Bottom-blowing oxidation rough smelting technology for antimony ore and metallurgical furnace
A technology of antimony ore and metallurgical furnace, which is applied in the field of antimony ore bottom blowing oxidation roughing and roughing process and metallurgical furnace, can solve the problems of low recovery rate, high slagging rate, low smelting recovery rate, etc., and achieve recovery rate improvement, The effect of low antimony loss rate in slag and uniform distribution of furnace gas
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
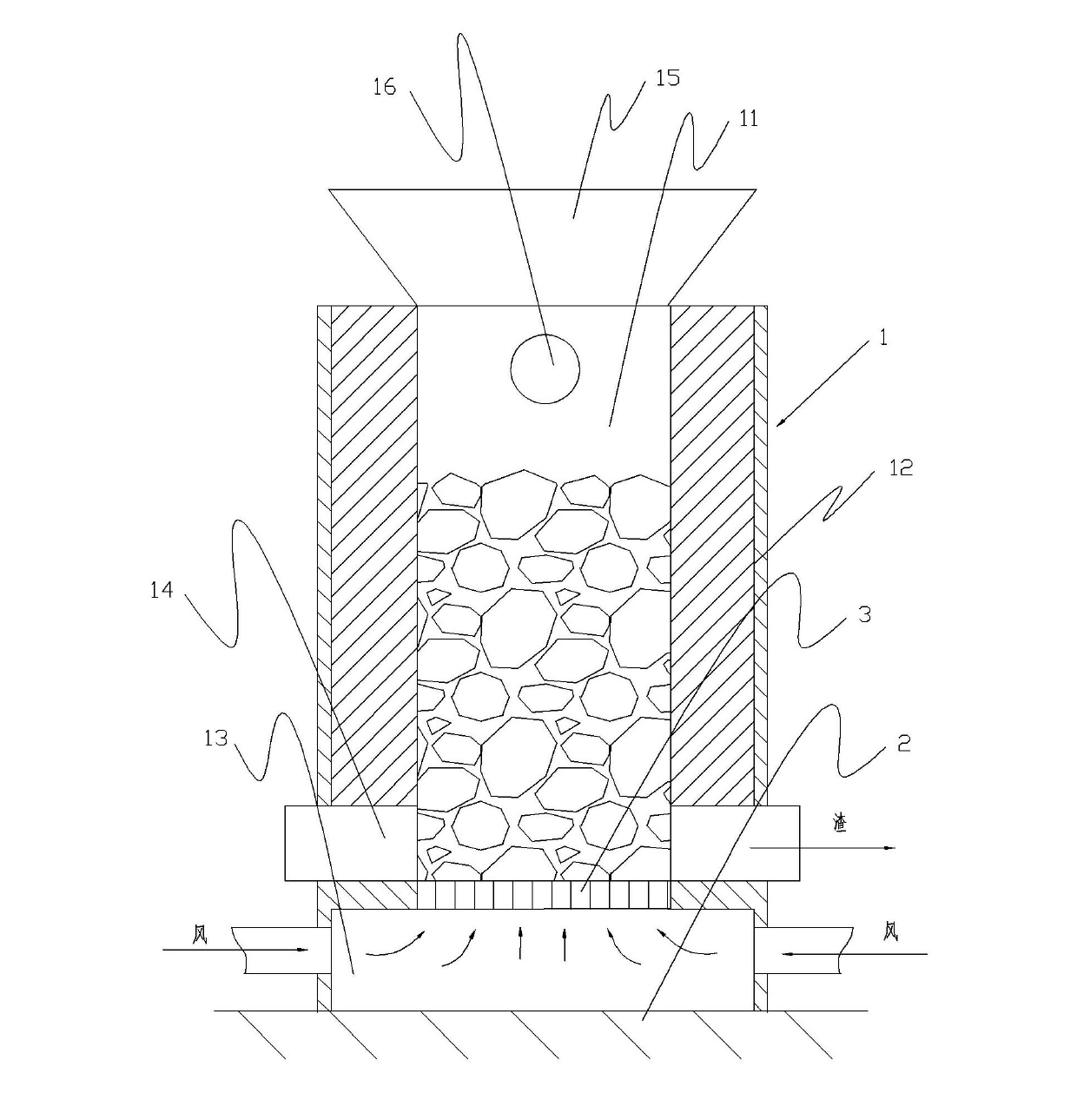
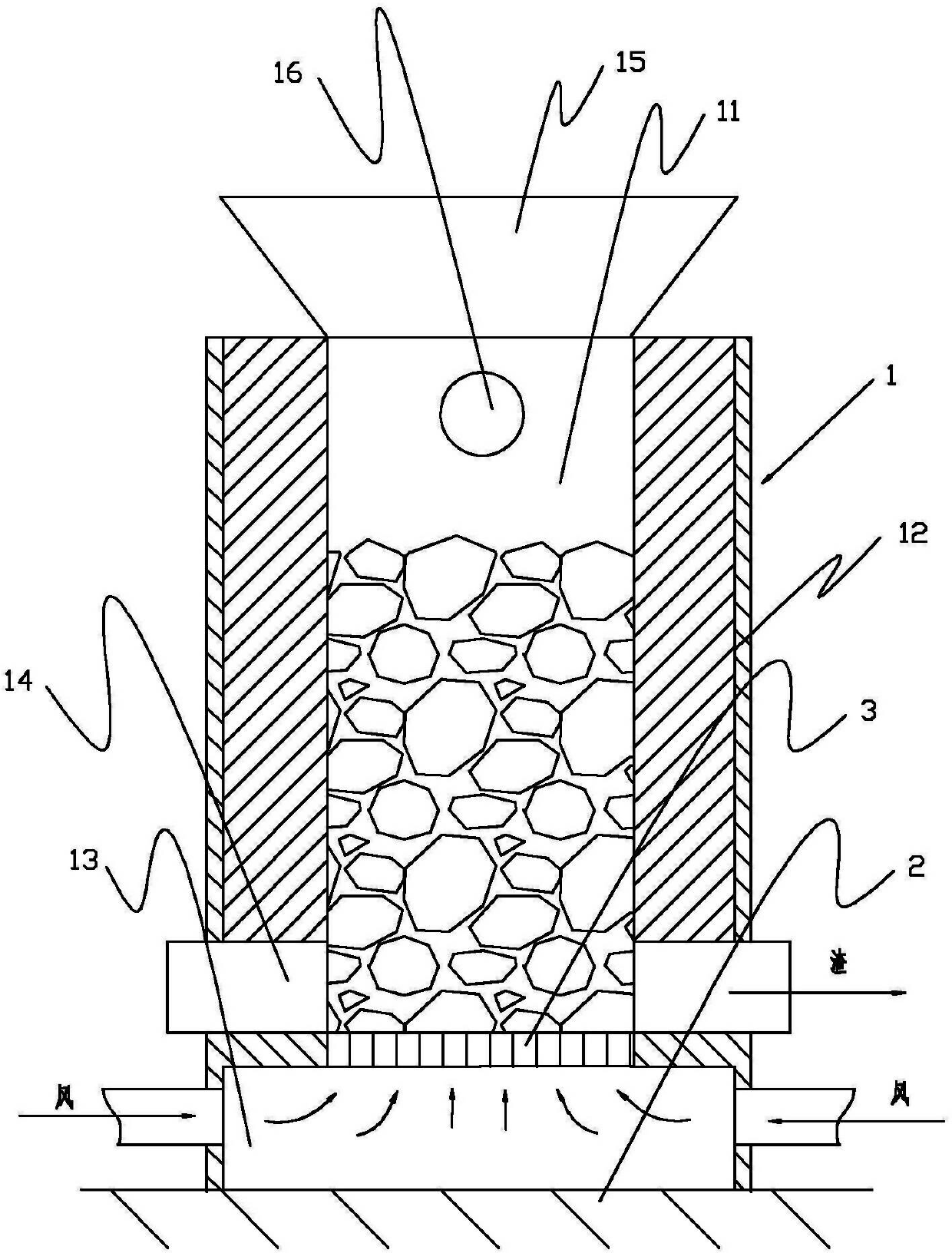
[0019] The heating and feeding method of the method of the present invention is the same as that of the existing blast furnace, which is also supplied by coking coal or lump coal, and the oxygen required for the reaction is supplied by a Roots blower or a centrifugal fan, and is preheated to 100-500°C in a high-efficiency heat exchanger Finally, air is supplied vertically upwards from the bottom of the furnace body through the bottom plane of the furnace charge. Coking coal and antimony ore charge are fed into the furnace from the top or upper side of the furnace body. The temperature in the central reaction zone of the furnace can reach 1200-1400°C. Condensation dust collection system, the main reaction formula is:
[0020] 2Sb 2 S 3 +9O 2 =2Sb 2 o 3 +6SO 2
[0021] C+O 2 =CO 2
[0022] S+0 2 = SO 2
[0023] 2C+O 2 =2CO
[0024] After the antimony component in the ore is oxidized and volatilized, the gangue component (mainly SiO 2 ) is deposited in the furnace...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com