Patents
Literature
153 results about "Prosthesis Implantation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
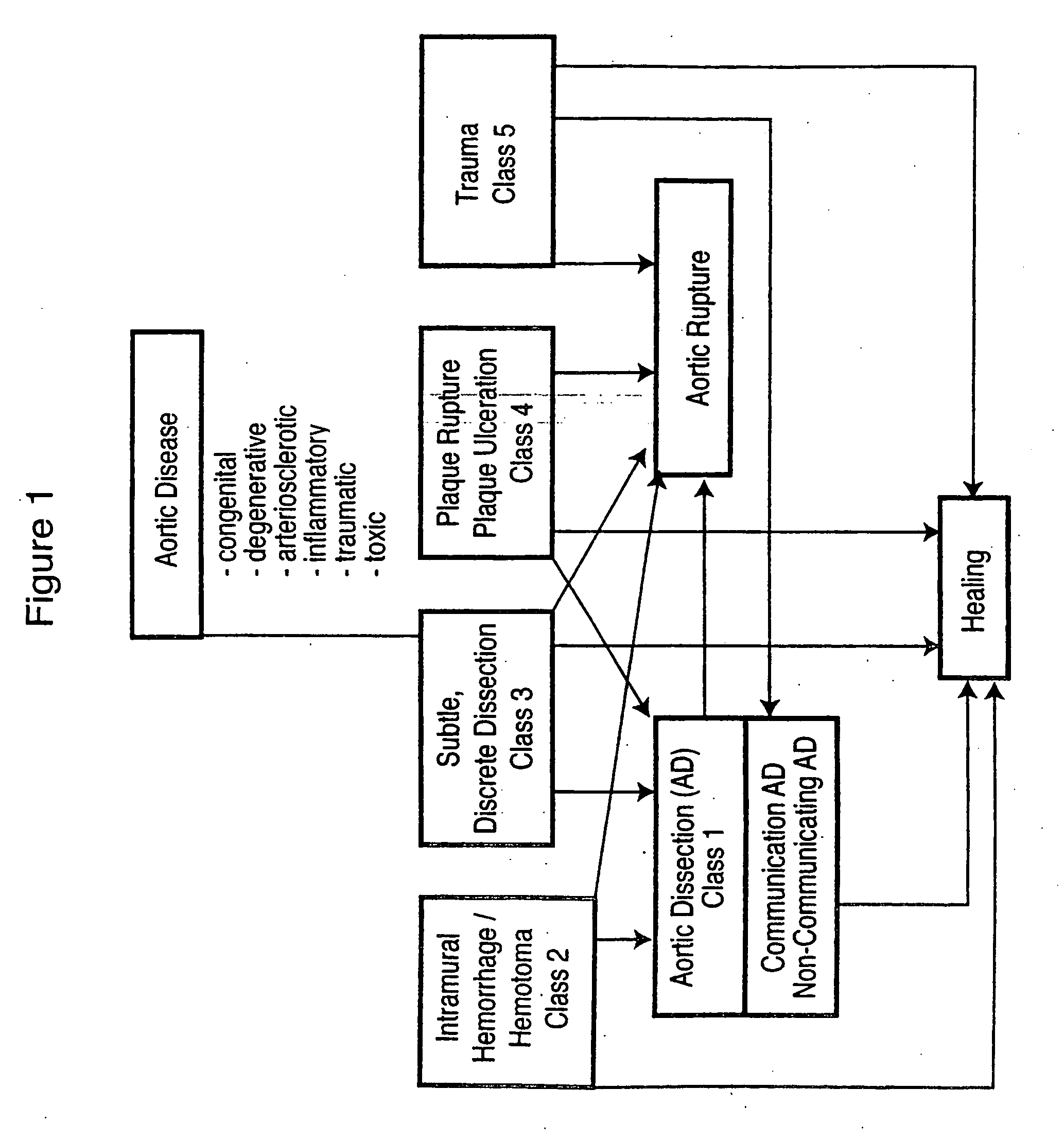
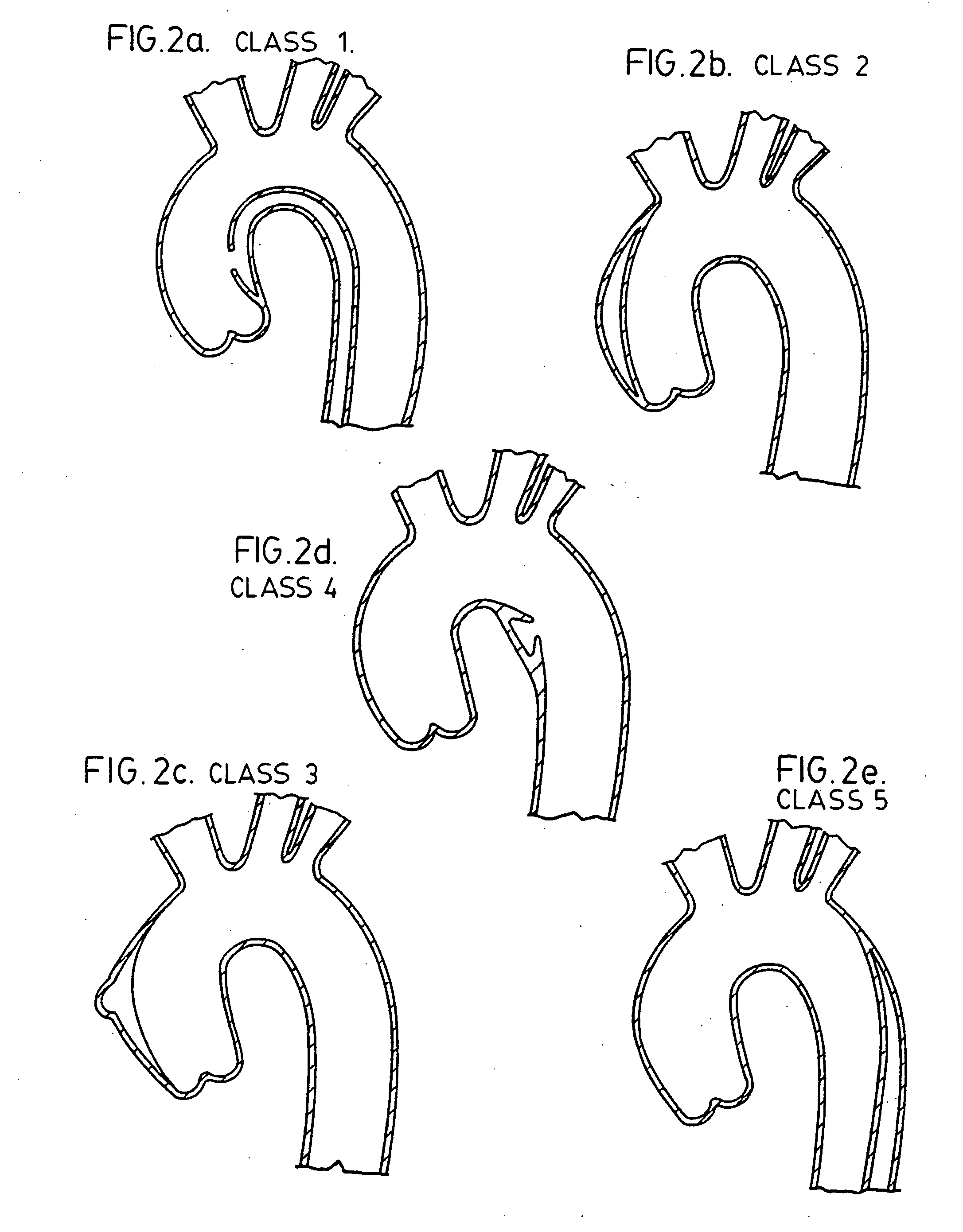
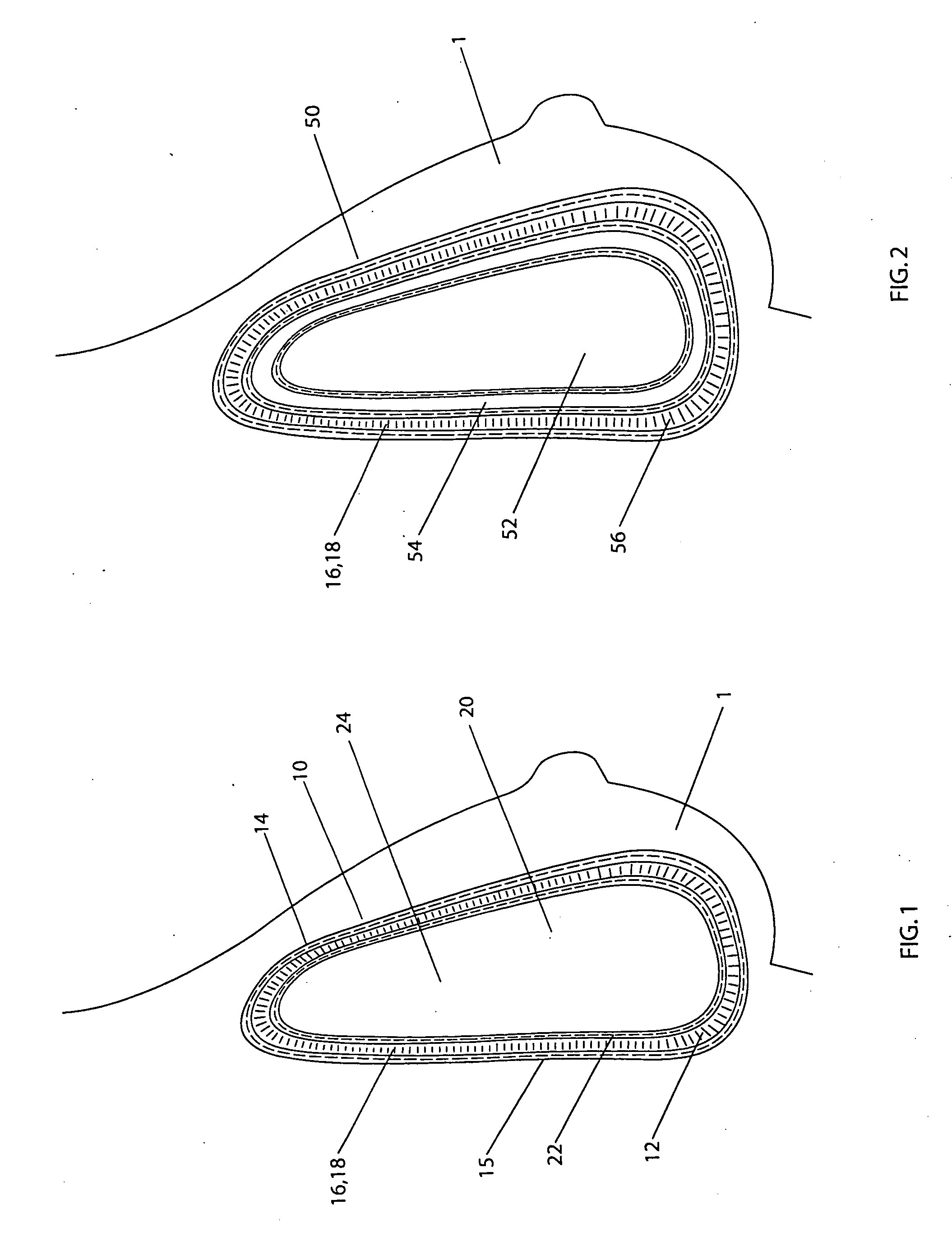
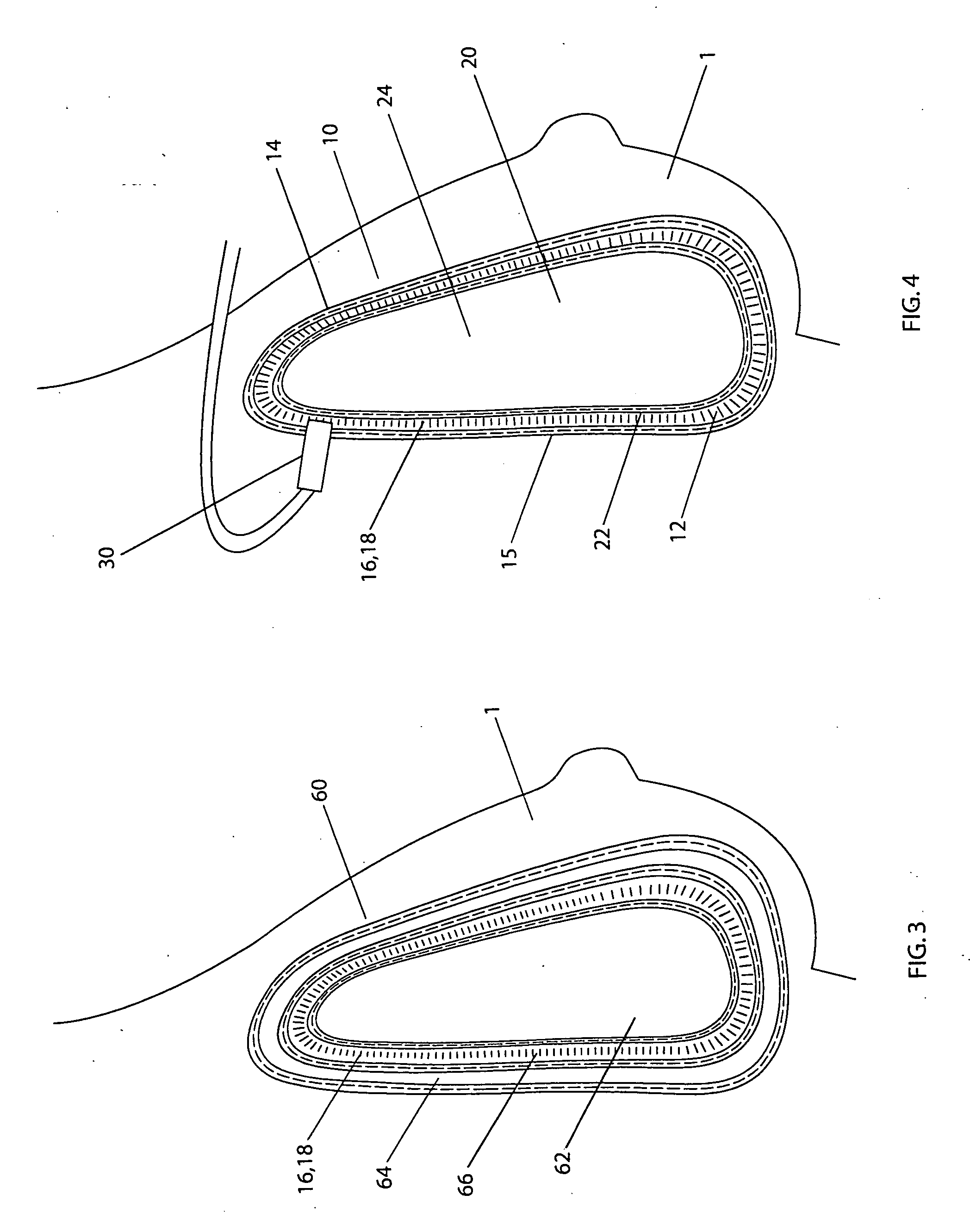
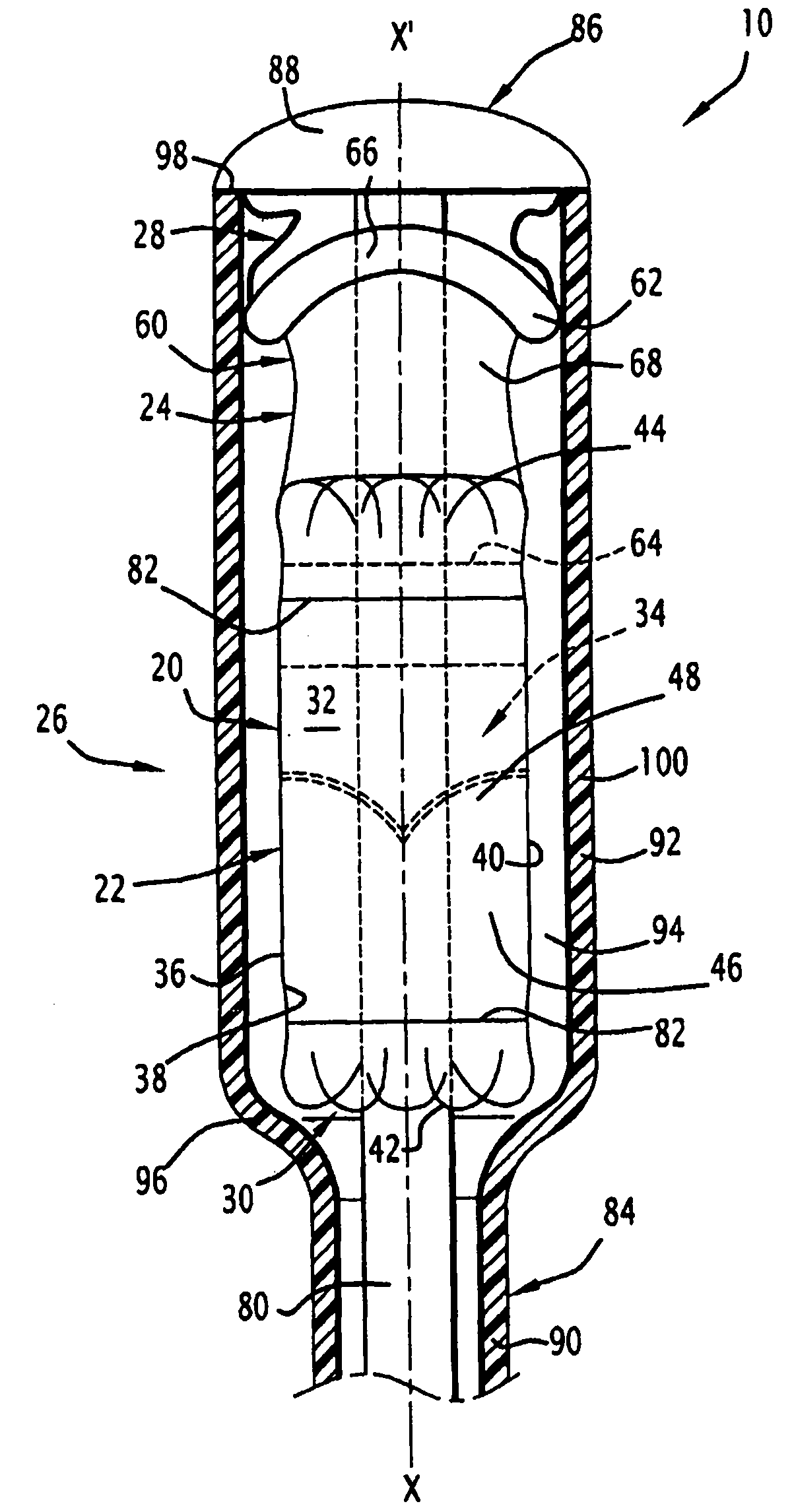
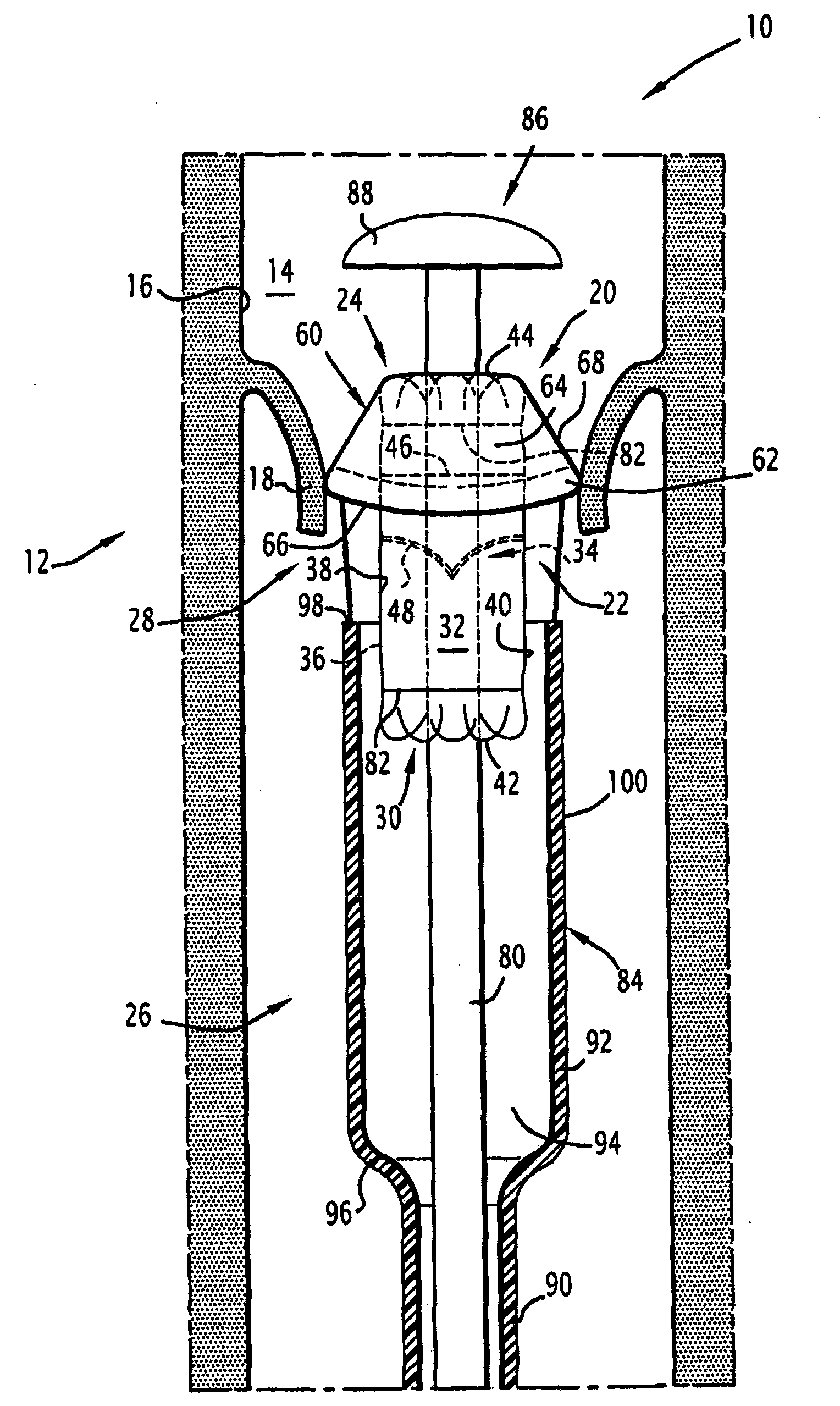
Surgical insertion of a prosthesis.
