Patents
Literature
41 results about "Fixed prosthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fixed prosthodontics are permanent prosthetics used in dental restoration to replace decayed or missing teeth or portions of teeth. Common examples of fixed prosthodontics include inlays, porcelain veneers, crowns, and bridges. They can be made of metal, porcelain, or resin,...
Endovascular aneurysm repair system
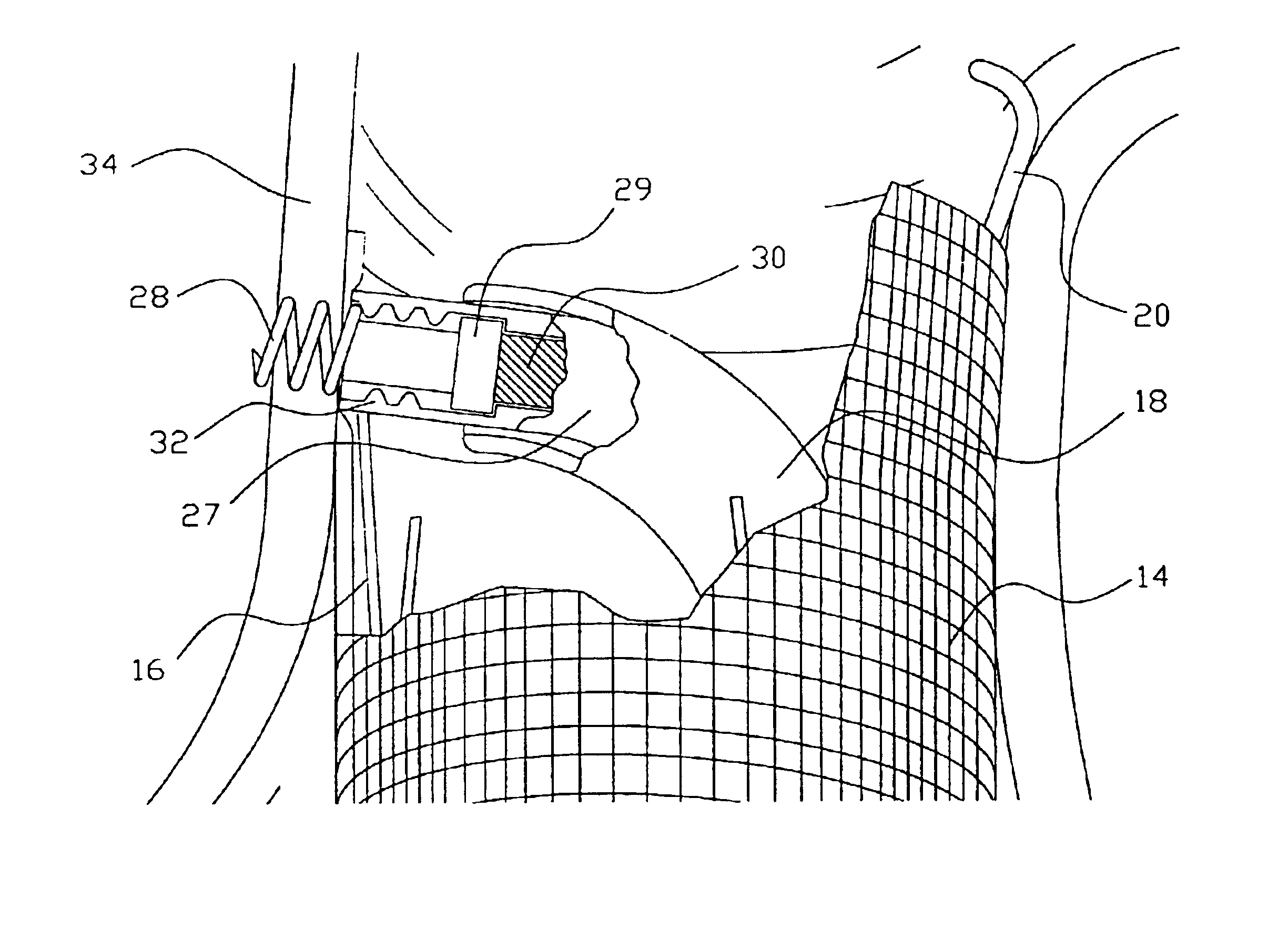
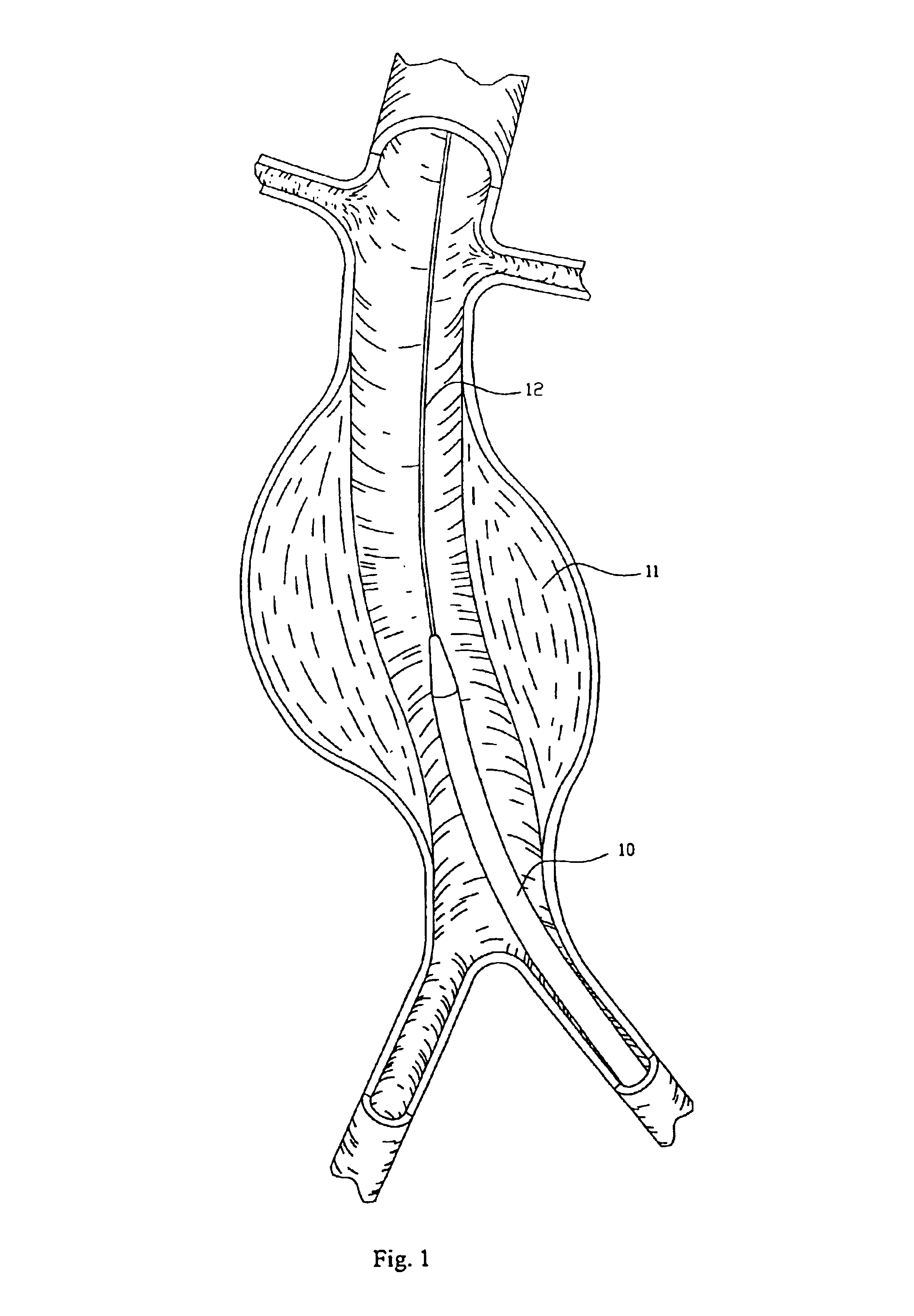
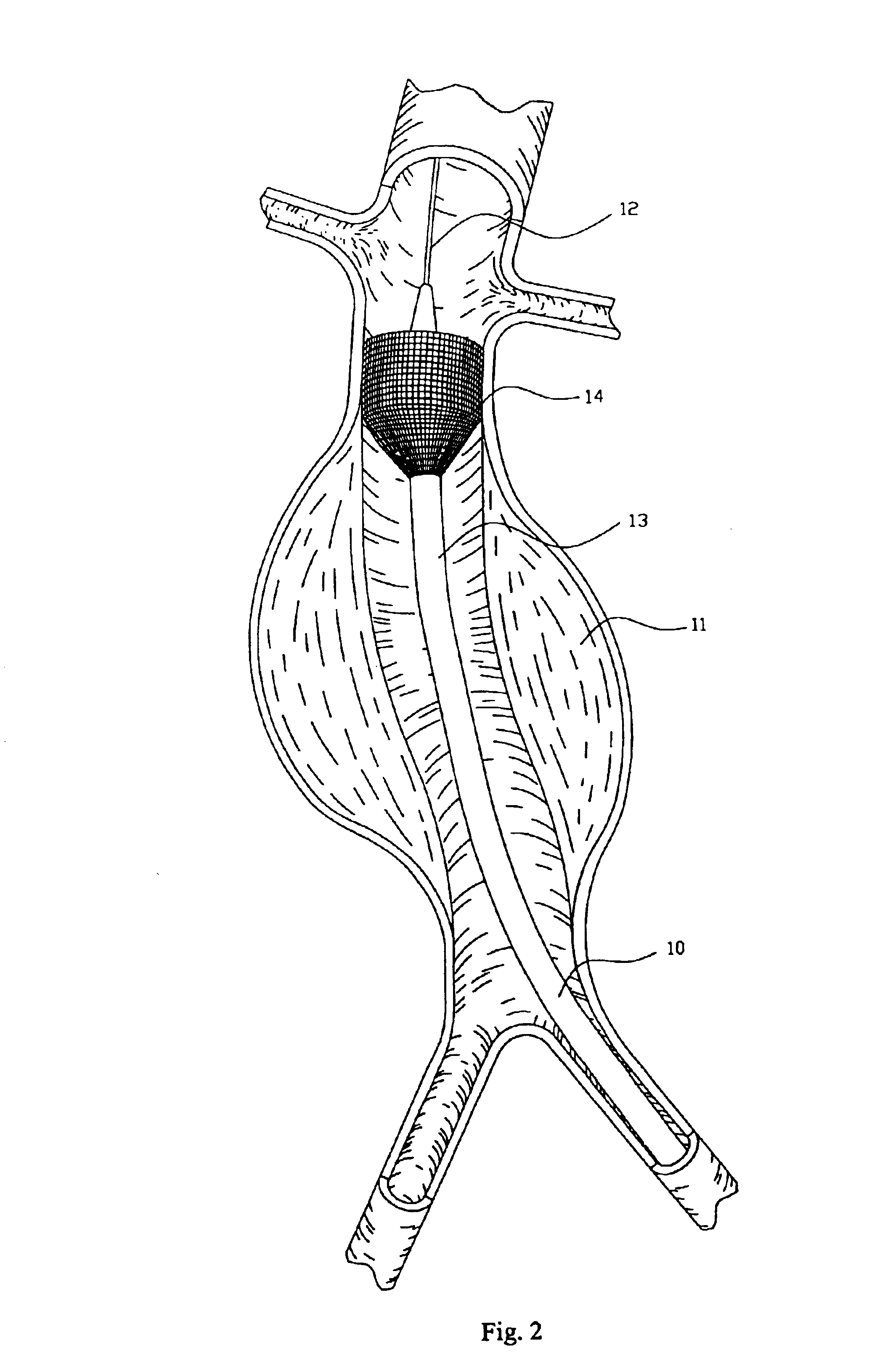
InactiveUS6960217B2Low profileEffective and less traumaticStentsEar treatmentEndovascular aneurysm repairBiomedical engineering
Method and apparatus for implanting radially expandable prostheses in the body lumens rely on tacking or anchoring of the prostheses with separately introduced fasteners. The prostheses may be self-expanding or balloon expandable. After initial placement, a fastener applier system is introduced within the expanded prostheses to deploy a plurality of fasteners at at least one prosthesis end, usually as each end of the prosthesis. The fasteners are usually helical fasteners which are delivered from a helical track in the fastener applier by rotation with a rotator wire. The fasteners will be applied singly, typically in circumferentially spaced-apart patterns about the interior of each end of the prosthesis.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Implantable preparations
Implantable preparation comprising a material which can be obtained from globin that has been modified, especially chemically, to be, at least partially, soluble at physiological pH, the material being biocompatible, and biodegradable in the organism. The material may be soluble at physiological pH, or insoluble at that pH. The preparation may be in the form of a solution, suspension, paste, gel, film, sponge, powder or granules, or a solid implant. Application in particular to the healing, protection or filling of external skin wounds, the filling of wrinkles and skin flaws, the filling of tissue, as means for fixing prostheses or biomaterials, or means for preventing adhesion.
Owner:KHORIONYX
Implantable preparations
An implantable preparation comprises a material which can be obtained from globin that has been modified, especially chemically, to be, at least partially, soluble at physiological pH. The material is biocompatible, and biodegradable in the organism. The material may be soluble at physiological pH, or insoluble at that pH. The preparation may be in the form of a solution, suspension, paste, gel, film, sponge, powder or granules, or a solid implant. The preparation can be used for the healing, protection or filling of external skin wounds, the filling of wrinkles and skin flaws, the filling of tissue, as a device for fixing prostheses or biomaterials, or as a device for preventing adhesion.
