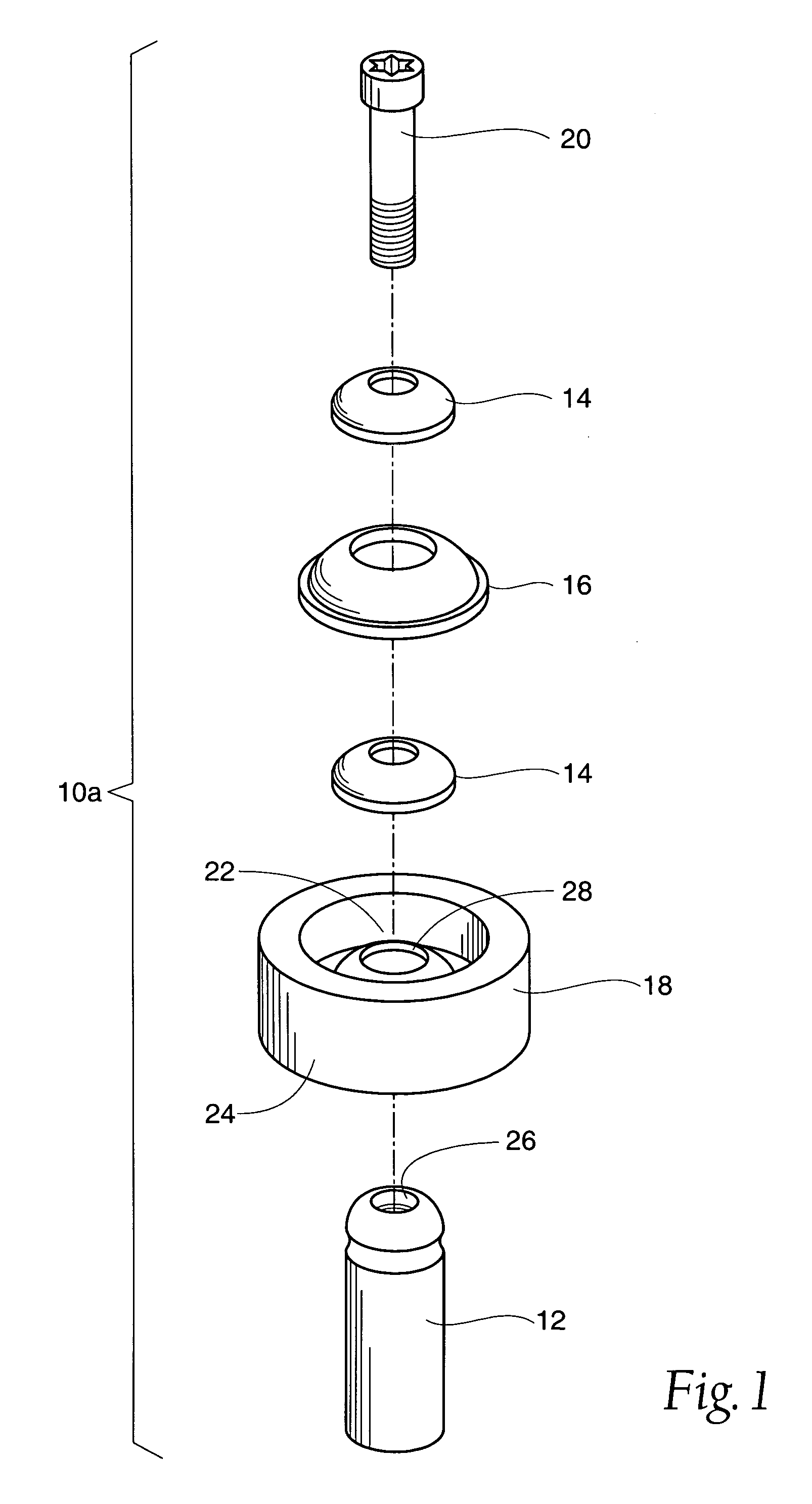
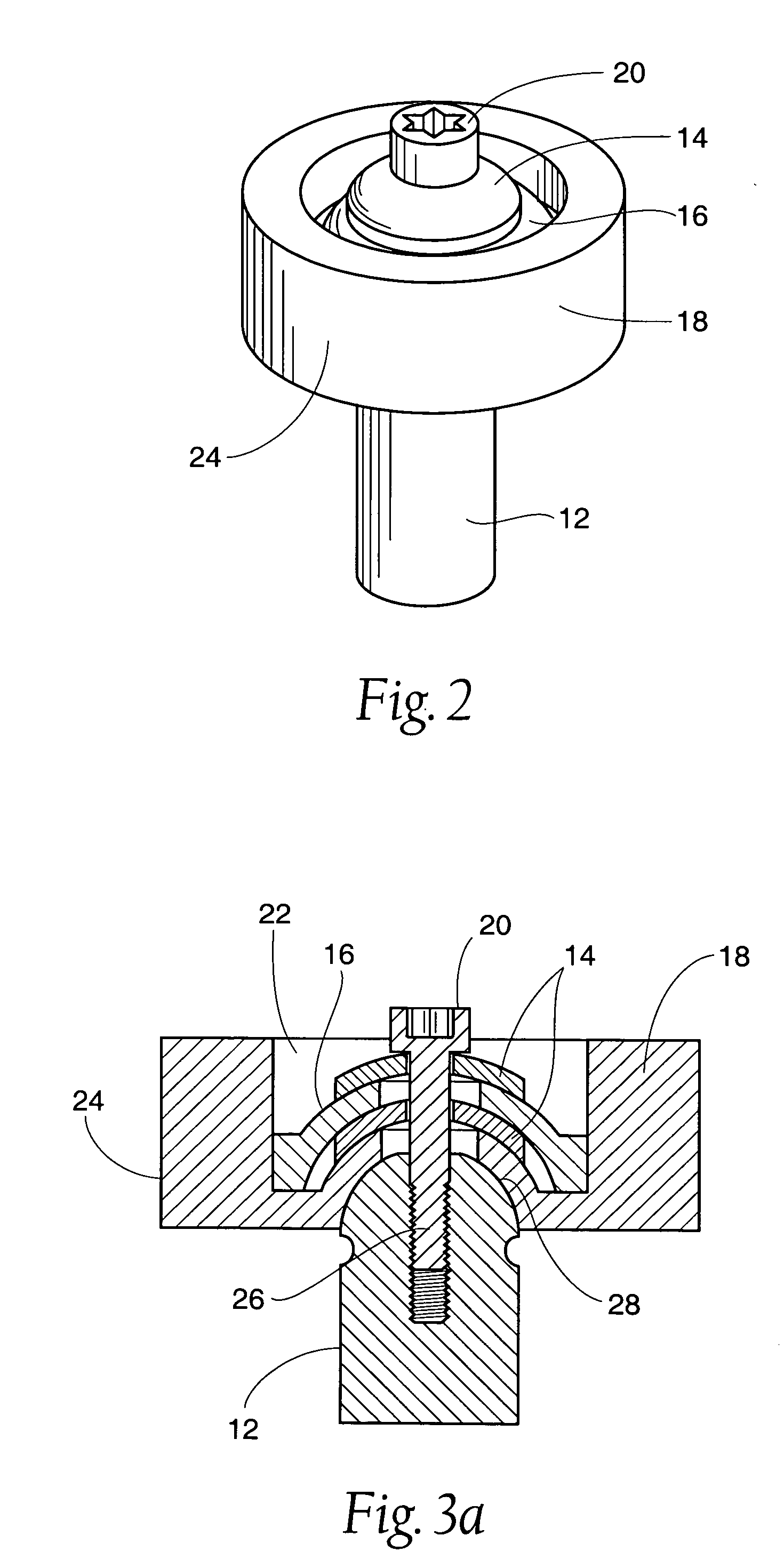
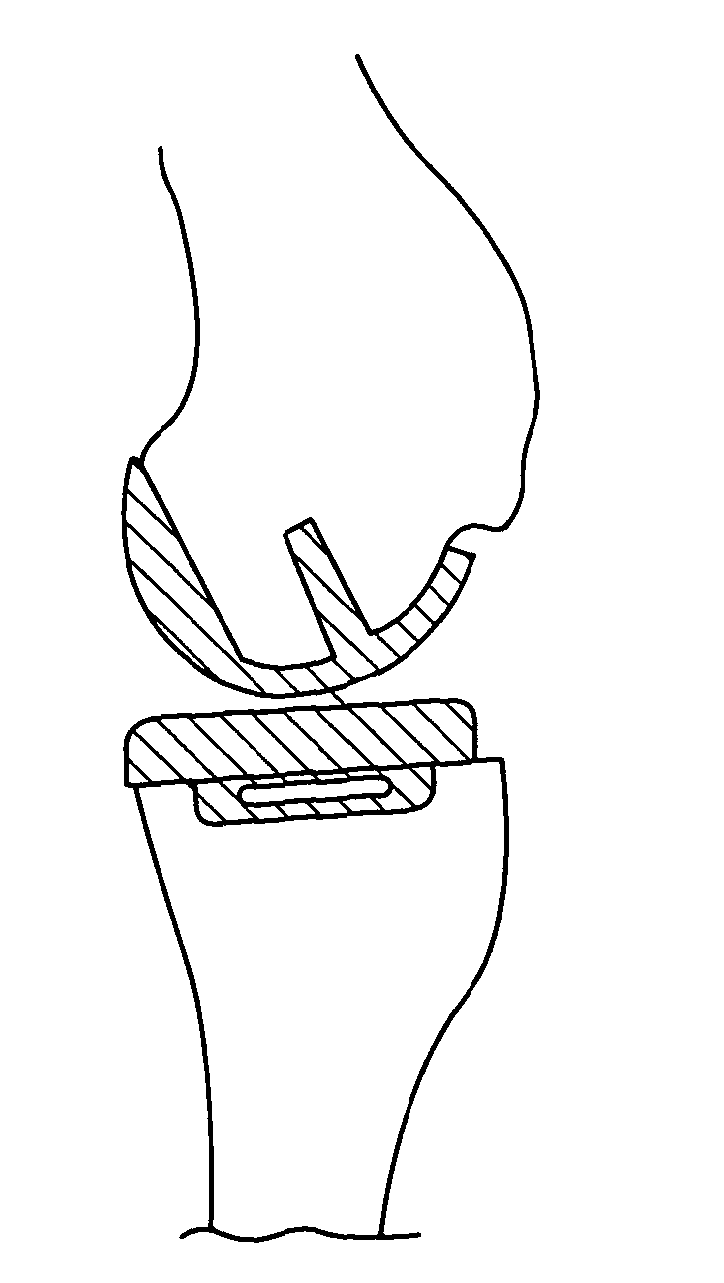
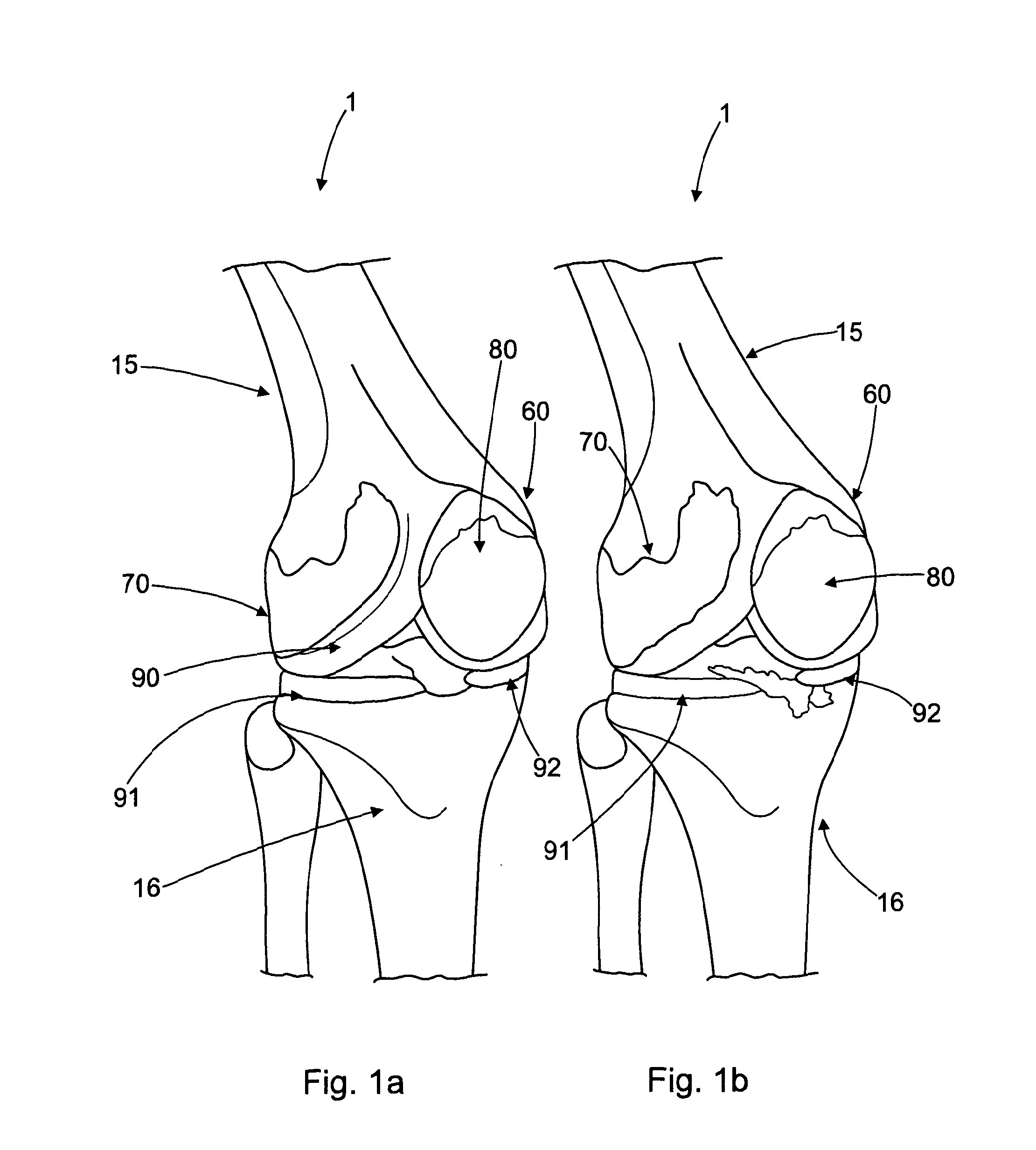
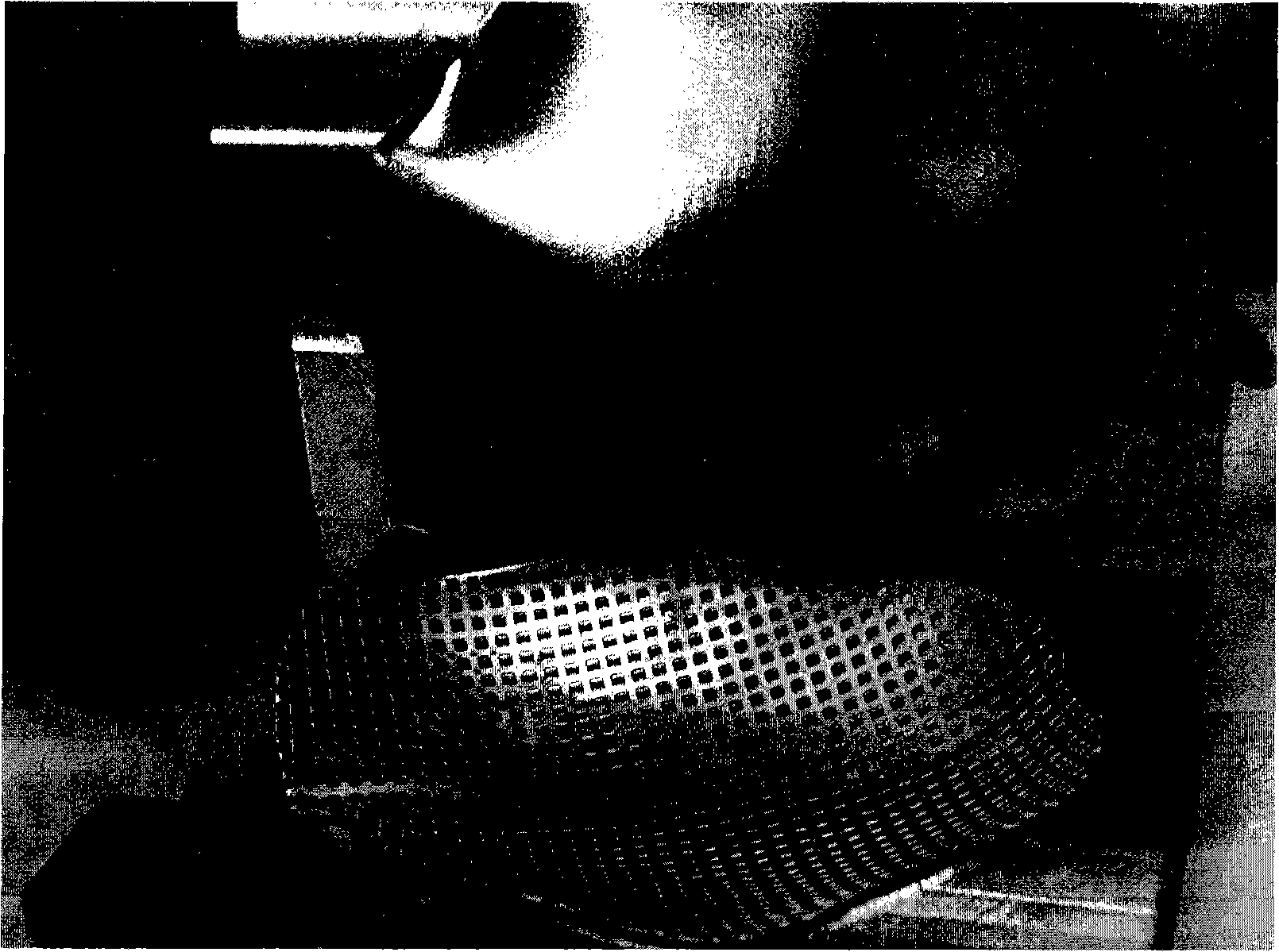Patents
Literature
173 results about "Bone prosthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Artificial substitute, constructed of either synthetic or biological material, which is used to partially or totally replace or repair injured or diseased bones.
