Patents
Literature
34 results about "Open hearth furnace" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Open hearth furnaces are one of a number of kinds of furnace where excess carbon and other impurities are burnt out of pig iron to produce steel. Since steel is difficult to manufacture due to its high melting point, normal fuels and furnaces were insufficient and the open hearth furnace was developed to overcome this difficulty. Compared to Bessemer steel, which it displaced, its main advantages were that it did not expose the steel to excessive nitrogen (which would cause the steel to become brittle), was easier to control, and it permitted the melting and refining of large amounts of scrap iron and steel.
Multi-purpose, multi-oxy-fuel, power burner/injector/oxygen lance device
InactiveUS20030075843A1Reduce the numberSmall sizeTuyeresCharge manipulationSteelmakingLiquid medium
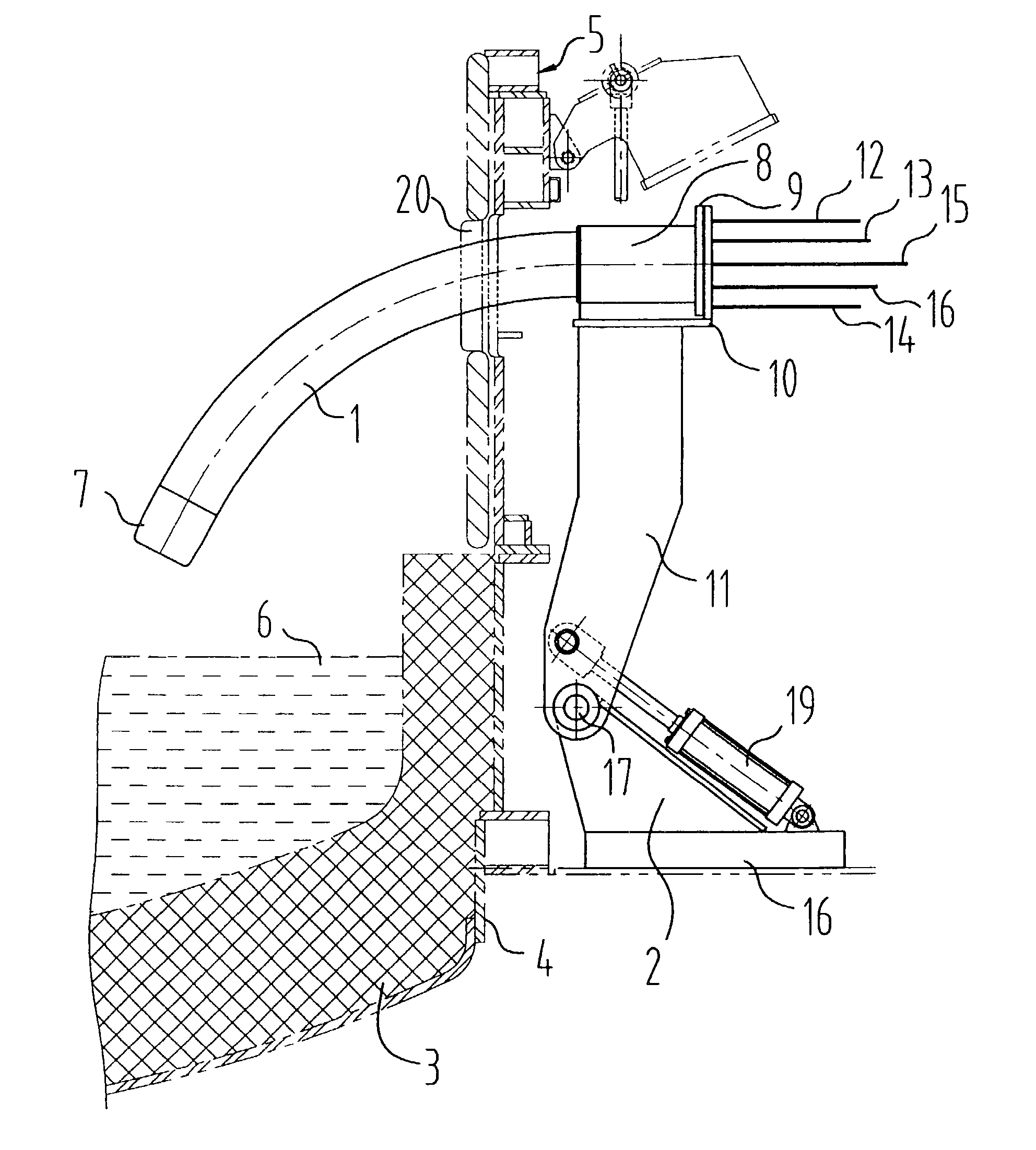
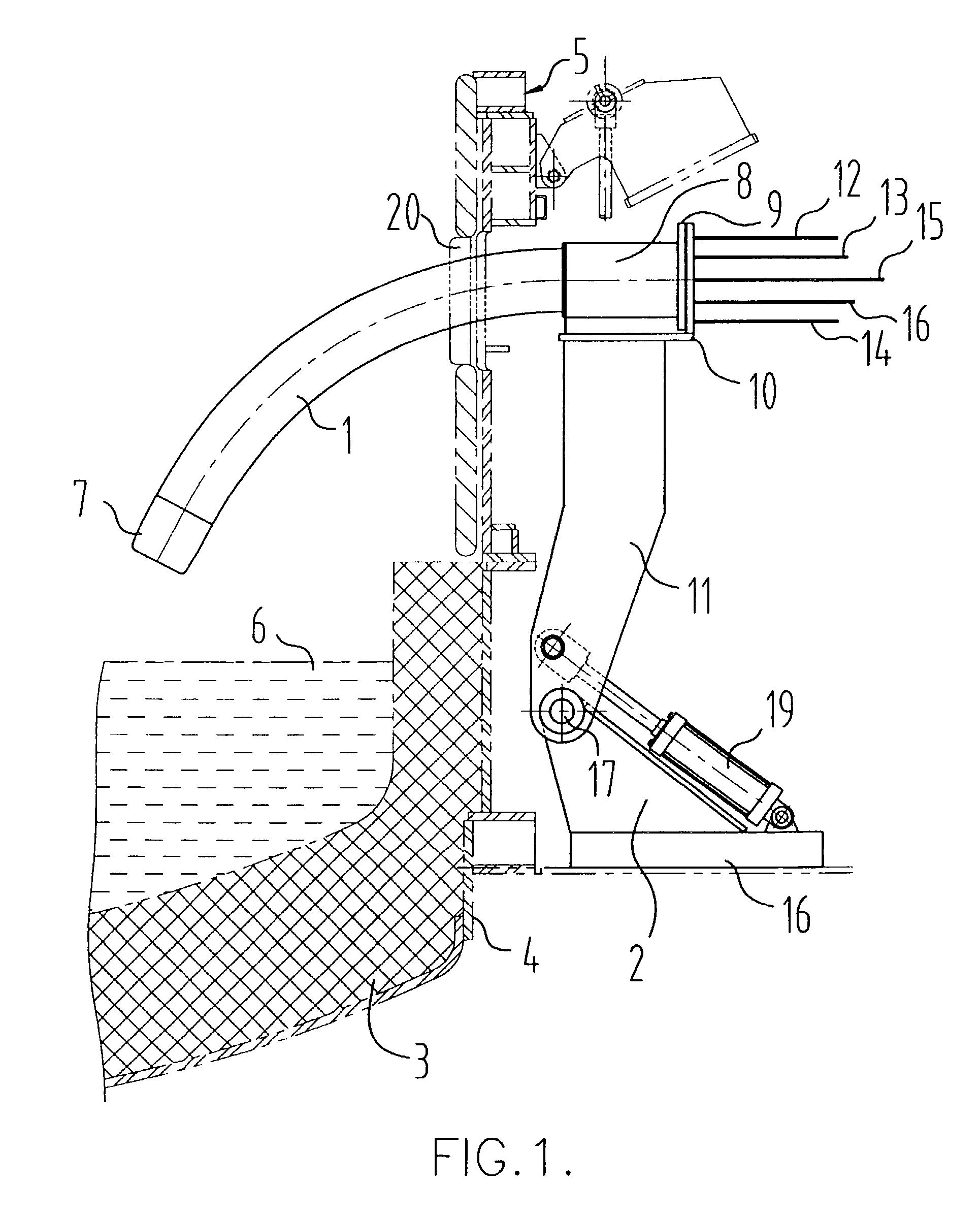
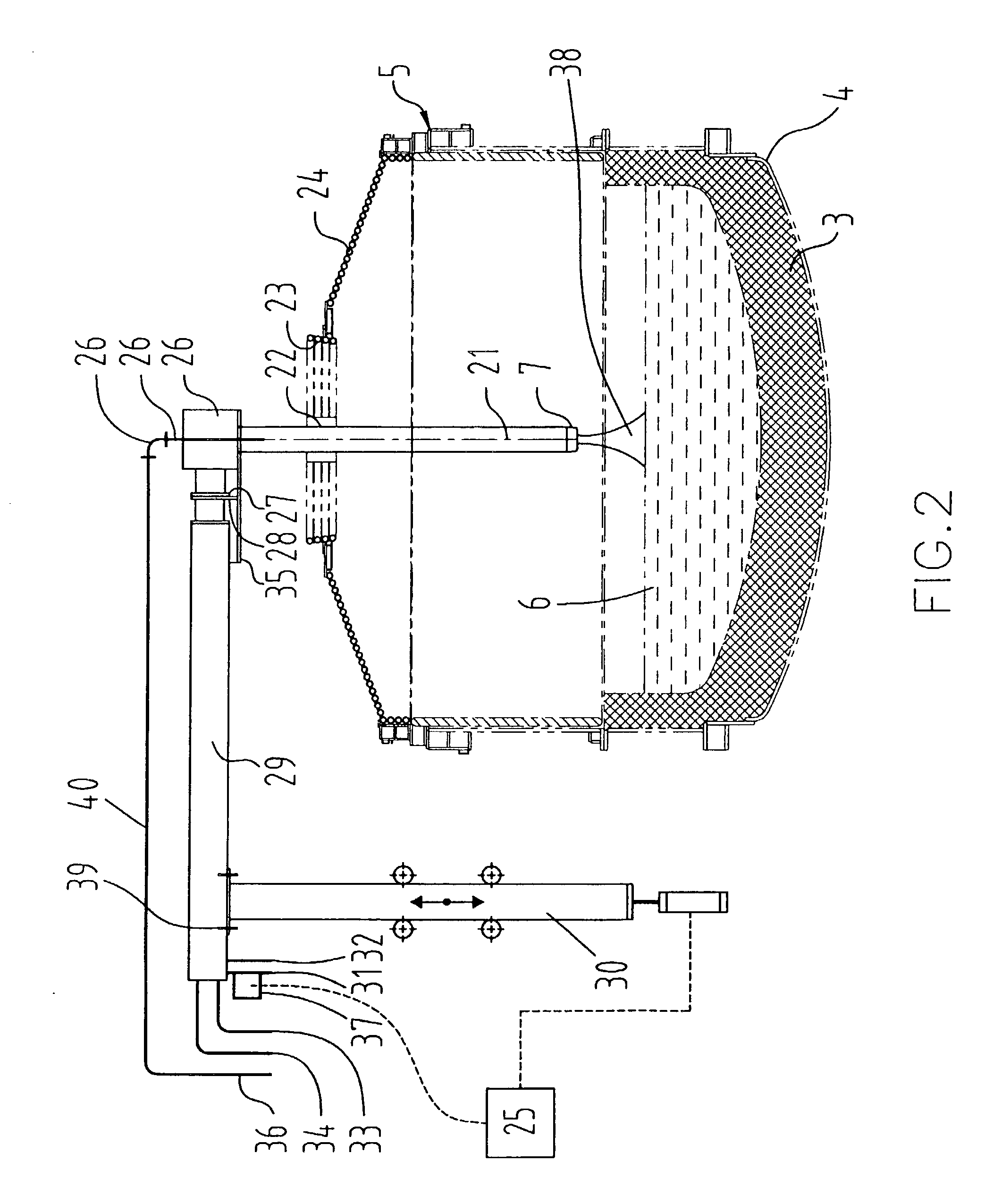
A multi-purpose, multi-oxy-fuel High Temperature Power Burner / Injector / Oxygen Lance, Mechanical System Apparatus Device, for steelmaking from recycled scrap and / or virgin ferrous charge, which can be employed in multi-oxy-fuel (natural gas; pulverized carbonaceous matter; heavy oil), especially by Oxygen Combusted mixture of Natural Gas / Pulverized Carbonaceous Matter in High Temperature Power Burner Mode, for efficient and rapid melting of solid ferrous charge (cold or preheated) in a special steelmaking Metallurgical Furnace or Open Hearth Furnace, Tandem Furnace, BOF, EAF, as its augmenting or only source of thermal energy; more than one Device in Oxygen-Natural Gas / Pulverized Carbonaceous Matter Power Burner Mode, can be employed as the only source of thermal energy in a modified, originally Electric Arc Furnace, as total replacement of Graphite Electrodes and Electric Arc System, the replacement being noticeably more primary energy efficient than the thermal energy provided by Graphite Electrode / Arc System; it also can be employed in an Solid Particles Injector Mode, for injecting of adequately granulated carbonaceous materials or lime into the molten steel for its carburizing or for foamy slag control; further it can be employed in a natural gas shrouded, pulsating oxygen stream, for vertically to the charge oriented soft blow supersonic Oxygen Injection Lance Mode, for decarburization of the molten metal contained in the hearth of the metallurgical furnace and foamy slag control; in one of the embodiments-generally arcuate-pivotally mounted, liquid media cooled composite body, is pivoted into and out of a furnace vessel through a small opening in the shell wall for auto-regulated constant optimal positioning of the Composite Body Tip against solid or molten charge, in each and all multi-purpose modes; furthermore, when inserted into the furnace vessel, the arcuate composite body can be rotated about its longitudinal axis for directing the oxy-fuel high temperature flame towards unmolten charge in the furnace; in an other-generally linear-embodiment, the liquid cooled composite body is attached to the mast type carrier allowing vertical movement of the composite body which enters the furnace vessel through a small opening in the furnace roof; the bimetallic, liquid cooled special tip assembly of both-arcuate and linear embodiments-of the composite body includes easy replaceable, independent, multi-opening nozzles, mounted in a protective, retracted position inside of the liquid cooled special tip assembly.
