Patents
Literature
89results about "Phosphorus oxyacids" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
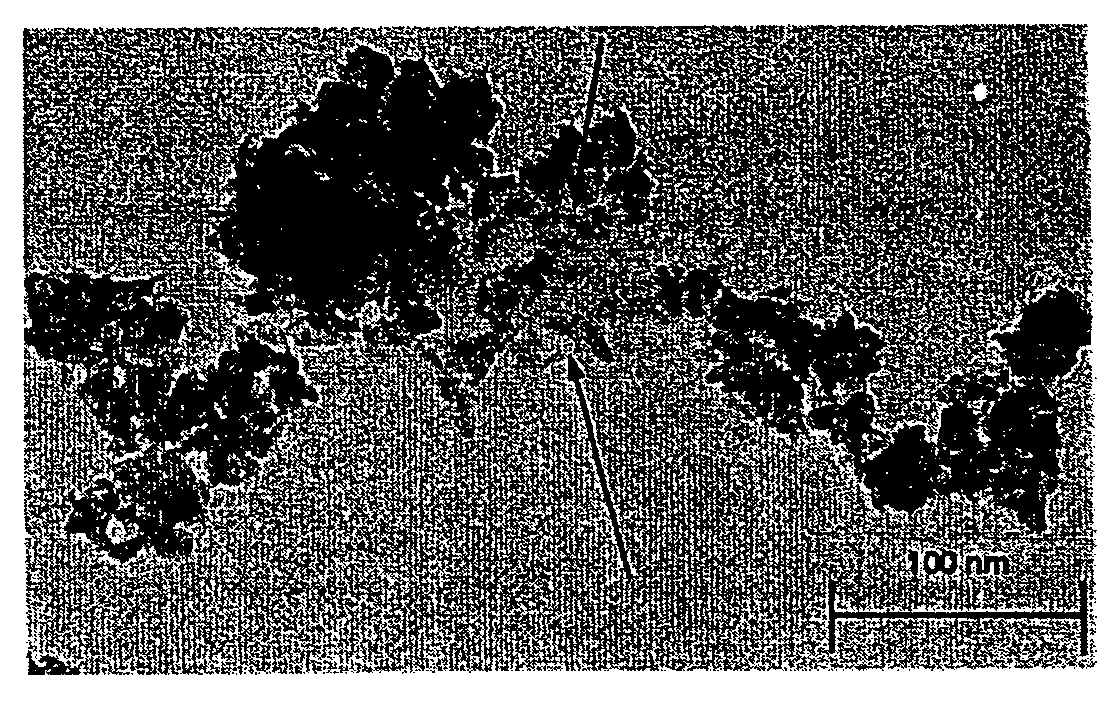
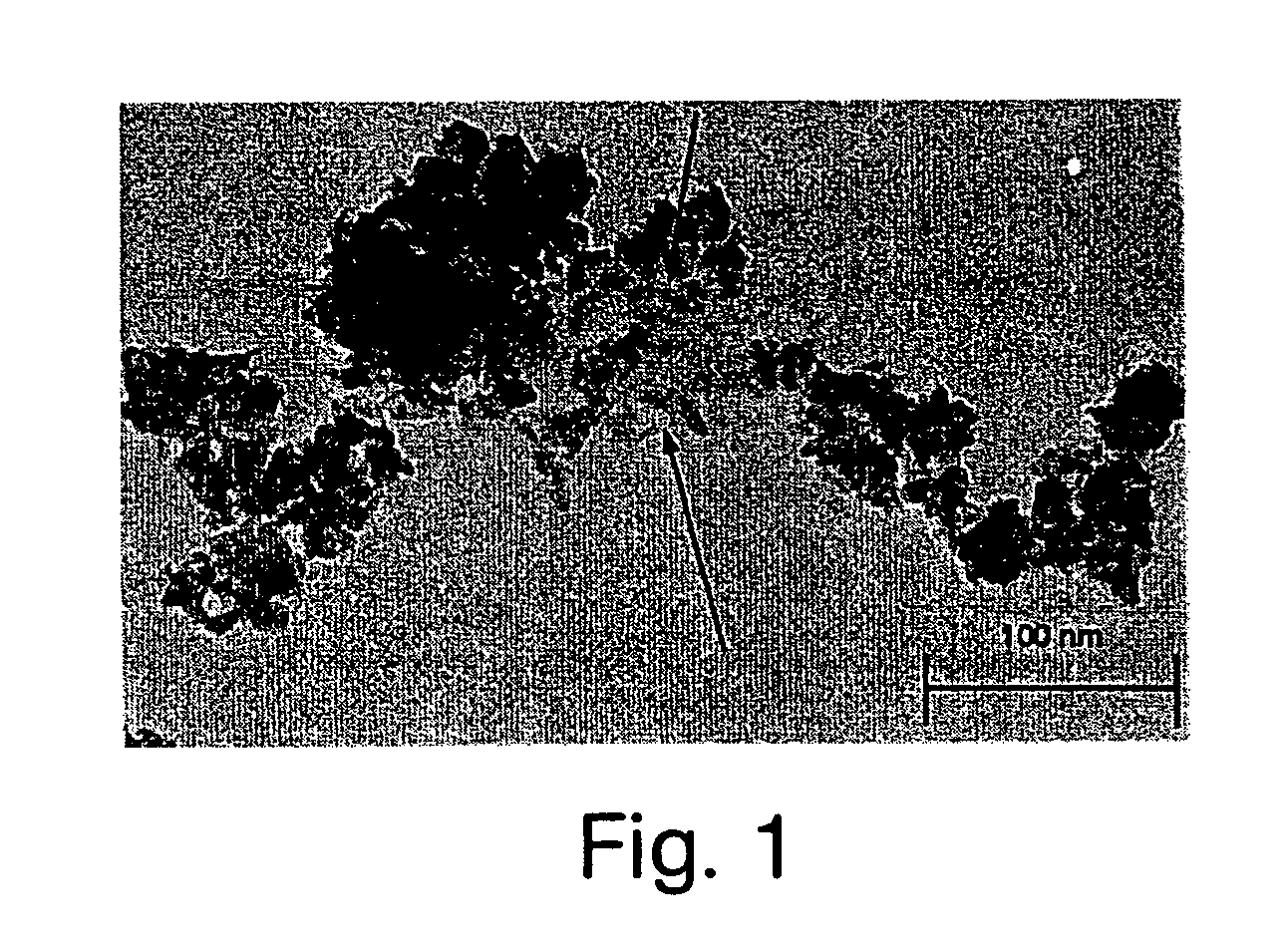
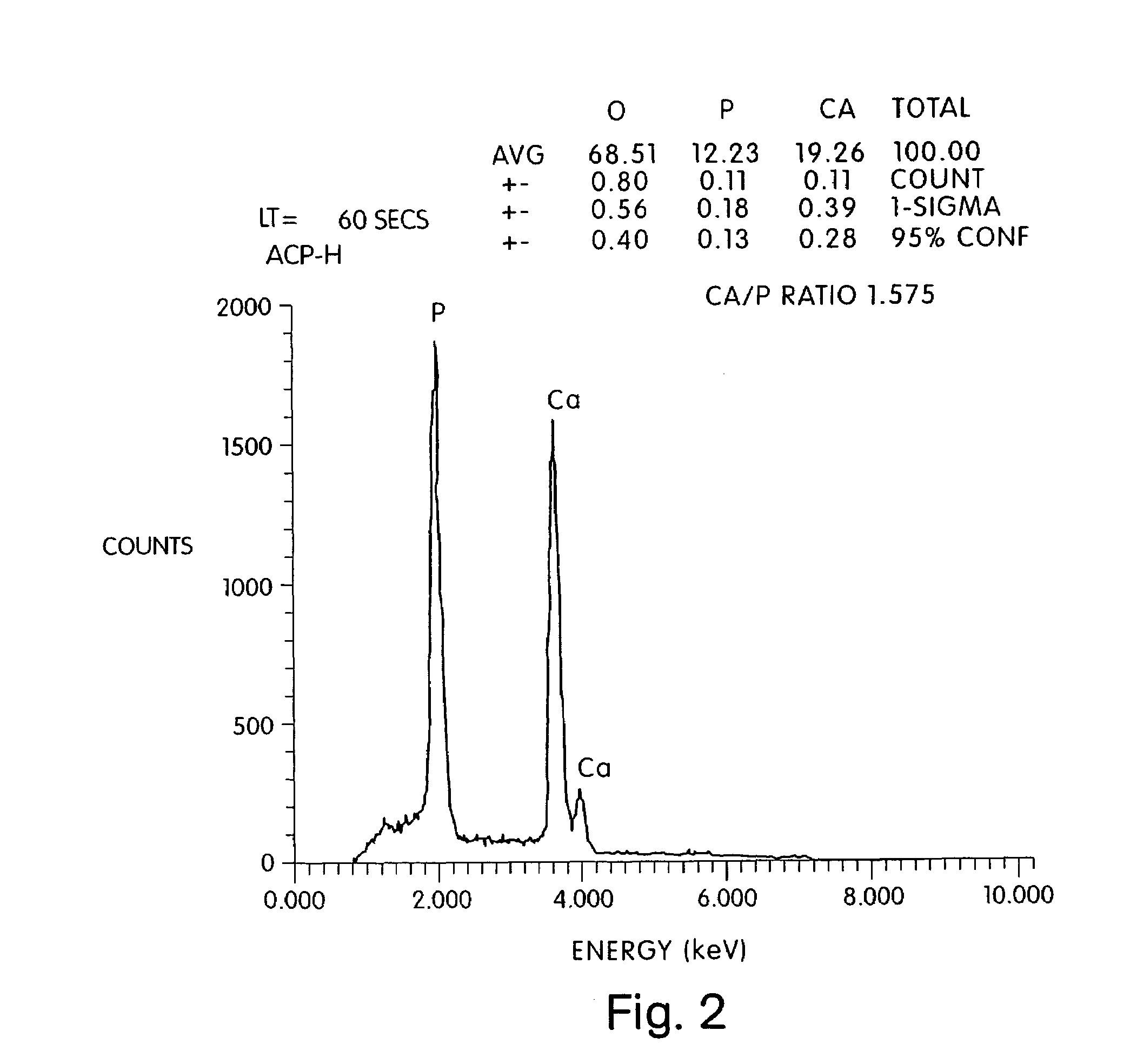
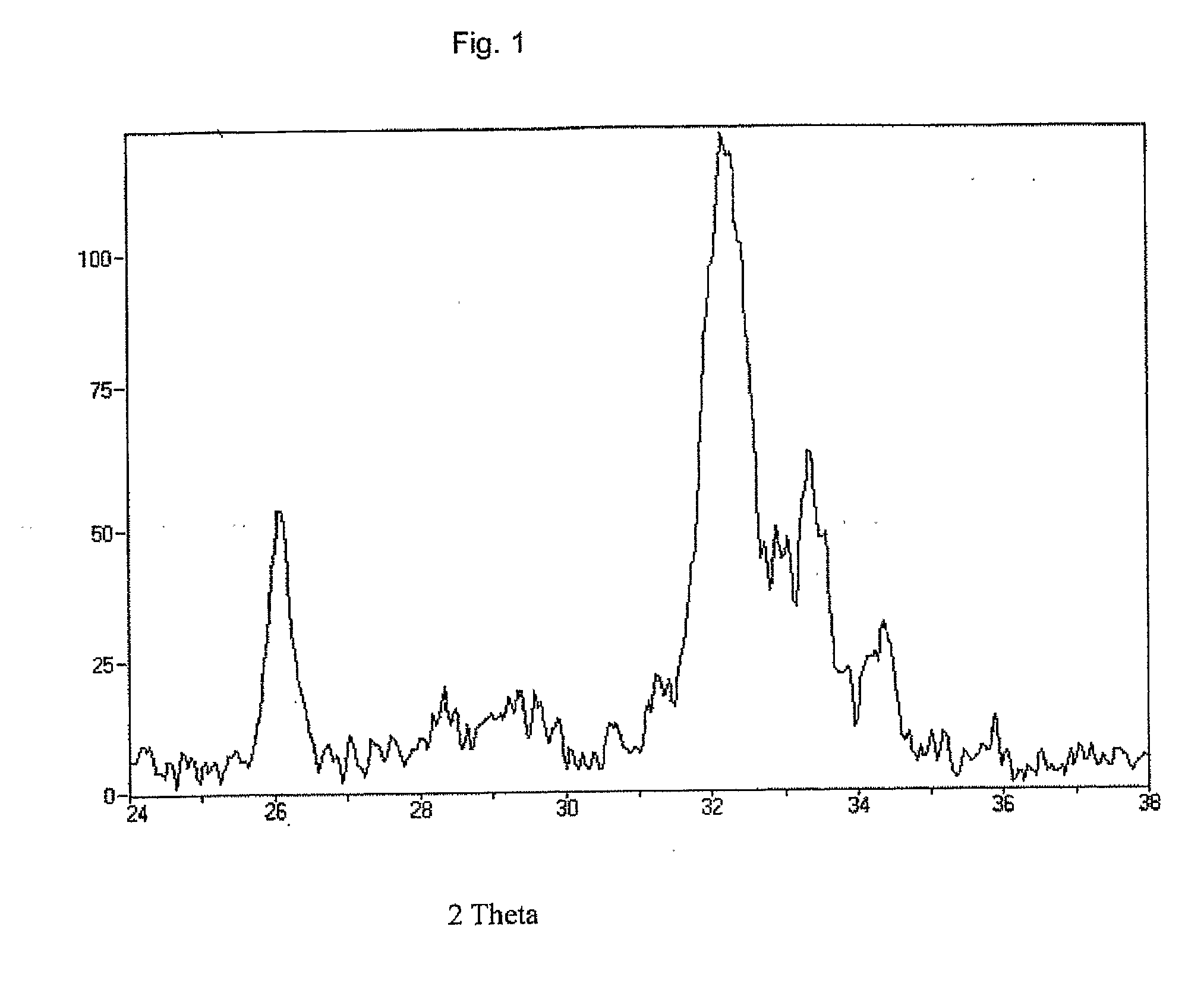
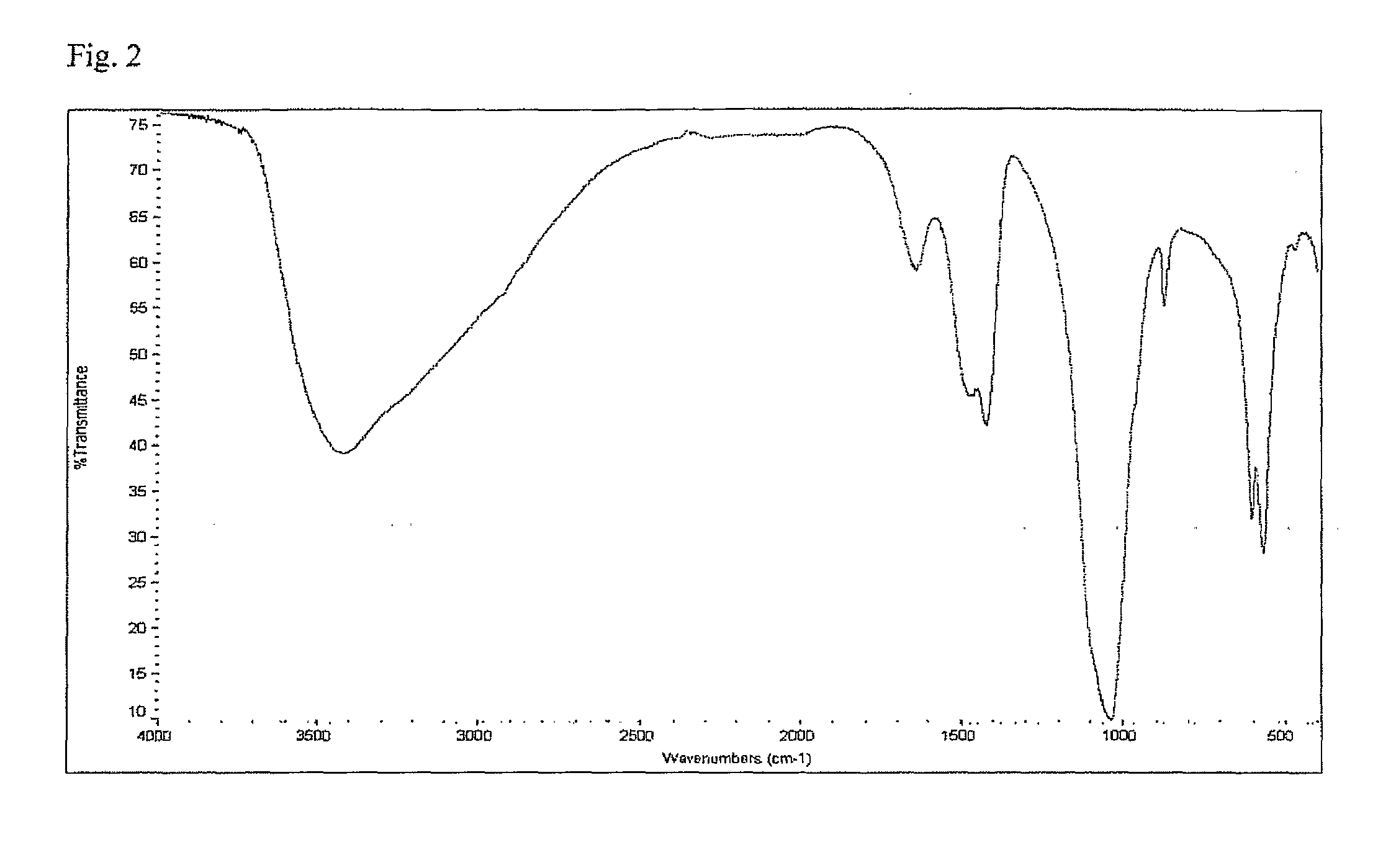
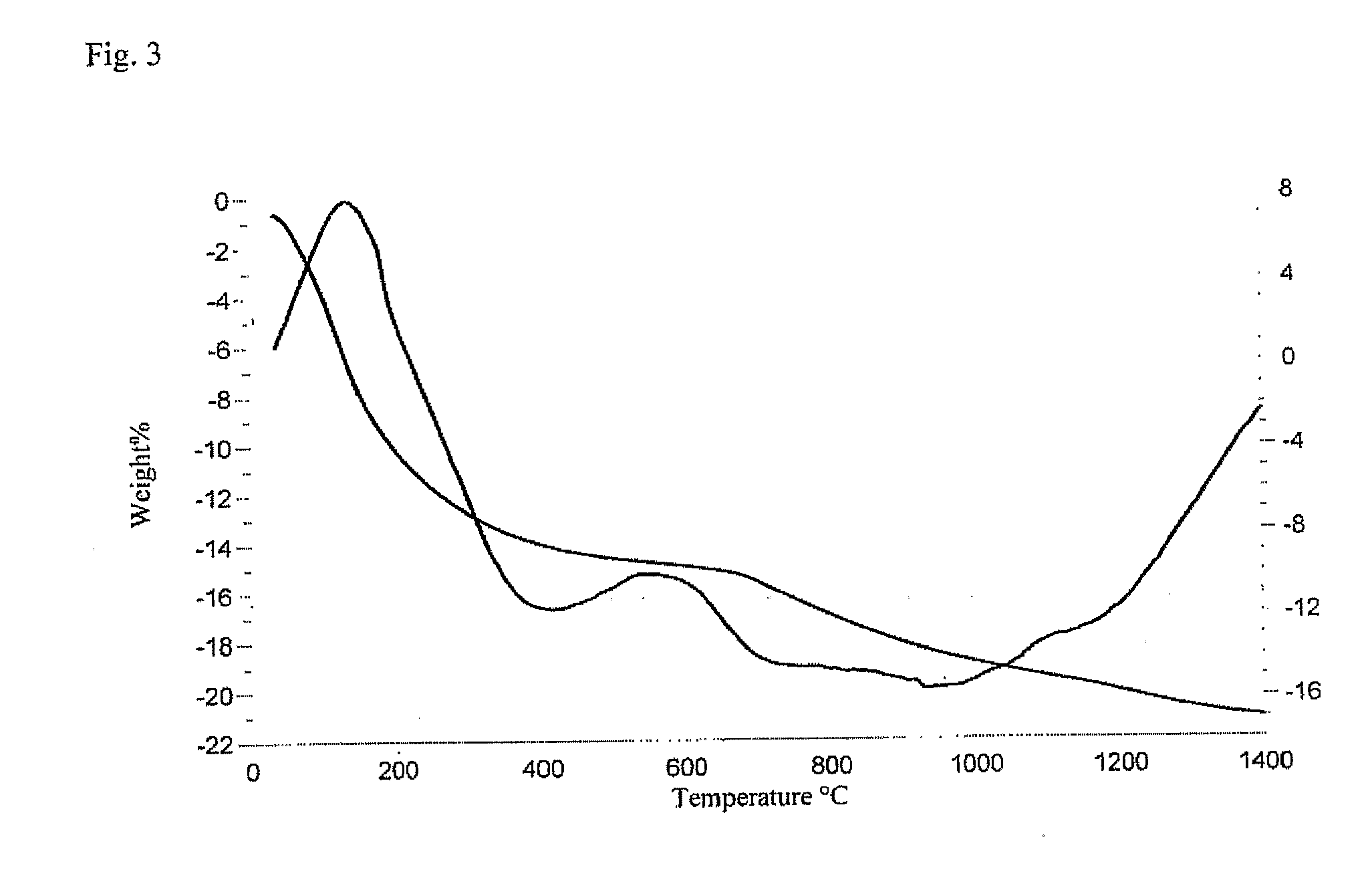
Method of preparing a poorly crystalline calcium phosphate and methods of its use
InactiveUS7517539B1Readily injectableHigh strengthBiocideSurgical adhesivesOsteoporotic boneIntervertebral spaces
The present invention provides a novel process for producing a calcium phosphate cement or filler which hardens in a temperature dependent fashion in association with an endothermic reaction. In the reaction a limited amount of water is mixed with dry calcium phosphate precursors to produce a hydrated precursor paste. Hardening of the paste occurs rapidly at body temperature and is accompanied by the conversion of one or more of the reactants to poorly crystalline apatitic calcium phosphate. The hardened cements, fillers, growth matrices, orthopedic and delivery devices of the invention are rapidly resorbable and stimulate hard tissue growth and healing. A composite material is provided including a strongly bioresorbable, poorly crystalline apatitic calcium phosphate composite and a supplementary material. The supplementary material is in intimate contact with the hydroxyapatite material in an amount effective to impart a selected characteristic to the composite. The supplemental material may be biocompatible, bioresorbable or non-resorbable. A method for treating a bone defect also is provided by identifying a bone site suitable for receiving an implant, and introducing a strongly resorbable, poorly crystalline apatitic calcium phosphate at the implant site, whereby bone is formed at the implant site. The implant site may be a variety of sites, such as a tooth socket, non-union bone, bone prosthesis, an osteoporotic bone, an intervertebral space, an alveolar ridge or a bone fracture.
