Patents
Literature
189 results about "Reactive intermediate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In chemistry, a reactive intermediate or an intermediate is a short-lived, high-energy, highly reactive molecule. When generated in a chemical reaction, it will quickly convert into a more stable molecule. Only in exceptional cases can these compounds be isolated and stored, e.g. low temperatures, matrix isolation. When their existence is indicated, reactive intermediates can help explain how a chemical reaction takes place.
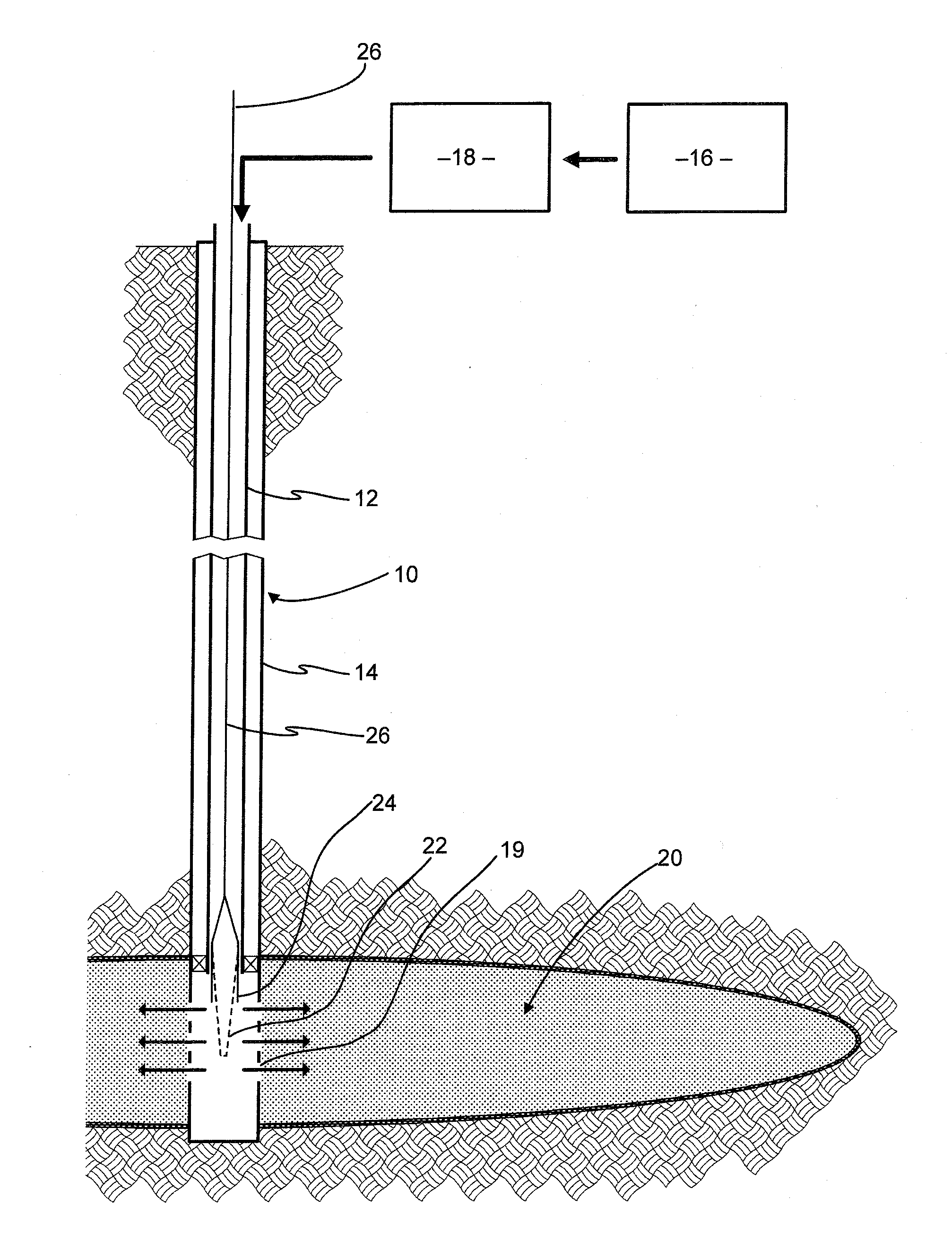
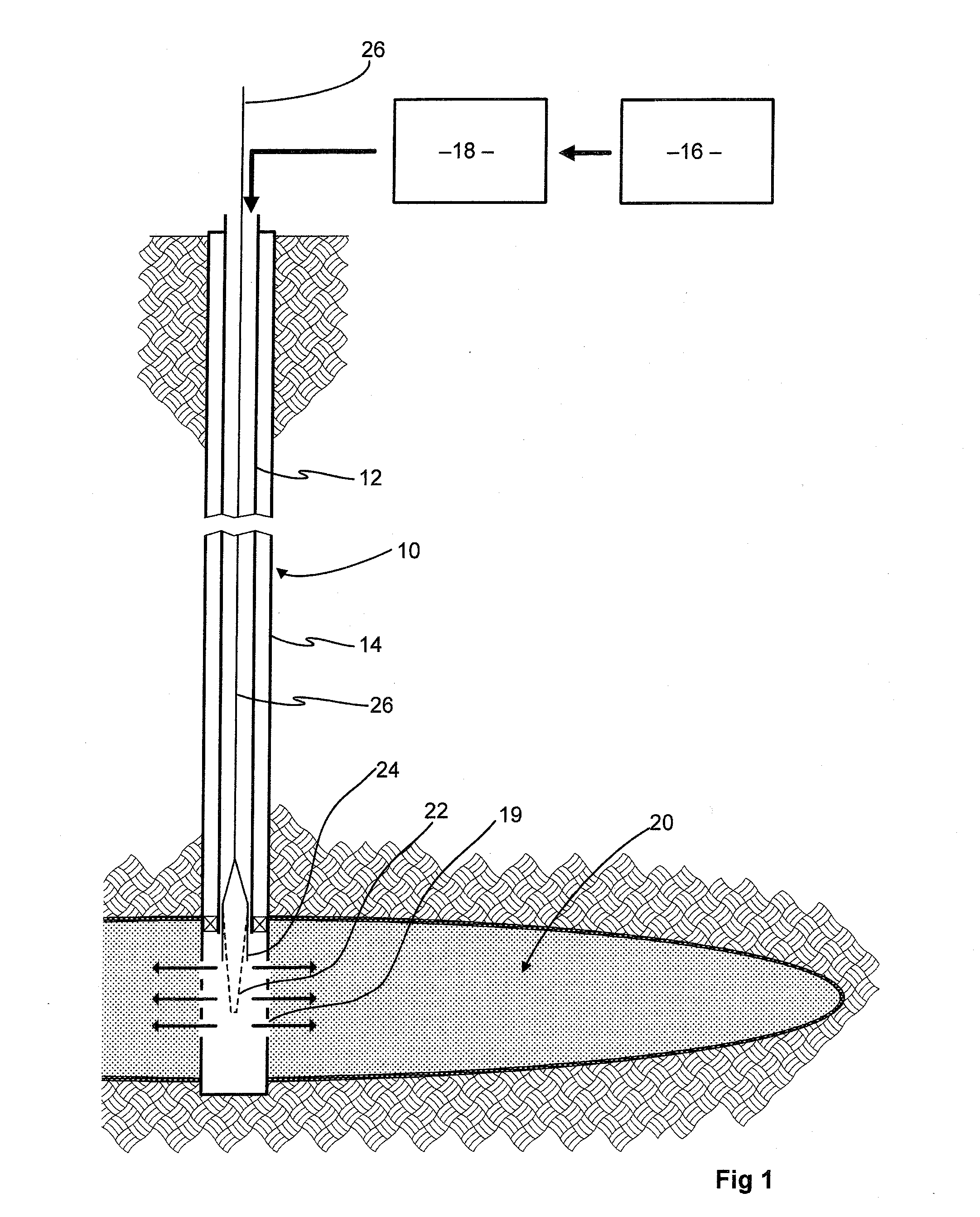
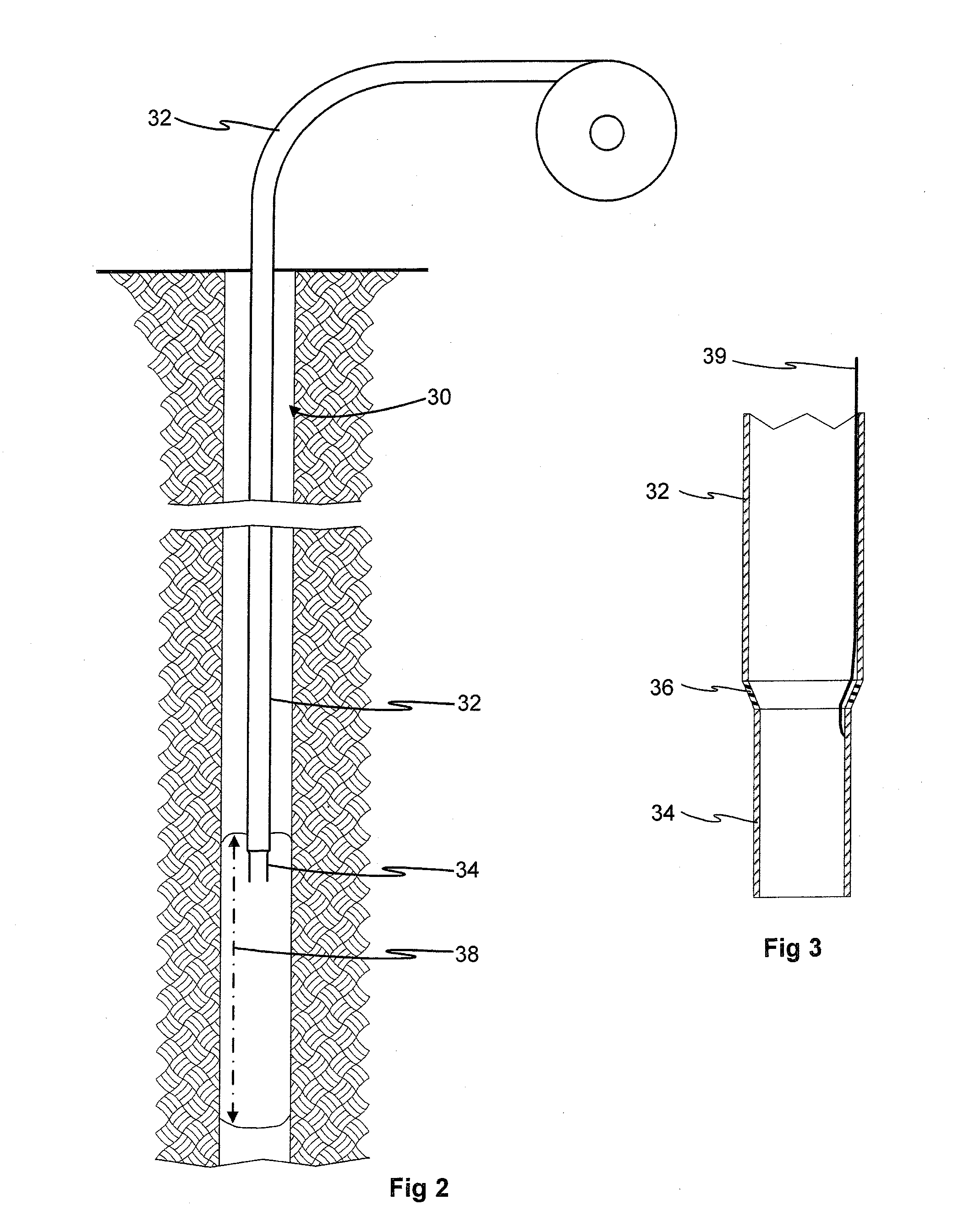
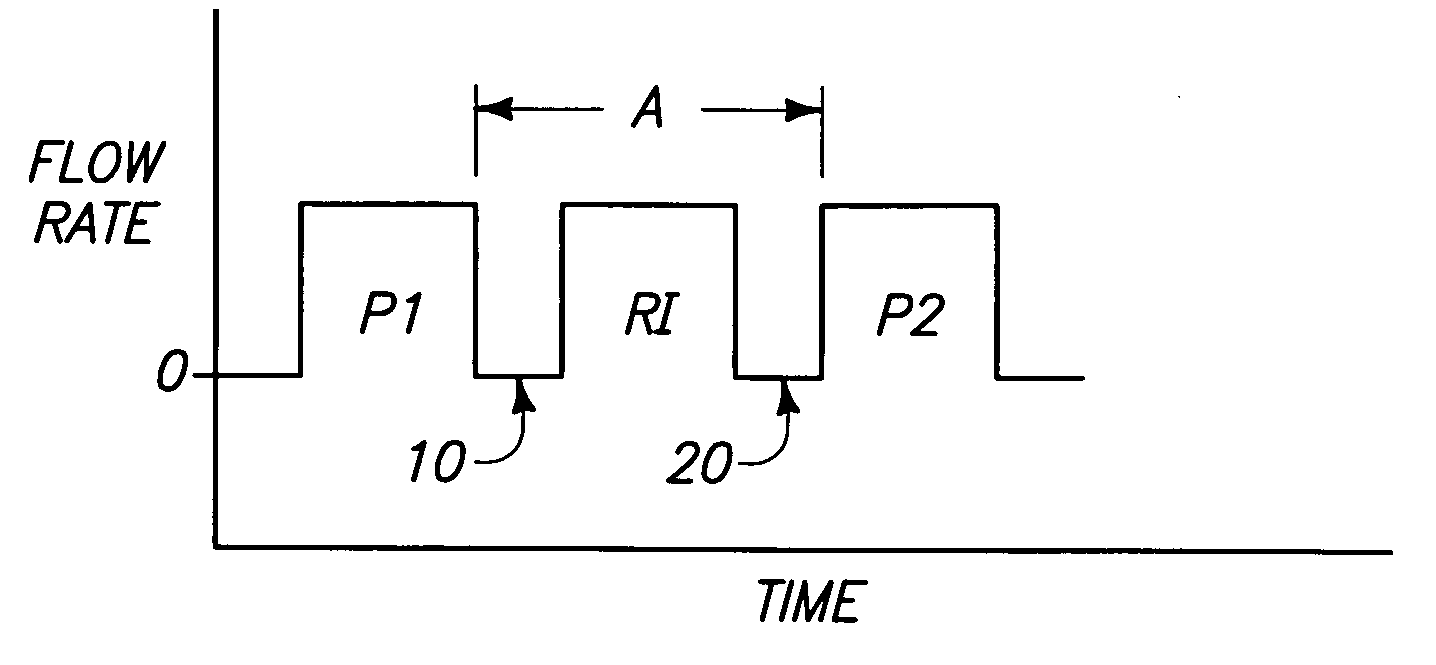
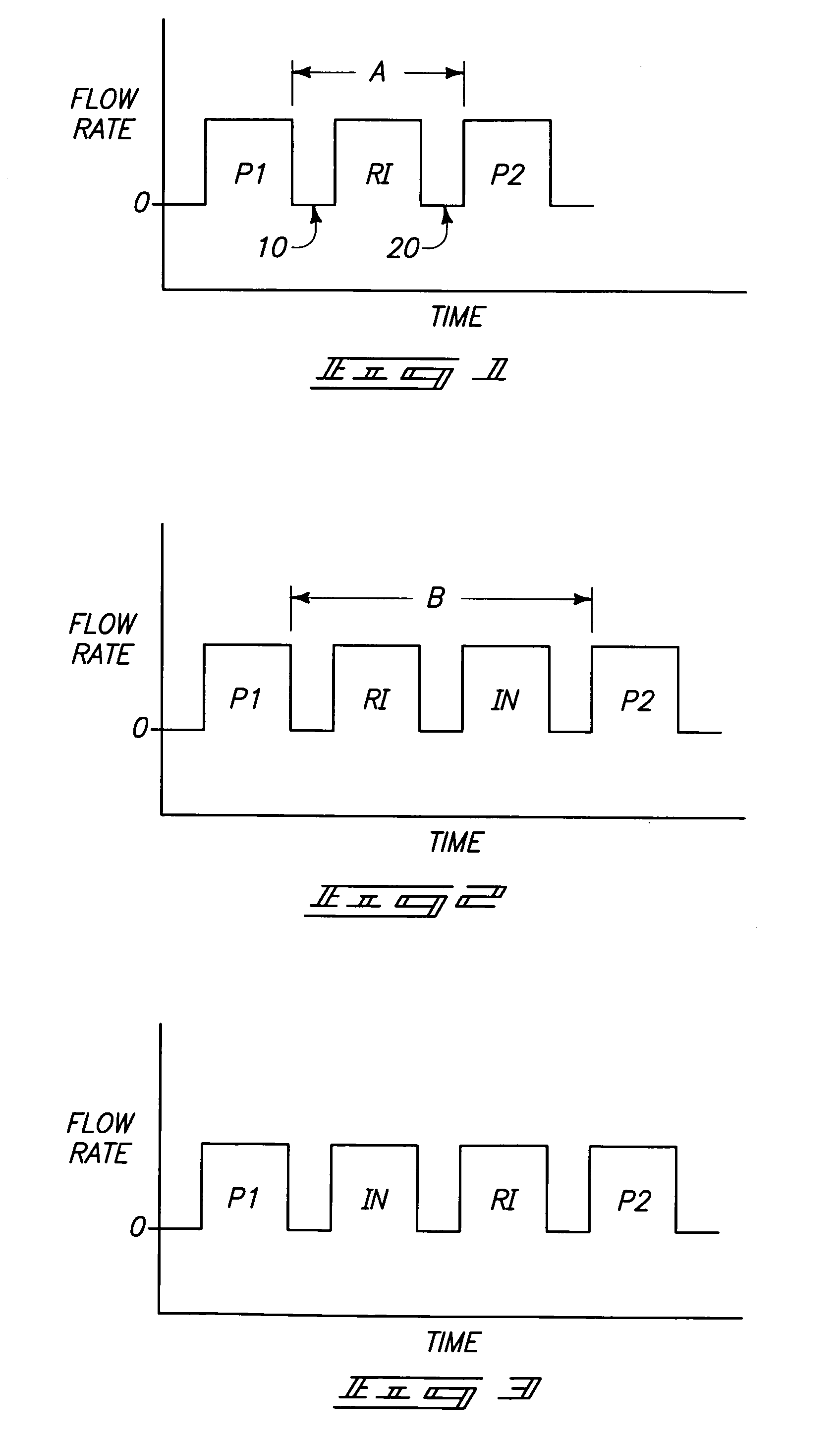
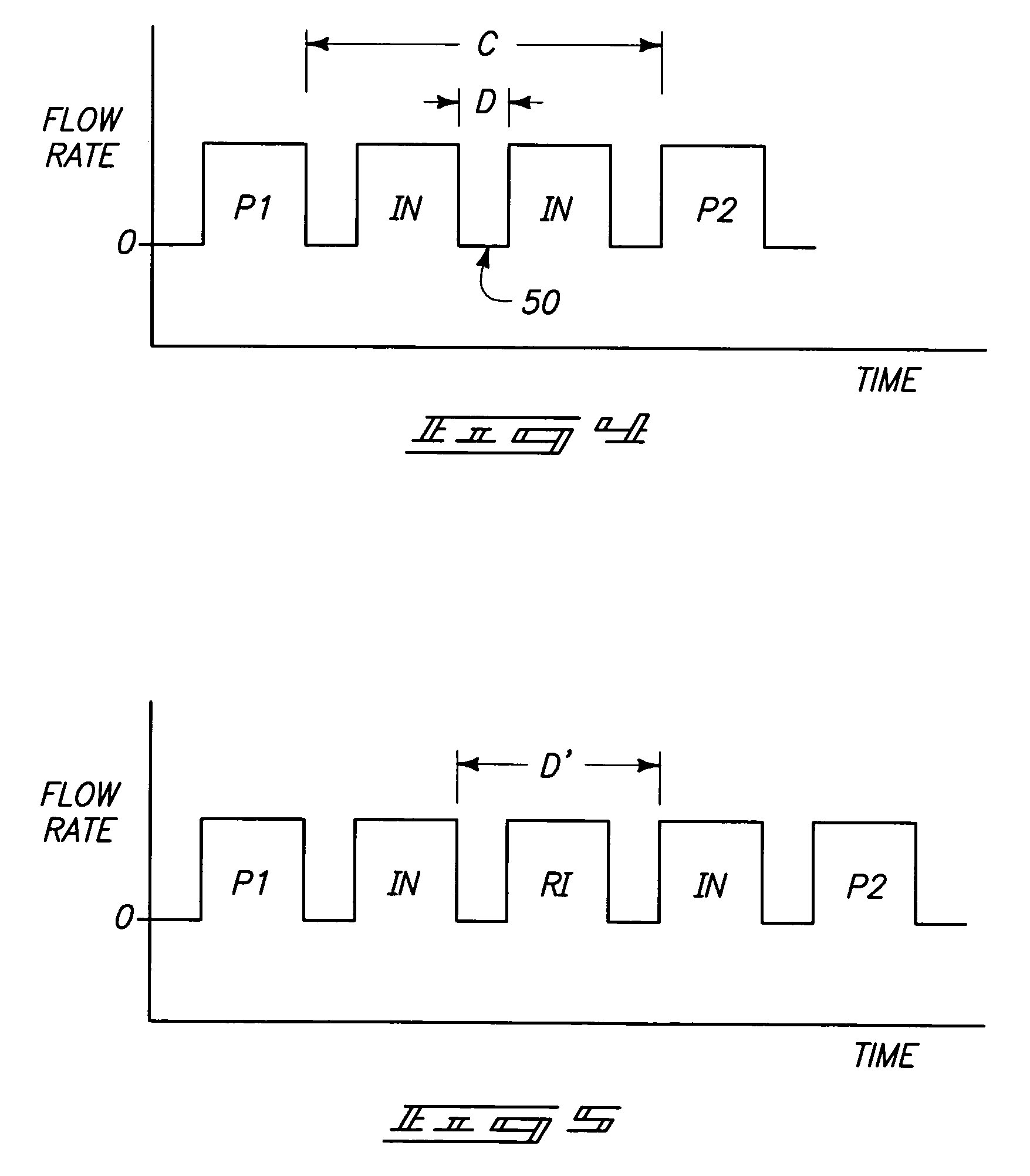
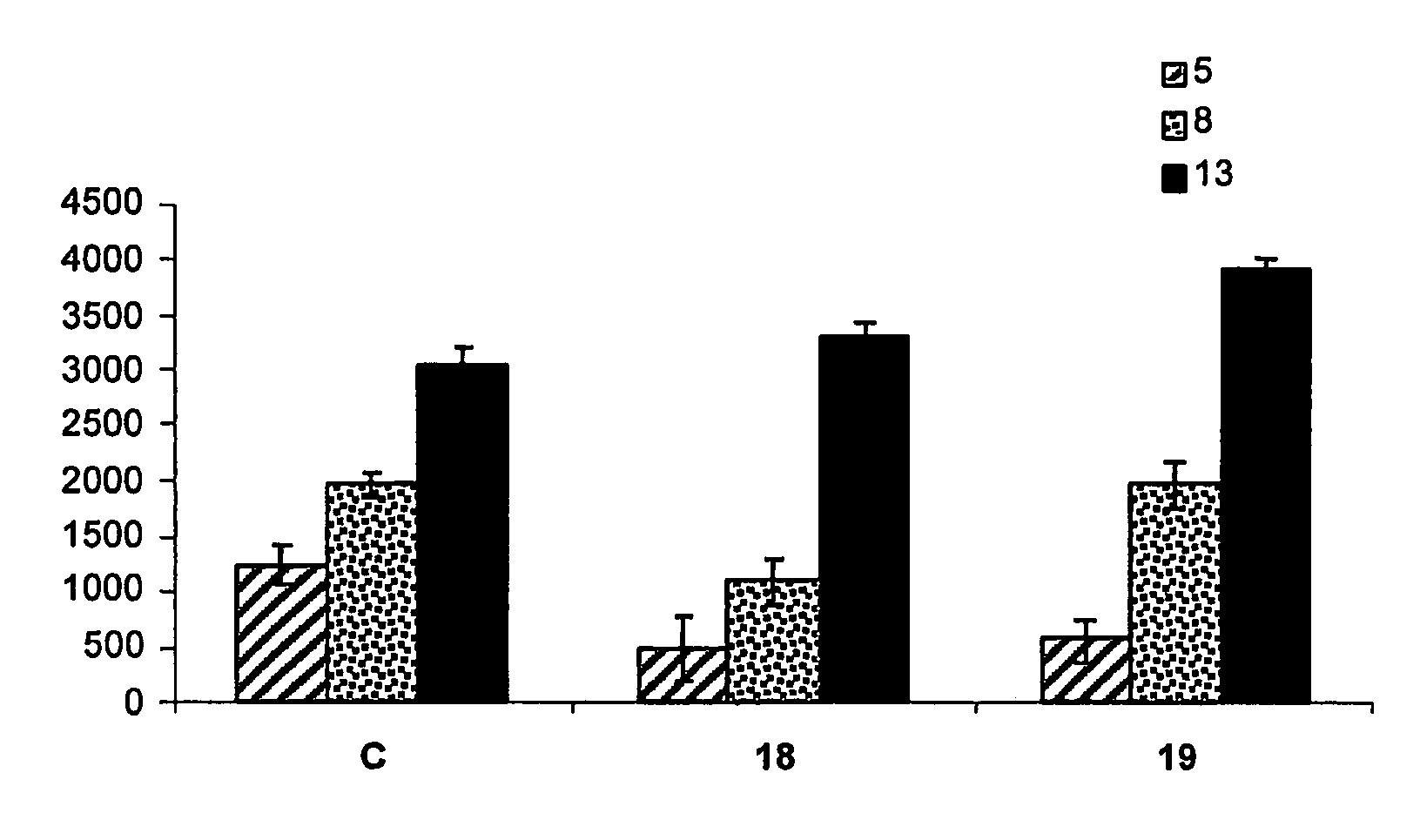
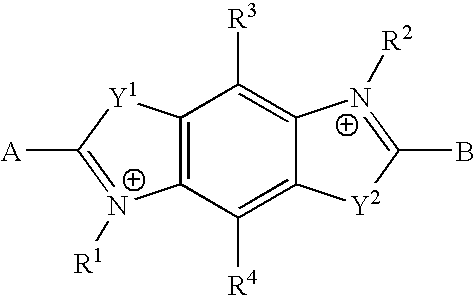
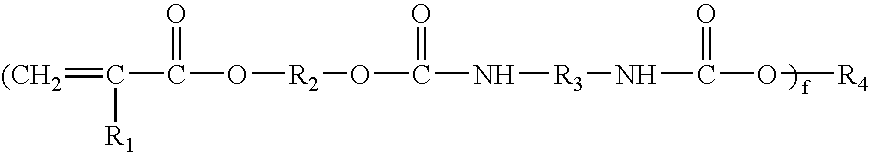
Formation of [2,2]paracyclophane and related compounds and methods for the formation of polymers from cyclophanes