Owner:EMPCO (CANADA) LTD
Molten steel component monitoring and analytical equipment
InactiveCN101183074AReduce volumeEasy to install on siteAnalysis by material excitationSteelmakingSteel jacket
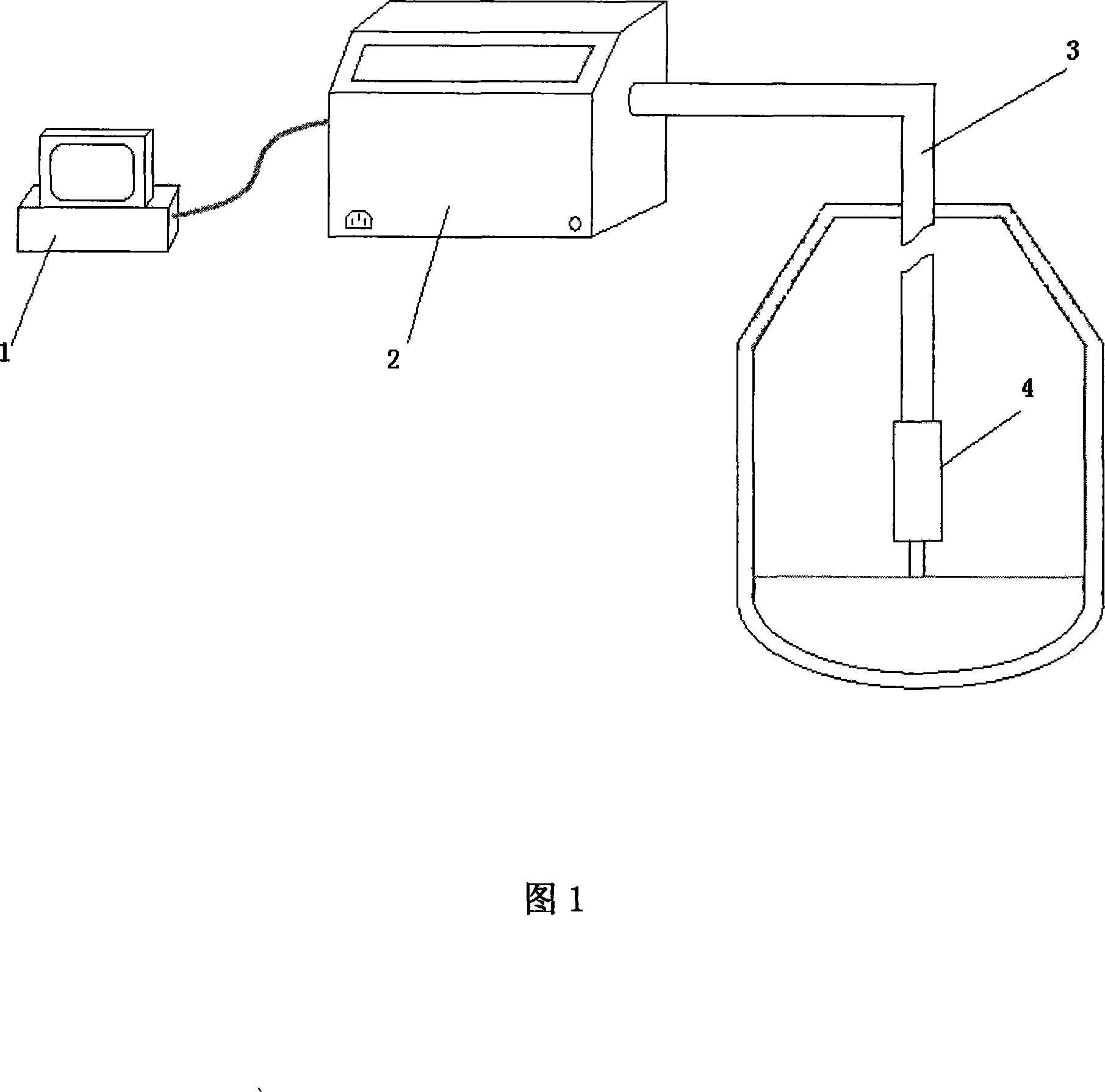
The liquid steel component monitoring and analyzing device belongs to the liquid steel analyzing device, and aims at monitoring the steelmaking process on-line, and directly and accurately judges the end point. The invention includes a detection probe, a telescopic tube, a signal generation and acquisition part and a processor. The detection probe structure is: a focusing lens is mounted in the air inside the metal cylinder, and two electrodes are mounted on the front end of the metal cylinder; the telescopic tube adopts a jointed steel pipe jacket, The inner hollow pipe passes through the conductive optical fiber, gas pipe and wire; the signal generation and collection part includes the laser controller, laser generator, optical path coupling components, spectrometer, charge coupled device CCD, blower, detection probe positioning control circuit; the processor receives the charge coupling The electrical signal transmitted by the CCD of the device is A / D converted and processed to analyze the spectral data; the start and stop of the laser generator and the parameter setting of the charge-coupled device CCD are controlled. The invention has the advantages of small volume, convenient on-site installation and fast analysis speed, and is suitable for technological processes such as converters, open hearth furnaces and refining outside furnaces.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Iron-making method for producing granular iron by smelting reduction of high-phosphorus oolitic low-grade hematite in rotary hearth furnace
The invention discloses an iron-making method for producing granular iron by smelting reduction of high-phosphorus oolitic low-grade hematite in a rotary hearth furnace. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) material preparation: preparing the following raw materials in parts by weight: 7 to 8 parts of high-phosphorus oolitic low-grade hematite, 1 to 3 parts of coal and 0 to 3 parts of fluxing agents; (2) smelting reduction in the rotary hearth furnace: uniformly mixing the above three raw materials, granulating, drying, delivering raw pellets to the rotary hearth furnace, heating to 1250 to 1450 DEG C, maintaining for 25 to 40 minutes, allowing the smelting reduction in the rotary hearth furnace, and discharging high-temperature granular iron intermediates and slag from the rotary hearth furnace; (3) indirect water cooling: delivering the high-temperature granular iron intermediates (600 to 1100 DEG C) and the slag to an indirect water cooling barrel which is introduced with nitrogen gas and performing cooling; and (4) dry magnetic separation: performing dry magnetic separation on the cooled granular iron intermediates and slag to obtain the final product of granular iron. The method provided by the invention has a simple process, a short flow and high efficiency, does not need charred coal, and is suitable for processing high-phosphorus oolitic low-grade hematite.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE METALLURGICAL DESIGN INST
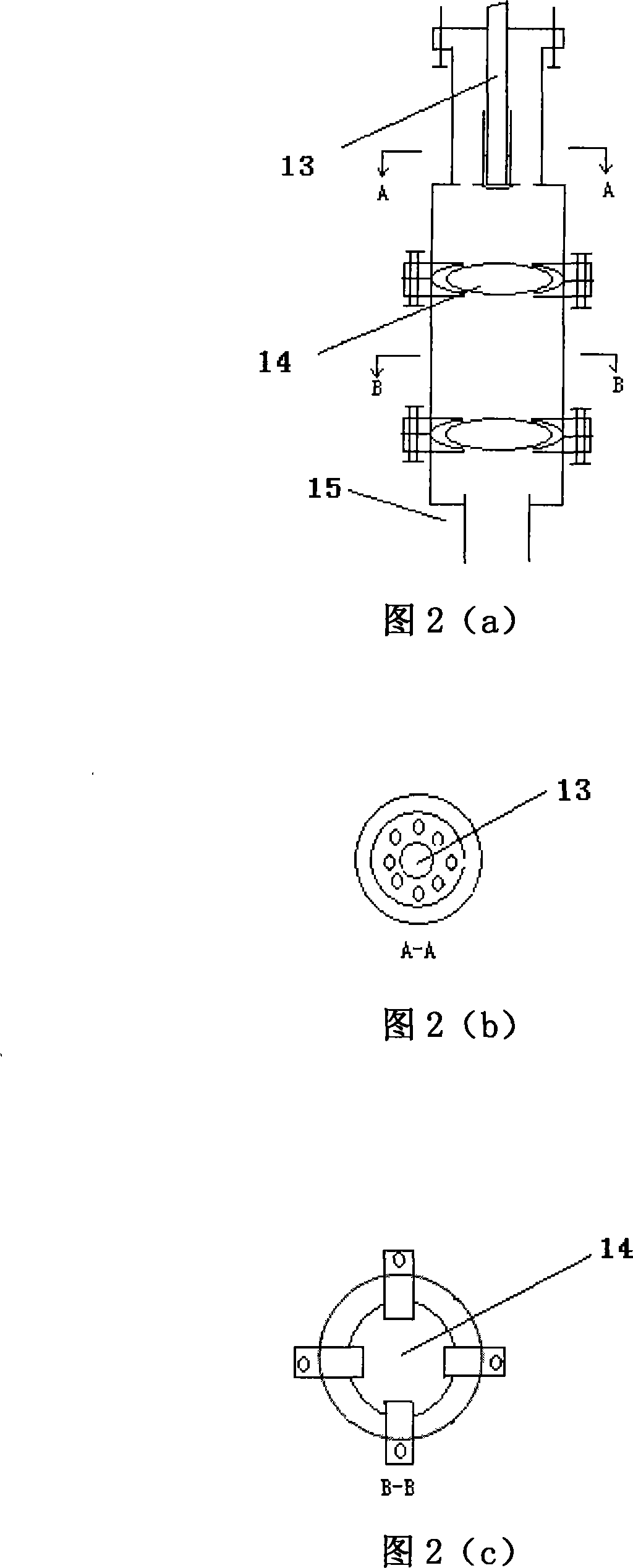
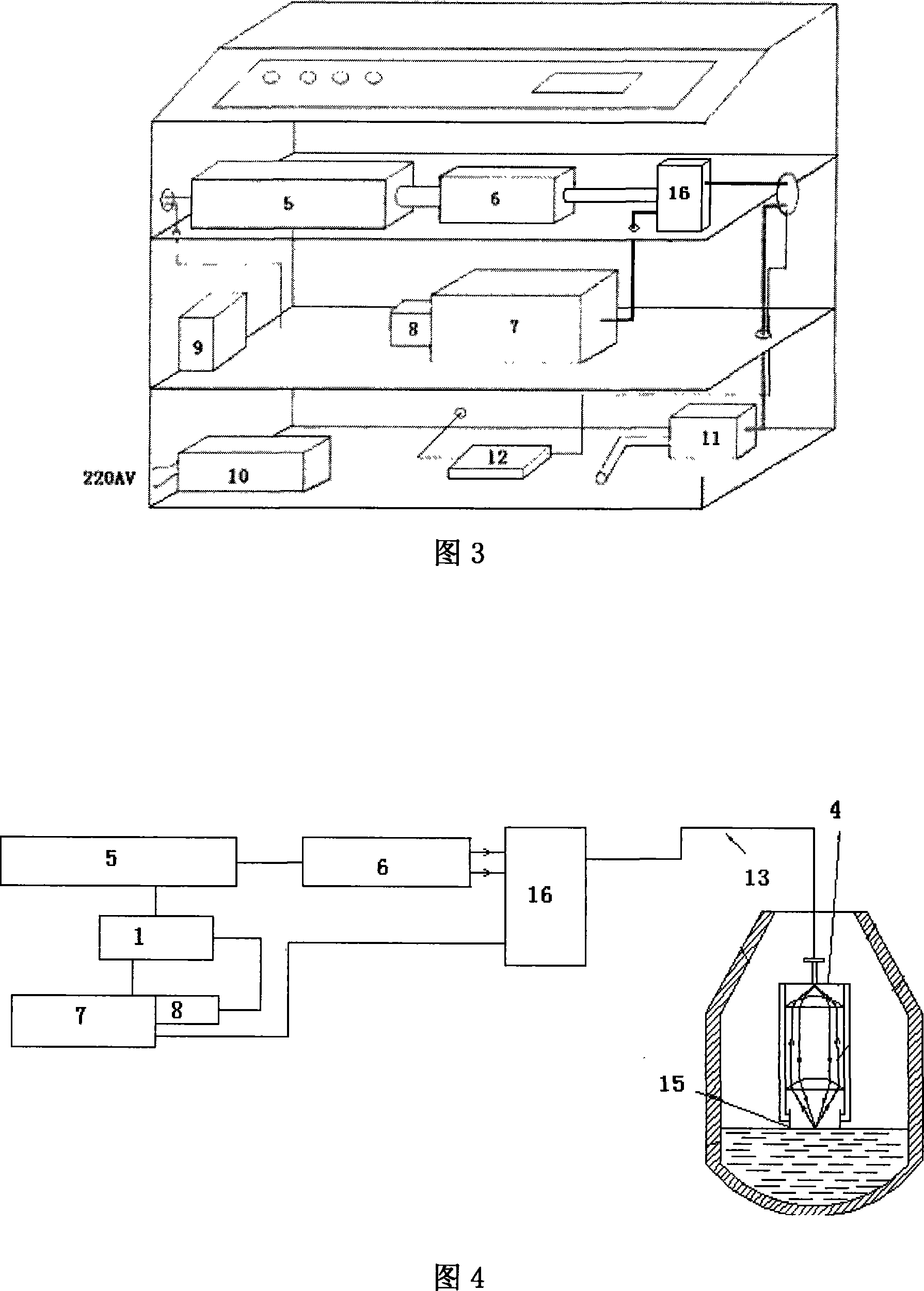
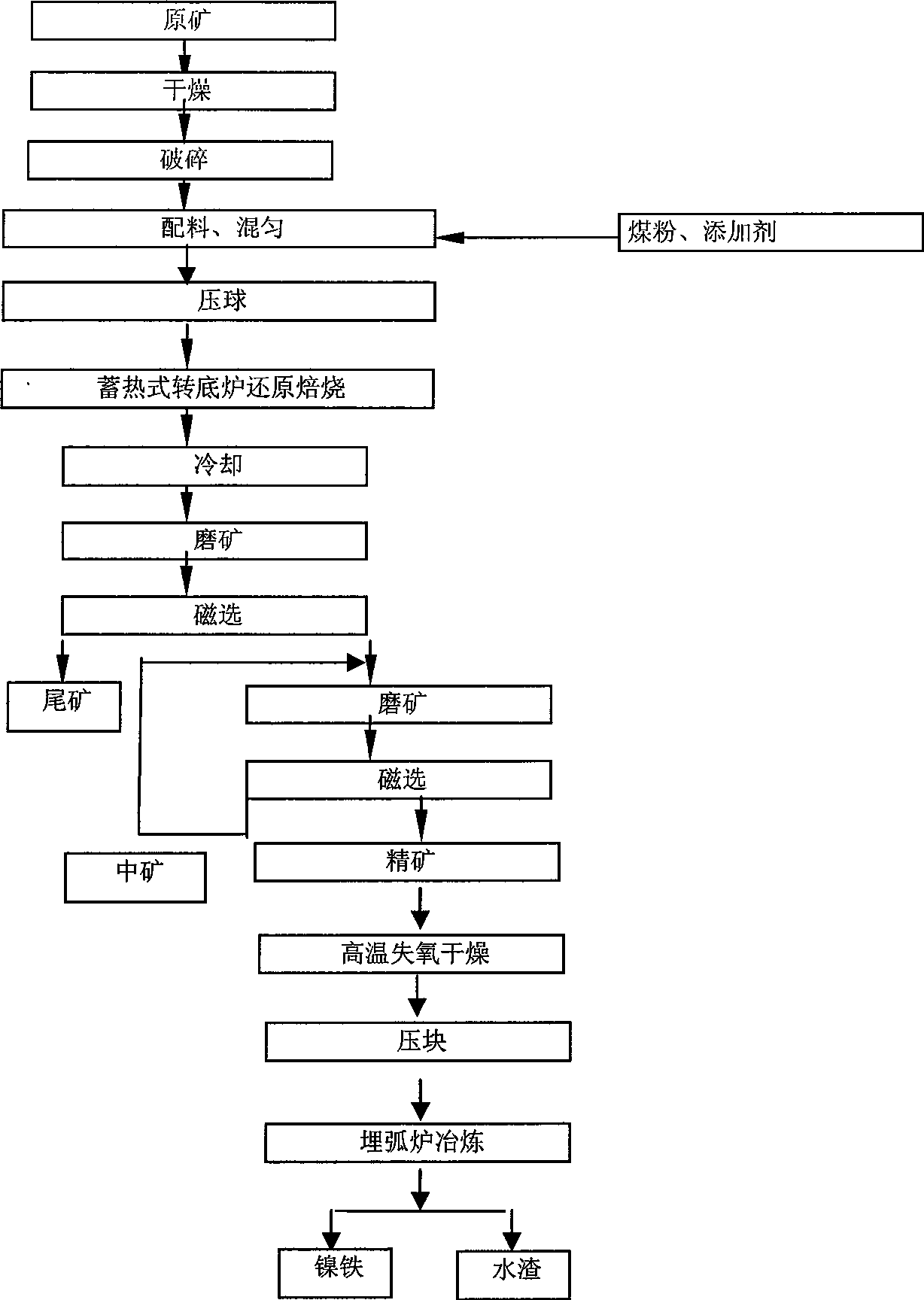
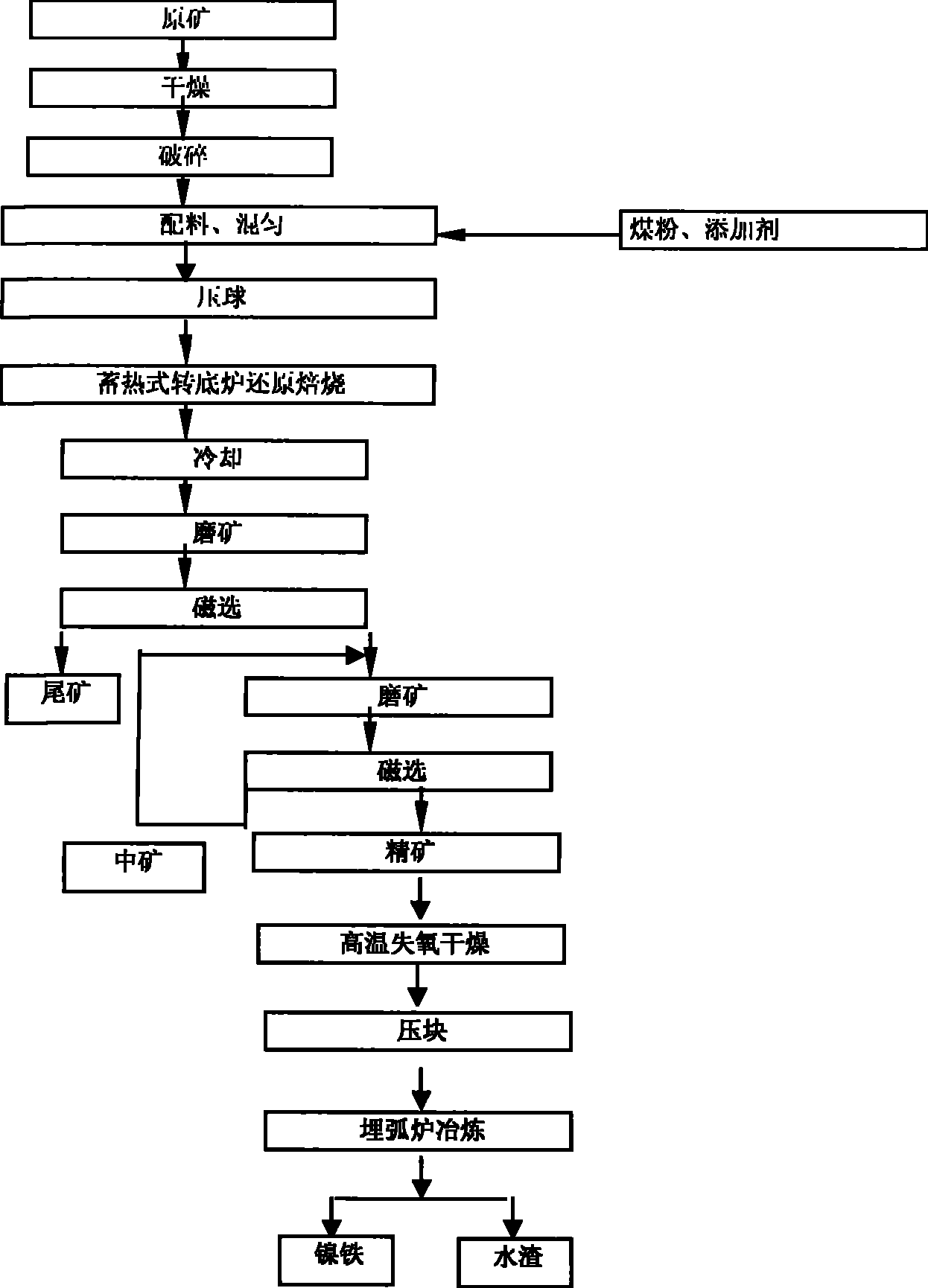
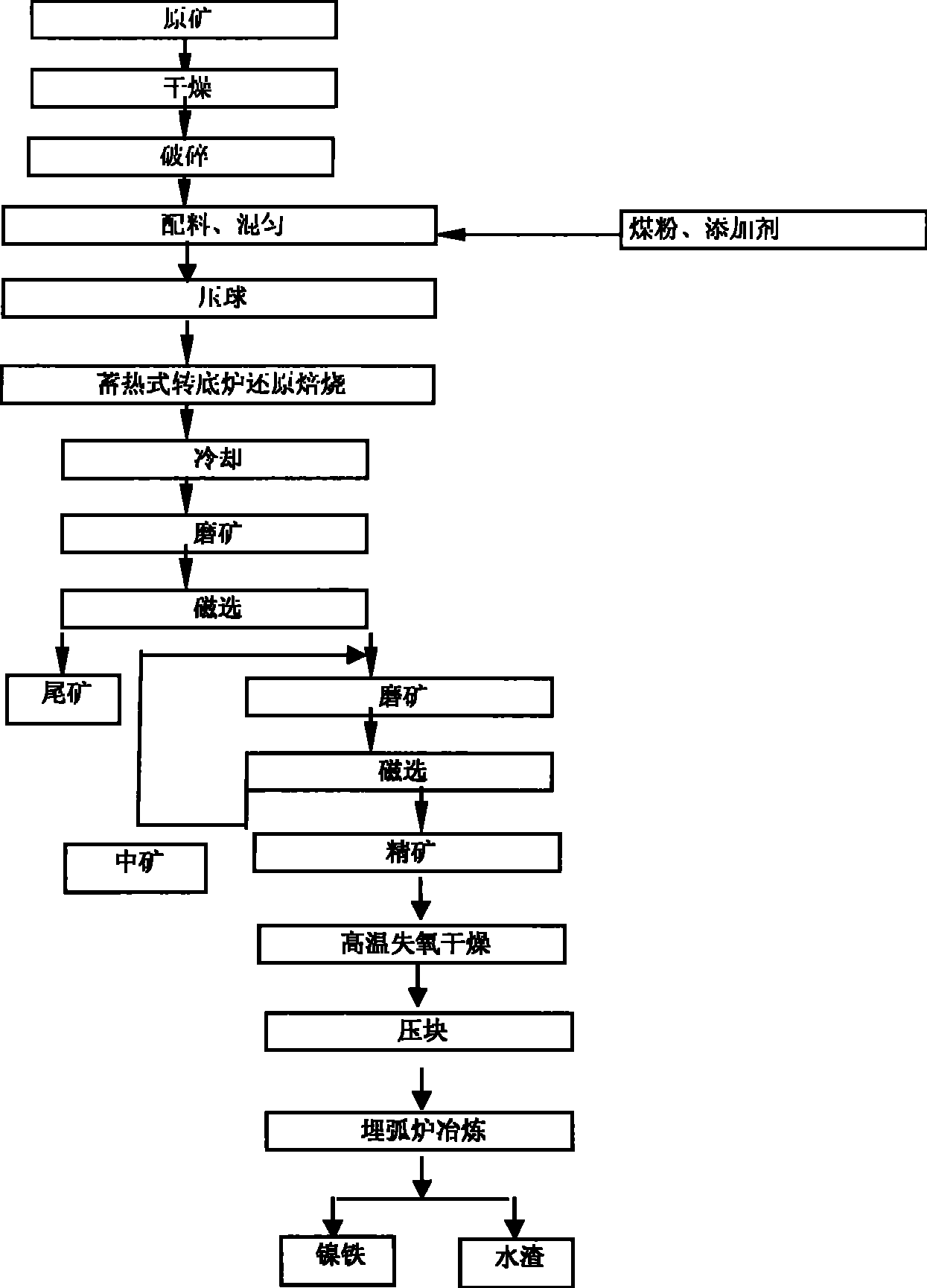
Heat accumulation type rotary hearth furnace-wet separation-buried arc furnace nickel ore smelting method
The invention discloses a heat accumulating type rotary hearth furnace-wet sizing-submerged arc furnace nickel ore smelting method which comprises the following steps: a certain amount of lateritic nickel raw ore is dried, crushed, mixed with coal powder and caking agent, pressed into a ball containing carbon, distributed to a rotary hearth furnace by a distributing device and heated to 900 DEG C to 1250 DEG C for 10min to 40min; the ball containing carbon is reduced into a metallic ball with 70 percent to 90 percent of metallization rate, discharged by a discharge device, and directly sent into water to be cooled, milled and sized. The iron material containing nickel after milling and sizing is dried by high-temperature oxygen losing waste gas, agglomerated and then sent into a submerged arc furnace or other melting equipment to separate the slag and the iron, and produce molten iron containing nickel. The method has simple process, short process, high efficiency, does not need coking coal, is applicable in the production of ferronickel with lateritic nickel of all grades, and no waste gas, waste water and waste solid is discharged during production.