Owner:KHORIONYX
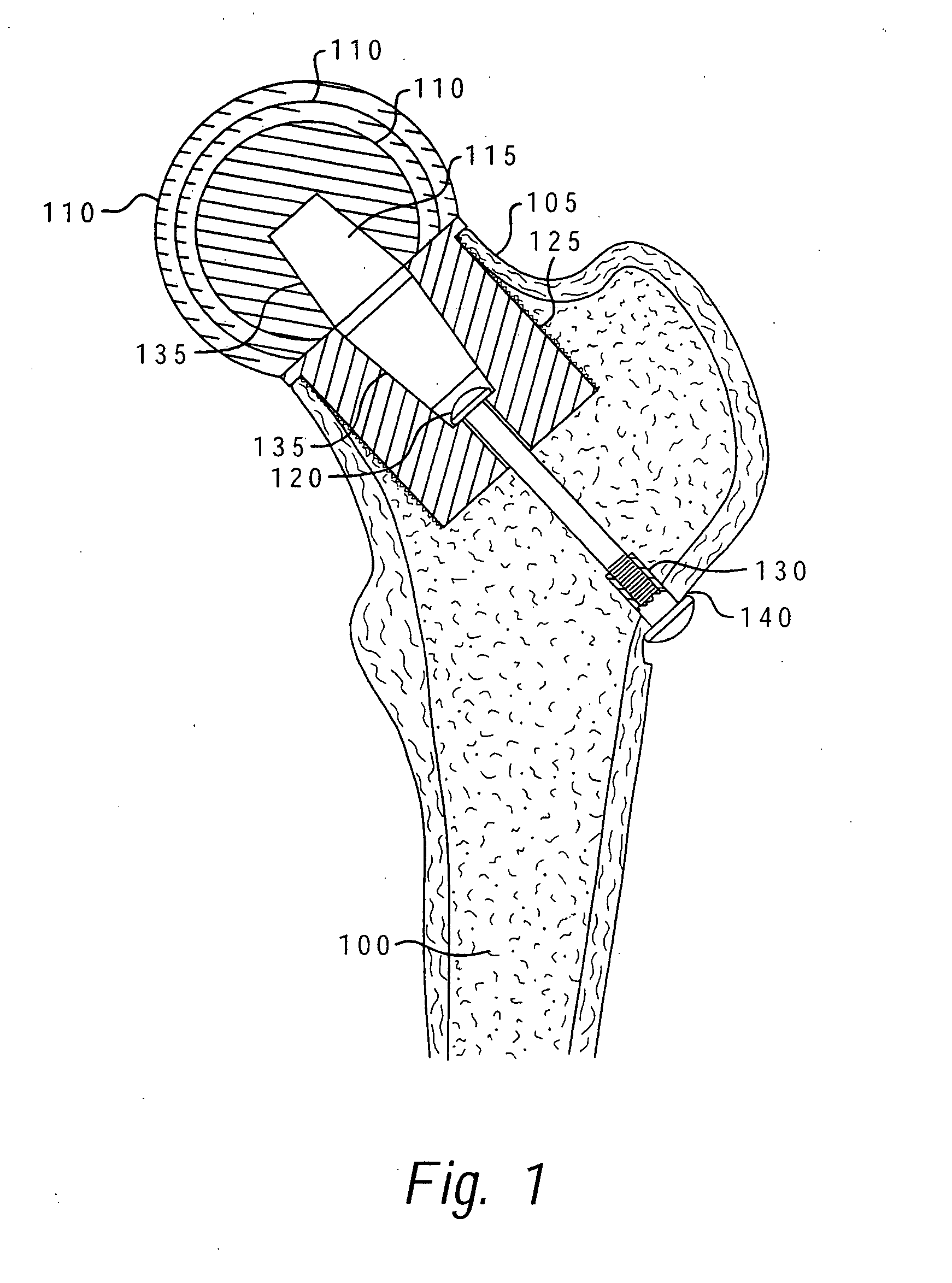
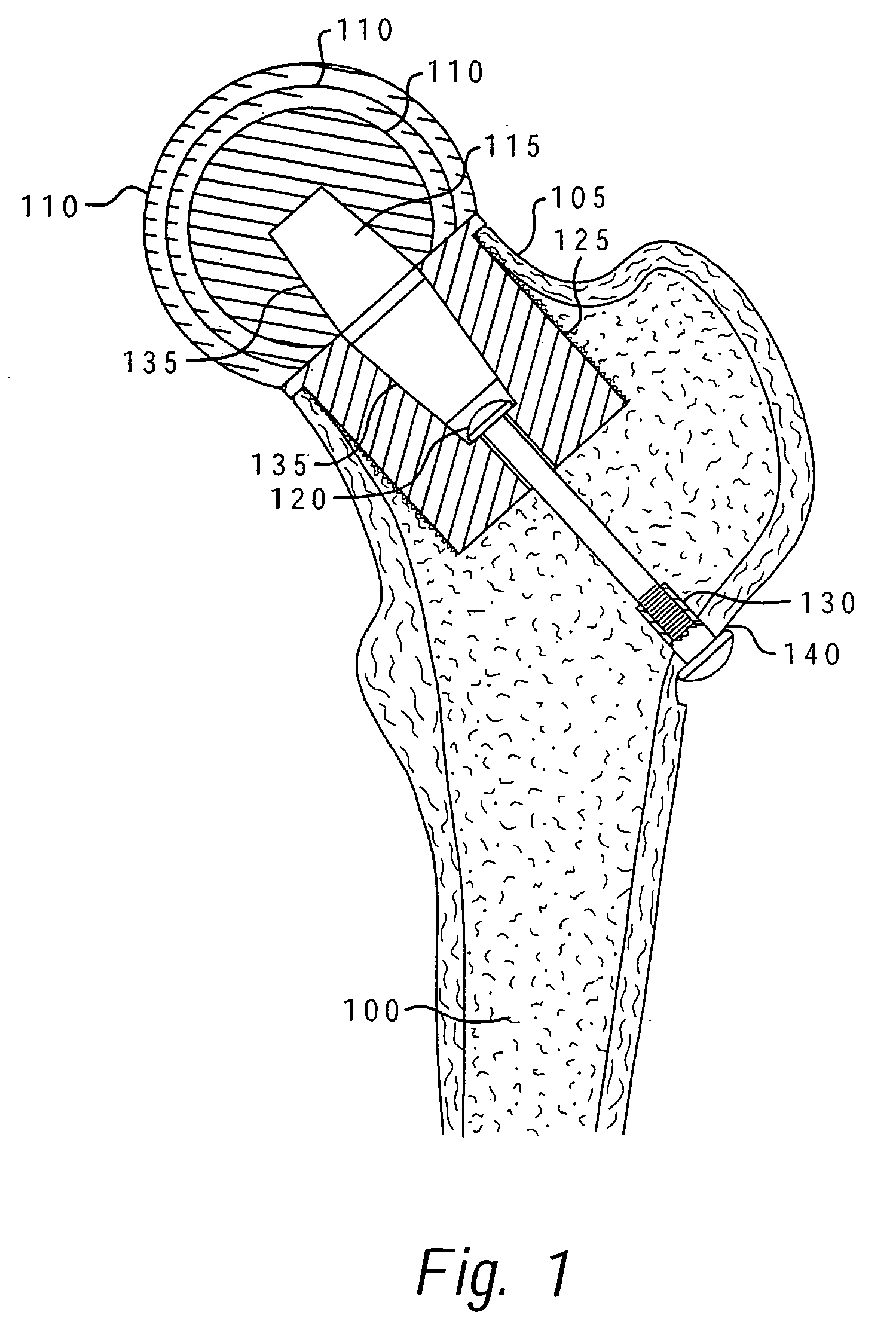
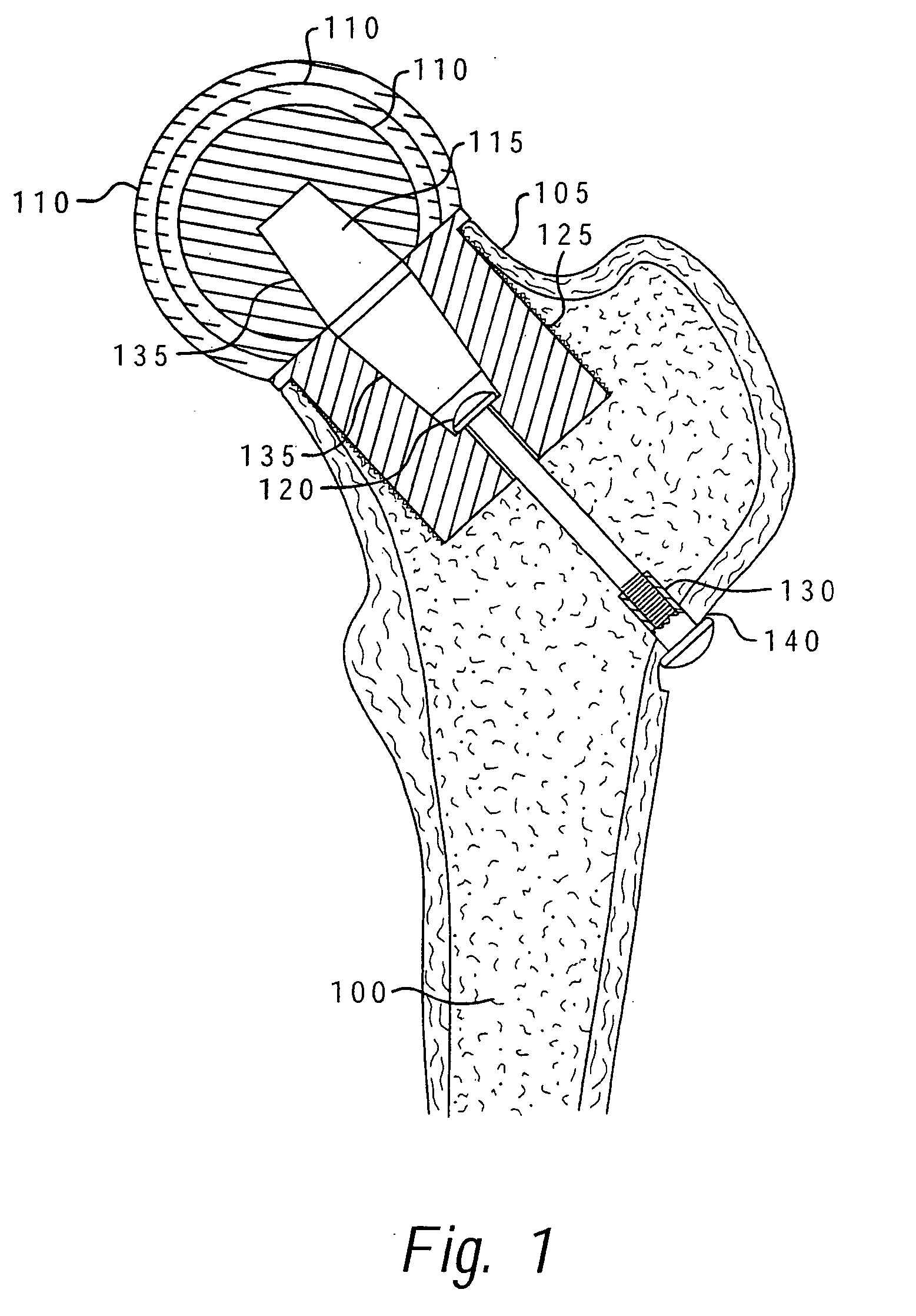
Method of implanting a femoral neck fixation prosthesis
InactiveUS20050010232A1Reduce bone lossReduce the amount requiredInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsRight femoral headMedicine
A femoral neck fixation prosthesis and method of using same which reduces bone loss and the avoids the other shortcomings of the prior art by allowing the fixation of a stable femoral head replacement while reducing the amount of the femur which must be reamed for the insertion of the prosthesis. The preferred embodiment provides that the femoral head is attached to a fixation prosthesis, which extends coaxially through the canal of the femoral neck, into the femur, and is then attached to the opposite lateral wall of the femur. In this manner, the prosthesis serves to imitate the original structure of the femoral neck. No other support members, either crosspins or arms extending into the length of the femur, are required.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Anatomic total disc replacement
An artificial spinal disc prosthesis that can be implanted to replace a damaged natural spinal disc. A nucleus of compressible elastomeric material is surrounded by a winding of a slender strand of flexible tension-bearing material oriented at a pitch angle relative to a central axis. The orientation of the winding provides the prosthesis a limited amount of freedom of movement and flexibility. A pair of end caps of the prosthetic implant include angulated grooves that allow for insertion of the device between vertebral bodies from any of several directions. Special fasteners provide protruding points useful in anchoring the prosthesis.
Owner:CARPENTER CLYDE T
Knee prosthesis with rotation bearing
A knee prosthesis including a femoral component, a tibial component and an intermediate piece which connects these forming a flexion bearing with the femoral component and a rotation bearing with the tibial component, which rotation bearing can be locked relative to the tibial part. To allow the physician to decide during the operation whether to use a rotation-free prosthesis or a rotationally fixed prosthesis, the intermediate piece is alternatively provided with a projection which engages in a matching recess in the tibial component.
Owner:WALDEMAR LINK GMBH & CO
Method of resecting a femoral head for implantation of a femoral neck fixation prosthesis
InactiveUS20050049714A1Substantially intact femoral neckReduce the amount requiredInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsRight femoral headLeft femoral head
A femoral neck fixation prosthesis and method of using same which reduces bone loss and the avoids the other shortcomings of the prior art by allowing the fixation of a stable femoral head replacement while reducing the amount of the femur which must be reamed for the insertion of the prosthesis. The preferred embodiment provides that the femoral head is attached to a fixation prosthesis, which extends coaxially through the canal of the femoral neck, into the femur, and is then attached to the opposite lateral wall of the femur. In this manner, the prosthesis serves to imitate the original structure of the femoral neck. No other support members, either crosspins or arms extending into the length of the femur, are required.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Method of implanting a femoral neck fixation prosthesis
InactiveUS20050010230A1Reduce bone lossReduce the amount requiredInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsRight femoral headLeft femoral head
A femoral neck fixation prosthesis and method of using same which reduces bone loss and the avoids the other shortcomings of the prior art by allowing the fixation of a stable femoral head replacement while reducing the amount of the femur which must be reamed for the insertion of the prosthesis. The preferred embodiment provides that the femoral head is attached to a fixation prosthesis, which extends coaxially through the canal of the femoral neck, into the femur, and is then attached to the opposite lateral wall of the femur. In this manner, the prosthesis serves to imitate the original structure of the femoral neck. No other support members, either crosspins or arms extending into the length of the femur, are required.
Owner:CROFFORD THEODORE W
Implant dentaire
InactiveUS20130157223A1Better respects the biological tissuesEasy to integrateDental implantsTeeth fillingDental implantBiomedical engineering
Dental implant having an internal geometry and an external geometry, the external geometry comprising at least three sections. This dental implant is provided with a fixing means implemented by a fixing of the Morse cone type in order to fix thereon a prosthetic stud and comprises an ovoid shaped cervical section or a ceramic ring.
Owner:SUDIMPLANT
Tibial component and articular prosthesis for the knee comprising said tibial component
A pin for the anchoring of articular prostheses includes a connecting portion (4) with a prosthesis (2) and an engagement portion (5) in a hole obtained within a bone. The engagement portion (5) is at least partly deformable in a radial direction and in a resilient way, in order to allow the instantaneous blocking of the pin (1) in the hole and the primary fixing of the prosthesis (2) on the bone, so as to al low an easy primary fixing of the prosthesis by simply introducing with a pressure the connecting portion in the hole obtained within the bone itself.