ActiveUS8633289B2Increase in costLimited utilityOrganic compound preparationHydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionReaction intermediateReactive intermediate
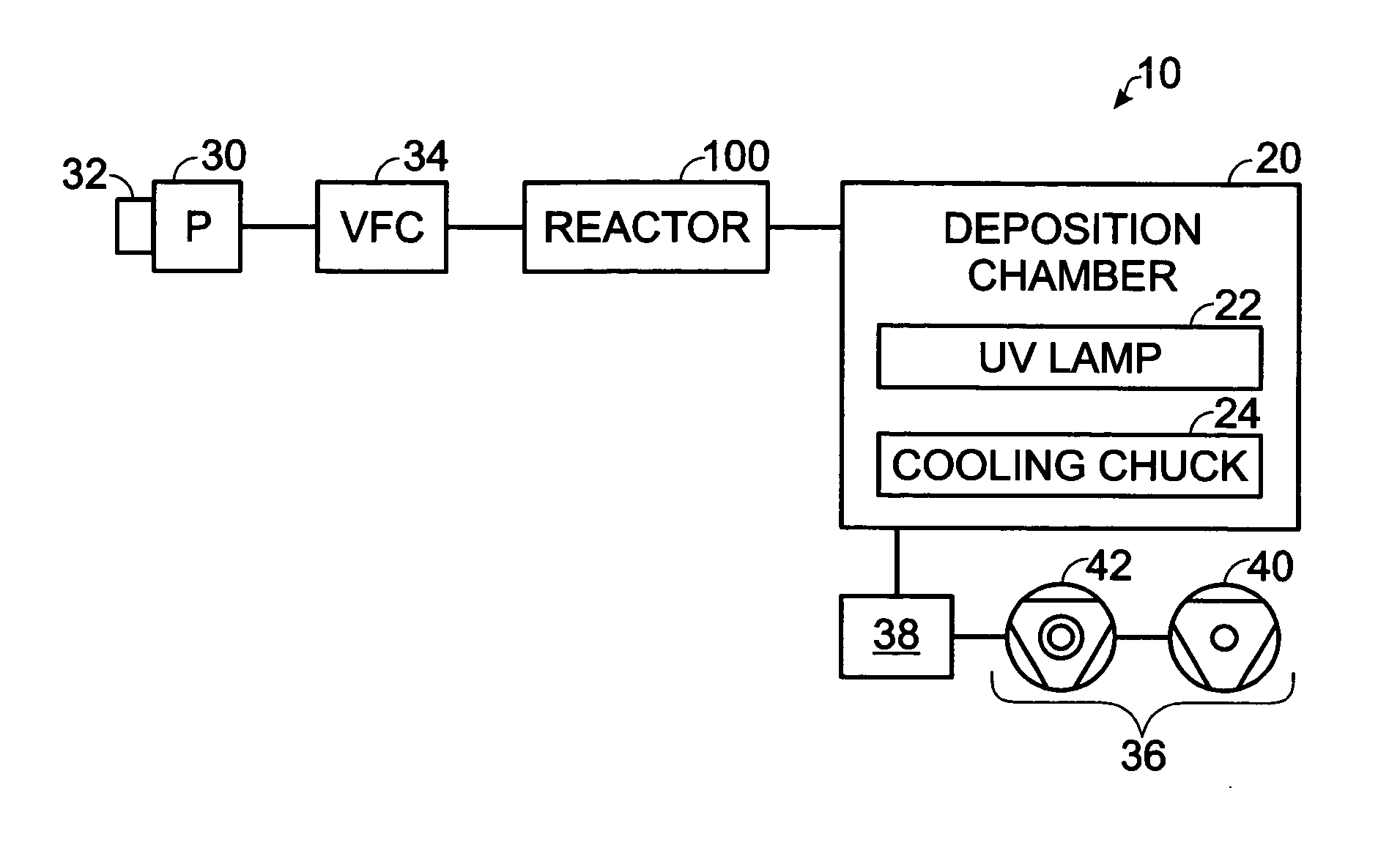
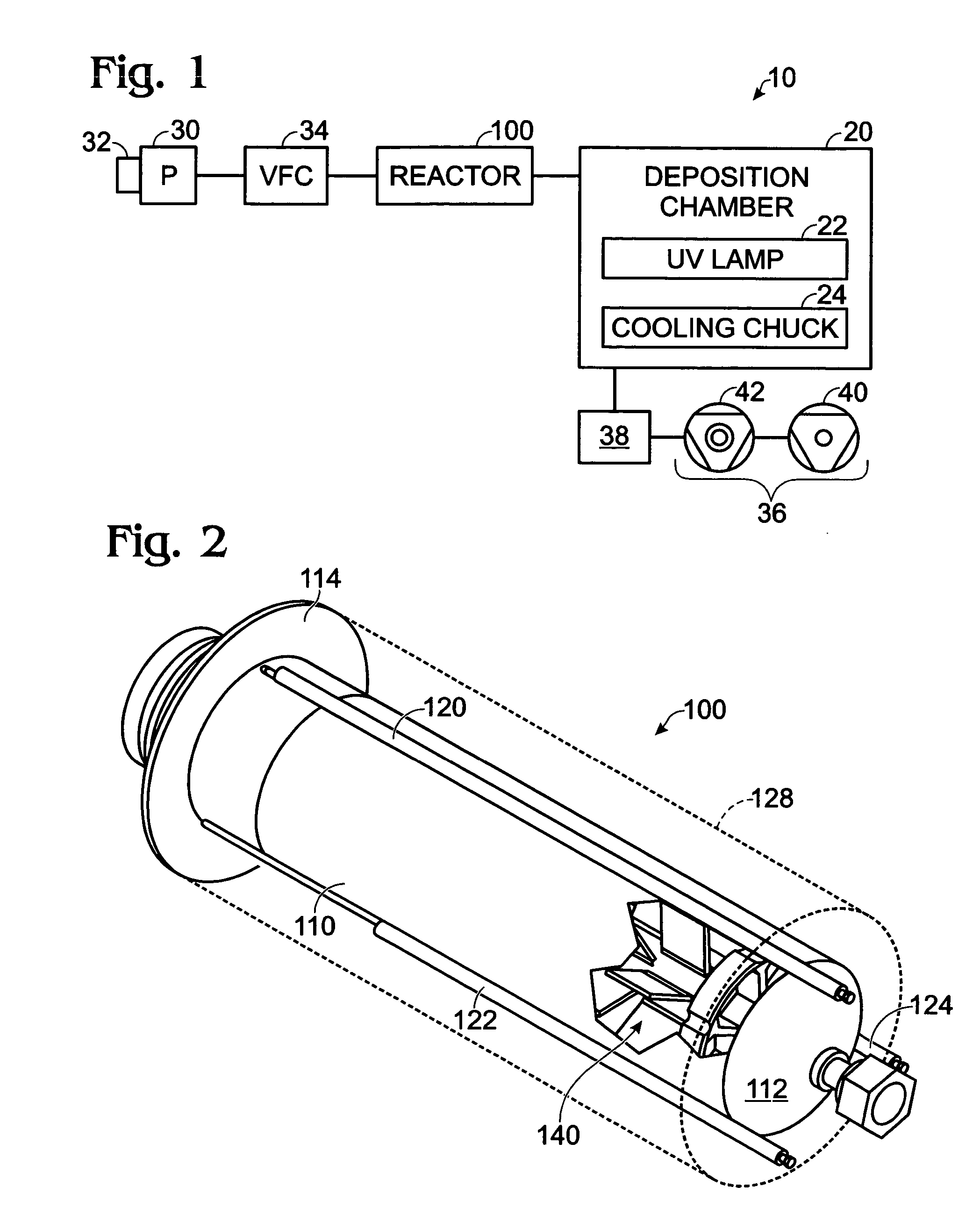
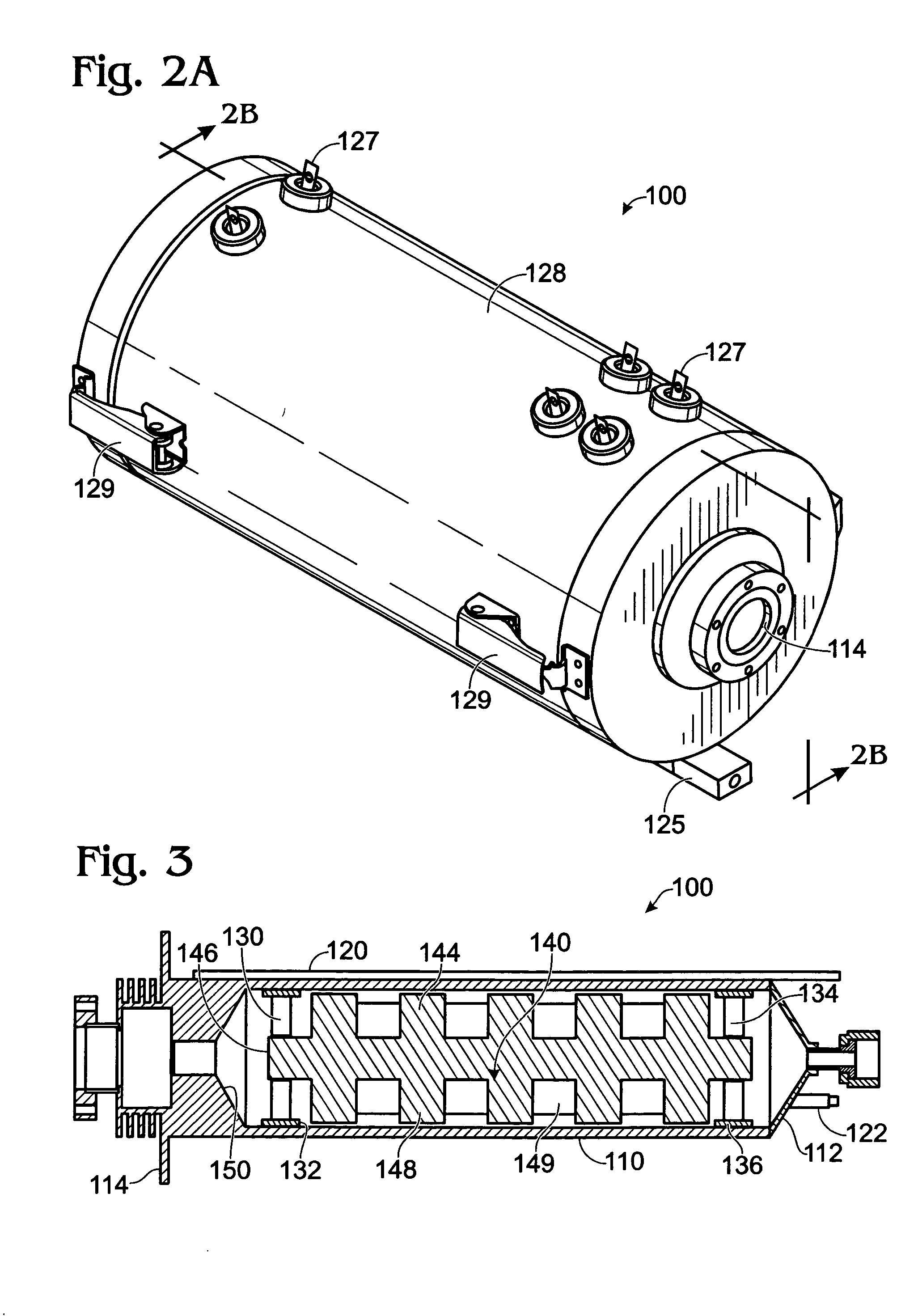
An improved process and method for the formation of stable intermediate cyclophanes. Embodiments describe a general method for the production of substituted and unsubstituted cyclophanes. The components include a pyrolysis reaction tube that may be electrically heated into which a flowing stream of nitrous oxide with xylene vapor in an optional inert carrier gas at atmospheric pressure. The exit gas is condensed resulting in the deposition of [2,2′]paracyclophane. Additionally a process and method whereby the reactive intermediates of the reaction described above can be directly deposited and polymerized at atmospheric pressures or thereabout is disclosed.
