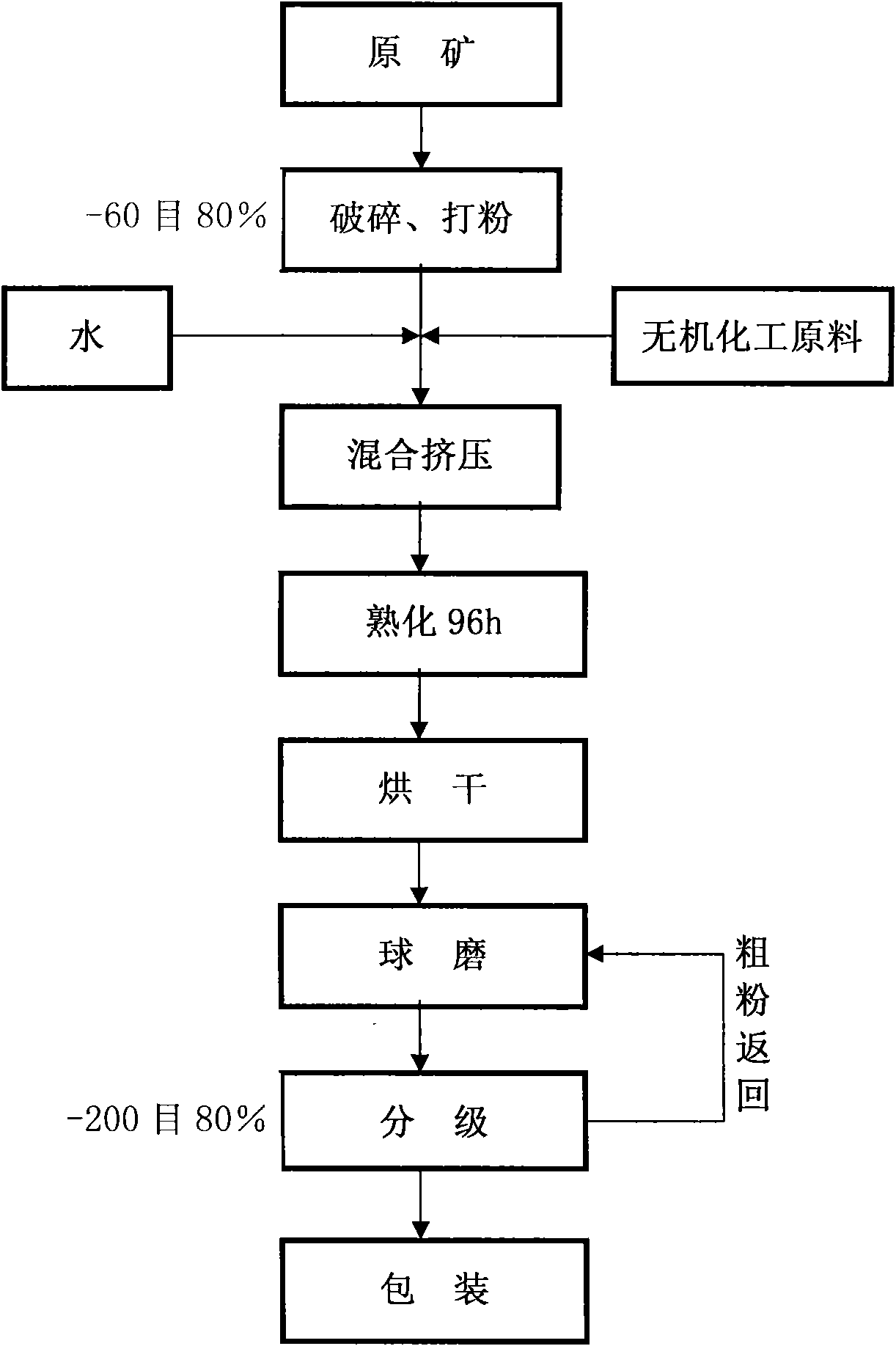
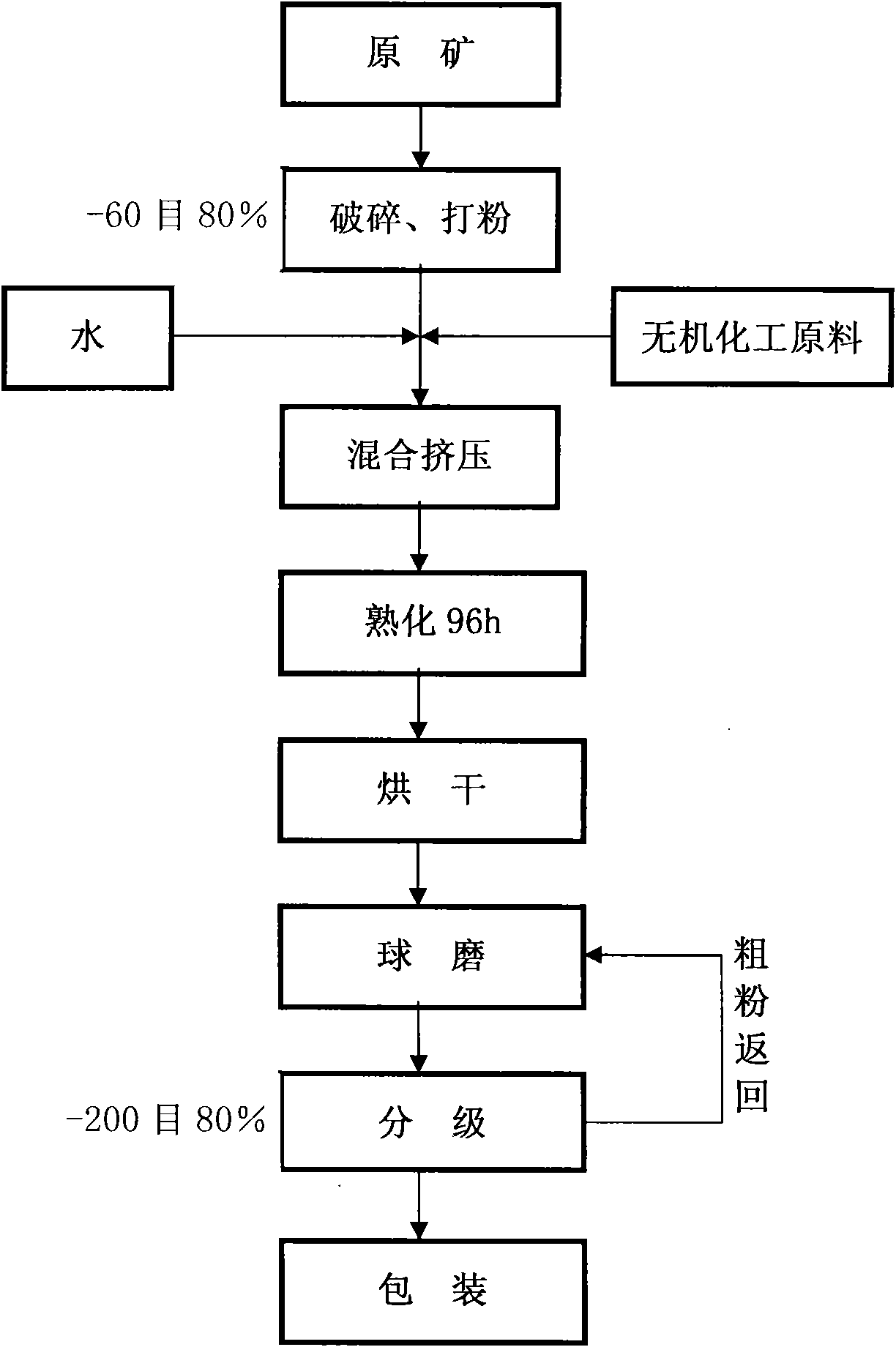
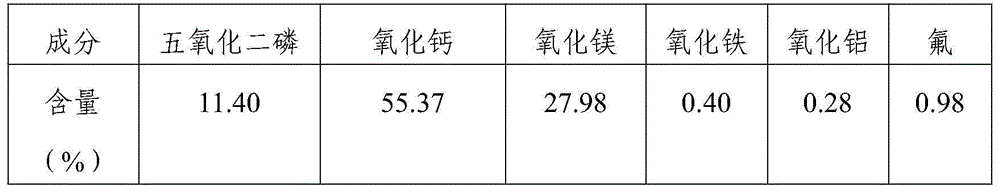
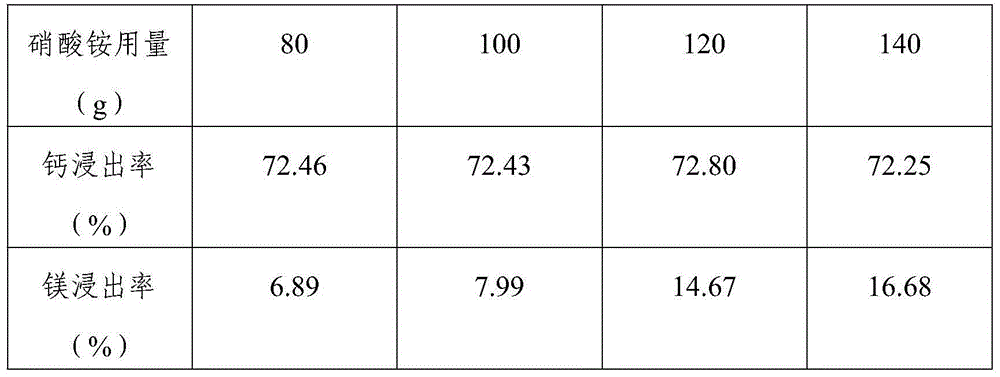
Patents
Literature
242results about "Raw phosphate material treatment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
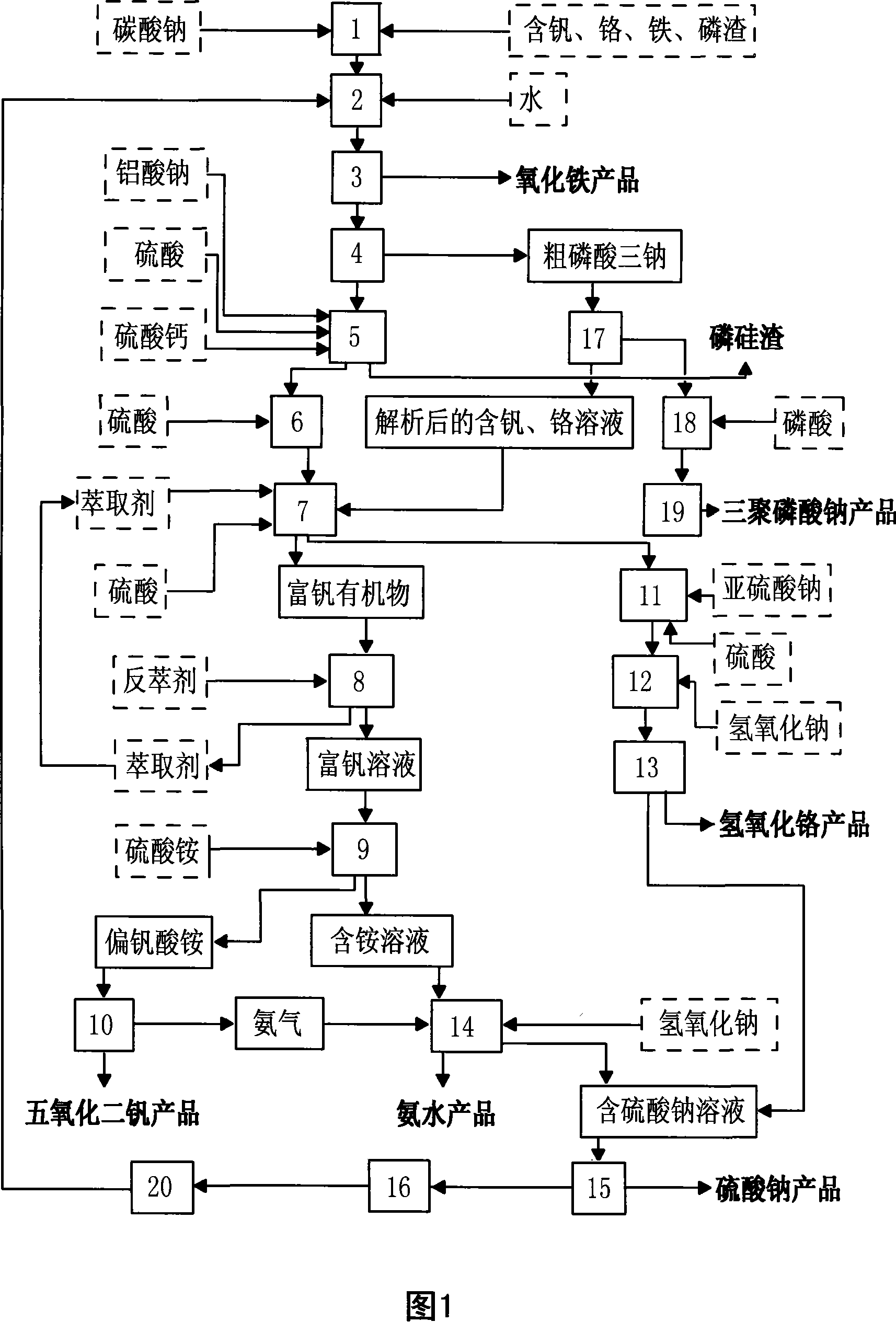
Method of reclaiming chemical industry products by using industrial slag containing vanadium, chromium, iron and phosphorous
ActiveCN101058853ATake advantage ofUsefulRaw phosphate material treatmentProcess efficiency improvementChemical industrySlag
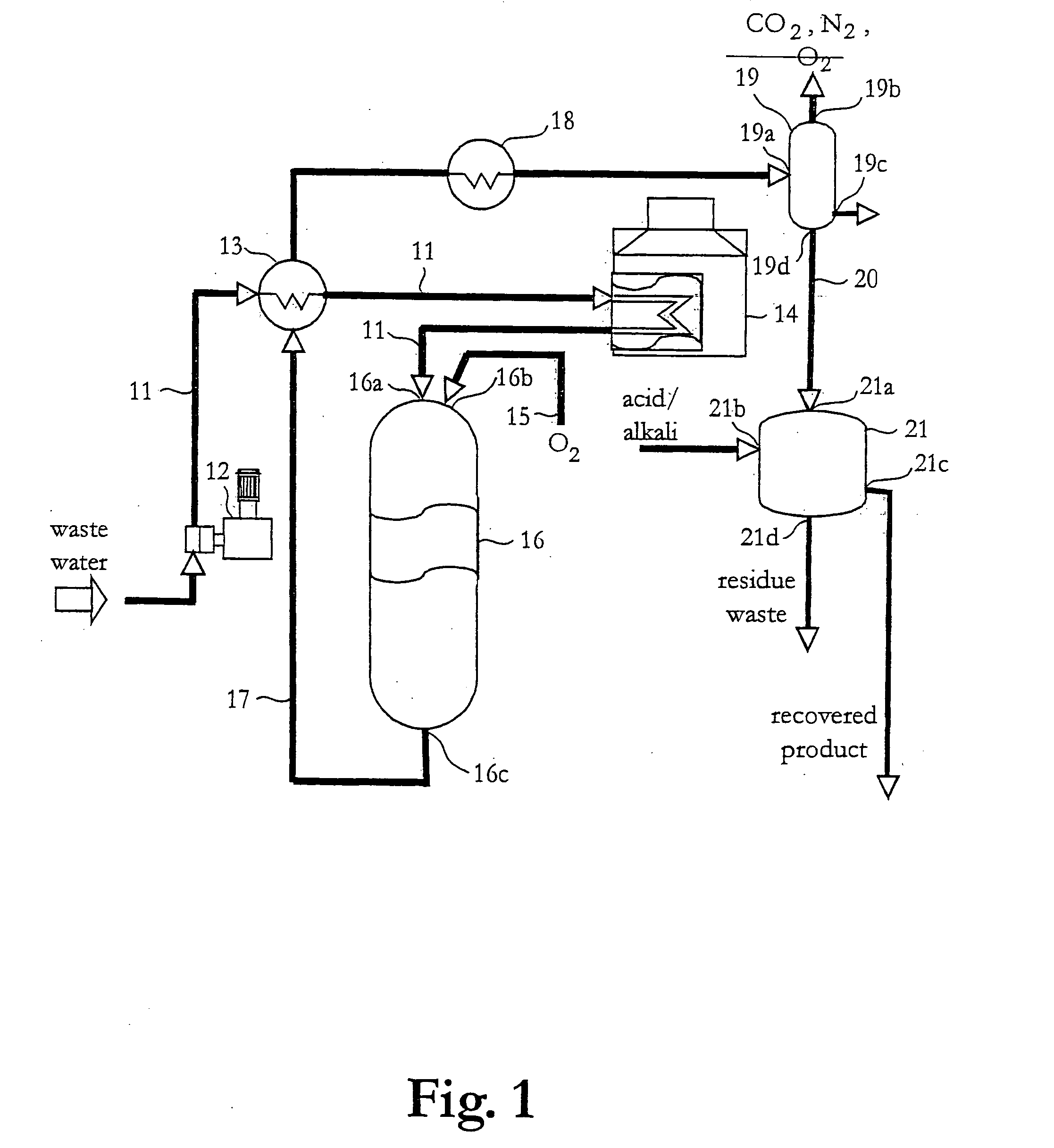
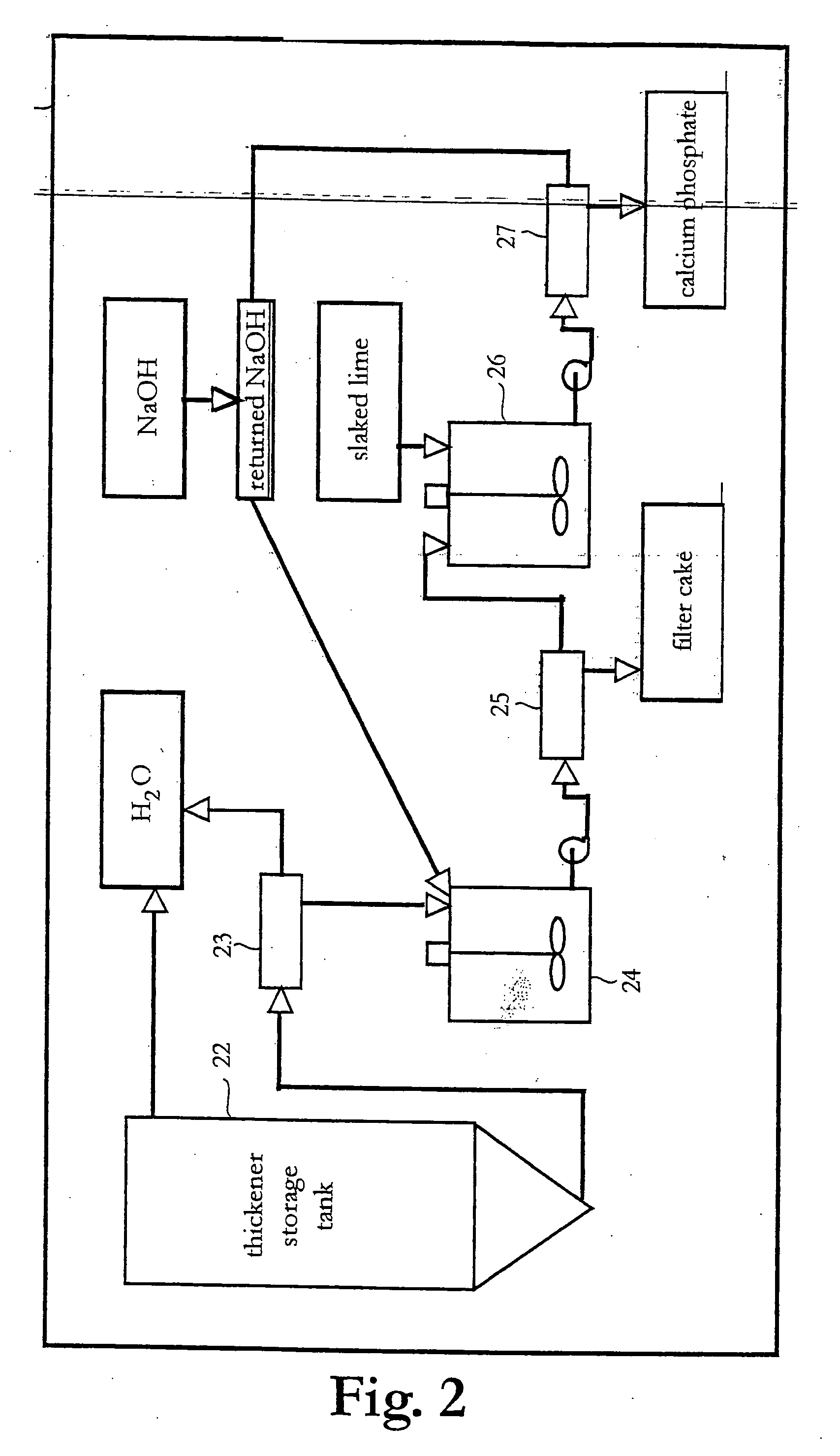
The invention discloses a recovering chemical product method with a V, Cr, Fe and P industrial muck in the chemistry field, which comprises the following steps: roasting raw materials; heating and leaching the clinkers; separating ferric oxide from the solution containing V, Cr, Fe and P; crystallizing the solution in order to removing to P; removing P deeply; removing Si; adjusting the acidity of the solution containing V and Cr; extracting V; extracting V reversely; settling V; roasting metammonium vanadate; reducing Cr; settling chromic hydroxide; separating chromic hydroxide from sodium sulfate; removing NH3; getting sodium sulfate crystallization; purifying sodium sulfate mother liquor; adsorbing V, Cr, tertiary sodium phosphate solution with rough tertiary sodium phosphate refining resin and reacting with phosphoric acid; drying and roasting sodium tripolyphosphate; getting V, Cr, Fe and P from the industrial muck containing V, Cr, Fe and P and separating the secondary product of ammoniacal liquor and sodium sulfate in the heat exchange procedure. The invention saves the energy, which adapts to an industrial appliance.