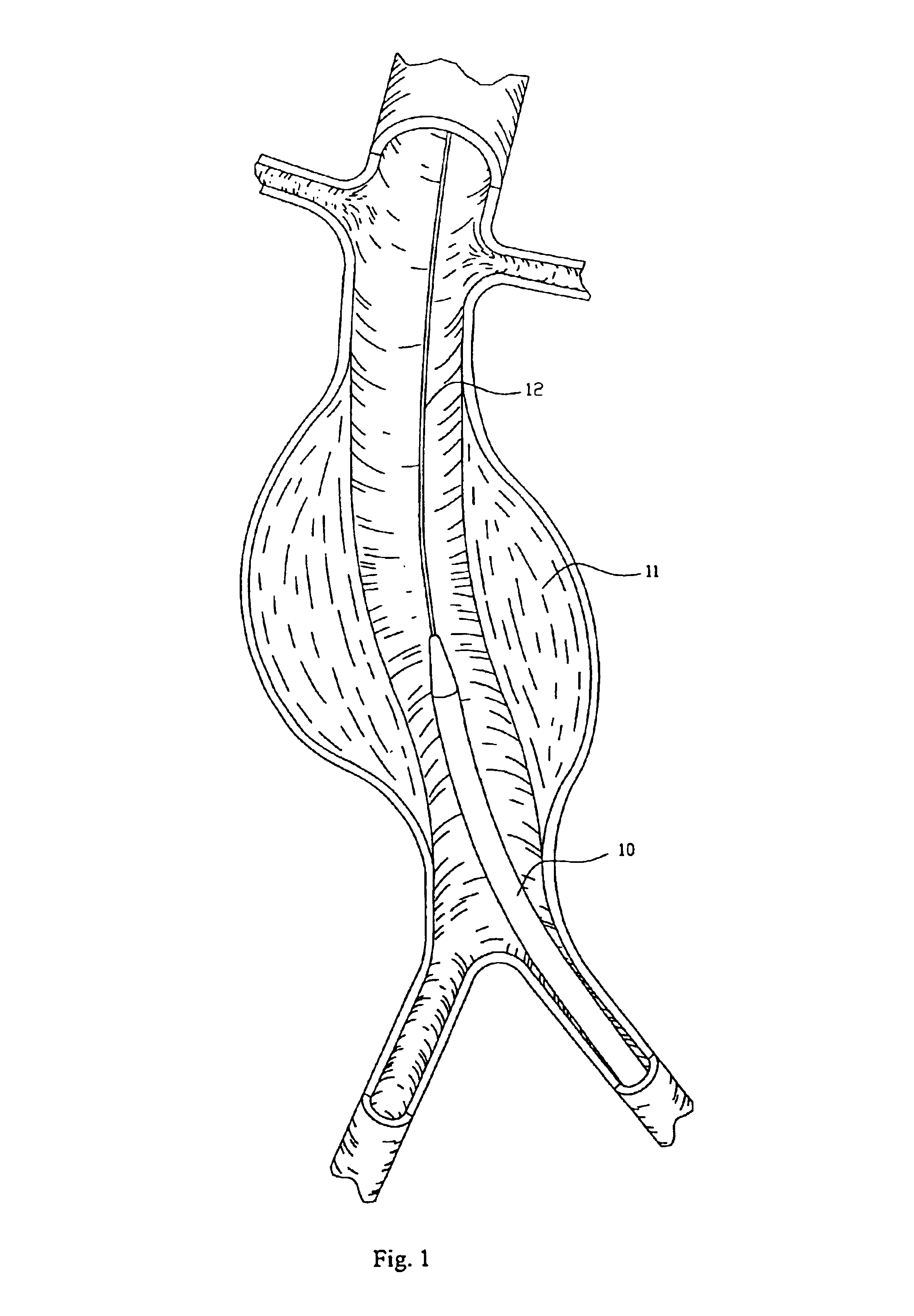
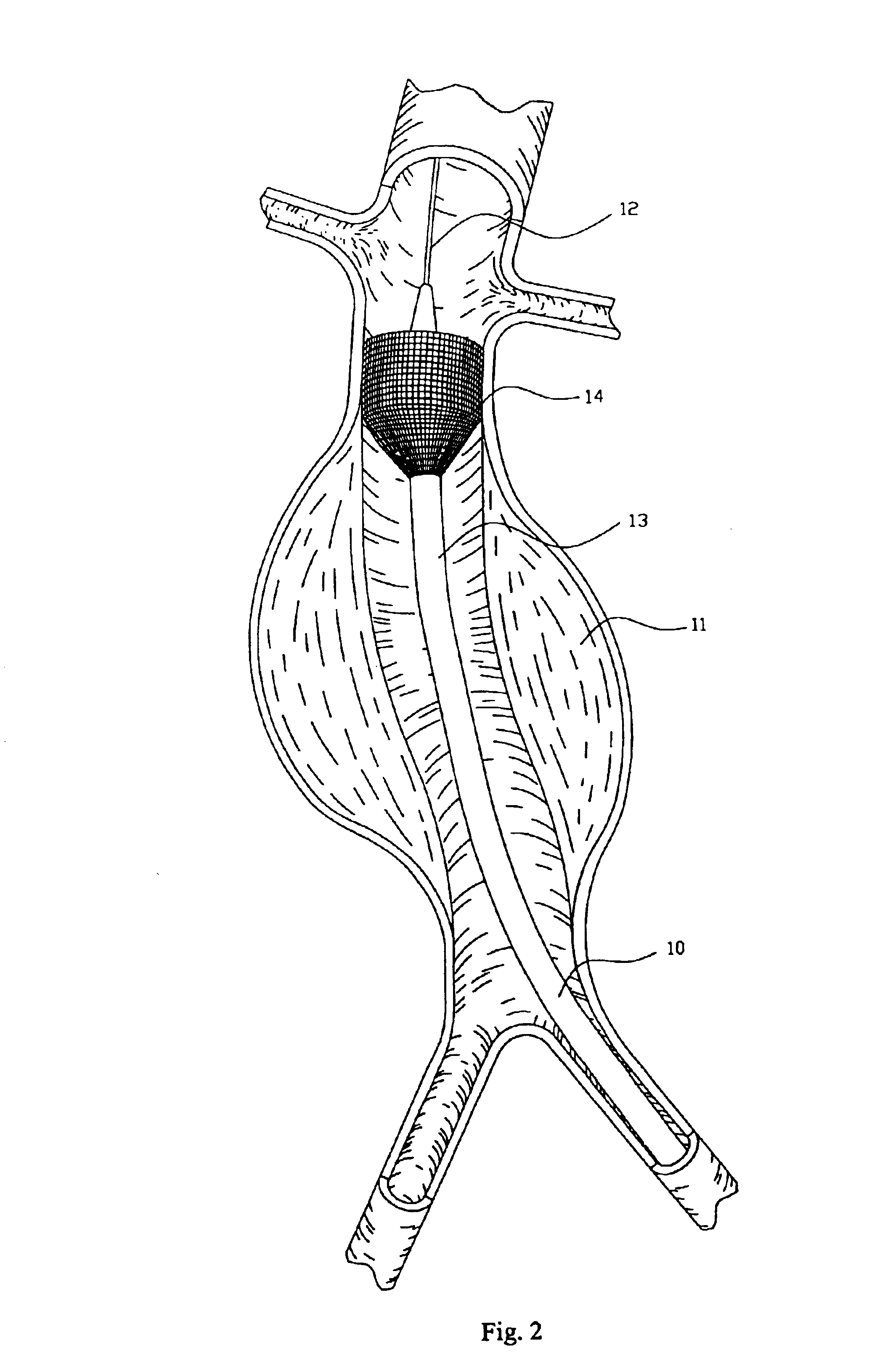
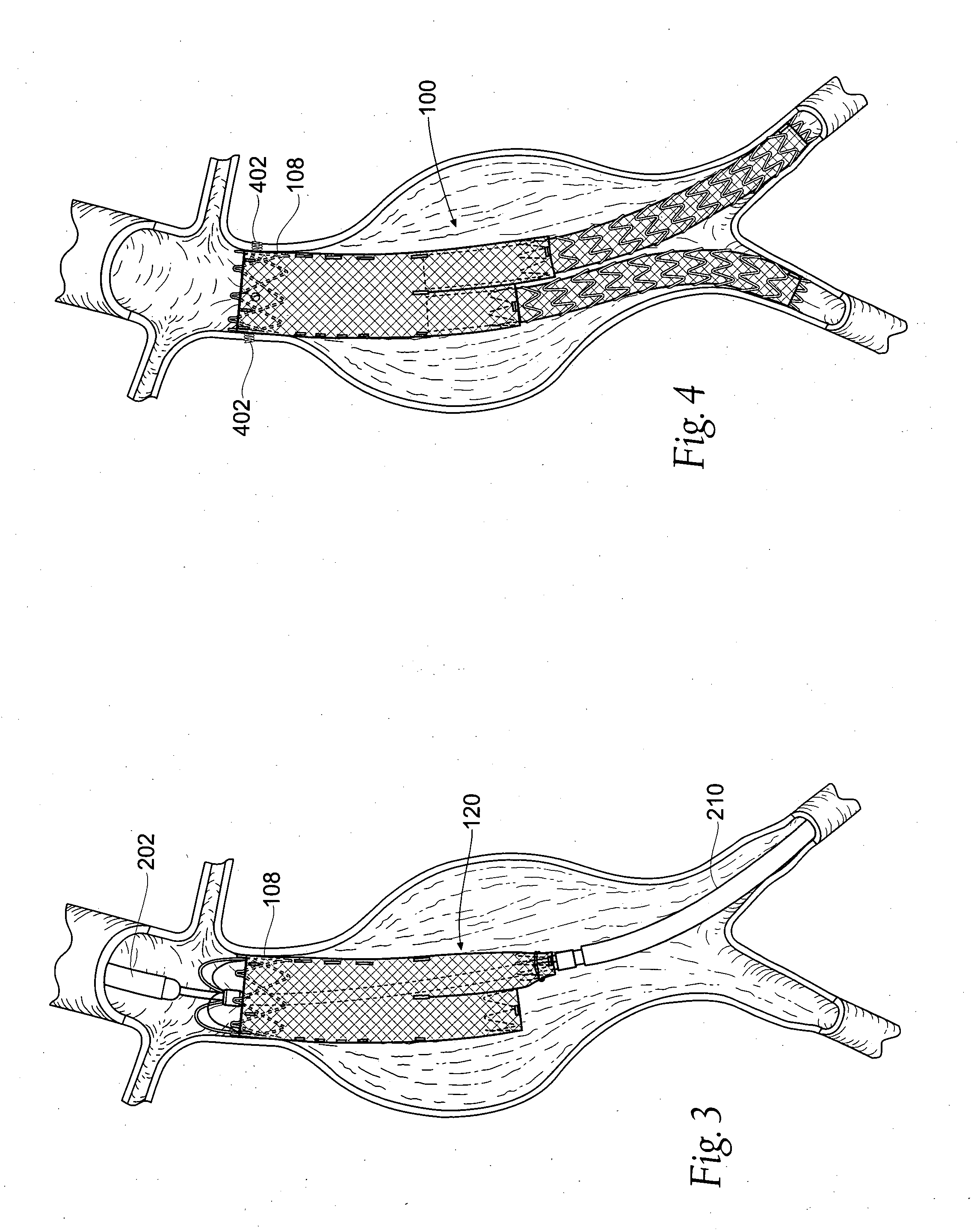
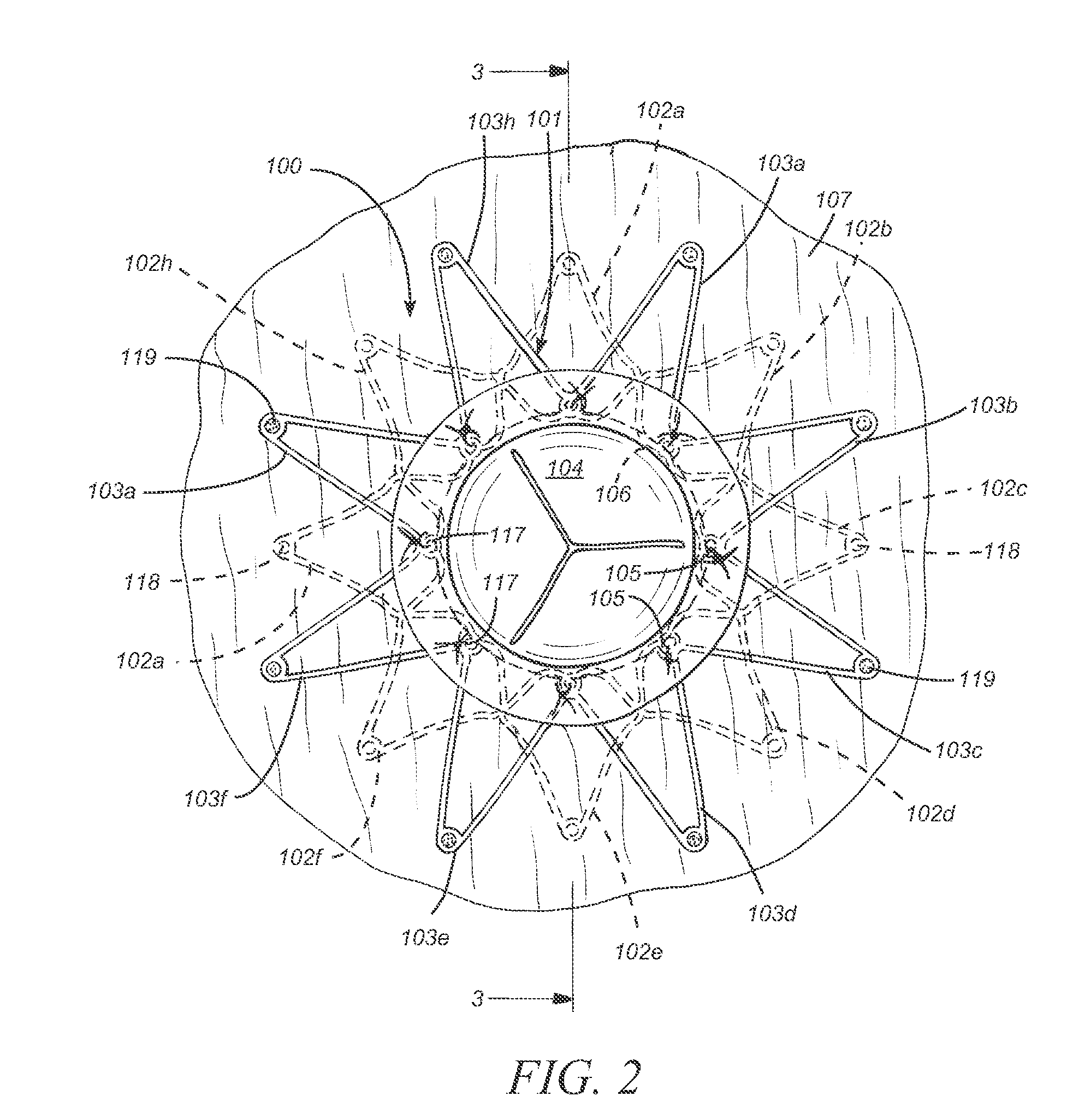
Endovascular aneurysm repair system
InactiveUS6960217B2Low profileEffective and less traumaticStentsEar treatmentEndovascular aneurysm repairBiomedical engineering
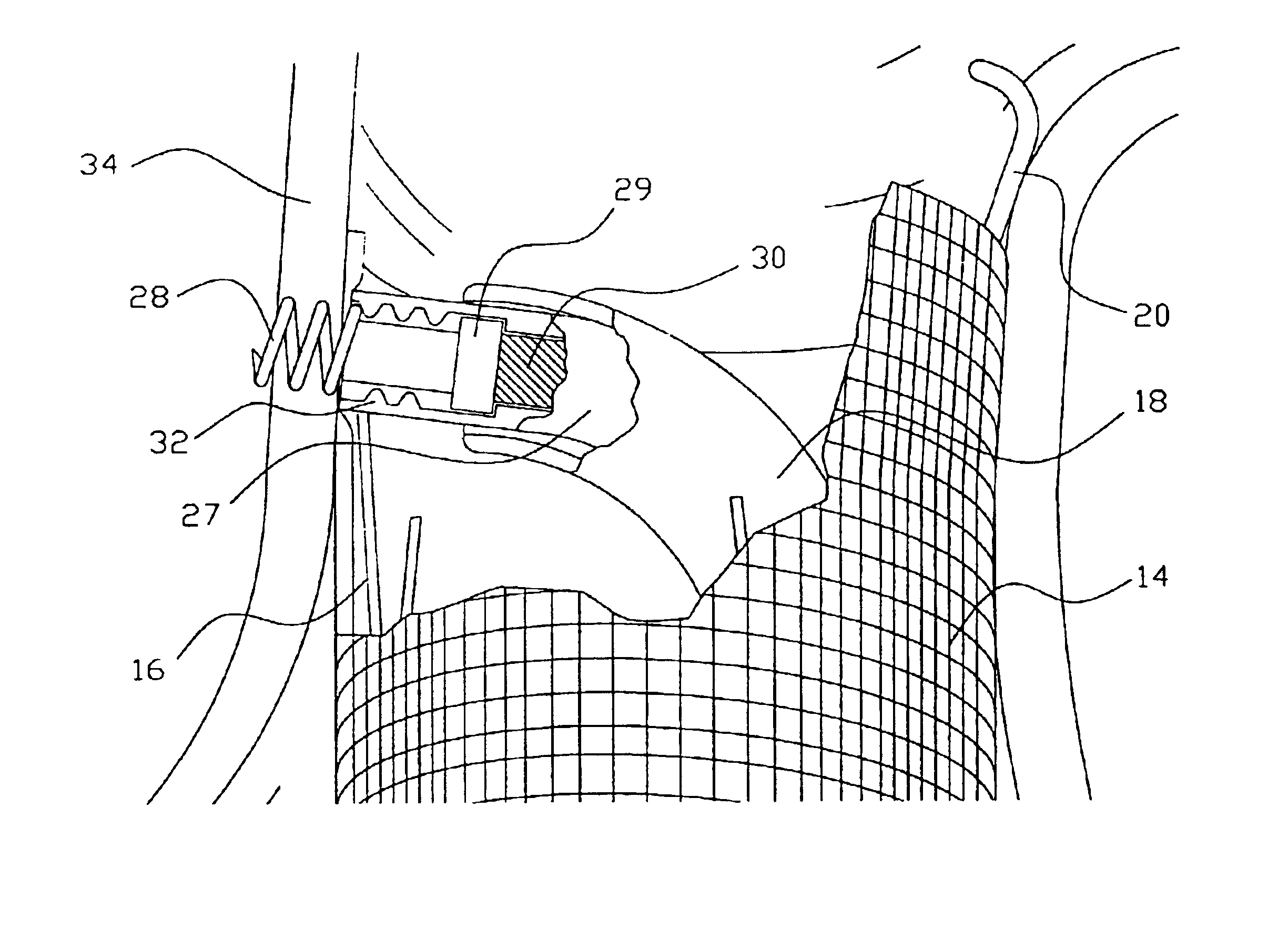
Method and apparatus for implanting radially expandable prostheses in the body lumens rely on tacking or anchoring of the prostheses with separately introduced fasteners. The prostheses may be self-expanding or balloon expandable. After initial placement, a fastener applier system is introduced within the expanded prostheses to deploy a plurality of fasteners at at least one prosthesis end, usually as each end of the prosthesis. The fasteners are usually helical fasteners which are delivered from a helical track in the fastener applier by rotation with a rotator wire. The fasteners will be applied singly, typically in circumferentially spaced-apart patterns about the interior of each end of the prosthesis.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Cutting guide apparatus and surgical method for use in knee arthroplasty
InactiveUS7104997B2Avoiding minimizing errorPrecise alignmentSurgical sawsProsthesisSurgical approachSurgical incision
Novel cutting guides and surgical methods for use in knee arthroplasty are described. Embodiments of the inventive cutting guide apparatus include fixed and adjustable cutting guide blocks having a series of slots designed to accommodate a cutting saw. The cutting guides and surgical method are designed to allow for the provision of all desired surgical cuts upon the distal end of the femur, for subsequent implantation of a prosthesis thereto, without having to remove the cutting guide block.
Owner:LIONBERGER DAVID +1
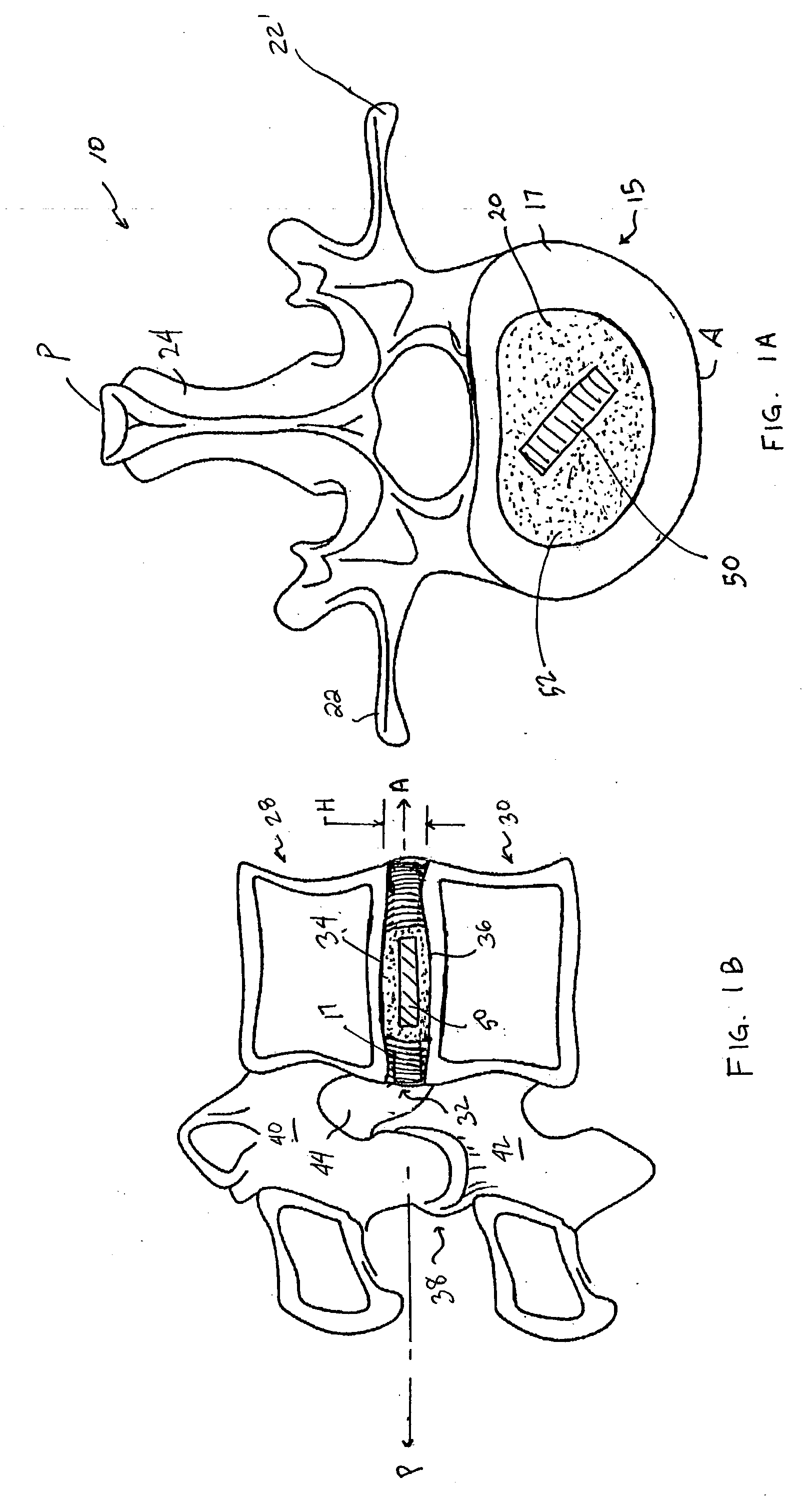
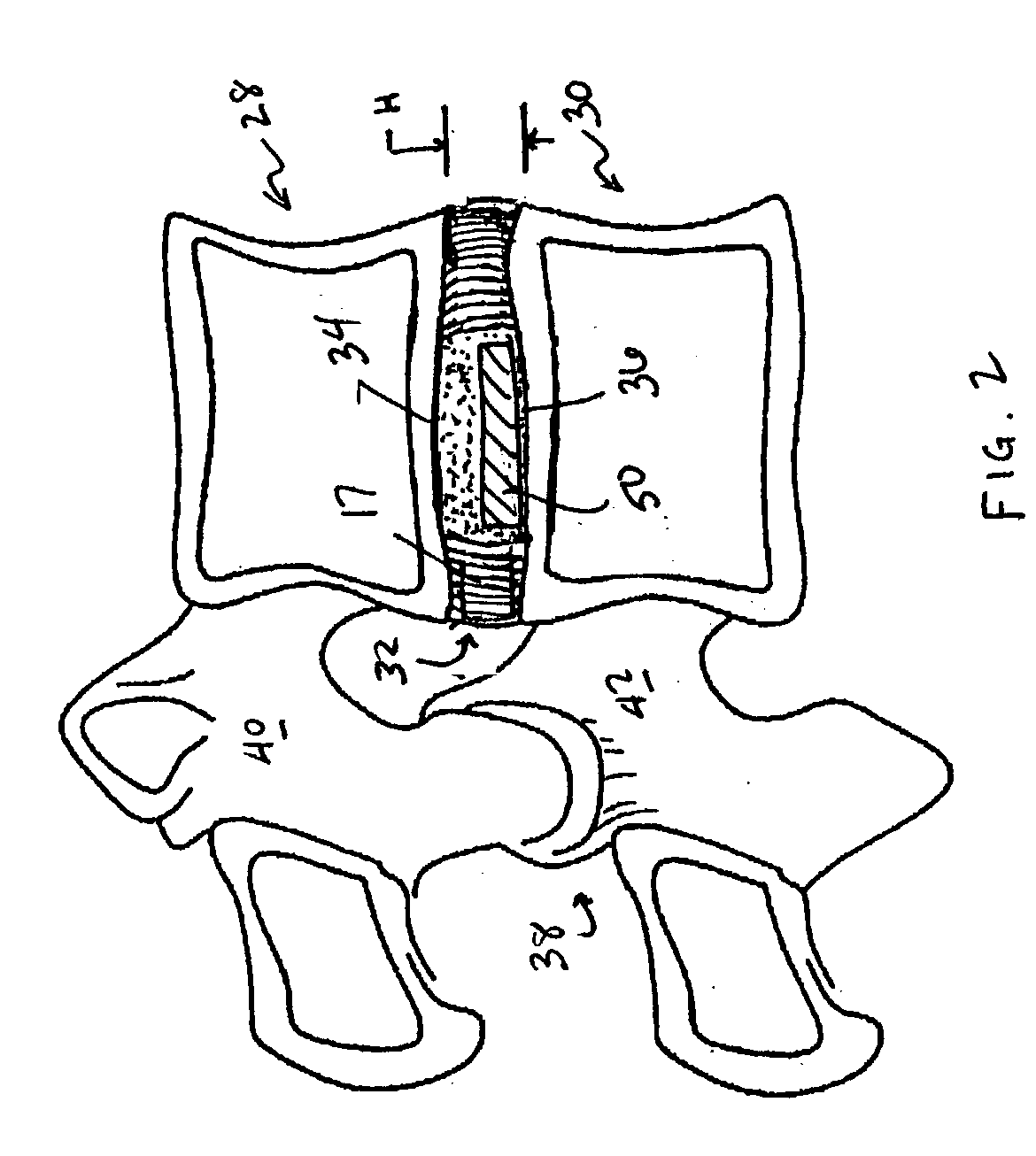
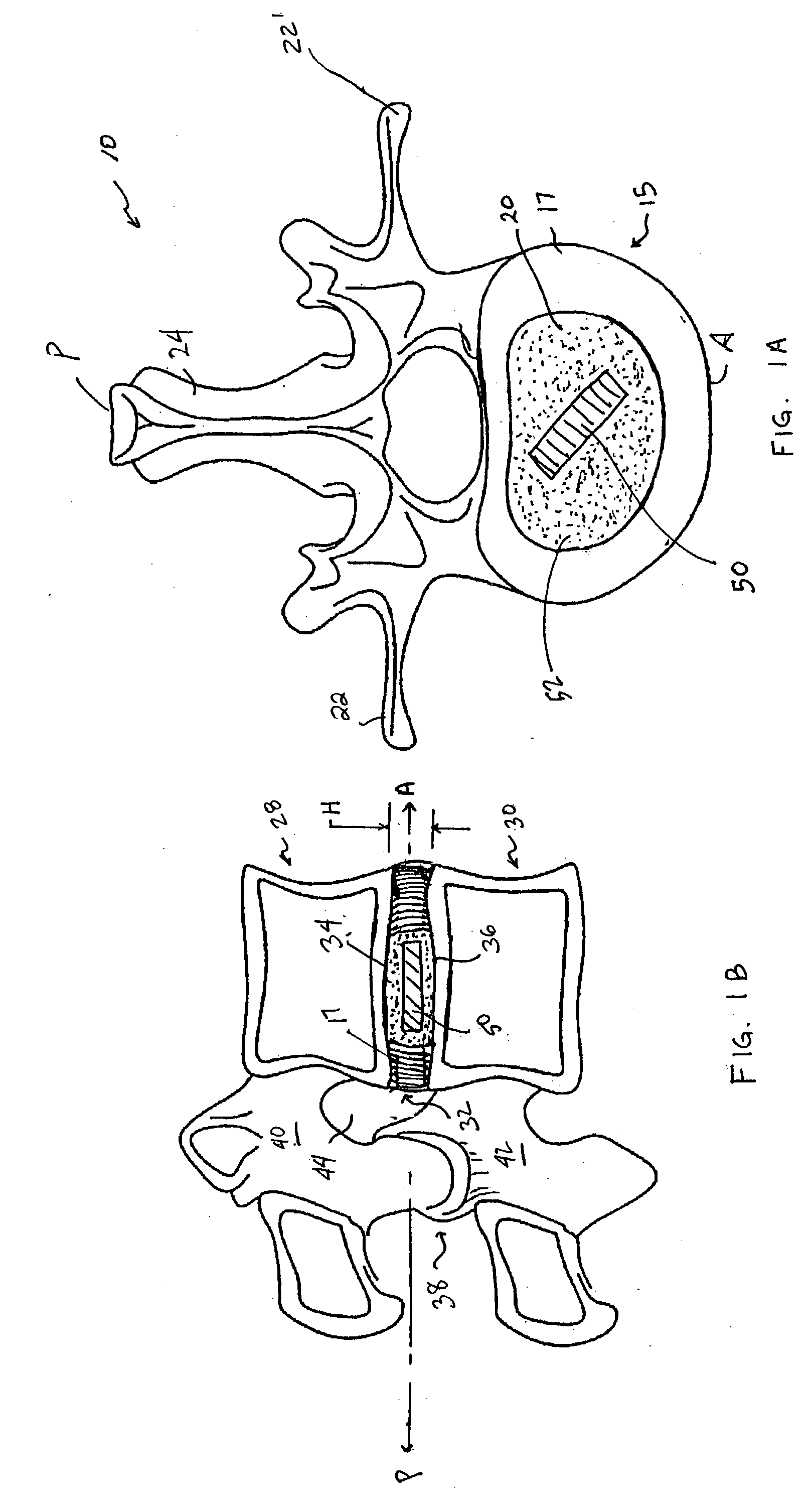
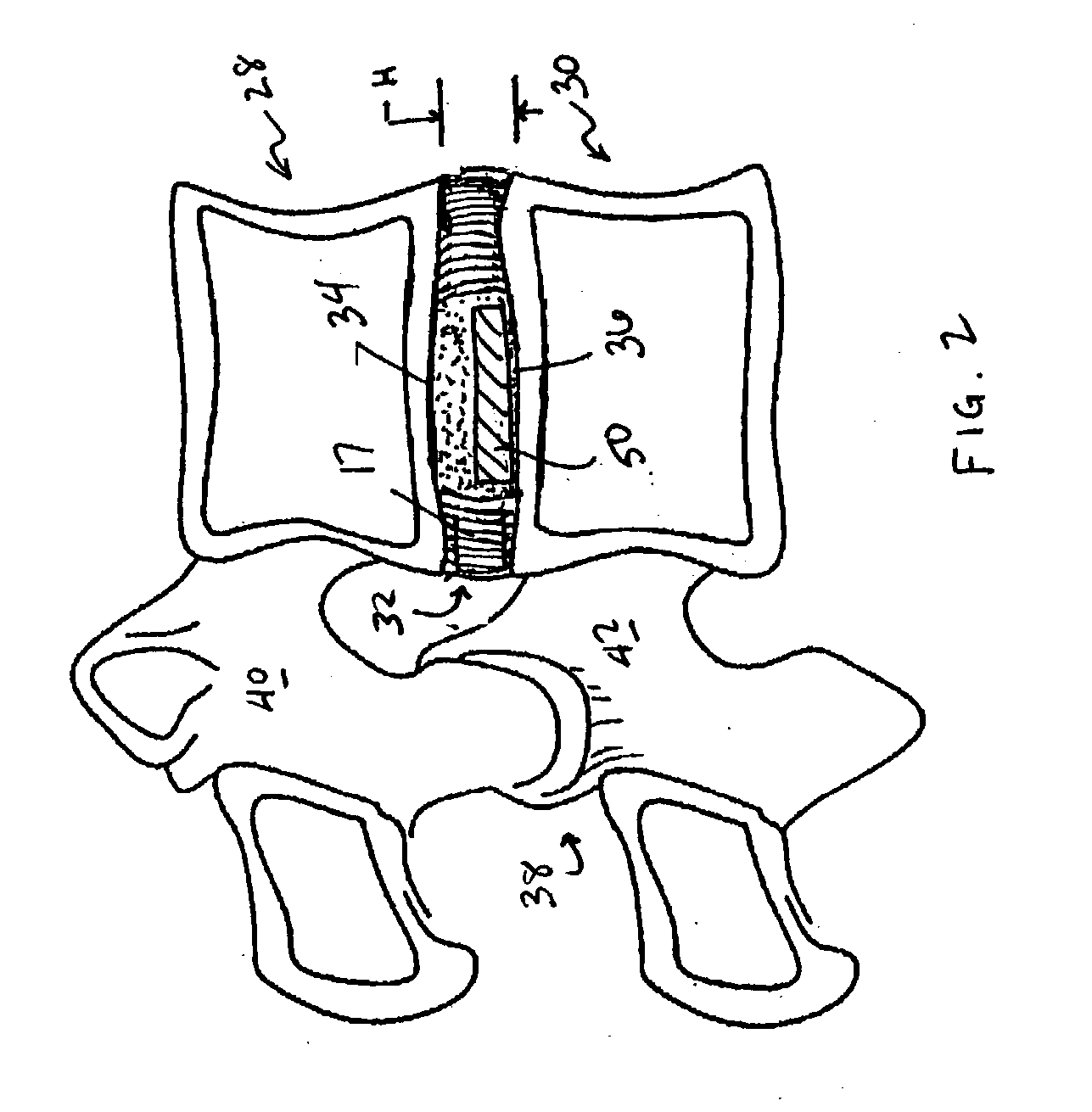
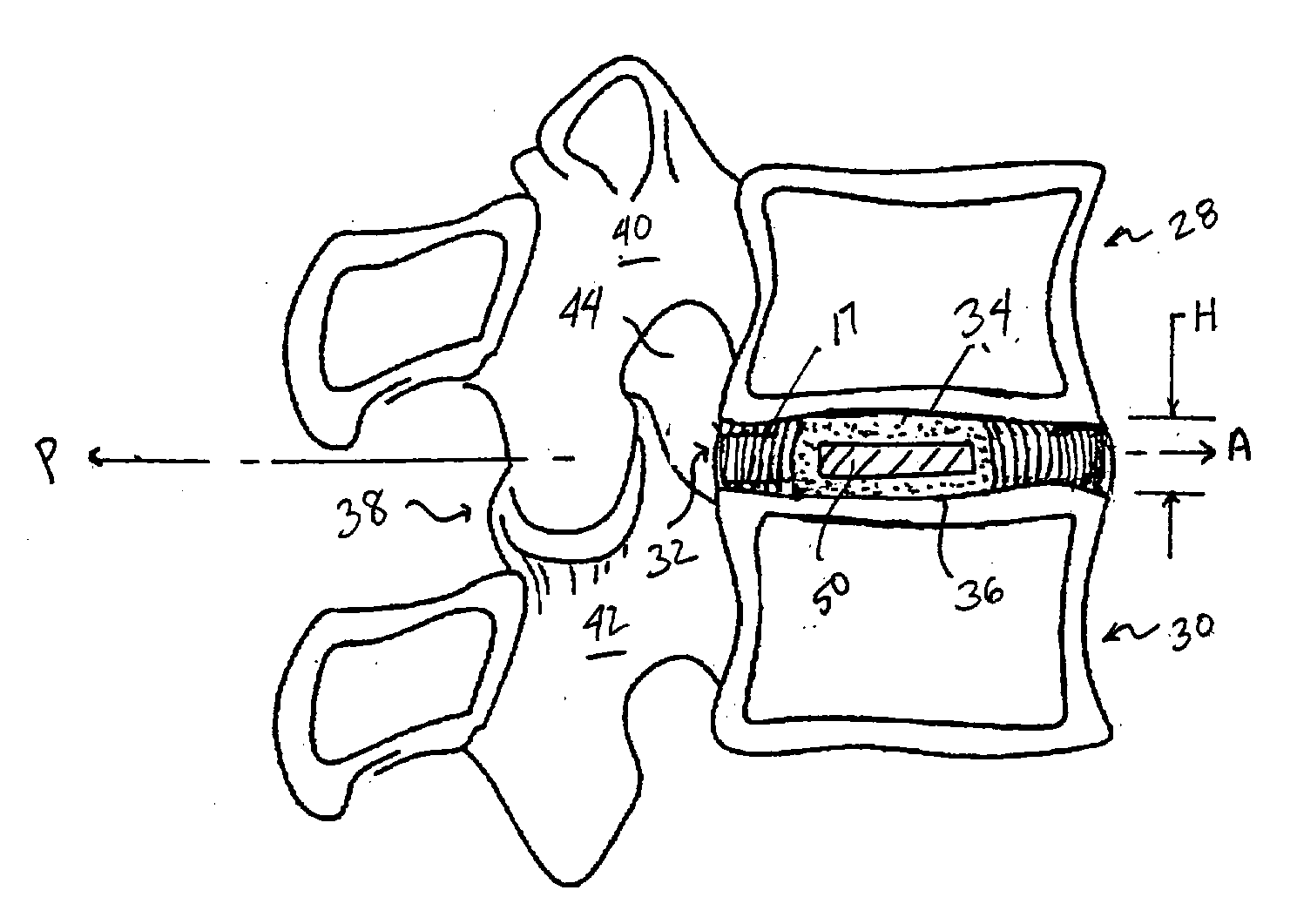
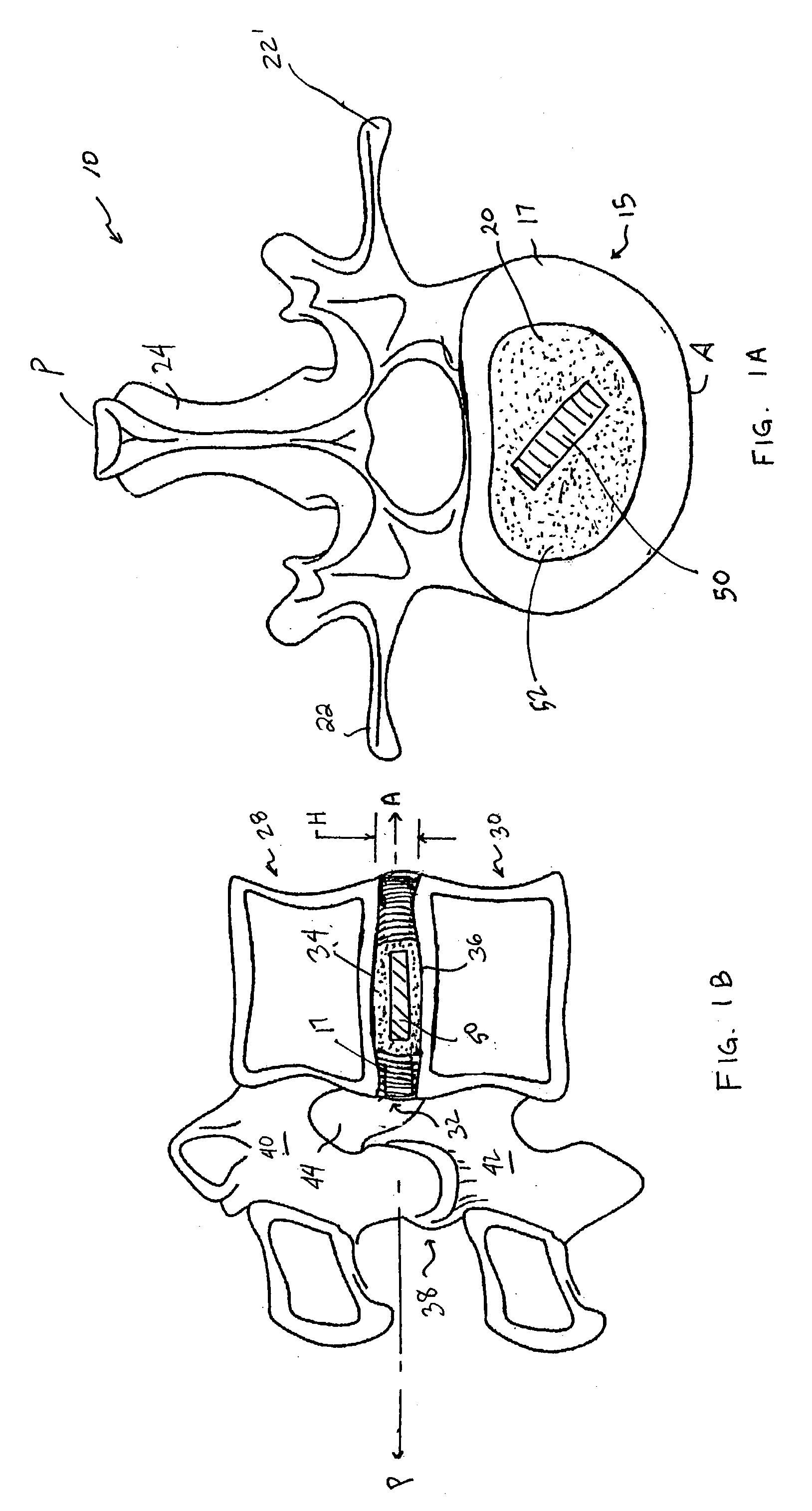
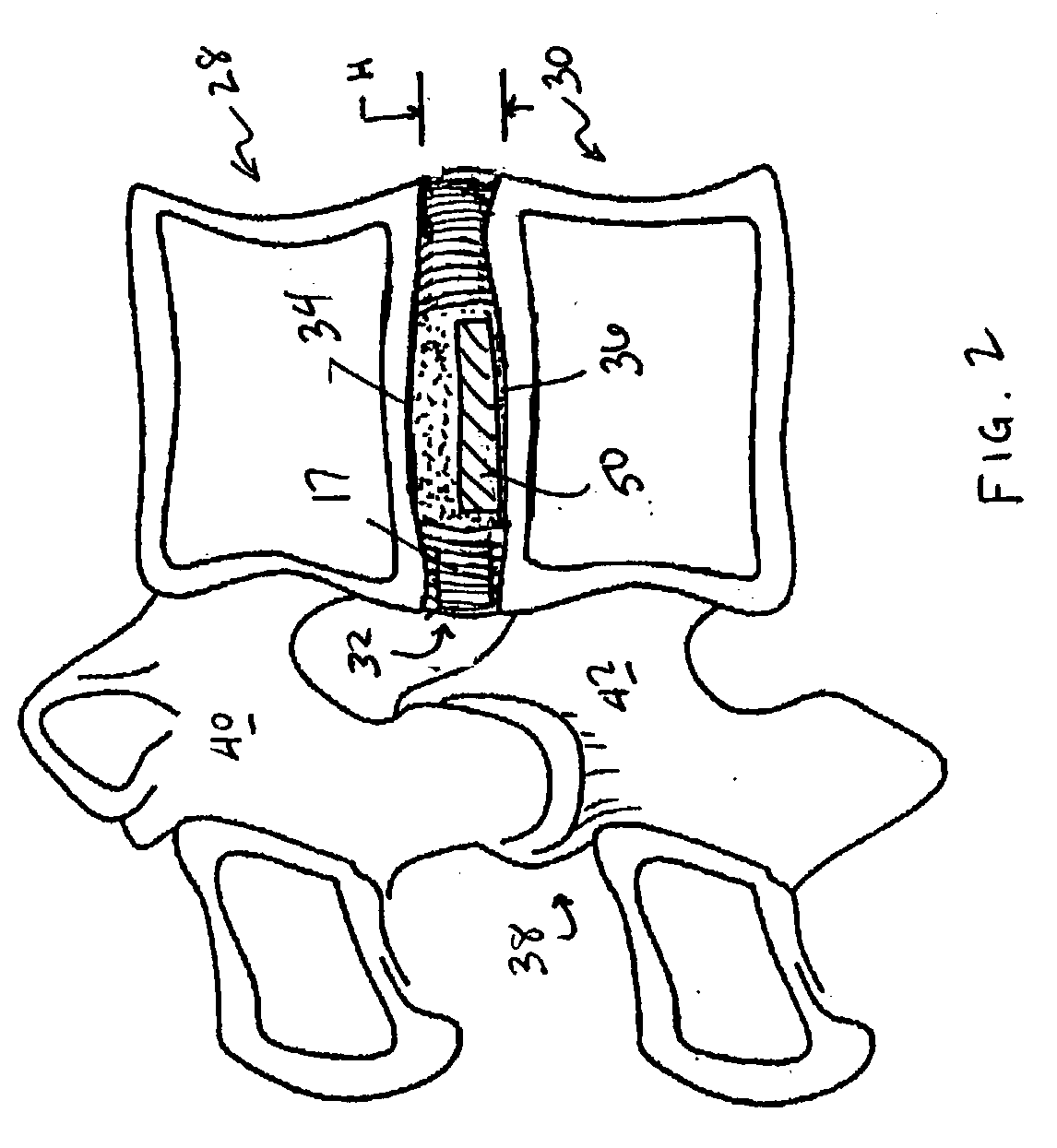
Devices and method for augmenting a vertebral disc
A vertebral disc prosthesis, a method of implanting a prosthesis and a deployment device is provided. The prosthesis may be implanted into the interior region of the vertebral disc so as to displace existing vertebral tissue, such as NP. The size or amount of the prosthesis inserted into the interior region of the vertebral disc may be a characteristic of the disc or the prosthesis. For example, the amount or size of prosthesis inserted into the disc may be dependent upon restoring the functionality of the disc (e.g., the ability of the disc to transfer nutrients or otherwise survive, the ability of the disc to carry the required loads and absorb stress or the reduction of pain). Restoring disc function may be determined by the resulting disc height desired, the resulting disc pressure desired or the resulting disc volume desired. The prosthesis may be sized or positioned within the interior of the vertebral disc such that it is spaced from at least one of the end plates of the vertebral disc. The prosthesis may be formed of a material having a compression strength that is less than 4 mn / m<2>. A deployment device may be used to facilitate placement of the prosthesis within the vertebral disc. The prosthesis may include a grouping of multiple components that can be deployed as group.
