Patents
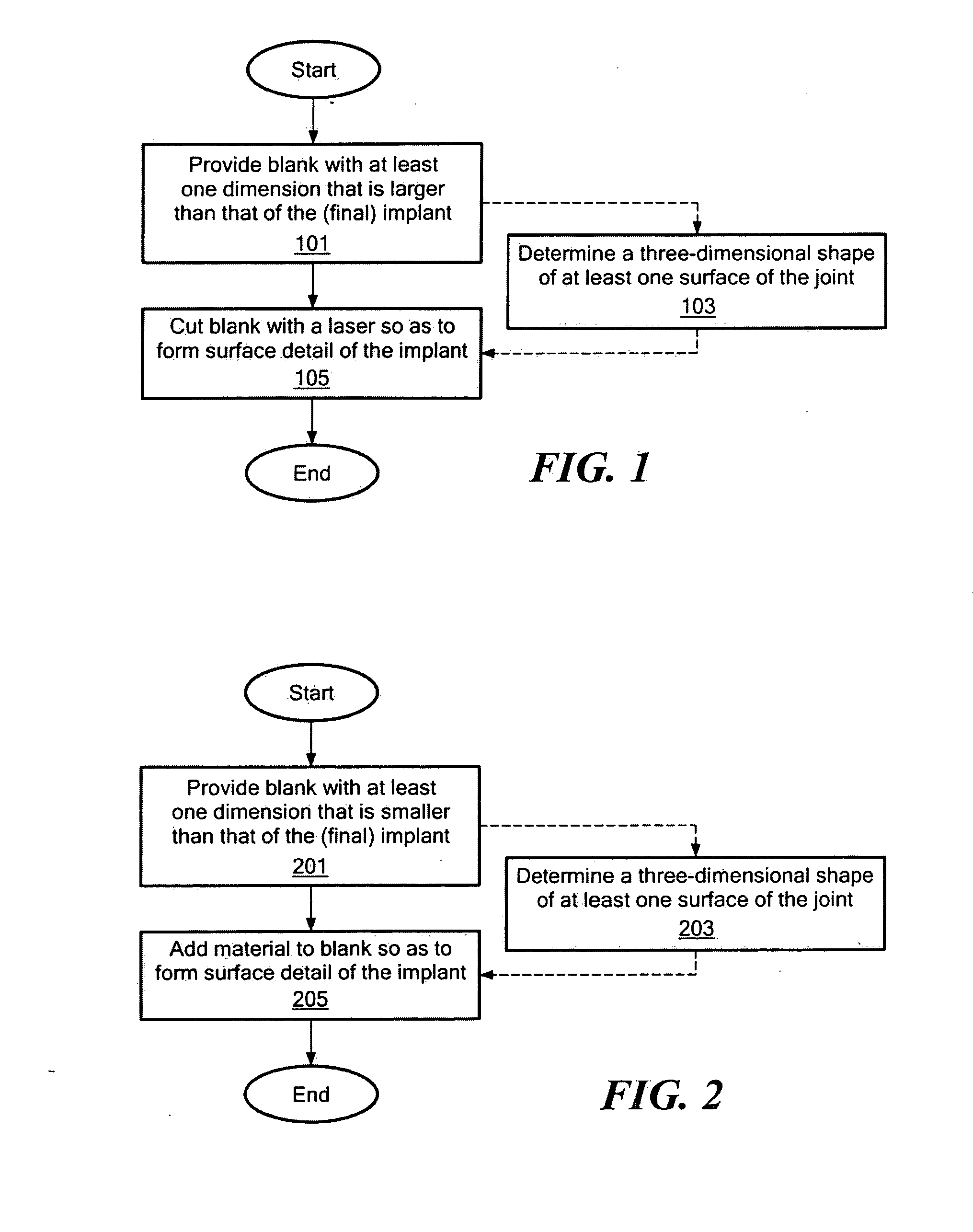
Literature
545results about "Hip joints" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
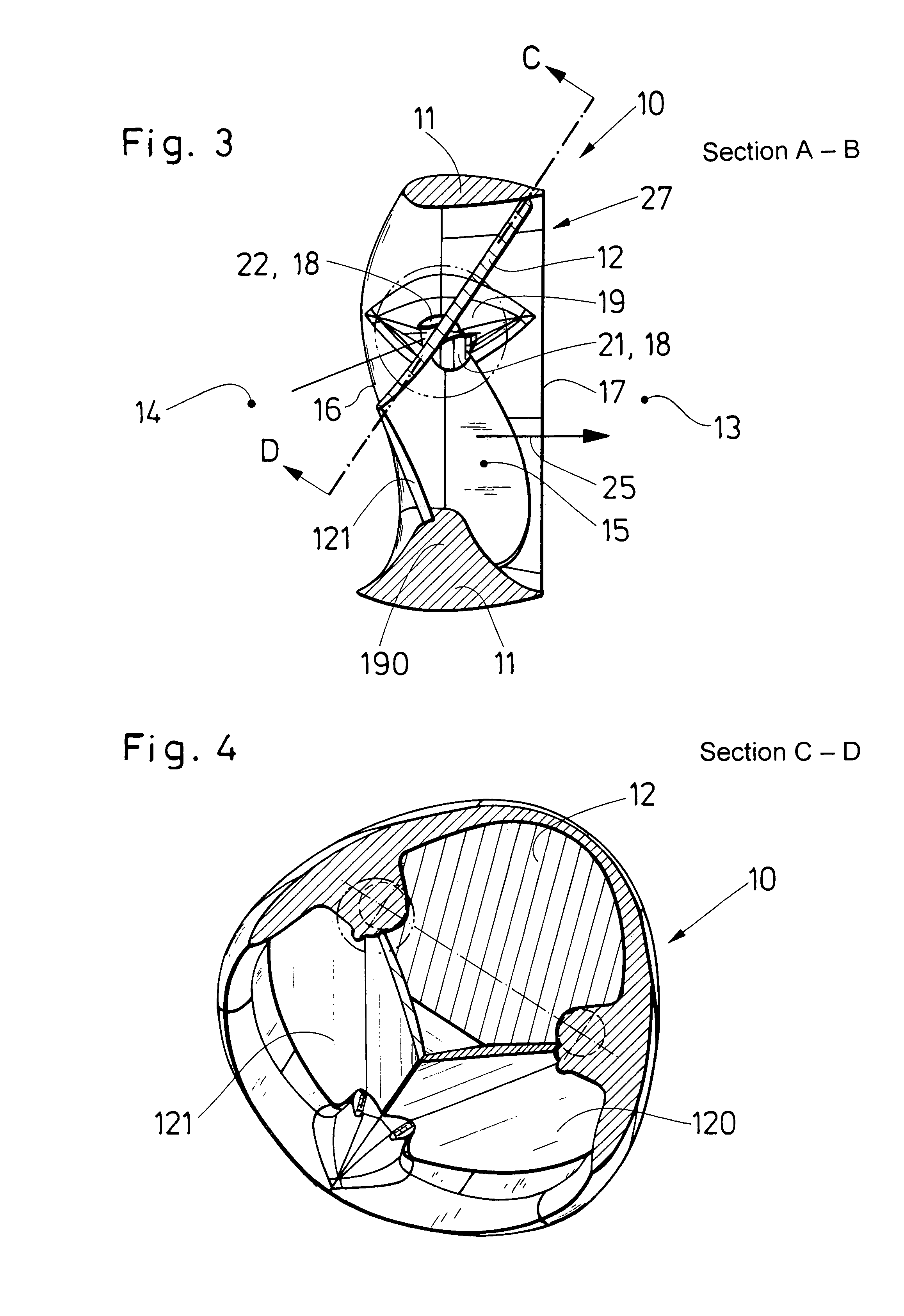
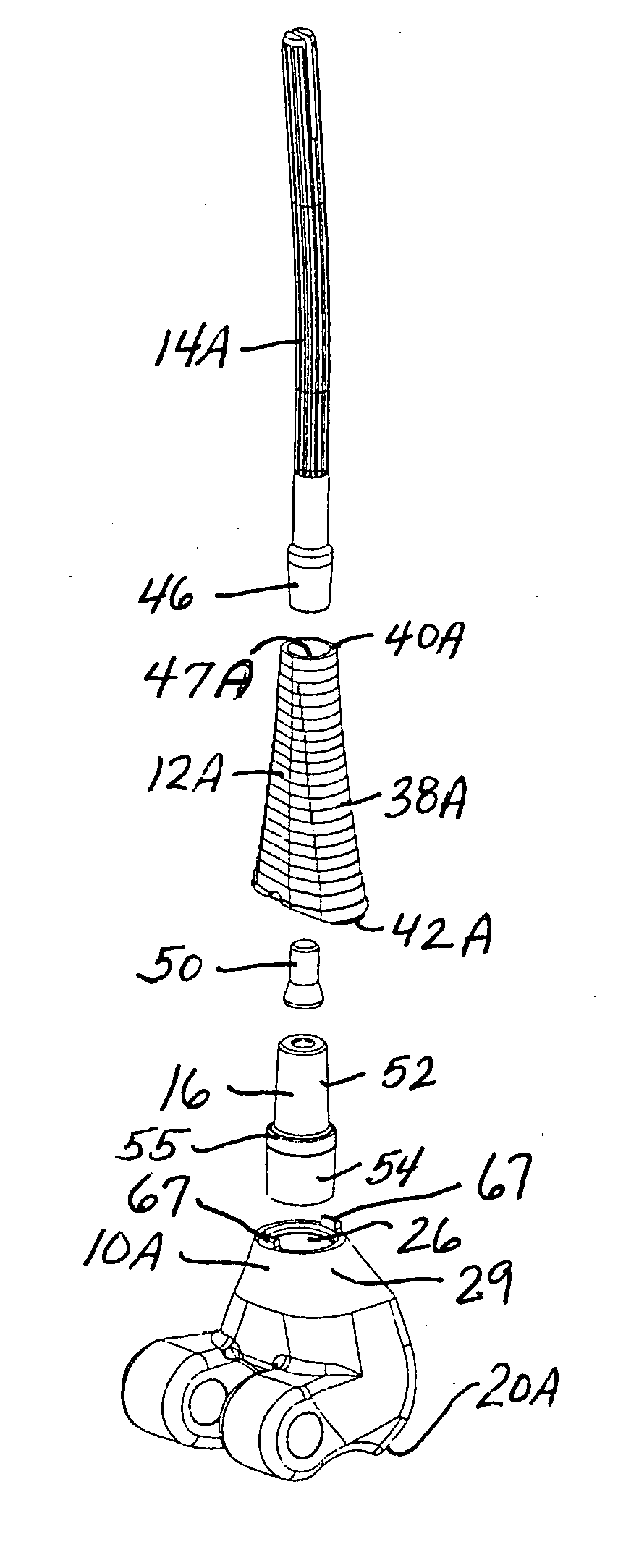
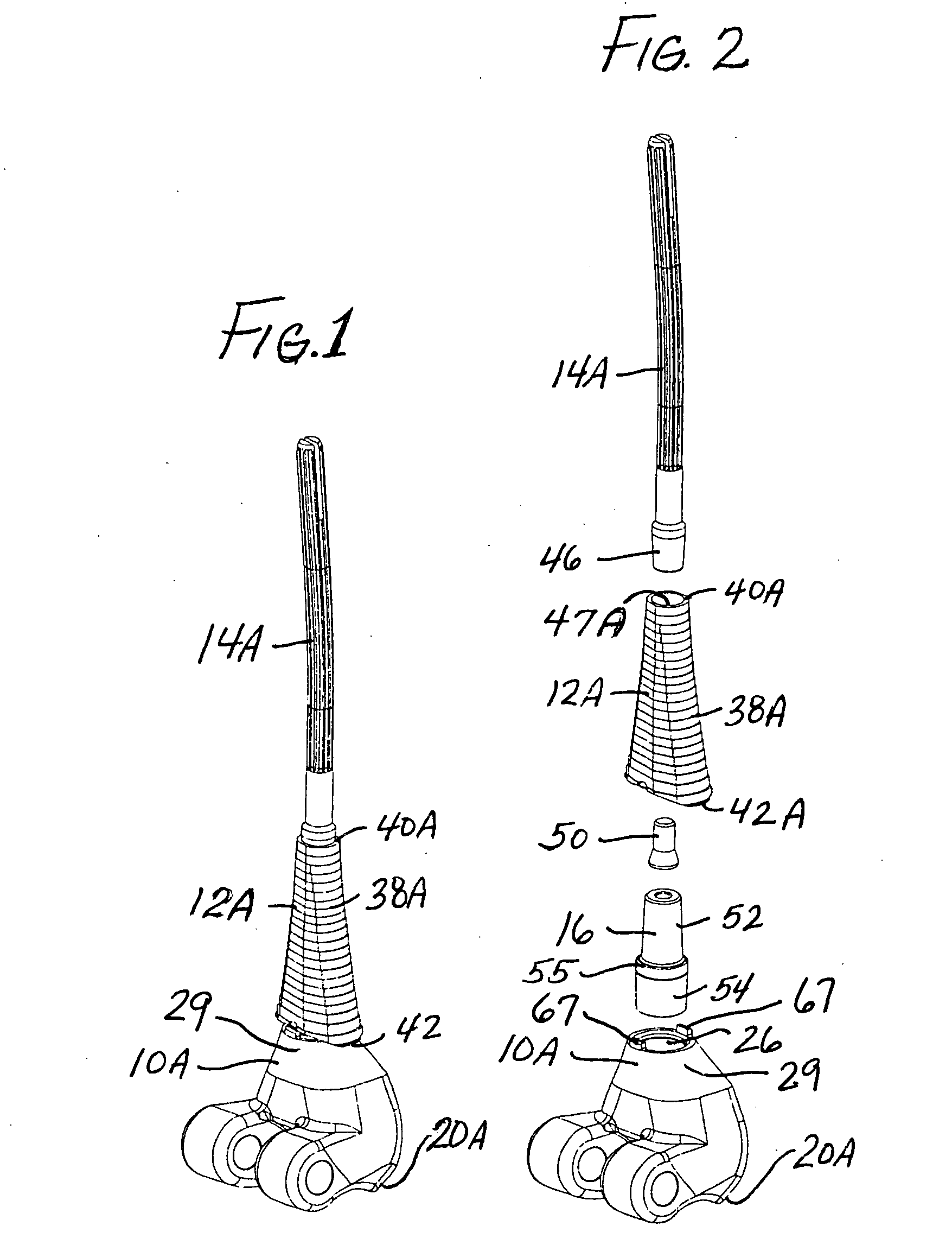
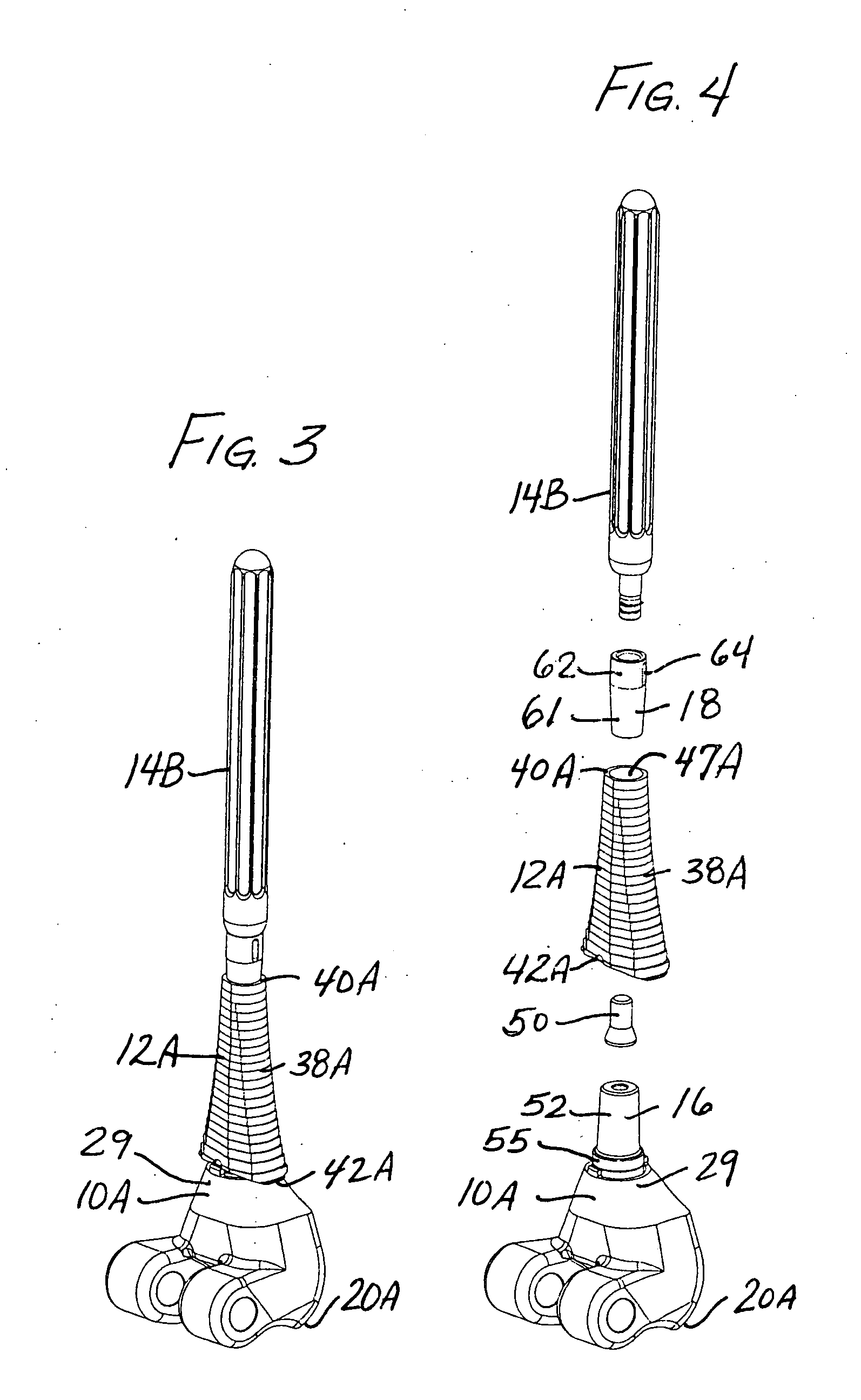
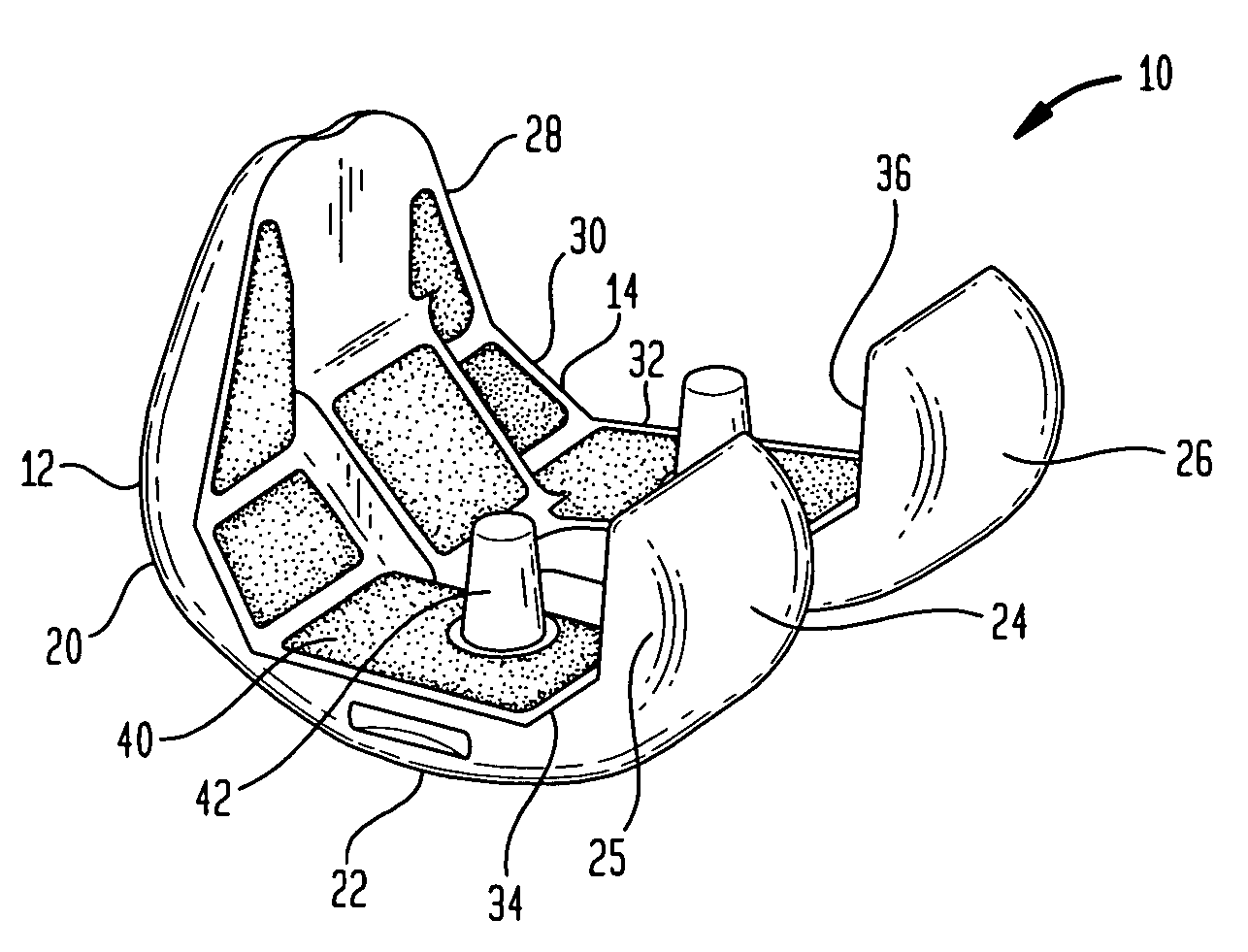
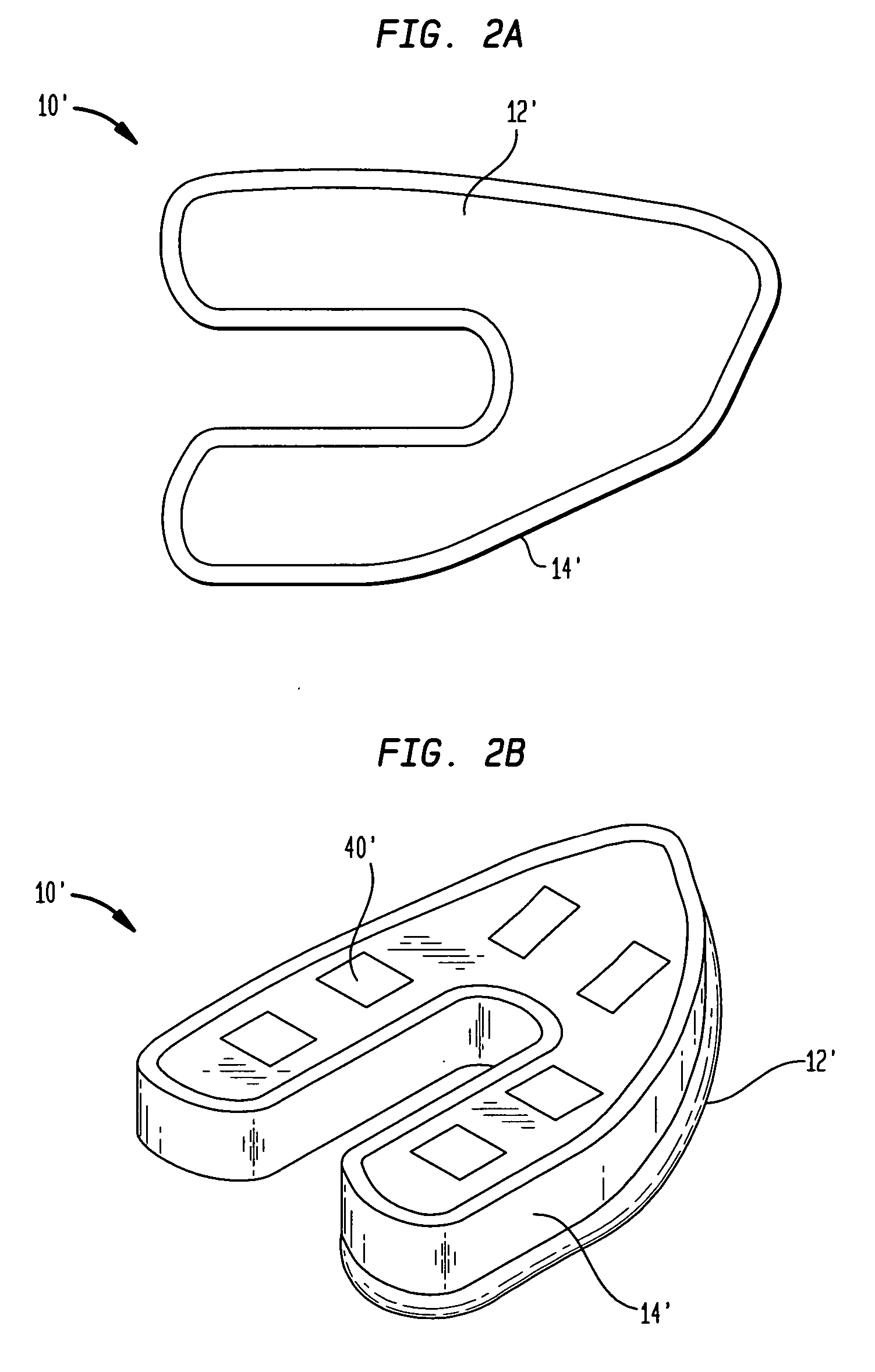
Cartilage repair implant with soft bearing surface and flexible anchoring device
InactiveUS9050192B2Strong and more permanent fixationSoft and bendableJoint implantsHip jointsCartilage repairSurgical implant
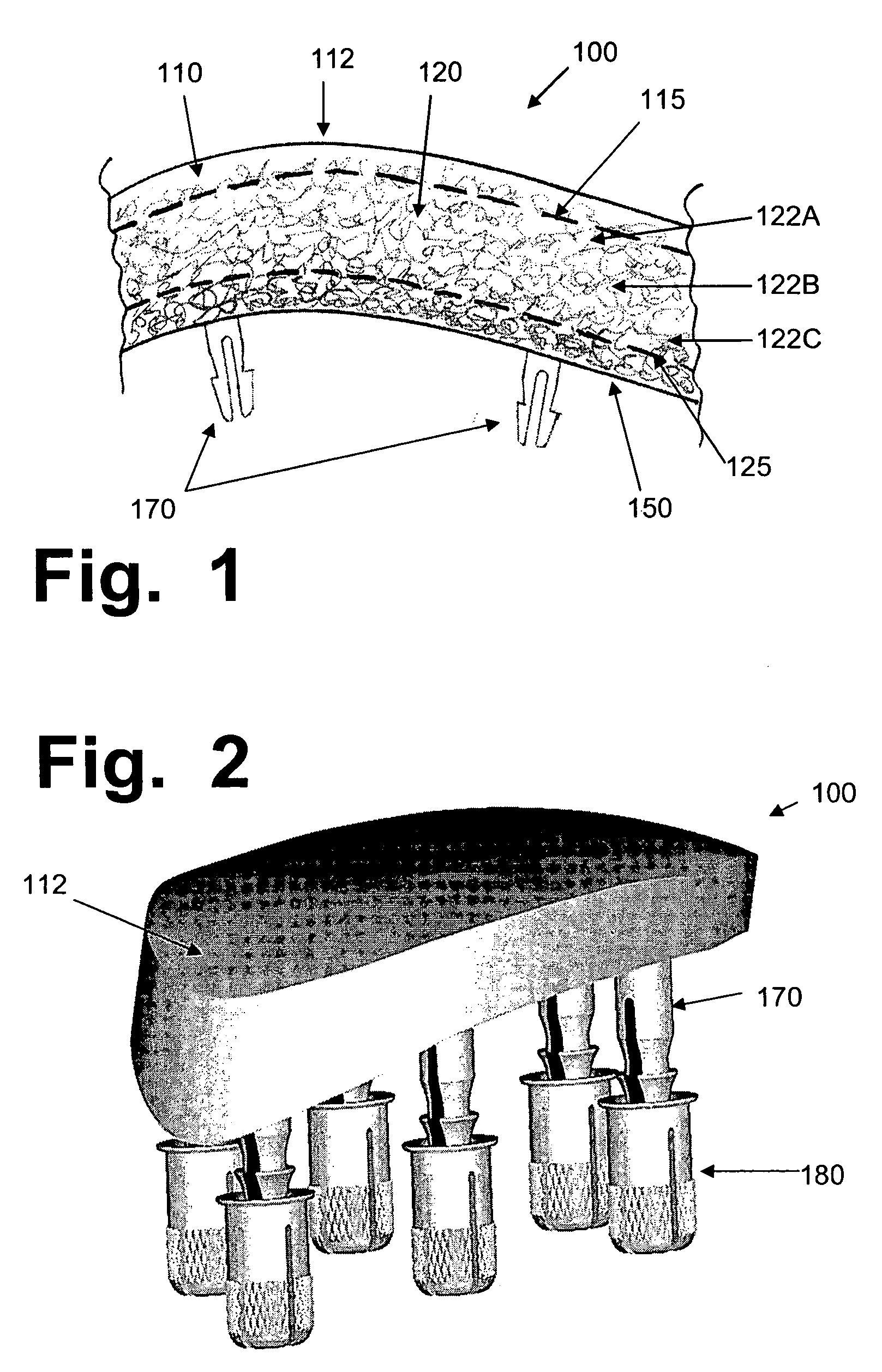
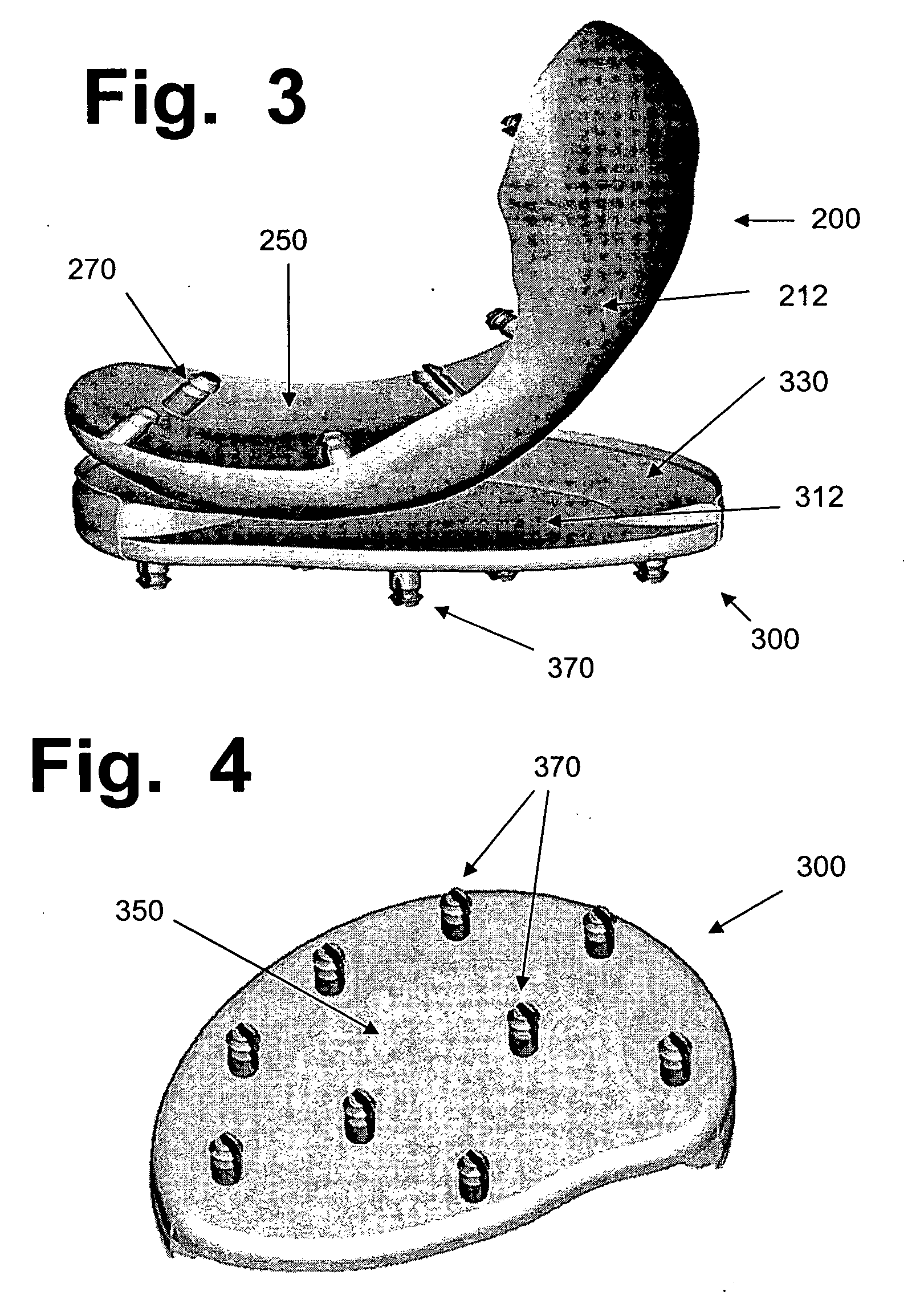
A surgical implant for replacing hyaline cartilage in a knee or other articulating synovial joint has an anchoring side on one side of the implant adapted for fixing the implant to one of the bones in the joint, and a bearing surface on the opposite side of the implant for lubricious rubbing and sliding contact with another bone in the joint. The anchoring side can be configured with an irregular surface for tissue ingrowth. The bearing side can include hydrogel. The implant can be rolled up from an original shape and surgically inserted by arthroscopic means, and opens into its original shape when released inside the joint.