Owner:CARVER SCI INC
Method for preparing phosphotungstic heteropoly acid with Keggin structure
InactiveCN102659181ASimple preparation processIncrease productivityTungsten compoundsHigh concentrationInorganic salts
The invention discloses a method for preparing phosphotungstic heteropoly acid with a Keggin structure. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) contacting a tungstate solution and an inorganic acid solution; (2) transferring the solution to a high-pressure reaction kettle, and activating at high temperature under high pressure to obtain an active intermediate; (3) contacting the obtained substance and phosphoric acid to obtain a phosphotungstic acid solution; and (4) adding an inorganic salt precipitator into the phosphotungstic acid solution, precipitating phosphotungstic acid by salting-out and crystallization, filtering, purifying and drying to obtain the Keggin phosphotungstic heteropoly acid. By the method, a process flow is simple, the yield of the heteropoly acid is high, and the preparation cost is reduced obviously; high-concentration strong acid in the conventional method is not used in the preparation process, so that the corrosivity to equipment is reduced greatly; and an inflammable low-boiling point organic extractant is not used, and the safety of preparation is improved greatly.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Altering a composition at a location accessed through an elongate conduit
InactiveUS20140060840A1Good effectLow viscosityFluid removalDrilling compositionCross-linkElectrochemical response
A composition flowing along an elongate conduit to a location accessed by that conduit contains a precursor substance which, arriving at the location, is converted electrochemically to chemically reactive intermediate. This intermediate reacts with another constituent of the composition, thereby bringing about a change in the composition. The reactive intermediate may be a cross-linking agent for a polymeric constituent of the composition so that the electrochemical reaction and subsequent cross-linking increases the viscosity of the composition as it arrives at the location where it is required.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
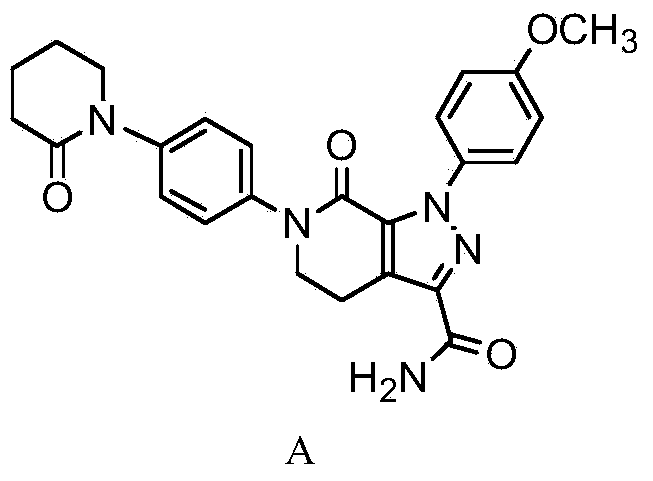
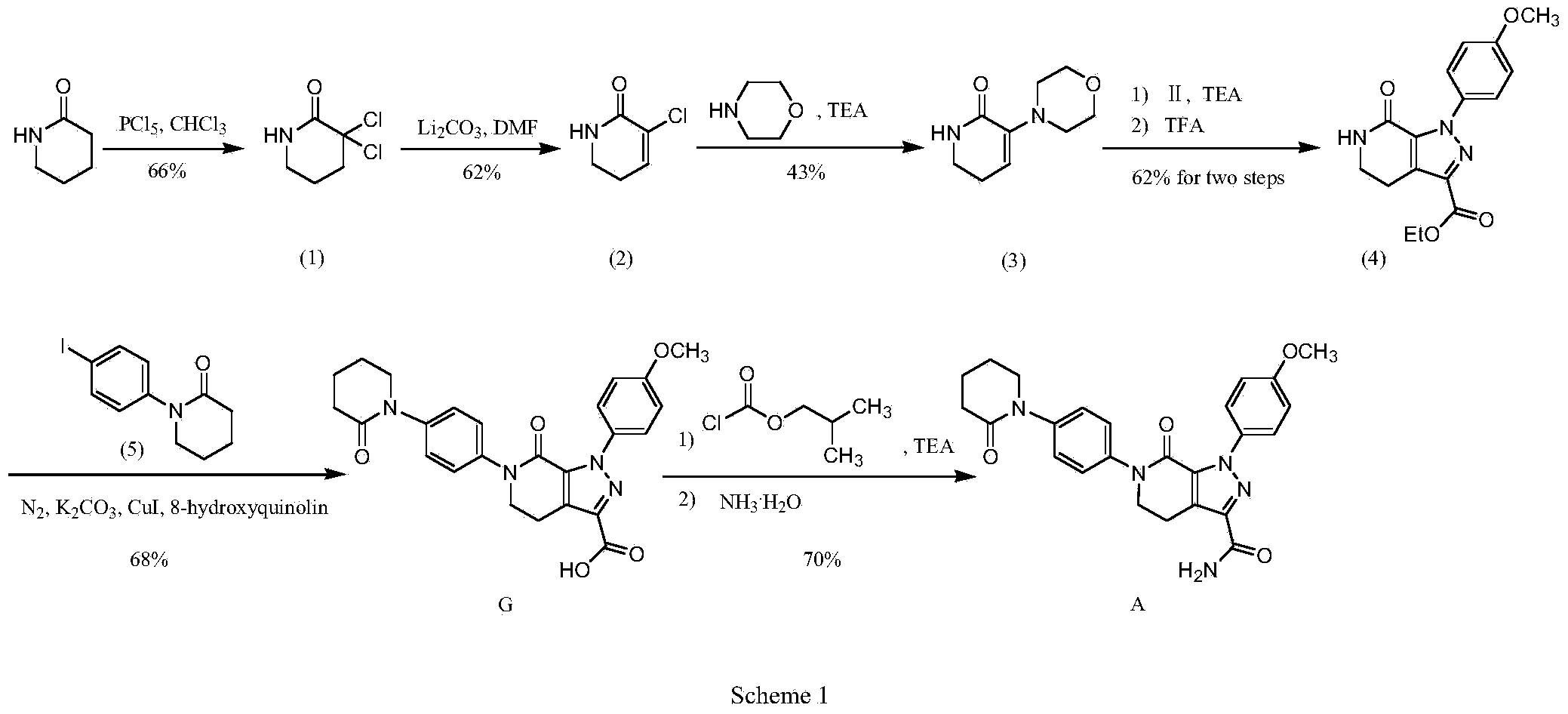
Apixaban preparation method
The invention discloses an Apixaban preparation method. The Apixaban preparation method comprises that 1, an intermediate I and an intermediate II undergo a [3+2] cyclization addition reaction under the alkali action to produce a compound B, and the compound B undergoes a morpholine ring removal reaction under the acid condition to produce a compound C, 2, the compound C is reduced by iron powder to form a corresponding amino compound D, 3, the amino compound D and 5-chlorovaleryl chloride undergo an amidation reaction under the triethylamine action to produce a compound E, 4, the compound E undergoes a cyclization reaction under the strong base action to produce a compound F, 5, the compound F undergoes a hydrolysis reaction under the strong base action to produce a corresponding carboxyl compound G, and 6, the carboxyl compound G and CDI undergo a reaction to produce an active intermediate H and the active intermediate H and ammonia water undergo an aminolysis reaction to produce the desired compound A. The Apixaban preparation method has simple processes, does not need strict reaction conditions, has low equipment requirements, has high reaction yield, utilizes stable intermediates thereby solving intermediate storage problems, and effectively improves product purity.
Owner:河北凯威恒诚制药有限公司
Composite electrode material and method of producing the same, negative electrode for metal-air battery, and metal-air battery
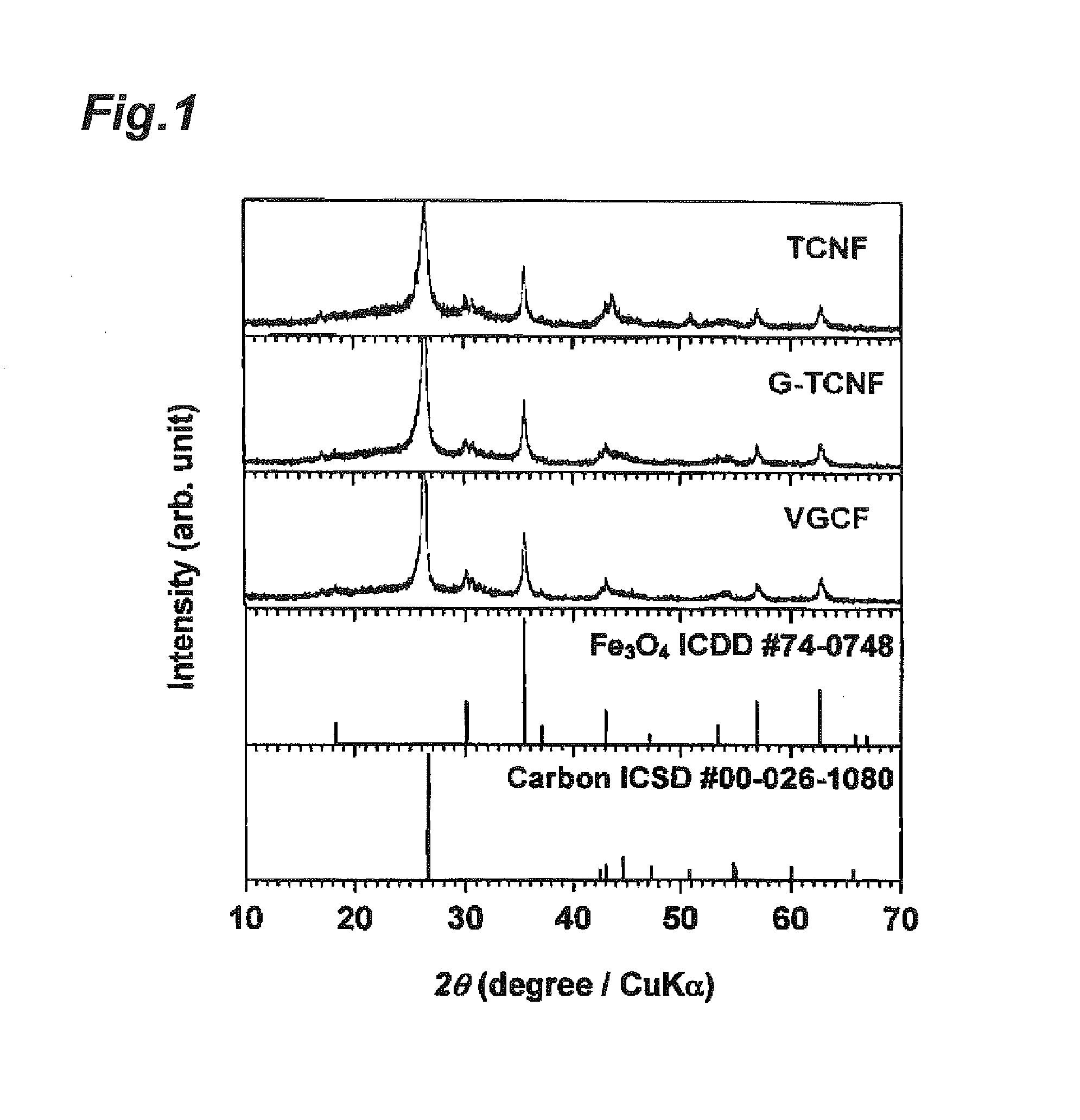
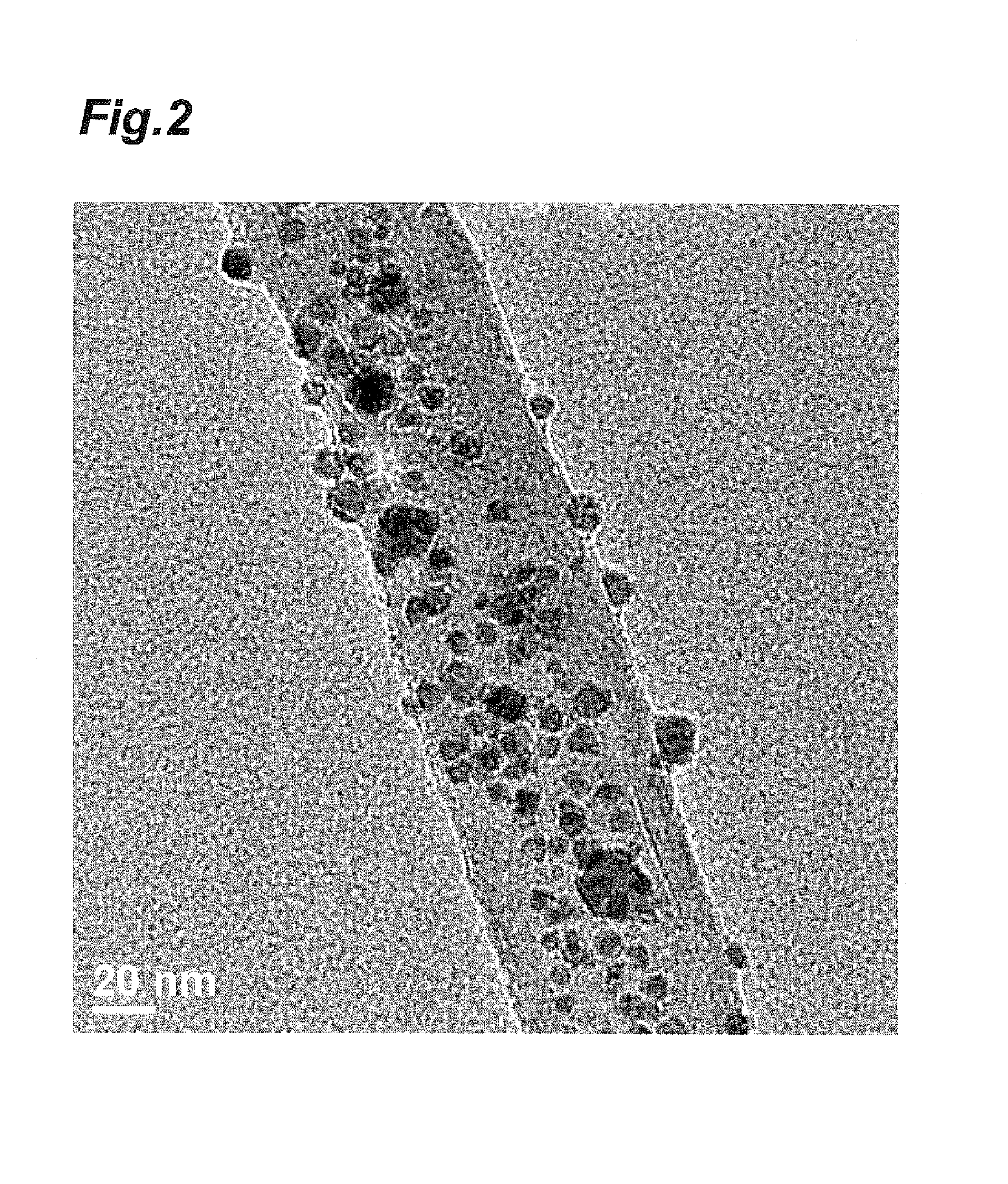
InactiveUS20120082922A1Superior electrode characteristicEasy to useMaterial nanotechnologyFuel and secondary cellsComposite electrodeReaction intermediate
The present invention relates to a composite electrode material having a carbon base material and iron oxide particles mainly containing Fe3O4 and being supported on the carbon base material and the particles have a D90 of 50 nm or less. In the composite electrode material, since the particle size of the iron oxide particles mainly containing Fe3O4 serving as an active material is small, the electron conductivity of the composite electrode material is not considerably reduced even when being covered with a Fe(OH)2 layer as a reactive intermediate for an electrode reaction. Thus, when the composite electrode material is used, an iron negative electrode having sufficient electron conductivity and charge-discharge cycle characteristics is provided. A negative electrode including the composite electrode material is favorably used as a negative electrode for a metal-air battery.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD +1
Method for preparing sorafenib
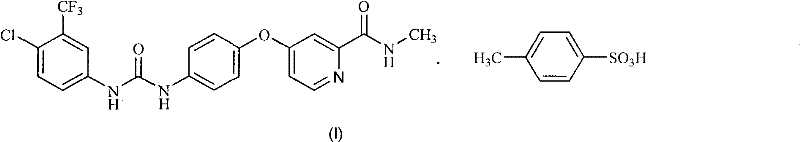
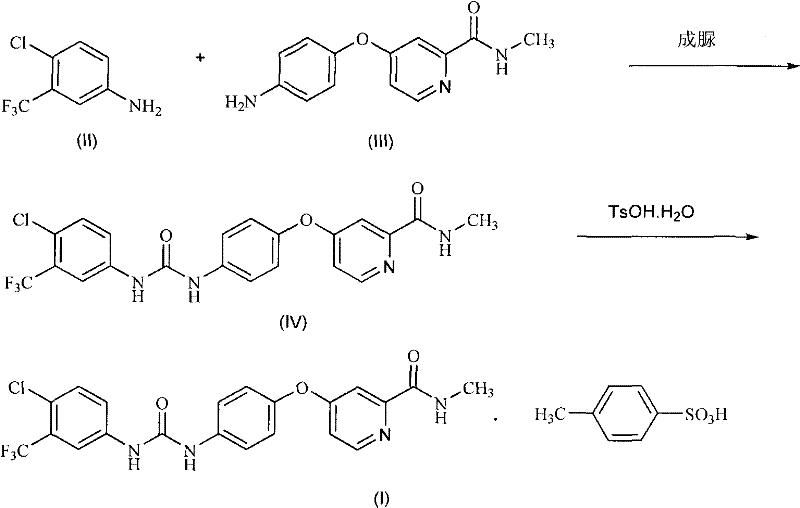
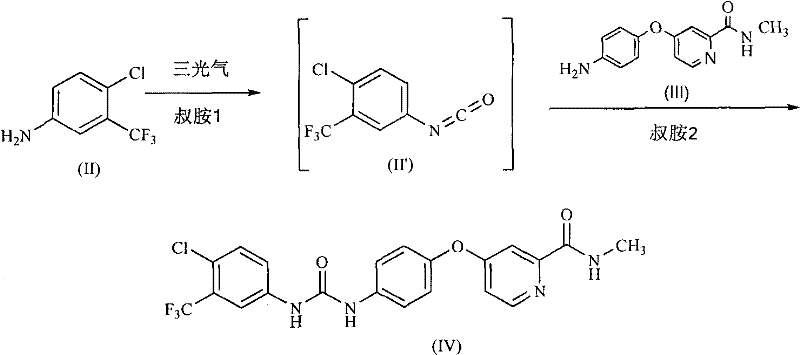
The invention discloses a method for preparing sorafenib, which comprises the steps of: 1) reacting triphosgene with 3-trimethyl fluoride-4-chloroaniline (II) in an inert solvent 1 under the existence of tertiary amine 1, thus obtaining a solution containing 3-trimethyl fluoride-4-chlorphenyl isocyanate (II'), wherein isolation and purification are not needed; and 2) reacting the 3-trimethyl fluoride-4-chlorphenyl isocyanate (II') with 4-(4-aminophenoxy)-N-methyl-2-pyridine carbonxamide (III) in an inert solvent 2 under the existence of tertiary amine 2, thus obtaining sorafenib (IV). The tertiary amine 1 and the tertiary amine 2 are the same or different, the inert solvent 1 and the inert solvent 2 are the same or different, and the feeding sequence of the 3-trimethyl fluoride-4-chloroaniline (II) and the 4-(4-aminophenoxy)-N-methyl-2-pyridine carbonxamide (III) can be interchangeable. The method is simple and convenient to operate, short for reaction time free from separation of intermediates with high reactivity, as well as is free from special equipment and conditions, and high in yield.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND CO LTD
Self-dispersing particles and methods for making and using the same
A method of modifying a particle that includes reacting a reactive compound having an X—[Y]n reactive group with a secondary compound N—S-ZM to form a substituted reactive intermediate [Y]a—X—(N—S-ZM)b, and reacting the particle with the substituted reactive intermediate [Y]a—X—(N—S-ZM)b to attach the substituted reactive intermediate to the surface of the particle to form a surface modified particle. The particle may comprise at least one of a dye particle, an inorganic pigment particle, an additive, or a combination thereof. X may be a sulfonyl, phosphoryl, or 1,3,5-triazinyl group. Y may be a halogen leaving group. N may be a nucleophilic group. S may be an organic group. ZM may be an ionizable end group. Also, n is an integer between 1 and 3, b is an integer between 1 and 3, and a=n−b. When n is equal to or greater than b, and wherein if b is 2 or 3, each N—S-ZM can be the same or different.