Owner:FIN CERAMICA FAENZA
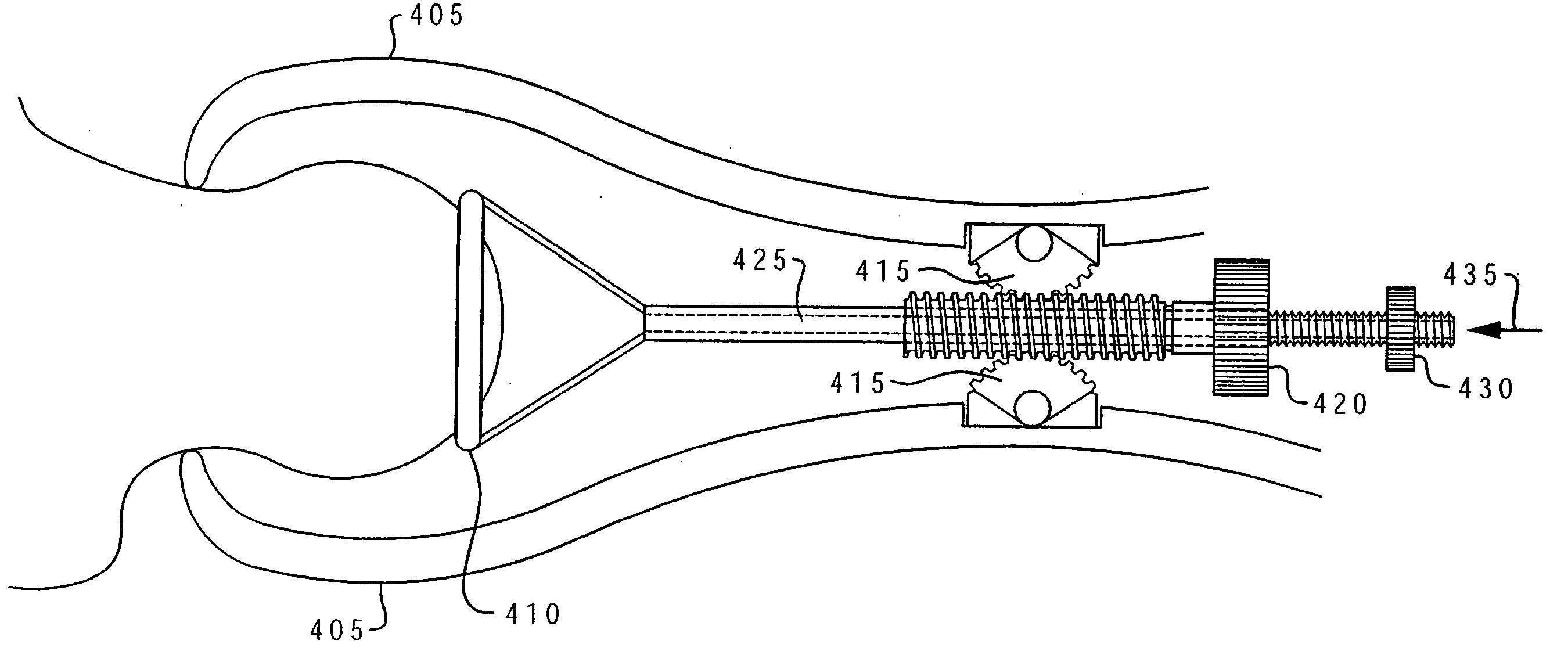
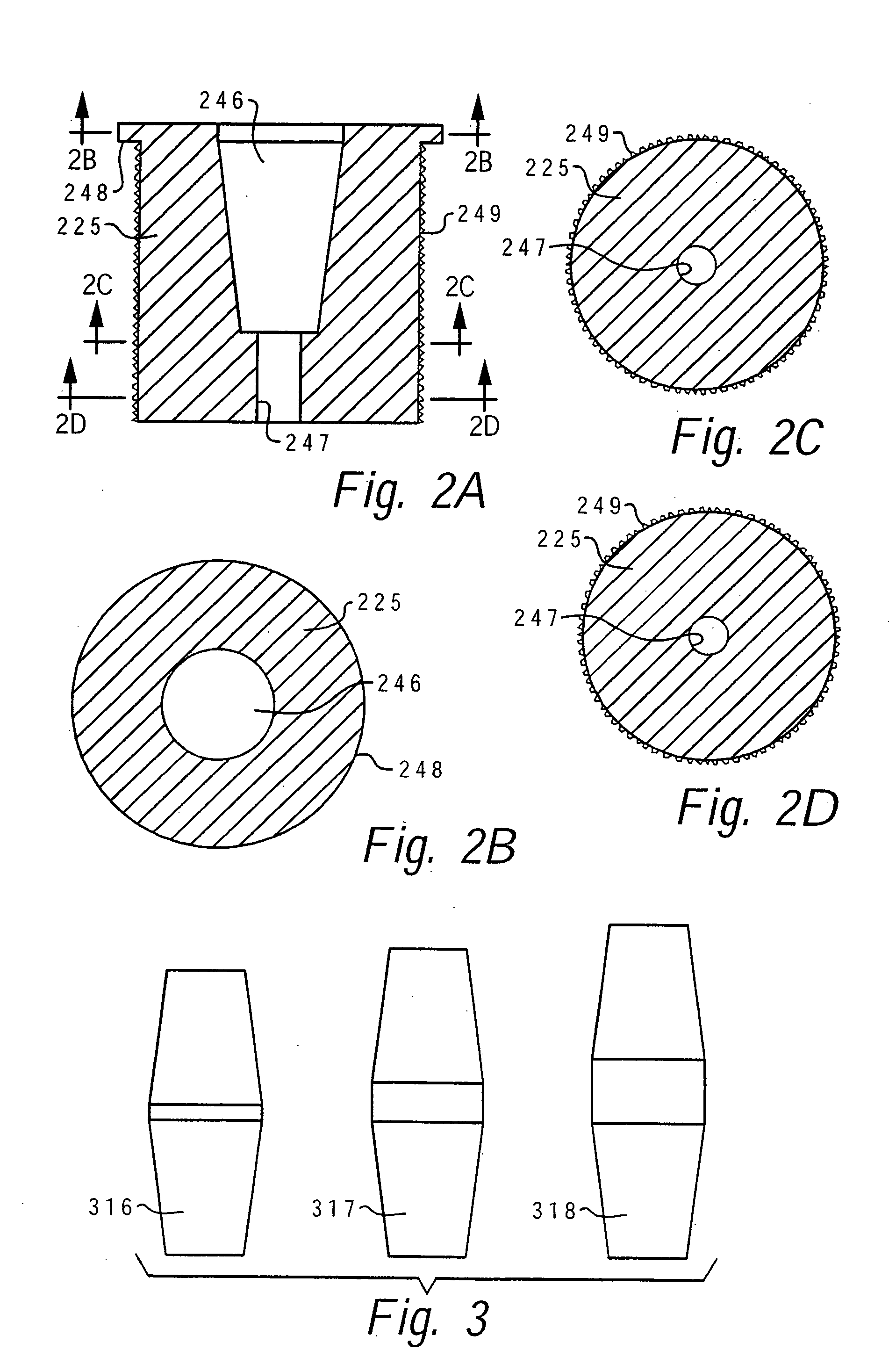
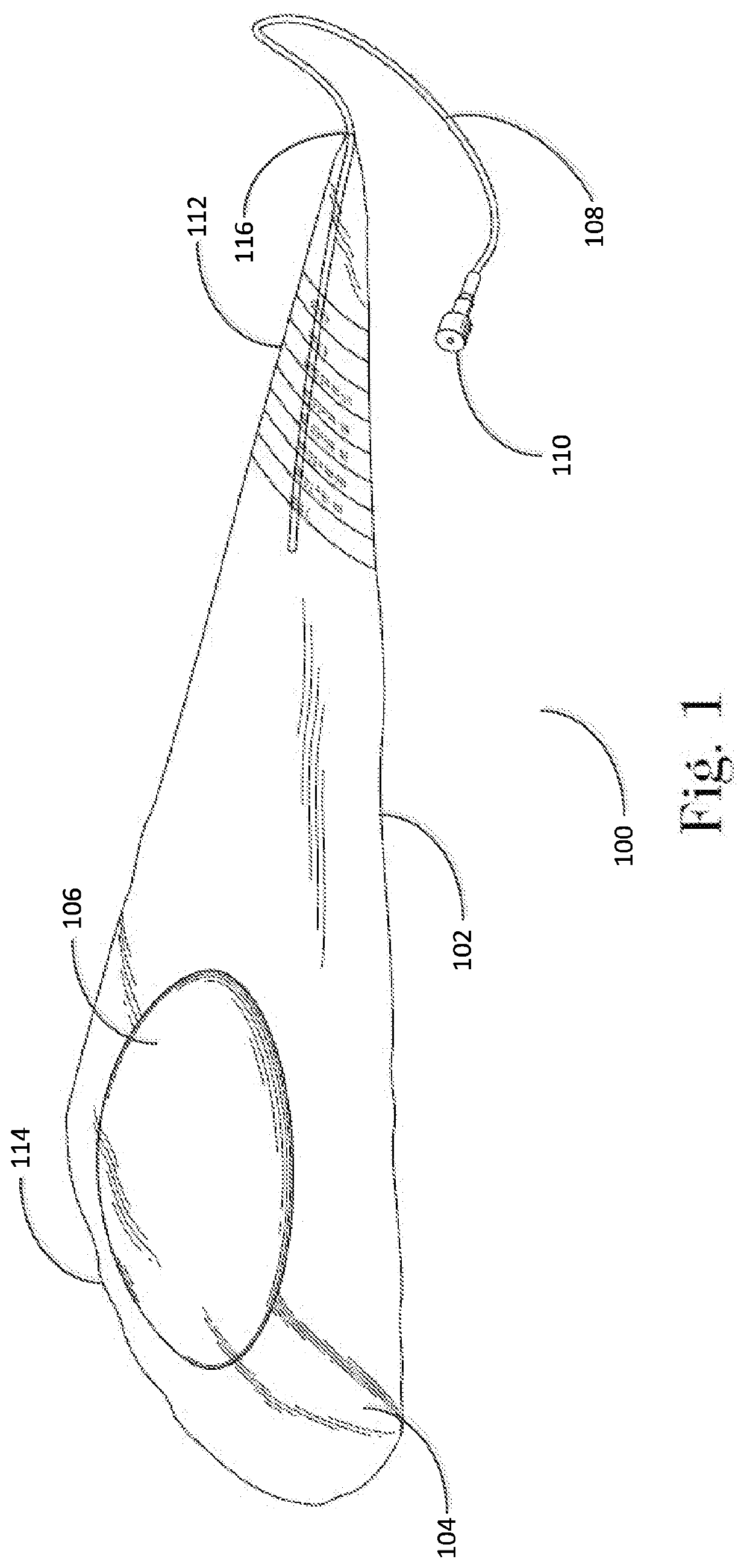
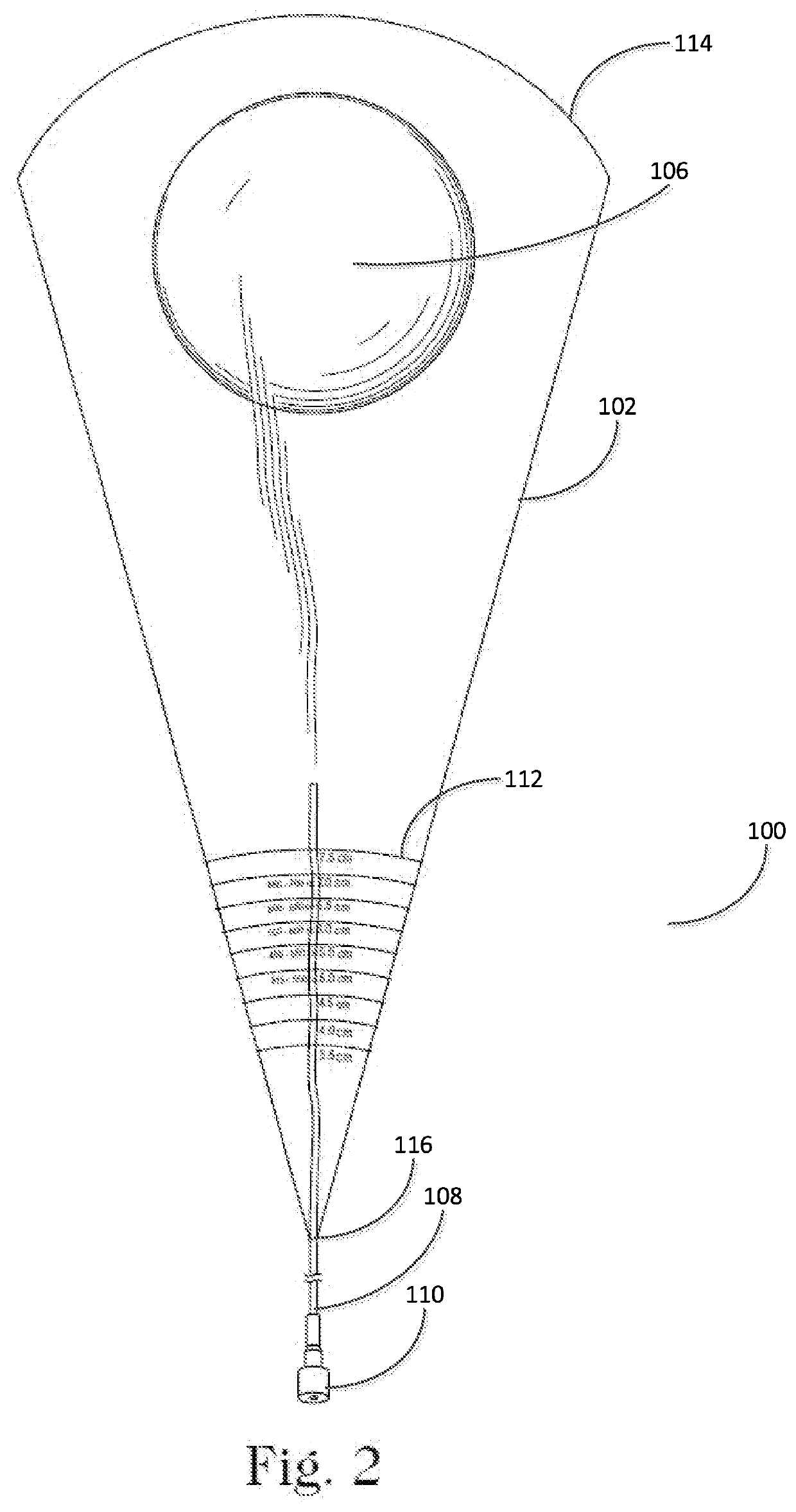
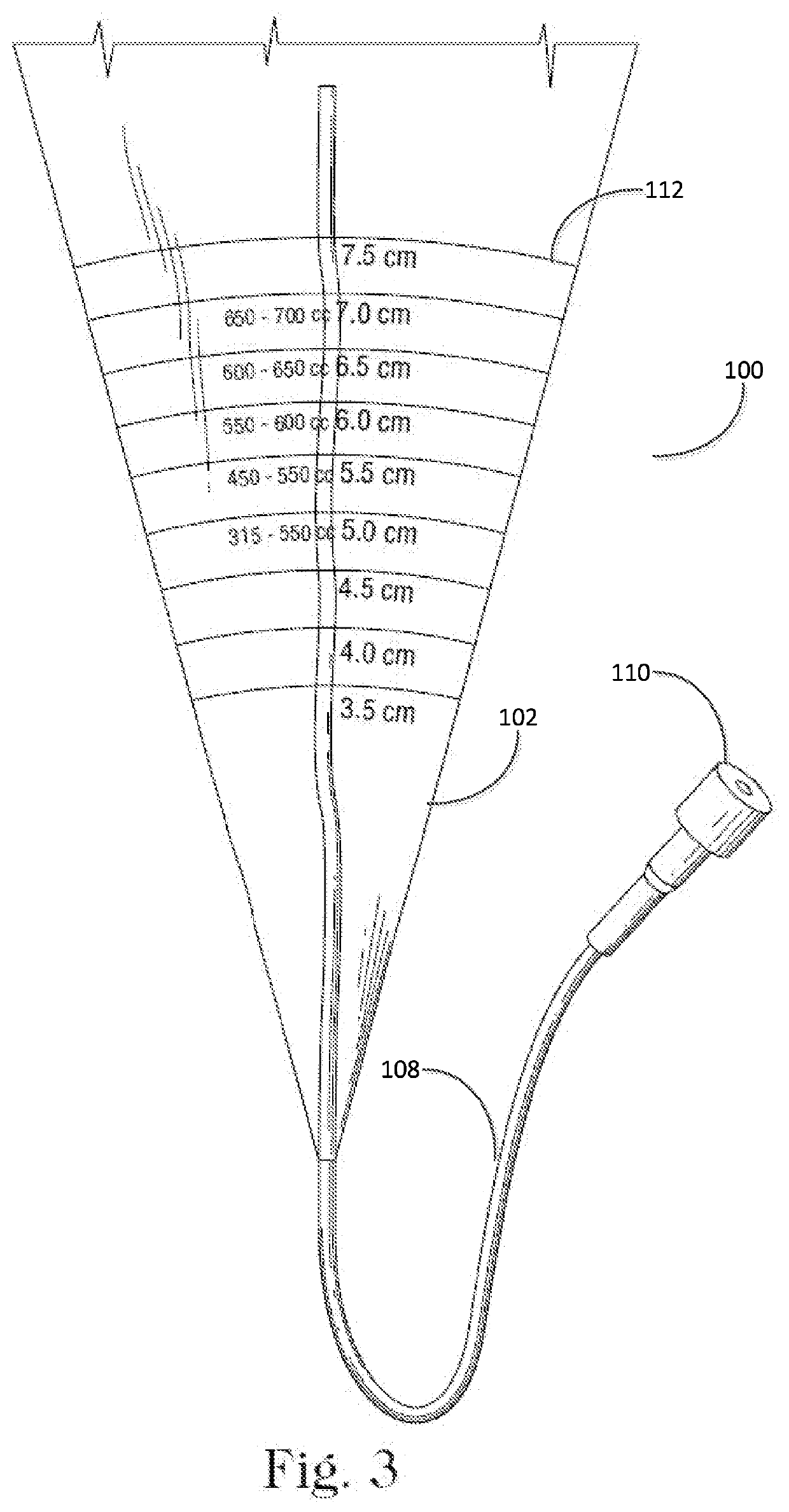
Closed funnel for the delivery of a prosthetic implant
InactiveUS20200222174A1Easily exit frustumReduce coefficient of frictionMammary implantsCosmetic implantsReoperative surgeryFixed prosthesis
A surgical device for assisting in the placement of a prosthetic implant within a surgical pocket of a patient. The surgical device according to one embodiment comprises one or more sheets of polymer shaped in the form of a conical frustum in which a proximal end of the frustum is sealed and a distal end of the frustum forms a tip, the interior cavity of the frustum sized to hold a prosthetic implant. A lumen extends into the interior of the frustum to allow the injection of fluid into the interior of the conical frustum and thereby activate any surface coatings applied thereto.
Owner:PROXIMATE CONCEPTS LLC
Titanium alloy hemipelvic prosthesis capable of individually retaining part of acetabulum through 3D printing
The invention discloses a titanium alloy hemipelvic prosthesis capable of individually retaining part of the acetabulum through 3D printing. The titanium alloy hemipelvic prosthesis comprises a prosthesis contact surface matched with the sacrum, a prosthesis contact surface matched with the rest acetabulum and a cylindrical structure for connecting the two prosthesis contact surfaces, wherein a porous structure is designed on the contact surface attached to the bone tissue, a covered edge is arranged outside the porous structure, two screw holes are formed in the middle of the porous structure, and the prosthesis and the adjacent bone tissue can be fixed by screws, so that early stability is obtained and long-term stability is achieved. The prosthesis contact surfaces are designed according to imaging data collected in the early stage and can be perfectly matched with the sacrum and the rest acetabulum of a patient, and the cylindrical structure is optimally designed through finite element mechanical analysis and a topological structure. The titanium alloy hemipelvic prosthesis is designed according to the remodeling requirement of the residual acetabulum of the underage patient after acetabulum tumor resection, and a relatively good hip joint function can be obtained by restoring the acetabulum structure after remodeling.
Owner:AIR FORCE MEDICAL UNIV
3D printing semi-pelvic prosthesis
InactiveCN110811935APrecise positioningReduce weightJoint implantsSpinal implantsPelvic regionBone ingrowth
The invention discloses a 3D printing semi-pelvic prosthesis. The 3D printing semi-pelvic prosthesis comprises a prosthesis contact surface matched with the sacrum, a prosthesis contact surface matched with the contralateral pubis, a semi-circular acetabular cup structure and a cylindrical structure connecting the prosthesis contact surfaces and the semi-circular acetabular cup structure. The prosthesis contact surfaces at two ends are designed with porous structures, edge wrapping structures outside and two screw holes in the middle, and the cylindrical structures are designed by finite element mechanical analysis and topological structure optimization. The prosthesis contact surfaces at two ends, designed through early collected imaging data, can perfectly fit the sacrum and the contralateral pubis of a patient, respectively; the prosthesis and the contacted bone can be fixed through screws, the position of the center of the semi-circular acetabular cup structure after reconstructionis consistent with that of the original acetabulum center, so that better hip joint function and early stability can be achieved, and the porous structures of the prosthesis contact surfaces are beneficial to later bone ingrowth, so as to achieve long-term stability.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Dental implant
The present disclosure relates to a dental implant used to support and secure the prosthetic elements replacing original teeth and especially for situations with aesthetic compromise and reduced available space due to the presence of adjacent teeth or due to the geometry of the bone, the dental implant including a threaded central body and a platform having a diameter between 3.1 and 3.5 mm with a conical outer and inner shape and extending by means of a threaded hole for retaining a pier for attachment to the prosthesis.