Owner:FORMAE
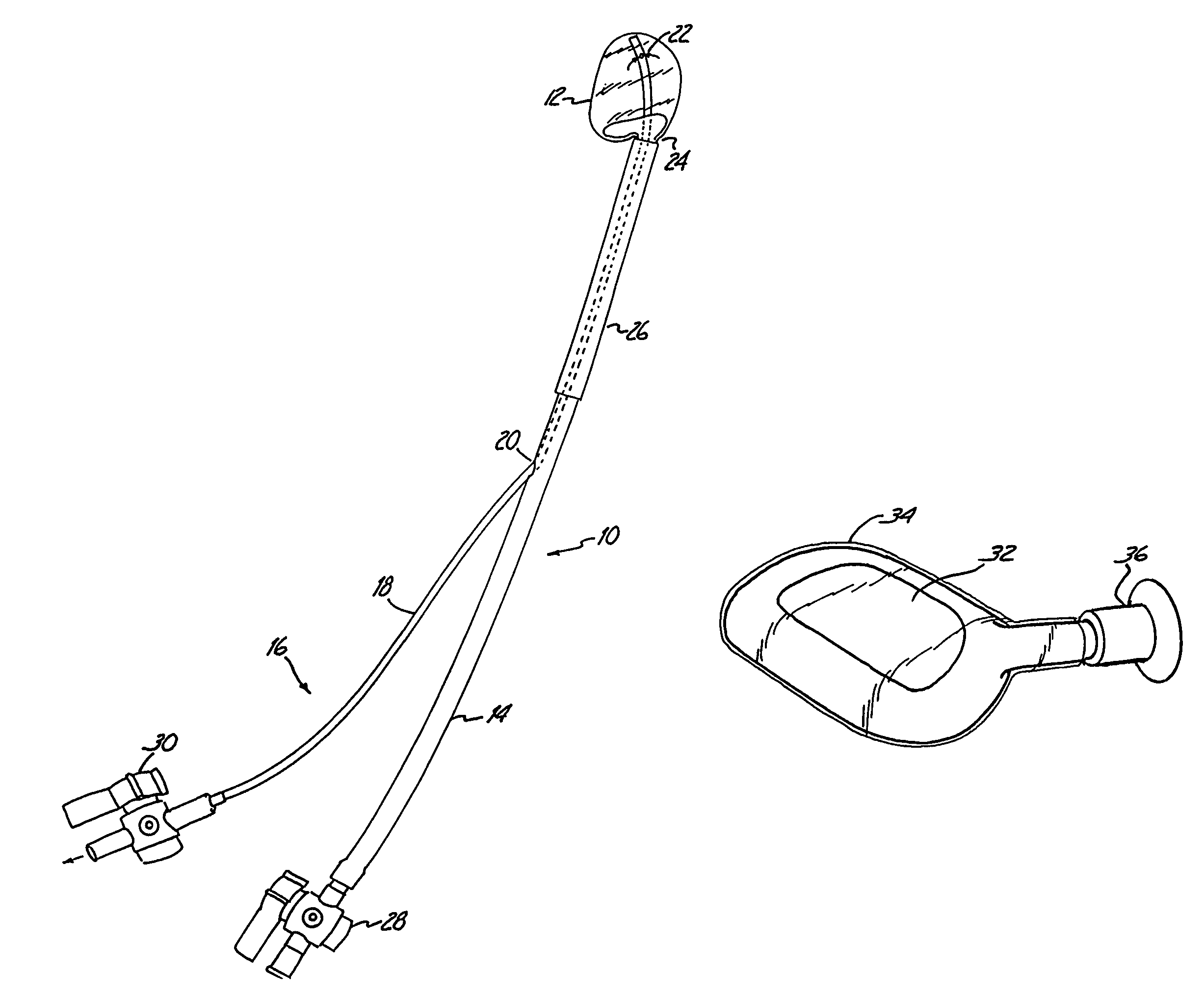
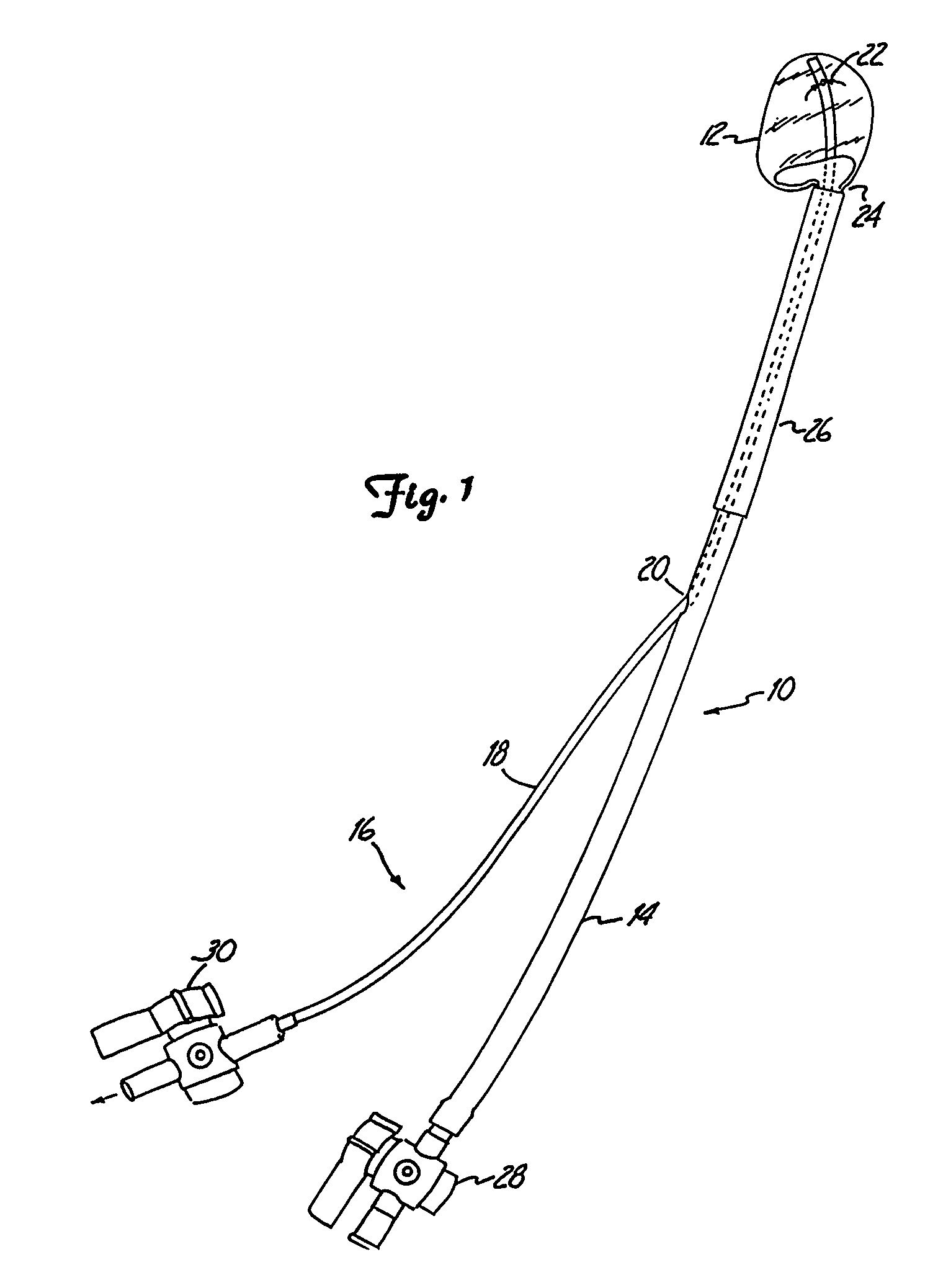
Intervertebral disc prosthesis
InactiveUS7001431B2Improved polymer cureImproved implant characteristicInternal osteosythesisAnkle jointsIntervertebral discPolymer
A system for repairing an intervertebral disc by delivering and curing a biomaterial in situ within the disc. The system includes both a device, having an insertable balloon and related lumen, controls and adapters, as well as an in situ curable biomaterial (and related biomaterial delivery means). The system can allow the doctor to determine a suitable endpoint for biomaterial delivery, by controlling distraction and / or biomaterial delivery pressure, and in turn, to deliver a desired quantity of biomaterial to the balloon in order to achieve improved polymer cure and implant characteristics. Also provided is a related method for repairing an intervertebral disc by using such a system to deliver and cure the biomaterial in situ. The system can be used to implant a prosthetic total disc, or a prosthetic disc nucleus in a manner that leaves the surrounding disc tissue substantially intact.
Owner:DISC DYNAMICS
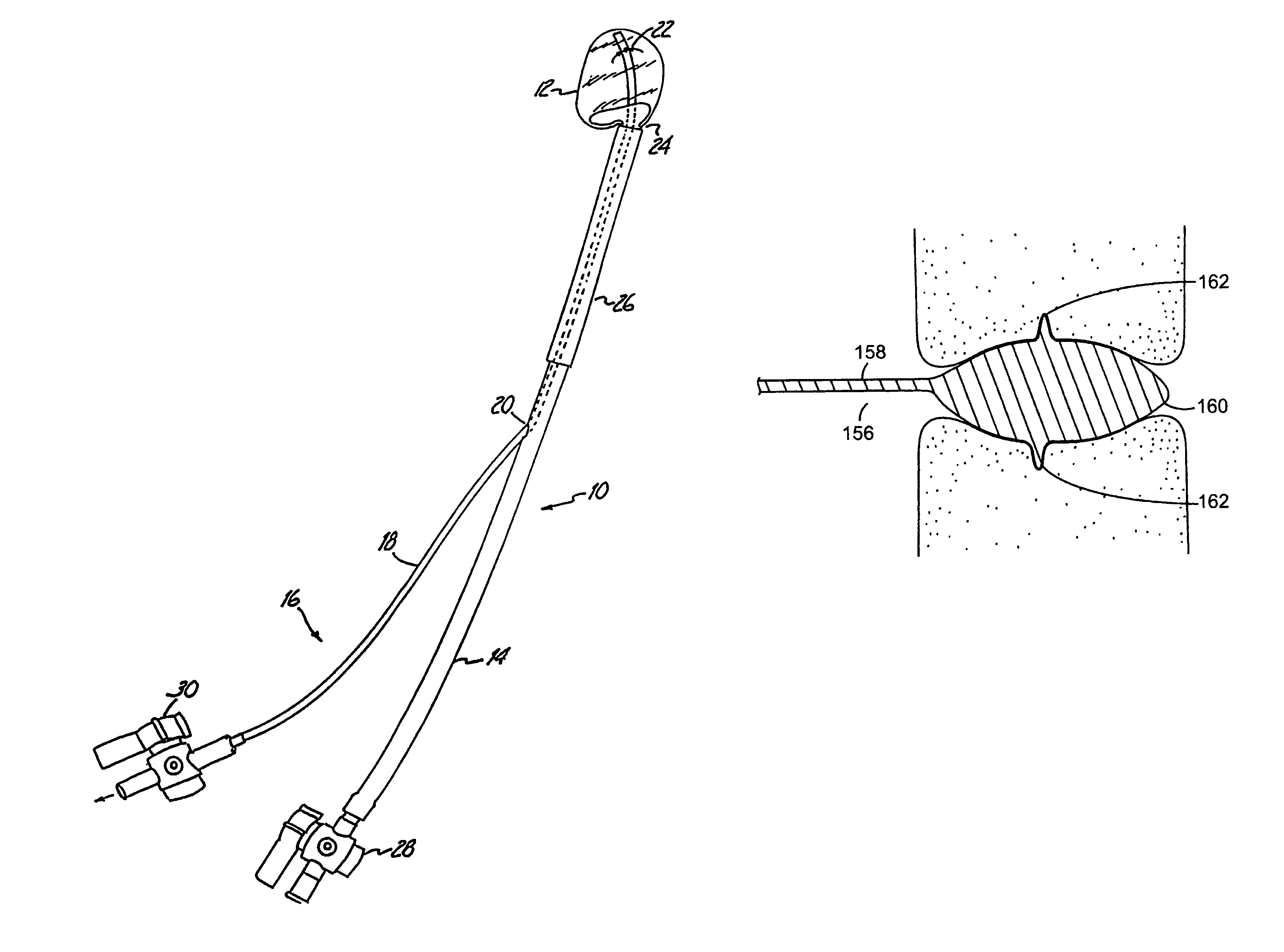
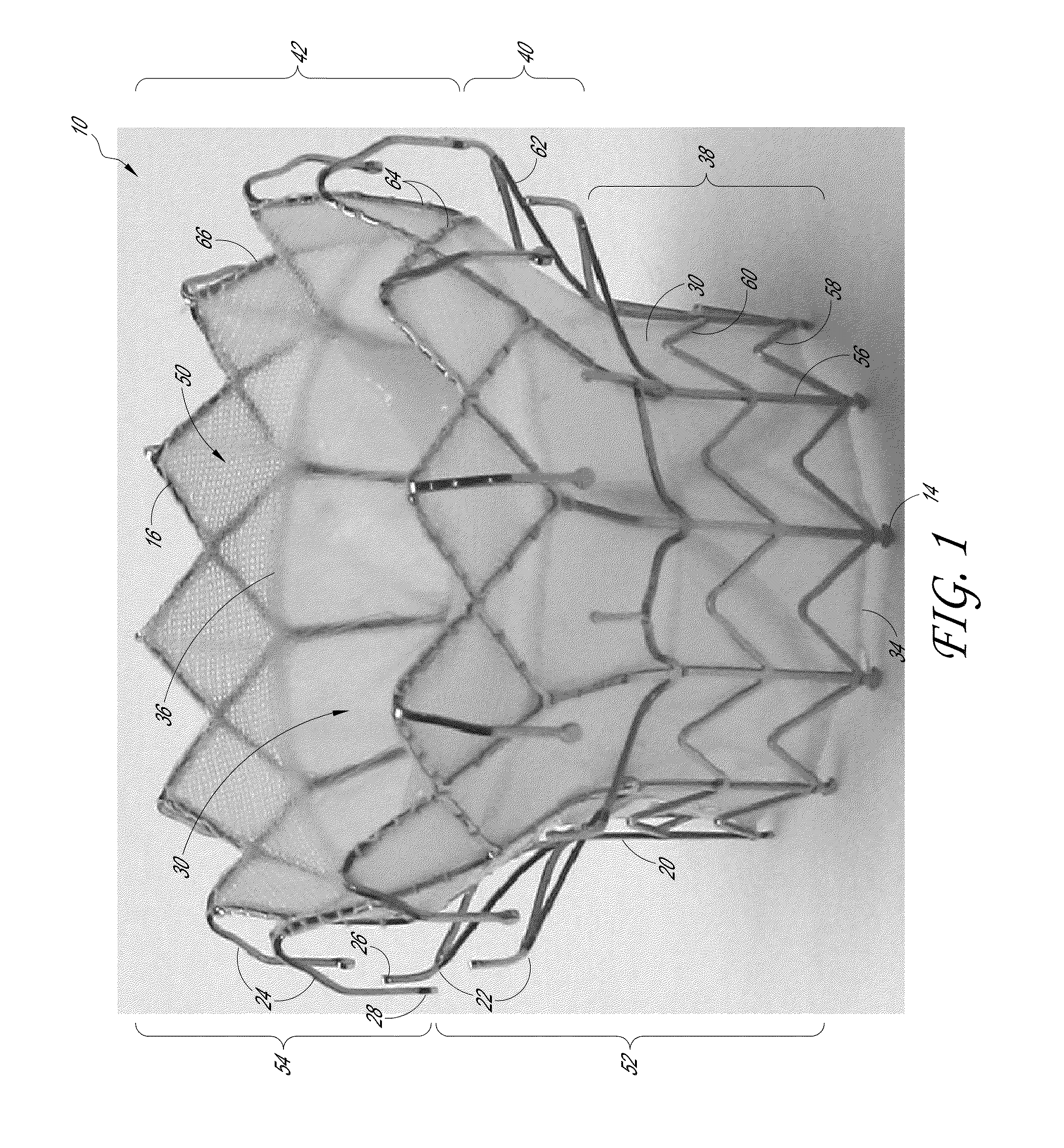
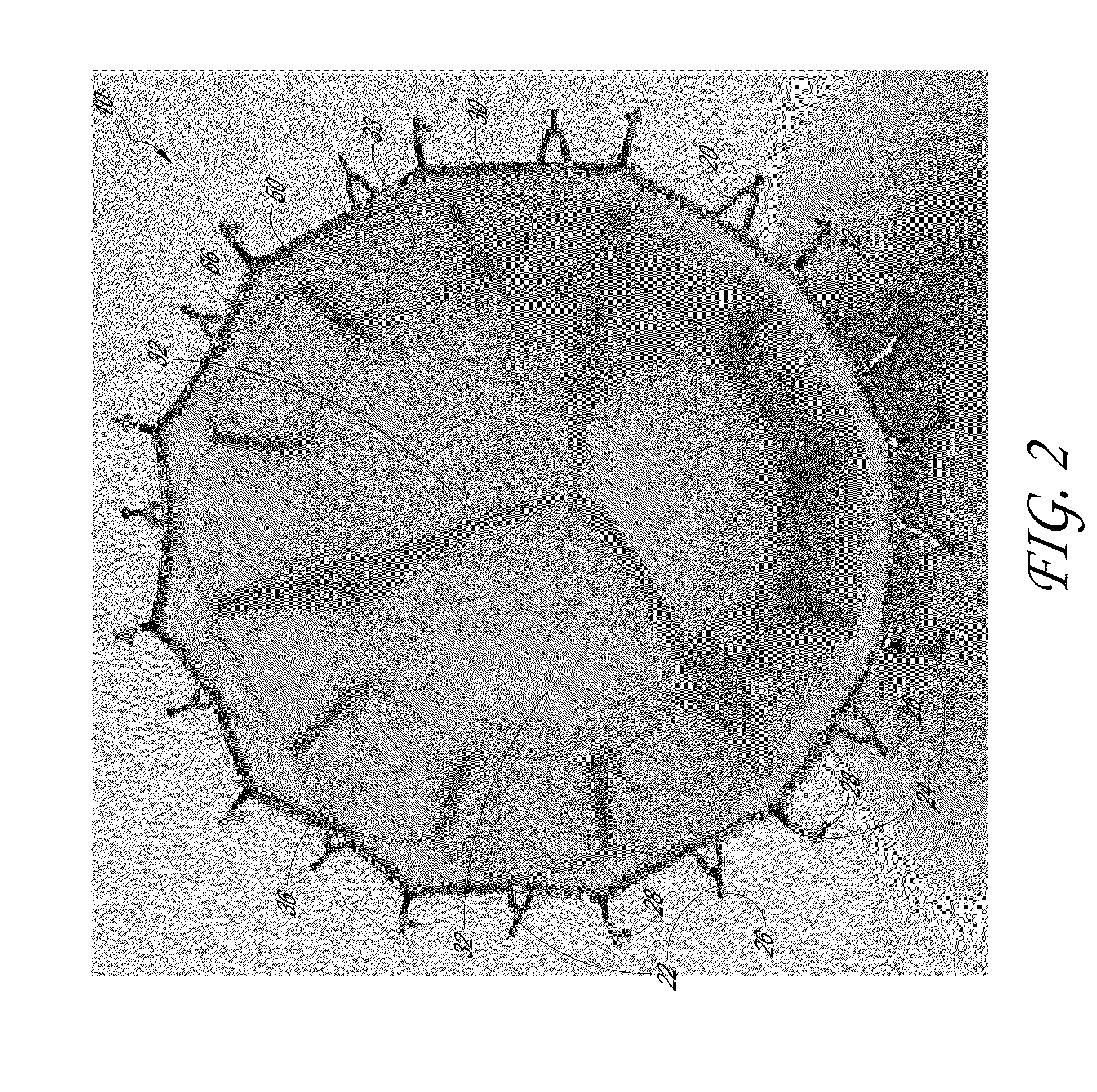
Percutaneous heart valve prosthesis
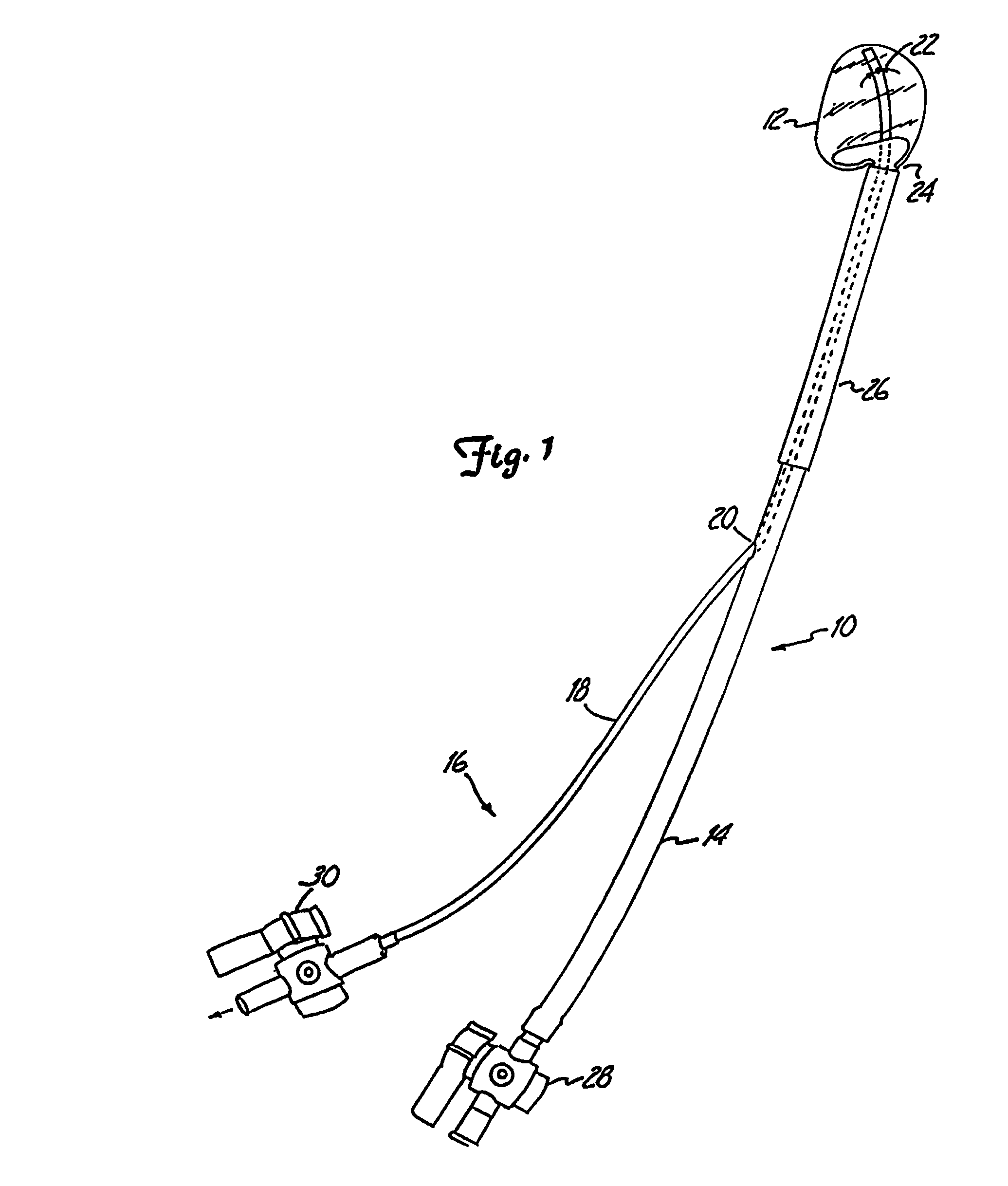
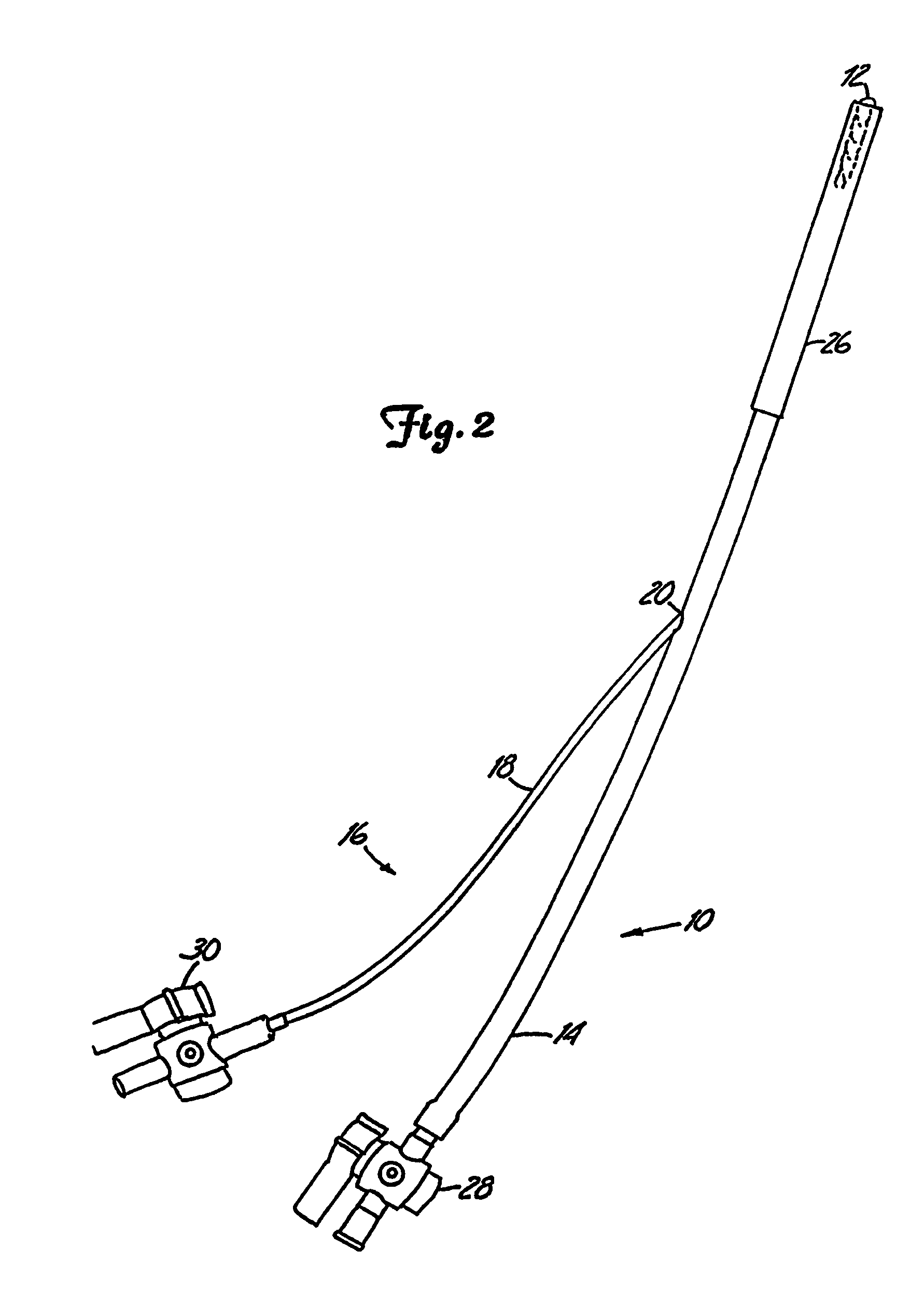
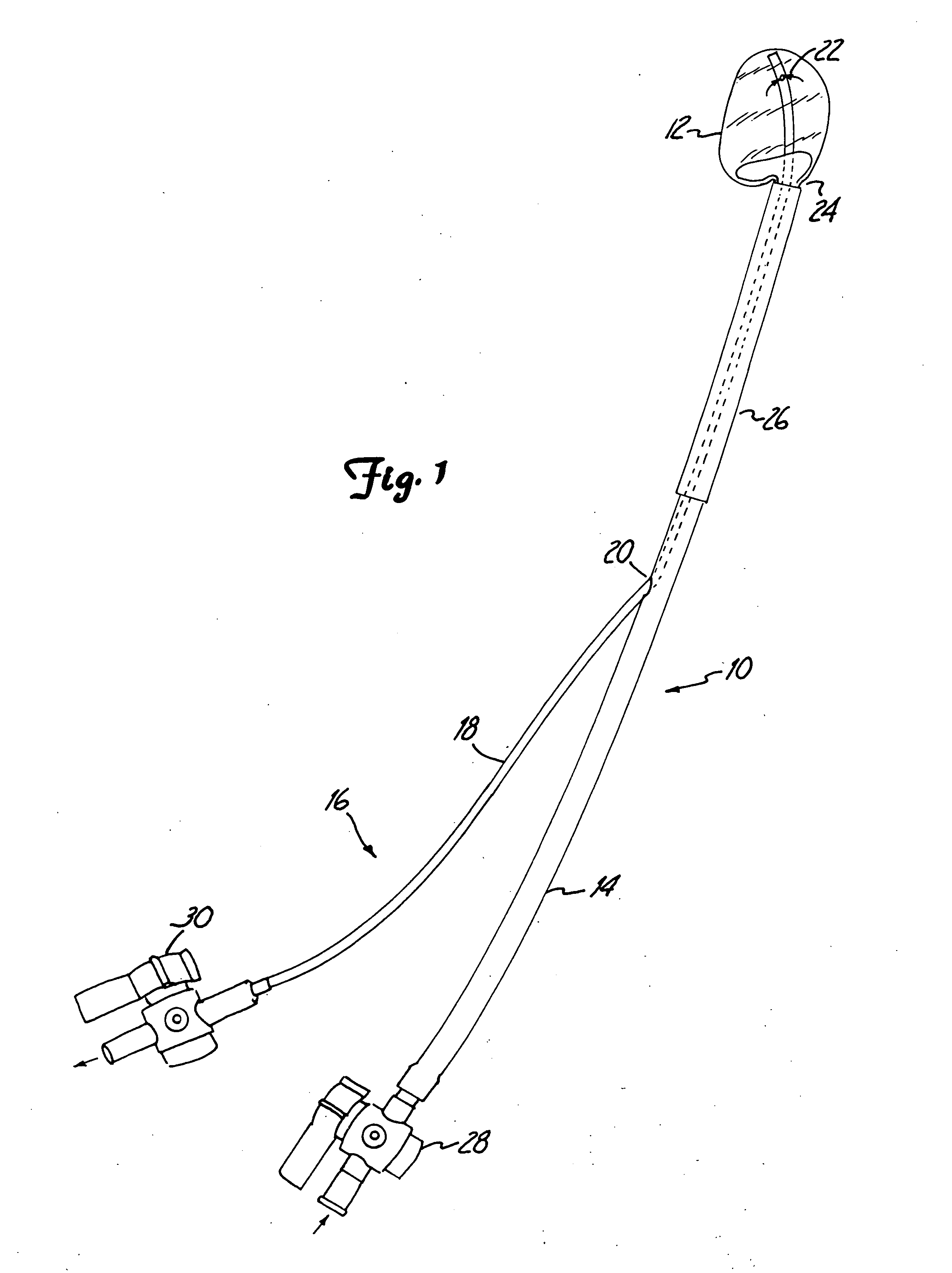
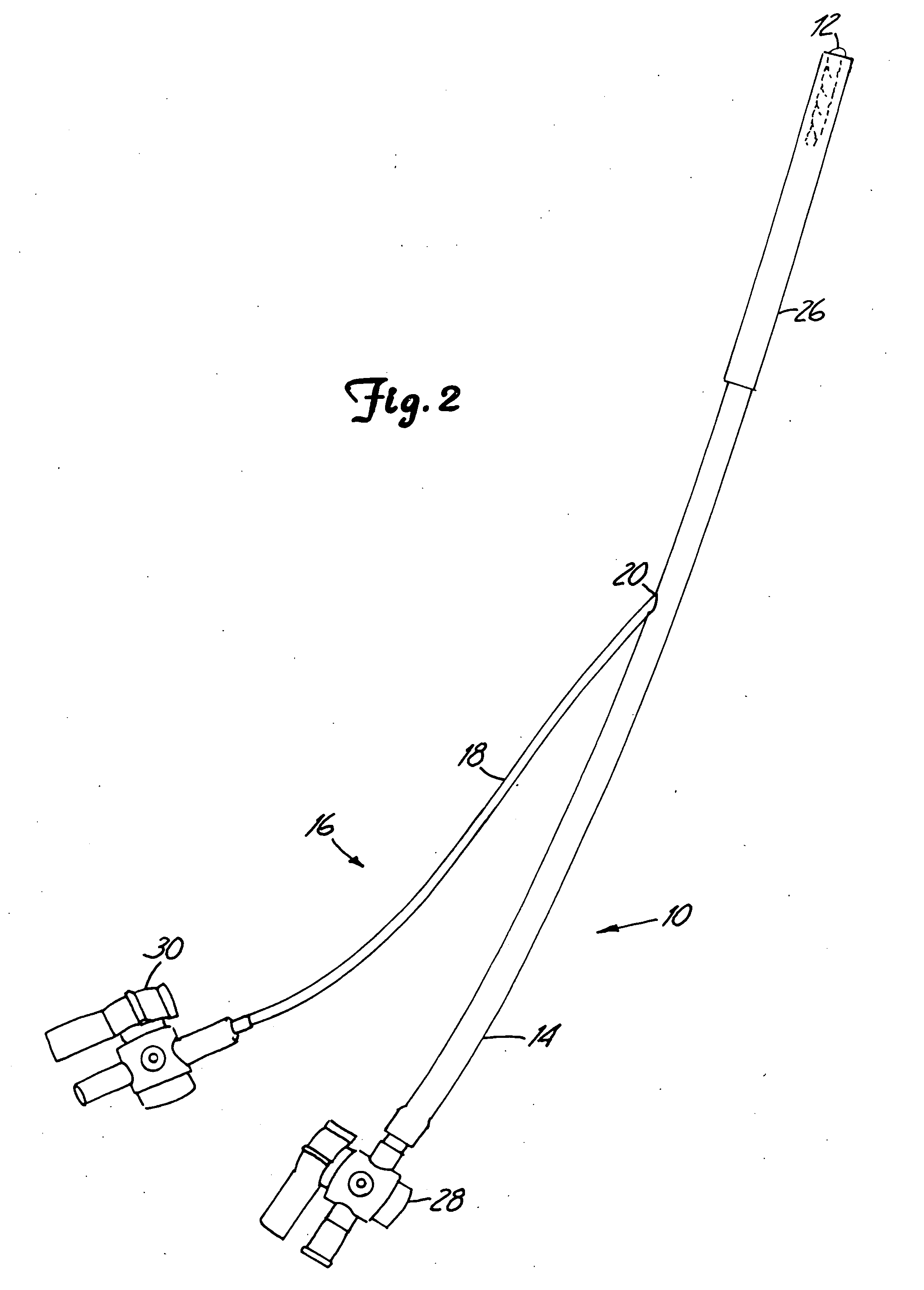
A percutaneous heart valve prosthesis (1) has a valve body (2) with a passage (9) extending between the first and second ends (7, 8) of the valve body (2). The valve body (2) is collapsible about a longitudinal axis (10) of the passage (9) for delivery of the valve body (2) via a catheter (18). One or more flexible valve leaflets (3, 4) are secured to the valve body (2) and extend across the passage (9) for blocking bloodflow in one direction through the passage (9). An anchor device (5), which is also collapsible for delivery via catheter (18), is secured to the valve body (2) by way of an anchor line (6). A failed or failing mitral heart valve (101) is treated by percutaneously locating the valve body (2) in the mitral valve orifice (102) with the anchor device (5) located in the right atrium (107) and engaging the inter-atrial septum (103), such that the taught anchor line (6) acts to secure the valve body (2) within the mitral valve orifice (102).
Owner:PERCUTANEOUS CARDIOVASCULAR SOLUTIONS PTY LTD
Implant Device and Method for Manufacture
A knee implant includes a femoral component having first and second femoral component surfaces. The first femoral component surface is for securing to a surgically prepared compartment of a distal end of a femur. The second femoral component surface is configured to replicate the femoral condyle. The knee implant further includes a tibial component having first and second tibial component surfaces. The first tibial component surface is for contacting a proximal surface of the tibia that is substantially uncut subchondral bone. At least a portion of the first tibial component surface is a mirror image of the proximal tibial surface. The second tibial component surface articulates with the second femoral component surface.
Owner:CONFORMIS
System and method for prosthetic fitting and balancing in joints
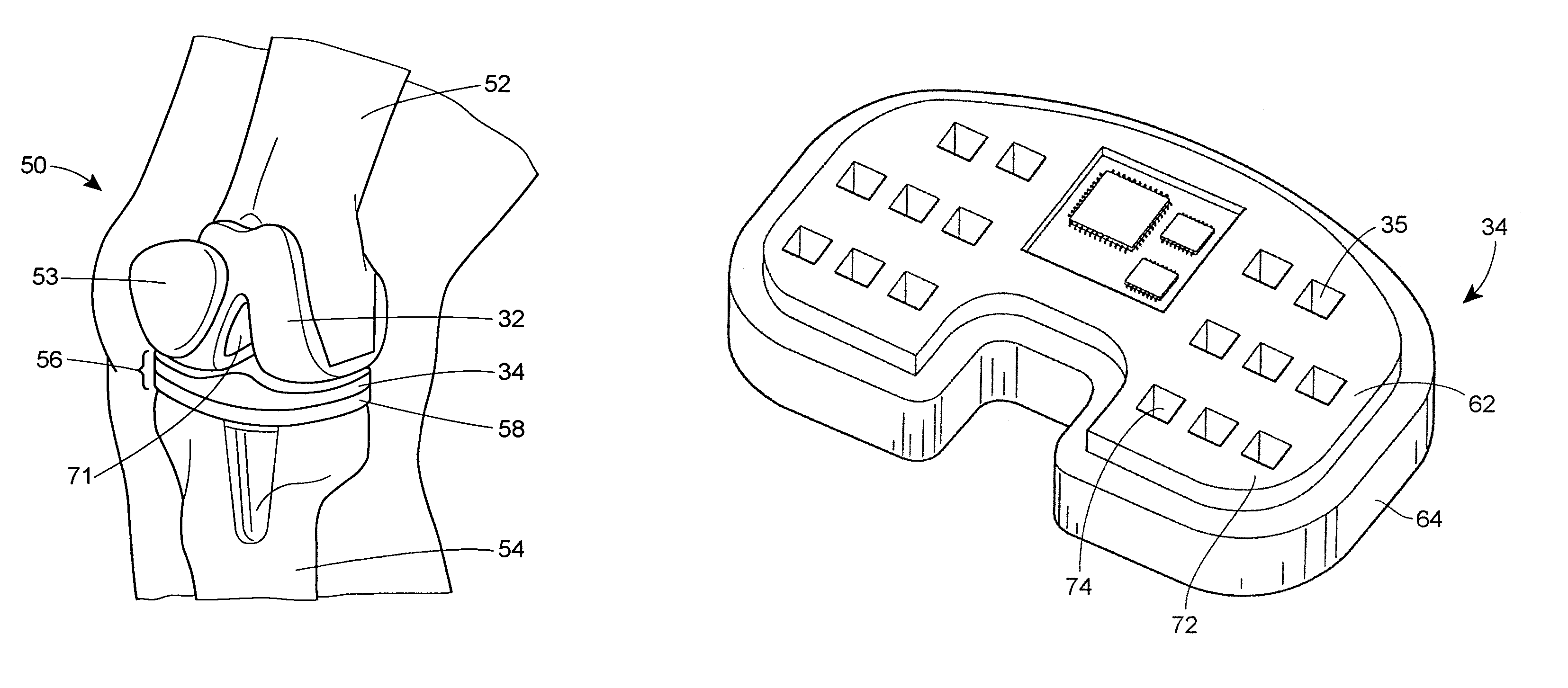
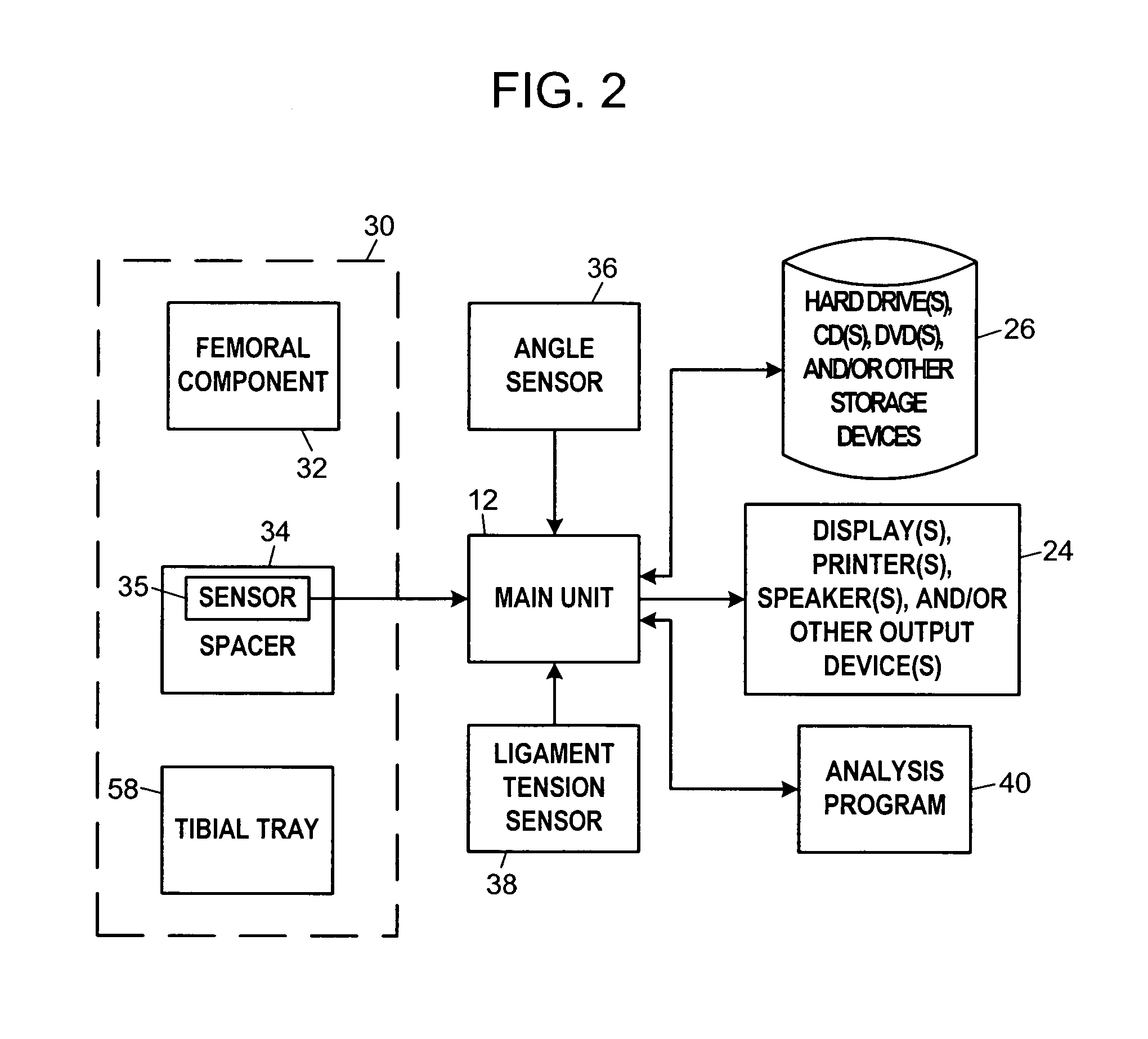
InactiveUS7575602B2Physical therapies and activitiesFinger jointsProsthesis fittingArtificial joints