Owner:LIFE SCI ENTERPRISES
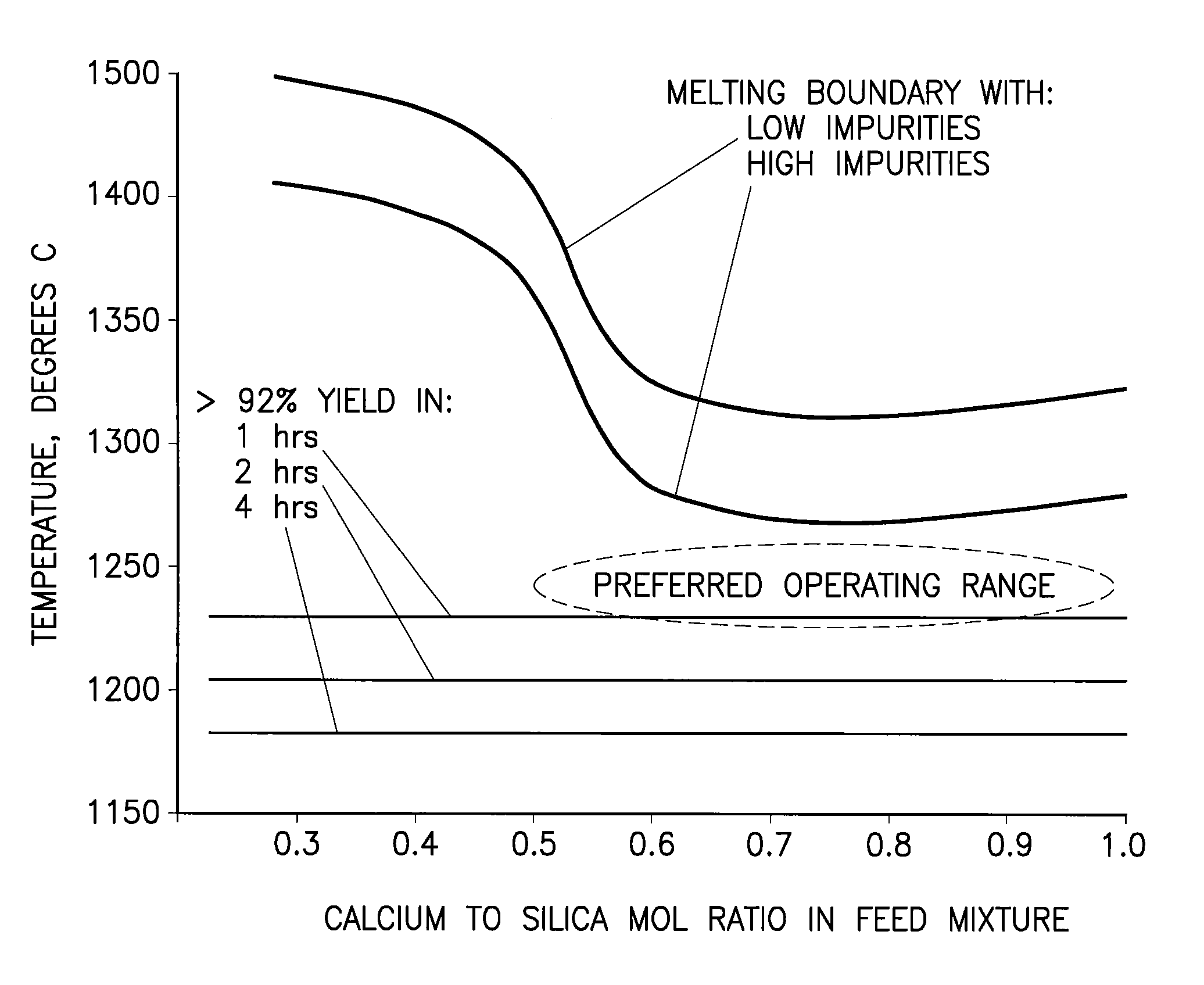
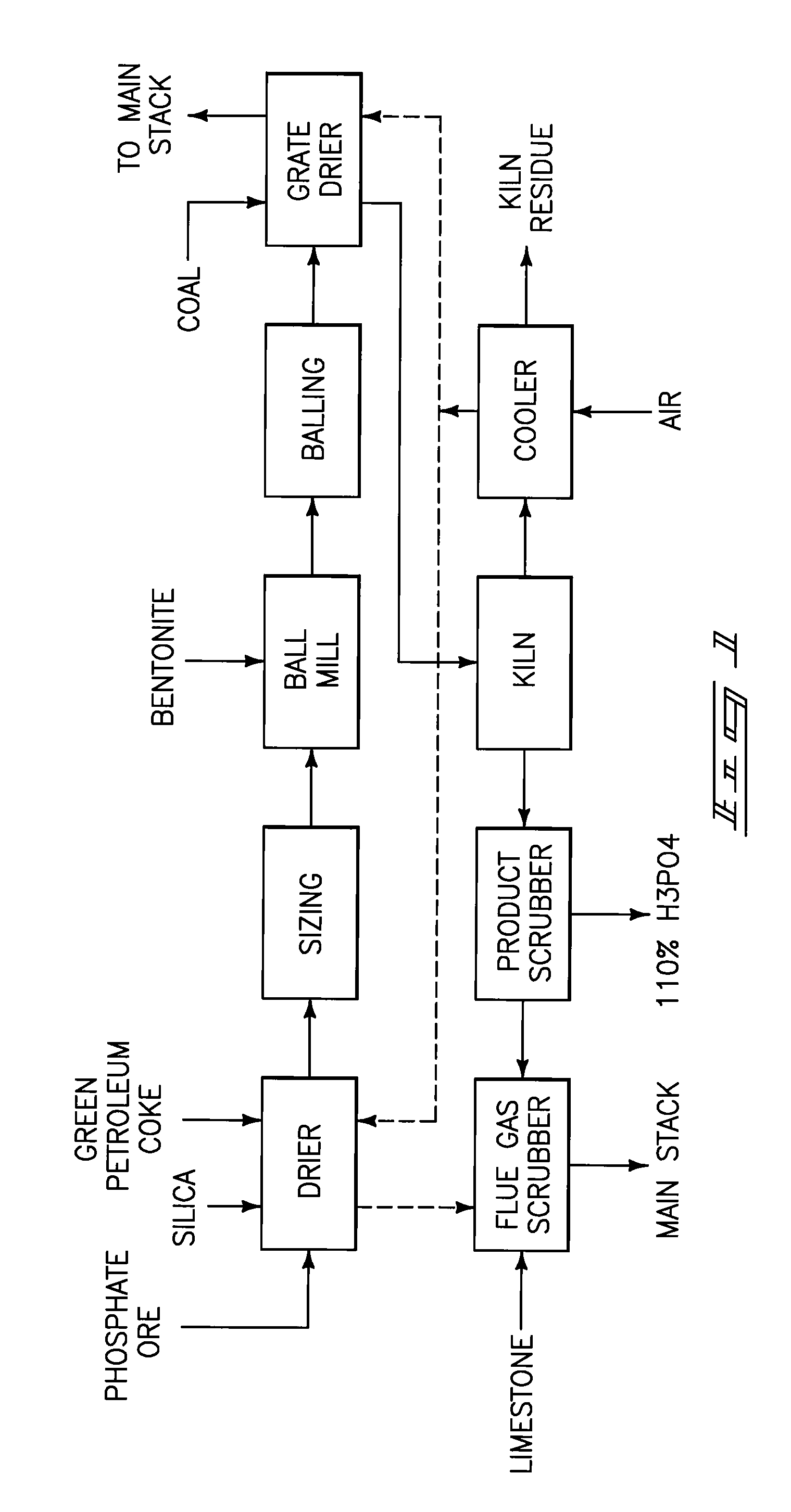
Phosphorous pentoxide producing methods
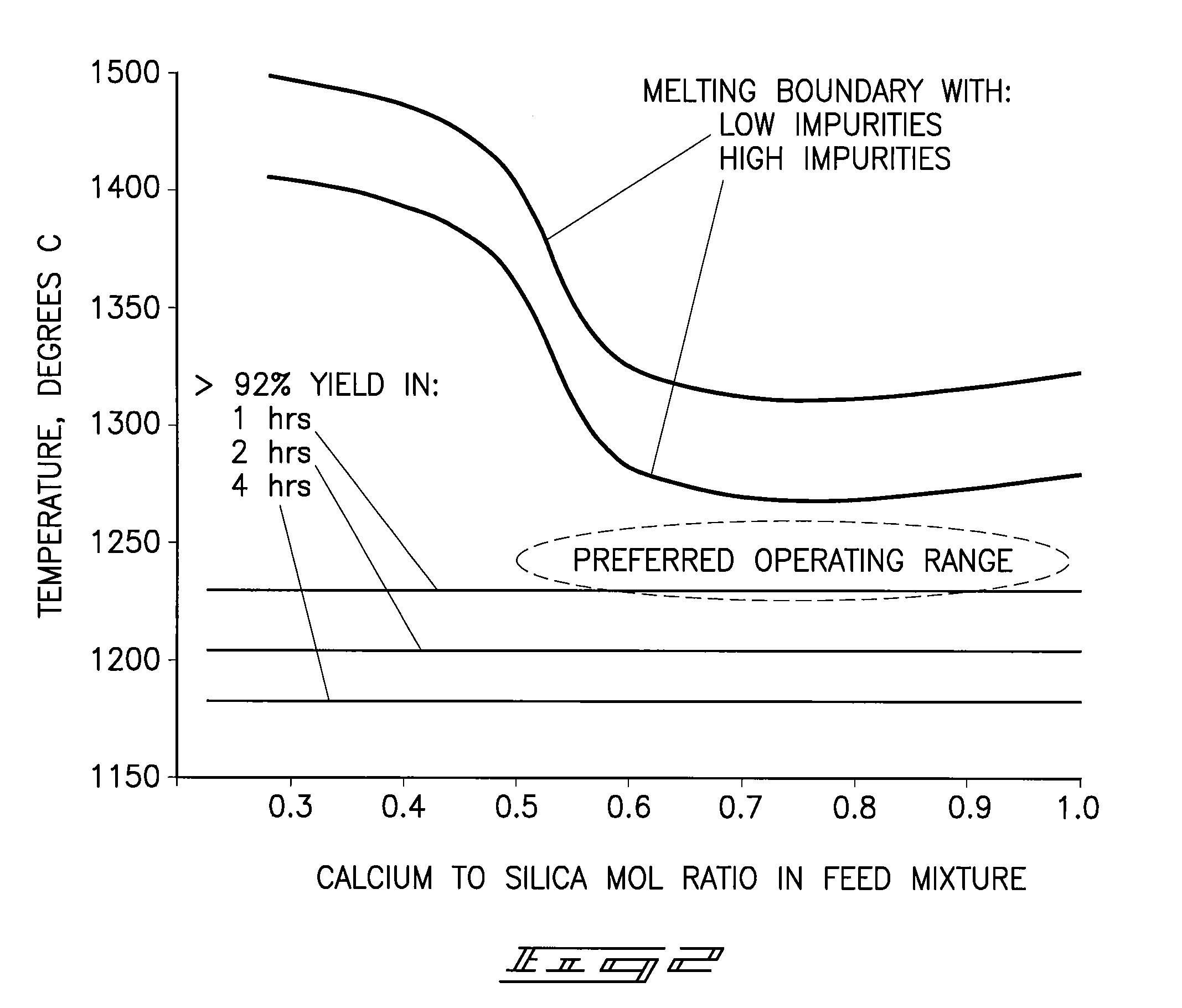
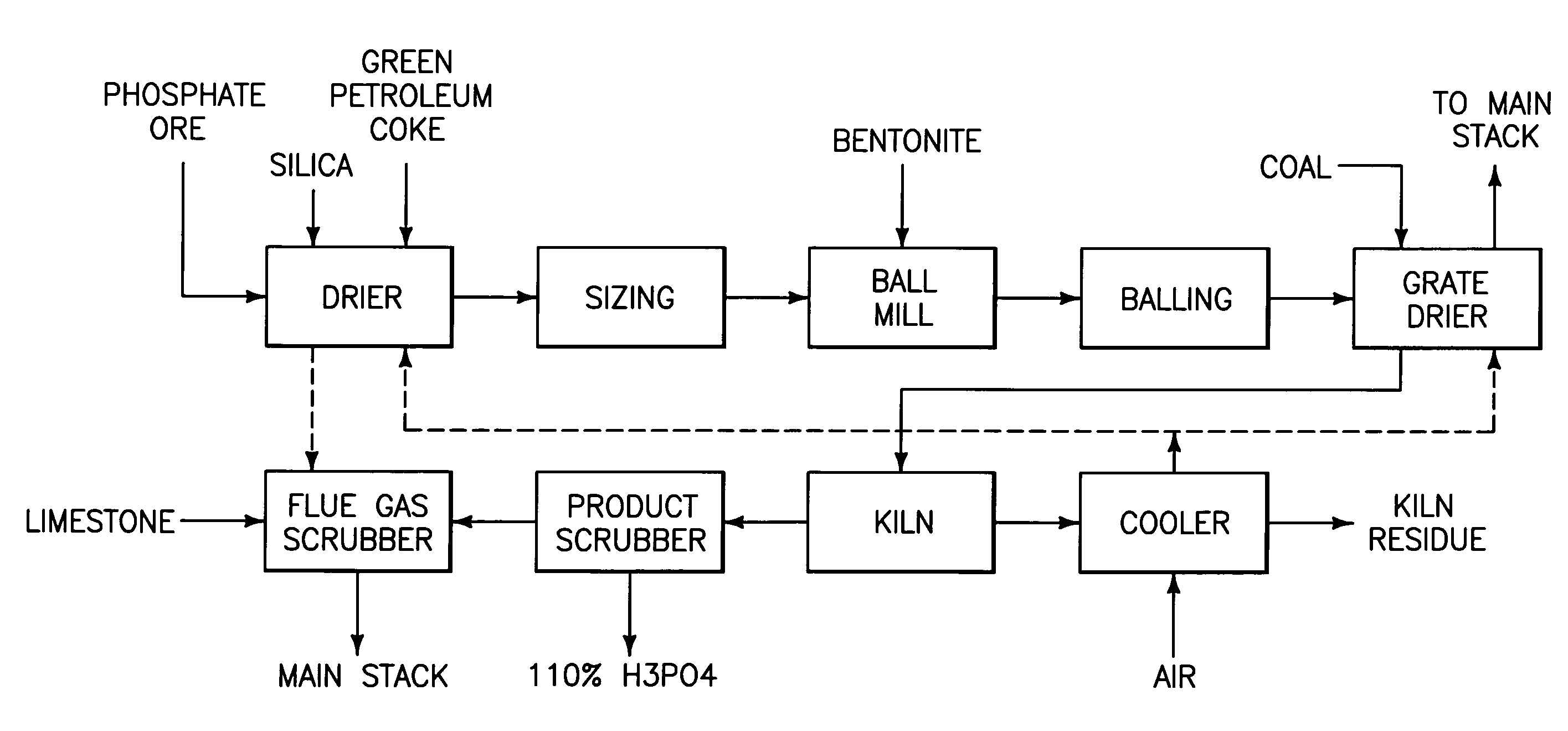
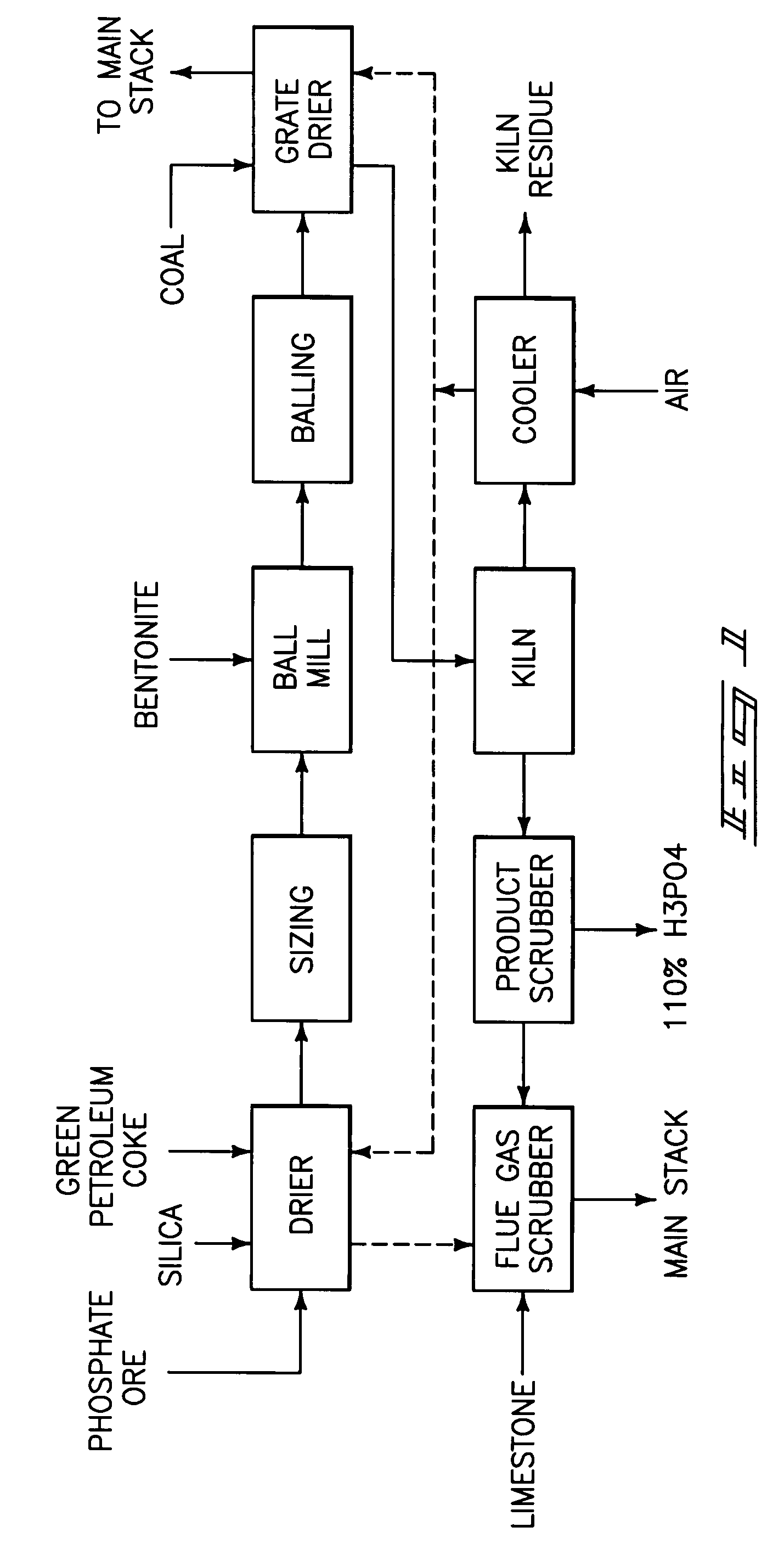
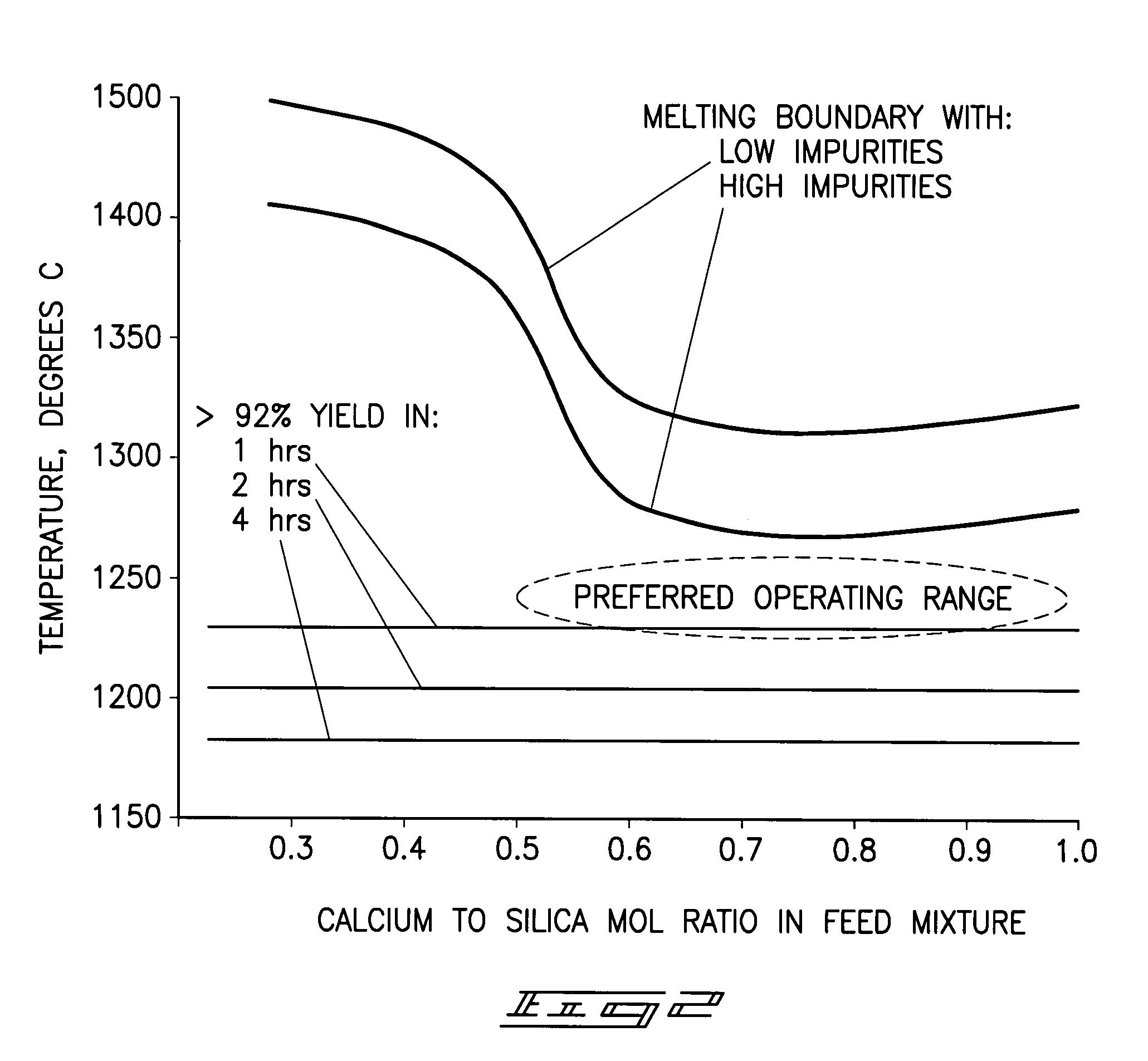
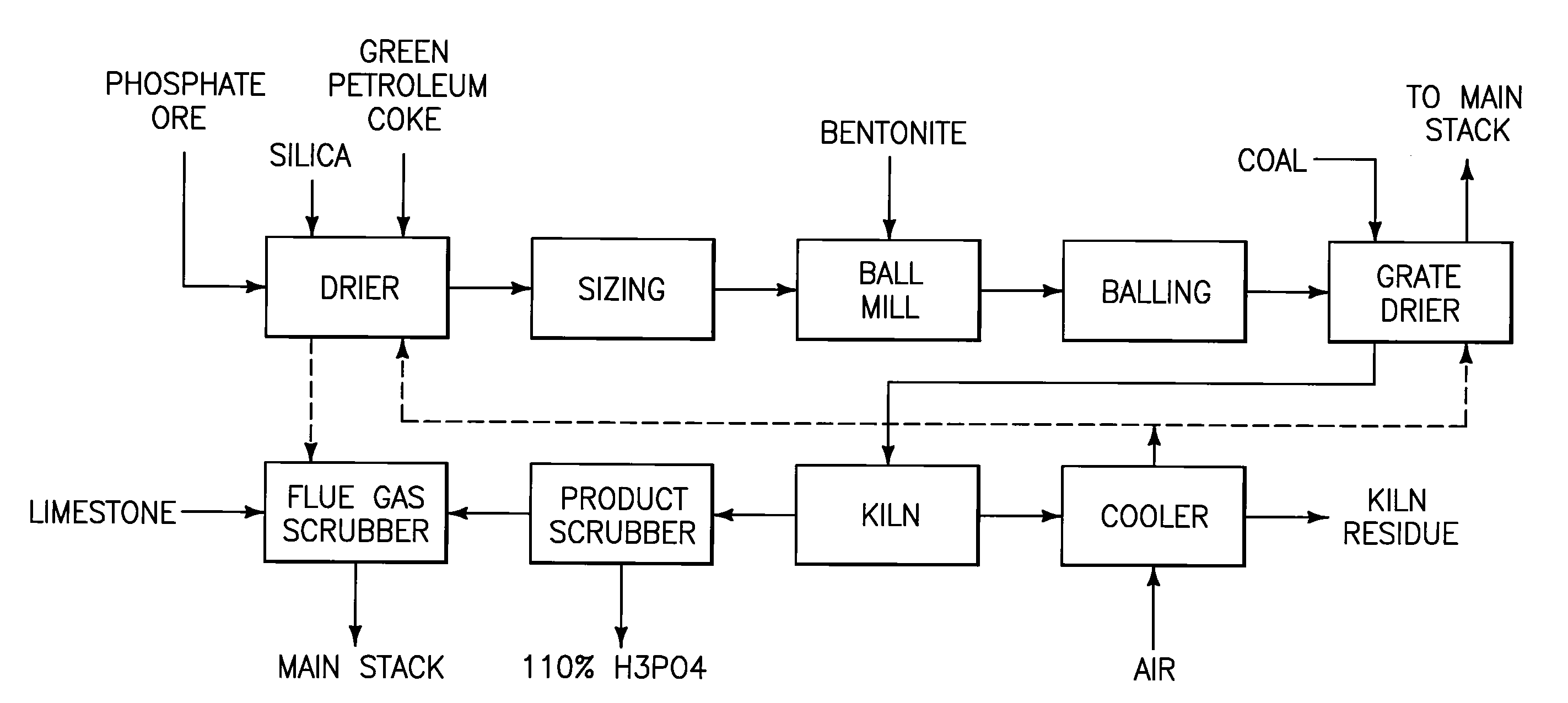
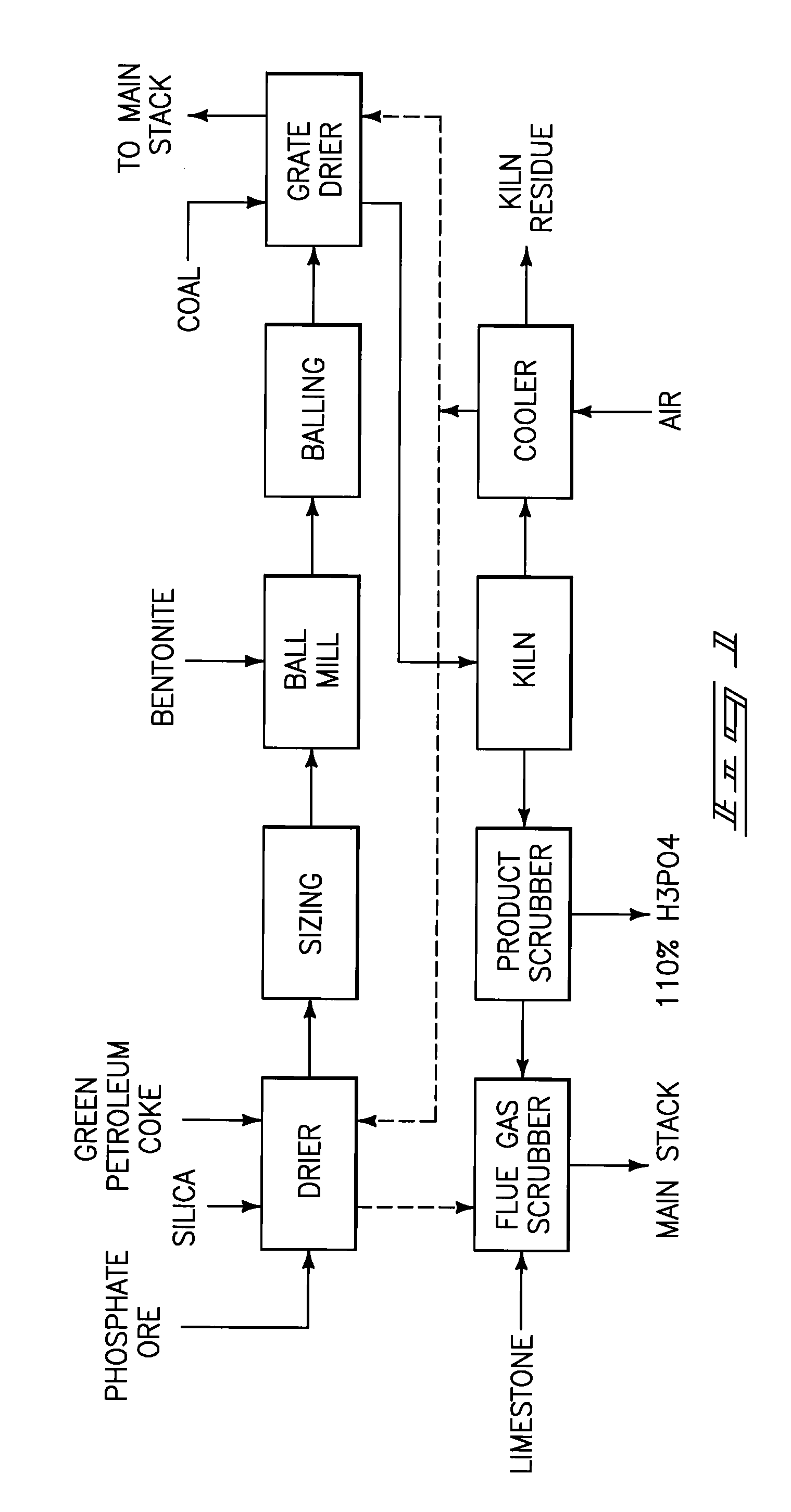
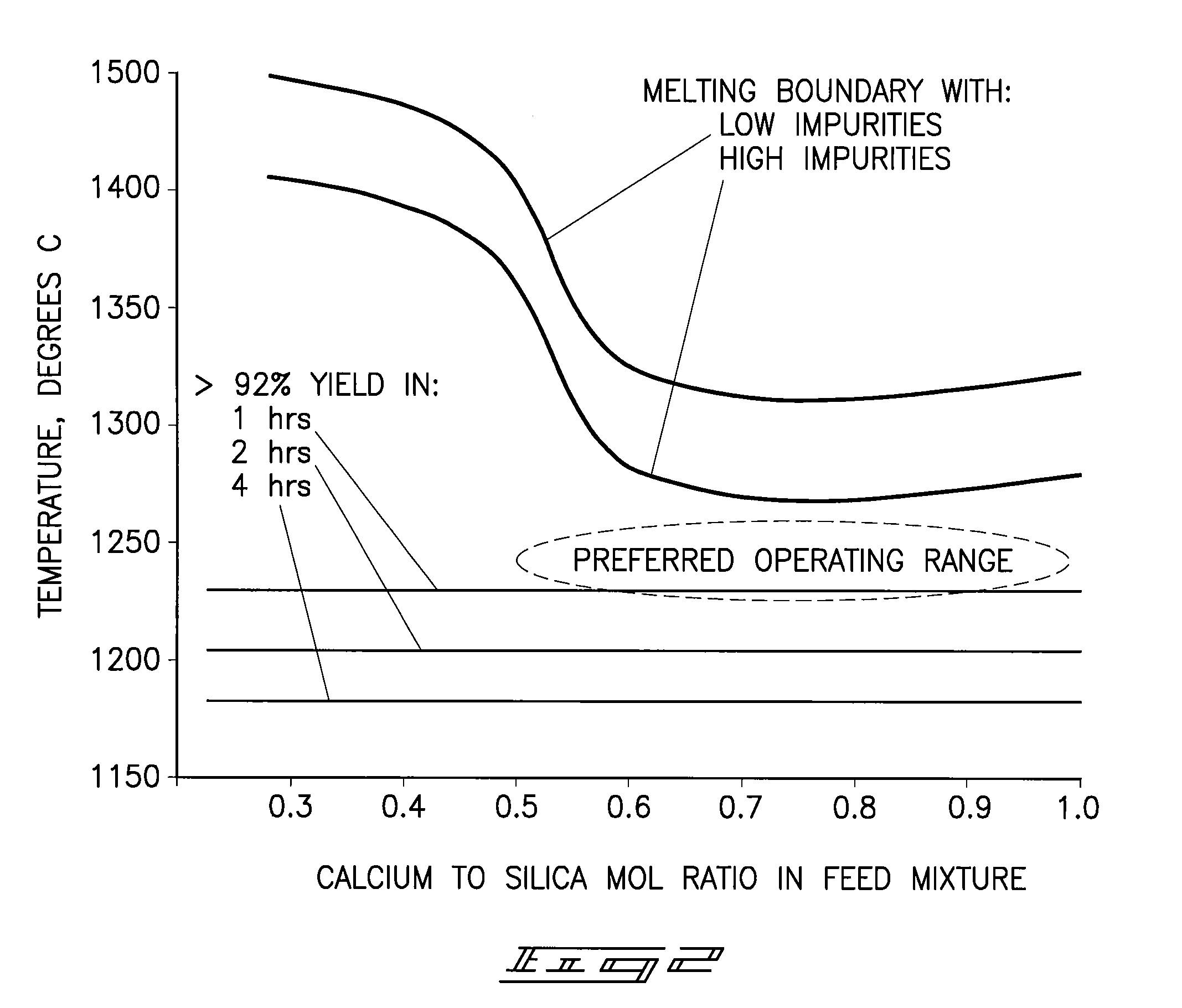
A phosphorous pentoxide producing method includes forming a kiln bed using feed agglomerates with a calcium-to-silica mole ratio of from 0.5 to 1.0 and maintaining a bed temperature at or above 1260° C. along a portion of the bed length without exceeding 1380° C. along the entire bed length. Less than 10% of the agglomerates' phosphate input to the kiln remains in the kiln residue as phosphate. Another method includes maintaining a bed temperature at or above 1180° C. along a portion of the bed length and establishing a bed surface-to-volume ratio multiplied by a time for bed heat up to 1180° C. of less than 50 minutes-ft2 / ft3.
Owner:NOVAPHOS INC
Sorbents for removing mercury from emissions produced during fuel combusion
InactiveUS20130157845A1Good predictor of thermal stabilitySuitable thermal stabilityUrea derivatives preparationNitrogen compoundsActivated carbonHalogen
Activated carbon is rendered more thermally stable by exposure to a non-halogenated additive, and optionally to a halogen and / or a halogen-containing compound. Such treated carbon is suitable for use in mitigating the content of hazardous substances in flue gases, especially flue gases having a temperature within the range of from about 100° C. to about 420° C.
Owner:ALBEMARLE AMENDMENTS LLC
Phosphorous pentoxide producing methods