Owner:INTRINSIC THERAPEUTICS
Devices and method for augmenting a vertebral disc
A vertebral disc prosthesis, a method of implanting a prosthesis and a deployment device is provided. The prosthesis may be implanted into the interior region of the vertebral disc so as to displace existing vertebral tissue, such as NP. The size or amount of the prosthesis inserted into the interior region of the vertebral disc may be a characteristic of the disc or the prosthesis. For example, the amount or size of prosthesis inserted into the disc may be dependent upon restoring the functionality of the disc (e.g., the ability of the disc to transfer nutrients or otherwise survive, the ability of the disc to carry the required loads and absorb stress or the reduction of pain). Restoring disc function may be determined by the resulting disc height desired, the resulting disc pressure desired or the resulting disc volume desired. The prosthesis may be sized or positioned within the interior of the vertebral disc such that it is spaced from at least one of the end plates of the vertebral disc. The prosthesis may be formed of a material having a compression strength that is less than 4 mn / m<2>. A deployment device may be used to facilitate placement of the prosthesis within the vertebral disc. The prosthesis may include a grouping of multiple components that can be deployed as group.
Owner:LAMBRECHT GREGORY +3
Cutting guide apparatus and surgical method for use in knee arthroplasty
InactiveUS20070073305A1Avoiding minimizing errorPrecise alignmentNon-surgical orthopedic devicesSurgical sawsKnee JointProsthesis
Novel cutting guides and surgical methods for use in knee arthroplasty are described. Embodiments of the inventive cutting guide apparatus include fixed and adjustable cutting guide blocks having a series of slots designed to accommodate a cutting saw. The cutting guides and surgical method are designed to allow for the provision of all desired surgical cuts upon the distal end of the femur, for subsequent implantation of a prosthesis thereto, without having to remove the cutting guide block.
Owner:LIONBERGER DAVID R +1
Devices and method for augmenting a vertebral disc
A vertebral disc prosthesis, a method of implanting a prosthesis and a deployment device is provided. The prosthesis may be implanted into the interior region of the vertebral disc so as to displace existing vertebral tissue, such as NP. The size or amount of the prosthesis inserted into the interior region of the vertebral disc may be a characteristic of the disc or the prosthesis. For example, the amount or size of prosthesis inserted into the disc may be dependent upon restoring the functionality of the disc (e.g., the ability of the disc to transfer nutrients or otherwise survive, the ability of the disc to carry the required loads and absorb stress or the reduction of pain). Restoring disc function may be determined by the resulting disc height desired, the resulting disc pressure desired or the resulting disc volume desired. The prosthesis may be sized or positioned within the interior of the vertebral disc such that it is spaced from at least one of the end plates of the vertebral disc. The prosthesis may be formed of a material having a compression strength that is less than 4 mn / m<2 >. A deployment device may be used to facilitate placement of the prosthesis within the vertebral disc. The prosthesis may include a grouping of multiple components that can be deployed as group.
Owner:INTRINSIC THERAPEUTICS
Method And Appartus For Acetabular Reconstruction
A trial system for a prosthesis is described. The prosthesis can include an acetabular prosthesis generally for implantation in an acetabulum and the surrounding pelvis. The acetabular prosthesis includes an acetabular cup having a substantially concave inner surface and a substantially convex outer surface. One trial shell or a collection of trial shells are provided to trial a range of motion of the hip joint before implanting a shell prosthesis into the acetabular prosthesis.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
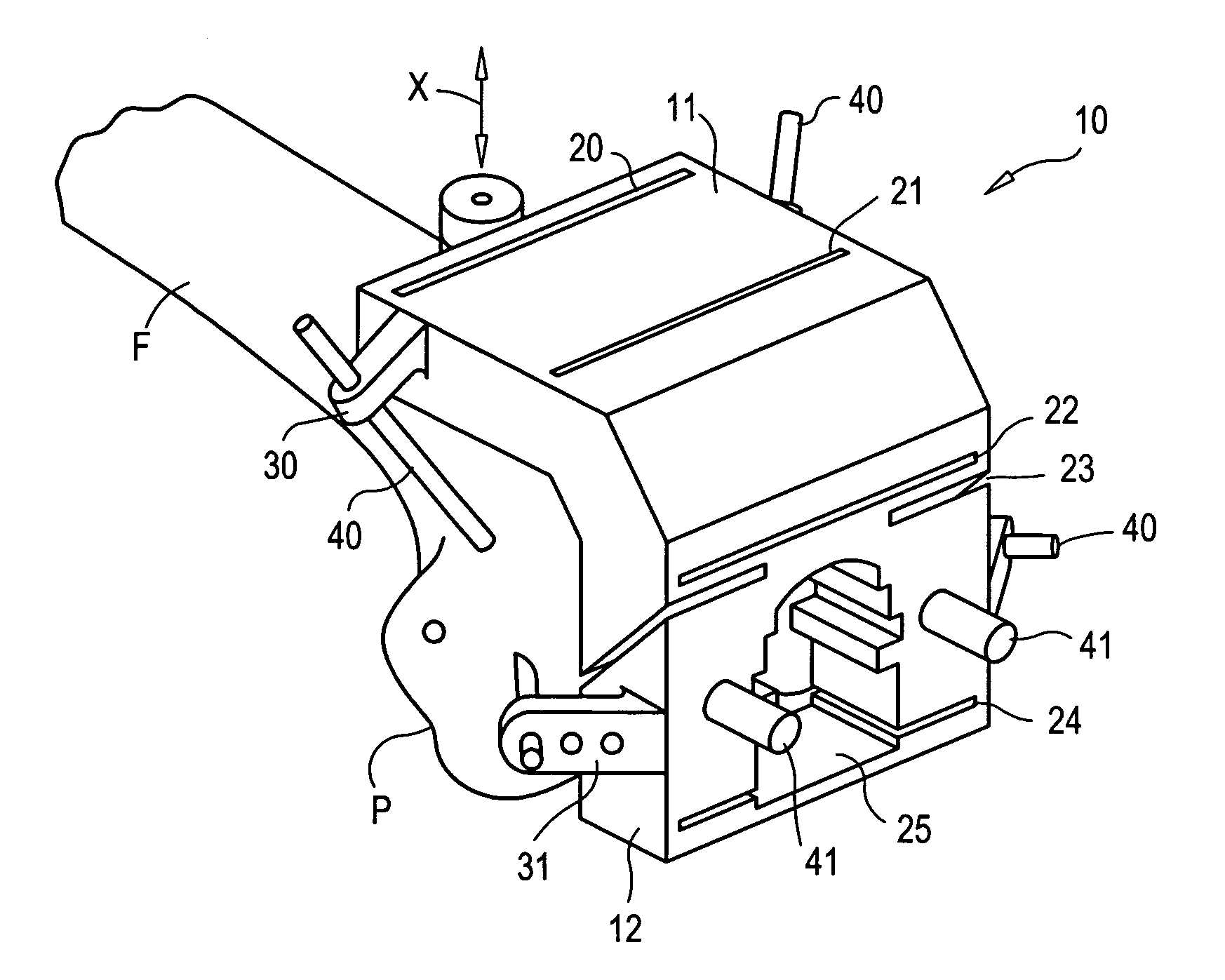
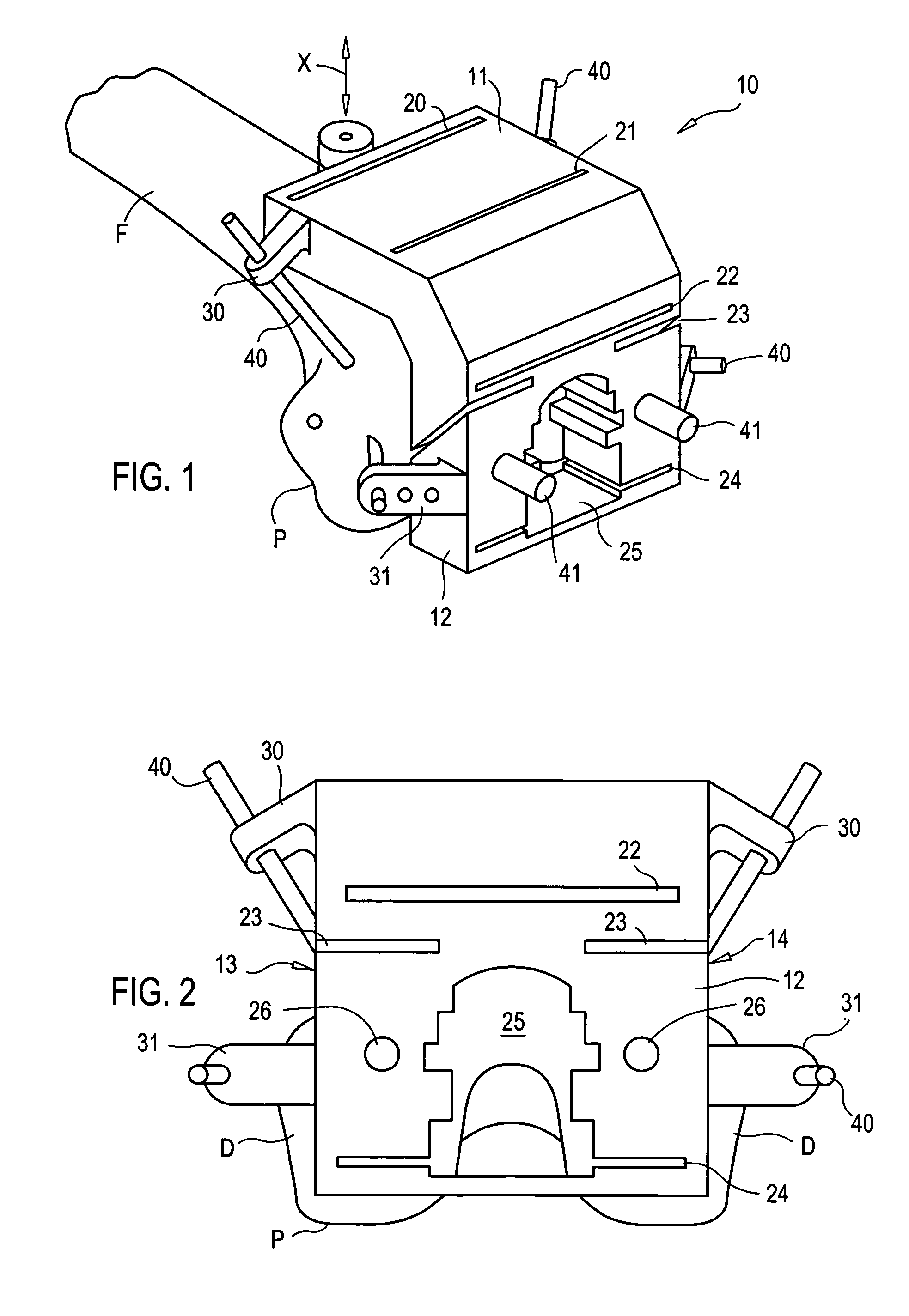
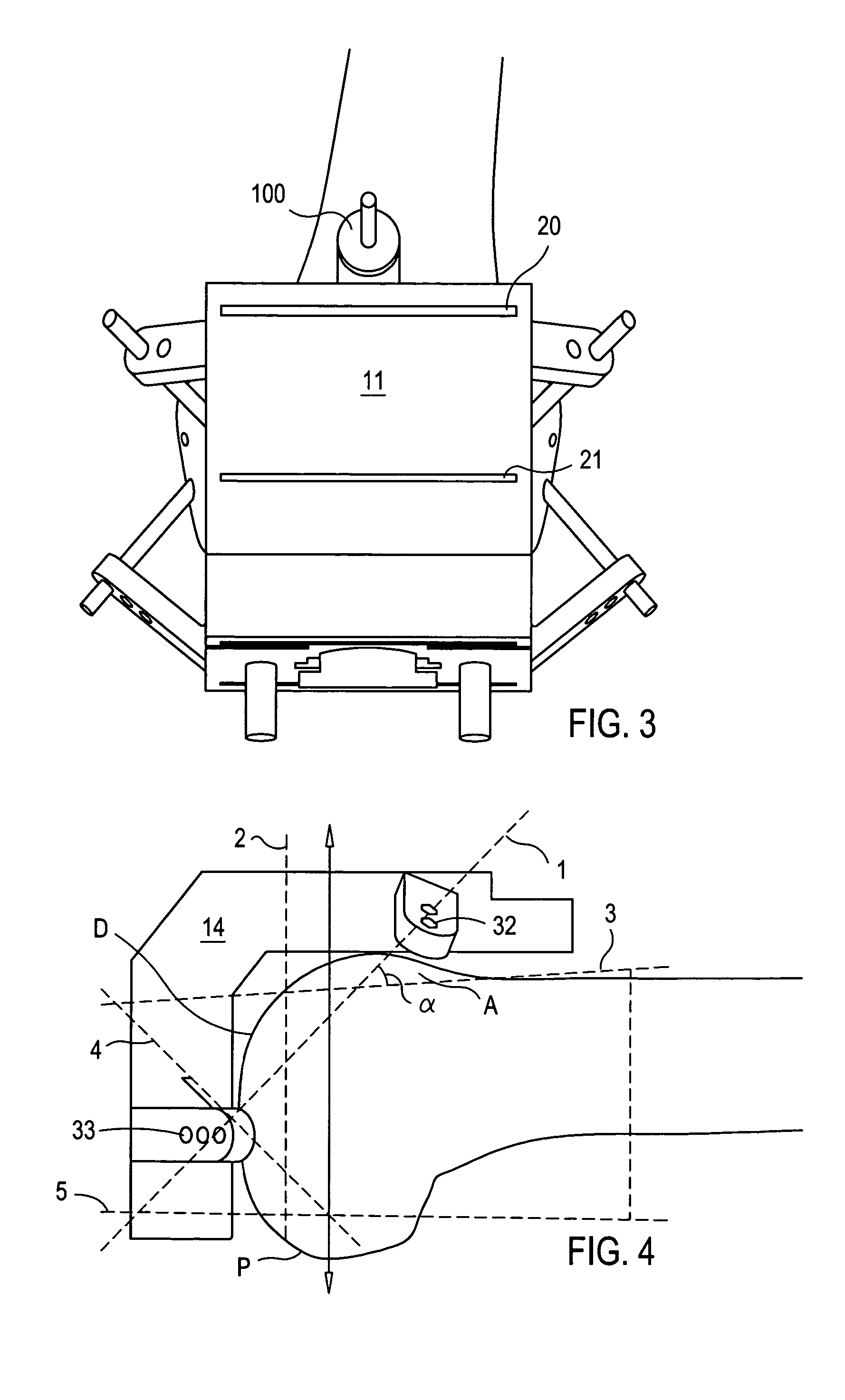
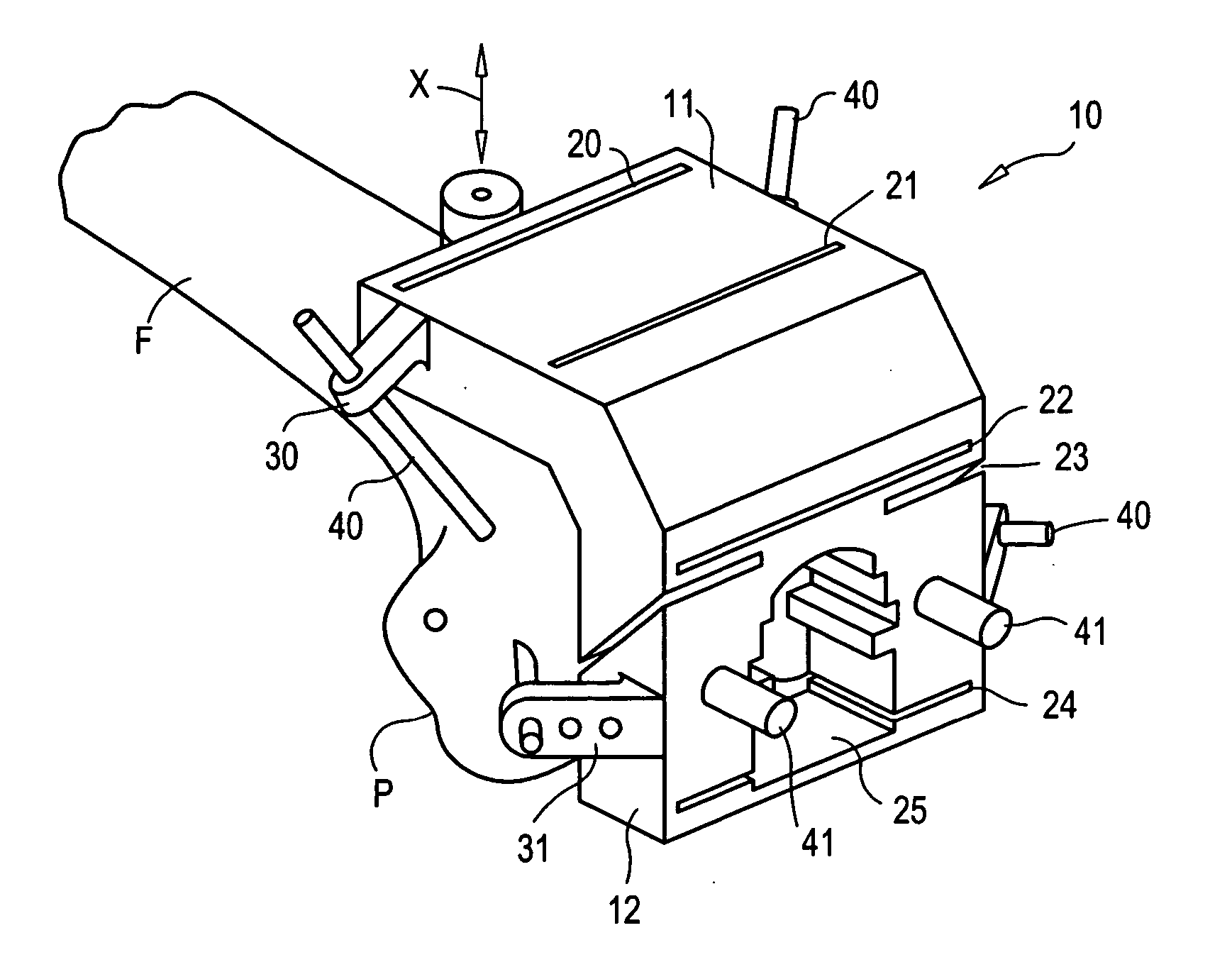
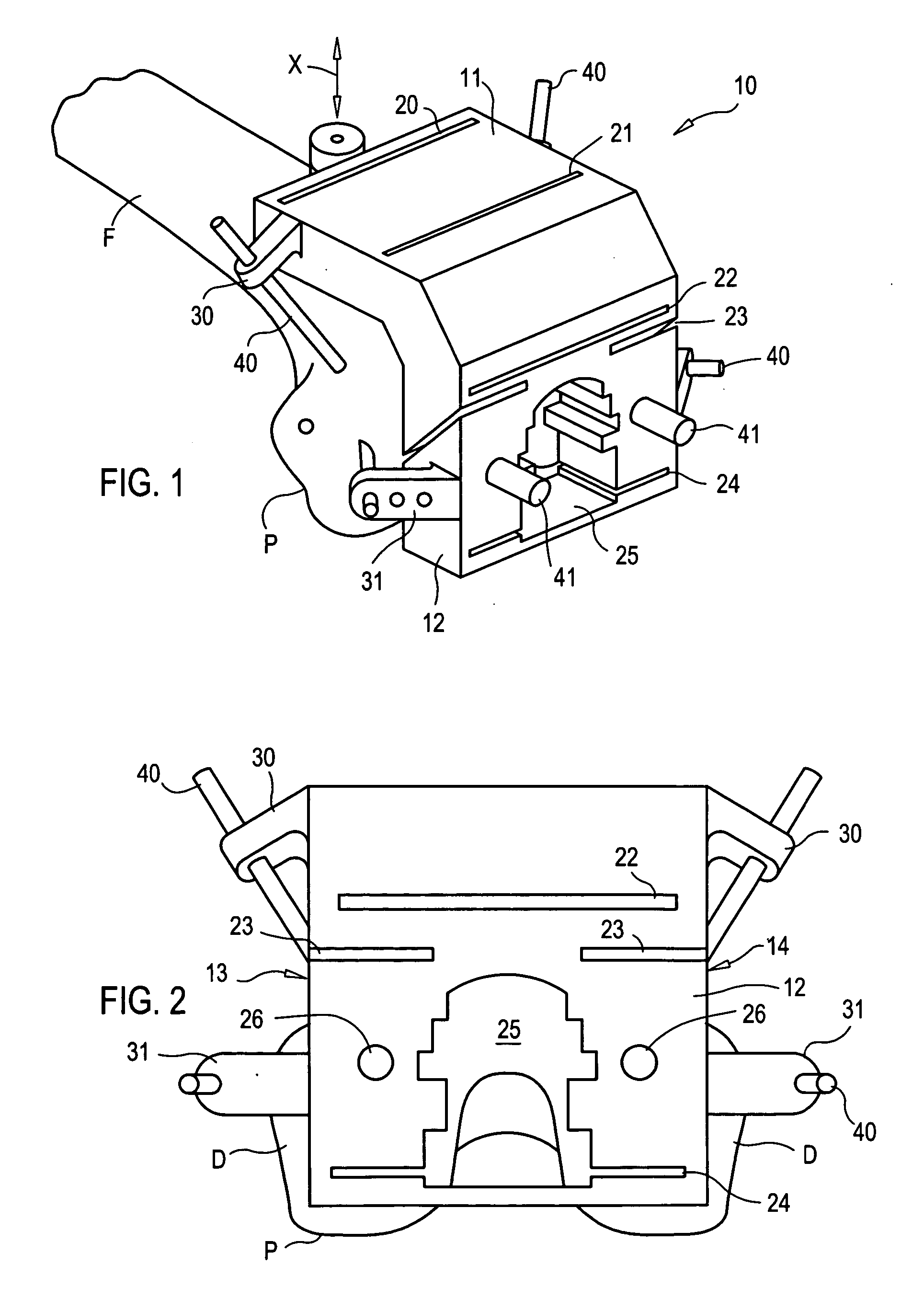
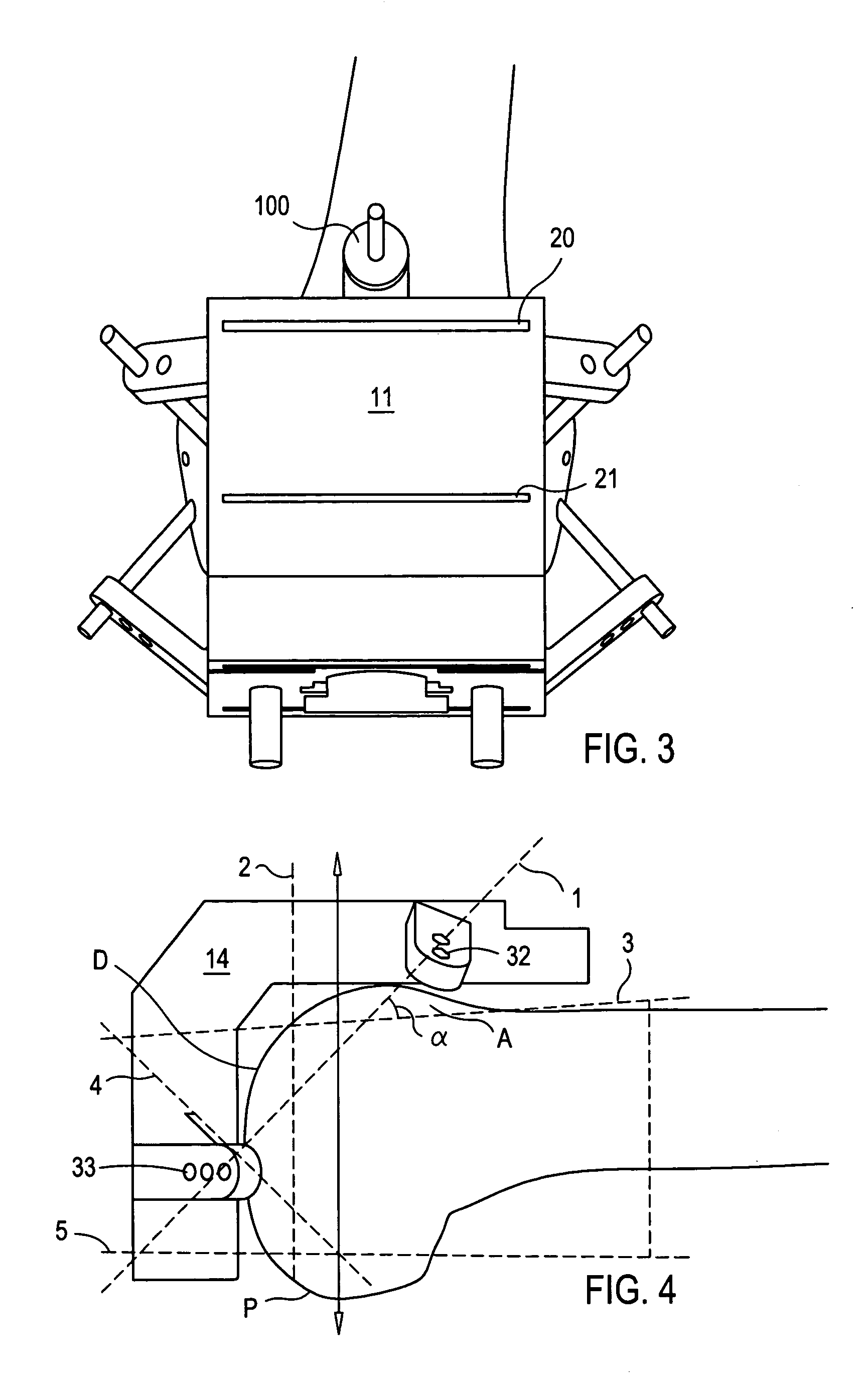
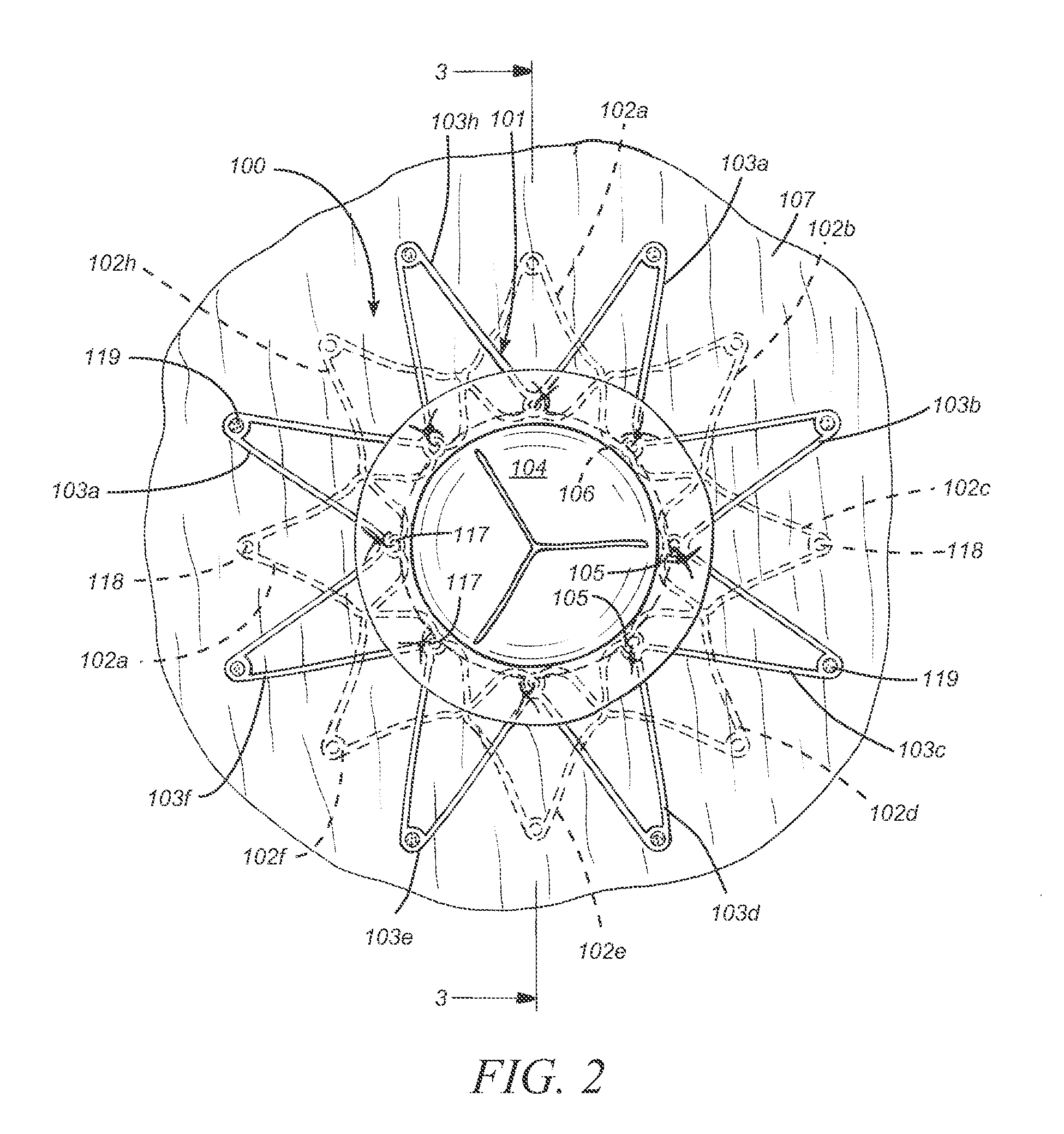
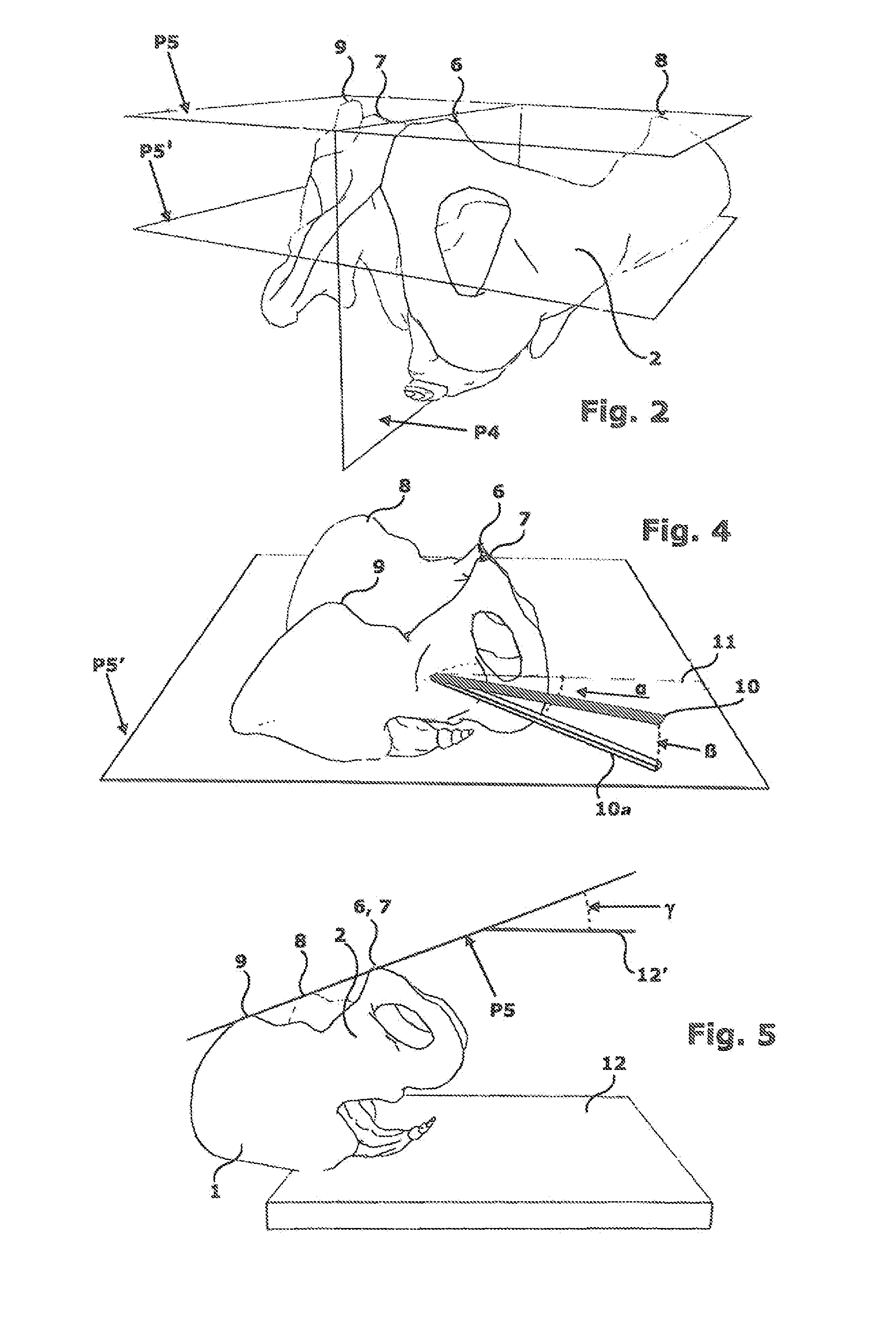
Tibial plateau and/or femoral condyle resection system for prosthesis implantation
According to the invention, the system enables a preoperative study to be carried out wherein the tibia and / or femur is modelled on a computer (6) in 3D, the ideal cutting plane is defined and the position of the resection instruments (1, 2, 3) used to cut the bone is modelled. Additionally, according to the invention, the system enables redefinition of the ideal cutting plane and the positioning and orientation of the resection instruments (1, 2, 3) on the tibia and / or femur, in such a manner that the plane of the slot (4) of the cutting guide (3) through which the cutting tool is introduced coincides with the ideal cutting plane.