A system and method for prosthesis fitting in joints comprising an artificial condyle and a spacer which cooperates with the condyle to form an artificial joint. The spacer embedded with at least one sensor which is responsive to a force generated between the condyle and the spacer. The artificial joint is adapted to move between a flexed position and an extended position defining a range of motion. The sensor is responsive to the force and generates an output representative of that force. The output is transmitted, either wirelessly or other, to a processor which utilizes an analysis program to display a representation of the forces applied. A practitioner utilizing the displayed analysis may intraoperatively determine the adjustments and balancing required within the artificial joint. The system may also utilize a ligament tension sensor which generates data representative of tension on a ligament of the artificial joint, and a joint angle sensor responsive to the range of motion of the artificial joint. The processor may be adapted to store the outputted sensor data to provide the practitioner with statistically relevant historical data.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Replacement heart valve
A replacement heart valve can have an expandable frame configured to engage a native valve annulus. A valve body can be mounted onto the expandable frame to provide functionality similar to a natural valve. The valve body has an upstream end and a downstream end, and a diameter at the downstream end is greater than a diameter at the upstream end.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI CARDIAQ
Artificial heart valve
InactiveUS6991649B2Increase flow ratePrevent thrombosisHeart valvesJoint implantsMitral valve leafletPivot joint
Owner:SIEVERS HANS HINRICH
In-vivo orthopedic implant diagnostic device for sensing load, wear, and infection
InactiveUS7097662B2Understand kinematics of jointReliable implantEndoradiosondesCatheterEngineeringIn vivo
A device for providing in vivo diagnostics of loads, wear, and infection in orthopedic implants having at least one load sensor associated with the implant, at least one temperature sensor associated with the implant, at least one vibration sensor associated with the implant, and at least one signal processing device operatively coupled with the sensors. The signal processing device is operable to receive the output signal from the sensors and transmit a signal corresponding with the output signal.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
Modular implant system with fully porous coated sleeve
A modular knee implant system allows a surgeon to select between several different styles of distal femoral implant components and several different styles of stem extensions while also allowing for use of a metaphyseal component. The metaphyseal component can be a universal one that is usable with all of the styles of distal femoral implant components through use of an adapter. A second adapter allows for use of stem extensions with different types of connectors with the metaphyseal component. A separate metaphyseal component could also be provided with a distal Morse taper post to mate with a distal femoral component having a proximal Morse taper bore. The metaphyseal component may have an outer surface that is configured to maximize contact area with the patient's bone, and may have a surface finish over a substantial part of its overall length that is conducive to bone ingrowth.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Knee joint prosthesis
InactiveUS20050043808A1Eliminate the effects ofImprove propertiesImpression capsAnkle jointsTissue repairProsthesis
