Patents
Literature
1955 results about "Graphite electrode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
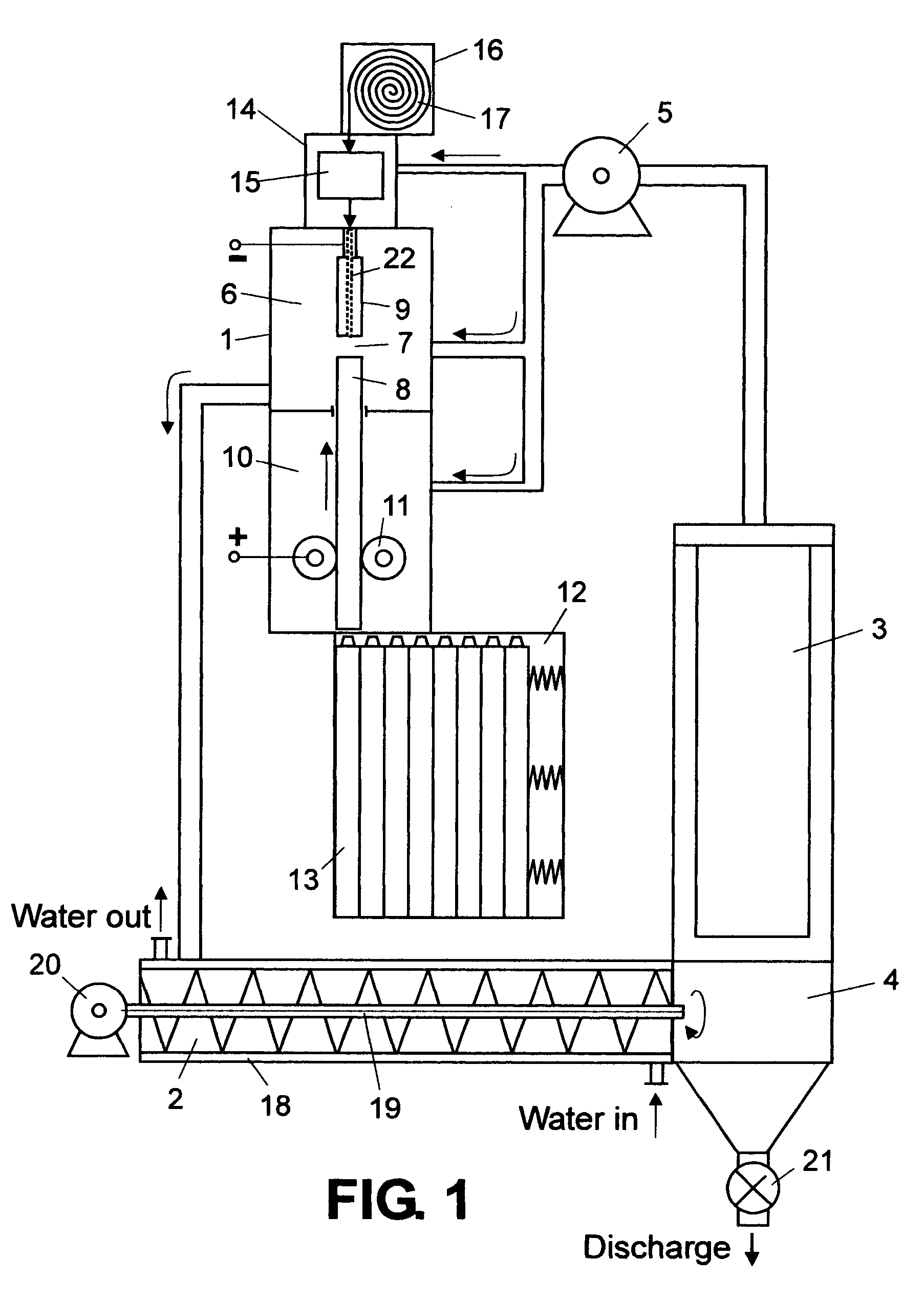
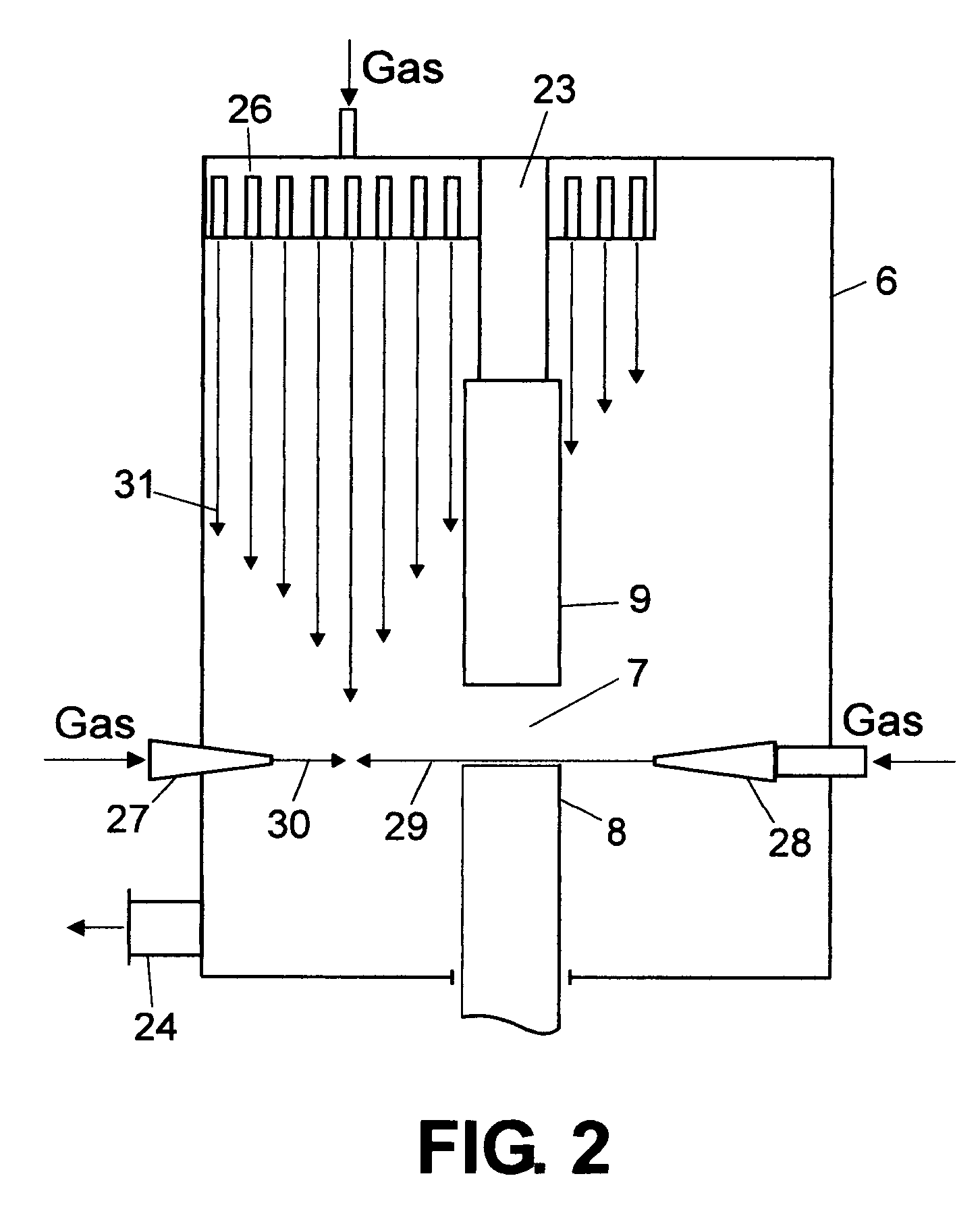
Multi-purpose, multi-oxy-fuel, power burner/injector/oxygen lance device
InactiveUS20030075843A1Reduce the numberSmall sizeTuyeresCharge manipulationSteelmakingLiquid medium
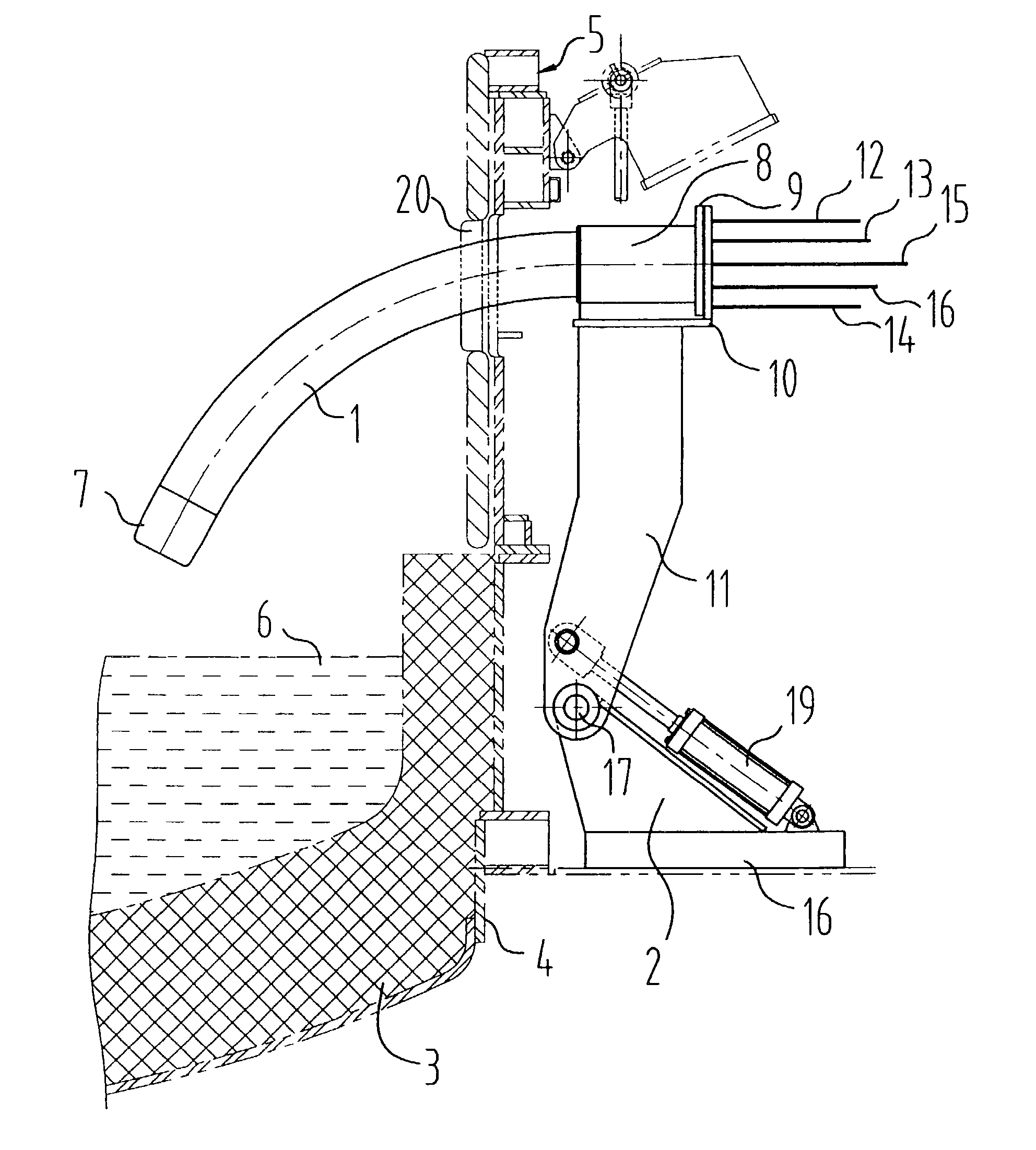
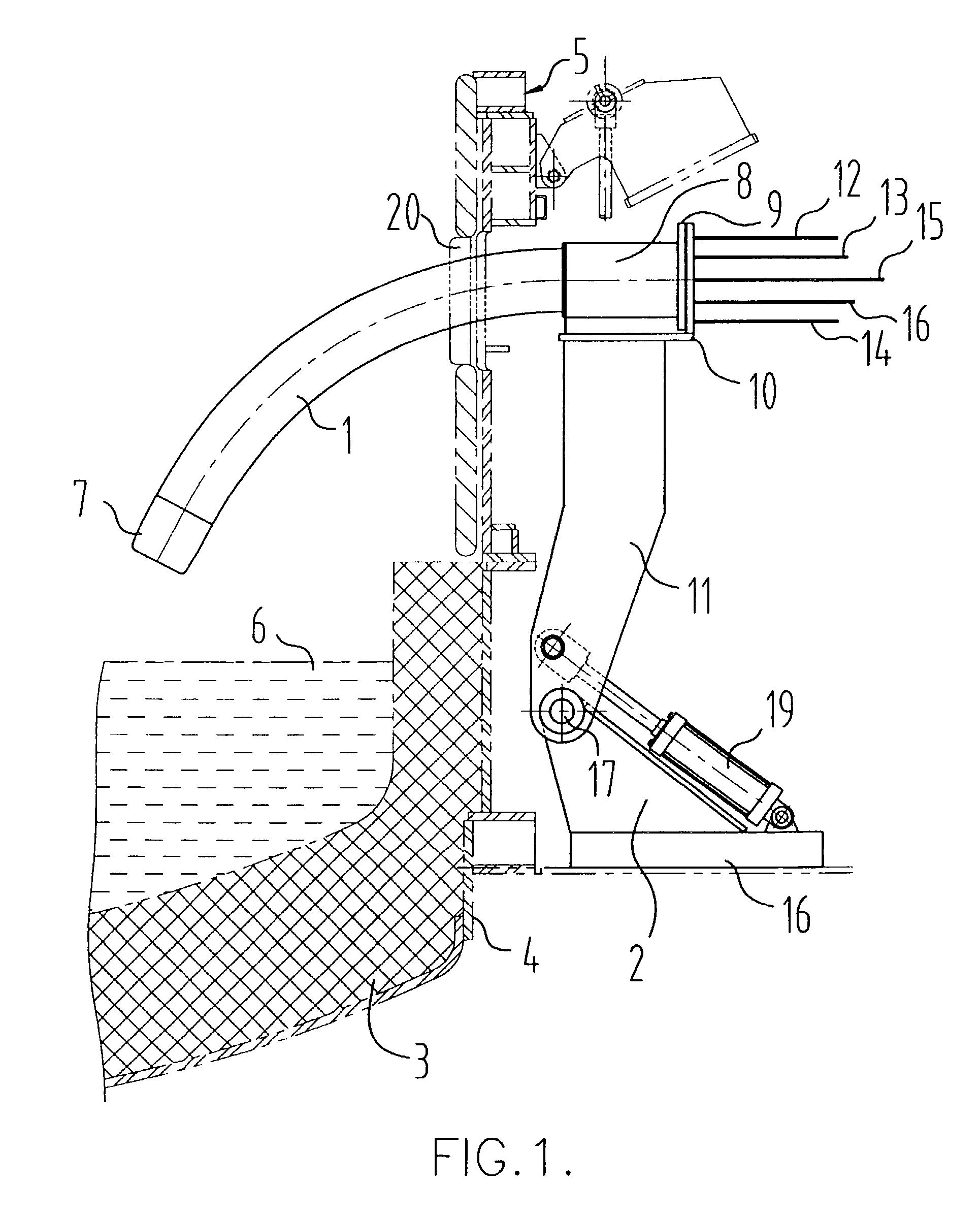
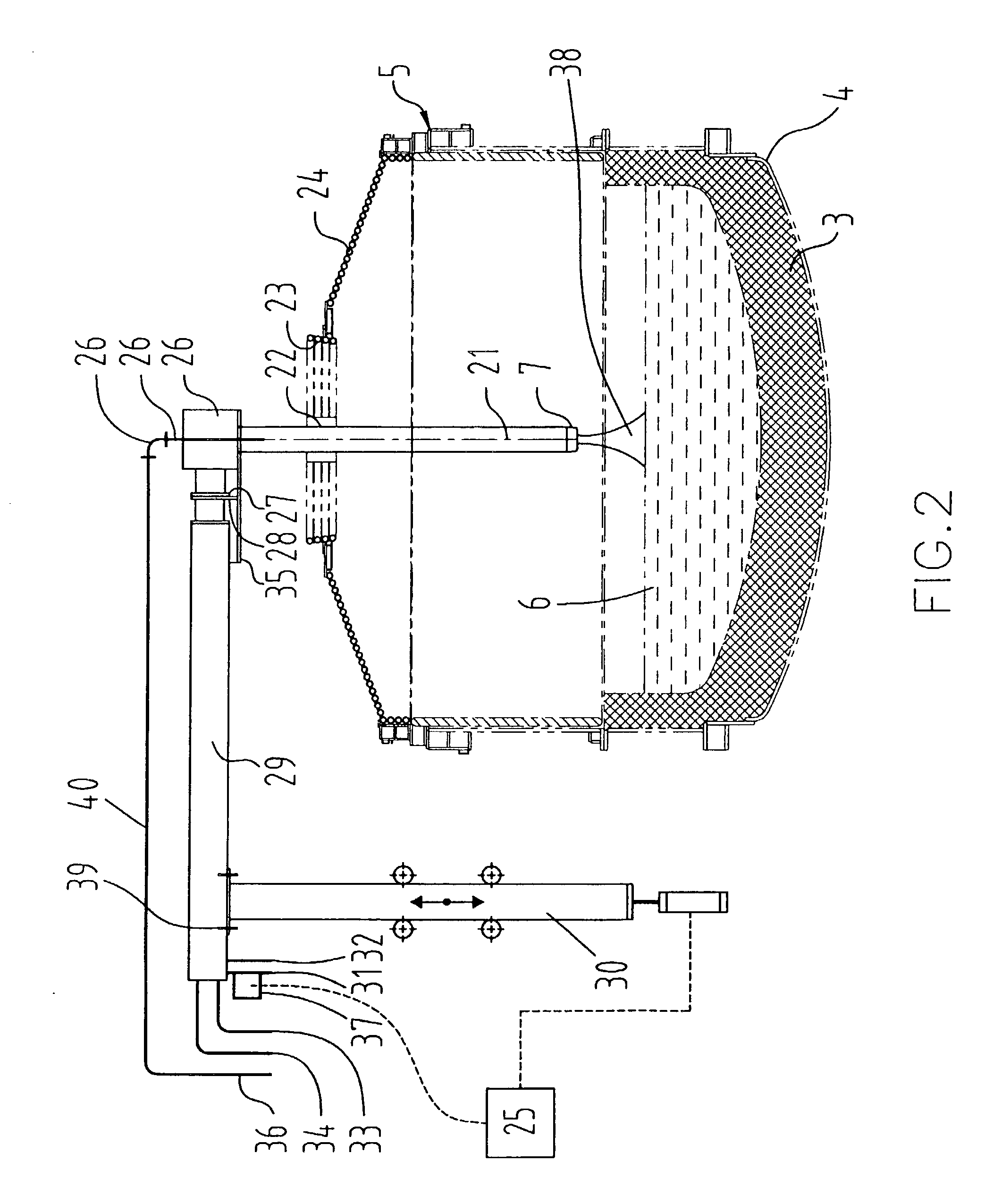
A multi-purpose, multi-oxy-fuel High Temperature Power Burner / Injector / Oxygen Lance, Mechanical System Apparatus Device, for steelmaking from recycled scrap and / or virgin ferrous charge, which can be employed in multi-oxy-fuel (natural gas; pulverized carbonaceous matter; heavy oil), especially by Oxygen Combusted mixture of Natural Gas / Pulverized Carbonaceous Matter in High Temperature Power Burner Mode, for efficient and rapid melting of solid ferrous charge (cold or preheated) in a special steelmaking Metallurgical Furnace or Open Hearth Furnace, Tandem Furnace, BOF, EAF, as its augmenting or only source of thermal energy; more than one Device in Oxygen-Natural Gas / Pulverized Carbonaceous Matter Power Burner Mode, can be employed as the only source of thermal energy in a modified, originally Electric Arc Furnace, as total replacement of Graphite Electrodes and Electric Arc System, the replacement being noticeably more primary energy efficient than the thermal energy provided by Graphite Electrode / Arc System; it also can be employed in an Solid Particles Injector Mode, for injecting of adequately granulated carbonaceous materials or lime into the molten steel for its carburizing or for foamy slag control; further it can be employed in a natural gas shrouded, pulsating oxygen stream, for vertically to the charge oriented soft blow supersonic Oxygen Injection Lance Mode, for decarburization of the molten metal contained in the hearth of the metallurgical furnace and foamy slag control; in one of the embodiments-generally arcuate-pivotally mounted, liquid media cooled composite body, is pivoted into and out of a furnace vessel through a small opening in the shell wall for auto-regulated constant optimal positioning of the Composite Body Tip against solid or molten charge, in each and all multi-purpose modes; furthermore, when inserted into the furnace vessel, the arcuate composite body can be rotated about its longitudinal axis for directing the oxy-fuel high temperature flame towards unmolten charge in the furnace; in an other-generally linear-embodiment, the liquid cooled composite body is attached to the mast type carrier allowing vertical movement of the composite body which enters the furnace vessel through a small opening in the furnace roof; the bimetallic, liquid cooled special tip assembly of both-arcuate and linear embodiments-of the composite body includes easy replaceable, independent, multi-opening nozzles, mounted in a protective, retracted position inside of the liquid cooled special tip assembly.