A phosphorous pentoxide producing method includes forming a kiln bed using feed agglomerates with a calcium-to-silica mole ratio of less than 1.0 and maintaining a bed temperature at or above 1180° C. along at least 50% of the bed length without exceeding 1380° C. along the entire bed length. Less than 10% of the agglomerates' phosphate input to the kiln remains in the kiln residue as phosphate. Another method includes maintaining a bed temperature at or above 1180° C. along a portion of the bed length and establishing a bed surface-to-volume ratio multiplied by a time for bed heat up to 1180° C. of less than 50 minutes-ft2 / ft3.
Owner:NOVAPHOS PHOSPHATE TECH LLC
Solvent extraction process for recovery of uranium from phosphoric acid (25-55% P2O5)
InactiveUS20030113247A1Cheaply and stablySpeed up the processSolvent extractionTransuranic element compoundsPhosphorous acidO-Phosphoric Acid
An improved process of extraction of uranium from phosphoric acid and in particular uranium VI from phosphoric acid especially strong phosphoric acid using a selective synergistic extractant mix of an organo-phosphorous acid and a neutral extraction agent. The process basically involves the steps of extraction comprising contacting said acid with a selective synergistic extractant system of di-nonyl phenyl phosphoric acid (DNPPA) and a neutral agent selected from di-butyl butyl phosphonate (DBBP) and tri-n-octyl phosphine oxide (TOPO); and recovering the uranium values from the loaded organic phase. The above process would provide for an improved process for recovery of uranium both from weak and strong phosphoric acids using a stable and relatively cheap extractant system. The process is directed to improved recovery of U-VI from phosphoric acid by way of a simple, industrially applicable and cost-effective process.
Owner:SEC DEPT OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Biometic compounds containing hydroxyapatites substituted with magnesium and carbonate, and the processes used to obtain them
Carbonate hydroxyapatites containing magnesium, composite materials consisting of said hydroxyapatites and natural polymers are described; processes for the preparation of said materials and their use in orthopaedics and dentistry fields are also described.