Owner:GARCIA SABAN JUAN CARLOS +2
Dental implant device
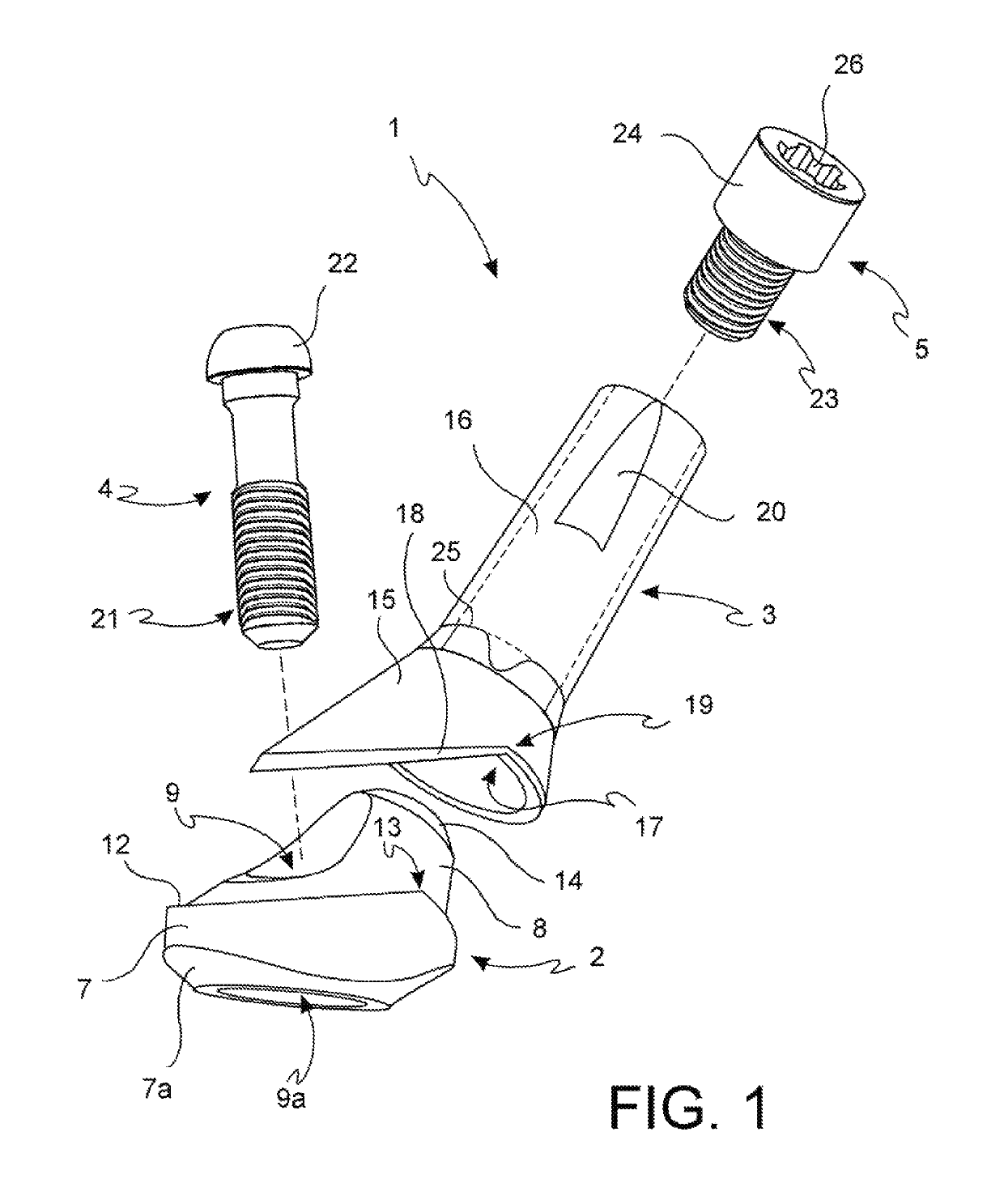
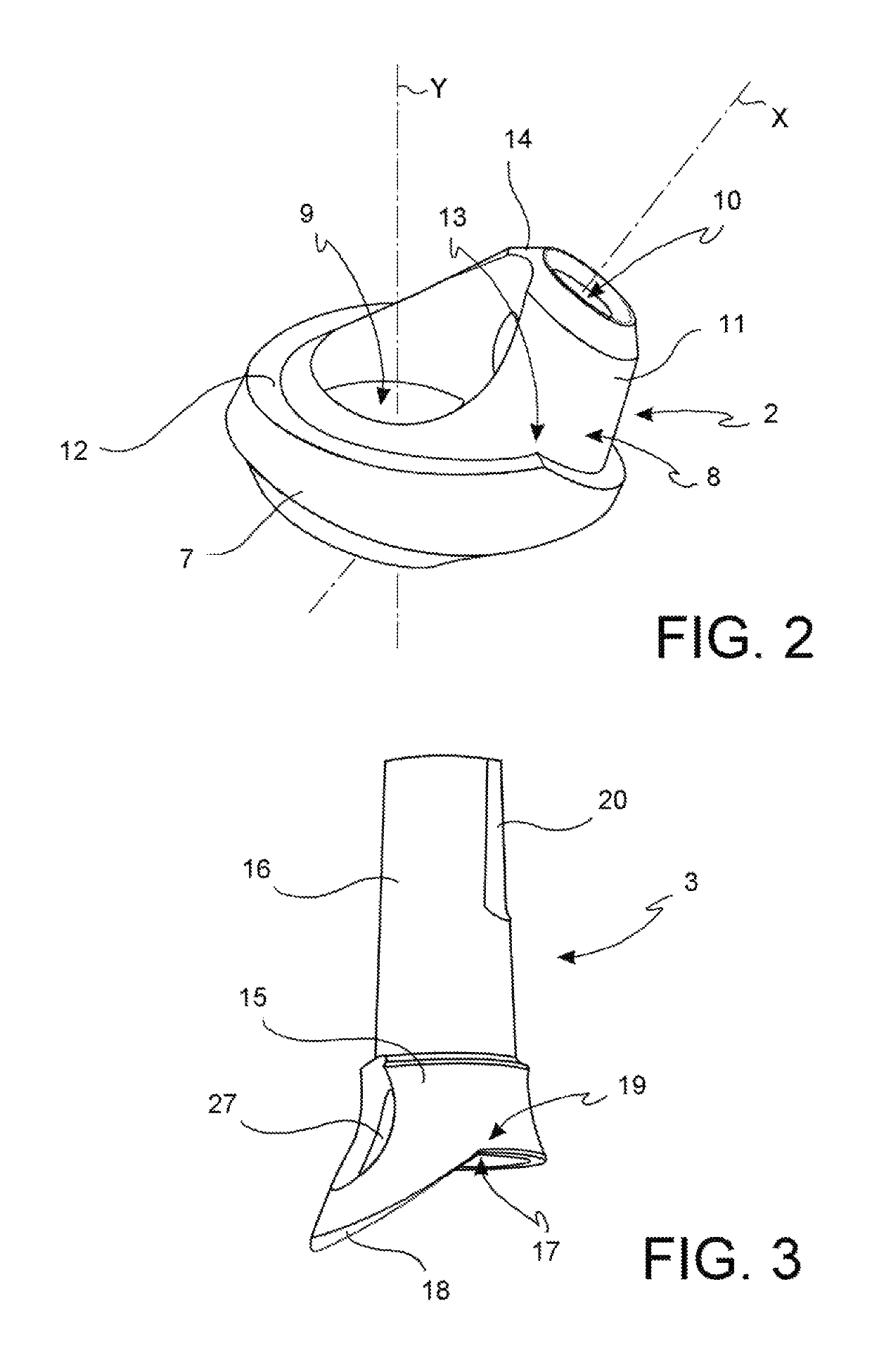
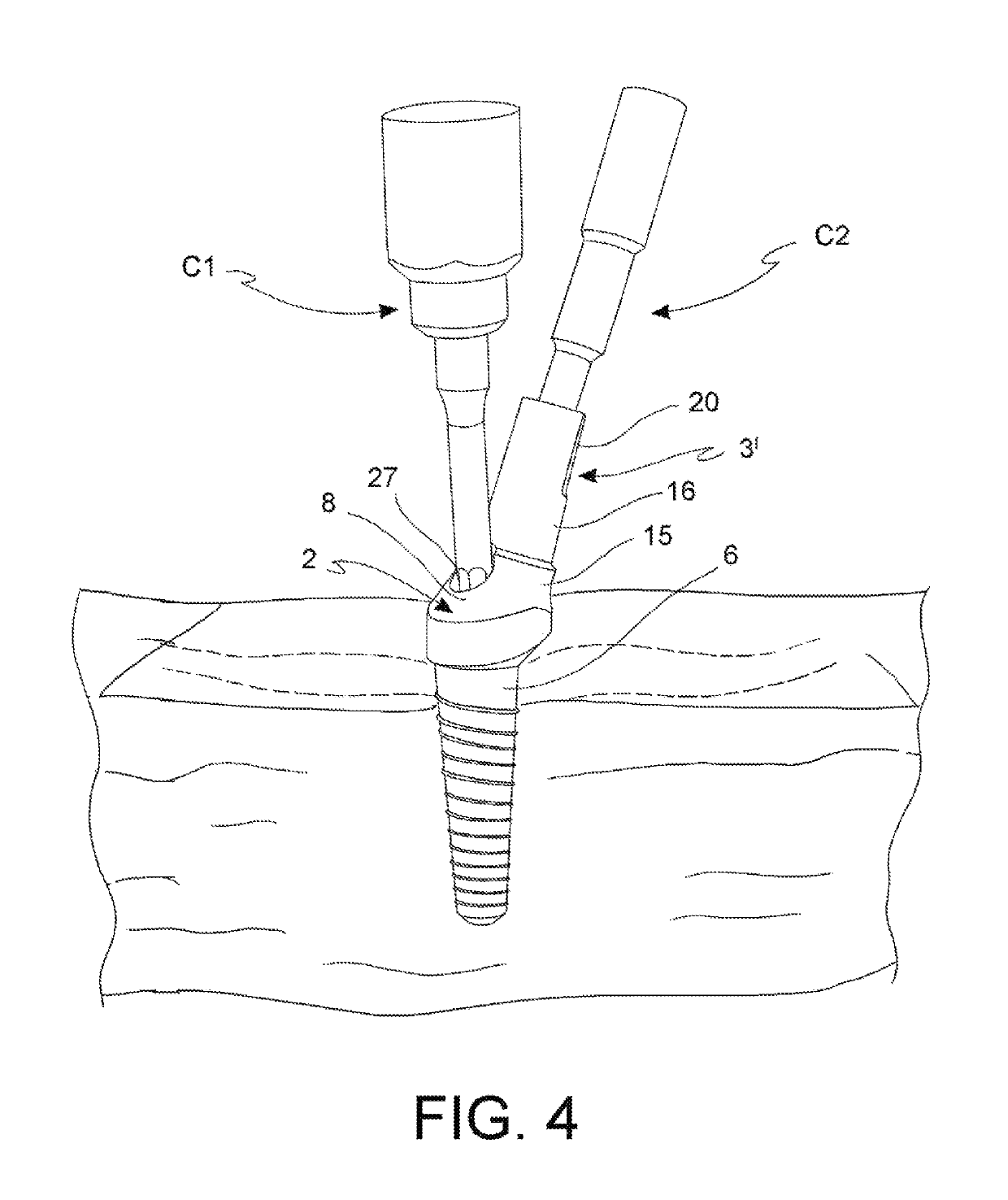
ActiveUS10285787B2Easy to assembleEasy to disassembleDental implantsImpression capsEngineeringDental implantology
This invention refers to a device exploitable within the scope of dental implantology, with specific reference to the set up and to the installation of a multi-teeth fixed prosthesis, either partial or total. The said invention specifically concerns a connection device (1) between a dental implant and the prosthesis. In particular, this invention concerns a connection device (1) including a bearing element (2) and a prosthesis connecting element (3, 3′), with the said connecting element (3, 3′) being matchable with the aforementioned bearing element (2), wherein the bearing element (2) includes a base portion (7) on which a conical portion (8) is further positioned and is characterized by the fact that between the base portion (7) and the conical portion (8) a shoulder (12) with a stop portion (13) is formed to prevent relative rotation of the connecting element (3, 3′) with respect to the bearing element (2).
Owner:DENTAL KNOWLEDGE
Preparation method of 3Y-TZP ceramic paste and preparation process of complete-implant fixed prosthesis
PendingCN113061028ARemove cleanFast curingAdditive manufacturing apparatusImpression capsPhotoinitiatorFixed prosthesis
The invention relates to a preparation method of 3Y-TZP ceramic paste and a preparation process of an upper structure of an implant prosthesis, wherein the preparation method of the 3Y-TZP ceramic paste comprises the steps: adding 3Y-TZP ceramic powder, a dispersing agent, a defoaming agent and a flatting agent into a photosensitive resin premixed solution, fully ball-milling to form ceramic slurry, then adding a photoinitiator, ball-milling again, then adding a rheological additive, and mixing to form the 3Y-TZP ceramic paste. The preparation process of the upper structure of the implant prosthesis comprises the steps of acquiring dentition data of a patient, designing, printing the upper structure of the implant prosthesis, degreasing, sintering, applying facing porcelain and carrying out heat treatment. The 3Y-TZP ceramic paste can be used for 3D printing of the upper structure of the implant prosthesis to replace a traditional cutting process, environmental pollution is avoided, material loss is reduced, manufacturing precision is improved, and product quality is improved.