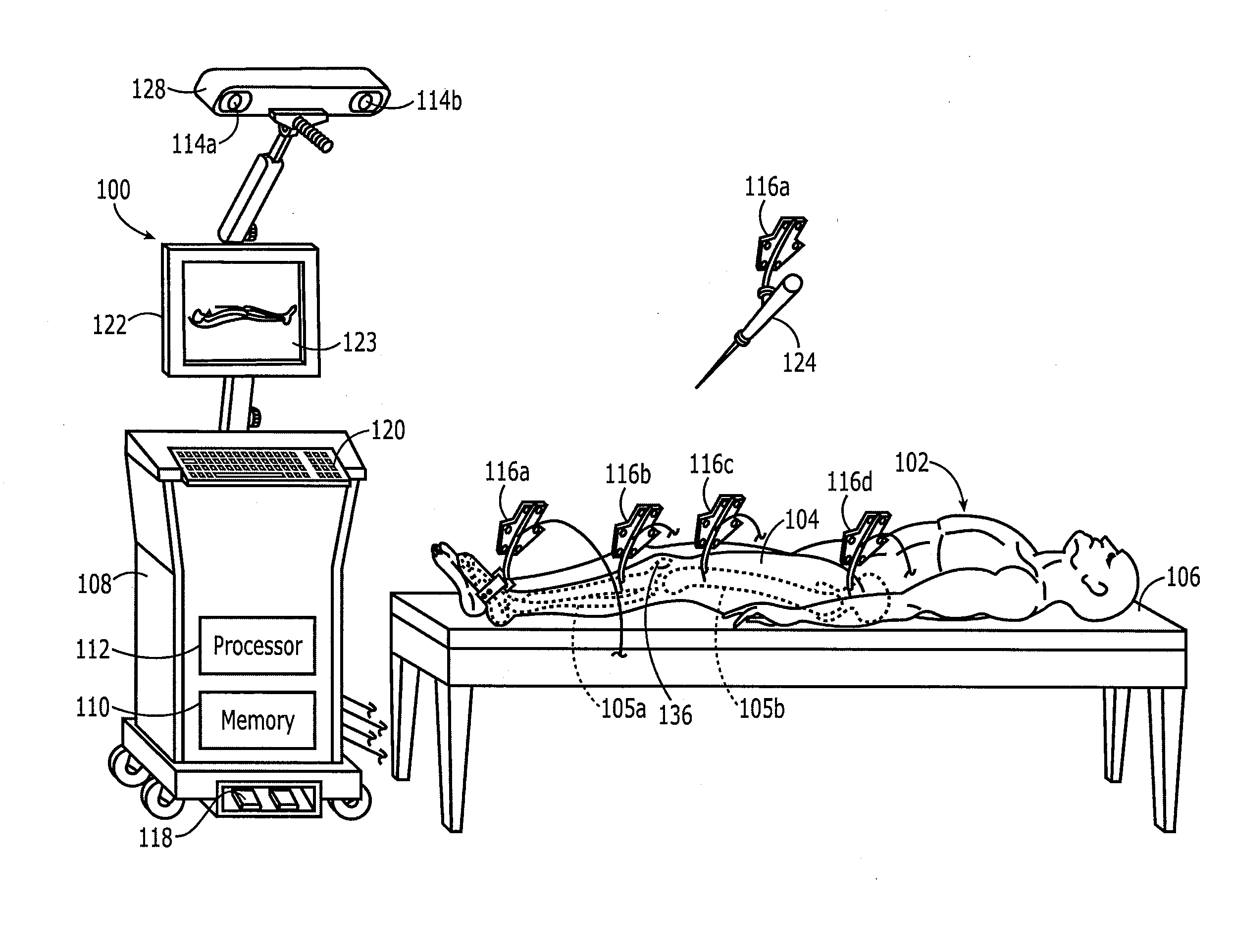
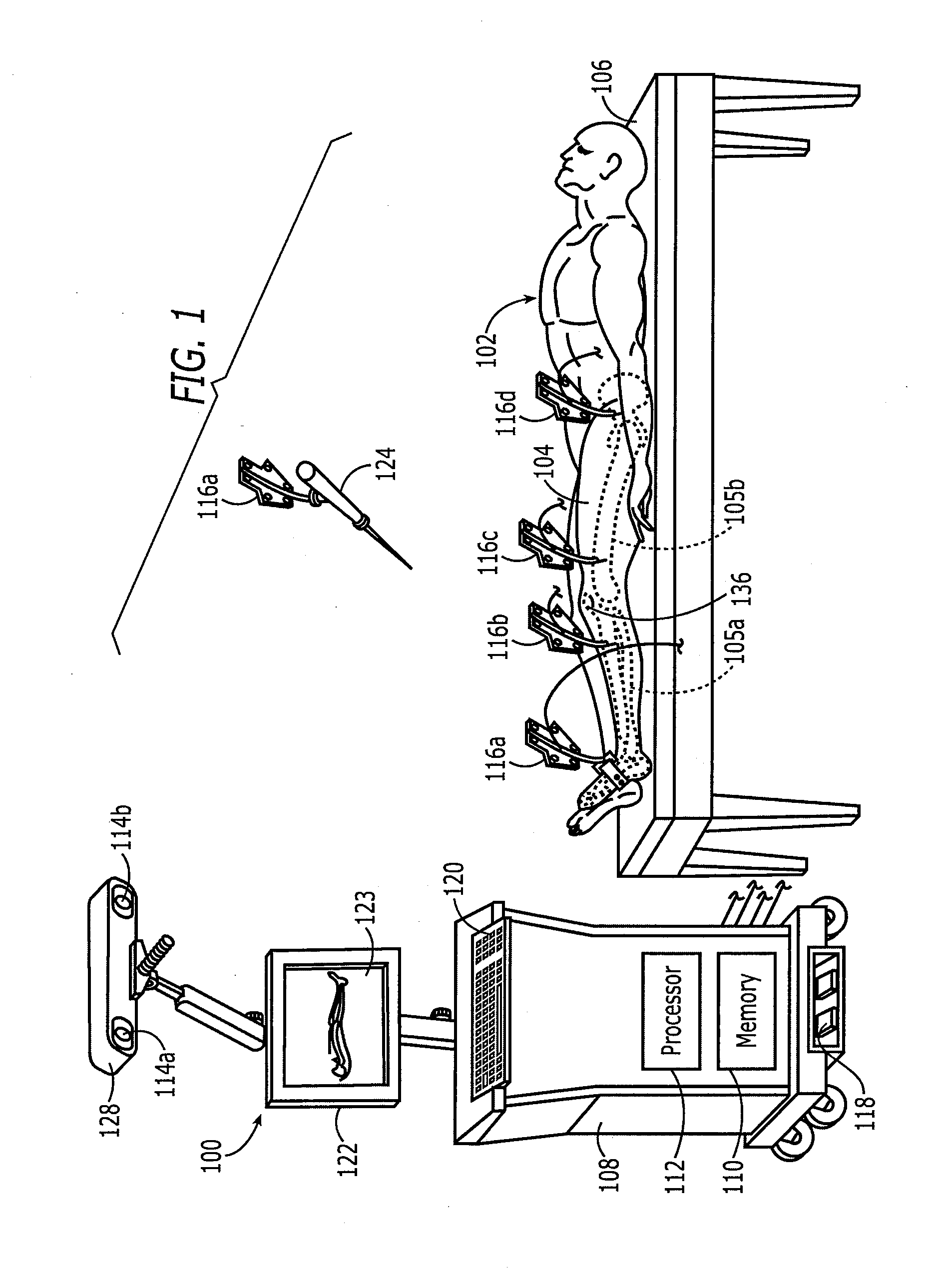
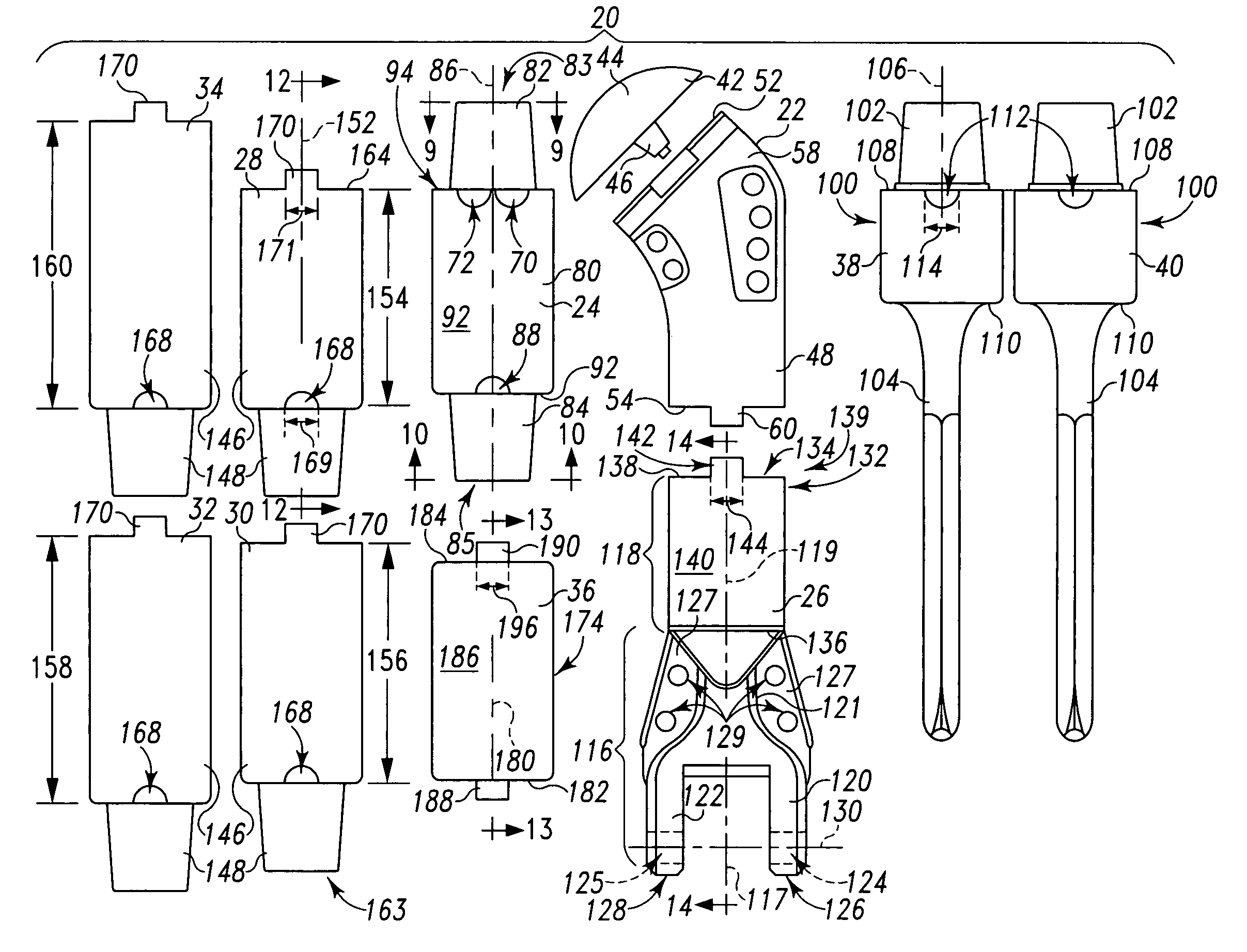
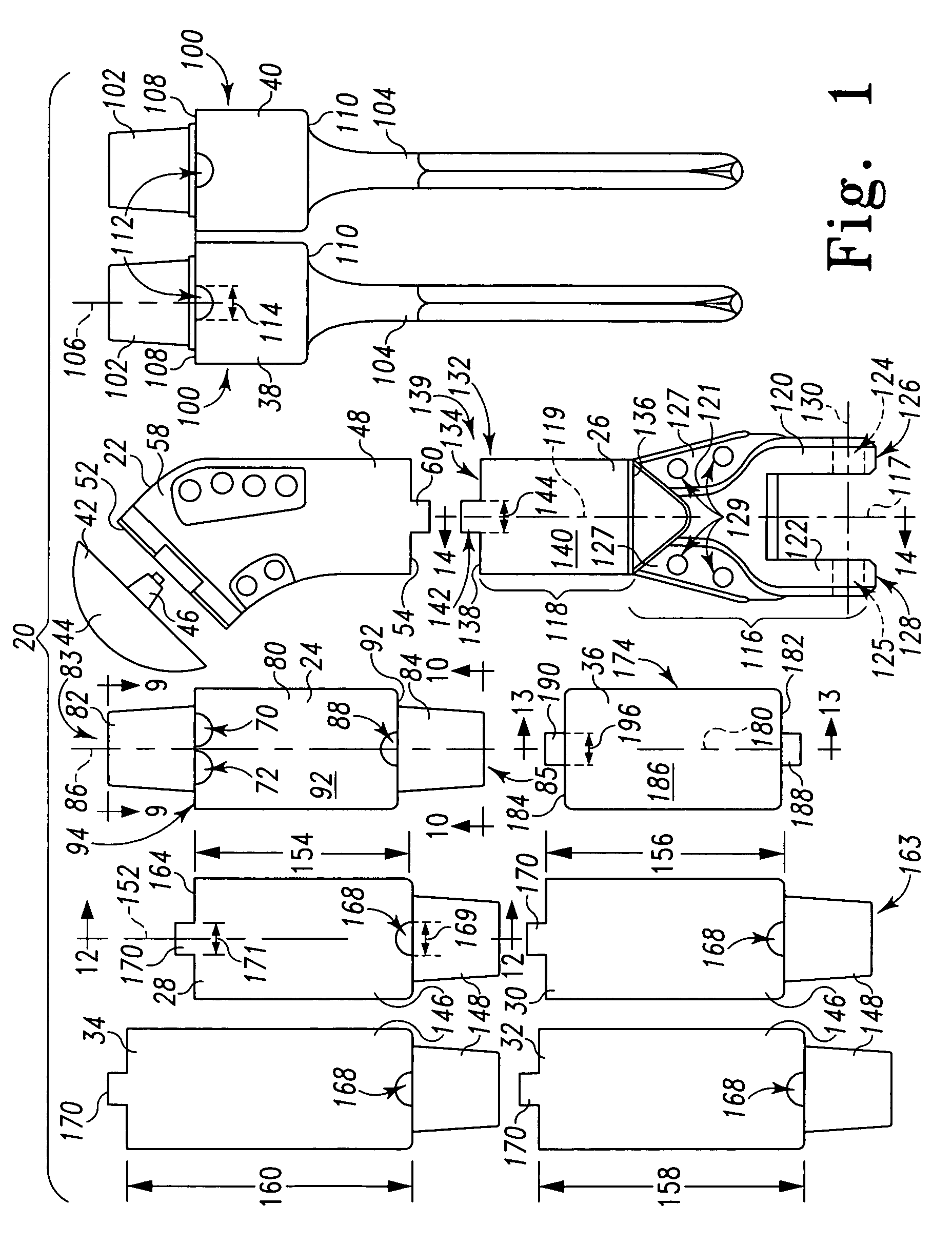
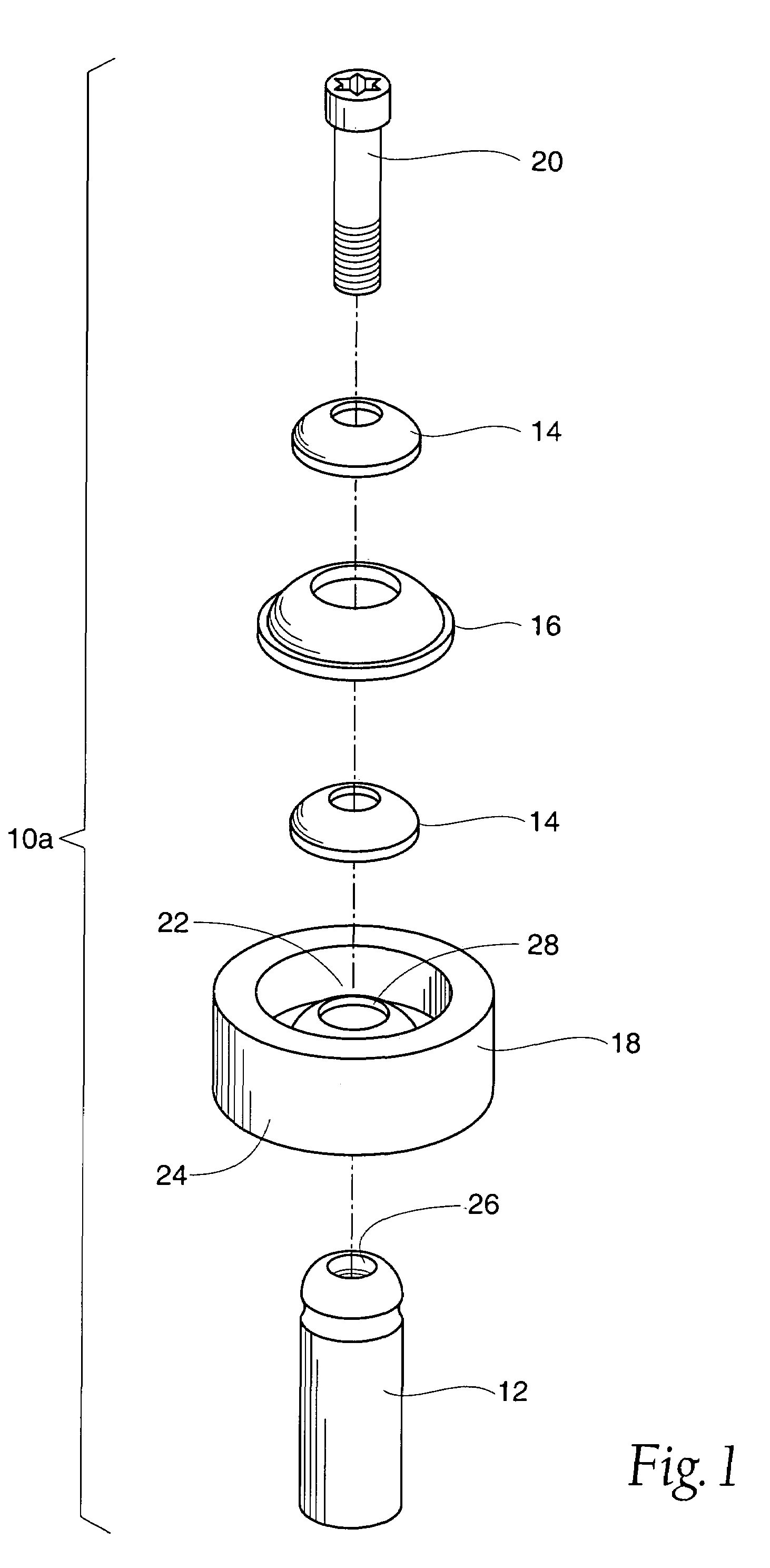
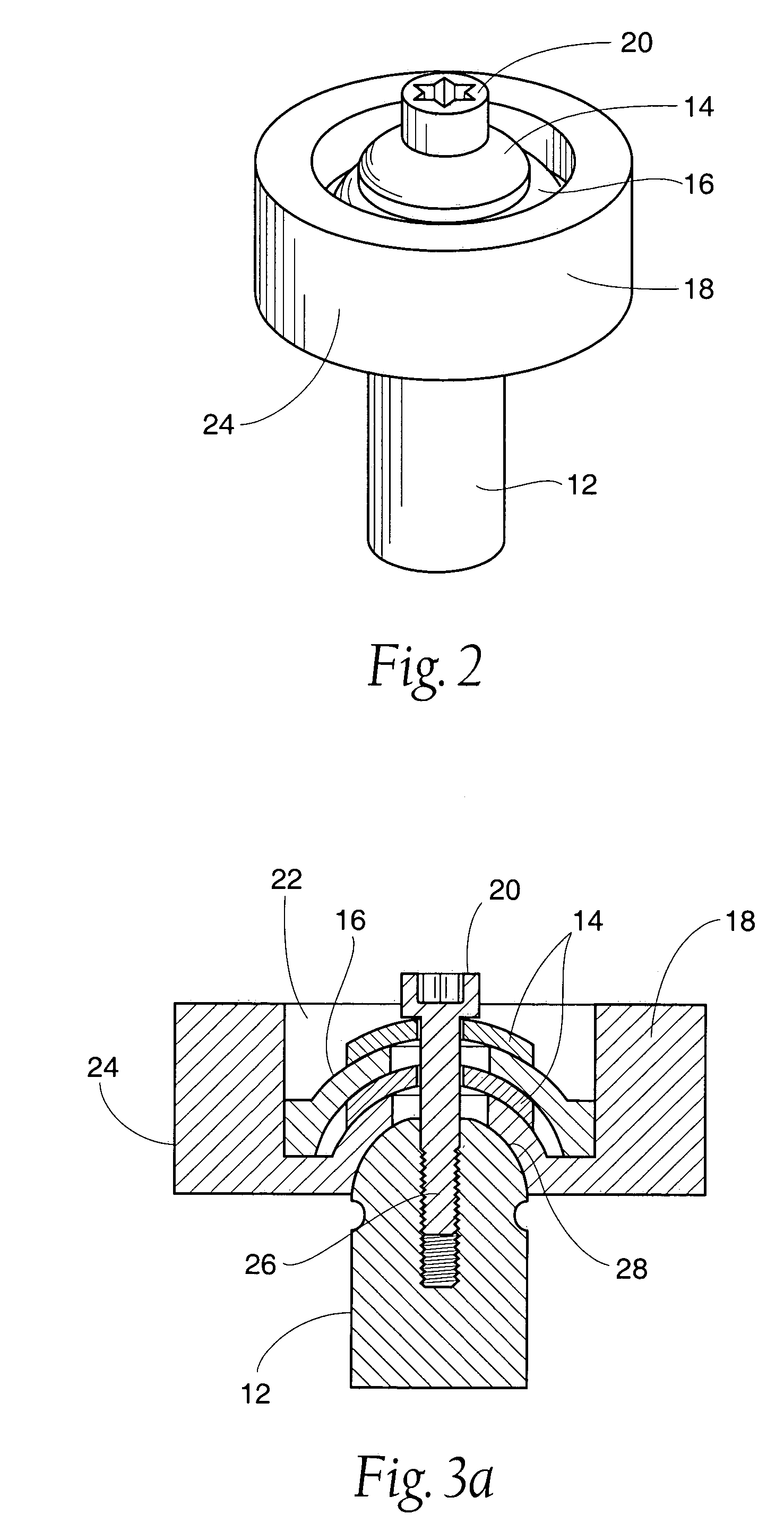
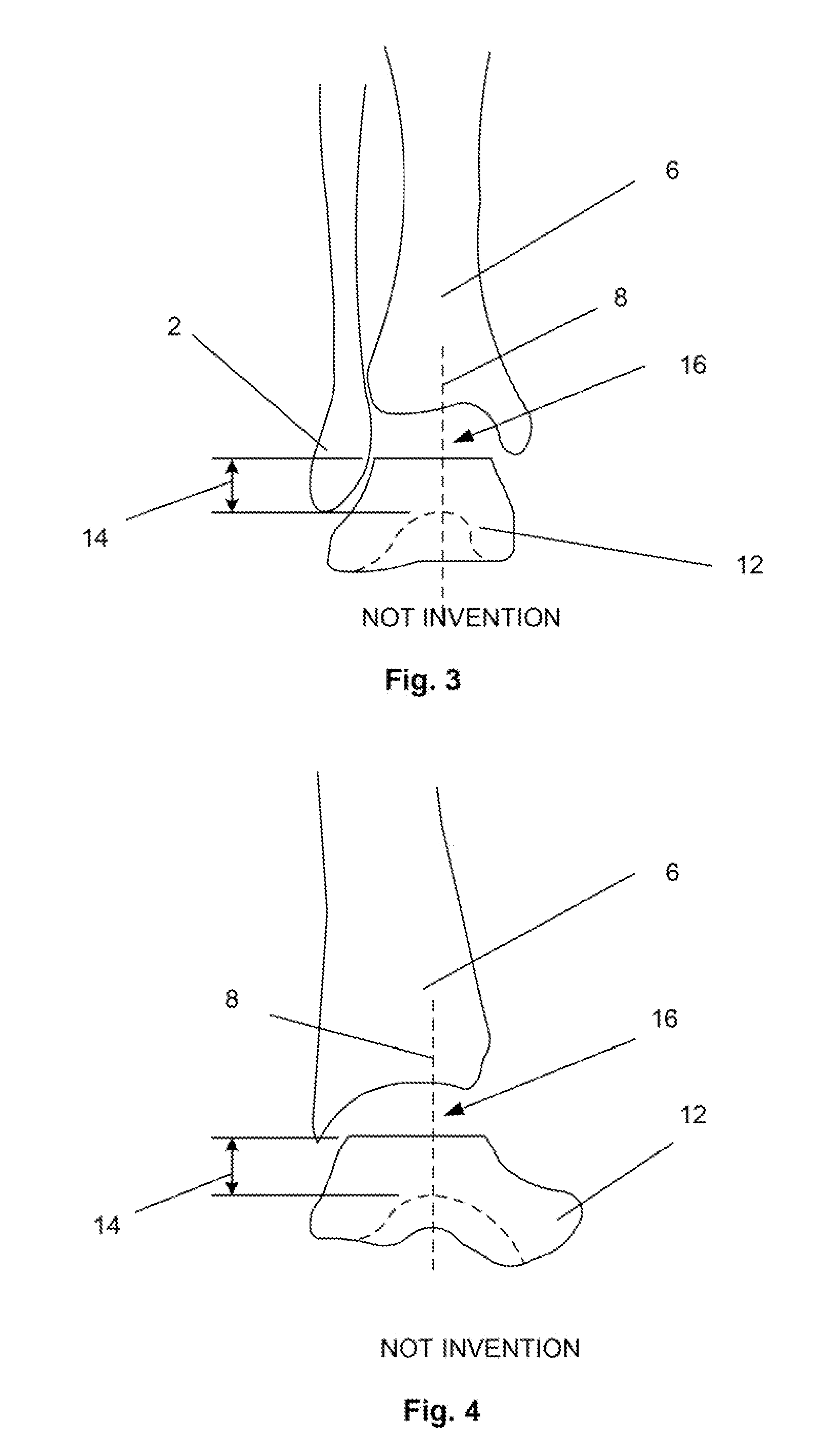
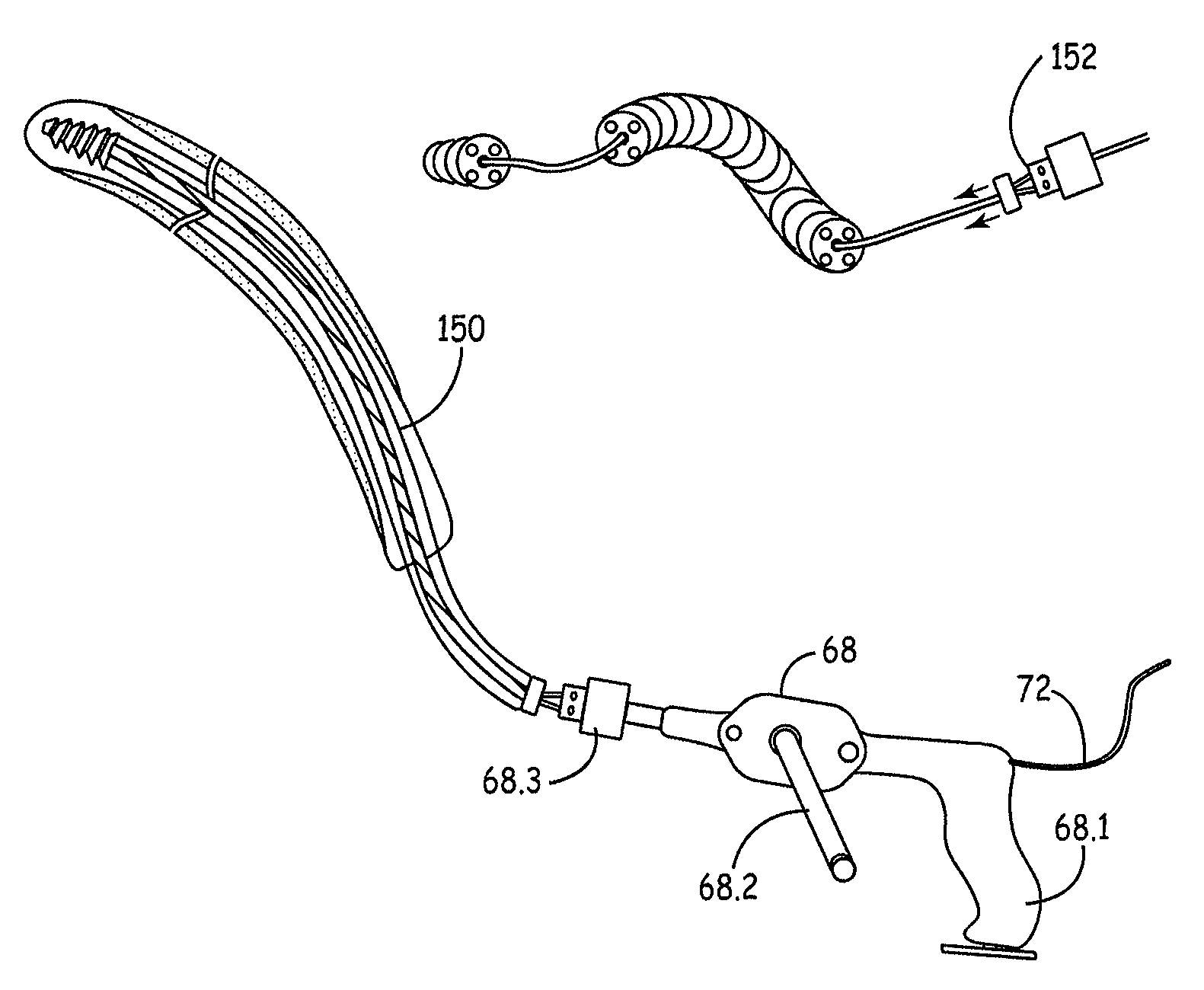
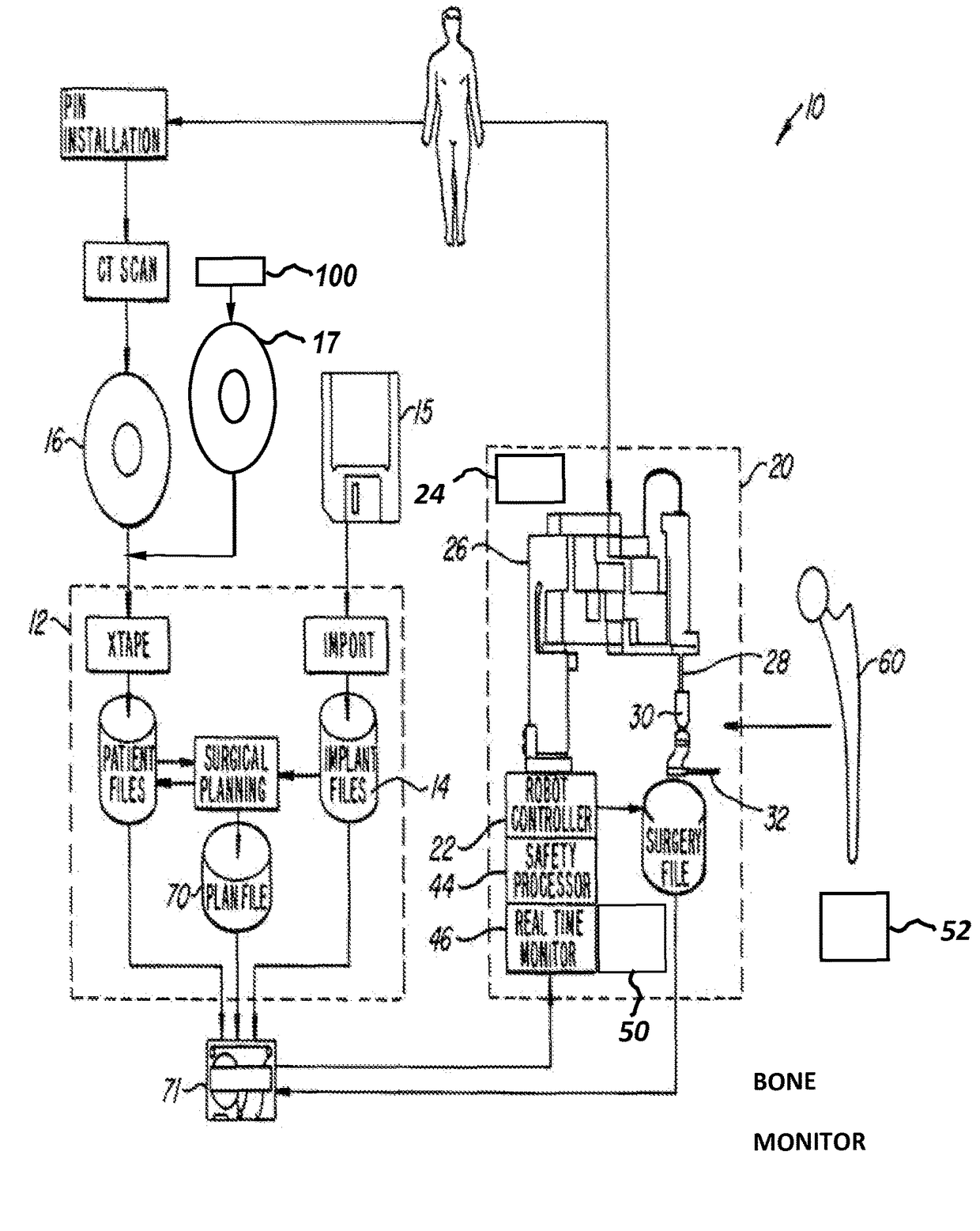
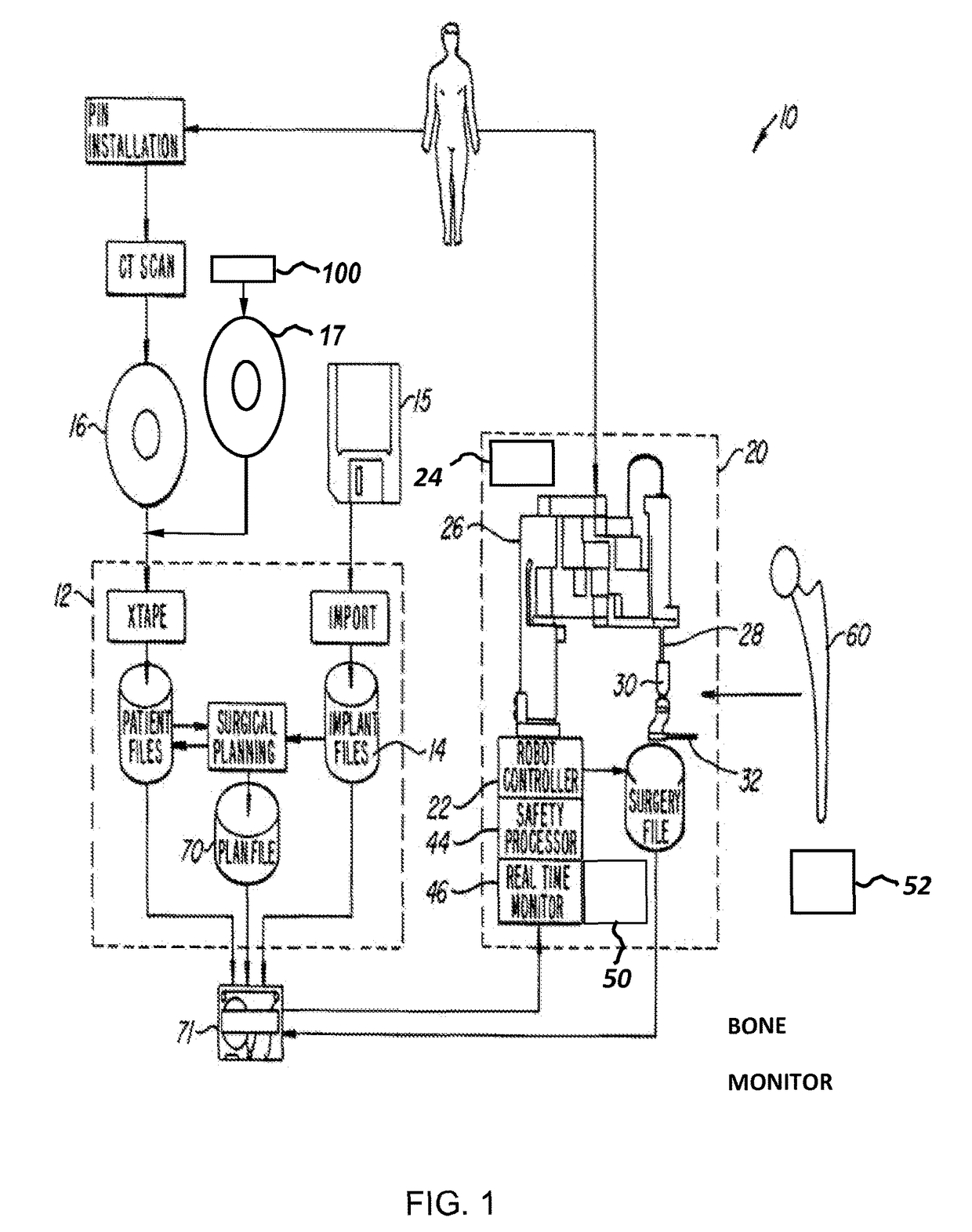
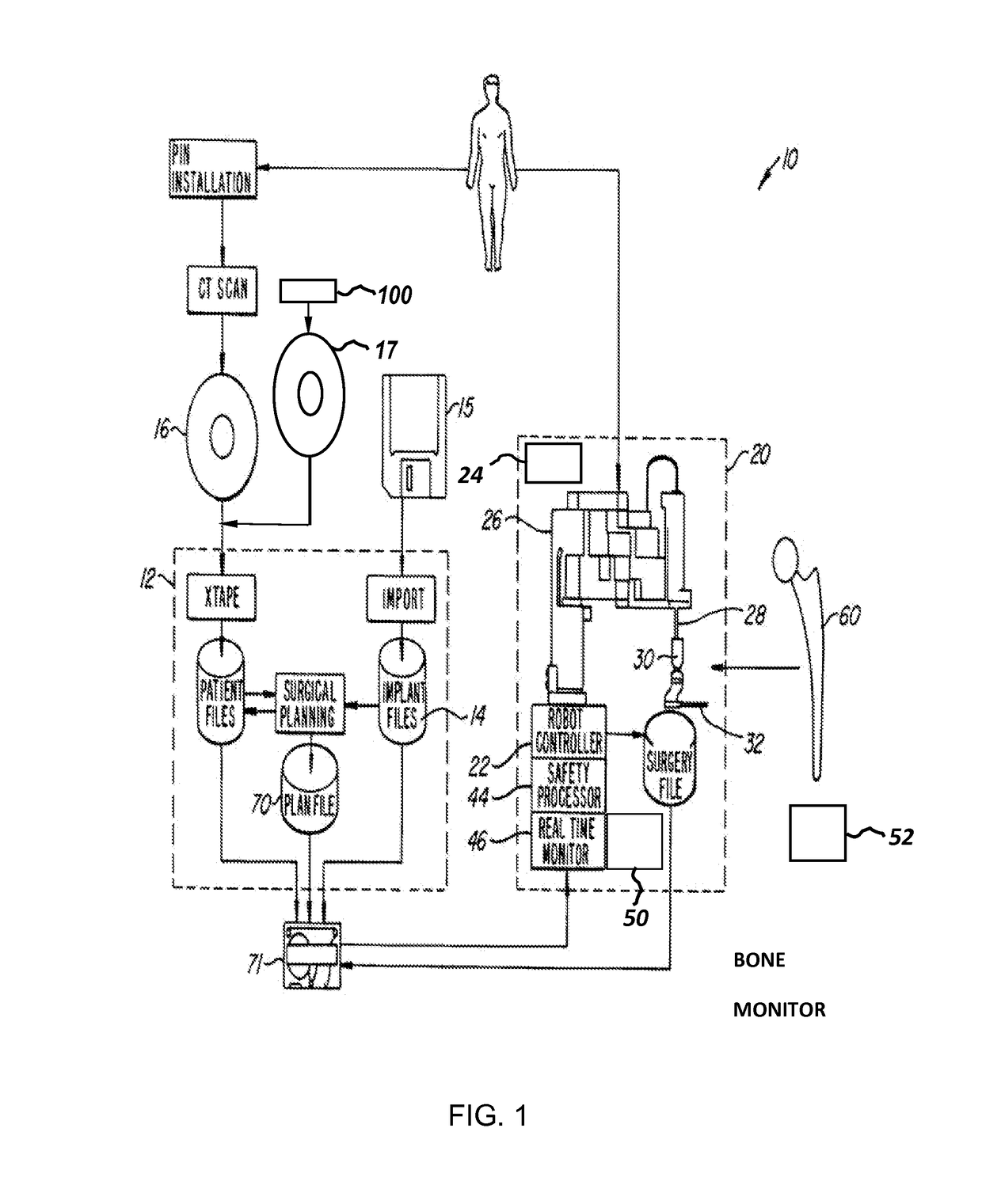
Method and apparatus for positioning a bone prosthesis using a localization system
InactiveUS20080051910A1Surgical navigation systemsSurgical systems user interfaceLocalization systemCoxal joint
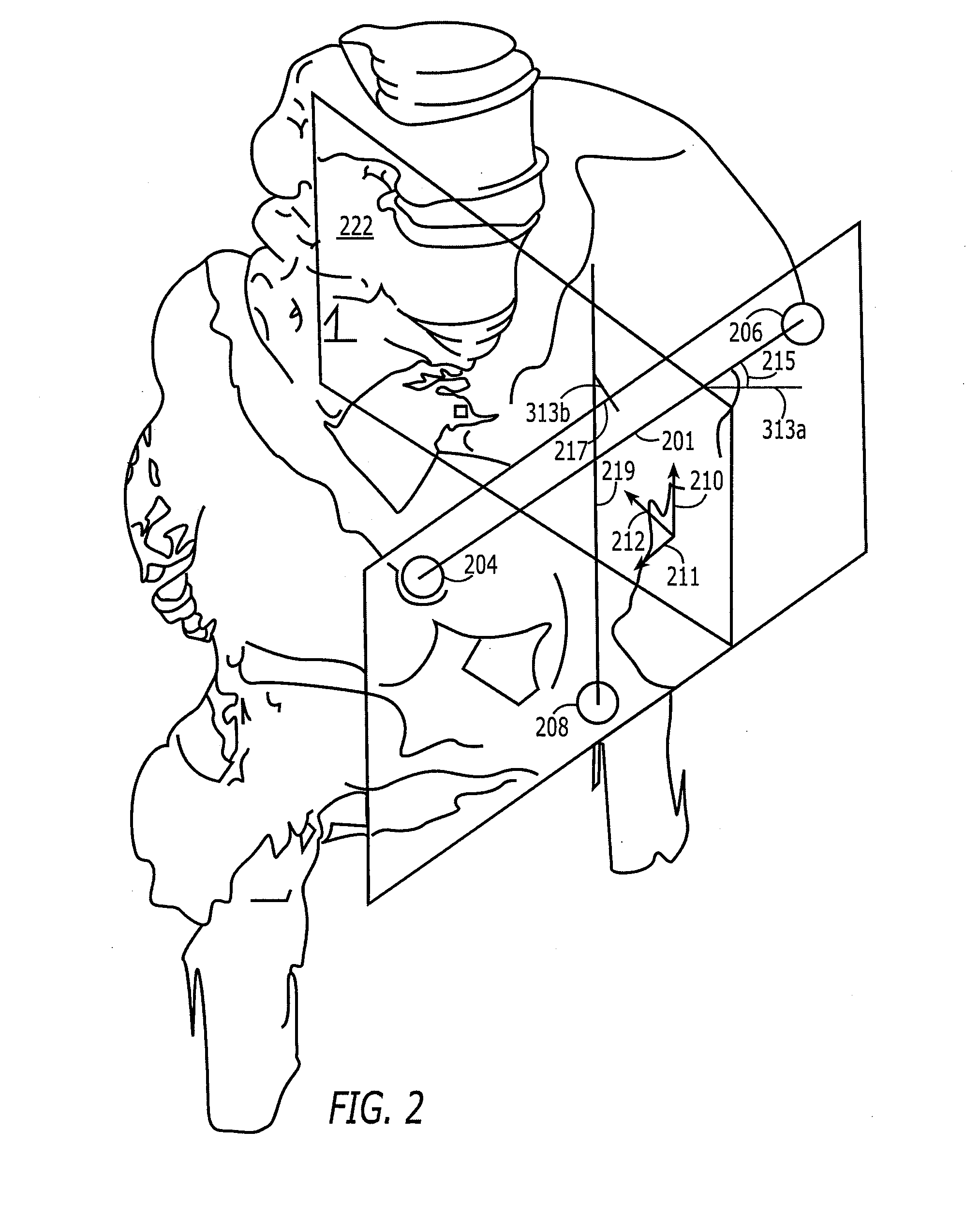
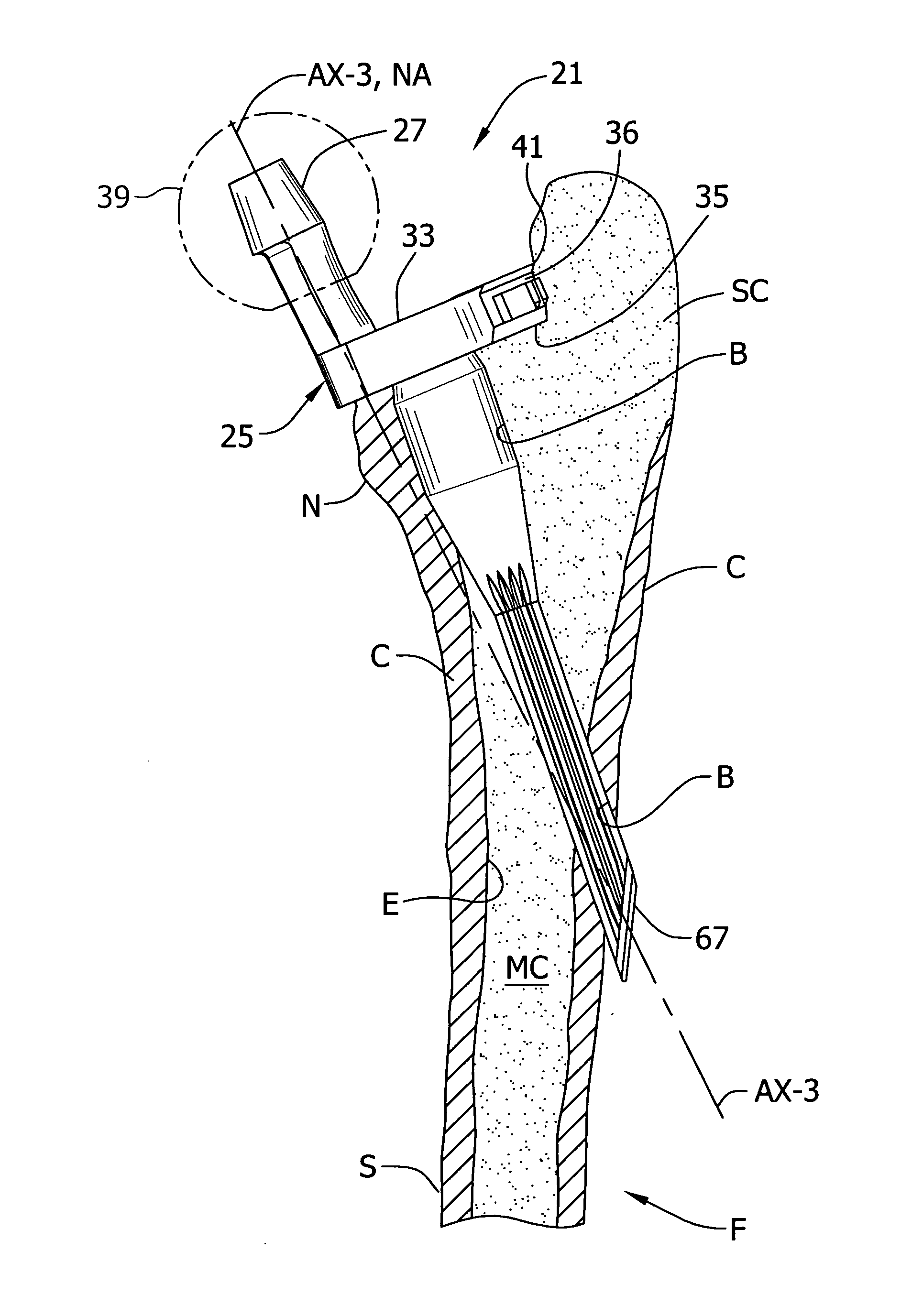
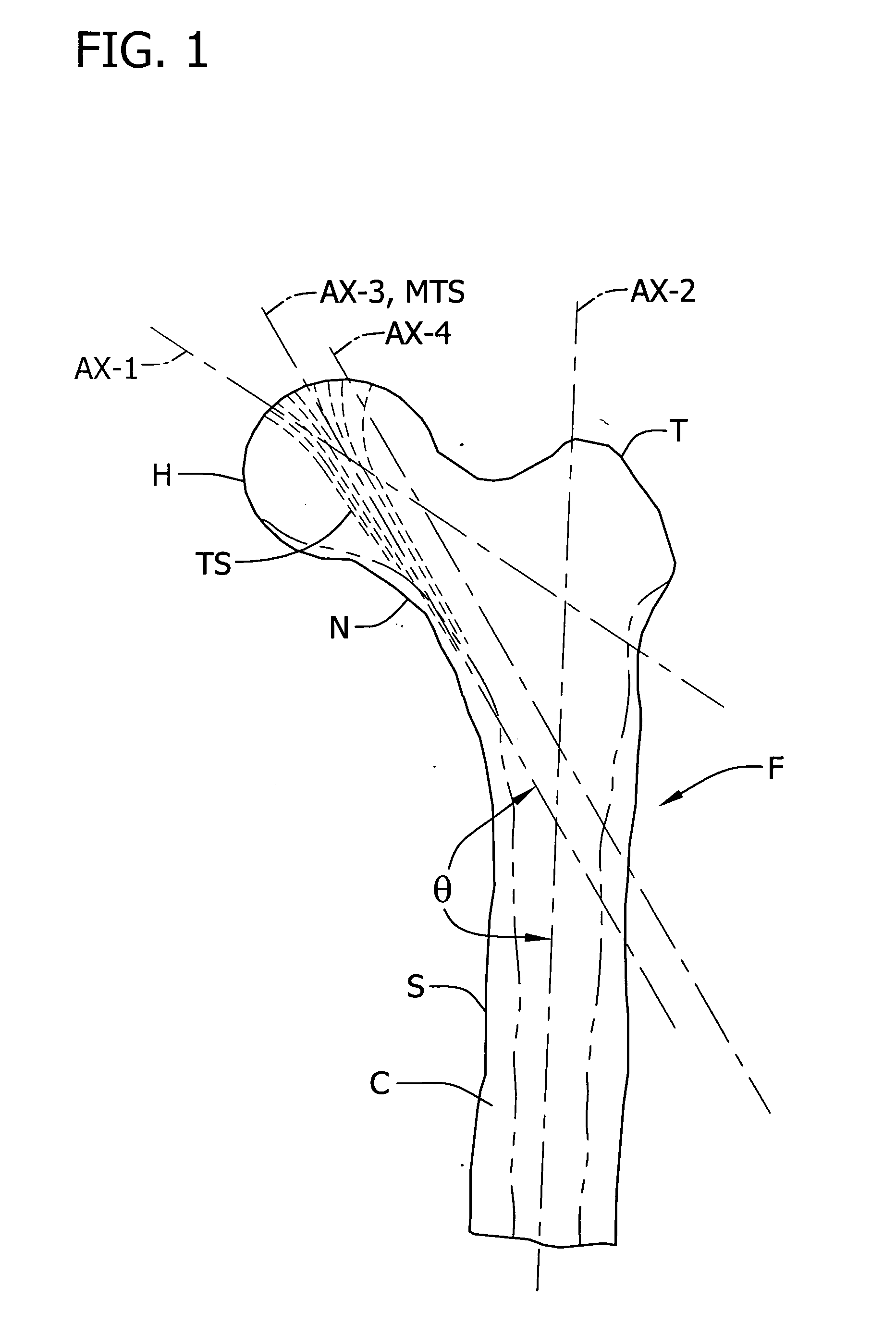
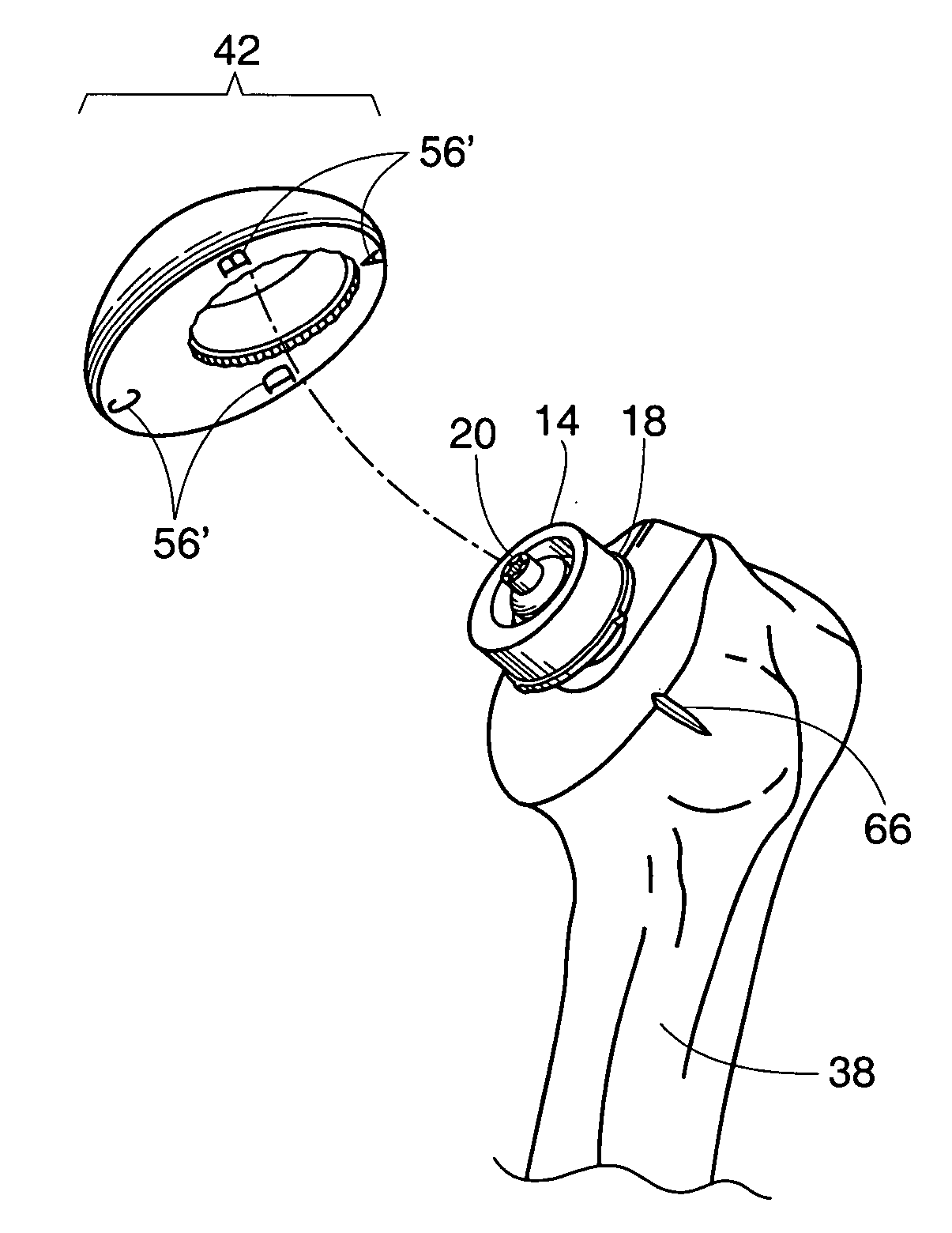
Methods and apparatus using a surgical navigation system to position the femoral component of a prosthetic hip during hip joint replacement surgery without separately affixing a marker to the femur. The navigation system acquires the center of rotation of the hip joint as well as at least one point on the femur in the pelvic frame of reference. From these two points, the navigation system calculates the position and length of a first line between the center of rotation of the hip joint and the point on the femur. Optionally, a second point on the femur that is not on the first line is palpated. The system can calculate the position and length of a second line that is perpendicular to the first line and that runs from