Owner:辽宁虹京实业有限公司
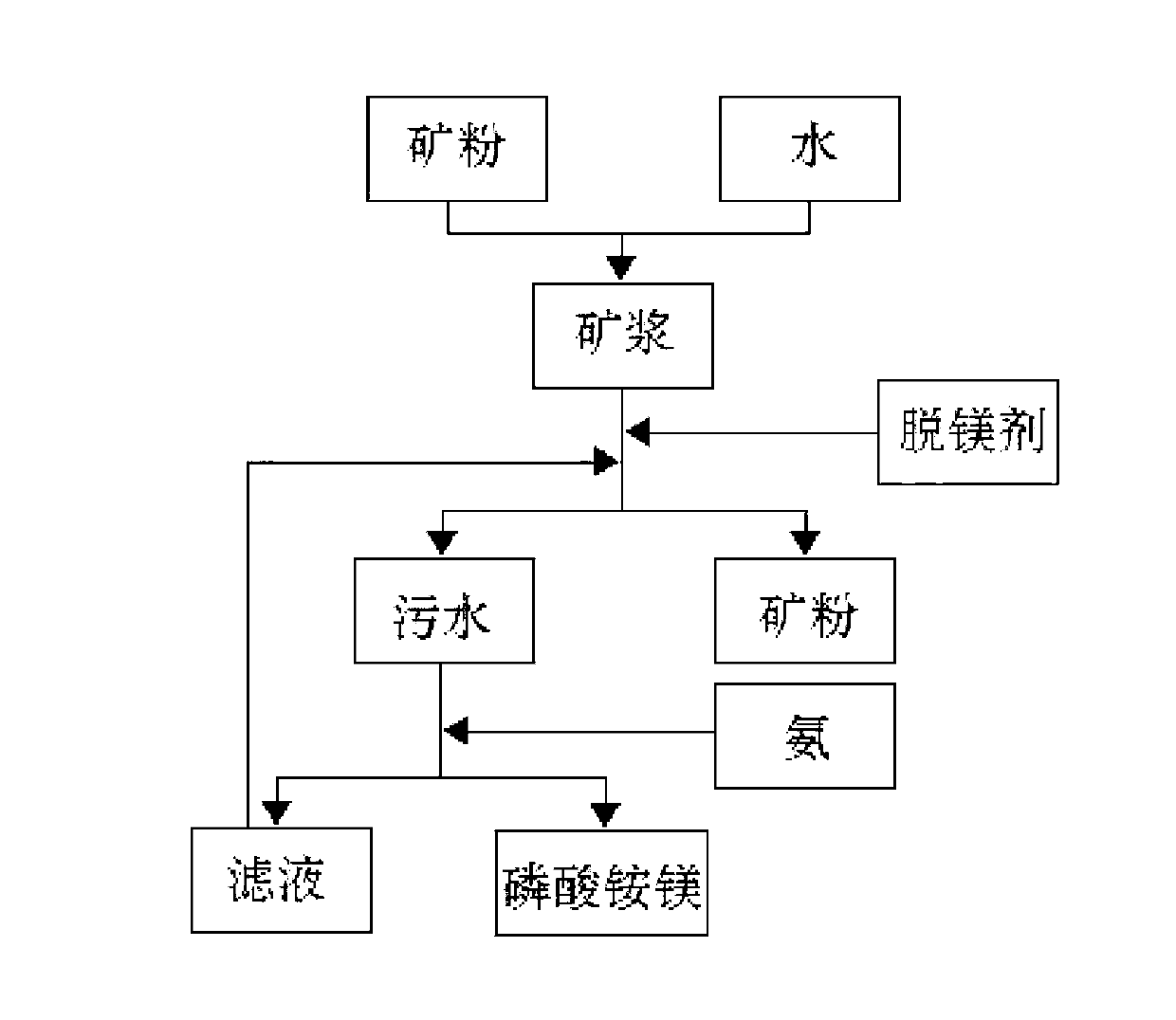
High-magnesium phosphorite de-magging method with by-product magnesium ammonium phosphate
InactiveCN102992284AHigh removal rateReduce contentRaw phosphate material treatmentPhosphoric acidMagnesium ammonium phosphate
The invention discloses a high-magnesium phosphorite de-magging method with a by-product magnesium ammonium phosphate. The method is as below: mixing a mineral powder and water to obtain a pulp; then adding a magnesium removal agent into the pulp for reaction; then separating wastewater and mineral powder after magnesium removal; adding ammonia into the wastewater to generate magnesium ammonium phosphate; filtering to obtain a magnesium ammonium phosphate product; and adding a recycled filtrate from filter into the pulp. The invention has advantages of economical equipment investment and good operating environment; sulfuric acid and / or phosphoric acid is used as a magnesium removal agent, has high removal rate of magnesium, significantly reduces magnesium content in the phosphate, and especially has obvious effect on phosphate with high magnesium content, so as to reduce loss of phosphorus pentoxide in the phosphate; the wastewater can be recycled to save water resource, and causes no impact on the environment; the treated concentrate in a wet production significantly improves bubble phenomenon and filtering performance, so as to improve production capacity and labor productivity of the whole device, and reduce the production cost; and magnesium in the phosphate can be used for production of a magnesium ammonium phosphate slow release fertilizer, and generates good economic benefit.
Owner:GUIZHOU KAILIN GRP CO LTD
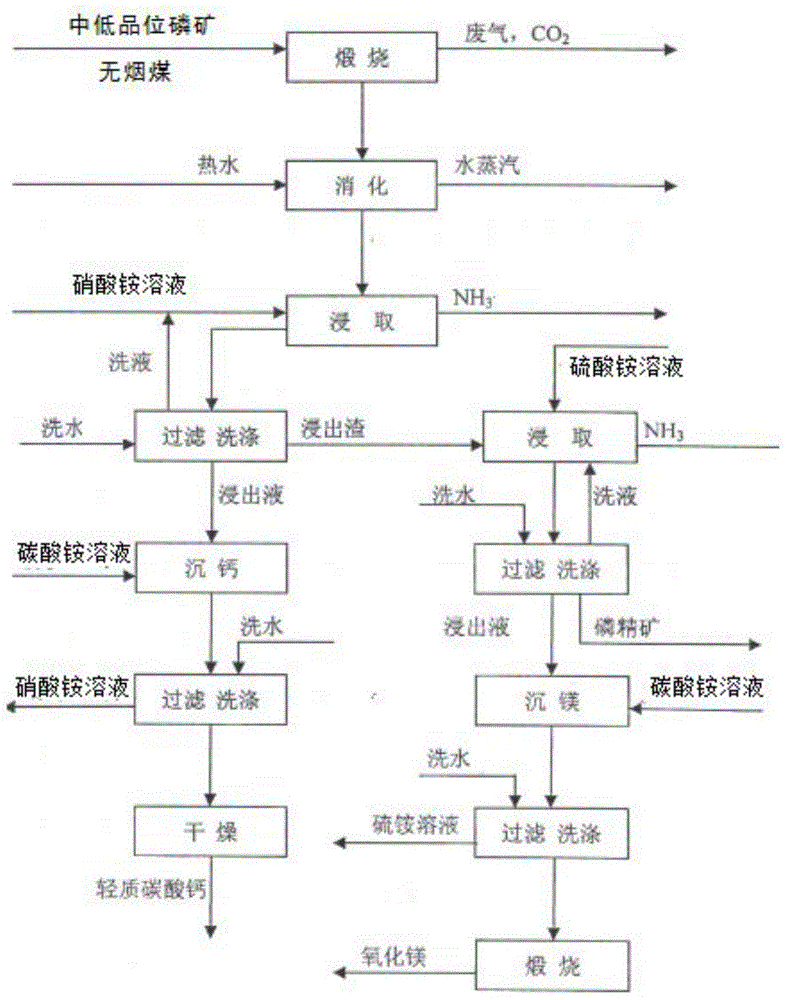
Process for preparing phosphate concentrate and by-products calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide from mid and low-grade phosphate rocks
InactiveCN104876197AEfficient recyclingSolve pollutionCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesRaw phosphate material treatmentAmmonium nitrateAmmonium sulfate
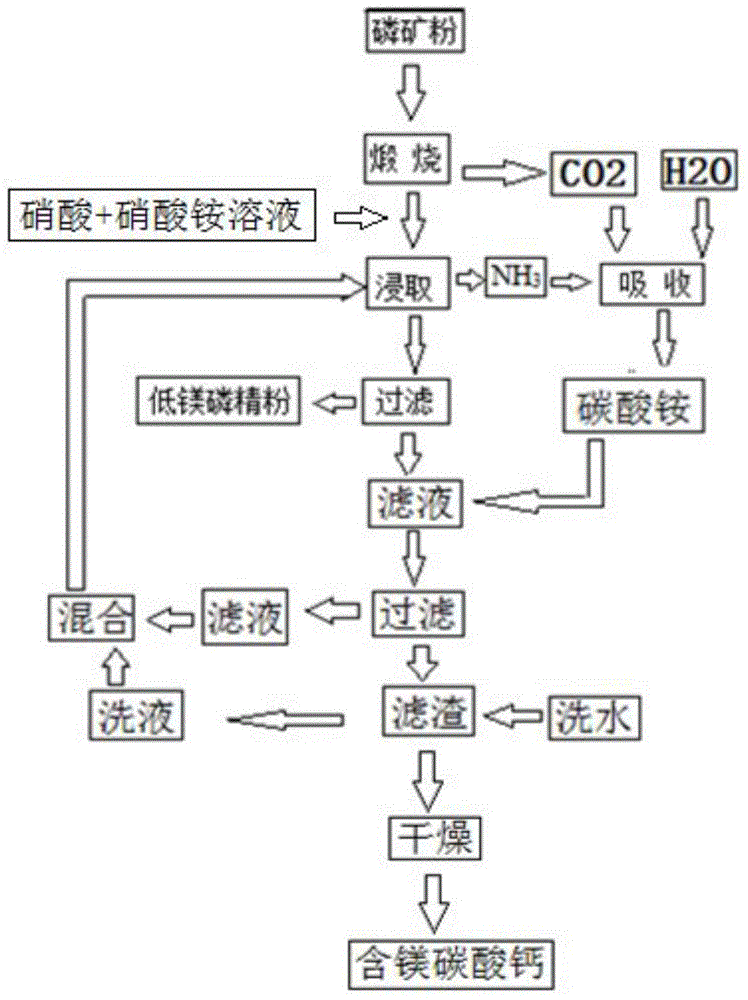
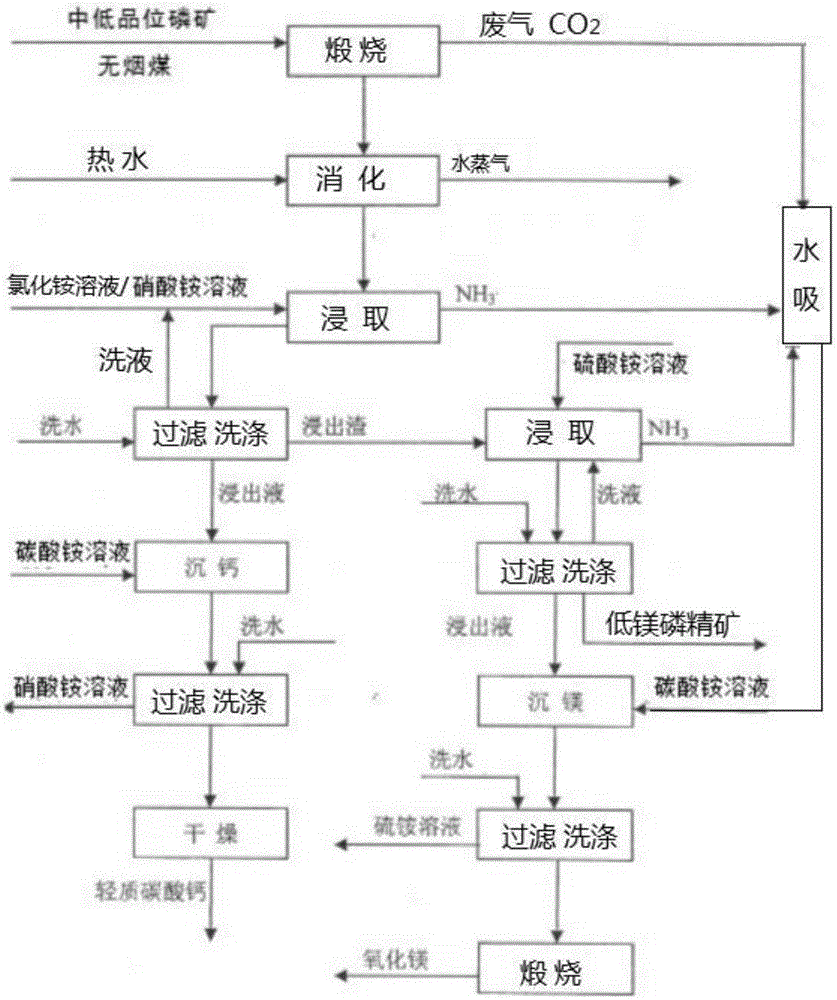
The invention provides a process for preparing phosphate concentrate and by-products calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide from mid and low-grade phosphate rocks, and belongs to the technical field of inorganic chemical industry. The process comprises the following steps: burning mid and low-grade phosphate rocks at 900-1100 DEG C; and then carrying out a series of treatment including digesting, leaching and participating to obtain phosphate concentrate, calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide. By virtue of the process, the phosphorus element is reserved in the prepared phosphate concentrate to the maximal extent; meanwhile, the by-products calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide are generated; calcium elements, magnesium elements and phosphorus elements in the mid and low-grade phosphate rocks are fully utilized; and meanwhile, ammonium nitrate and ammonium sulfate are recycled in the treatment process, so that the target of saving raw materials is reached.