Owner:EMPCO (CANADA) LTD
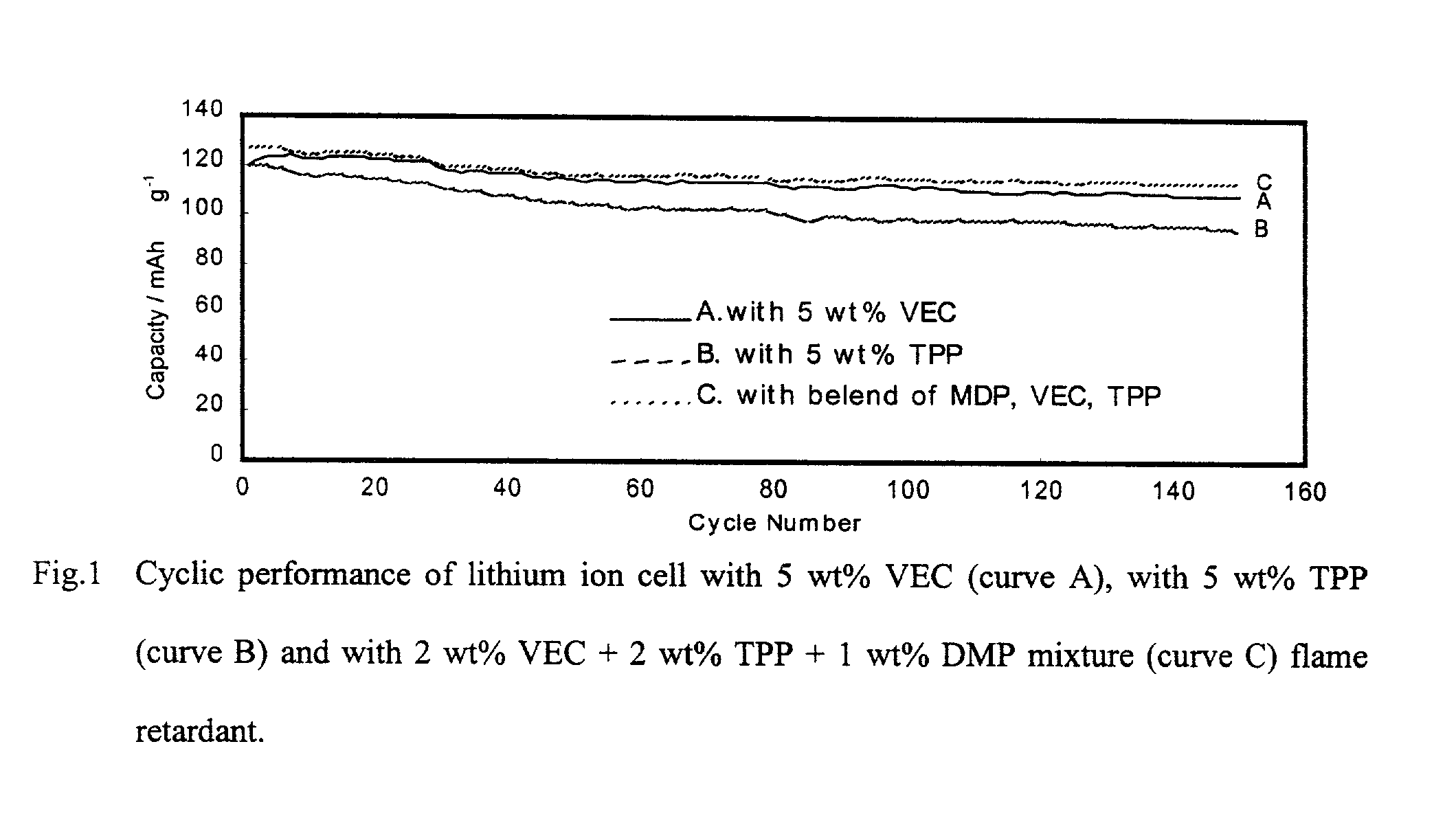
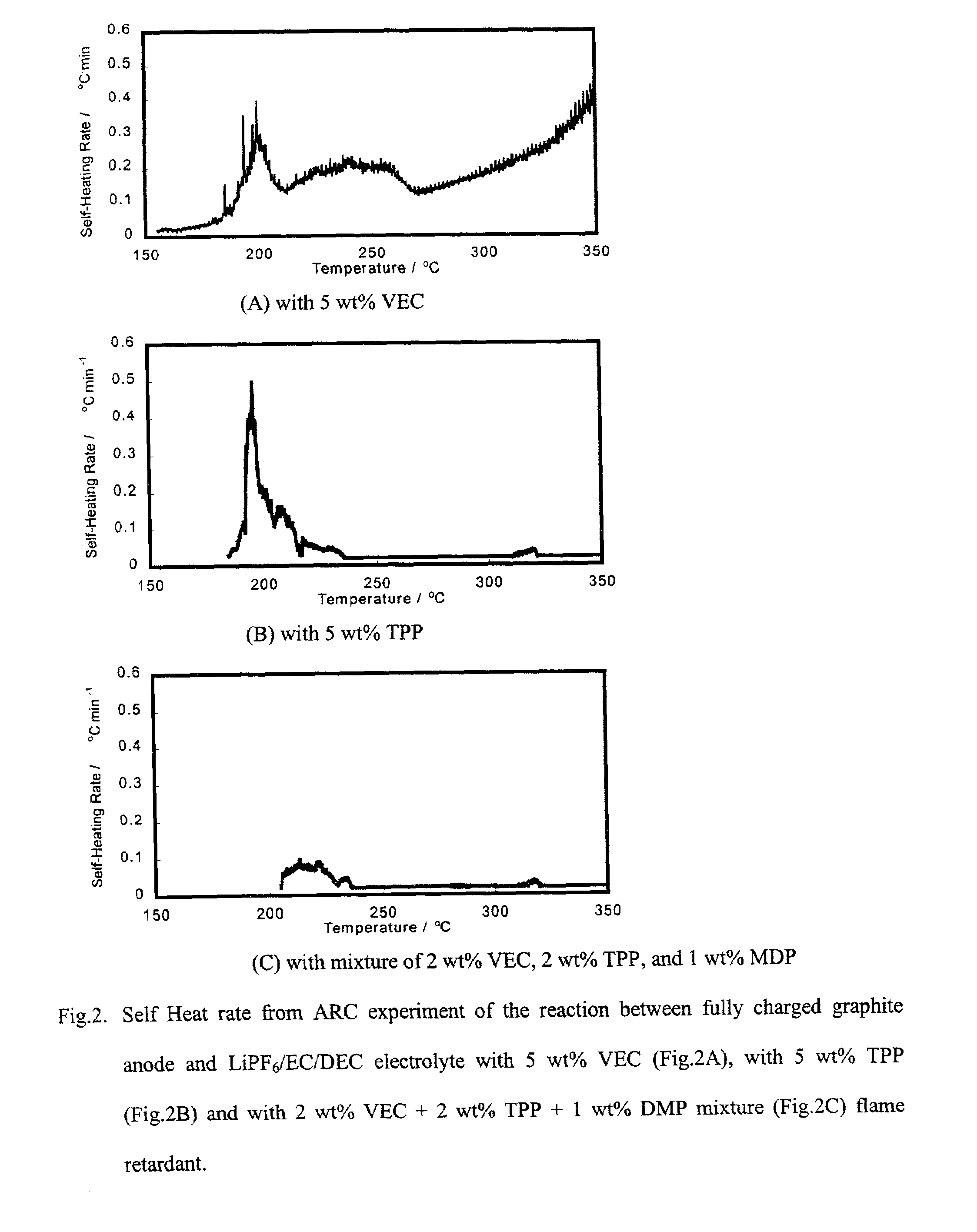
Lithium ion battery with improved safety
InactiveUS7026074B2Superior thermal safety behaviorSuppress gas productionOrganic electrolyte cellsLi-accumulatorsOrganic solventGraphite electrode
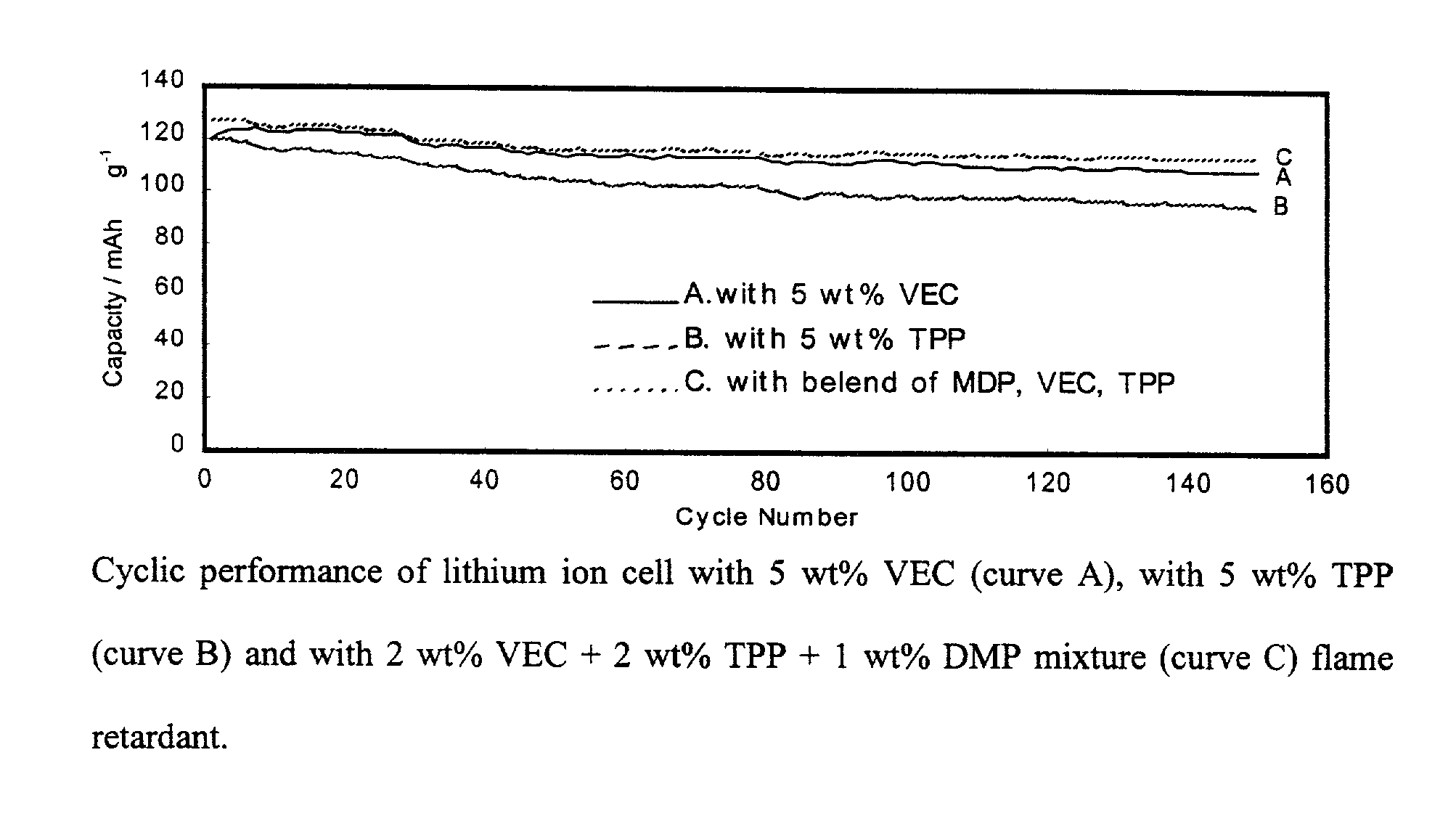
A lithium battery with improved safety that utilizes one or more additives in the battery electrolyte solution wherein a lithium salt is dissolved in an organic solvent, which may contain propylene, carbonate. For example, a blend of 2 wt % triphenyl phosphate (TPP), 1 wt % diphenyl monobutyl phosphate (DMP) and 2 wt % vinyl ethylene carbonate additives has been found to significantly enhance the safety and performance of Li-ion batteries using a LiPF6 salt in EC / DEC electrolyte solvent. The invention relates to both the use of individual additives and to blends of additives such as that shown in the above example at concentrations of 1 to 4-wt % in the lithium battery electrolyte. This invention relates to additives that suppress gas evolution in the cell, passivate graphite electrode and protect it from exfoliating in the presence of propylene carbonate solvents in the electrolyte, and retard flames in the lithium batteries.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
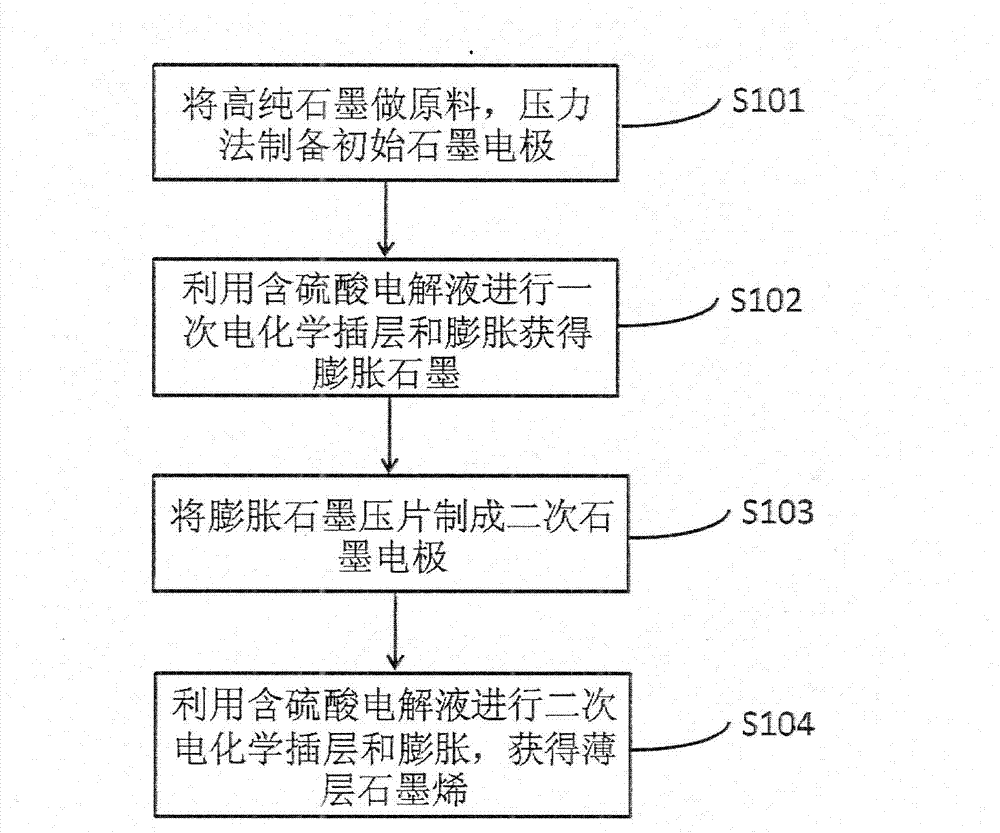
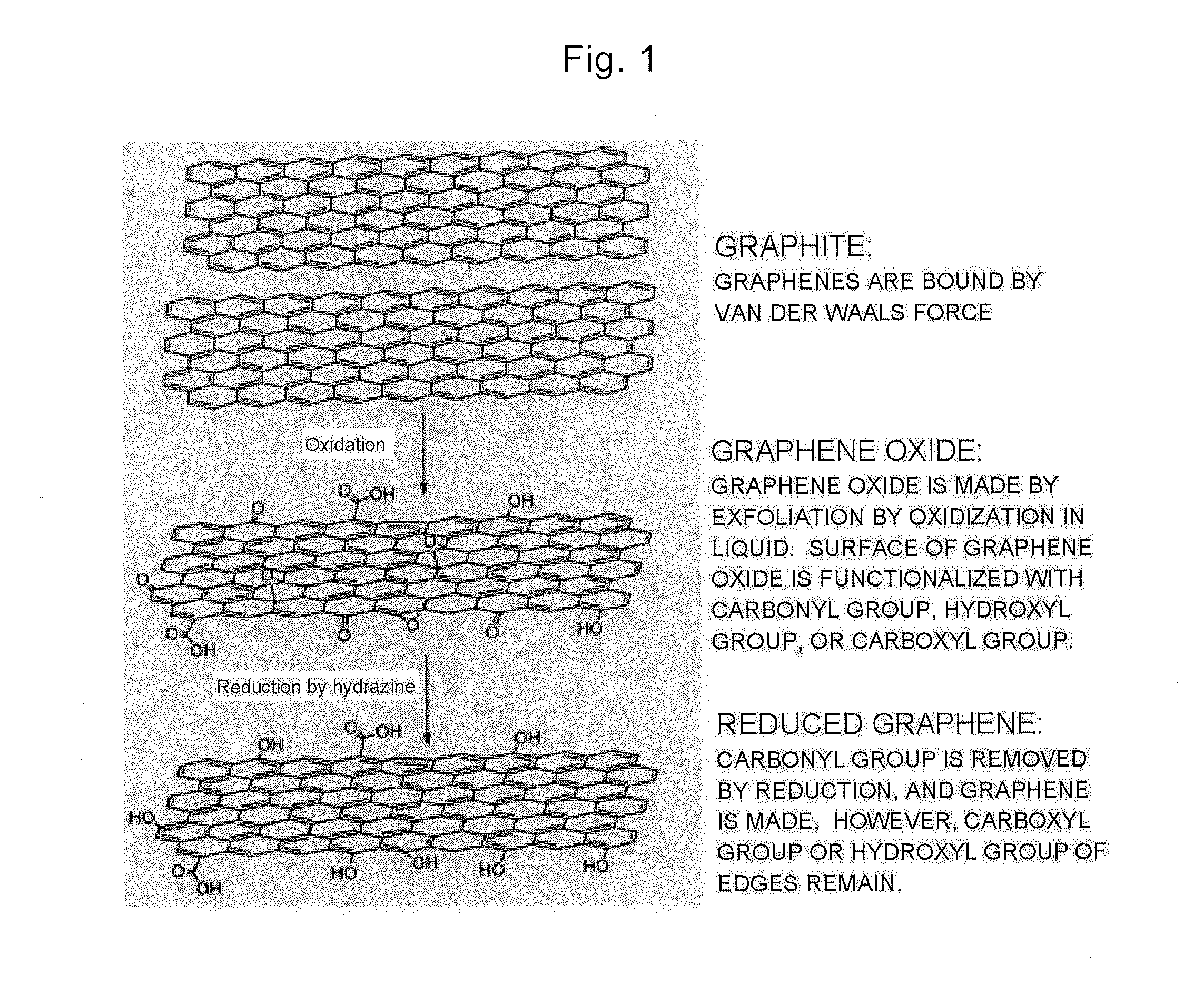
Method for electrochemically preparing graphene
The invention discloses a method for electrochemically preparing graphene, which preferably comprises the steps of pressing a high-purity graphite raw material to form a graphite electrode, carrying out anodization through the graphite electrode by using sulfuric acid aqueous solution or acetic acid and the like mixed acid solution as an electrolyte to prepare a graphite intercalation product, and obtaining expanded graphite by high temperature or microwave and other methods; and then pressing the expanded graphite to prepare a reaction electrode, and carrying out secondary electrochemical intercalation and expansion to finally obtain laminar graphene. According to the invention, in the preparing process, potassium permanganate and other strong oxidizers are not used, and the damage of the strong oxidizers to the structure and performance of graphene are avoided; alkali metal, fuming sulfuric acid oxydol and other inflammable and explosive dangerous substances are not used, and toxic or harmful substances are not introduced, so that the production is safe and environment friendly; and at the same time, the method is simple in process flow, easy to operate, low in cost, high in yield, mild in reaction conditions and low in energy consumption, and is suitable for industrialized large-scale production.