Owner:A MENARINI IND FARM RIUNITE SRL
Wet-process technique for refining phosphoric acid
A process for purification by multistage countercurrent extraction of wet-process phosphoric acid includes the steps of (a) preparing an aqueous phosphoric acid by decomposition of crude phosphates with sulfuric acid and prepurification thereof; (b) providing an organic solvent mixture consisting of one of (A) a water immiscible solvent and a fully water-miscible solvent or (B) a partially water-miscible solvent and a fully water-miscible solvent; (c) extracting water from the acid by contacting with the solvent mixture in a volumetric ratio of acid to solvent mixture of 1:1 to 1:10 at a temperature of 5 to 90° C.; (d) recovering the fully water-miscible solvent by distillation and washing; (e) recycling the fully water-miscible solvent to step (b) to provide a recycled solvent mixture; and (f) repeating steps (c), (d) and (e) with the recycled solvent mixture to provide a phosphoric acid having a preselected degree of purity.
Owner:BK GIULINI CHEM
Phosphorous Pentoxide Producing Methods
A phosphorous pentoxide producing method includes forming a kiln bed using feed agglomerates with a calcium-to-silica mole ratio of from 0.5 to 1.0 and maintaining a bed temperature at or above 1260° C. along a portion of the bed length without exceeding 1380° C. along the entire bed length. Less than 10% of the agglomerates' phosphate input to the kiln remains in the kiln residue as phosphate. Another method includes maintaining a bed temperature at or above 1180° C. along a portion of the bed length and establishing a bed surface-to-volume ratio multiplied by a time for bed heat up to 1180° C. of less than 50 minutes-ft2 / ft3.
Owner:NOVAPHOS INC
Indole compounds useful for the treatment of cancer
InactiveUS7151100B1Reduced expression levelGood curative effectBiocideOrganic chemistryCancer cellMedicine
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
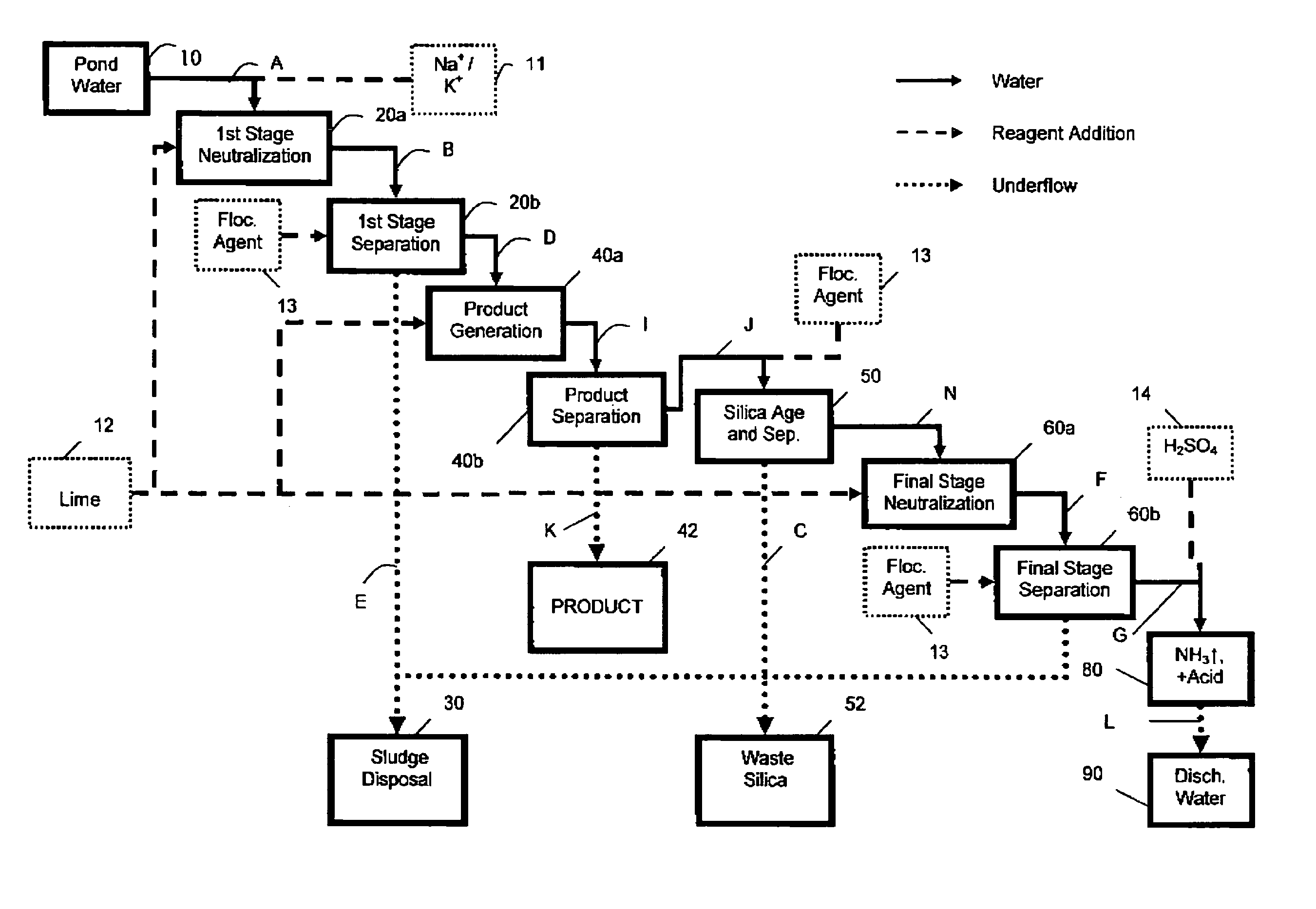
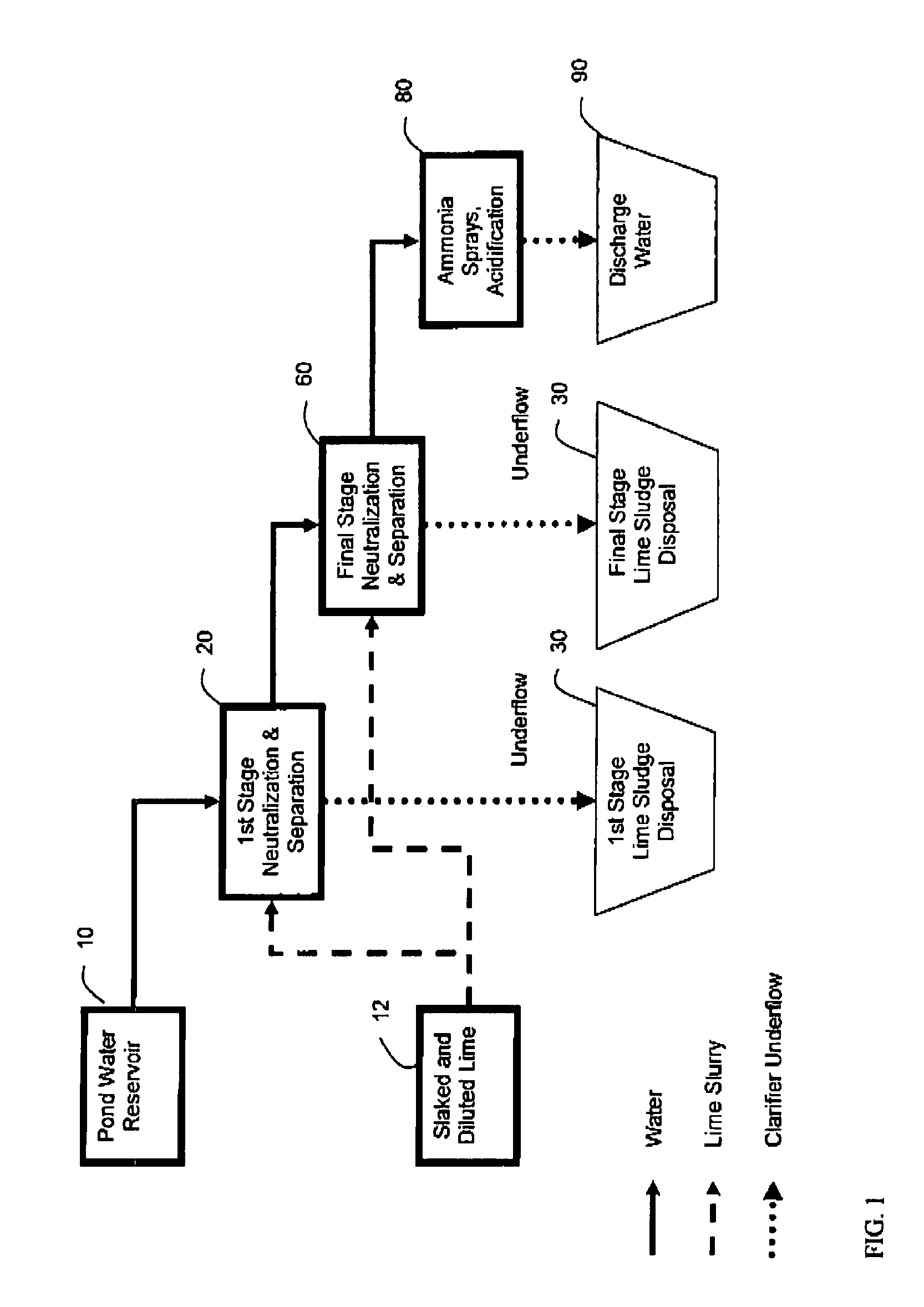
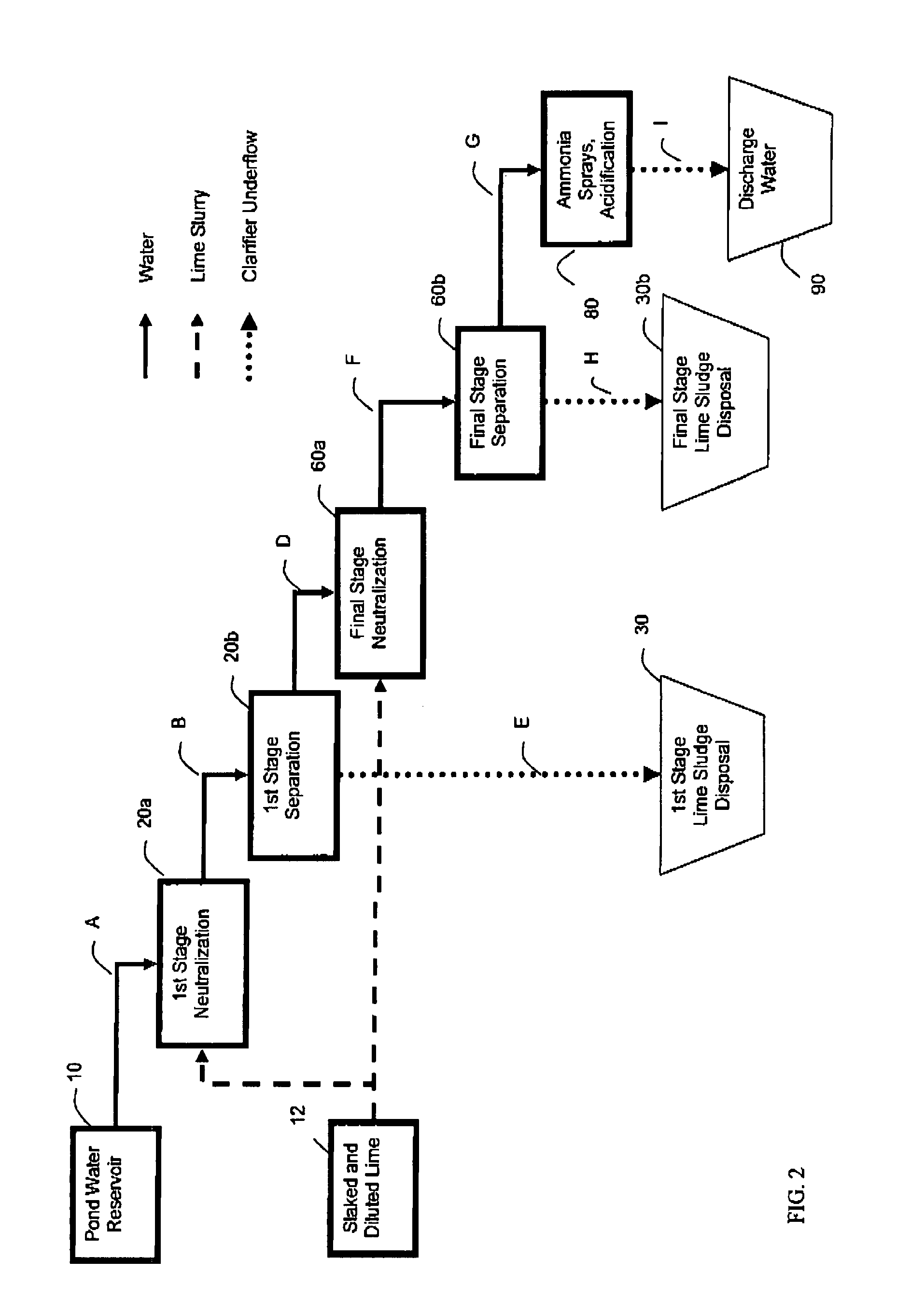
Process for treating pond water
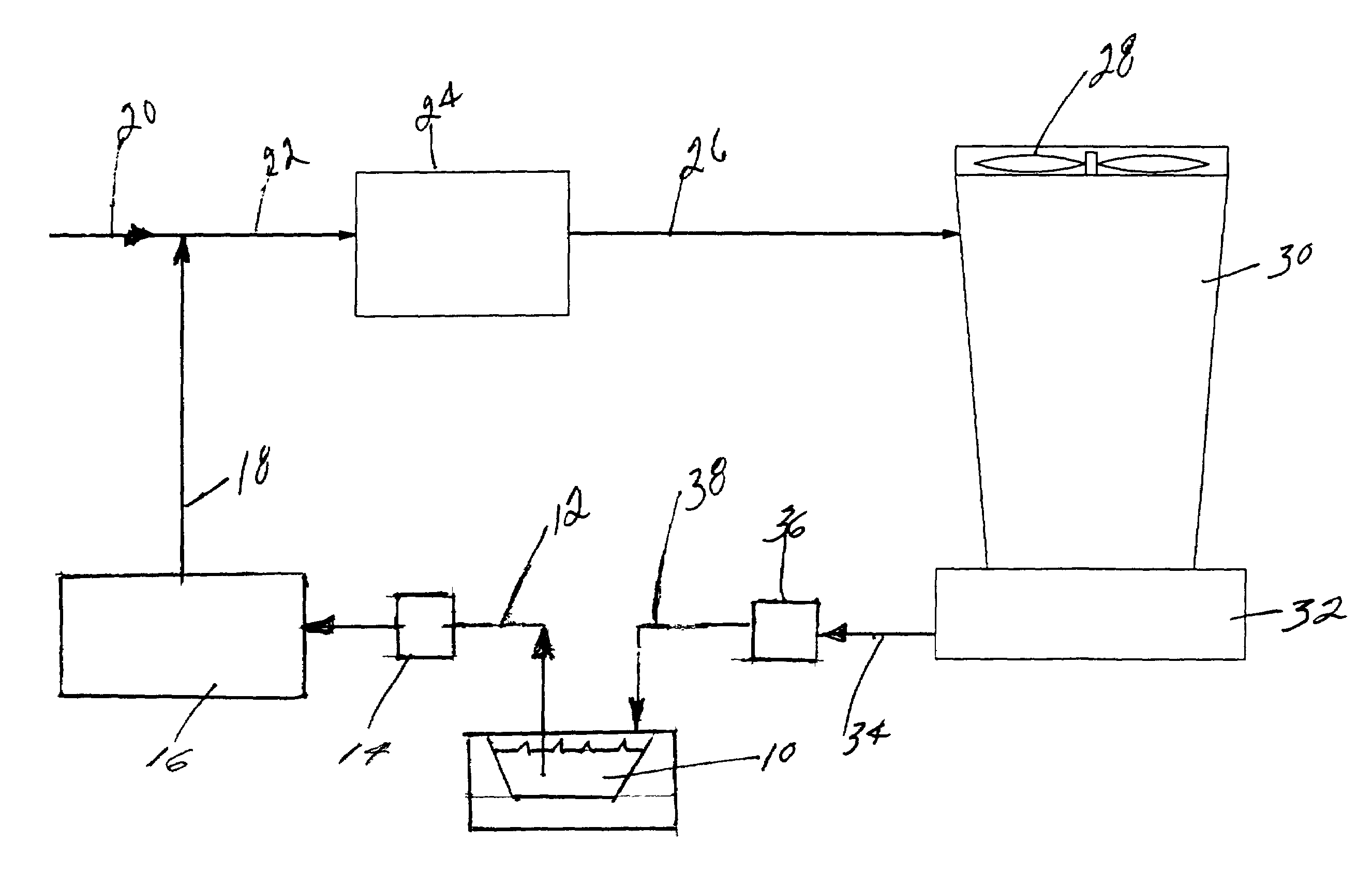
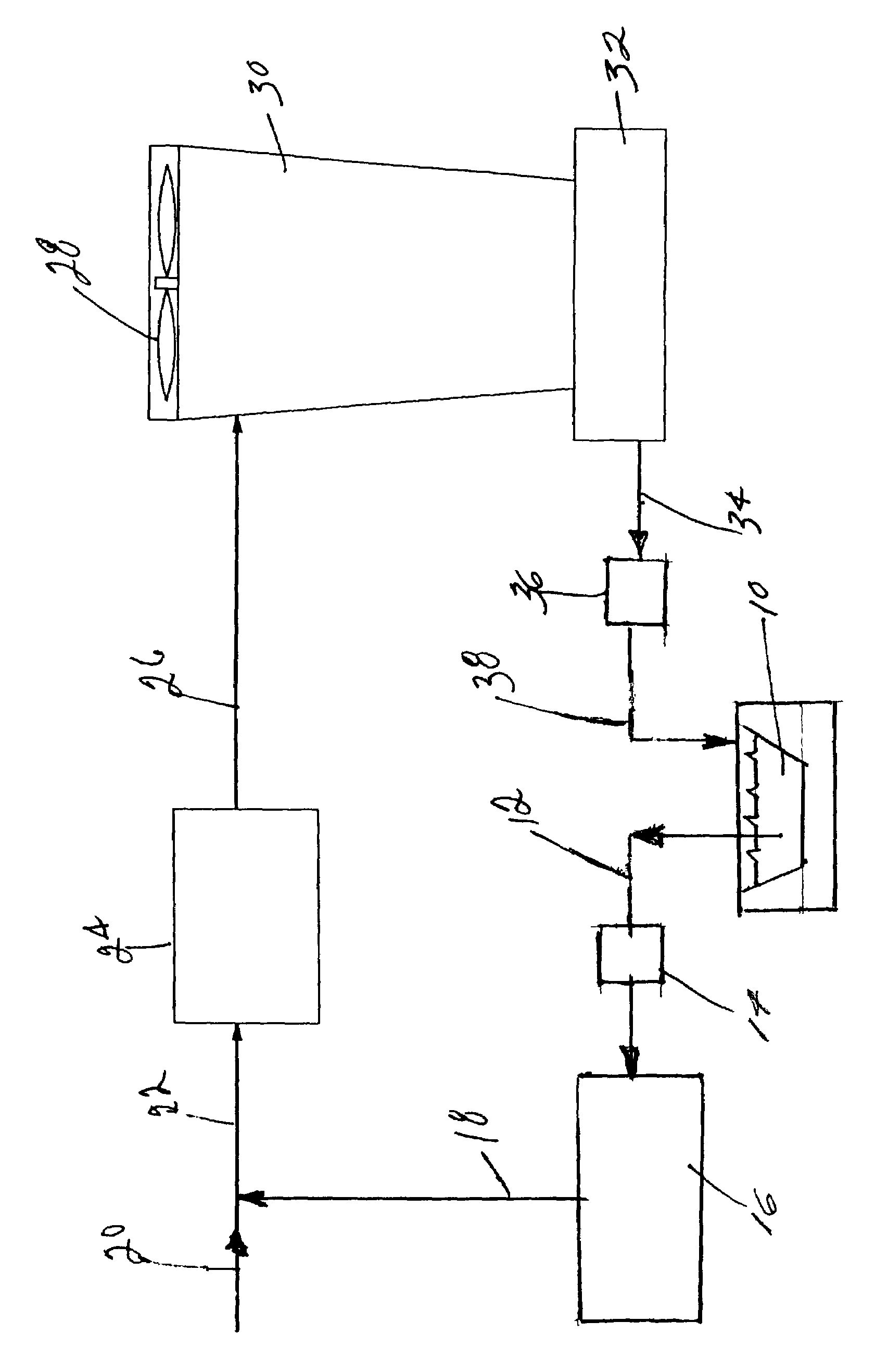
ActiveUS7560031B1Promote recoveryLow fluoride valueWater contaminantsPhosphorus oxyacidsSludgePhosphate product
A process for the treatment of phosphoric acid plant pond water facilitating the recovery of phosphorus values from the input pond water. In certain aspects the process recycles solids from a later stage neutralization and separation into the clarified liquid stream from an initial clarification and neutralization stage. A sufficient amount of solids are added to the clarified liquid stream to effect the pH-dependent precipitation of a phosphate product. In alternative aspects an intermediate pH-dependent precipitation of a phosphate product is achieved through the addition of a neutralizing agent. The phosphate product is further characterized by a low concentration of fluoride. In addition the phosphate product can be further processed to a high purity technical grade phosphoric acid. In certain aspects the process employs flocculating agents to enhance the formation of precipitates. In further aspects, methodologies taught herein facilitate the reduction of silica in the process streams. Processes according to the present invention are further characterized by an enhanced recovery of treated water, reduced sludge impoundment and reduced lime consumption when compared to conventional double liming processes.