Owner:TRAIBER
Total elbow arthroplasty system
A total elbow arthroplasty system, incorporating a humeral component, a radial component and a ball component, may be used as a total elbow replacement in the canine, as well as in other species. The implant of the present invention has an isometric humeral component and an isometric radial component. An isometric ball component having an isometric articular surface is mounted on the radial component. The humeral and radial components have stems for mounting in the medullary canals of the respective bones, which are angled so as to approximate the configuration of the original humerus and radius. The components work together to form a nonconstrained ball and socket joint. The invention is also directed to methods for implanting the novel endoprosthesis of the present invention in a canine elbow joint. The apparatus and methods of the present invention are useful in the treatment of elbow osteoarthritis in canines, as well as in other species, including other quadrupeds and humans.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
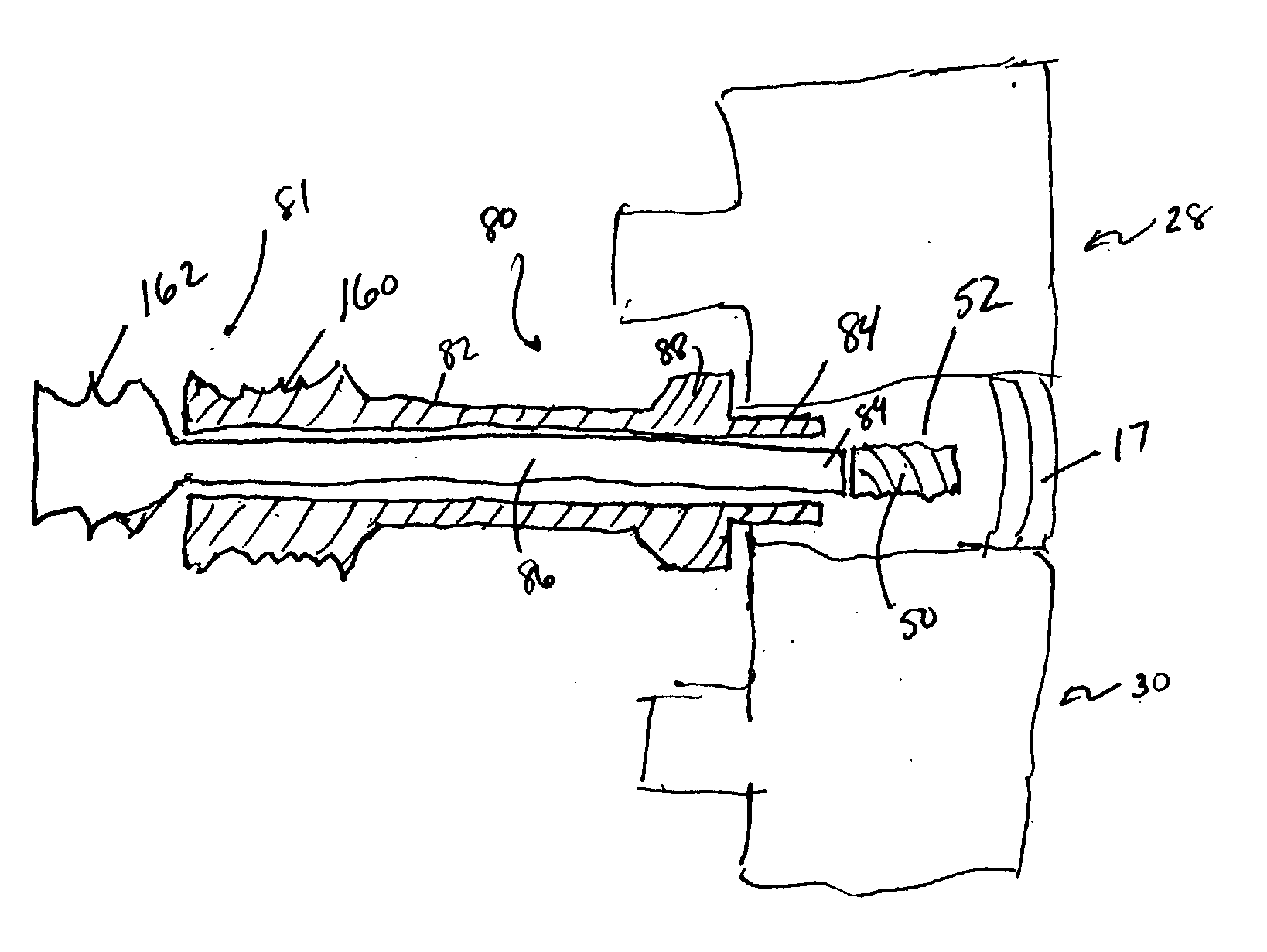
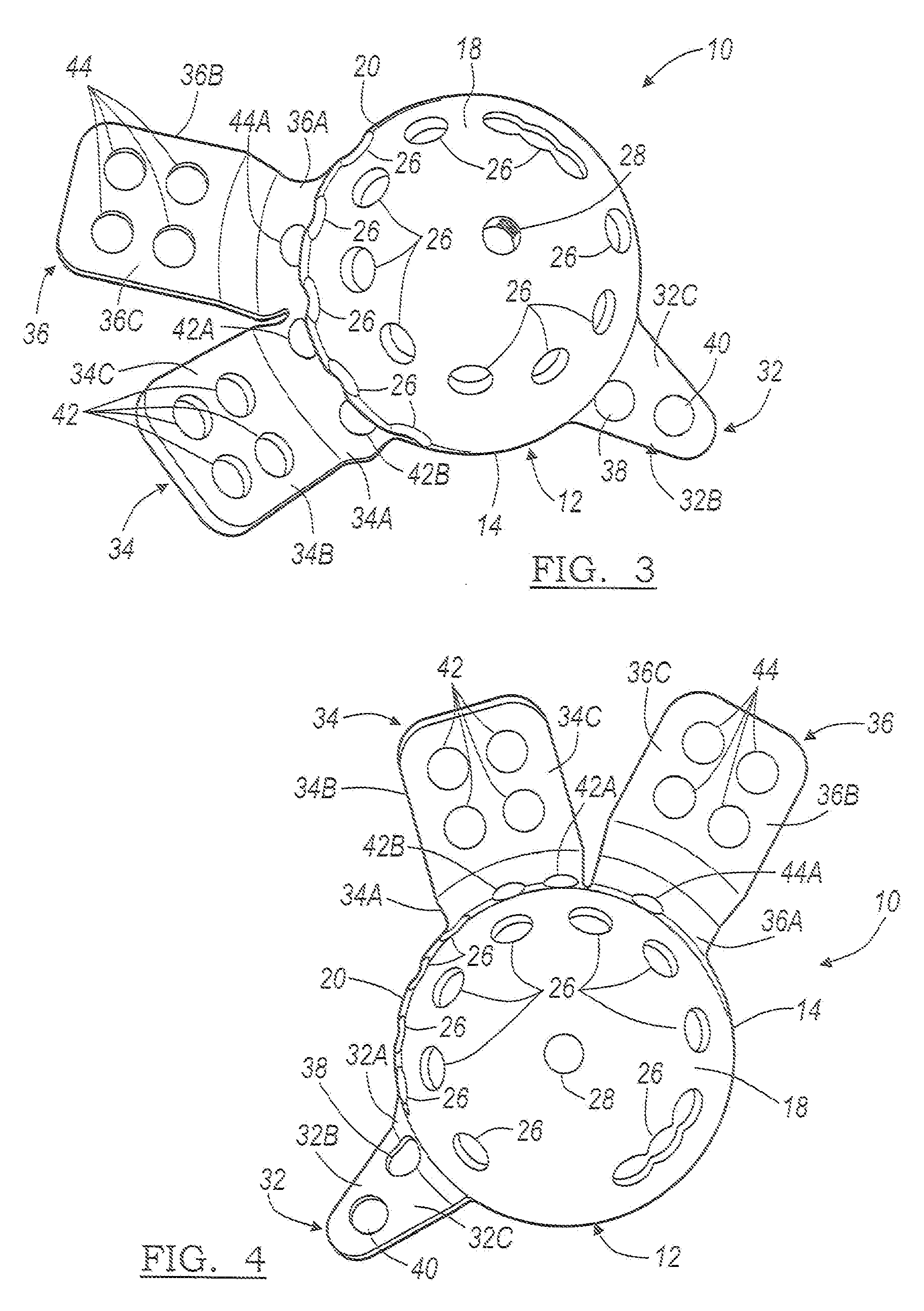
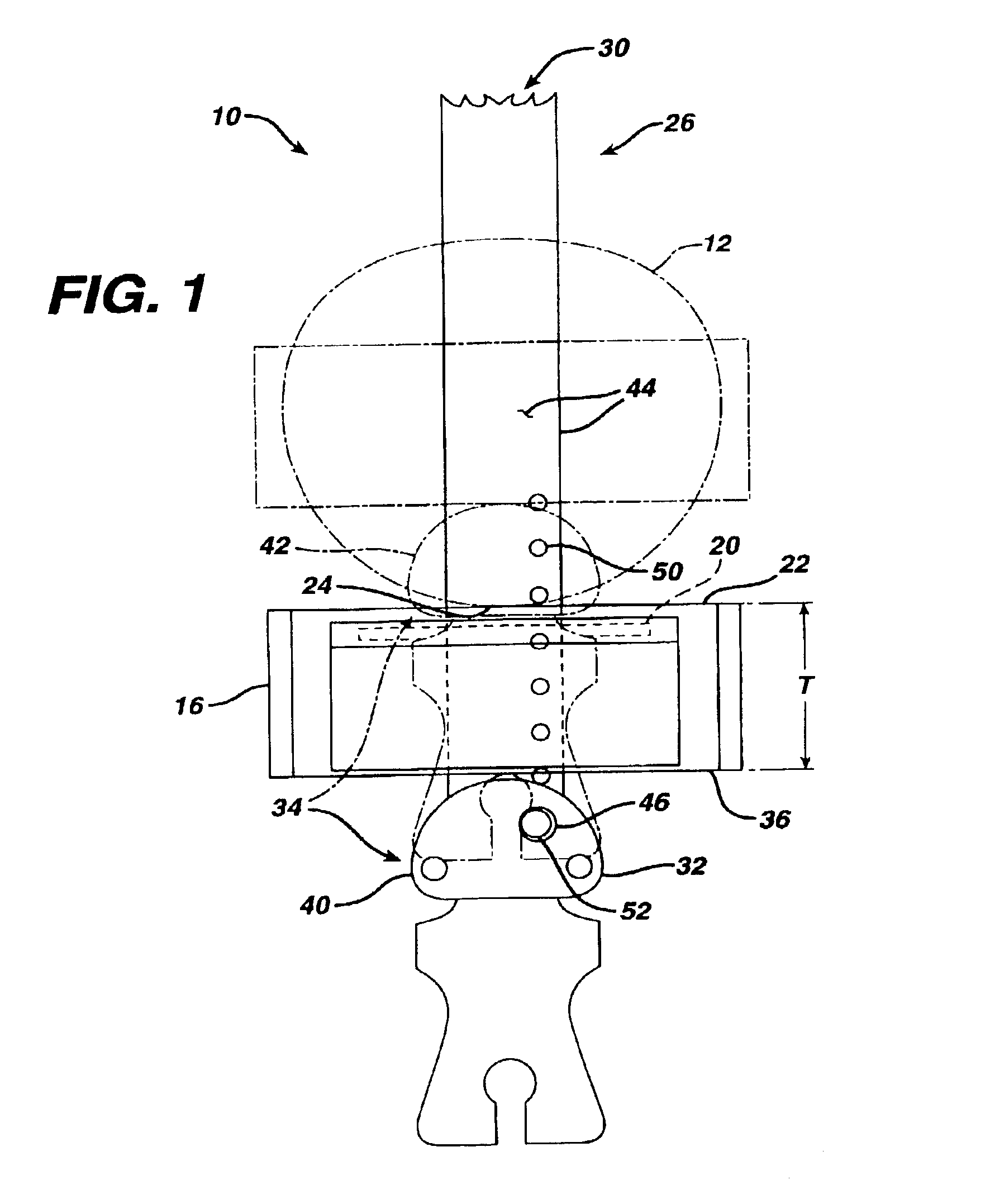
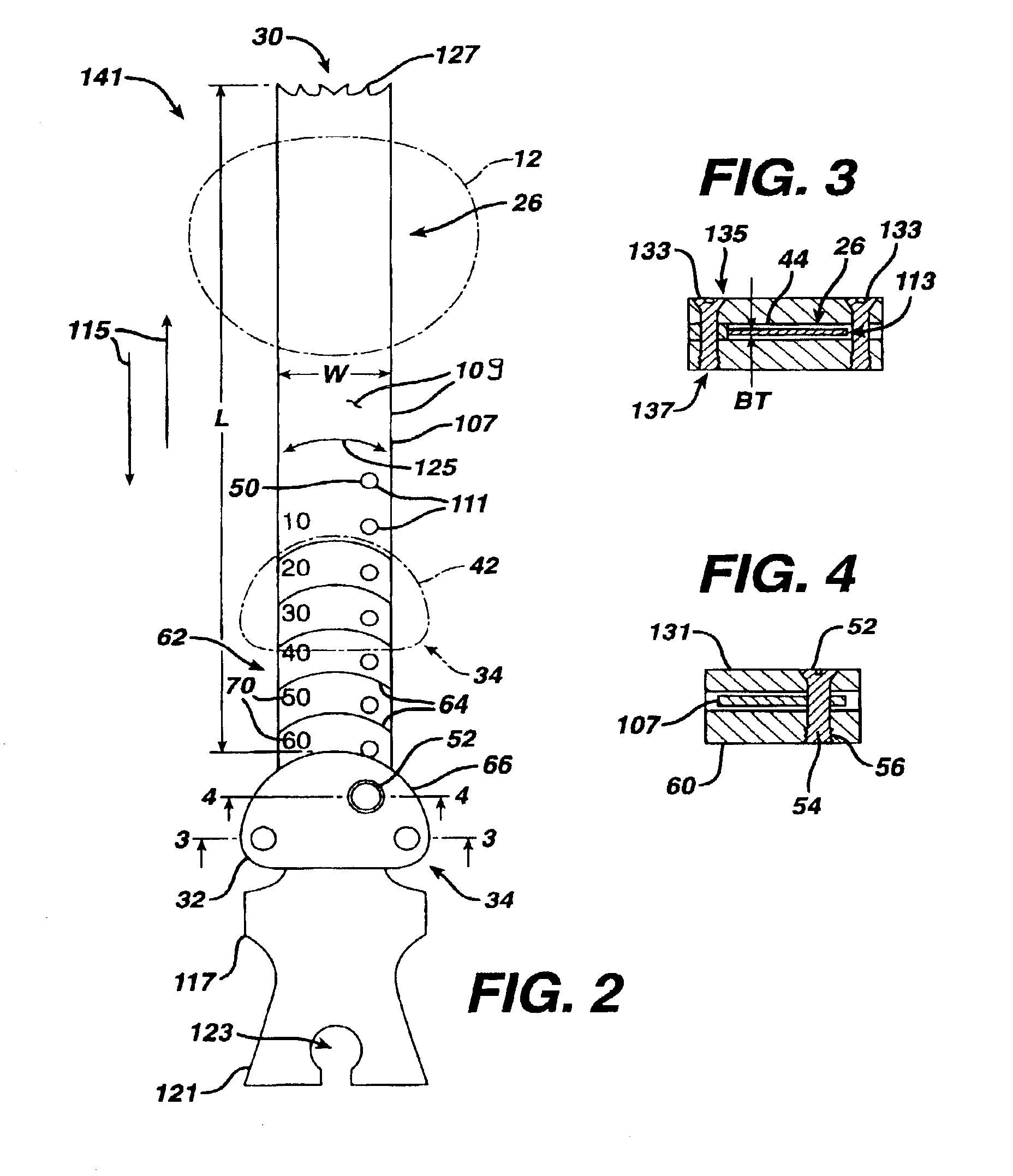
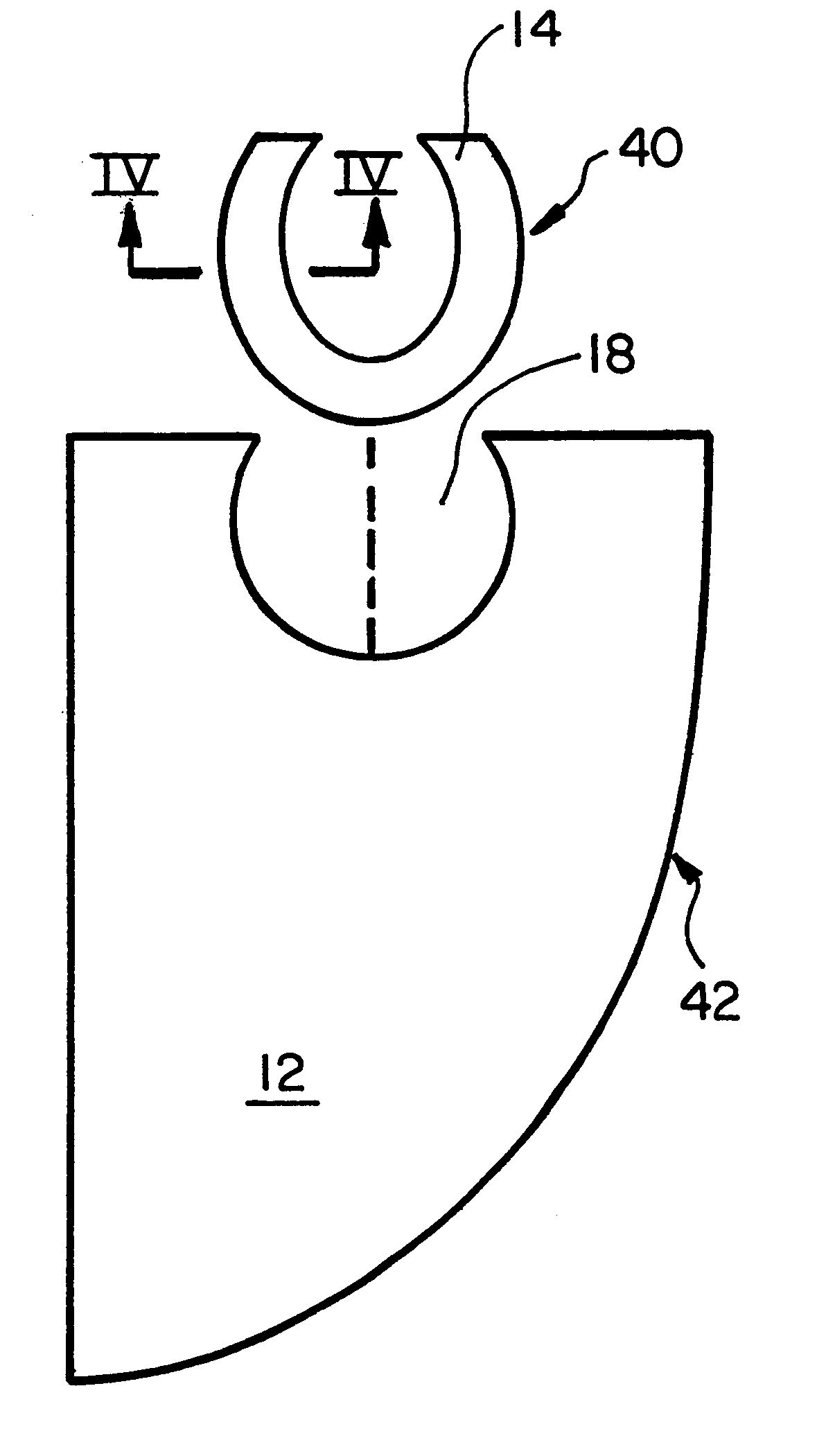