Owner:GUIZHOU RES INST OF CHEM IND
Penicillium, as well as preparation method and application
InactiveCN101434909AReach pollutionReduce pollutionFungiMicroorganism based processesEcological environmentPhosphate
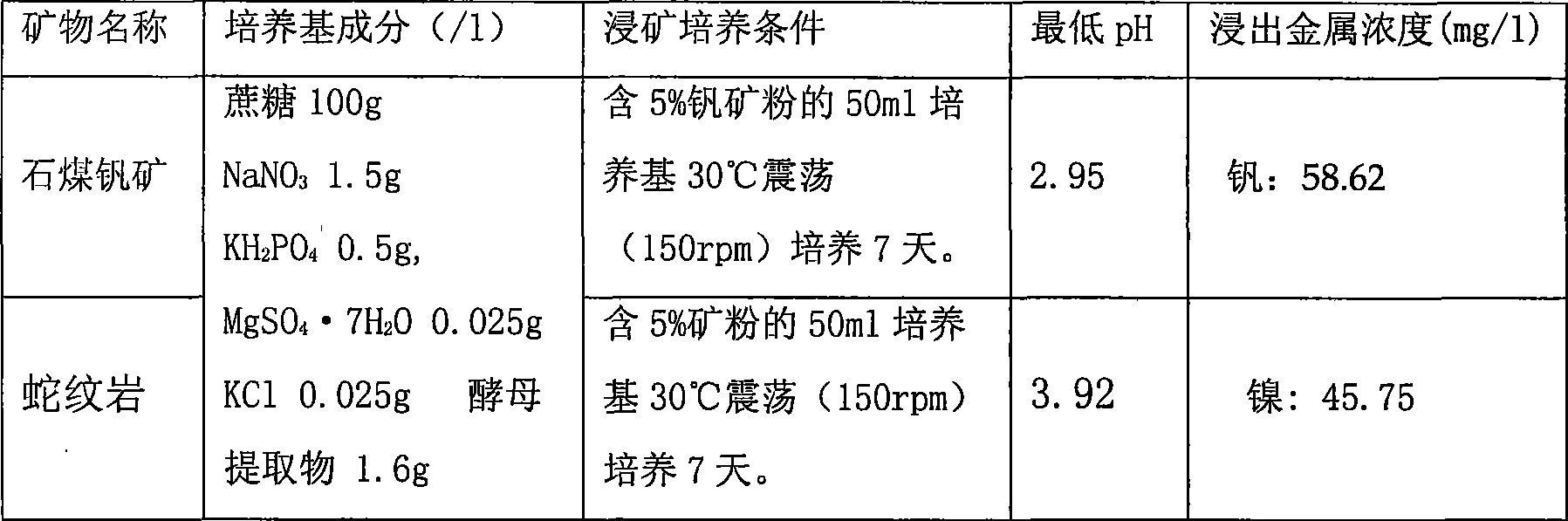
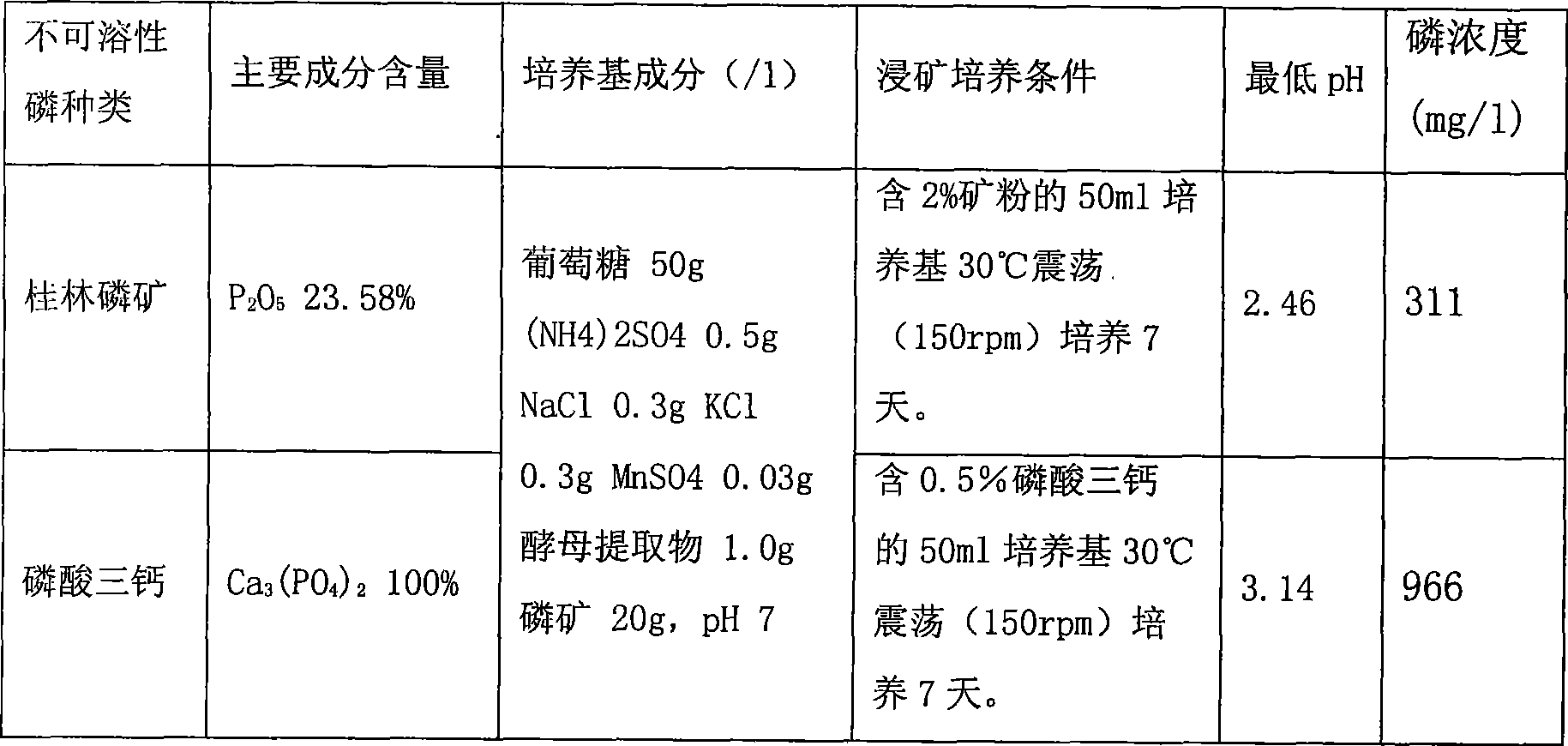
The invention discloses a Penicillium, a preparation method and applications thereof, Penicillium fungus PSM11-5 is separated from a vanadium ore sample; insoluble tricalcium phosphate, sodium metavanadate, cobalt hydroxide and basic nickel carbonate are taken as indicating compounds; and a fungal strain is screened by testing the capability of decomposing the tricalcium phosphate, the sodium metavanadate, the cobalt hydroxide and the basic nickel carbonate. The Penicillium PSM11-5 is Penicillium sp.PSM11-5 CCTCCM208207. The strain is utilized for carrying out biological leaching of phosphorus and biological metallurgy, metals of phosphorus, vanadium, nickel, cobalt and the like are leached from lean ores, discarded ores, submarginal ores, difficult-to-mine ores, difficult dressing ores and refractory ores, thereby fully utilizing the mineral resources, reducing the metallurgical costs and protecting the ecological environment. The PSM11-5 is utilized for leaching the phosphorus from low-grade phosphate rock powder, a biological fertilizer is prepared to be applied to the soil, thereby leading the soil to contain higher content of soluble phosphorus which can be utilized by crops; the strain further leaches insoluble phosphorus which is deposited in the soil before, thereby reducing phosphorus fertilizer and reducing gas pollution caused by the phosphorus fertilizer and water pollution caused by the phosphorus fertilizer.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Powdered rock phosphate oxygen-enriched binder
ActiveCN102381690AOxygenatedWith combustionRaw phosphate material treatmentFertilizer mixturesRare-earth elementPhosphate
A powdered rock phosphate oxygen-enriched binder is characterized in that on a weight basis, a drug is prepared by rare earth elements, sodium chloride, calcium chloride, zinc chloride, sodium carbonate, and potassium carbonate; according to a ratio of the drug:montmorillonite=1:2.80-3.60, a finished product is obtained by mixing, curing, drying, ball milling into powder; wherein the drug is obtained by adding sufficient water in 3%-5% of rare earth elements, 5%-10% of sodium chloride, 5%-10% of calcium chloride, 5%-10% of zinc chloride, 5%-10% of sodium carbonate, and 2-11% of potassium carbonate, and dissolving to obtain liquid with a concentration of 20-45%. The invention is applicable to the bonding of single-element or multi-element ore powder such as powdered rock phosphate, serpentine powder, iron ore powder, manganese ore powder and the like, facilitates pelletization, granulation, and air permeability improvement of material layers, and can increase the heat transfer rate andthe sintering speed; the calcining process of pellets prepared by adding the binder saves fuel by more than 30% per ton product when compared with a crude sintering method; and the P2O5 content is increased by 0.5%-1% when compared with the content of original ore powder.
Owner:宣威市恒邦磷化工业有限公司
Method for extracting phosphate concentrate from phosphate tailings and cooperatively producing calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide
InactiveCN104860278AHigh economic valueEfficient recyclingCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesRaw phosphate material treatmentDigestion TreatmentPhosphate
The invention discloses a method for extracting phosphate concentrate from phosphate tailings and cooperatively producing calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide. First, phosphate tailings are calcined under high temperature, hot water is added into the calcined material for digestion treatment, an ammonium nitrate solution is added to the calcined material, the mixture is stirred, calcium is extracted under a certain temperature, calcium-containing leaching liquid and leaching residues are obtained, phosphate concentrate and magnesium-containing leaching liquid are obtained after magnesium is extracted from the leaching residues with an ammonium sulfate solution, calcium carbonate is obtained after the calcium-containing leaching liquid is precipitated by an ammonium carbonate solution, magnesium carbonate is obtained after the magnesium-containing leaching liquid is precipitated by an ammonium carbonate solution, and magnesium oxide is obtained after the magnesium carbonate is calcined. According to the method, phosphate concentrate, calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide are prepared with phosphate tailings as the main raw materials, large-scale treatment can be carried out on the phosphate tailings, the problem that because phosphate tailings pile up in quantity, the phosphate tailings occupy a lot of land and pollute the environment is solved, and the products of phosphate concentrate, calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide are obtained.
Owner:GUIZHOU RES INST OF CHEM IND
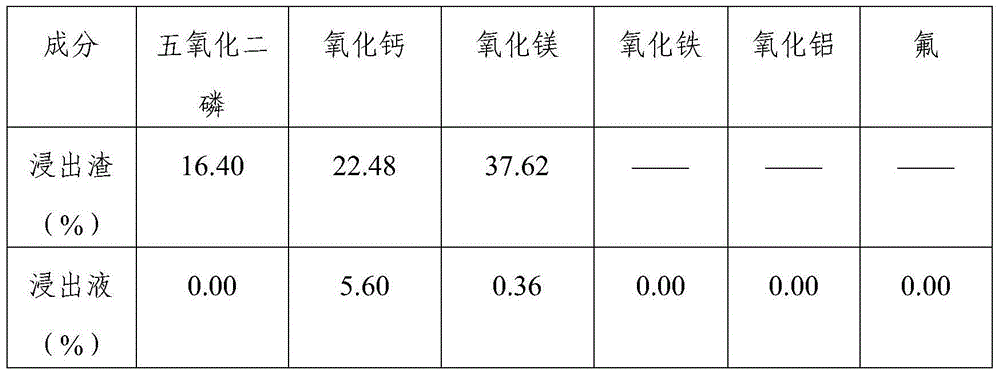
Method of preparing magnesium hydroxide and calcium carbonate and separating out phosphorus ores by taking phosphate tailings as raw materials through ammonia circulation process
The invention provides a method of preparing magnesium hydroxide and calcium carbonate and separating out phosphorus ores by taking phosphate tailings as raw materials through an ammonia circulation process. The method can be used for preparing three products, namely magnesium hydroxide, calcium carbonate and phosphorus ores by sufficiently utilizing residual tailings after raw phosphorus ore separating through circulation of ammonia. The method has the characteristics of low cost, simple process and good product quality, and is used for providing an effective utilization way for utilizing the industrial waste phosphate tailings.
Owner:QIANNAN NORMAL UNIV FOR NATTIES
Process for upgrading raw phosphate ore
InactiveUS20040067187A1High-purity phosphorusIncrease productionPhosphatesPeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesO-Phosphoric AcidSludge
Fluorapatite mineral deposits in middle Tennessee were formerly beneficiated by washing out most of the clay, but some of the clay remained in the beneficiated ore. The ore was agglomerated by heating to temperatures high enough to melt clay remaining in the ore thereby obtaining a fluid phase for agglomeration in rotary kilns. The agglomerated phosphatic material was mixed with silica rock and metallurgical coke and the mixture was smelted in electric furnaces to produce elemental phosphorus. The feedstock had a percent P O in the phosphate-plus-silica of about 25.7. Phosphate ore deposits amenable tp beneficiation by washing were used up. Furthermore, mud ponds containing the washed-out clay polluted ground water and water courses. An endeavor was made to smelt feedstock prepared from raw phosphate ore but the percent P O in the feedstock was too low for smelting. The present invention is a process for upgrading feedstock prepared from raw phosphate ore. Phosphorus sludge is burned to produce impure phosphoric acid and the acid is combined with beneficiated phosphate ore to prepare anhydrous monocalcium phosphate. Feedstock prepared from raw phosphate ore is blended with anhydrous monocalcium phosphate to upgrade the feedstock.