Owner:江苏京科智镕新材料科技有限公司
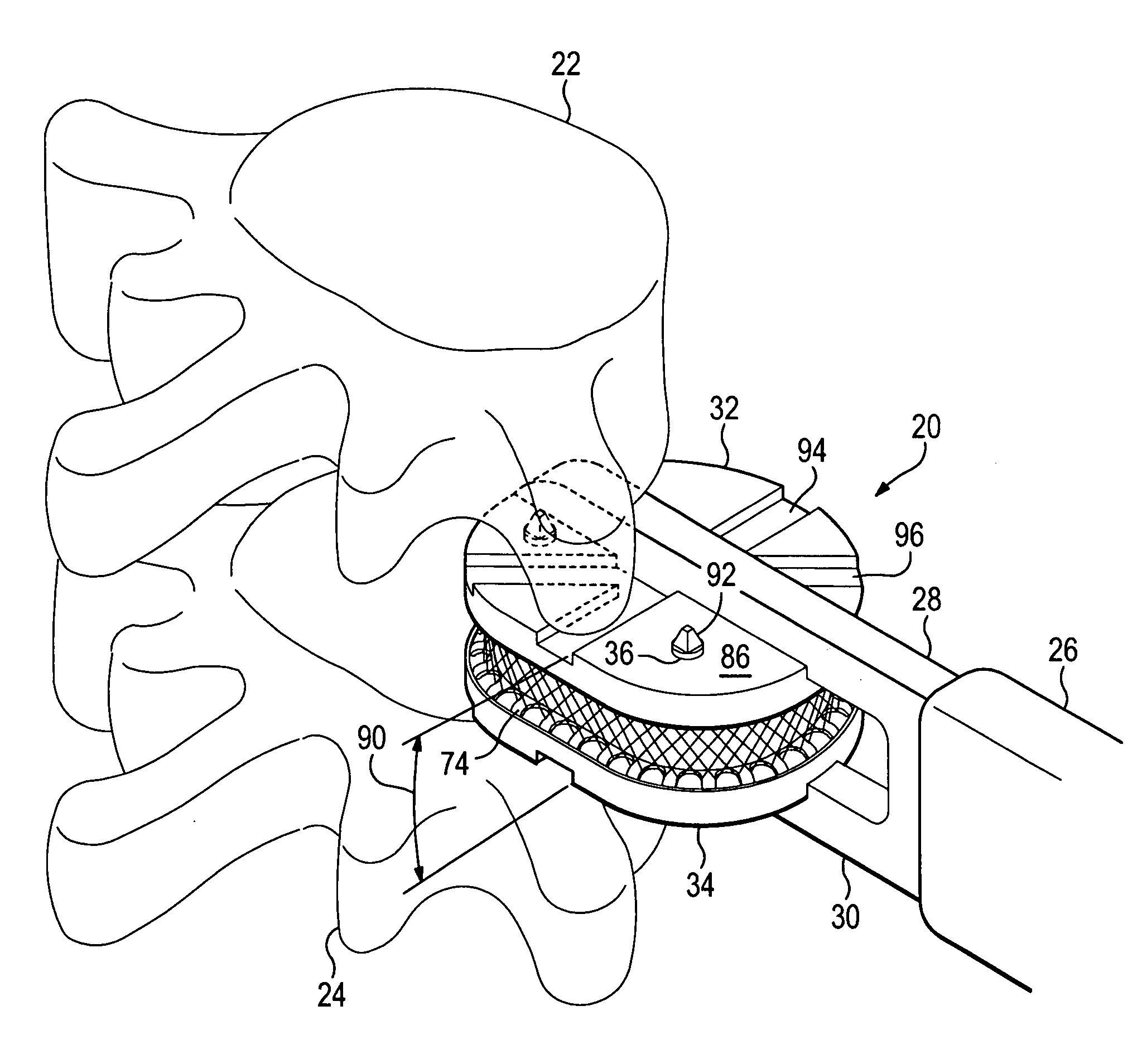
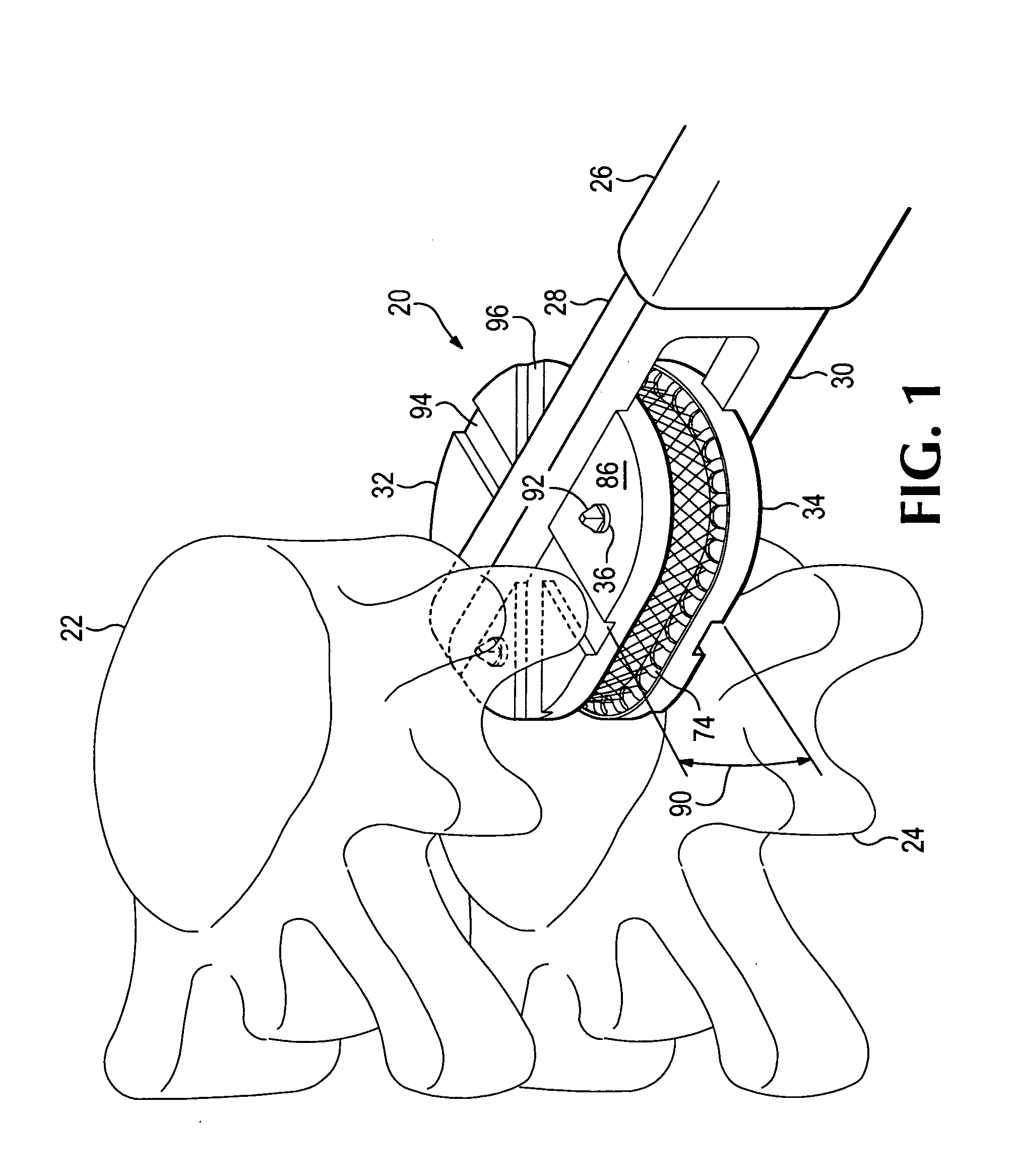
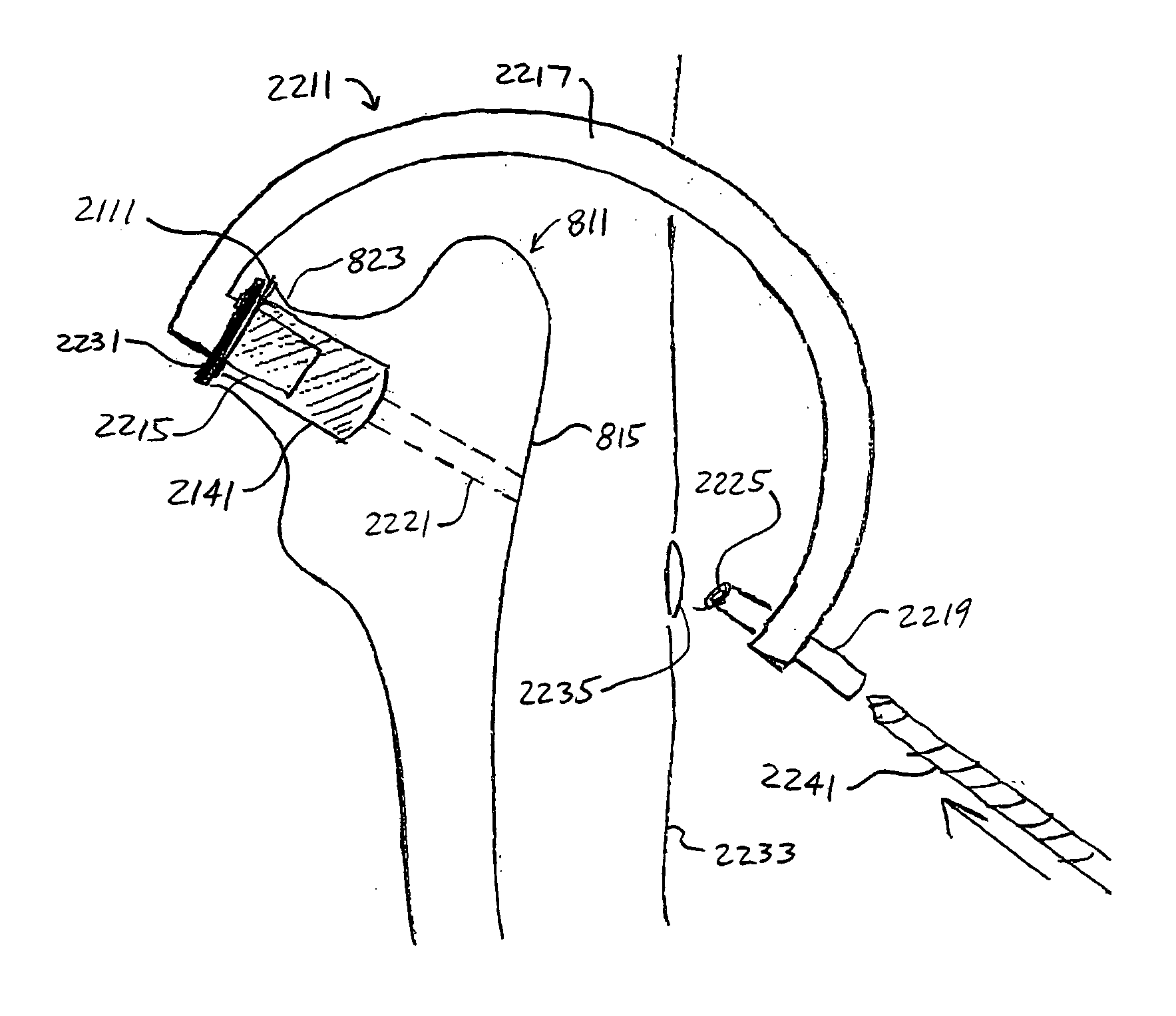
Methods and devices for the endoluminal deployment and securement of prostheses
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Pin for anchorage of articular prosthesis, articular prosthesis comprising said pin, tibial component and articular prosthesis for the knee comprising said tibial component
A pin for the anchoring of articular prostheses includes a connecting portion (4) with a prosthesis (2) and an engagement portion (5) in a hole obtained within a bone. The engagement portion (5) is at least partly deformable in a radial direction and in a resilient way, in order to allow the instantaneous blocking of the pin (1) in the hole and the primary fixing of the prosthesis (2) on the bone, so as to al low an easy primary fixing of the prosthesis by simply introducing with a pressure the connecting portion in the hole obtained within the bone itself.
Owner:FIN CERAMICA FAENZA
Vertically fixed substitute prosthesis for occlusalf surface
ActiveCN102988123AAvoid the possibility of breakingAvoid the effects of smoothnessBone implantAtrophyEngineering
The invention discloses a structure design of a vertically fixed substitute prosthesis for an occlusalf surface. Screw pores for vertically fixing the substitute prosthesis are formed on the section of the prosthesis, and matched with drill bushings and screws, the drill bushings and the screw pores are in clearance fit, and the drill bushings and the screws are in clearance fit. The traditional extender fixing technology is changed by the vertically fixed prosthesis, so that the periosteum and soft tissues are prevented from being peeled in a large area in the fixing process, and the possibility of prosthesis cracking is reduced. More importantly, the vertical fixing method does not change the main stress mode of lower jawbone of a patient, and the stress shielding effect of the extender on the lower jawbone covered by the extender in the transverse fixation can be avoided, and post-operation bone atrophy can be effectively prevented.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Knee joint prosthesis structure
PendingCN112869918AImprove long-term stabilityReduce the probability of looseningJoint implantsFemurSurgical RevisionKnee Joint
A knee joint prosthesis structure comprises a thighbone component, a cushion block component, a tibia component and a patella component, the thighbone component is provided with an intercondylar fixing block, the intercondylar fixing block is provided with a protruding part, the inner wall of the thighbone component is provided with a first coating used for bone ingrowth or bone growth, the cushion block component is located between the thighbone component and the tibia component, the outer wall of the lower end of the tibia component is provided with a second coating used for bone growth or bone length, the patella component is located in front of the thighbone component, and the inner wall of the patella component is provided with a third coating used for bone growth or bone length. The knee joint prosthesis structure is a biological type fixed prosthesis structure, various defects and complications caused by bone cement fixation can be avoided, harm to patients and surgical related medical staff due to current bone cement application is reduced, the long-term stability of the prosthesis is improved, the prosthesis loosening rate and the surgical revision rate are reduced, the cost is saved, and the cost is reduced. and the problem of precious medical observation is solved, and great social effect and economic benefit are achieved.
Owner:邬黎平
Intraoral insertion path visualizer
An intraoral insertion path visualizer is applied in the field of oral fixed prosthesis, especially in fixed prosthodontics requiring that abutments share the same insertion path. The intraoral insertion path visualizer mainly comprises two parallel visualizing rulers, a crossbeam and a handle. One of the visualizing rulers is disposed at an end of the crossbeam and is rotatable, and the other visualizing ruler is disposed at the other end of the crossbeam and can slides in a sliding groove in the crossbeam. The handle is flat so that the handle is convenient to grasp. The intraoral insertion path visualizer is characterized in that: during a visualizing process, the sharp end of one of the visualizing rulers is disposed at the shoulder of an abutment and the sharp end of the other visualizing ruler is disposed at the shoulder of another abutment, and therefore the same insertion path of the abutments can be visualized. One of the visualizing rulers is fixed relatively and the other visualizing ruler can be adjusted by allowing the visualizing ruler to slide along the crossbeam according to the different distances between the two abutments. The two visualizing rulers are both rotatable so as to suit each axial surface of the abutments.
Owner:崔荣新
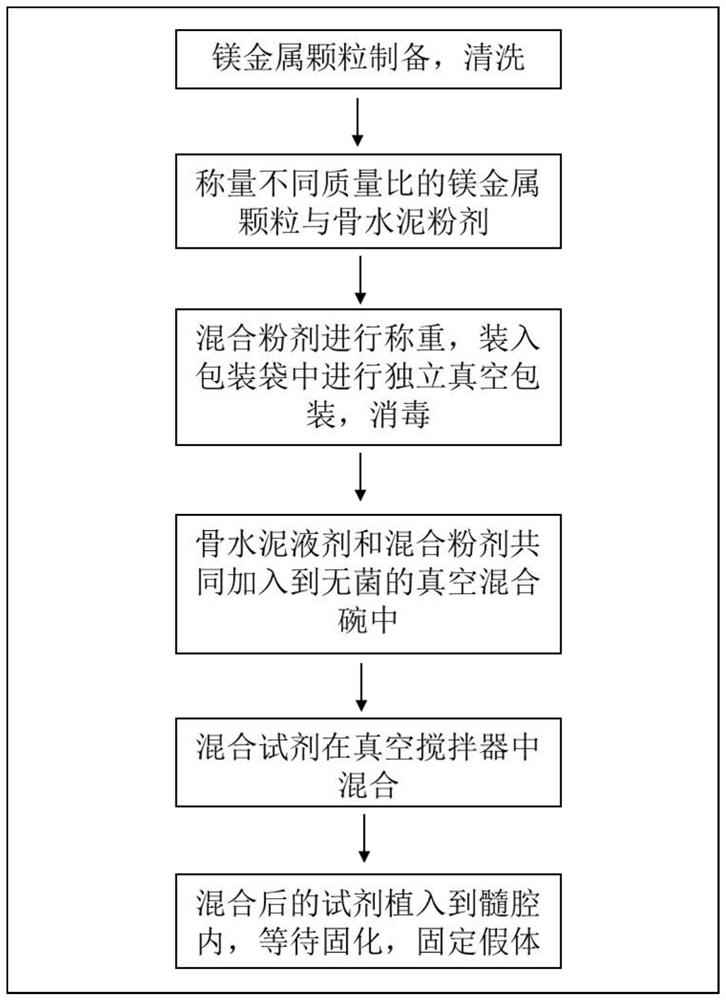
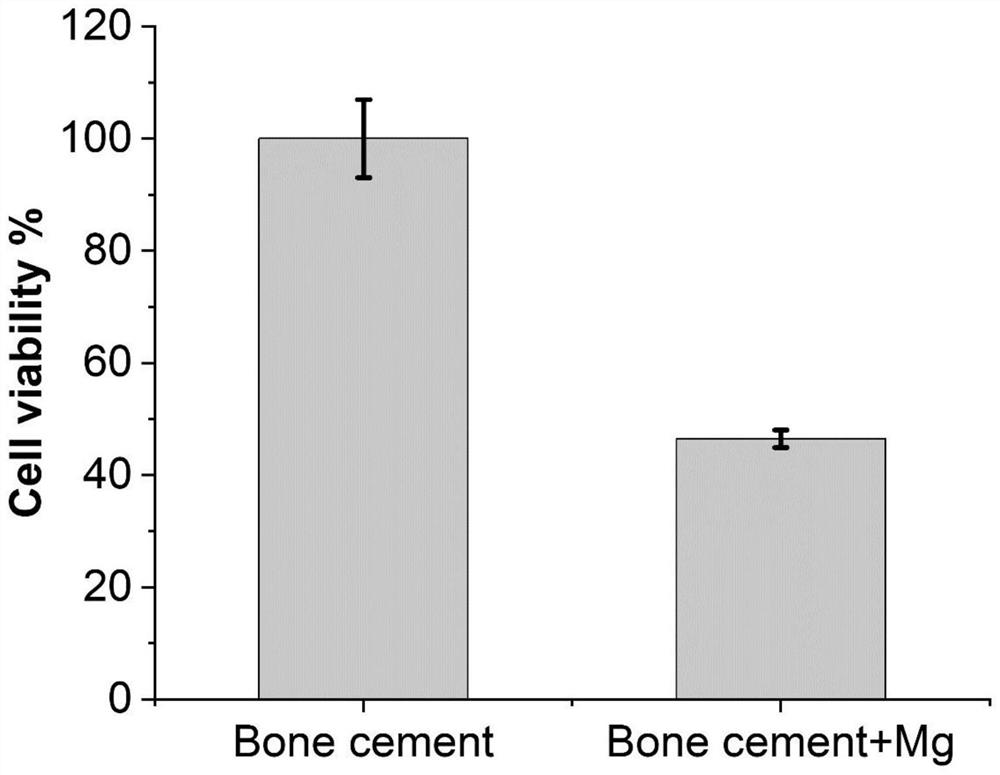
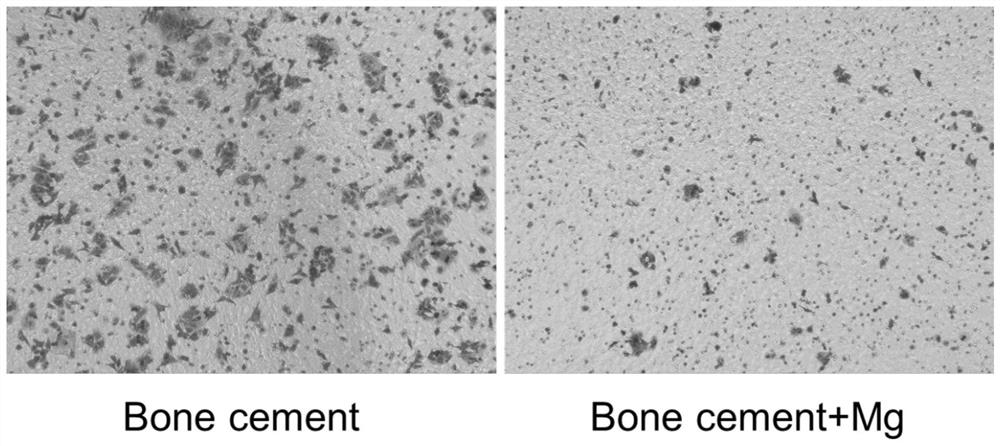
Preparation method of tumor bone cutting edge filler for preventing prosthesis loosening and tumor postoperative recurrence
PendingCN113367787AReduced risk of aseptic looseningImprove the quality of lifeOsteosynthesis devicesBone marrow cavityMaterial resources
The invention provides a preparation method of a tumor bone cutting edge filler for preventing prosthesis loosening and tumor postoperative recurrence. The preparation method comprises the following production steps of: (1) preparing metal particles containing magnesium elements, and carrying out cleaning; (2) respectively weighing the mass of the bone cement powder and the mass of the metal particles at a ratio; (3) loading the mixed powder weighed in the step (2) into a packaging bag for carrying out independent vacuum packaging and disinfection; (4) during utilization, adding the mixed powder and the bone cement liquid into a sterile vacuum mixing bowl; (5) preventing the magnesium particles from being oxidized in air, and mixing the mixed reagent in the step (4) in a vacuum stirrer; and (6) when stirring is carried out for certain time, implanting the mixture of the bone cement and the magnesium particles into the medullary cavity, waiting for solidification, and fixing the prosthesis. By use of the tumor bone edge cutting filler, the risk of secondary surgery is reduced, the postoperative living quality of a patient is greatly improved, manpower and material resources are saved, and the tumor bone edge cutting filler is suitable for being popularized and used.
