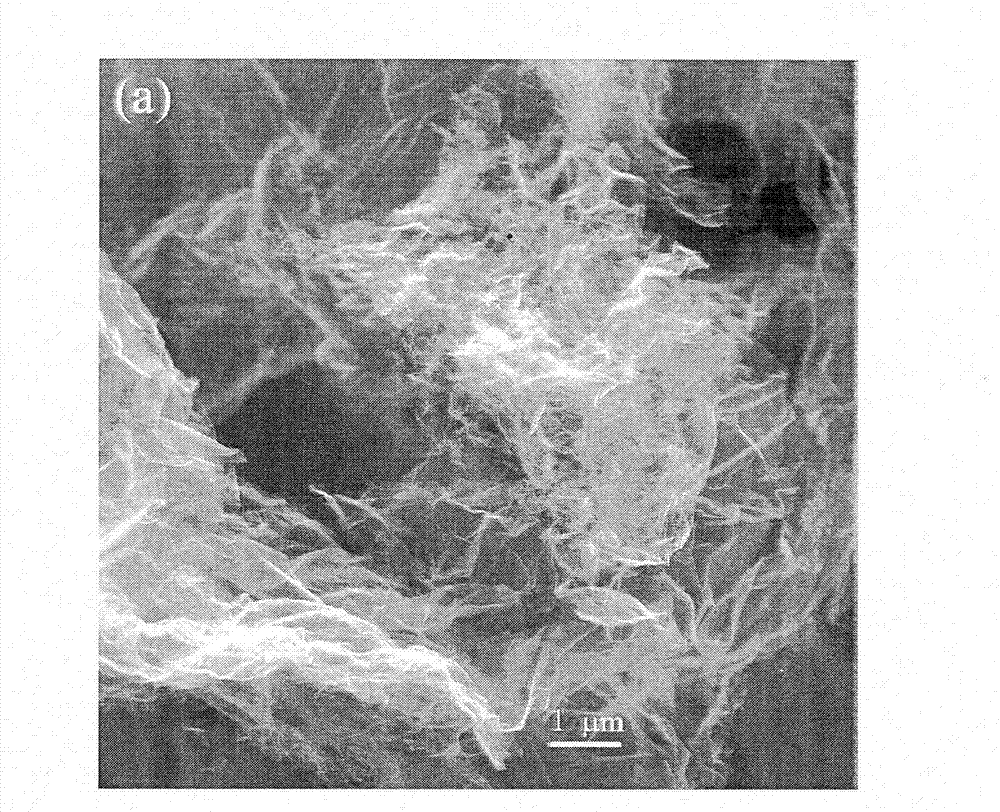
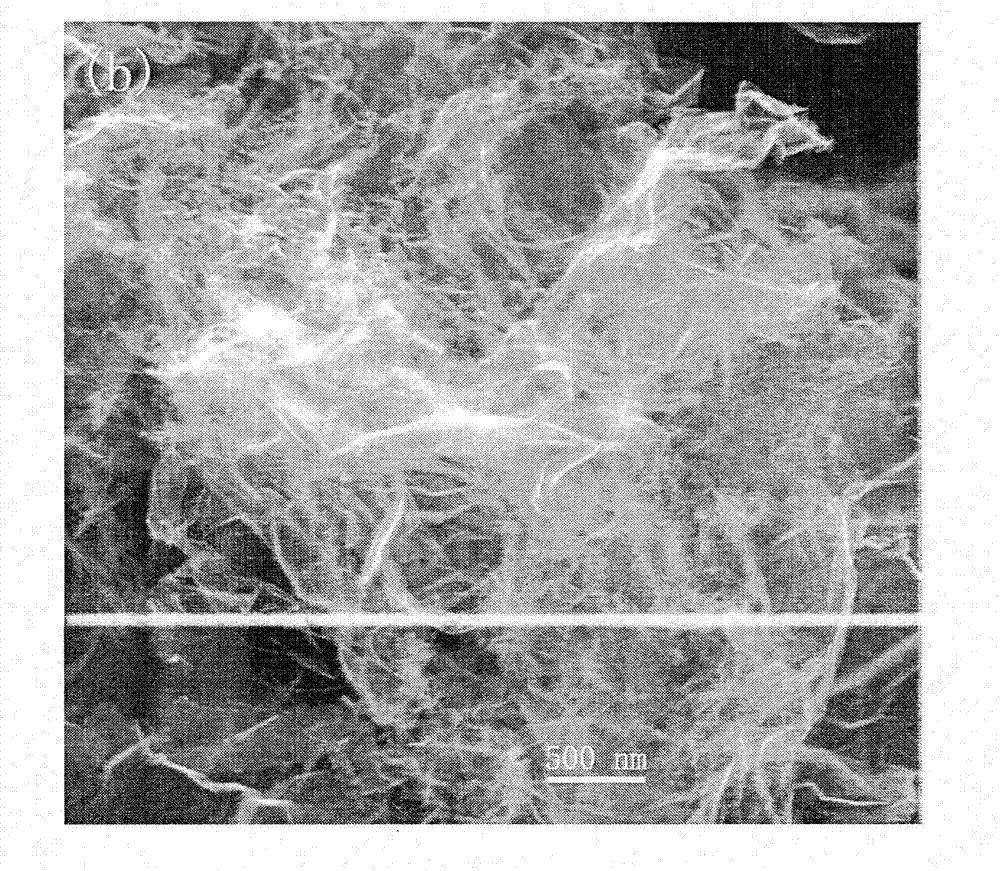
Method for electrochemically preparing graphene
An electrochemical and graphene technology, applied in the field of materials, can solve problems such as high cost, influence of electronic properties, thickness of graphene sheets, etc., and achieve the effect of low cost, environmental friendliness and less defects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
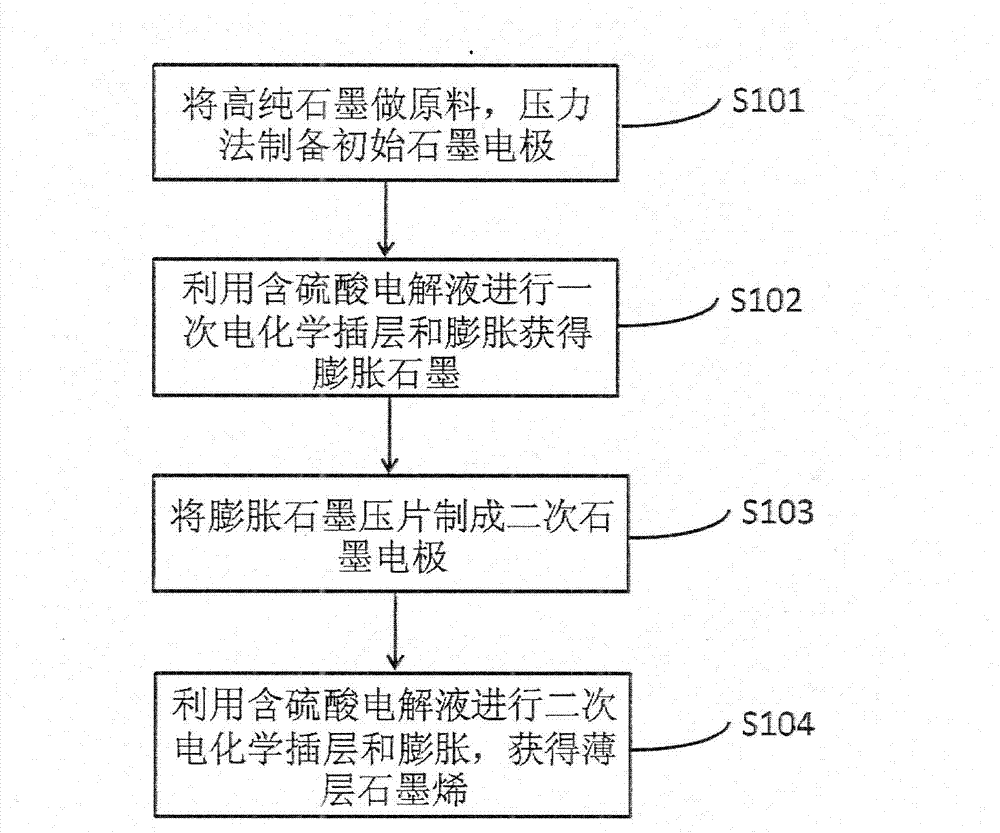
[0042] Embodiment 1 A kind of preparation method of high-purity thin-layer graphene, its technological process is as follows:
[0043] Step S101: Press 250 mg of high-purity graphite to form a film under a pressure of 10 MPa, and use Ag glue to connect the pressed graphite disc to a copper wire to form a graphite electrode as an anode.
[0044] Step S102: 10 mL of 5 M sulfuric acid aqueous solution was used as the electrolyte, and a platinum sheet was used as the cathode, and the anodic oxidation of the graphite electrode was carried out under the condition of a constant voltage of 5 V, and the reaction time was 1 hour. The reaction product was drained and washed with water, and then dried in air for 3 hours. The dried product was subjected to microwave expansion at a power of 800 W for 30 seconds to obtain worm-like expanded graphite.
[0045] Step S103: Press 100 mg of worm-like expanded graphite to form a film under a pressure of 10 MPa, and connect it to a copper wire wit...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Embodiment 2 A kind of preparation method of high-purity thin-layer graphene, its technological process is as follows:
[0048] Step S101: Press 200 mg of high-purity graphite to form a film under a pressure of 20 MPa, and use Ag glue to connect the pressed graphite disc to a copper wire to form a graphite electrode as an anode.