the first line to the second palpated point on the femur. The prosthetic cup is implanted and its center of rotation is recorded. A tool for forming the bore within which the stem of the femoral implant component will be placed is tracked by the navigation system. While the tool is fixed to the femur, the surgeon re-palpates the same point(s) on the femur that were previously palpated. The navigation system calculates the position and length of a first line between the center of rotation of the prosthetic cup and the re-palpated first point. If a second point on the femur was re-palpated, the navigation system also calculates the position and length of a perpendicular line between the first line and the second point. The surgical navigation system uses this information to calculate and display to the surgeon relevant information about the surgery, such as change in the patient's leg length and / or medialization / lateralization of the joint.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
Prosthesis and method of implantation
InactiveUS20060015188A1Easy to implantAvoid crackingBone implantJoint implantsLess invasive surgeryBone prosthesis
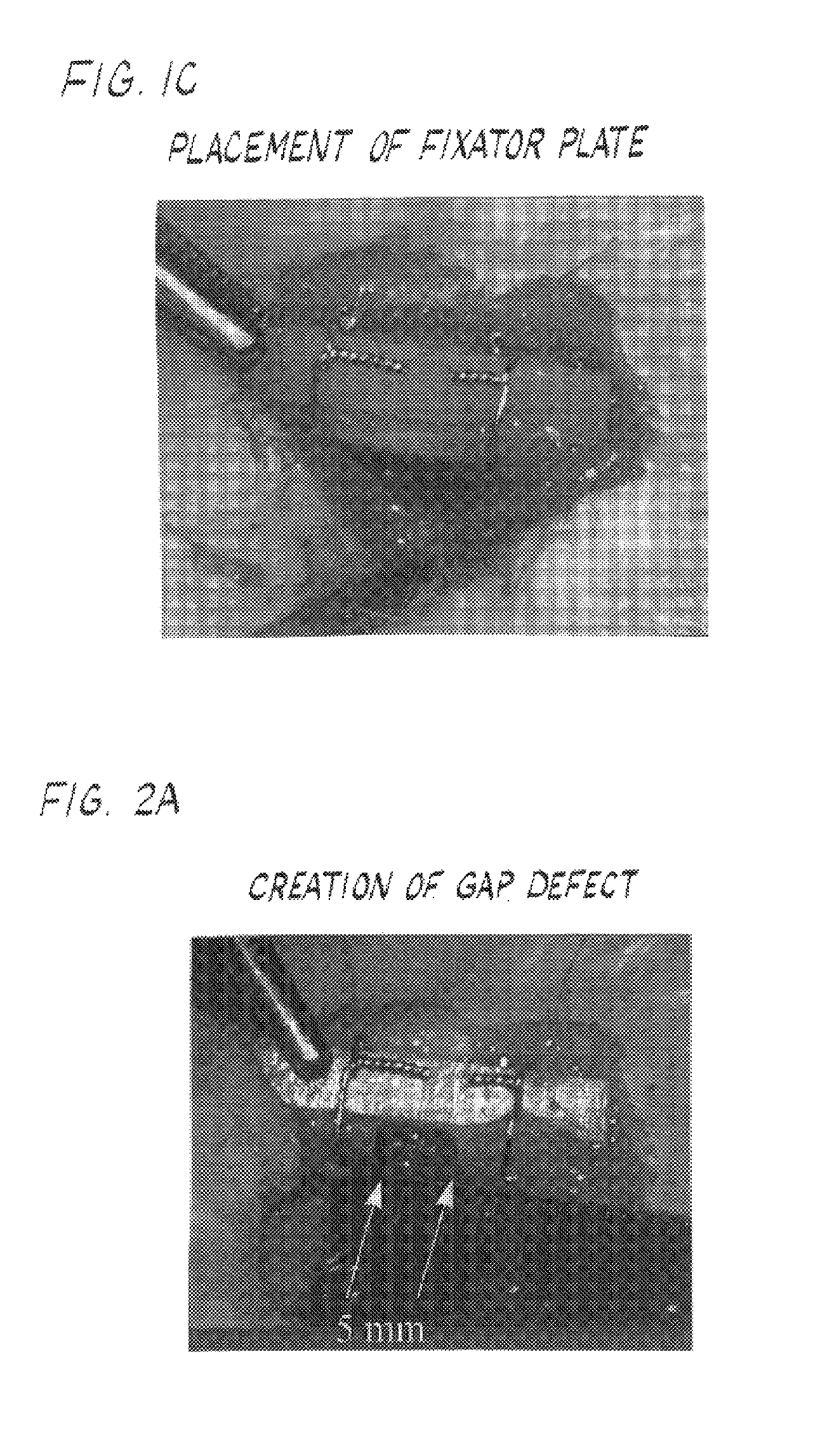
A bone prosthesis for implantation at a joint is adapted to closely replicate the normal loading of the femur and is suitable for implantation using a single incision anterior approach, a form of minimally invasive surgery (MIS). The bone prosthesis comprises a stem adapted for orientation with a medial trabecular stream of the femur.