Owner:SENSIENT COLORS
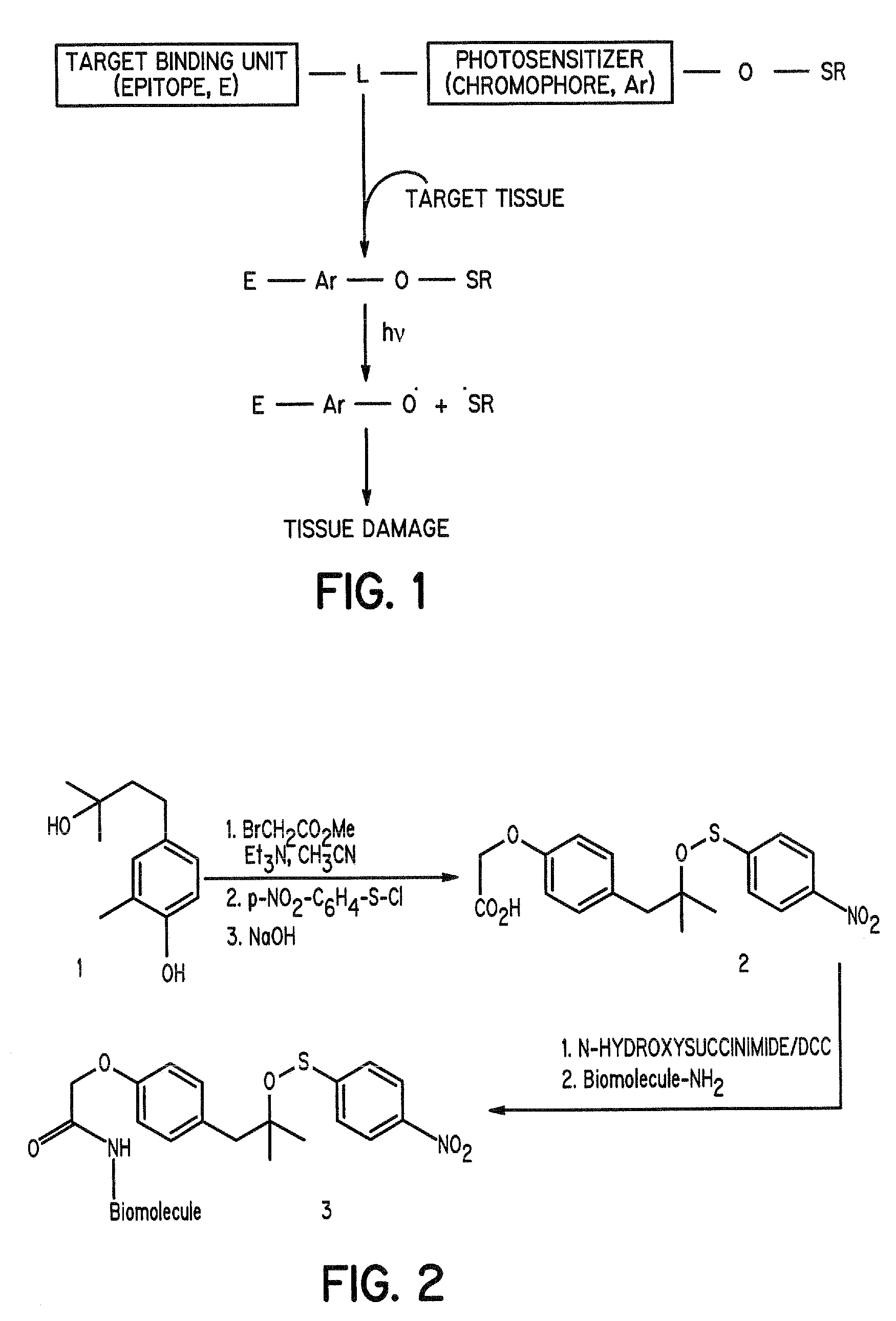
Aromatic sulfenates for type I phototherapy
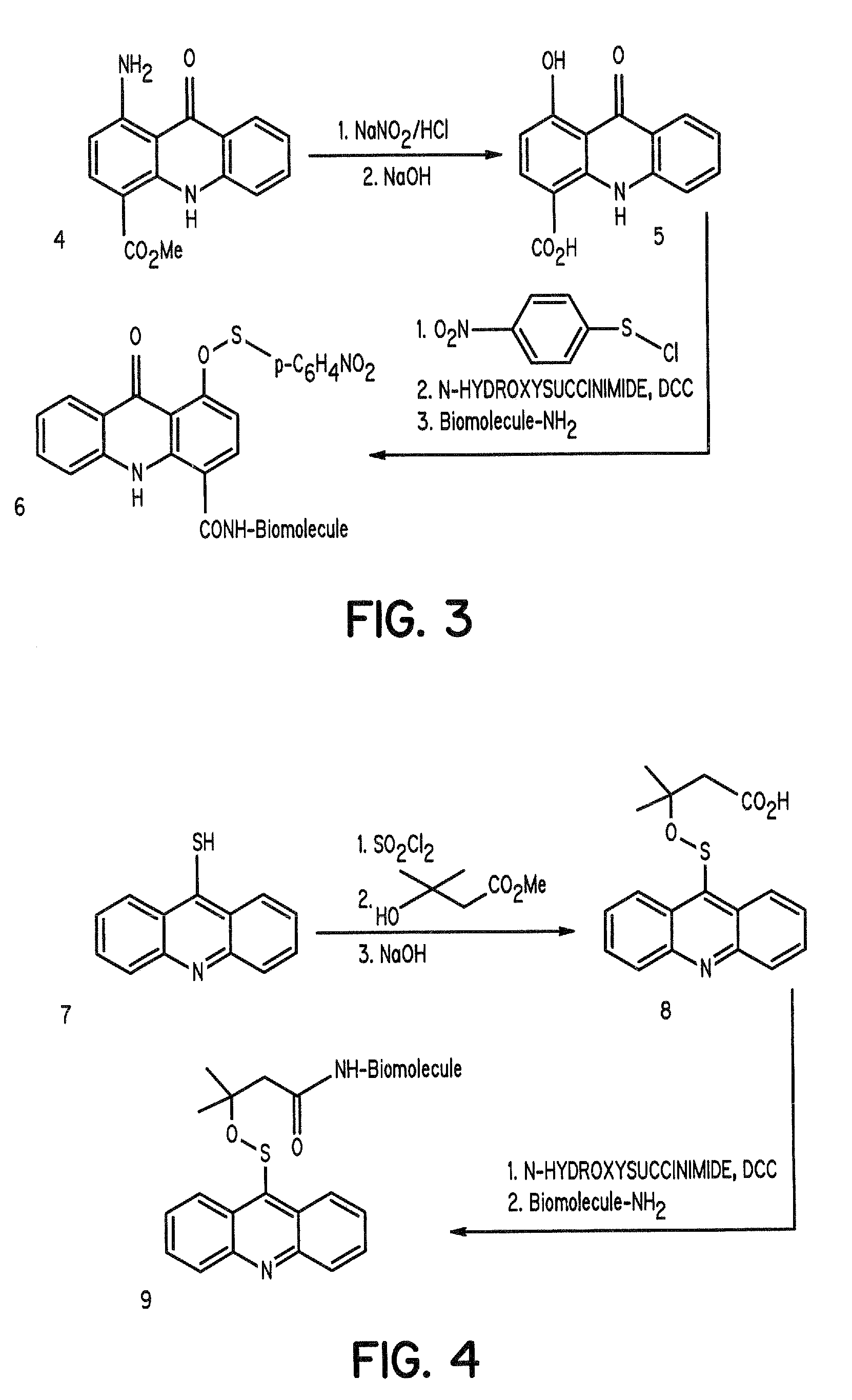
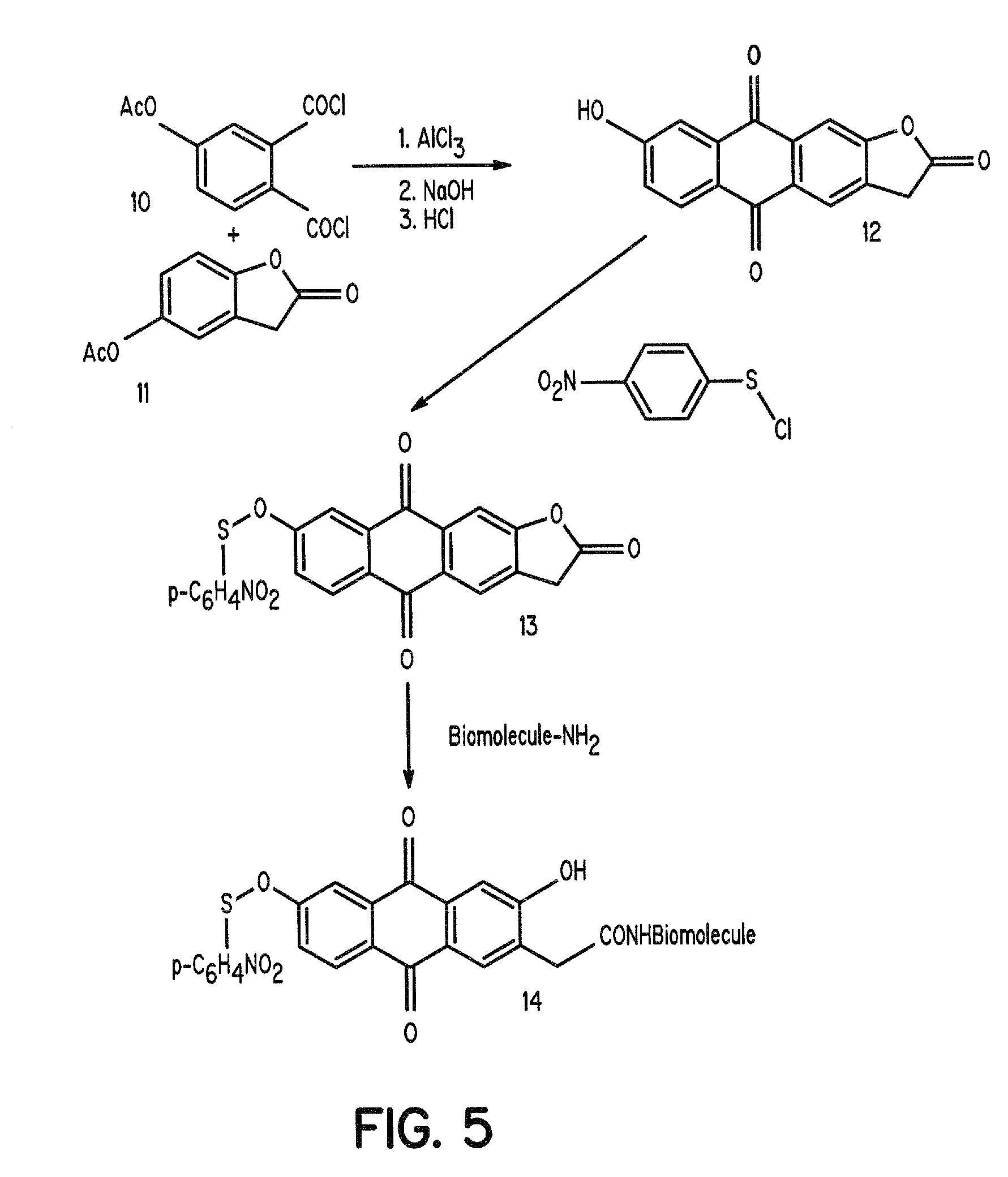
InactiveUS7235685B2Sufficient fluenceSufficient powerOrganic active ingredientsElectrotherapyAbnormal tissue growthLight treatment
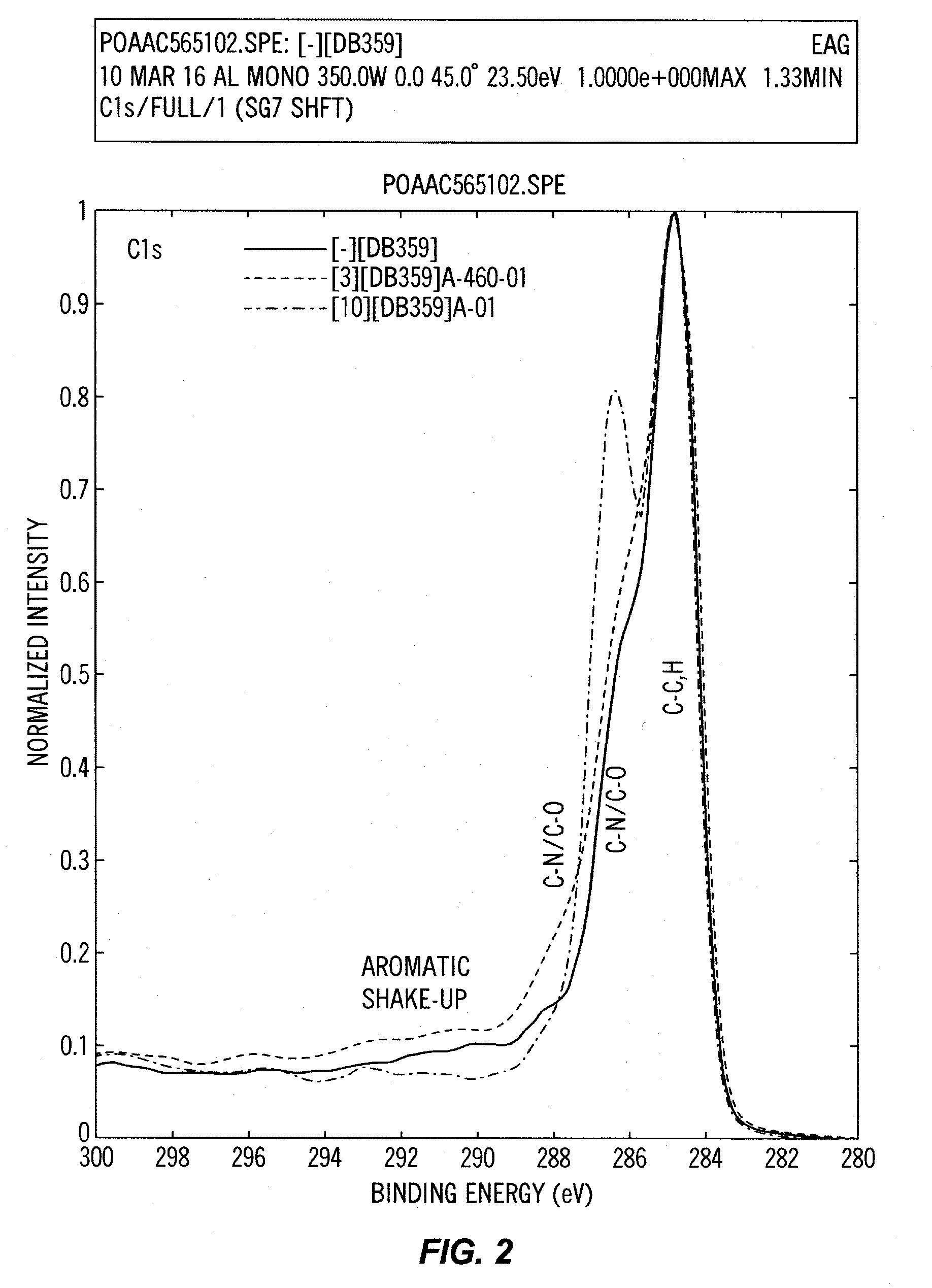
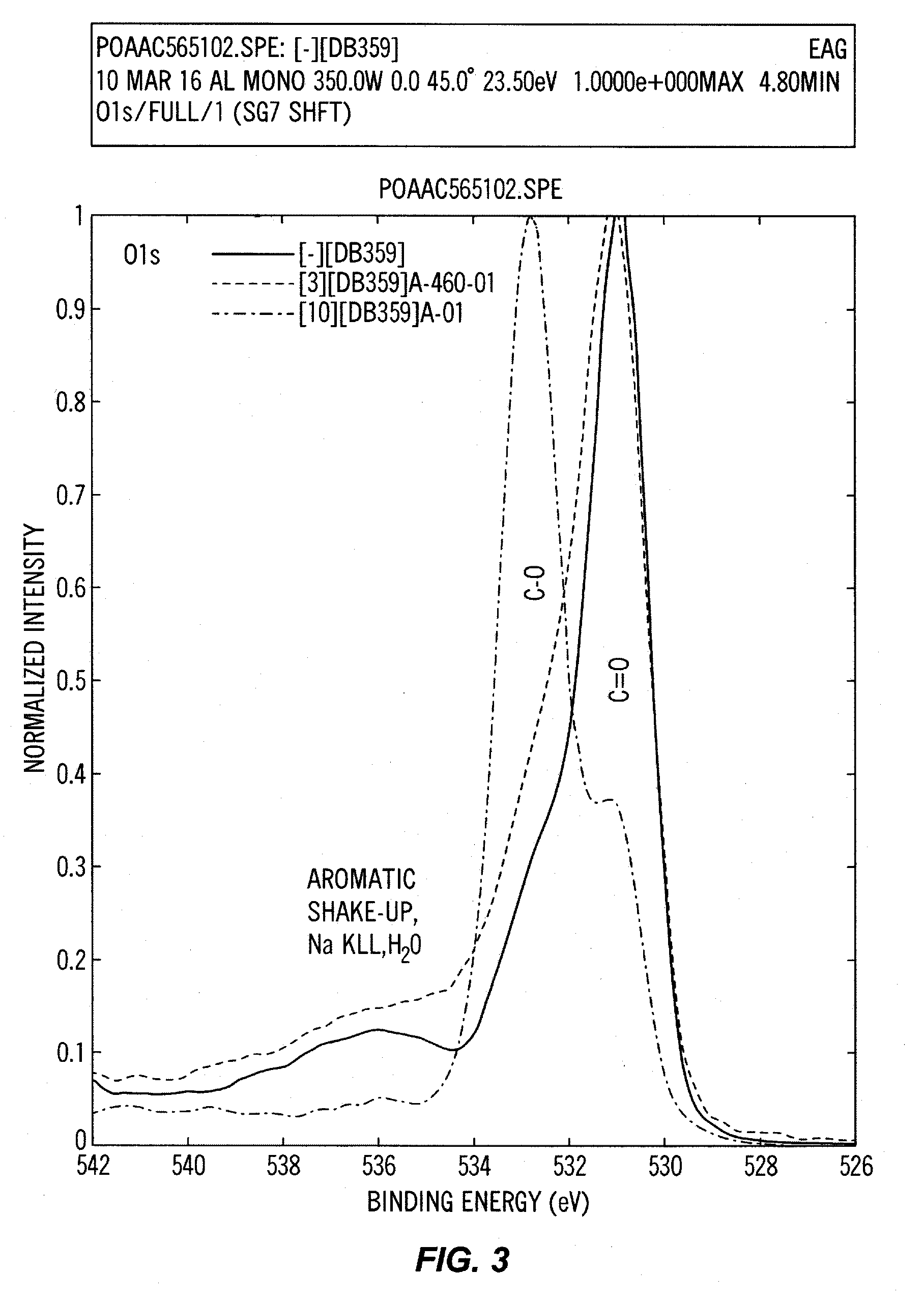
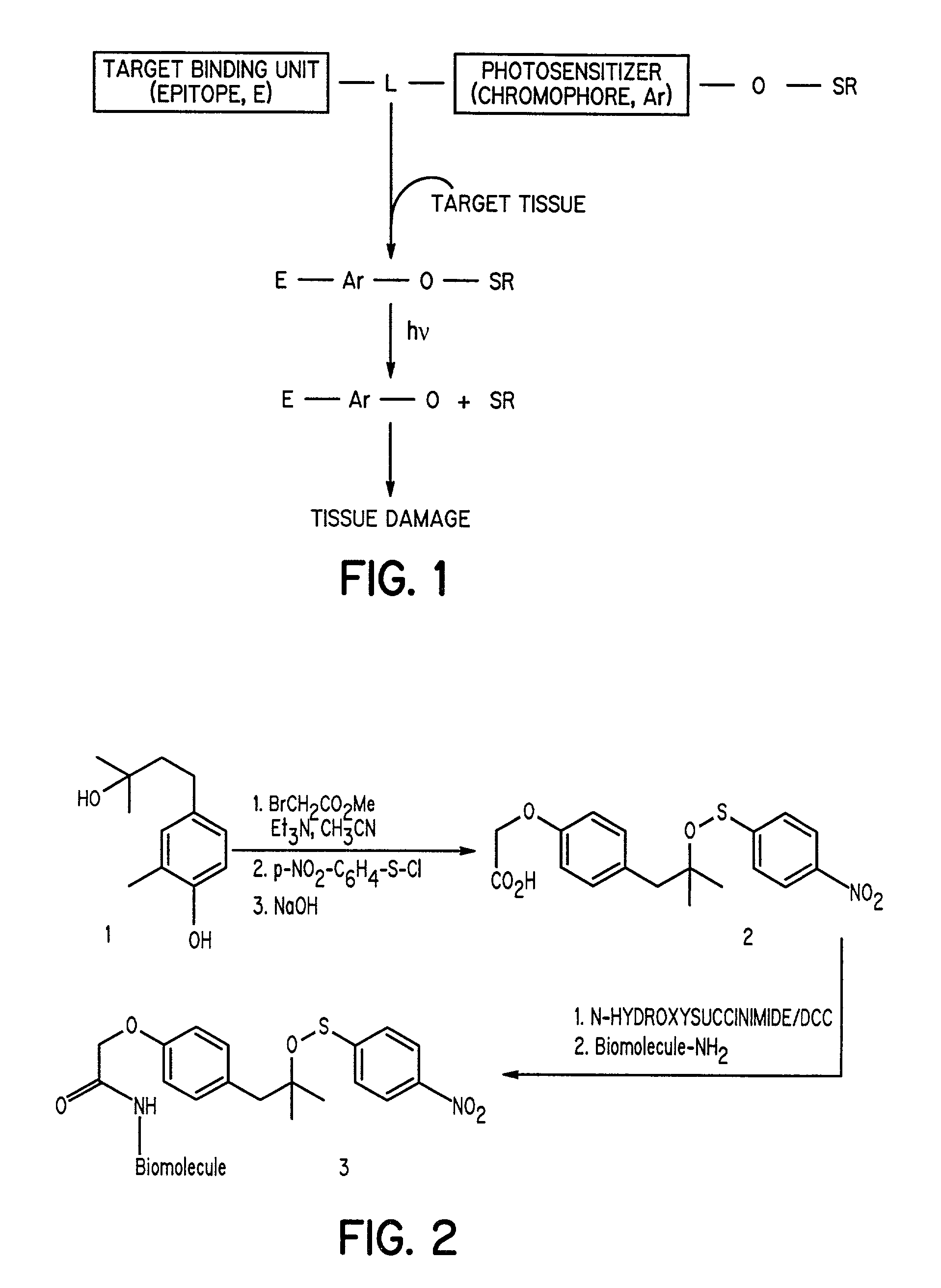
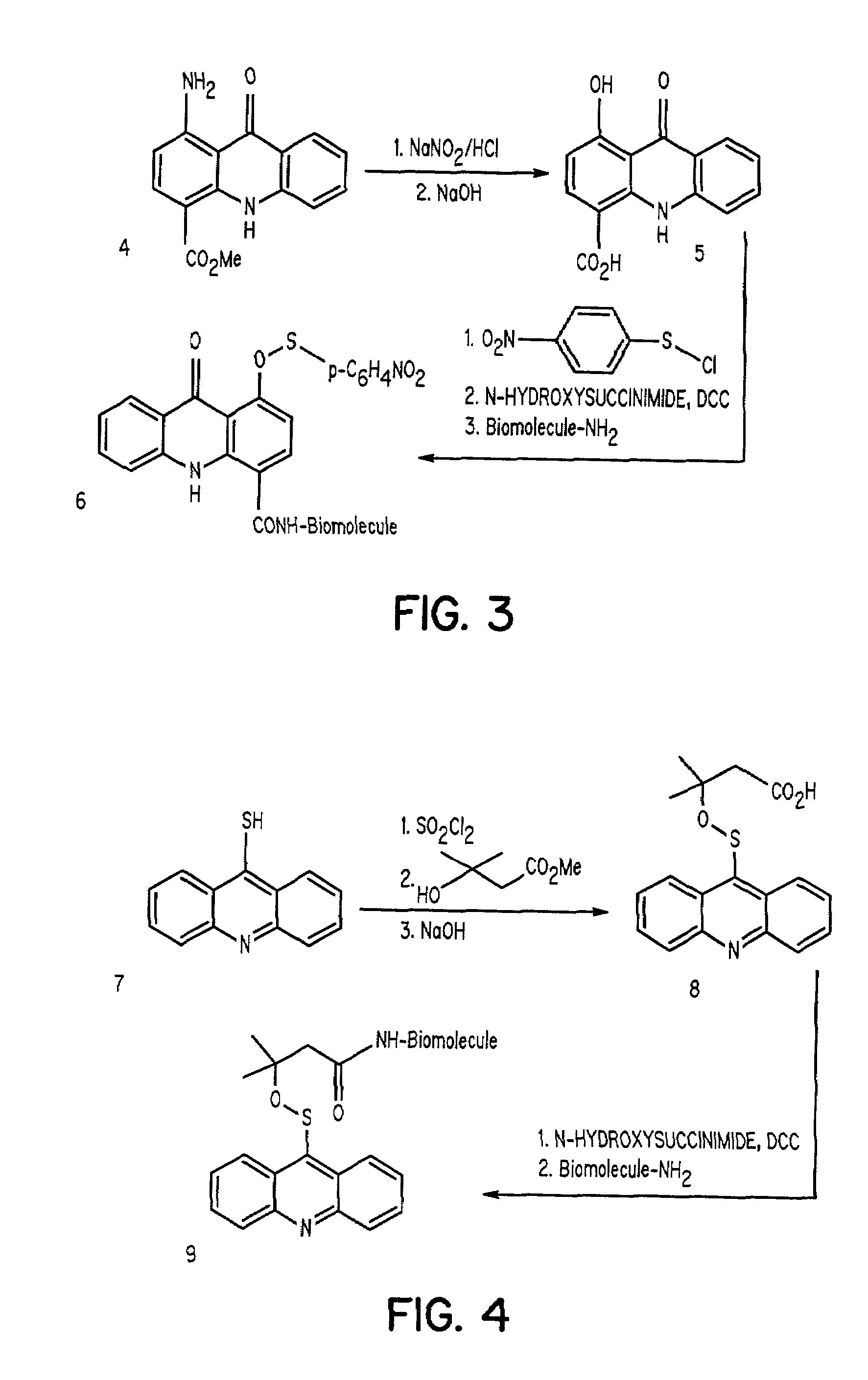
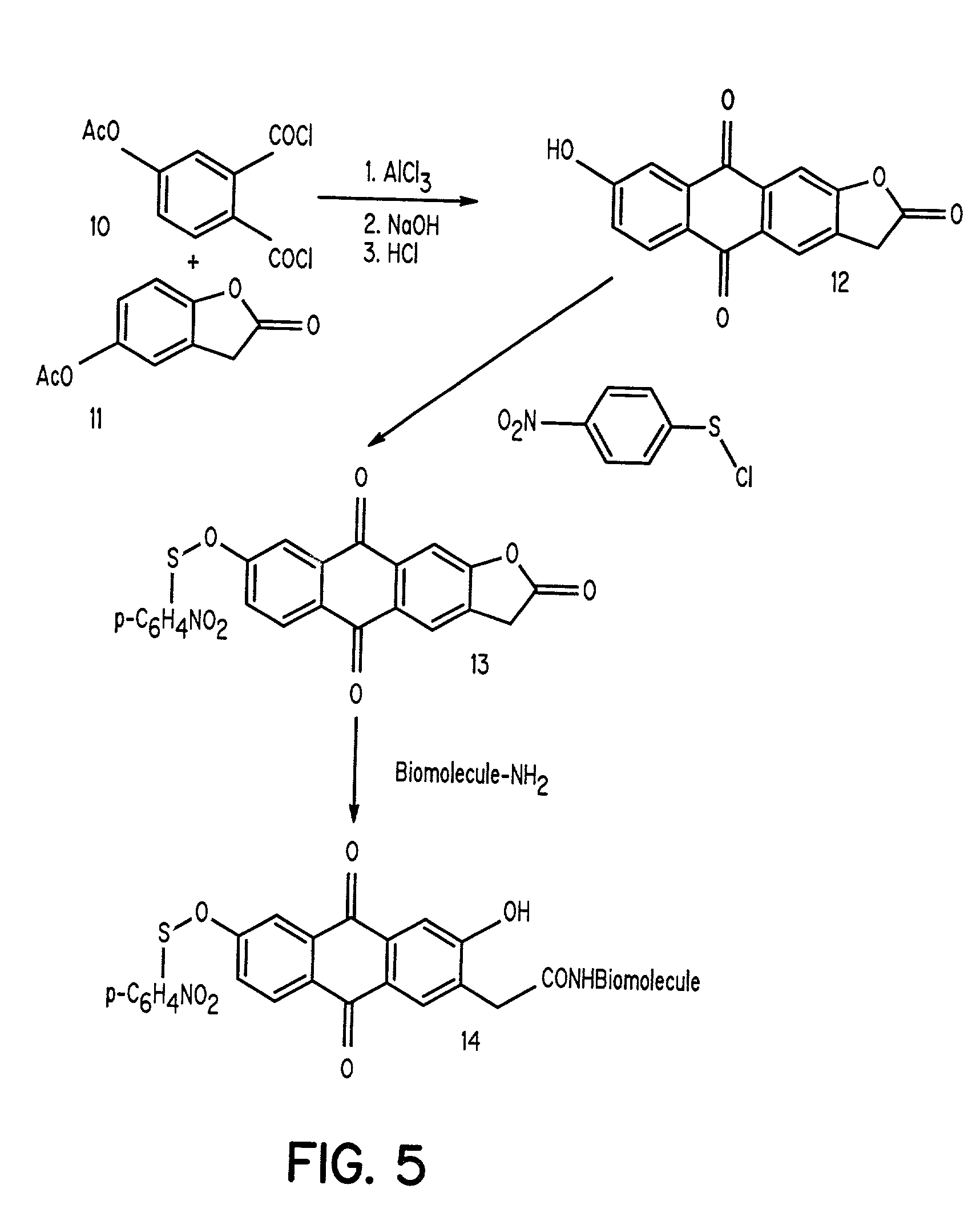
The present invention discloses novel sulfenate derivatives and their bioconjugates for phototherapy of tumors and other lesions. The sulfenates of the present invention are designed to absorb low-energy ultraviolet, visible, or near-infrared (NIR) region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The phototherapeutic effect is caused by direct interaction of free radicals, the reactive intermediate produced upon photofragmentation of the sulfenate moiety, with the tissue of interest.
Owner:MALLINCKRODT INC
Reactor for producing reactive intermediates for low dielectric constant polymer thin films
InactiveUS20050000435A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesReaction intermediateReactive intermediate
A reactor for forming a reactive intermediate from a precursor for the deposition of a low dielectric constant polymer film via transport polymerization is disclosed. The reactor includes an inlet for admitting a flow of the precursor into the reactor, an interior for converting the precursor to the reactive intermediate, an outlet for admitting a flow of the reactive intermediate out of the interior, and at least one of an energy source and an oxidant source associated with the outlet for decomposing residues in the outlet.