Owner:SUZHOU ORIGIN MEDICAL TECH
Method for duplicating a denture
The fabrication of an implant-supported fixed complete denture involves multiple clinical and laboratory steps. One of the main steps is to provide the patient with an interim fixed prosthesis to evaluate the patient's esthetic and function al needs as well as to enhance the patient's psychology before proceeding to the definitive prosthesis. Different techniques for fabricating interim prostheses have been described in the literature. This disclosure describes a method of fabricating an implant-supported fixed interim prosthesis using self-curing acrylic resin. The interim prosthesis may be used as a blueprint for the definitive implant-supported hybrid prosthesis.
Owner:IMAM ABDULRAHRNAN BIN FAISAL UNIVERSITY
Biomaterial and method for its realisation
Porous biocompatible composite biomaterial, useable as a drug delivery system or as spacer or as bone substitute, such as for example for filling bone lacunae or for substituting damaged parts of bone tissue, or for fixing prosthesis of various types, or for thickening bones weakened by illness such as osteoporosis or the like, including a component adapted to form a porous structural matrix and a soluble component, wherein the soluble component is in form of powder and granules or other similar agglomerates so as to have mechanical support characteristics and osteoinductive and osteoconductive characteristics in the entire volume occupied by the biomaterial, and a method for obtaining the biomaterial.
Owner:TECRES SPA
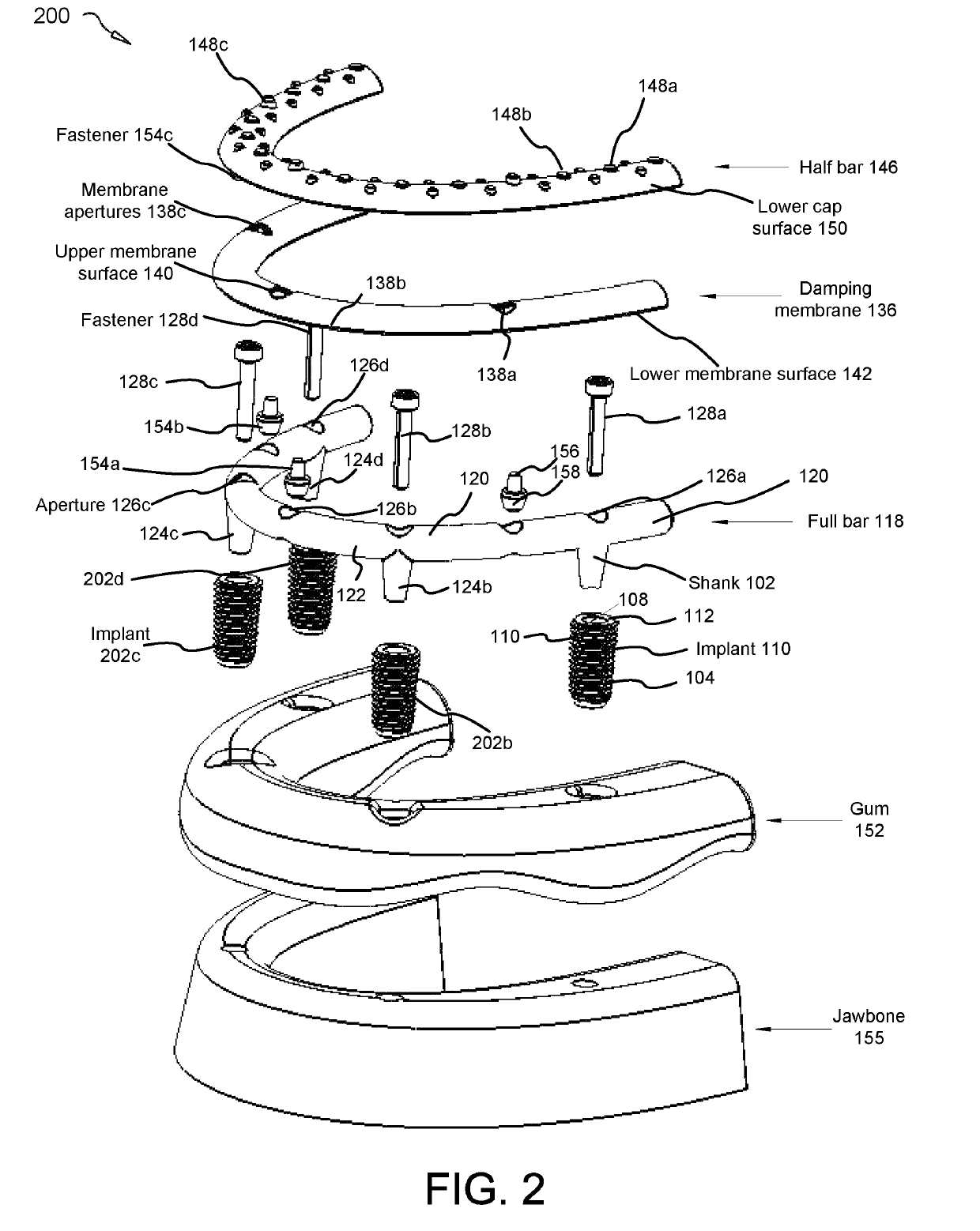
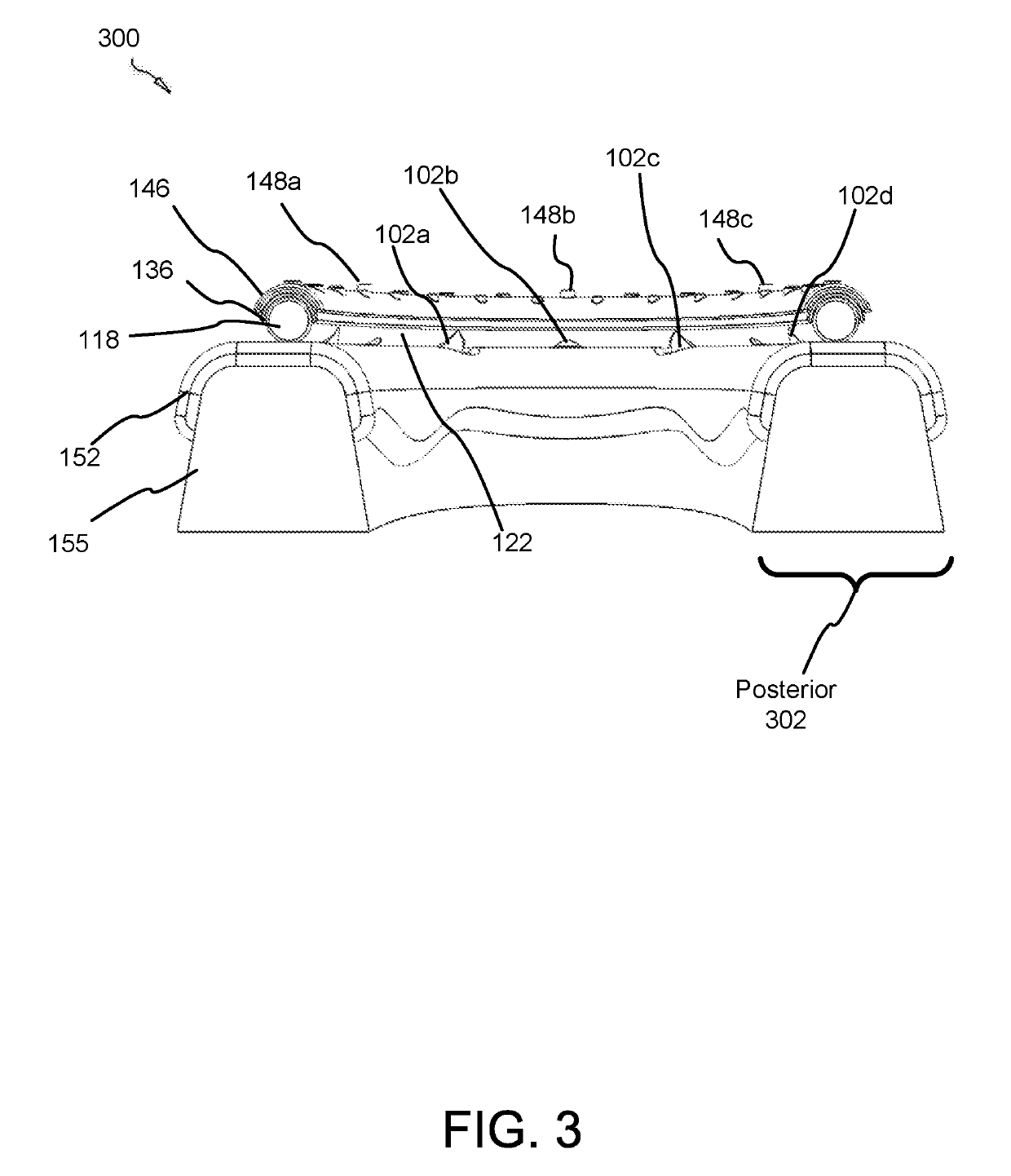
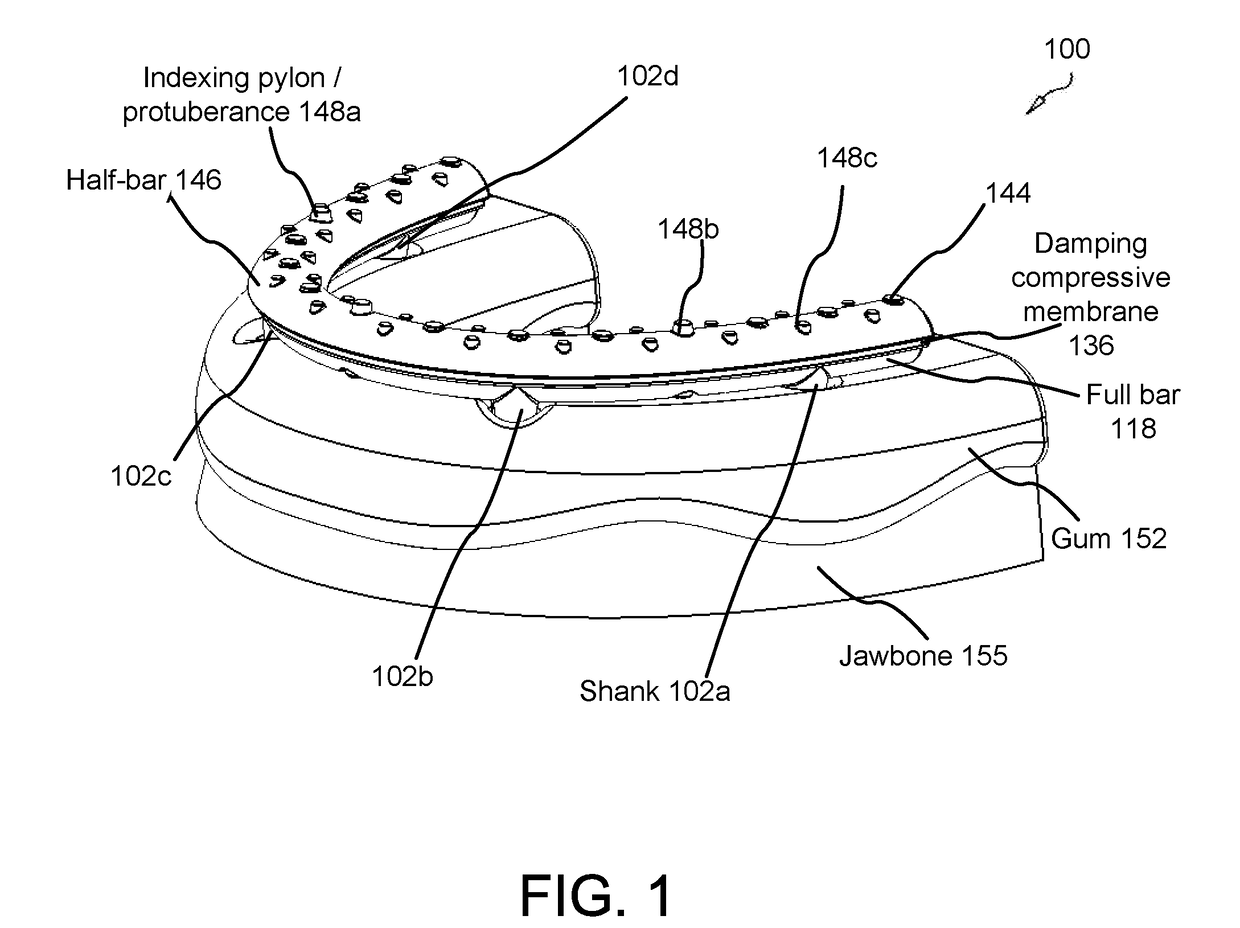
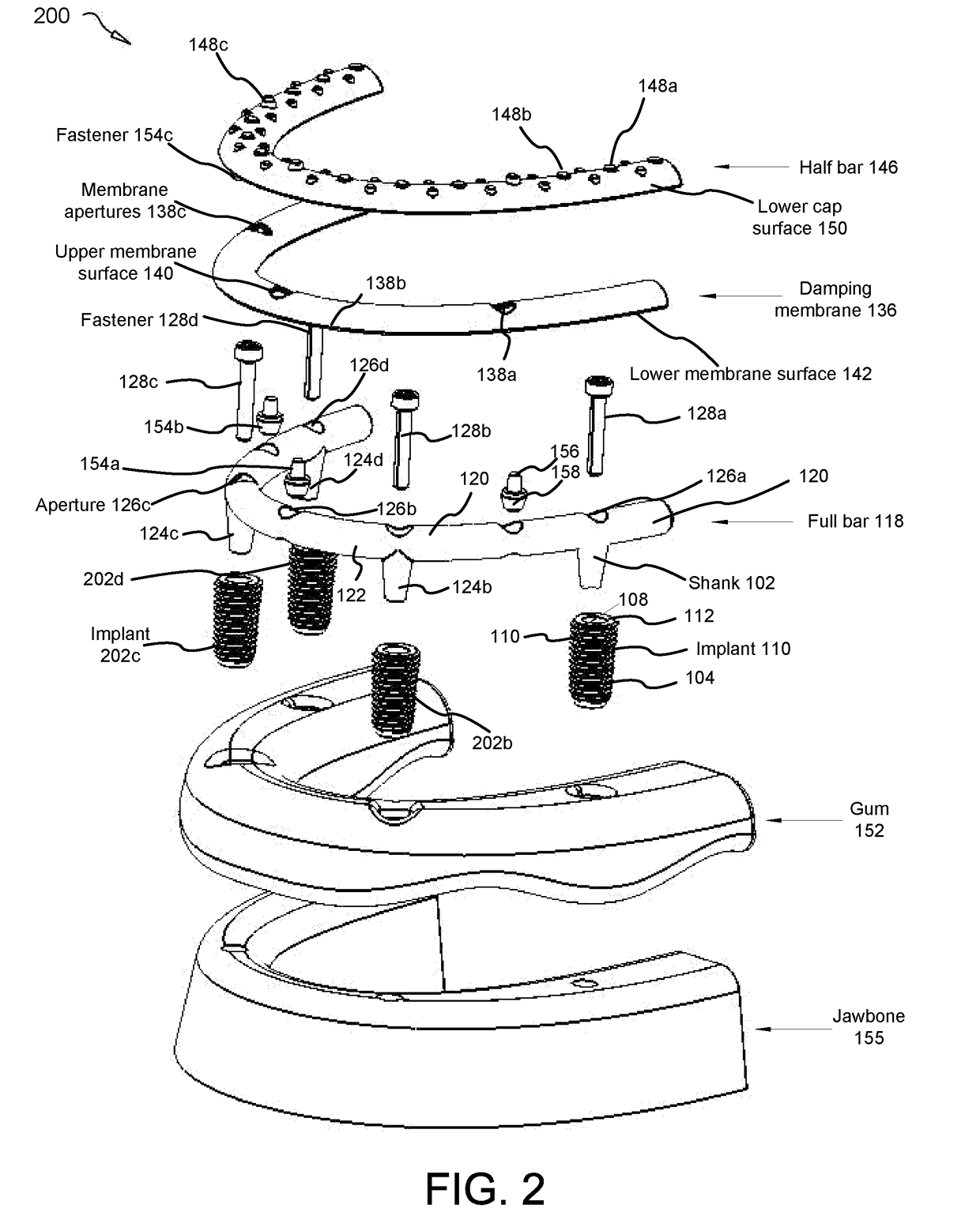
Force damping dental bridge assembly with synthetic periodontal ligament fibers
Owner:CLARK JR PAUL KENNETH
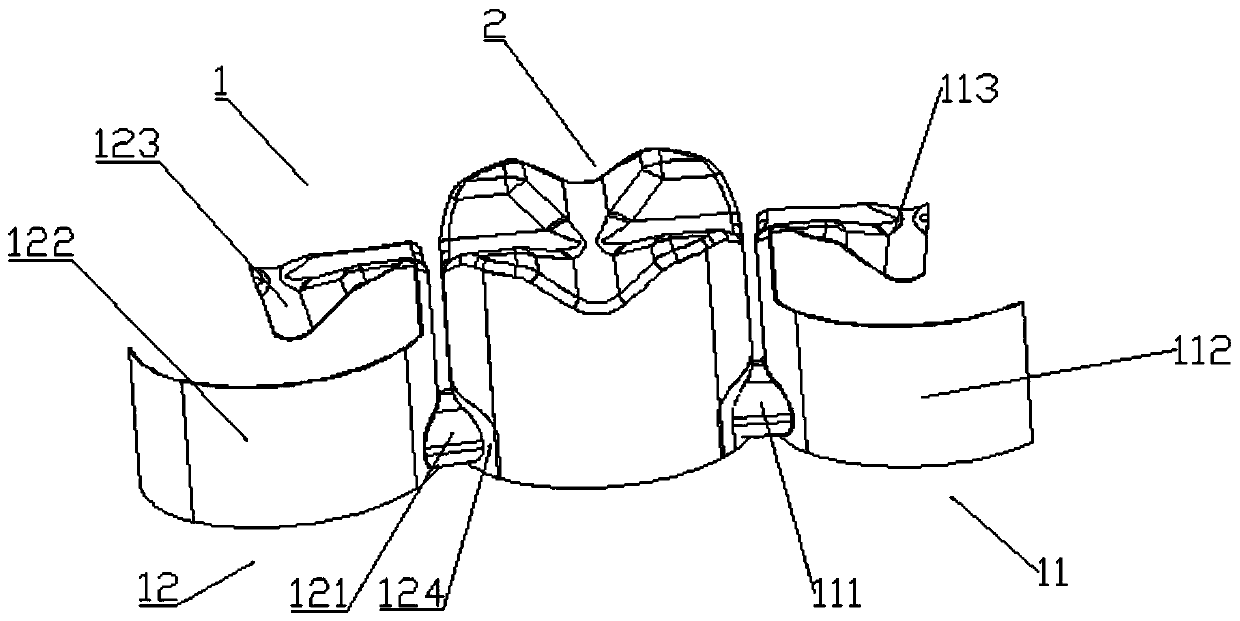
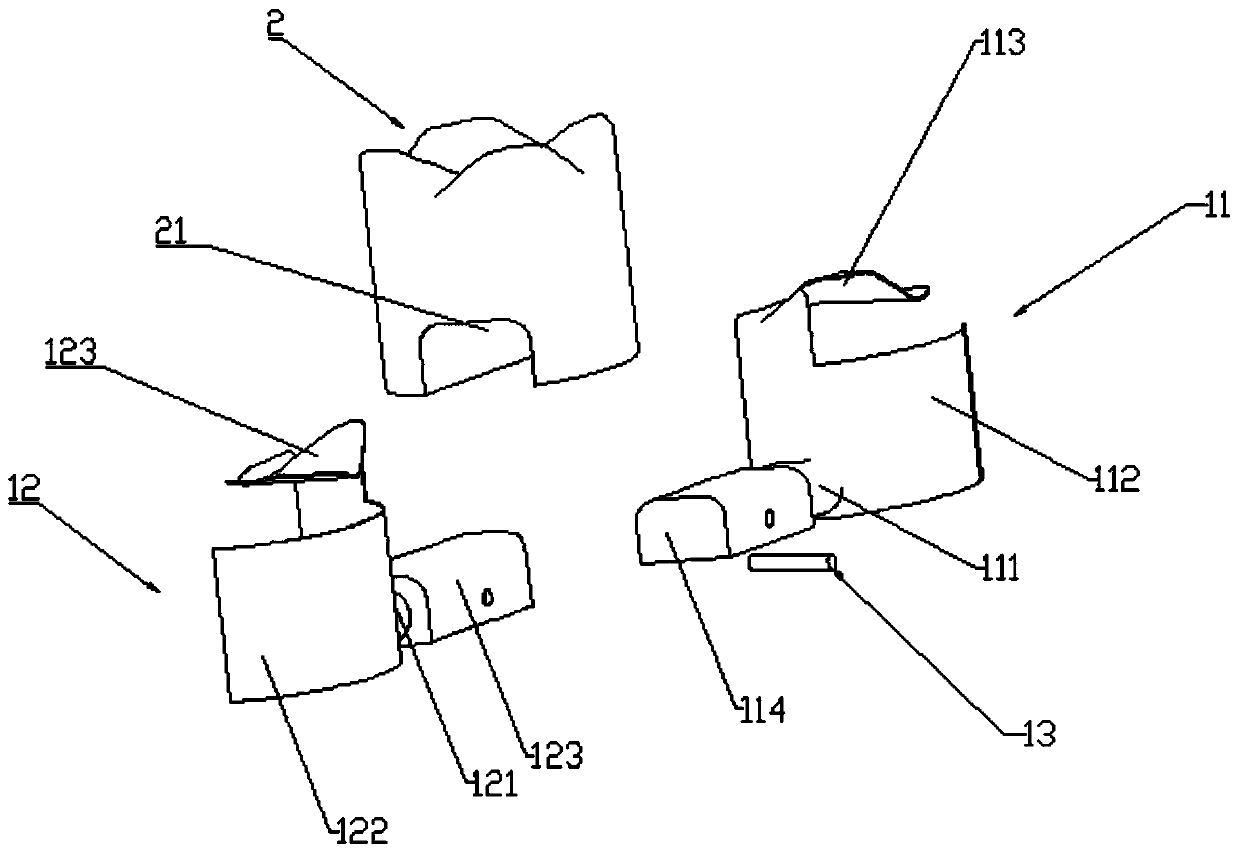
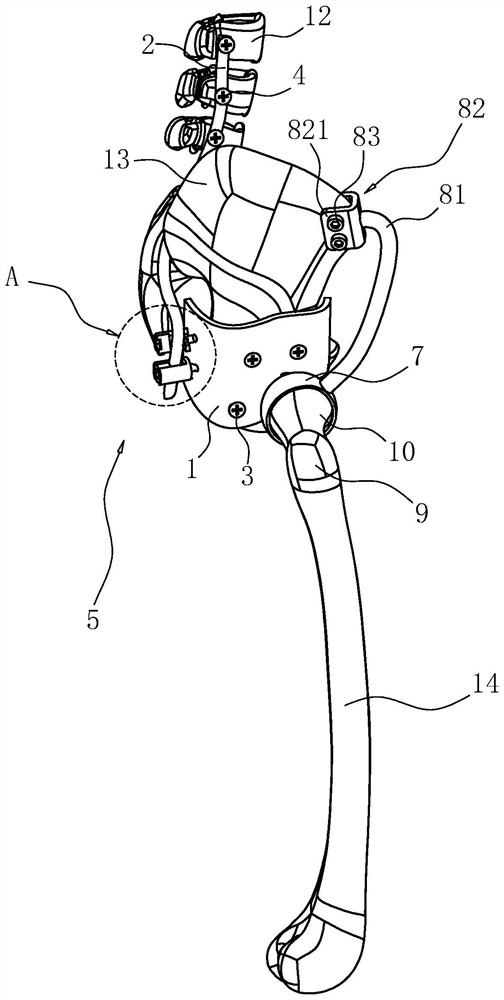
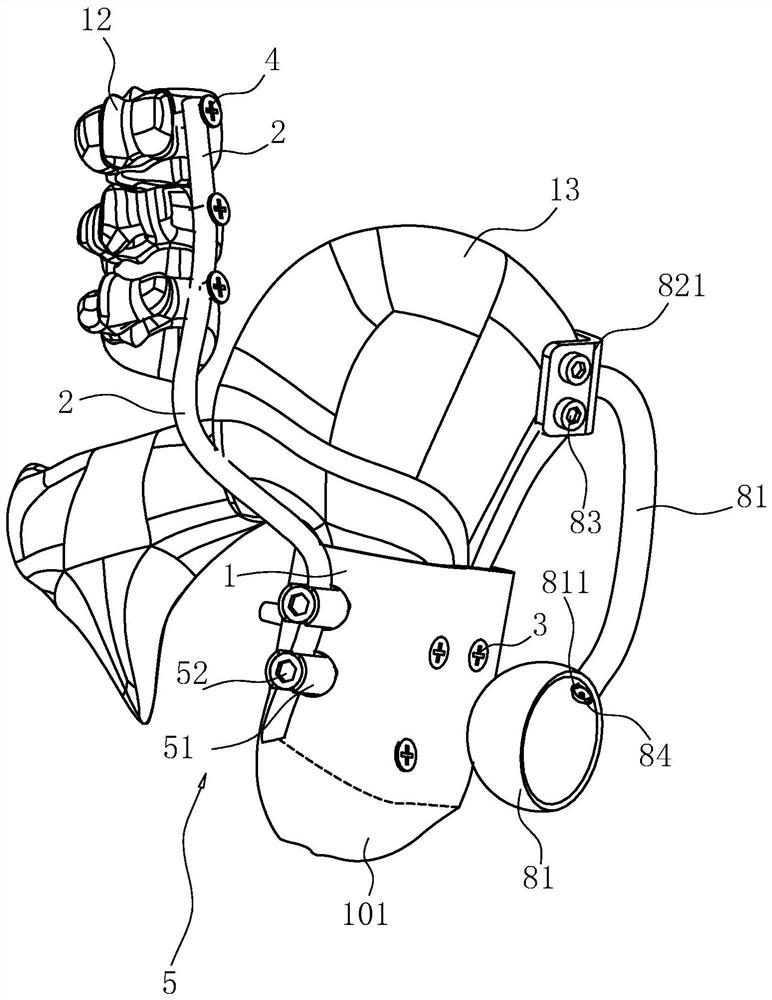
Fixed prosthesis for partially missing teeth and manufacturing method of fixed prosthesis
PendingCN110301990AProtect healthPrevent impactTeeth fillingArtificial teethMissing toothMissed tooth