Owner:THE JAMES B GRIMES & TRACIE LYNN GRIMES 1998 TRUST
Method of preparing a poorly crystalline calcium phosphate and methods of its use
InactiveUS7517539B1Readily injectableHigh strengthBiocideSurgical adhesivesOsteoporotic boneIntervertebral spaces
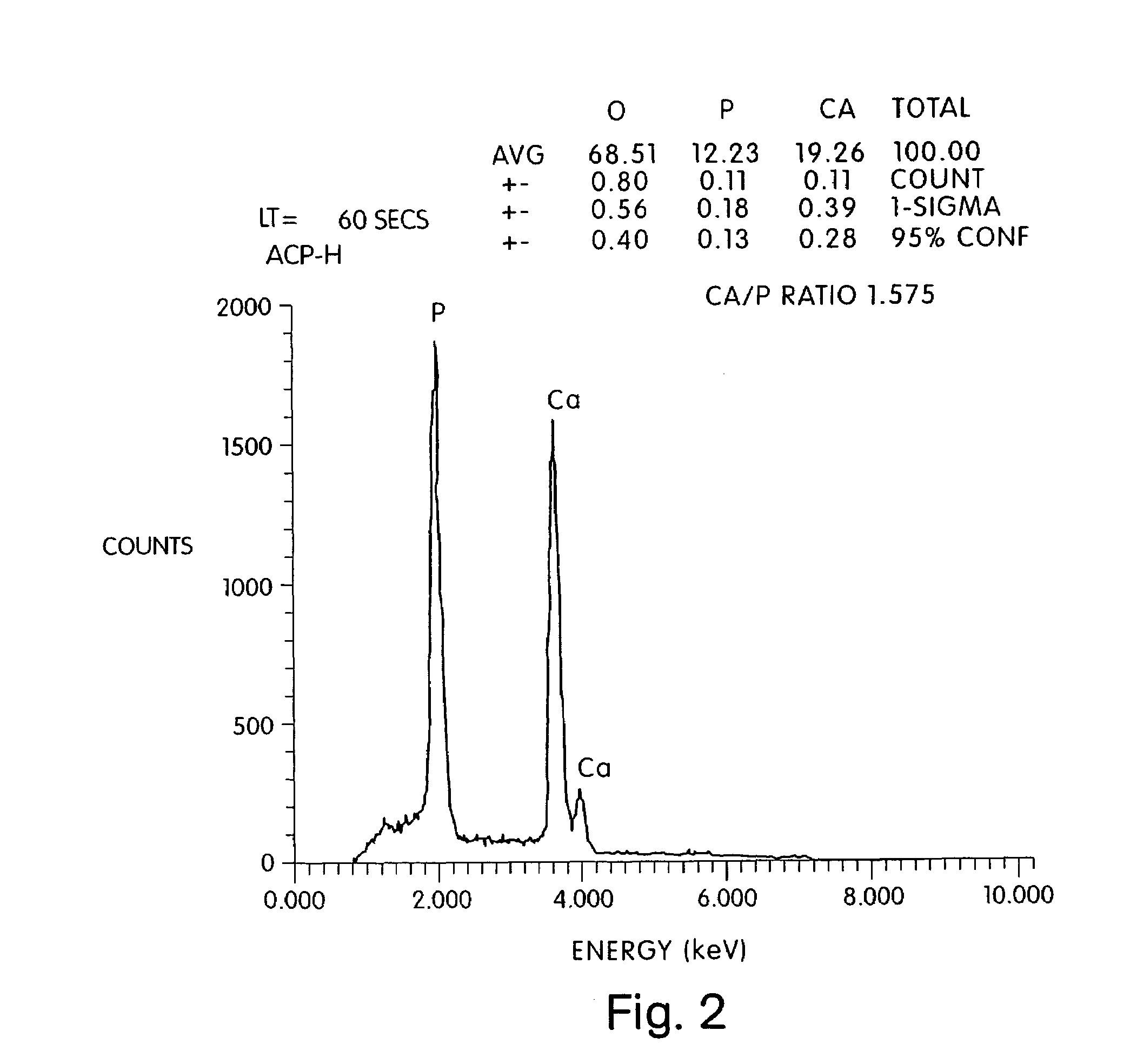
The present invention provides a novel process for producing a calcium phosphate cement or filler which hardens in a temperature dependent fashion in association with an endothermic reaction. In the reaction a limited amount of water is mixed with dry calcium phosphate precursors to produce a hydrated precursor paste. Hardening of the paste occurs rapidly at body temperature and is accompanied by the conversion of one or more of the reactants to poorly crystalline apatitic calcium phosphate. The hardened cements, fillers, growth matrices, orthopedic and delivery devices of the invention are rapidly resorbable and stimulate hard tissue growth and healing. A composite material is provided including a strongly bioresorbable, poorly crystalline apatitic calcium phosphate composite and a supplementary material. The supplementary material is in intimate contact with the hydroxyapatite material in an amount effective to impart a selected characteristic to the composite. The supplemental material may be biocompatible, bioresorbable or non-resorbable. A method for treating a bone defect also is provided by identifying a bone site suitable for receiving an implant, and introducing a strongly resorbable, poorly crystalline apatitic calcium phosphate at the implant site, whereby bone is formed at the implant site. The implant site may be a variety of sites, such as a tooth socket, non-union bone, bone prosthesis, an osteoporotic bone, an intervertebral space, an alveolar ridge or a bone fracture.
Owner:LIFE SCI ENTERPRISES
Modular long bone prosthesis for partial or total bone replacement
A modular long bone prosthesis is provided having a proximal component and a retroversion component. The proximal component is configured at a proximal end to receive a head forming a portion of a joint and is formed at a distal end to mate with additional prosthesis components. The proximal component is formed to simulate an angle inherent in the proximal end of the bone to be replaced and includes an indicator adjacent the distal end to facilitate rotational alignment of the proximal component and additional prosthesis components. The retroversion component includes a proximal end configured to mate with the distal end of the proximal component. The proximal end includes alignment indicia for positioning relative to the indicator on the proximal component. When the indicator is in a first position relative to the alignment indicia the proximal component and the retroversion component establish a first alignment orientation forming an angle simulating the angle inherent in the proximal end of the right long bone of the long bone to be replaced. When the indicator is in a second position relative to the alignment indicia the proximal component and the retroversion component establish a second alignment orientation forming an angle simulating the angle inherent in the proximal end of the left long bone of the long bone to be replaced.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Adjustable bone prostheses and related methods
InactiveUS7166132B2Straightforward and yet robustYielding couplingBone implantBone prosthesisBiomedical engineering
Adjustable prostheses and related methods provide a wide range of adjustment along or about multiple axes. The prostheses and related methods make possible a straightforward, yet robust way of securing, e.g., a humeral head prosthesis in a desired position and maintaining the prosthesis in the desired position during use.
Owner:TORNIER INC
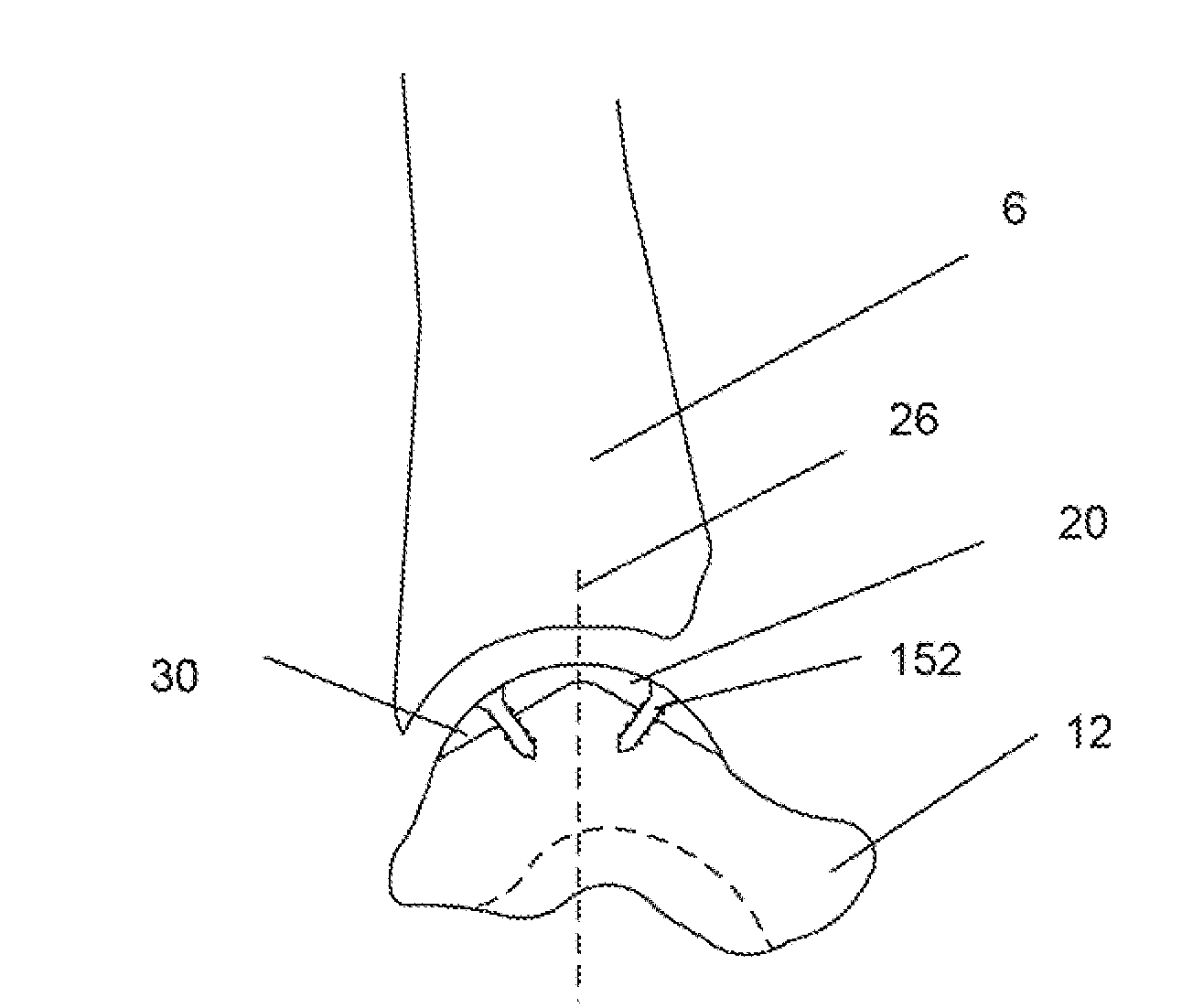
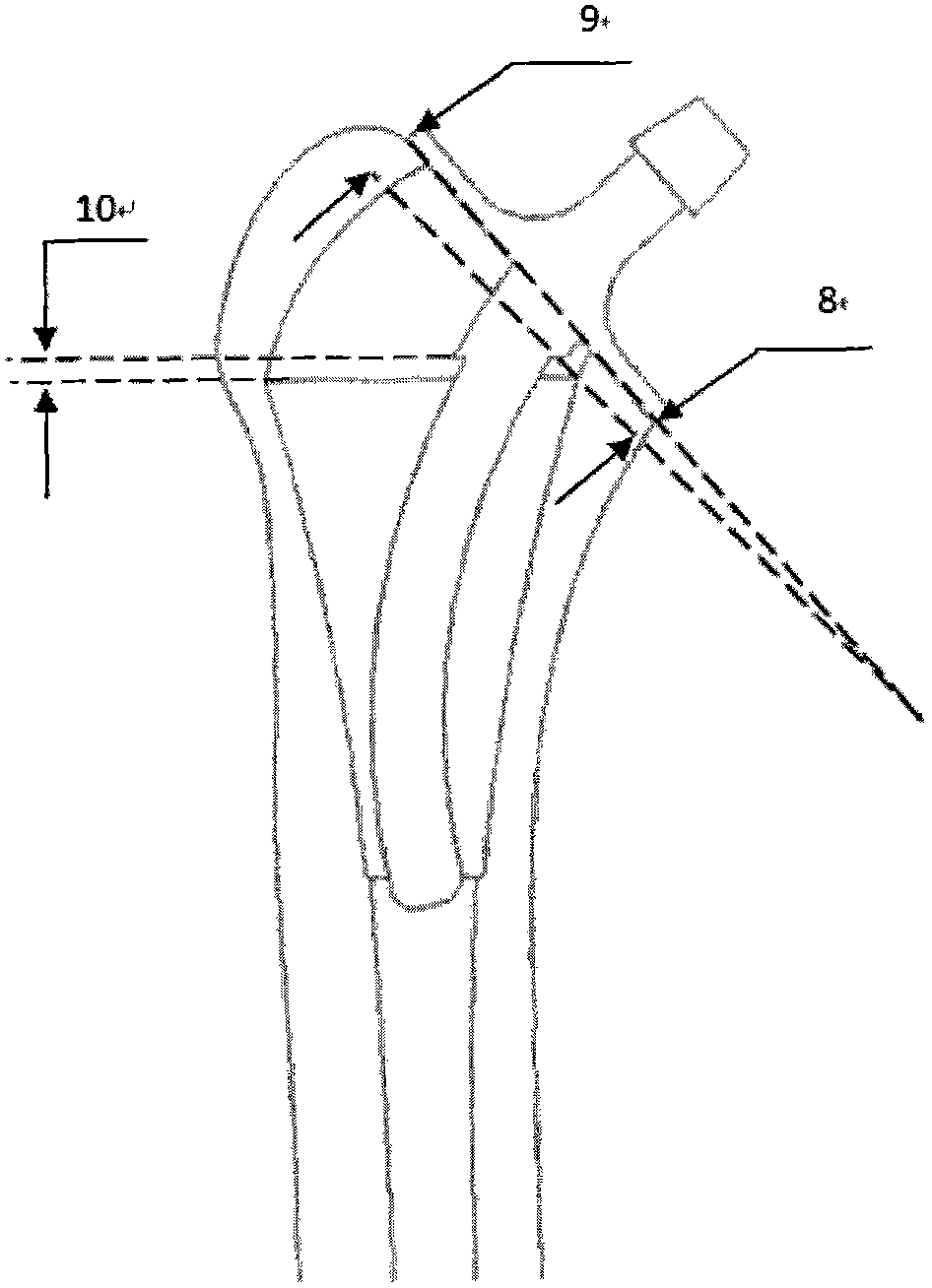
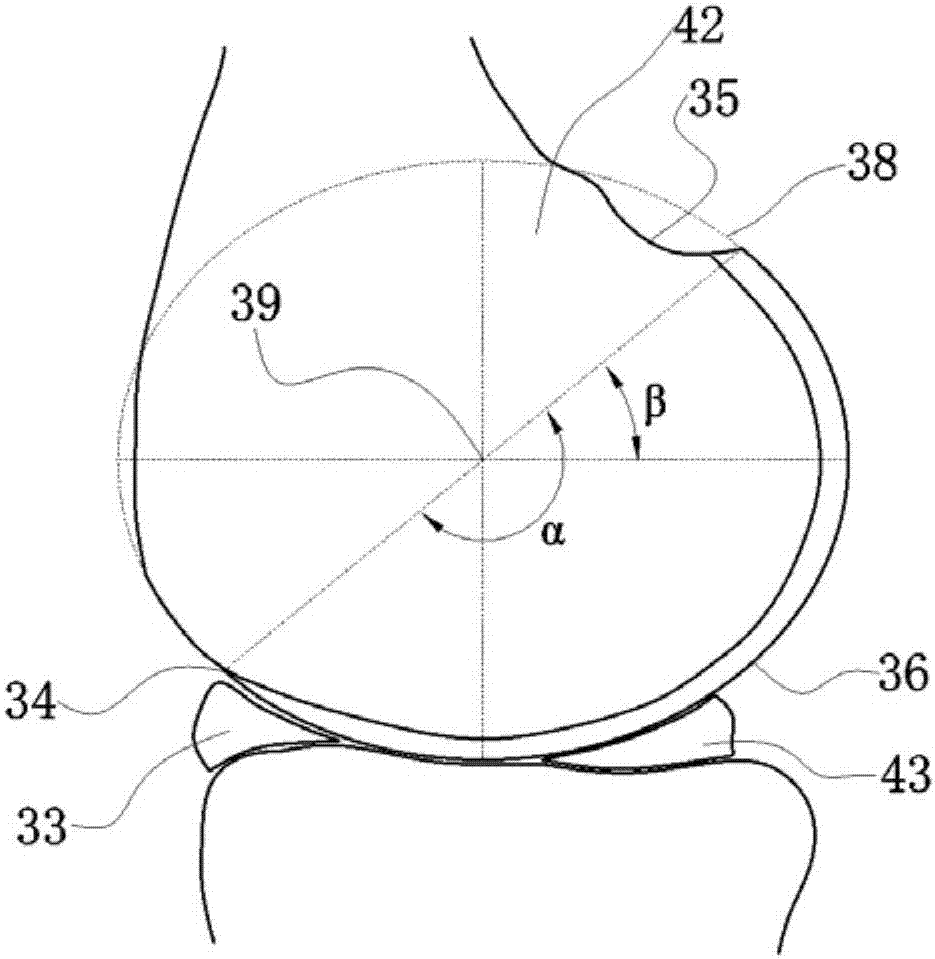
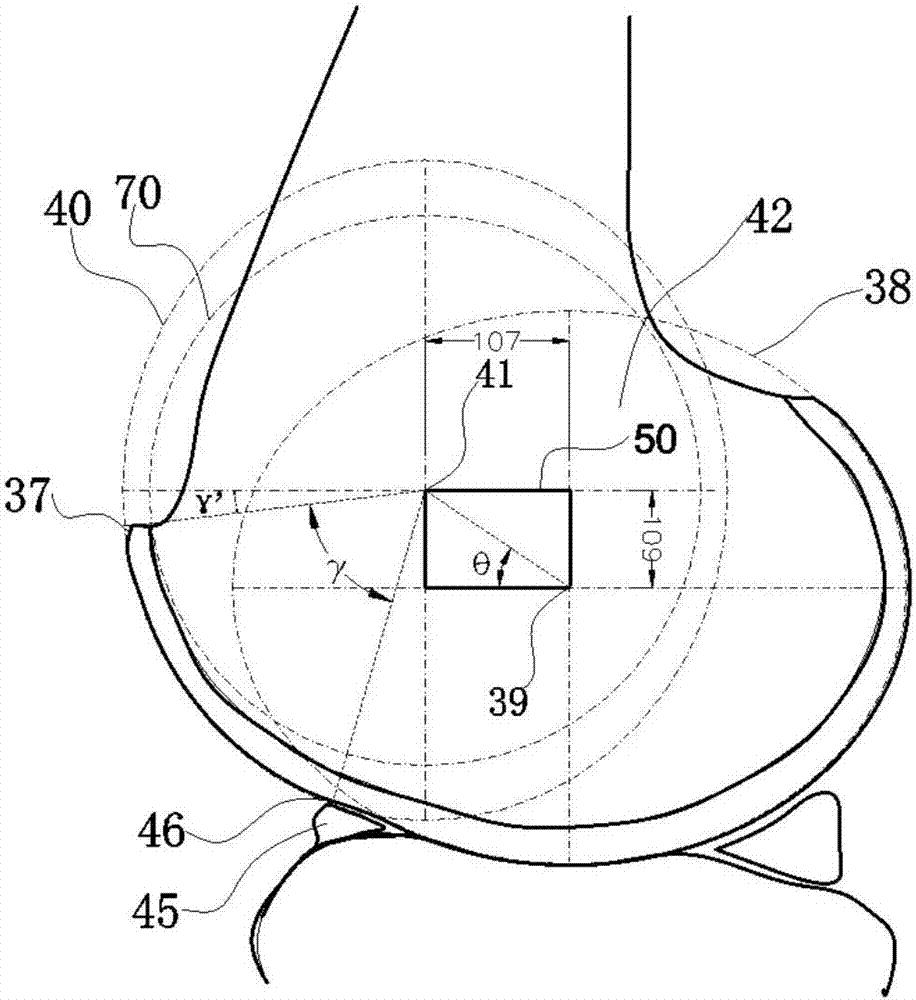
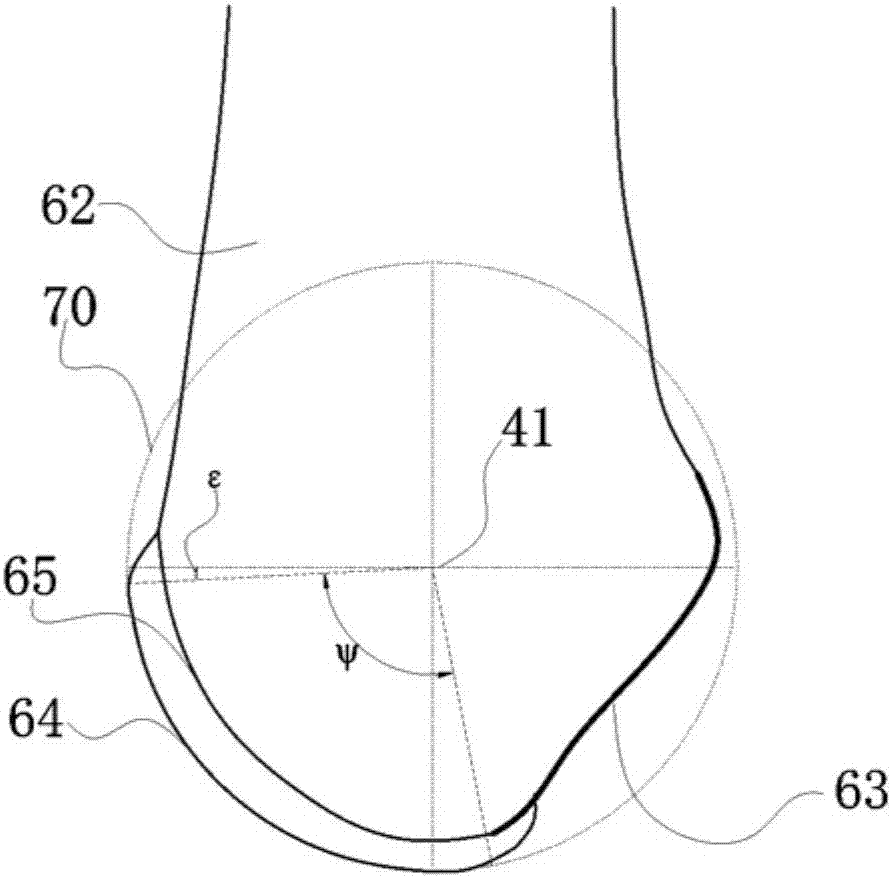
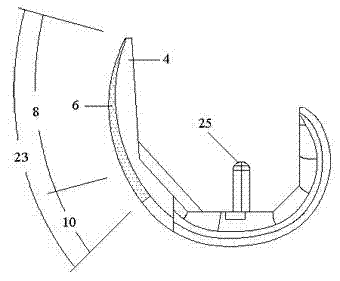
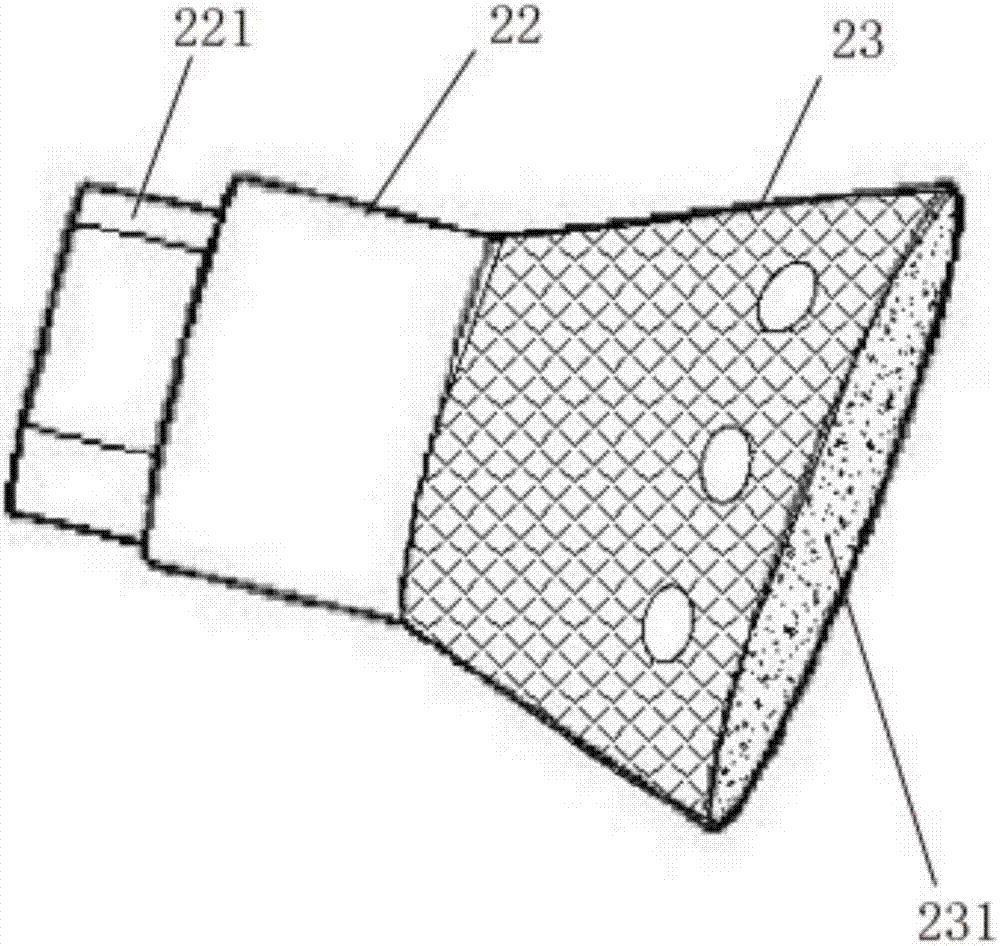
Bone prosthesis
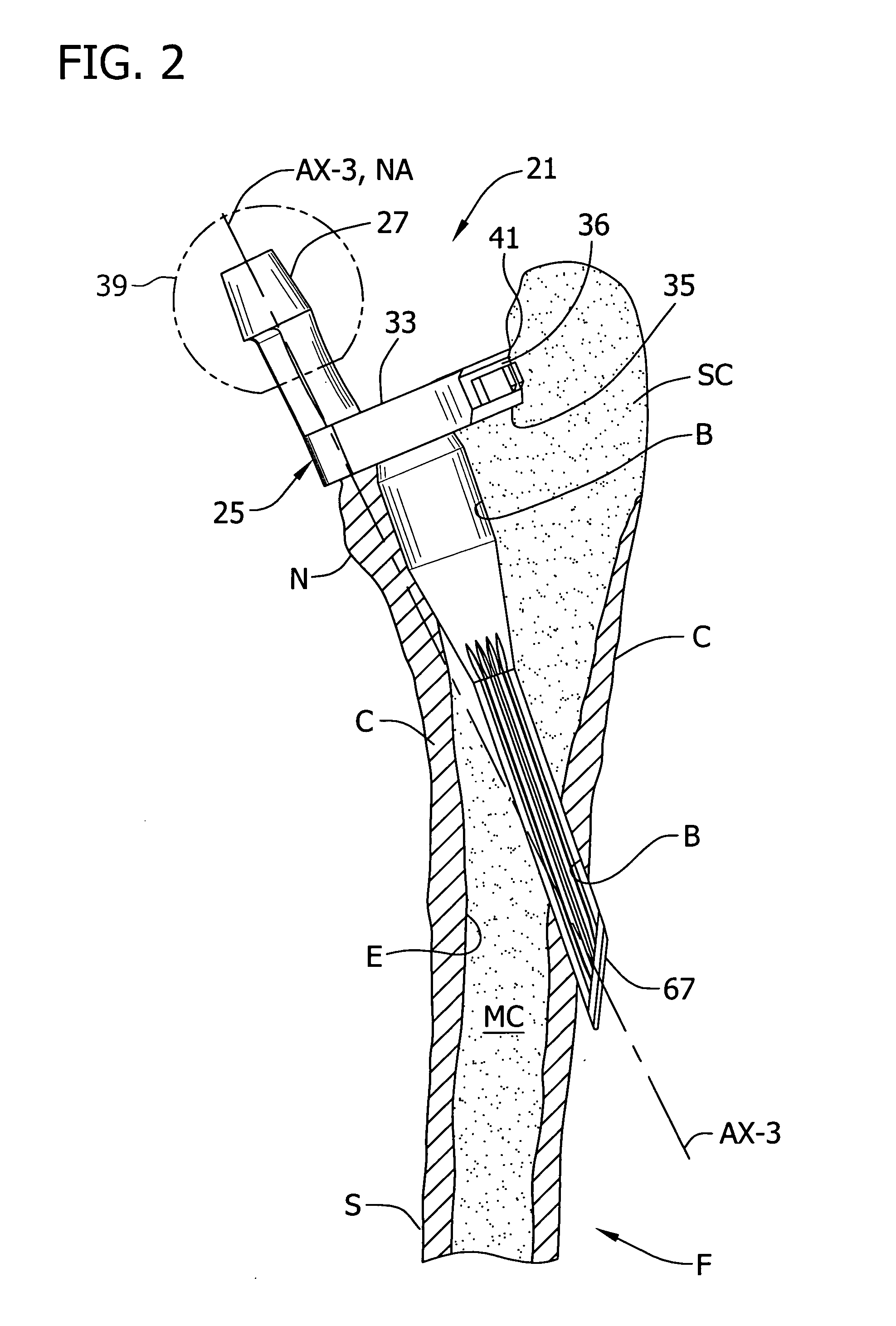
A partial bone prosthesis and methods of using the same are disclosed herein. The partial bone prosthesis can be configured for use, for example, on the superior side of the talus or an end of a long bone, such as the tibia. The partial bone prosthesis can anchor to the perimeter of the contact patch between the bone and the prosthesis. For example, the prosthesis can be attached to the talus without drilling holes through the talus, preserving structural integrity and blood flow within the talus.