A method, and related composition and apparatus for repairing a tissue site. The method involves the use of a curable polyurethane biomaterial composition having a plurality of parts adapted to be mixed at the time of use in order to provide a flowable composition and to initiate cure. The flowable composition can be delivered using minimally invasive means to a tissue site and there fully cured provide a permanent and biocompatible prosthesis for repair of the tissue site. Further provided are a mold apparatus, e.g., in the form of a balloon or tubular cavity, for receiving a biomaterial composition, and a method for delivering and filling the mold apparatus with a curable composition in situ to provide a prosthesis for tissue repair.
Owner:ADVANCED BIO SURFACE
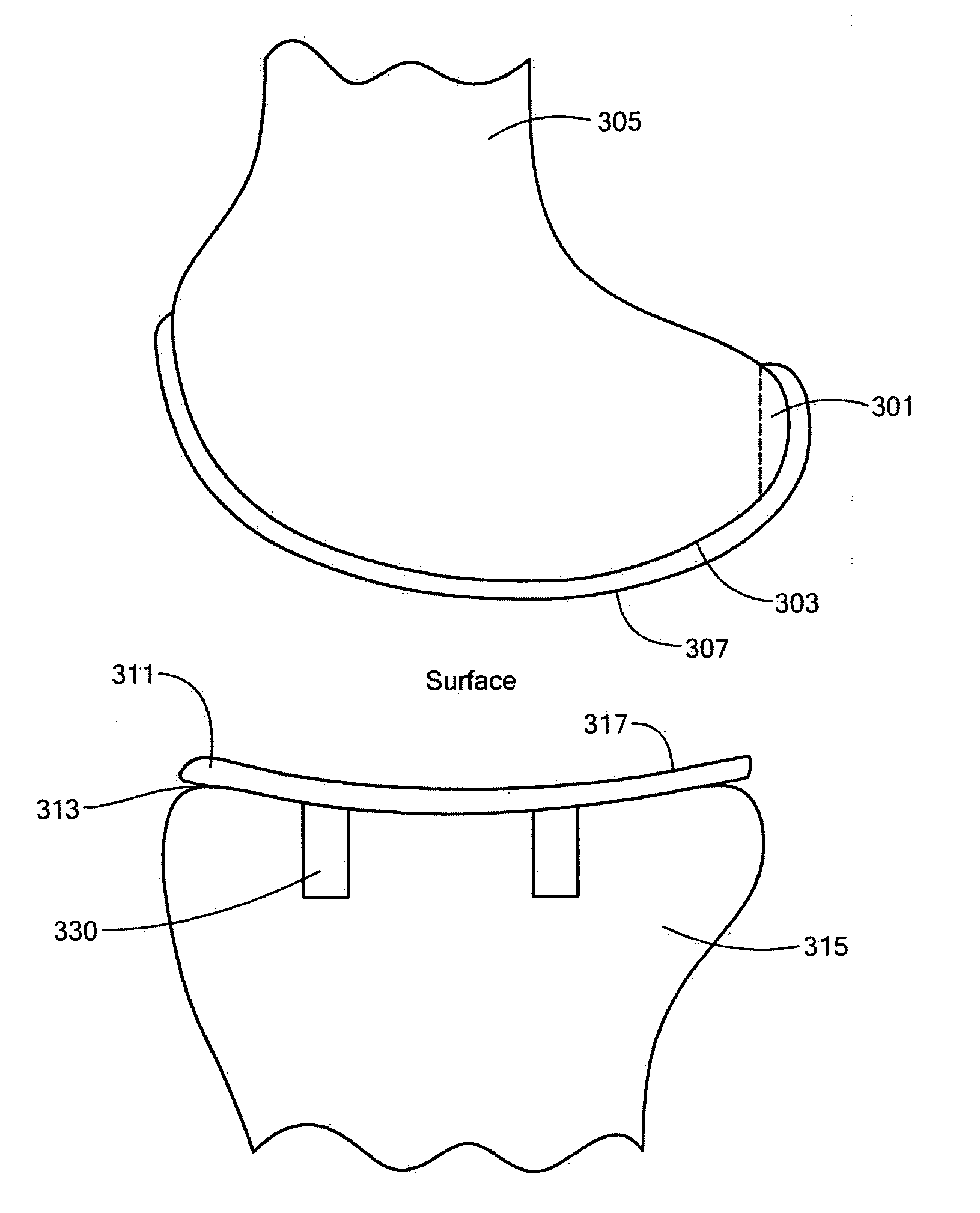
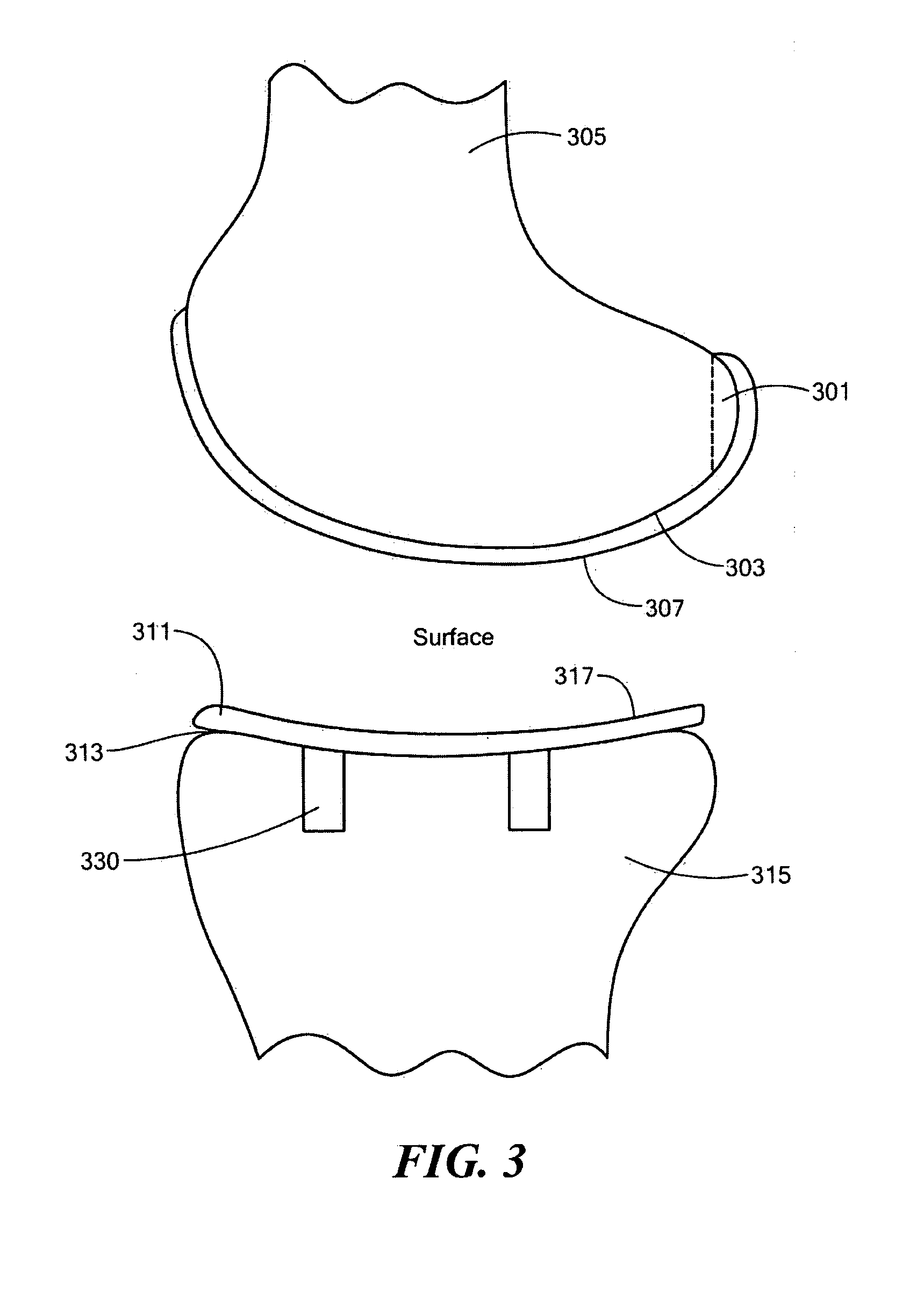
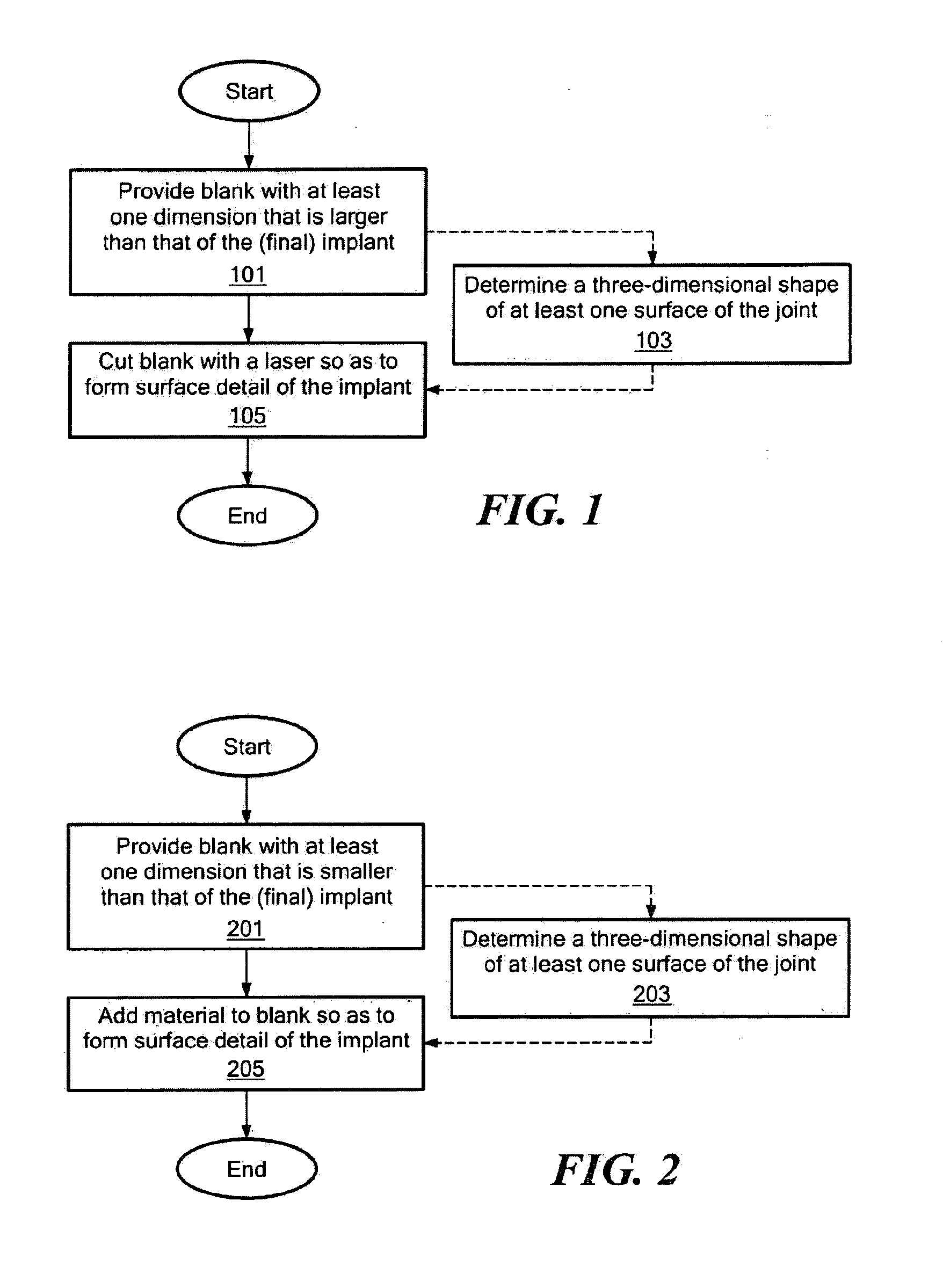
Implant device and method for manufacture
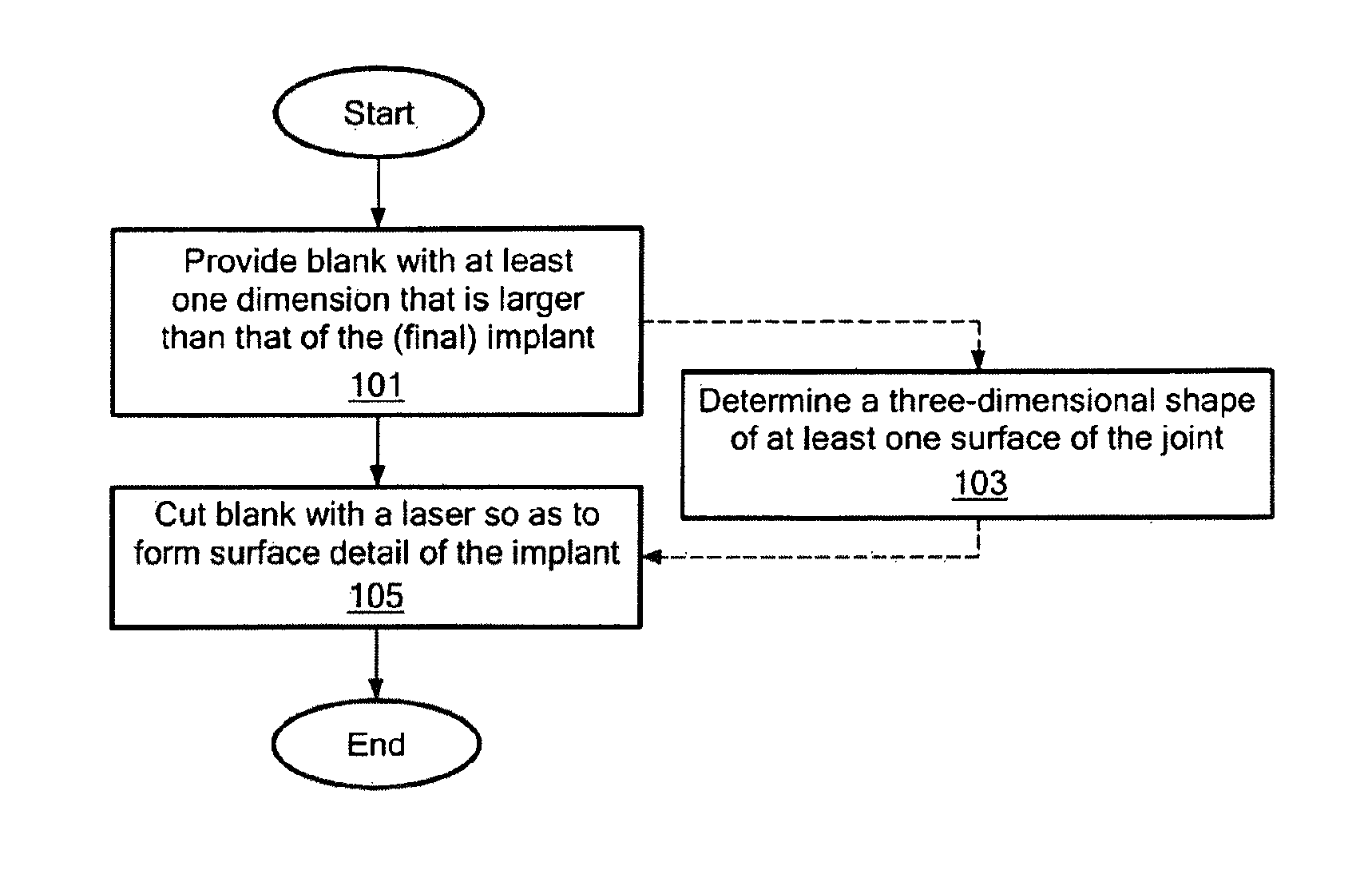
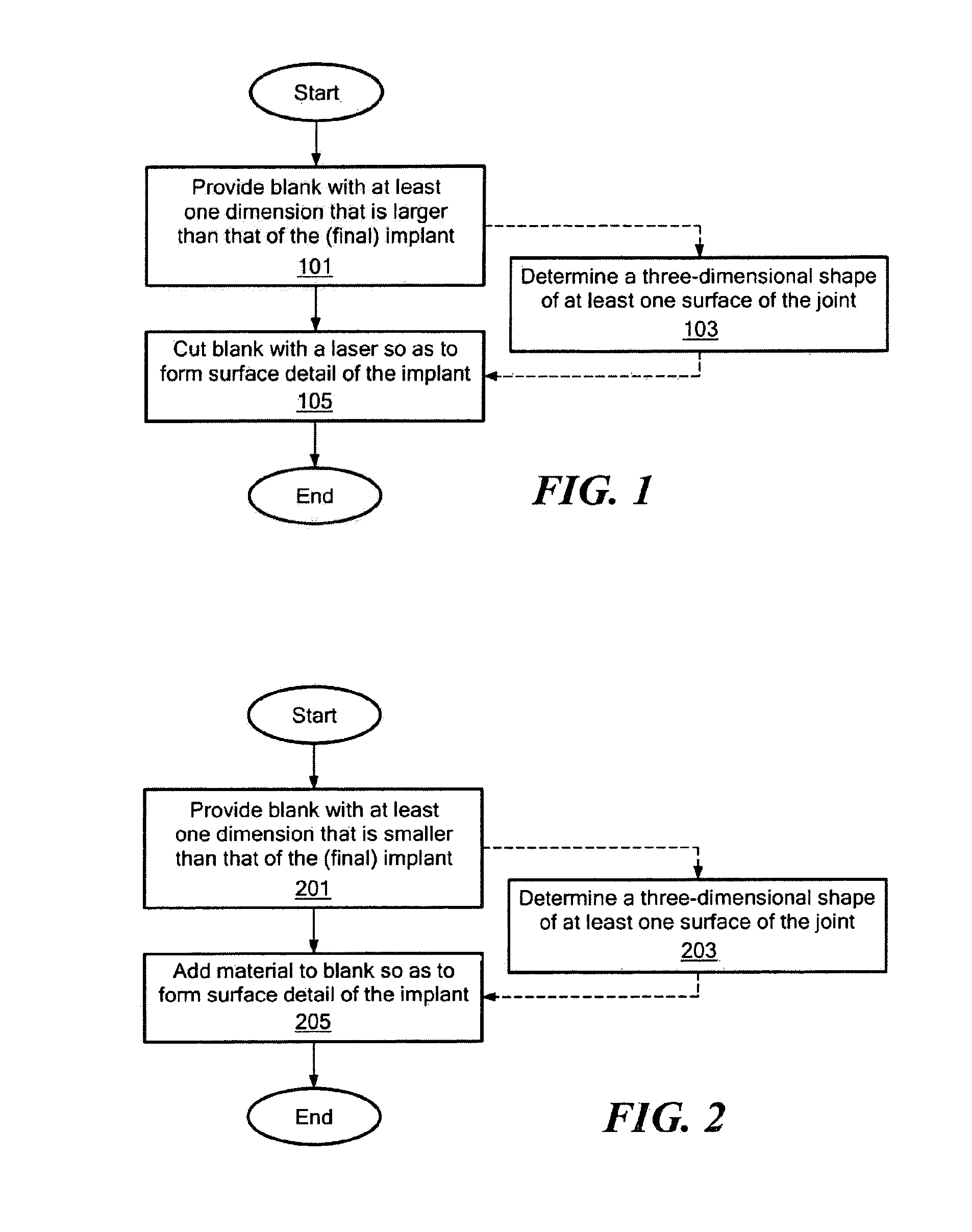
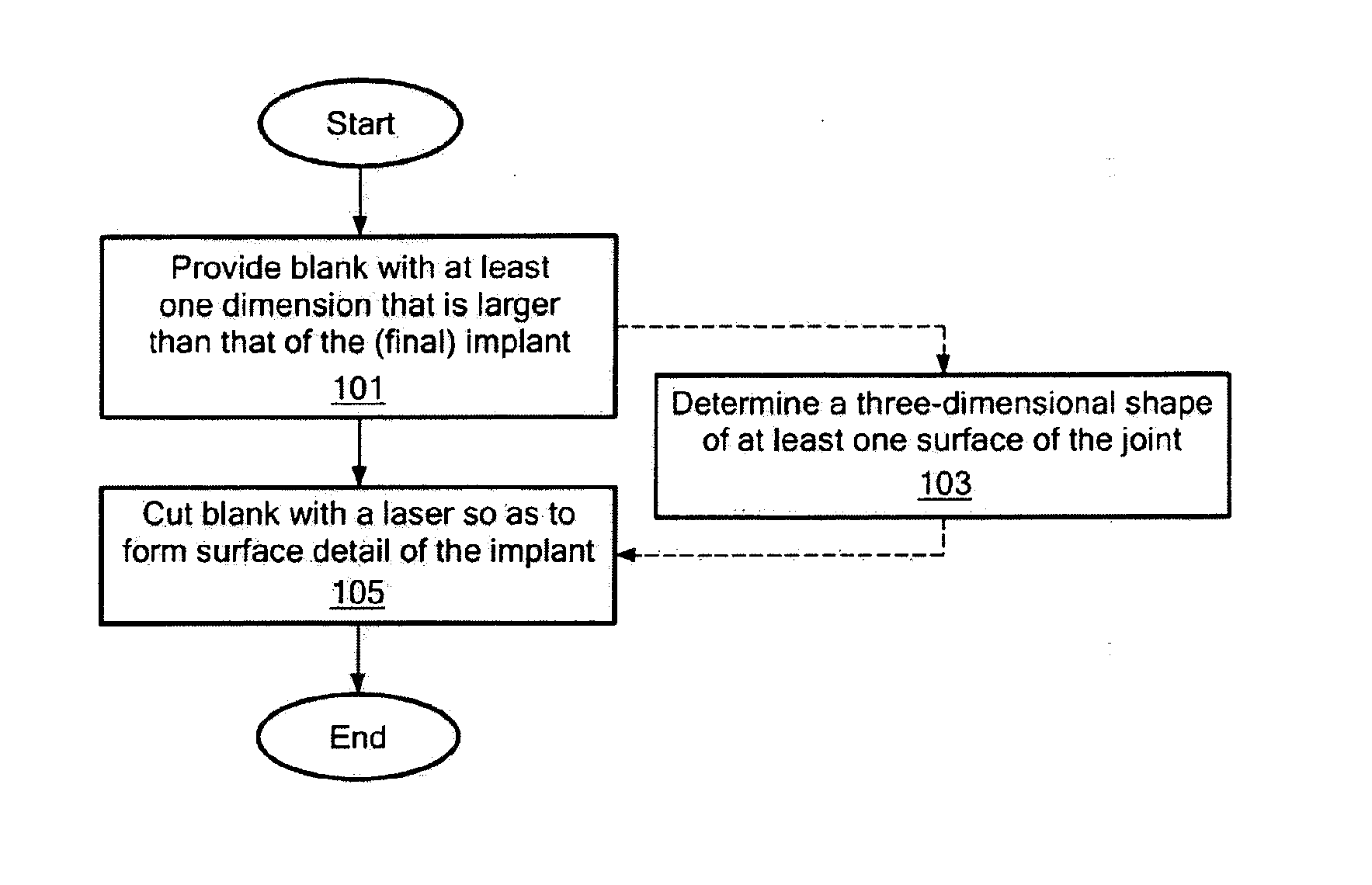
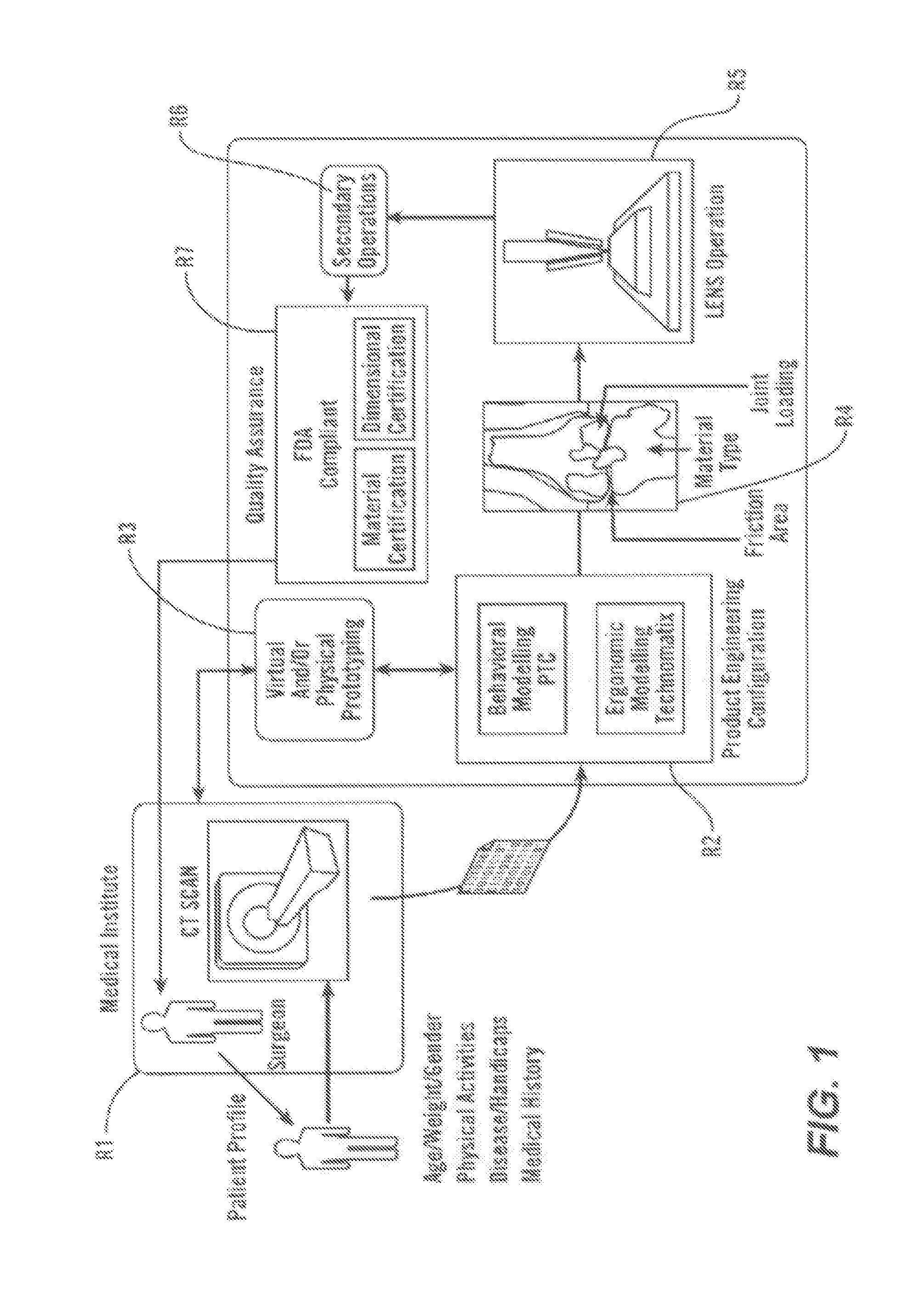
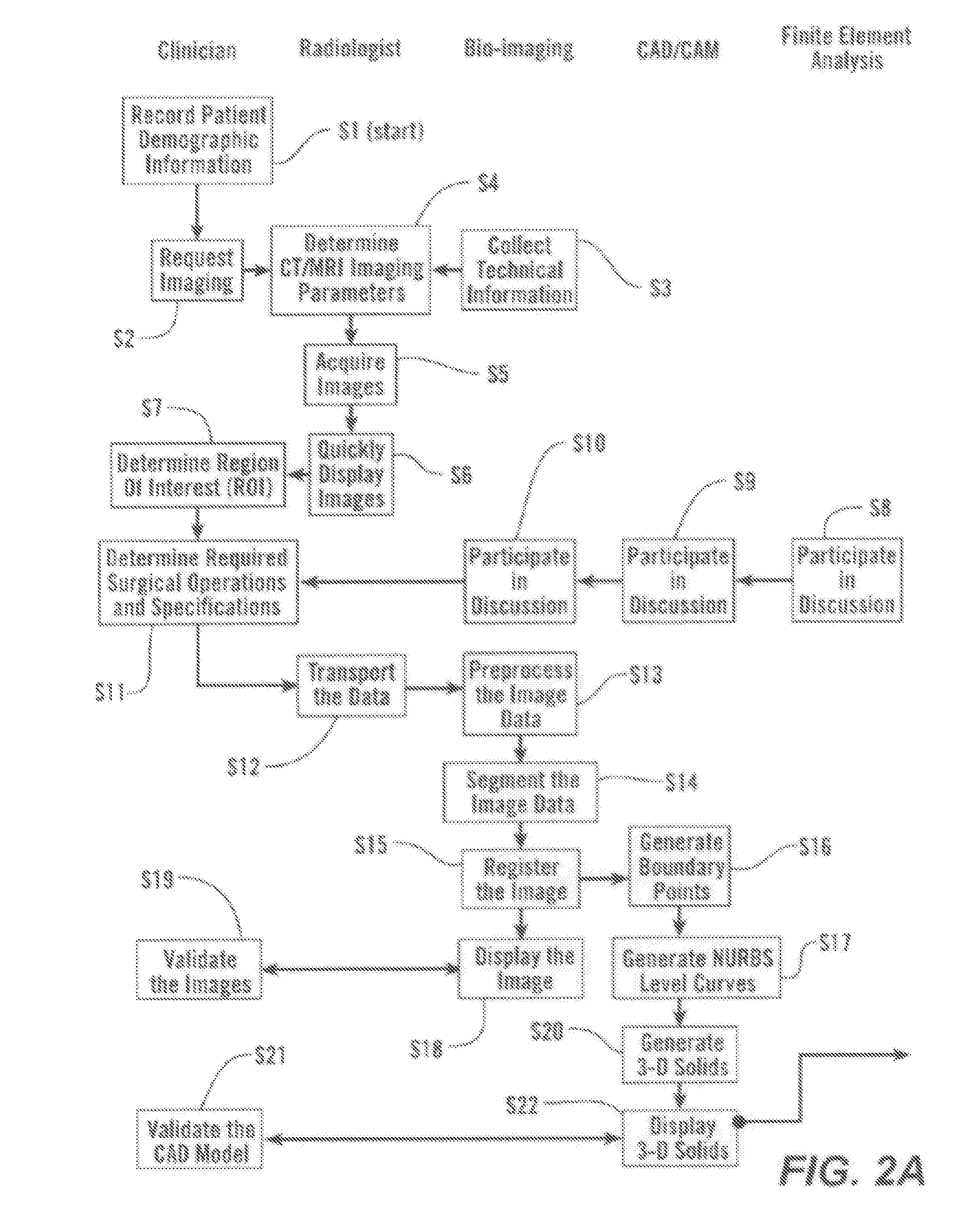
Disclosed are systems, devices and methods for optimizing the manufacture and / or production of patient-specific orthopedic implants. The methods include obtaining image data of a patient, selecting a blank implant to be optimized for the patient, and modifying the blank implant utilizing techniques disclosed herein to alter specific features of the implant to conform to the patient's anatomy.
Owner:CONFORMIS
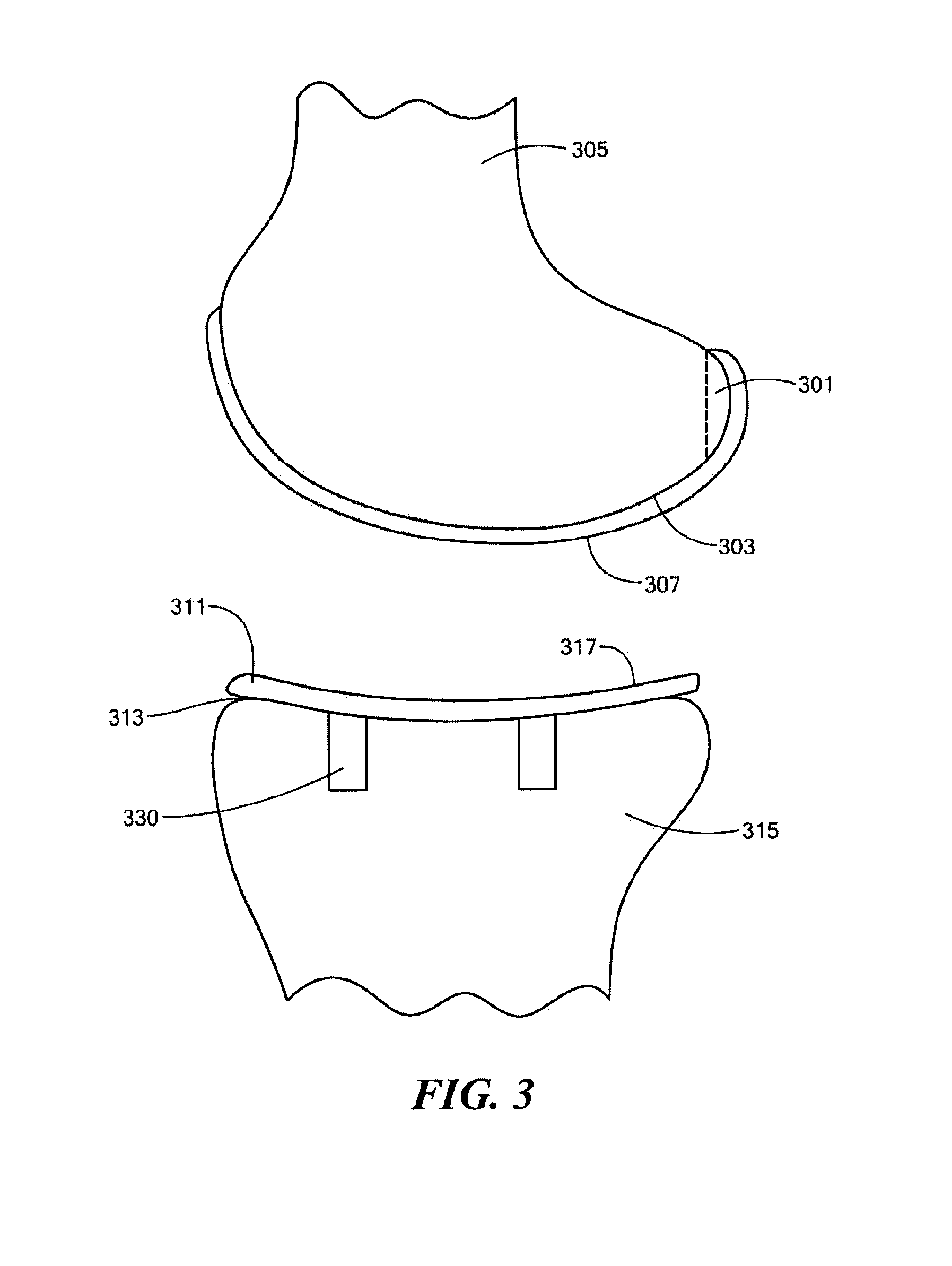
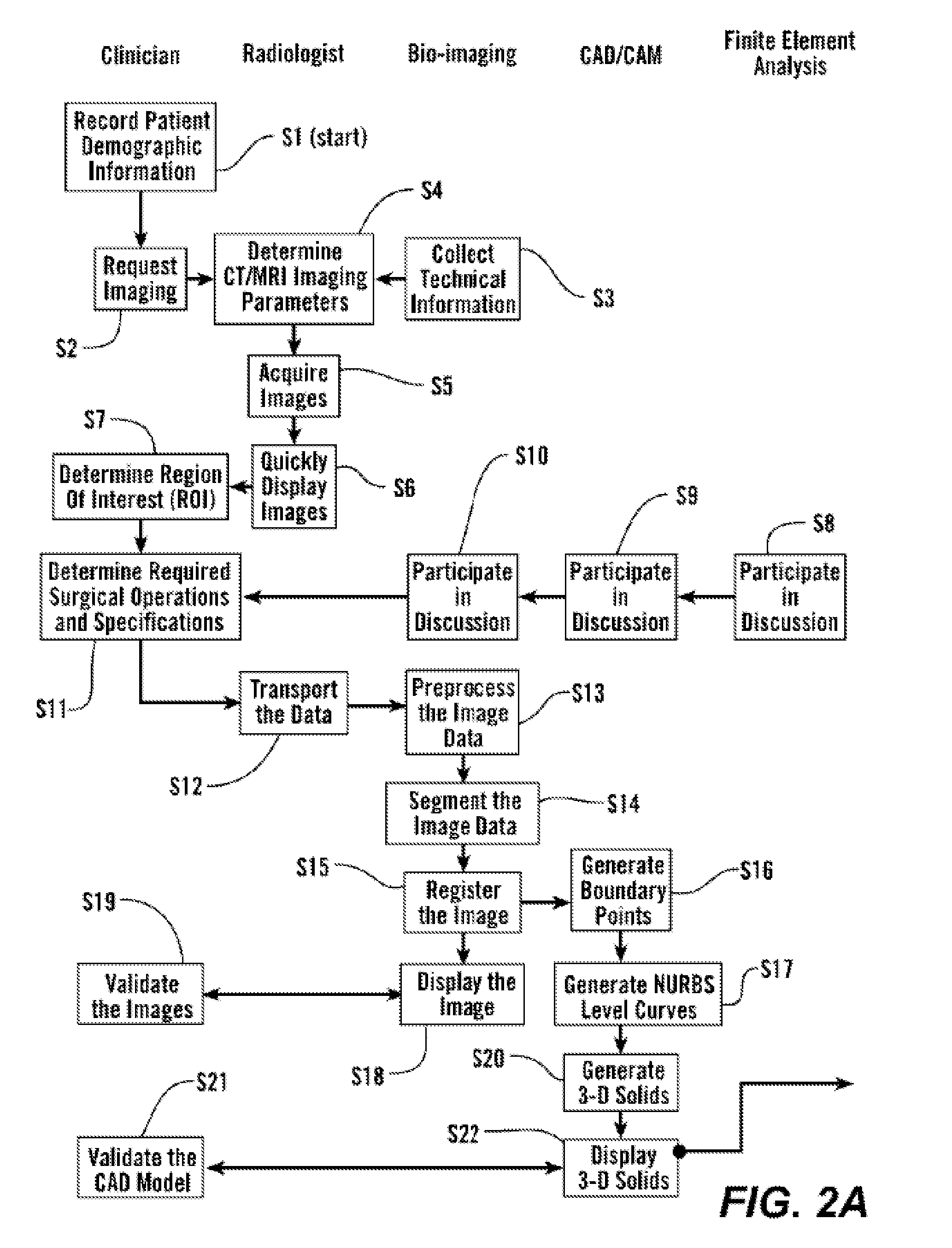
Personalized fit and functional designed medical prostheses and surgical instruments and methods for making
ActiveUS8457930B2Simple designFast learningMedical simulationAdditive manufacturing apparatusCamMedical treatment
Owner:SCHROEDER JAMES
Modular humeral head resurfacing system
A two piece humeral component for use in joint arthroplasty which is adapted to be implanted into a joint and engaged by a socket component of the joint. The joint component includes a body having a first articulating surface and a second medial surface opposite the first articulating surface. The first articulating surface is adapted to be engaged by the socket and the second medial surface is adapted to be secured to mounting portion. The mounting portion has a first surface and a second medial surface. The first surface is adapted to be fixably engaged to the second mounting portion of the humeral component. The second medial surface is adapted to be secured to the humerus. A peg which has a first end adapted to engage a cavity found in the humerus is disposed on the mounting portion's second medial surface.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
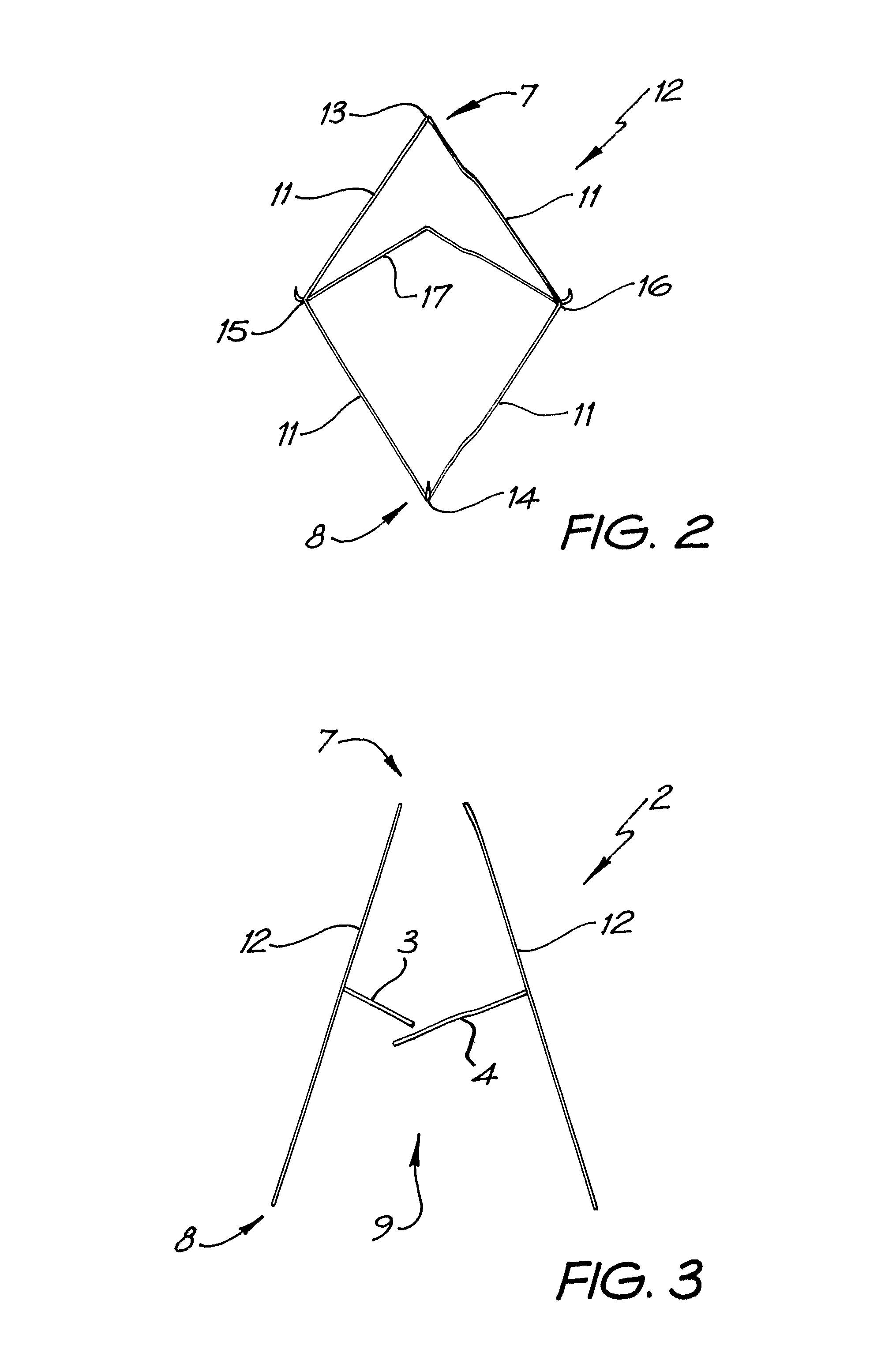
Laser-produced implants
A method of producing an orthopedic implant including the steps of building a flat open model of at least a portion of an implant. The flat open model may be built using a selective laser center process. The flat open model preferably includes at least one groove along either a first surface or a second surface of the model. Next a force may be applied to the flat open model at predetermined locations to thereby cause the model to bend and assume a shape similar to a desired result. The now bent model may be resurfaced by either applying additional material such that the bent flat open model assumes the shape of a desired implant or the bent open model may be snap fit to an additional element.