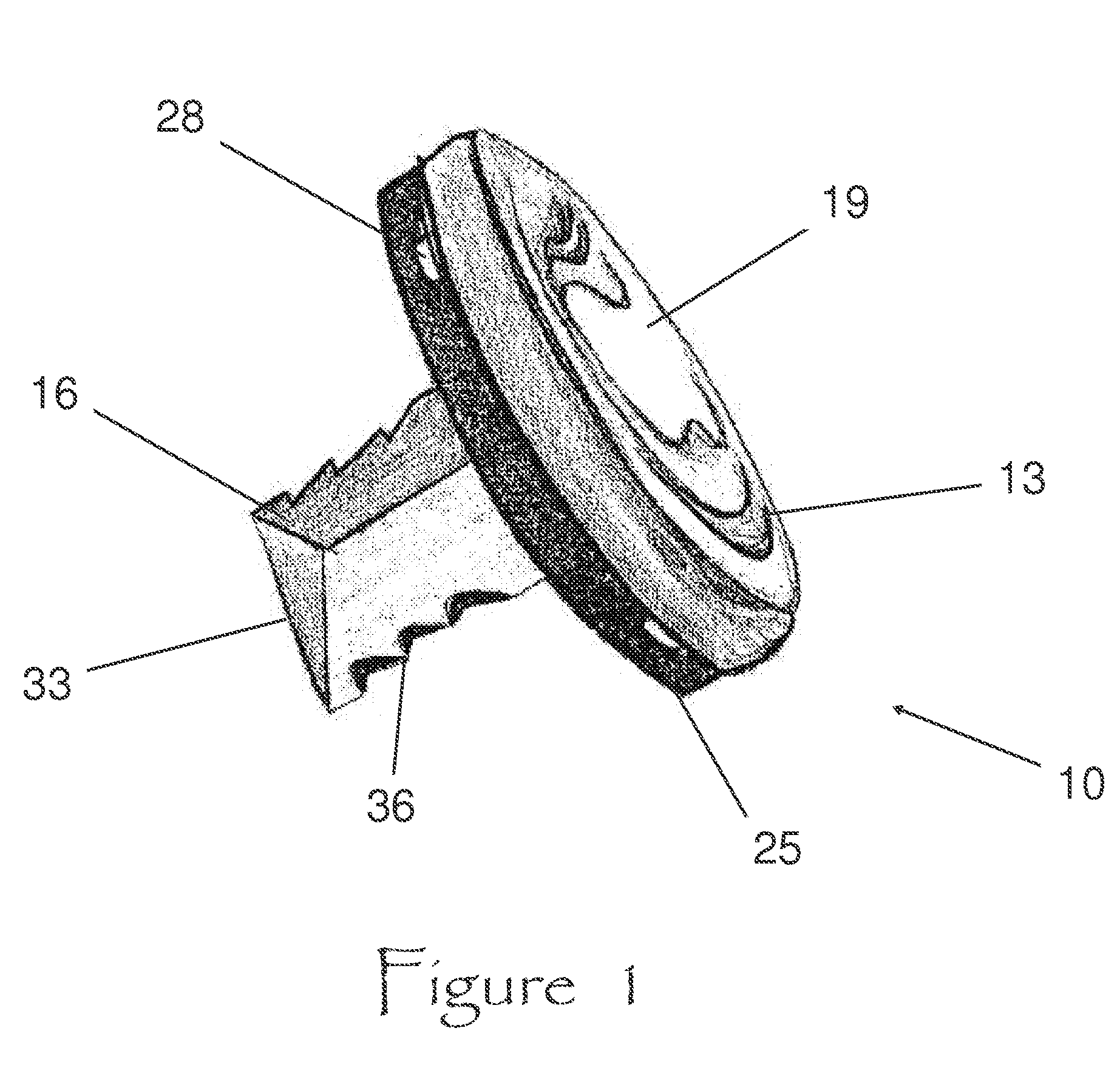
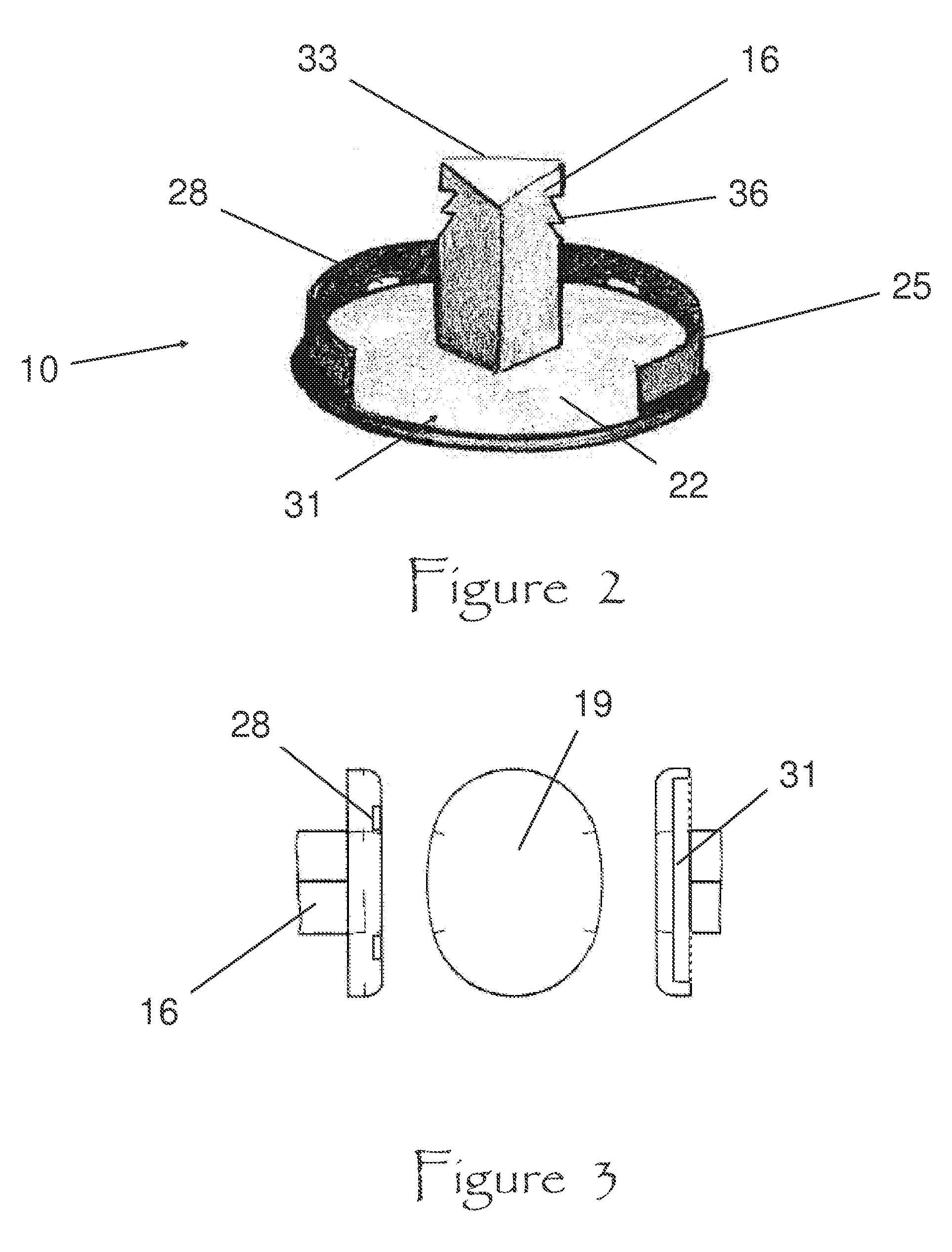
Blade for resection of bone for prosthesis implantation, blade stop and method
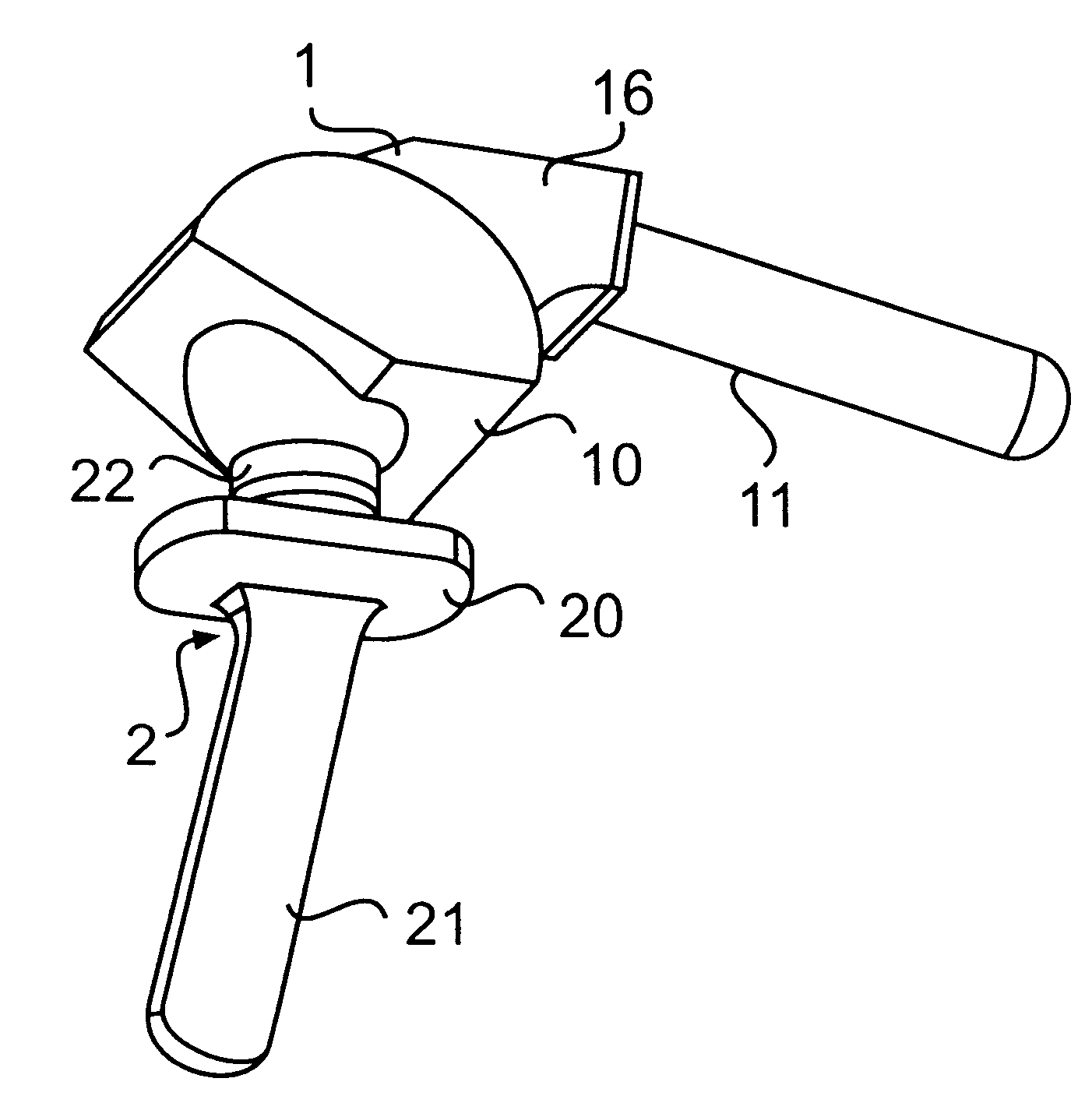
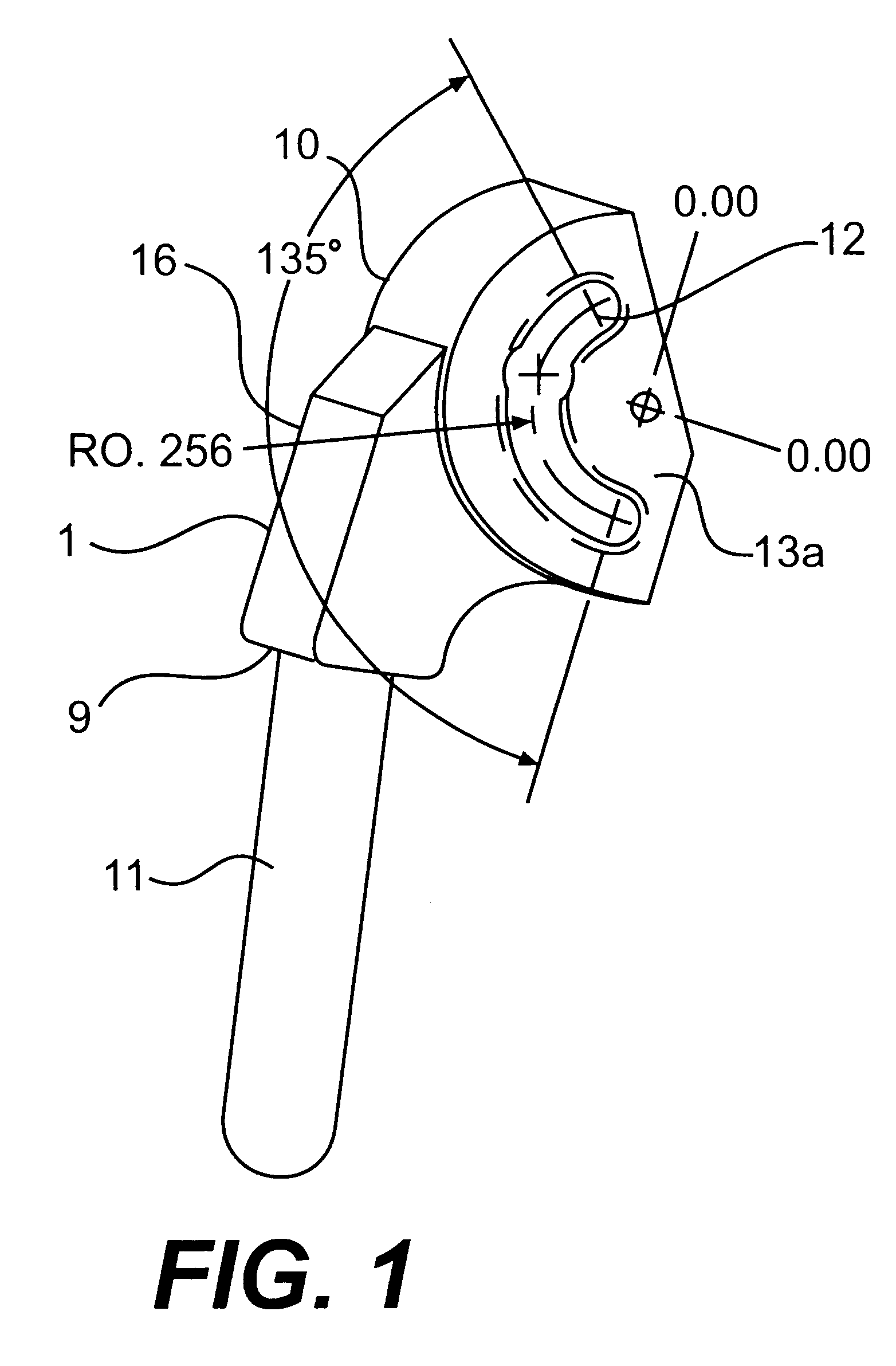
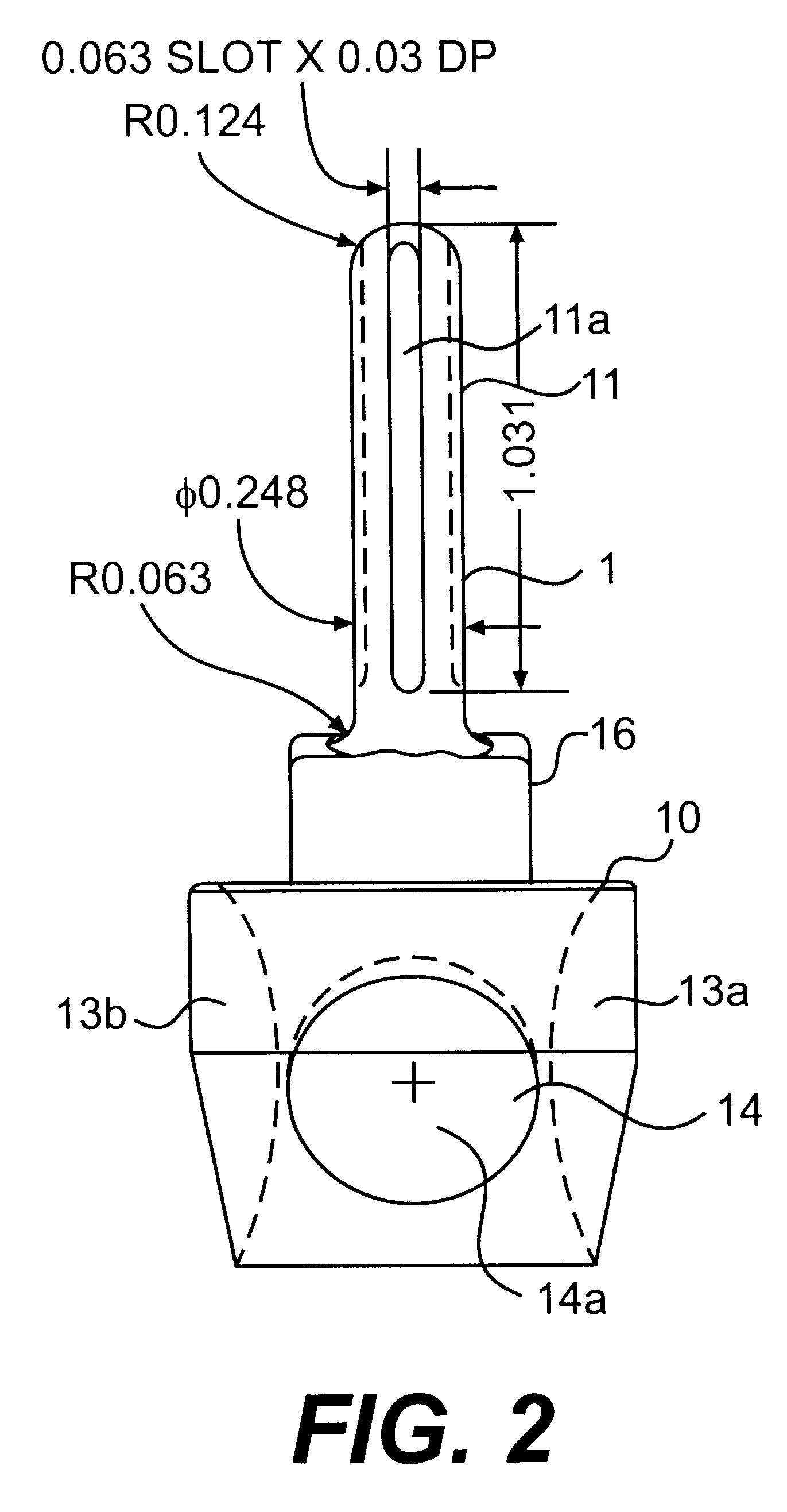
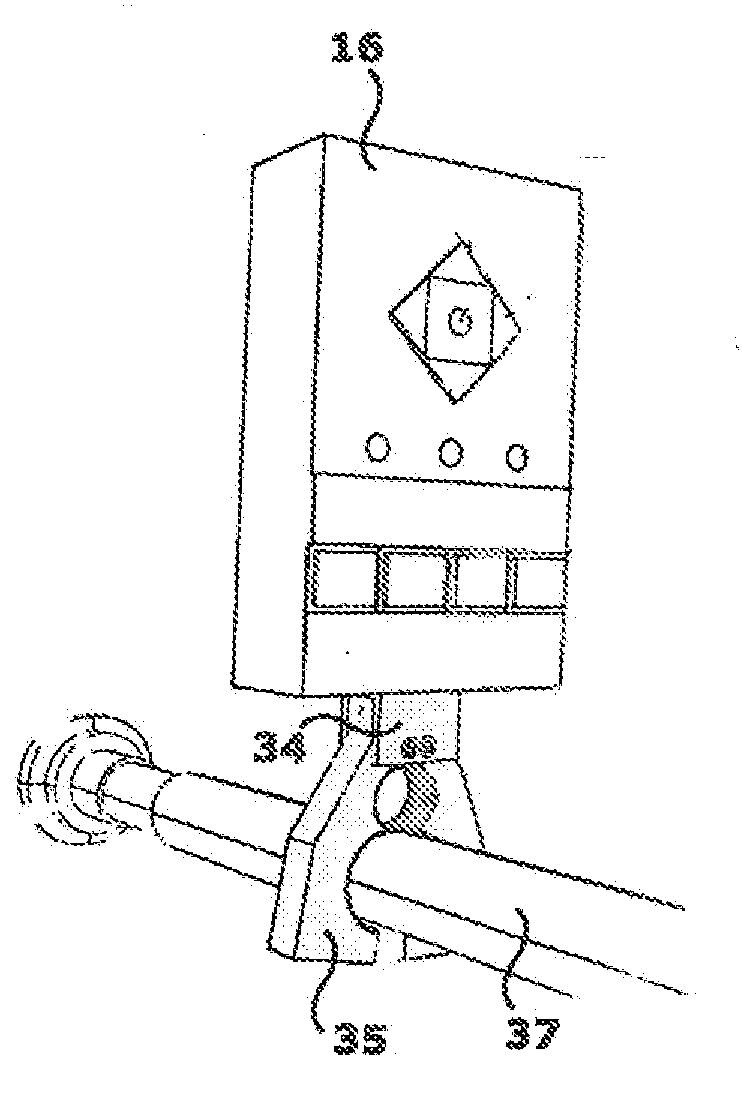
InactiveUS6875222B2Few instrumentsReduce in quantityMetal sawing devicesMetal sawing accessoriesProsthesis ImplantationSacroiliac joint
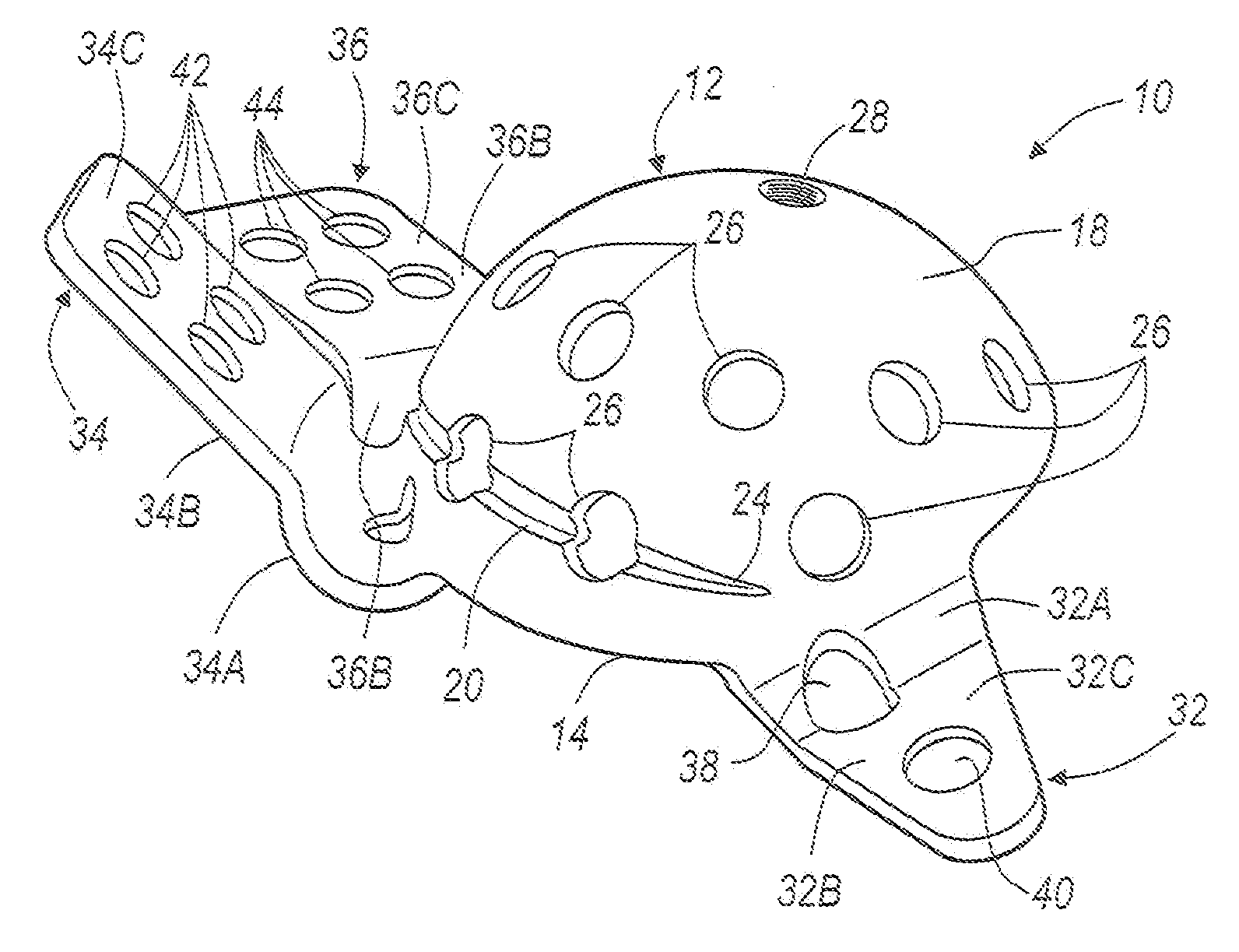
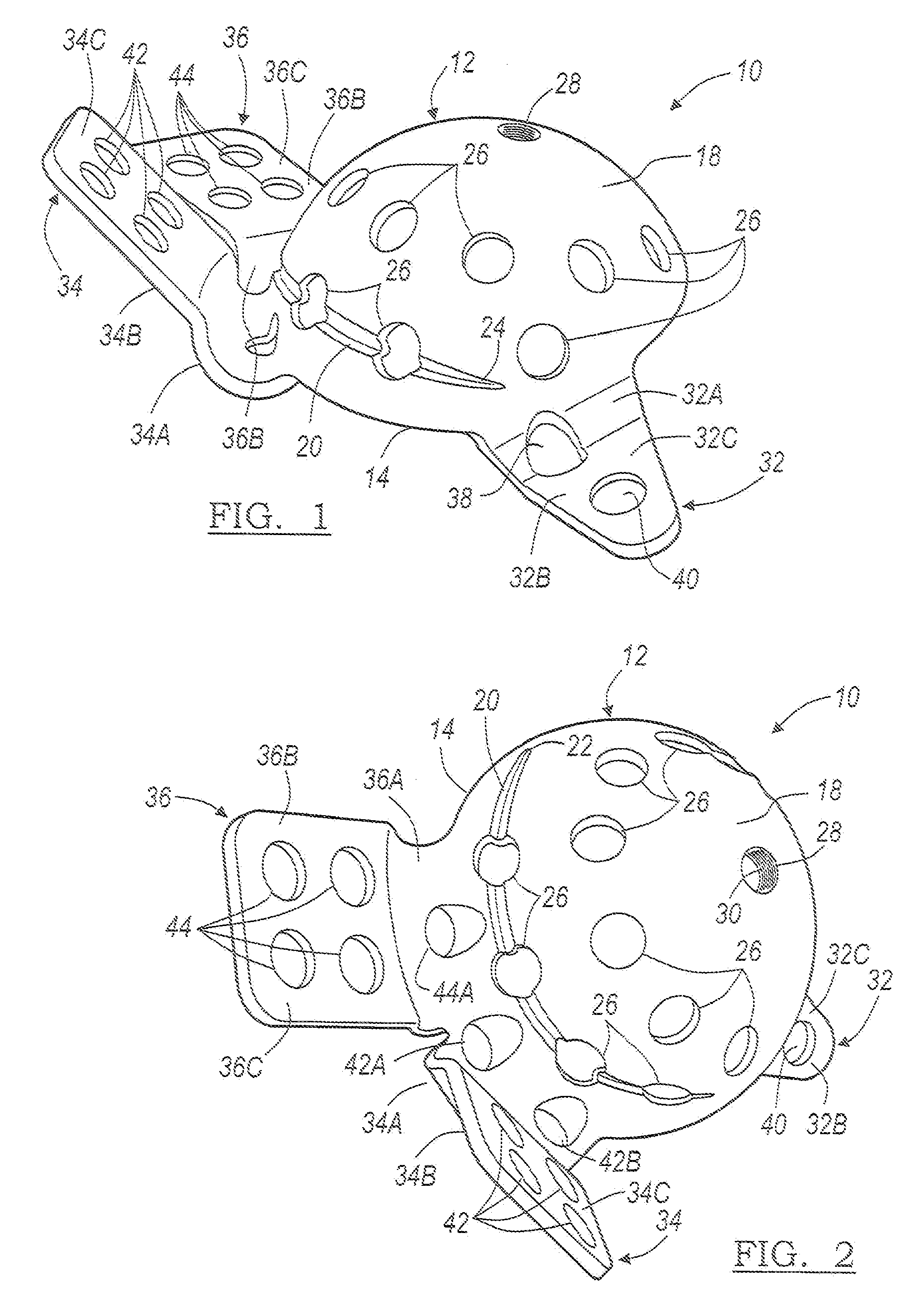
A kit (10) for resection of bone (12) for use in implantation of a joint prosthesis (14) is provided. The kit (10) includes a guide (16), a tool (26) and a stop (32). The guide (16) defines an opening (20) through the guide (16). The guide (16) is in cooperation with the bone (12). The tool (26) may be constrained within the opening (20) of the guide (16). The tool (26) includes a cutting edge (30) for resection of bone (12). The stop (32) cooperates with the guide (16) and the tool (26) to limit the movement of the tool (26) within the guide (16) so that the position of the cutting edge (30) with respect to the bone (12)m may be controlled. The stop (32) includes a plurality of positions (34) with respect to the tool (26) and the guide (16).
