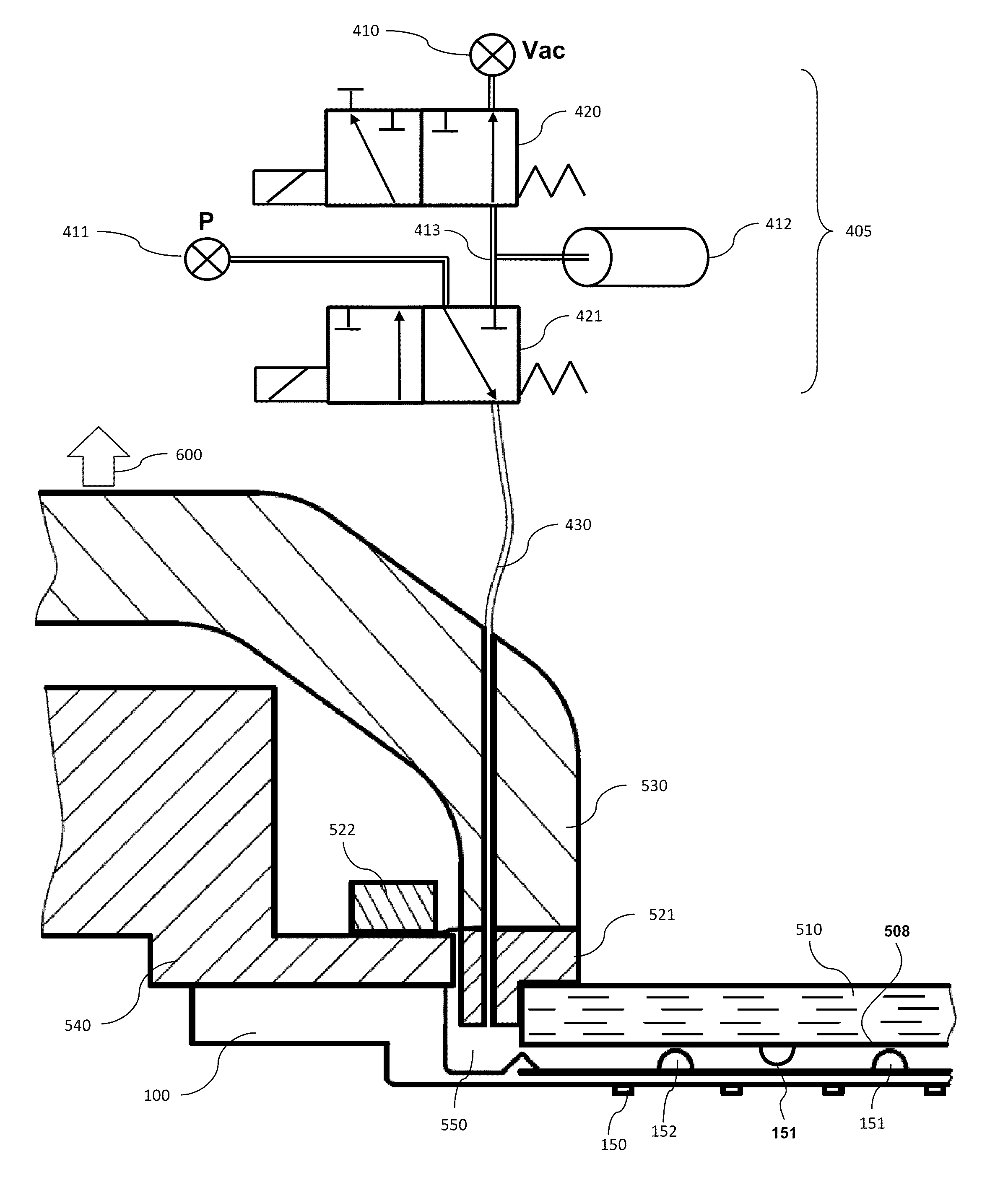
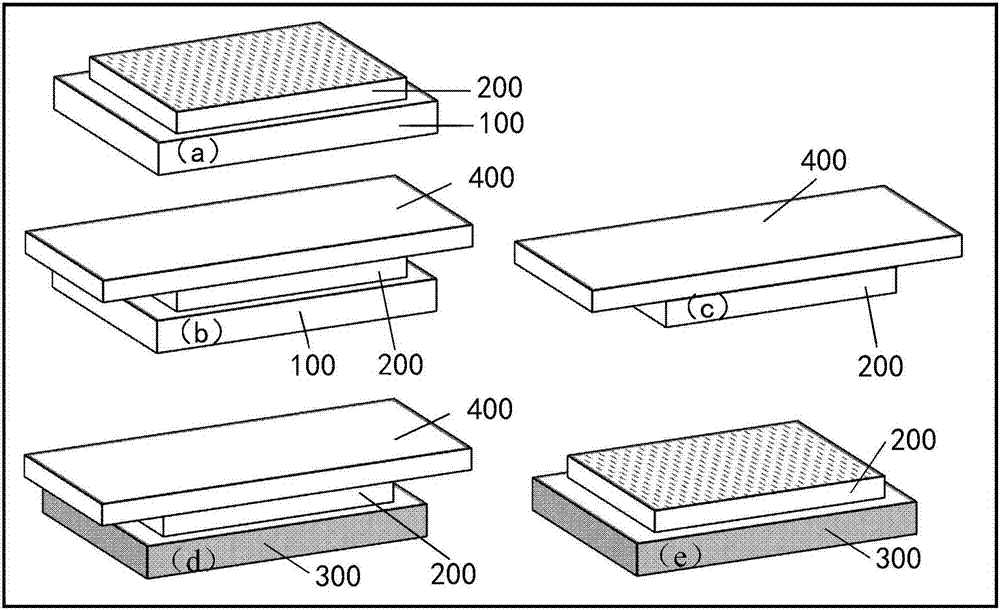
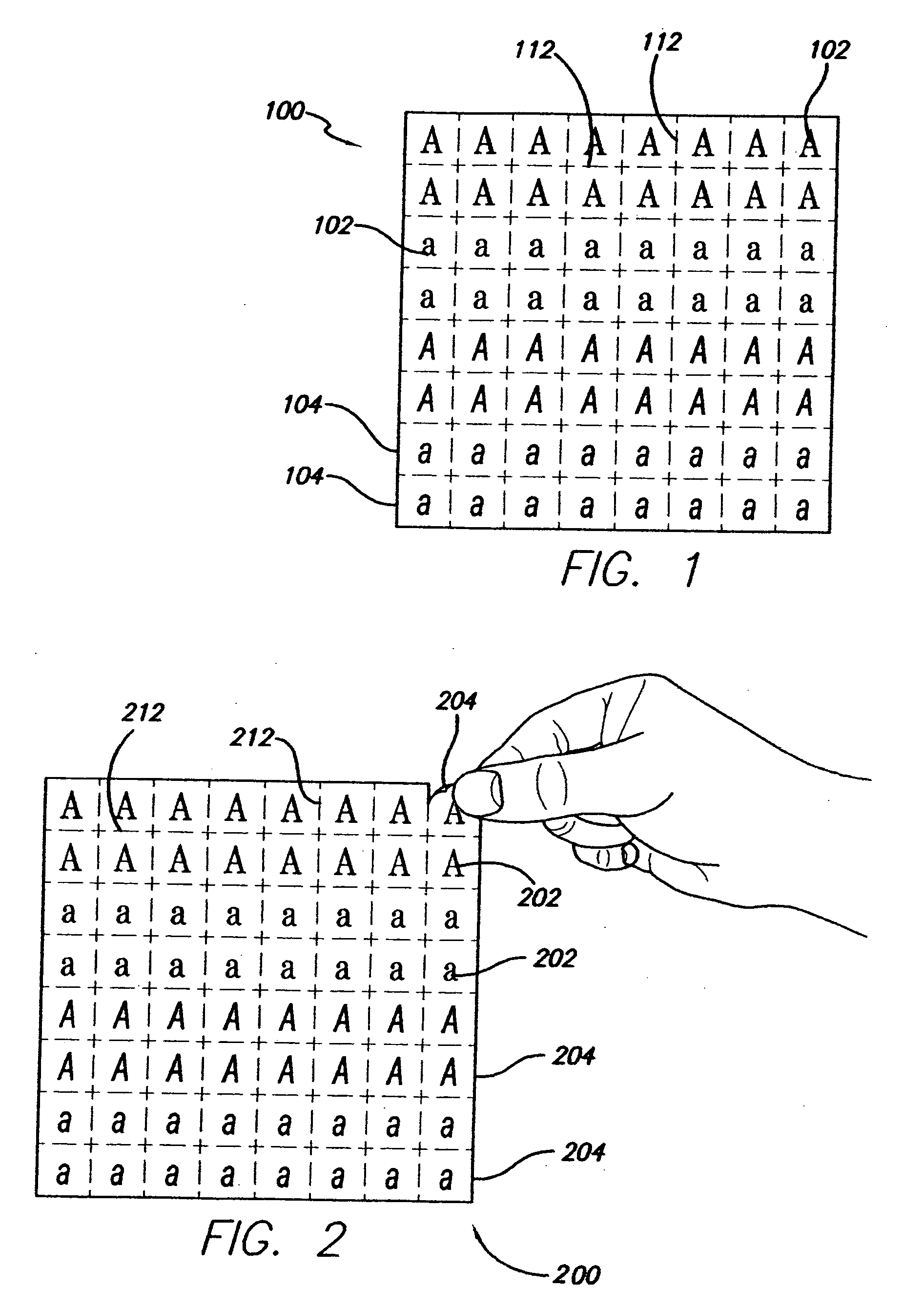
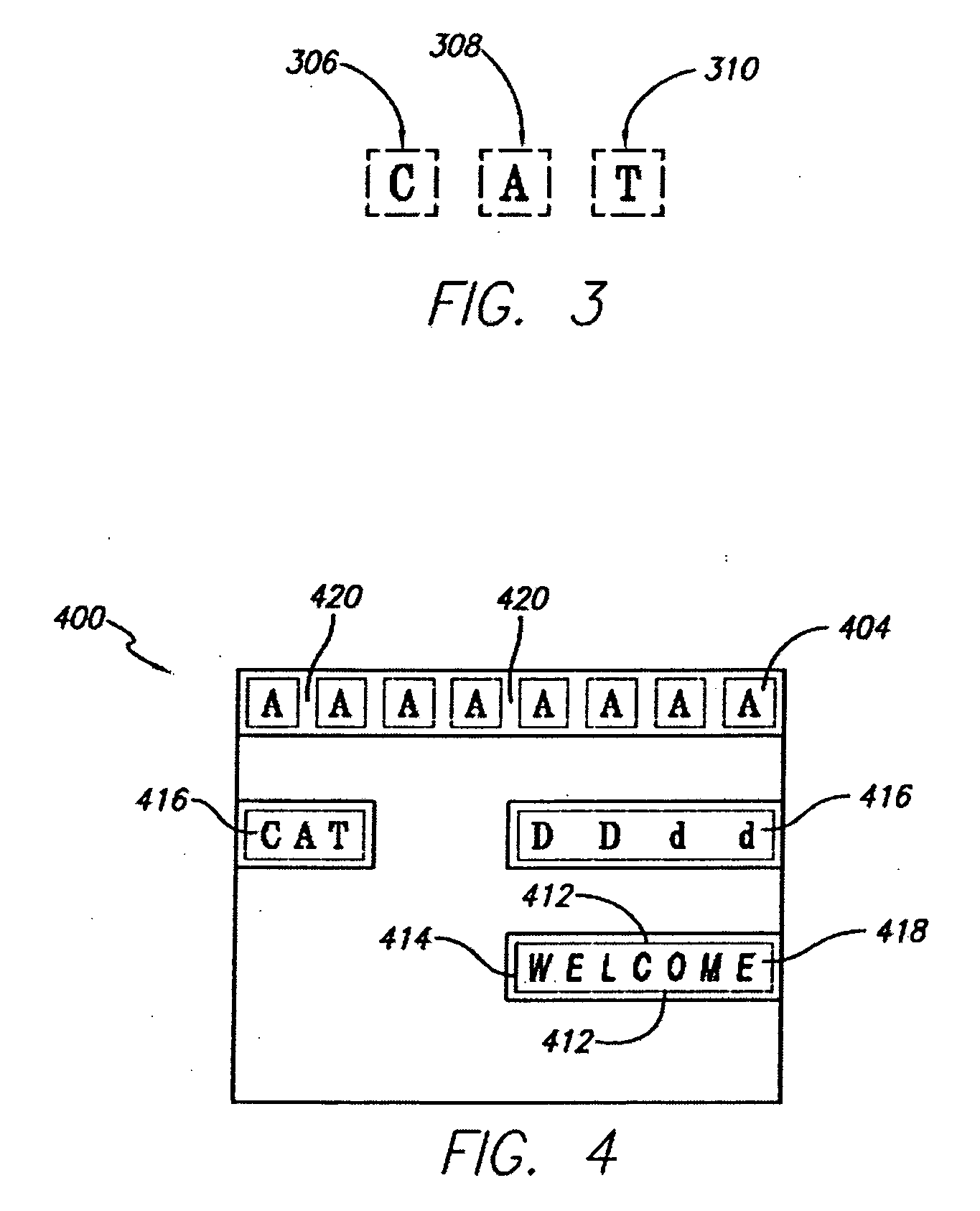
Dry transfers (also called rub-ons or rubdowns) are decals that can be applied without the use of water or other solvent. The decal itself is on a backing material such as paper or plastic sheeting much like a transparency. The dry transfer is placed in the desired location with the backing side up. The decal is then applied by burnishing the backing with a stylus or similar object such as a ballpoint pen. The contact side of the decal includes a pressure-sensitive adhesive; the combination of heat and pressure causes the decal to stick more strongly to the new surface than to the backing. When the backing is removed, the decal remains. This allows for ink only where needed even if the pattern is delicate, because the backing supports the decal while it is being applied.