Owner:UNIV OF LIVERPOOL +2
Method of making an intervertebral disc prosthesis
InactiveUS7077865B2Excellent characteristicsImprove curingInternal osteosythesisAnkle jointsDistractionMedicine
A system for repairing an intervertebral disc by delivering and curing a biomaterial in situ within the disc. The system includes both a device, having an insertable balloon and related lumen, controls and adapters, as well as an in situ curable biomaterial (and related biomaterial delivery means). The system can allow the doctor to determine a suitable endpoint for biomaterial delivery, by controlling distraction and / or biomaterial delivery pressure, and in turn, to deliver a desired quantity of biomaterial to the balloon in order to achieve improved polymer cure and implant characteristics. Also provided is a related method for repairing an intervertebral disc by using such a system to deliver and cure the biomaterial in situ. The system can be used to implant a prosthetic total disc, or a prosthetic disc nucleus in a manner that leaves the surrounding disc tissue substantially intact.
Owner:DISC DYNAMICS
In-vivo orthopedic implant diagnostic device for sensing load, wear, and infection
InactiveUS20060047283A1Understand kinematics of jointReliable implantEndoradiosondesJoint implantsEngineeringIn vivo
A device for providing in vivo diagnostics of loads, wear, and infection in orthopedic implants having at least one load sensor associated with the implant, at least one temperature sensor associated with the implant, at least one vibration sensor associated with the implant, and at least one signal processing device operatively coupled with the sensors. The signal processing device is operable to receive the output signal from the sensors and transmit a signal corresponding with the output signal.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
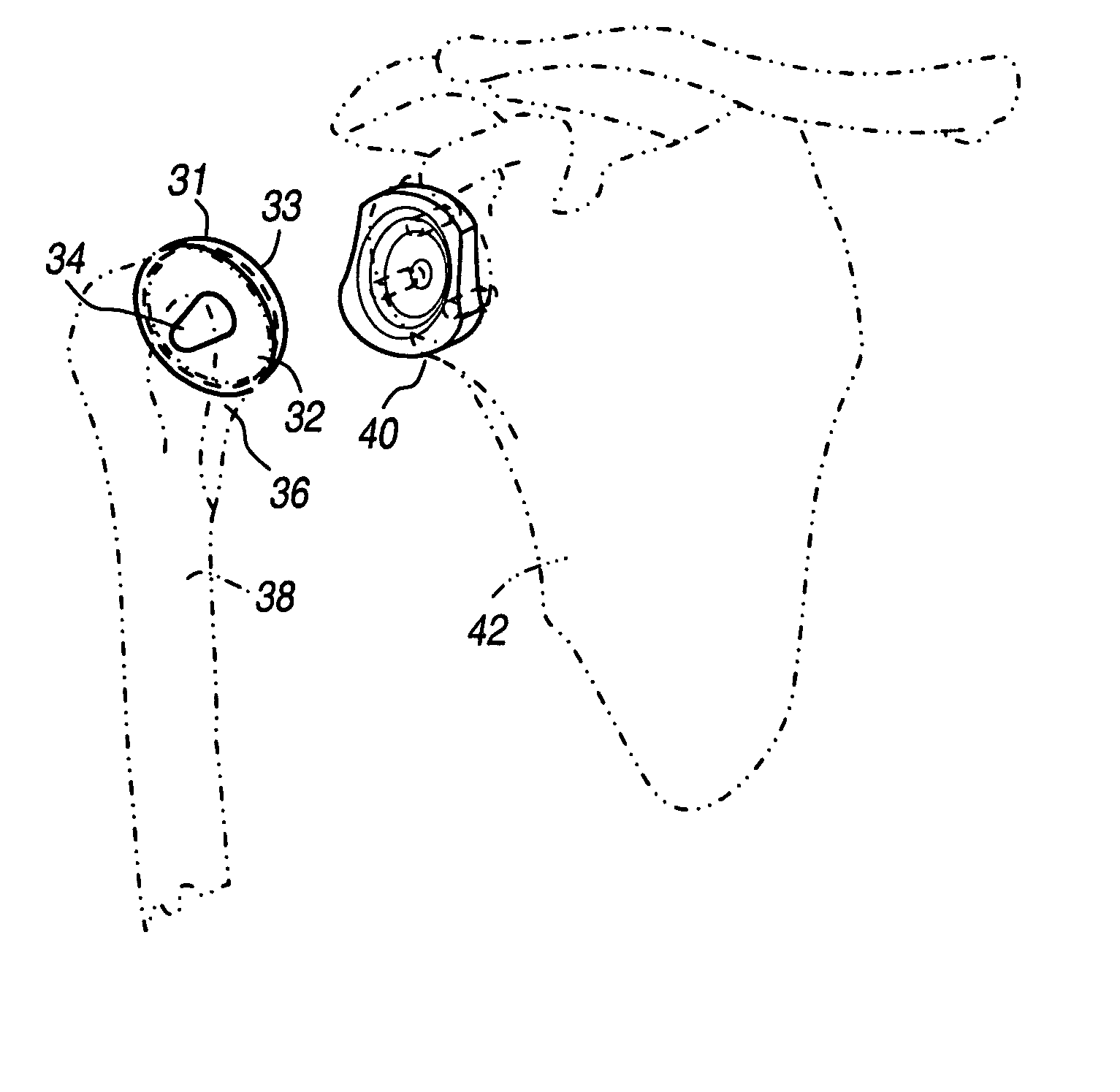
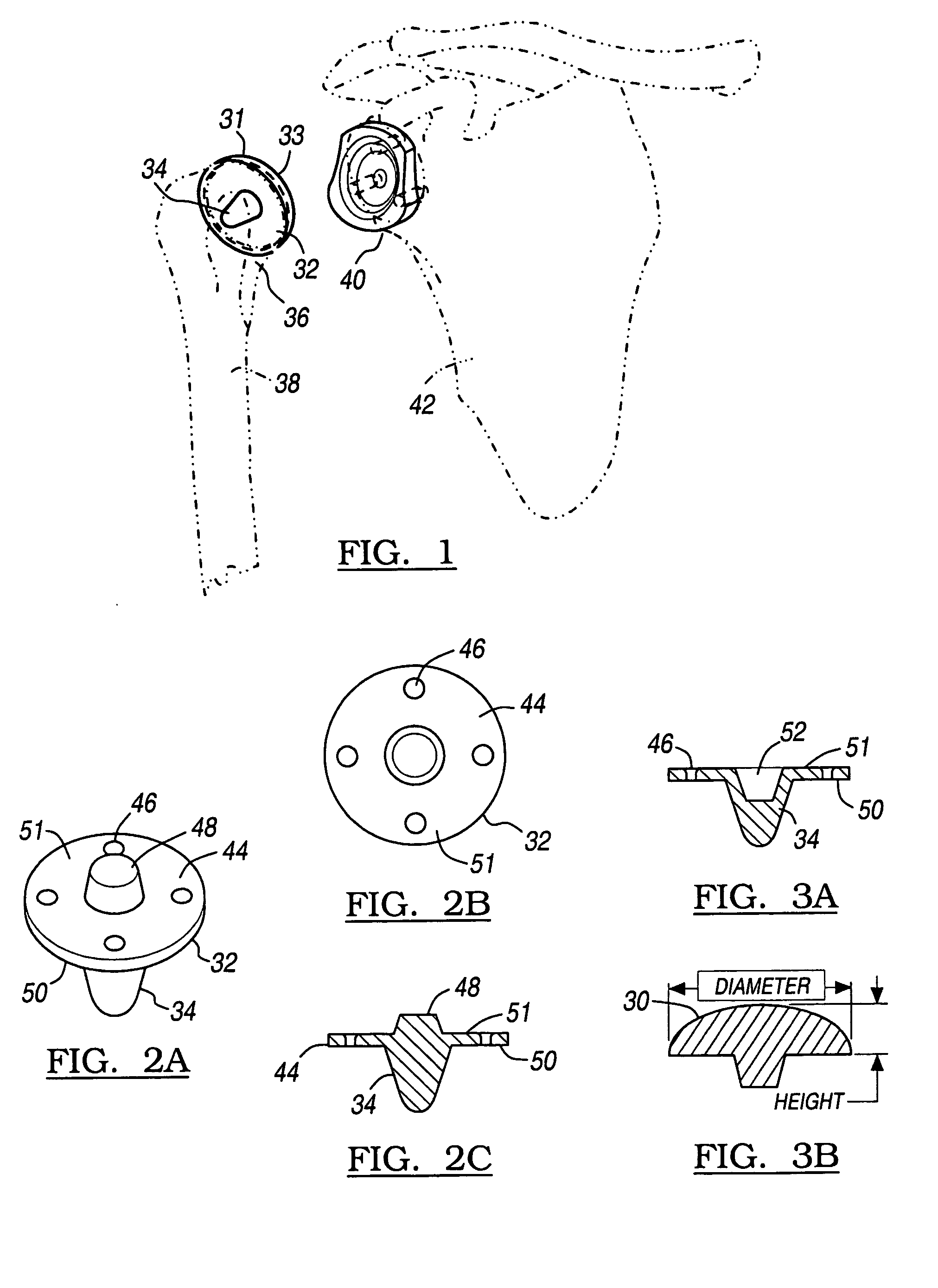
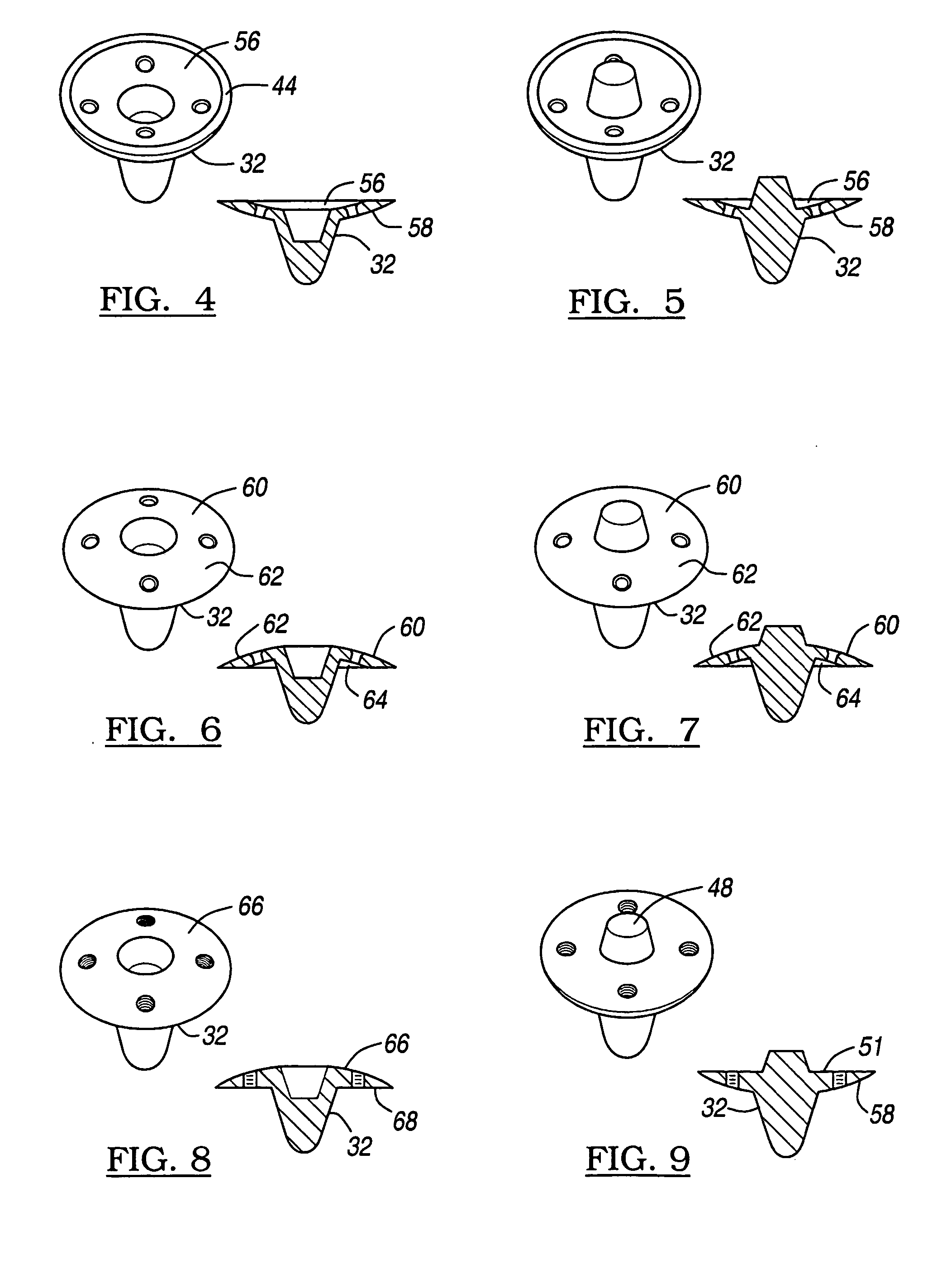
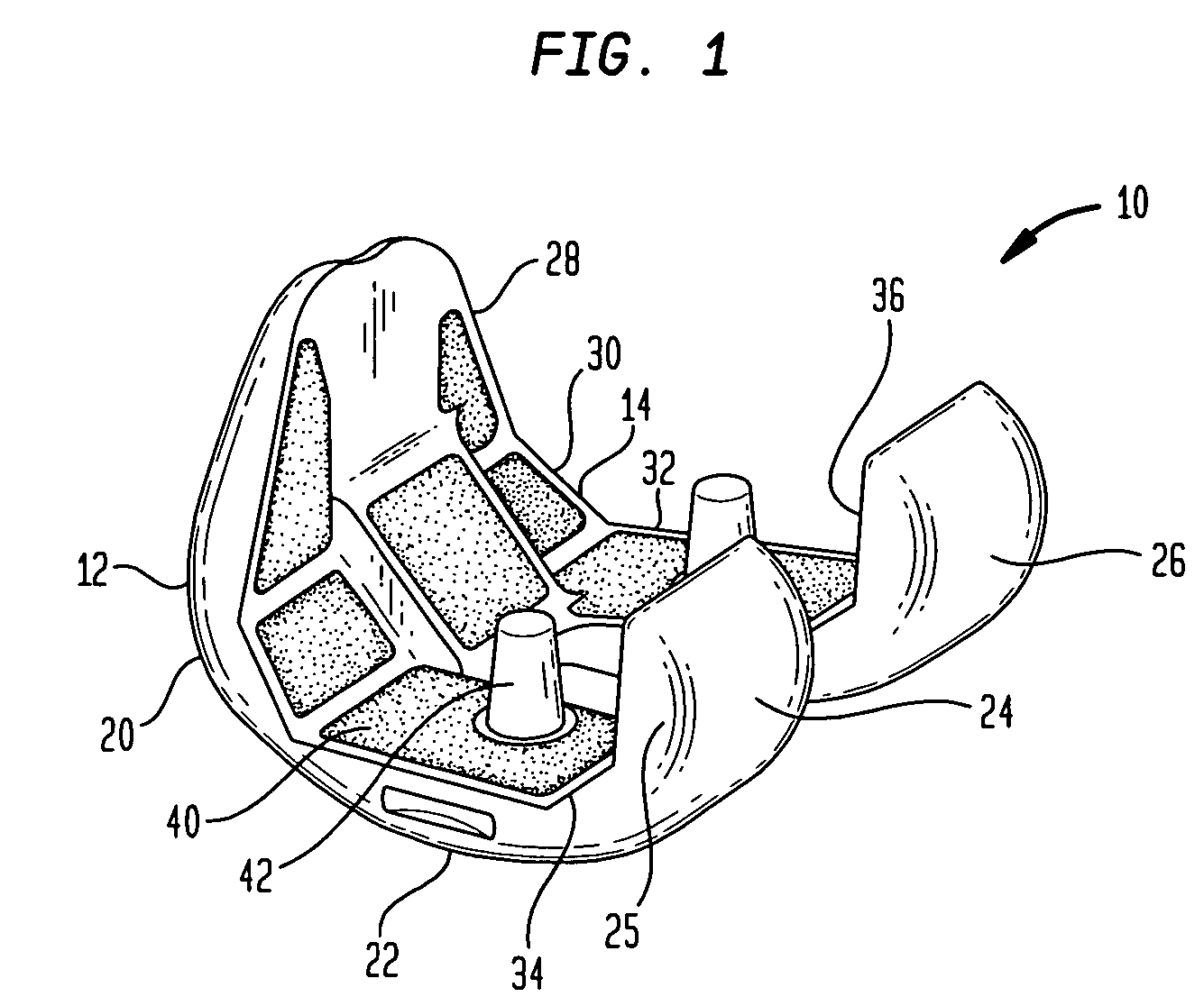
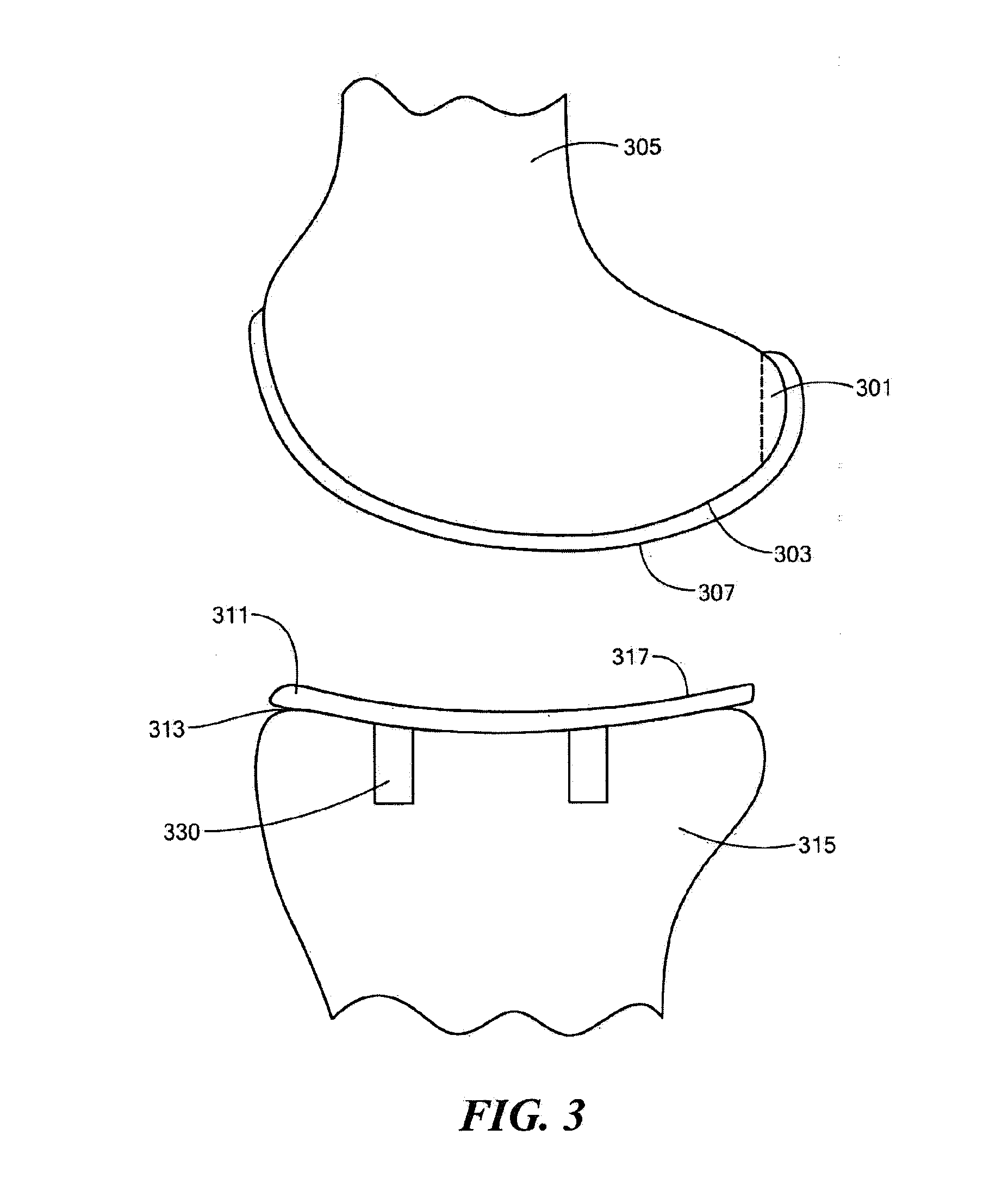
Hydrogel implants for replacing hyaline cartilage, with charged surfaces and improved anchoring
InactiveUS20050287187A1High strengthIncreased durabilityFinger jointsWrist jointsKnee JointVolumetric Mass Density
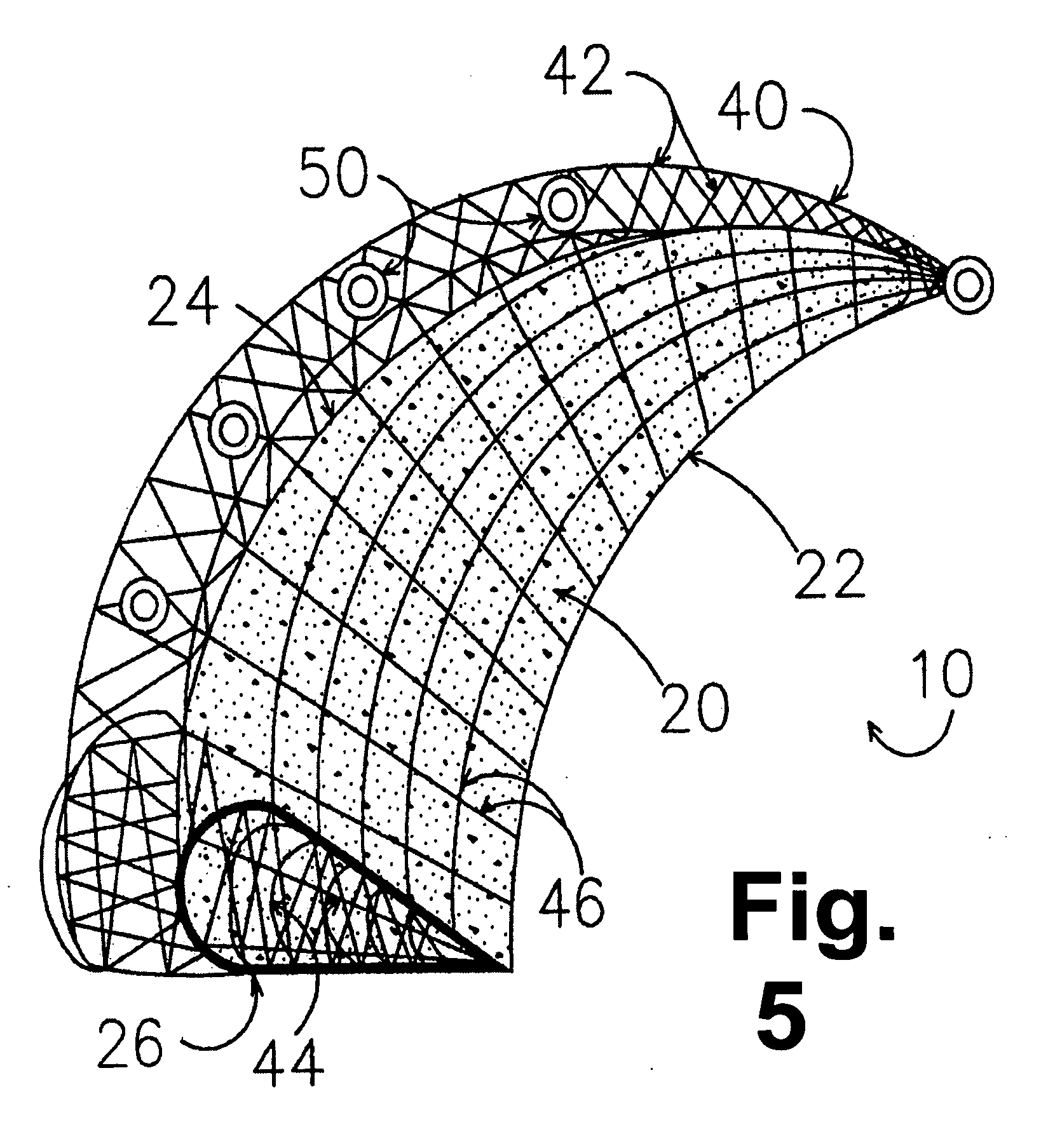
Hydrogel devices for surgical implantation to replace damaged cartilage in a mammalian joint (such as a knee, hip, shoulder, etc.) are disclosed, with one or more of the following enhancements: (1) articulating surfaces that have been given negative surface charge densities that emulate natural cartilage and that interact with positively charged components of synovial fluid; (2) anchoring systems with affixed pegs that will lock into accommodating receptacles, which will be anchored into hard bone before the implant is inserted into a joint; (3) a three-dimensional reinforcing mesh made of strong but flexible fibers, embedded within at least a portion of the hydrogel.