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
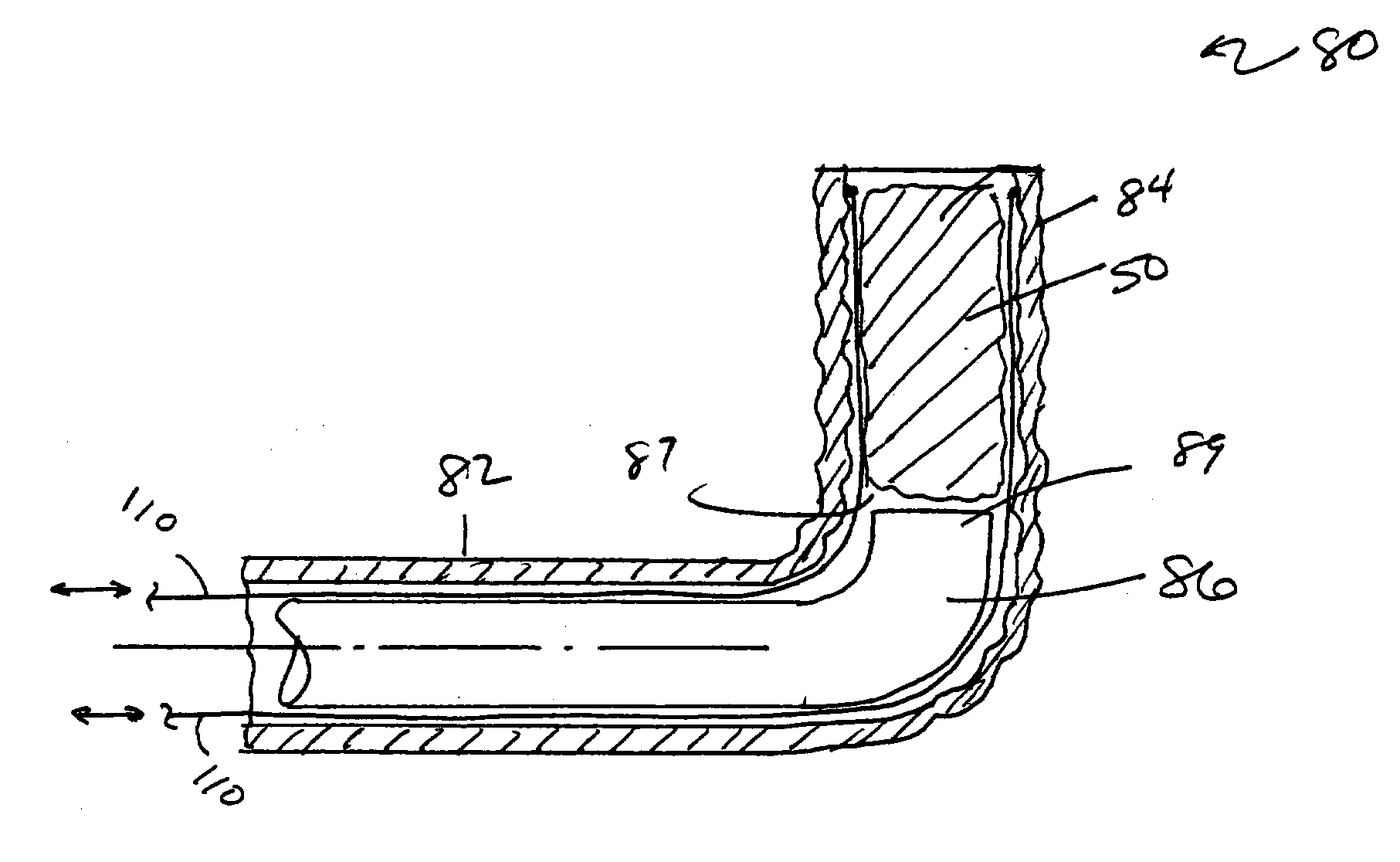
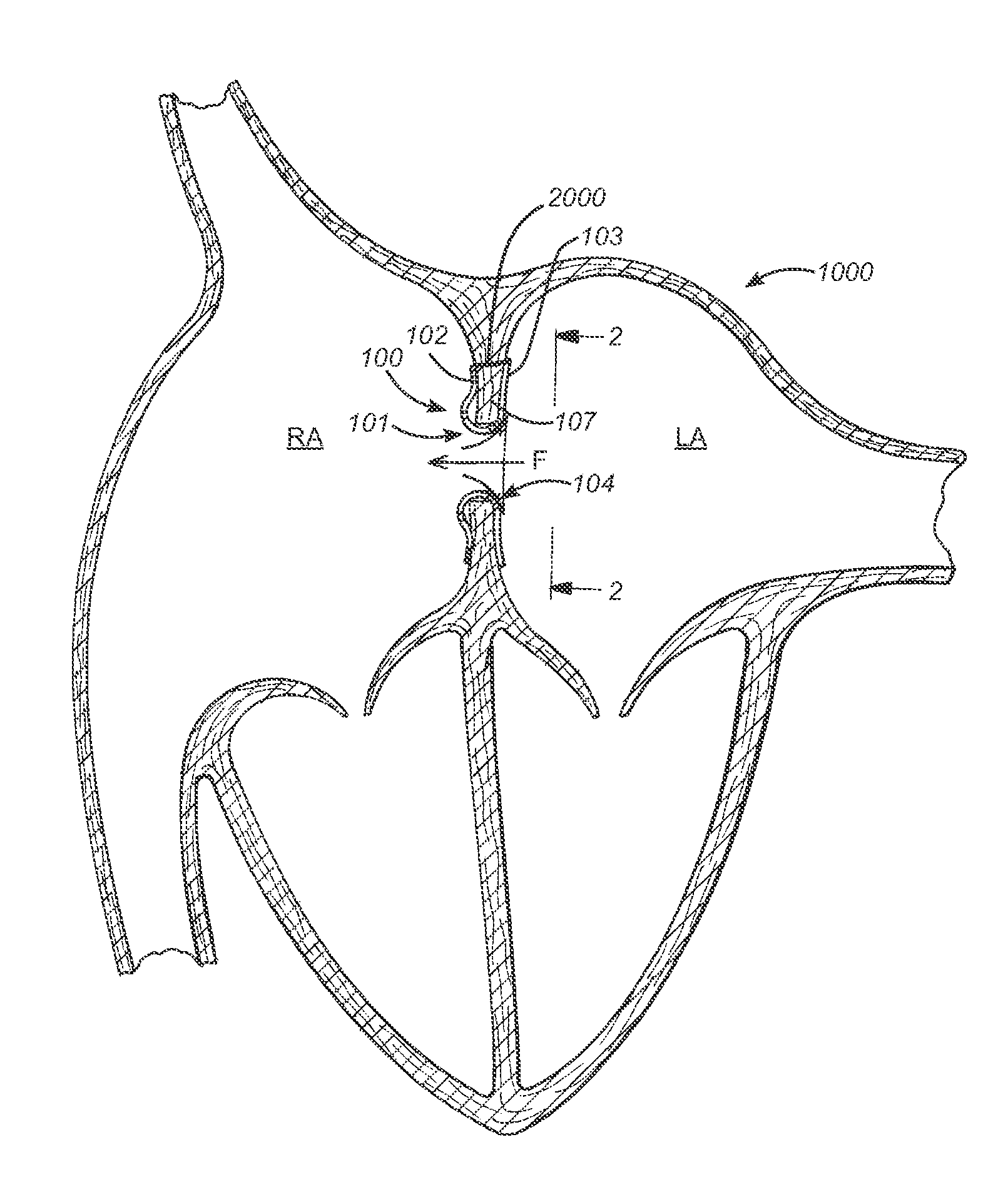
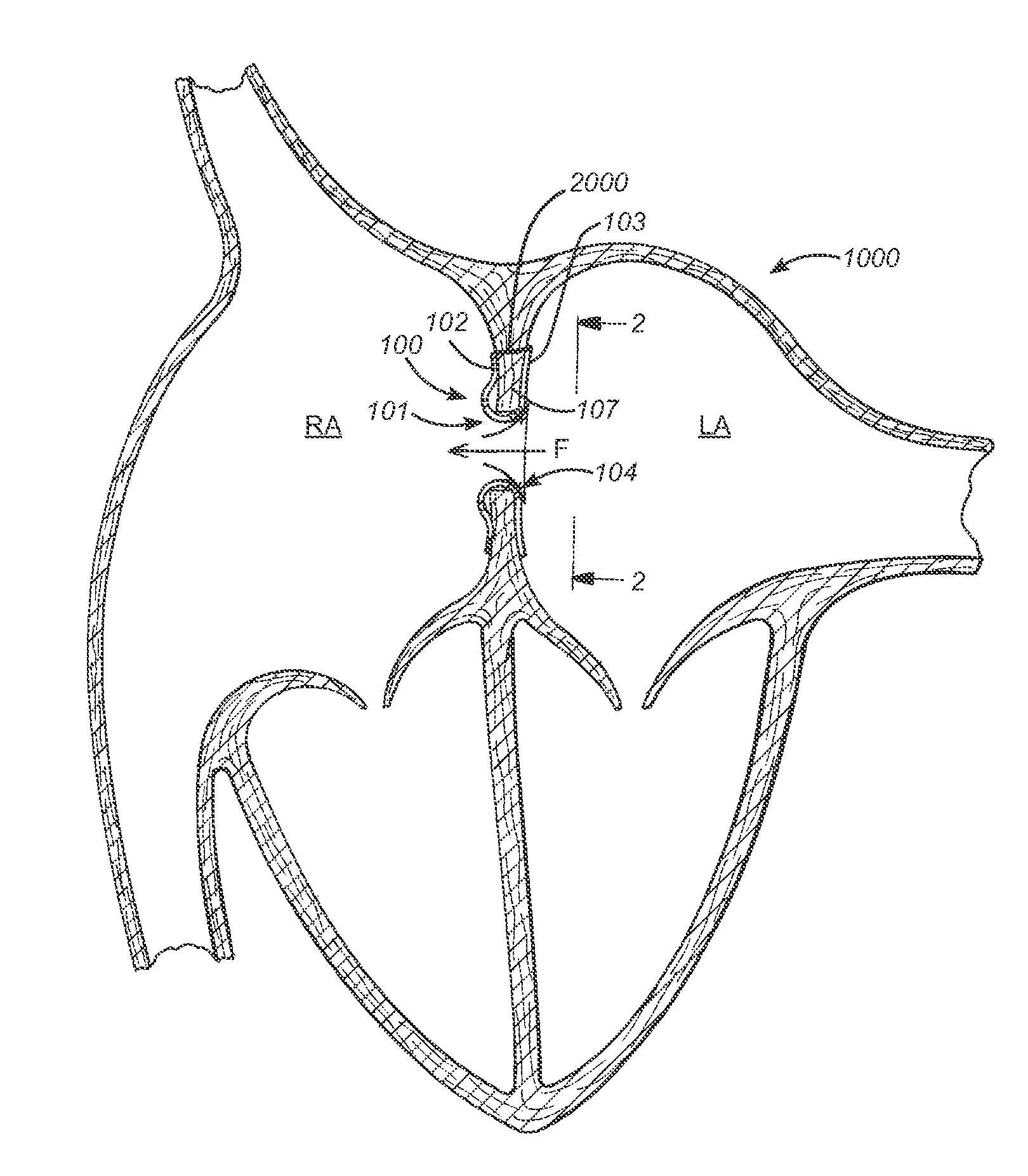
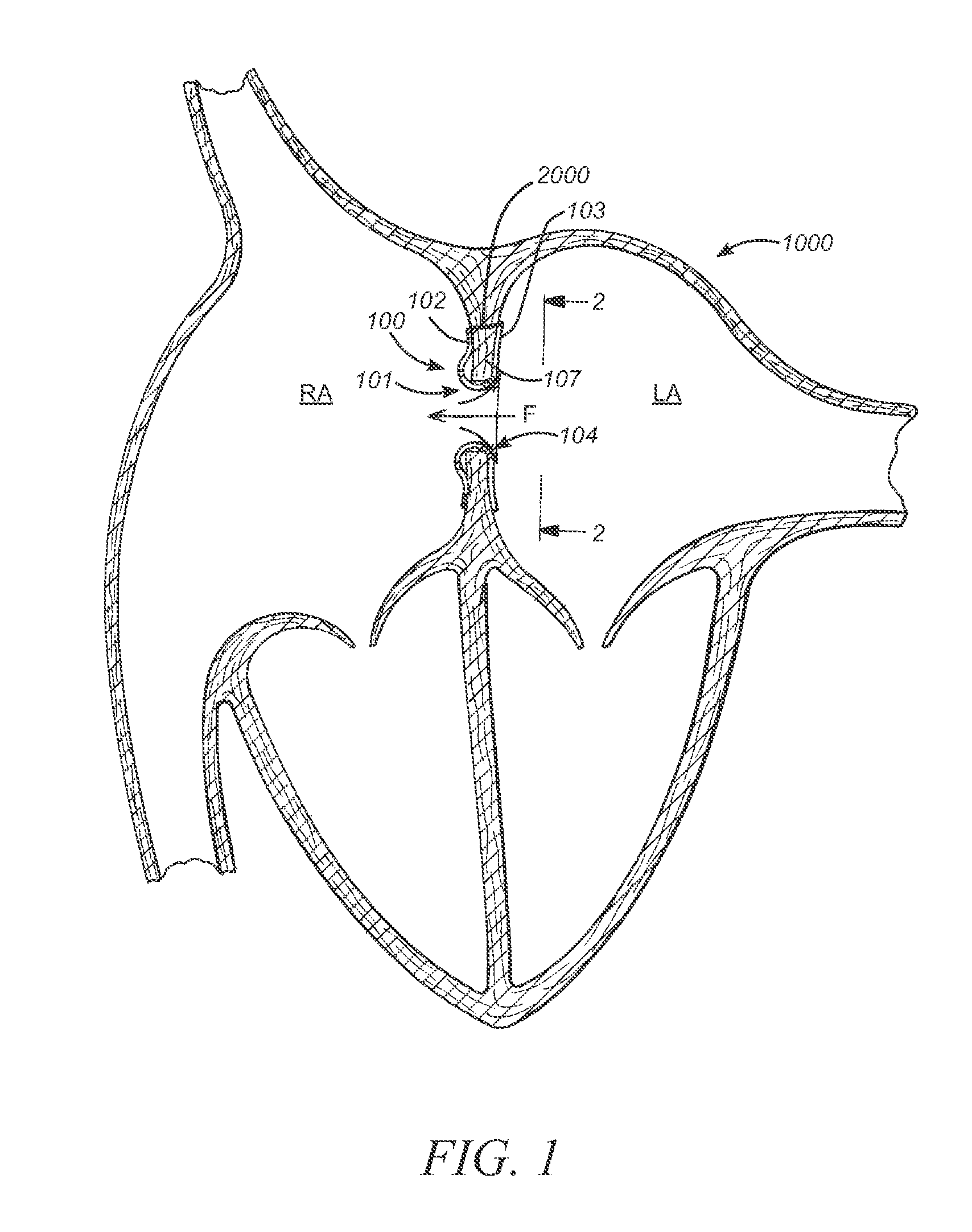
Prosthesis for reducing intra-cardiac pressure having an embolic filter
ActiveUS20120053686A1Reducing pressure necrosisImprove radiopacityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsHeart valvesPatients symptomsProsthesis
The present disclosure relates to devices and methods for implanting a prosthesis into a heart of a mammal, such as a person. The disclosure includes a prosthesis that acts as a pressure vent between the left and right atria of the heart. The intracardiac pressure vents disclosed allow sufficient flow from the left atrium to the right atrium to relieve elevated left atrial pressure and resulting patient symptoms. The devices also limit the amount of flow from the right atrium to the left atrium to minimize the potential for thrombi or other embolic material from entering arterial circulation.
Owner:CORVIA MEDICAL
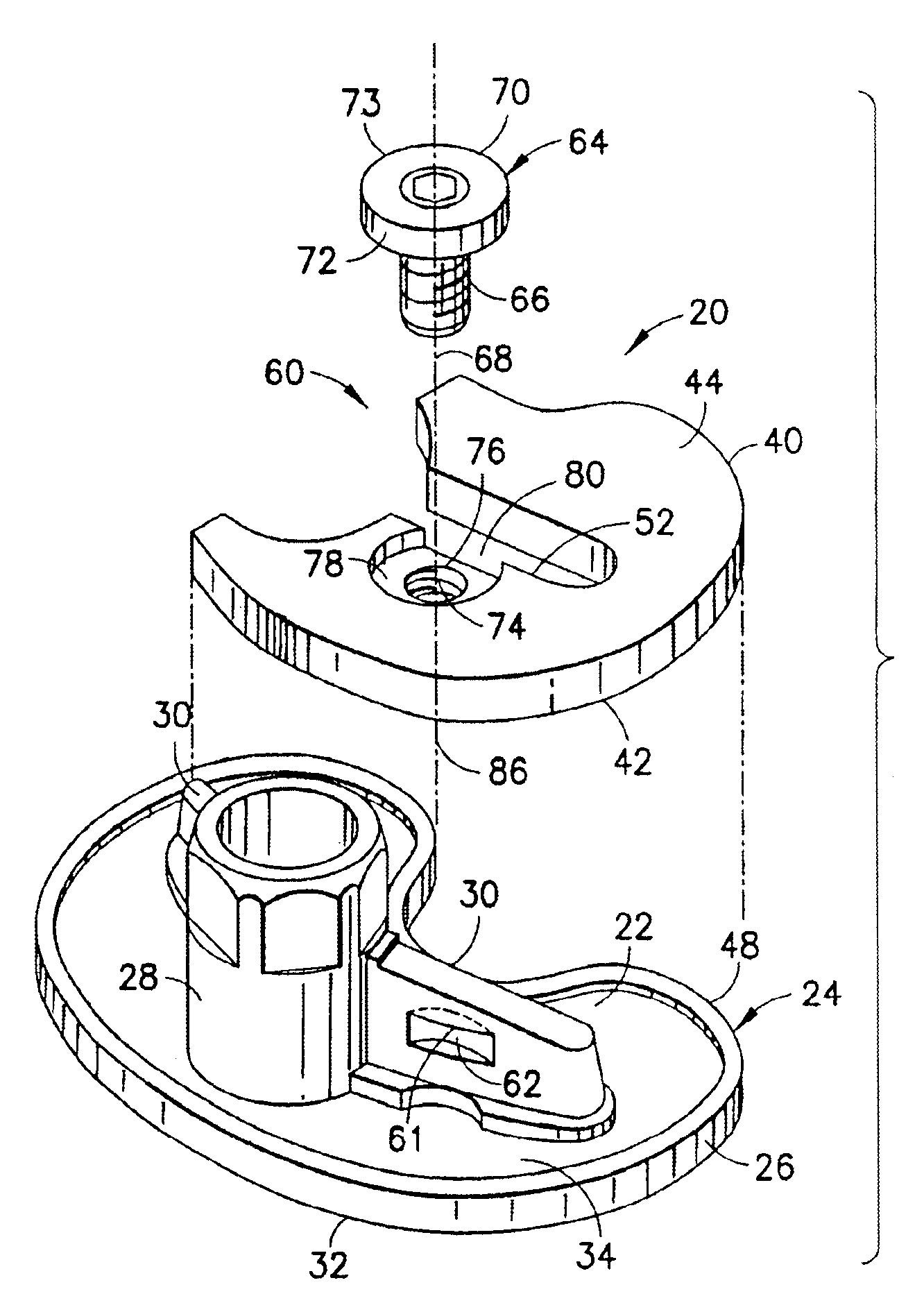
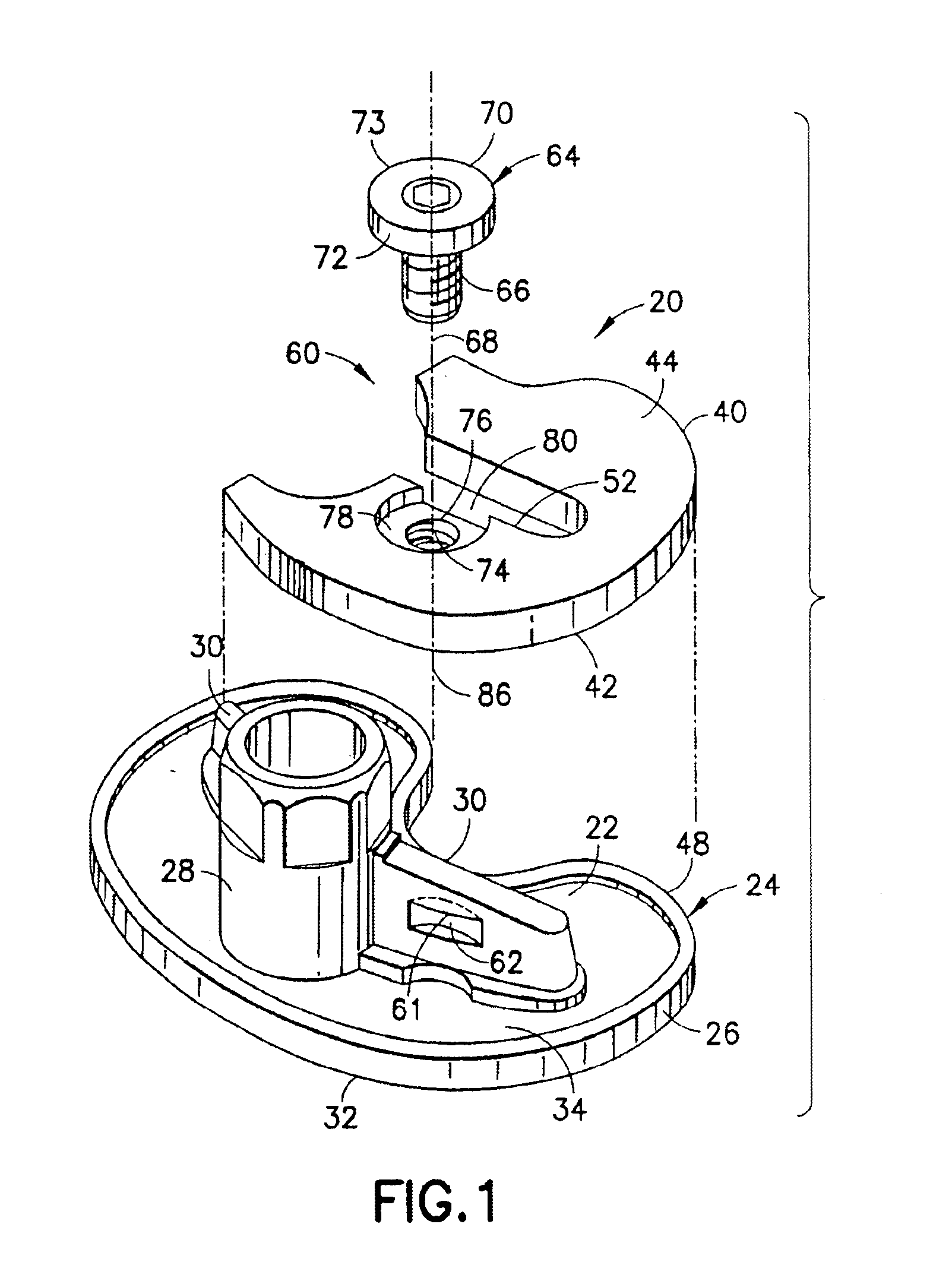
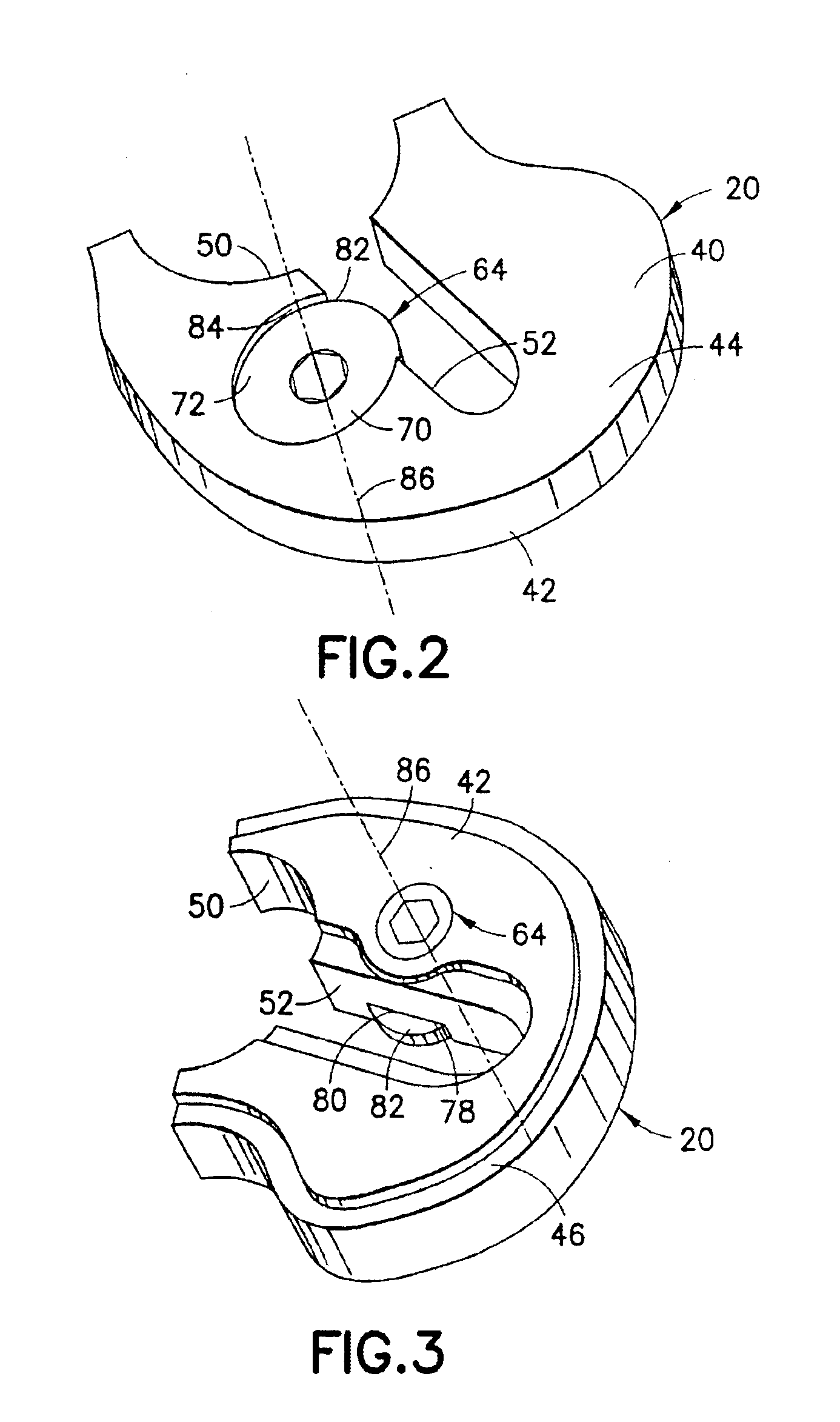
Securing an augment to a prosthetic implant component
InactiveUS6896702B2Improve securityEasy selectionJoint implantsKnee jointsTibiaProsthesis Implantation
A selected augment, shown as a tibial augment, is secured at an augmentation location on a prosthetic implant component, shown as a tibial implant component, by a securing element assembled with the body of the augment for displacement relative to the augment body to selectively engage an abutment located on a depending structure of the implant component, adjacent the augmentation location, so as to establish a securing force between the securing element and the depending structure for urging the augment against the implant component, and thereby secure the augment to the implant component at the augmentation location. In the tibial augment, a distal surface includes surface portions extending in anterior-posterior directions and oriented essentially normal to medial-lateral directions.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Hernia prosthesis
A prosthesis and a method for repairing a tissue or muscle wall defect, such as an inguinal hernia, near a cord-like structure, such as the spermatic cord. The prosthesis comprises a layer of repair fabric having a cord opening therethrough that is adapted to receive the cord-like structure when the prosthesis is implanted at the repair site. The prosthesis also includes a cord protector that is attachable to the repair fabric at the opening to isolate the cord-like structure from the fabric in proximity to the opening. The repair fabric may be formed from a material which is susceptible to the formation of adhesions with sensitive tissue and organs. The cord protector may be formed from material which inhibits the formation of adhesions with sensitive tissue and organs. The cord protector may overlie a portion of at least one of the first and second surfaces of the repair fabric. The cord protector may extend substantially farther away from the opening edge on one of the first and second surfaces than on the other of the first and second surfaces. The cord protector may be configured as an insert that is separate from and attachable to the repair fabric. Alternatively, the cord protector may be integral with the repair fabric to form a composite prosthesis.