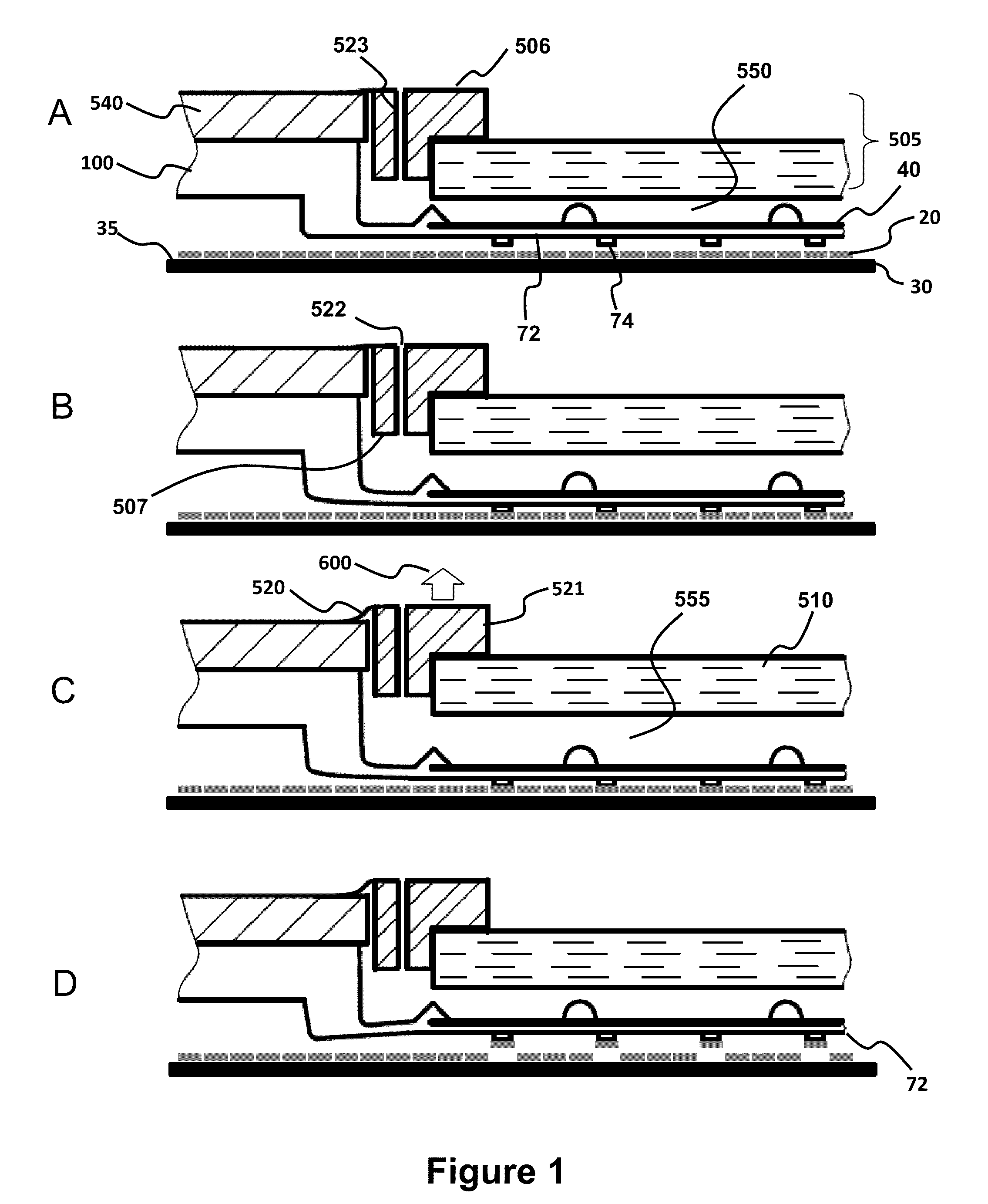
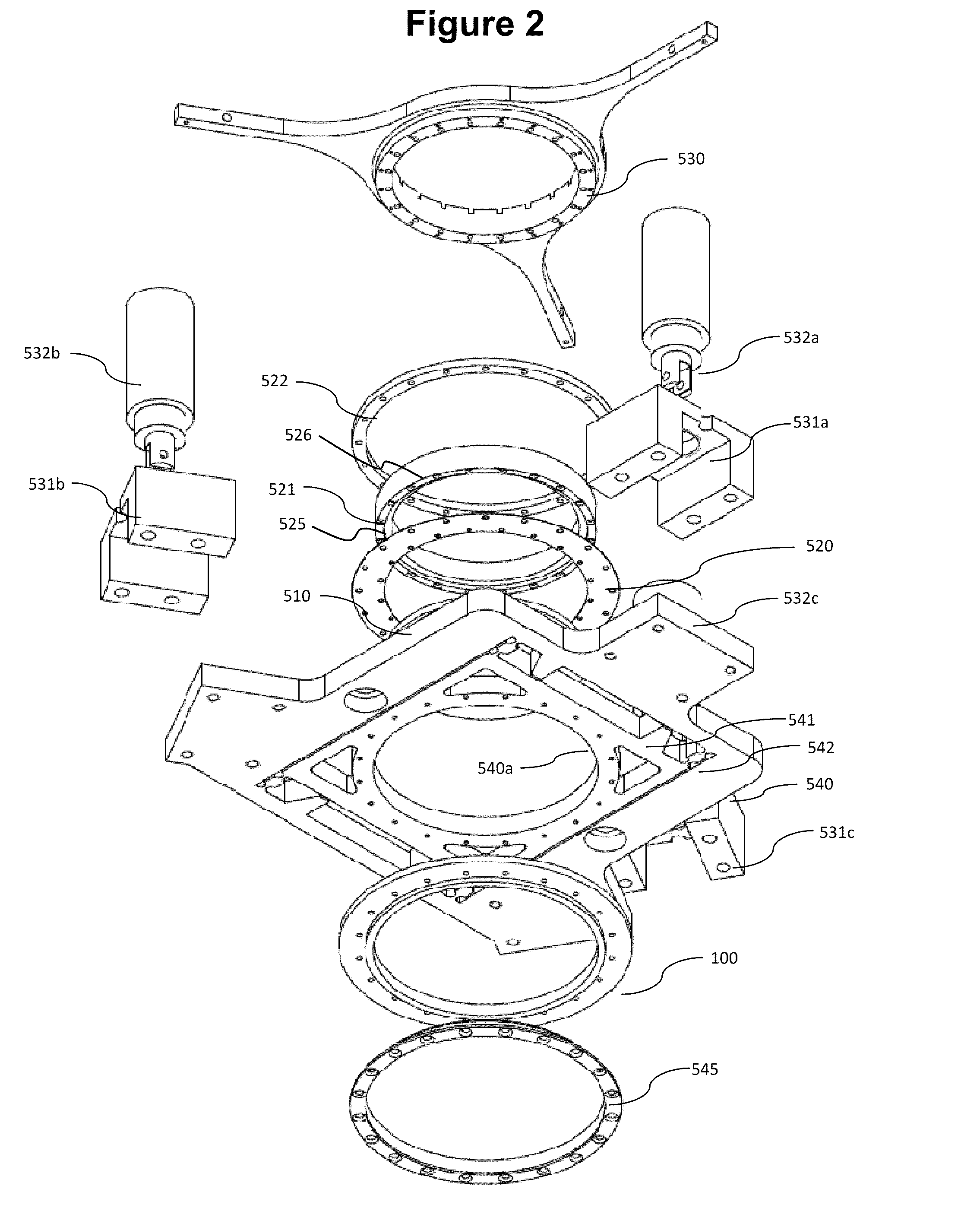
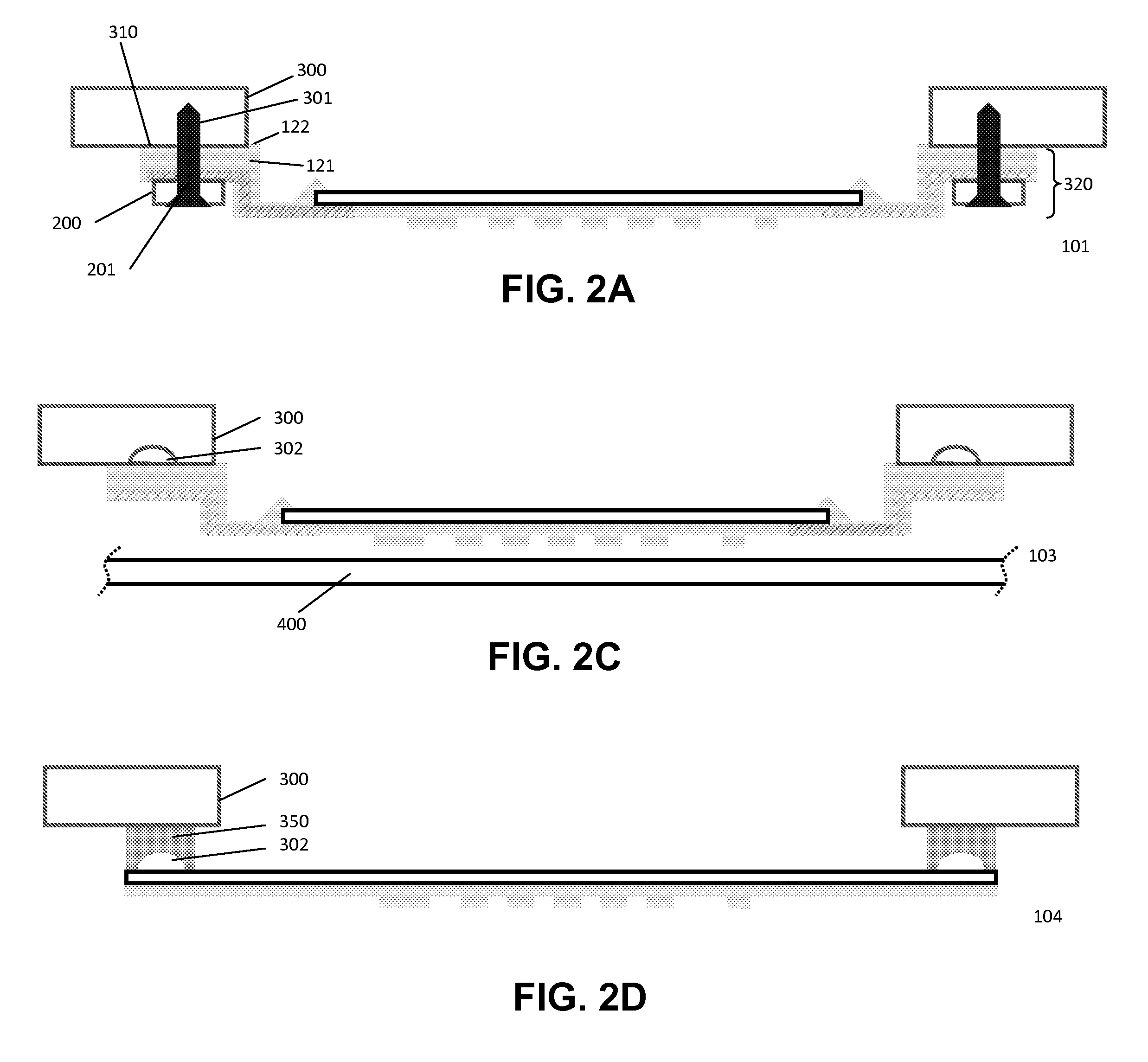
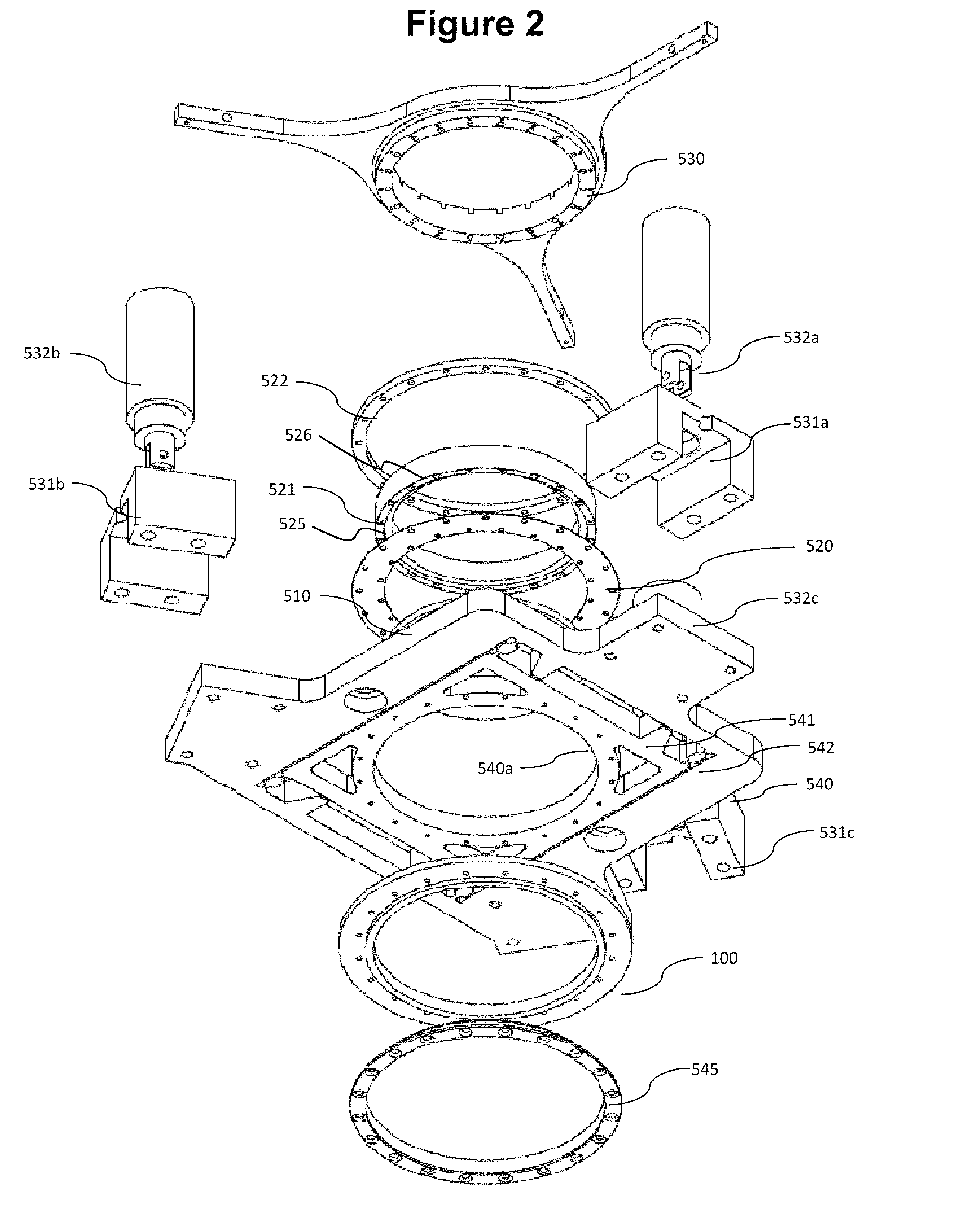
Reinforced composite stamp for dry transfer printing of semiconductor elements
ActiveUS7927976B2Easy to controlPrecise and repeatable vertical motionTurning machine accessoriesMouldsSemiconductor structureContact force
Provided are reinforced composite stamps, devices and methods of making the reinforced composite stamps disclosed herein. Reinforced composite stamps of certain aspects of the present invention have a composition and architecture optimized for use in printing systems for dry transfer printing of semiconductor structures, and impart excellent control over relative spatial placement accuracy of the semiconductor structures being transferred. In some embodiments, for example, reinforced composite stamps of the present invention allow for precise and repeatable vertical motion of the patterned surface of the printing apparatus with self-leveling of the stamp to the surface of a contacted substrate. Reinforced composite stamps of certain aspect of the present invention achieve a uniform distribution of contact forces between the printing apparatus patterned surface and the top surface of a substrate being contacted by the reinforced composite stamp of the printing apparatus.
Owner:X DISPLAY CO TECH LTD
Vacuum coupled tool apparatus for dry transfer printing semiconductor elements
InactiveUS8261660B2Improvement in printing yield and placement accuracy and fidelityReduce pressureMechanical working/deformationDecorative surface effectsEngineeringThin glass
Owner:X DISPLAY CO TECH LTD
Reinforced Composite Stamp for Dry Transfer Printing of Semiconductor Elements
ActiveUS20100018420A1Easy to controlPrecise and repeatable vertical motionTurning machine accessoriesNanoinformaticsSemiconductor structureContact force
Provided are reinforced composite stamps, devices and methods of making the reinforced composite stamps disclosed herein. Reinforced composite stamps of certain aspects of the present invention have a composition and architecture optimized for use in printing systems for dry transfer printing of semiconductor structures, and impart excellent control over relative spatial placement accuracy of the semiconductor structures being transferred. In some embodiments, for example, reinforced composite stamps of the present invention allow for precise and repeatable vertical motion of the patterned surface of the printing apparatus with self-leveling of the stamp to the surface of a contacted substrate. Reinforced composite stamps of certain aspect of the present invention achieve a uniform distribution of contact forces between the printing apparatus patterned surface and the top surface of a substrate being contacted by the reinforced composite stamp of the printing apparatus.
Owner:X DISPLAY CO TECH LTD
Preparation method of inner decoration material for automobile
ActiveCN1966265AOvercome the shortcoming that some functions are easily weakenedSoft touchLamination ancillary operationsFibre treatmentMetallurgySlurry
The invention relates to a method for producing decorates material of vehicle, wherein it comprises that: (1), pretreating base cloth, while the base cloth is immerged with disinfection and flameproof, dried, cooled and coiled; (2), wet solidifying coat that rolling the base cloth, scraping on coating machine, while the slurry amount is 100-300g / m2, drying, solidifying in solidifying groove, washing, drying and shaping, cooling and coiling; (3), dry transfer surface shaping that special paper transfer adhering; (4), rolling and drying the semi-product, coiling and packing. The inventive product has water resistance, etc.