Owner:JAMES C BARBER & ASSOCS
Silicide compositions containing alkali metals and methods of making the same
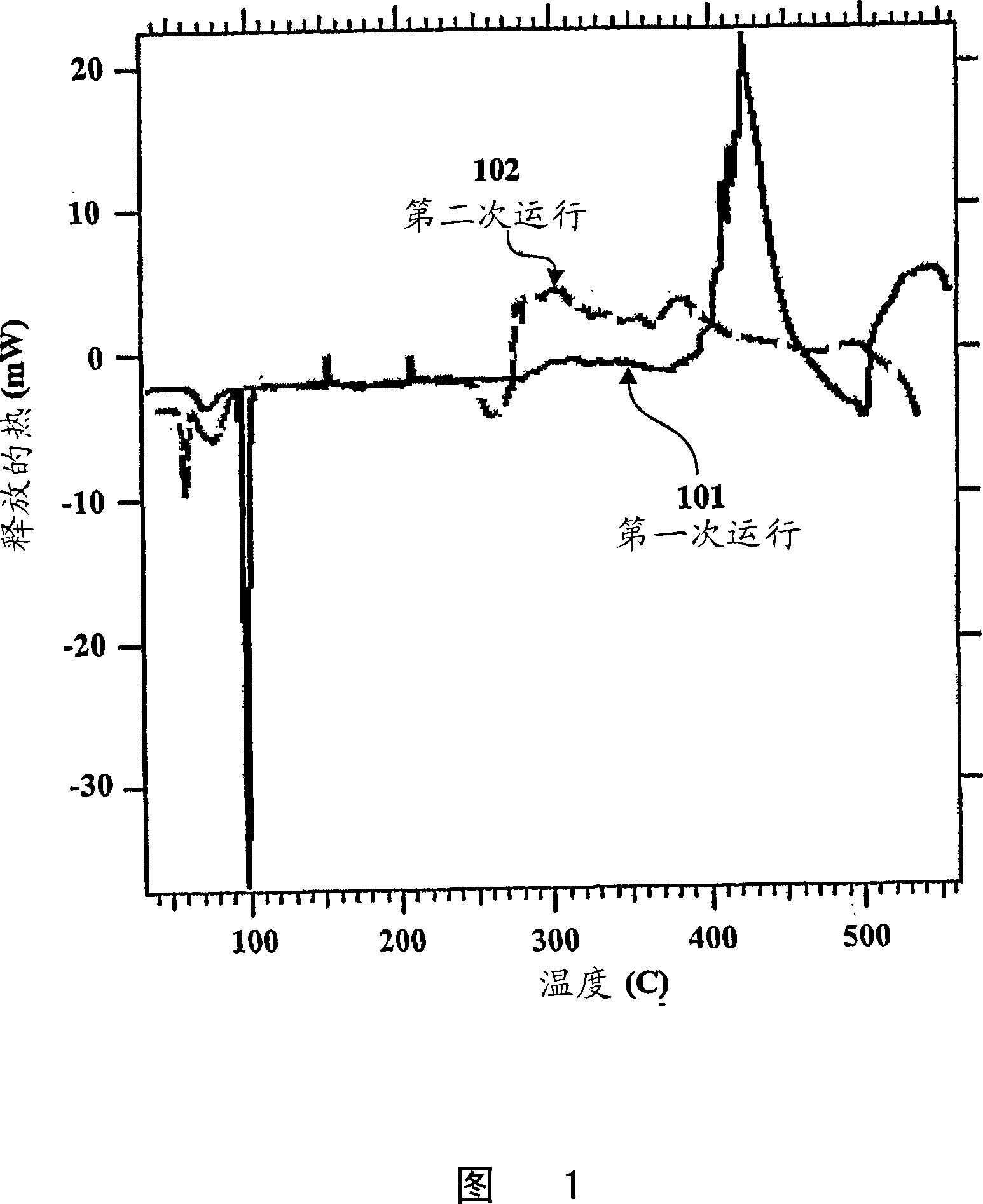
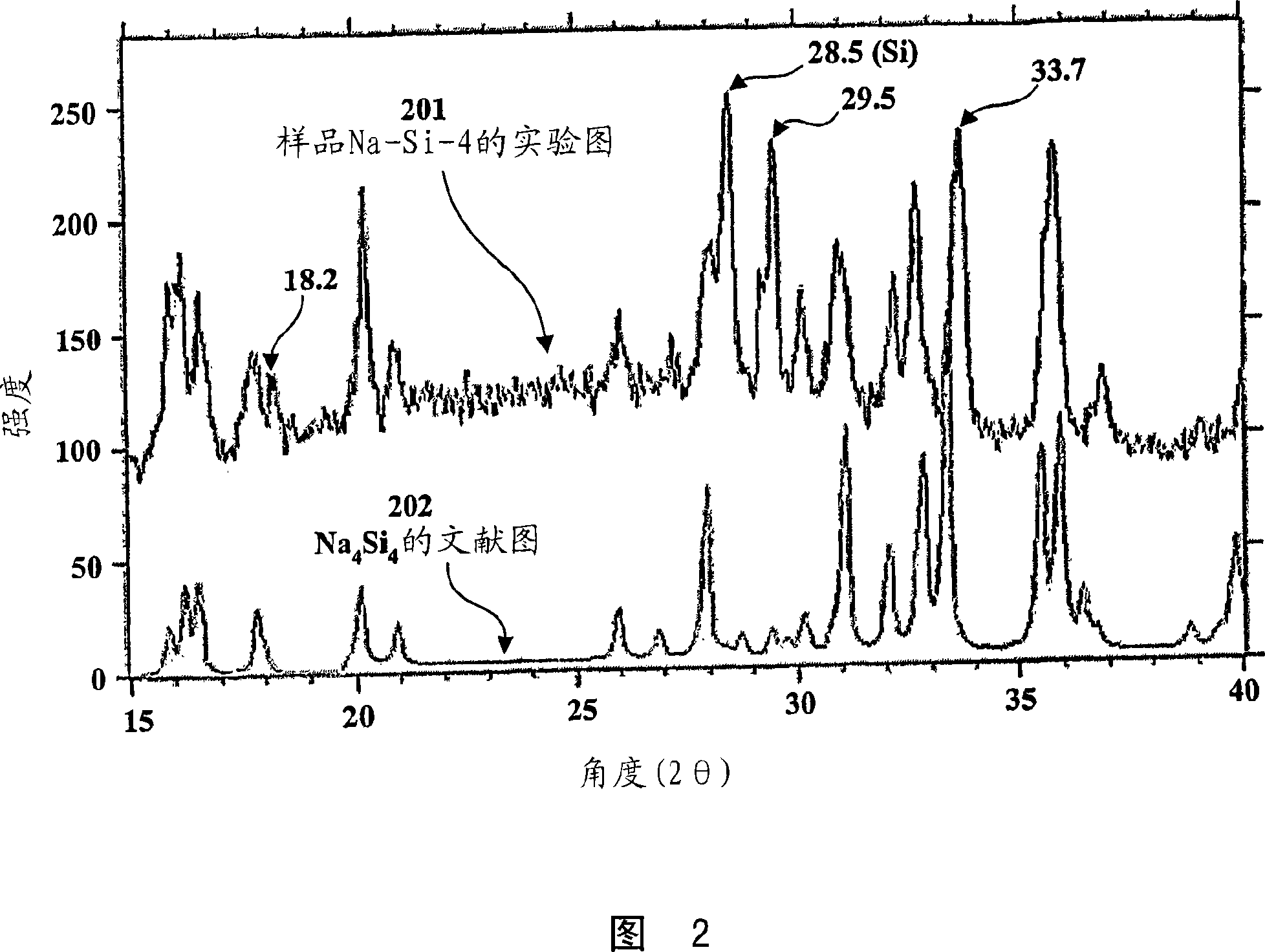
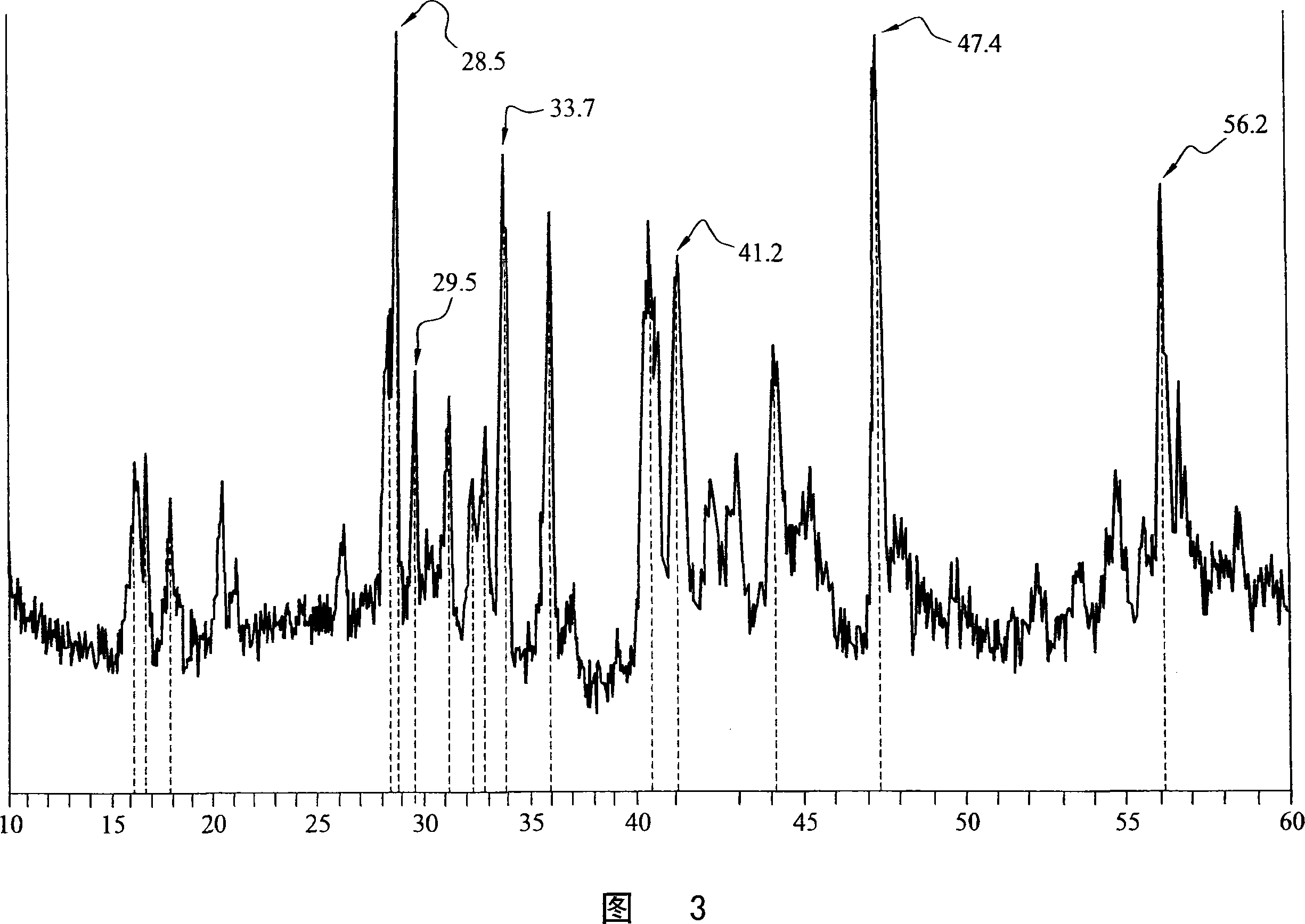
The invention relates to Group 1 metal / silica gel compositions comprising silica gel and an alkali metal or an alkali metal alloy. The compositions of the inventions are described as Stage 0, I, II, and III materials. These materials differ in their preparation and chemical reactivity. Each successive stage may be prepared directly using the methods described below or from an earlier stage material. Stage 0 materials may, for example, be prepared using liquid alloys of Na and K which are rapidly absorbed by silica gel (porous Si02) under isothermal conditions, preferably at or just above room temperature, to form loose black powders that retain much of the reducing ability of the parent metals. When the low melting Group 1 metals are absorbed into the silica gel, a mild exothermic reaction produces Stage I material, loose black powders that are indefinitely stable in dry air. Subsequent heating to 400 DEG C produces Stage II materials, which are also loose black powders. Further heating above 400 DEG C forms Stage III material with release of some Group 1 metal. It is believed that Stage I, II and III materials represent reductions of the silica gel after absorption of the Group 1 metal. Preferred Group 1 metal / silica gel compositions of the invention are those containing sodium, potassium, or sodium-potassium alloys with sodium and sodium- potassium alloys being most preferred. Each stage of the Group 1 metal / silica gel composition of the invention may be used as a reducing agent reacting with a number of reducible organic materials in the same manner known for alkali metals and their alloys.
Owner:SIGNA CHEM INC +1
Method for comprehensively utilizing low-grade phosphate ores
ActiveCN103193213ARealize comprehensive utilizationReduce use costProcess efficiency improvementRaw phosphate material treatmentPhosphateLaterite
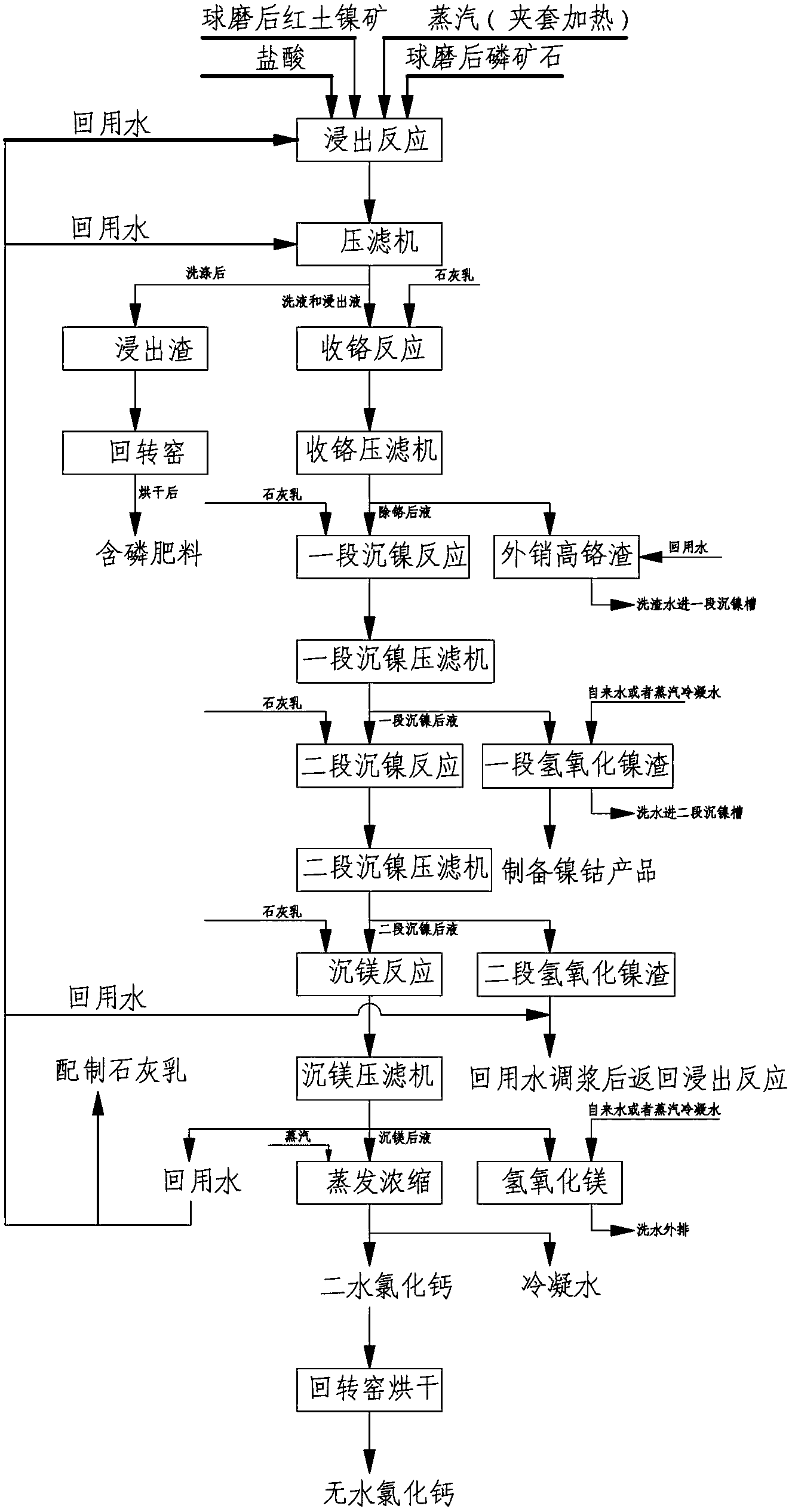
The invention discloses a method for comprehensively utilizing low-grade phosphate ores. In the traditional method, acid phosphate is used as a catalyst to participate in a reaction and used for removing iron and recovering iron hydroxide and phosphate radicals, the investment is increased because novel working sections and equipment are additionally provided in the process, and in addition, the liquid-solid separation process is more difficult because the iron hydroxide is a colloid. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out ball-milling treatment on nickel laterite ores and low-grade phosphate ores in respective ore grinding systems; mixing the obtained nickel laterite ores and low-grade phosphate ores and concentrated hydrochloric acid with the mass percentage of 20-35%, and carrying out leaching reaction; carrying out solid-liquid separation on the obtained leaching residues and leaching liquid in a filter press, wherein the residue cleaning process is also carried out in the filter press; and mixing a cleaning solution and the leaching liquid, settling by using lime milk to obtain chromium, and then, carrying out a nickel settlement reaction and a magnesium settlement reaction by using the lime milk. According to the invention, the characteristics of components of the phosphate ores and the nickel laterite ores are reasonably utilized, and the comprehensive utilization of the leaching residues of the nickel laterite ores is realized.