Owner:苏州格瑞丰纳米科技有限公司
Method for preparing high-quality graphene through electrochemical high-efficiency exfoliation
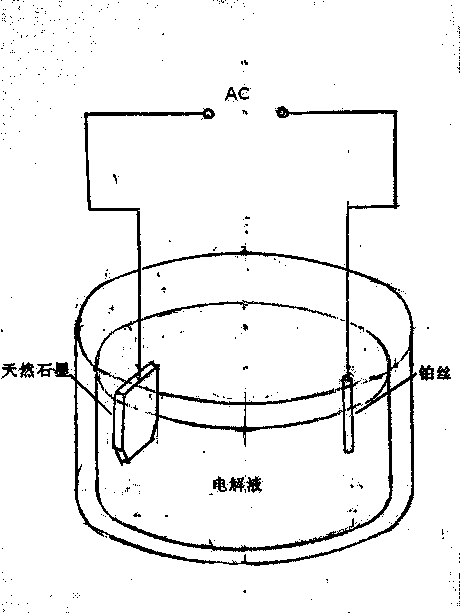
The invention relates to a preparation method for graphene, especially to a method for preparing high-quality graphene through electrochemical high-efficiency exfoliation. The method mainly overcomes the technical problems that the honeycomb lattice structure of graphene is severely destroyed in the process of oxidation, an obtained membrane resistance is 1 K to 70 K omega / square (wherein light transmittance is less than 80%), the resistance is too high and much higher than requirements of ITO, etc. The method comprises the following steps: with graphite as a positive electrode and a platinum filament as a negative electrode, repeatedly applying high offset voltage and negative offset voltage on the graphite electrode, which enables graphite to be rapidly disassociated and decomposed into double-layer graphene floating on the surface of an electrolyte; collecting graphene and then filtering and drying graphene; dispersing obtained powder of a graphene film in a DMF solution; and carrying out water-bath ultrasonic treatment and centrifugation so as to obtain desired 1.5-nm-grade graphene flakes.
Owner:杭州金马新能源科技有限公司
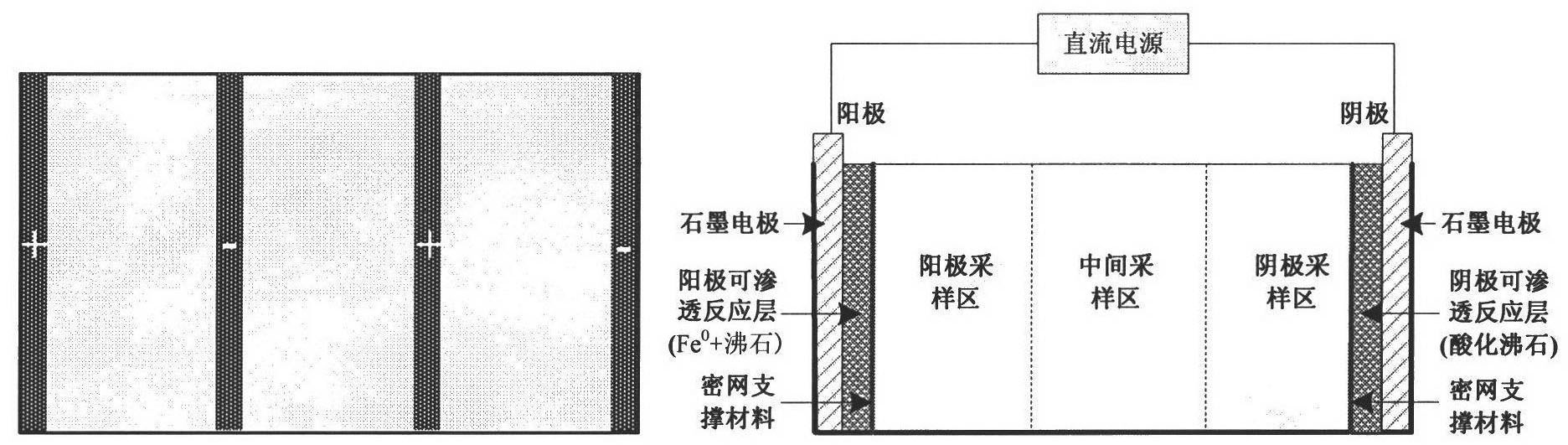
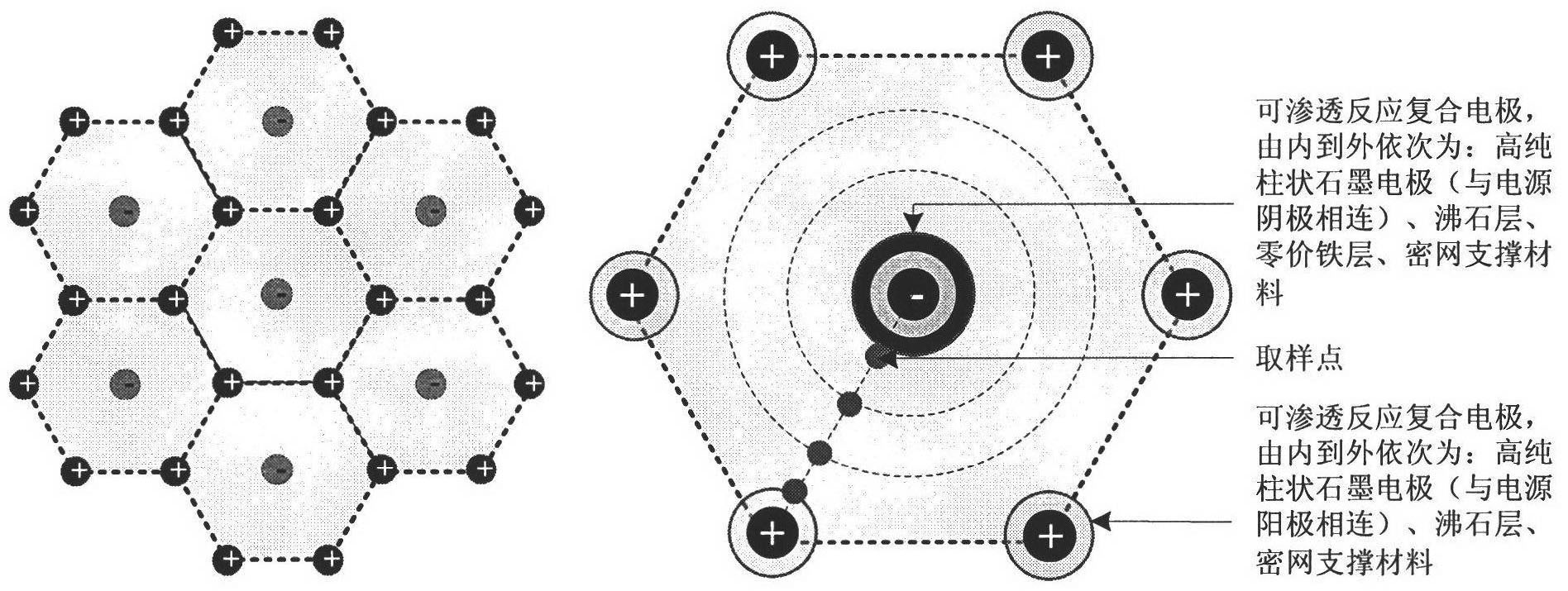
Electrokinetic remediation method of heavy metal polluted soil by composite electrodes
ActiveCN102441564AEffective pH controlWeaken the big changeContaminated soil reclamationGraphite electrodeElectrokinetic remediation
The invention relates to composite electrodes and an electrokinetic remediation method of heavy metal polluted soil by using the composite electrodes. According to the electrodes, an active material layer is adhered to the surface of graphite electrodes or metal electrodes of an anode and a cathode so as to form integrated composite electrodes with permeable reactive performance. By the permeablereactive layer, on one hand, H<+> and OH<-> generated from the electrode reaction can be neutralized and adsorbed, the pH value of the soil can be effectively controlled, and the heavy metal can be prevented from being prematurely deposited in the soil. On the other hand, migrated heavy metal pollutants can be captured, and in situ removal of the heavy metal pollutants in the soil can be realizedby removing the composite electrodes.
Owner:上海环境保护有限公司
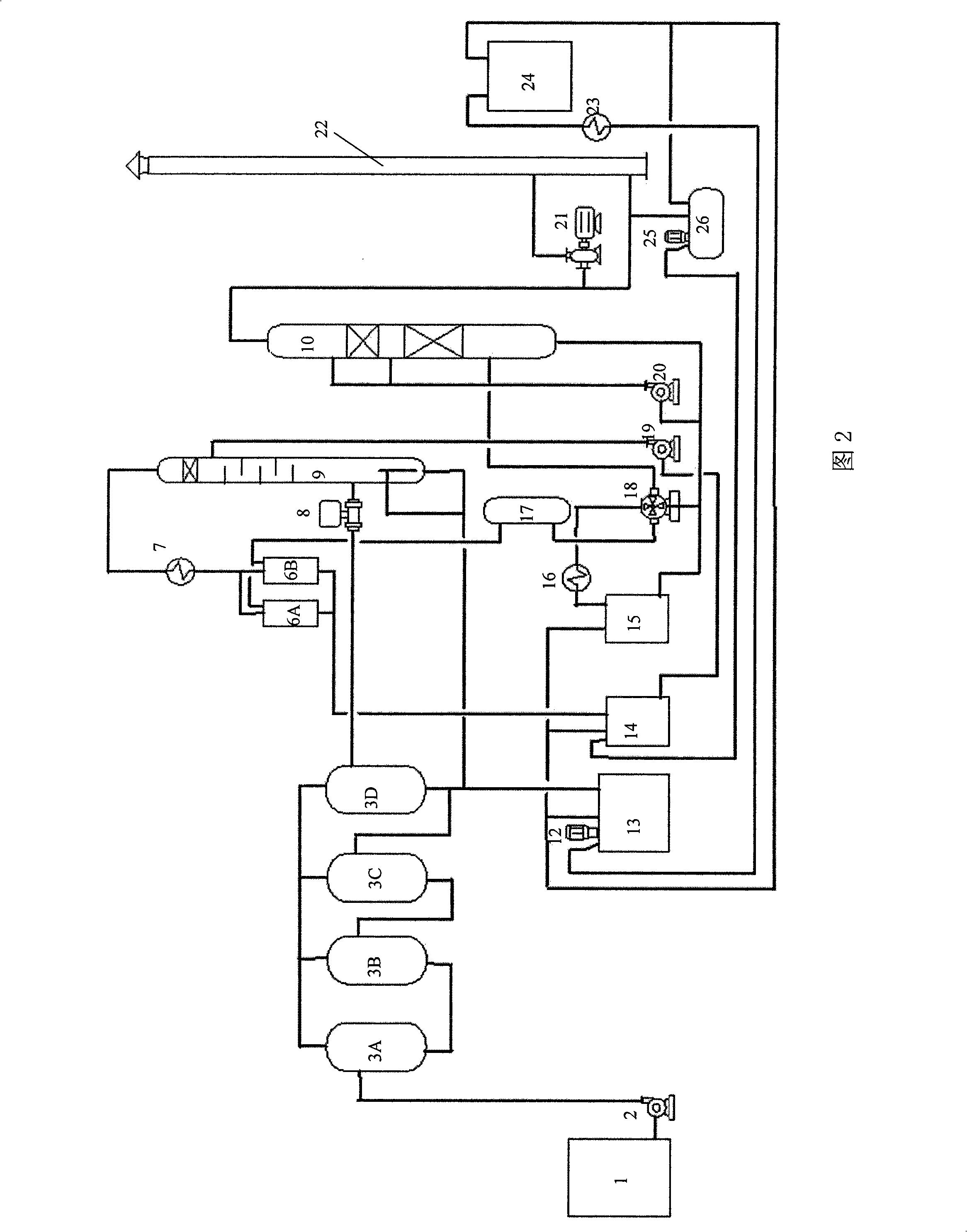
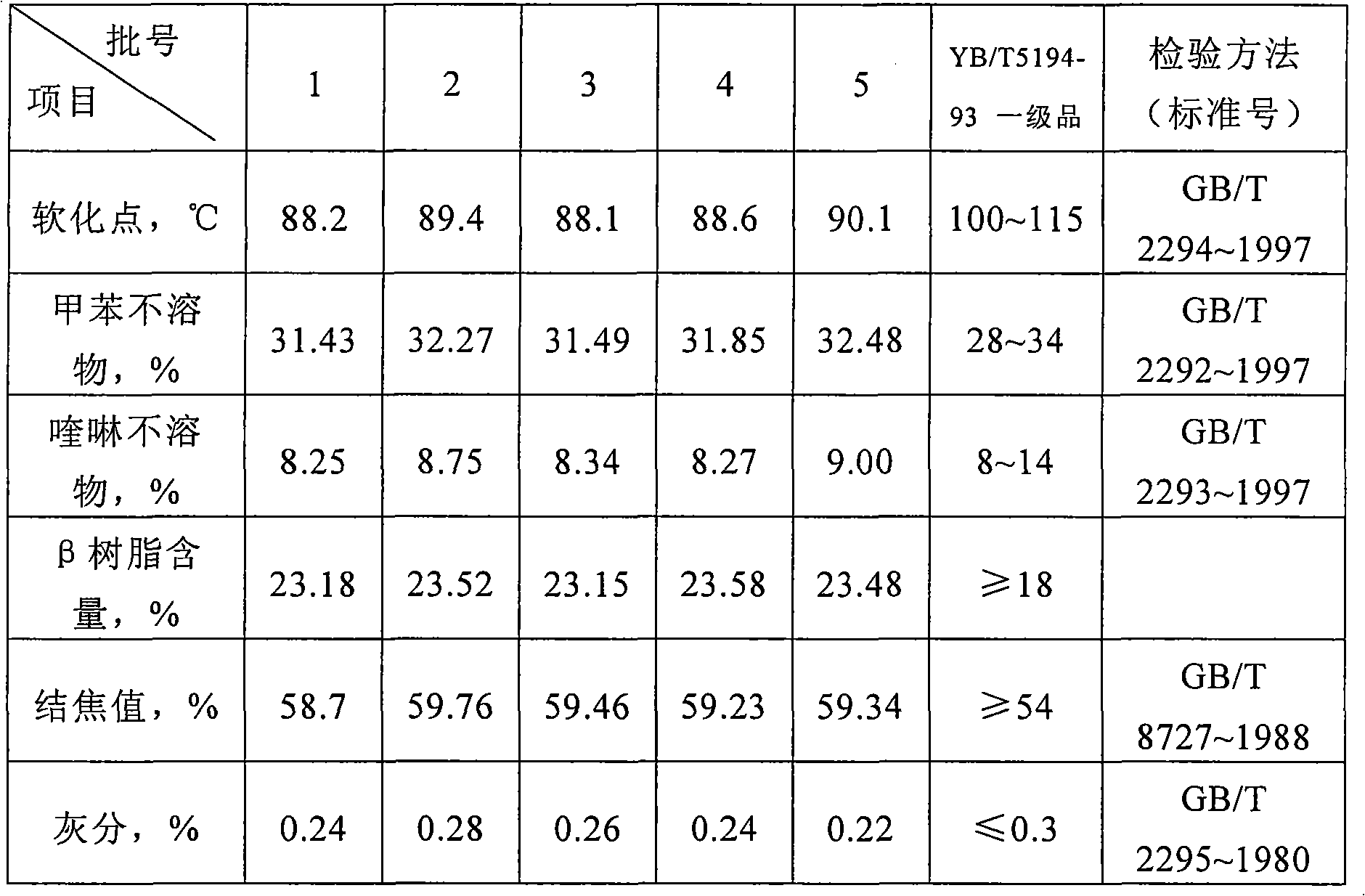
Fine purification method for coal tar pitch
InactiveCN101294090AImprove continuityImprove efficiencyWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumenOrganic filmFiber
The invention relates to a coal tar pitch refining method, in particular to a method for refining pitch for coal tar pitch needle coke, impregnant and binding agent for manufacturing high-power and ultrahigh-power graphite electrodes and pitch for manufacturing coal tar pitch carbon fibers. The method is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: diluting coal tar pitch and the liquid containing coal tar pitch with organic solvent at a weight ratio of the organic solvent to coal tar pitch and the liquid containing coal tar pitch of 1:(5 to 30), removing impurities in the pitch solution by the combination of separation by a centrifuge and filtering with an organic film, and distilling and recovering the solvent in the refined mixture solution to obtain the coal tar pitch free of quinoline insoluble materials. The method has the advantages of good continuity of the separation process and high efficiency, and the pitch contains no quinoline insoluble materials.