Owner:HAININ JINDA COATING
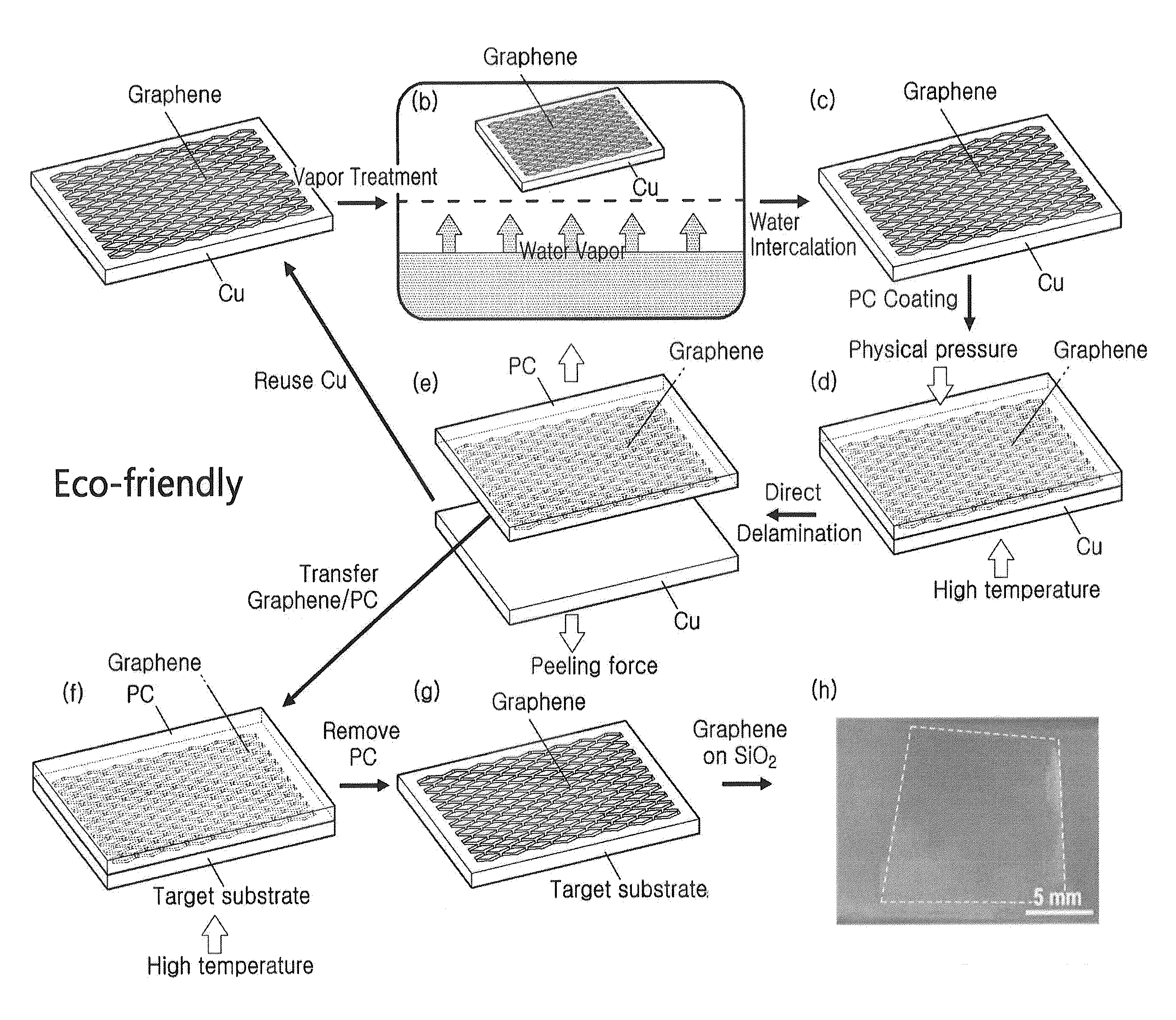
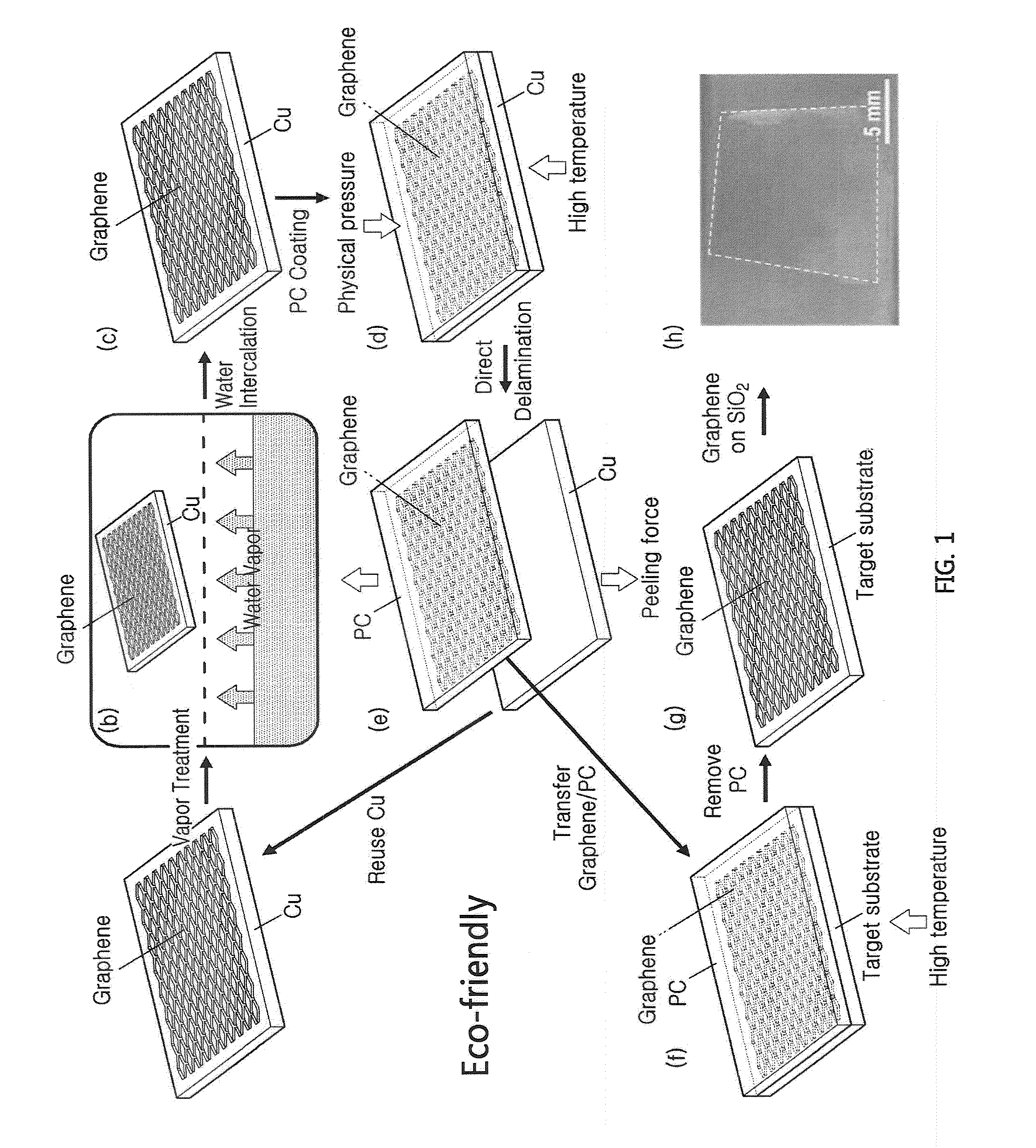
Large-area graphene transfer method
InactiveUS20160137507A1Low costLikely industrial scalabilityLayered product treatmentCarbon compoundsWater vaporSingle crystal
A graphene transfer method using water vapor-assisted determination of CVD-grown graphene film on the Cu foil. By using the polymer film as a supporting layer, we found that graphene can be directly detached from the Cu foil as a consequence of water intercalated at the graphene-Cu interface(s), by a ‘dry transfer’ method. The delaminated graphene films are continuous over large area. This nondestructive method also worked for the transfer of graphene grown on a Cu single crystal without sacrificing the expensive crystal, thus affording the possibility of producing high-quality graphene and reusing the substrate. The Cu foil and single crystal can both be repeatedly used for many times, which may reduce the cost of graphene synthesis and is environmentally more benign. Our method affords the advantages of high efficiency, likely industrial scalability, minimal use of chemicals, and the reusability of the Cu foil in multiple growth and delamination cycles.
Owner:UNIST ULSAN NAT INST OF SCI & TECH +1
Pattern adhesive seal products and method of production
The present invention is drawn to a method of making a sealing product, by a) selecting an a sealing material of an optimum film, mat or multi-well plate surface material for a specific sealing application; b) treating the sealing material; and c) directly coating the sealing material with an adhesive in a pattern format using Gravure, screen, rotary screen, flexographic, pad printing or dry transfer techniques. The present invention is further drawn to a sealing product made using the aforementioned method.
Owner:RAZAVI ALI
Wet method for preparing waterborne polyurethane space leather
The invention discloses a wet method for preparing a waterborne polyurethane space leather. The method uses anionic waterborne polyurethane emulsion immersion liquid and a demulsification crosslinking agent solution to treat a base cloth; the base cloth is coated with a waterborne polyurethane foam slurry, and subjected to condensation, washing, drying and dry transfer veneer to obtain the waterborne polyurethane space leather. The wear additives, wax powder and breathable additives added in the waterborne topping slurry system improve the scratch abrasion resistance of space leather, and endow the space leather with smooth surface, good handle, and excellent air and moisture permeability. The waterborne polyurethane space leather obtained by the method has the advantages of safety, environmental protection, good cut, fine compact structure, no crack or wear, and flexible handle.
Owner:HEFEI KETIAN WATERBORNE TECH CO LTD +2
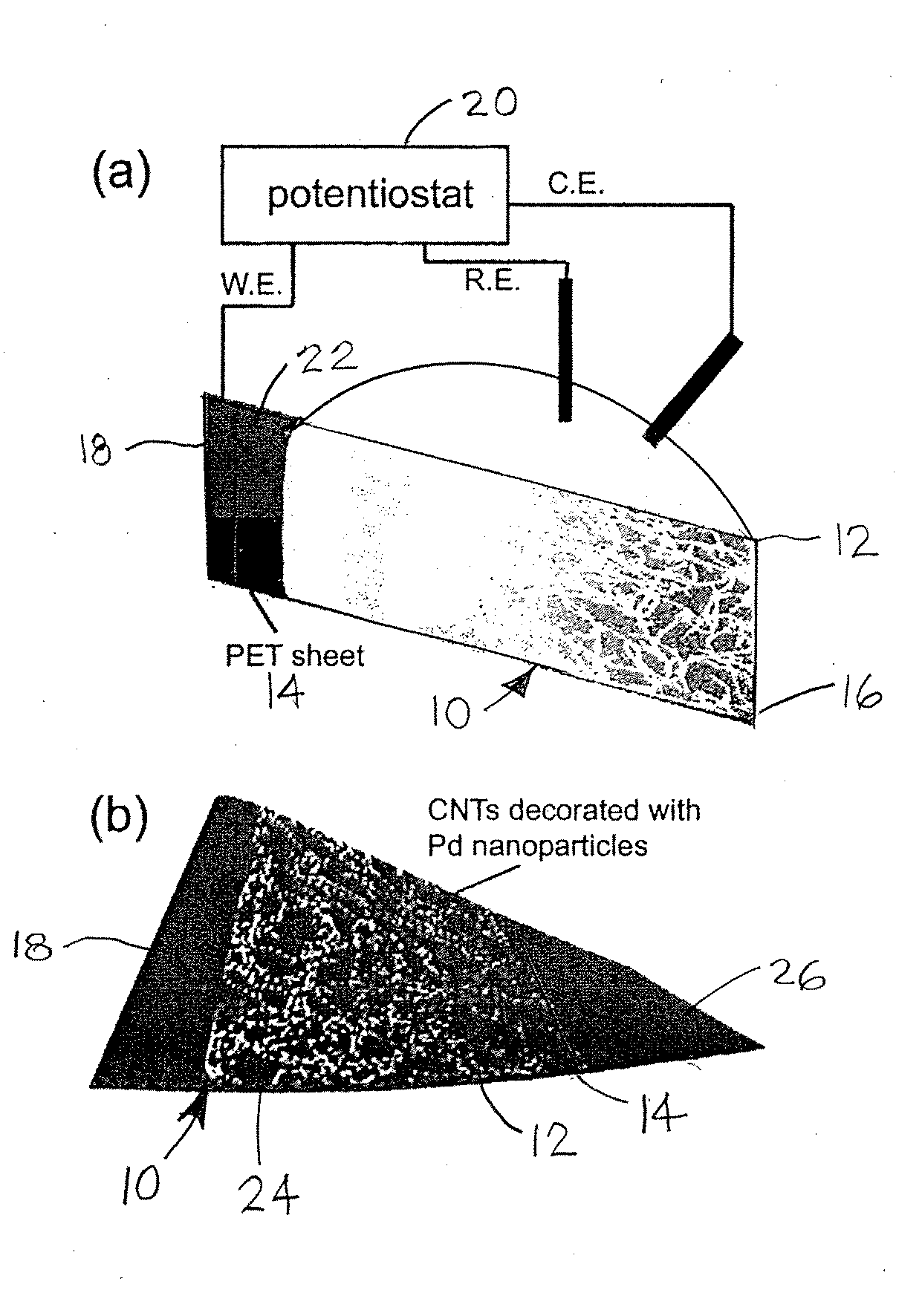
High-Performance Flexible Hydrogen Sensors
InactiveUS20090084159A1Easy to conformFast recovery timeAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNanotechCarbon nanotubeEvaporation
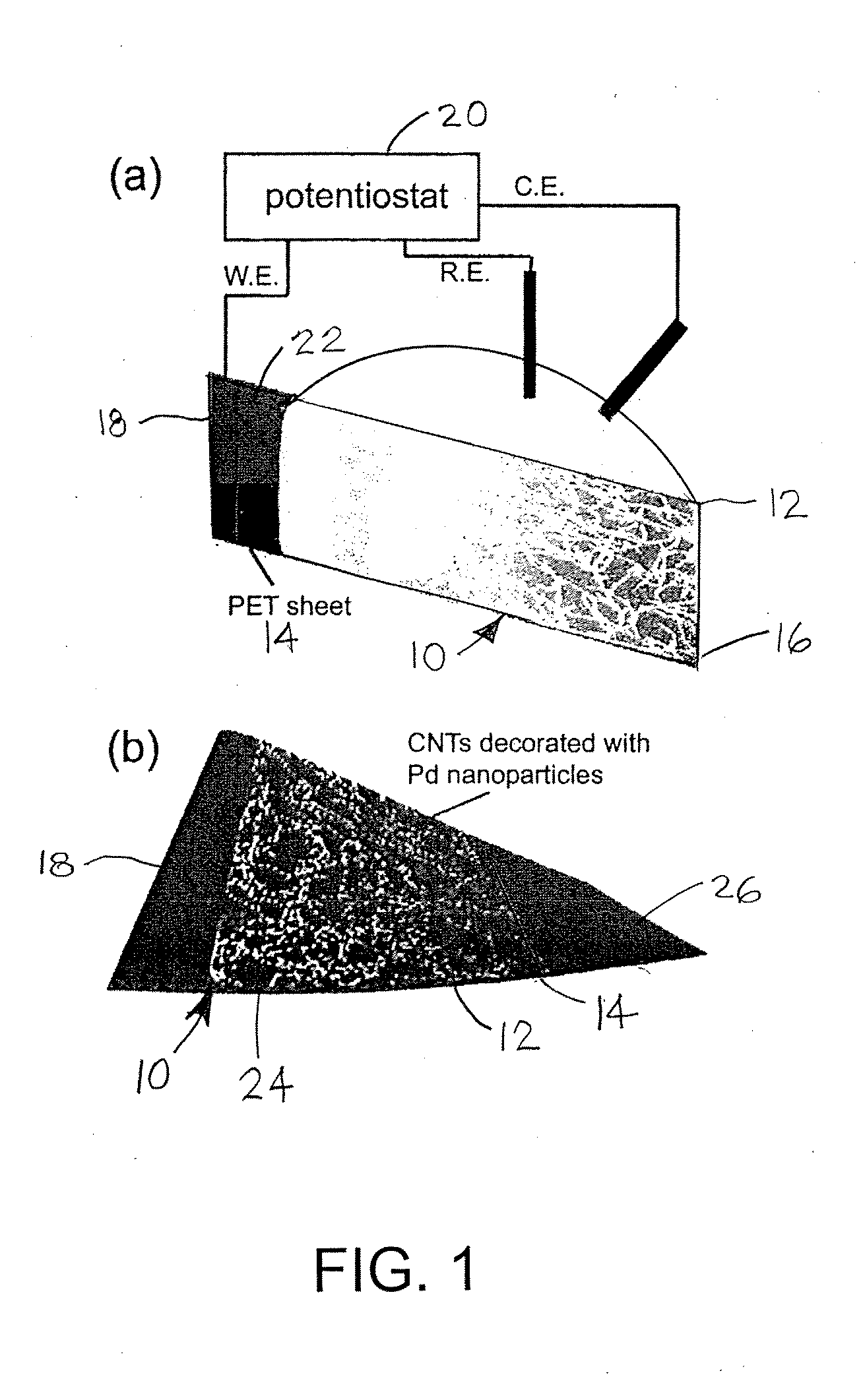
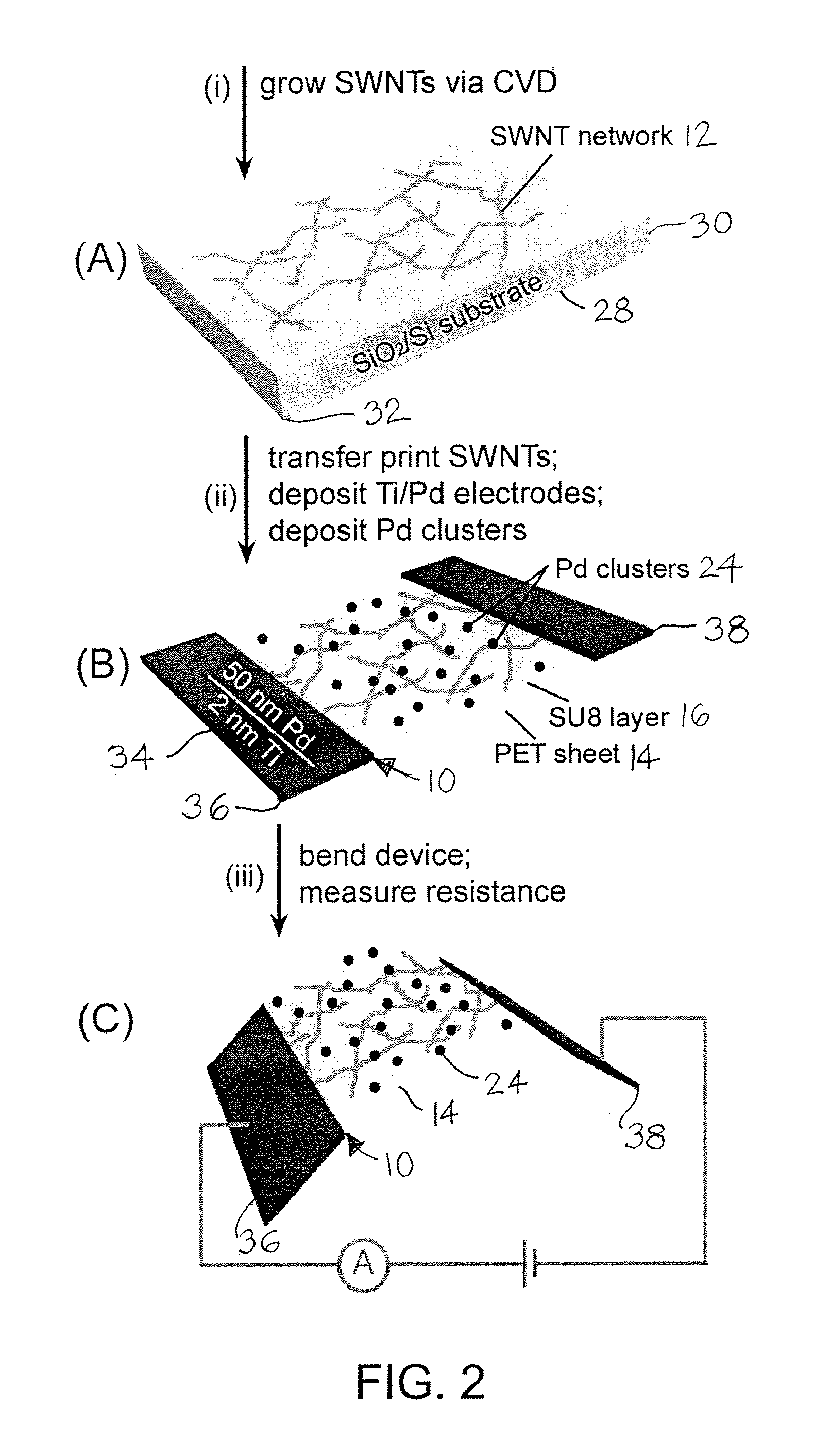
Single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNTs) are decorated with metal nanoparticles to form high-performance flexible hydrogen sensors. The special process to form the high-performance flexible hydrogen sensors can combine a dry transfer printing technique and modification of SWNTs with palladium (Pd) nanoparticles to provide high-performance hydrogen sensors with excellent mechanical flexibility on plastic substrates. Two approaches can be used to decorate the SWNTs. One is physical deposition, such as electron beam evaporation (EBE) and the other is electrochemical deposition which can selectively grow palladium nanoparticles on the surface of the SWNTs, resulting in significantly decreasing the use of palladium. Preferably, the Pd nanoparticles are deposed on the SWNTs in a discontinuous arrangement so that the Pd nanoparticles are spaced away from each other to form individual discontinuous Pd nanoparticles rather a continuous Pd film. Advantageously, the SWNTs are arranged with substantial semiconducting pathways. Desirably, the high-performance flexible hydrogen sensors have an excellent response and recovery time, provide superior sensitivity for detecting hydrogen, and are bendable to conform to the contours of other structures.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Vacuum Coupled Tool Apparatus for Dry Transfer Printing Semiconductor Elements
InactiveUS20110018158A1Shorten the timeReduce waiting timeMechanical working/deformationDecorative surface effectsDry transferSemiconductor components
Provided are an optimized tool apparatus and methods for dry transfer printing of semiconductor elements with high yield and good placement accuracy. The tool apparatus comprises a vacuum coupled fast peel apparatus that provides high pickup yield of the semiconductor elements. In an aspect, this vacuum coupled apparatus provides high pickup rates during pickup of the semiconductor elements from a donor / source wafer. Provided is a tool apparatus for dry transfer printing with a reinforced composite stamp having a thin glass-backing. The tool apparatus also comprises a pressure regulated micro-chamber which provides precise control of a composite stamp lamination and de-lamination. In an aspect, the micro-chamber has an internal cavity volume that is variably controlled, thereby providing precise control of the force on the stamp, and corresponding separation velocity, and improved semiconductor element pick-up and / or placement.
Owner:X DISPLAY CO TECH LTD
Method of dry transfer printing of synthetic fibrous material with disperse dye and transfer paper
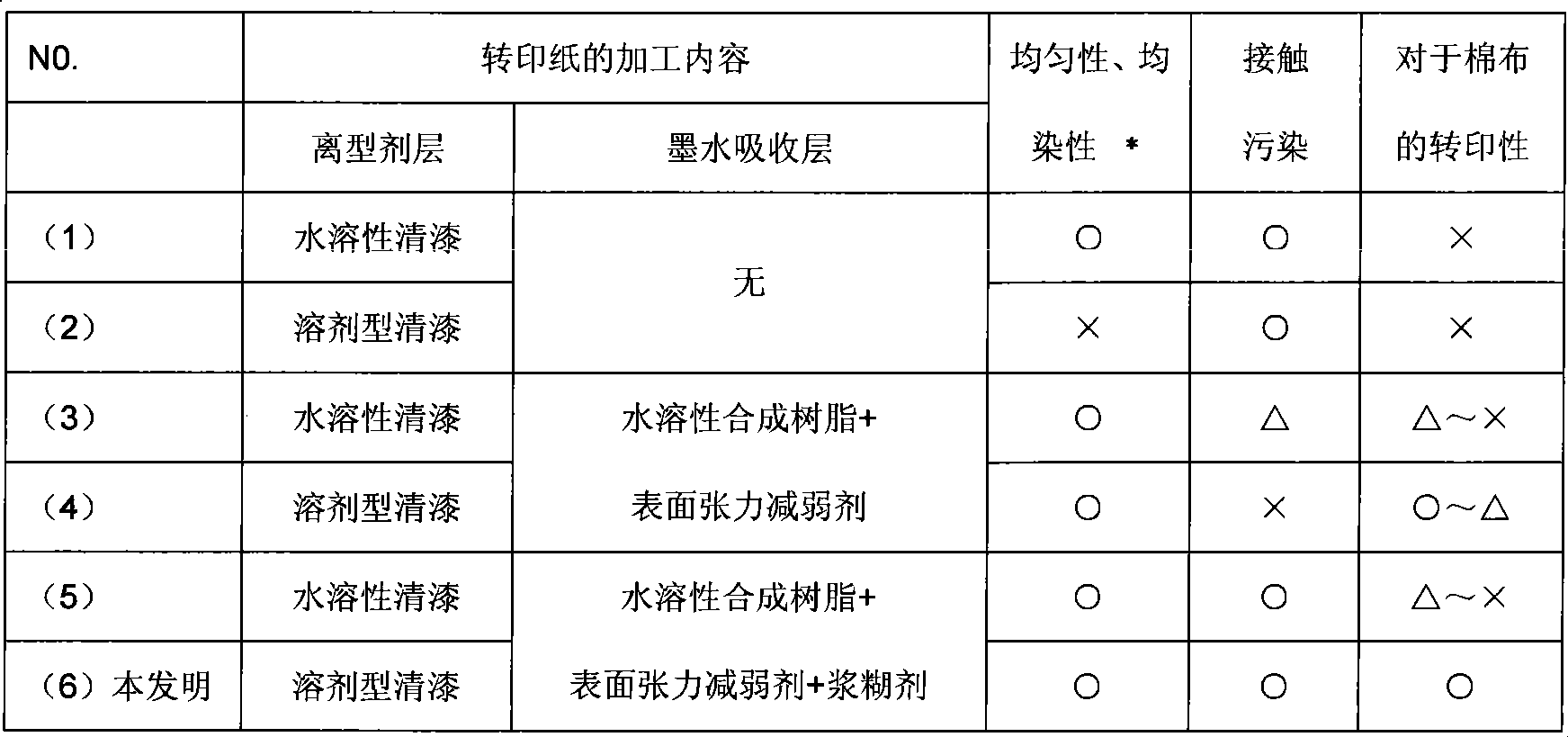
InactiveCN101688358AImprove qualityFeel goodNon-fibrous pulp additionSpecial paperDisperse dyeOrganic solvent
A transfer paper which comprises a transfer paper base and a disperse dye ink printed thereon or imparted thereto. The transfer paper is used in a dry transfer printing method in which the transfer paper is pressed against a synthetic fibrous material with heating to thereby transfer the dye (pattern) from the transfer paper to the fibrous material. The transfer paper is characterized in that thetransfer paper base has a releasant layer comprising a synthetic resin soluble in organic solvents and an ink-receiving layer made from a mixture comprising a hydrophilic synthetic resin which softensor melts upon heating, a hydrophilic binder, and various aids, the ink-receiving layer being superposed on the releasant layer. With this transfer paper for dry transfer printing, a highly fine pattern can be printed with excellent reproducibility. Furthermore, the transfer paper enables quick delivery by so-called printing without platemaking. The method of dry transfer plating employs this transfer paper.