Owner:胡雷
Plasma display unit
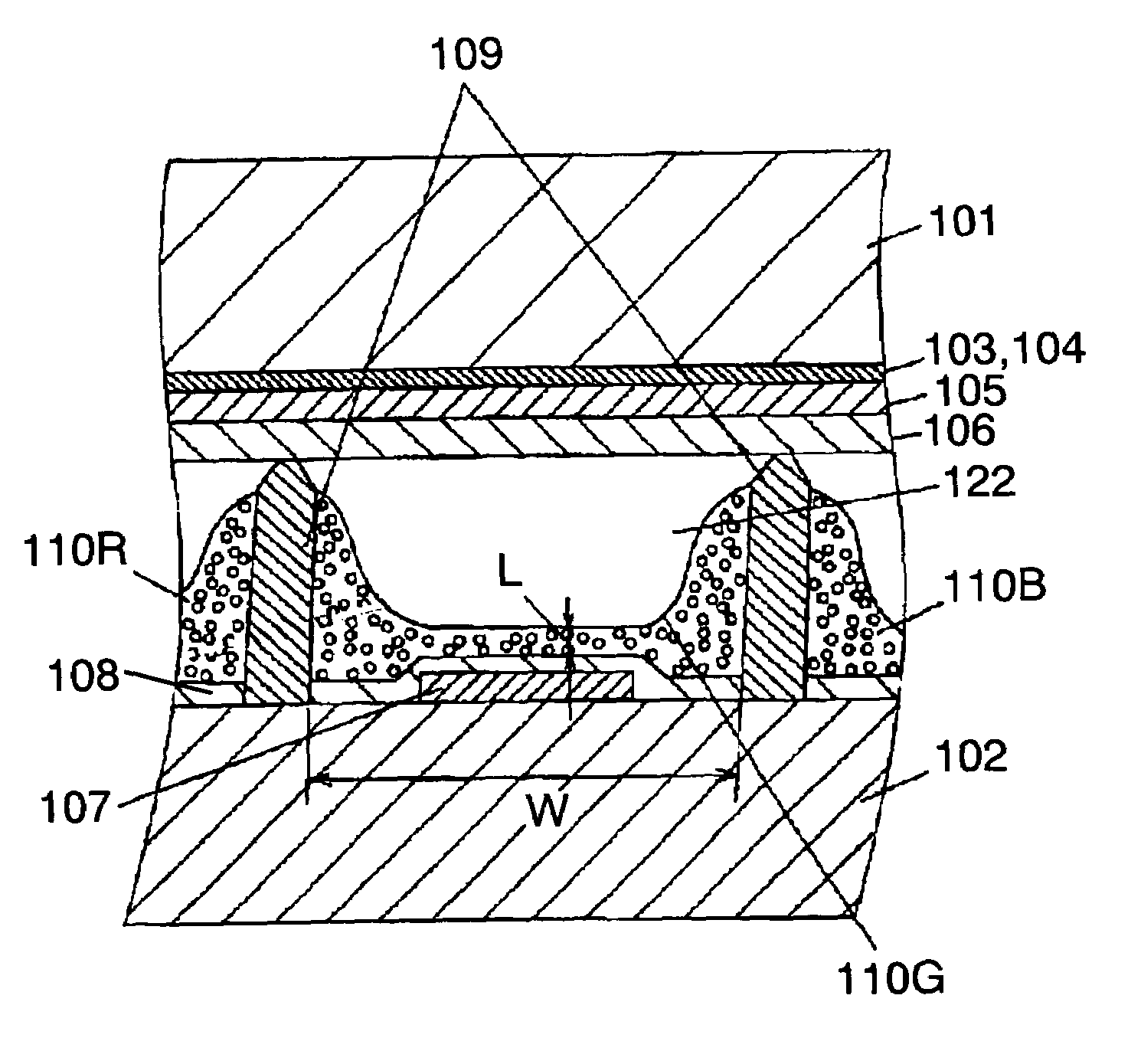
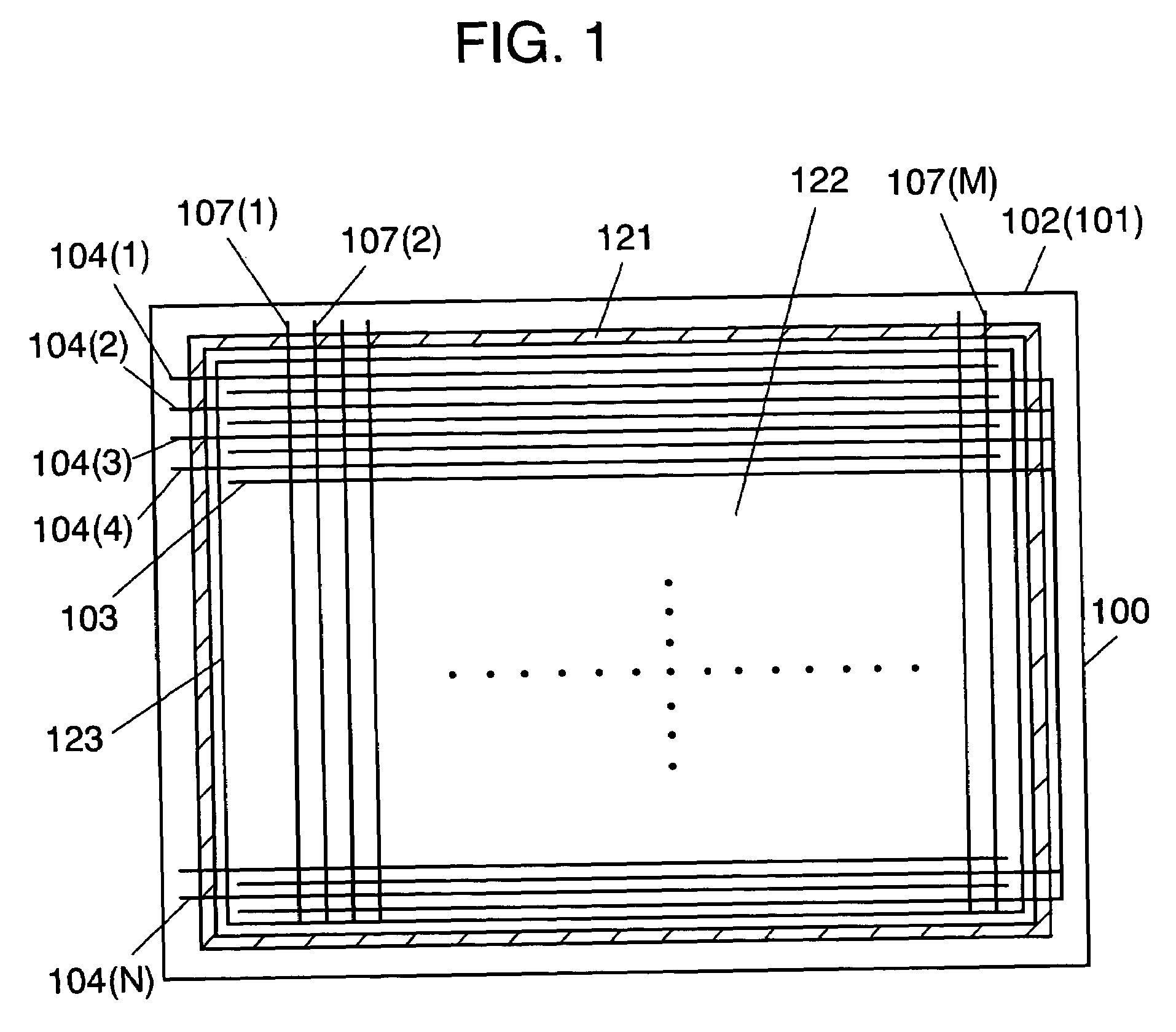
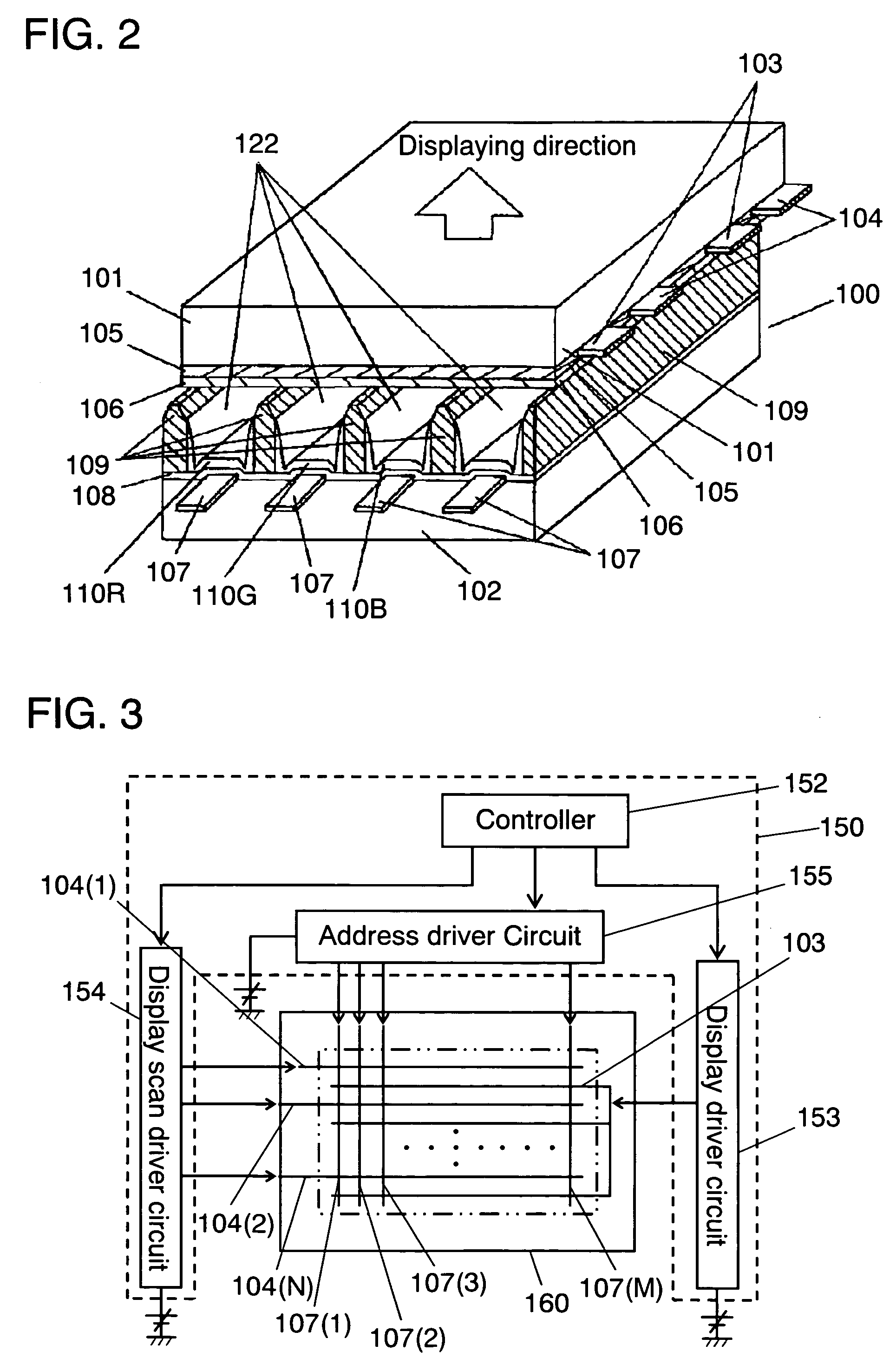
InactiveUS7161298B2Inhibition of adsorptionReduce changesAddress electrodesSustain/scan electrodesFluorescenceDisplay device
A plasma display device includes a blue phosphor composed of a compound represented by Me3MgSi2O8:Eu (where, Me is at least calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), or barium (Ba)). Concentration of bivalent Eu ions is 45 to 95% and concentration of trivalent Eu ions is 5 to 55%, of the europium (Eu) atoms contained in the blue phosphor layer. The plasma display device has less luminance degradation in a panel manufacturing process, high luminance, and long lifetime.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Process for comprehensive using waste water of phosphatic fertilize and phosphorous chemical industrial
ActiveCN1724340AGuarantee product qualityReduce processing costsWater/sewage treatmentRaw phosphate material treatmentIndustrial waste waterSewage
A process for comprehensive utilization of the acidic sewage generated by preparing P fertilizer and P chemicals includes such steps as pulverizing or grinding phosphorus ore, adding clean water, stirring, adding it to acidic sewage, stirring, regulating pH=3-5, floatation while adding floating capture, filling air and removing foam to obtain P ore concentrate.
Owner:WENGFU (GRP) CO LTD
Method of filtering phosphate utilizing a rotary table filter or horizontal table filter
Owner:THOMPSON INDAL SERVICES
Method and preparation technology used for producing yellow phosphorus from low-grade phosphate ore
ActiveCN105329865AReduce wasteAvoid wastingRaw phosphate material treatmentHalogenated silanesEnvironmental resistanceLower grade
The invention relates to a method used for producing yellow phosphorus from low-grade phosphate ore. According to the method, phosphate ore powder with appropriate silicon content and low iron content is obtained via selectively adapting silicon concentrating or removing technology and removing iron-containing compounds in smashing period based on the difference of phosphate ores in mining period; a first time P2O5 enrichment and a second time P2O5 enrichment are carried out respectively via drying, roasting, or obverse flotation, or reverse flotation, drying,, curing, and obtaining of phosphate ore balls. The method is low in cost, high in efficiency, is friendly to the environment, is capable of improving yellow phosphorus quality, avoiding accidents or faults such as arch structure formation, material collapse, and electrode broken, and ensuring safe, stable, and high efficiency operation of electric furnaces.
Owner:成都天屿新磷科技有限公司
Urban manure disposal method
InactiveCN103408203AAchieve harmless disposalAchieve recyclingSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningDispersed particle separationAgricultural engineeringSlurry
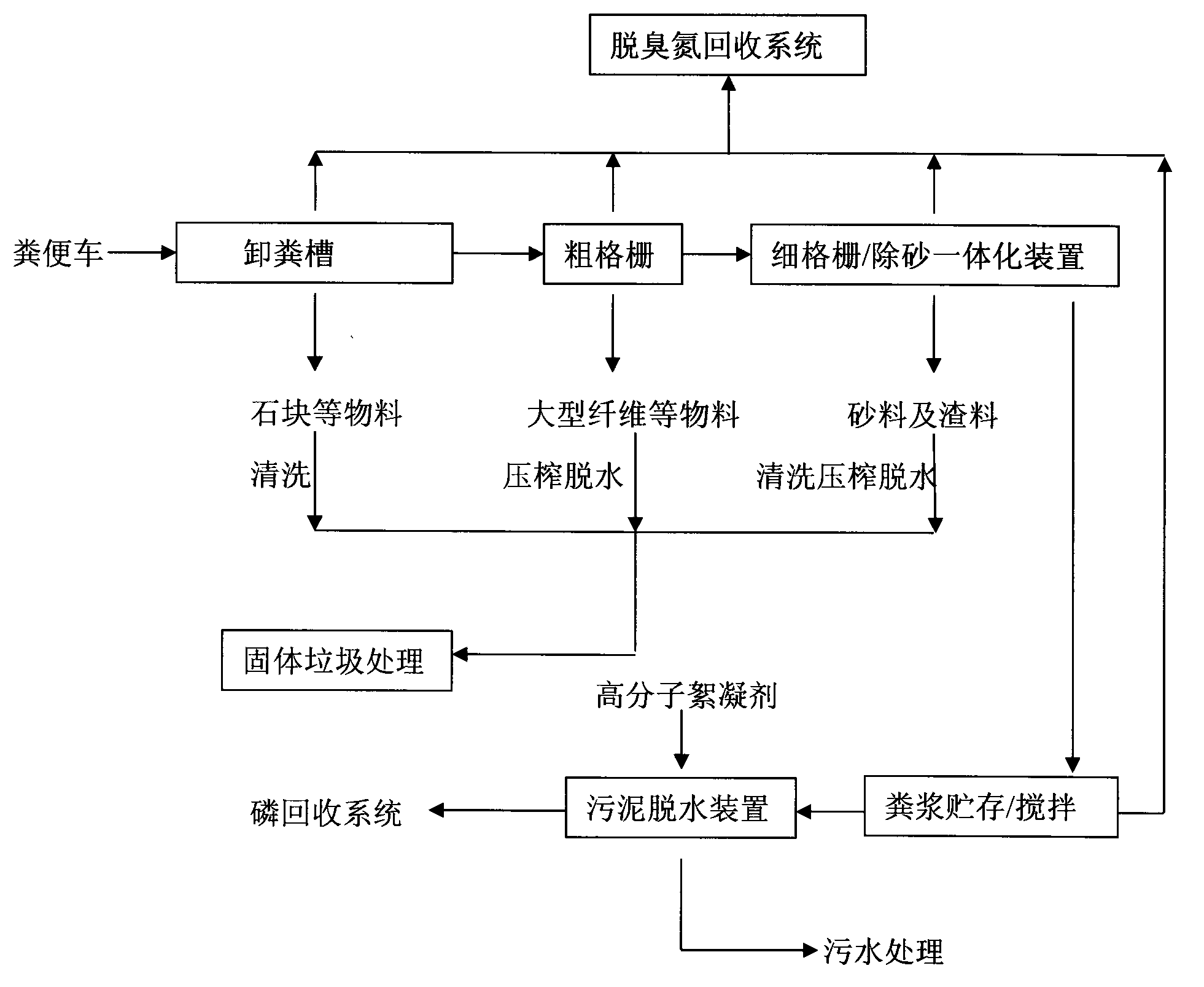
The invention provides an urban manure disposal method. According to the method, on one hand, harmless disposal can be performed on manure; on the other hand, phosphorus element in the manure can be recovered. After the manure passes through a manure unloading slot, a coarse grid and a solid-liquid separation integrated machine, manure slurry filtrate can form a mud cake with the solid content of 35-45% after being subjected to flocculation and dehydration treatment, the mud cake can be used as an agricultural fertilizer and can also be used for recovering phosphorus, liquid produced during the treatment process is fed into a sewage treatment plant to be treated, and disgusting odor can be treated specially.
Owner:ATK HLDG GRP CO LTD
Method for producing powdered rock phosphate balls by using powdered rock phosphate
ActiveCN103964404AIncrease contentRaise the gradeRaw phosphate material treatmentCO2 contentCalcium Binder
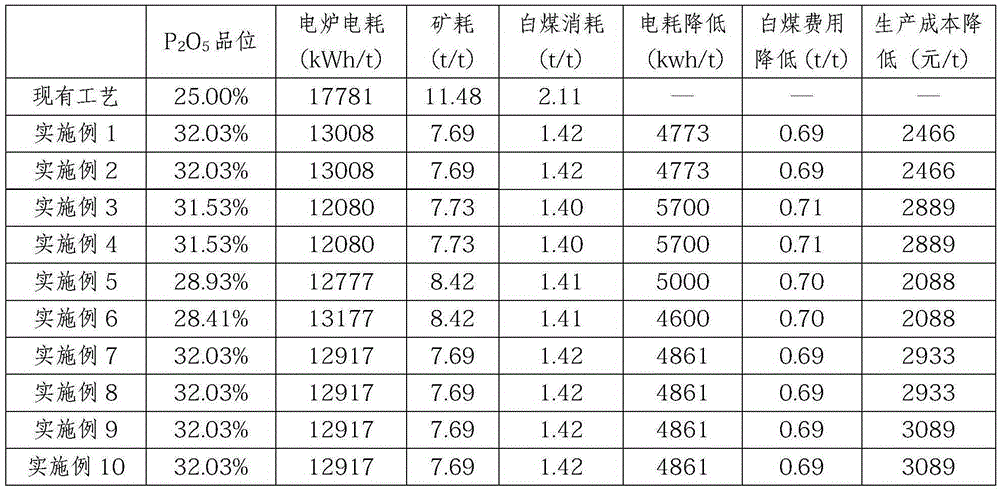
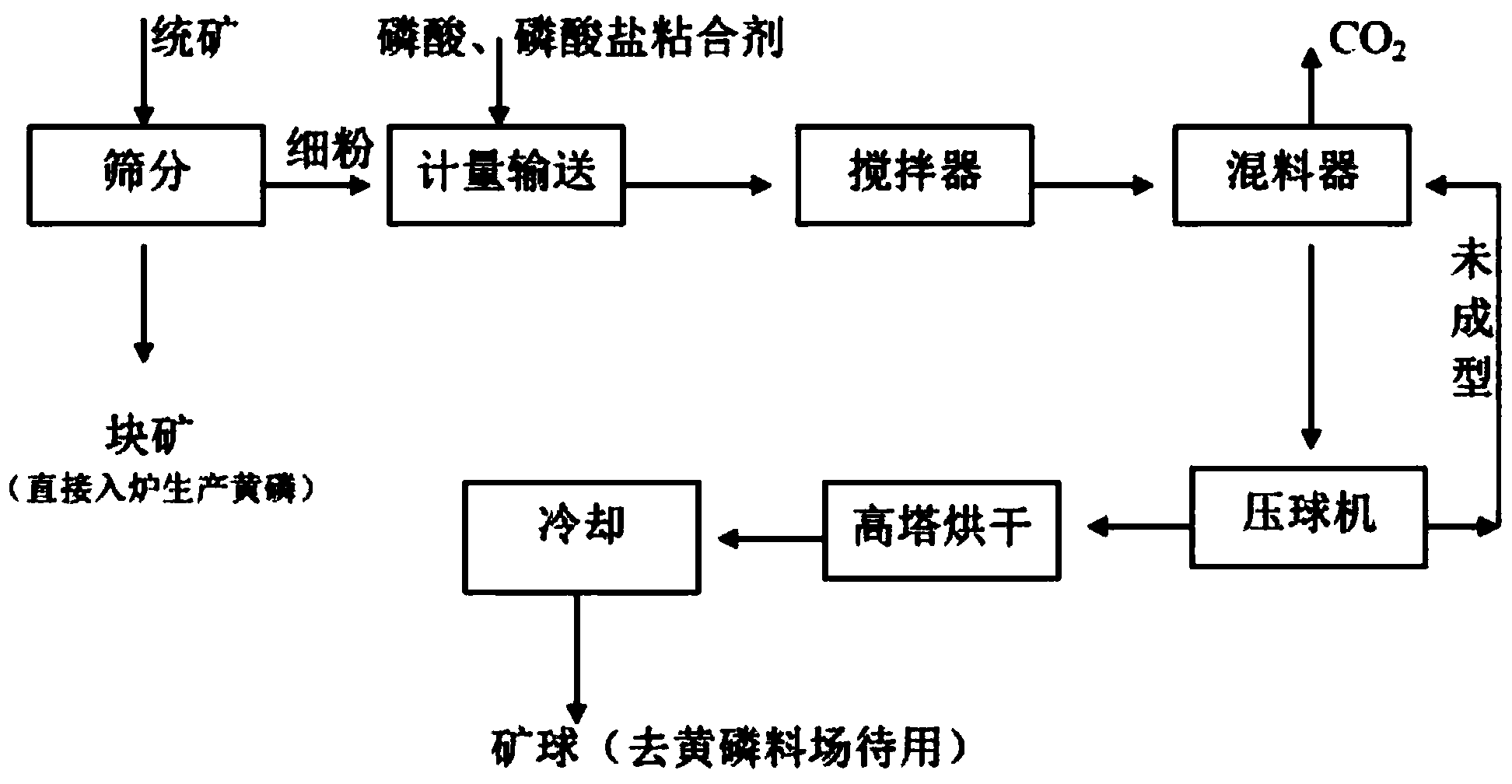
The invention relates to the technical field of mineral processing, in particular to a method for producing powdered rock phosphate balls by using powdered rock phosphate screened out by enterprises or mineral powder left after mine production with low-concentration phosphoric acid. The method comprises the steps of screening, batching, mixing, ball pressing, drying and cooling; in the method, the content of P2O5 in phosphate rock is increased as a phosphate acid and phosphate binder is adopted and the P2O5 in the binder ultimately enters a furnace and participates the phosphorus producing reaction, and the quality of phosphate rock is improved; carbonate impurities in the added phosphoric acid and phosphate rock are subjected to chemical replacement reaction, and mixing is carried out by a double-roll mixer, so that carbon dioxide and organic matters harmful to the electric furnace during production can be fully released; in the production of yellow phosphor, the power consumption of the electric furnace can be reduced by 190 kilowatt hour as long as 1% of CO2 content is reduced, the consumption of coke can be reduced by 29 kilograms, and the production costs of the enterprises can be greatly reduced.