Owner:北京锦泰诚瑞科技发展有限公司
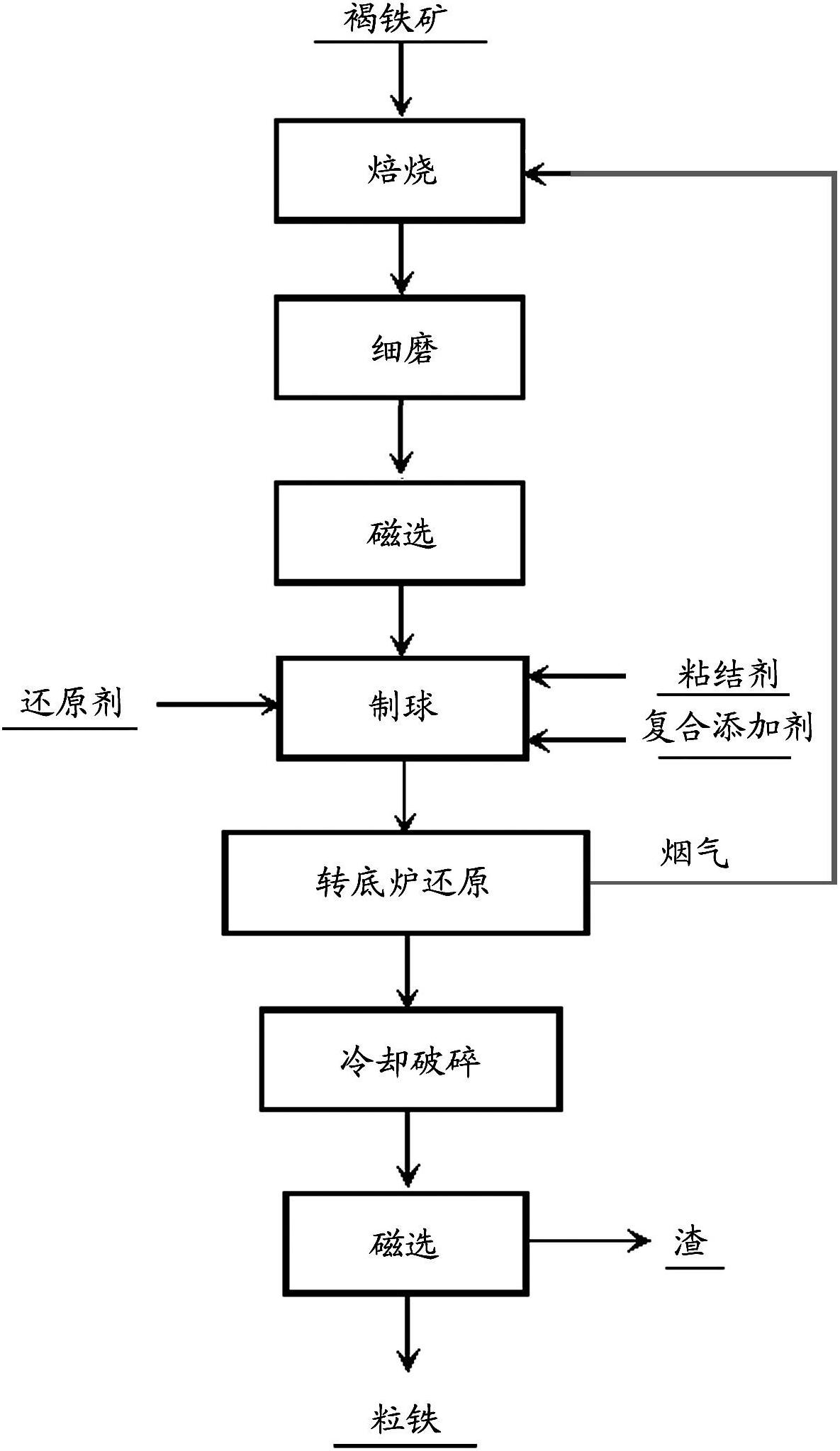
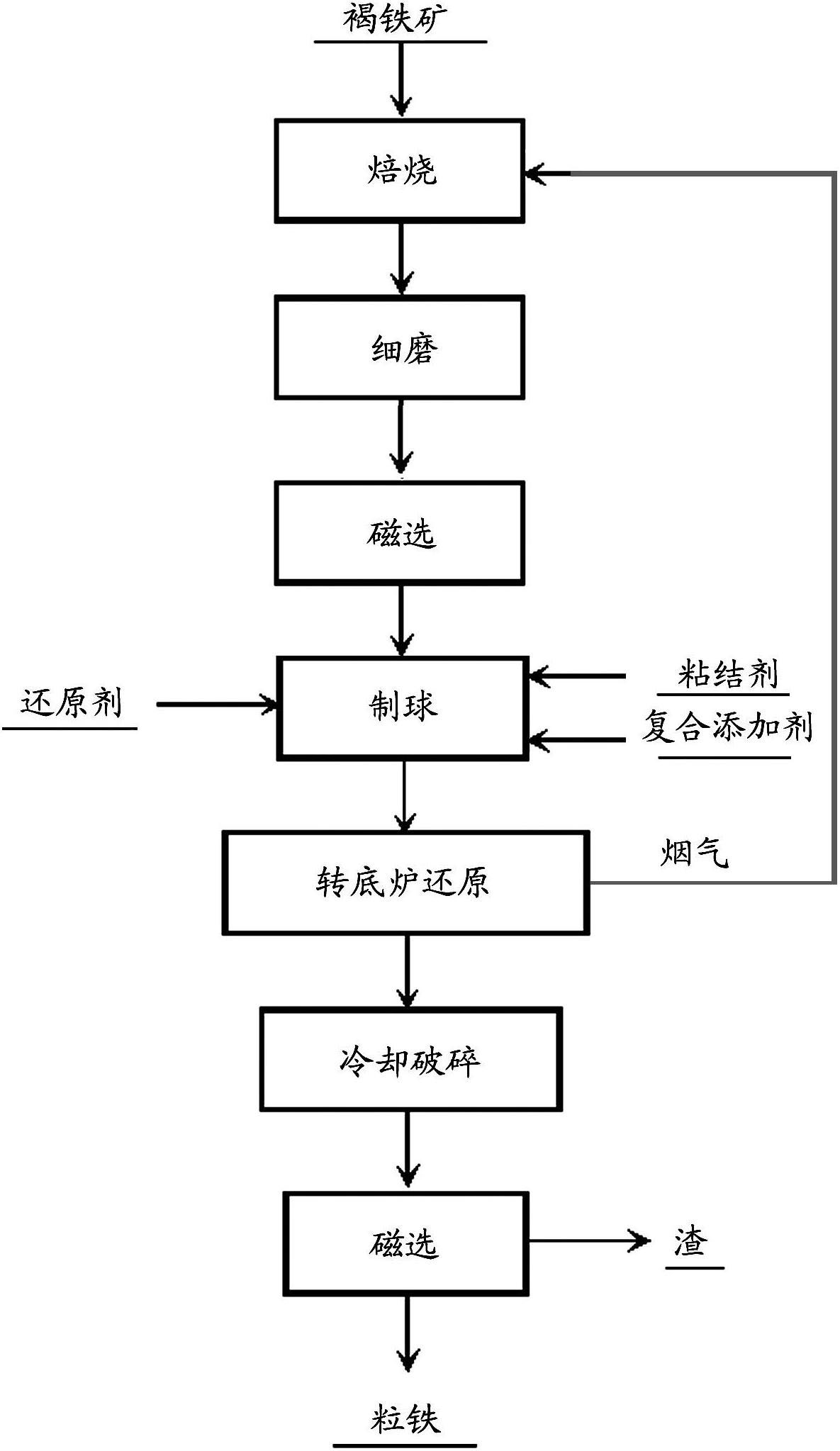
Method for producing granular iron by magnetically roasting and reducing low-quality limonite with rotary hearth furnace
InactiveCN102653804AReduce consumptionReduce smelting costFluidised-bed furnacesHearthReducing agent
The invention provides a method for producing granular iron by magnetically roasting and reducing low-quality limonite with a rotary hearth furnace. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out reduction roasting, fine grinding and magnetic concentration on limonite; adding carbonaceous reducing agents, compound additives and binders to concentrated ore after magnetic concentration and mixing the materials uniformly; then preparing pellets with pelleting equipment and drying the pellets; and carrying out quick reduction by adopting the rotary hearth furnace, and carrying out cooling, grinding and magnetic separation with a magnetic separator so as to obtain the granular iron, wherein the reducing agents for reduction roasting of limonite are flue gases generated by the rotary hearth furnace. The method has the advantages of high degree of automation, high reaction speed, high reduction efficiency, low smelting cost and the like.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
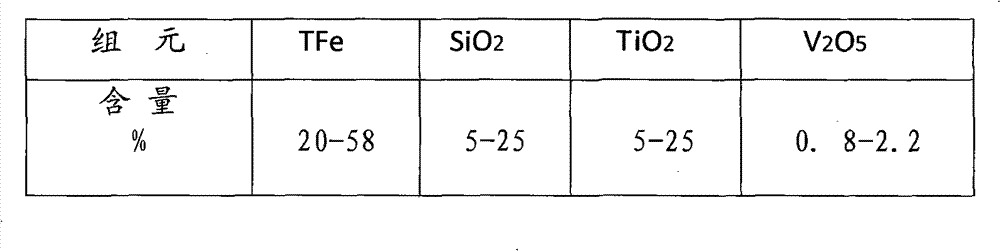
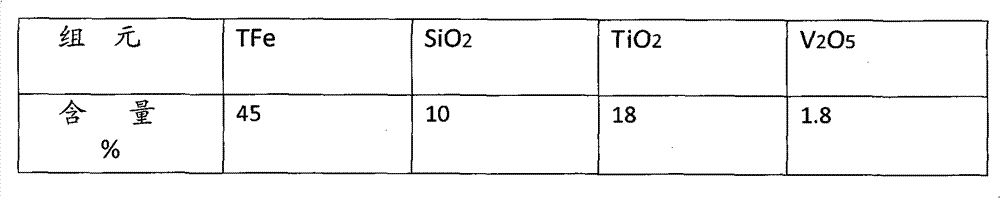
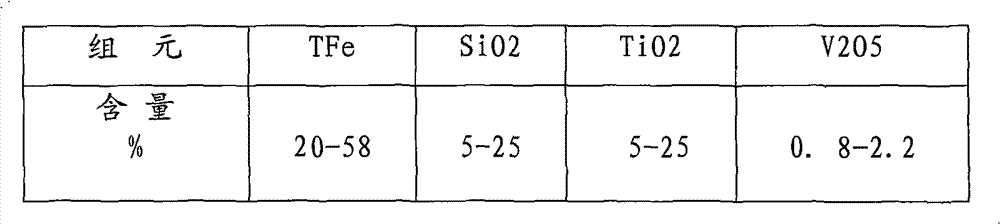
Process for smelting vanadium-containing pig iron by high-silicon vanadium titanomagnetite concentrate powder
The invention provides a process for smelting vanadium-containing pig iron by high-silicon vanadium titanomagnetite concentrate powder, which comprises the following steps: preparing raw material particles with a particle size of 5-150 mm of carbon-containing cold-bonded pellets (blocks), sinter, roasted acidic pellets, and metallized pellets (blocks) from the concentrate powder, mixing the raw material particles with a solvent and a reducing agent, smelting in a smelting furnace to obtain vanadium-containing pig iron; according to the different components of the raw material particles, the solvent ratio during smelting is that raw material particle:limestone:dolomite:fluorite = 1:(0-0.25):(0-0.15):(0-0.10); the material blending principle is that the CaO:SiO2:TiO2 in the slag is controlled to be within a weight ratio range of 1:(0.5-1.2):(0.6-1.8); the invention solves the problem of difficult smelting of the vanadium titanomagnetite concentrate powder with high silicon, high titanium, and low iron; the smelting furnace relates to a blast furnace, an open hearth furnace, a submerged arc furnace and a hot blast cupola.
Owner:王洪东
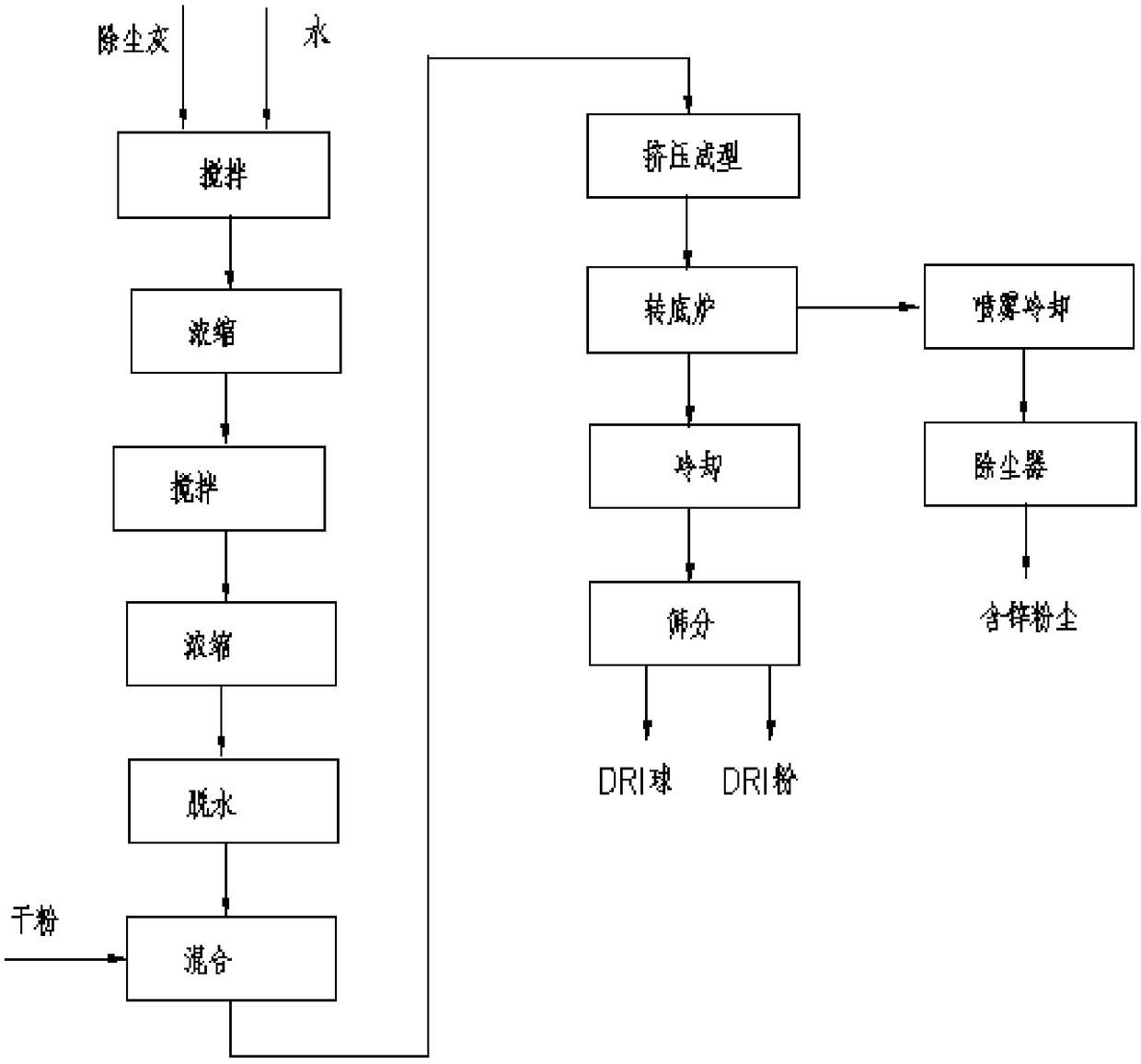
Treatment technology for zinc-containing dust of rotary hearth furnace
InactiveCN109055726ALow investment costSo as not to damageCombination devicesProcess efficiency improvementHearthSpray cooling
The invention belongs to the technical field of metallurgy, and relates to a treatment technology for zinc-containing dust of a rotary hearth furnace. K, Na, Cl and other elements in the zinc-containing dust are fully removed by adopting a wet way technology, wherein the wet way technology is to make the zinc-containing dust of a steel and iron mill to be mixed with water and subjected to multiplestirring, concentration and then dehydration; a mode of coal rod machine extrusion is adopted to make raw materials form at a moisture content of 15-20%, meanwhile, drying, preheating, heating and reducing roasting of the raw materials are completed in the rotary hearth furnace, thus raw material drying does not need to be configured with a dryer, drying is directly carried out in the rotary hearth furnace, and the cost is saved; and meanwhile, flue gas of the rotary hearth furnace is cooled by adopting a mode of spray cooling, no boiler or heat exchanger is required to be configured, the investment cost of flue gas treatment of the rotary hearth furnace is reduced, the flue gas of the whole rotary hearth furnace can meet the treatment requirements of the zinc-containing dust of medium and small steel mills, and the production cost is saved.