Owner:NORITZ CORP
Formula and technology for producing synthetic leather from graphene modified waterborne polyurethane
InactiveCN105926308AAbrasion fastness exceedingImprove breathabilityPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsTextiles and paperWater basedFiltration
The invention discloses a formula for producing synthetic leather from graphene modified waterborne polyurethane. The formula comprises a coating solution. The coating solution comprises 51-88.999% of waterborne polyurethane emulsion, 5-15% of filler, 3-10% of stearic acid ammonium emulsion, 0.5-3% of foaming agent, 0.001-1% of graphene, 0.5-10% of water-based color paste, 0.5-2% of ammonium hydroxide, 0.5-5% of flatting agent and 1-3% of thickener. The technology comprises the steps of adding raw materials in the formula, and conducting stirring, filtration and viscosity regulation to obtain the coating solution; making the coating solution into coating foams, and applying the coating foams onto a leather base cloth; conducting drying to obtain a foam base; conducting aftertreatment to obtain the graphene modified waterborne polyurethane synthetic leather. By producing the foaming synthetic leather from graphene modified waterborne polyurethane, the wear resistance of a membrane is improved greatly, the dry transfer coating procedure is omitted, and antistatic, flame retardant and waterproof effects are realized.
Owner:宋婷婷 +1
Transfer paper for dry transfer printing and method of dry transfer printing with the same
InactiveCN101448999AImprove qualityFeel goodDecorative surface effectsDuplicating/marking methodsFiberAdhesive
The present invention provides a transfer paper for use in dry transfer printing in which a transfer paper is pressed with heating against a natural or synthetic fibrous material to transfer an ink thereto. It is characterized in that it is produced by applying a water-soluble dye ink to a transfer paper having a release agent layer and an ink-receiving layer overlying the layer and the ink-receiving layer comprises a hydrophilic synthetic resin and a hydrophilic adhesive, the hydrophilic adhesive being contained in an amount of 1-50 parts by weight per 100 parts by weight of the hydrophilic synthetic resin. Also provided is a method of dry transfer printing characterized by pressing the transfer paper for dry transfer printing against a natural or synthetic fibrous material with heating to thereby transfer the water-soluble dye ink applied to the transfer paper to the fibrous material and subsequently fixing the ink.
Owner:环宇企业集团有限公司 +1
Preparation method of fuel cell membrane electrode
InactiveCN110459774AAvoid curling problemsAvoid easy turning over film layingCell electrodesFinal product manufactureSpray coatingProton
The invention discloses a preparation method of a fuel cell membrane electrode, which comprises the following steps: first catalyst slurry is applied to a side A of a proton exchange membrane by spraying; a transfer medium is coated with second catalyst slurry and dried; the dried transfer medium is attached to the proton exchange membrane spray-coated with the first catalyst slurry, the side, spray-coated with the second catalyst slurry, of the transfer medium faces an uncoated side B of the proton exchange membrane, the side A, spray-coated with the first catalyst slurry, of the proton exchange membrane is covered with a protective film, a heat transfer printing process is adopted, and after hot pressing, the transfer medium is peeled off to obtain a fuel cell membrane electrode. Throughspray coating first and then transfer printing, the problem that it is not easy to turn over and lay a membrane and the proton exchange membrane is easy to roll up in a single ultrasonic spray coating method is avoided, the production efficiency is improved, the problem of high interface resistance between the catalytic layer and the proton exchange membrane in a single transfer printing method is avoided, and the ohmic impedance loss is reduced.
Owner:KUSN INNOVATION INST OF NANJING UNIV +2
Device structure with grapheme as contact electrode and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN105070347AImprove protectionReduce performanceElectrolytic capacitorsSuperconductor detailsEtchingSemiconductor materials
The invention provides a device structure with grapheme as a contact electrode and a manufacturing method thereof, and relates to the technical field of device structures with grapheme as contact electrodes. A novel device structure of an h-BN-grapheme-superconductive / semi conducting material-h-Bh is formed through a dry transfer method, and pollution and damage of material crystal lattices due to wet transferring method, graphical etching and metallic deposition technology. h-BN services as a substrate and an encapsulated layer, which facilitates grapheme carrier mobility, and protects the device from absorbing O2, H2O and particles in air. The electric performance of the device structure is improved. The grapheme serves as contact electrode, and one-dimensional linear contact between the depositing metal and the cross section of the grapheme is formed. The contact resistance of superconductive / semiconductor devices is substantially reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multilayer composite for the dry transfer of graphics to receptive substrates
InactiveUS6875497B2High strengthLow wear resistanceDecorative surface effectsDuplicating/marking methodsGraphicsDry transfer
A multilayer composite for applying printed graphics to a receptive substrate, comprising: a carrier sheet; a transparent breakcoat having an upper surface releasably bonded to the carrier sheet, and a lower print receptive surface on which graphics are permanently printed; and a layer of pressure sensitive adhesive having an upper surface permanently adhered to the thus printed graphics, and a lower surface releasably adhered to a protective liner. The protective liner is separable from the adhesive without disrupting the bond between the carrier sheet and the breakcoat, and the adhesive, and the adhesive is removably bondable to the substrate during a wet out period, after which the carrier sheet is separable from the breakcoat, allowing the breakcoat / graphics / adhesive residue to remain firmly bonded to the substrate.