Owner:CR BARD INC +1
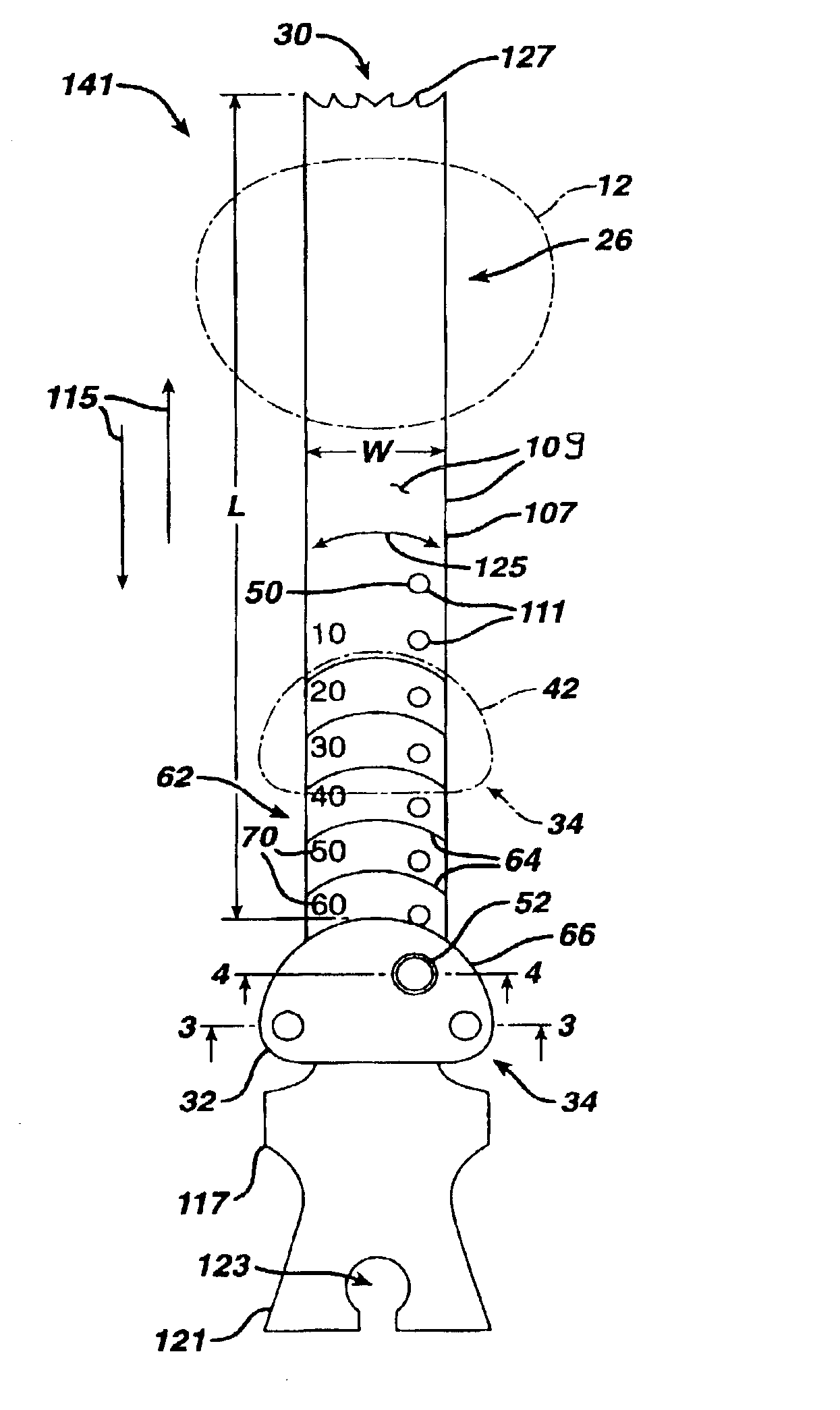
Prosthetic implant, trial and associated method
InactiveUS7338498B2Shorten the timeLow costJoint implantsFemoral headsJoint arthroplastyProsthesis Implantation
A kit (100) for use in performing joint arthroplasty on a head of a long bone (4) is provided. The kit (100) includes a first trial (102) including a first trial articulating surface (106) and an opposed first trial mounting surface (108) having a first trial location feature (110). The kit (100) also includes a second trial (104) including a second trial articulating surface (112) and an opposed second trial mounting surface (114) having a second trial location feature (116). The first trial articulating surface (106) and the second trial articulating surface (112) have different geometries and the first trial location feature (110) and the second trial location feature (116) have substantially identical geometries whereby different trials may be used with a common location feature.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
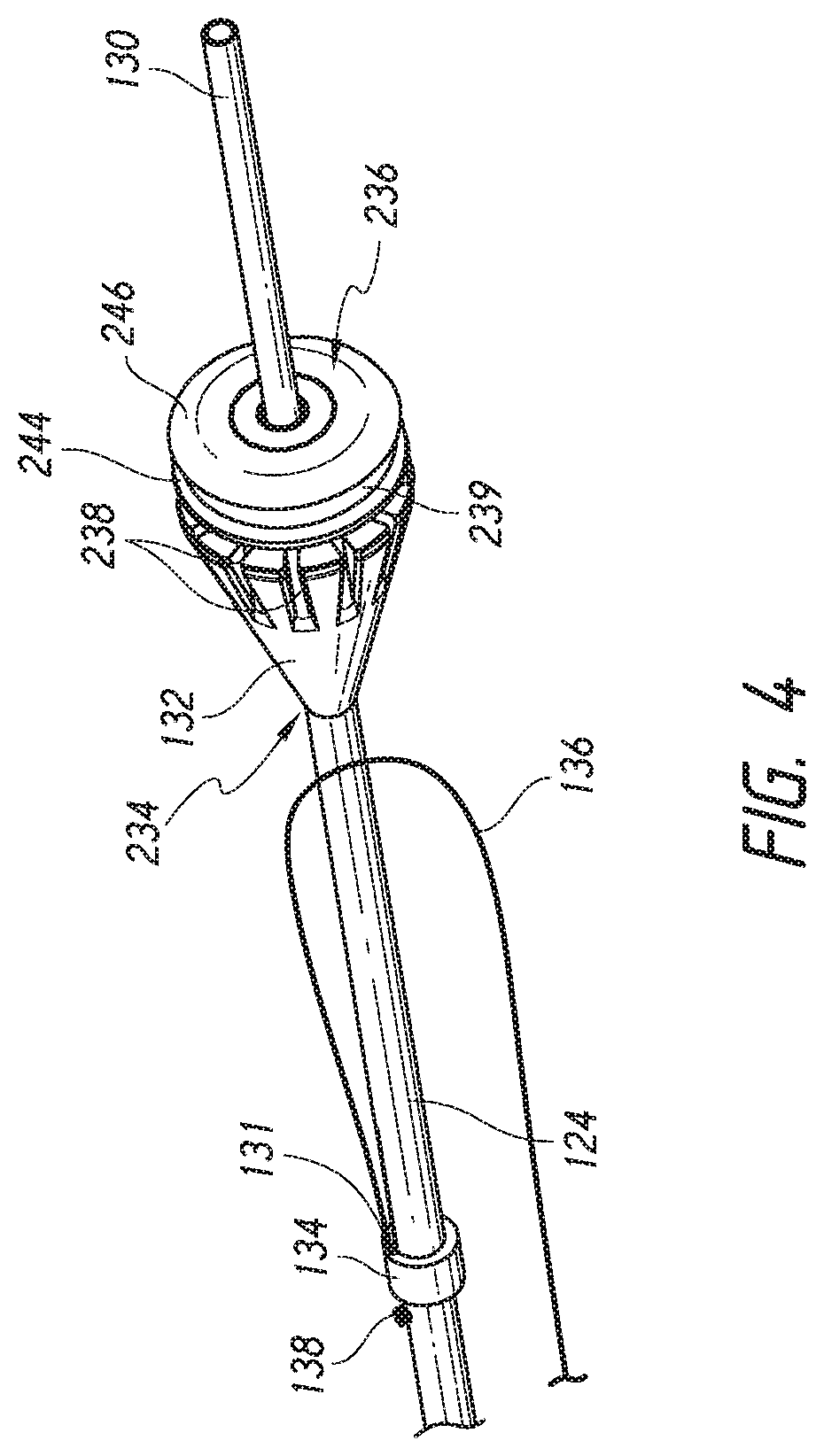
Devices, systems, and methods for prosthesis delivery and implantation, including the use of a fastener tool
Devices, systems, and methods for implanting radially expandable prostheses in the body lumens rely on tacking or anchoring the prostheses with separately introduced fasteners. The prostheses may be self-expanding or balloon expandable, and may include a single lumen or more than one lumen. After initial placement, a fastener applier system is introduced within the expanded prostheses to deploy a plurality of fasteners to at least one prosthesis end. The fasteners are usually helical fasteners which are releasably restrained on the fastener driver, and are delivered by rotation of the fastener driver. The fasteners may be applied singly, typically in circumferentially spaced-apart patterns about the interior of at least one end of the prosthesis. A lumen extension or lumens may be coupled to the prosthesis to extend the reach of the prosthesis within the implantation site. Fasteners may also be applied to the lumen extensions.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
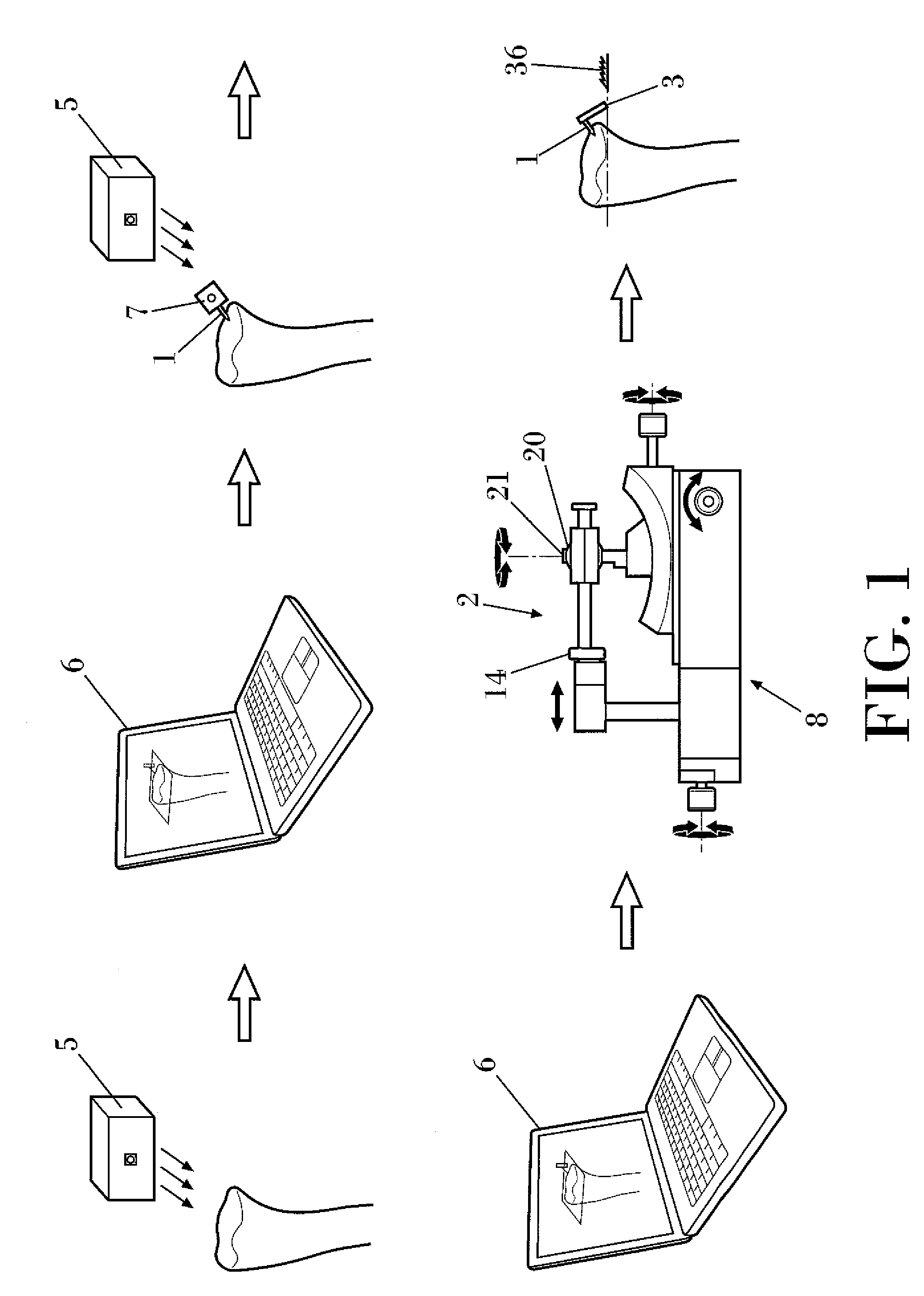
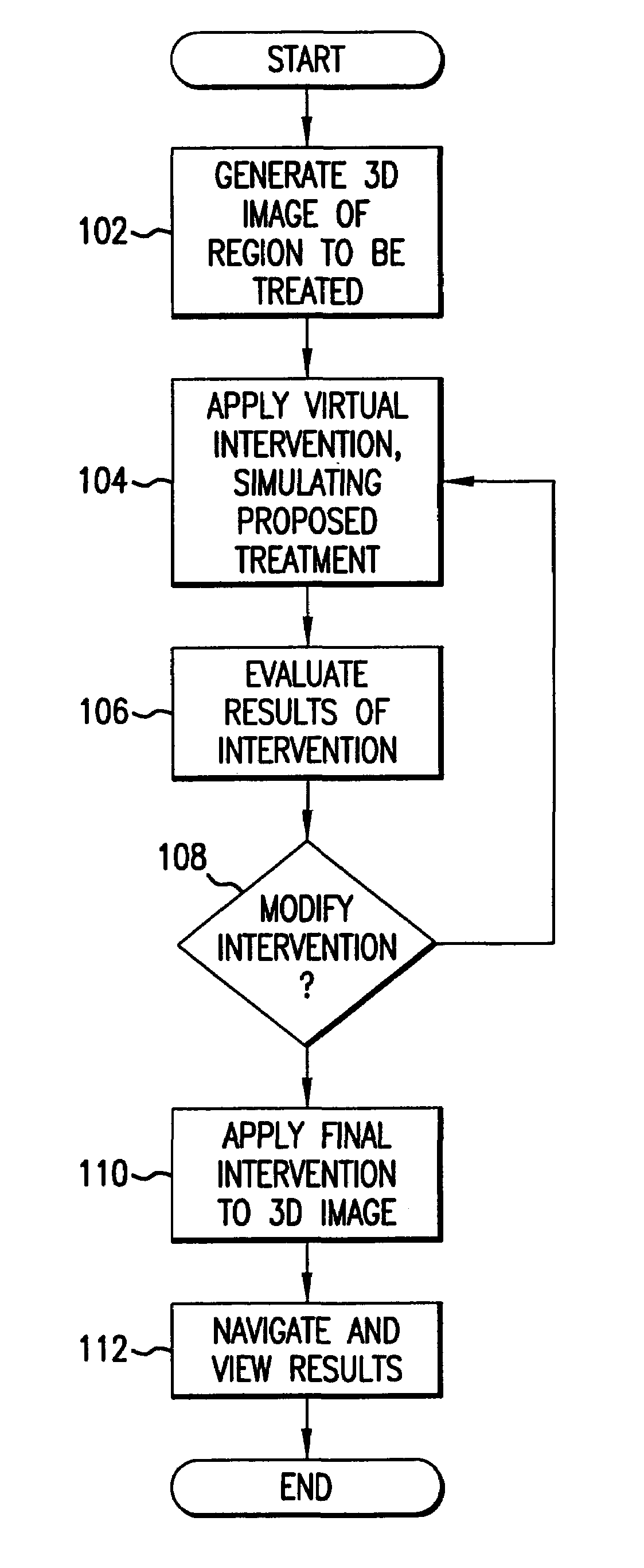
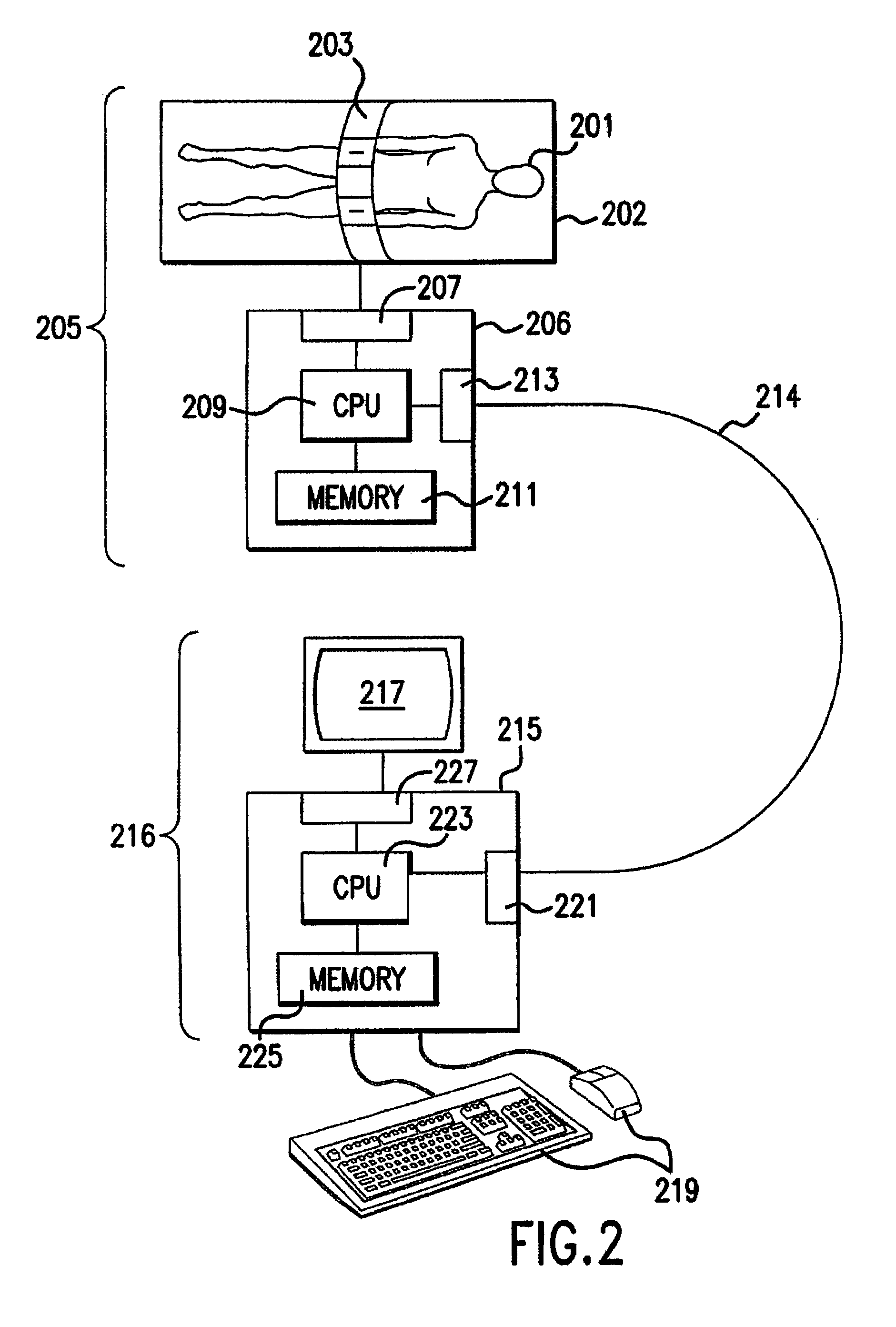
Computer aided treatment planning
InactiveUS7630750B2High riskManipulation of the 3D image can be costlyCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringAnatomical structures3d image
A method of computer aided treatment planning is performed by generating and manipulating a three dimensional (3D) image of a region which includes at least one anatomical structure for which treatment, such as surgery, biopsy, tissue component analysis, prosthesis implantation, radiation, chemotherapy and the like, is contemplated. A virtual intervention, which simulates at least a portion of the contemplated treatment, is performed in the 3D image. The user can then determine the effect of the intervention and interactively modify the intervention for improved treatment results. Preferably, a warning is automatically provided if the intervention poses a risk of detrimental effect. The user can navigate through the contemplated region in the 3D image and assess the results. The treatment plans can be saved for comparison and post treatment evaluation.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
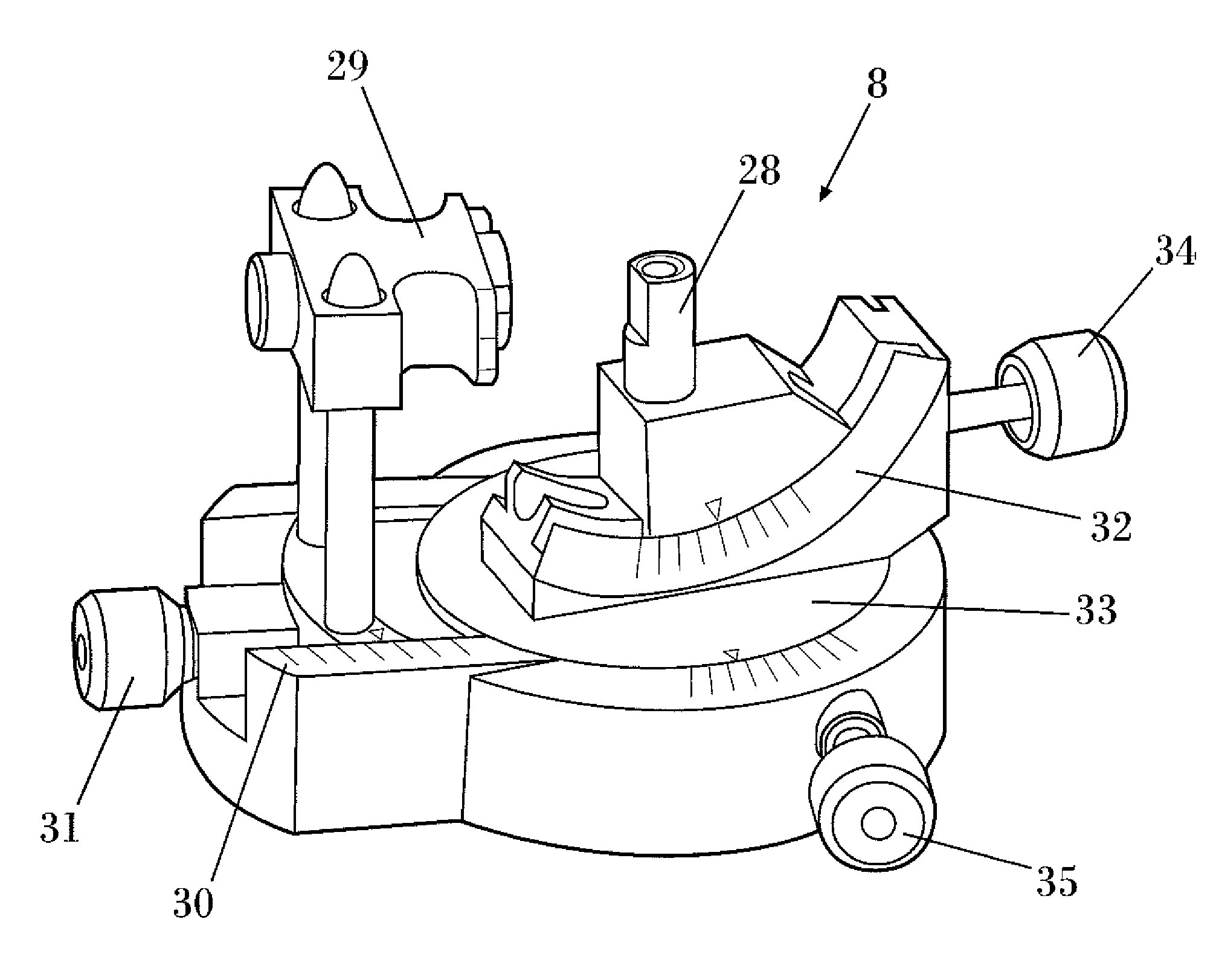
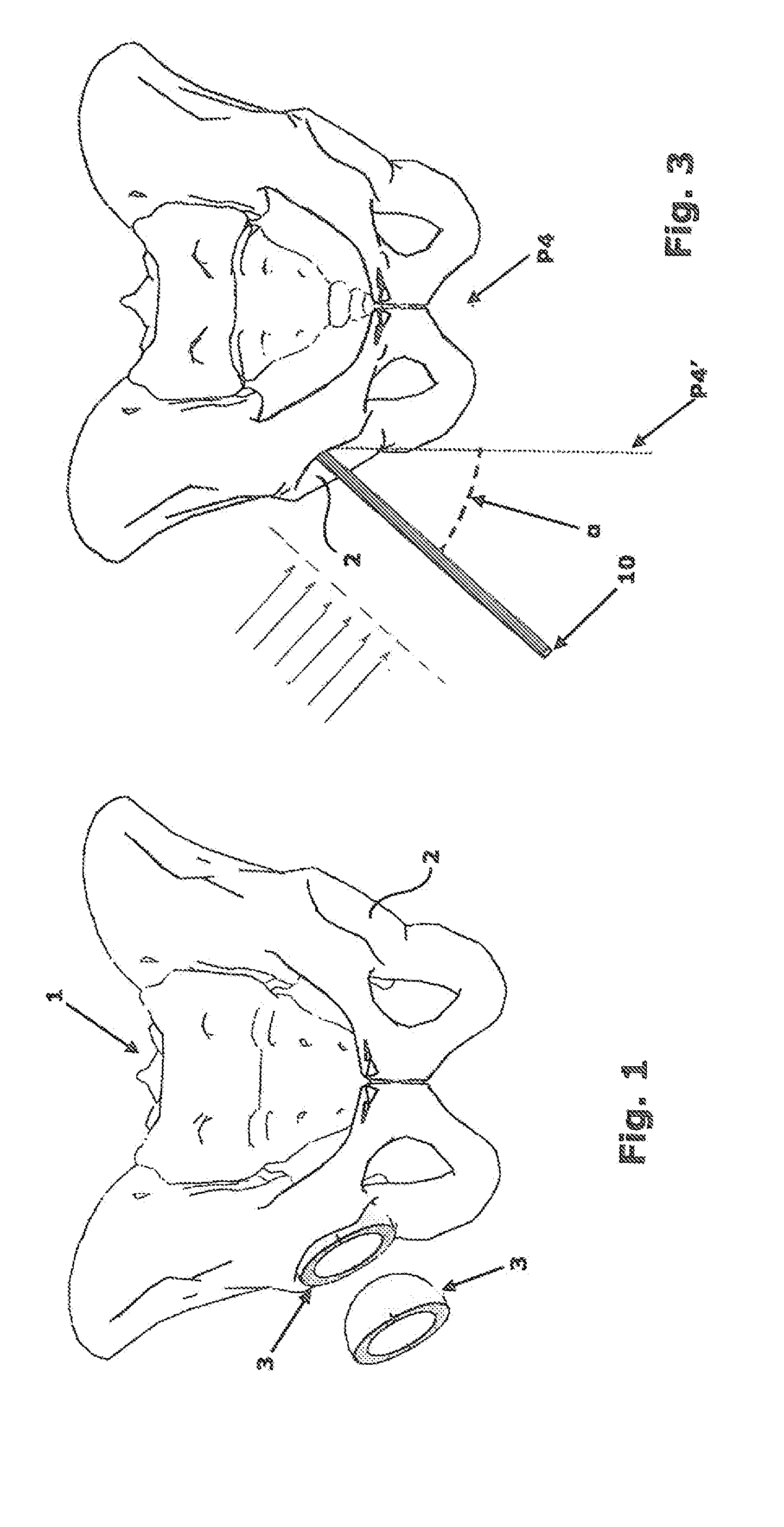
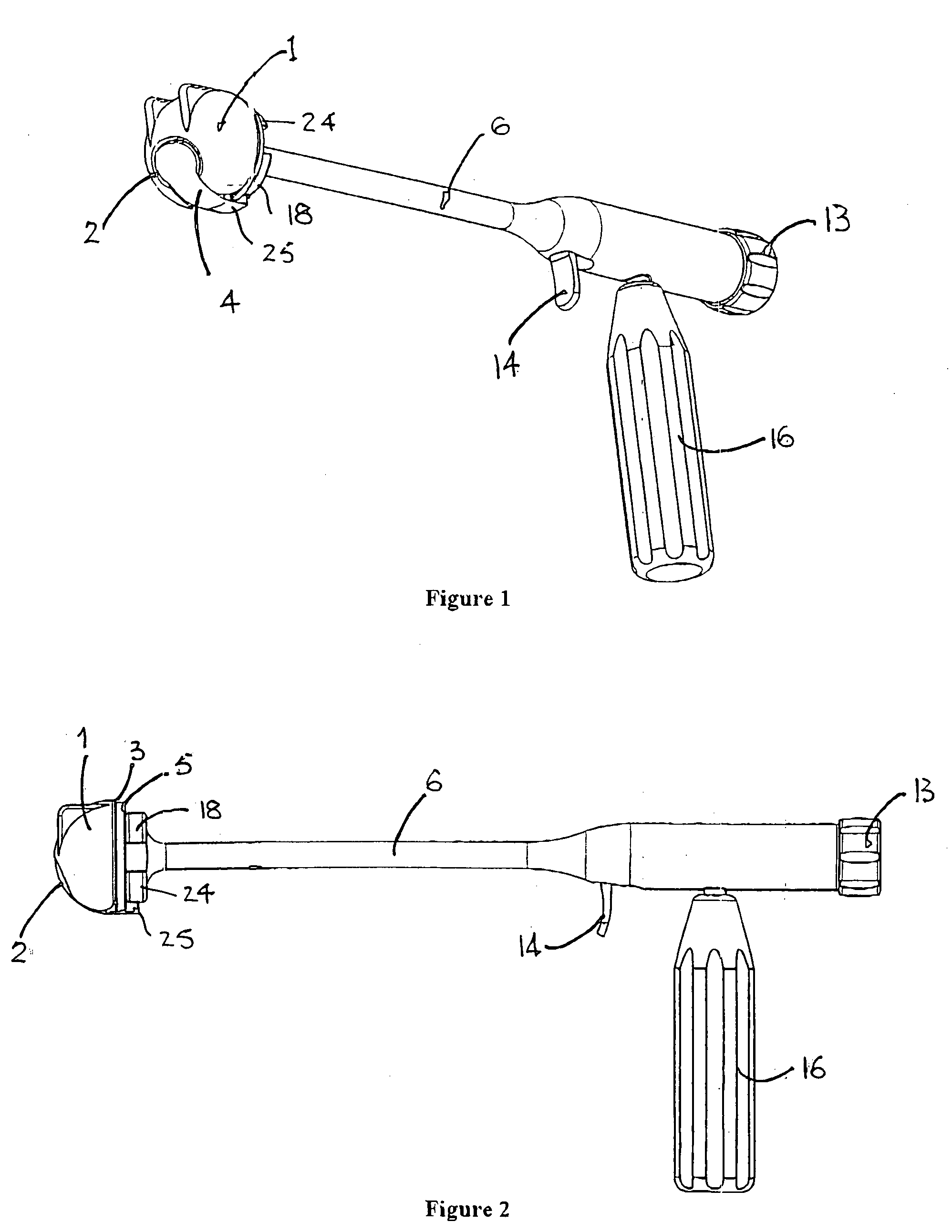
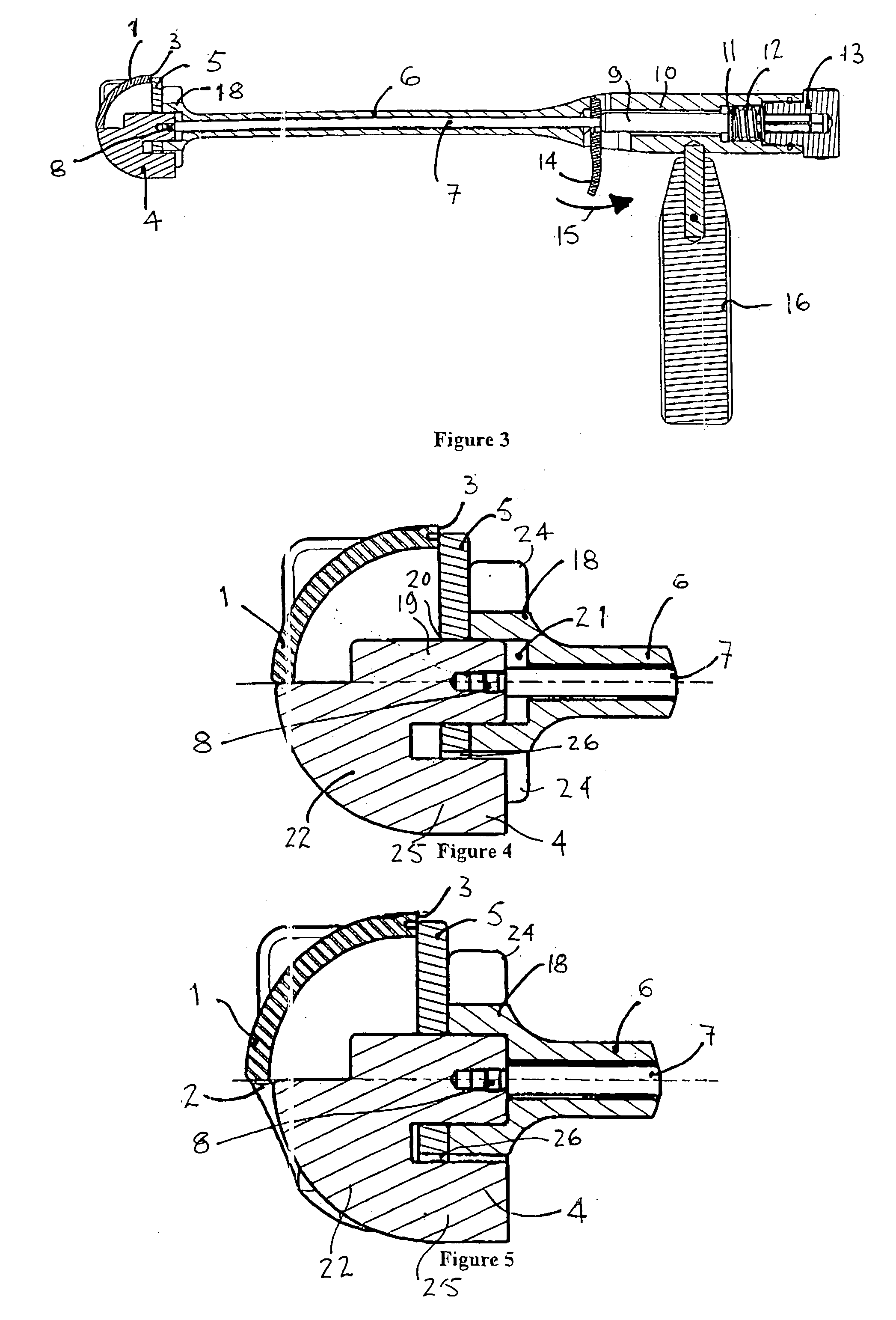
Apparatus for the orientation and positioning of surgical instruments and of implantation prosthesis in a bone seat
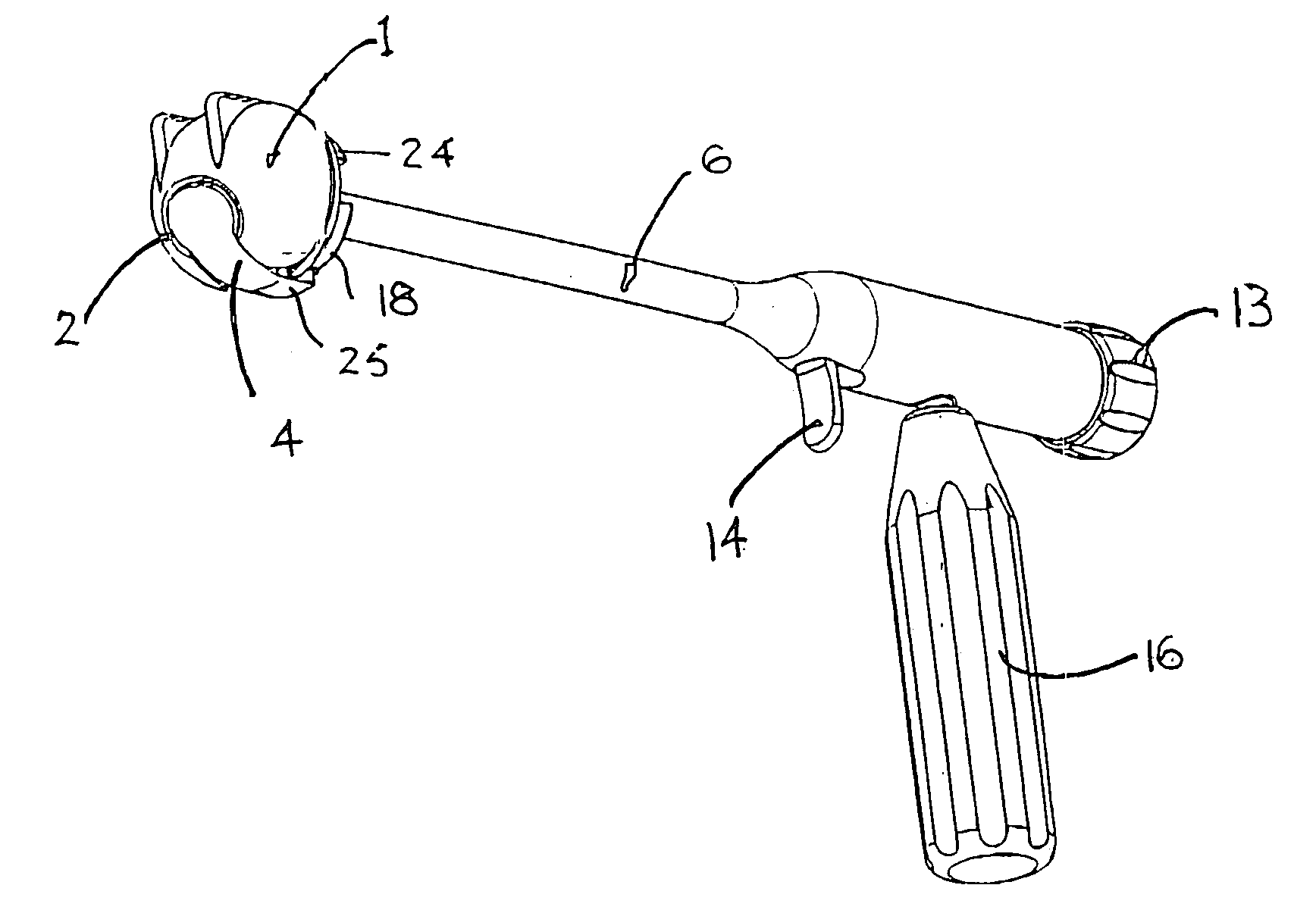
Apparatus for the fast angular orientation of a surgical instrument with respect to an implantation seat of a prosthesis in a patient's bone, of the type comprising a moving sensor, which may be associated with the surgical instrument, and a fixes sensor, which may be integrally fastened to the bone during a surgical operation, the moving sensor and the fixed sensor being provided with a position detection device and with a device for signaling of the detected position to a central memory and processing unit. The central memory and processing unit comprises calibration device which detect the position of the moving sensor when it is associated with a line passing through two known points of the bone and, simultaneously, they detect the position of the fixed sensor when it is integrally fastened to the bone, and they record such position as initial work position.