Owner:ZIBO MINING GRP
High efficient laminated graphic discharge gap device
ActiveCN101090197AImprove conductivityHigh melting pointOvervoltage arrestors using spark gapsCapacitanceGraphite electrode
This invention relates to an efficient laminated graphite discharge arc gap device including: N+1 arc gaps and a pi-shaped connection capacitor set with N capacitors in the same capacitance value, in which, the gaps are serial to each other, the first one is connected with the live wire, the last one is connected to the earth, one end of each capacitor in the set is connected with the conduction piece between the two arc gaps and the other end is connected to the earth, the arc gap is made of graphite, insulation ring pad is set between the graphite electrodes, the arc gaps are assembled in lamination, parameter of each capacitor in the set is selected according to C=In / 2pifVK, in which, In is the induced discharge current on the capacitors, In=I / N, I is the total current of the set, N is the number of capacitors, f is a lightning wave frequency, V is a rating voltage and K is a safety factor greater than or equal to 1.
Owner:SICHUAN ZHONGGUANG LIGHTNING PROTECTION TECH
Method for regenerating graphene by recovering waste lithium ion battery
ActiveCN103259062APromote oxidationImprove propertiesFinal product manufactureWaste accumulators reclaimingGraphite electrodeGraphite
The invention discloses a method for regenerating graphene by recovering a waste lithium ion battery. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: S1, recovery of an active substance of a battery electrode: carrying out pre-charge or pre-discharge treatment on the waste lithium ion battery which takes graphite as an anode material, and then separating a cathode coating and an anode coating from a current collector and an outer package to obtain a cathode and anode blending material; S2, separation of an intercalated graphite electrode material: drying and crushing the cathode and anode blending material, and separating the active substances of a positive electrode and a negative electrode by adopting a physical method to obtain intercalated graphite powder; and S3, preparation of graphene from the intercalated graphite powder: preparing the graphene by an oxidation-reduction method or an ultrasonic stripping method based on the intercalated graphite powder as a raw material. After the method is adopted, the industrial recovery of the lithium ion battery is realized, and a graphene material can be regenerated by a graphite anode with high added value, so that the method has better application prospect and feasibility, and can produce greater economic benefit and social benefit.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
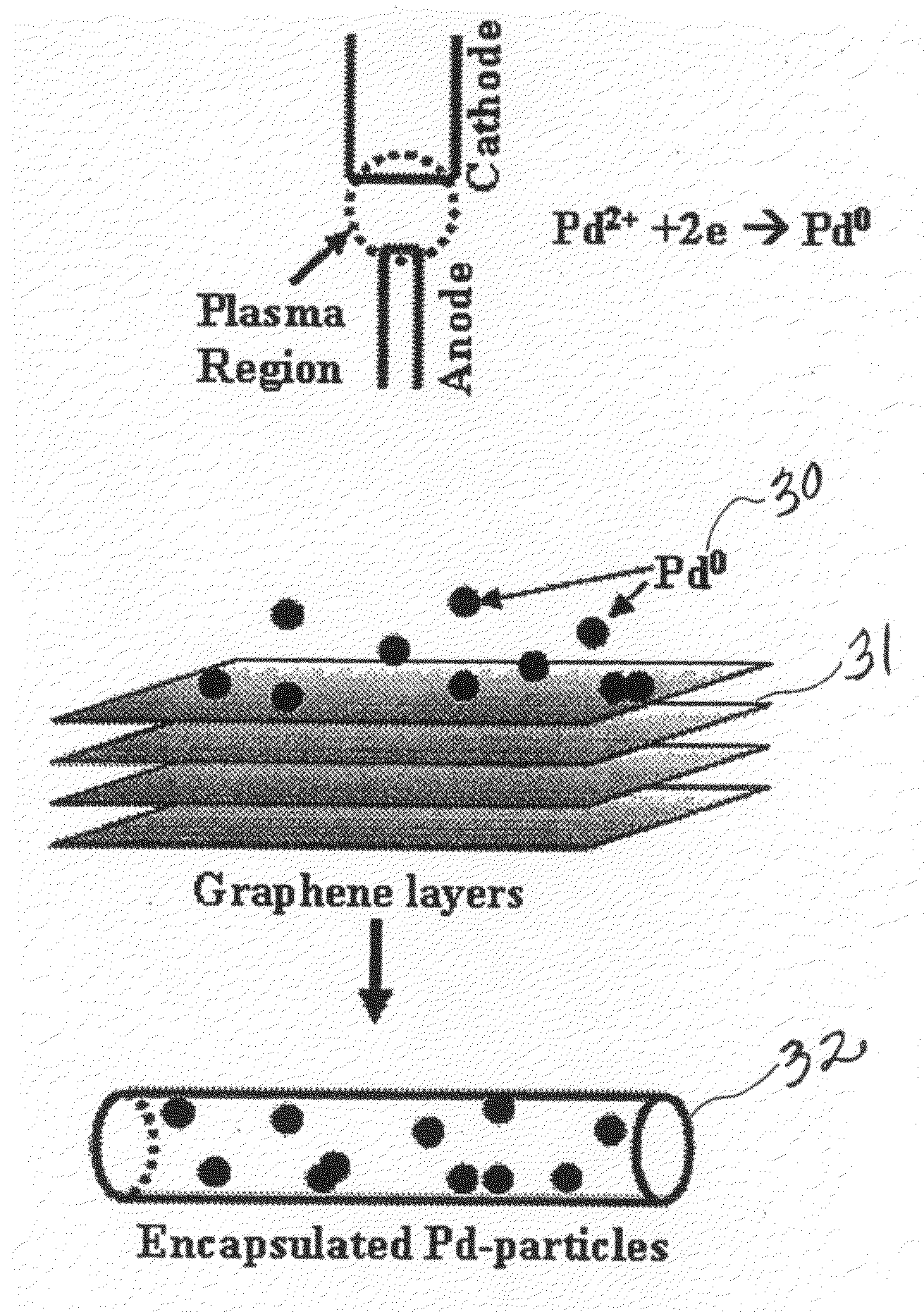
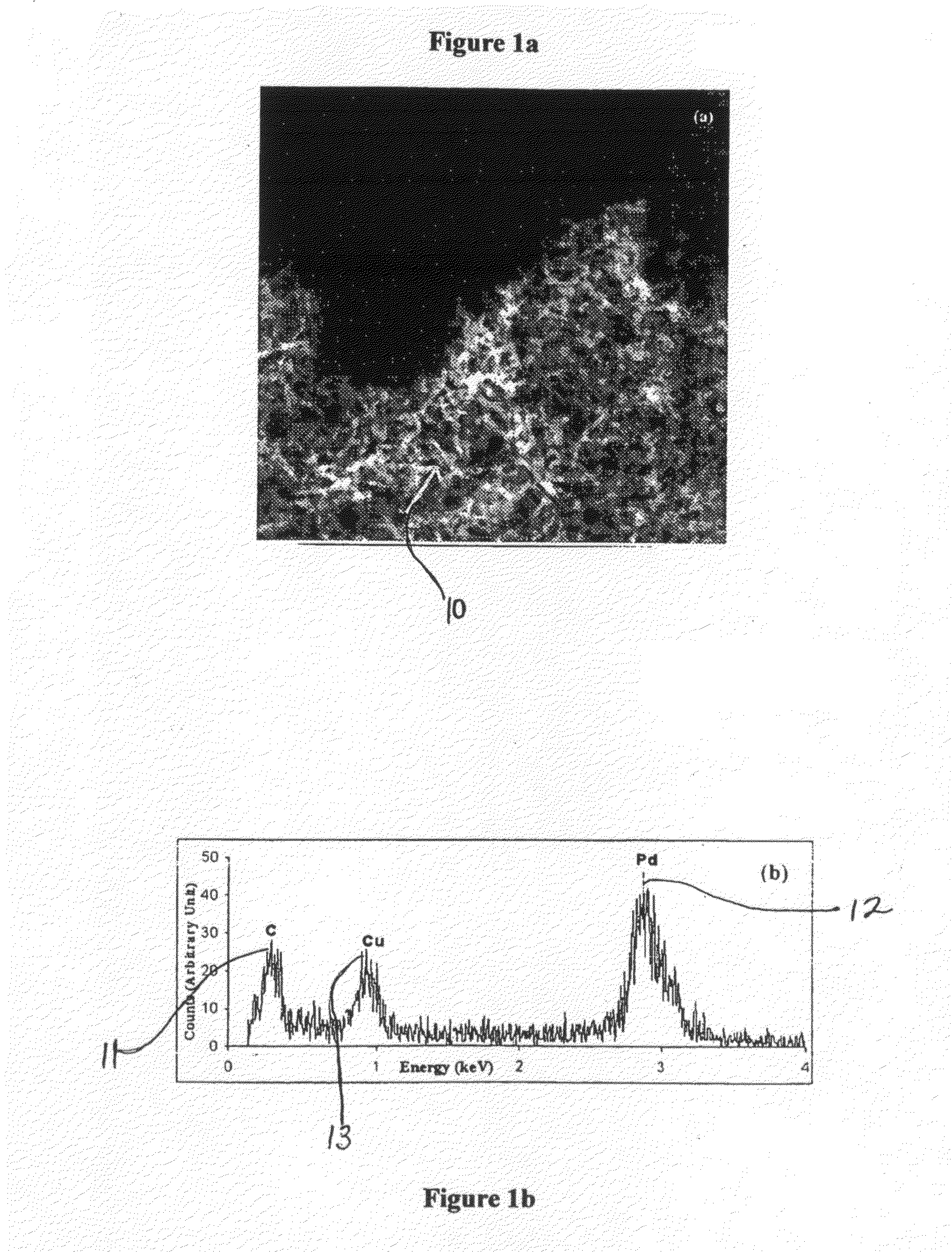
Synthesis of carbon nanotubes filled with palladium nanoparticles using arc discharge in solution
InactiveUS20090072192A1Improve abilitiesMaterial nanotechnologyOther chemical processesNanotubeMaterials science
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
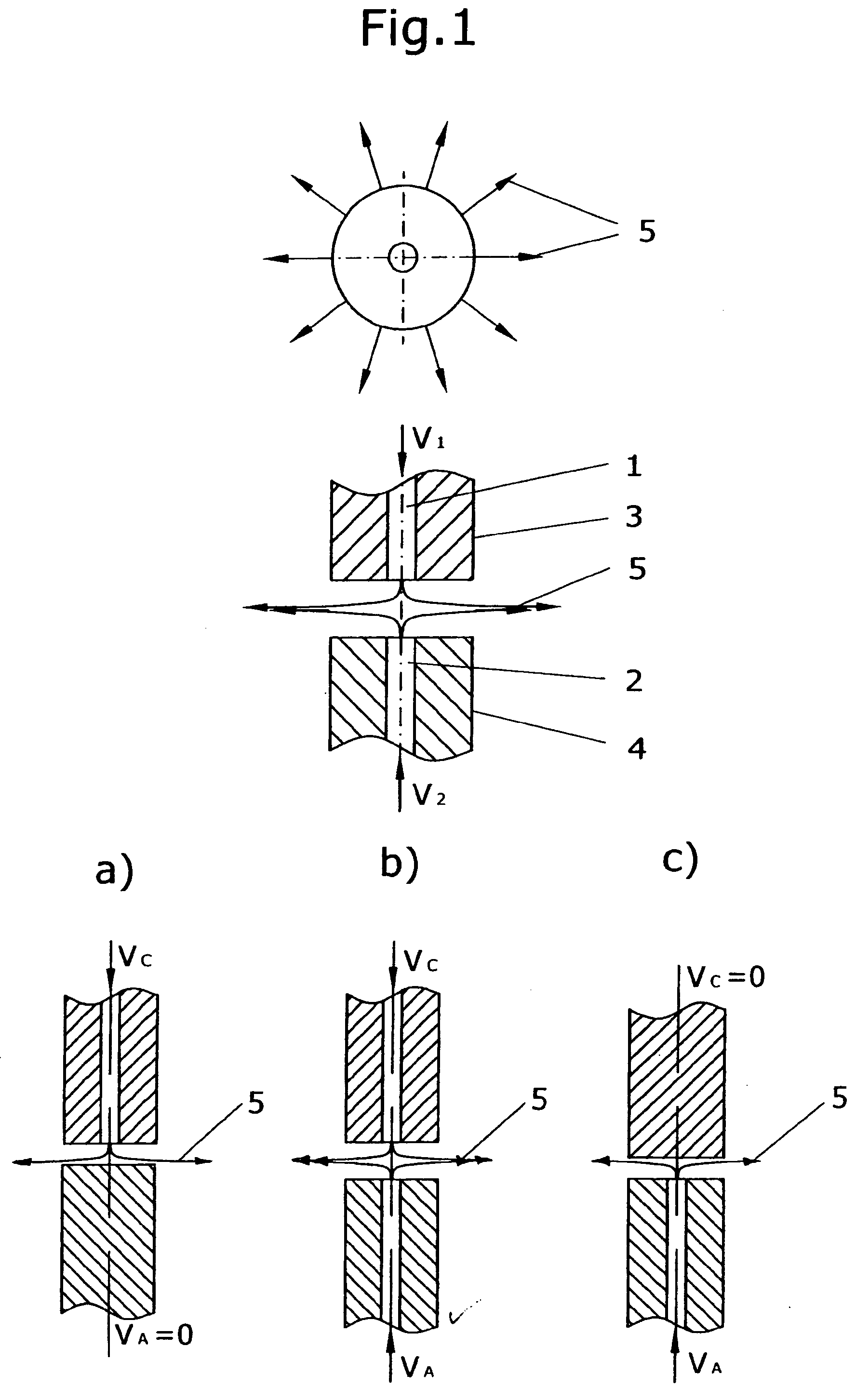
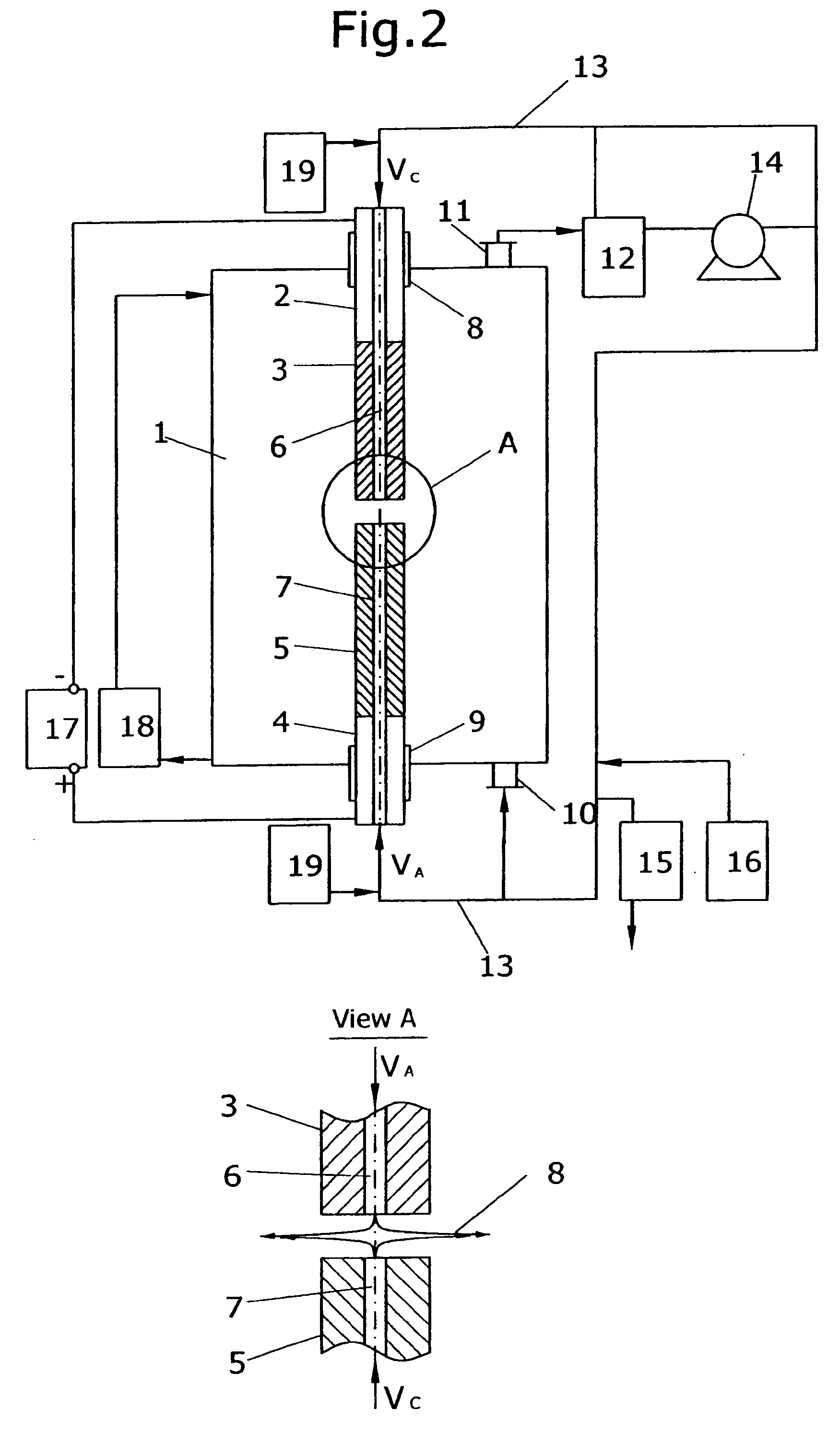
Method and apparatus for carbon allotropes synthesis
InactiveUS20050230240A1Easy and inexpensiveEliminate the problemMaterial nanotechnologyFullerenesOxygenCarbon allotrope
A method and apparatus for synthesis of fullerenes and nanotubes in large quantities at an economical cost from graphite in electric arc plasma process are presented. Different embodiments of channeled graphite electrodes for both direct current (DC) and alternative current (AC) processes are disclosed. High productivity of the carbon allotropes is achieved by feeding consumable graphitic electrode into hot plasma zone, injecting of feedstock, catalyst and buffer gas flow through the longitudinal inner channel electrodes into the hot plasma zone and creating the radial gas outflow in the gap between electrodes, and following removal of produced carbon and catalytic vapors from the hot plasma zone into an oxygen deprived reaction vessel for quenching and condensing. Deposited after condensation soot containing carbon allotropes is collected and carbon allotropes are recovered by known techniques. The final products of recovering are fullerenes C60, C70 and higher fullerenes or nanotubes.