Owner:FLEXCON
Method for manufacturing nano-wire piezoelectric device
InactiveCN101859731AImprove stabilityIncrease output powerPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingEngineering
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a nano-wire piezoelectric device, which comprises the following steps of: arranging prefabricated nano-wires on a polyimide film to form parallel nano-wire arrays by using direct dry transfer; preparing a source electrode and a drain electrode of the piezoelectric device on the nano-wire arrays by adopting a micro or nano photo-etching method; and finally, adding a connecting point and a lead for connection on one side of the source electrode and one side of the drain electrode, and packing the surface of the piezoelectric device by adopting polydimethylsiloxane. The manufacturing method has the advantages of simple manufacturing process, wide application range, cost saving and the like, and greatly improves the yield of the piezoelectric device; the nano-wire piezoelectric device manufactured by implementing the method can realize simultaneous work of a large amount of nano-wires to generate electrical energy; and the stability and the output power of the piezoelectric device are improved by combining a packing process.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
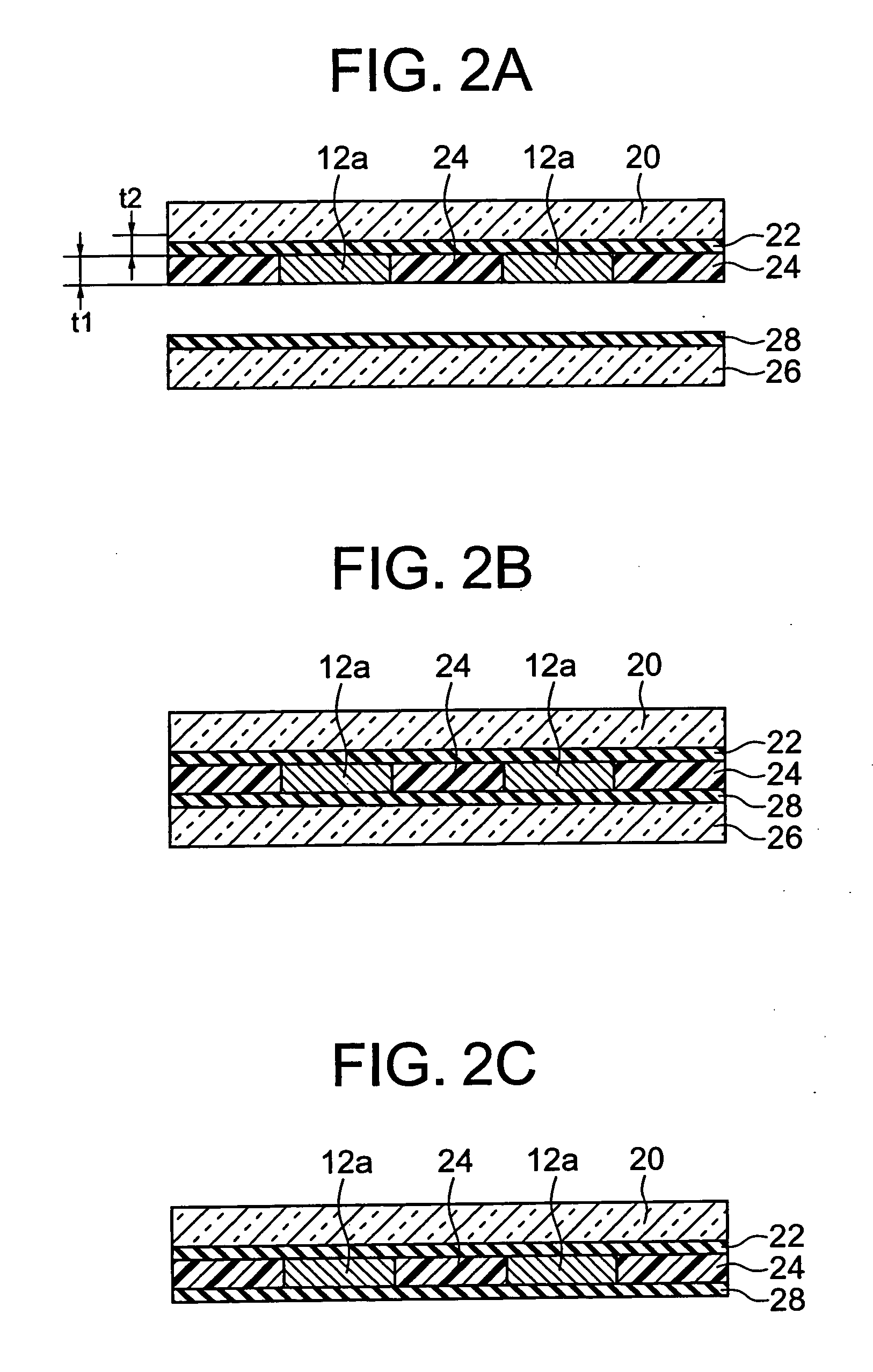
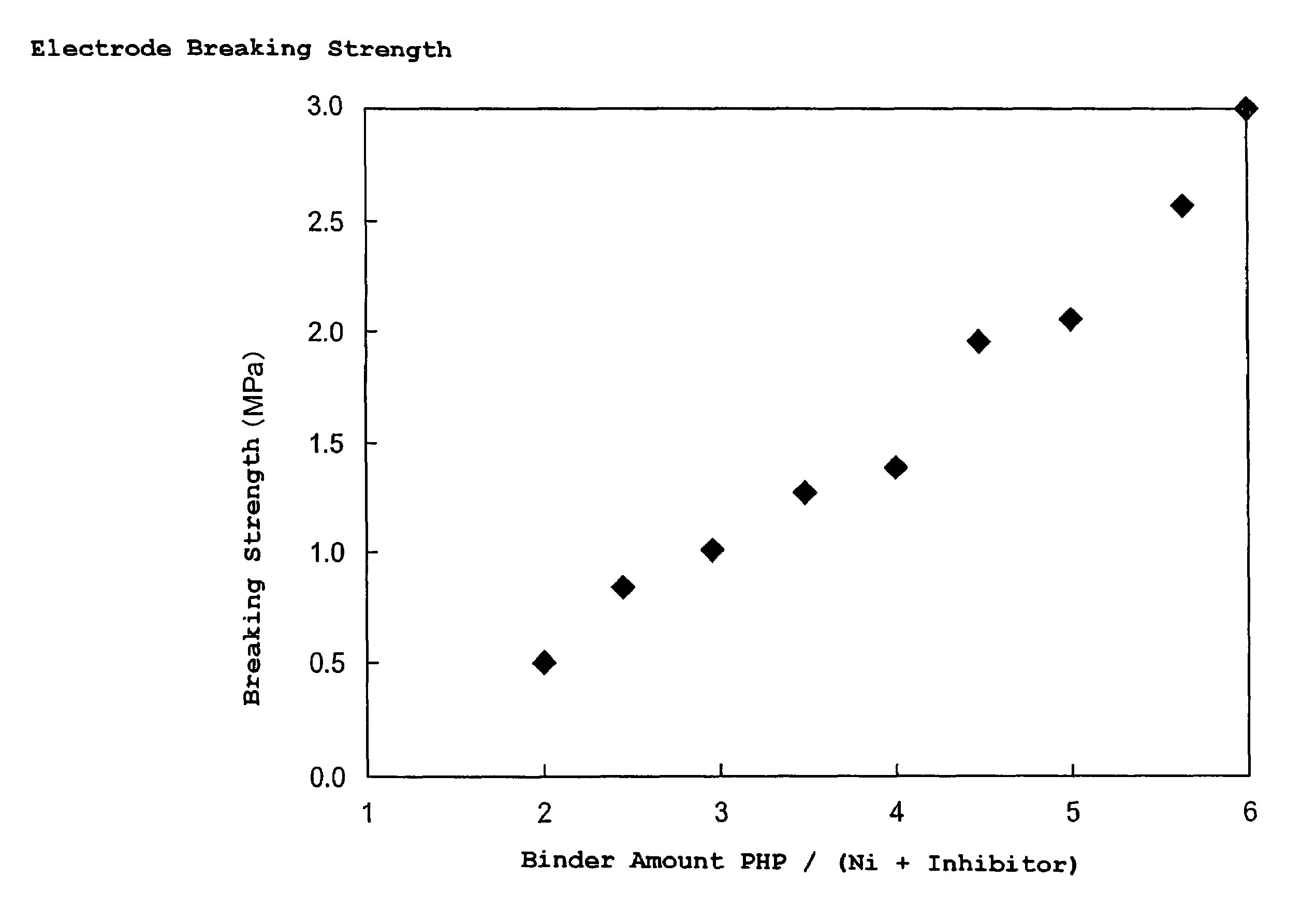
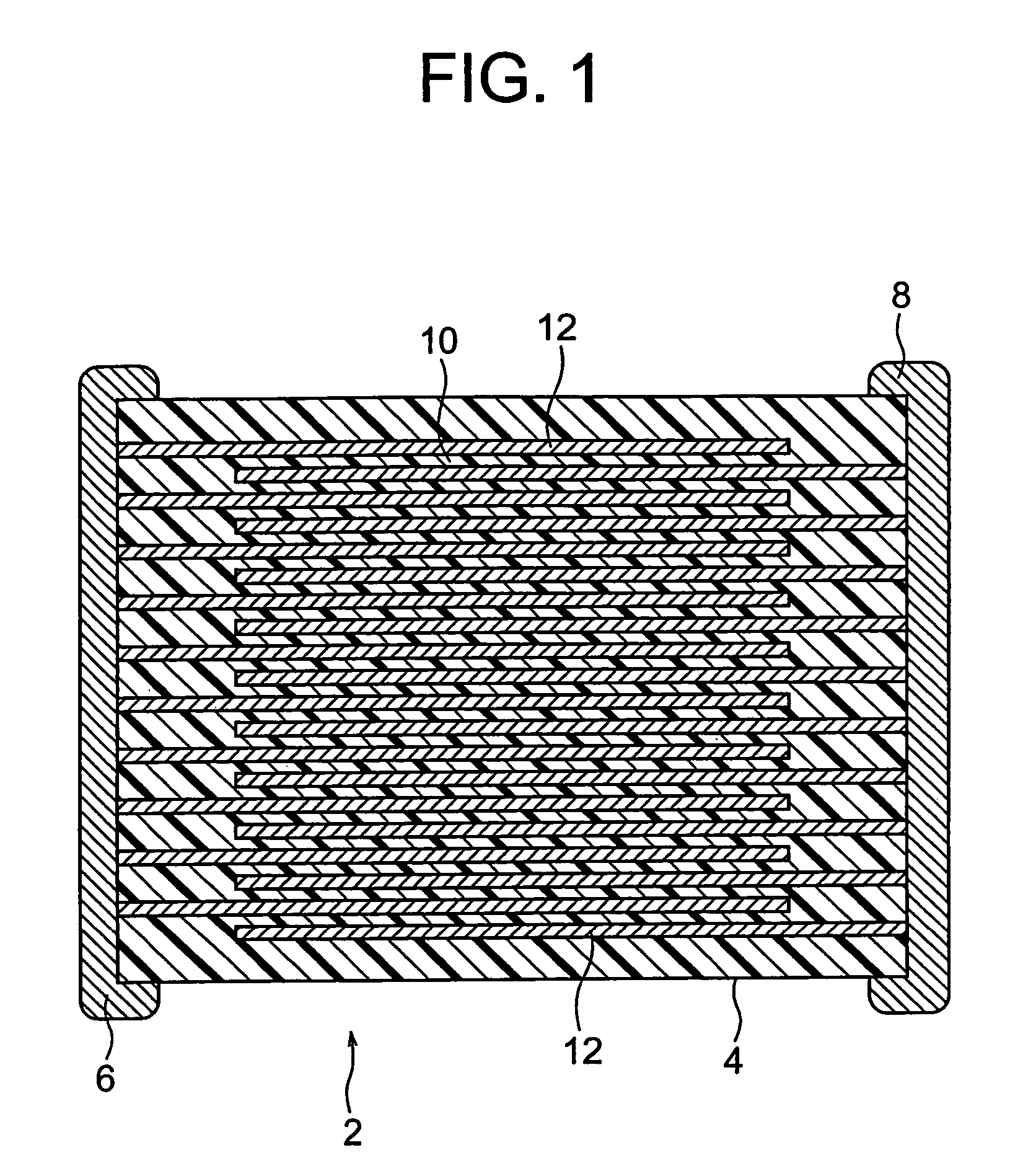
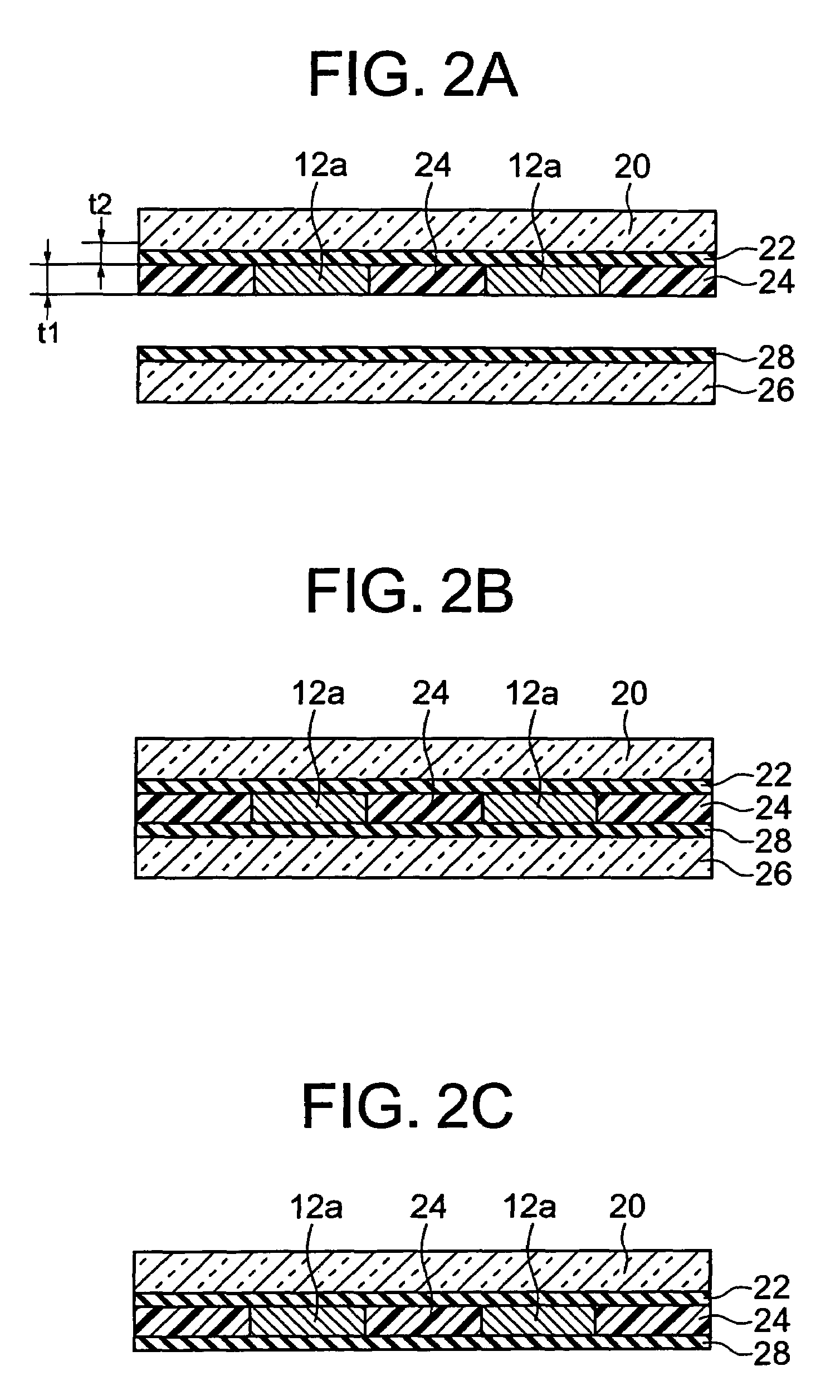
Paste for internal electrode and process for producing electronic part
InactiveUS20060197062A1Easy to controlIncrease ratingsFixed capacitor electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricPlasticizerSolvent
An internal electrode paste comprises electrode material powder, a binder resin containing a polyvinyl butyral resin as the main component, and a solvent. The internal electrode paste furthermore comprises a plasticizer, and the plasticizer is contained by 25 parts by weight or more and 150 parts by weight or less with respect to 100 parts by weight of the binder resin. The binder resin is contained by 2.5 to 5.5 parts by weight with respect to 100 parts by weight of the electrode material powder. It is possible to provide an internal electrode paste having enough strength and an adhesive force for the dry transfer method, and a production method of an electronic device using the paste.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Method of dry transfer printing of synthetic fibrous material with disperse dye and transfer paper
InactiveUS20100043152A1Fast deliveryEasy to produceNon-fibrous pulp additionSpecial paperDisperse dyeOrganic solvent
A transfer paper which comprises a transfer paper base and a disperse dye ink printed thereon or imparted thereto. The transfer paper is used in a dry transfer printing method in which the transfer paper is pressed against a synthetic fibrous material with heating to thereby transfer the dye (pattern) from the transfer paper to the fibrous material. The transfer paper is characterized in that the transfer paper base has a releasant layer comprising a synthetic resin soluble in organic solvents and an ink-receiving layer made from a mixture comprising a hydrophilic synthetic resin which softens or melts upon heating, a hydrophilic binder, and various aids, the ink-receiving layer being superposed on the releasant layer. With this transfer paper for dry transfer printing, a highly fine pattern can be printed with excellent reproducibility. Furthermore, the transfer paper enables quick delivery by so-called printing without platemaking. The method of dry transfer plating employs this transfer paper.