The invention relates to a tooth fixed prosthesis, in particular to a fixed prosthesis for partially missing teeth. The fixed prosthesis includes a bracket and a prosthesis body, the bracket includesa first bracket and a second bracket, the first bracket is a positive bracket, and includes a first connection body, a first wing plate, an adjacent tooth near-the-center support and a precise attachment positive bolt; the second bracket is a negative bracket, and includes a second connection body, a second swing plate, an adjacent tooth far-from-the-center support and a precise attachment negative channel. According to the fixed prosthesis for the partially missing teeth, reversed recesses formed by adjacent teeth at both ends and the adjacent teeth are fully used for enhancing retention force of products, operations are not needed, prepared adjacent tooth tissue is little, the adjacent teeth and tooth tissue are not damaged, and the health of the adjacent teeth is protected.
Owner:刘友烈
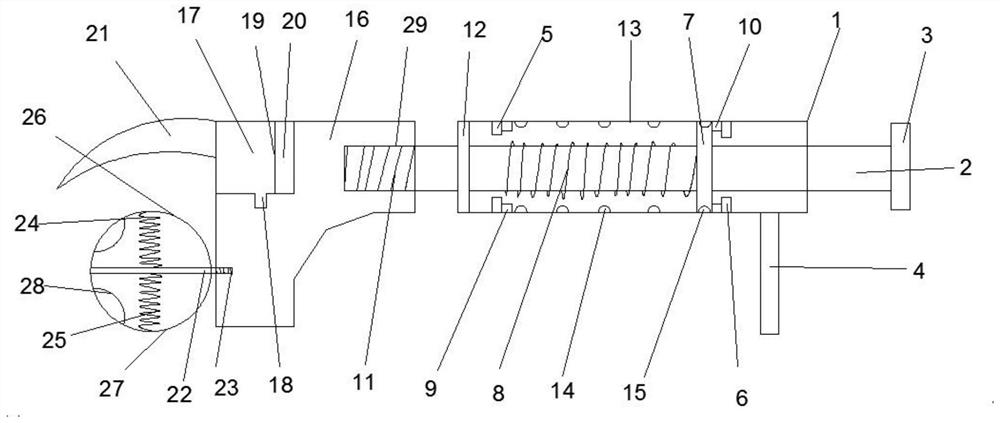
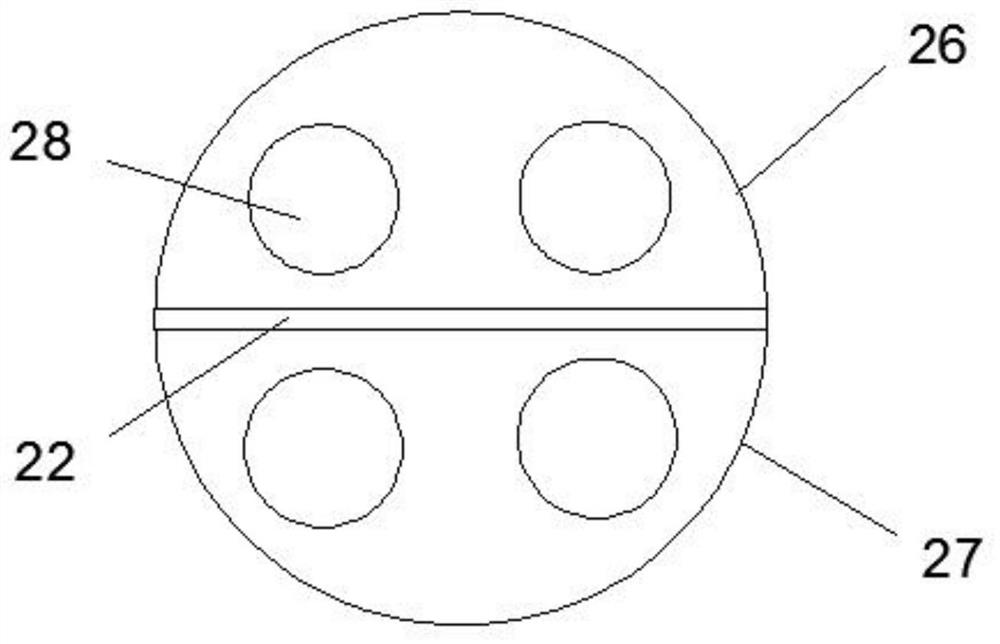
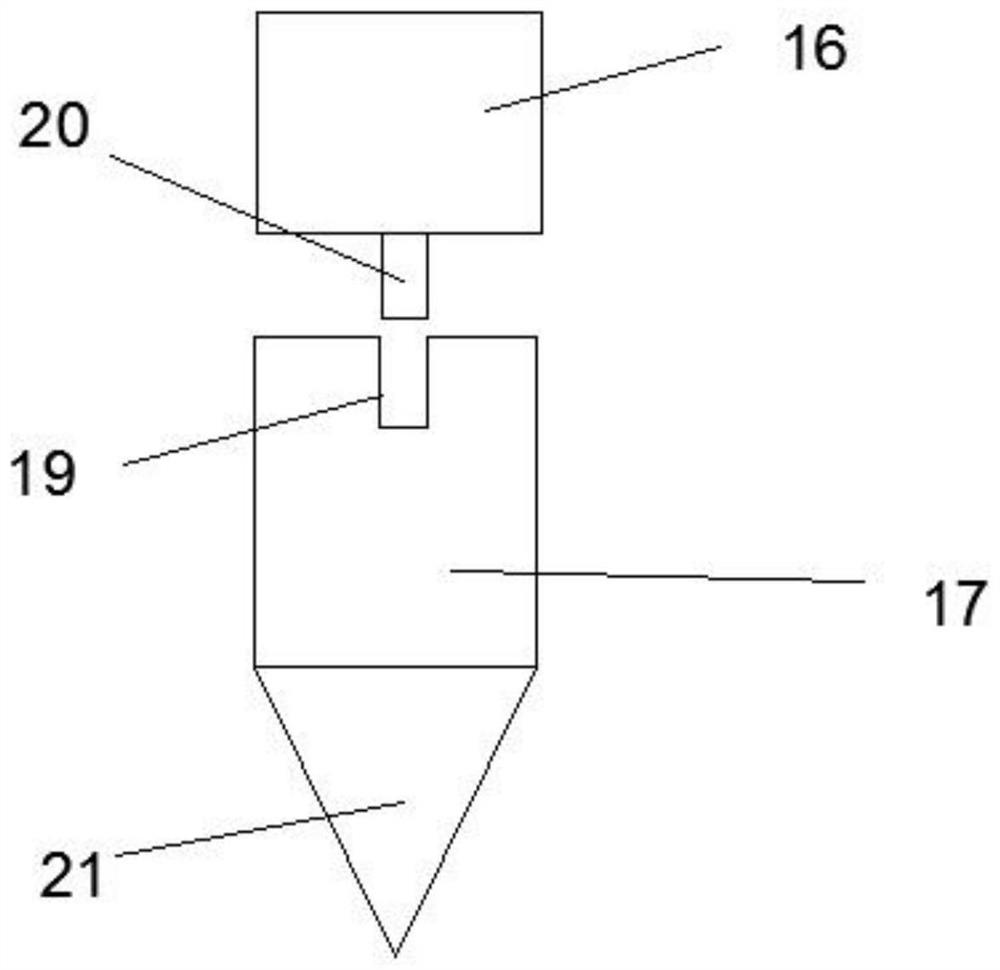
Acetabulum prosthesis extractor for revision
InactiveCN111839843AImprove convenienceImprove effectivenessJoint implantsAcetabular cupsAnatomyEngineering
The invention discloses an acetabulum prosthesis extractor for revision. The acetabulum prosthesis extractor comprises an acetabulum prosthesis supporting outer rod, a movably connected rotating rod is arranged on the outer side of the acetabulum prosthesis supporting outer rod; a movably connected acetabulum prosthesis supporting inner rod is arranged in the acetabulum prosthesis supporting outerrod in a sleeving manner; a fixedly connected third buffer layer is arranged at one end of the acetabulum prosthesis supporting outer rod, a first baffle plate and a second baffle plate which are fixedly connected are arranged in the acetabulum prosthesis supporting outer rod, a fixedly connected pressing handle is arranged at one end of the acetabulum prosthesis supporting inner rod, and the pressing handle and the acetabulum prosthesis supporting inner rod are of an integrated structure. The extractor has the beneficial effects that through a first spring and a second spring in a first bonetest head and a second bone test head, the spherical size can be changed according to bones of different sizes, the effectiveness of an operation is improved, and the progress of the operation is accelerated; due to the arrangement of the suction cups, the tightness of the fixing prosthesis is greatly improved.