Owner:贵州福泉川东化工有限公司
Medium and low grade phosphorus ore magnesium removal treatment method
ActiveCN104860277AAvoid emissionsIncrease added valueRaw phosphate material treatmentPhosphoriteLower grade
The invention relates to the technical field of medium and low grade phosphorus ore pretreatment, particularly to a medium and low grade phosphorus ore magnesium removal treatment method. A magnesium element in a phosphorus ore is converted into an oxide from carbonate after steps of calcining digestion, leaching, absorption, separation and ammonium carbonate treatment, the ionic state is presented in a solution to enable the magnesium element to be separated out, and the treatment is performed on obtained filtrate to enable nitrate in the filtrate to be recycled; absorption and utilization are performed on the waste gas produced in the calcining process and the ammonia gas produced in the leaching process to obtain ammonium carbonate; the ammonium carbonate is reacted in the filtrate to obtain an ammonium nitrate solution and magnesium contained calcium carbonate, the ammonium nitrate solution is returned to the leaching step, and accordingly the discharge of the waste liquid is avoided, the magnesium contained calcium carbonate additional product is obtained, and the additional process value is increased.
Owner:贵州盛源新材料股份有限公司
Making method of fluor apatite
InactiveCN1475436AGood response densityImpression capsDentistry preparationsCalcium hydroxideLithium
A process for preparing the fluorapatite (FAP) includes proportionally mixing calcium fluoride with hydroxyapatite, adding excipient, die pressing and sintering. It has high biological compatibility,so using it as biomedical material for curing teeth, etc.
Owner:文国琴
Method for granulating, molding and calcining ground phosphorite
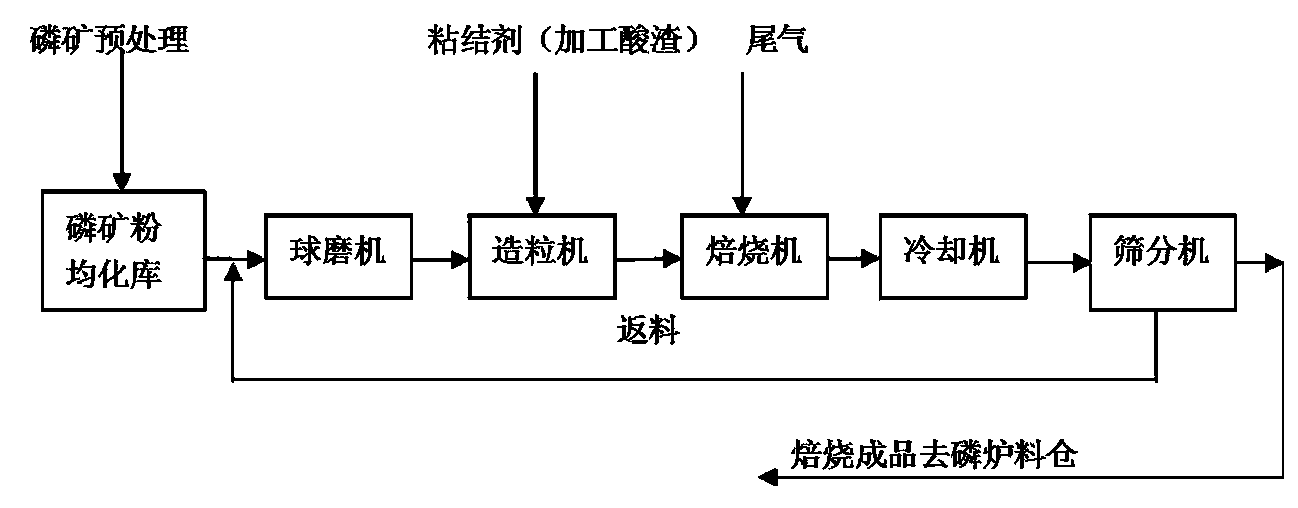
ActiveCN104261363ANo increase in Si-Ca ratioEfficient use ofRaw phosphate material treatmentCircular discSlag
The invention relates to a method for granulating, molding and calcining ground phosphorite. The method comprises the steps of crushing phosphorite, screening, drying and carrying out homogenizing pretreatment to obtain ground phosphorite, feeding the ground phosphorite into a ball mill for grinding, adding fine ground phosphorite into a circular-disc granulator, evenly adding a binder prepared from an intermediate product acid slag in production of phosphoric acid by virtue of a dihydrate wet process in proportion so that the fine ground phosphorite is bound with each other and phosphorite pellets of which the particle sizes reach 20-30mm are prepared, introducing phosphorus furnace tail gas into a chain-grate-type calcining machine, calcining at a temperature of 850-950 DEG C and cooling with air to obtain the phosphorite pellets for production of yellow phosphorus. According to the method, the intermediate product in the production process is fully utilized, is processed into an auxiliary material and directly returns back to the production process, newly added other raw auxiliary materials and the consumption of energy, such as coke powder are not needed; by virtue of phosphorus furnace tail gas and unique calcining and air cooling processes, the content of P2O5 in the ground phosphorite pellets is increased by 8-10% and the silicon-calcium ratio (acidity coefficient Mk) in the phosphorite pellets is not increased, and thus the efficient comprehensive utilization of phosphate resources is achieved.
Owner:YUNNAN TIANAN CHEM CO LTD
Collector for beneficiating carbonaceous phosphate ores
ActiveUS20180043373A1Calcium/strontium/barium carbonatesSurface-active detergent compositionsAlkaline earth metalPhosphate
The invention is related to a flotation process using an improved collector to remove alkaline earth metal carbonate impurities from phosphate ores. The flotation feed may be conditioned with the improved carbonate collector at acidic pH, and subjected to a reverse flotation. The cell overflow may be collected as waste in which carbonate minerals dominate, and the cell underflow may be the phosphate concentrate. The collector may be a combination of chemicals, comprising: (1) any kind of fatty acids, either conventional fatty acid, saponified fatty acid, or modified fatty acid; (2) chemicals with sulfonate or sulfate groups, such as dodecylbenzene sulfonic acid (DDBSA) or its salt, sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), sodium coco sulfate (SCS), etc.; and (3) phosphorous-bearing chemicals, such as sodium tripolyphosphate (STPP), sodium hexametaphosphate (SFMP), trisodium phosphate (TSP), Tetrasodiumpyrophosphate (TSPP), etc. With the improved collector, the separation selectivity and phosphate recovery may be significantly improved.
Owner:ARRMAZ PROD INC
Technology for preparation of low-magnesium phosphate concentrate and byproducts calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide from medium and low grade phosphate rock
ActiveCN105540560AEfficient recyclingSolve pollutionCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesRaw phosphate material treatmentInorganic ChemicalPhosphorite
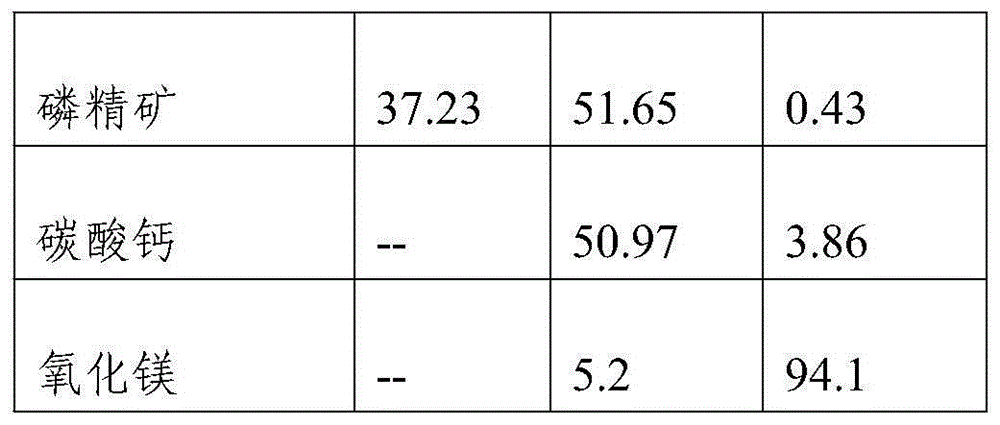
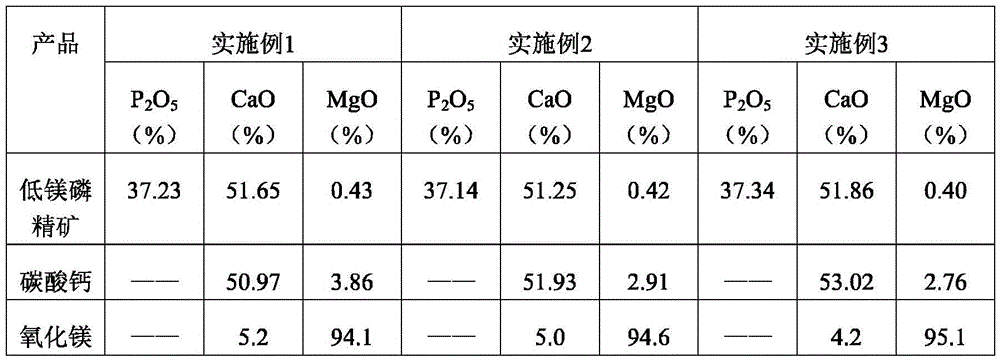
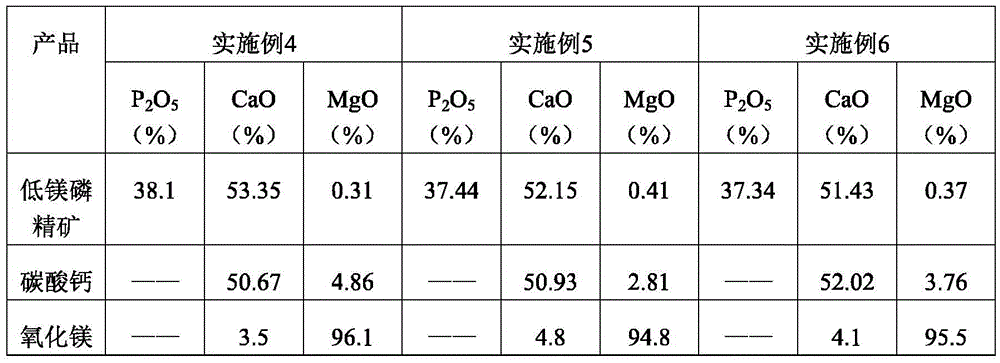
Belonging to the technical field of inorganic chemical industry, the invention provides a technology for preparation of low-magnesium phosphate concentrate and byproducts calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide from medium and low grade phosphate rock. The technology includes the steps of: calcining medium and low grade phosphate rock at 900-1100DEG C; and then carrying out slaking, leaching, precipitation and a series of treatment to obtain low-magnesium phosphate concentrate, calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide. The technology maximumly retains phosphorus element in the prepared low-magnesium phosphate concentrate, and produces calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide as the byproducts, so that the calcium, magnesium and phosphorus elements in the medium and low grade phosphate rock can be fully utilized. In the obtained low-magnesium phosphate concentrate, calcium carbonate and magnesium oxide products, the low-magnesium phosphate concentrate has a phosphorus pentoxide content of more than 37% and a magnesium oxide content of less than 0.5%, the calcium carbonate has a calcium oxide content of more than 50%, and the magnesium oxide has purity of over 94%. Therefore, the increase percentage point of phosphorus pentoxide in the low-magnesium phosphate concentrate is over 10.13.