Owner:DUBROVSKY ROMAN +1
Ultra high power graphite resistor rod with 600mm diameter and method for producing the same
ActiveCN101553060ASolve capacitySolve the scale-up problemElectric discharge heatingVolumetric Mass DensityCoal
The present invention provides an ultra high power graphite resistor rod with 600mm diameter and a method for producing the same. The method utilizes domestic coal series acicular coke with low true density in main physicochemical standard, high heat expansion coefficient and sulphur content for producing the large-size ultra high power graphite resistor rod with 600mm diameter. Volumetric density, bending strength, elastic modulus, electric resistivity and heat expansion coefficient of the product reaches the international standard after detecting which can solve difficult problem that the domestic coal series acicular coke can not produce the large-size ultra high power graphite resistor rod with 600mm diameter because of low true density in main physicochemical standard, high heat expansion coefficient and sulphur content, and can realize localization for raw material acicular coke of the large-size ultra high power graphite resistor rod, simultaneity, also can solve problem that the acicular coke depends on importation in a long time and has high cost for restricting expanding yield and scale of the ultra high power graphite resistor rod in carbon industry. The product can reduce cost and improve economic performance.
Owner:KAIFENG CARBON CO LTD OF CHINA PINGMEI SHENMA GRP
Poisonous waste treating method and special apparatus
InactiveCN101088581AAvoid secondary pollutionReduce processingDispersed particle separationCombined combustion mitigationHigh energyPolychlorinated biphenyl
The present invention relates to poisonous waste treating method and apparatus, and belongs to the field of waste treating technology. The poisonous waste treating apparatus is plasma apparatus comprising a furnace body, a main graphite electrode and an auxiliary graphite electrode connected to the cover of the furnace body, carrier gas supplier connected to the main graphite electrode, a feeder, a vitreous body exhausting heat pump, a metal melt heat pump, a crucible inside the furnace body, a lower electrode in the bottom of the furnace body, a liquid level sensor connected to the sensor controller, and a tail gas exhausting system connected to the furnace body. It is used in treating polychlorinated biphenyl and other high dangerous waste through instantaneous high temperature, and has no secondary pollution, capacity of recovering high energy gas, and capacity of recovering metals.
Owner:HOOTECH
Graphite electrode for electrothermic reduction furnaces, electrode column, and method of producing graphite electrodes
InactiveUS20050254545A1Low production costElectric discharge heatingConductive materialGraphite electrodeCrystal structure
A graphite electrode for an electrothermic reduction furnace is formed from anode grade coke and graphitized at a graphitization temperature below 2700° C. The resulting electrode is particularly suited for carbothermal reduction of alumina. It has an iron content of about 0.05% by weight, a specific electrical resistivity of above 5 μOhm·m, and a thermal conductivity of less than 150 W / m·K. The graphite electrode is manufactured by first mixing calcined anode coke with a coal-tar pitch binder, and a green electrode is formed from the mixture at a temperature close to the softening point of the pitch binder. The green electrode is then baked to carbonize the pitch binder to solid coke. The resultant carbonized electrode, after further optional processing is then graphitized at a temperature below 2700° C. for a time sufficient to cause the carbon atoms in the carbonized electrode to organize into the crystalline structure of graphite.
Owner:SGL CARBON SE
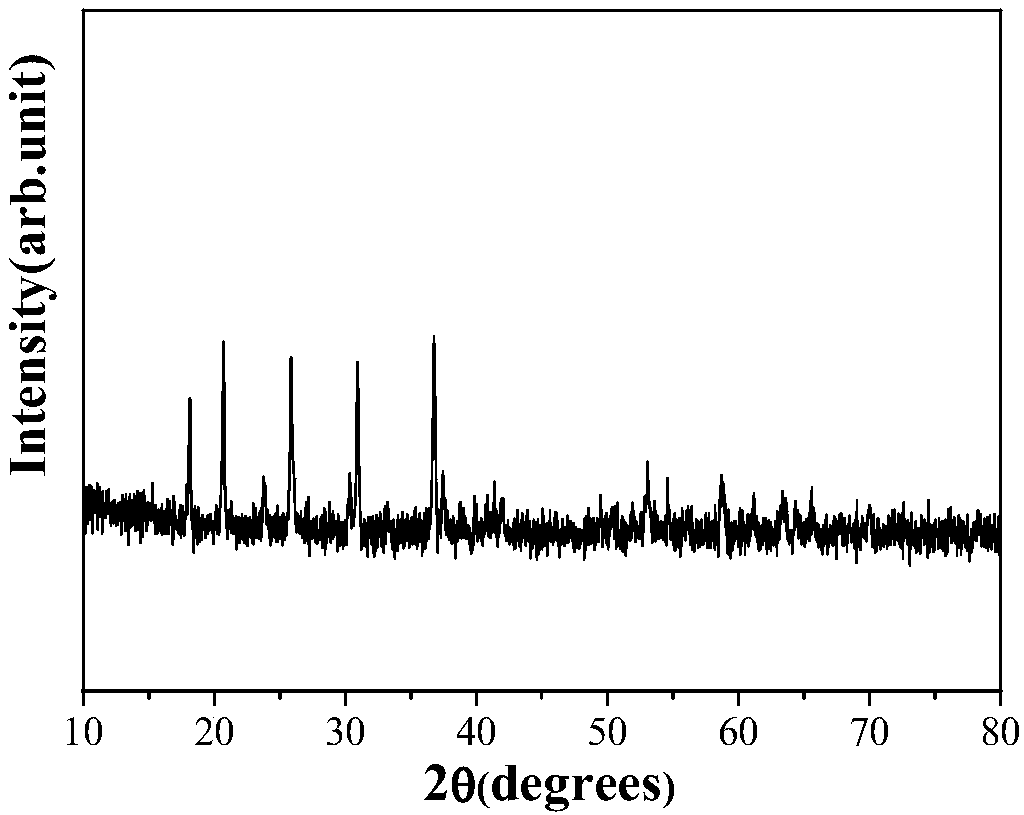
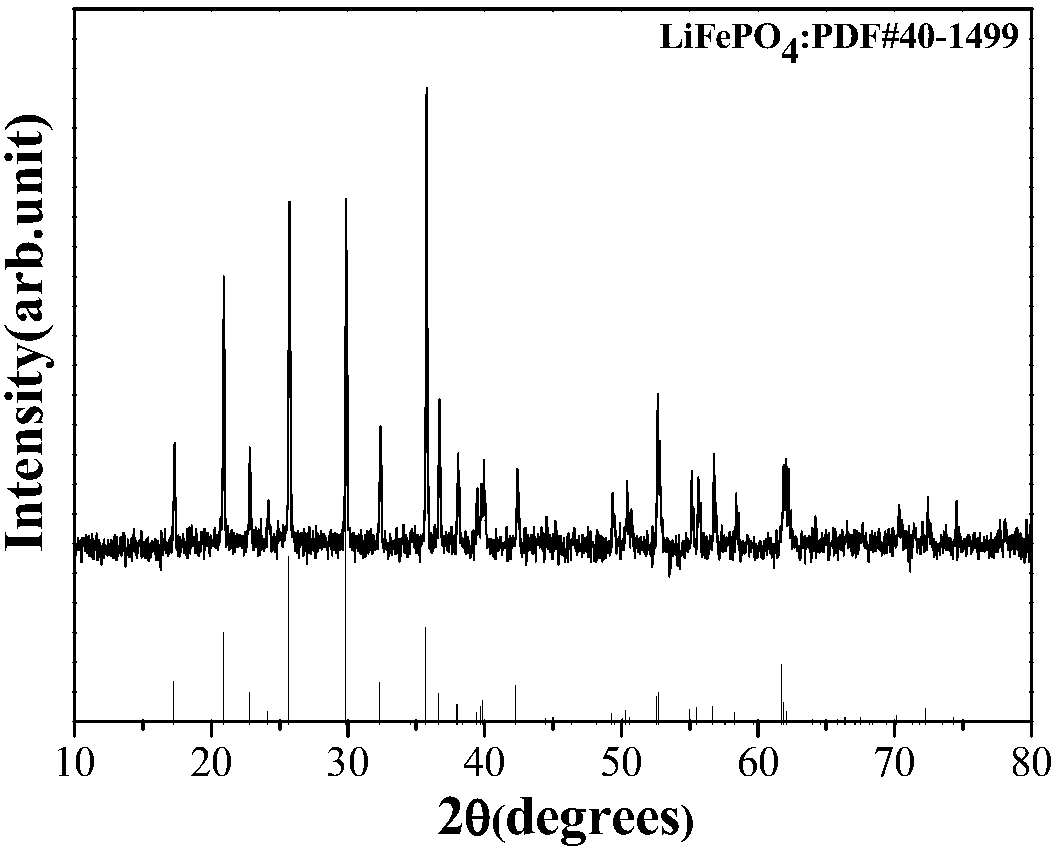
Recycling method of retired lithium iron phosphate battery positive-electrode materials
InactiveCN108417923ASimple processImprove escape rateWaste accumulators reclaimingBattery recyclingElectrolysisPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a recycling method of retired lithium iron phosphate battery positive-electrode materials. The method includes the steps: soaking and dissolving binding agents in an N-methylpyrrolidone solvent by the aid of the N-methylpyrrolidone solvent to strip LiFePO4 positive-electrode materials and aluminum foil fluid collectors; mixing the stripped waste LiFePO4 positive-electrode materials and binding agents; coating a carbon fabric or titanium mesh with mixture of the waste LiFePO4 positive-electrode materials and the binding agents to serve as a positive electrode; taking a graphite electrode as a negative electrode; building an electrolytic tank in electrolyte solution; driving lithium removal by the aid of a direct-current electric field to collectively recycle lithiumions and lithium removal product iron phosphate. According to the method, lithium removal is driven and adjusted by the direct-current electric field, lithium can be basically completely removed, subsequent treatment of the electrode materials after lithium removal is performed, so that treated electrode materials can be converted into the iron phosphate, and the iron phosphate can be used for preparing lithium iron phosphate positive-electrode materials and is good in electrochemical performance. The method is simple and convenient in operation process, controllable in condition, high in recycling rate and environmentally friendly, and popularization and application are facilitated.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Electrically enhanced internal anaerobic zero-valent iron reactor
InactiveCN101928066APromote generationRegulated DissolutionTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesDecompositionDissolution
The invention discloses an electrically enhanced internal anaerobic zero-valent iron reactor, belonging to the technical field of water treatment. Two graphite electrodes are arranged inside an anaerobic reactor and connected with an external direct current regulated power supply through a wire to simulate growth of microorganisms; meanwhile, the oxidation reduction process of the graphite electrodes also strengthens reductive decoloration of azo dyes. The graphite electrodes are arranged in the anaerobic internal biological zero-valent iron reactor, dissolution of iron is regulated by applying micro-voltage, and the buffer capacity of the reactor to acidification is strengthened. Coupling of an external power supply and zero-valent iron can also accelerate sludge granulation, efficiently enhance the decomposition capacity to organic compounds and realize rapid starting and high-efficiency running of the anaerobic reactor. A bench scale experiment shows that after the micro-voltage is applied, the rapid starting and the sludge granulation of the anaerobic reactor can be realized within 41 days, and the electrically enhanced internal anaerobic zero-valent iron reactor has stronger shock resistance.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Three-level acceleration type spiral wave plasma propulsion device
InactiveCN104653422AAcceleration and efficiencyImprove performanceMachines/enginesUsing plasmaThree levelGraphite electrode
The invention discloses a three-level acceleration type spiral plasma propulsion device. The three-level acceleration type spiral wave plasma propulsion device is characterized in that an antenna is connected with an RF (Radio Frequency) power source, the antenna and a discharge chamber are fixedly arranged in a sleeve, and an electromagnetic coil is fixedly arranged on the outer circumferential surface of the sleeve in a surrounding way; the rear part of the discharge chamber is provided with a rotating electric field ion acceleration system, and the rotating electric field ion acceleration system comprises four graphite electrodes which are uniformly and symmetrically arranged on the outer circumferential surface of the sleeve; the tail end of the rotating electric field ion acceleration system is provided with an electromagnetic spray pipe ion acceleration system, and the electromagnetic spray pipe ion acceleration system comprises a conical expanding spray pipe of which one end is connected with the tail part of the discharge chamber, and the electromagnetic coil. According to the three-level acceleration type spiral plasma propulsion device disclosed by the invention, the rotating electric field acceleration system is adopted for carrying out secondary acceleration on a plasma, acceleration is further carried out through the electromagnetic spray pipe, and a three-level acceleration effect is formed, thus the thrust is generated by efficiently accelerating ions, the work of a propulsor under high power can be realized, the reliable performance of high ion ejecting speed and high propulsion capacity can be realized, wide application prospect is obtained, and a high-performance power platform can be provided for future space technology development.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Protective atmosphere vacuum sintering furnace with high temperature of 1800 DEG C
InactiveCN101655310ASolve insulation problemsSolve the sealing problemMuffle furnacesRetort furnacesGraphite electrodeControl system
The invention discloses a protective atmosphere vacuum sintering furnace with high temperature of 1800 DEG C. A control system is connected with an electronically-controlled execution component arranged in an apparatus, a graphite sealing box is arranged in a heating chamber, an air inlet pipeline and an exhaust pipeline of a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace are connected with the graphite sealing box. The protective atmosphere vacuum sintering furnace is characterized in that the furnace has two techniques of atmosphere sintering and vacuum sintering, and a function conversion measurement is actualized by a control program; a furnace shell is provided with a thermoelectric couple and a copper electrode; the part of a shell column body is provided with a pipe joint communicated with an evacuation unit of a vacuum system; and a square heating chamber is arranged in the furnace shell, heaters are fixed on four walls in the heating chamber, and the heater is internally provided with a sealing box and a support material frame; and the air inlet pipeline and the exhaust pipeline communicated with the sealing box passes through an upper wall and a lower wall of the heating chamber and the sealing box through a graphite pipe to communicate with the inside of the sealing box, one end of the furnace shell is provided with a gas circulating cooling blower, an inner wall of the sealing box is provided with the thermoelectric couple and the copper electrode, and the copper electrode is connected with the heater through a graphite electrode. A volatile substance sealed in the sealing box can not disperse during vacuum sintering, thereby effectively preventing the volatile substance from polluting and damaging the heater, and simultaneously achieving the effect of enabling the protective gas to take the volatile substance away to protect furnace materials, and improving the utilization ratio of the protective gas.