Owner:MANSMANN KEVIN A
Femoral neck resection guide
InactiveUS7488325B2Shorten the timeRelieve painThread cutting machinesJoint implantsFemoral neckSurgery
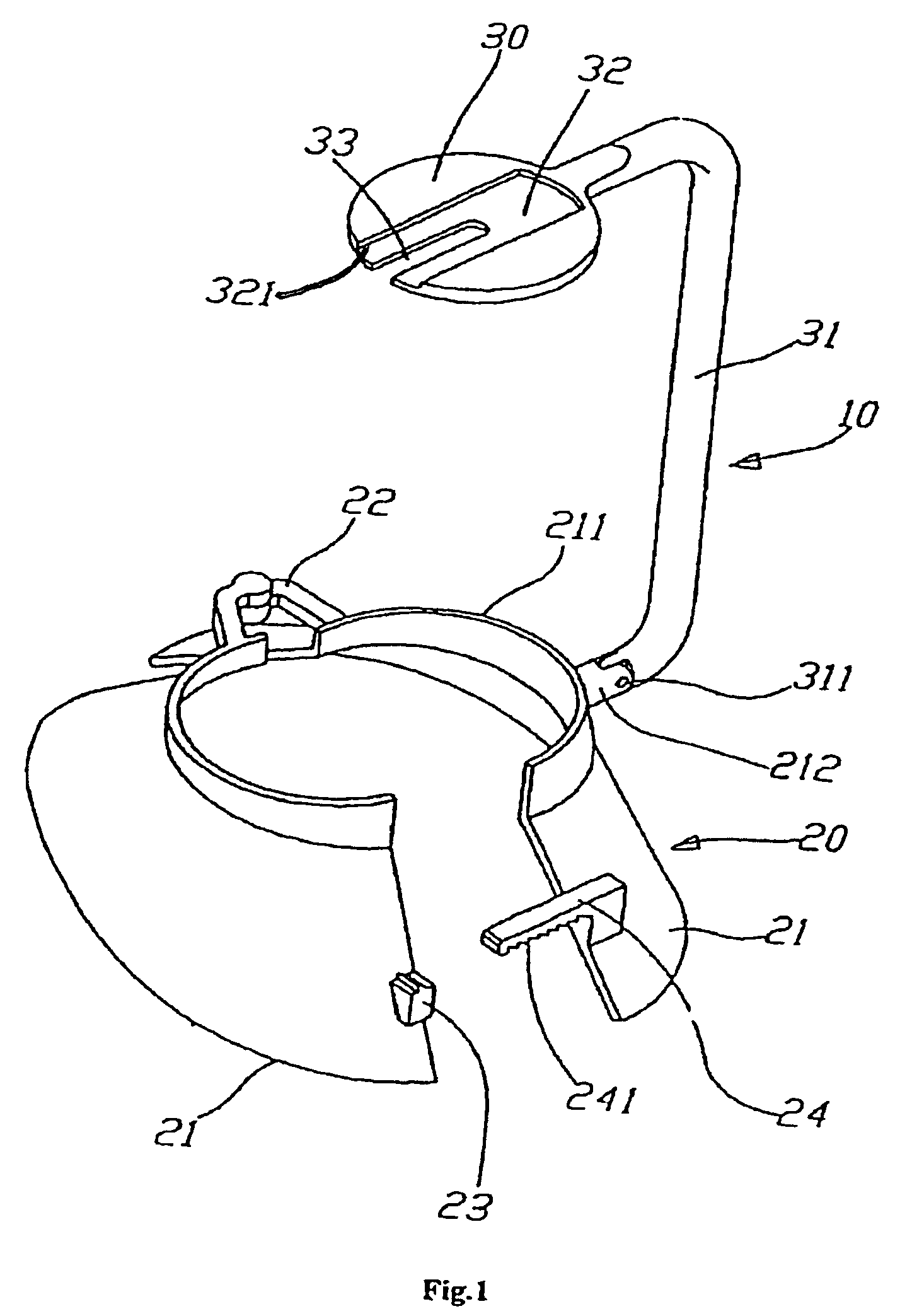
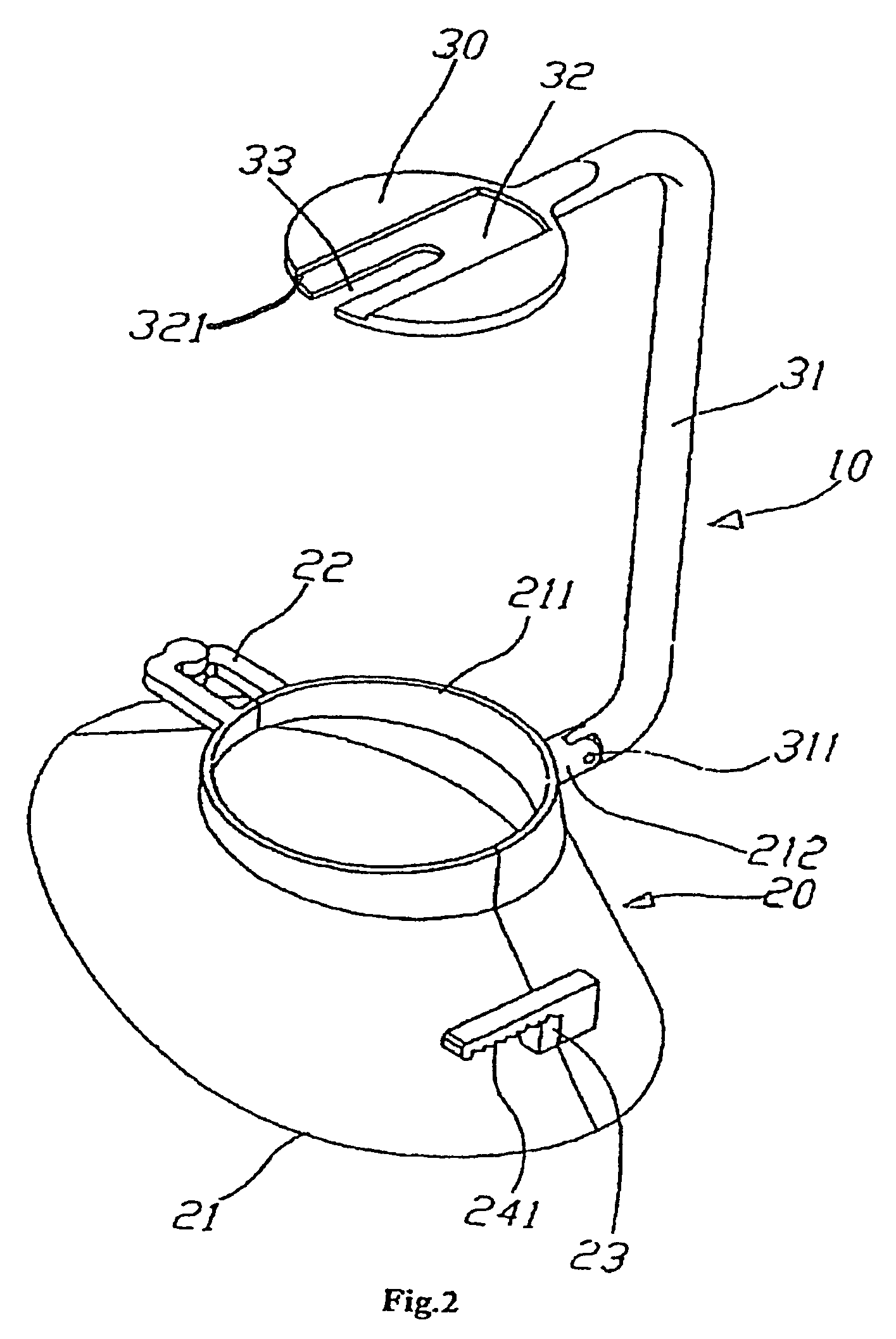
The present invention relates to an apparatus for fitting a protecting femoral neck device. The said apparatus includes a clamping base. A fixation element whose circumference size can be adjusted according to the size of the femoral neck in mounted on an end of the said clamping base and a locating element is mounted on the other end of the said clamping base. An element for shaping the bone can be fixed on the said locating element.
Owner:QIAN BENWEN
Laser based metal deposition of implant structures
InactiveUS20050123672A1Improved bearing propertyIncrease bone ingrowth propertyDental implantsFinger jointsArtificial jointsBone ingrowth
Owner:MEDICINELODGE
System and method for performing arthroplasty of a joint and tracking a plumb line plane
ActiveUS20060095047A1Improve stabilityMinimal potential for impingementSurgical navigation systemsPerson identificationRange of motionNavigation system
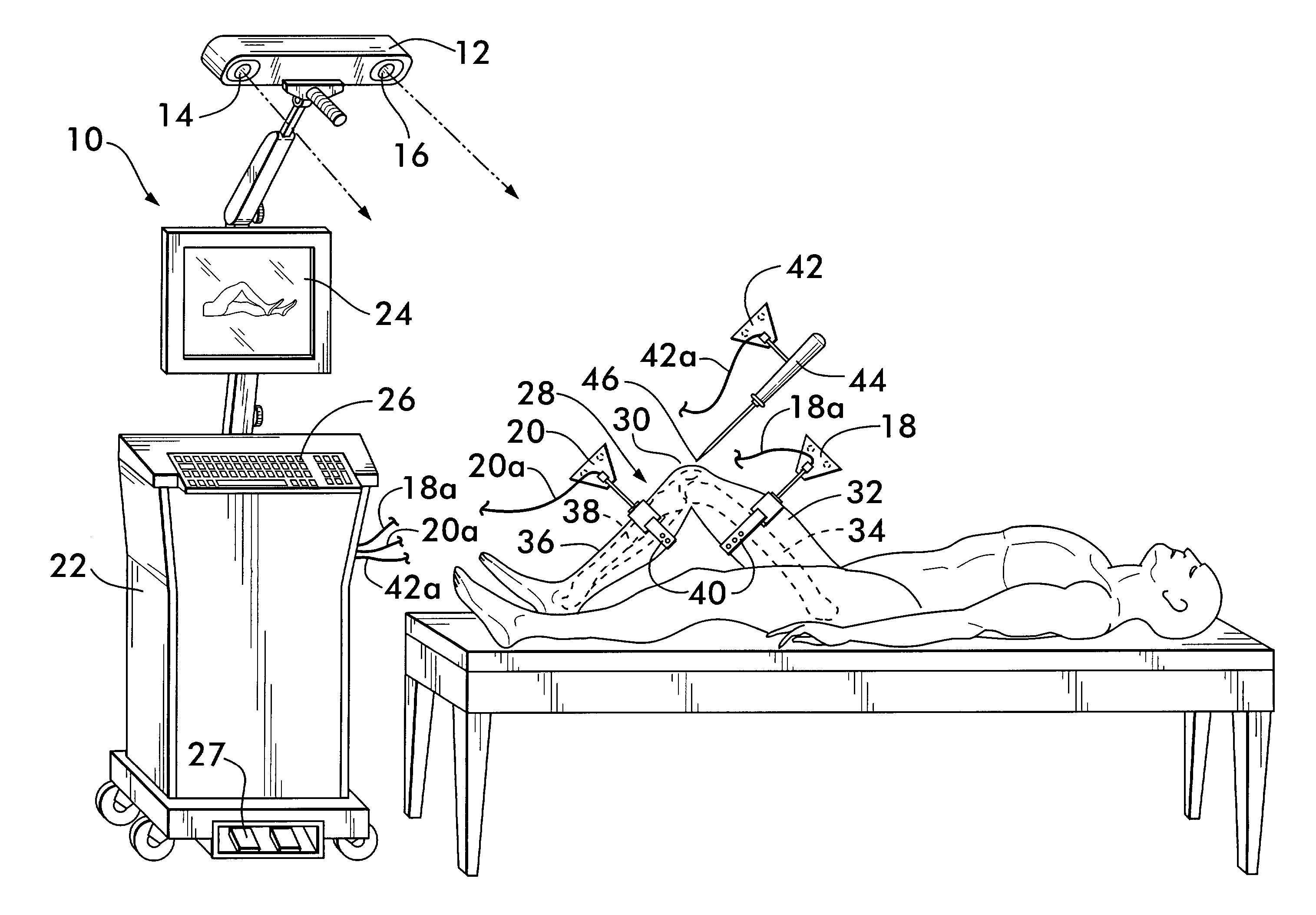
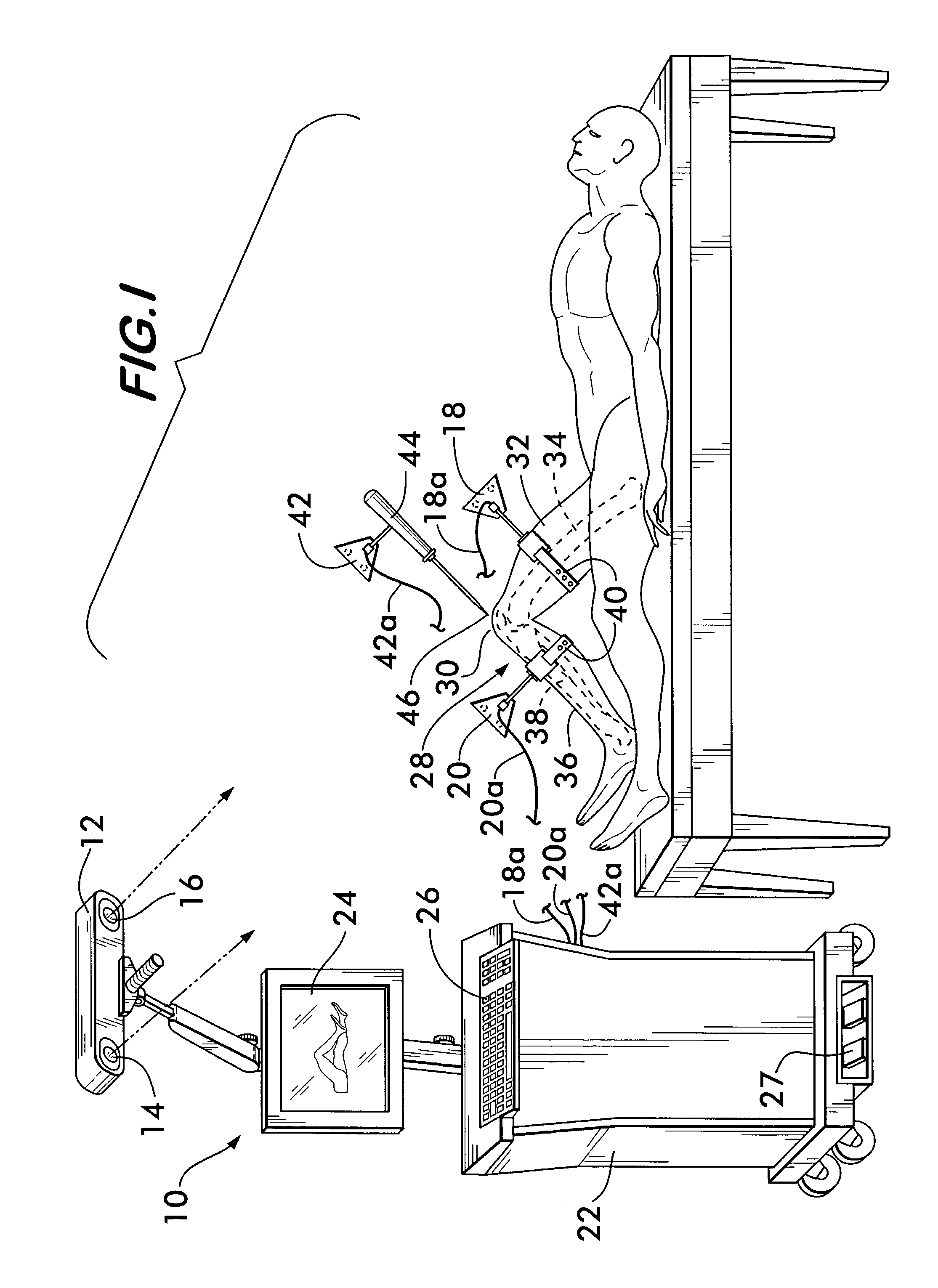
A method of performing an arthroplasty of a ball and socket joint with a surgical navigation system includes the step of digitizing landmarks to provide geometrical parameters of the joint and a limb depending there from, including digitizing aspects of a socket region of the ball and socket joint. A range of motion parameter is determined. A soft tissue tension parameter is determined. A functional goal is computed based on landmark data, the range of motion parameter, the soft tissue tension parameter, and a database of potential implants. An optimal socket position is solved for to minimize impingement of potential implants. An implant is chosen based on the optimal socket position and the functional goal. The joint is prepared to receive the chosen implant. The chosen implant is installed into the joint.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
Method and apparatus for reducing femoral fractures
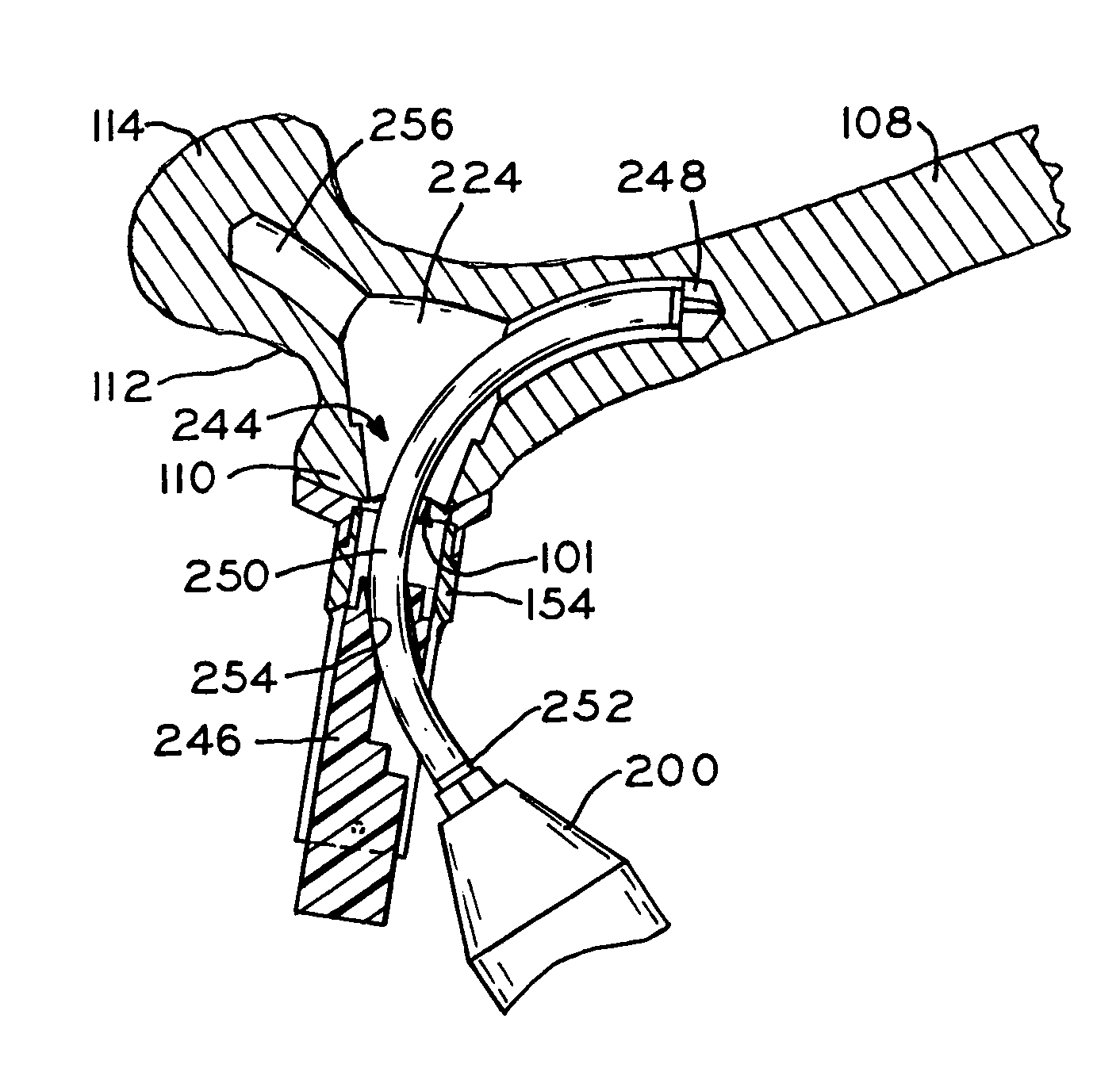
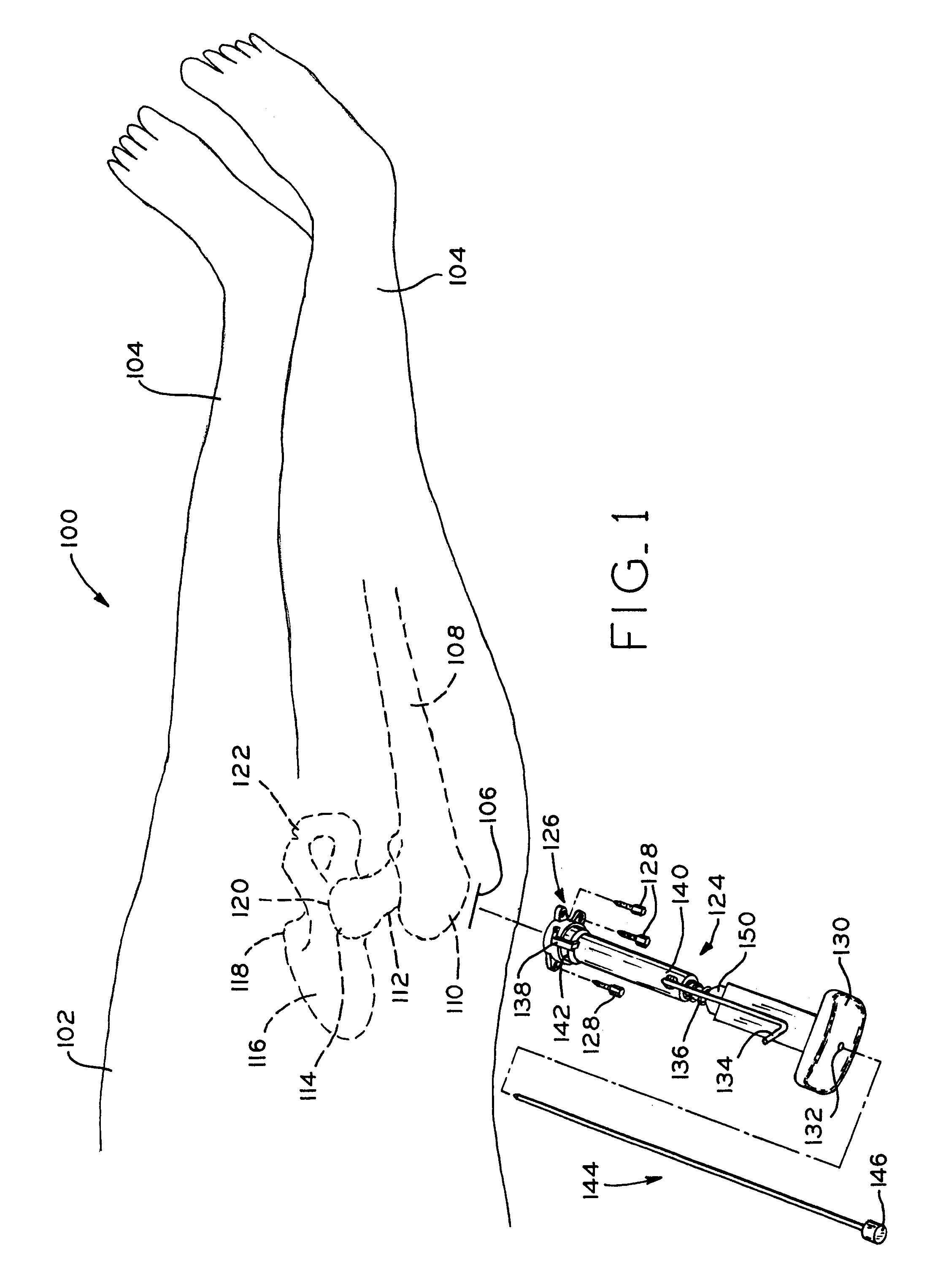
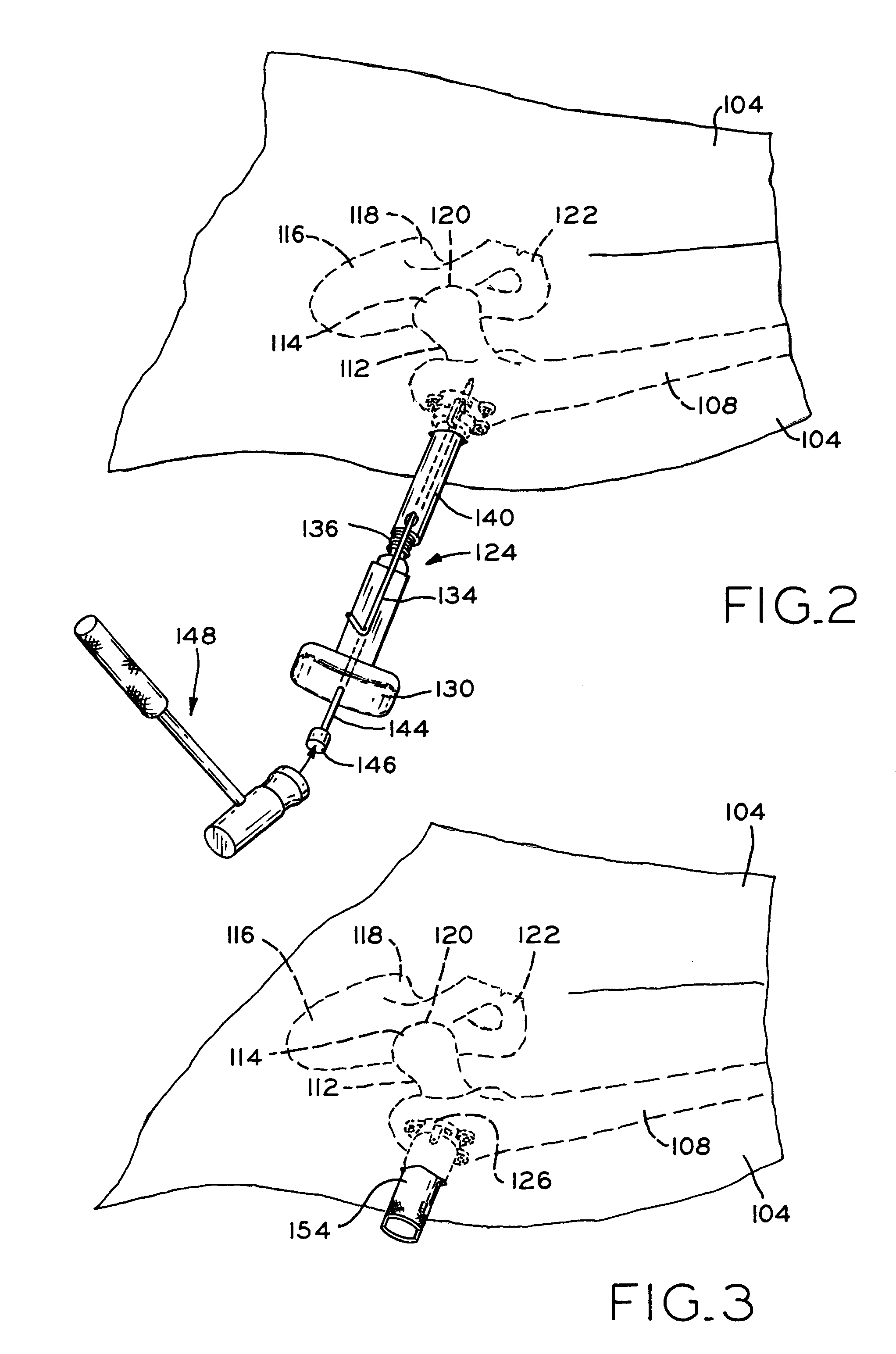
InactiveUS7258692B2Reducing a hip fracturePrevent escapeInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsRight femoral headHip fracture
An improved method and apparatus for reducing a hip fracture utilizing a minimally invasive procedure which does not require incision of the quadriceps. A femoral implant in accordance with the present invention achieves intramedullary fixation as well as fixation into the femoral head to allow for the compression needed for a femoral fracture to heal. To position the femoral implant of the present invention, an incision is made along the greater trochanter. Because the greater trochanter is not circumferentially covered with muscles, the incision can be made and the wound developed through the skin and fascia to expose the greater trochanter, without incising muscle, including, e.g., the quadriceps. After exposing the greater trochanter, novel instruments of the present invention are utilized to prepare a cavity in the femur extending from the greater trochanter into the femoral head and further extending from the greater trochanter into the intramedullary canal of the femur. After preparation of the femoral cavity, a femoral implant in accordance with the present invention is inserted into the aforementioned cavity in the femur. The femoral implant is thereafter secured in the femur, with portions of the implant extending into and being secured within the femoral head and portions of the implant extending into and being secured within the femoral shaft.
Owner:ZIMMER TECH INC
Implant Device and Method for Manufacture
Disclosed are systems, devices and methods for optimizing the manufacture and / or production of patient-specific orthopedic implants. The methods include obtaining image data of a patient, selecting a blank implant to be optimized for the patient, and modifying the blank implant utilizing techniques disclosed herein to alter specific features of the implant to conform to the patient's anatomy.
Owner:CONFORMIS
Soft tissue implants with improved interfaces
InactiveUS20060293760A1Facilitates dual functionInduce new tissue formationAnkle jointsBone implantHost tissueDual function
Specialization of the end(s) or host tissue contact points of biocompatible scaffolds brings a functionality to the scaffold that facilitates the dual function of inducing new tissue formation and facilitating attachment and site-specific tissue formation at the scaffolds' functionalized points of fixation.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US) +1
Sacroiliac joint immobilization
Improved tools and procedures relate to the immobilization of the sacroiliac joint for the treatment of pain associated with the joint. Kits comprise, for example, a guide element and an immobilization element of a biocompatible material with a size and shape suitable for placement within the sacroiliac joint. Suitable immobilization elements include, for example, pins, nails, screws, darts, wedges, shims and hardening material. A bioactive agent can be delivered into the joint to compliment the immobilization and promote healing. Suitable procedures can be done in a less invasive procedure through a cannula or the like.