Owner:TALUS MEDICAL
Method and apparatus for positioning a bone prosthesis using a localization system
InactiveUS7594933B2Surgical navigation systemsSurgical systems user interfaceHip joint replacement operationLocalization system
Methods and apparatus using a surgical navigation system during hip joint replacement surgery without separately affixing a marker to the femur. The navigation system acquires the center of rotation of the hip joint as well as at least one point on the femur in the pelvic frame of reference. From these two points, the navigation system calculates the position and length of a first line between the center of rotation of the hip joint and the point on the femur. A prosthetic cup is implanted and its center of rotation is recorded. A tool for forming the bore within which the stem of the femoral implant component will be placed is tracked by the navigation system. The navigation system calculates the position and length of a first line between the center of rotation of the prosthetic cup and the re-palpated first point. The surgical navigation system uses this information to calculate and display to the surgeon relevant information about the surgery.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
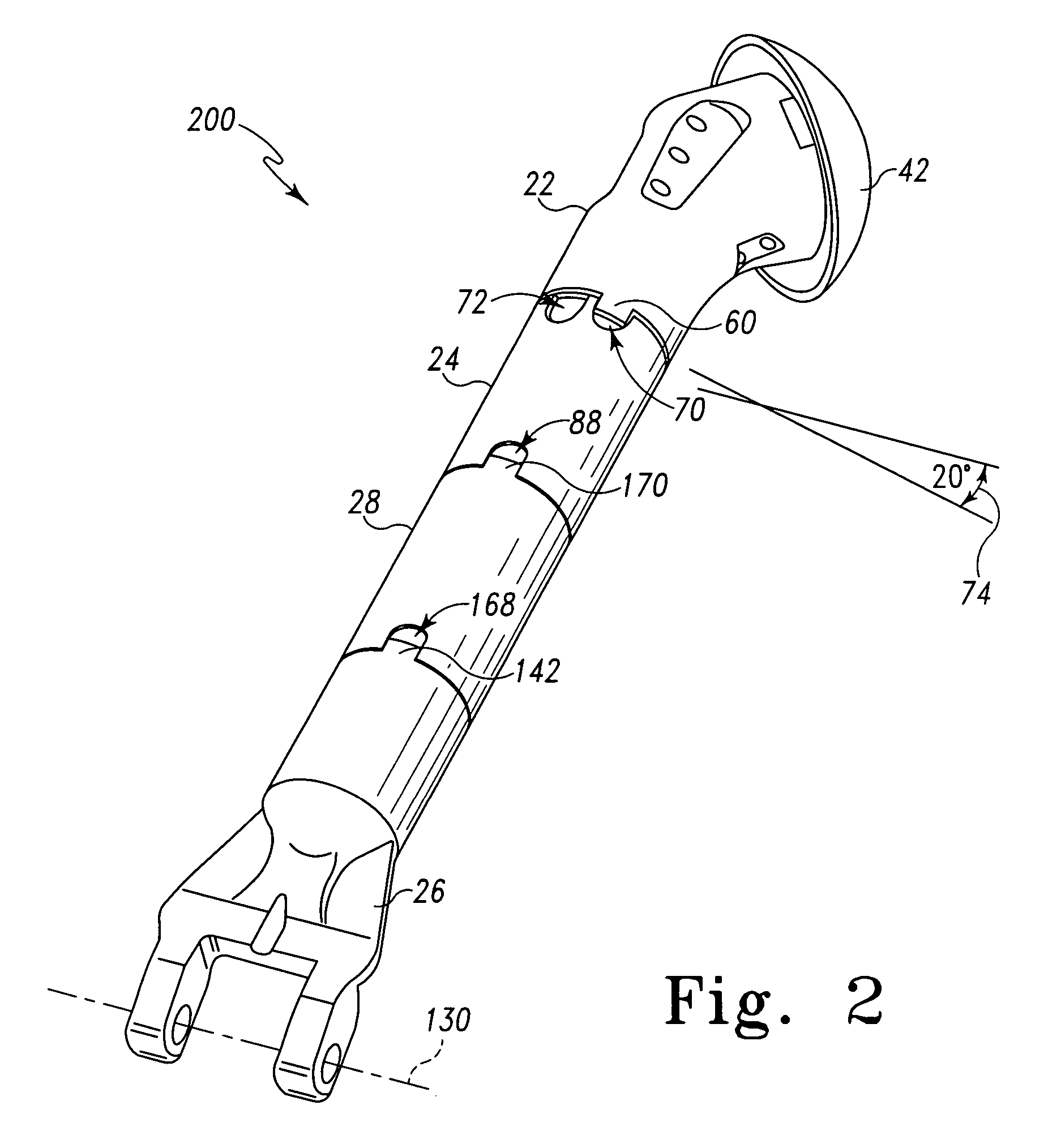
Internal cord fixation device
InactiveUS7410489B2Prevent and reduce particulate sheddingProvide resistanceSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisCompressive resistanceBone prosthesis
Methods and apparatuses for fixing a bone fragment or a bone prosthesis onto a bone. To affix a bone fragment to the bone, an internal fastener is attached from within the interior of the bone to a bone fragment with a length of flexible, inelastic cord extending within the bone interior and attached to the fastener and passing outwardly through an opening in a second bone fragment. An axially rigid tubular support may be placed along the cord to reduce particulate shedding, to reduce ingrowth of bone into the cord, to provide compressive resistance to the cable, or to deliver antibiotics or other pharmaceuticals. The fastener and cord are so positioned as to draw respective fracture surfaces together to reduce the fracture when the cord is pulled outwardly of the opening in the second bone fragment. A second fastener desirably is attached to the bone opening, this fastener including an open bore to receive the cord and a lock to secure the cord to this fastener and maintain the cord under tension.
Owner:DAOS
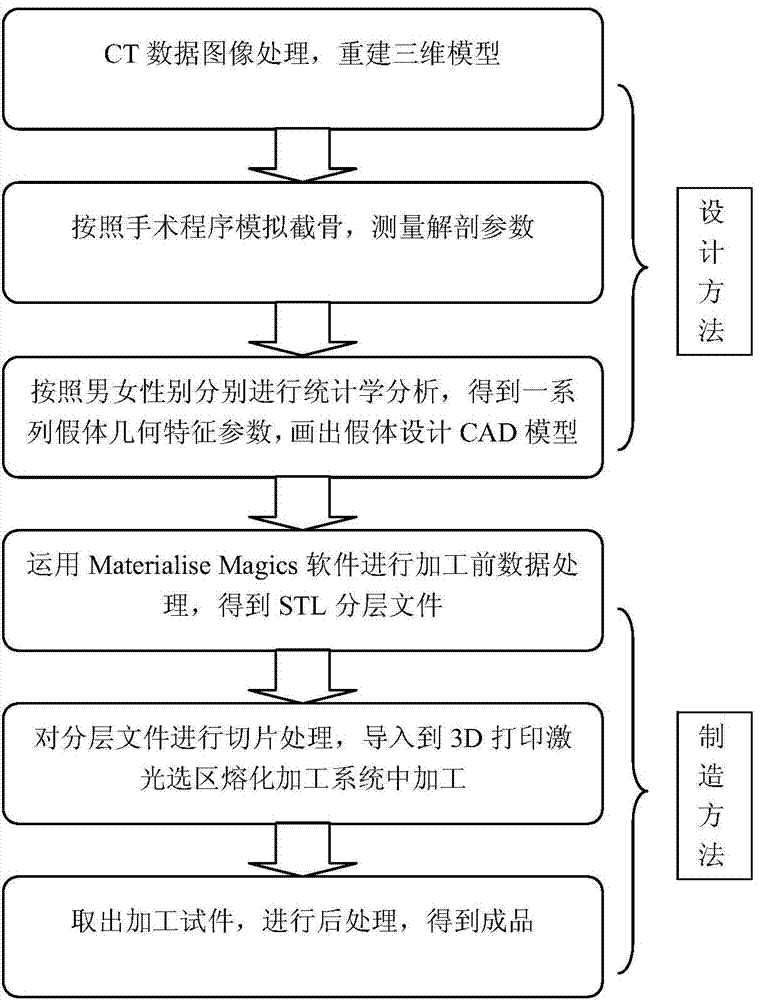
Designing method and manufacturing method of knee joint femoral prosthesis used for total knee arthroplasty
ActiveCN103584932AGood compatibilityShort processing cycleJoint implantsKnee jointsTotal hip arthroplastyDICOM
The invention discloses a designing method and a manufacturing method of a knee joint femoral prosthesis used for total knee arthroplasty. The designing method includes the following steps: S11, on the basis of CT (computed tomography) data of a normal Chinese person and in a medical image DICOM format, applying medical image software Mimics to build a three-dimensional digital model of a femur, and outputting a PLY-format file; S12, leading the digitalized femoral model PLY file in Geomagic Studio software, establishing a three-dimensional coordinate system, and utilizing a measuring tool to collect geometric parameters related to prosthesis designing; S13, performing statistical analysis on collected data by utilizing statistical software, and utilizing three-dimensional drawing software to draw a solid entity of the knee joint femoral prosthesis. The designing method and the manufacturing method have the advantages that a series of femoral prostheses different in type exist for men and women respectively, different knee joint femoral skeleton anatomical morphological features of men and women in China can be met, and matching degree of prostheses and knee joints is increased.
Owner:BEIJING NATON TECH GRP CO LTD +1
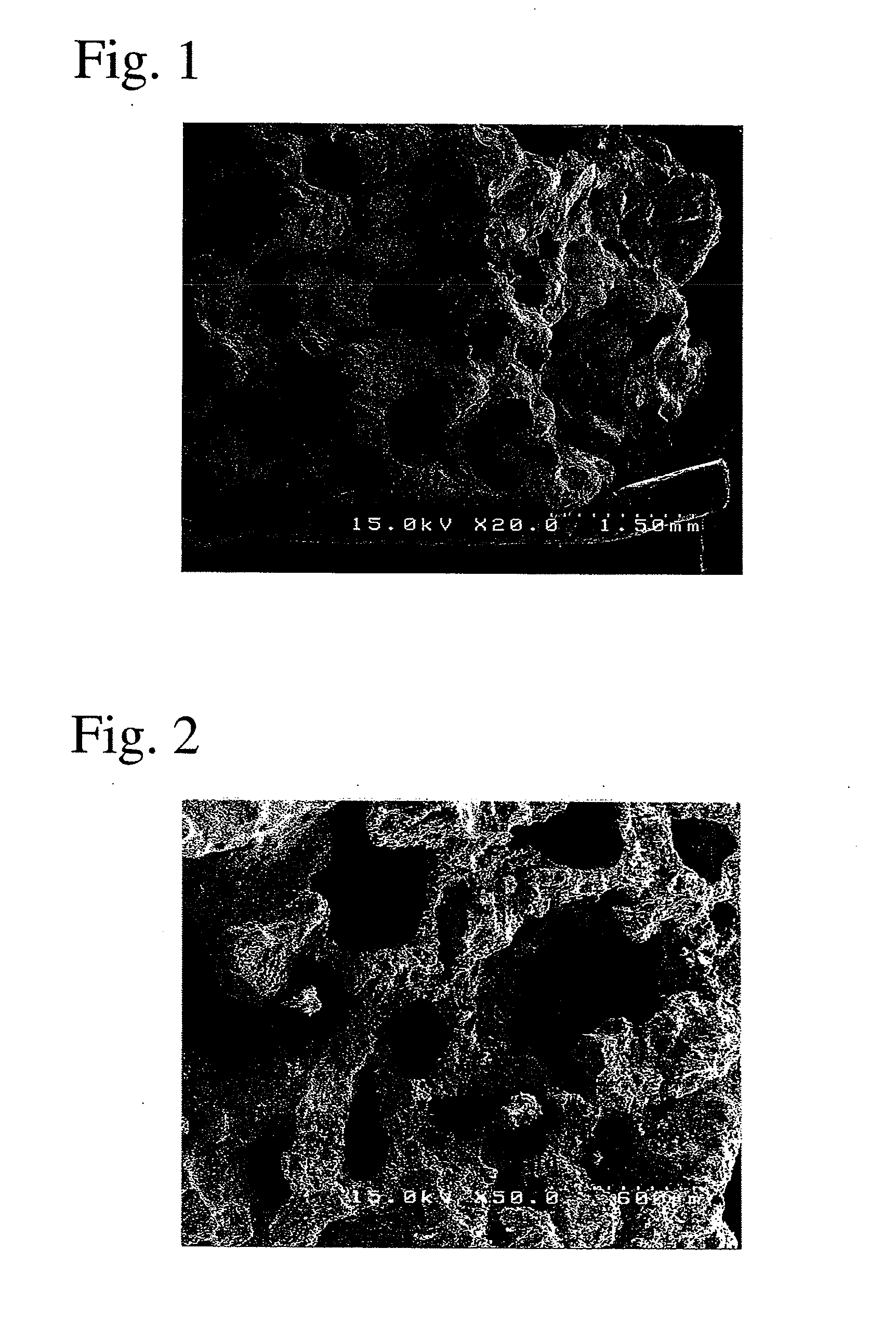
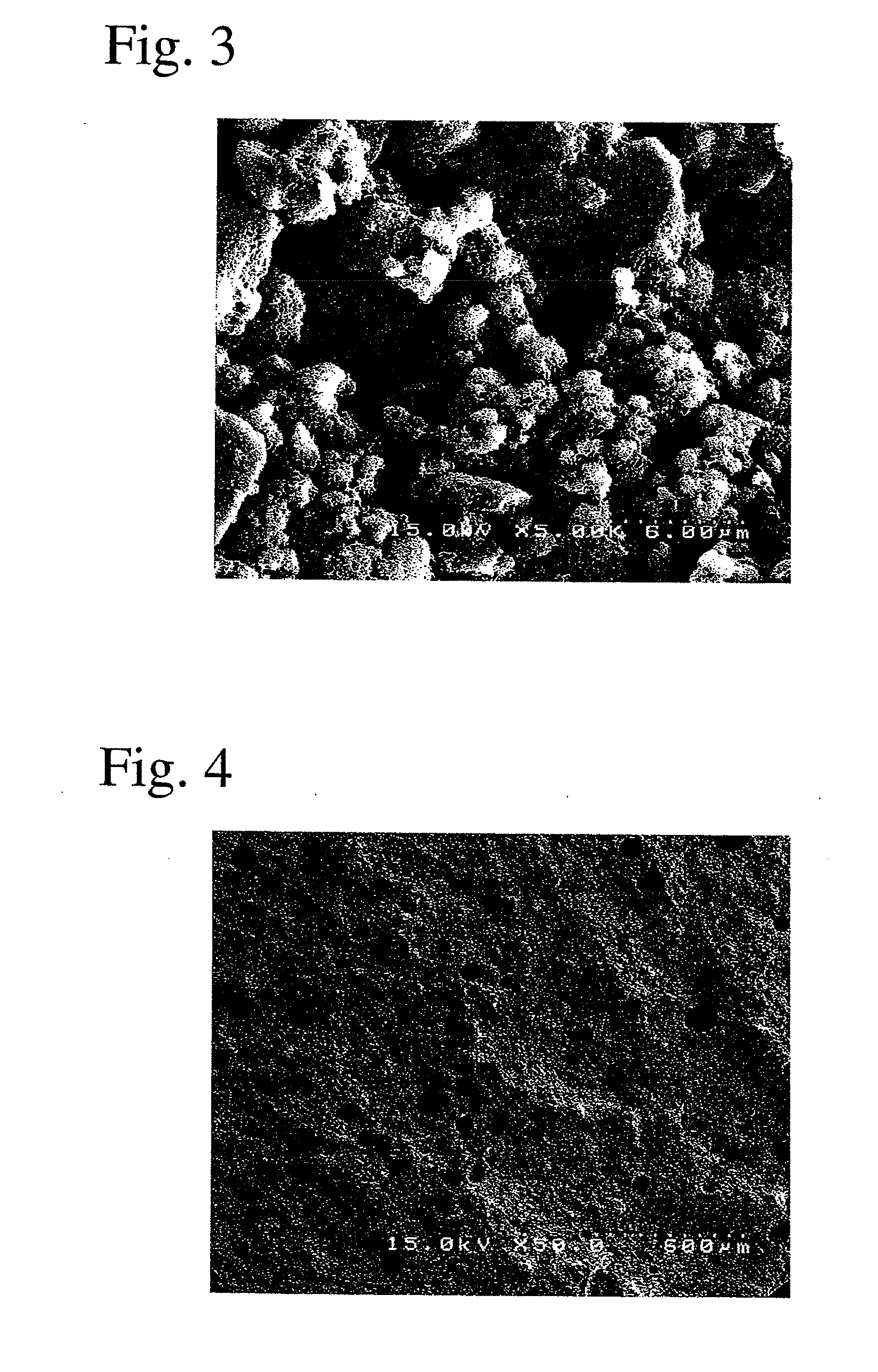
Porous bone prosthesis containing hydroxy apatite component and its preparation method
The porous bnoe prosthesis with good biological compatibility and biological activity is formed from nano hydroxyapatite and polyamide component with weight ratio of 1 / 1-0.3, and has mutual through pores whose pore size is 1-300 micrometers, and its total porosity is 30-70%. Its preparation method includes the following steps: according to the described ratio mixing fine hydroxyapatite powder and polyamide fine powder, then mixing them with ethyl alcohol solution containing calcium chloride to make solidifiation, and using water to dissolve the above-mentioned obtained material to remove water solubility component from solidified material and form porous structure in the bone prosthesis material.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Compositions and methods for forming and strengthening bone
Compositions are provided which stimulate bone growth. Also provided are methods for utilizing the compositions for filling in bone defects, promoting rapid fusion of bone fractures, grafts, and bone-prostheses, and promoting strengthening of osteoporotic bones.
Owner:MARFLY 2
Micropore processing method of bone repairing body rough surface
ActiveCN101254138AGood adhesionProliferation effect is goodBone implantSurgeryControllabilityMaterials science
The invention discloses a micropore processing method for an open surface of a bone-prosthesis. The micropore processing method comprises the steps as follows: in the step of laser ablation, a plurality of micropores which are distributed uniformly and continuously are etched on the surface of the bone-prosthesis to be processed by using a laser engraving machine according to the conventional laser ablation method, the laser output power is 10 to 25W, the distance between a laser eradiating port and the etched surface is 1.5 to 2.5 mm when in etching, the cross-sectional area of each micropore is 1950 to 200000 micrometers<2>, and the depth is 5 to 500 micrometers; in the step of chemical milling, acid solution used for chemical milling is prepared by using HF, HNO3 and H2O, or HNO3, HF, H2O2 and H2O in an acid corrosion resistance container, then the etched bone-prosthesis is put in the acid solution to act the chemical milling on the open surface of the micropores, and then is washed by water. The steps are simple, the operation is simple and convenient, the controllability is good, the manufacturing cost is low, and the micropore processing method solves the difficult problem that the uniform and continuous micropore structure is formed on the surface of surgical implants.
Owner:XIAN CONTINENTAL BIOMATERIALS CO LTD
Adjustable bone prostheses and related methods related applications
InactiveUS20070118230A1Straightforward and yet robustBone implantJoint implantsBone prosthesisDevice prosthetic
Adjustable prostheses and related methods provide a wide range of adjustment along or about multiple axes. The prostheses and related methods make possible a straightforward, yet robust way of securing, e.g., a humeral head prosthesis in a desired position and maintaining the prosthesis in the desired position during use.