Owner:SHENYANG HENGJIN VACUUM TECH
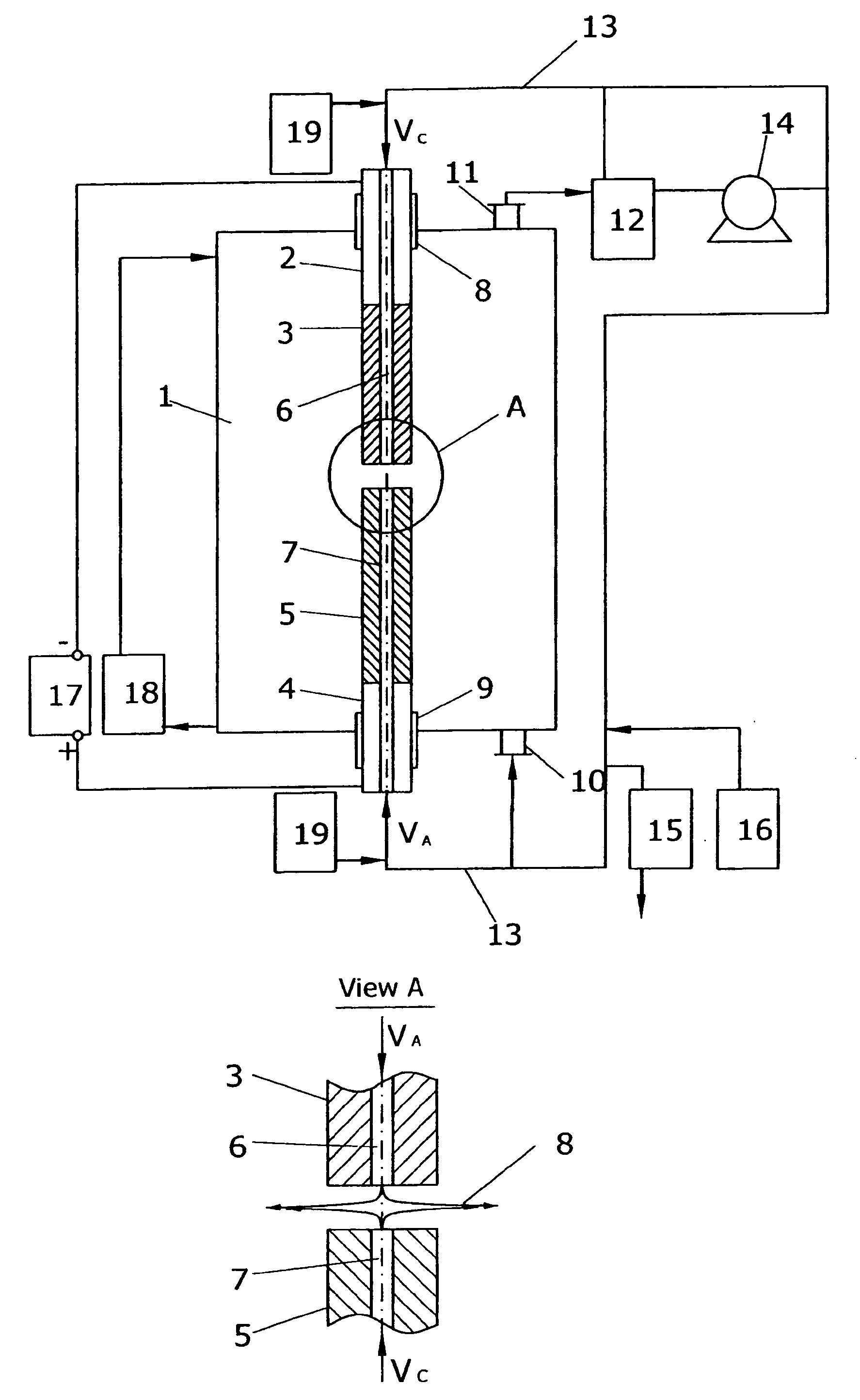
Continuous production of carbon nanotubes and fullerenes
A method and a device for production of fullerene-related carbon nanotubes and fullerenes in direct current arc discharge between two graphite electrodes are disclosed. Two features distinctive from conventional arc discharge technique providing remarkably high productivity of the present method are introduced. The first feature comprises means for maintaining an optimal temperature of anode end surface to suppress formation of large carbon clusters and micro-crystallite carbon particles useless for synthesis of carbon nanotubes and fullerenes. The second one comprises means for maintaining an optimal concentration of carbon and catalyst vapor in vapor generation zone to ensure optimal yields of carbon nanotubes and fullerenes. Airtight plug-in cartridges are used to supply consumable electrodes and catalyst material inside closed-loop device without process being stopped. The means to perform automatic continuous feeding of consumable electrodes and catalyst, pneumatic transportation of condensables and their automatic continuous discharge are also described.
Owner:KOULIKOV DMITRI
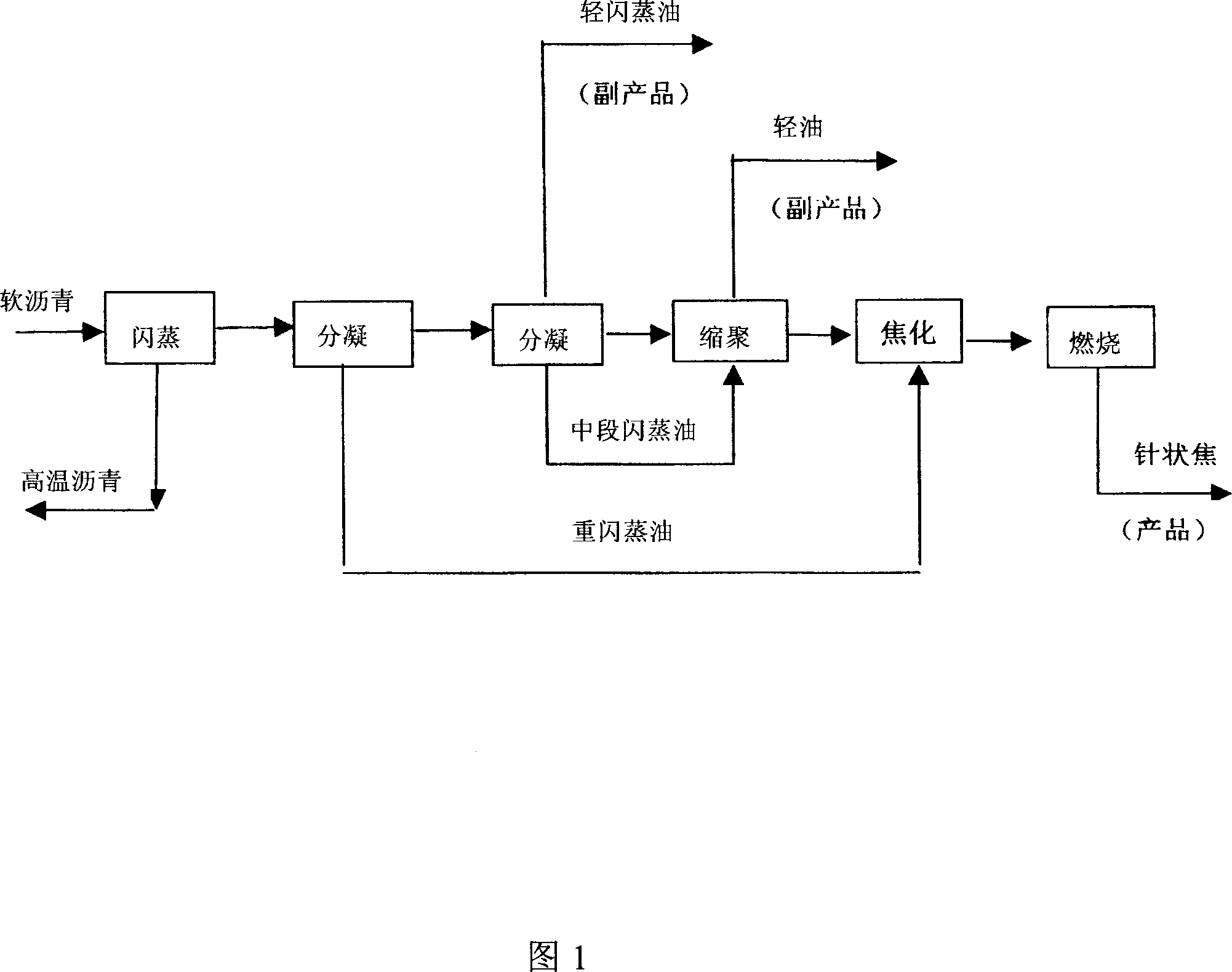
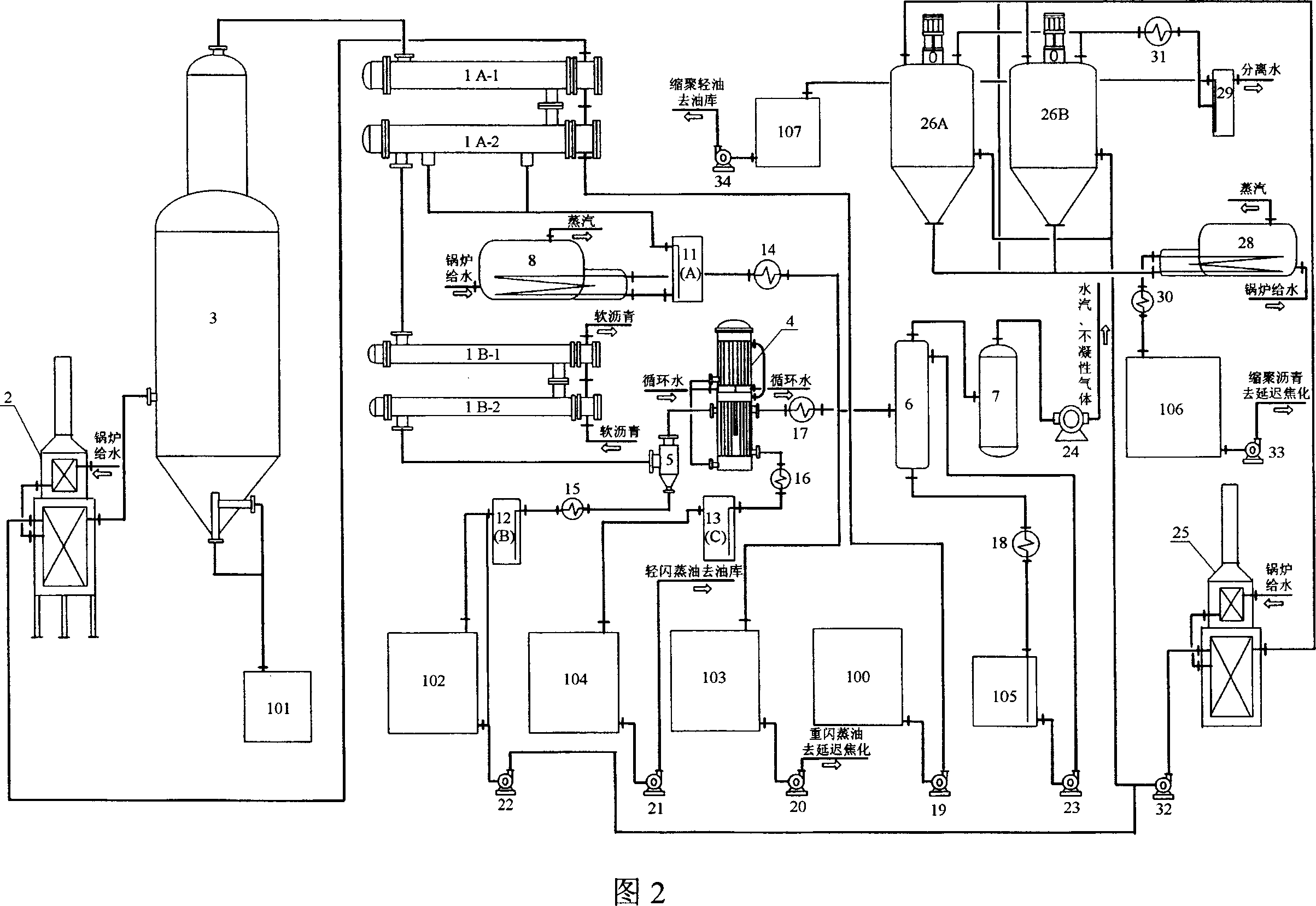
Industrial producing process for coal series needle coke
ActiveCN1944578AHigh molecular weightSmall molecular weightCoking carbonaceous materialsGraphite electrodeGraphite
The industrial producing process of coal series needle coke includes the following steps: stepped condensing the flash oil produced in vacuum flashing of coal tar pitch to obtain three, heavy, medium and light, fractions; polycondensating the medium fraction in an improved pitch circulating process to obtain condensed pitch; delay coking the condensed pitch and the heavy fraction and injecting N2 into the un-coked oil in the later coking stage to perform the final heating and coke drawing of the needle coke forming course; and final high temperature calcining to obtain coal series needle coke. Thus produced coal series needle coke has low thermal expansion coefficient and may be used in producing high power and super high power graphite electrode.
Owner:山西宏特煤化工有限公司
Remedying method for removing chrome in contaminated soil of chromium slag site in situ
The invention discloses a remedying method for removing chrome in contaminated soil of a chromium slag site in situ. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) smashing the air-dried chromium-contaminated soil of the chromium slag site, and sieving the smashed soil; (2) mixing the soil sieved in the step (1) and a citric acid solution to ensure that the moisture content of the soil reaches a set value, carrying out uniform stirring and then carrying out balancing for one day; (3) putting the soil balanced in the step (2) in a soil sample chamber of an electrokinetic remediation device, wherein the two ends of the soil sample chamber of the electrokinetic remediation device are respectively a cathode chamber and an anode chamber; and (4) adding an electrolyte to the cathode chamber and the anode chamber, respectively inserting graphite electrodes in the cathode chamber and the anode chamber, and connecting a power source to ensure that electric currents pass through the soil chamber to carry out electrokinetic remediation, wherein the electrolyte is a KCI solution. For the high-chromium-content alkaline contaminated soil of the chromium slag site, the remedying method is simple in technology, higher in removal efficiency of chrome in comparison with a common electrokinetic remediation method, low in unit energy consumption and lowered in cost, and can effectively reduce the bioavailability of residual chromium in the soil.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Phi 800mm general power graphite electrode and production method thereof
ActiveCN102158999AReduce consumptionImprove product quality levelElectric discharge heatingAdhesiveStearic acid
The invention provides a phi 800mm general power graphite electrode and a production method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing dry materials by using large delay petroleum coke particles, middle delay petroleum coke particles, delay petroleum coke powder materials and graphite powder; after pre-heating the dry materials, putting into a kneading boiler, adding ferric oxide powder and stearic acid which serve as additives in the kneading boiler, adding middle-temperature modified coal pitch serving as adhesives and wetly mixing to prepare paste materials; and putting the paste materials into a material cooling boiler and cooling, extruding, roasting and graphitizing to produce the phi 800mm general power graphite electrode. According to the method, the ideal extrusion molding manner of the graphite electrode is adopted, and novel technique formula, technology and mature production equipment are used to produce the general power graphite electrode capable of replacing the original carbon electrodes and vibration molding electrodes; moreover, the smelting input power is improved and the smelting energy consumption is reduced. Both the quality index and theuse performance of the produced products reach the national standards; the use consumption of the phi 800mm general power graphite electrode is reduced; and the economic benefit is improved.