Owner:VEOLIA WATER NORTH AMERICA OPERATING SERVICES
Preparing method of difluorophosphoric acid and lithium difluorophosphate
The invention relates to a preparing method of difluorophosphoric acid and lithium difluorophosphate. The preparing method of lithium difluorophosphate comprises the following steps of 1, carrying outa reaction between dichloro phosphate and a fluorinated reagent to prepare the difluorophosphoric acid, wherein the fluorinated reagent is AsF3, NH4F, NH4HF2 and / or MFx, for MFx, x is equal to 1 or 2or 3, and M is hydrogen, alkali metal, alkaline-earth metal or transition metal; 2, carrying out a reaction between difluorophosphoric acid and a lithium source material in a non-aqueous agent. According to the preparing method of lithium difluorophosphate, dichloro phosphate, the fluorinated reagent and the lithium source material serve as raw materials to carry out the reactions to prepare lithium difluorophosphate, and the raw materials are wide in source and low in cost; a fluoridation reaction and a substitution reaction of the lithium source material easily take place, the side reactionis small, a crude product of lithium difluorophosphate with few impurities is conveniently obtained under the condition of a high conversion rate, and thus good conditions are created for obtaining high-quality products of lithium difluorophosphate at low cost.
Owner:DO FLUORIDE CHEM CO LTD
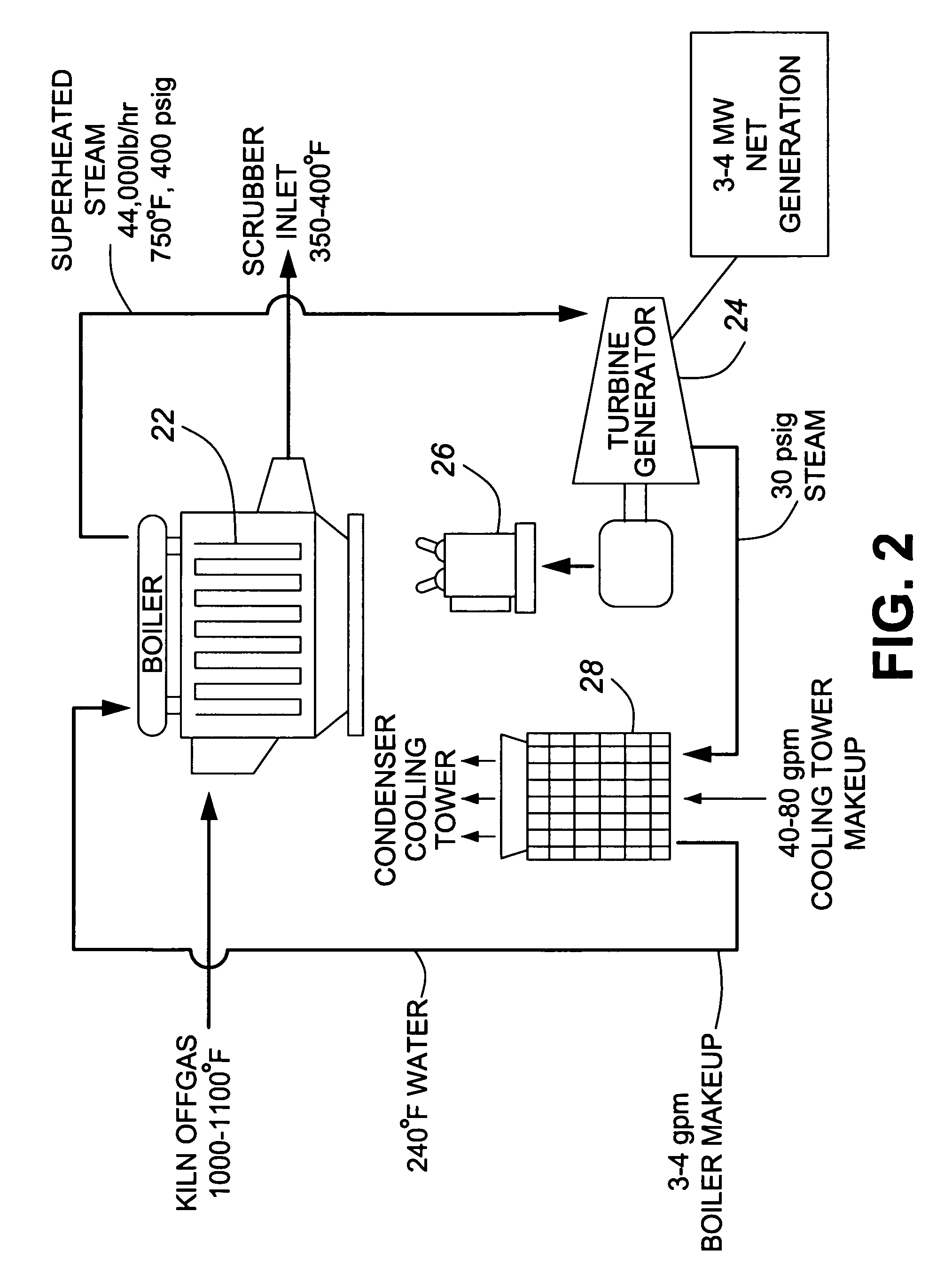
Integrated lime kiln process
ActiveUS20080031794A1Optimizing pollutantSimple technologyUsing liquid separation agentRotary drum furnacesWaste heat recovery unitPlate heat exchanger
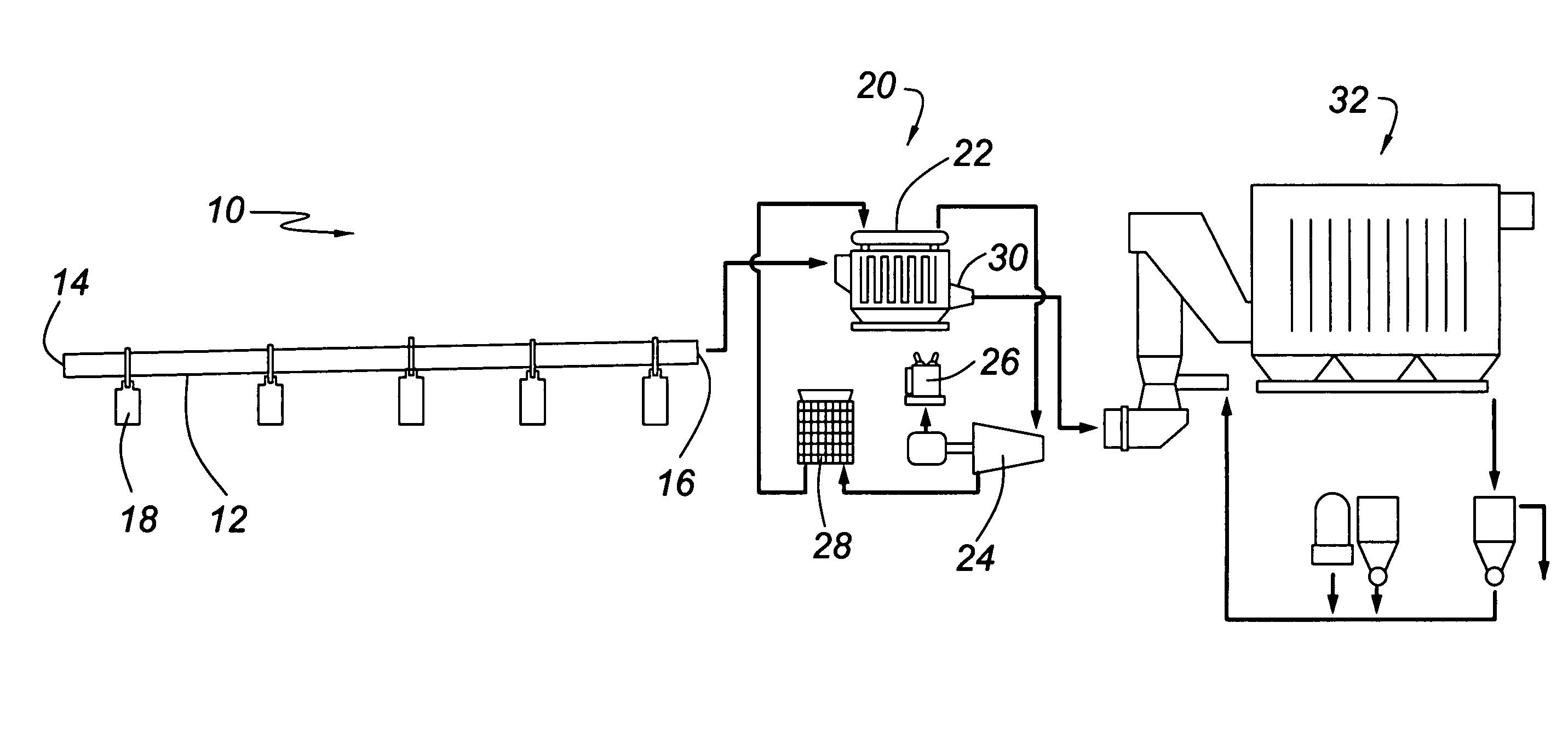
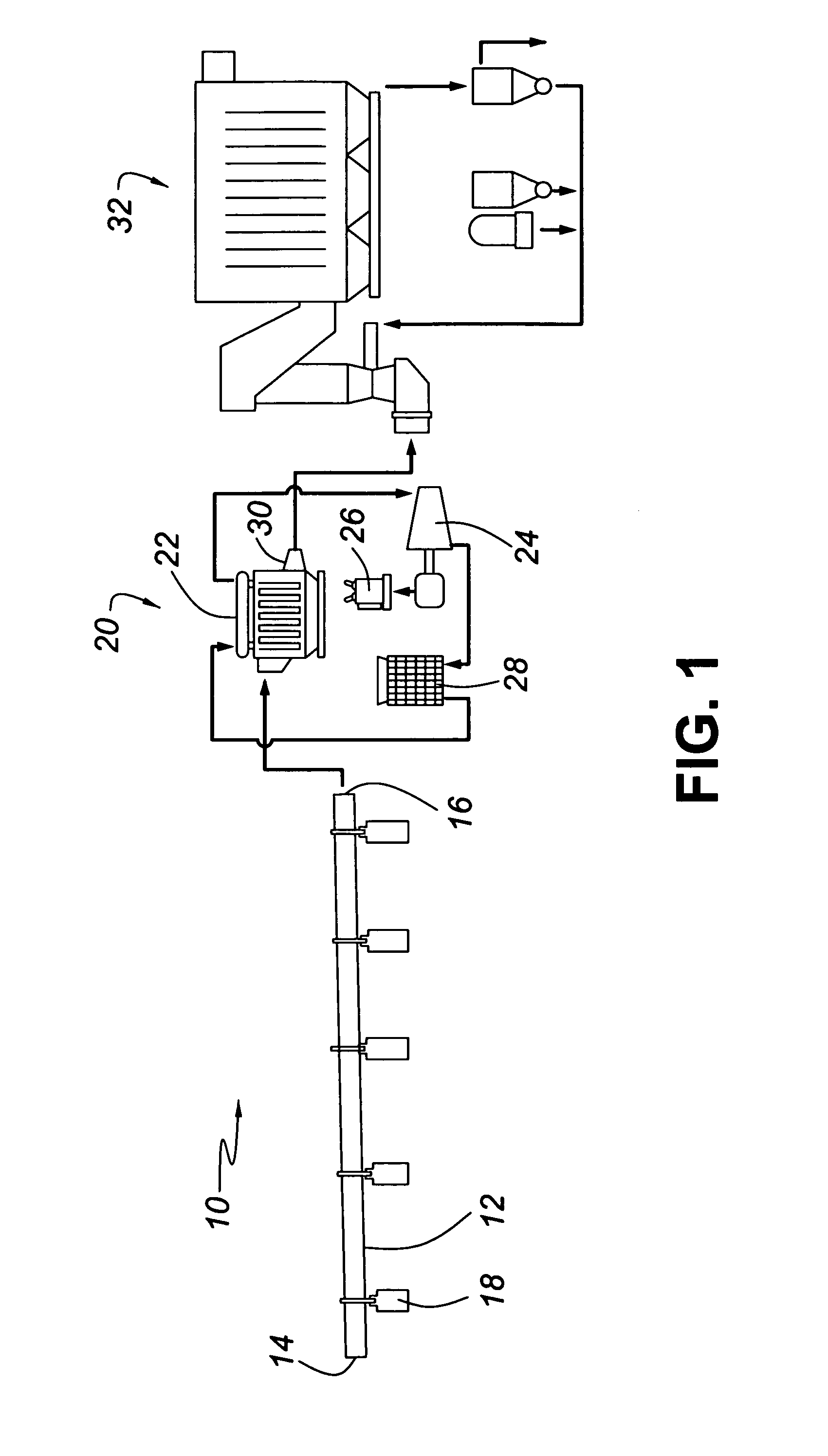
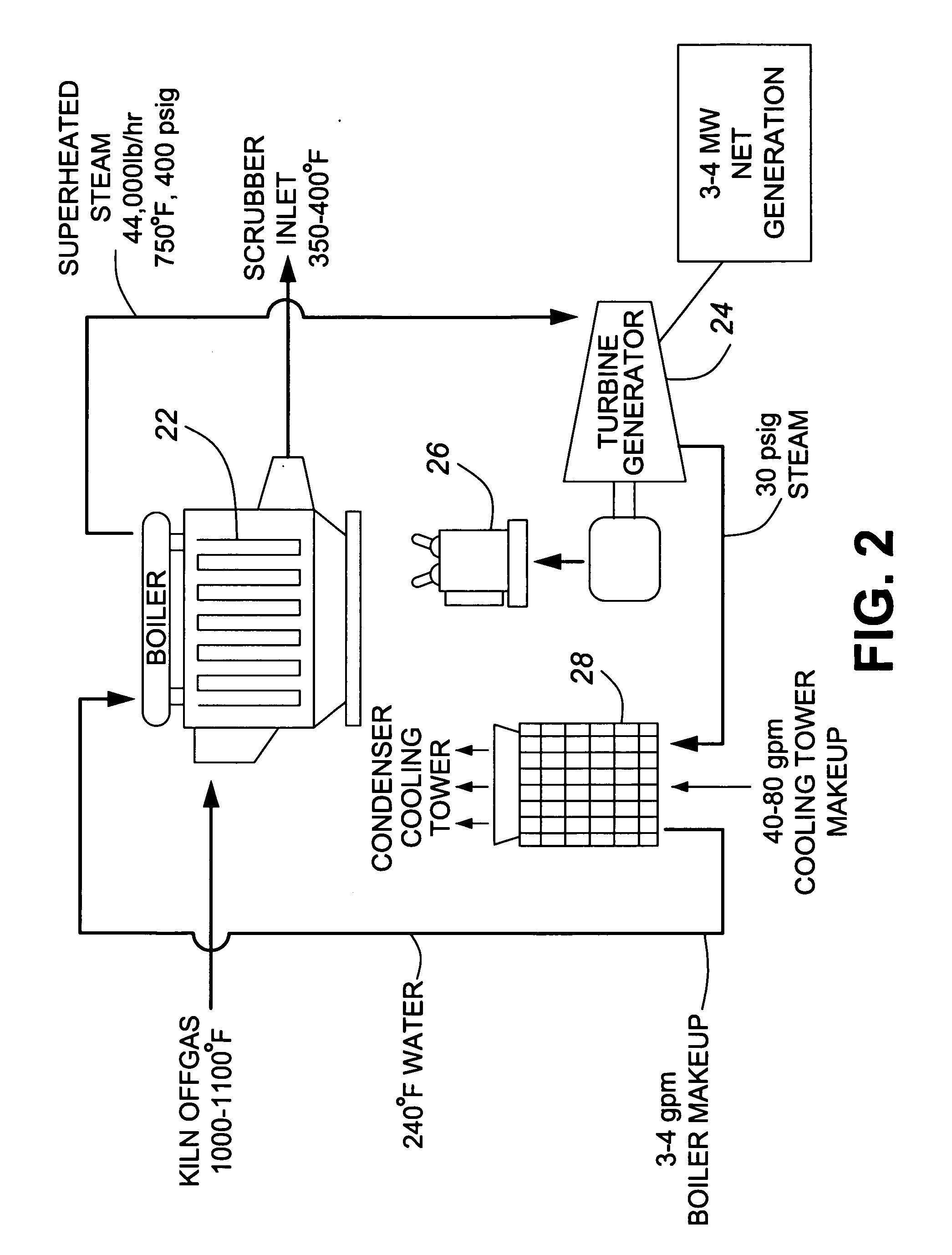
A process and system for recovering waste heat from a kiln used for lime or cement production. The system unifies the kiln, a waste heat recovery and power generation circuit and a dry scrubber for scrubbing the pollutants from the kiln offgas. Essentially, the system employs the boiler component of the waste heat recovery and power generation circuit as a heat exchanger to recover the waste heat from the kiln, which is used to drive the steam turbines. The heat absorption from the latter stage lowers the temperature of the kiln offgas sufficiently for optimum performance from the scrubber. The presence of lime particles in the offgas effectively protects the boiler tube surfaces from corrosion which would occur at optimum scrubber temperatures, and subsequently provides the lime required as a scrubbing medium for the dry scrubber. Further, the efficient scrubbing allows for the use of any fuel for firing the kiln inclusive of high sulphur content compounds. A process for effecting the technology is also provided.
Owner:GRAYMONT PA INC
Method for preparing Dawson heteropolyphosphatotungstate
InactiveCN103613082AEasy to operateShort reaction processPhosphorus oxyacidsInorganic saltsTungstate
The invention discloses a method for preparing Dawson heteropolyphosphatotungstate. The method comprises the following steps: (1) enabling a tungstate solution to come into contact with an inorganic acid solution, so as to obtain a reactive intermediate; (2) continuously enabling the solution to come into contact with a phosphoric acid solution, so as to obtain a phosphotungstic acid solution; (3) transferring the phosphotungstic acid solution to a high-pressure reactor, and carrying out high-temperature and high-pressure reaction; (4) adding an inorganic salt precipitant to the obtained phosphotungstic acid solution, carrying out salting-out crystallization to obtain phosphotungstate, filtering, purifying and drying, so as to obtain the Dawson heteropolyphosphatotungstate. Compared with the prior art, the method is simple in technological process, short in reaction cycle, high in yield and product purity, and low in cost; meanwhile, strong acid acidification and diethyl ether extraction used in the traditional method are avoided; the safety of the preparation process is greatly improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method of filtering phosphate utilizing a rotary table filter or horizontal table filter
Owner:THOMPSON INDAL SERVICES
Process for recycling waste acid
ActiveUS20080056982A1Quality improvementWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOrganic compound preparationSULFATE IONSpent acid
A recycling process is presented to treat spent waste acid solutions whereby useful products are produced. Spent waste acid containing inorganic and organic contaminants is mixed with a magnesium compound containing aluminum and iron compounds that form oxyhydroxide flocs that complex, react, sequester and / or co-precipate the contaminates from the admixture. The magnesium reacts with sulfate ions to form a high quality magnesium sulfate solution.