Owner:贵州盛源新材料股份有限公司
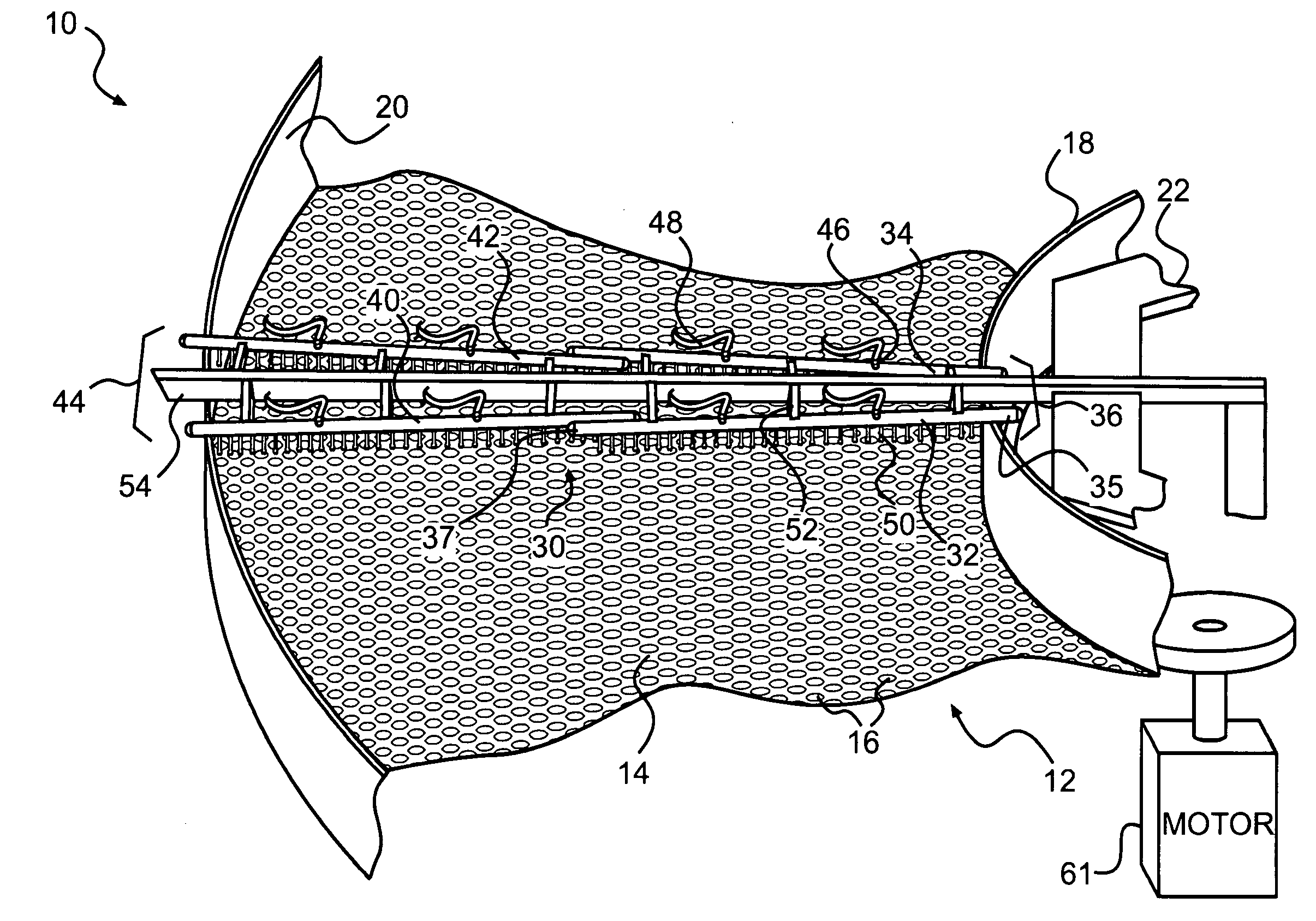
Process and plant for the recovery of phosphorus and coagulants from sludge
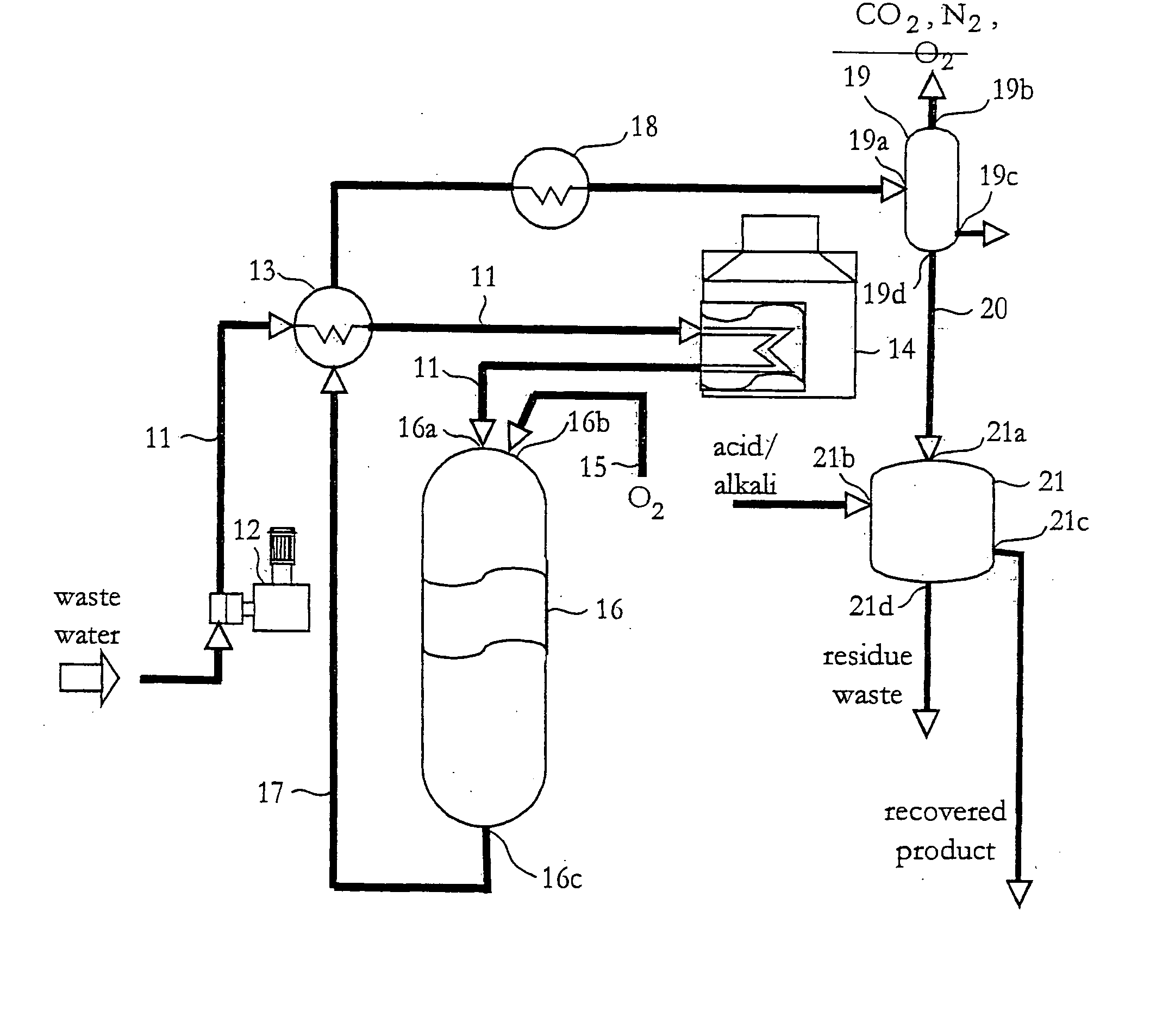
InactiveUS20040232088A1Improve performanceSludge treatment by oxidationWater contaminantsSludgeSupercritical water oxidation
A process for treatment of waste containing organic material, phosphorous and water in suitable amounts to be a pumpable sludge and in order to be oxidizable through supercritical water oxidation, comprises the steps of: putting the sludge into conditions being supercritical for water; adding oxidant, particularly, oxygen to the sludge, wherein the organic material contained in the waste is substantially completely oxidized by means of supercritical water oxidation; separating the phosphorous from water and from carbon dioxide formed during the oxidation; and recovering the phosphorous by means of dissolving the phosphorous in an alkali.
Owner:CHEMATUR ENG +1
Method for dissolving mid-low-grade rock phosphate by utilizing thermoacidophile
InactiveCN102173399AScientific and effective useReduce manufacturing costMicroorganism based processesRaw phosphate material treatmentSolubilityPhosphate
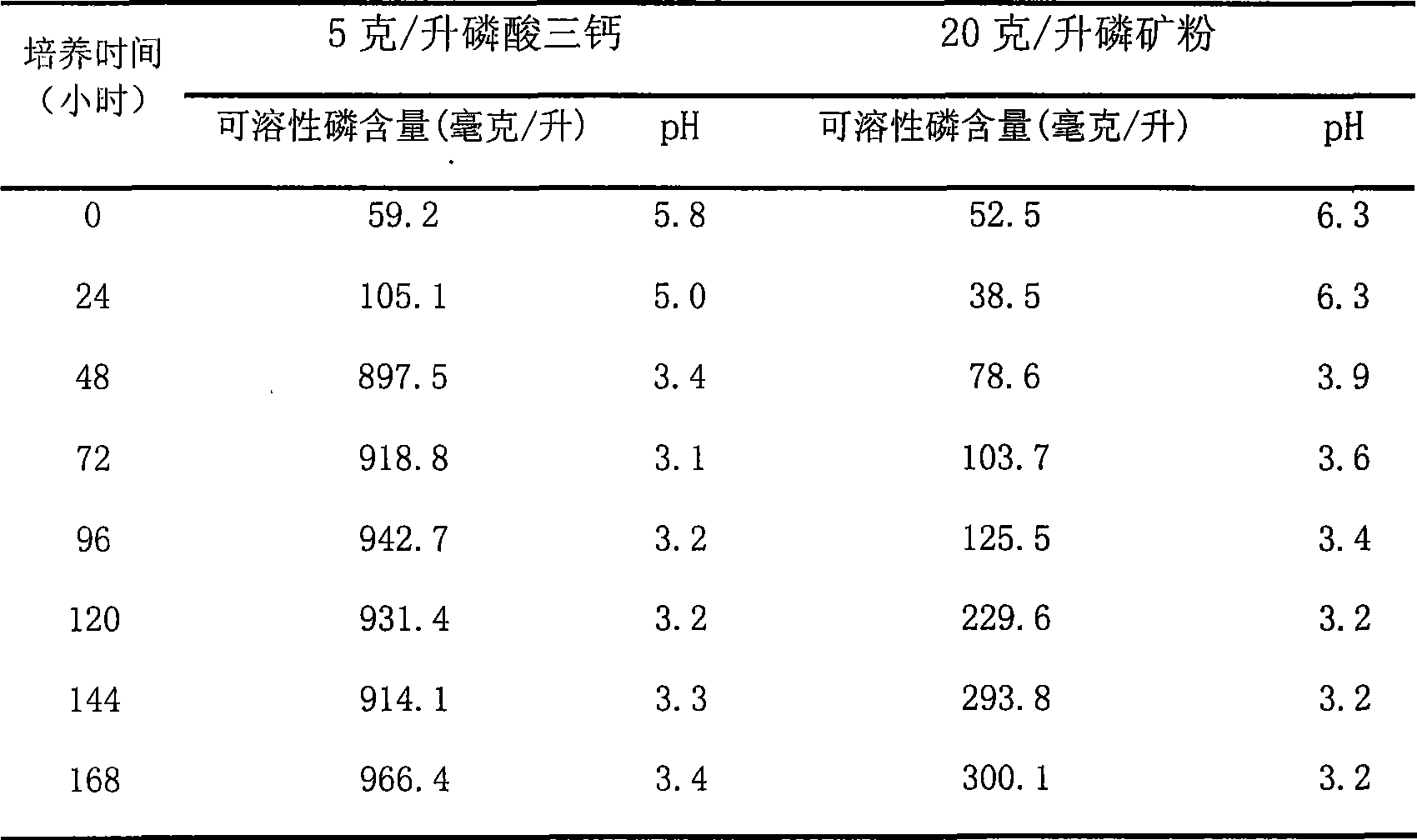
The invention relates to a method for dissolving mid-low-grade rock phosphate by utilizing thermoacidophile. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1) activating the original thermoacidophile liquid to obtain activated thermoacidophile liquid; 2) domesticating the obtain activated thermoacidophile liquid to obtain domesticated thermoacidophile liquid; and 3) putting a culture medium into a container and adding pyrite powder and mid-low-grade rock phosphate to obtain culture liquid C, adjusting the pH value of the culture liquid C to be 2.0-3.0 with sulfuric acid with concentration being 10-20wt% and then adding the domesticated thermoacidophile liquid; and then putting the container in a shaker at the constant temperature of 40-55 DEG C and carrying out shaking culture at a speed of 120-180r / min for 15-20 days to obtain soluble phosphorus. The method has the characteristics of high phosphorus solubility, simple process and low production cost.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Washing and direct flotation method of low-grade refractory argillaceous phosphorite
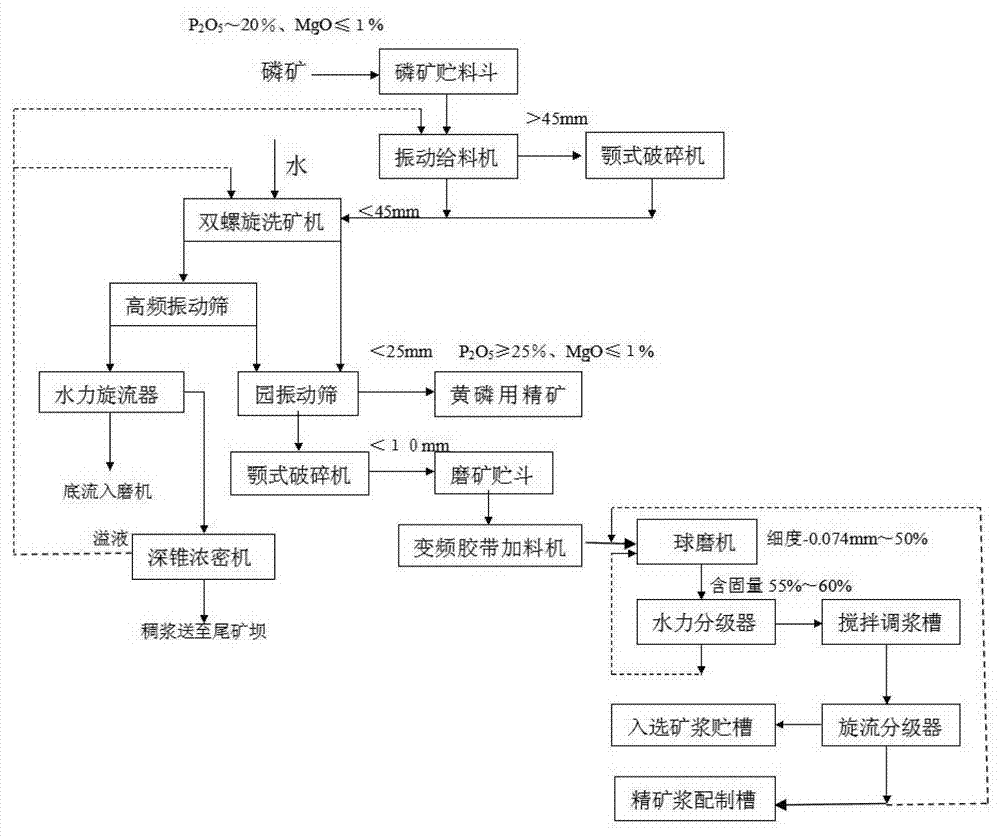
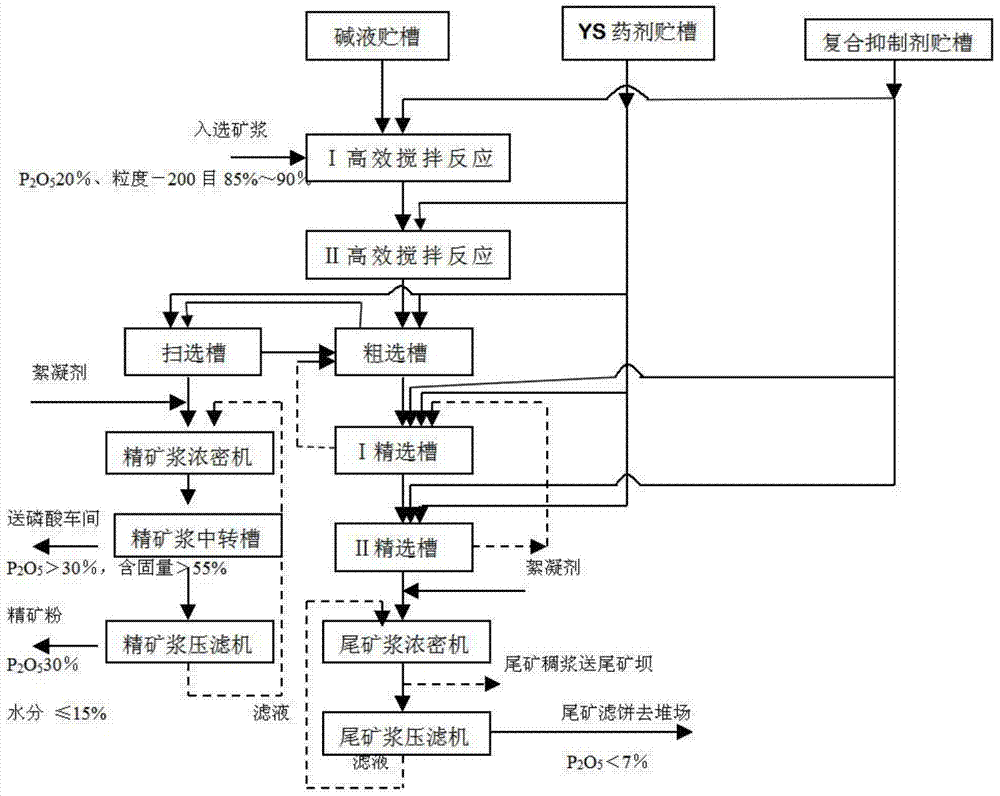
ActiveCN104261361AReduce grinding energy consumptionTo achieve hierarchical useFlotationRaw phosphate material treatmentWet grindingLow graded
The invention relates to a washing and direct flotation method of low-grade refractory argillaceous phosphorite, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: a. phosphorite closed coarse crushing, fine crushing, screening, water washing and fine ore closed wet grinding grading; and b. phosphorite rough separation, twice concentrating, once scavenging direct flotation, thickening and pressure filtration direct flotation. The step a is performed to prepare the phosphorus concentrate for yellow phosphorus production, of which the mass percent of P2O5 is greater than or equal to 25% and the particle size is less than or equal to 25mm, and prepare the phosphorite slurry for phosphoric acid production, extraction and slurry preparation without flotation, of which the content of particles with the particle size of 100 meshes is greater than 85% and the mass percent of P2O5 is 28.5%. By adopting the more-crushing / less grinding-closed screening-washing technique, the method can lower the grinding energy consumption by 10kw.h / t, and has the advantages of obvious separating effect between the phosphorite and gangue mineral and favorable separation indexes. Compared with the traditional technique, the phosphorus concentrate recovery rate is enhanced by 10% or so, and the tailing remaining phosphorus is lowered by 2-3%.
Owner:YUNNAN HONGFU CHEM FERTILIZER
Method for removing magnesium oxide in phosphate concentrate through phosphatic fertilizer and phosphorus chemical industry acid wastewater
InactiveCN102838097AReduce loss rateQuality improvementRaw phosphate material treatmentChemical industryPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a method for removing magnesium oxide in phosphate concentrate through phosphatic fertilizer and phosphorus chemical industry acid wastewater. The method comprises the steps as follows: adding the acid wastewater and the phosphate concentrate pulp to a reacting groove to be reacted for 0.5 to 6 hours at 15 to 50 DEG C, so as to obtain reactive size; carrying out solid-liquid separation to the reactive size, wherein the solid phase produced by the separation is the phosphate concentrate with the magnesium oxide removed; and then preparing via a phosphoric acid by wet process. The method provided by the invention is simple in technology, easy to operate in the reaction, high in removal rate of magnesium oxide, low in loss ratio of the phosphorus in the phosphate concentrate, and high in economy.
Owner:WENGFU (GRP) CO LTD
Method for extracting phosphate concentrate from phosphate tailings and cooperatively producing calcium ammonium nitrate and magnesium ammonium sulphate
InactiveCN104860279AEfficient recyclingAlleviate the status quo of depletionMagnesium compoundsCalcium/strontium/barium nitratesPhosphateDigestion Treatment
The invention discloses a method for extracting phosphate concentrate from phosphate tailings and cooperatively producing calcium ammonium nitrate and magnesium ammonium sulphate. Phosphate tailings are calcined under high temperature, hot water is added into the calcined material for digestion treatment, an ammonium nitrate solution is added to the calcined material, the mixture is stirred, calcium is extracted under a certain temperature, calcium-containing leaching liquid and leaching residues are obtained, phosphate concentrate and magnesium-containing leaching liquid are obtained after magnesium is extracted from the leaching residues with an ammonium sulfate solution, and calcium ammonium nitrate and magnesium ammonium sulphate are obtained after the calcium-containing leaching liquid and the magnesium-containing leaching liquid are concentrated and dried. According to the method, phosphate concentrate, calcium ammonium nitrate and magnesium ammonium sulphate are prepared with phosphate tailings as the main raw materials, large-scale treatment can be carried out on the phosphate tailings, the problem that because phosphate tailings pile up in quantity, the phosphate tailings occupy a lot of land and pollute the environment is solved, and the obtained phosphate concentrate, calcium ammonium nitrate and magnesium ammonium sulphate can bring certain economic interests.