Owner:FANGDA CARBON NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Photoelectrical chemical synergistic catalytic reaction waste water treatment method and device
InactiveCN1966421AImprove catalytic degradation efficiencyImprove degradation efficiencyWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsUltraviolet lightsCatalytic oxidation
The invention disclosed a kind of water treatment method through photoelectricity concerted catalytic oxidation as well as its device. The invention uses the TiO2 membrane electrode (Ti as the base) as the positive pole, graphite electrode as the negative pole and the calomel electrode as the reference electrode; it uses UV-lamp to irradiate the positive pole and the negative pole to form a photoelectricity catalyzing reactor; under the electric field and the ultraviolet ray, the positive pole degrade the organics in the positive tank with photoelectricity catalysis; at the same time, the negative pole generate H2O2 which degrades under ultraviolet light; so the pollutants both in the negative tank and the positive tank are degraded. The invention has reconstructed the UV / H2O2 system on the negative pole, on the basis of the degradation on the positive pole, the negative pole can degrade the organics through photoelectricity catalyst which increased the degrading efficiency of the organics which are hard to degrade.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Process for united repairing heavy metal polluted soil by electric power and iron permeable reaction lattices
InactiveCN1899717AChange physical and chemical propertiesAvoid secondary pollutionContaminated soil reclamationMetal contaminationElectric power
The in-situ efficient heavy metal polluted soil repairing technology without secondary pollution is to combine electric power and in-situ PRB technology. Graphite electrodes are mounted on two sides of the polluted soil and PRB is set inside the soil between these two electrodes, so that under the action of the electric field, metal anions, such as Cr ion can migrate to anode, metal cations, such as Cd2+ and Hg2+ can migrate to cathode and heavy metals can react with PRB to be adsorbed, reduced and precipitated. The said technology can eliminate polluting heavy metals from soil completely, avoid the secondary pollution to water and reduce the changes of soil in physical and chemical properties.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
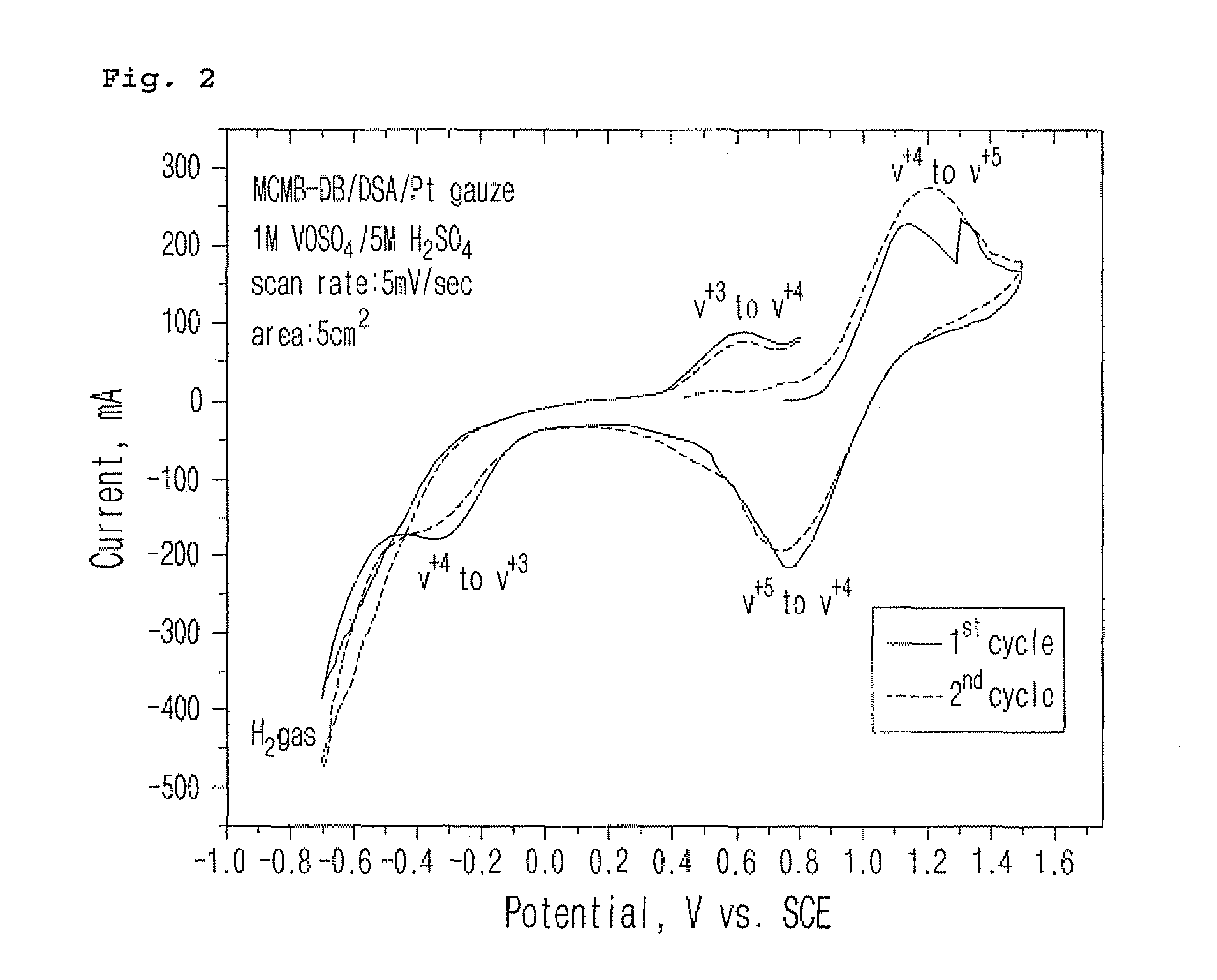
Graphite/DSA assembled electrode for redox flow battery, method of manufacturing the same and redox flow battery including the same
InactiveUS8518572B2High densityIncreased durabilityElectrode manufacturing processesElectrode carriers/collectorsGraphite electrodeRedox
Disclosed is a graphite / DSA assembled electrode for a redox flow battery, obtained by assembling a graphite electrode made of micro-sized graphite and a DSA electrode using rolling thus improving cell performance including electrode durability, corrosion resistance, power density, energy efficiency and cycle properties. A method of manufacturing the graphite / DSA assembled electrode is also provided, which includes preparing a mixture composed of a graphite active material, a conductive material and a binder into a slurry using an alcohol, evaporating the alcohol from the slurry thus preparing a paste, thinly spreading the paste into an electrode sheet, and rolling the electrode sheet along with a DSA electrode thus obtaining the assembled electrode. A redox flow battery including the electrode thus obtained is also provided, which has increased electrode durability and corrosion resistance and enhanced power properties, energy efficiency and cycle performance.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH +1
Boron contg. multi-element low alloyed wearable cast steel and prepn. thereof
InactiveCN1834279AHigh strengthImprove wear resistanceHeat treatment process controlRare earthPotassium
This invention discloses a multi-element low alloy abrasion-resisting cast steel, which is composed of C 0.20-0.45 wt.%, Mn 1.1-1.8 wt.%, Si 0.8-1.5 wt.%, Cr 0.3-1.2 wt.%, B 0.05-0.20 wt.%, Ti 0.08-0.30 wt.%, N 0.03-0.20 wt.%, Ca 0.05-0.15 wt.%, K 0.04-0.15 wt.%, and the rest is Fe and inavoidable impurities. The cast steel is manufactured by: (1) mixing scrapped steel, silicon iron, chromium iron and manganese iron, (2) carrying out carburization by using scrapped graphite electrode or pig iron, (3) melting to obtain liquid steel and adjusting the components until being qualified, (4) heating the liquid steel to 1620-1660 deg.C, (5) adding Si-Ca alloy, boron iron, titanium iron and nitrogen-containing chromium iron, and then pouring out of the furnace, (6) pulverizing Y-based rare earth magnesium alloy and potassium-containing substances to granules whose sizes are less than 15 mm, (7) drying at 130-180 deg.C, (8) placing at the bottom of the ladle, (9) carrying out modification treatment by pour-over process, and casting at 1480-1520 deg.C, (10) austenitizing at 830-1050 deg.C for 0.5-4 h, (11) rapidly cooling, (12) keeping the temperature at 150-300 deg.C, and (13) cooling in a furnace or in the air.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
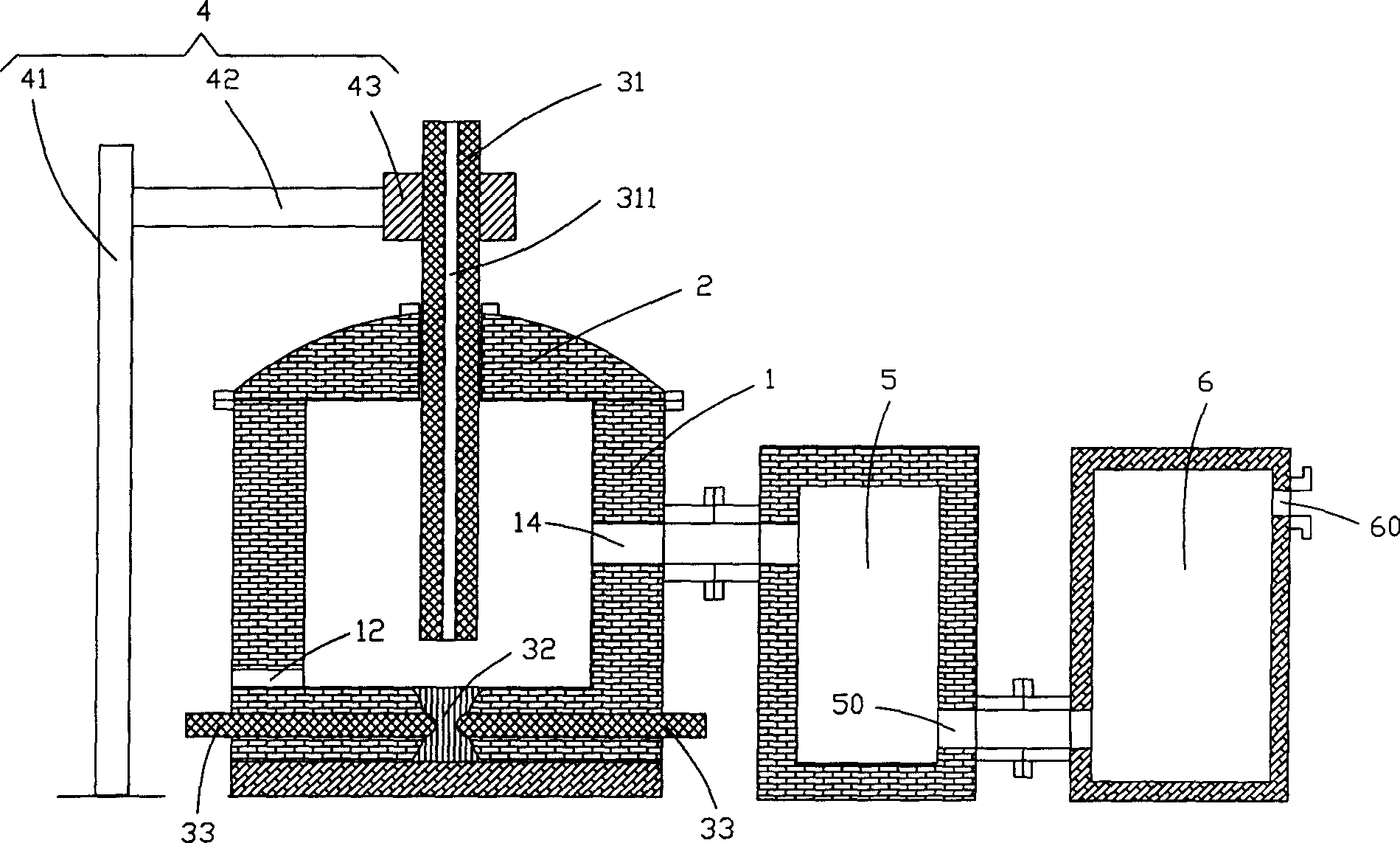
Ultrahigh-temperature thermal current simulation system used for spacecraft vacuum thermal test
InactiveCN104015942ASolve the technical problems of ultra-high temperature and extremely high heat flow simulationSolve temperature problemsCosmonautic condition simulationsThermal insulationHeater Rod
The invention discloses an ultrahigh-temperature thermal current simulation system used for a spacecraft vacuum thermal test in a vacuum container. The ultrahigh-temperature thermal current simulation system mainly comprises a semi-cylindrical graphite heating array, high-reflectivity high-temperature thermal insulation assembly units, a graphite heating array installing support, an ultrahigh temperature measuring unit and a power-regulator power control unit. A plurality of graphite heating rods are arranged and combined into the semi-cylindrical graphite heating array according to the requirements for the density and uniformity of thermal currents. Each graphite heating rod is composed of a graphite heating body and a graphite electrode, alternating-current electricity supply is adopted, and wiring electrode leads penetrate through a high-current cabin-penetrating electricity supply flange arranged on a container wall of the vacuum low-temperature environment simulation container and are electrically connected with the temperature measuring unit and the power-regulator power control unit respectively. Through the unique design of the graphite heating array, the high-reflectivity high-temperature thermal insulation assembly units and the ultrahigh temperature measuring unit, measurement of and control over temperatures over 1800 DEG C in the space environment simulation container are achieved, and the ultrahigh-temperature thermal current simulation system is also suitable for high-temperature and high-thermal-current environment simulation requirements in vacuum thermal tests of all types of spacecraft.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT ENVIRONMENT ENG