Owner:VEOLIA & TECHN SOLUTIONS
Adsorbent for phosphoric acid
InactiveUS20050107253A1Improve performanceEasy to manufactureOrganic active ingredientsOther chemical processesCarrageenanO-Phosphoric Acid
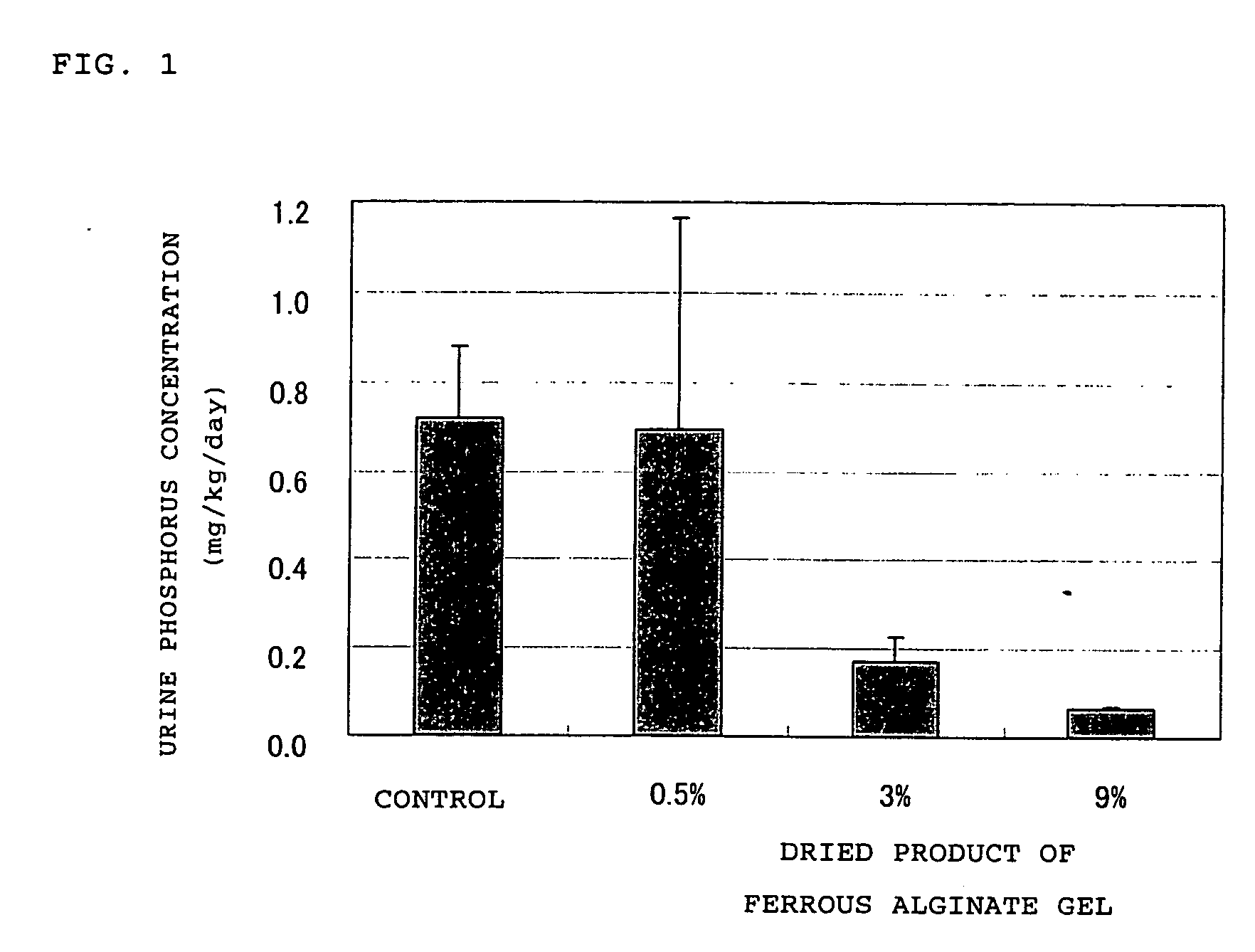
Provided is an adsorbent for phosphoric acid which can be produced with ease, exhibits high adsorbability of phosphoric acid and is free from any problems in use thereof. The adsorbent for phosphoric acid which includes a water-insoluble reaction product formed by mixing an iron ion and a natural polysaccharide having a carboxylic functional group or a sulfuric acid functional group such as alginate, pectin and carrageenan in a solution, or a dried product thereof. The additional incorporation of a hydrophilic polymer such as agar into the adsorbent prevents the reduction in adsorbability of phosphoric acid in the case where a trivalent iron ion is used to produce the dried product of a water-insoluble reaction product.
Owner:MUROMACHI CHEM +1
Method of preparing wet process phosphoric acid
InactiveUS7172742B2Concentration maximizationImprove crystallization conditionsCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesPhosphorus oxyacidsFiltrationPhosphate
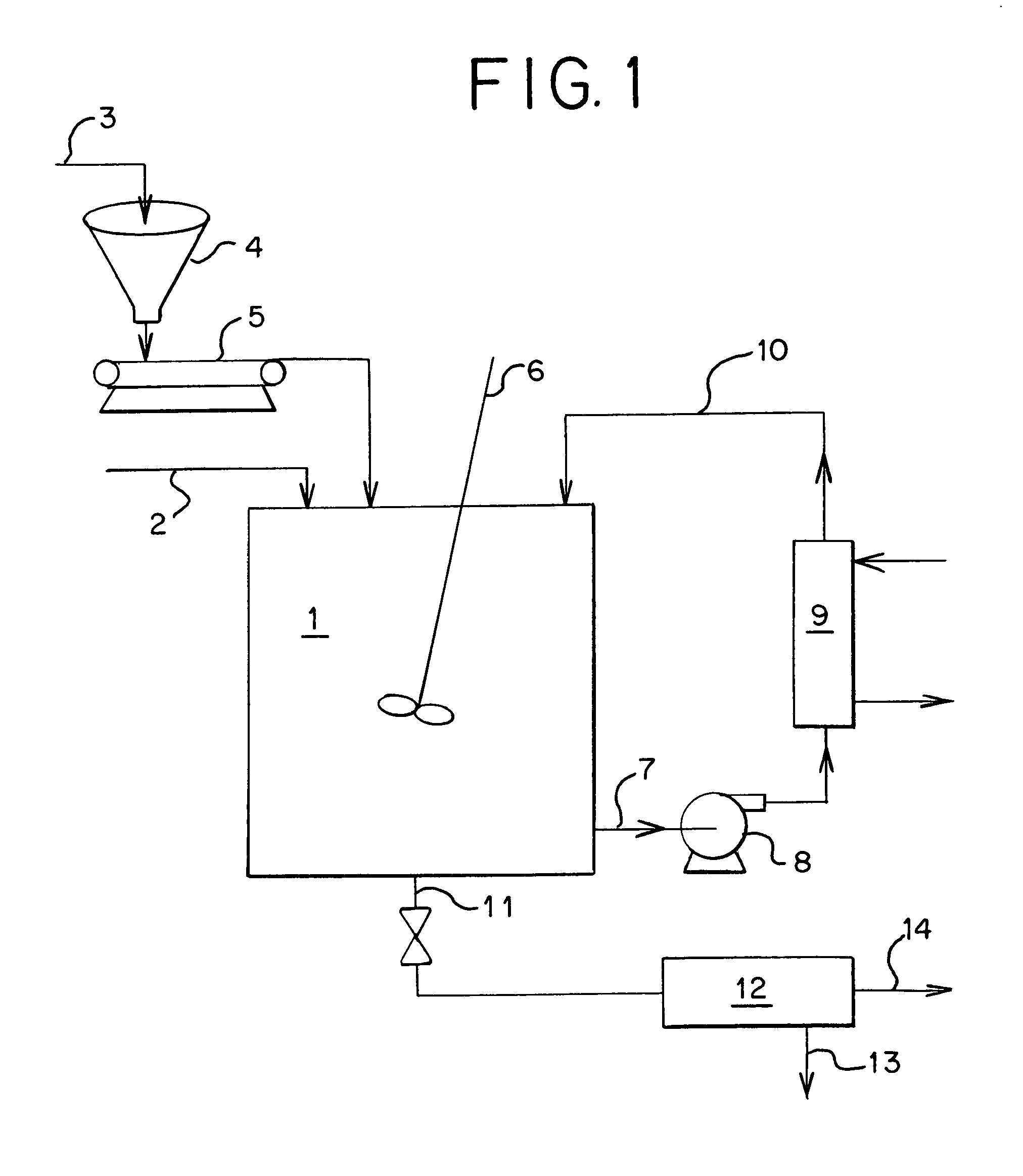
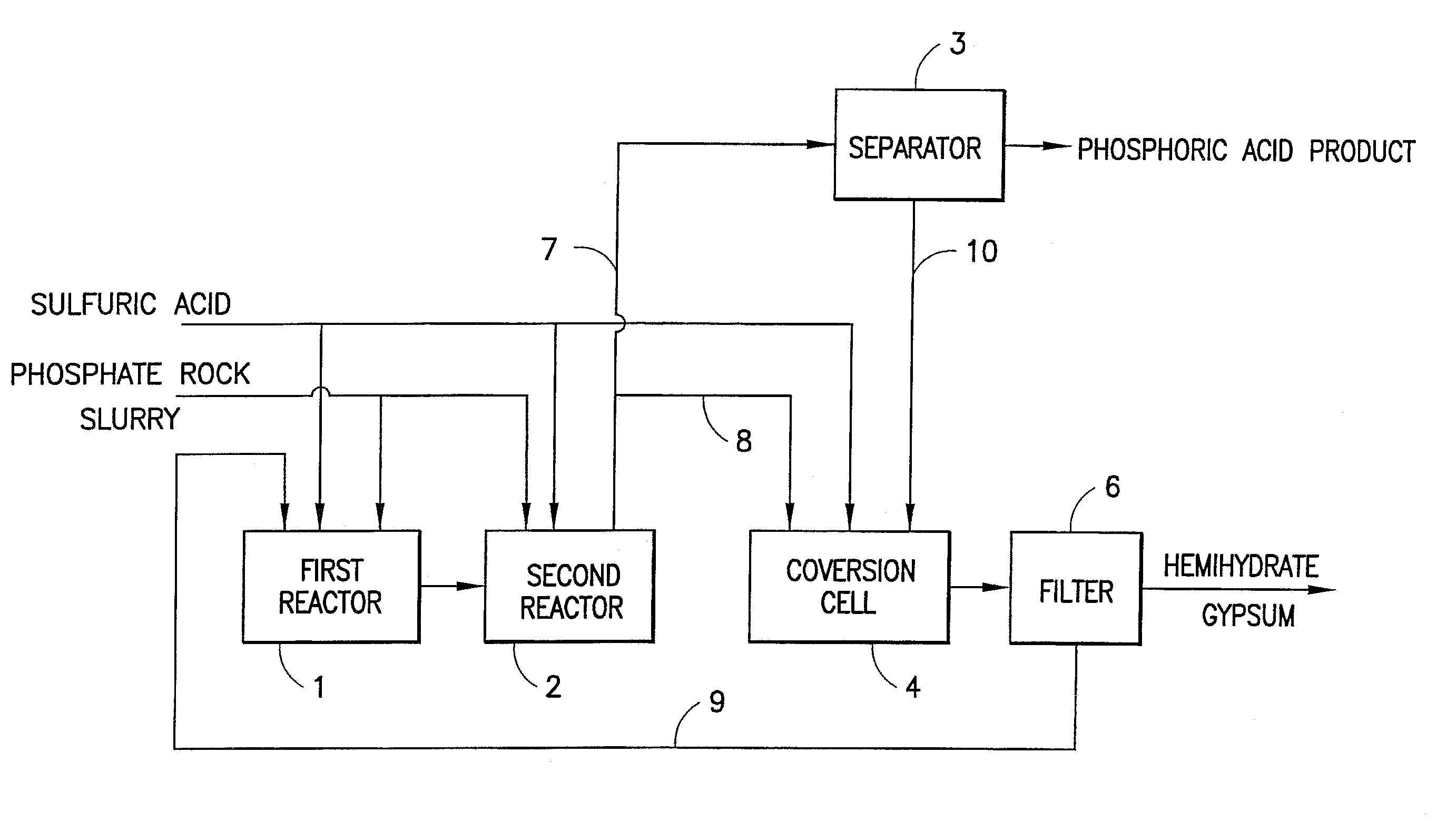
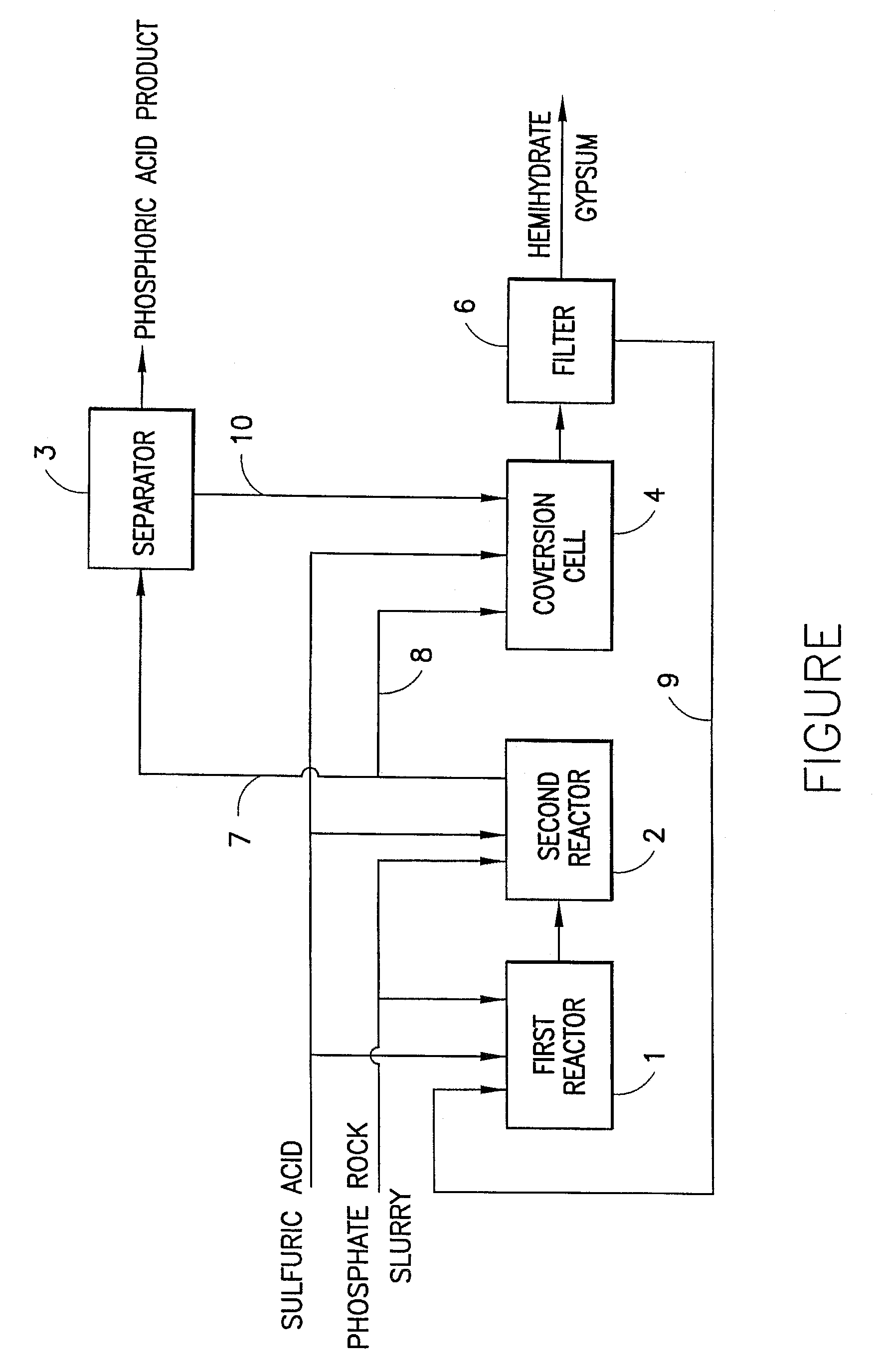
The present invention relates to a method of preparing wet process phosphoric acid, which comprises: dividing raw materials which contain phosphate rock slurry and sulfuric acid into two parts, and then feeding these two parts into two reactors separately. In the first reactor, feeding 70–90 wt. % of the total amount of the slurry and sulfuric acid, in which the ratio of phosphate rock slurry to sulfuric acid to recycled phosphoric acid is set to be 1:0.6˜0.8:1.0˜2.5. 10˜30% of the reaction solution directly flows into conversion cell, participating in the conversion reaction of dihydrate gypsum. Thus resulted phosphoric acid concentration is 33˜39 wt. %. The recovery efficiency of P2O5 is 99% or more. When putting coke powders in the conversion solution as filter aid, the filtration efficiency can be improved by 10˜30%, and in so produced hemihydrate gypsum, P2O5 is 0.05˜0.2%, water of hydration is 4˜8%. The product can be used for producing sulfuric acid and cement without baking dry.