Owner:TORNIER INC
Tibial prosthetic component for a partial or unicondylar bearing knee replacement, method of selecting such a tibial prosthetic component, method of implanting such a tibial prosthetic component and a kit for a surgeon
ActiveUS20130166037A1Great capacity to handle stressReduce the amount requiredBone implantJoint implantsKnee JointBone tibia
The invention concerns a tibial prosthetic component comprising a plate (100) for forming a tibial plateau of a tibia (16), wherein a peripheral region of the plate (100) has a thickness of less than 3 mm. The invention also concerns a tibial prosthetic component having a keel of depth less than 9 mm. The invention also concerns a method of selecting a tibial prosthetic component comprising receiving measurements of at least one physical attribute of an individual into whom the tibial prosthetic component is to be implanted, selecting a thickness of a plate (100) and depth of keel of the tibial prosthetic component based on the measurements and providing a tibial prosthetic component comprising a plate (100) having the selected thickness and a keel having the selected depth. The invention may also comprise implanting a tibial prosthetic component selected in accordance with this method into an individual and a kit comprising a plurality of prosthetic components comprising plates having different thicknesses with keels of different depths.
Owner:OCONNOR JOHN +3
Humeral prosthesis
A humeral prosthesis, for the articulation of a humerus in a scapula of a shoulder having a glenoid cavity, includes an articulation device able to be associated both with an articulation element mounted on the glenoid cavity, and also at the top of said humerus by an attachment element. The articulation device comprises a first element able to articulate with the articulation element and a second element associated with the attachment element, the first element and the second element being pivoted to each other around a pivoting axis to allow a free relative rotation thereof around the pivoting axis.
Owner:LIMA CORPORATE SPA
Calcium phosphate cement composition and its kit for bone prosthesis
A calcium phosphate cement composition kit comprising (A) a powdery agent comprising 100 parts by mass of calcium phosphate powder, and 5-50 parts by mass of a powdery apatite / collagen composite, and (B) an aqueous blending liquid; a paste-like mixture being obtained by blending the powdery agent with the aqueous blending liquid, in such a proportion that the aqueous blending liquid is 15-50 parts by mass per the total amount (100 parts by mass) of the calcium phosphate powder and the powdery apatite / collagen composite, and filled in a predetermined prosthetic site in a human body to form a hardened calcium phosphate / collagen composite.
Owner:HOYA TECHNOSURGICAL CORP
Method for obtaining human body defect skelecton titanium alloy restoring body by mould stamping
InactiveCN101354579ARealize the designMethod implementationProgramme controlComputer controlNumerical controlHuman body
The invention relates to a method for obtaining a titanium alloy prosthesis for human defective bone through mould stamping. The method provides the titanium alloy bone prosthesis which has high precision and meets the individual requirements of a patient for patients with bone defects and particularly for those with defective bones of complex structures. The method constructs a curved surface of the defective bone prosthesis according to the CT DICOM format data or MR DICOM format data of the bone of the patient; a titanium plate forming mould is designed according to the curved surface; then, the data of the mould is input into a digital control machine tool; a stamping mould needed by the design is machined by the machine tool; and the titanium plate is carried out stamping forming by the mould. Moreover, the CT DICOM format data or MR DICOM format data of the bone of the patient undergoes 3D reconstruction, and a reconstructed bone image is input to the digital control machine tool; and the digital control machine tool machines a bone prosthesis, and matching check between the bone prosthesis and a bone model of the patient is carried out so as to ensure that the prosthesis is completely matched with a skull of the patient.
Owner:苏州泰美医疗科技有限公司
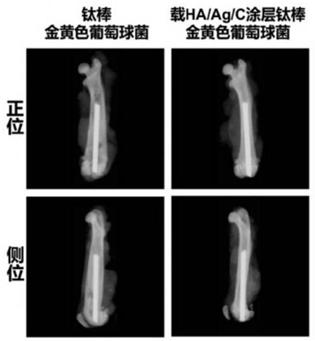
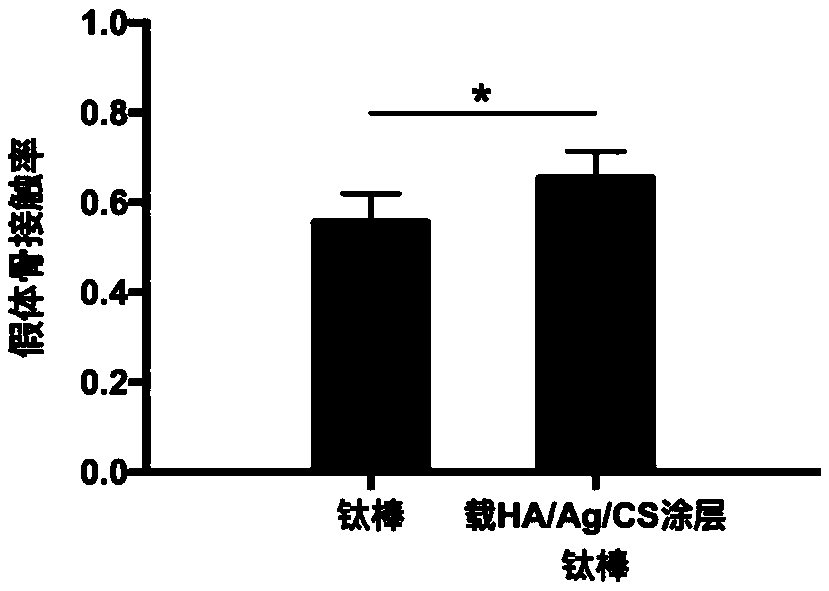
Titanium alloy implant with effects of resisting infection and promoting bone formation and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109453425AReduce releaseLow cytotoxicityPharmaceutical delivery mechanismLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingUltraviolet lightsBone formation
The invention discloses a titanium alloy implant with effects of resisting infection and promoting bone formation and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following stepsof S1, preparing a titanium alloy implant body; S2, performing alkaline heat treatment on the surface of the titanium alloy implant body, and activating dopamine; S3, performing HA (hydroxyapatite) grafting, and activating the dopamine again; S4, under the room temperature environment, soaking the titanium alloy implant body treated in step 3 into 1 to 4 mM of silver nitrate solution for 0.5 to 8h, fetching out, airing, radiating by ultraviolet light for 0.5 to 2 h, and reducing, so as to obtain a nanometer Ag (silver) particle layer; S5, soaking the titanium alloy implant body treated in step 4 into 1 to 4 mg / ml of chitosan for 30 s to 5 min, and drying, so as to complete the preparation of the HA / Ag / Cs-loaded coating titanium alloy implant. Compared with the titanium alloy implant, theprepared HA / Ag / Cs-loaded coating titanium alloy implant has excellent antibacterial property, and can promote the bone formation and the integration of bone-prosthesis interface.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
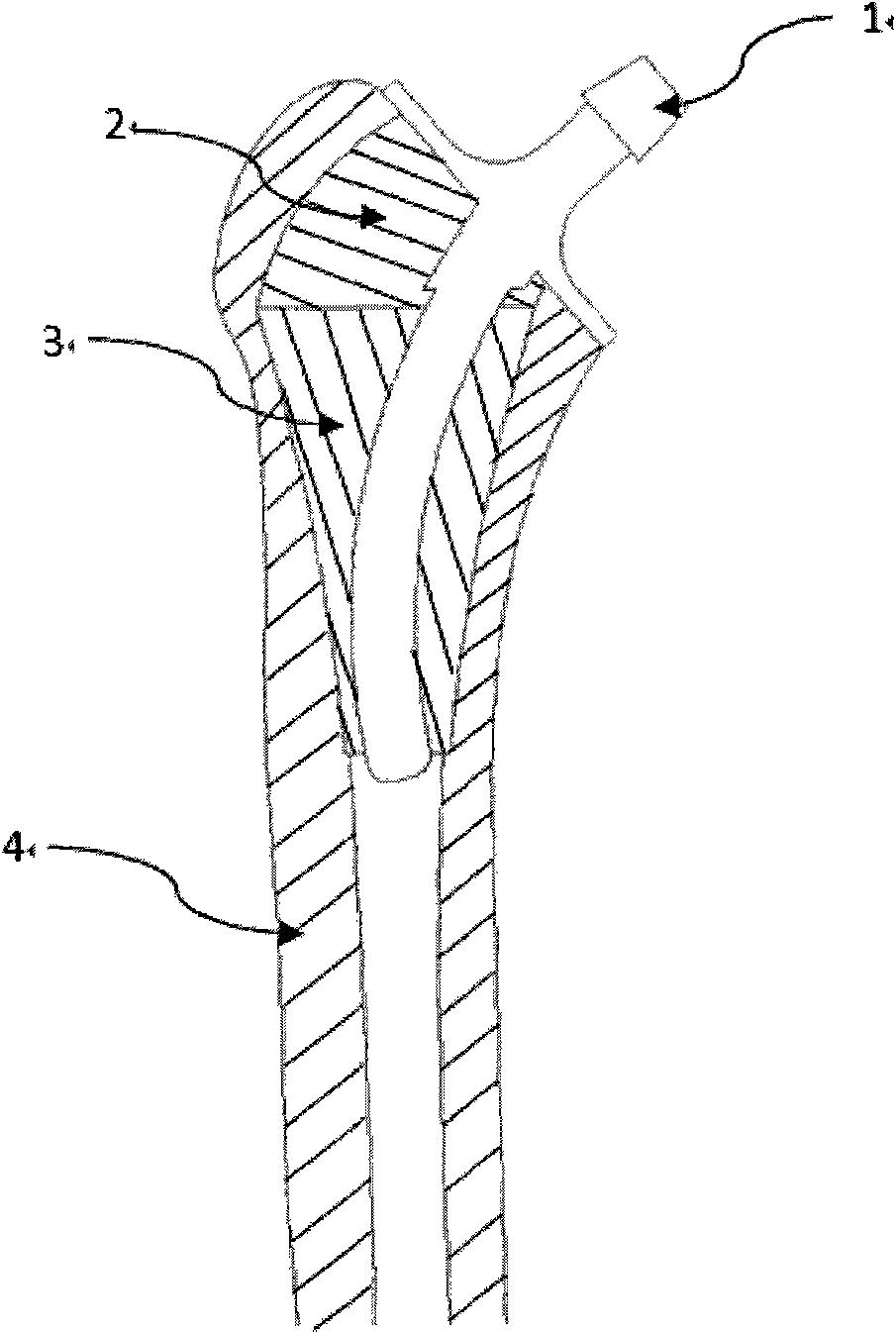
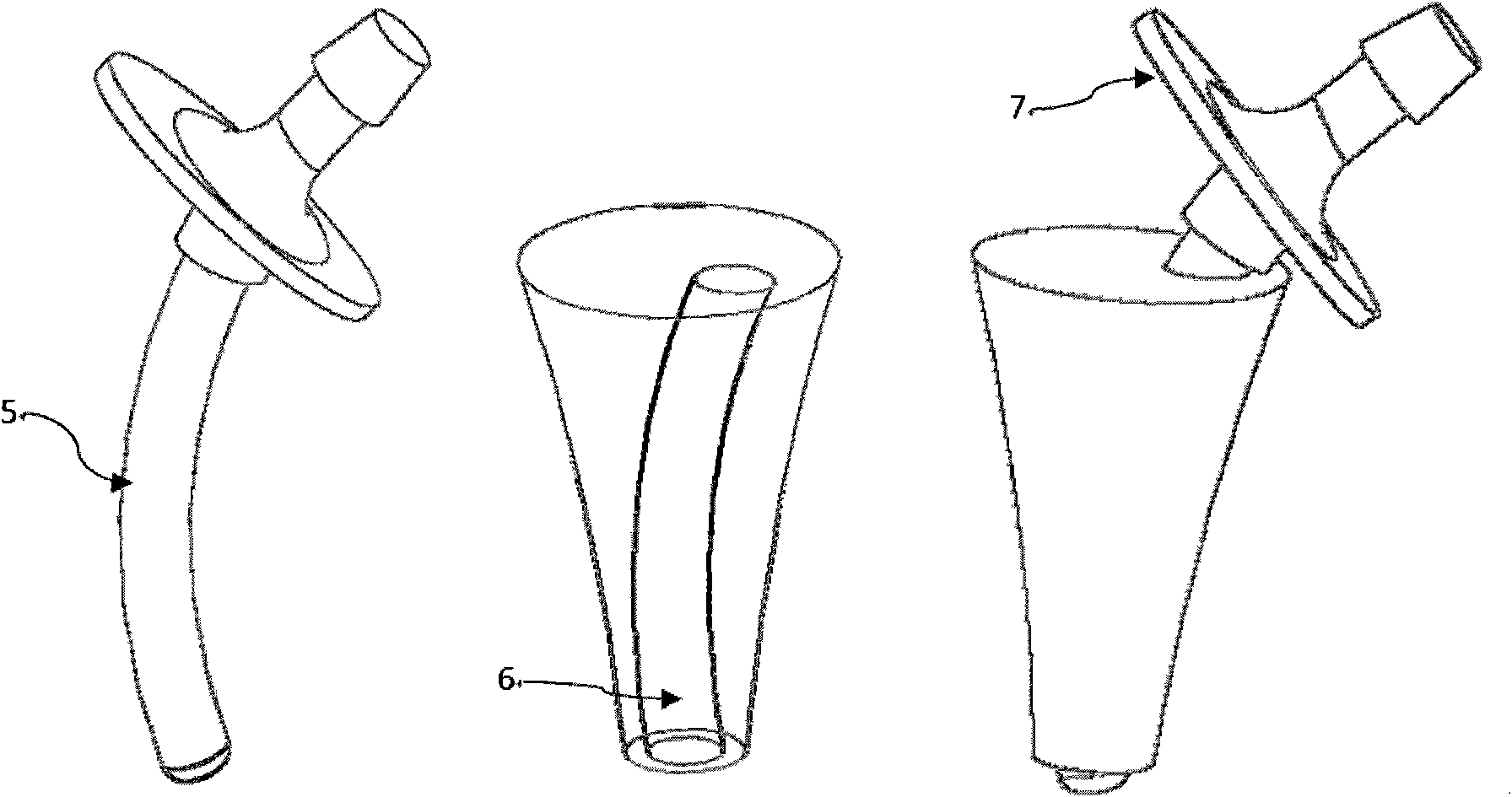
Artificial femoral prosthesis
InactiveCN101889913AImprove stabilityAdd a heavy insurance to achieve stabilityJoint implantsFemoral headsNatural stateTransfemoral prosthesis
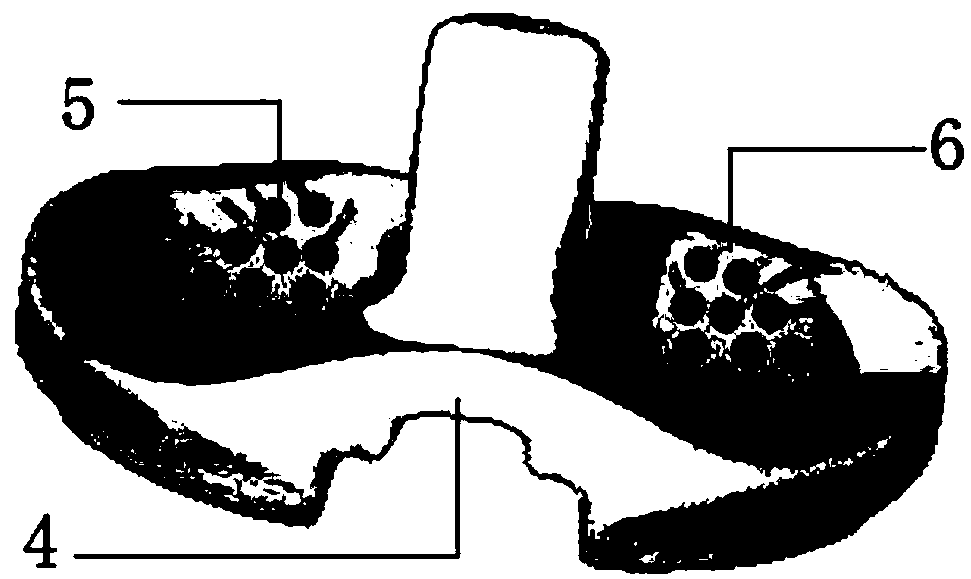
The invention discloses an artificial femoral prosthesis, which consists of a femoral stem (1), bone grafts (2) and an outer sleeve (3). Particularly, the outer sleeve (3) is implanted into the medullary space of femora (4); a femoral stem far end (5) is inserted into an outer sleeve track (6); and the gap between the outer sleeve (3) and the femora (4) is filled with the bone grafts (2). The aim of the invention is that: through long term fusion of the femora (4) and the bone grafts (2), the artificial femoral prosthesi bears the stress from a femoral stem collar (7); through the annular design of the outer sleeve track (6), after the femoral stem collar (7) is stressed, inside displacement (8) is smaller than outside displacement (9), so that the stress outside the femora is larger; by controlling the contact position of the outer sleeve track (6) and the femoral stem far end (5), the stress of the femora (4) is distributed close to the natural state; through anatomy covering of the femoral stem collar (7), grains are prevented from entering the bone-prosthesis joint surface; and by changing the shape size of the outer sleeve (3), the artificial femoral prosthesis adapts to different medullary spaces and indications.
Owner:孙瑞财
Medial femoral single condyle prosthesis, lateral femoral single condyle prosthesis, and femoral trochlea prosthesis
PendingCN107280817ASimplified Design Parameter ValuesJoint implantsKnee jointsArticular surfacesArticular surface
The invention discloses a medial femoral single condyle prosthesis (201), a lateral femoral single condyle prosthesis (301), and a femoral trochlea prosthesis (401). The medial femoral single condyle prosthesis comprises an articular surface which is a surface making contact with the medial patella and the medial tibial plateau during the knee joint motion process, wherein the articular surface is presented as a segmental arc (203) on a first ellipse (38) on the sagittal position, and is presented as a segmental arc (95) on a first circle (94) on a coronal position; and an inside surface, which is the part adjoining femoral condyle cut bone surface and bone cement after prosthesis implantation, and is presented as a medial posterior condyle (202) with a straight line section and a medial distal end (209) consistent with the segmental arc (203). The prosthesis can be closer to the geometric shape of the normal human femoral condyle, and design parameter values of femoral prostheses of various types are simplified.
Owner:温晓玉
Calcium phosphate cement and use and method for making same
InactiveCN1333196AEasy to hardenGood dispersionImpression capsSurgical adhesivesCalcium biphosphateBone prosthesis
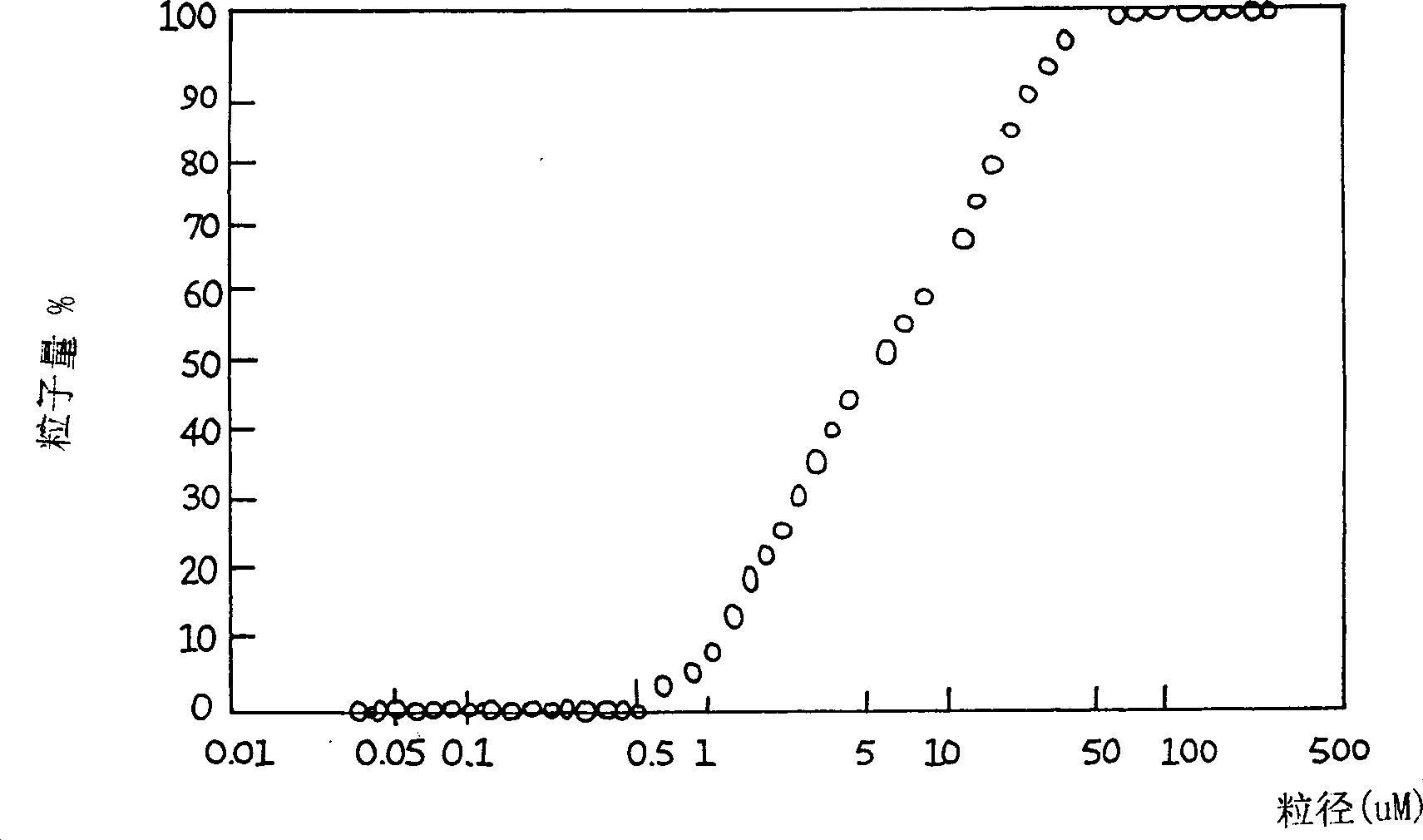
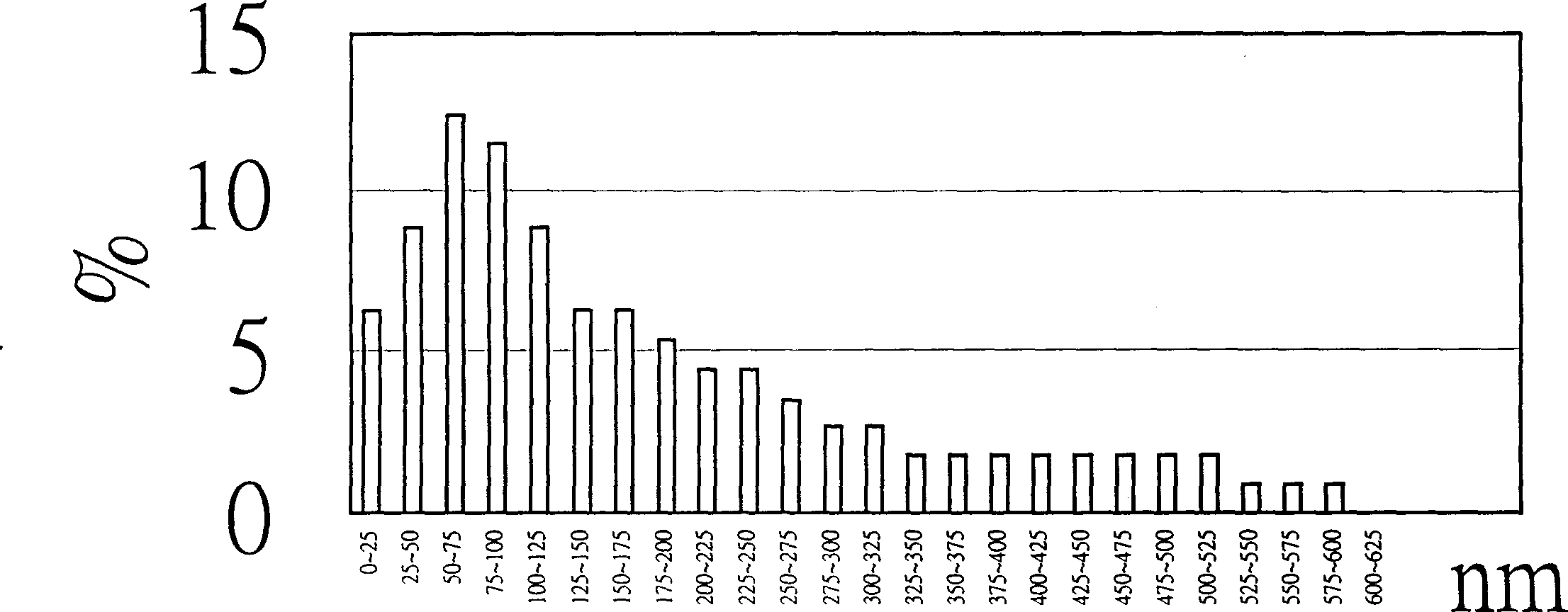
A calcium phosphate cement suitable for use in dental and bone prosthesis is disclosed, which include calcium phosphate particles having a diameter of 0.05 to 100 microns, wherein said calcium phosphate particles on their surfaces have whiskers or fine crystals having a width ranging from 1 to 100 nm and a length ranging from 1 to 1000 nm..