Owner:DIELECTRIC SYST INT
Atomic layer deposition method
InactiveUS7128787B2Polycrystalline material growthVacuum evaporation coatingProduct gasReactive intermediate
An atomic layer deposition method includes positioning a semiconductor substrate within an atomic layer deposition chamber. A first precursor gas is flowed to the substrate within the atomic layer deposition chamber effective to form a first monolayer on the substrate. After forming the first monolayer, a reactive intermediate gas is flowed to the substrate within the deposition chamber. The reactive intermediate gas is capable of reaction with an intermediate reaction by-product from the first precursor flowing under conditions of the reactive intermediate gas flowing. After flowing the reactive intermediate gas, a second precursor gas is flowed to the substrate within the deposition chamber effective to form a second monolayer on the first monolayer. Other aspects and implementations are contemplated.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Galactosylated chitosan scaffold material for bioartificial liver and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a galactosylated chitosan scaffold material for a bioartificial liver, which is a galactosylated chitosan biological material with a three-dimensional porous structure which is cross-linked by an oxidized sodium alginate biological crosslinking agent. Its main preparation process: chitosan and lactobionic acid are dissolved in tetramethylethylenediamine / hydrochloric acid mixed solution in an equimolar ratio, and active intermediates are added to activate the reaction to prepare galactosylated chitosan; galactosylated chitosan is dissolved in Acetic acid solution and oxidized sodium alginate are dissolved in ultrapure water, and the two solutions are mixed in a certain proportion to carry out cross-linking reaction. After the reaction is completed, pour it into a mold for molding, freeze-dry to obtain a scaffold material, and then immerse it in sodium hydroxide- The residual acetic acid was removed by ethanol aqueous solution, and then washed by ethanol aqueous solution and freeze-dried twice to obtain the galactosylated chitosan scaffold material cross-linked by oxidized sodium alginate. The galactosylated chitosan scaffold material of the invention has a pore size suitable for the growth of liver cells and good biocompatibility.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Biocide and bleach compositions and related methods
InactiveUS20120207858A1Improve stabilityHigh of efficacyBiocideOrganic chemistryBleachReactive intermediate
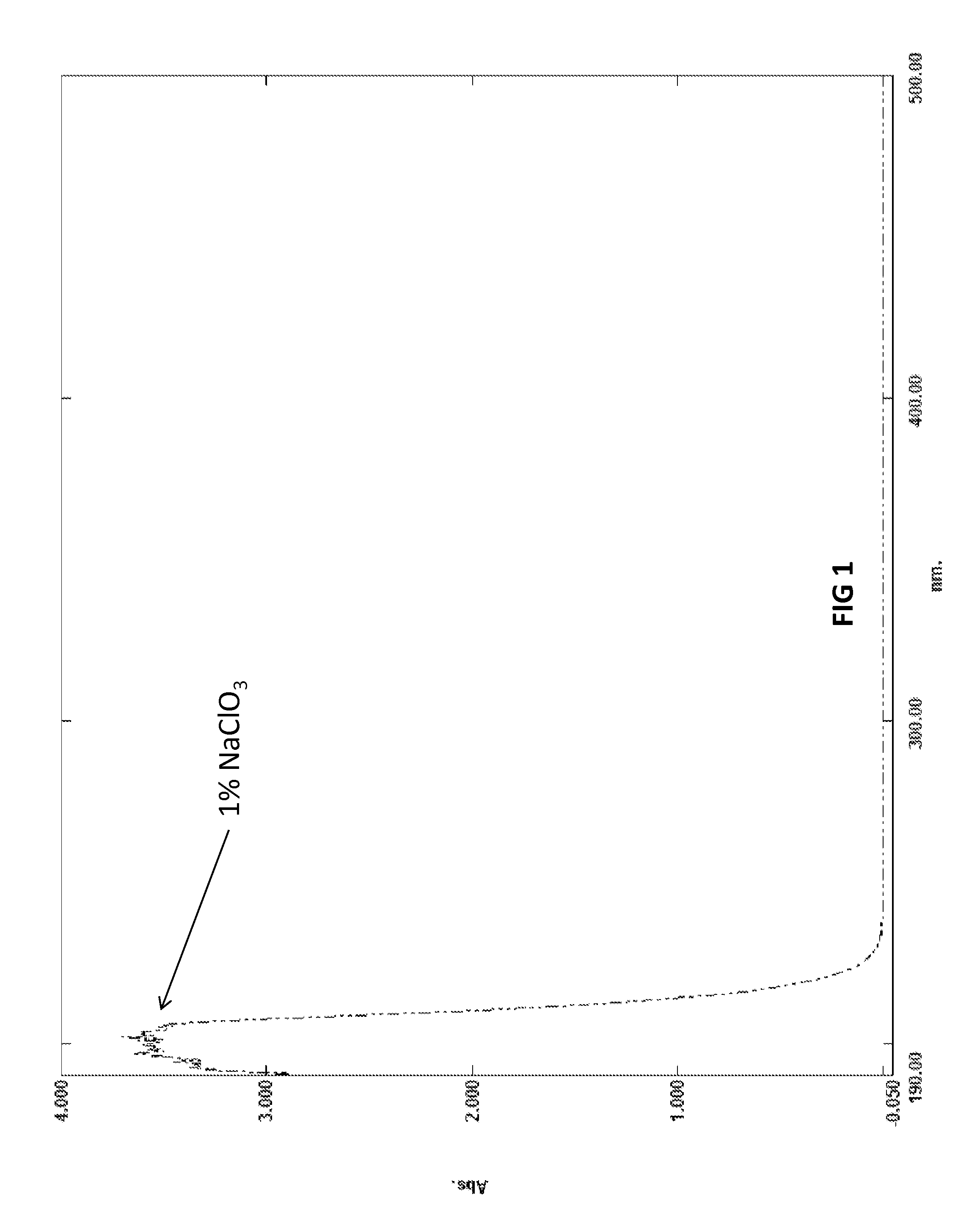
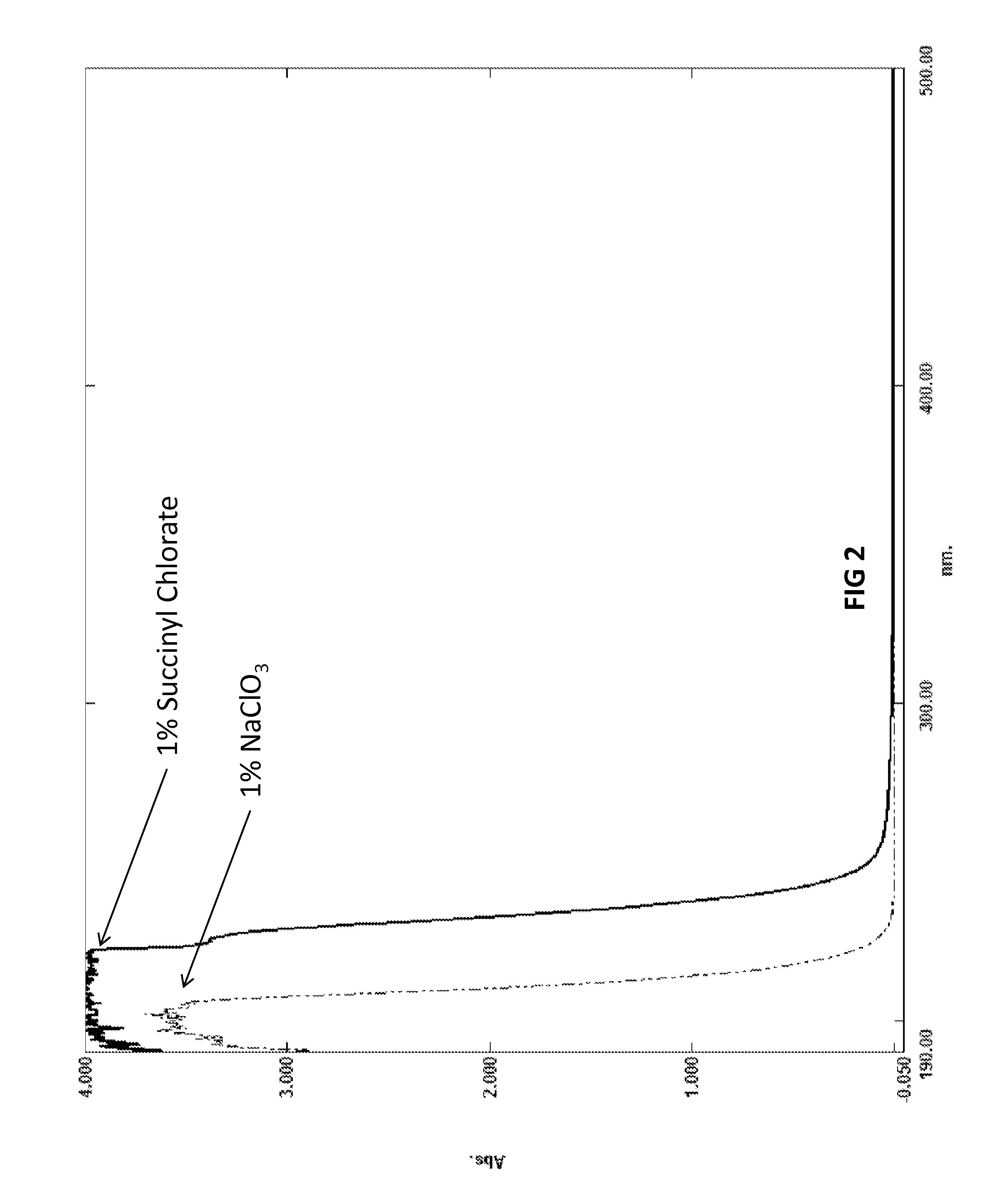
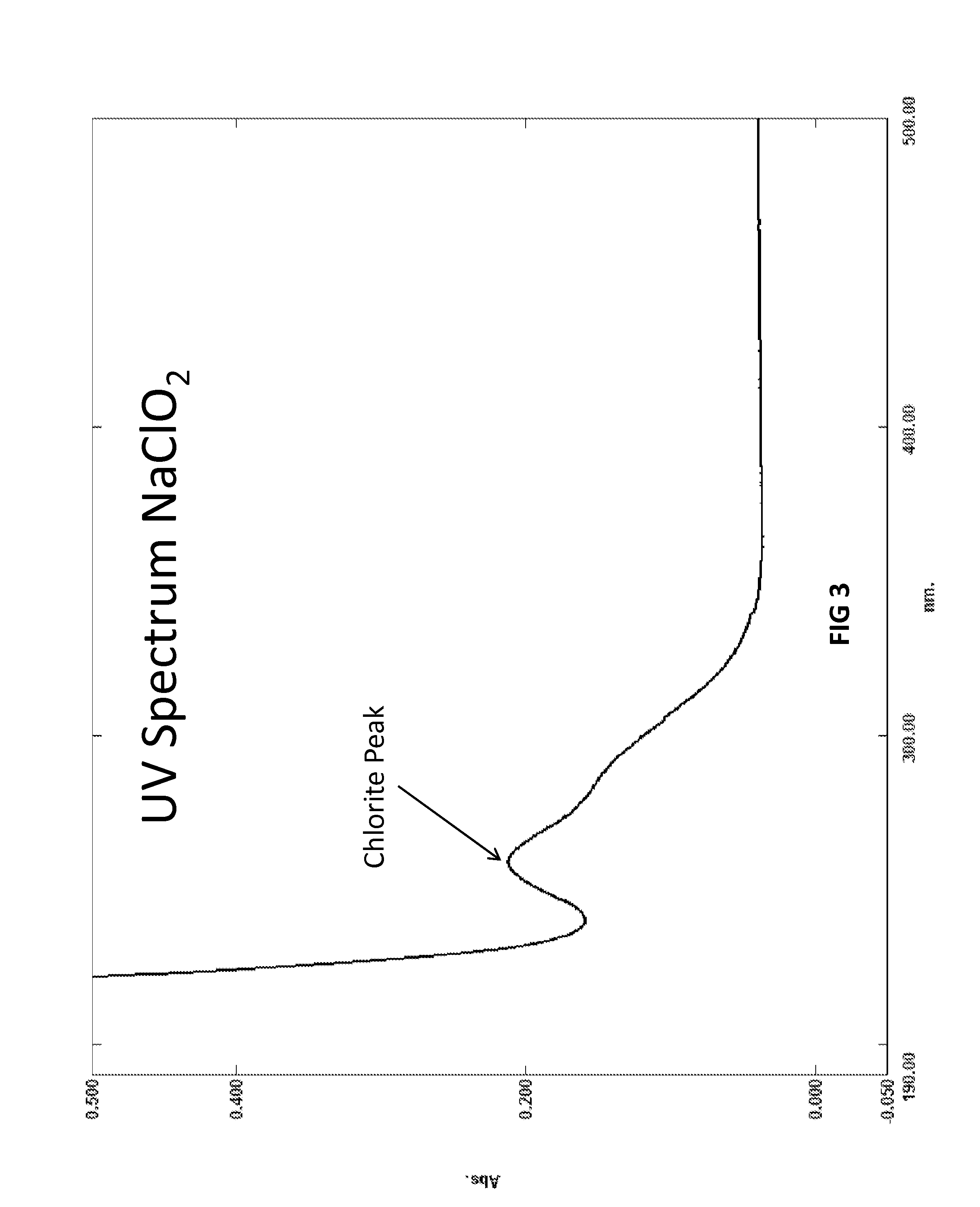
Provided are biocide compositions and bleach compositions comprising organic acyl polyoxychlorine and related methods. The reduction of the acyl polyoxychlorine group releases a reactive intermediate that undergoes a series of cascading reduction steps, resulting in termination products Generally Recognized As Safe.
Owner:TRUOX
Novel method for creating, suspending and stabilizing electronically modified oxygen derivatives, along with creating, suspending and stabilizing electronically modified reaction intermediates, in a bio compatible fluorocarbon suspension, for the purpose of inducing a cascading immune response in mammalian patients
InactiveUS20120039796A1Positive resultFacilitates release of oxygenPowder deliveryBiocideUltrasonic cavitationReaction intermediate
A bio compatible free radical suspension, comprising of oxygen and electronically modified reaction intermediates, where a fluorocarbon is used as an inert medium for stabilization of reaction intermediates. A stabilized bio compatible electronically modified derivative suspension is produced by the subjecting a fluorocarbon to certain stressors, such as oxidizing agents, reactive intermediates, physiological gases, benzo-γ-pyrone derivatives, ultrasonic-cavitation, electric fields, magnetic fields, UV radiation, active metal catalyst, surfactant reactants, buffers, electrolytes, glucose, glucose derivatives, for the purpose of inducing a cascading immune response.
Owner:MARKOU DEMETRIOS
Method for preparing Dawson heteropolyphosphatotungstate
InactiveCN103613082AEasy to operateShort reaction processPhosphorus oxyacidsInorganic saltsTungstate
The invention discloses a method for preparing Dawson heteropolyphosphatotungstate. The method comprises the following steps: (1) enabling a tungstate solution to come into contact with an inorganic acid solution, so as to obtain a reactive intermediate; (2) continuously enabling the solution to come into contact with a phosphoric acid solution, so as to obtain a phosphotungstic acid solution; (3) transferring the phosphotungstic acid solution to a high-pressure reactor, and carrying out high-temperature and high-pressure reaction; (4) adding an inorganic salt precipitant to the obtained phosphotungstic acid solution, carrying out salting-out crystallization to obtain phosphotungstate, filtering, purifying and drying, so as to obtain the Dawson heteropolyphosphatotungstate. Compared with the prior art, the method is simple in technological process, short in reaction cycle, high in yield and product purity, and low in cost; meanwhile, strong acid acidification and diethyl ether extraction used in the traditional method are avoided; the safety of the preparation process is greatly improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Salt-free dyeing method for active dye