Owner:ILION MEDICAL
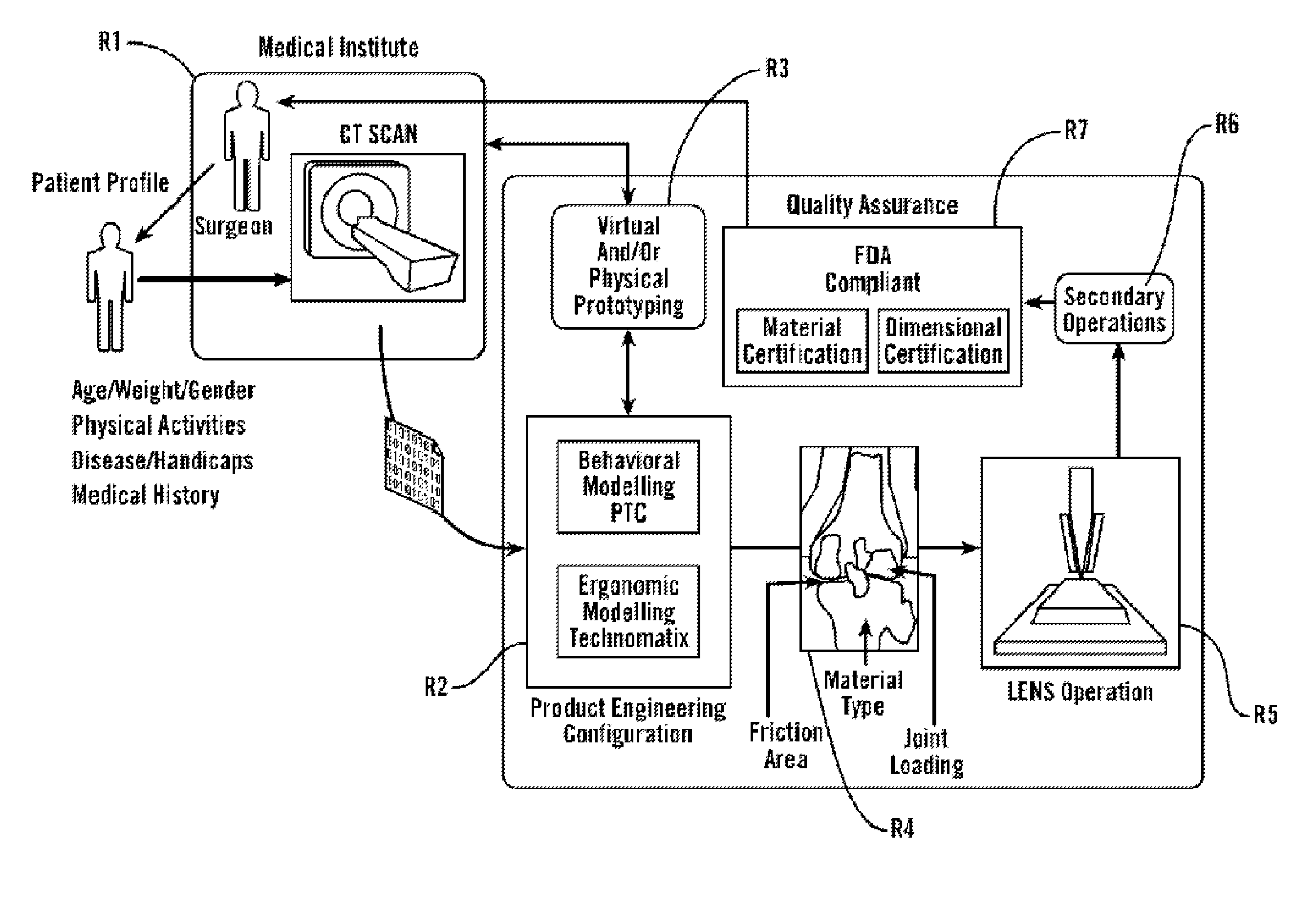
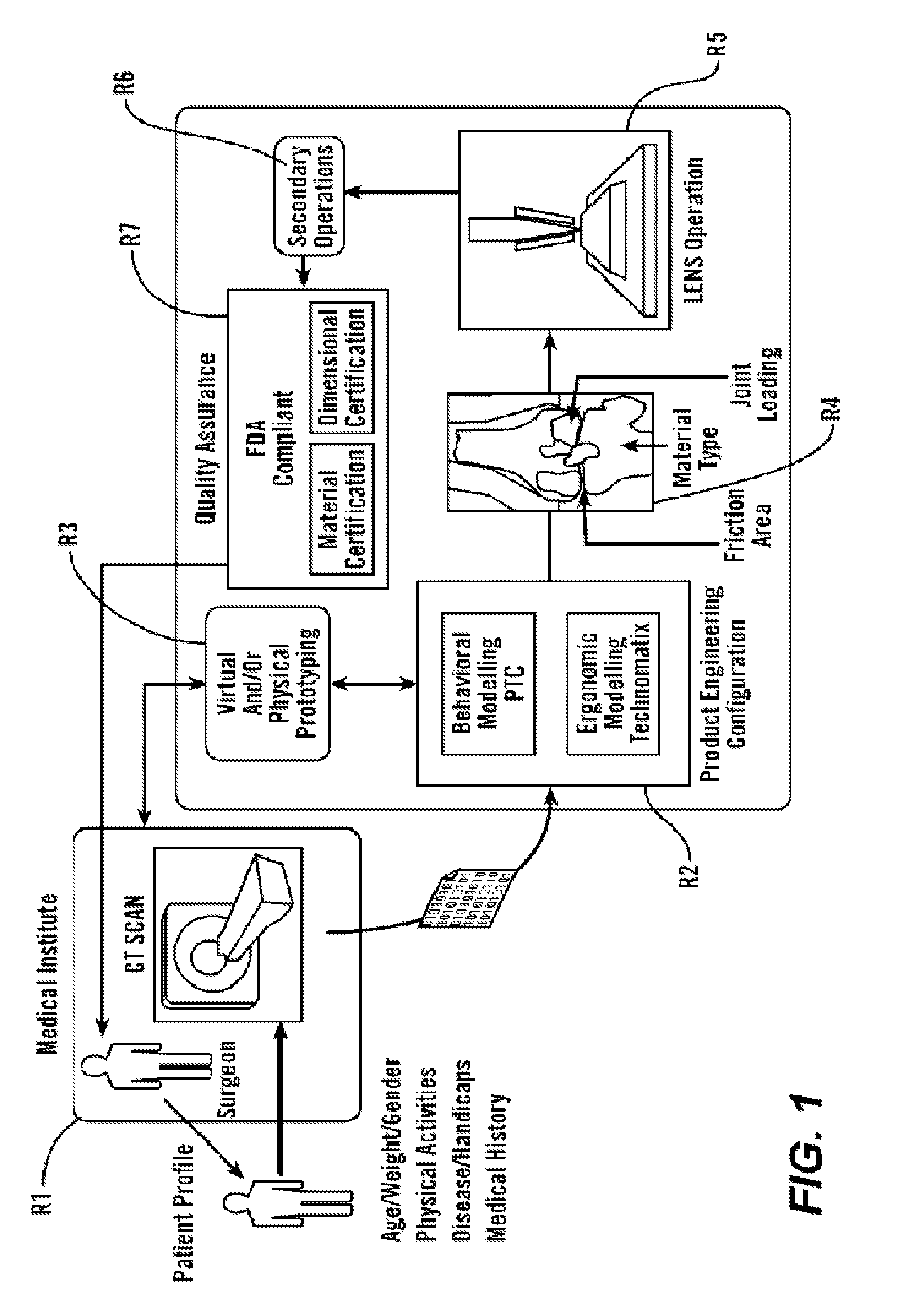
Personalized Fit and Functional Designed Medical Prostheses and Surgical Instruments and Methods for Making
ActiveUS20130245801A1Simple designFast learningMedical simulationAdditive manufacturing apparatusPersonalizationManufacturing technology
Methods, devices and systems for virtual, remote and real-time collaboration between surgeons and engineers using system learning and intelligent and timely disbursement of design and performance information to engineering teams embarking on the preliminary design event of a personalized orthopedic implant or personalize surgical instrument utilizing a case-based reasoning expert system. Additive manufacturing technology and statistically controlled advanced manufacturing processes quickly produce personalized medical devices worldwide.
Owner:SCHROEDER JAMES
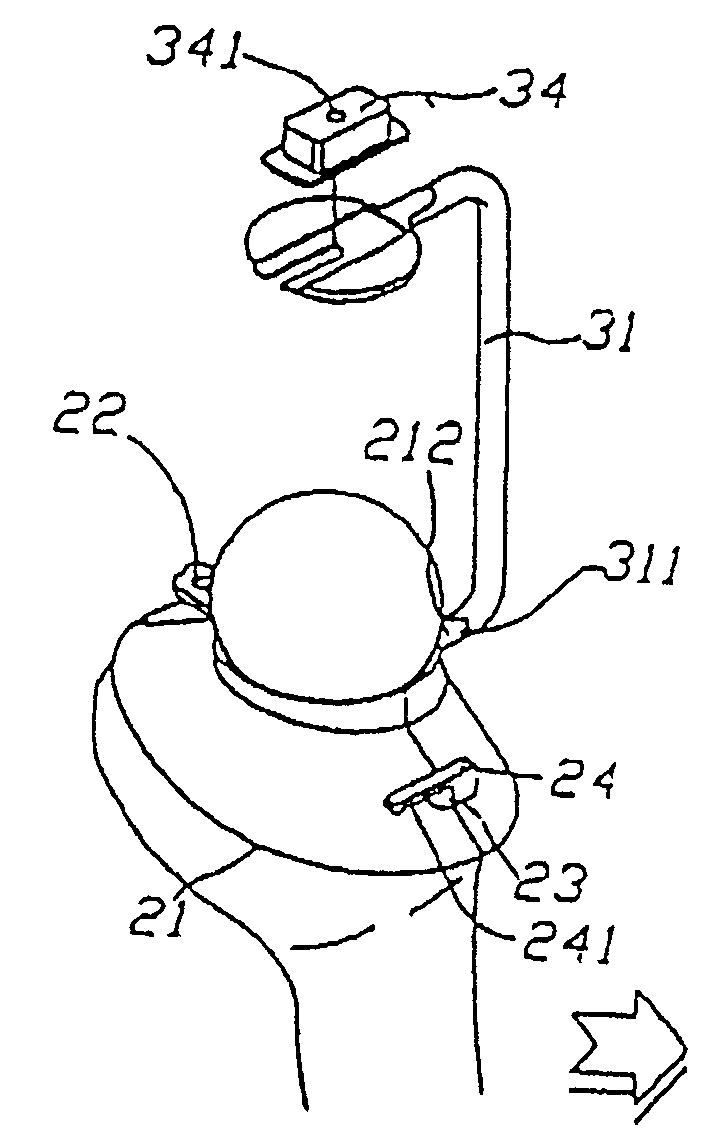
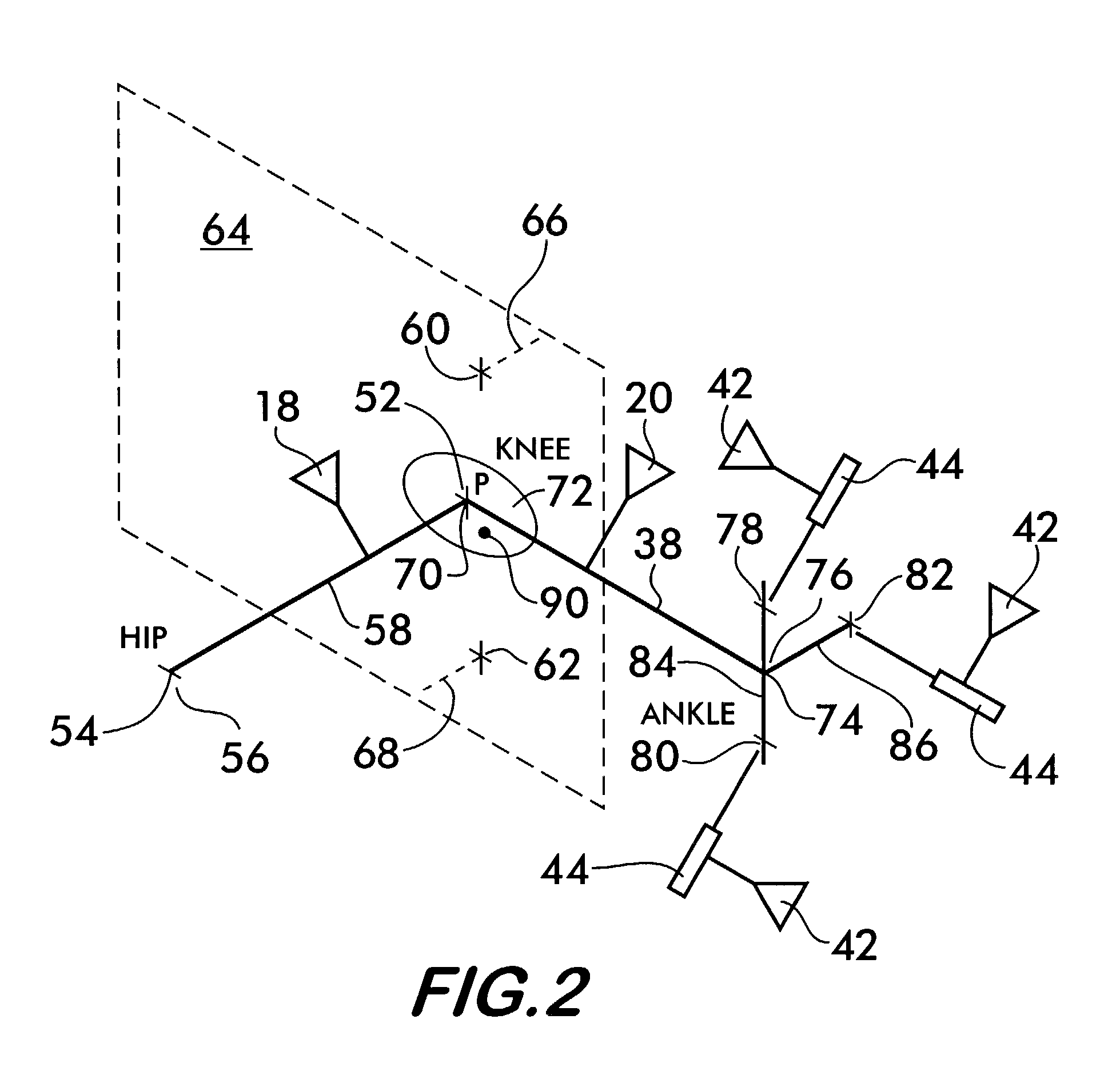
Method of determining the position of the articular point of a joint
A non-invasive method for determining the articular point of a joint is disclosed. The method uses a surgical navigation system having a stereoscopic cameras which tracks the positions of infrared emitting or reflecting markers attached to appendages on either side of the joint. A movable marker is used to palpate known landmarks on the appendages to determine their positions. The appendages are moved to determine the trajectories of the landmarks relative to the joint. Positional information from the cameras is fed to a data processing system with resident software which uses the positional information and trajectories to mathematically determine the position of the joint articular point according to the laws of kinematics.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
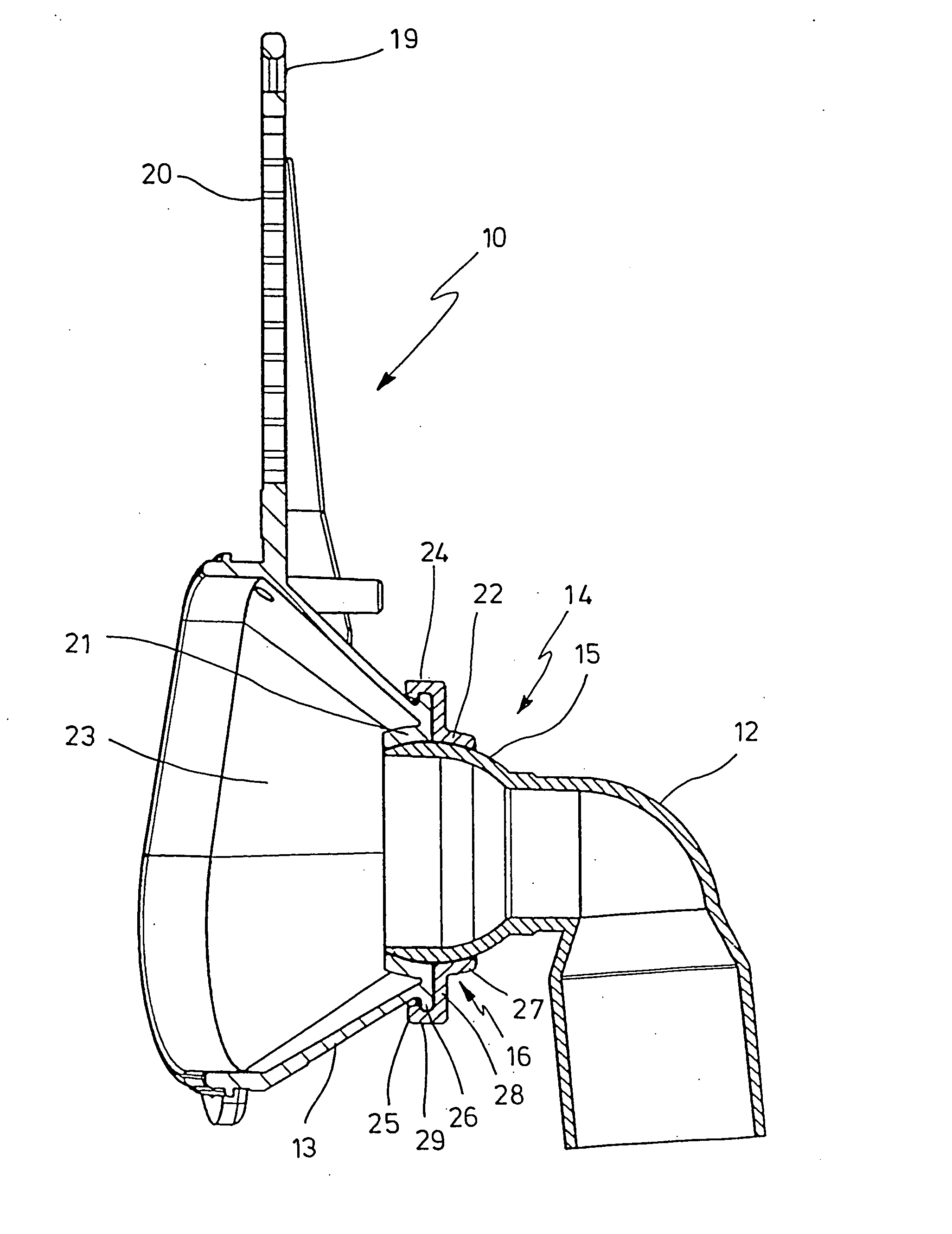
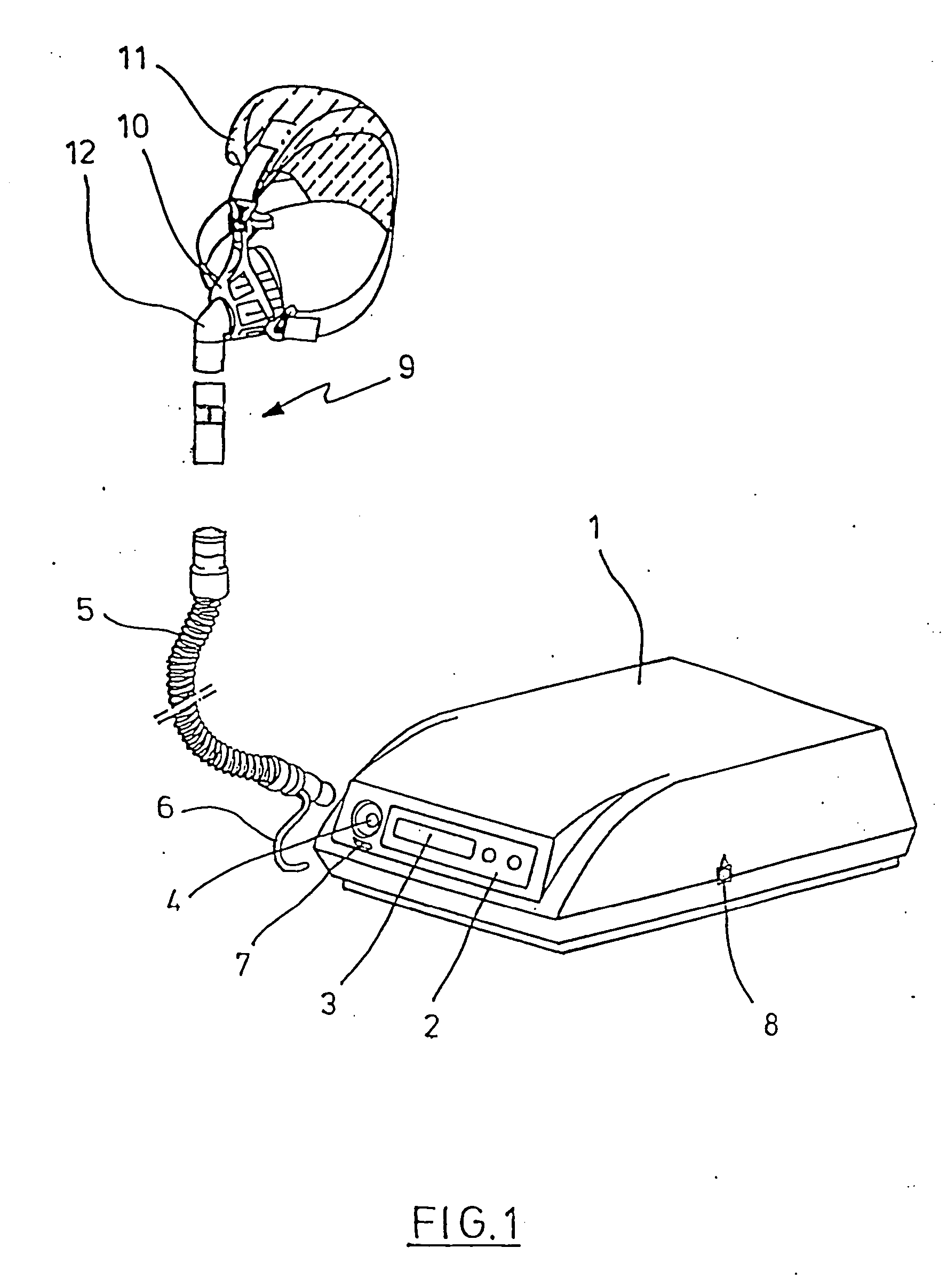
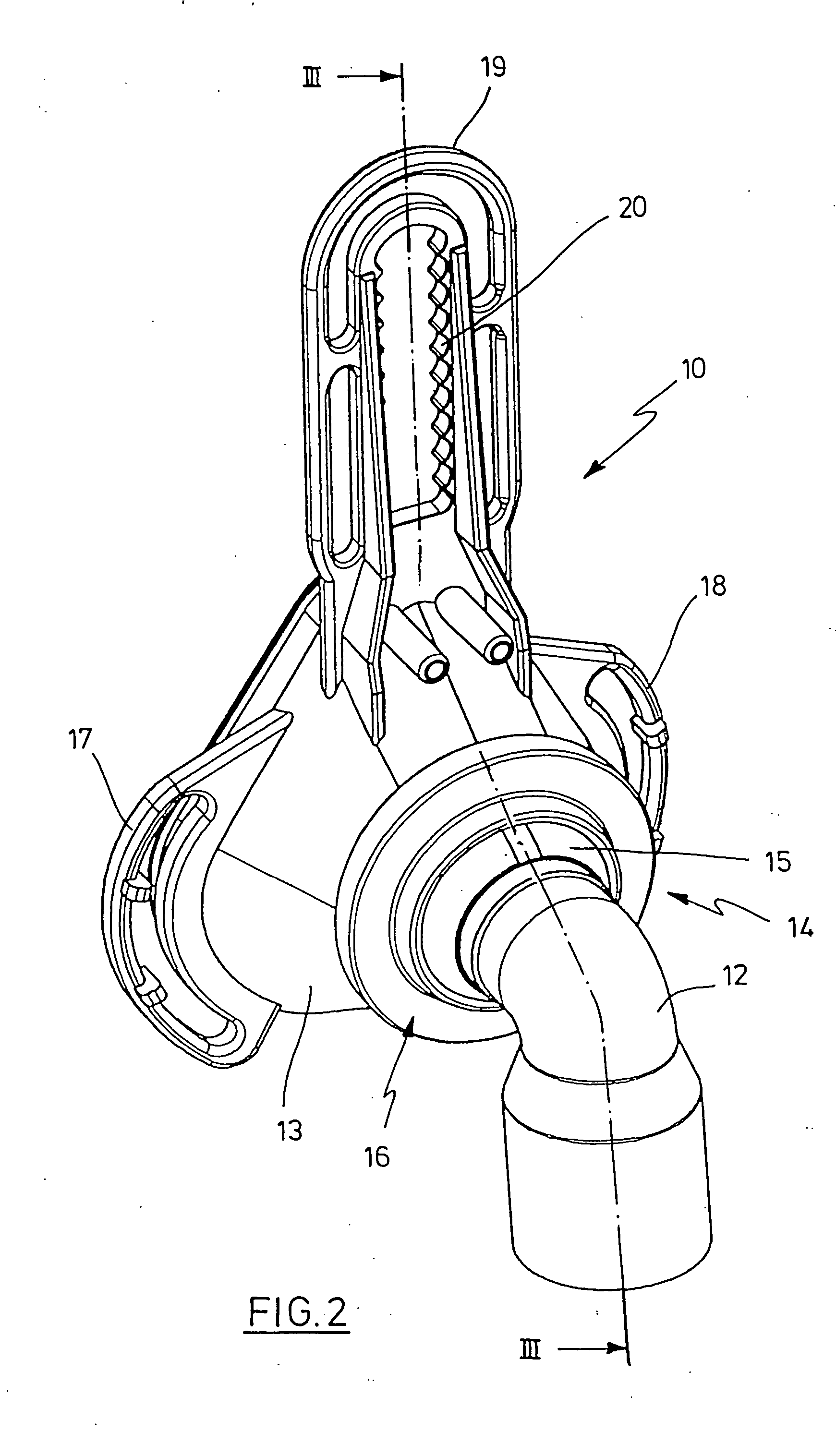
Ventilation device
InactiveUS20050150497A1Improve mechanical stabilityEasy to assembleRespiratory masksBreathing masksBreathing gasEngineering
A device used for ventilation includes a ventilation mask that can be connected to a respiratory gas hose. The ventilation mask has a respiratory gas hose coupling that is movably connected by a joint with the base of the ventilation mask. The joint is a ball-and-socket joint, which has an inner part that is shaped like a spherical segment and an outer shell for guiding the inner part. The outer shell is constructed from at least two shell segments that can be connected with each other.