Owner:卡茨特科公司
Infection preventing and osteoblast differentiation promoting antibacterial peptide modified titanium alloy prosthesis and making method thereof
InactiveCN105816912AExcellent antibacterial biological activityImprove the shortcomings of clinical applicationPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMetallic material coating processesCell-Extracellular MatrixOsteoblast
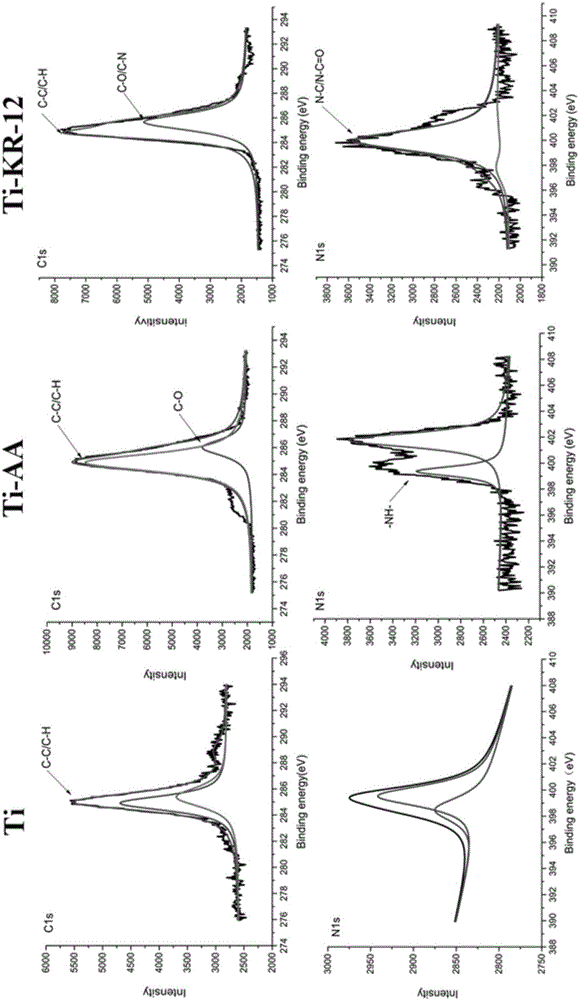
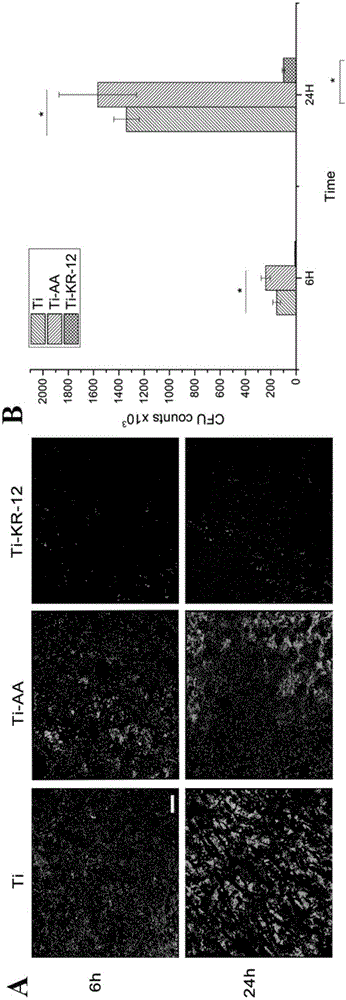
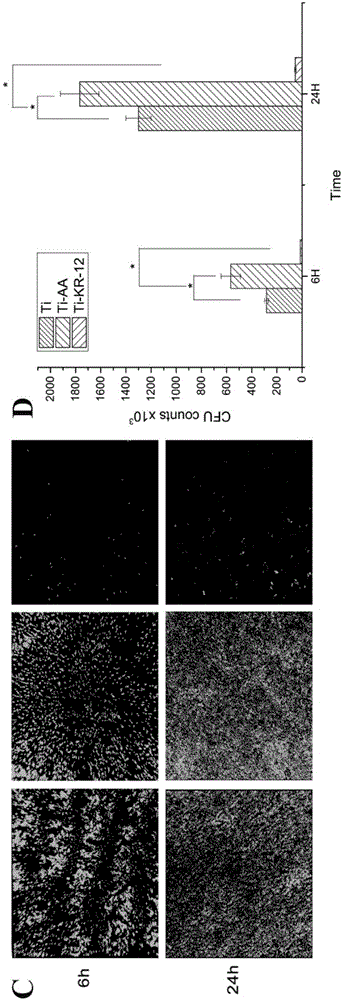
The invention relates to an anti-infection and osteogenic differentiation-modified titanium alloy prosthesis and a preparation method thereof. The present invention fixes KR-12, a biologically active fragment of human antimicrobial peptide LL-37, on a titanium plate by means of covalent grafting, and the KR-12 antimicrobial peptide fixed on the titanium plate can maintain its antibacterial biological activity and can Promote osteogenic differentiation and extracellular matrix mineralization of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. The invention has simple process and low production cost, but at the same time solves the two major complications of infection and loosening that traditional orthopedic prostheses face in clinical application, and has very important significance in the field of titanium alloy biofunctionalization.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Artificial knee joint prosthesis
InactiveCN102727327AImprove wear resistanceReduce thicknessJoint implantsKnee jointsPatella prosthesisProsthetic graft
The invention relates to an artificial knee joint prosthesis which comprises a patella prosthesis and a femur prosthesis, wherein the patella prosthesis is made of metal and is 3-4mm, preferably 3.5mm in thickness; the femur prosthesis is provided with a tackle part which is made of metal; a polyethylene joint surface is arranged on the surface of the tackle part; and the polyethylene joint surface is gradually thickened from a near end to a far end and no gap exists between the polyethylene joint surface and the tackle part. The artificial knee joint has the following advantages: the patella prosthesis is made of metal, so that the wear resisting property is good, the thickness is thin, the patella cut amount is decreased, then the application scope of the existing knee joint prosthesis is enlarged, the postoperative fracture occurrence rate is reduced, benefit is brought to overhauling and the problem of uneven patella stress distribution is solved at the same time; the tackle part of the femur prosthesis is covered by a layer of ultra-high molecular polyethylene joint surface, so that the abrasion is reduced and the 'soft landing' of femur quadriceps tendon is realized; and no gap exists between the polyethylene joint surface and the metal backing and the polyethylene joint surface and the metal backing are integrally pressed and shaped, so that a polyethylene / metal friction surface is not added.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
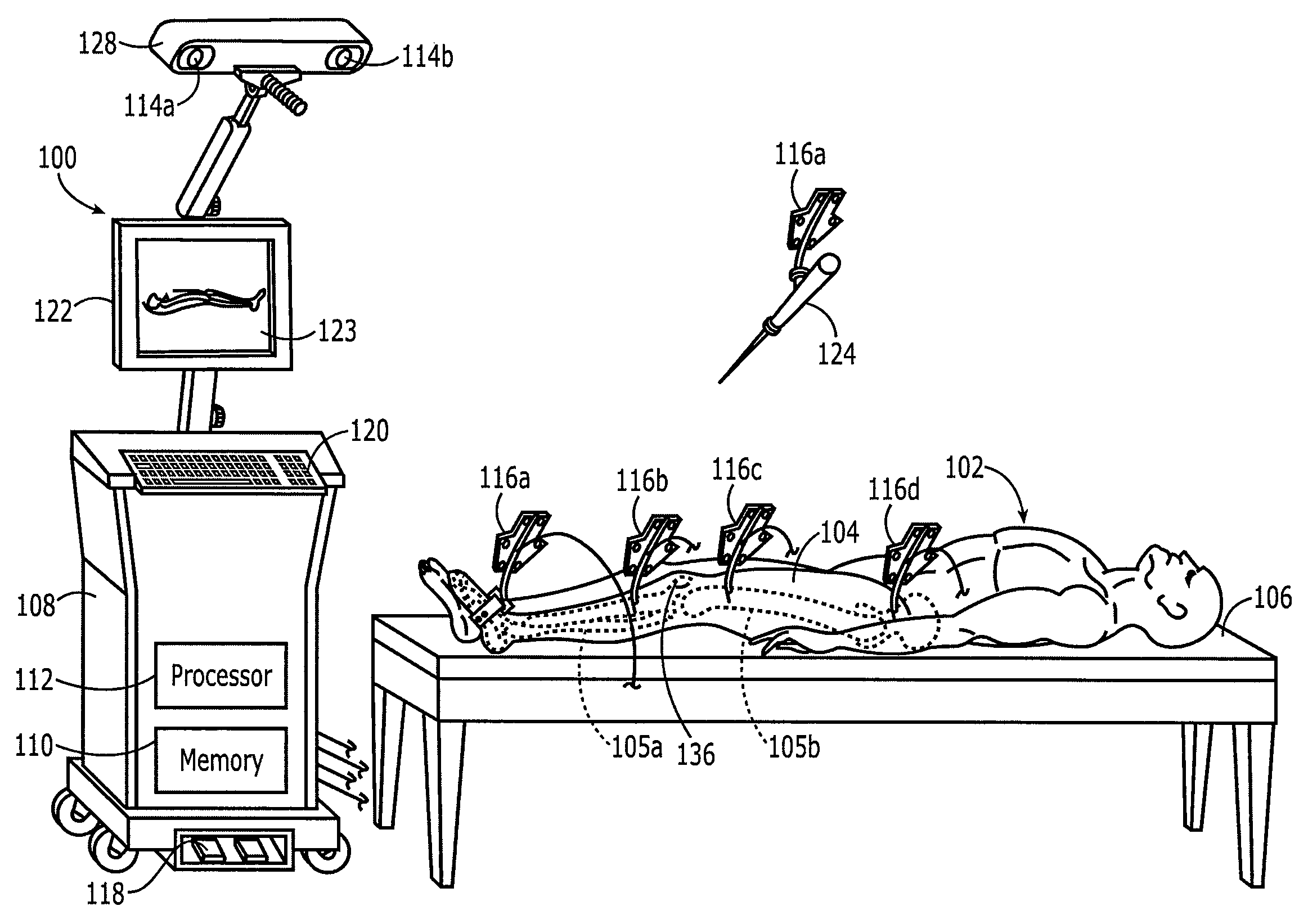
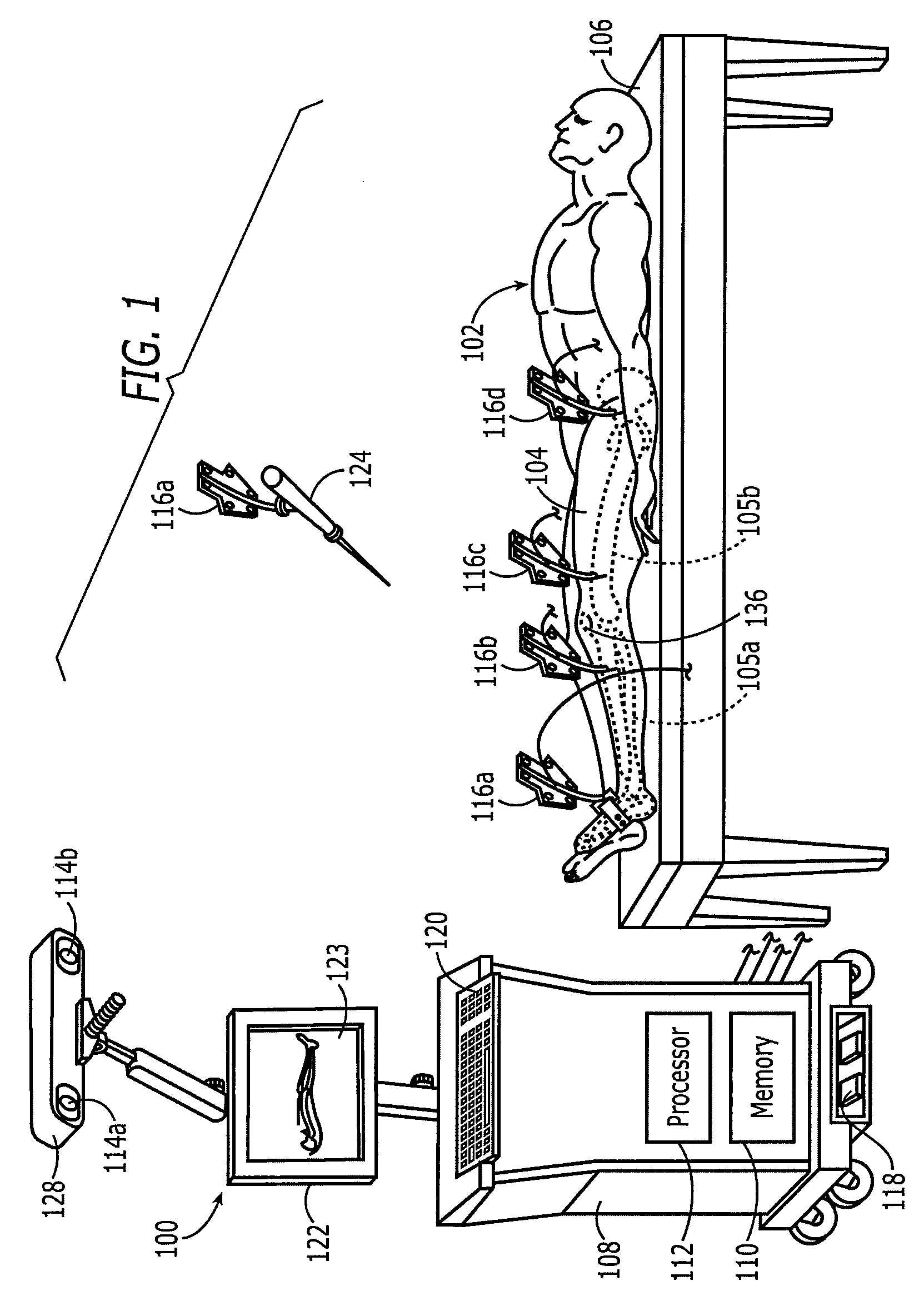
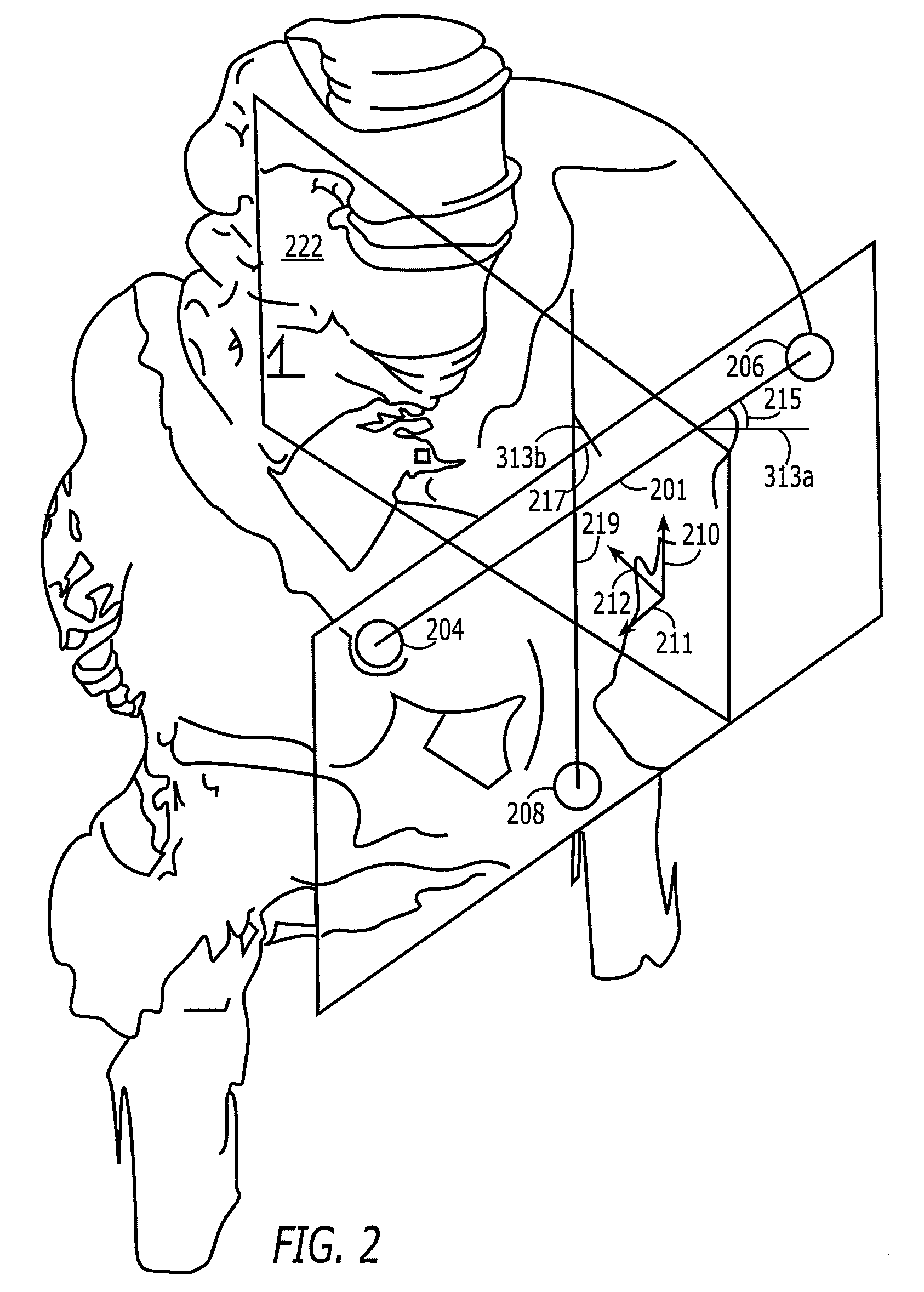
Systems and processes for revision total joint arthroplasty
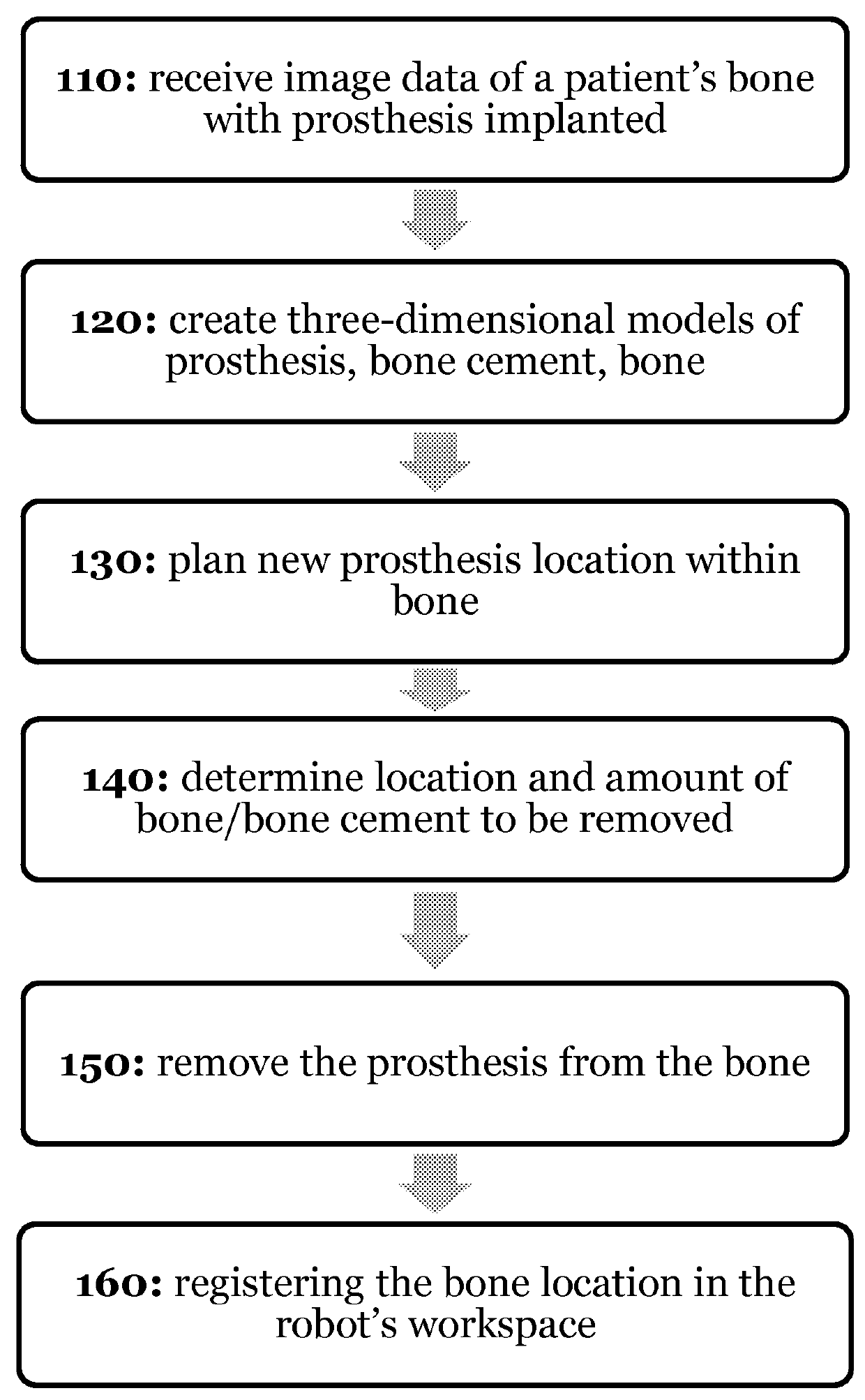
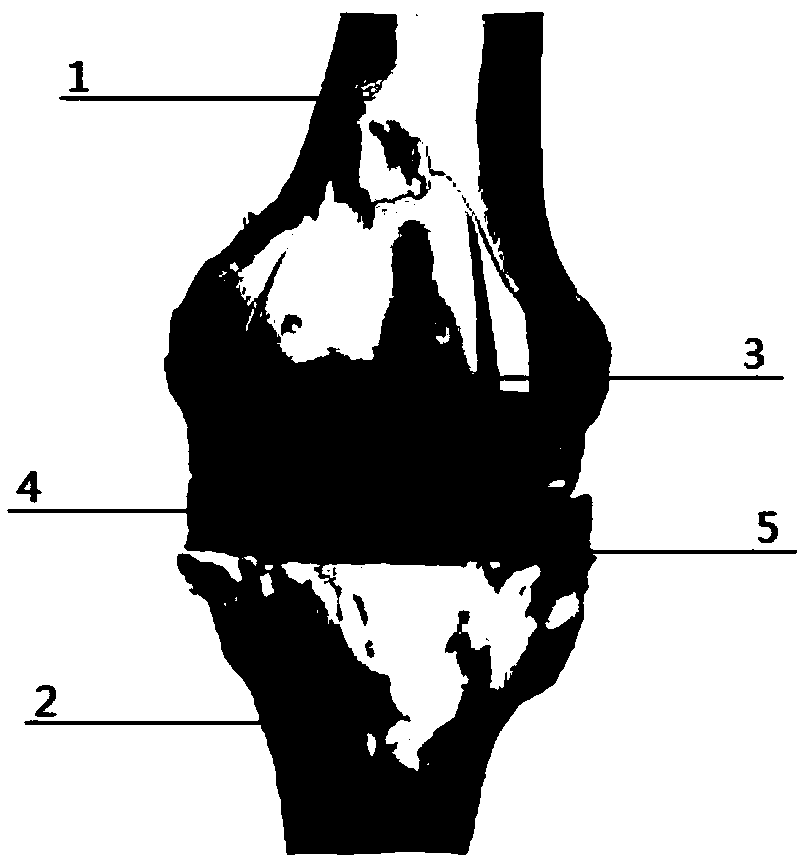
A process and system for performing orthopaedic surgery with the use of computer systems and robotic assistance to remove bone, bone cement, and a bone prosthesis, typically a bone prosthesis used in hip replacement surgery, knee replacement surgery, and the like. The process for replacing one or more bone prostheses using a robotic system includes receiving image data comprising an image of each bone, including at least one prosthesis implanted within each bone; creating three-dimensional models of the prosthesis, and the bone; creating a plan for positioning new prostheses within the bone; determining the location and amount of bone and any non-bone material to be removed for the new prostheses; and removing the bone prosthesis from the bone. The inventive process may be used for the replacement of hip joints, shoulder joints, ankle joints, wrist joints, finger joints, toe joints, or other joints.
Owner:THINK SURGICAL
Knee joint balance detection system in total knee replacement and balance discrimination method thereof
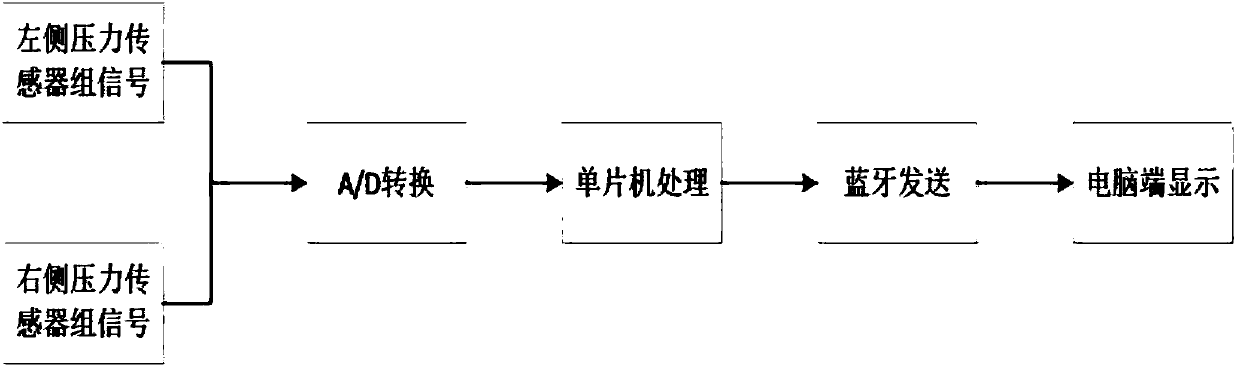
PendingCN107802382AImprove accuracyImprove quality of life after surgeryJoint implantsKnee jointsTotal knee replacement surgeryTibial tray
The invention discloses a knee joint balance detection system in total knee replacement and a balance discrimination method thereof. The system is characterized in that a left pressure sensor set anda right pressure sensor set are attached to the left and right regions of a gasket, in the operation process, the gasket is placed in a gap between the thigh bone prosthesis and the tibia bracket, data of the left and right sensor sets can be obtained during 0-degree knee bending, 90-degree knee bending, internal rotation and ectropion, due to data analysis, whether the knee joints are located inthe balanced state or not is judged, and if the knee joints are in the non-balanced state, by properly repairing bones or adjusting the position of a prosthesis, the knee joints are in the balanced state finally. By keeping the position unchanged, surgical suturing is performed. By improving the accuracy of surgical knee joint balance, the important role in prolonging the service life of the postoperation prosthesis of a patient, reducing postoperative complications, and improving the postoperation living quality of the patient is achieved.