Owner:CISDI RES & DEV CO LTD
Calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer and production method thereof
The invention relates to a calcium-magnesia phosphate fertilizer and a production method thereof. The calcium-magnesia phosphate fertilizer is prepared by mixing ferrophosphorus and phosphorus ore according to the mass ratio of 1:1.8-2.2, placing the obtained mixture in a high-temperature open-hearth furnace for melting, and hardening the mixture. The production method of the calcium-magnesia phosphate fertilizer comprises the following steps: mixing the ferrophosphorus and the phosphorus ore according to the mass ratio of 1:1.8-2.2, placing the obtained mixture into the high-temperature open-hearth furnace for heating to 1800-2200 DEG C to oxidize and burn phosphor in the mixture, and performing furnace tapping on a product and hardening the product, thus obtaining a semi-finished product of the calcium-magnesia phosphate fertilizer, and finally making the semi-finished product into a finished product of the calcium-magnesia phosphate fertilizer. The phosphor in the mixture is oxidized and burned by the way of direct air blasting to raise the temperature of the high-temperature open-hearth furnace. The production method is adopted to produce the calcium-magnesia phosphate fertilizer with high phosphor conversion rate, resources saving and low energy consumption.
Owner:徐辉石
Steel slag modification and steel slag cement
InactiveCN100357208CAchieve separationReduce manufacturing costCement productionRecycling and recovery technologiesIngotUltimate tensile strength
A process for preparing modified steel scrap by adding reforming agent in the scrap at agitation and separating iron from scrap while steel furnace discharging. The quality of pig obtained reaches the standards of clean steel scrap and ingot iron. Changing the formula of reforming agent, three kinds of modified steel scrap can be used for making ordinary cement, moderate cement and road cement. All steel scrap of electric furnace, rotary furnace and open-hearth furnace are reclaimable.
Owner:叶德敏
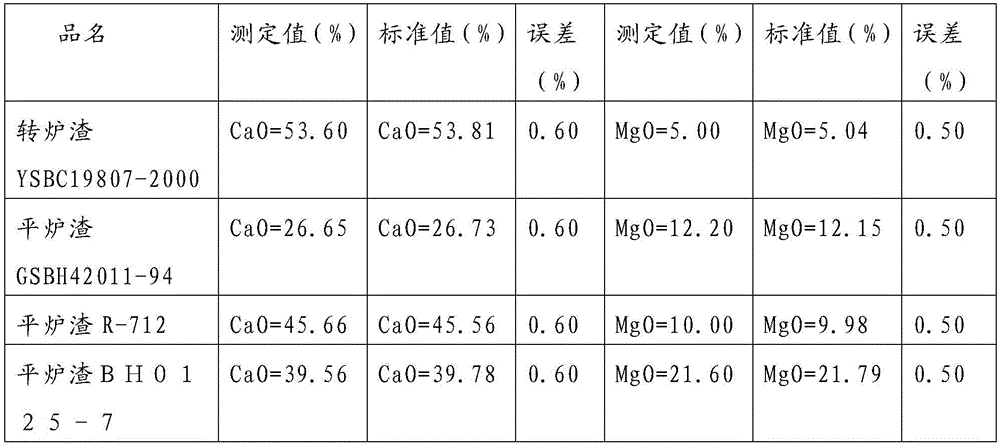
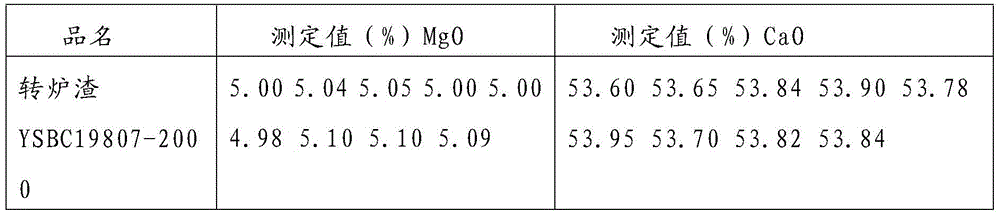
Measuring method for content of calcium oxide and magnesium oxide in open-hearth furnace slag, converter slag and electric furnace slag
InactiveCN105606762AReduce consumption costReduce labor costsChemical analysis using titrationSlagHydroxylamine Hydrochloride
The invention discloses a measuring method for the content of calcium oxide and magnesium oxide in open-hearth furnace slag, converter slag and electric furnace slag. The measuring method has the advantages of being rapider, more accurate and more efficient. A sample is dissolved with hydrochloric acid, nitric acid-hydrofluoric acid, perchloric acid is added for smoking, and after taking down and cooling, hydrochloric acid is added to heat and dissolve salt; the pH value of the test solution is adjusted to be 7 with ammonium hydroxide, the test solution is heated to be boiled, taken down, slightly cooled and filtered in a volumetric flask, sediment is washed 7-8 times with a hot ammonium chloride solution, after being cooled, the solution is diluted to scales for volume setting, two parts of equal solutions are taken respectively and put in two flasks, triethanolamine, water and a small amount of hydroxylamine hydrochloride are added to one part, the