Owner:NORITZ CORP
Internal electrode paste and production method of electronic device
InactiveUS7485244B2Increase ratingsImprove flatnessFixed capacitor electrodesFixed capacitor dielectricPlasticizerSolvent
An internal electrode paste comprises electrode material powder, a binder resin containing a polyvinyl butyral resin as the main component, and a solvent. The internal electrode paste furthermore comprises a plasticizer, and the plasticizer is contained by 25 parts by weight or more and 150 parts by weight or less with respect to 100 parts by weight of the binder resin. The binder resin is contained by 2.5 to 5.5 parts by weight with respect to 100 parts by weight of the electrode material powder. It is possible to provide an internal electrode paste having enough strength and an adhesive force for the dry transfer method, and a production method of an electronic device using the paste.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Prestretching-based graphene flexible strain sensor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109520411AImprove stabilityGood repeatabilityElectrical/magnetic solid deformation measurementAdhesiveRepeatability
The invention discloses a prestretching-based graphene flexible strain sensor and a preparation method thereof. The prestretching-based graphene flexible strain sensor comprises a released substrate;a graphene sensitive layer is arranged on the released substrate; conductive silver adhesives are arranged at the joints of the two ends of the graphene sensitive layer and the released substrate, andelectrodes are arranged on the upper surfaces of the conductive silver adhesives. The preparation method of the prestretching-based graphene flexible strain sensor comprises the following steps: prestretching a substrate before transferring a graphene film, and completing the transferring of the graphene film through a dry transfer method, thereby preparing the graphene flexible strain sensor based on prestretching. Larger strain measurement is achieved by the sensor provided in the invention through pre-stretching, and good stability and repeatability are achieved; the manufacturing successrate is increased through a dry transfer method, the preparation method is simplified, and large-scale manufacturing is achieved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
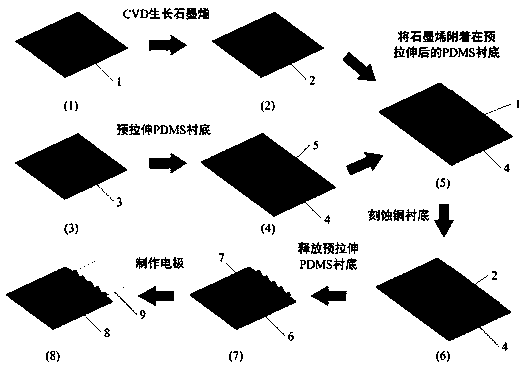
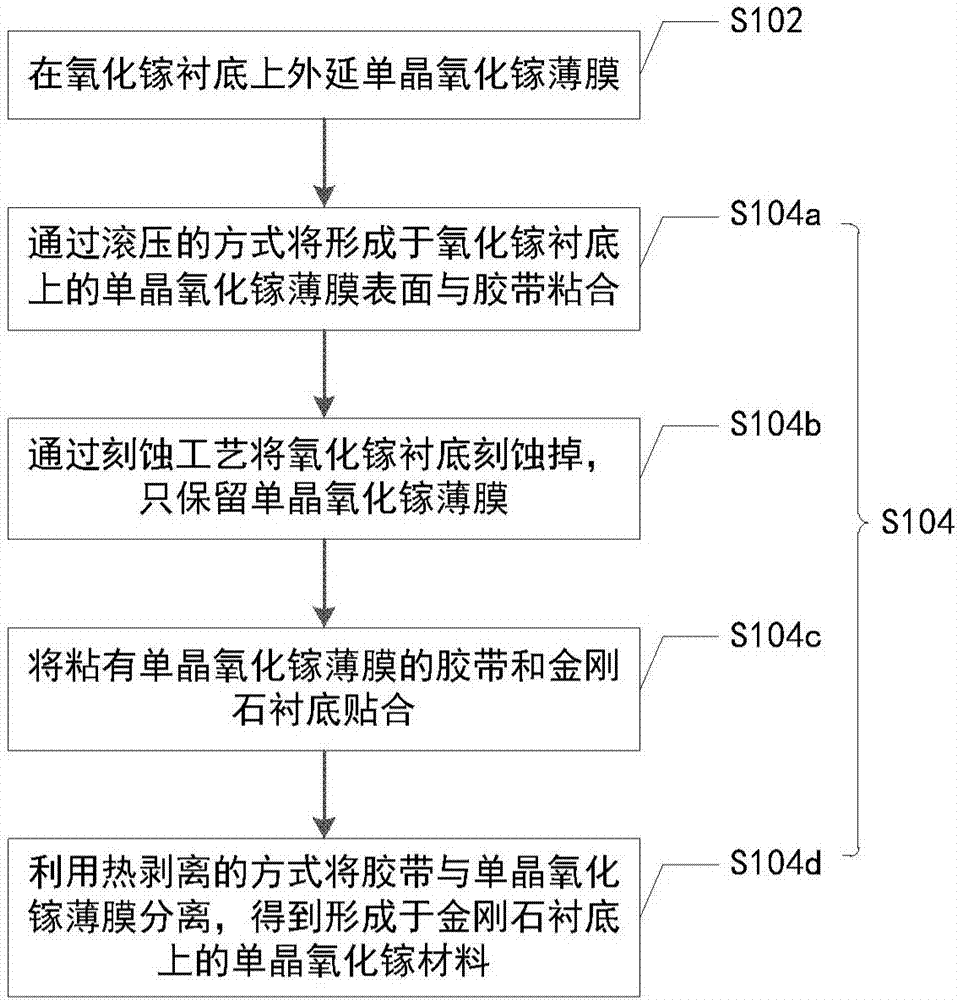
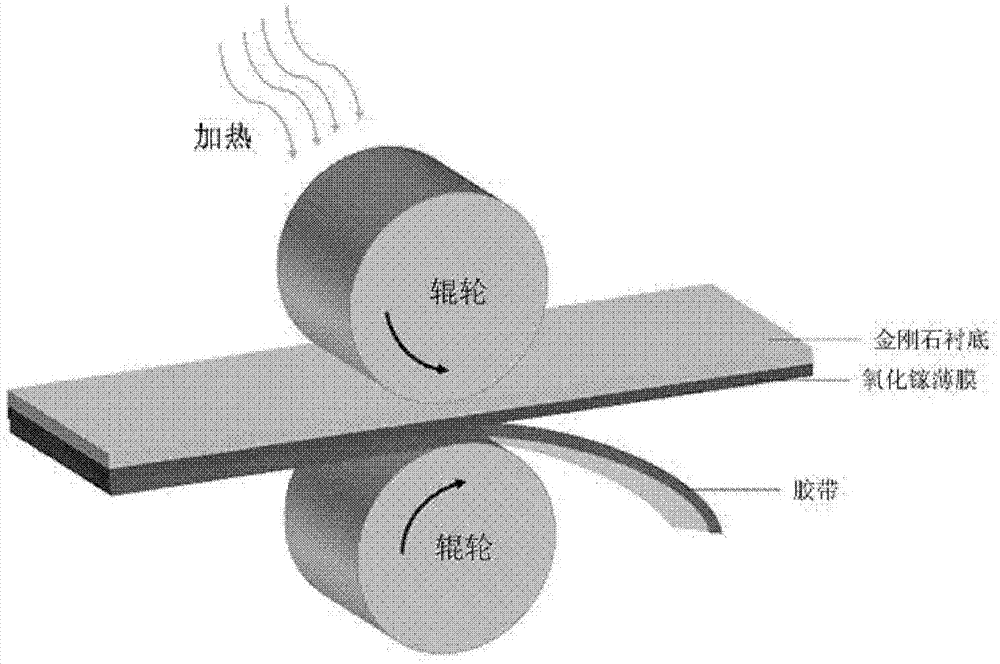
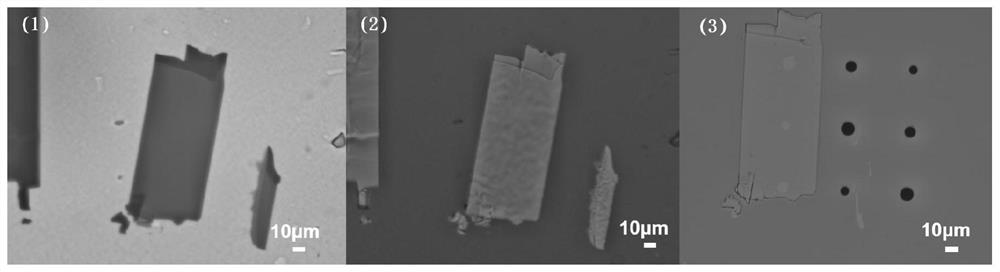
Method for improving thermal conductivity of gallium oxide material
ActiveCN107039245AHigh thermal conductivityImprove product qualitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesComposite substrateSingle crystal
The invention provides a method for improving thermal conductivity of a gallium oxide material. The method comprises: an epitaxial monocrystalline gallium oxide film is grown on a gallium oxide substrate; the monocrystalline gallium oxide film is transferred to a substrate material which has a thermal conductivity of more than 200 W / m.K and is compatible with semiconductors by means of an etching process combined with two-dimensional material transfer, and a monocrystalline gallium oxide material formed on the substrate is obtained. By transferring the monocrystalline gallium oxide film to a substrate which has a thermal conductivity of more than 200 W / m.K and is compatible with semiconductors, including diamond, an AlN substrate, a GaN substrate, a SiC substrate or a composite substrate composed of a Si substrate and diamond deposited on the Si substrate, the thermal conductivity of the gallium oxide material is effectively improved; and the process of dry transfer technique is simple, more mature process can be formed easily, thus the method is easy to promote, facilitates improving the production quality, and has high value for practical use.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing coated aluminium alloy strips for producing photographic quality decorations by dry transfer
The invention relates to a method for continuously producing an aluminium alloy strip for transferring a sublimable decoration from a temporary carrier consisting in using the aluminium alloy strip having a gloss and high-gloss quality, in anodising and sealing said strip and in coating the anodised strip with a transparent lacquer consisting of a polyester and polyurethane mixture. Said anodisation and sealing are substitutable by a HELIA process under EP 0 745 703 patent in order to form a compact oxide barrier whose thickness ranges from 140 to 200 nm. The thus produced aluminium alloy strip for sublimation transfer and a strip or sheet decorated after said transfer from the temporary carrier are also disclosed.
Owner:金属及合金处理有限公司
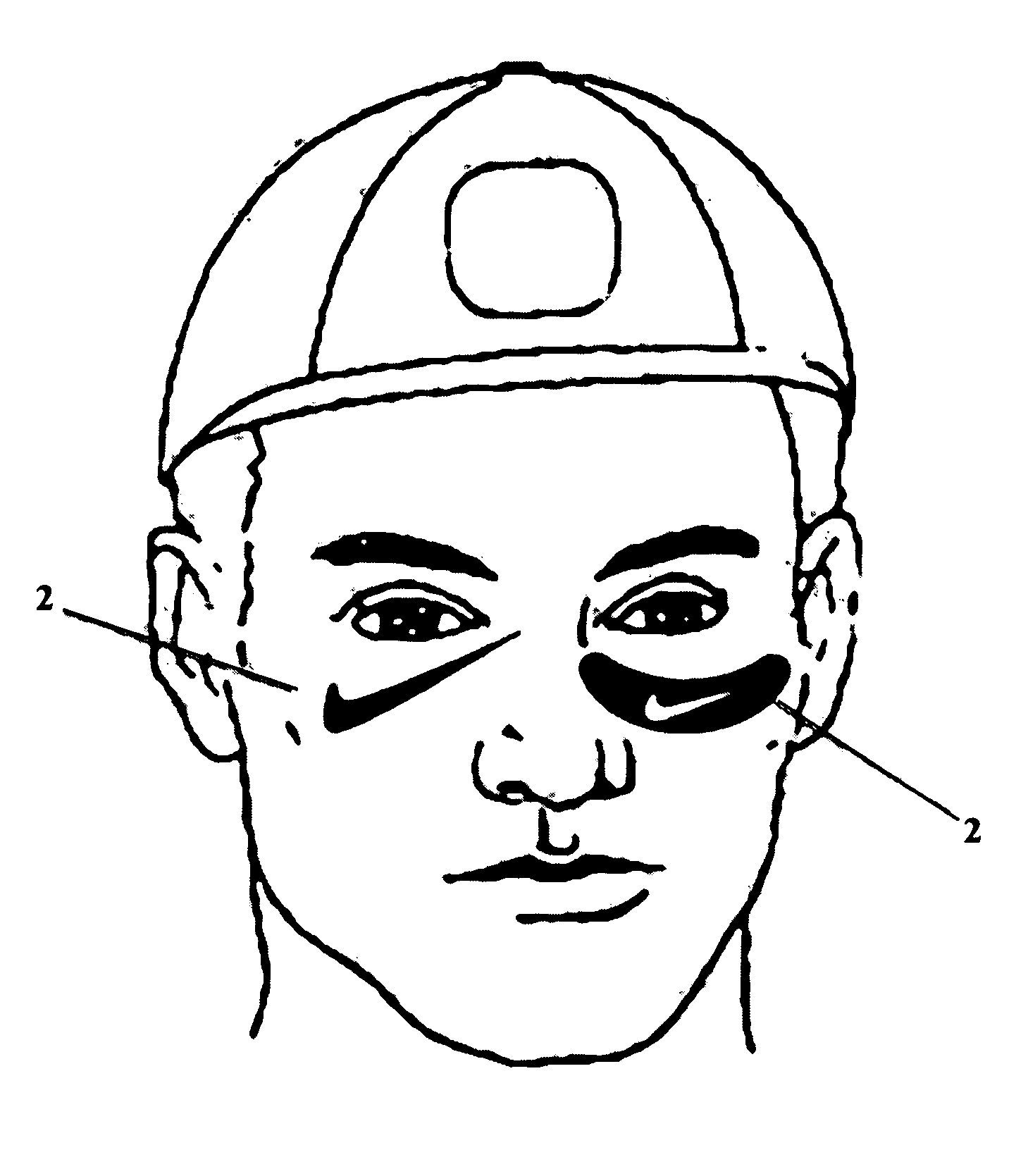
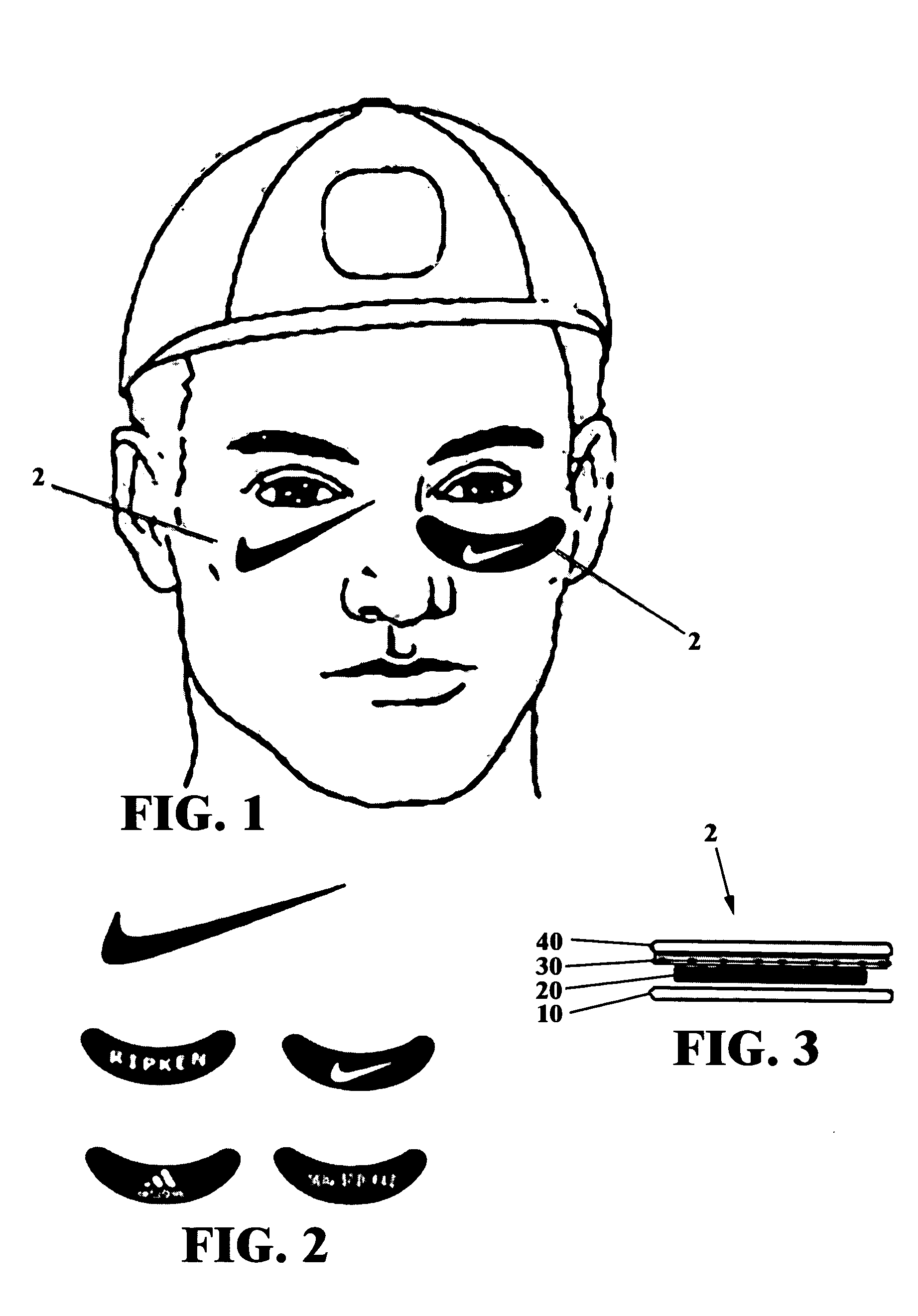
Under-eye anti-glare sport tattoos
A temporary under-eye anti-glare sport tattoo comprised of a solid dermatological composition with anti-glare properties. The composition forms a film that is deposited on a person's skin underneath the eyes and over the cheekbones by a dry transfer method. The film thus applied reduces eye glare and increases contrast sensitivity. By incorporating team or business logos, trademarks or the like, into the film, the present invention also serves as either an advertising mechanism for businesses or a mechanism to promote team spirit. The film is able to sustain a predefined shape, has adhesive properties, is water resistant, color fast, and heat resistant. The composition comprises oil, a gelling compound, dyes and a mixture of wax and carbon.