Owner:吴小玲 +1
Assembly type artificial sacral prosthesis
PendingCN107496061AIncrease stressImprove stabilitySpinal implants3D printingLumbosacral regionSacral tumors
The invention relates to an assembly type artificial sacral prosthesis. The assembly type artificial sacral prosthesis comprises a prosthesis main body, a first sacral combination body and a second sacral combination body; the first sacral combination body and the second sacral combination body are connected with the prosthesis main body in a knocking and inserting manner; the first sacral combination body or the second sacral combination body comprises a connecting body and a bone setting body; each bone setting body is provided with a pore structure; and the first sacral combination body and / or the second sacral combination body is prepared by using a 3D printing technology. The assembly type artificial sacral prosthesis has the advantages that when the sacral bone is rebuilt, the assembly type artificial sacral prosthesis can be accurately matched with different excision faces of sacral tumors due to personalized customization, stress conduction recovery and stability of a lumbosacral portion are good, the length is conveniently adjusted so that the assembly type artificial sacral prosthesis is fixedly connected with the lumbar vertebra, the lumbar vertebra is prevented from hanging in the air and falling off, the assembly type artificial sacral prosthesis can be completely fused with the tumor excision faces, seamless joint is achieved, and long-term stability and recovery are good.
Owner:SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV
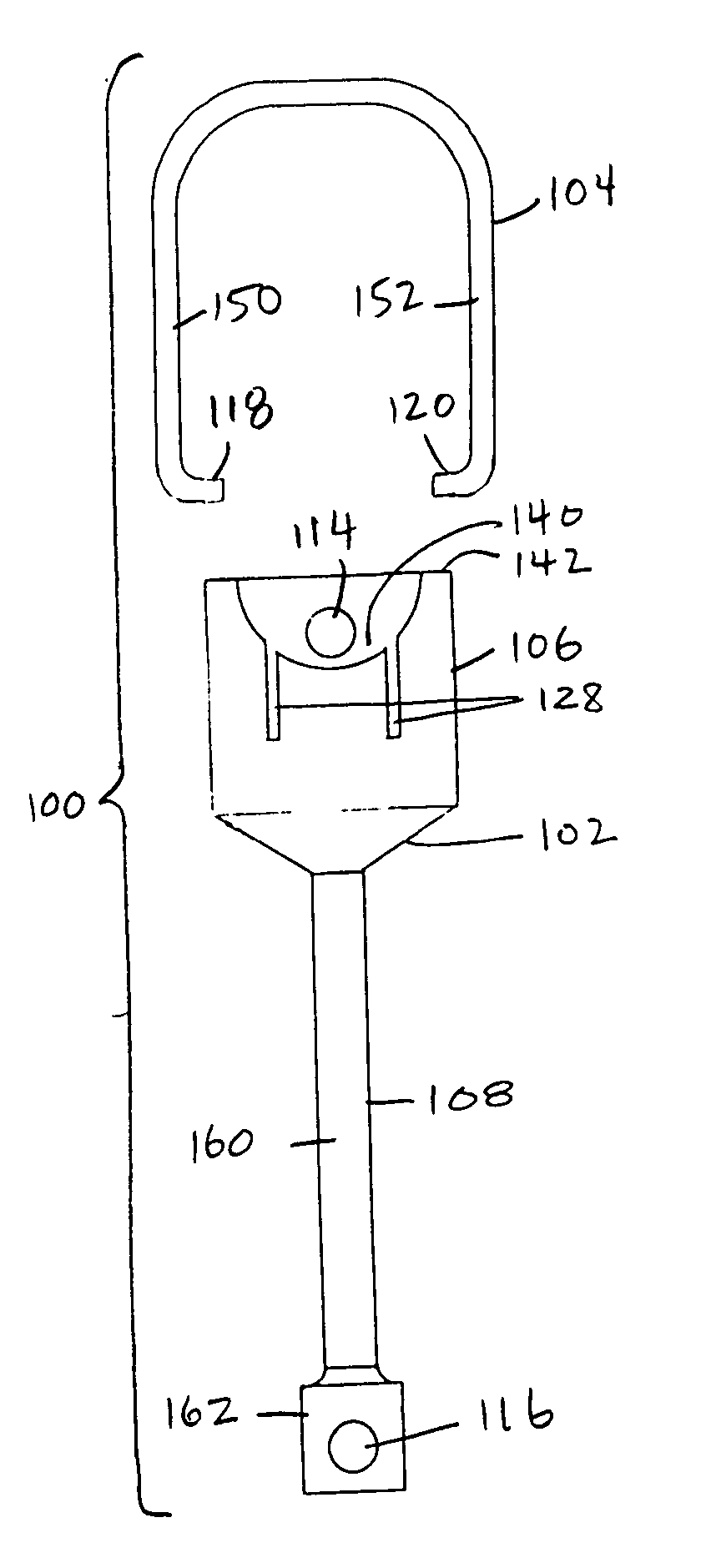
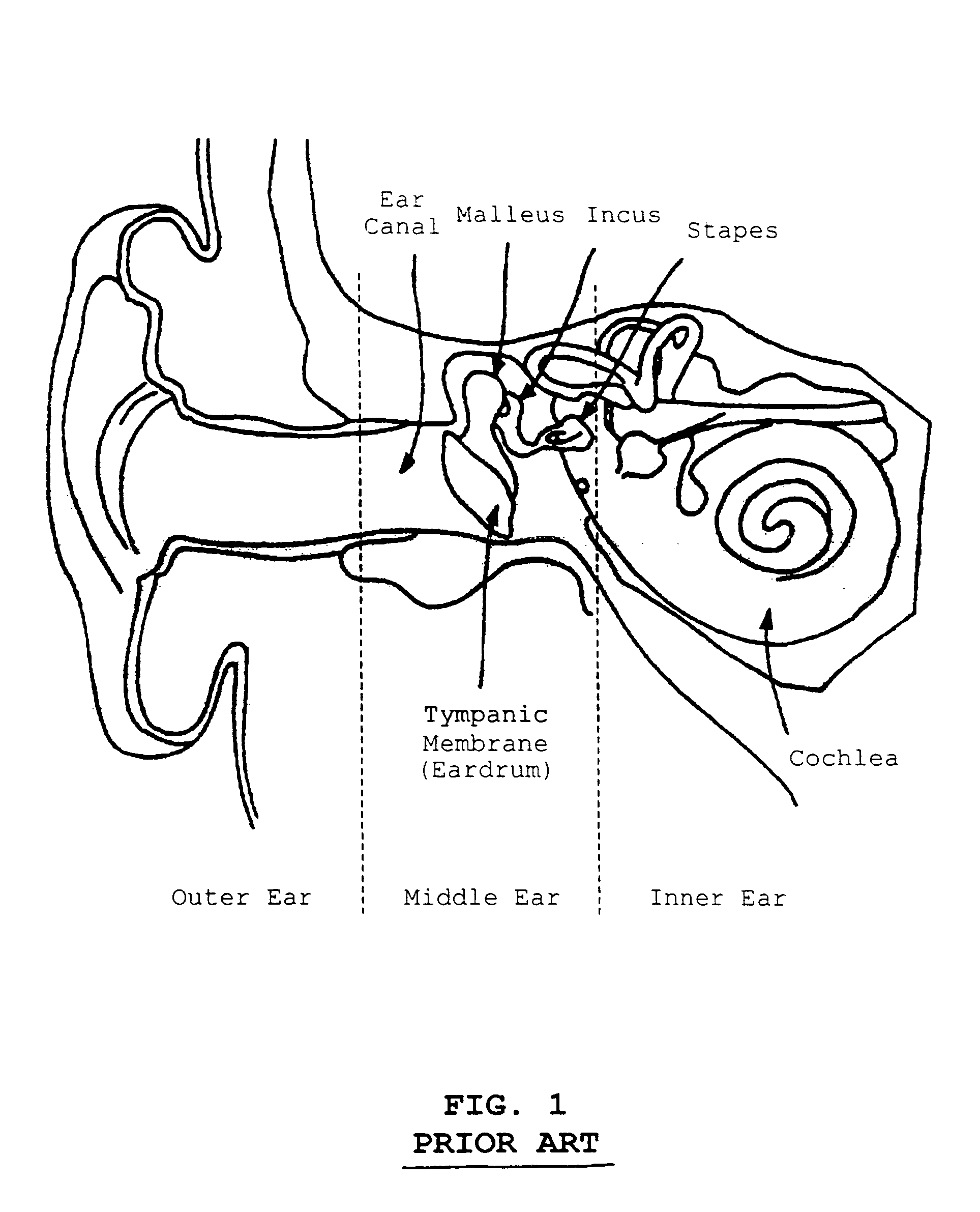
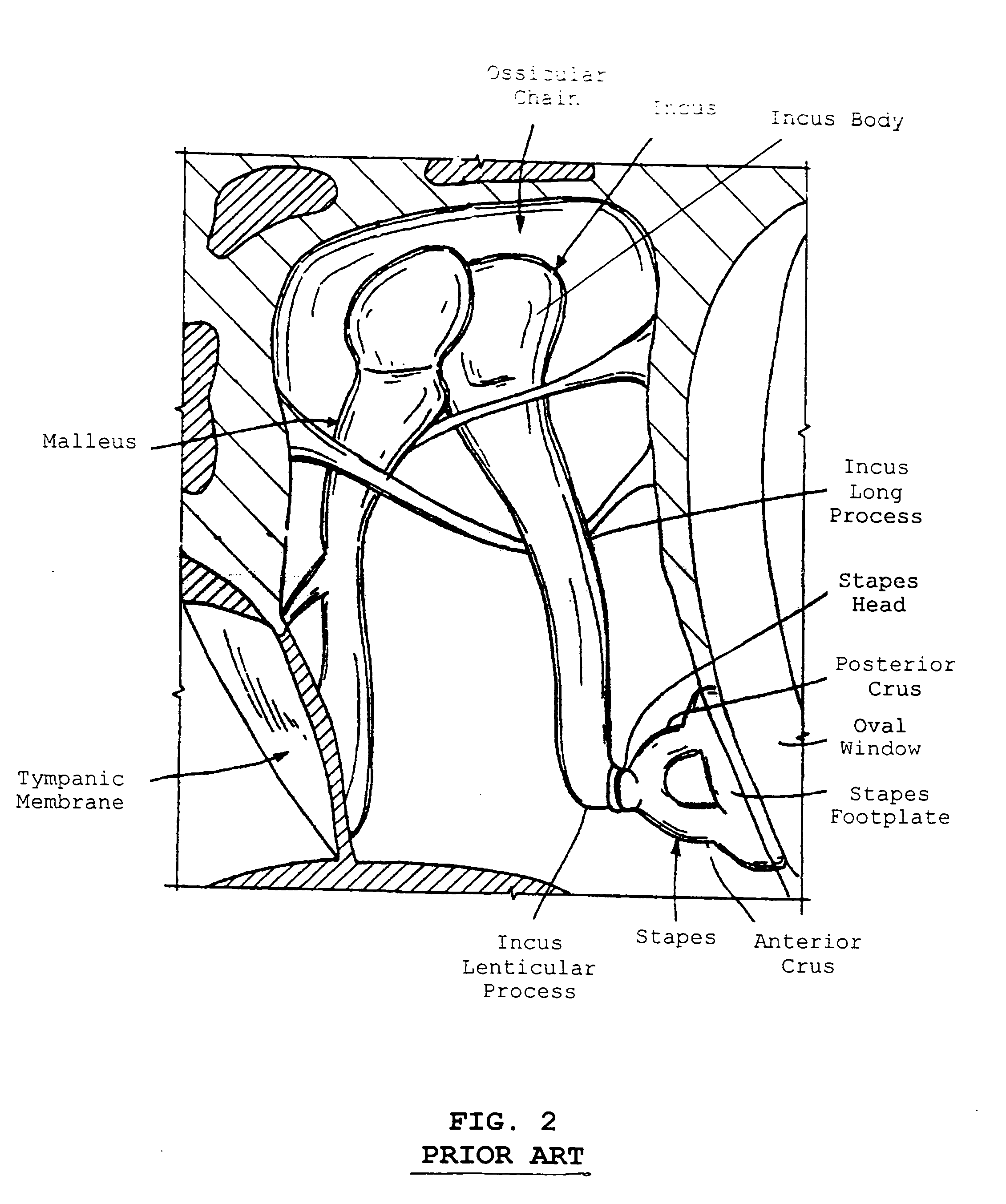
Stapedial prosthesis and method of implanting the same
InactiveUS20050065603A1Uniform fit and movementLess imaging artifactEar implantsProsthesisDistal portion
A stapedial prosthesis includes a body defining a bucket and a shaft, and a bail handle coupled to the bucket. The bucket is preferably adjustable in diameter to fit the incus lenticular process. The shaft preferably has a varying diameter, with a central portion of a smaller diameter than a distal portion which aids in depth perception during implantation and reduces mass to permit better sound energy transmission by the prosthesis. The bail handle is preferably spring-loaded and preferably constructed of titanium. The bail handle is preferably coupled to the body without crimping, twisting or welding and preferably biases the incus toward the bucket. A method of implanting a stapedial prosthesis is also provided.
Owner:CLARITY
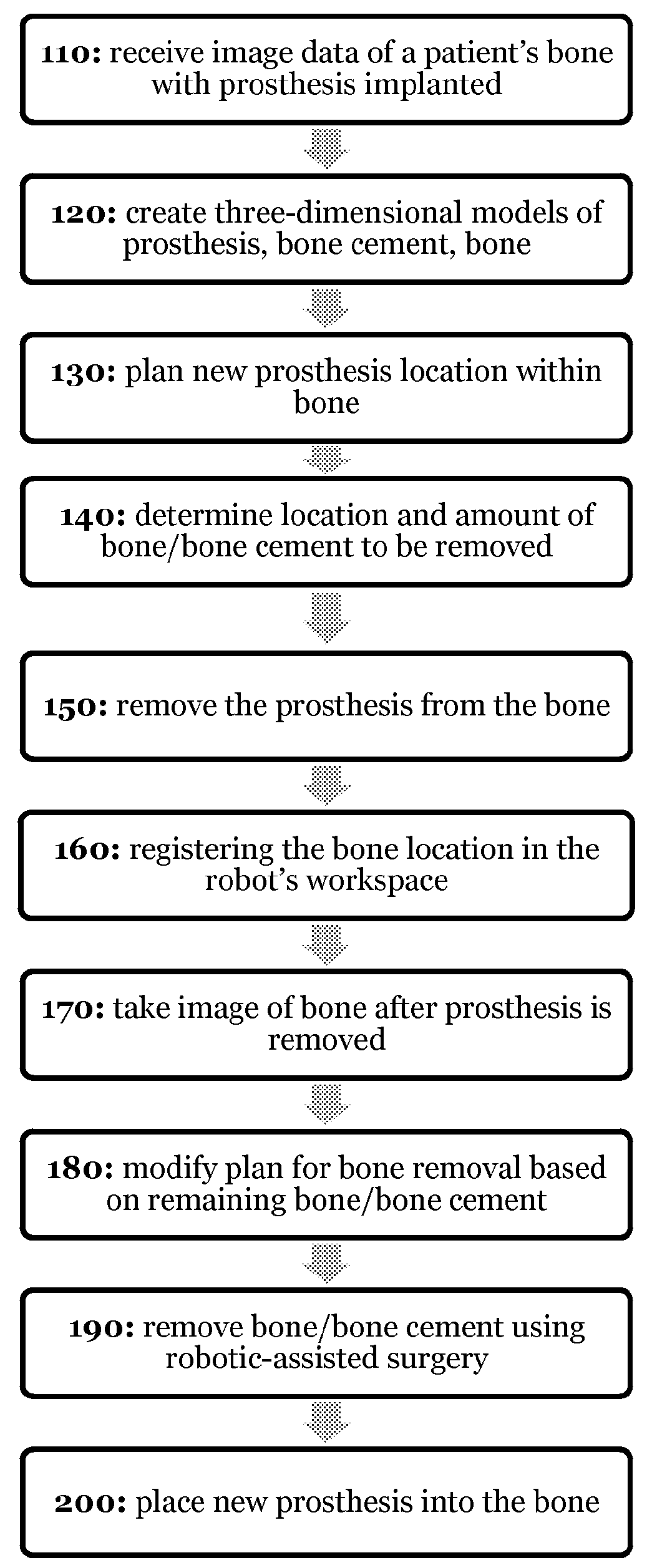
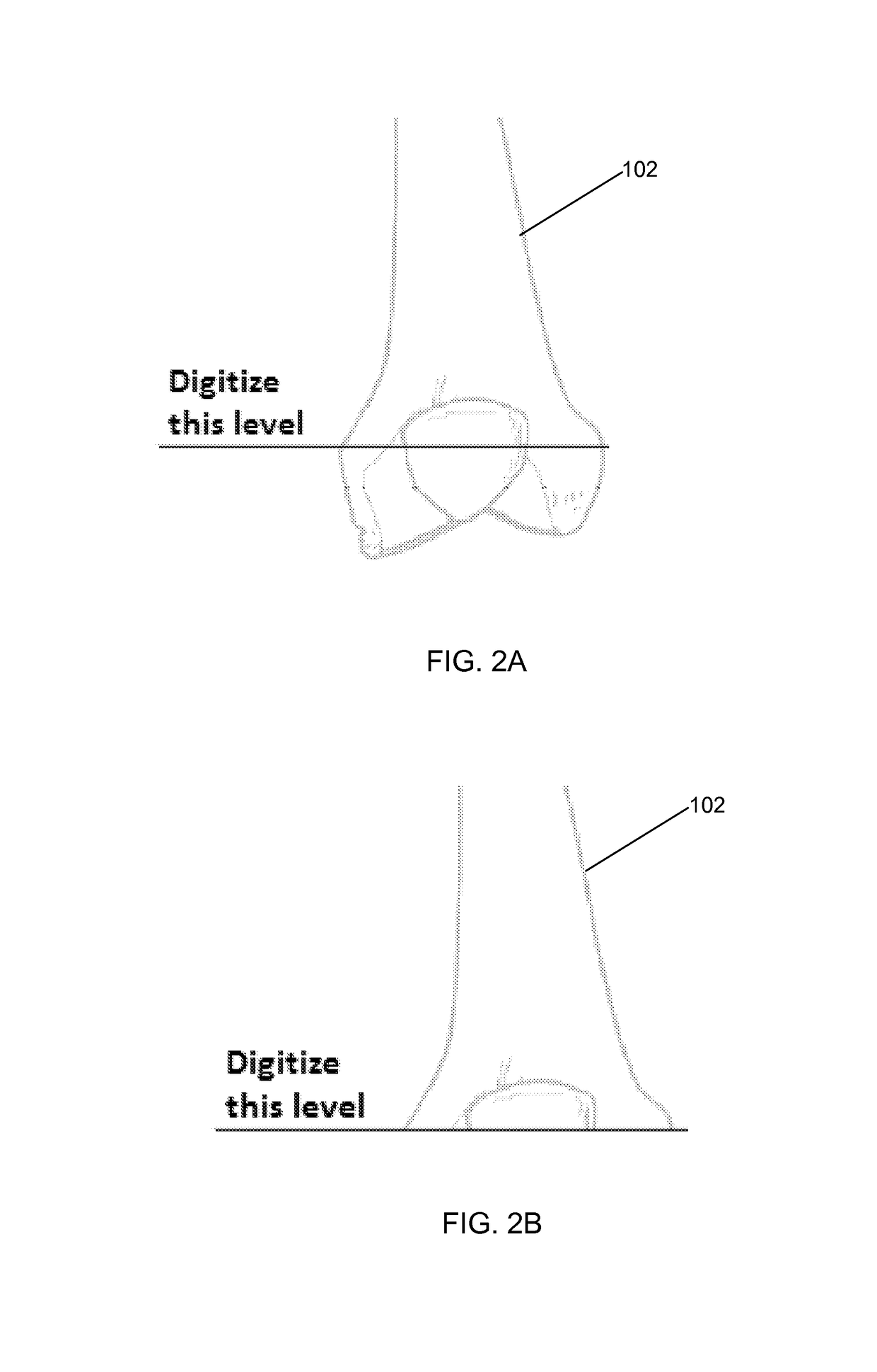
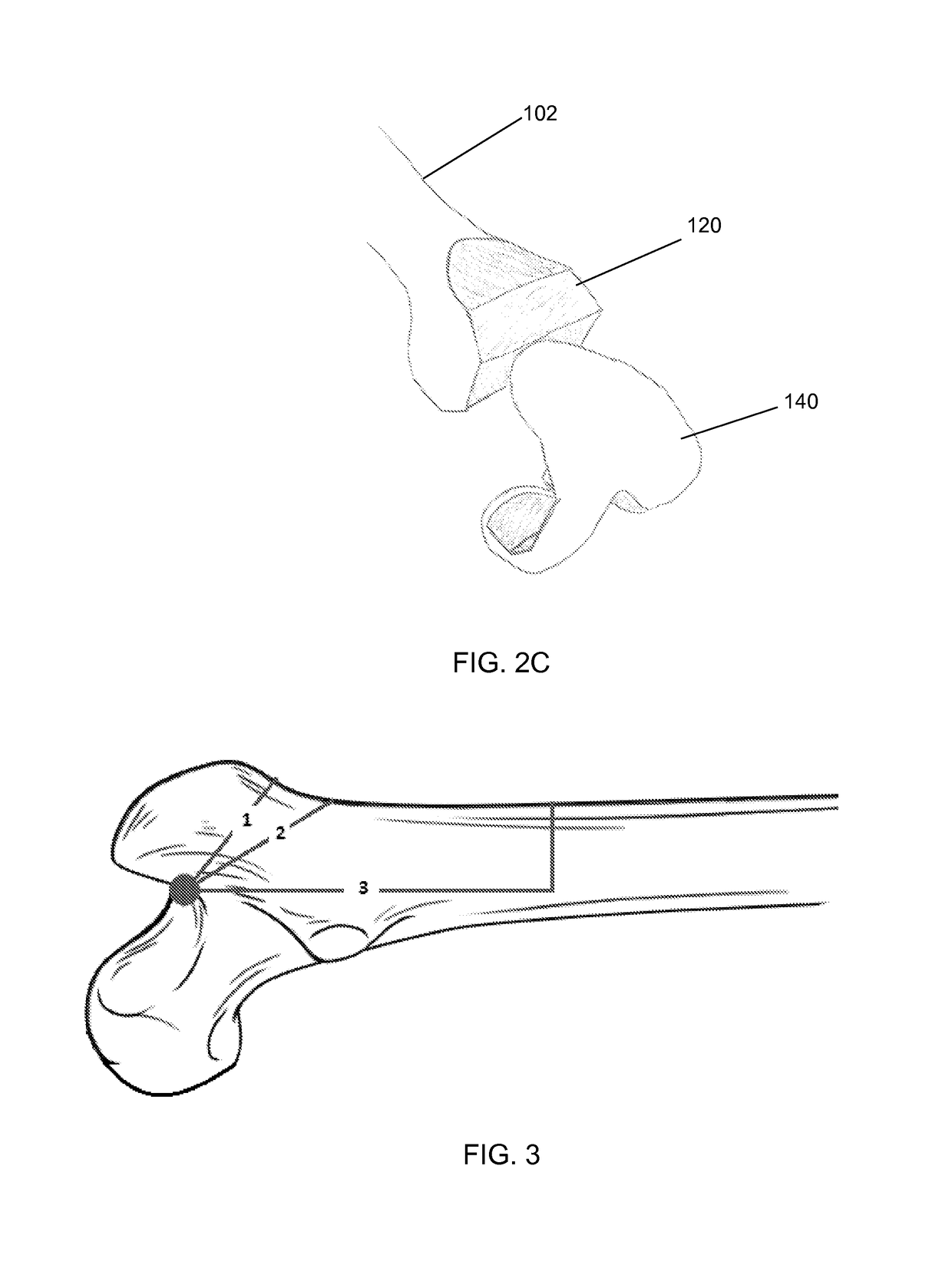
Implant based planning, digitizing, and registration for total joint arthroplasty
A system and process for performing orthopedic surgery is provided that uses a patient's existing implant as a registration tool in an orthopedic surgical procedure. The systems and processes may be used with computer assisted systems or navigation systems to aid in the removal of bone, bone cement, or a bone prosthesis, typically a bone prosthesis used in hip replacement surgery, knee replacement surgery, and the like. The removal of the prosthesis may be done by conventional methods, with navigation systems, robotic assistance or articulating hand held systems. The removal of bone and / or bone cement may be performed with navigated systems, robotic systems, articulating hand-held systems and combinations thereof.
Owner:THINK SURGICAL
Implant based planning, digitizing, and registration for total joint arthroplasty
A system and process for performing orthopedic surgery is provided that uses a patient's existing implant as a registration tool in an orthopedic surgical procedure. The systems and processes may be used with computer assisted systems or navigation systems to aid in the removal of bone, bone cement, or a bone prosthesis, typically a bone prosthesis used in hip replacement surgery, knee replacement surgery, and the like. The removal of the prosthesis may be done by conventional methods, with navigation systems, robotic assistance or articulating hand held systems. The removal of bone and / or bone cement may be performed with navigated systems, robotic systems, articulating hand-held systems and combinations thereof.
Owner:THINK SURGICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com