pH value is adjusted to be 12 after a potassium hydroxide solution is added, a proper amount of calcein is added, and titration is conducted with an EDTA standard solution till an end point that fluorescent green disappears and the amount of calcium is obtained; triethanolamine, water and a small amount of hydroxylamine hydrochloride are added to the other part, the pH value is adjusted to be 10 after an ammonia-ammonium chloride buffer solution is added, eriochrome black T serves as an indicator, and titration is conducted with the EDTA standard solution till an end point of pure blue and the resultant amount of calcium and magnesium is obtained.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA BAOTOU STEEL UNION
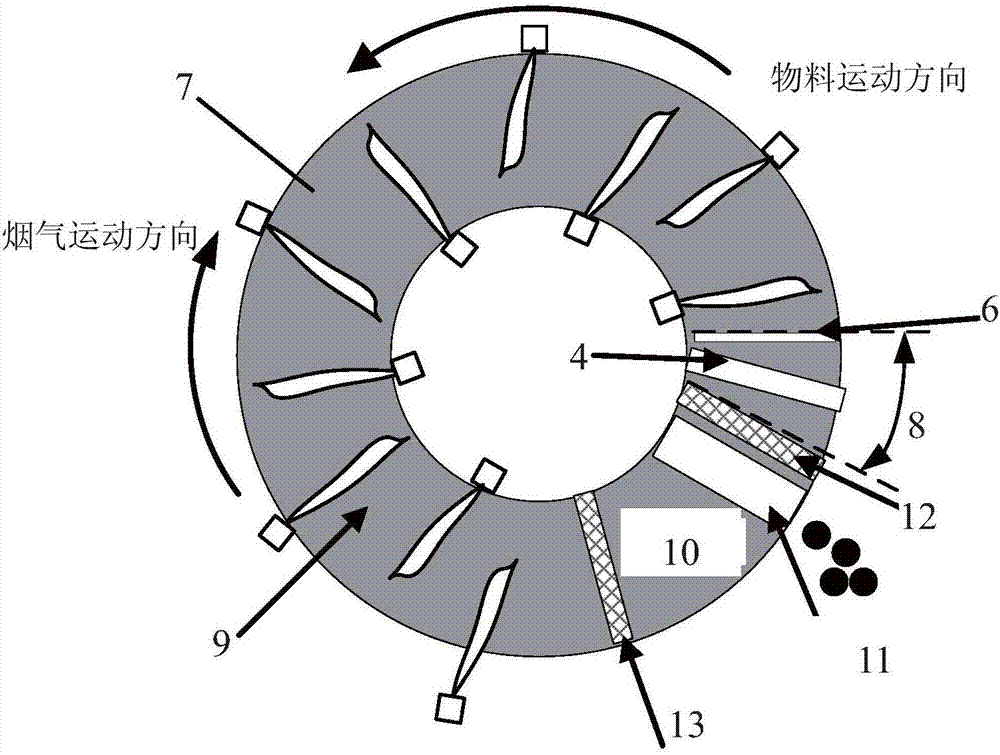
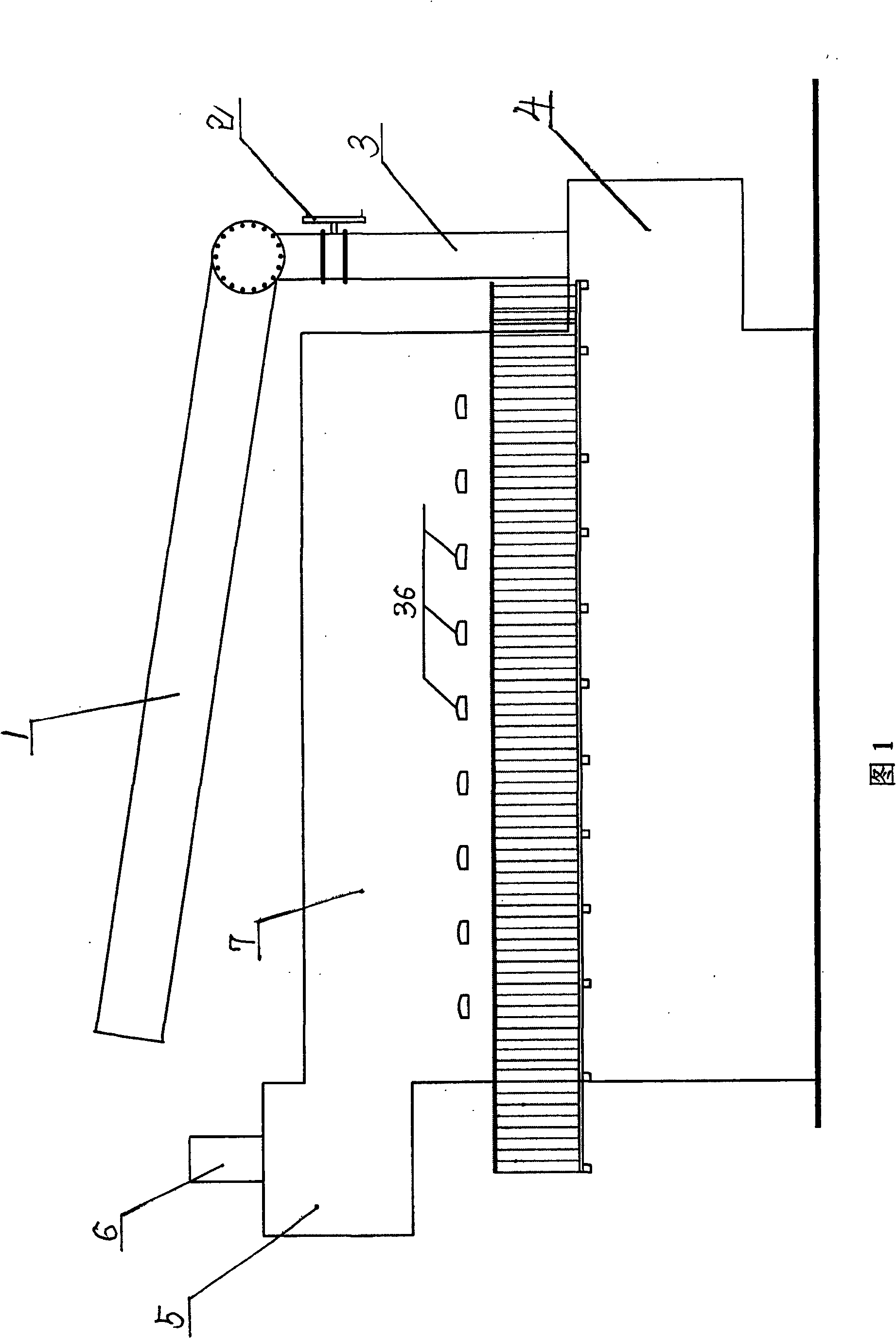
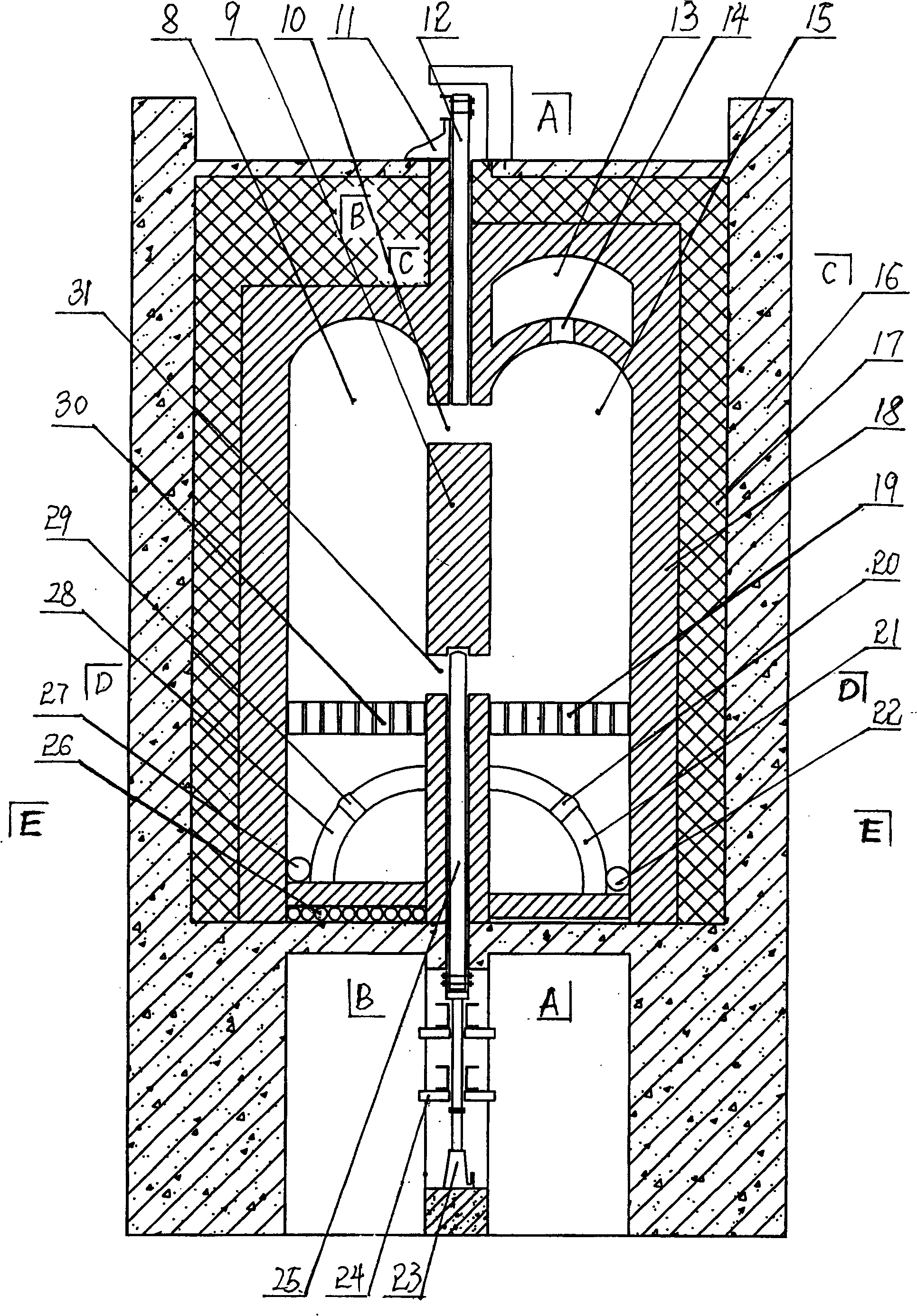
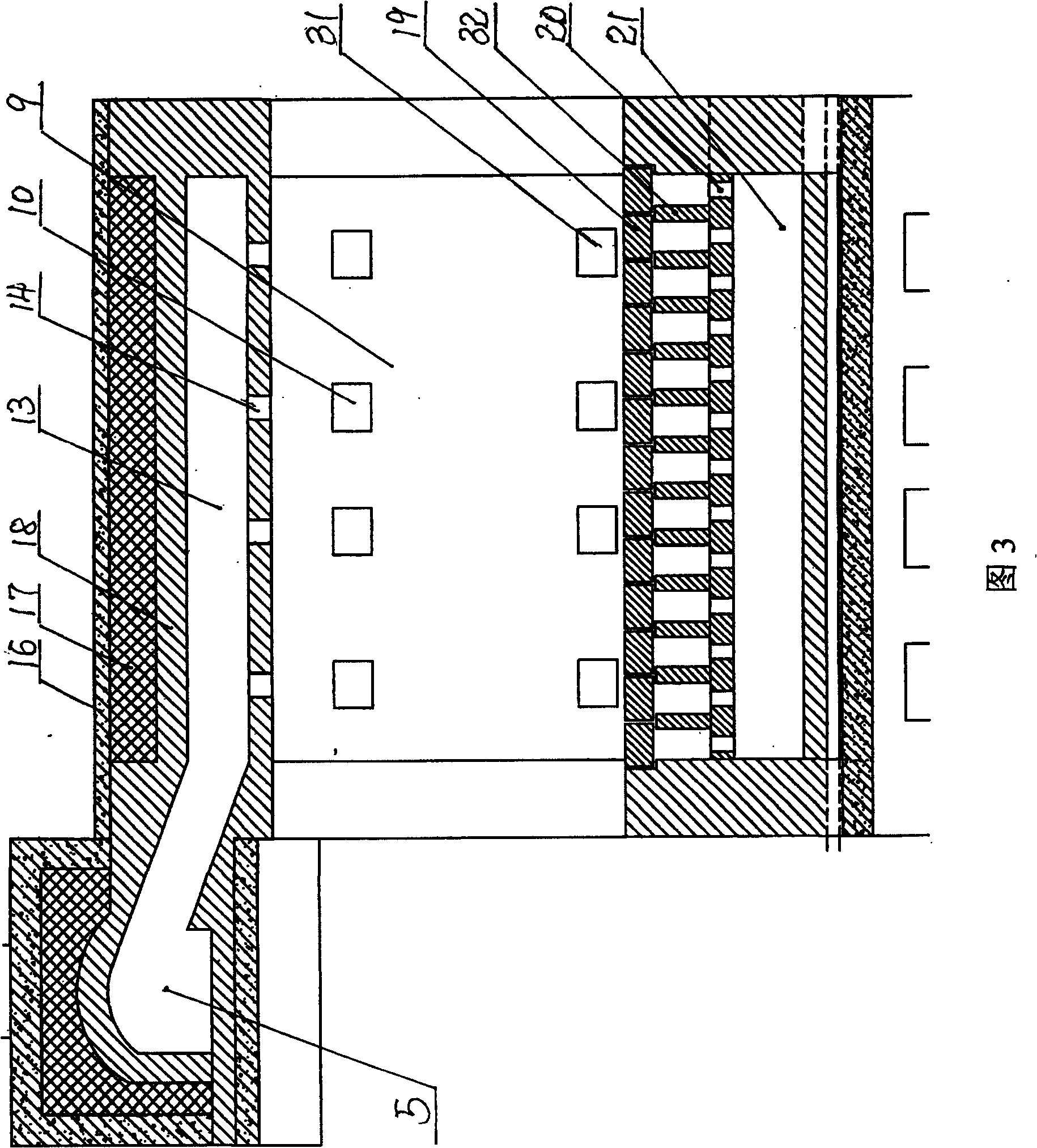
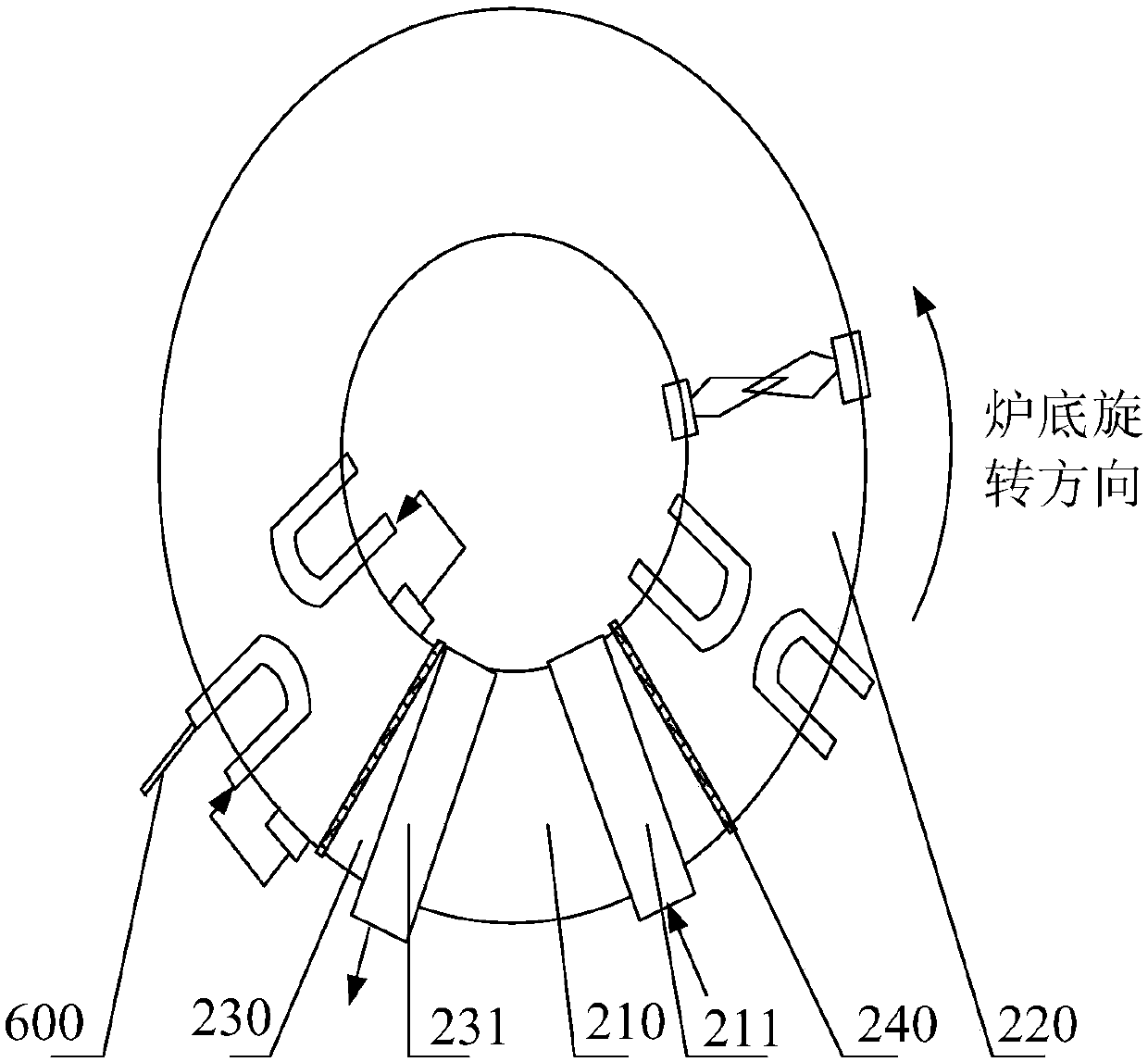
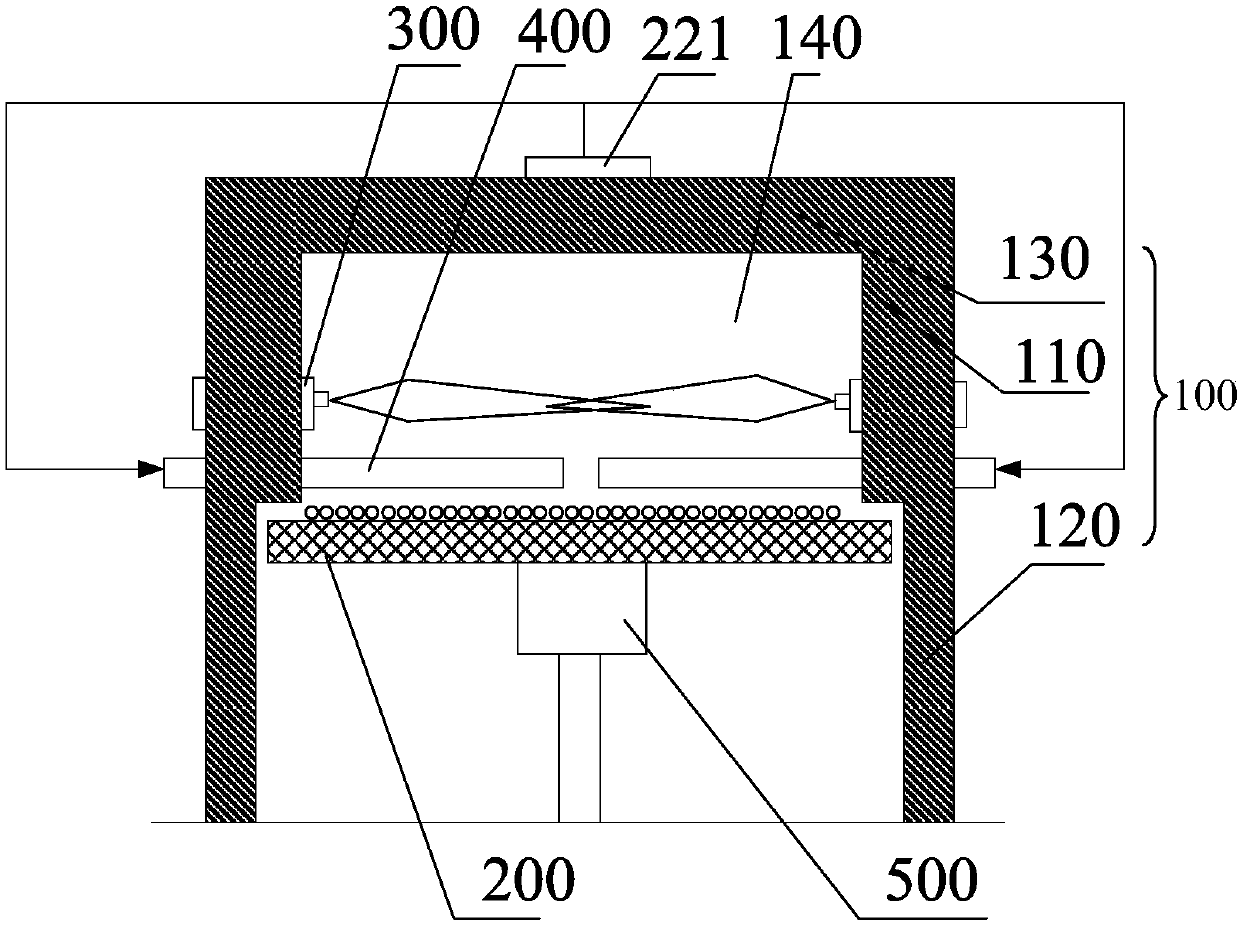
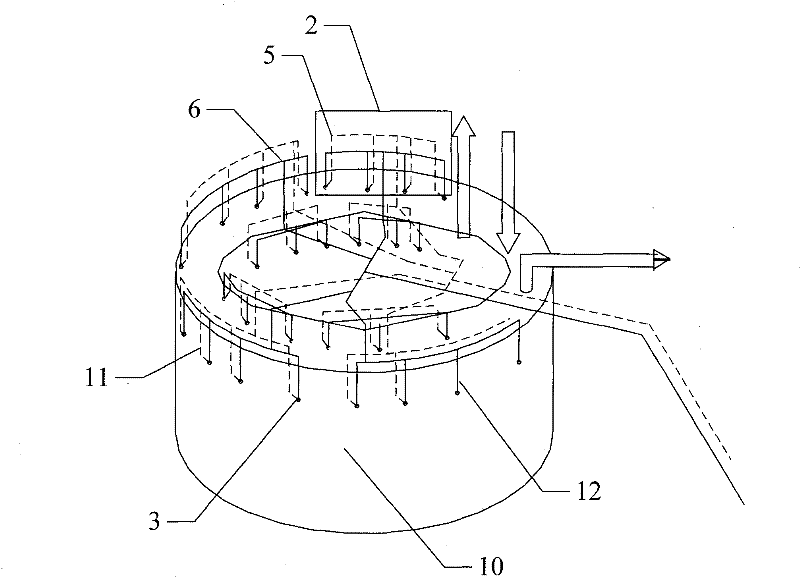
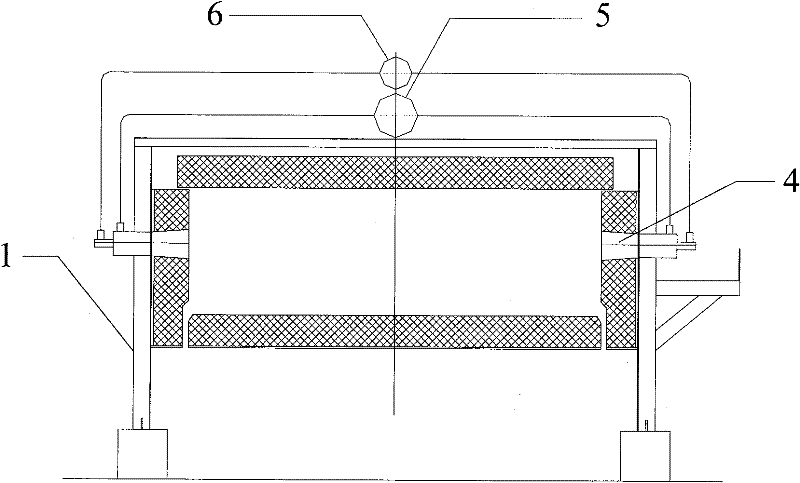
Rotary hearth furnace
The invention relates to a rotary hearth furnace. The rotary hearth furnace comprises an annular furnace body, an annular hearth, a heat power engineering system, a discharge mechanism, a distributionmechanism and a smoke discharge mechanism. The rotary hearth furnace effectively solves low CO utilization rate, and meanwhile, fully uses the smoke afterheat; more CO participates in indirect reduction; materials are preheated by the smoke afterheat; compared with a traditional rotary hearth furnace technology, the rotary hearth furnace can reduce adding of the material carbon dosage, effectively reduces the smelting energy consumption, and reduces the production cost; and the angle of a high-temperature reduction area is increased, so that the reduction time is prolonged, the reduction effect is improved, and meanwhile, the treatment capacity of the rotary hearth furnace is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE METALLURGICAL DESIGN INST
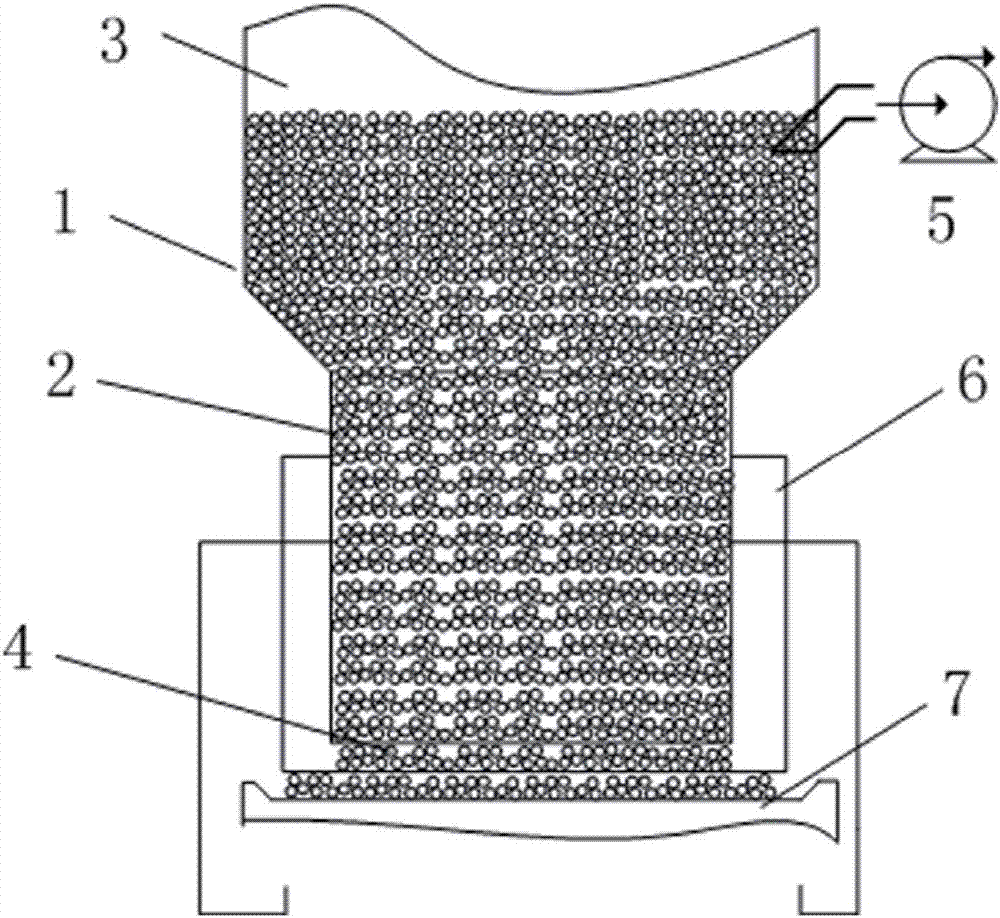
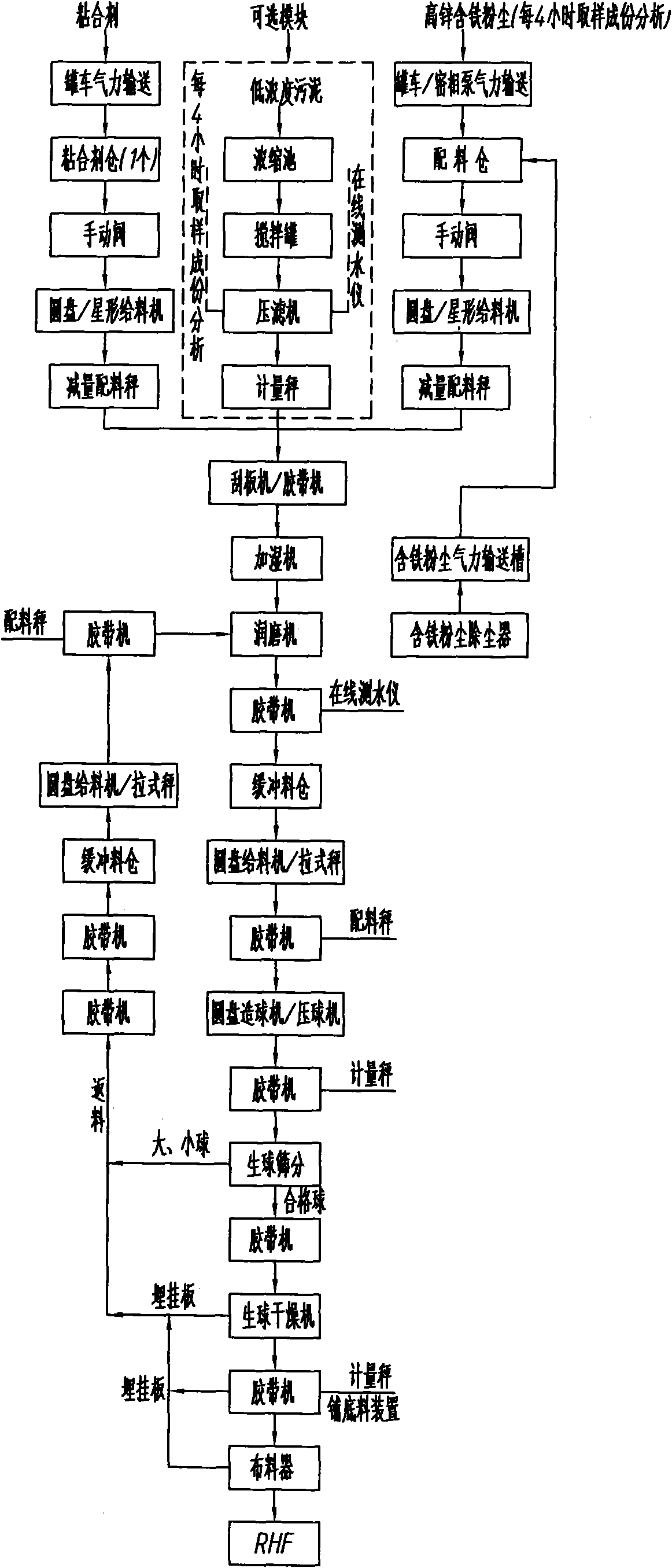
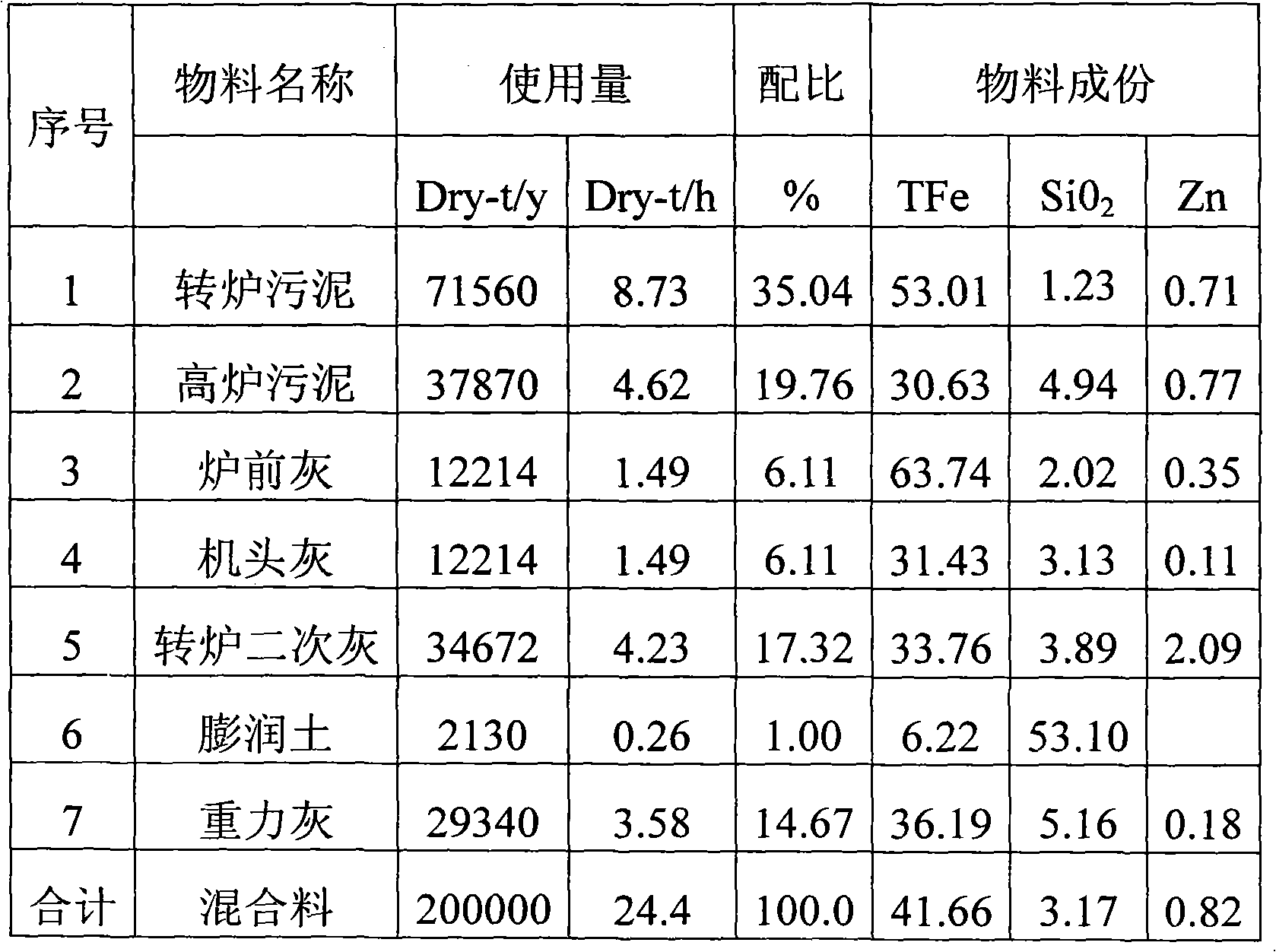
Raw material treatment and pelletizing system process for rotary hearth furnace
InactiveCN101962717AEvenly distributedParticle size specific surface area increasesProcess efficiency improvementSludgeHearth
The invention discloses a raw material treatment and pelletizing system process for a rotary hearth furnace (RHF). The process comprises the following steps of: conveying various high-zinc iron-containing dusts to be treated to a mixing tank for mixing; and moistening, grinding and pelletizing the dusts and adhesive mixture required by pelletizing to produce the high-zinc iron-containing pellets which meet the high index parameter requirements of the RHF. The process effectively overcomes the adverse factors, such as large fluctuation, poor pelletizing performance and the like, of the raw material components, such as zinc-containing dust, sludge and the like, by combining the actual conditions of the high-zinc iron-containing sludge and dust raw materials of each iron and steel plant, and has the advantages of perfect function, accurate ingredients, compact layout and reasonable manufacturing cost; and the high-zinc iron-containing pellets which meet the high index parameter requirements of the RHF can be stably produced.