Owner:SHANDONG LUBEI ENTERPRISE GROUP
Energy saving type phosphorus reaction tower for producing high pure phosphoric acid
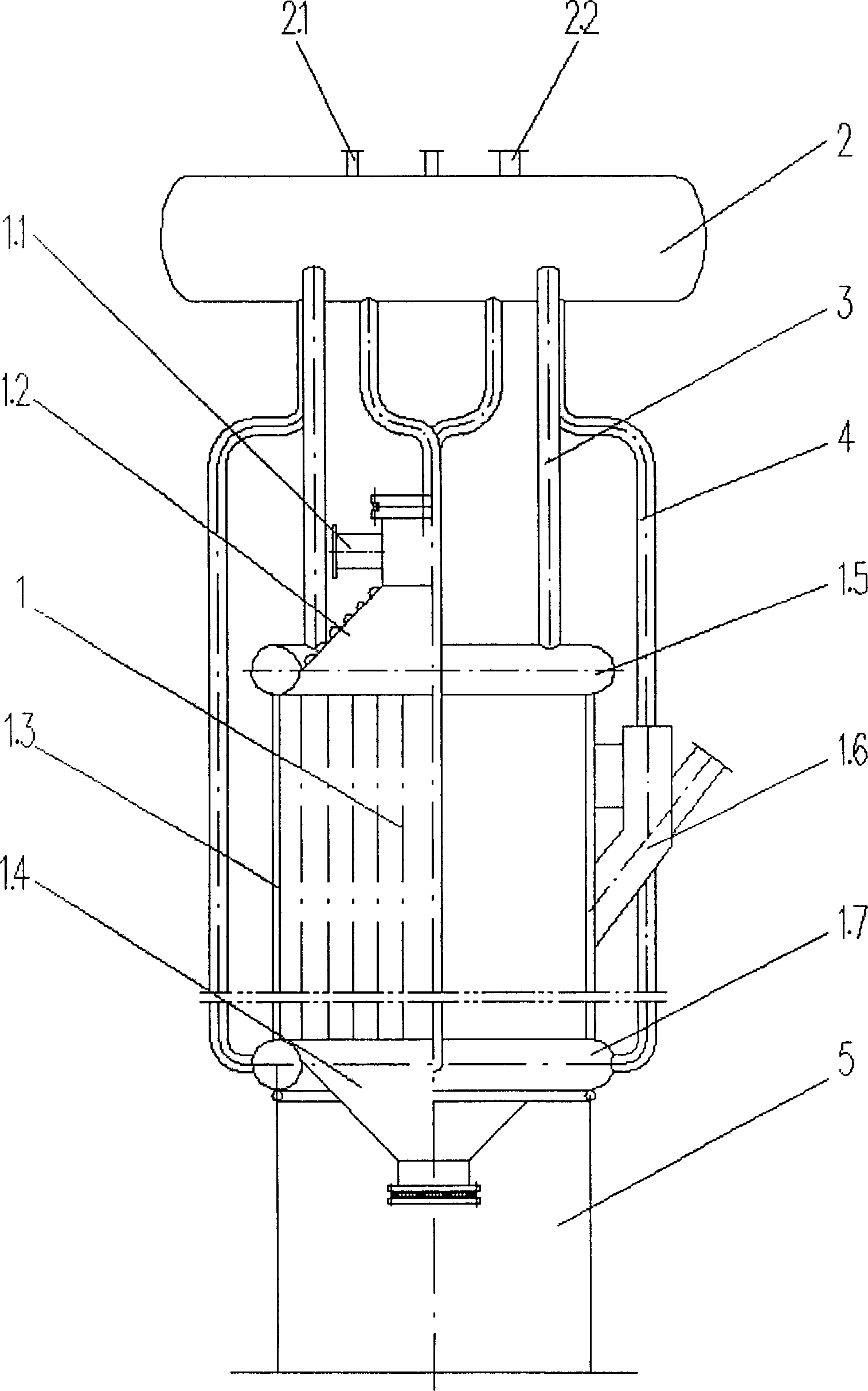
InactiveCN1857996ASimple structureRealize waste heat recoveryPhosphorus oxyacidsMouth piecePhosphoric acid
The present invention discloses a kind of energy saving phosphorus reaction tower for producing high purity phosphoric acid. The vertical sealed tower has ring film type water cooling wall formed with stainless steel pipes and finned sheets through welding, upper header tank and upper conic end with fume outlet connected to the upper end of the ring film type water cooling wall, lower header tank and lower conic end connected to the lower end of the ring film type water cooling wall, inclined phosphorus spraying gun mouth piece in the lower part, apron type pedestal connected to the lower header tank, steam collector connected between the steam-water separator and the upper header tank, down take connected between the steam-water separator and the lower header tank, and the steam-water separator with steam outlet pipe and cold water inlet pipe. The present invention realizes the afterheat recovery of phosphoric acid producing process, and has high heat efficiency and phosphoric acid as high as 99 %.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A kind of preparation method of difluorophosphoric acid and lithium difluorophosphate
ActiveCN108640096BPhosphorus oxyacidsSecondary cells servicing/maintenanceAlkaline earth metalHydrogen
The invention relates to a preparing method of difluorophosphoric acid and lithium difluorophosphate. The preparing method of lithium difluorophosphate comprises the following steps of 1, carrying outa reaction between dichloro phosphate and a fluorinated reagent to prepare the difluorophosphoric acid, wherein the fluorinated reagent is AsF3, NH4F, NH4HF2 and / or MFx, for MFx, x is equal to 1 or 2or 3, and M is hydrogen, alkali metal, alkaline-earth metal or transition metal; 2, carrying out a reaction between difluorophosphoric acid and a lithium source material in a non-aqueous agent. According to the preparing method of lithium difluorophosphate, dichloro phosphate, the fluorinated reagent and the lithium source material serve as raw materials to carry out the reactions to prepare lithium difluorophosphate, and the raw materials are wide in source and low in cost; a fluoridation reaction and a substitution reaction of the lithium source material easily take place, the side reactionis small, a crude product of lithium difluorophosphate with few impurities is conveniently obtained under the condition of a high conversion rate, and thus good conditions are created for obtaining high-quality products of lithium difluorophosphate at low cost.
Owner:DO FLUORIDE CHEM CO LTD
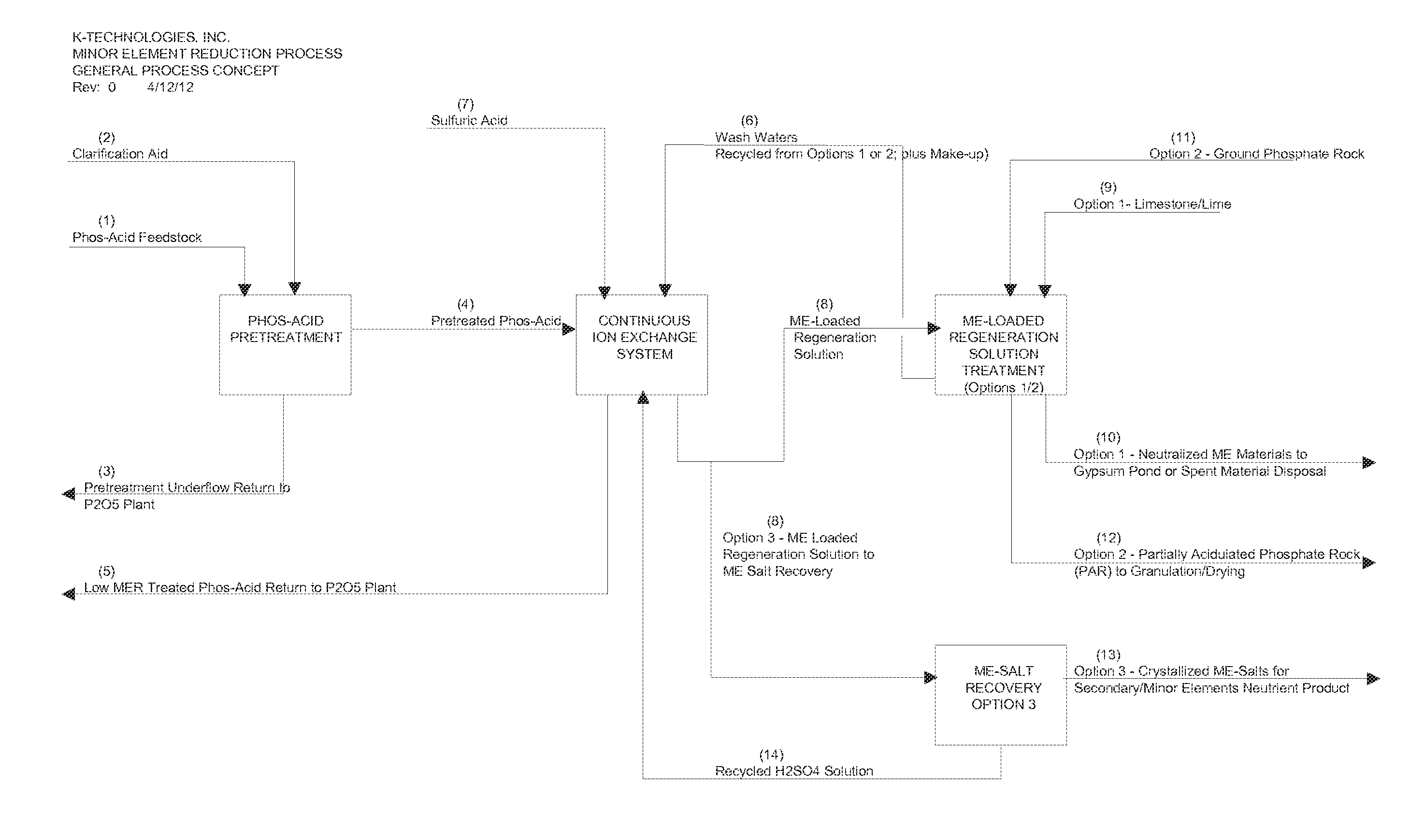
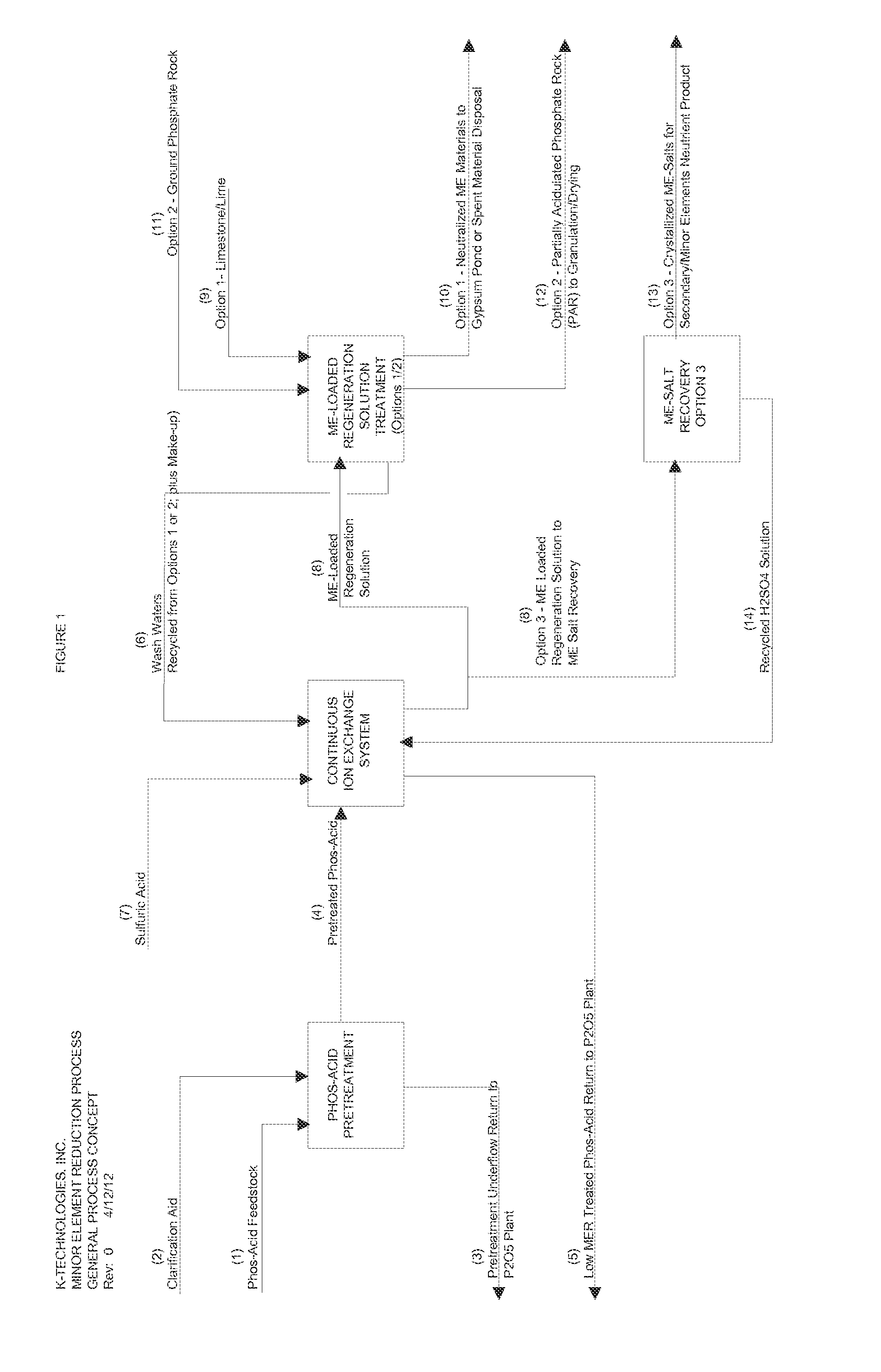
Processes for the removal and recovery of minor elements in wet-process phosphoric acid
ActiveUS20150166343A1Minimal phosphate lossSuitable for productionCation exchanger materialsIon-exchanger regenerationMinor elementPhosphoric acid
In alternative embodiments, the invention provides processes and methods for the recovery or the removal of the so-called “Minor Elements” consisting of iron, aluminum and magnesium (expressed as oxides), from wet-process phosphoric acid using a continuous ion exchange approach. In alternative embodiments, use of processes and methods of the invention allows for the reduction of these Minor Elements with minimal phosphate losses and dilution in order to produce a phosphoric acid that is suitable for the production of fertilizer products such as world-class diammonium phosphate (DAP), merchant-grade phosphoric acid, superphosphoric acid, and other phosphoric acid products. Further, use of the invention would allow the use of lower grade phosphate rock or ore, which would greatly expand the potential phosphate rock reserve base for phosphate mining activities, and allow for better overall utilization of resources from a given developed mine site.
Owner:OCP
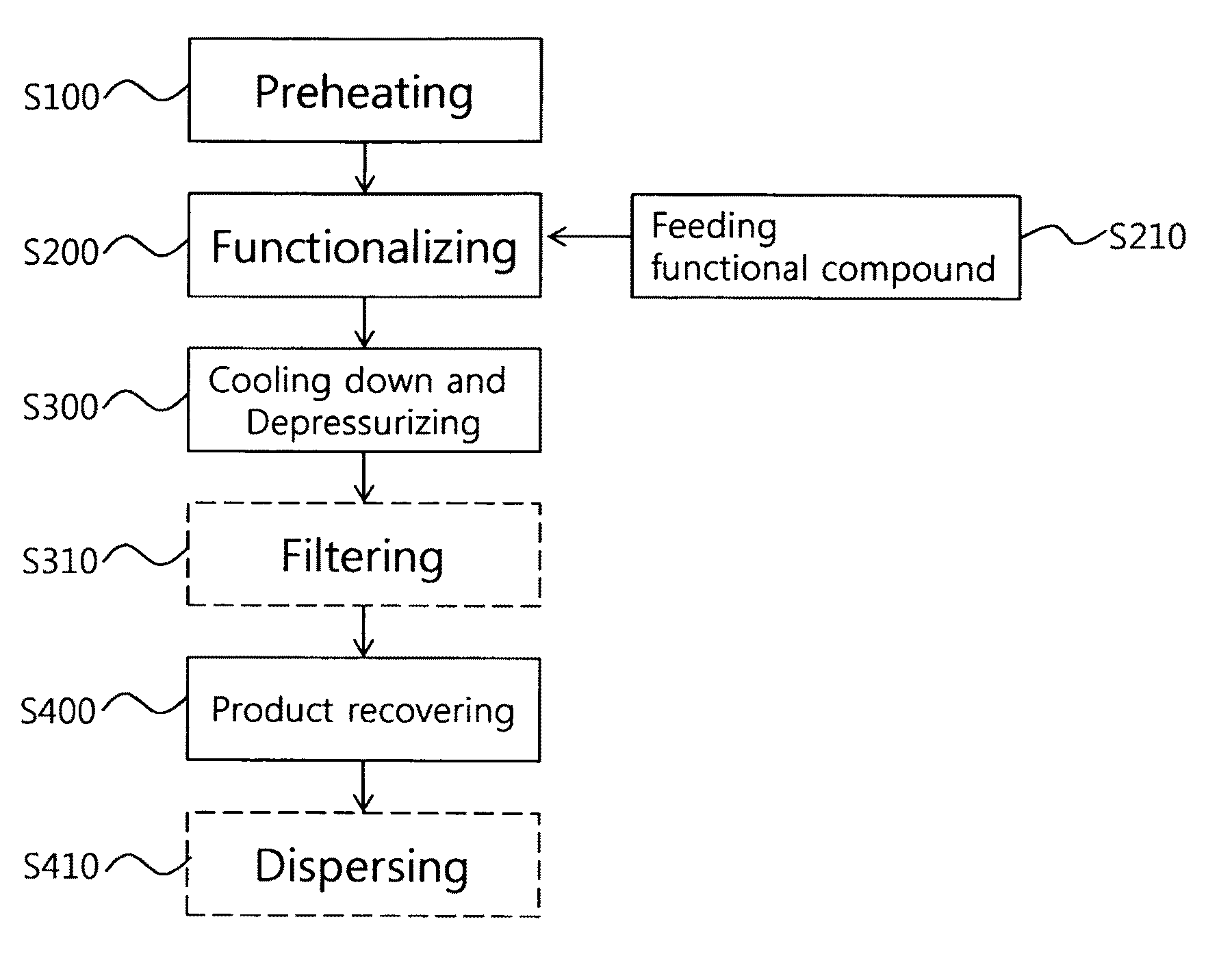
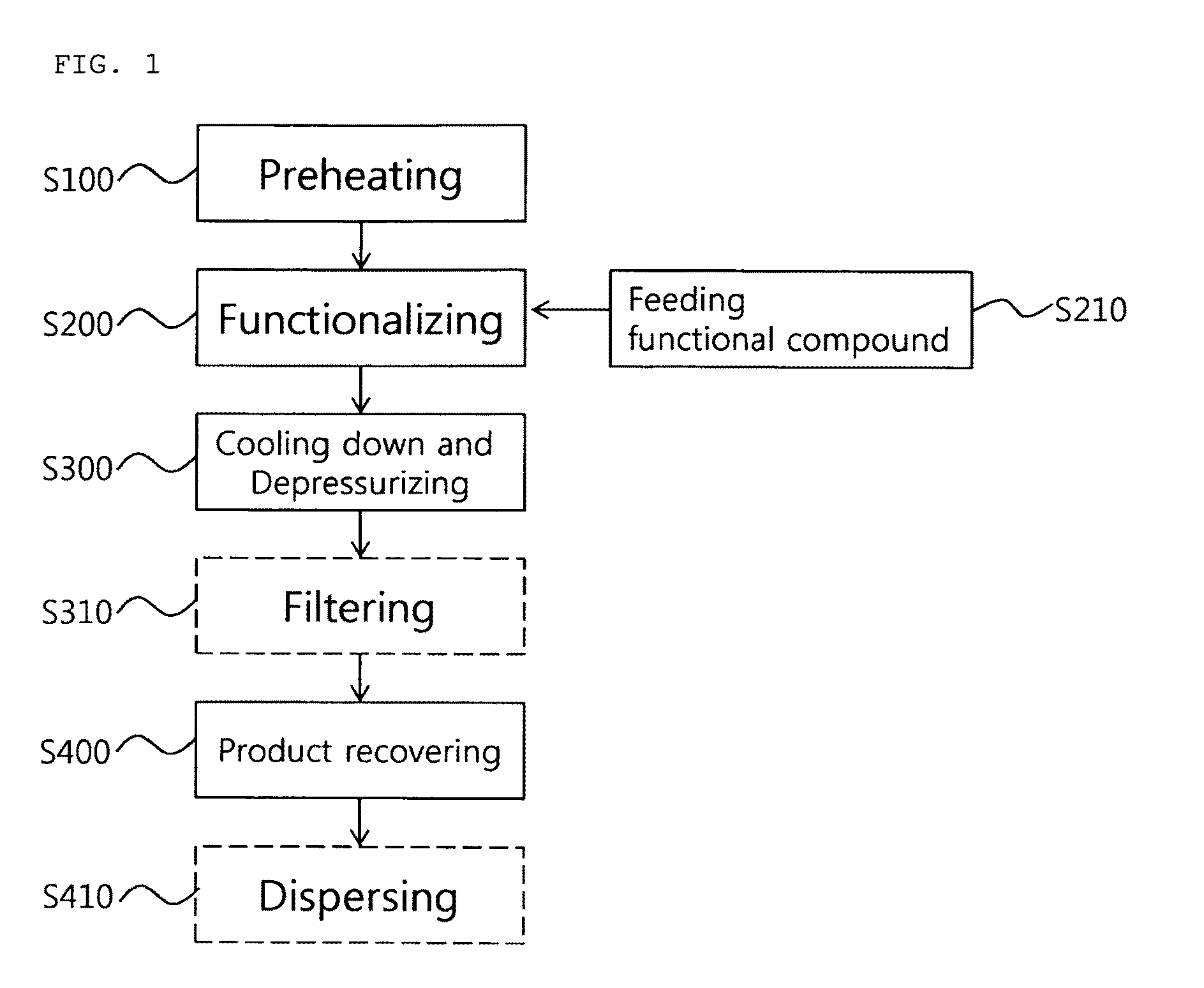
Continuous method and apparatus of functionalizing carbon nanotube
ActiveUS8187566B2Increase functionalizing effectGood dispersionMaterial nanotechnologyOxygen-containing compound preparationCarbon nanotubeOxidizing agent
Owner:HANWHA CHEMICAL CORPORATION
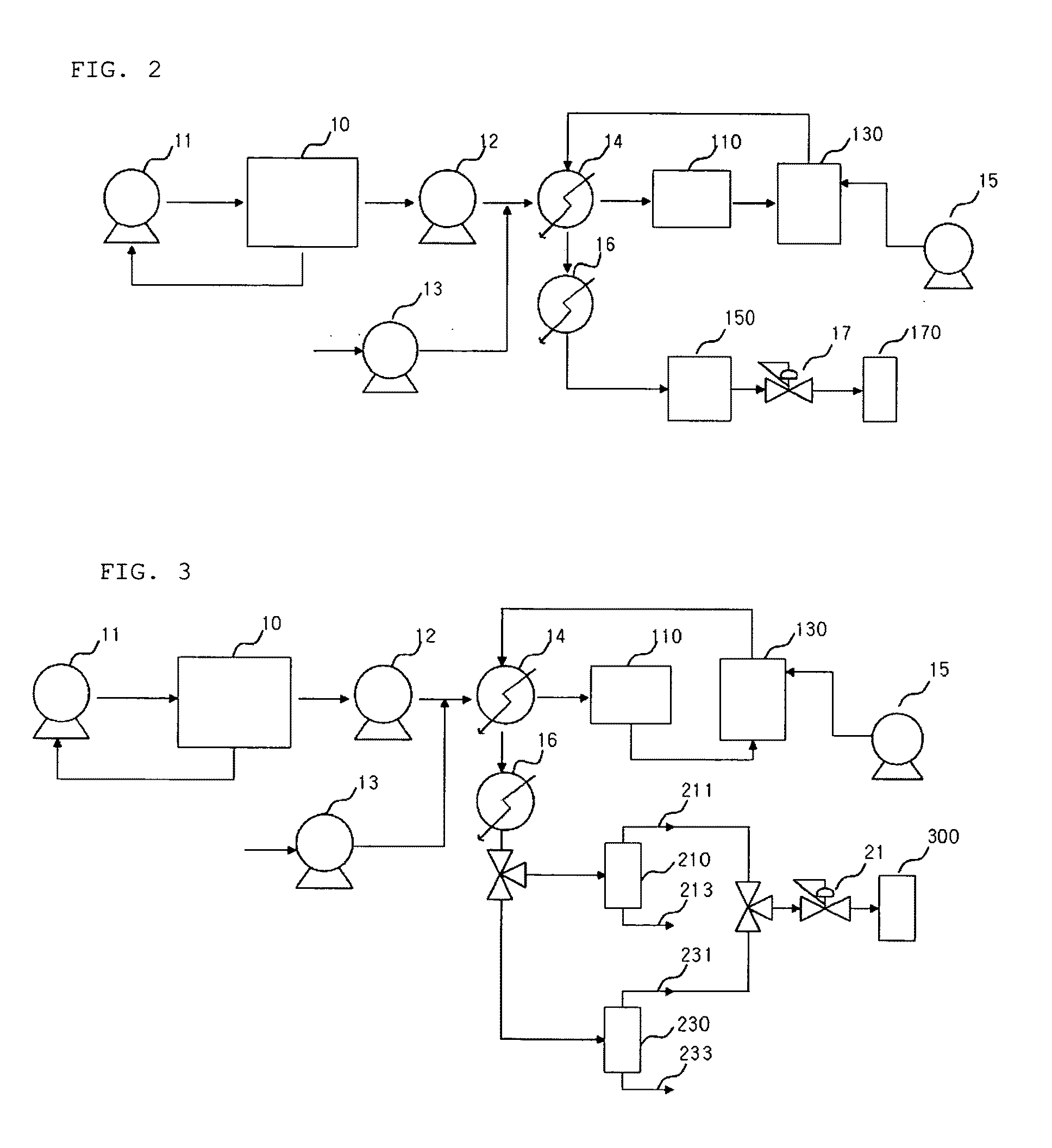
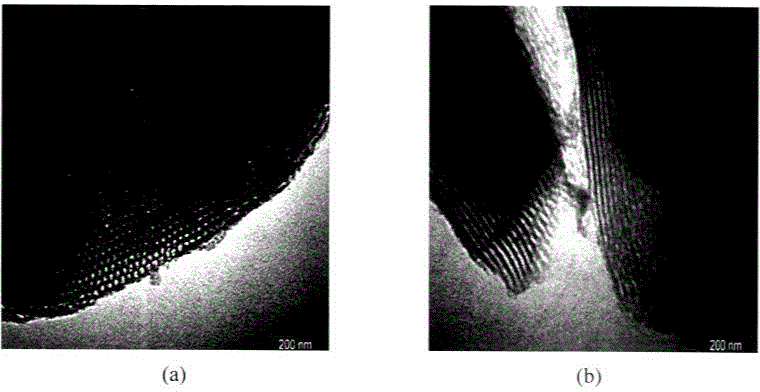
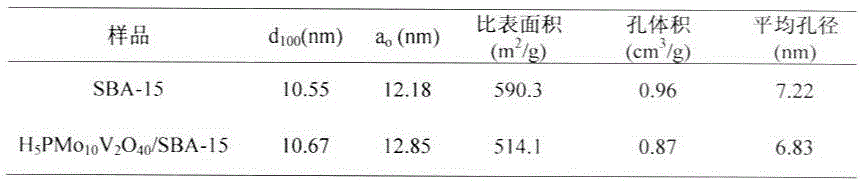
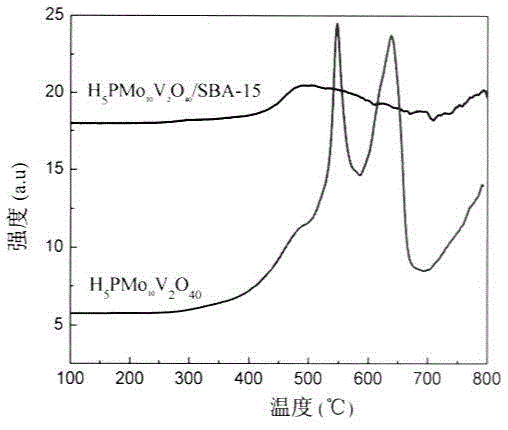
Preparation and applications of composite SBA-15 molecular sieve catalysts
The present invention provides a class of heteropolyacid loaded mesoporous molecular sieve SBA-15 catalysts and a preparation method thereof, and applications of the catalysts in oxidation of benzene into phenol. According to the present invention, the catalyst adopts the mesoporous molecular sieve SBA-15 is adopted as the carrier, and the Keggin type heteropolyacid H5PMo10V2O40 is loaded on the mesoporous molecular sieve SBA-15 by using the sol-gel method to prepare the catalyst; and in the oxidation reaction of benzene into phenol, the loaded catalyst has characteristics of high selectivity and good catalyst recycling.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF COMMERCE
Reduction of wastewater in phosphate manufacturing
InactiveUS7022242B2Reduce fresh water consumptionDischarging to environmentDrying using combination processesPhosphorus oxyacidsPhosphatePhosphoric acid
Use and reduction of wastewater or “pond water” created by the wet-process phosphoric acid manufacturing there is created a large amount of wastewater or “pond water” to substantially reduce or eliminate the discharge of pond water with contaminants to the environment. By partially treating pond water with known industry standard processes and using the treated pond water for use as required makeup or cooling water in an electric power generator or any other Industry requiring makeup, cooling or process water will substantially reduce or eliminate the need for the phosphoric acid manufacturers to discharge the contaminated water to the environment and reduce the quantity of fresh water that would normally be required by these other industries using the treated pond water for cooling or makeup water.