Owner:MARKEY III STEPHEN A
Laser-engraving transfer printing technology
InactiveCN103991300AEasy to manufactureImprove printing effectDecorative surface effectsDuplicating/marking methodsLaser engravingPulp and paper industry
The invention discloses a transfer printing technology, and especially relates to a laser-engraving transfer printing technology. The laser-engraving transfer printing technology is relatively stable in printing effect and relatively good in printing effect, and successively comprises the following six steps: pasting a photogelatin, specifically coating transfer printing paper with the photogelatin by employing rolls; drying the photogelatin, specifically placing the transfer printing paper coated with the photogelatin into a dryer for drying, and controlling the drying temperature to be 150-200 DEG C; performing laser irradiation, specifically placing the dried transfer printing paper into a paper printing machine, and irradiating under laser; pasting a color slurry, specifically pasting the color slurry on the transfer printing paper subjected to laser irradiation; drying the color slurry, specifically drying the transfer printing paper subjected to color-slurry pasting; and performing heat transfer printing by employing a printer, specifically placing the prepared transfer printing paper and raw-material cloth in a printing machine, so as to finish printing-machine heat transfer printing.
Owner:SHAOXING SHOUCHUANG TEXTILE FINISHING
Photoelectric memory based on two-dimensional heterojunction optical wavelength induction and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109817756AImplement multi-value storageAchieve non-volatile performanceFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionLength wave
The invention belongs to the technical field of photoelectric memories, and particularly relates to a nonvolatile photoelectric memory based on two-dimensional heterojunction optical wavelength induction and a preparation method thereof. According to the invention, different optical responses are generated on light with different wavelengths by using defect energy levels in a two-dimensional material, different charge storage states are realized under the driving of an electric field, and nonvolatile multi-value storage of the device is realized through bipolar change of a channel two-dimensional material and stepped change of the number of charges in a light absorption layer. The preparation method comprises the following steps: obtaining a two-dimensional material serving as a light absorption layer on a substrate by utilizing mechanical stripping or chemical vapor deposition, and then stacking the two-dimensional material with double polarities on the light absorption layer by utilizing a dry transfer technology to serve as a channel of a device. The novel nonvolatile photoelectric memory with the multi-value storage capability prepared by the invention has a wide application prospect in the field of future data photoelectric storage.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
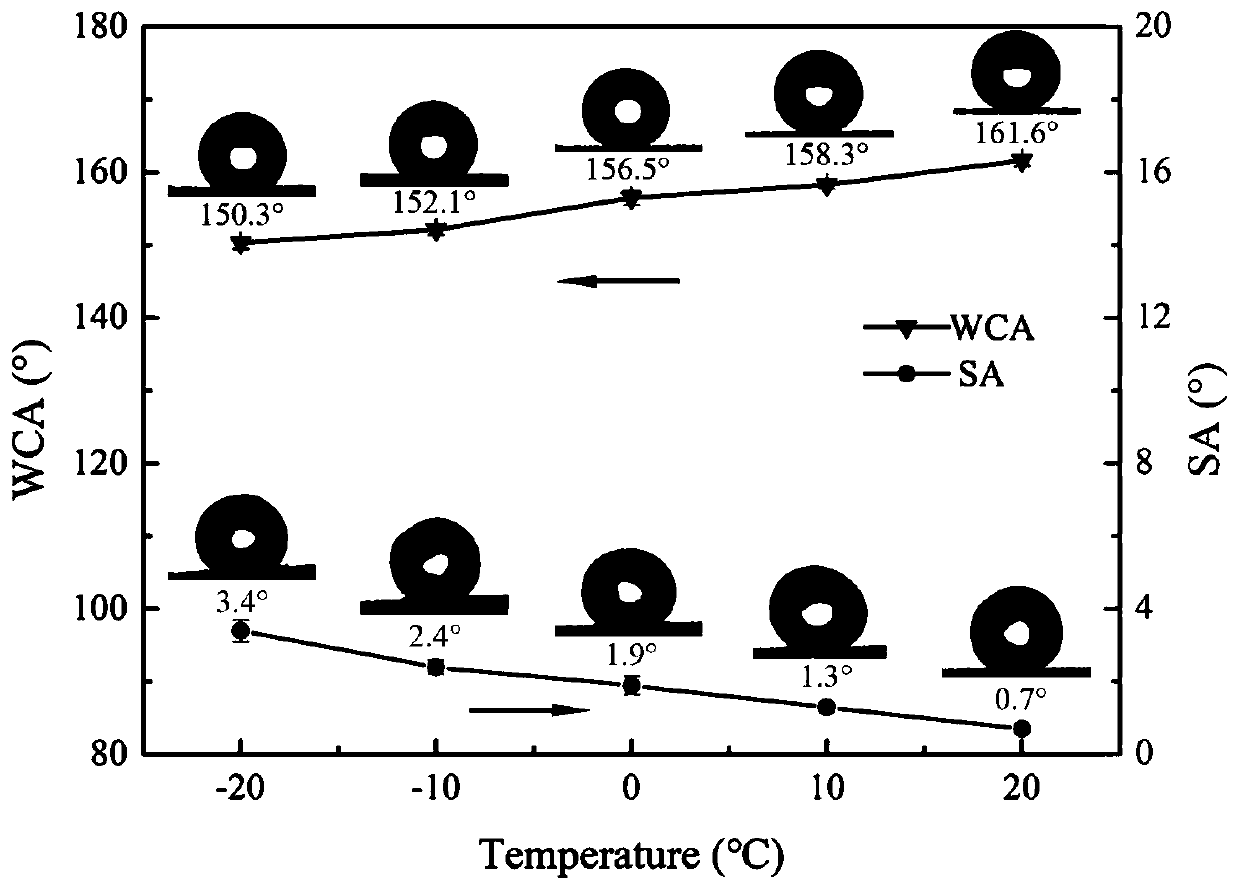
Preparation method of super-hydrophobic graphene-based wrinkled film capable of controlling springback direction of water drops
ActiveCN110775962AMaintain superhydrophobic propertiesBounce direction controllablePretreated surfacesGraphenePolymer scienceAqueous droplet
The invention discloses a preparation method of a super-hydrophobic graphene-based wrinkled film capable of controlling the springback direction of water drops, belonging to the field of ice prevention. With the wrinkled film in the invention, the bouncing direction of cold water drops can deviate from a surface after the cold water drops are impacted, so anti-icing efficiency is greatly improved.According to the invention, a rGO film is transferred to a biaxially stretched substrate film through dry transfer, and forces in four directions of the substrate film are sequentially retracted to obtain an irregular wrinkled film; and in virtue of a Stober method, SiO2 nanoparticles grow on the surface of rGO, and the SiO2 / rGO wrinkled film with a micro-nano hierarchical structure is obtained through FDTS modification. At -20 DEG C, the water contact angle of the film is still larger than 150 degrees, and the rolling angle of the film is smaller than 4 degrees, so the film shows excellent low-temperature super-hydrophobic characteristics. Meanwhile, at a temperature of -10 DEG C, the supercooled water drops impact the surface of the film, and due to the fact that the irregular microstructure of the supercooled water drops enables the viscous force between solid and liquid to be asymmetrically distributed, the water drops retract asymmetrically, so the springback direction deviates in the fixed direction.