Owner:马钢设计研究院有限责任公司
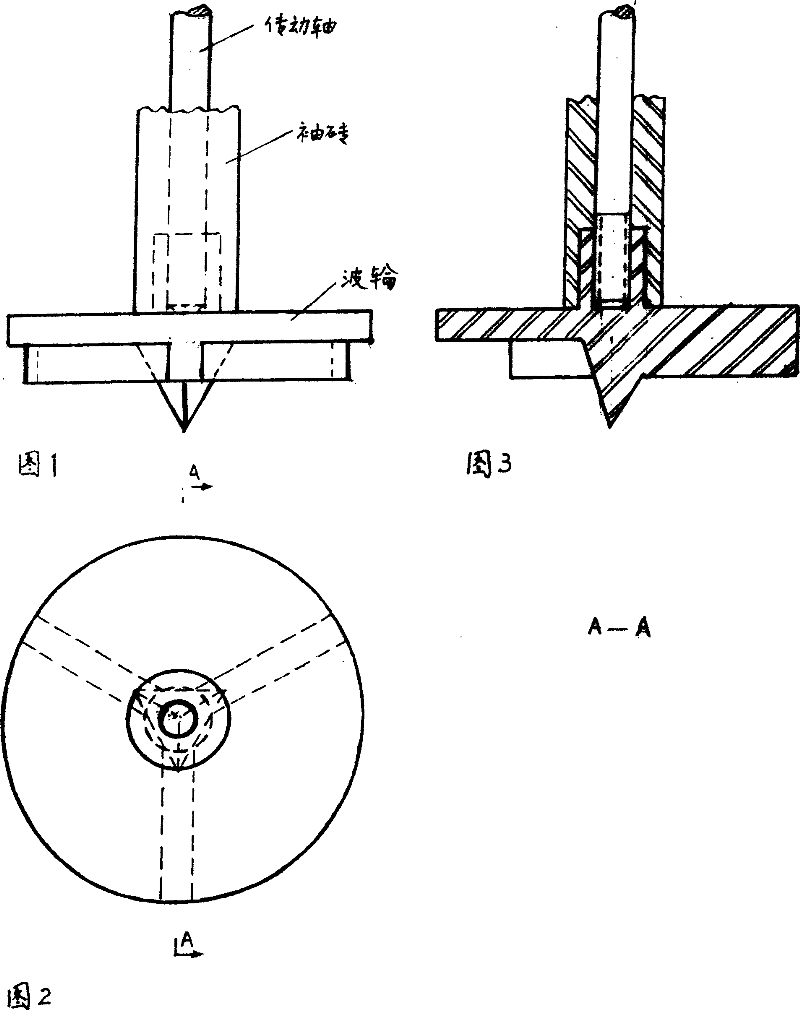
Rotary hearth furnace and screw rod for discharging reduced iron
The invention discloses a reduced iron discharging screw of a rotary hearth furnace, which is used for self-forming a hearth reduced iron on the discharging port of periphery, and discharging the hearth reduced iron to the outside of the furnace body. The reduced iron discharging screw has screw blade outside of the rotating axis, the inside of the discharging screw is cooled by the flow of cooling water, and the fireproof layer in the middle is formed outside of the rotating axis.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Bottom-blowing oxidation rough smelting technology for antimony ore and metallurgical furnace
The invention discloses a bottom-blowing oxidation rough smelting technology for antimony ore and a metallurgical furnace. The bottom-blowing oxidation rough smelting technology for antimony ore includes the steps as follows: supplying heat by coking coal or lump coal, supplying air and oxygen into a hearth by a fan, adding coal and antimony ore burden into the hearth from the top or the upper side surface of the furnace body, enabling the air of the fan to blow into the hearth from bottom to top after the air passes through a distribution plate from the bottom of the hearth, allowing flue gas to enter a condensation dust-collection system from the upper side surface or the top of the furnace body, and discharging solid-state slag from the bottom or the lower side surface of the furnace body. The metallurgical furnace comprises the furnace body, wherein the top or the upper side surface of the furnace body is provided with a burden feed hole; the furnace body is provided with an air flow distribution plate at the bottom of the furnaced; the fan supplies air upwards from the bottom of the furnace through the air flow distribution plate; the top or the upper side surface of the furnace body is provided with a flue gas outlet for leading the flue gas to enter the condensation dust-collection system; and the bottom of the furnace body is provided with a slag discharge hole. The metallurgical furnace integrates the characteristics of an existing blast furnace, an open-hearth furnace and a roasting furnace and has the characteristics of high stock columns, thin stock layers, low coke rate and high recovery rate.
Owner:娄底市兴华有色金属有限公司
Method for melting copper through line frequency furnace
ActiveCN105274354AImprove airtightnessImprove energy savingProcess efficiency improvementIngotShaft furnace
The invention discloses a method for melting copper through a line frequency furnace. The method comprises the following steps that 1, a waste copper piece and waste are subjected to primary treatment; 2, screening is carried out; 3, classification is carried out; 4, accessories are fed into furnaces, wherein the accessory I, the accessory II and the accessory III are fed into the shaft furnace, the open-hearth furnace and the line frequency cored copper melting copper to be refined, and a product I, a product II and a product III are obtained; 5, the product I and the product II are transported to a copper continuous casting and rolling unit for casting treatment, a steel rod is obtained, and the product III is placed in a pig casting machine to be machined and treated, and a copper ingot is obtained; and 6, the steel rod in the step 5 is drawn, and a qualified copper piece is obtained. The method for melting copper through the line frequency furnace achieves energy saving and is environmentally friendly, and manufactured steel is good in quality.
Owner:NINGXIA RUIYIN NONFERROUS METAL TECH CO LTD
Environmental protection type vanadium extraction process through replace of sodium chloride with soda
InactiveCN102531058AEmission complianceConserve waterEnergy inputVanadium oxidesWater useIon exchange
The present invention relates to an environmental protection type vanadium extraction process through replace of sodium chloride with soda. Compared to the vanadium extraction process by a traditional fire baking method, the main characteristic of the process of the present invention is that: an efficient vertical baking furnace is adopted to replace the open hearth furnace in the vanadium extraction process by the traditional fire baking to carry out baking, the formula of the additive is optimized so as to reduce the pollutant discharge, a tank type circulating dump leaching process is adopted to replace the acid leaching extraction or an ion exchange step, at the same time, an aeration evaporator is adopted to treat the vanadium precipitating waste water and the waste gas generated from the furnace by using the baking furnace flue gas waste heat. According to the present invention, the whole mechanical operation is adopted, such that the vanadium recovery rate can be improved by 30%, the labor intensity of the worker is substantially reduced, and the water use amount is saved by 80%; the sodium salt in the waste water can be recovered when the vanadium precipitating waste water is treated, the dust and other harmful components in the waste gas are absorbed, and the recovered sodium salt returns to a material stirring system, such that the assistant material can be reused, and the remaining part can be sold as by-products.
Owner:张广林
Acid-resistant, fire-resistant and thermal-insulation material high in comprehensive performance
The invention relates to the technical field of materials, in particular to an acid-resistant, fire-resistant and thermal-insulation material high in comprehensive performance. The material is prepared from 90%-95% of silica bricks, 5%-10% of clay, 3%-10% of caprolactam, 1%-2.5% of hydroxy propyl cellulose and 1%-2.5% of hydroxyethyl cellulose. Accordingly, compared with the prior art, the preparation method is simple, the practicability of a finished product is good, technological operation is easy and convenient, the acid-resistant slag erosion capacity is high, refractoriness under load ishigh, the volume does not shrink after repeated calcination and even slightly swells, and the material is mainly used for thermal equipment such as coke ovens, glass melting furnaces and acid open hearth furnaces.
Owner:绵阳旺通科技有限公司
Reverse flow carbonization horizontal stove
InactiveCN1963363AAchieve waste heat recovery and utilizationTo achieve the purpose of low-temperature residue removalMuffle furnacesRetort furnacesCarbonizationProcess engineering
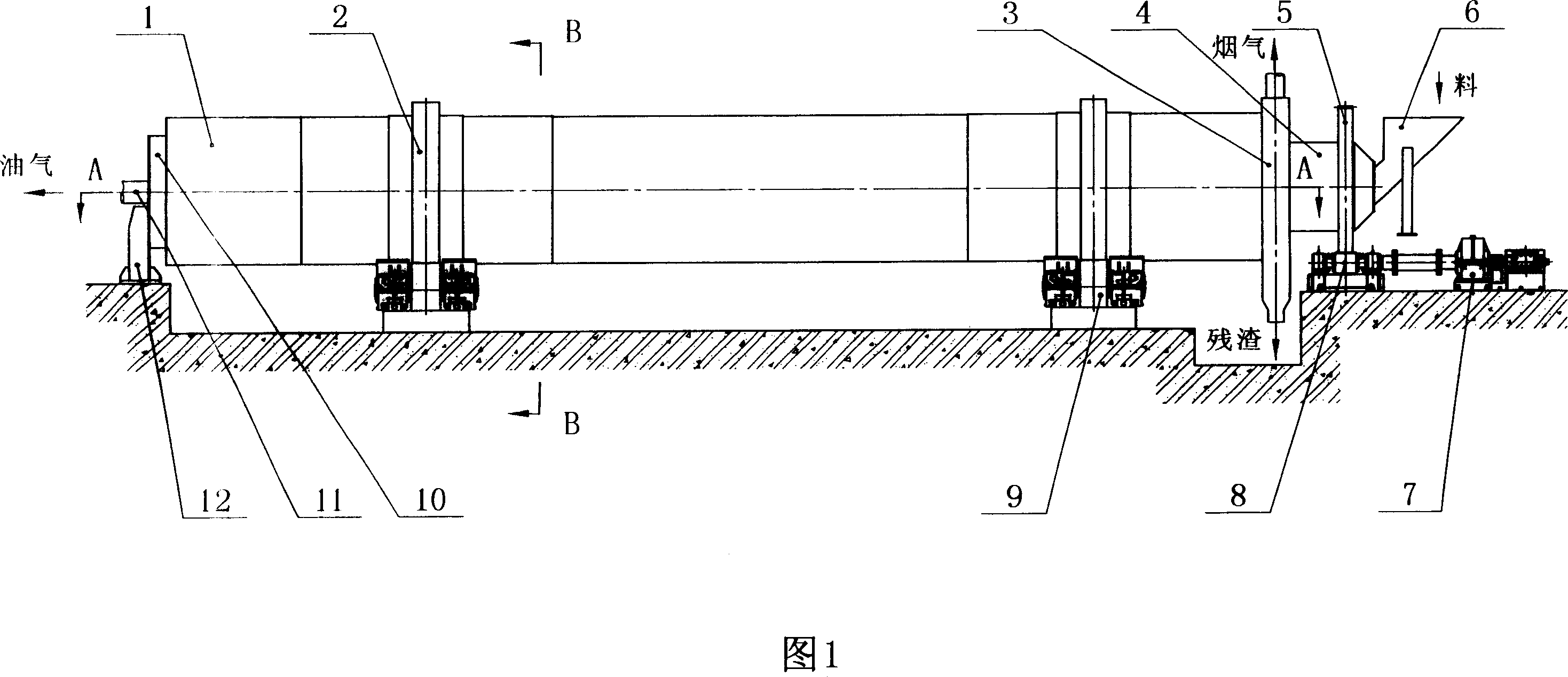
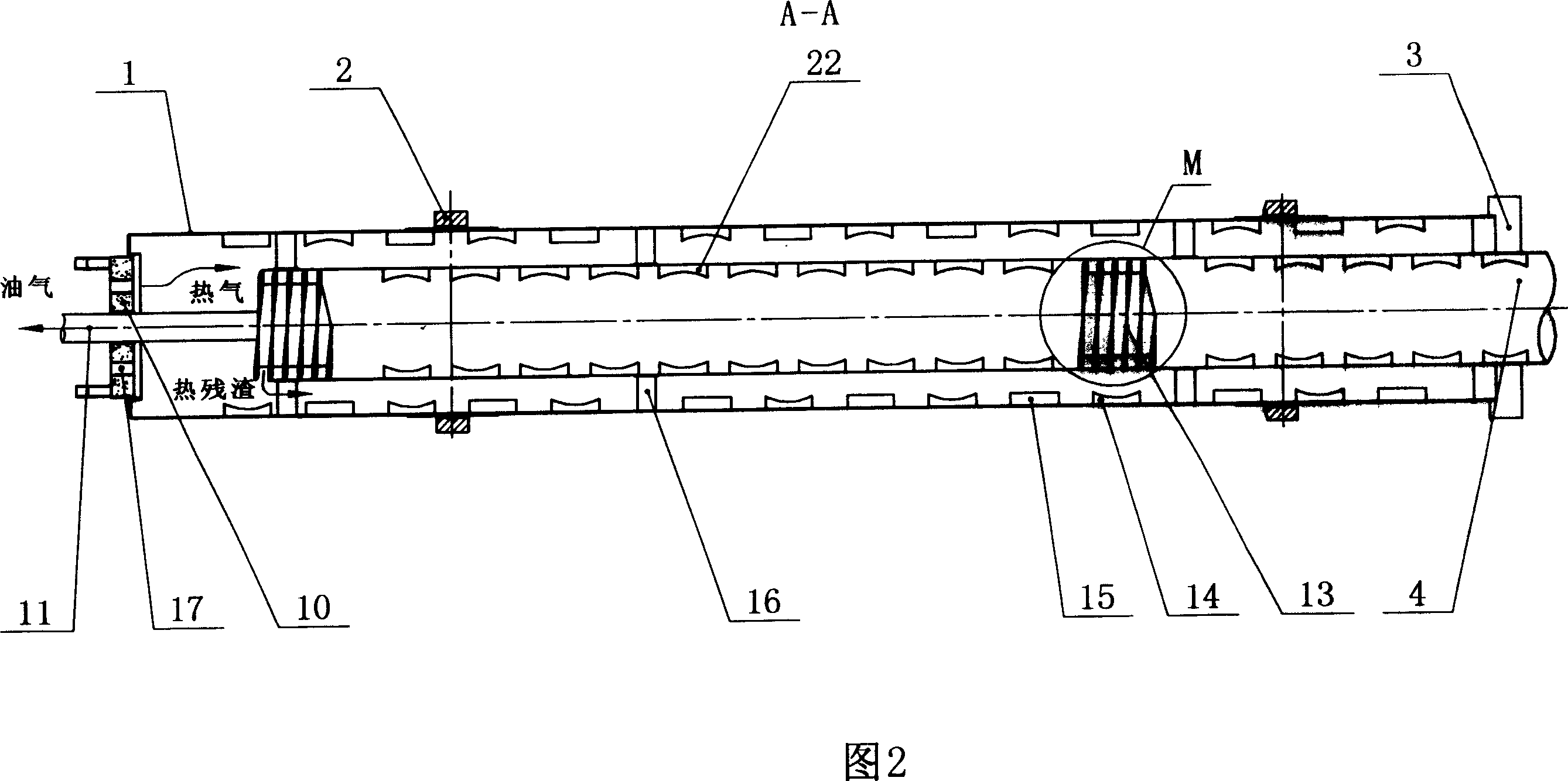
A return flow retorting open hearth furnace is made of inside and outside barrels, built in material encapsulating device, supporting device and drive device. The residue heat of oil contained solid material after retorting can be recovered with improved heat efficiency and reduced energy consumption.