Owner:SACCHI RICHARD EDWIN
Novel materials useful as electrolytic solutes
InactiveUS20050084763A1Light-sensitive devicesOrganic electrolyte cellsHeteroatomCompound (substance)
The invention concerns novel ionic compounds with low melting point whereof the onium type cation having at least a heteroatom such as N, O, S or P bearing the positive charge and whereof the anion includes, wholly or partially, at least an ion imidide such as (FX1O)N−(OX2F) wherein X1 and X2 are identical or different and comprise SO or PF, and their use as solvent in electrochemical devices. Said composition comprises a salt wherein the anionic charge is delocalised, and can be used, inter alia, as electrolyte.
Owner:ACEP +2
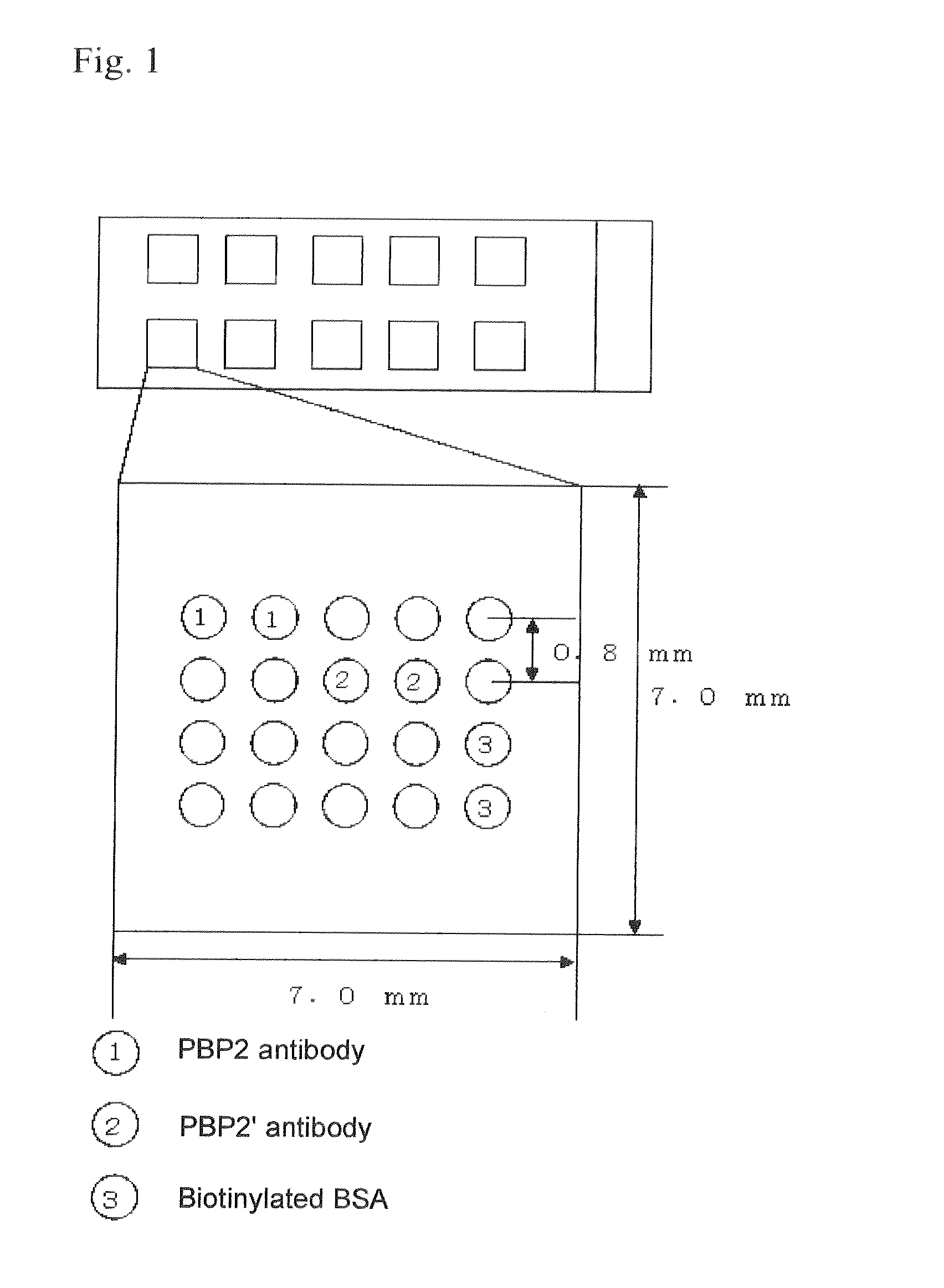
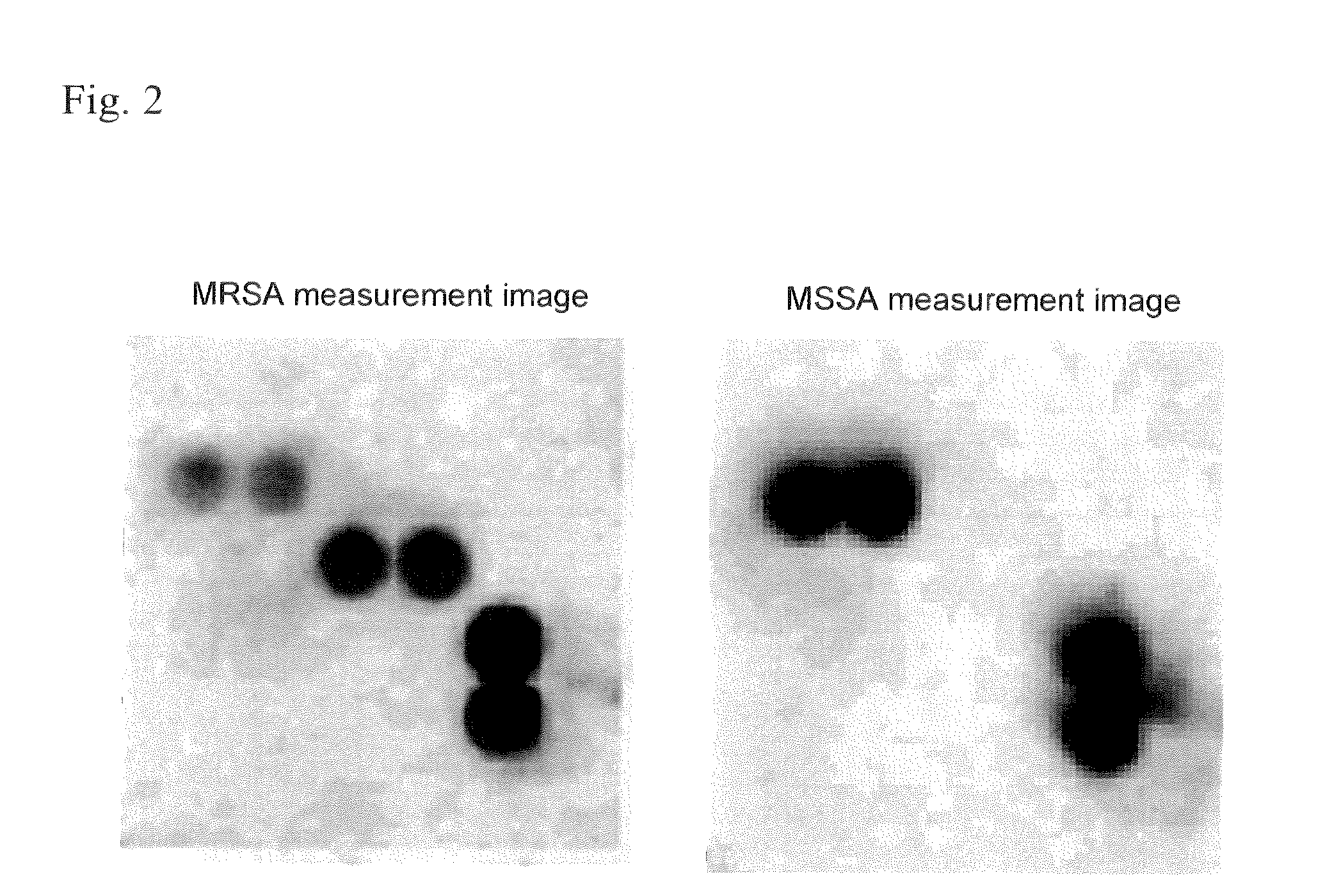
Method for extracting Staphylococcus aureus antigen, reagent for extracting Staphylococcus aureus antigen, and method for assessing Staphylococcus aureus
ActiveUS8679812B2Efficiently extract PBP2′Reliably assess whether a specimenChlorine/hydrogen-chlorideNitrogen compoundsAntigenStaphylococcus cohnii
The invention provides a method for extracting a Staphylococcus aureus antigen which comprises using an extraction reagent with a pH of no higher than 5.0, containing one or more acids selected from among hydrochloric acid, acetic acid, citric acid, phosphoric acid, sulfuric acid and nitric acid, to extract a Staphylococcus aureus antigen comprising a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus antigen and / or a methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus antigen, from Staphylococcus aureus in a specimen. The invention further provides a method for assessing Staphylococcus aureus.
Owner:KIKKOMAN CORP
Process for removing fluorinated compounds from an aqueous phase originating from the preparation of fluoropolymers
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Method of filtering phosphate utilizing a rotary table filter or horizontal table filter
Owner:THOMPSON INDAL SERVICES
Integrated lime kiln process
ActiveUS7678354B2Optimizing pollutant dry scrubbingSimple technologyUsing liquid separation agentRotary drum furnacesWaste heat recovery unitPlate heat exchanger
A process and system for recovering waste heat from a kiln used for lime or cement production. The system unifies the kiln, a waste heat recovery and power generation circuit and a dry scrubber for scrubbing the pollutants from the kiln offgas. Essentially, the system employs the boiler component of the waste heat recovery and power generation circuit as a heat exchanger to recover the waste heat from the kiln, which is used to drive the steam turbines. The heat absorption from the latter stage lowers the temperature of the kiln offgas sufficiently for optimum performance from the scrubber. The presence of lime particles in the offgas effectively protects the boiler tube surfaces from corrosion which would occur at optimum scrubber temperatures, and subsequently provides the lime required as a scrubbing medium for the dry scrubber. Further, the efficient scrubbing allows for the use of any fuel for firing the kiln inclusive of high sulphur content compounds. A process for effecting the technology is also provided.
Owner:GRAYMONT PA INC
High-temperature gas cooled nuclear reactor coupled iodine selenium thermochemical cycle phosphorous reduction hydrogen production method
ActiveCN110407167AAvoid the problem of inability to carry out large-scale regular hydrogen productionReduce manufacturing costIodinePhosphorus oxyacidsNuclear reactor coreDecomposition
The invention relates to an iodine selenium thermochemical cycle phosphorous reduction hydrogen production method, and belongs to the technical field of hydrogen energy. The method comprises the stepsthat water serves as a raw material, selenium and iodine are added for a reaction under normal pressure, and a seleninic acid solution and hydroiodic acid are obtained; the hydroiodic acid is rectified and concentrated, the rectified and concentrated hydroiodic acid is decomposed, hydrogen obtained after decomposition is output as a product, and iodine is recycled; a reducing agent white phosphorus or red phosphorus or phosphorus trioxide are added into the obtained seleninic acid solution, selenium and a by-product are obtained and output, and the selenium as the raw material is recycled. The highest temperature required by the reaction process in the method is 400-500 DEG C, and the problem is avoided that due to too high reaction temperature, large-scaled hydrogen production cannot beconducted. The reacting agent iodine and selenium in the method can be recycled, and accordingly, the hydrogen production cost is greatly reduced. The method can be well coupled with the latest cleanenergy, namely a high-temperature gas cooled nuclear reactor, the heat energy, electric energy and mechanical energy of the high-temperature gas cooled nuclear reactor can be utilized by the iodine selenium thermochemical cycle hydrogen production process.
Owner:CHINERGY CO LTD
Iron phosphomolybdate smoke suppression PVC plate and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108456374AHigh oxygen indexSmoke suppressionPhosphorus oxyacidsPhosphomolybdic acidFerric hydroxide
The invention belongs to the application field of high polymer materials, and relates to an iron phosphomolybdate smoke suppression PVC plate and a preparation method thereof. The iron phosphomolybdate smoke suppression PVC plate comprises the following components in parts by weight: 100 parts of PVC resin powder, 2-3 parts of a stabilizer, 2-3 parts of a processing aid, 0.5-1 part of a lubricant,3-5 parts of a flexibilizer, 8-15 parts of a filler, and 4-6 parts of a flame-retardant smoke suppressant. According to the iron phosphomolybdate smoke suppression PVC plate provided by the invention, phosphomolybdic acid and ferric hydroxide are used as raw materials, the iron phosphomolybdate prepared by a hydrothermal method is used as a flame-retardant smoke suppressant, and is added to PVC plate production in combination with other additives, the process is simple, the yield is high, and the flame-retardant and smoke-suppression effect is obvious.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com