Owner:GUIZHOU RES INST OF CHEM IND
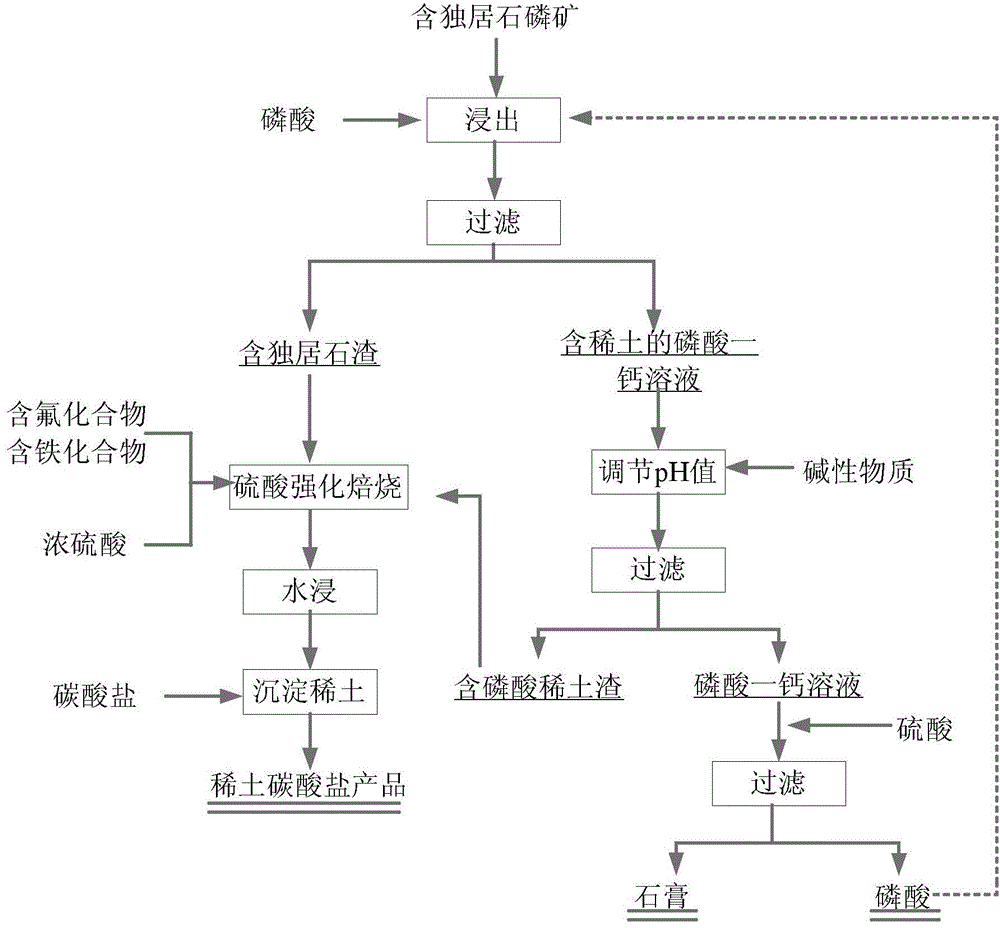
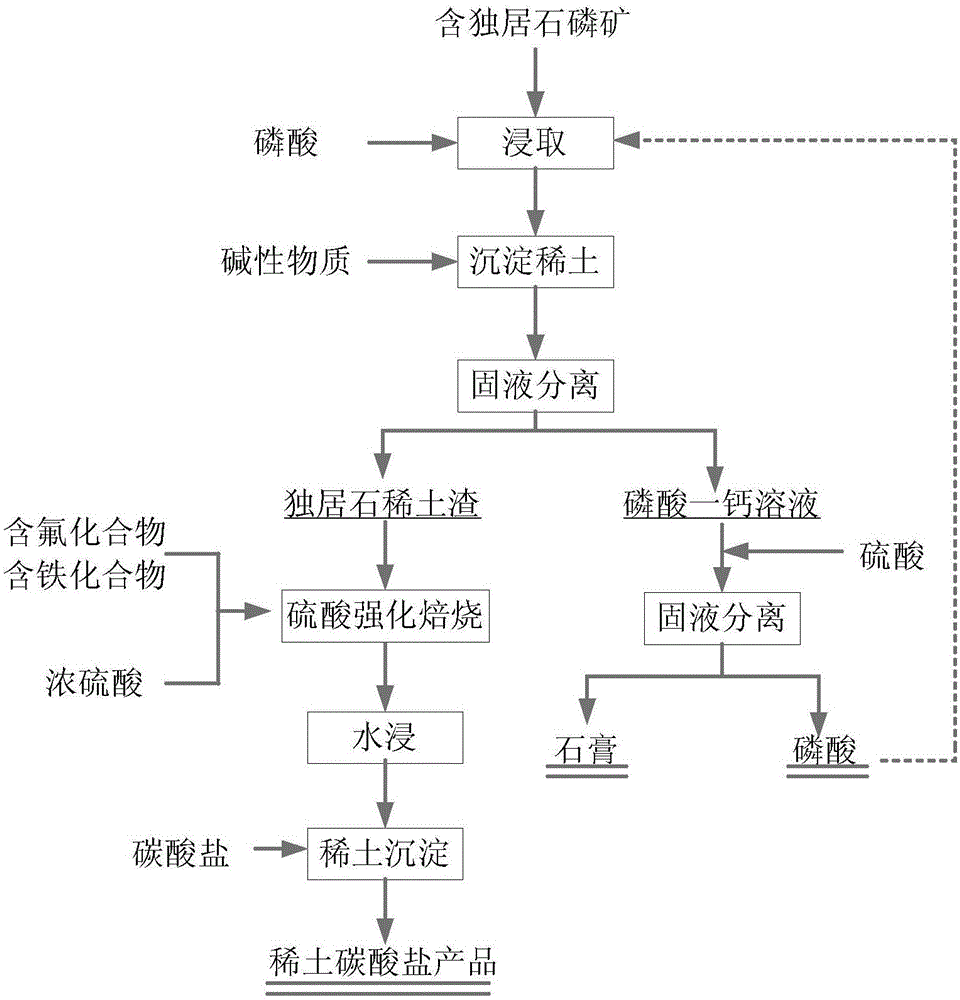
Method for comprehensively recycling phosphorus and rare earth from rare earth phosphorite containing monazite
ActiveCN105331812AHigh recovery rateEfficient separationProcess efficiency improvementRaw phosphate material treatmentSolubilitySlag
The invention discloses a method for comprehensively recycling phosphorus and rare earth from rare earth phosphorite containing monazite. The method includes the following steps that rare earth phosphorite containing monazite is obtained from phosphoric acid in a leaching manner, and a monocalcium phosphate solution containing rare earth and slag containing monazite are obtained through filtration; the monocalcium phosphate solution containing rare earth is processed through a precipitation method, dissolved rare earth precipitates, a monocalcium phosphate solution and rare earth slag containing phosphoric acid are obtained through filtration, and the rare earth slag containing phosphoric acid and slag containing monazite are mixed to form mixed slag; and phosphorus in the monocalcium phosphate solution is recycled, and rare earth in the mixed slag is recycled. Acid leaching is conducted by adding phosphoric acid, phosphorus in rare earth phosphorite containing monazite forms monocalcium phosphate high in solubility, and therefore monazite existing in a precipitation manner and phosphorus can be separated. Then, the monocalcium phosphate solution containing rare earth is processed through the precipitation method, and rare earth and phosphorus elements in phosphorite can be effectively separated. Rare earth and phosphorus are effectively separated through two times of separation steps, and therefore the rare earth recycling rate is increased.
Owner:GRIREM ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Method for processing phosphate rock tailings
ActiveCN106315530APromote decompositionFully leachedCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesMagnesium carbonatesEcological environmentPhosphorite
The invention relates to a method for processing phosphate rock tailings. According to the invention, the phosphate rock tailing pre-treated by sulfuric acid is processed through calcination digestion, then a processing mode with two-step leaching is used, a magnesium element in the phosphate tailing is fully separated, and the phosphate tailing quality is enhanced. Waste liquid and waste gas which are generated in the process are recycled, a treated solvent is reused, a filtrate is subsequently processed while the high-quality phosphate rock is obtained, the obtained calcium and magnesium are effectively recycled, discharge of the waste liquid and the waste gas is avoided, tailings are prevented from accumulating, and therefore, the ecological environment is improved.
Owner:铜仁市万山区盛和矿业有限责任公司
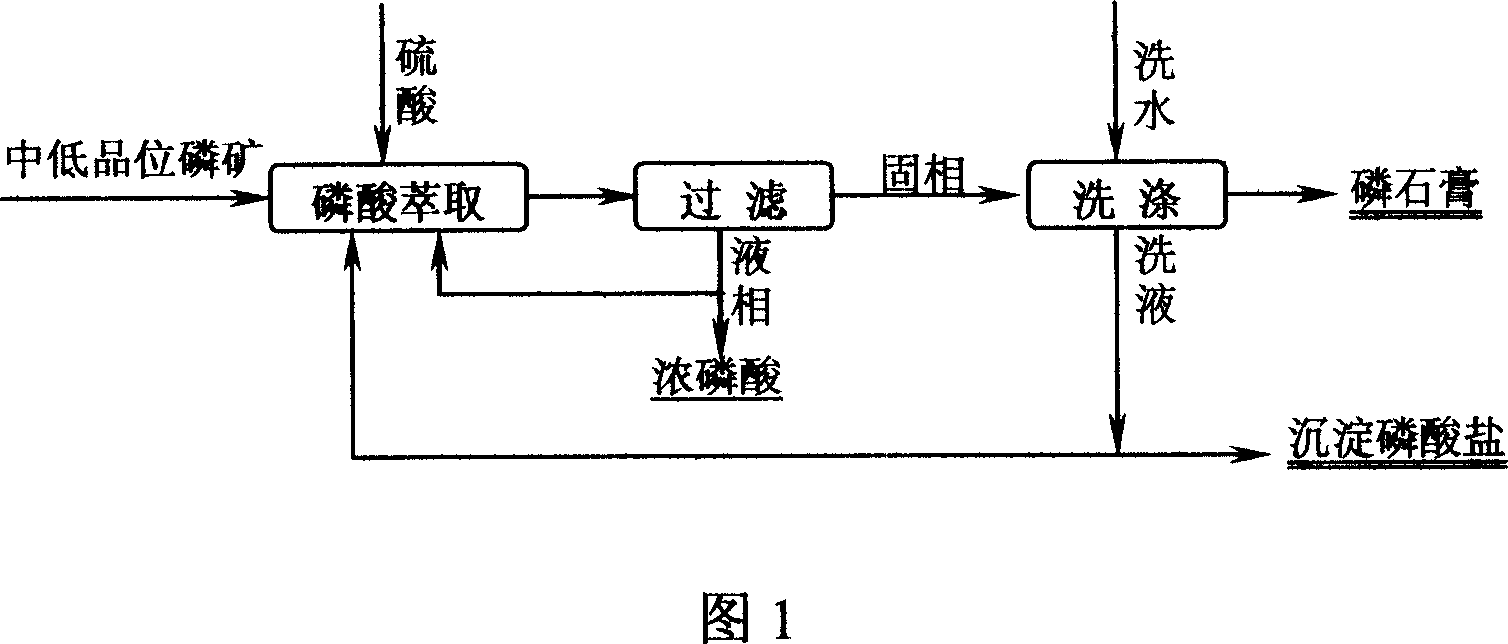
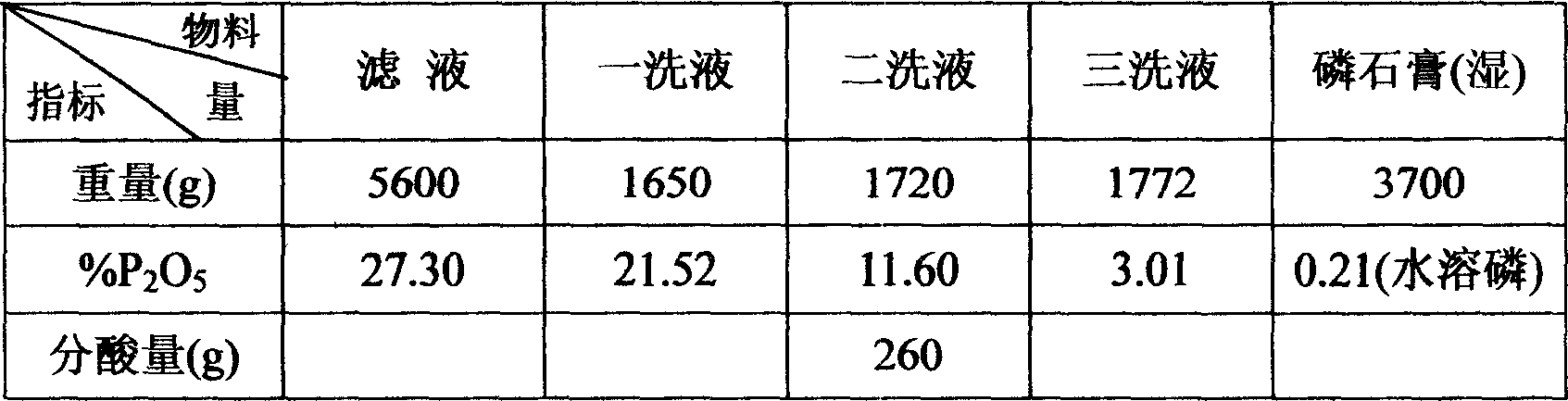
Process for preparing high concentration phosphoric acid from middle-and low-grade phosphorus ore
InactiveCN1994870ALow water solubilitySave upfront processing costsPhosphatesRaw phosphate material treatmentHigh concentrationPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a making method of high-density phosphic acid based on middle or low grade phosphoric ore, which comprises the following steps: separating extracted phosphic acid system from washing quantity of phosphogypsum; manufacturing sediment phosphate; avoiding the unflavored effect due to increasing present system; using partial phosphor element to manufacture refined sediment phosphoric acid salt; reducing the loss of phosphor; circulating mother liquid of phosphate into grinding system or washing water of phosphogypsum.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Efficient and low-pollution phosphorous-slurry recycling method
ActiveCN105883736AStrong targetingEliminate poor recyclingRaw phosphate material treatmentChemical industryState of art
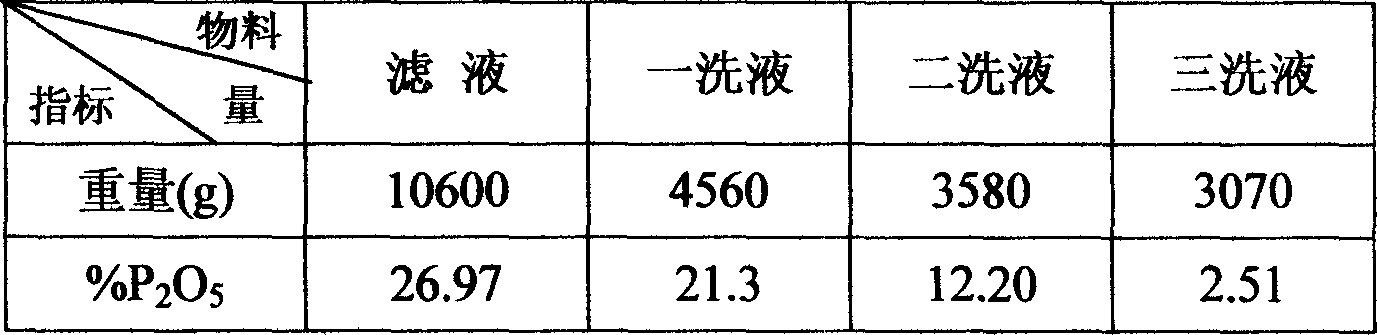
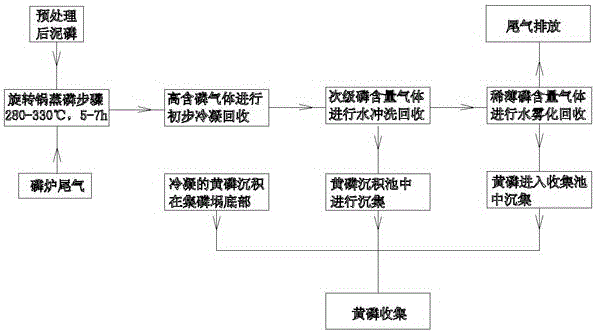
The invention provides an efficient and low-pollution phosphorous-slurry recycling method, and relates to the technical field of phosphorus chemical industry. The problems that multiple processes and multiple superposition devices are adopted in an existing dry-blowing phosphorous-slurry recycling method, the superposition effect can not be achieved, the recycling rate is low, the safety factor of the device is low, and tail gas is not up to the standard are solved. According to the efficient and low-pollution phosphorous-slurry recycling method, it is not followed that single-stage recycling processes are infinitely extended in the prior art, and multistage recycling processes with different acting objects and different function emphasis points are set; in other words, high phosphorus-containing gas is primarily condensed and recycled, secondary phosphorus-containing gas is washed and recycled with cooling water, and thin phosphorus-containing gas is atomized and recycled with cooling water. The all stage technologies of phosphorous-slurry recycling are optimized, pertinence is higher, and the problems that as yellow phosphorus is condensed and collected through a plurality of purely-added series phosphorus receiving troughs or a plurality of purely-added series phosphorus collecting crucibles in the prior art, the whole recycling effect is poor, the device is seriously idled and wasted, the safety factor is decreased, and investment and operation cost are increased are solved.
Owner:云南澄江志成磷业化工有限责任公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com