Owner:贲道春
Heat accumulation type rotary hearth furnace-wet separation-buried arc furnace nickel ore smelting method
Owner:北京锦泰诚瑞科技发展有限公司
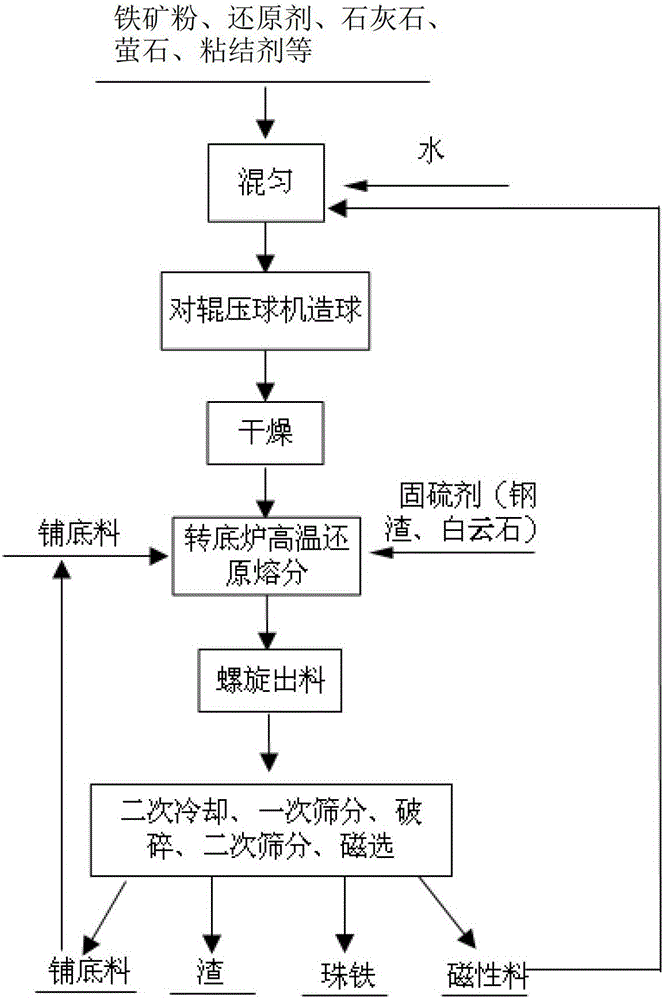
A method for producing low-sulfur steelmaking pig iron using a rotary hearth furnace
The invention relates to a method for producing low-sulfur pig iron for steel manufacture by using a rotary hearth furnace. The method uses low grade iron ore powder, a carbonaceous reducing agent, limestone, fluorite, soda and an organic binder as raw materials for pelletizing; the materials are subjected to preheating, reduction, melt-phase separation and cooling in the rotary hearth furnace to realize iron and slag separation; and the materials are discharged, subjected to secondary cooling, first screening, crushing, second screening and magnetic separation to achieve recovery of grate-layer material and separation of iron and slag, so as to obtain high-quality low-sulfur iron beads. The method provided by the invention achieve rapid reduction and melt-phase separation of carbon-containing pellet by adjusting the slag system, adding a sulfur fixing agent and optimizing temperature and air flow in the rotary hearth furnace, so as to obtain the lower-sulfur iron bead, which can be used as fine raw material for electric furnace or converter steelmaking. The method has the advanategs of low temperature for melt-phase separation and short time for high temperature maintenance, thereby reducing energy consumption.
Owner:LAIWU IRON & STEEL GRP
Coating for iron founding and founding method
InactiveCN109365742ARaise the ratioNot easy to stickFoundry mouldsFoundry coresCasting moldSodium silicate
The invention discloses a coating for iron founding and a founding method. The coating comprises the following components including sodium silicate, talcum powder, argil, white clay, microcrystallinewax and a siloxane compound. Iron ore and waste iron are added into an open-hearth furnace, and argon is introduced; the temperature is increased till the iron ore and the waste iron are all molten, apreheated smelting agent is added; and after the preheated smelting agent is added, stirring is carried out for 5 min to 8 min till uniform stirring is achieved; surface dross is skimmed, the furnacetemperature is reduced to 800 DEG C, a refining agent is added for refining, a casting mold is preheated to range from 100 DEG C to 150 DEG C, a coating is sprayed, and the casting mold is dried at the temperature being 150 DEG C for standby application; and molten iron is poured into the mold, and demolding is carried out after cooling. The coating is simple in ratio and is not prone to adheringto the surface of pig iron; and after the coating is adopted, the surface of the mold is directly coated with the coating, operation is simple, the demolding speed can be increased, and operation time is greatly saved.
Owner:徐州善势信息科技有限公司
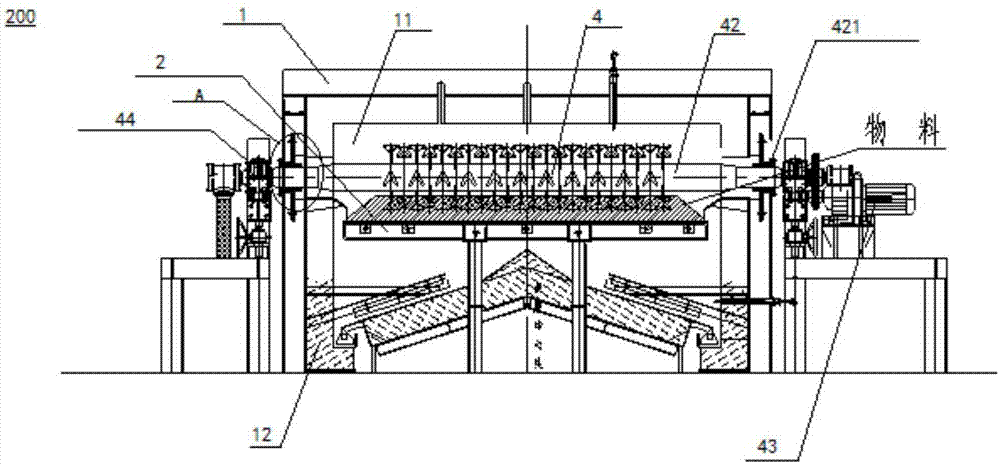
Rotary hearth furnace
InactiveUS20120214118A1Improve the mixing effectMaximizes timeMuffle furnacesRetort furnacesCombustible gasHearth
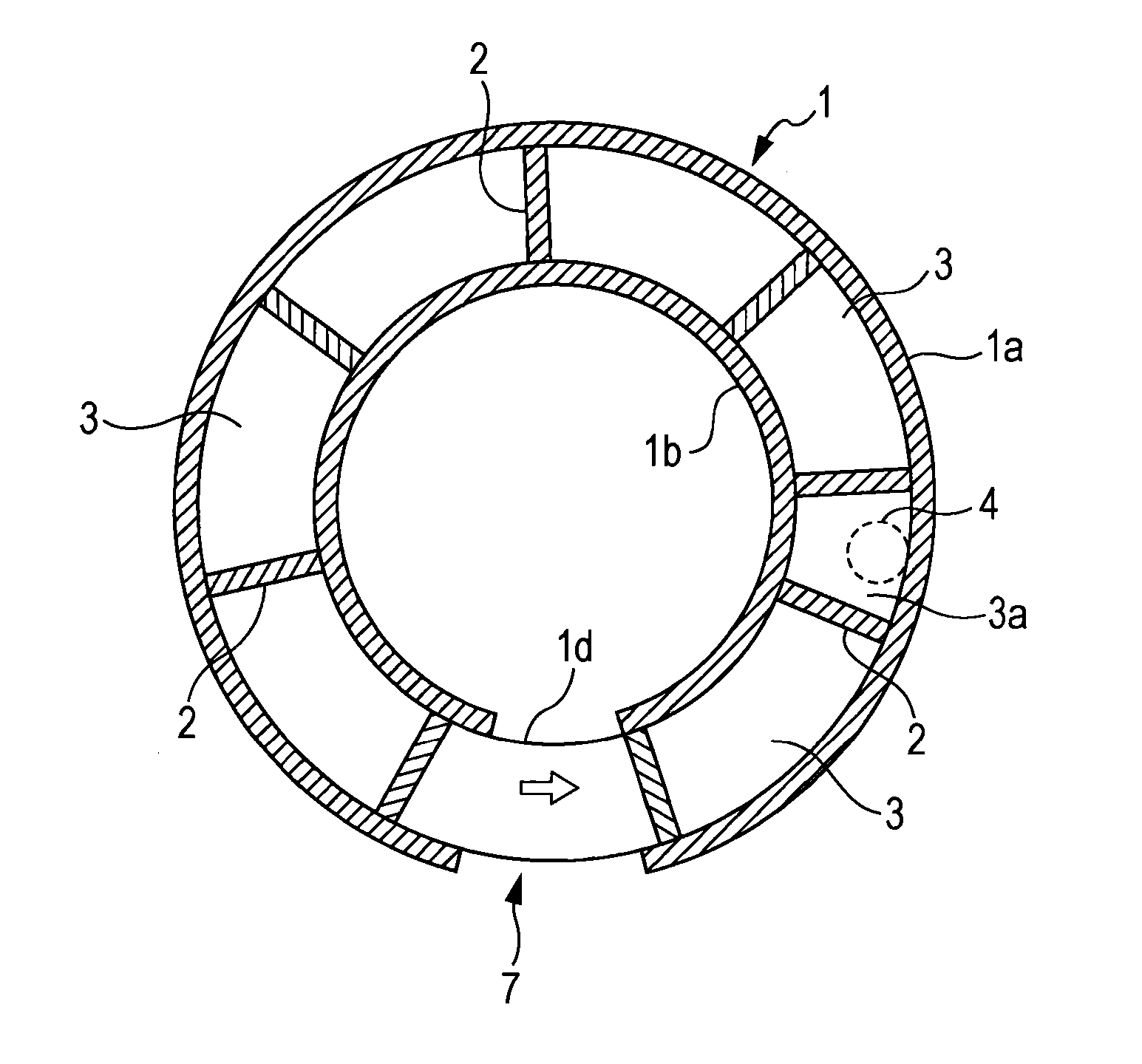
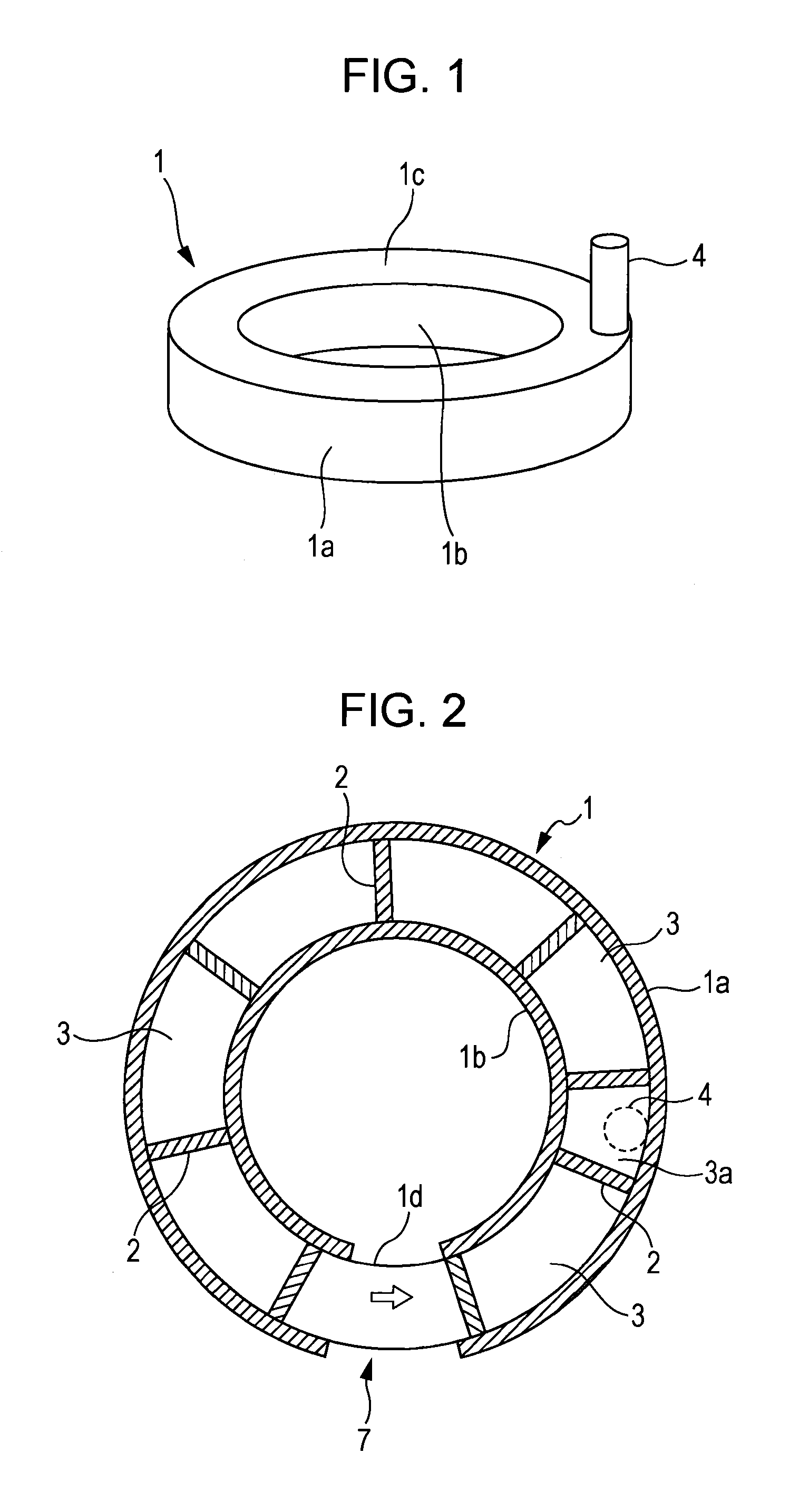
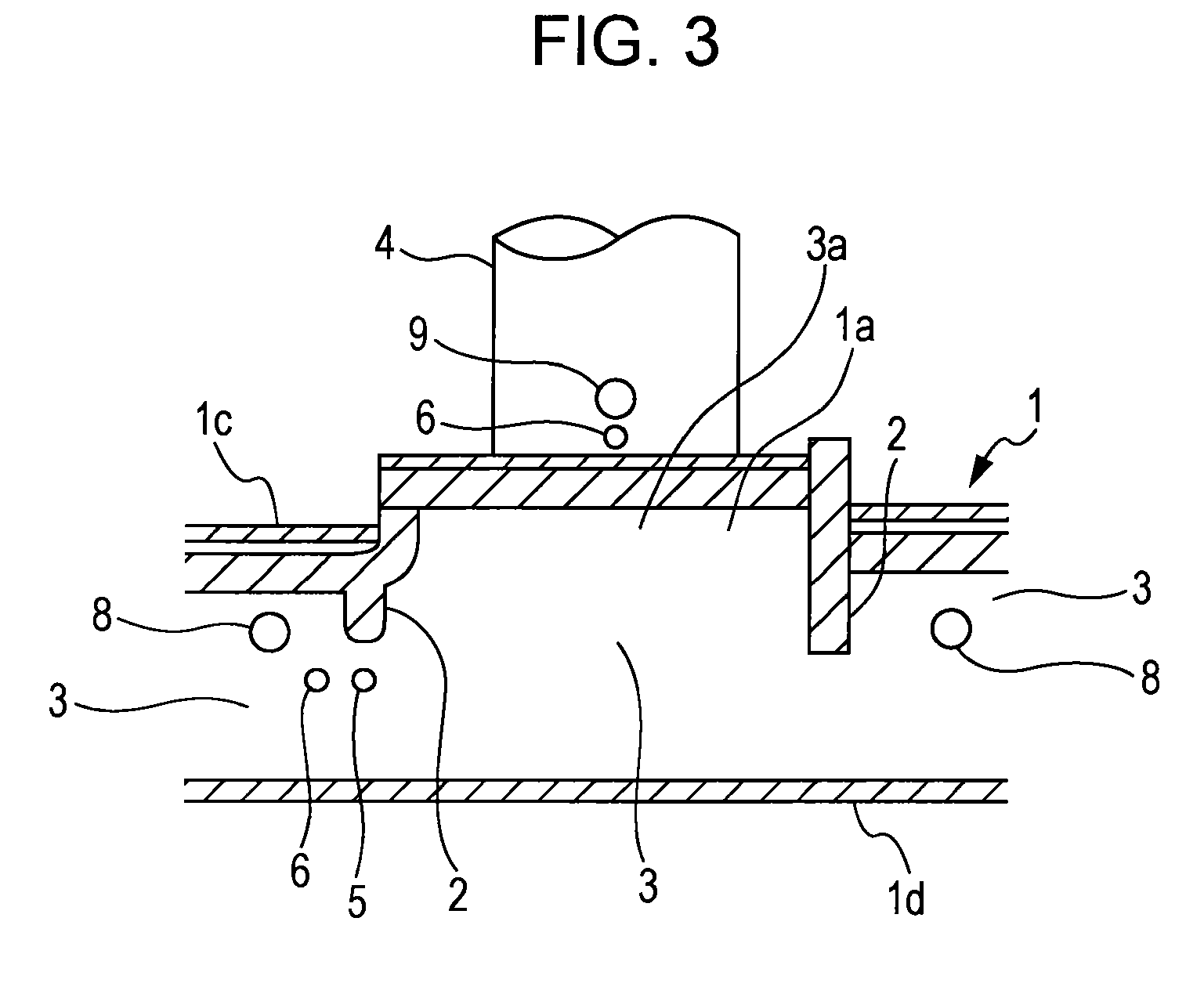
Provided is a rotary hearth furnace which can stir exhaust gas within a furnace, to efficiently burn flammable gas within the exhaust gas and to efficiently heat an object to be heated, and which can contribute to reduction of specific energy consumption and improvement of productivity. A rotary hearth furnace (1) has therein a series of zone spaces (3) which are divided by vertical walls (2) hanging from a ceiling (1c). Among the zone spaces (3), the zone space to which an exhaust gas duct (4) is attached is constructed as an exhaust zone (3a). An oxygen-containing gas supply unit (5) is provided in the vicinity of the lower edge of the vertical wall (2) which divides the exhaust zone (3a) from the other zone spaces (3). Further, the exhaust gas duct (4) is disposed on the outer periphery side or the inner periphery side from the center of the width of the zone space (3).