Owner:姜杰
Connecting prosthesis for bone defects
The invention discloses a connecting prosthesis for bone defects and relates to the medical field. The connecting prosthesis comprises a fixed prosthesis body and an adjusting prosthesis body, wherein a connecting component is arranged at one end of the fixed prosthesis body, and a first medullary canal stem is arranged at the other end and is integrally formed with the fixed prosthesis body; a blind hole is formed in the connecting part, a first locating hole is formed in the blind hole, and a first locking screw is arranged at the first locating hole; one end of the adjusting prosthesis body is arranged in the blind hole and detachably connected with the blind hole through the first locking screw, and a second medullary canal stem is arranged at the other end of the adjusting prosthesis body and integrally formed with the adjusting prosthesis body; an adjuster is arranged on the adjusting prosthesis body and can slide on the adjusting prosthesis body, a second locating hole is formed in the adjuster, a second locking screw is arranged at the second locating hole, and the adjuster is detachably connected with the adjusting prosthesis body through the second locking screw. With the adoption of the design, the connecting prosthesis can be adjusted properly according to actual conditions and is enabled to have better mechanical performance and support effect after mounted, and the function can be restored early.
Owner:佟文
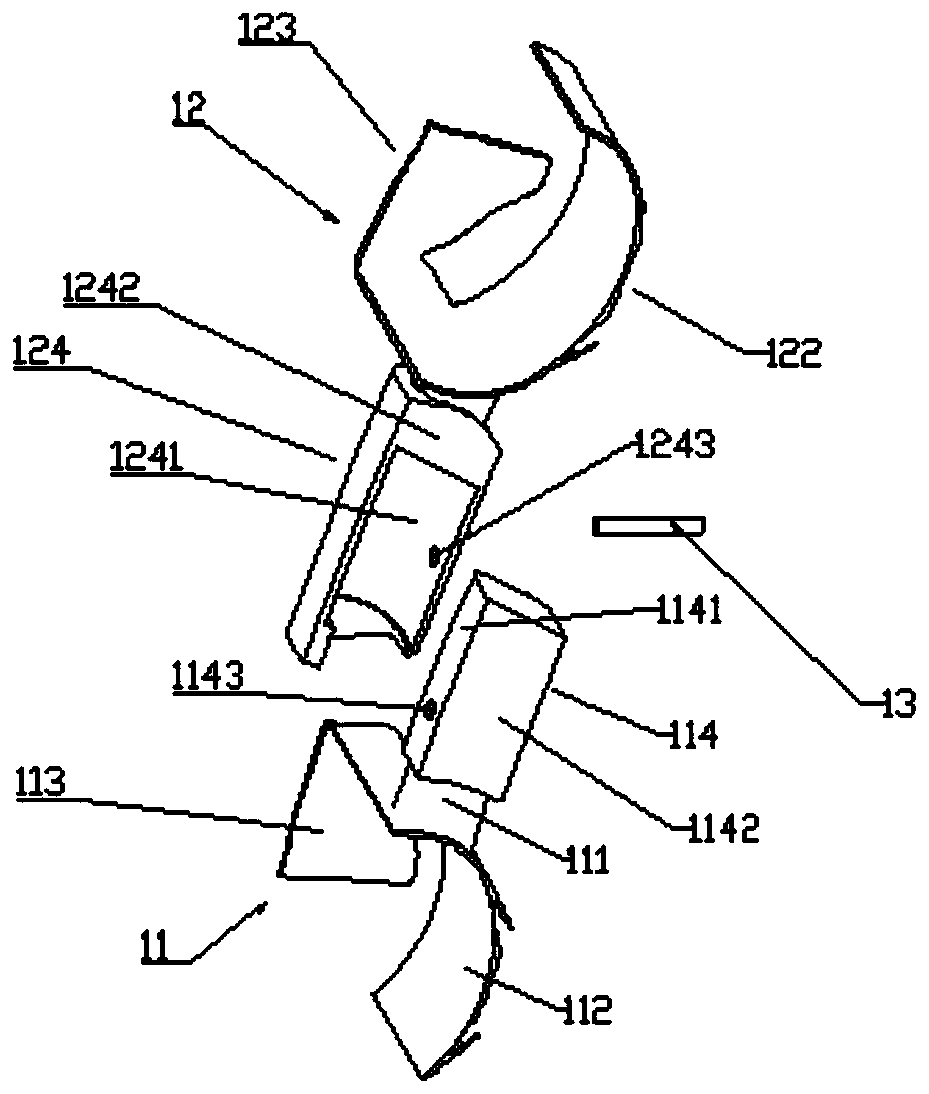
Fixing prosthesis for osteolysis therapy
ActiveCN113367847AAchieve support fixationRealize multi-point support positioningJoint implantsHip jointsIliac screwBiomedical engineering
The invention relates to a medical instrument, in particular to an osteolysis treatment fixing prosthesis which is characterized in that the osteolysis treatment fixing prosthesis comprises a fixing plate, a fixing rod and a plurality of fixing screws, the fixing rod extends towards one side of the fixing plate, and a fixing assembly used for fixing the fixing rod to the fixing plate is arranged on the fixing plate; part of the fixing screws are arranged on the fixing plate and used for fixing the position of the fixing plate, and the other part of the fixing screws are arranged on the fixing rod and used for fixing the position of the fixing rod. And the purposes that the multi-point supporting effect on the fixing plate is achieved, and then the stability of the fixing plate is improved are achieved.
Owner:BEIJING LIDAKANG TECH
Force damping dental bridge assembly with synthetic periodontal ligament fibers
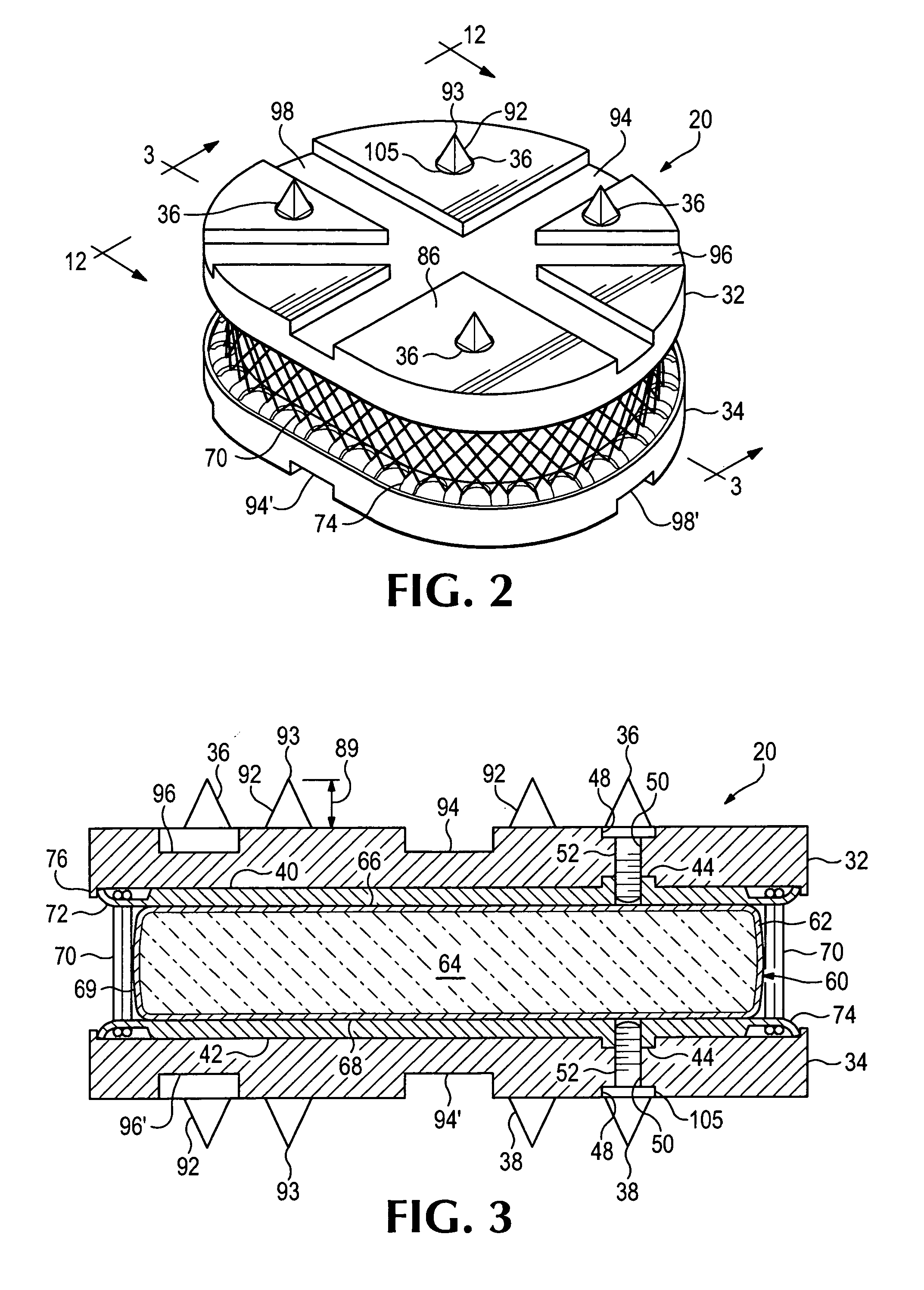
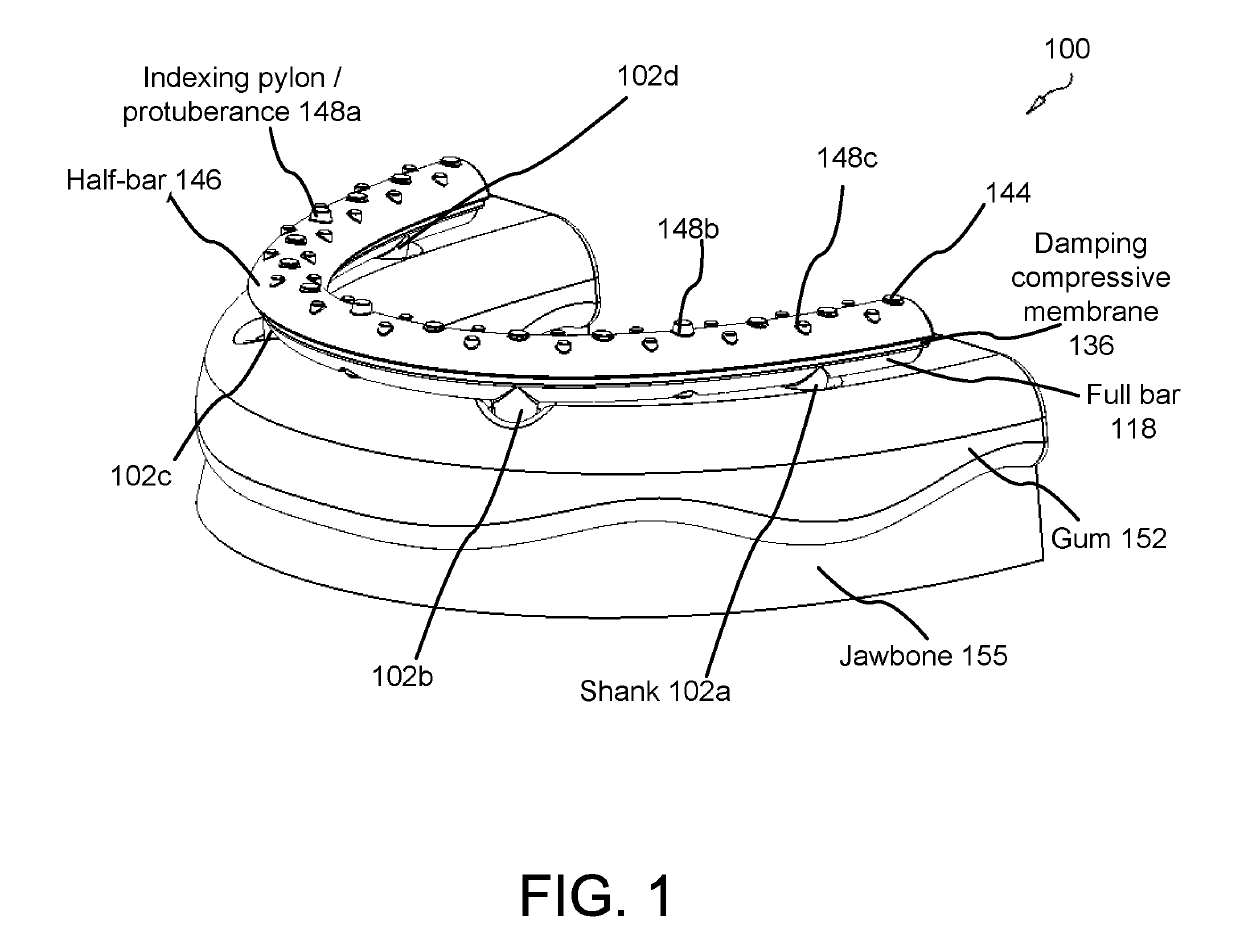
A force damping dental bridge assembly which damps compressive, tensile, and lateral forces on a prosthetic tooth and jawbone through use of synthetic periodontal ligament fibers in the form of a damping membrane. Multiple layers of arcuate components and Morse taper interconnections secure the assembly. A threaded implant that penetrates the jawbone defining a tapered, conical inner cavity which receives a shank protruding downwardly from a full bar. An arcuate damping membrane positions on the bar and a half-bar positions over the membrane; whereby the damping membrane is sufficiently resilient to enable lateral and axial movements by the prostheses affixed to the half-bar. A plurality of protuberances extend from an upper surface of the half-bar to enable sculpting and affixation of prostheses thereon; and whereby a plurality of fasteners detachably connect the prostheses to the bar and / or implants in a snap-fit relationship that can be detached with an implement adapted to unsnap the assembly from a patient's mouth.
Owner:CLARK JR PAUL KENNETH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com