[0049] Step S102: Use 10 mL of 10 M sulfuric acid aqueous solution as the electrolyte, and a platinum sheet as the cathode, with a constant current of 30 mA / cm 2 The anodic oxidation of the graphite electrode was carried out under the following conditions, and the reaction time was 1 hour. The reaction product was drained and washed with water, and then dried in air for 3 hours. The dried product was subjected to microwave expansion at a power of 800 W for 30 seconds to obtain worm-like expanded graphite.
[0050] Step S103: Press 100 mg of worm-like expanded graphite to form a film under a pressure of 10 MPa, and connect it to a copper wir...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Embodiment 3 A kind of preparation method of high-purity thin-layer graphene, its technological process is as follows:
[0053] Step S101: Press 300 mg of high-purity graphite to form a film under a pressure of 20 MPa, and use Ag glue to connect the pressed graphite disc to a copper wire to form a graphite electrode as an anode.
[0054] Step S102: Use 10 mL of sulfuric acid-acetic acid mixture (volume ratio: 5:5) as the electrolyte, and a platinum sheet as the cathode, and perform anodic oxidation of the graphite electrode under the condition of a constant voltage of 2.5 V, and the reaction time is 1 hour. After the reaction product was pumped dry, it was expanded in argon at high temperature, the gas flow rate was 200 sccm, and the temperature was 800 o C, the expansion time is 5 minutes, and the worm-like expanded graphite is obtained.
[0055] Step S103: Press 200 mg of worm-like expanded graphite to form a film under a pressure of 10 MPa, and connect it to a coppe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com