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Flyash ceramisite sintered open-hearth furnace
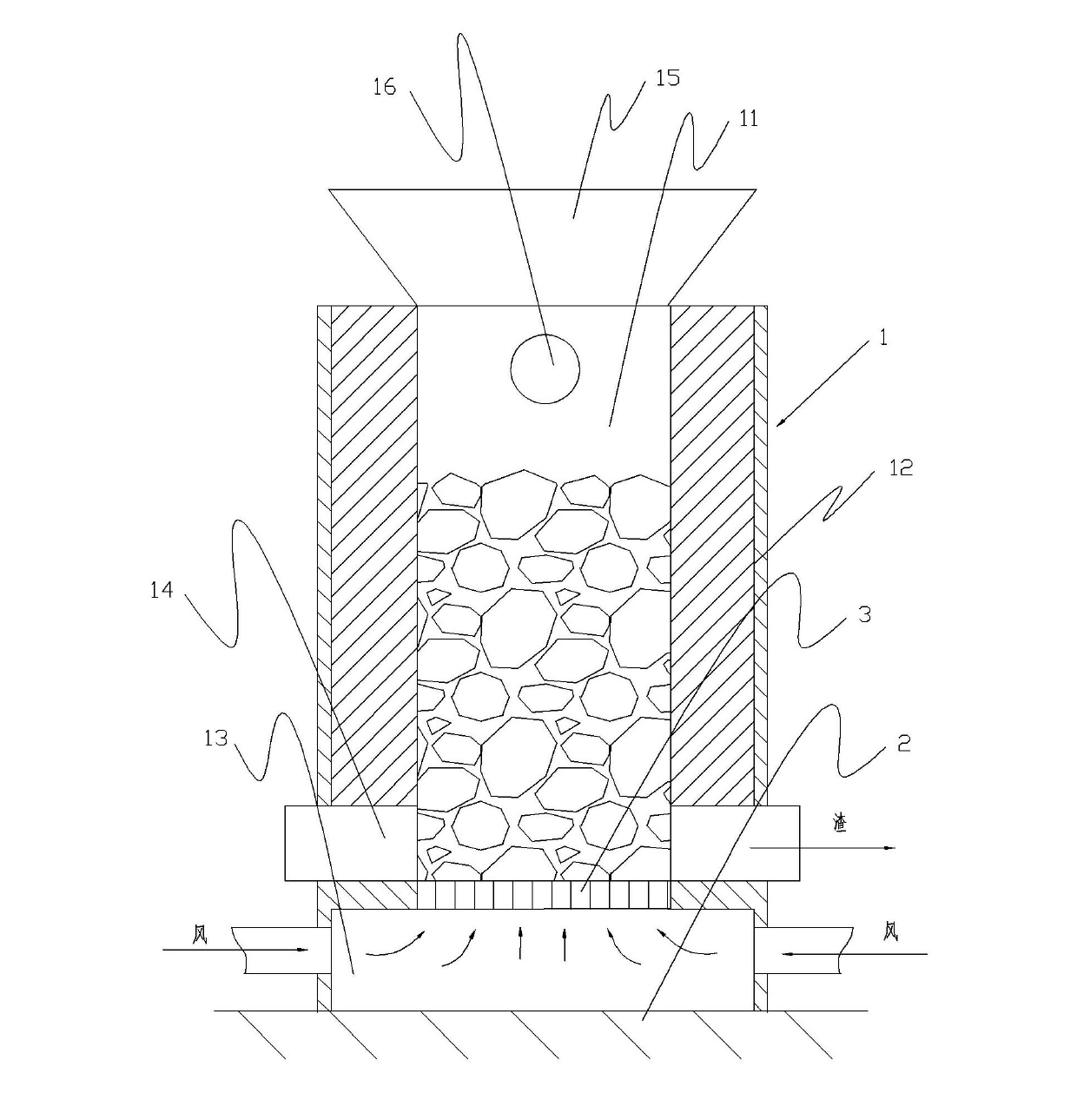
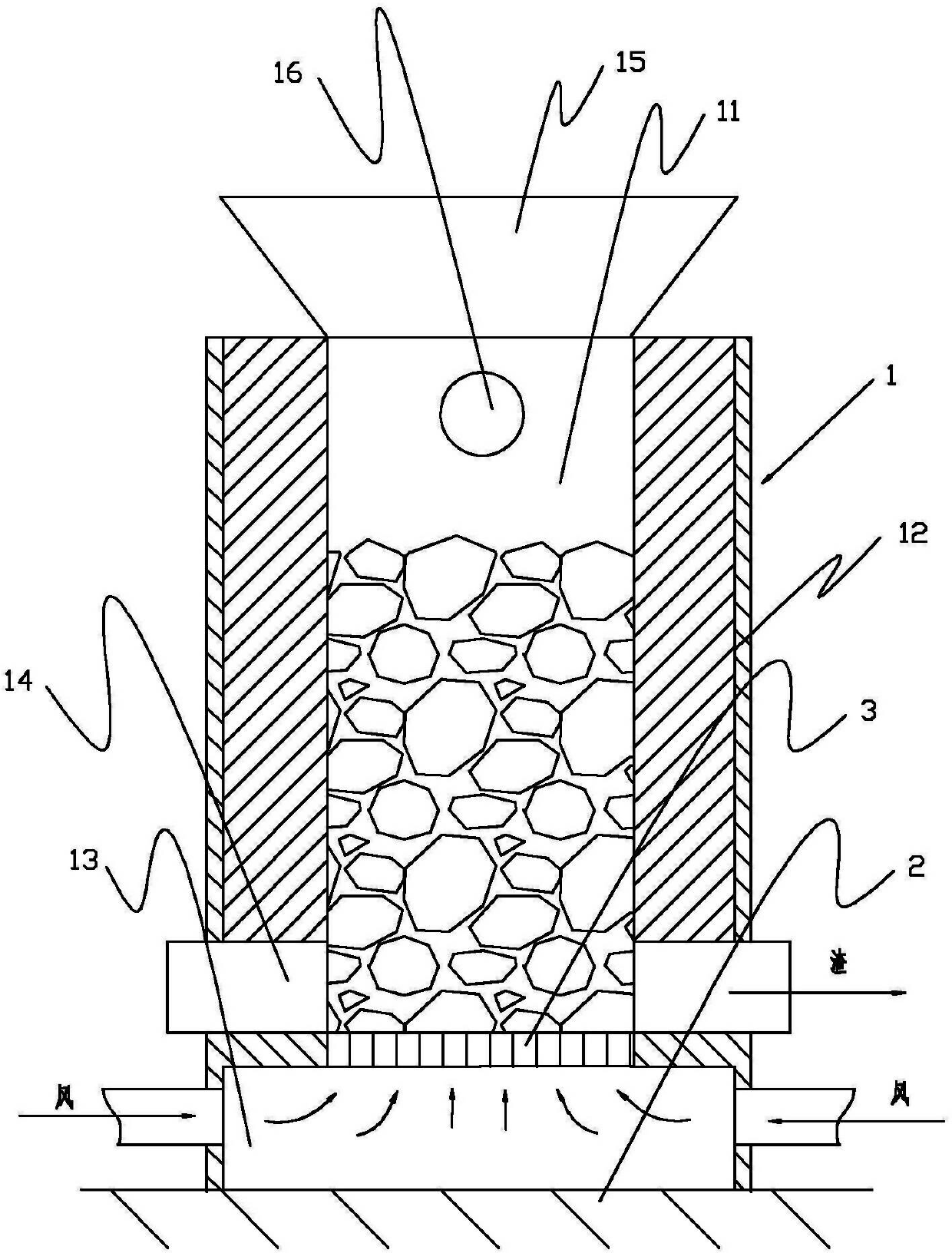
ActiveCN100458338CAgglomerates burn evenlyQuality improvementLighting and heating apparatusCombustion chamberBottom gate
Owner:CHINA CHEM ENG SECOND CONSTR
Rotary hearth furnace
PendingCN106698370AEfficient use ofGuarantee product qualityRaw phosphate material treatmentPhosphoric acidEngineeringFlue
The invention discloses a rotary hearth furnace which comprises an annular furnace body, a rotatable annular hearth, a plurality of nozzles and a plurality of radiation tubes, wherein the annular hearth is arranged on the lower portion of the annular furnace body, located between the inner side wall and the outer side wall and sequentially divided by partitions in the rotating direction of the annular hearth into a feeding section, a reaction section and a discharging section. The feeding section is provided with a feeding component, the reaction section is provided with a flue outlet, and the discharging section is provided with a discharging component. The plurality of nozzles are arranged on the reaction section along the circumference. The plurality of radiation tubes are arranged on the reaction section along the circumference. By arrangement of the radiation tubes, reduction reaction and oxidation reaction are divided clearly, and the reduction reaction and the oxidation reaction are performed smoothly respectively on the premise of guarantee efficient utilization of heat energy and atmospheres required for the reduction reaction and the oxidation reaction respectively.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE METALLURGICAL DESIGN INST
Direct reduction process of iron ore powder with carbon porous block
ActiveCN104195276BImprove internal and external heat transfer efficiencyImprove reduction efficiencyFluidised-bed furnacesTunnel kilnIron powder
Owner:临泉县非凡装饰工程有限公司
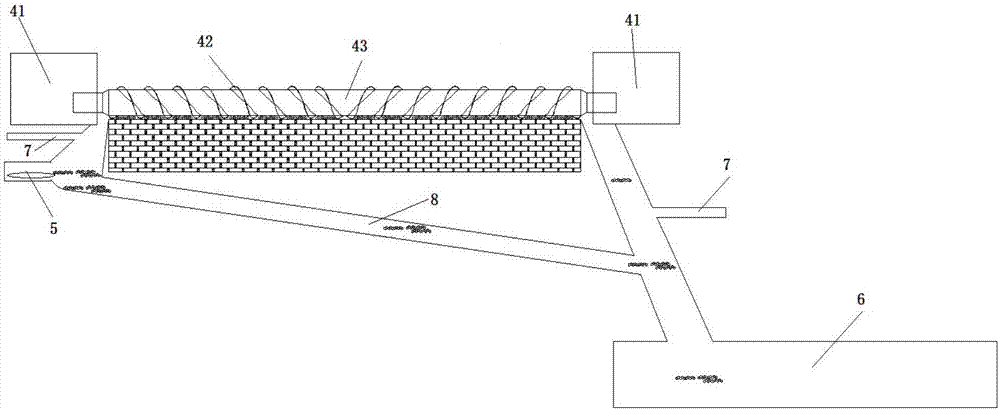
Burning pipeline system for rotary hearth furnace
The invention discloses a burning pipeline system for a rotary hearth furnace. The burning pipeline system for the rotary hearth furnace comprises a combustion-supporting medium conveying pipeline, a fuel medium conveying pipeline and a valve group consisting of a plurality of valves, wherein the valve group is arranged on a cover body of the rotary hearth furnace section by section; the combustion-supporting medium conveying pipeline and the fuel medium conveying pipeline are independently and respectively connected with the valves in the valve group section by section; and the number of sections of the combustion-supporting medium conveying pipeline and the fuel medium conveying pipeline is the same as the number of sections of the valve group. By adopting the burning pipeline system ofthe rotary hearth furnace and using the sectioned valve group arranged on the cover body of the rotary hearth furnace, the valves independently exist in groups and sections; meanwhile, independent control over the quantity of the gas conveyed to each valve according to different process requirements can be realized by using the combustion-supporting medium conveying pipeline and the fuel medium conveying pipeline which are independently connected with the valves in each section of valve group, so the demanded quantity of the gas of each section in the rotary hearth furnace can be controlled precisely.
Owner:ZHONGYE-CHANGTIAN INT ENG CO LTD
A method for melting copper in a power frequency furnace
ActiveCN105274354BImprove airtightnessImprove energy savingProcess efficiency improvementIngotShaft furnace
The invention discloses a method for melting copper through a line frequency furnace. The method comprises the following steps that 1, a waste copper piece and waste are subjected to primary treatment; 2, screening is carried out; 3, classification is carried out; 4, accessories are fed into furnaces, wherein the accessory I, the accessory II and the accessory III are fed into the shaft furnace, the open-hearth furnace and the line frequency cored copper melting copper to be refined, and a product I, a product II and a product III are obtained; 5, the product I and the product II are transported to a copper continuous casting and rolling unit for casting treatment, a steel rod is obtained, and the product III is placed in a pig casting machine to be machined and treated, and a copper ingot is obtained; and 6, the steel rod in the step 5 is drawn, and a qualified copper piece is obtained. The method for melting copper through the line frequency furnace achieves energy saving and is environmentally friendly, and manufactured steel is good in quality.
Owner:NINGXIA RUIYIN NONFERROUS METAL TECH CO LTD
Process for efficiently processing zinc-containing iron metallurgical dust sludge in rotary hearth furnace
The invention discloses a process for efficiently processing zinc-containing iron metallurgical dust sludge in a rotary hearth furnace. A pellet material made of zinc-containing iron metallurgy dust sludge or mineral is placed on a moving bed for drying treatment, pre-heat treatment and fuel igniting treatment in sequence, the pellet material is preheated by introducing hot air generated by heat exchange of the rotary hearth furnace gas, the hot air generated by secondary combustion of the rotary hearth furnace gas is introduced to perform the fuel igniting treatment on the pellet material, and the waste gas generated by the fuel igniting treatment is used for pellet drying; the pellet material after the fuel igniting treatment is transferred into the rotary hearth furnace and directly enters a reduction stage, and zinc is collected, condensed and recycled from the flue gas. The process overcomes the problem of thin material and low production efficiency caused by heat transfer throughradiation of a traditional rotary hearth furnace process, realizes recycling of gas resources, reduces energy consumption and secondary pollution, and efficiently cleans the zinc-containing iron metallurgical dust sludge in the rotary hearth furnace.
Owner:广西锐异资源循环工程技术有限公司
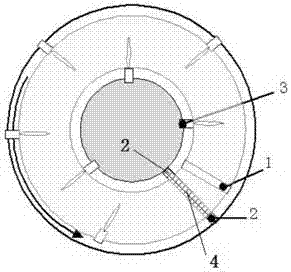
Rotary hearth furnace
PendingCN107881283AAvoid stickingReduce energy consumptionRotary drum furnacesProduction rateCombustor
The invention relates to a rotary hearth furnace. The rotary hearth furnace comprises a furnace body, a furnace bottom, a discharging device, a burner and a material water quenching device, and the cross section of the furnace body is in a circular ring shape, the furnace body is provided with a feeding opening, and discharging openings are formed at the bottoms of the inner ring side wall and theouter ring side wall of the furnace body; an annular reaction space is defined by the inner ring side wall and the outer ring side wall of the furnace body and the upper surface of the furnace bottom; the burner is mounted on the side wall of the furnace body, the discharging device is mounted on the furnace body, and a discharging opening body of the discharging device communicates with the discharging openings; and the material water quenching device is arranged on the outer side of the furnace bottom and comprises a material water quenching channel and a water quenching pool which communicate with each other, and the material water quenching channel communicates with the discharging openings. According to the rotary hearth furnace, the discharging device is designed to be the mode of discharging on both sides, materials in the rotary hearth furnace are completely discharged in time to prevent the furnace bottom and the furnace wall from being jammed due to multiple times of heatingand melting of the stored materials, sensible heat of the materials is fully utilized, and the rotary hearth furnace has the characteristics of long service life, high productivity and low energy consumption.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE METALLURGICAL DESIGN INST
Rotary hearth furnace
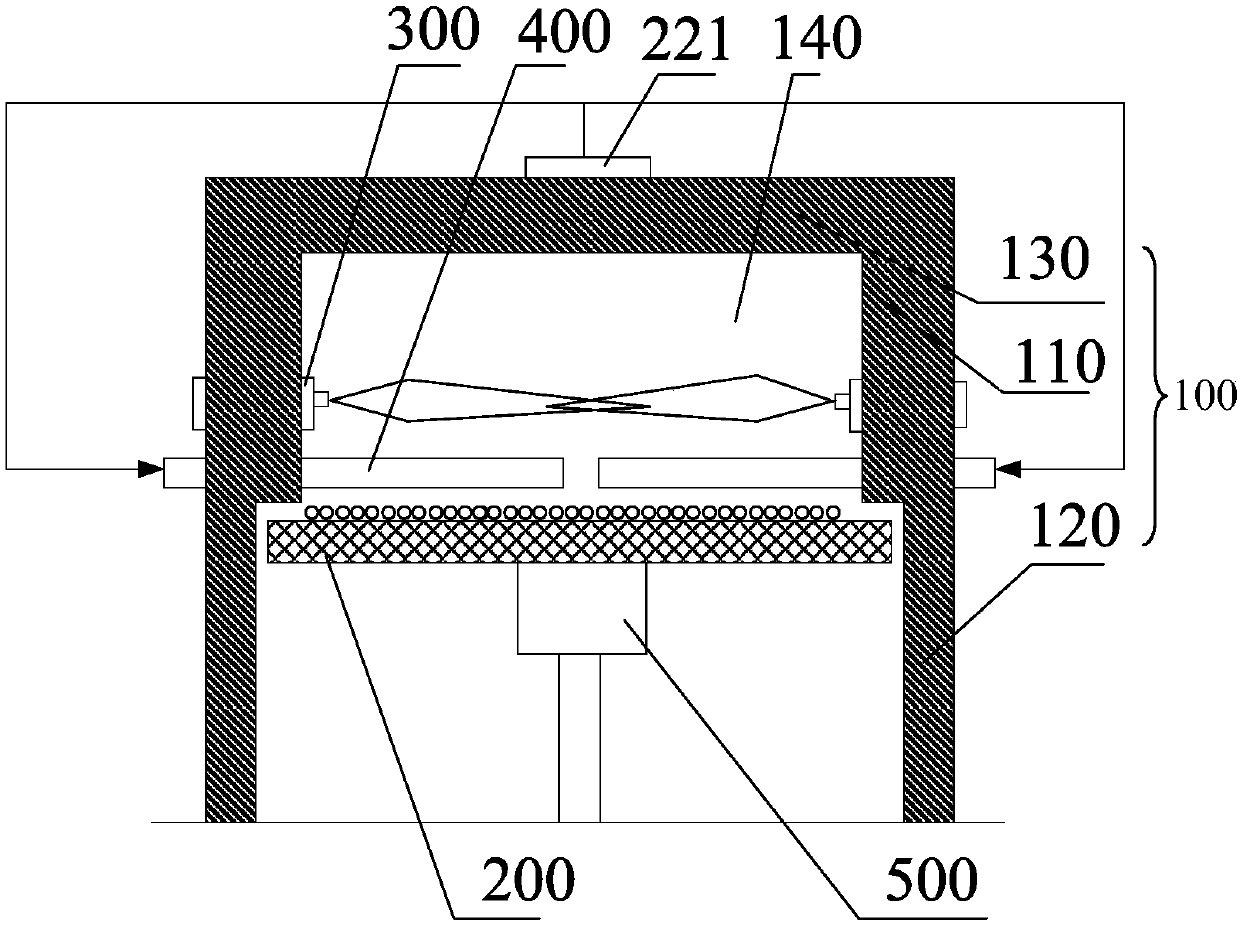
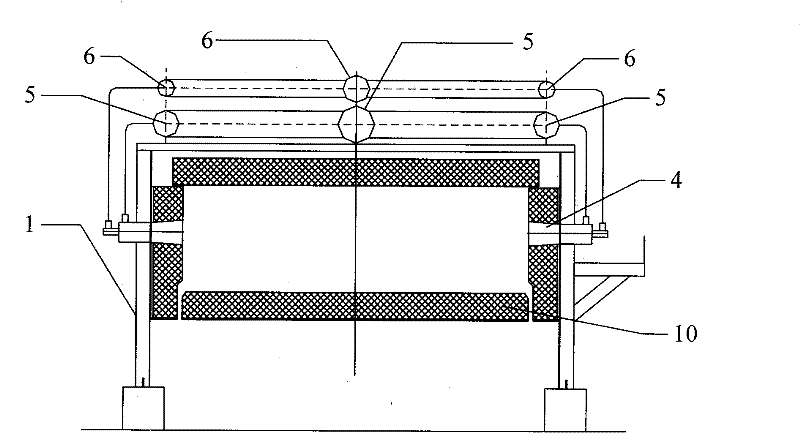
The invention discloses a rotary hearth furnace, which comprises: an annular furnace body, a hearth, a burner and a material turning device. The furnace body defines a furnace chamber; the hearth is arranged in the furnace chamber, and the hearth rotates horizontally around the central axis of the furnace body; the burner is arranged on the furnace body; the turning The charging device includes a turning member for turning up materials on the hearth, and the turning member is arranged in the furnace cavity and above the hearth. According to the rotary hearth furnace of the embodiment of the present invention, by setting the turning member on the upper part of the hearth, the turning member can turn the material during the movement of the material, so that the upper and lower layers of materials are scattered and rearranged, and the heating device can realize the Uniform heating of materials, thereby improving the production efficiency and product quality of the rotary hearth furnace.
Owner:SHENWU TECH GRP CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com