Owner:成都泰格尔航天航空科技股份有限公司
Dry transfer lettering with separable units
InactiveUS20070036950A1Good transferabilityDecorative surface effectsDuplicating/marking methodsEngineeringDry transfer
A carrier sheet with completely or partially detachable perforated sheet units improves the transferability of dry transfer symbols. A carrier sheet of dry transfer symbols may be comprised of a plurality of dry transfer symbols removably affixed to a plurality of perforated sheet units. At least one dry transfer symbol may be removably affixed to at least one side of the plurality of perforated sheet units
Owner:ROYAL BRUSH MFG
Method for transferring two-dimensional material to hole substrate
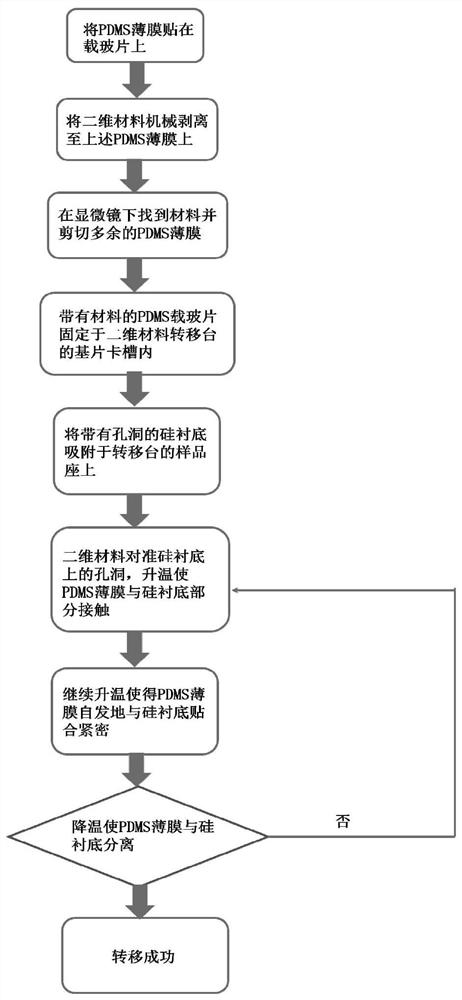
PendingCN113851371AGood technical effectSticky precisionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThin membraneMaterial transfer
The invention discloses a method for transferring a two-dimensional material to a hole substrate, and relates to two-dimensional material transfer. The method comprises: pasting a PDMS thin film on the glass slide; stripping a two-dimensional material block onto the PDMS film; shearing the redundant part of the PDMS film under a microscope; fixing the obtained glass slide with the material in a substrate clamping groove of a two-dimensional material transfer table; adsorbing the silicon substrate with the hole on a sample seat of a transfer table; aligning the material to the hole in the Si substrate, and heating to make the PDMS film partially contact with the Si substrate; continuously raising the temperature to enable the PDMS film to be spontaneously and tightly attached to the Si substrate; and carrying out cooling to separate the PDMS film from the Si substrate. The viscosity of the PDMS film is adjusted by changing the temperature, so that the two-dimensional material is transferred to the silicon substrate with the holes. The method is a pure dry transfer method, the surface of the transferred sample is clean, the operation is simple, and the method can be realized only by controlling the temperature of the PDMS film without the help of excessive experimental instruments except a transfer table.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for treating surface of transfer printing concrete
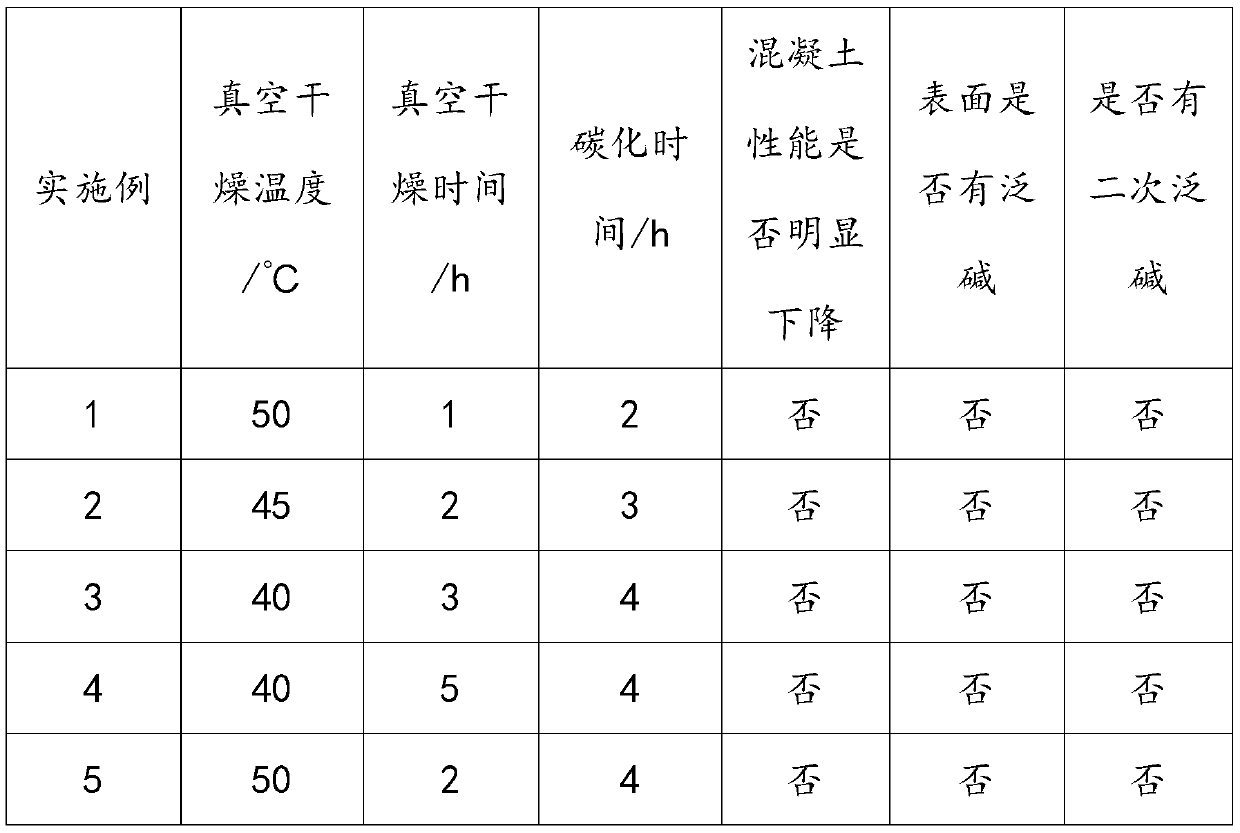
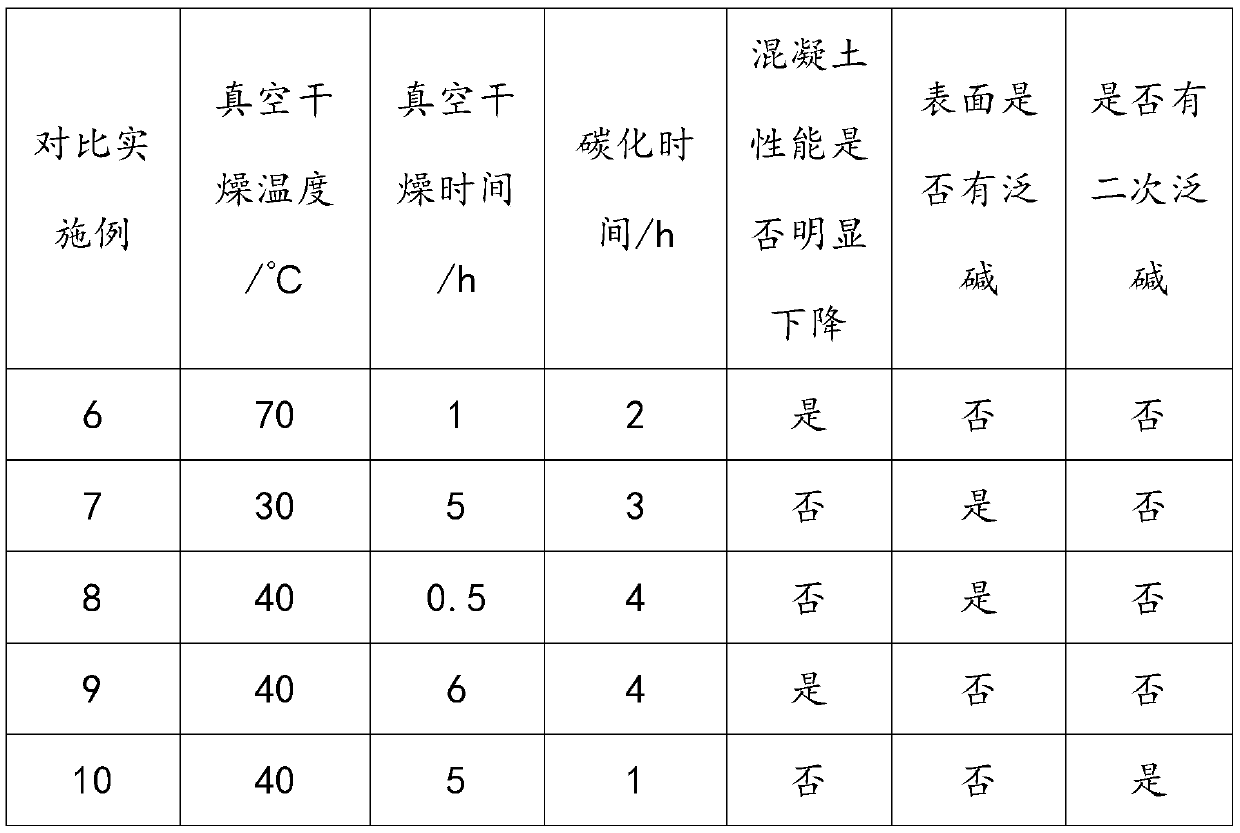
InactiveCN110480811ASolve the ubiquitous problemSolve chromatic aberrationCeramic shaping apparatusEngineeringVacuum drying
The invention discloses a method for rapidly treating the surface of transfer printing concrete. The method solves the problem that the color difference is caused due to the fact that the surface of existing transfer printing concrete is prone to whiskering. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps: putting the just-scoured transfer printing concrete into a vacuum drying oven for vacuum drying; and then carrying out surface accelerated carbonation treatment on the dried transfer printing concrete. The method has a remarkable anti-whiskering effect, is stableand reliable, and is capable of effectively improving the yield and impression quality of the transfer printing concrete.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Method for Fabricating Organic Optoelectronic Multi-Layer Devices
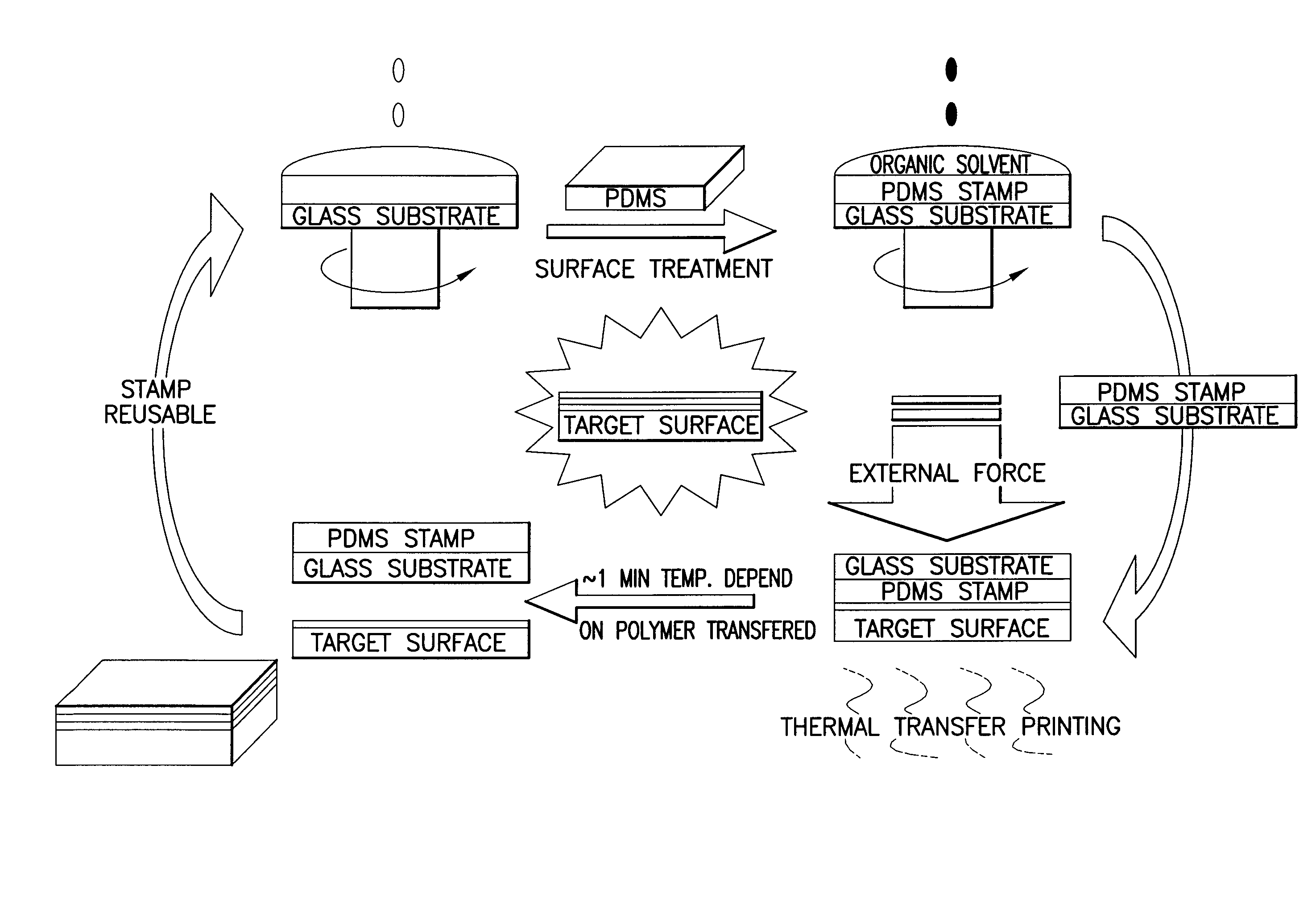
InactiveUS20100084081A1Stable and fast and wayAdded fabricationLayered product treatmentDecorative surface effectsOrganic solventDimethyl siloxane
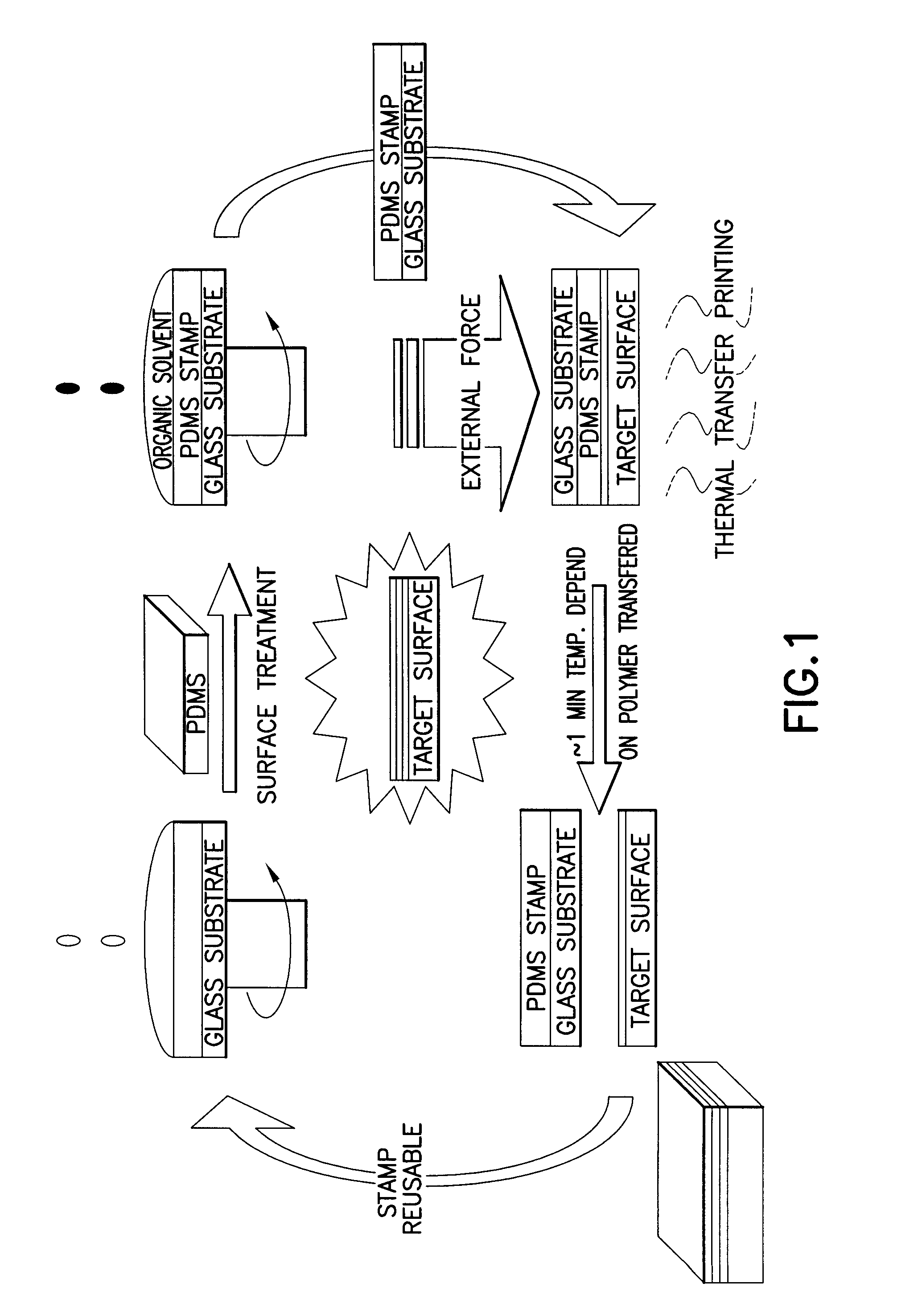
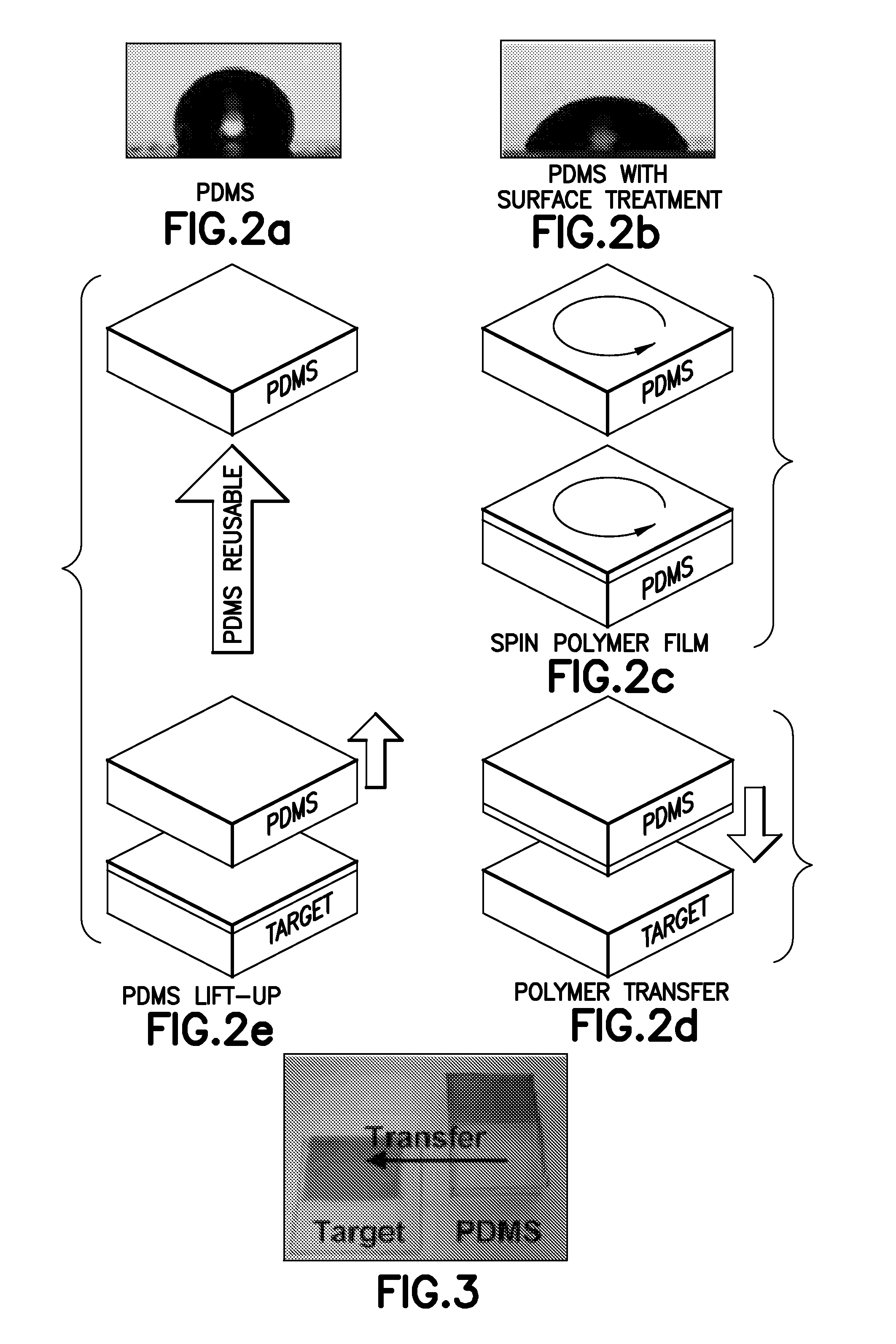
A method for fabricating organic optoelectronics multi-layer devices is disclosed. A polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) surface is pretreated with an organic solvent and used to directly form a uniform optoelectrical thin-film from organic solution by spin coating. The optoelectrical thin-film films that are formed on the PDMS surface are easily transferable to any substrate by a slight, externally applied force for providing conformal contact with a target substrate and thermal annealing, depending on the polymers to be transferred. Pretreatment of the PDMS surface with the organic solvent combined with a dry transfer process provides an easier way to cascade polymer architecture fabrication. In addition, the method increases the performance of various types of organic photo electronics, and permits an extension of the types of research that can be performed in the field of photo electronics.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com