Owner:WEINMANN GERATE FUR MEDIZIN
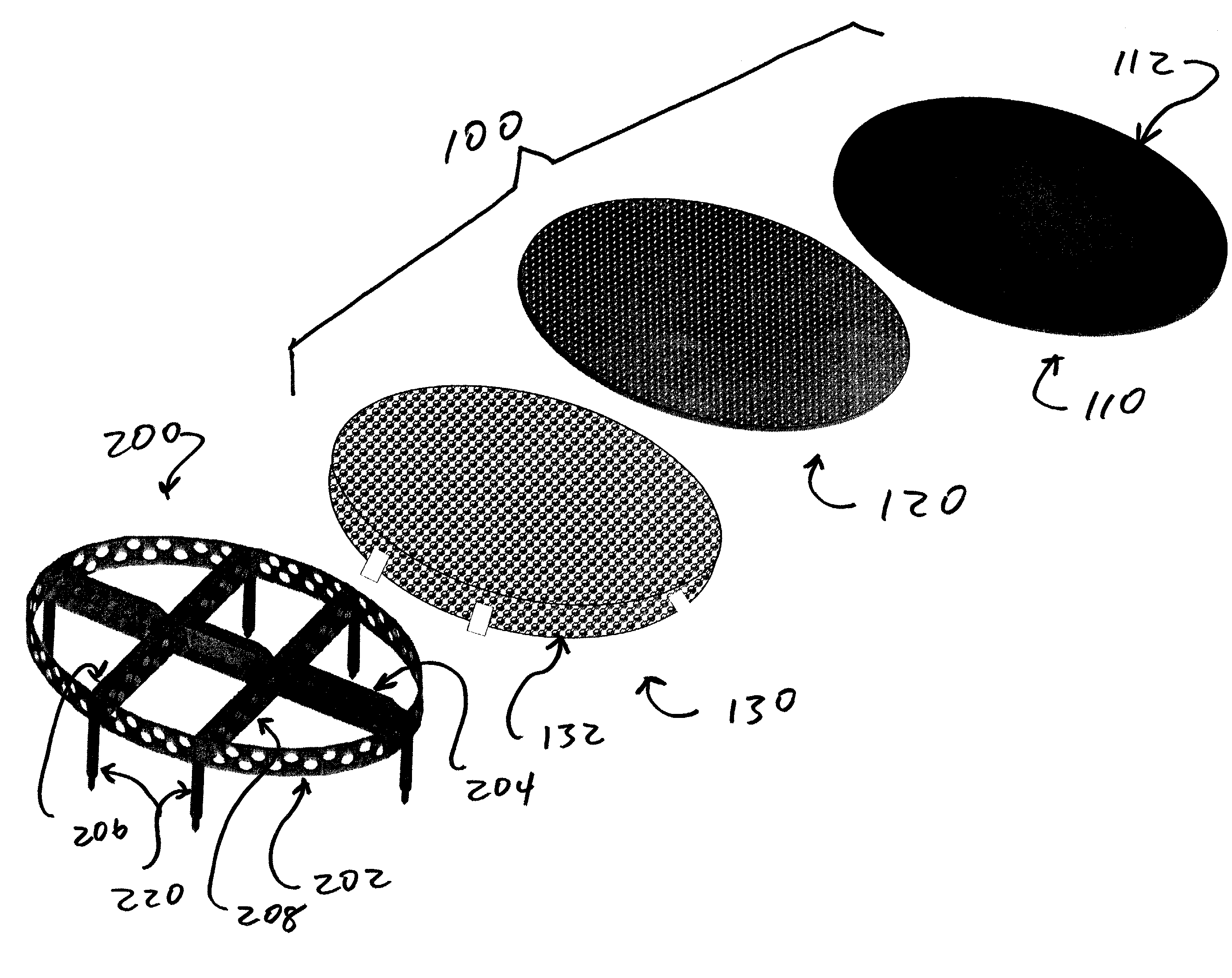
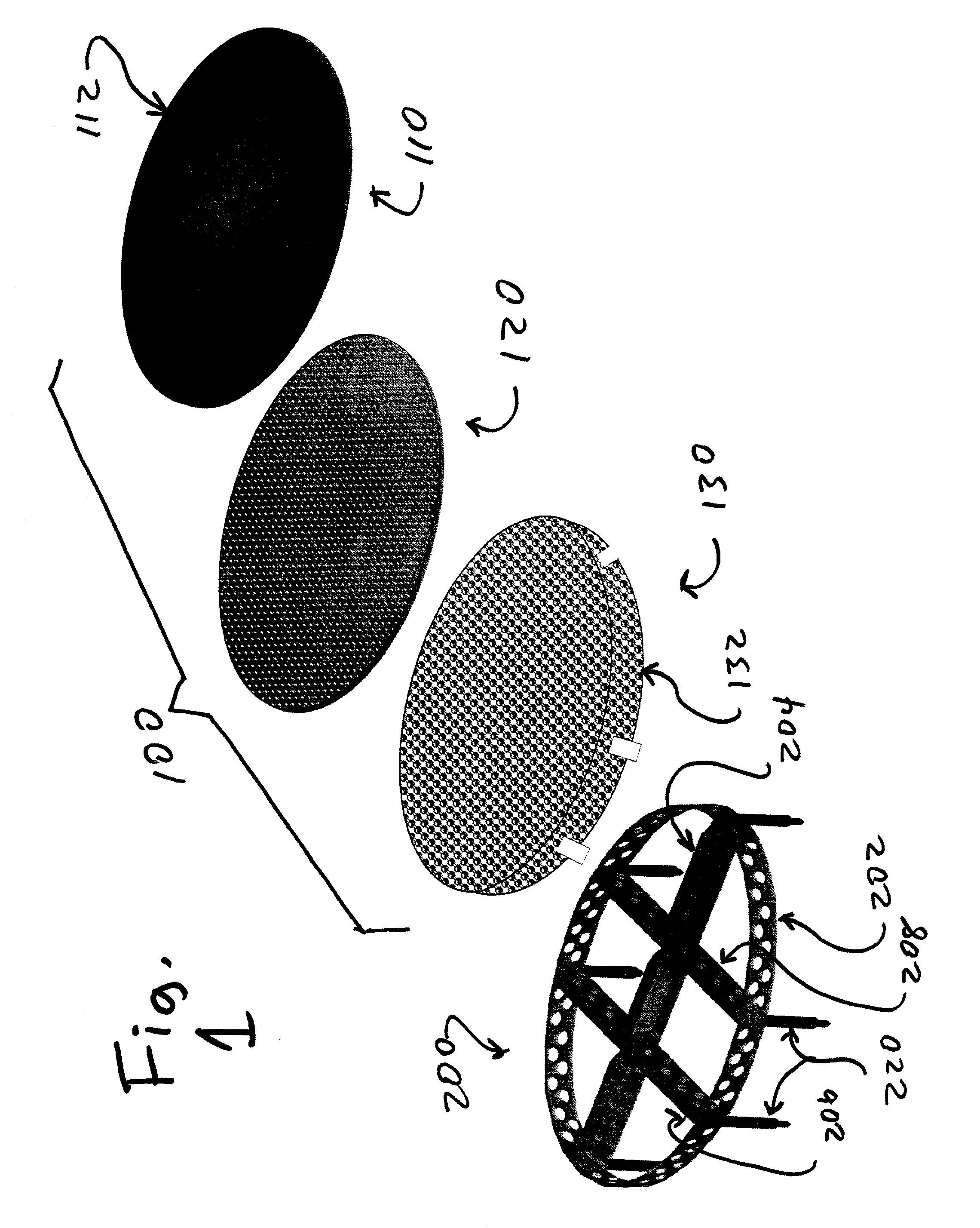
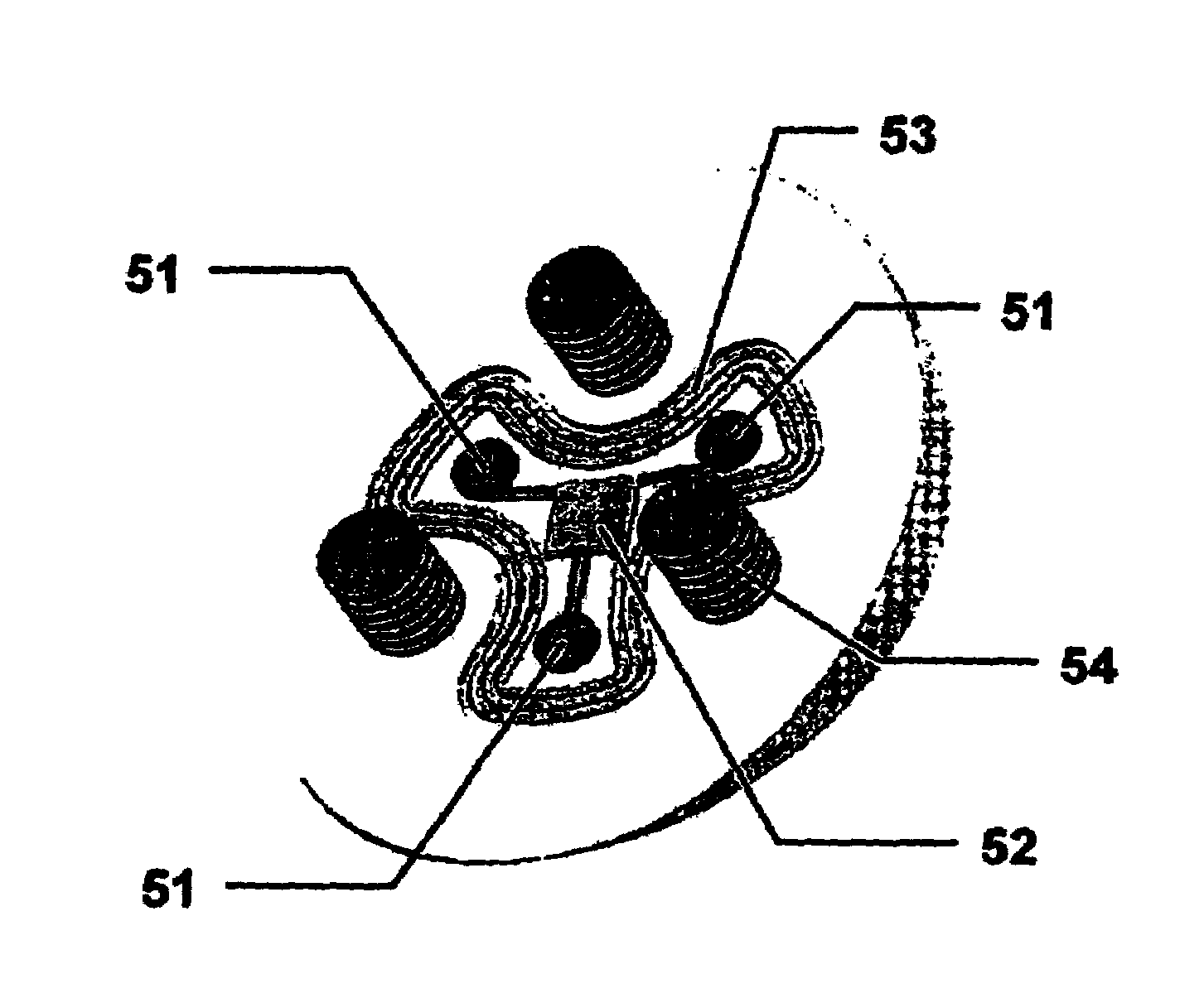
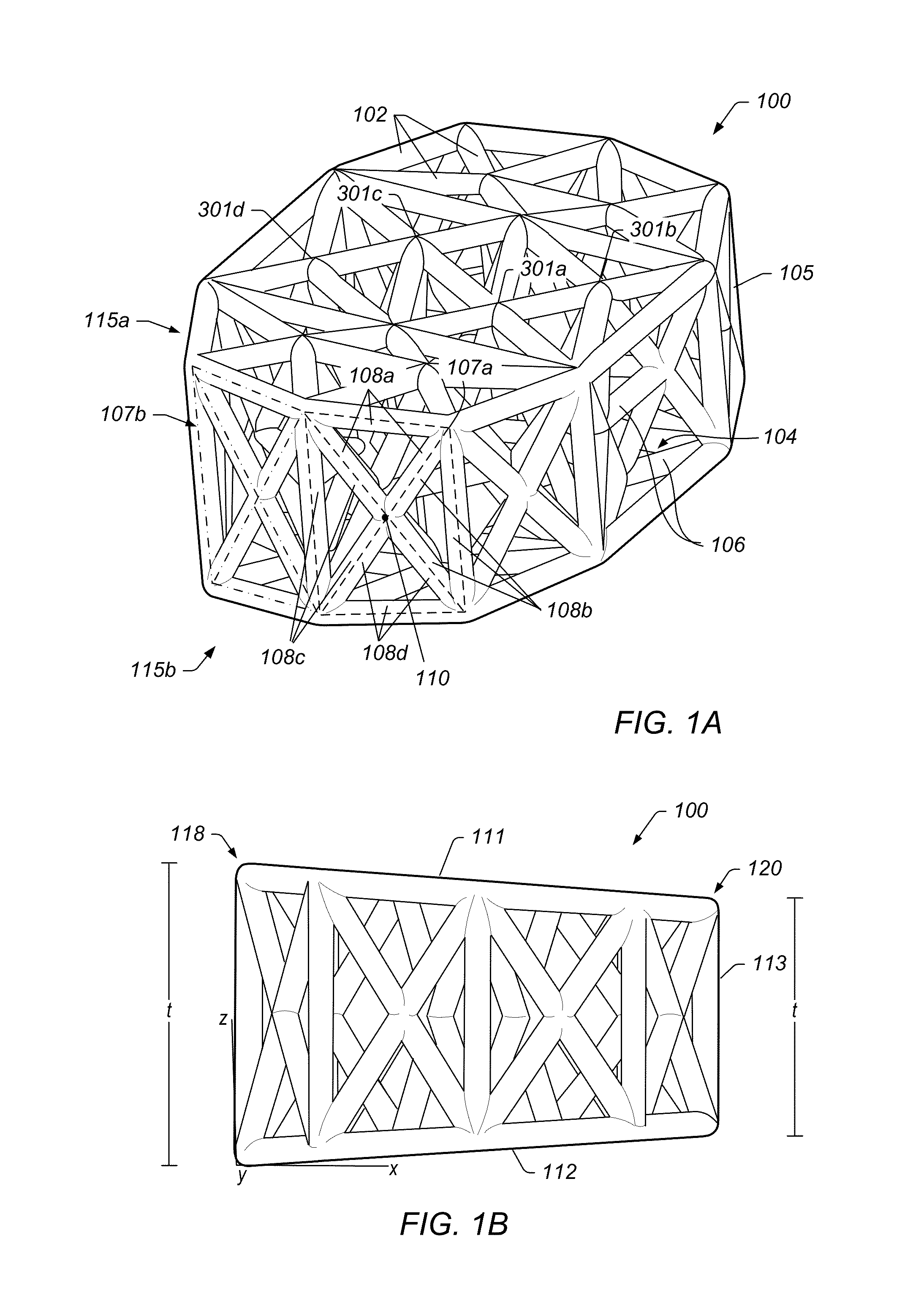
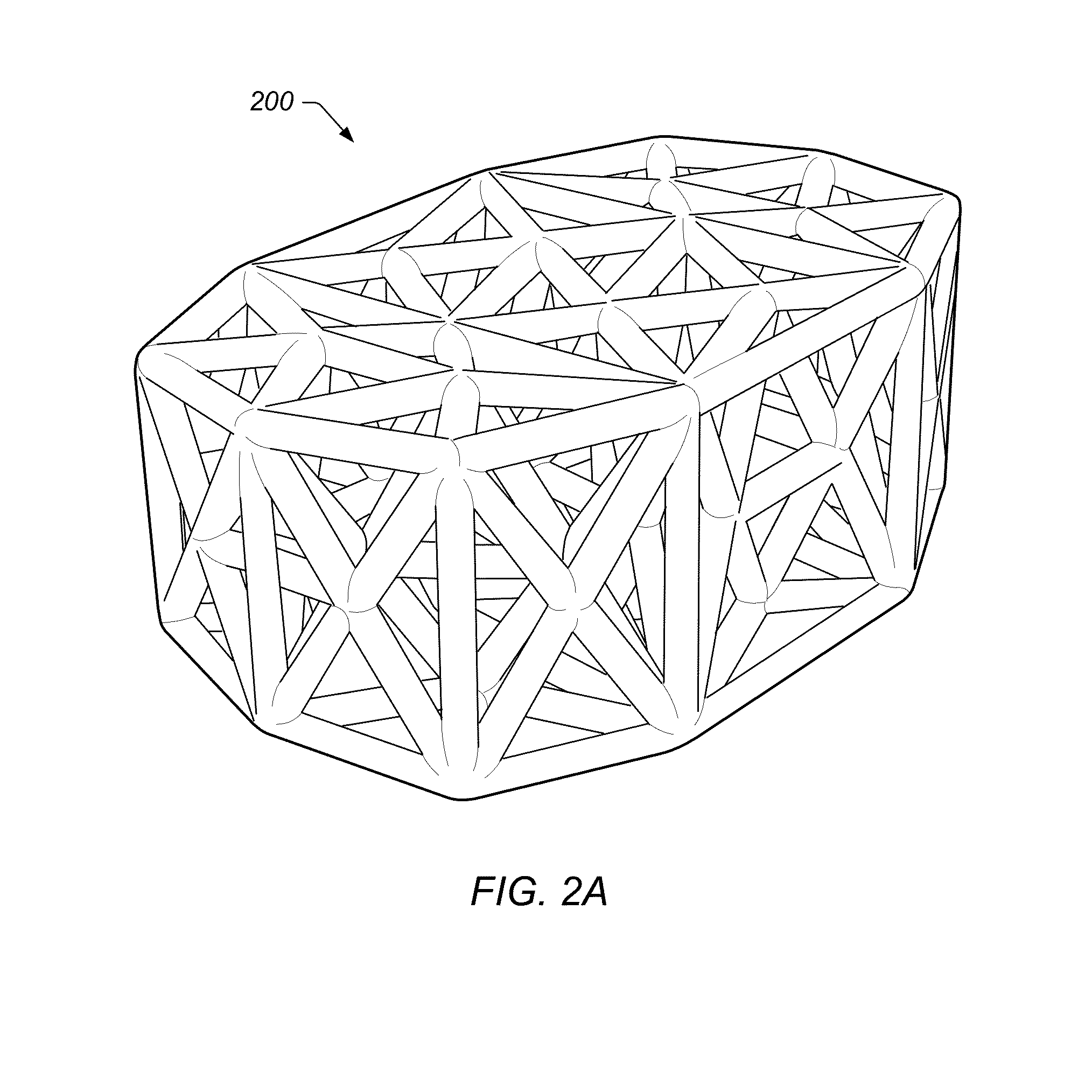
Programmable implants and methods of using programmable implants to repair bone structures
Various embodiments of implant systems and related apparatus, and methods of operating the same are described herein. In various embodiments, an implant for interfacing with a bone structure includes a web structure, including a space truss, configured to interface with human bone tissue. The space truss includes two or more planar truss units having a plurality of struts joined at nodes. Implants are optimized for the expected stress applied at the bone structure site.
Owner:4-WEB
Method and apparatus for reducing femoral fractures
InactiveUS20070225721A1Reducing a hip fractureHigh strengthInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsRight femoral headHip fracture
Owner:ZIMMER TECH INC
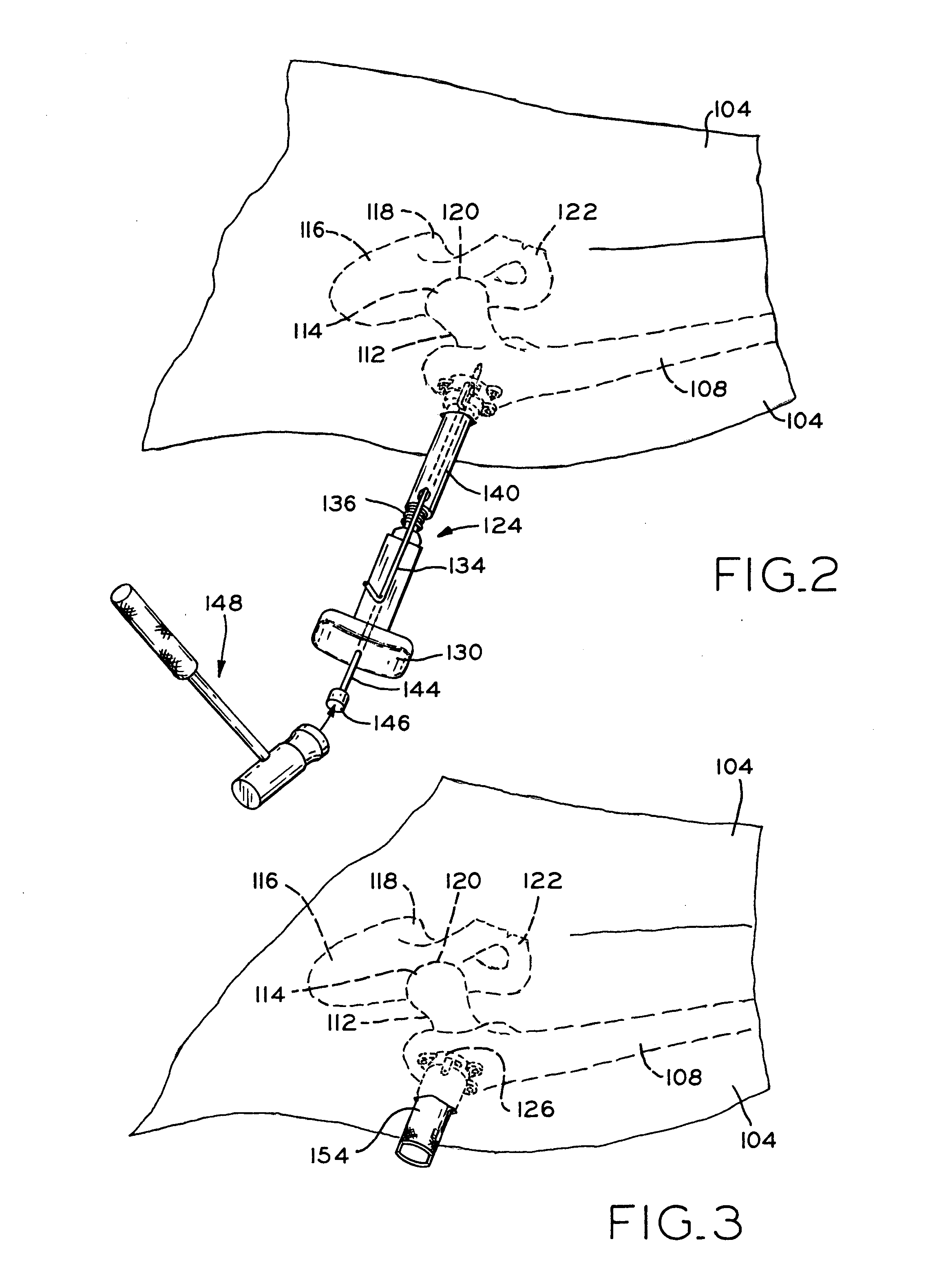
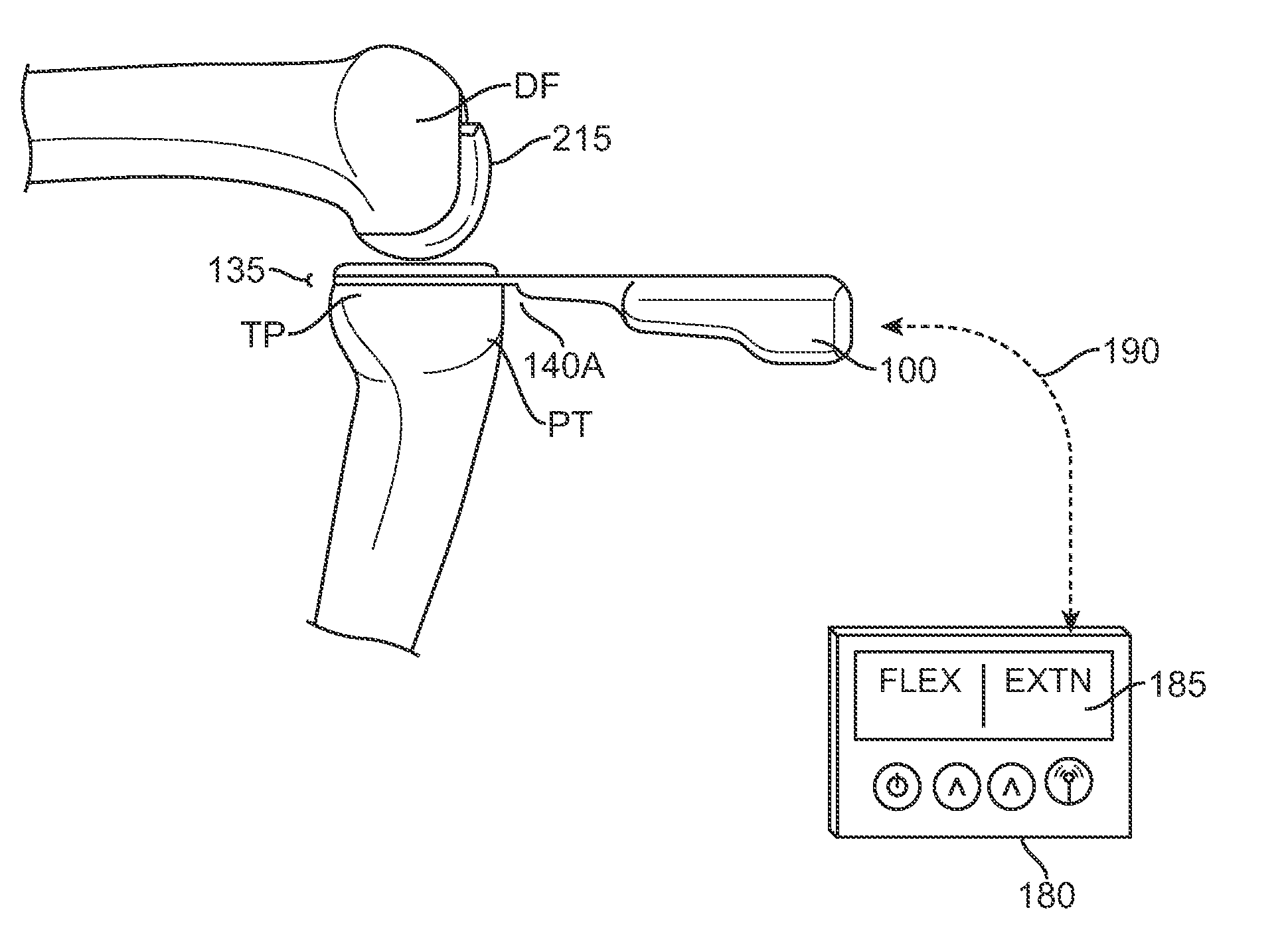
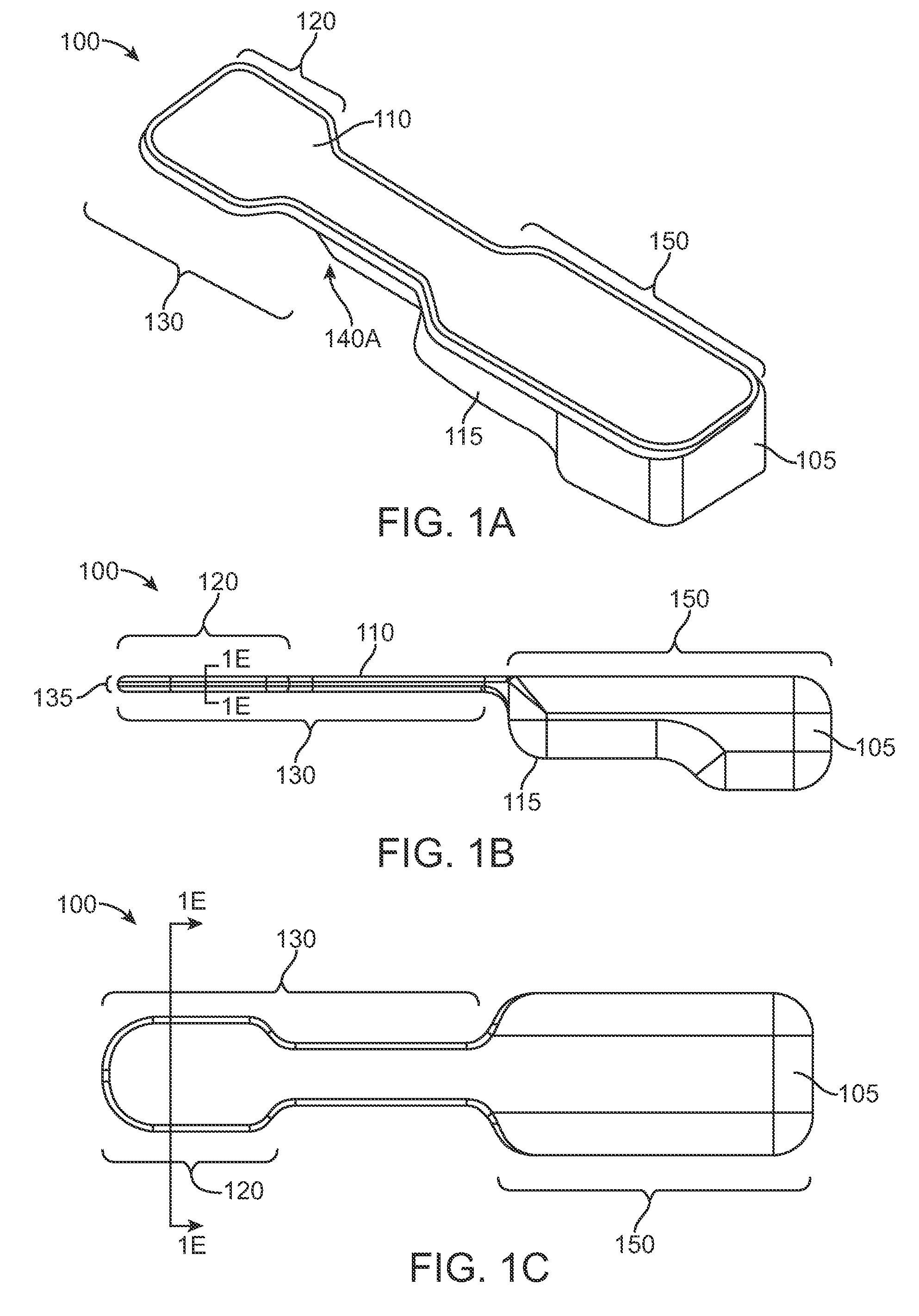
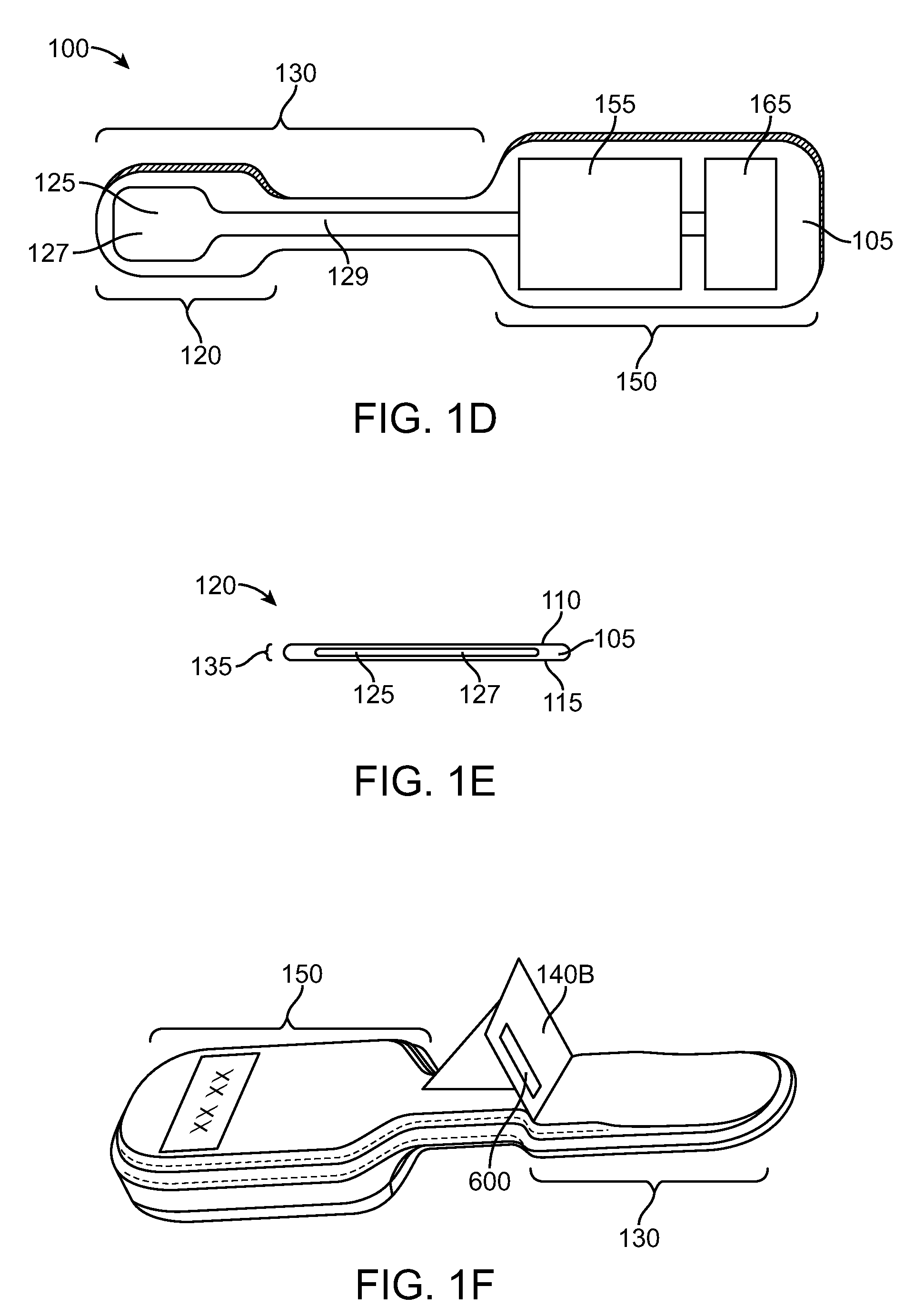
Sensing force during partial and total knee replacement surgery
ActiveUS8211041B2Accurate and quantifiable measurementPrecise tensionAnkle jointsPerson identificationTibiaTotal knee replacement surgery
Systems, devices, and methods are provided for measuring forces in the space of a knee during surgery. Such forces can be caused by tension in the ligaments of the knee. A femoral member is engaged with a distal femur. While the knee is flexed, partially extended, or fully extended, a force sensor and a gauge shim can be placed in the gap between the femoral member and the tibial plateau to measure the forces therebetween. The force sensor provides an accurate and quantifiable measurement of force, making knee replacement surgery and ligament tension balancing more accurate, standardized and repeatable. The force sensor comprises an elongate housing which comprises a thin force sensing distal portion and a proximal handle portion.
Owner:SYNVASIVE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com