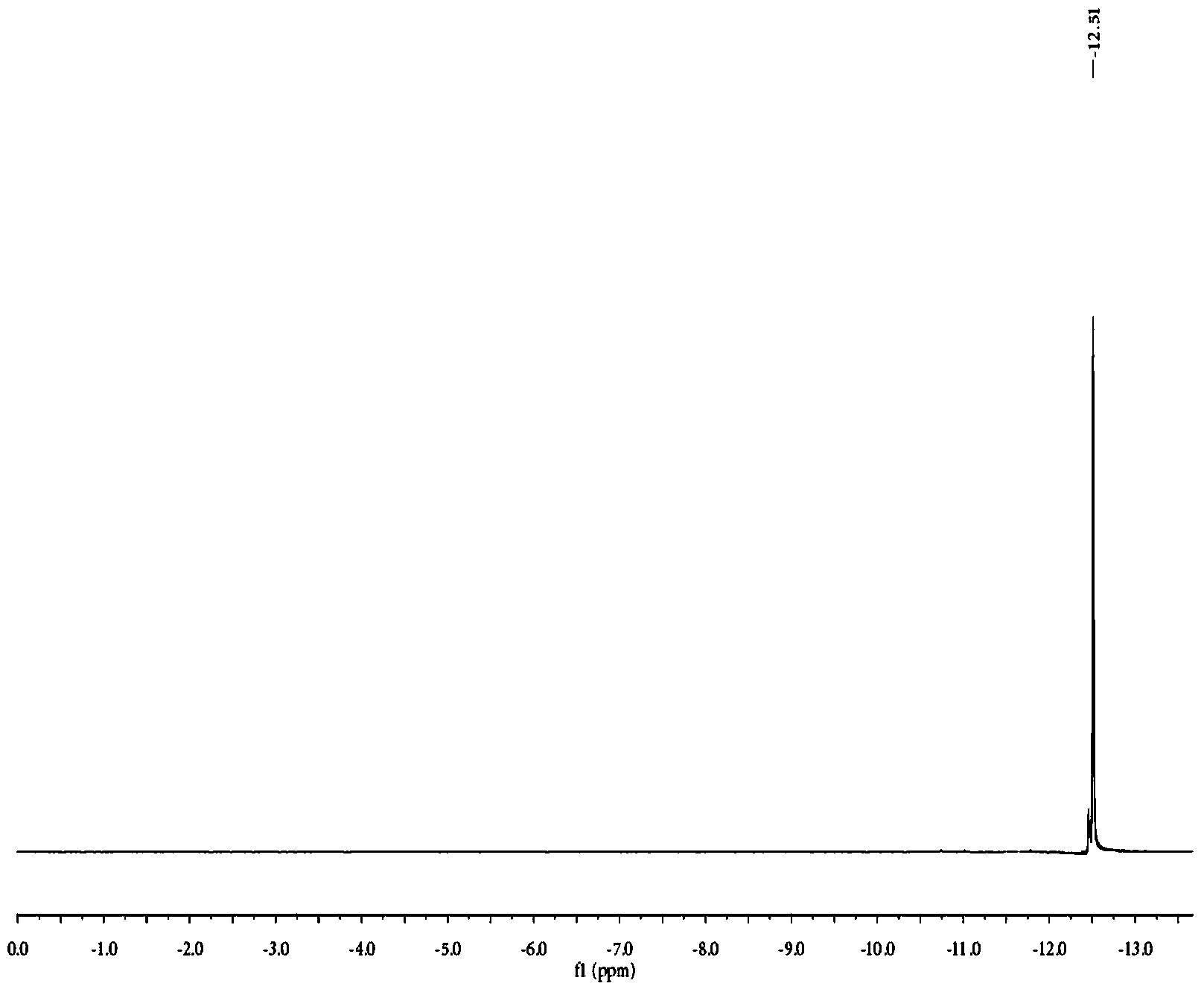
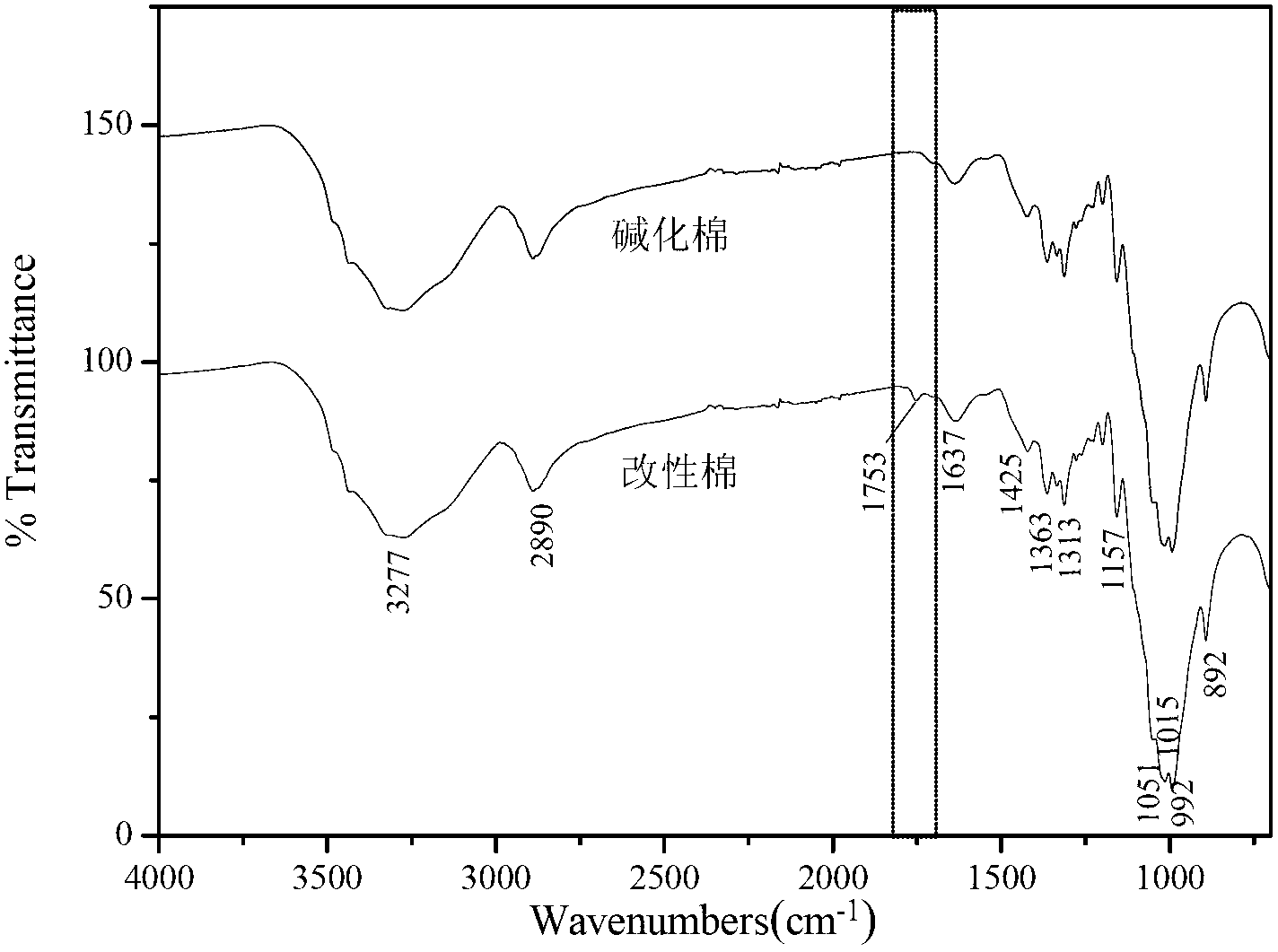
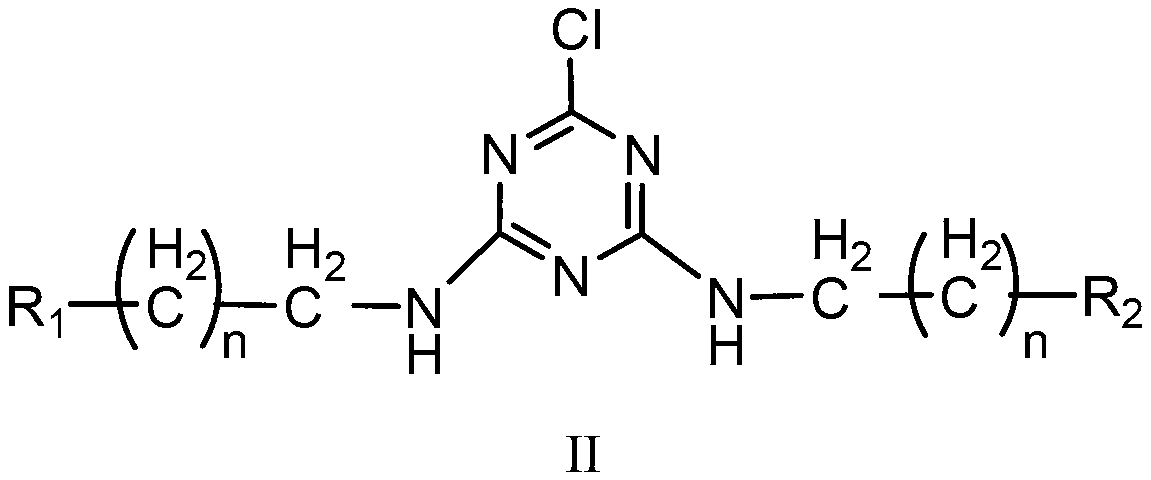
ActiveCN103215805AHigh reactivityShorten the cationic modification reaction timeDyeing processVegetal fibresFiberSalt free
The invention relates to a salt-free dyeing method for an active dye, belonging to the field of printing and dyeing of active dyes. The salt-free dyeing method for the active dye comprises a modification treatment step and a dyeing step, wherein the modification treatment step comprises the following sub-steps of: (1) alkalinizing cotton fibers; (2) impregnating the alkalinized cotton fibers obtained by the sub-step (1) in an active intermediate solution for cotton fiber modification; and (3) impregnating the modified alkalinized cotton fibers obtained by the sub-step (2) in a carboxylic acid group-containing cationic reagent solution for cotton fiber cationic modification. By the alkalinization of the cotton fibers and the introduction of a plurality of carboxyl groups and amino groups, the reactivity of the cotton fibers is improved, and further cationization and reaction with the active dye are facilitated.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
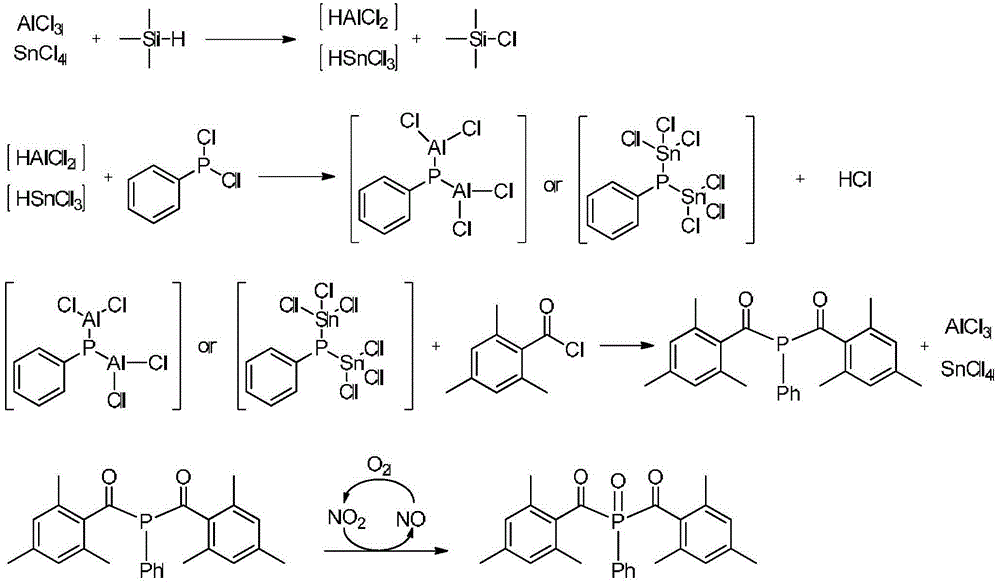
Preparation method for photoinitiator bis(2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl)phenylphosphine oxide
InactiveCN104151358ALess prone to fireHigh reaction safety factorGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPotassiumPhenylphosphine
The invention discloses a preparation method for a photoinitiator bis(2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl)phenylphosphine oxide. The preparation method comprises the synthesis steps: under the protection of inert gas, carrying out a reaction of aluminium trichloride or tin tetrachloride and trimethylsilane in the temperature range of 0-100 DEG C to obtain aluminium dichloride ions, and rapidly acting with dichlorophenyl phosphine in the reaction system, to obtain a bis(aluminium trichloride or tin tetrachloride)phosphine salt intermediate; then carrying out a reaction of the intermediate and 2,4,6-trimethyl benzoyl chloride, to obtain bis(2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl)phenyl phosphine; and under the condition of the temperature of 20-50 DEG C, oxidizing by nitrogen dioxide, to obtain the target product. The method avoids use of a dangerous active metal potassium or sodium, and adopts aluminium trichloride or tin tetrachloride with relatively low price and trimethylsilane for on-site generation of the active intermediate to achieve the reaction. The method has the characteristics of low preparation cost, simple and safe operation process, easy control of the reaction process, high product yield, good purity, easy realization of mass production and the like.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG JIMUTE CHEM TECH
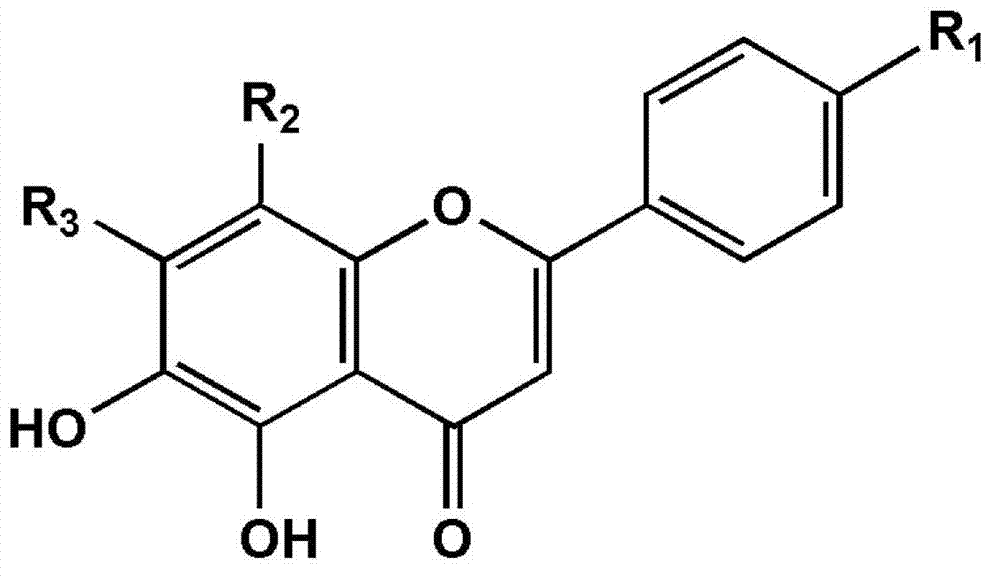
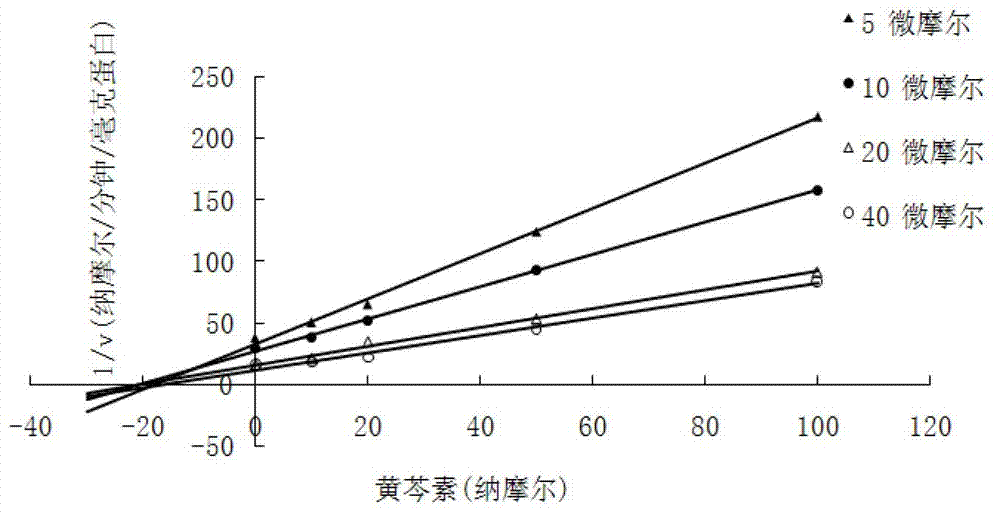
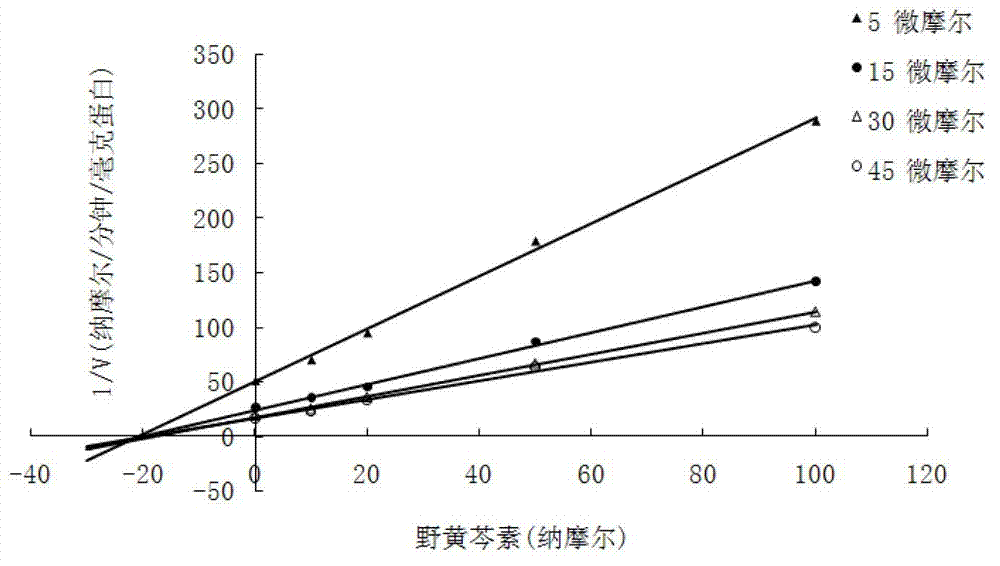
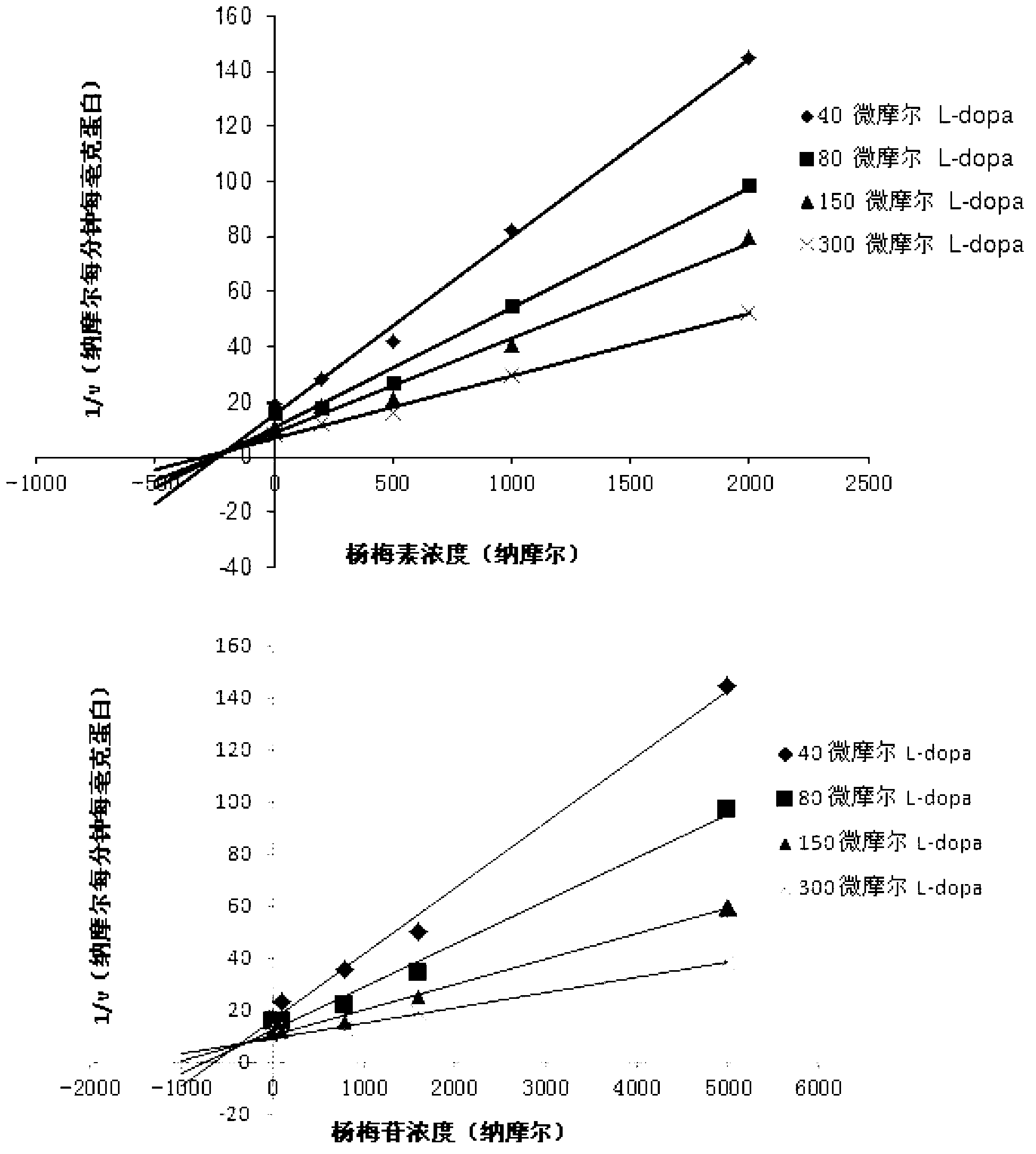
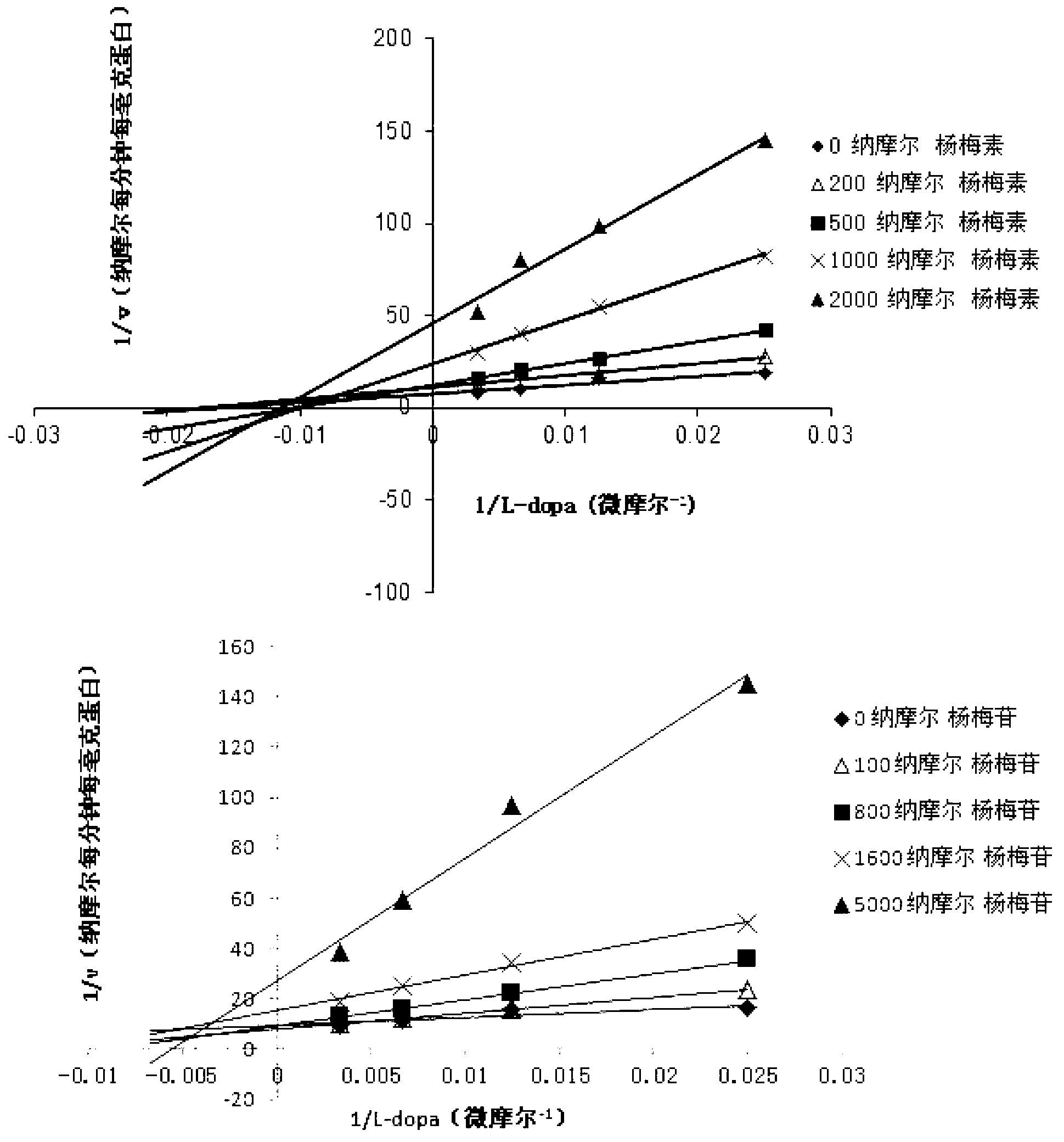
Application of compound with flavone skeleton structure as Parkinsonism treating medicine
InactiveCN102755312AWon't happenImprove securityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderScutellareinBiological activation
The invention relates to application of a compound with a flavone skeleton structure as a Parkinsonism treating medicine. The compound with a flavone skeleton structure is an inhibitor for the catechol methylation transferase; and the compound specifically comprises radix scutellariae, scutellarein and structure derivatives of radix scutellariae and scutellarein, and can be used as a synergist of the Parkinsonism treating medicine levodopa. In-vitro activity test indicates that IC50 of the compound in inhibiting catechol methylation transferase can reach nanomole level, wherein the COMT(Catechol O Methyl Transferase) inhibition activity of scutellarein and the derivatives of scutellarein is superior to that of medicine tolcapone on the market. The rat overall pharmacokinetic study shows that by the joint application of scutellarein and levodopa, the blood concentration of levodopa can be obviously increased. Moreover, the compound does not generate active intermediate through metabolism activation or form toxic adduct together with biological macromolecules, thus the hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity caused by metabolism activation are avoided, and the compound has good prospect of patent medicine.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Self-dispersed pigments and methods for making and using the same
A method of modifying a pigment that includes reacting a reactive compound having an X-[Y]n reactive group with a secondary compound N-S-ZM to form a substituted reactive intermediate [Y]a-X-(N-S-ZM)b. A pigment is reacted with the substituted reactive intermediate [Y]a-X-(N-S- ZM)b to attach the substituted reactive intermediate to the surface of the pigment to form a surface modified pigment. X may be a sulfonyl, phosphoryl, or 1,3,5-triazinyl group, Y may be a halogen leaving group, N may be a basic nucleophilic group, S may be an organic group, and ZM may be an ionizable end group. Also, n is an integer between 1 and 3, b is an integer between 1 and 3, and a = n-b. When n is equal to or greater than b, and if b is 2 or 3, each N-S- ZM can be the same or different.