Plasma reaction furnace for processing waste
InactiveCN1825042AIncrease profitImprove processing efficiencyIncinerator apparatusBell type furnacesGraphite electrodeRefractory
The invention comprises a furnace body and a furnace lid. There is a refractory furnace liner and a thermal-protective insulating layer inside of the furnace body. A molten mass portal is disposed on the side of the hearth bottom. An air outlet is disposed on the furnace wall. A hollow graphite electrode disposed in the center of the furnace lid extends into the furnace. In the hollow graphite electrode there is a passageway. A second electrode against the hollow graphite electrode and a graphite lead-out electrode connected with the second electrode are disposed at the bottom of the furnace body. An arc zone is formed between the hollow graphite electrode and the second electrode to generate hot plasma.
Owner:黄建军
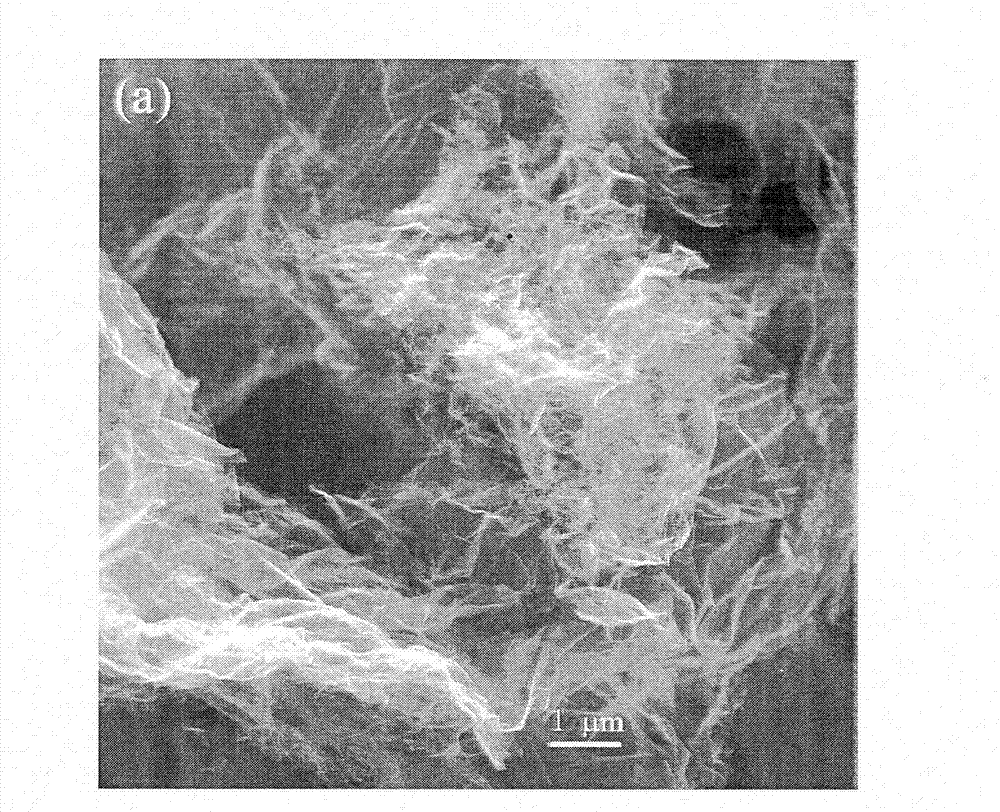
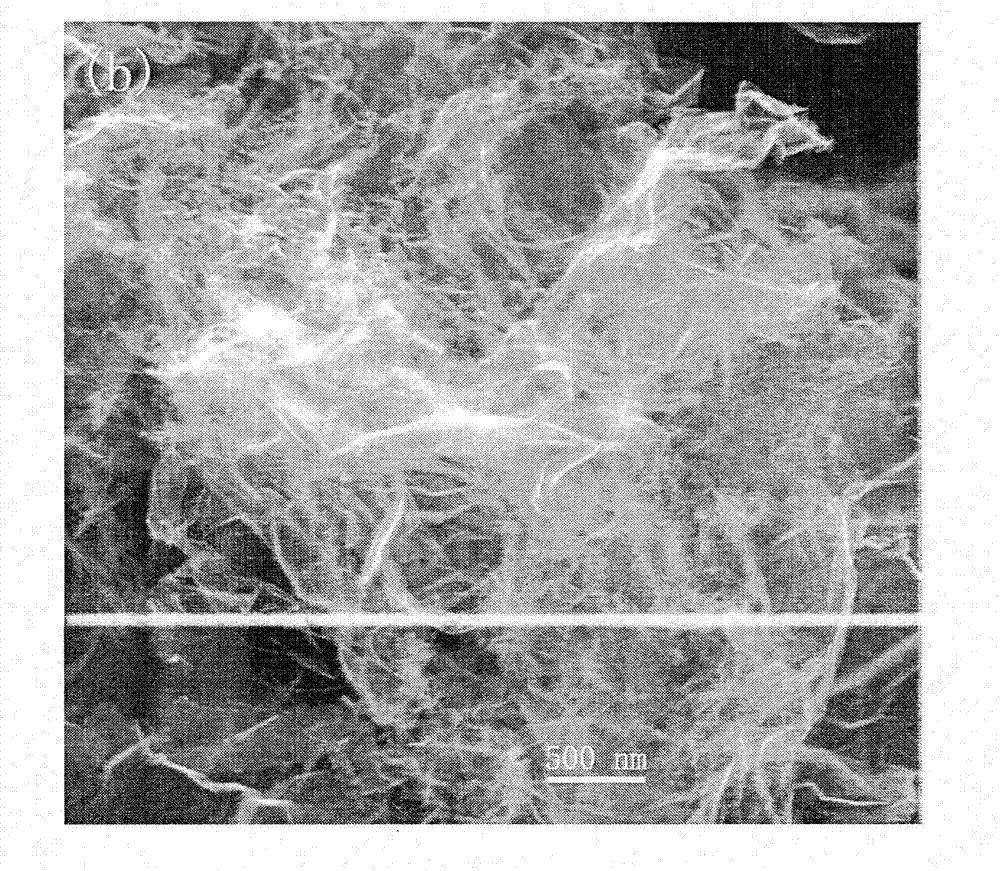
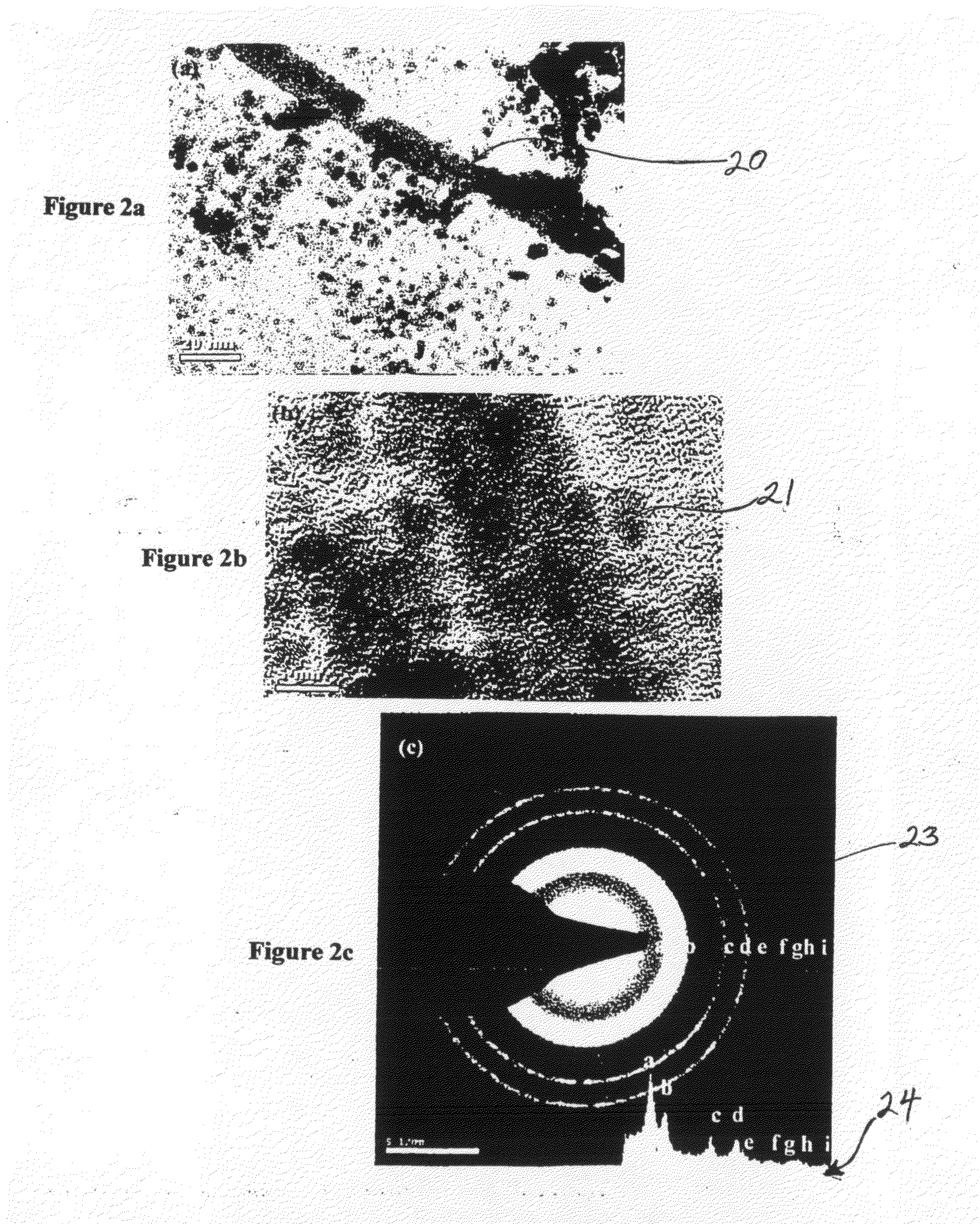
Ultrathin graphene piece, apparatus for preparing ultrathin graphene piece, method for preparing ultrathin graphene piece, capacitor, and method of manufacturing capacitor
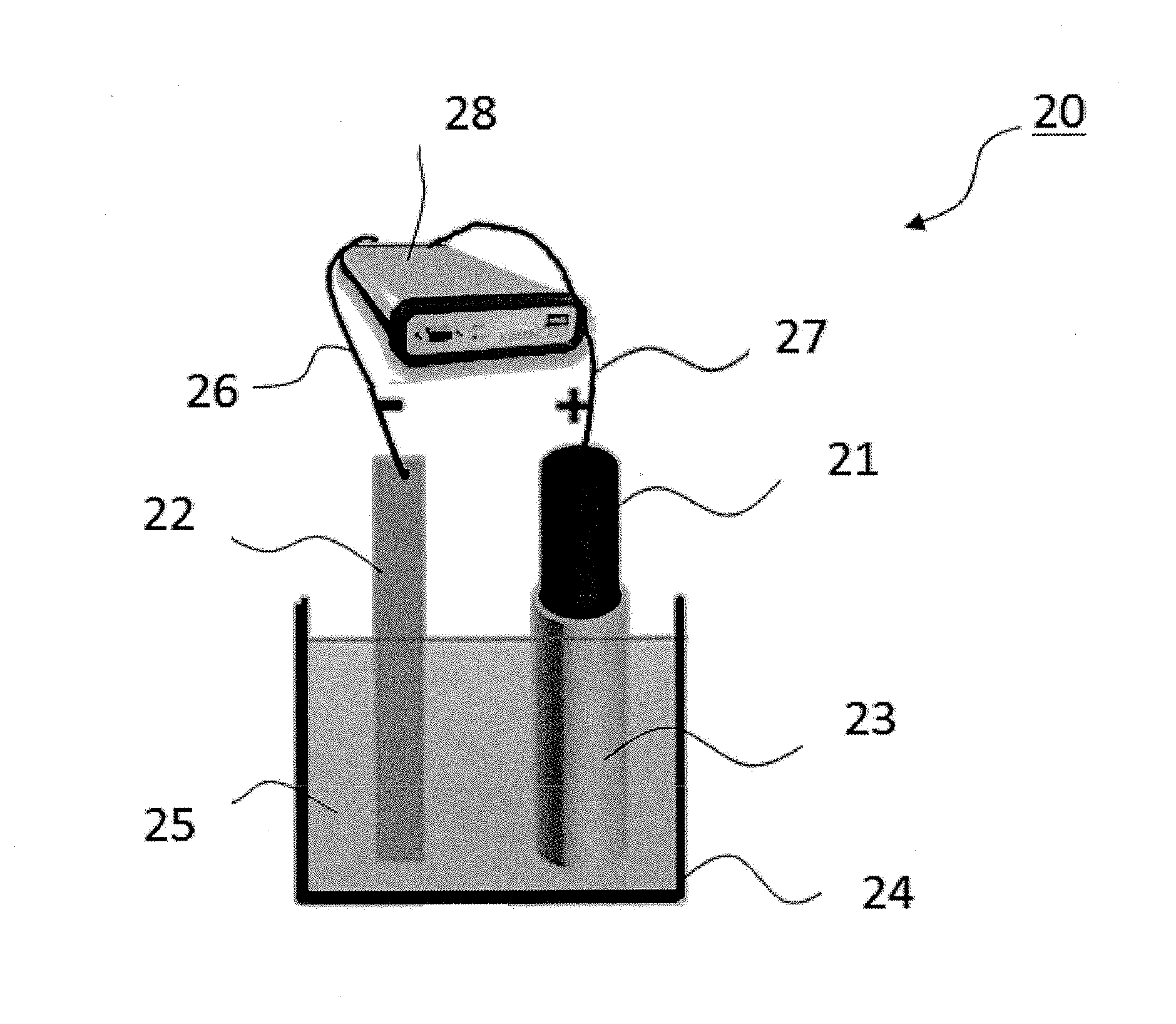
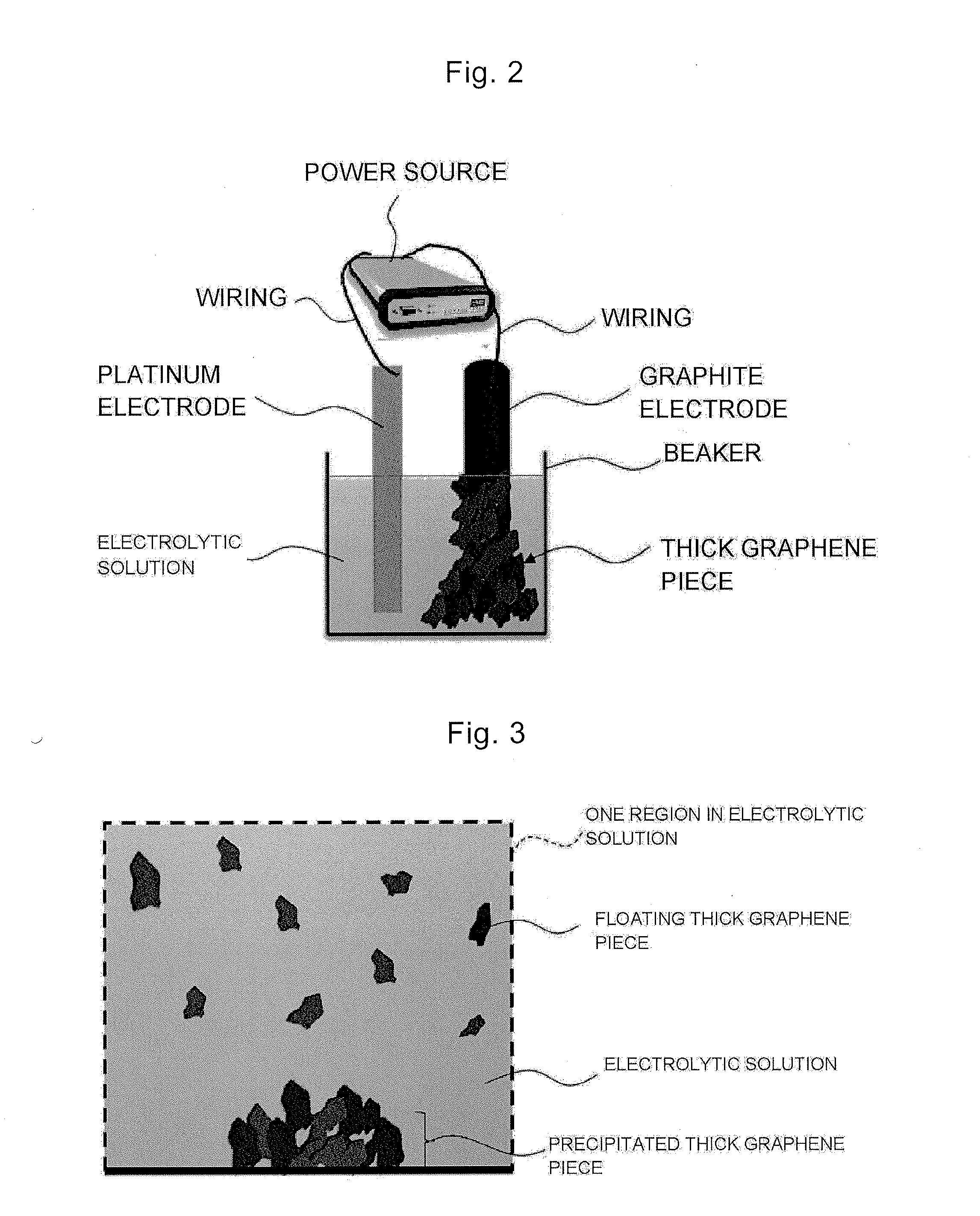
InactiveUS20150291431A1Raise the ratioQuality improvementMaterial nanotechnologyPhotography auxillary processesCorrosion resistant alloyGraphite electrode
The problem addressed by the present invention is to provide an apparatus for preparing ultrathin graphene pieces capable of preparing ultrathin graphene pieces in which less than 10 pieces of graphene are overlapped in large quantities, a method for preparing ultrathin graphene pieces capable of preparing the ultrathin graphene pieces with high yield, an ultrathin graphene piece in which less than 10 pieces of graphene are overlapped, a capacitor having high performance by using the ultrathin graphene piece as an electrode, and an efficient method of manufacturing the capacitor. The above-described problem can be solved by using an apparatus 20 for preparing ultrathin graphene pieces, the apparatus comprising: a graphite electrode 21; a counter electrode 22 which is made of graphite, a corrosion resistant alloy, or a precious metal; an electrolytic solution 25 in which one end sides of the two electrodes 21 and 22 are immersed; a container 24 which stores the electrolytic solution 25; and a power source 28 which is connected to the two electrodes 21 and 22 via wirings 26 and 27. The apparatus is also provided with a porous filter 23 so as to cover at least the immersed part of the graphite electrode 21 that is immersed in the electrolytic solution 25.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
Process for producing moderate temperature modified bitumen by continuously pressurizing and hot-polymerizing at two stages connected in series
ActiveCN101289624AIncrease flexibilityLow equipment requirementsWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by chemical meansQuinolineEngineering
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing high-quality intermediate temperature modified pitch through two-section serial continuous pressurizing hot polymerization. The method comprises the following steps that: mid-temperature pitch is made into modified pitch by a two-section serial reaction kettle through low-pressure heating polycondensation; heating precracking reaction is carried out during a first section, while heating polycondensation reaction is carried out quickly during a second section so as to increase the content of toluene insoluble and reduce the content of quinoline insoluble, thereby increasing a beta value; the reacted material is fed in a flash tower, and the softening point of the modified pitch is adjusted inside the flash tower; and the tail gas of a flash system is fed in a flue gas absorption system to be absorbed by circular wash oil, and then is discharged through a chimney. The method can manufacture intermediate temperature modified pitch which meets special requirements and has a lower softening point (80 to 90 DEG C), a controllable softening point amplitude of between 1 DEG C below zero and 1 DEG C and higher beta resin content (more than 18 percent), thereby providing a high-quality raw material for making an ultra-high power graphite electrode.
Owner:山西宏特煤化工有限公司
Process for the production of needle coke
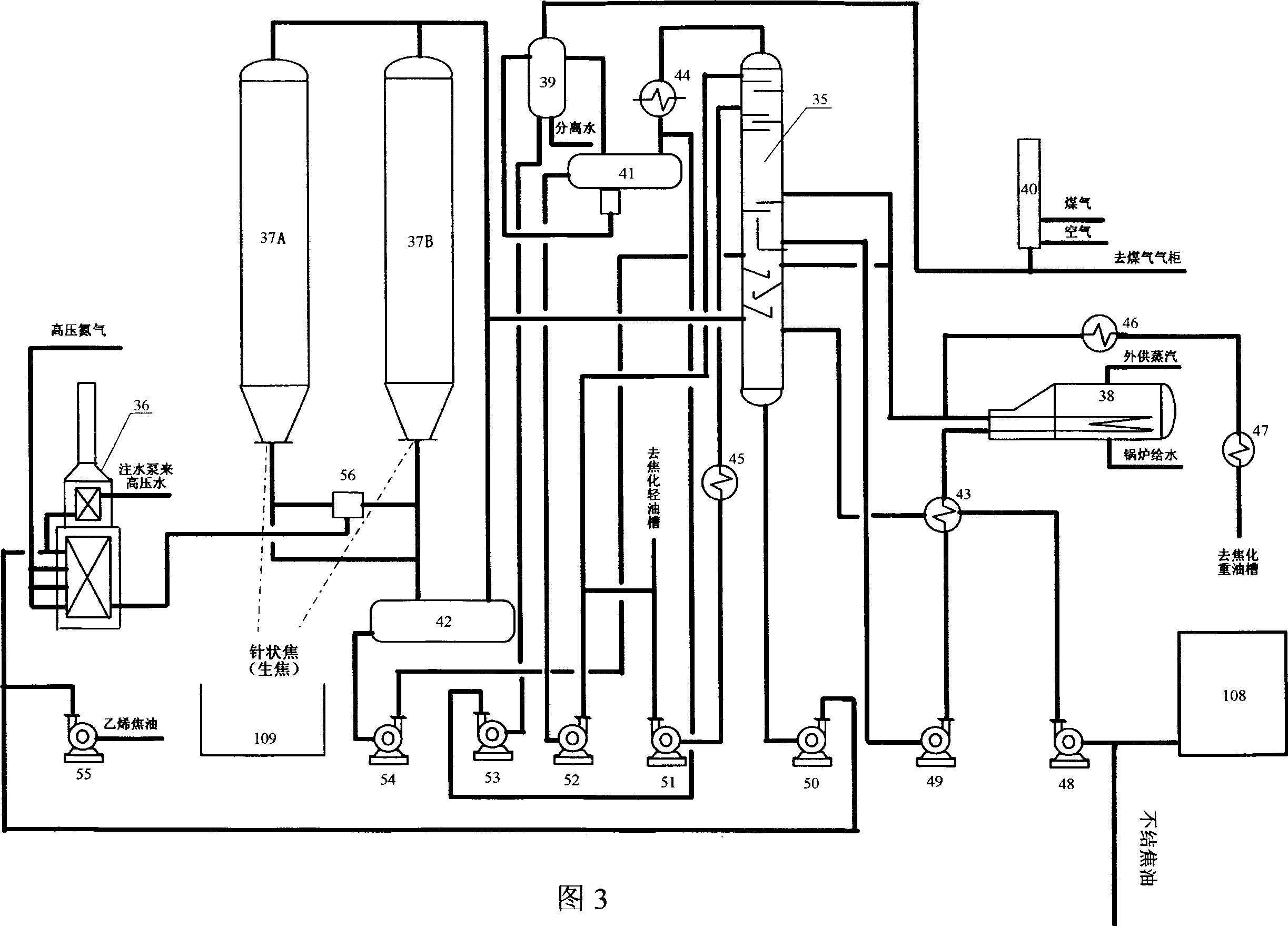
ActiveUS20050284793A1Yield minimizationPromote formationThermal non-catalytic crackingTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyGraphite electrodeBoiling point
A process is disclosed for producing needle coke from heavy atmospheric distillation residues having sulfur no more than 0.7 wt %, which process involves the steps of heating the feedstock to a temperature in the range of 460 to 540° C. for thermal cracking in a soaking column under pressure in the range of 1 to 10 kg / cm2 to separate the easily cokable material, separating the cracked products in a quench column and a distillation column and then subjecting the hydrocarbon fraction from the bottom of the quench column and a heavy gas oil fraction having 10% true boiling point more than 370° C. and 90% true boiling point not less than 480° C. from the distillation column and / or any other suitable heavier hydrocarbon streams in a definite ratio depending on certain characteristic parameters to thermal cracking in a second soaking column at a temperature of 440 to 520° C., pressure in the range of 2 to 20 kg / cm2 in presence of added quantity of steam for formation of a mesophase carbonaceous structure which on steam stripping and cooling forms a solid crystalline coke suitable for manufacturing of graphite electrode of large diameter having co-efficient of thermal expansion lower than 1.1×10−6 / ° C. measured on graphite artifact in the temperature range of 25 to 525° C.
Owner:INDIAN OIL CORPORATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com