Owner:DIAL MEDICALI
Endovascular prosthesis
InactiveUS20040098091A1Convenient lengthReduce occlusionStentsBlood vesselsProsthesis ImplantationEndovascular prosthesis
A endovascular prosthesis for implantation in a body passageway. The prosthesis comprises a tubular wall which is: (i) movable between a first longitudinal length and a second longitudinally length, and (ii) radially expandible for implantation of the prosthesis in the body passageway. In one embodiment, the tubular wall has a longitudinally length which is variable by an "accordian"-like action. In another embodiment, the tubular wall has a longitudinally length which is variable by an "telescoping"-like action. The longitudinal length of the tubular wall may be varied in vivo to optimize deployment of the endovascular prosthesis.
Owner:ERBEL RAIMUND +3
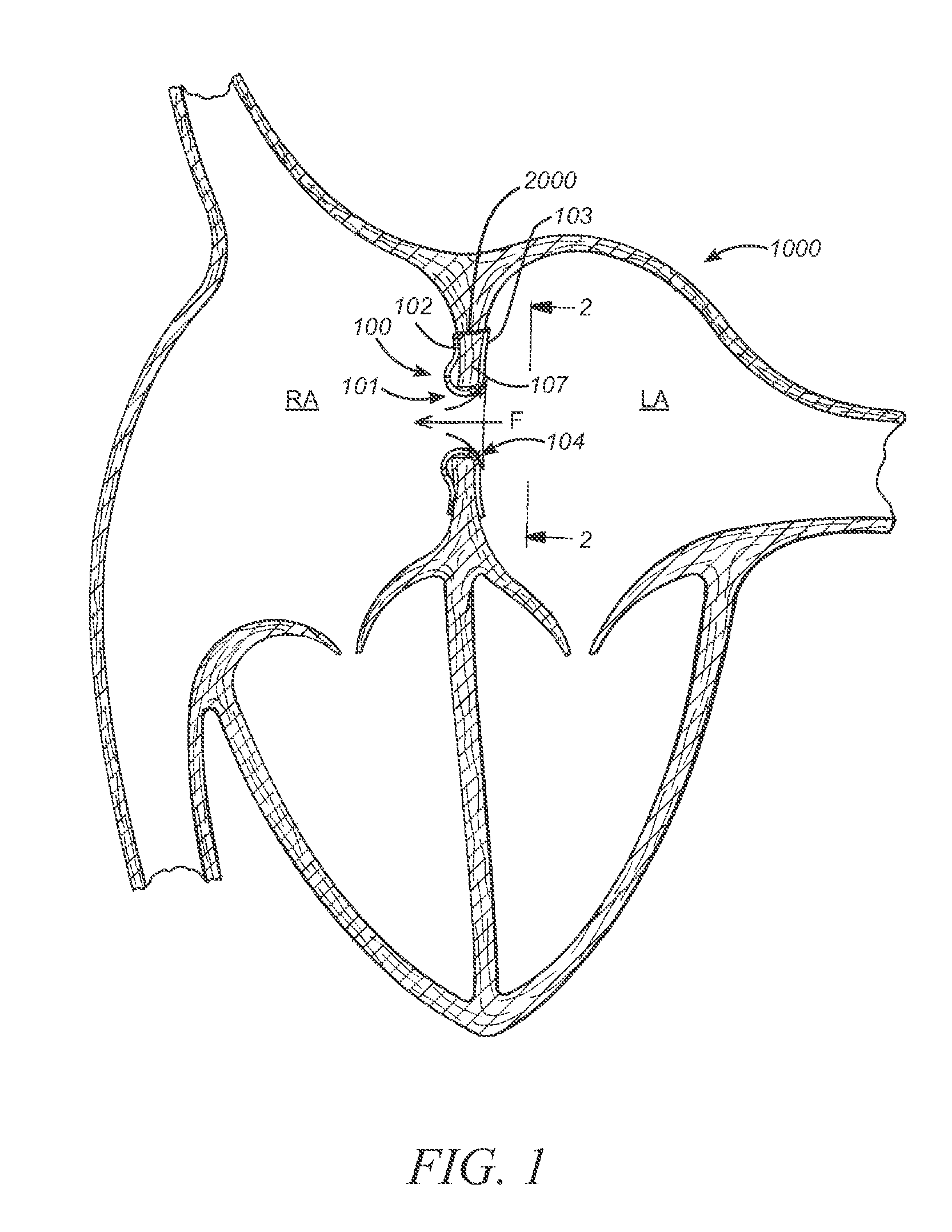
Prosthesis for retrieval and deployment
ActiveUS20110295362A1Reduce pressureRelieve symptomsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsHeart valvesProsthesis ImplantationPatients symptoms
The present disclosure relates to devices and methods for implanting a prosthesis into a heart of a mammal, such as a person. The disclosure includes a prosthesis that acts as a pressure vent between the left and right atria of the heart. The disclosure also includes a mounting tool for mounting the prosthesis onto a loading tool, the loading tool useful for loading the prosthesis onto a device for delivering the prosthesis into the patient's heart. Control devices and methods for using these devices are also disclosed. The intracardiac pressure vents disclosed allow sufficient flow from the left atrium to the right atrium to relieve elevated left atrial pressure and resulting patient symptoms. The devices also limit the amount of flow from the right atrium to the left atrium to minimize the potential for thrombi or other embolic material from entering arterial circulation.
Owner:CORVIA MEDICAL
Biomimetic artificial hip joint with internal growth function
ActiveCN105105875AImprove tribological propertiesImprove fault toleranceJoint implantsHip jointsArticular surfacesBiomechanics
The invention discloses a biomimetic artificial hip joint with an internal growth function. The joint is composed of an artificial cartilage layer, an interface bonding layer and a porous bracket, wherein the artificial cartilage layer and the porous bracket have elliptic surfaces; the surface wrapping angle of the joint is 60-120 degrees; when the wrapping angle is 80-120 degrees, 3-6 convex columnar bodies, which are uniformly distributed, are designed on the inner surface of a prosthesis along the peripheral direction; a porous coating with biological activity is prepared on the outer surface of a femoral component and materials of the coating have gradient changes from inside to outside; the porous bracket is designed into a porous structure with gradient according to a finite element optimization result, and the pore diameter is 300-800 microns; the porosity is 20%-85%. According to the biomimetic artificial hip joint disclosed by the invention, bone mass and biomechanical characteristics of thigh bones can be kept to the greatest extent; the biomimetic artificial hip joint has good mechanical properties and tribological properties; the growth of bone cells is induced or promoted so as to guarantee effective interface bonding intensity between a prosthesis implantation material and a natural bone, the stability of the planted prosthesis is improved and the service life is prolonged.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Disk Replacement Endoprosthesis
A disk replacement endoprosthesis and a procedure for implantation of the endoprosthesis to treat pain, nerve root compression, and neural injury caused by degeneration or injury to vertebral disks. The endoprosthesis may include an intervertebral wedge or other body having a lead-in distractor. A fastening plate may be attached to the intervertebral wedge by a joint such that the first fastening plate may move from a first configuration in which the first fastening plate is in-line with the intervertebral wedge to facilitate insertion of the endoprosthesis to a second configuration in which the first fastening plate is in contact with an anterior surface of the inferior vertebral body for attachment thereto.
Owner:KYPHON
Cosmetic and reconstructive prosthesis containing a biologically compatible rupture indicator
InactiveUS20050149186A1High strengthReduce diffuseMammary implantsDiagnosticsElastomerFilling materials
A prosthesis containing a rupture indicator is disclosed, which includes an indicator lumen enclosed by an indicator lumen envelope made of at least one layer of elastomer containing therein a biologically compatible chemical indicator and a carrier medium; and at least one implant lumen enclosed by an implant lumen envelope made of at least one layer of elastomer, disposed within the indicator lumen. The implant lumen contains therein an implant filling material. Also disclosed is a single lumen prosthesis which includes an envelope made of elastomer containing therein an implant filling material and a biocompatible chemical indicator in a carrier medium. Further disclosed is a method of detecting rupture of a prosthesis, which includes surgically implanting the prosthesis containing a biologically compatible chemical indicator in a desired location of a patient's body and monitoring a change of a body excretion or secretion for indication of prosthesis rupture.
Owner:TONABA HEALTHSCI
Device for treating a blood circulation conduit
Owner:CORMOVE
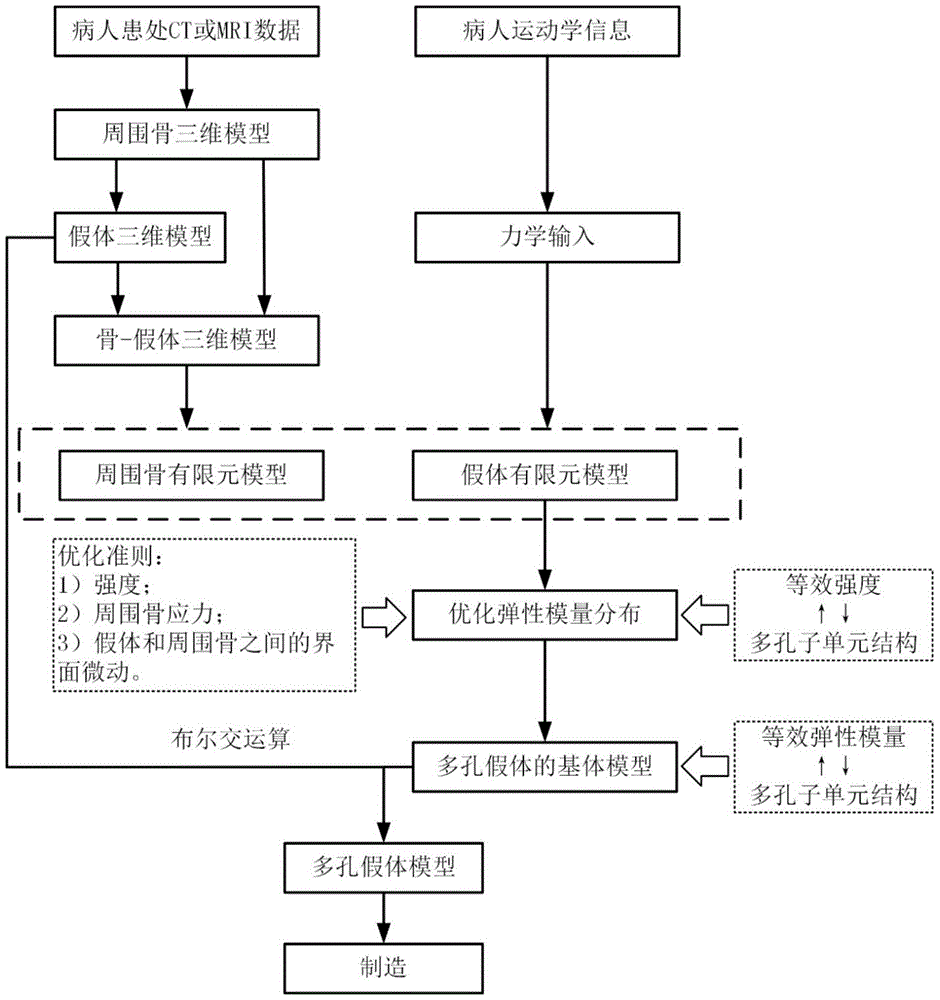
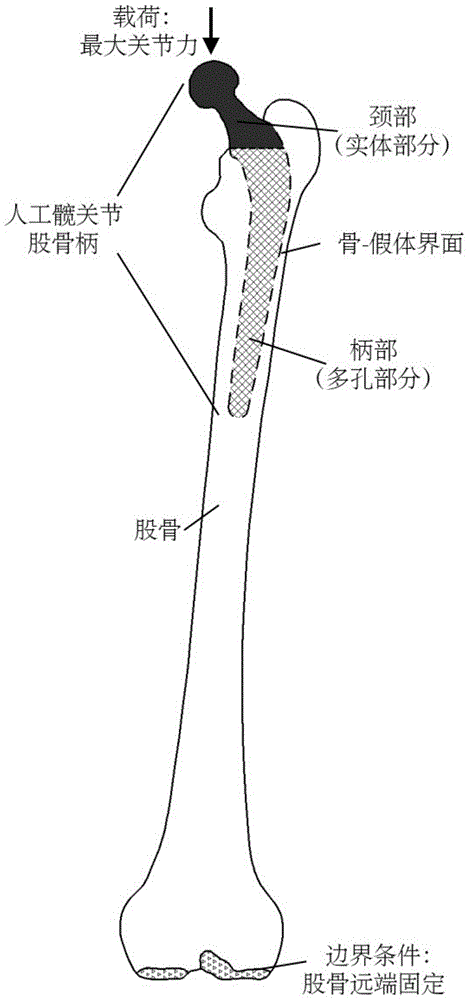
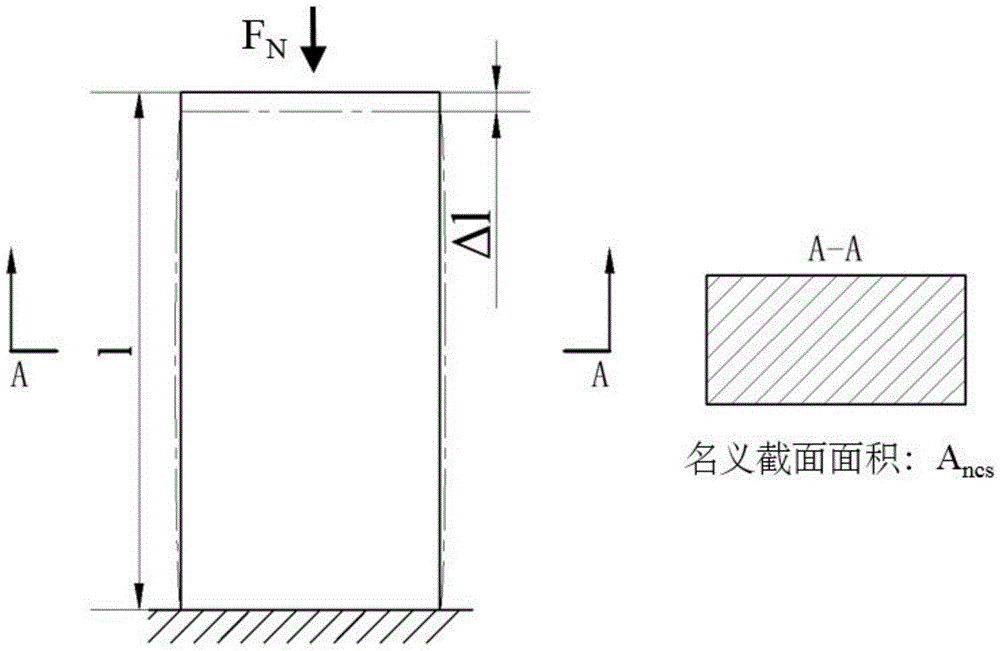
Host bone stress environment based custom prosthesis optimization design method
ActiveCN105740523AAdapt to boneAdapt to the situationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsPersonalizationBones stress
The invention, for reducing a stress shielding effect after prosthesis implantation, proposes a host bone stress environment based custom prosthesis optimization design method. Three criteria, namely, the strength, the surrounding bone stress and the interface micro-motion between a prosthesis and a bone, in prosthesis elastic modulus optimization calculation are proposed, and the mechanical property of the host bone and a personalized kinematic input are considered in optimization; the prosthesis elastic modulus distribution is optimized through finite element software to achieve the purpose of optimizing a porous structure in the prosthesis; and for the designed prosthesis, on the premise of meeting the strength requirement, the stress shielding effect after implantation is reduced and the service life of the prosthesis after implantation is prolonged.
Owner:深圳协同创新高科技发展有限公司
Methods for accelerating bone and cartilage growth and repair
InactiveUS6916783B2Strengthen bonesEnhancing cartilage repairAngiotensinsPeptide/protein ingredientsProsthesis ImplantationAgonist
The present invention provides improved methods, kits, and compositions for enhancing bone, cartilage and cartilage repair, bone and prosthesis implantation, and attachment and fixation of cartilage and cartilage to bone or other tissues, and chondrocyte proliferation composing the administration of an effective amount of angiotensinogen, angiotensin I (AI), AI analogues, AI fragments and analogues thereof, angiotensin II (AII), AII analogues, AII fragments or analogues thereof or AII AT2 type 2 receptor agonists.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Inserter for a flexible acetabular cup
ActiveUS20060167462A1Compromising positionCompromising stabilityJoint implantsAcetabular cupsProsthesis ImplantationBiomedical engineering
A prosthesis implantation inserter is used with a flexible acetabular cup which has an opening or openings in its peripheral rim. The inserter has engagement elements which in an operational position frictionally engage the opening or openings in the flexible cup rim. A release is provided which can be operated to withdraw the engagement element from the opening or openings. When the cup is held §in position it can be guided and inserted into the acetabulum and impacted. Once the position of the prosthesis satisfies the surgeon the engagement element can be removed by operating the release and the cup inserter is removed without any risk of compromising the position or the stability of the implant.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
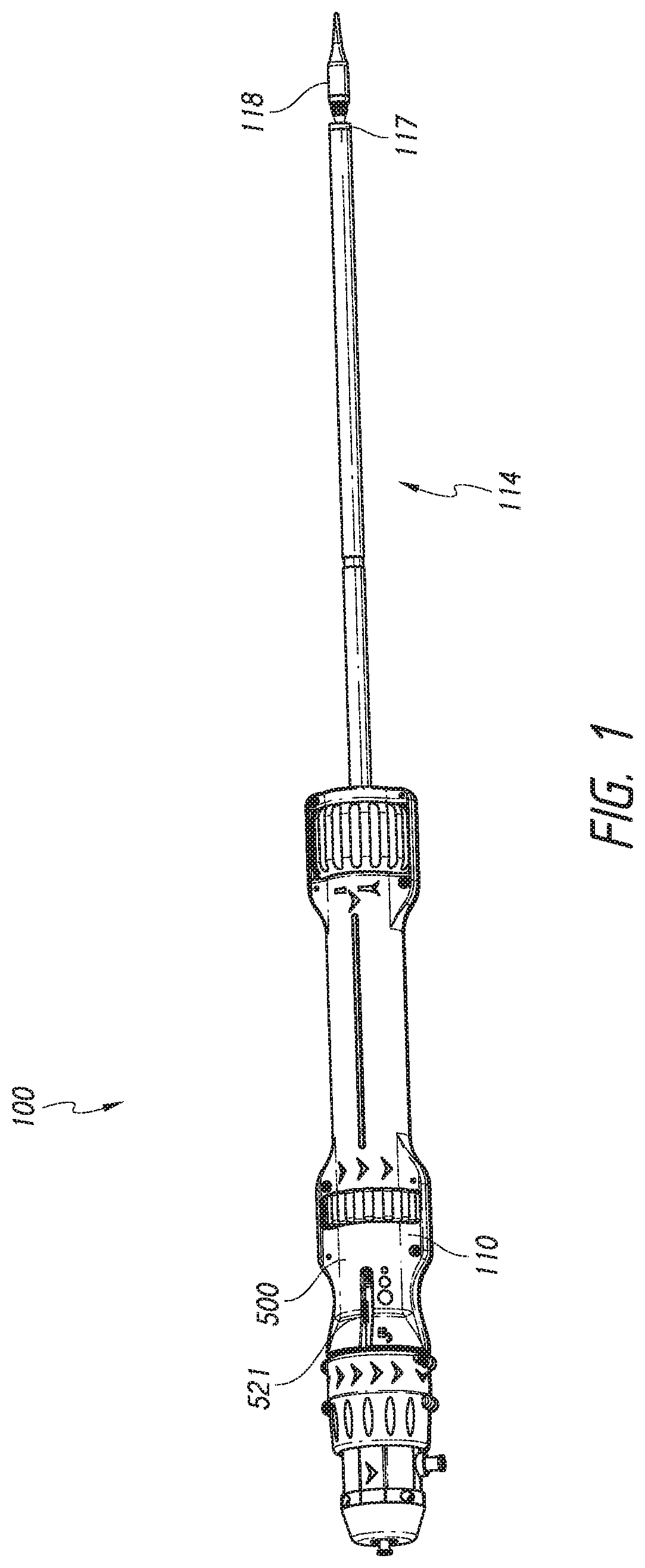
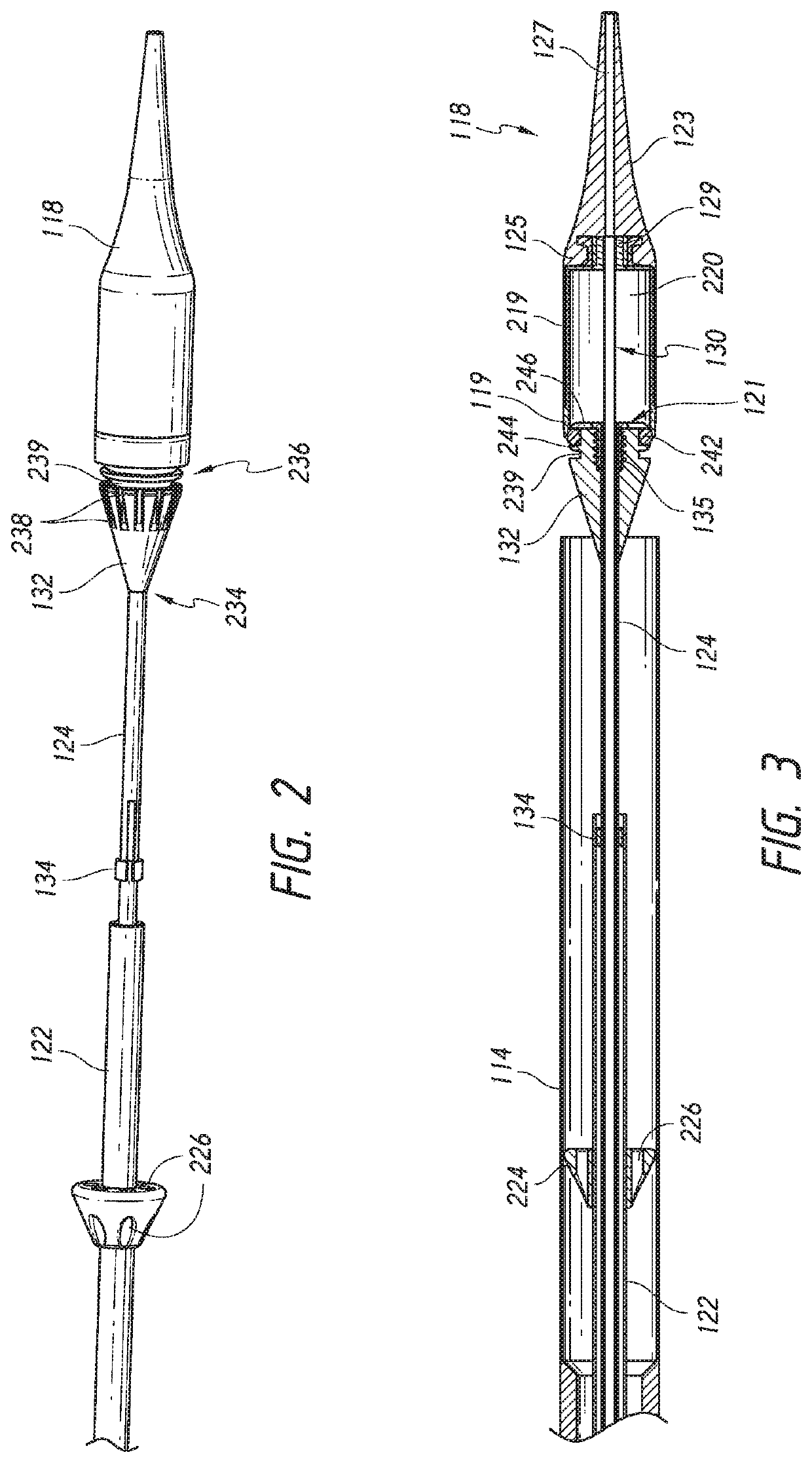
Delivery device and methods of use for transapical delivery of replacement mitral valve
Devices, systems and methods are described for implantation of a prosthesis within a lumen or body cavity and delivery systems for delivering the prosthesis to a location for implantation. A delivery system can include a tether connected to a single directional handle knob for release of the prosthesis within the lumen or body cavity and retraction of the tether towards the handle.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI CARDIAQ
Individualized customized implantation material shaping device for 3D printing and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN105726168ARelieve painEasy to acceptAdditive manufacturing apparatusBone implantCustom made implantTissue defect
The invention discloses an individualized customized implantation material shaping device for 3D printing and a manufacturing method thereof. The individualized customized implantation material shaping device is characterized in that the shaping devices are divided into three types: a guide plate or mold with the skeleton surface as a basis after a most ideal digital reset, para-position and alignment skeleton model is established, a guide plate or mold with establishment of a digital most-ideally installed most-ideal implantation material model of an implantation material as basic design and a shaping device mainly used for a tissue defect repairing implantation material and a prosthesis implantation material. The manufacturing method comprises the steps that firstly, the digital skeleton model is obtained through modeling based on a reverse engineering technology; secondly, reset or osteotomy shape-correcting operation is conducted on the skeleton model according to the operation purpose to make skeleton model reach a final ideal state required by an operation, and material obtaining is performed on the basis to establish various characteristics gradually. The individualized customized implantation material shaping device has the advantages of saving operation time, relieving the suffering of patients, more facilitating the operation, being low in access threshold and the like.
Owner:佛山市三水区人民医院
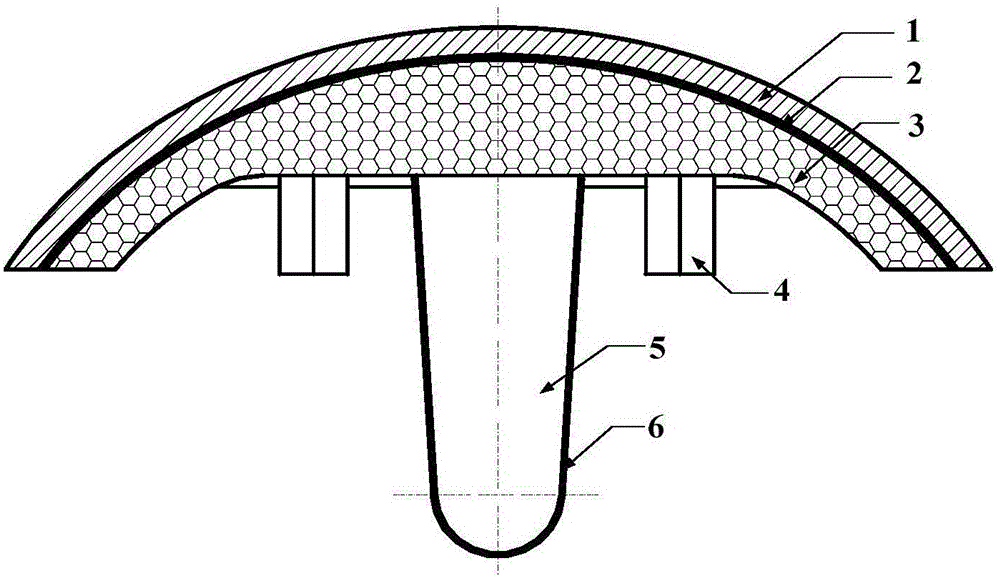
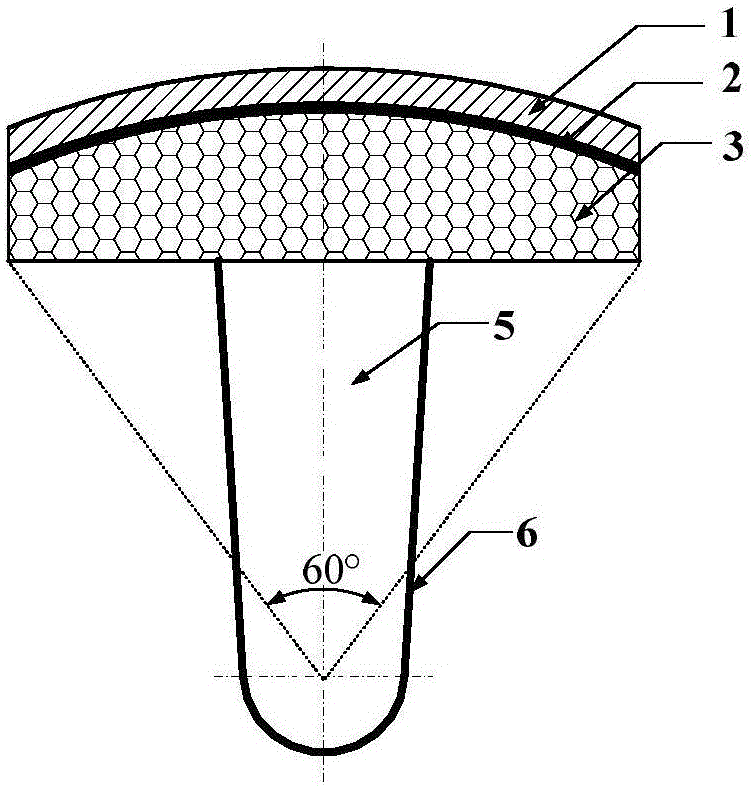
Method for preparing prosthesis with tantalum coating
InactiveCN101862231AGood roughnessGood porosityDental implantsImpression capsProsthesis ImplantationBone tissue
The invention discloses a method for treating surface pores of artificially implanted prosthesis and particularly to a method for preparing a prosthesis with a tantalum coating. The method comprises: preparing a tantalum microporous coating, which may has different surface porosities, on the surface of the part, to be implanted in a bone, of the prosthesis by selecting spraying powers of 25, 30, 35 and 40kW respectively under the conditions of a spraying distance of 100 to 150 millimeters and a powder feeding rate of 70 to 80 grams per minute, wherein the thickness of the tantalum microporous coating is 30 to 300, and the porosity is between 20 and 50 percents; and the substrate of the prosthesis is made of stainless steel 00Cr18Ni14Mo3 or 00Cr18Ni15Mo3N, titanium ( Ti), a titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4A or a C-Cr-Mo alloy (Co30Cr6Mo0.35C) material. The method aims to make the coating of the prosthesis high reliably in bonding strength and high selectable in surface porosity and to reduce the adverse factors which influence the stability of the prosthesis after the prosthesis is implanted. Thus, the anchoring area of the bone and the prosthesis can be increased, preconditions are created for the growth of the newly born bone tissues toward the inside of the pores, the loosening and dislocation of the prosthesis are avoided and the immobilization effect and the service life of the prosthesis are ensured.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Joint Resurfacing Prosthetic Implant System
ActiveUS20120296439A1Low production costAvoid collisionFinger jointsToe jointsProsthesis ImplantationReamer
A joint resurfacing prosthetic implant system is disclosed having an anatomically-shaped implant to replace a joint at a pedal digit or finger, including a head having an elliptical bearing surface disposed for engaging the end of an adjacent bone and a seating surface opposite the bearing surface, an elongated stem extending distally from the seating surface, and a flange on the circumference of the device and extending distally from the seating surface. The flange includes one or more portals and a removed section configured to avoid impinging upon a tendon during and after implantation of the prosthetic. A specialized tool is also provided to facilitate the resection of the bone for implantation. The specialized tool includes an elliptical template having a cutting edge and a center insert that is sized and configured to match a reamer used to bore into the bone for insertion of the implant.
Owner:SLAVITT JEROME A
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com