Owner:SENSIENT COLORS
Tailored control of surface properties by chemical modification
InactiveUS20100068783A1Big economySignificant technical bulk advantageHydrazine preparationGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsArylReactive intermediate
A process for producing a substrate having an adhesive surface, which process comprises: (a) contacting the substrate with a carbene precursor, which carbene precursor is a compound of the following formula (1): whose substituent groups are SP defined herein, provided that when R is aryl or heteroaryl, said aryl or heteroaryl may be substituted by one, two, three, four or five groups, which groups are independently selected from various groups including -LB-WB; and (b) either: (i) when WA or WB comprises an adhesive functional group, generating a carbene reactive intermediate from the carbene precursor so that it reacts with the substrate to functionalise the surface, thereby yielding said substrate having an adhesive surface; or (ii) when WA or WB comprises a group which is a precursor of an adhesive functional group, generating a carbene reactive intermediate from the carbene precursor so that it reacts with the substrate to functionalise the surface, and (c) converting said group which is a precursor into an adhesive functional group thereby yielding said substrate having an adhesive surface. The invention further relates to carbene precursor compounds for use in the process, substrates produced by the process and to processes for preparing certain precursor compounds.
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD
Selective plugging agent for horizontal well and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102102012ASynthetic production is convenientStable chemical propertiesDrilling compositionSweep efficiencyOil field
The invention discloses a selective plugging agent for a horizontal well and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the technical field of oil field chemistry. The plugging agent comprises the following components in part by weight: 6.50 to 7.50 parts of polymer monomer, 4.50 to 5.75 parts of surface active intermediate, 0.85 to 1.00 part of modifier, 85.75 to 88.15 parts of water. The method comprises the following steps of: adding the surface active intermediate into water, adding the polymer monomer and uniformly stirring; making the surface active intermediate react with the polymer monomer, adding the modifier and stirring to react; and drying a reaction product, grinding the dry product into particles, and screening to obtain selective plugging agent particles for the horizontal well. The plugging agent provided by the invention has the advantages of high oil and water selectivity, convenience in synthesizing and producing, stable chemical properties, high adaptability and simple construction technology; simultaneously, the sweep efficiency of the development of a high-water-cut old oilfield horizontal well is improved, the swept volume is expanded, and the petroleum recovery ratio is increased.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Carbene precursor compound for producing an adhesive surface on a substrate
InactiveUS8530212B2Big advantageHydrazine preparationGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsArylReactive intermediate
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD
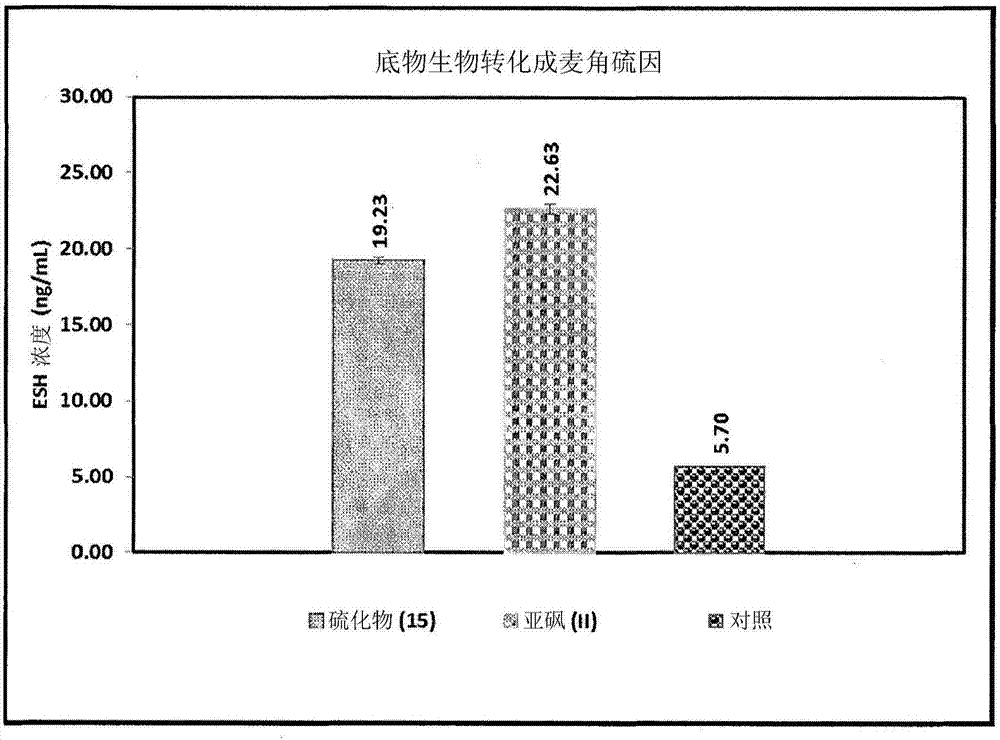
Process for synthesizing ergothioneine and related compounds
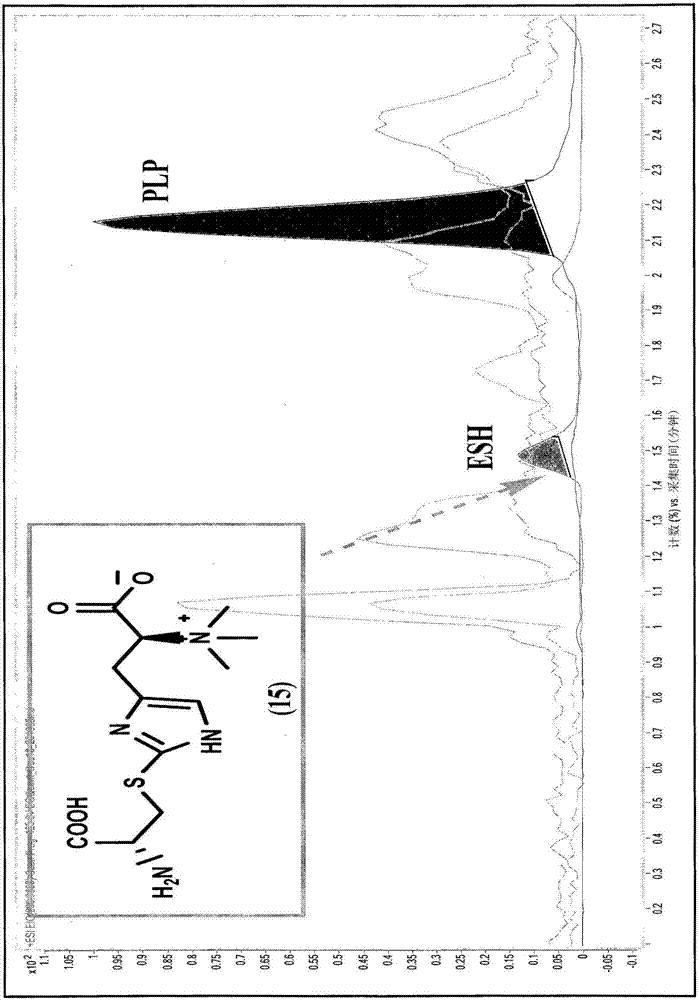
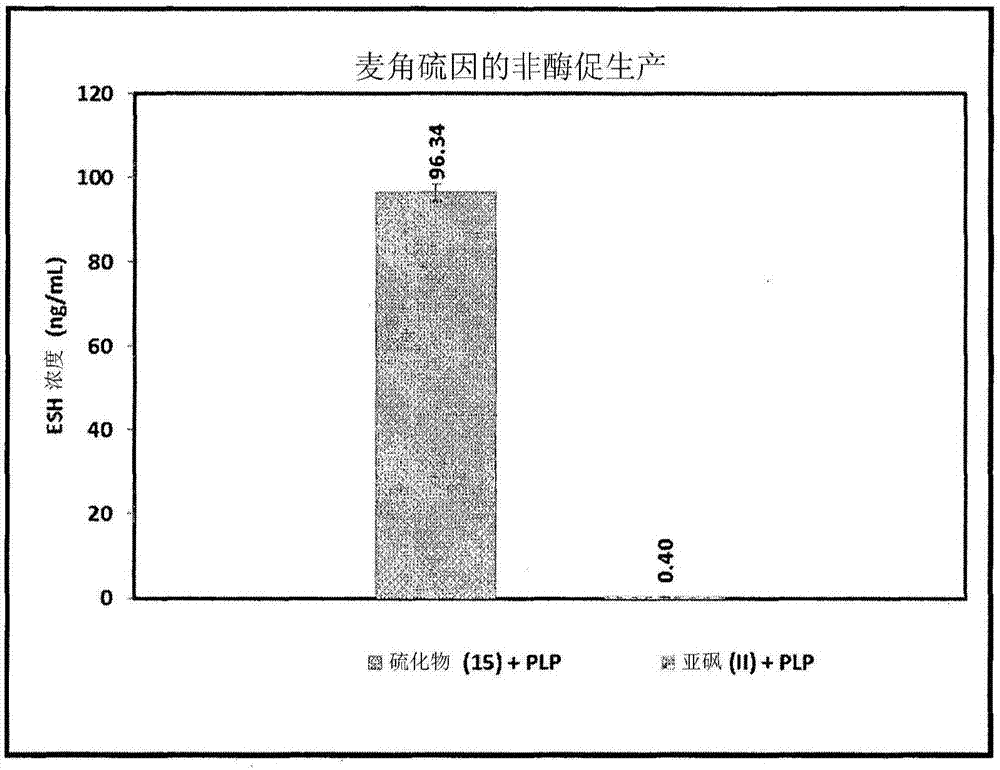
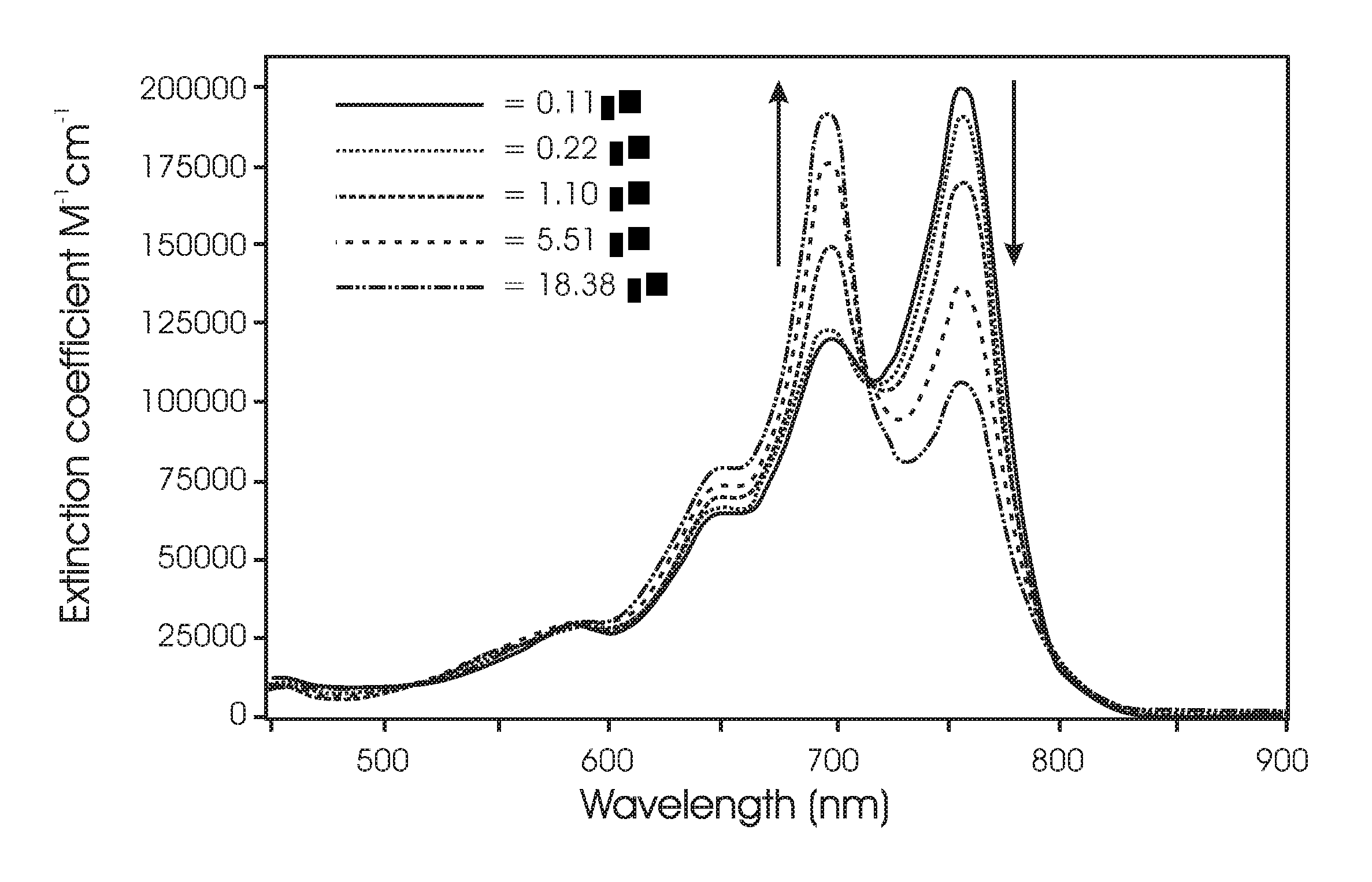
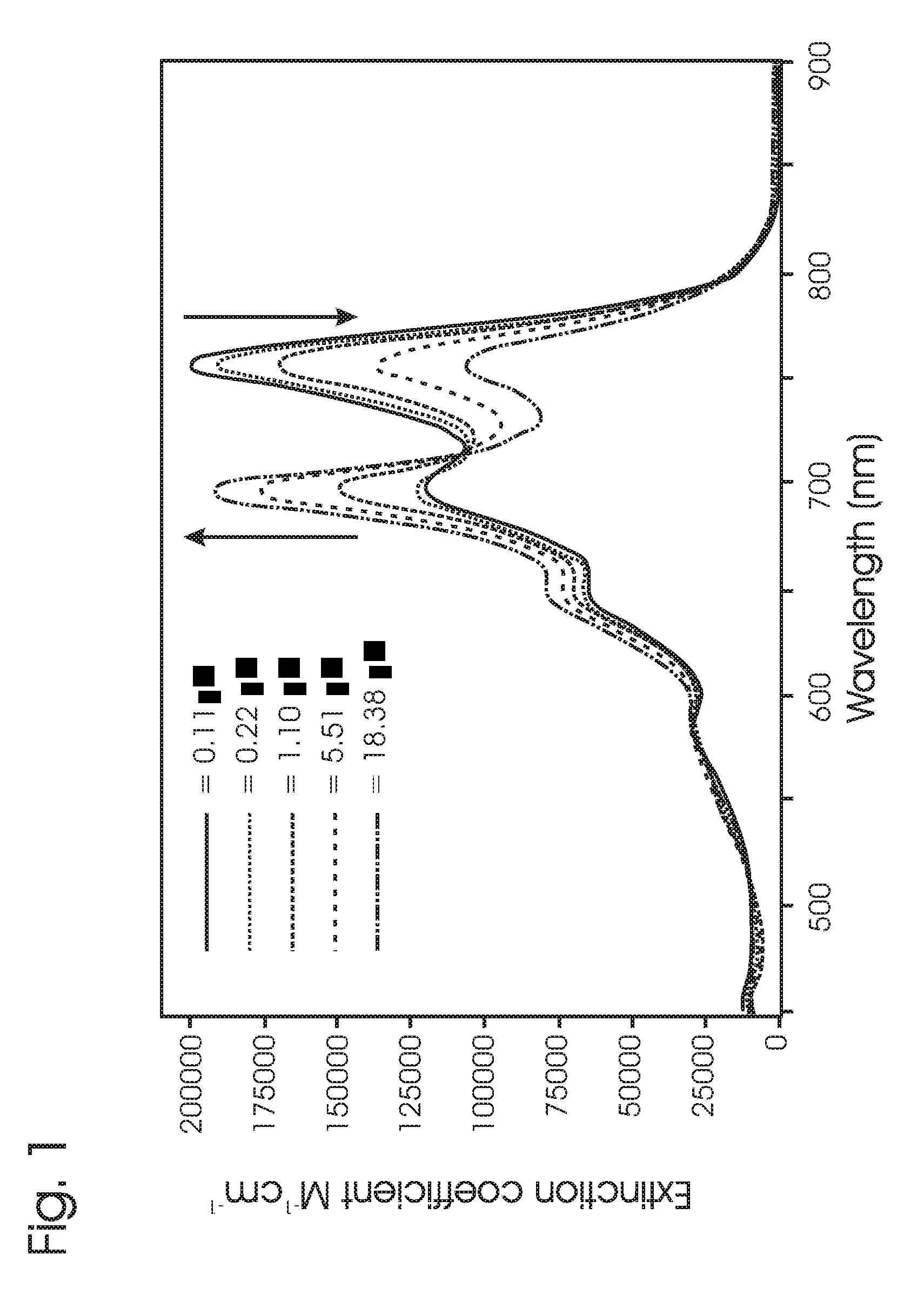
The invention provides a process for synthesising a compound of formula (V) wherein: formula (z) or a physiologically acceptable salt, tautomer, stereoisomer or mixture of stereoisomers thereof. The process utilizes a / V-benzyl protected histidine rather than the unprotected form of histidine. The process of the invention comprises the steps of: (a) deprotecting a / V-benzyl protected histidine of formula 11 to form A / -benzyl histidine of formula 12; (b) converting compound 12 to (S)-3-(1 -benzyl-1 H-imidazol-4-yl)-2-(dimethylamino)propanoic acid of formula 13; (c) converting compound 13 to (2S)-N,N,N-2-trimethylethanaminium-3-(1 -benzyl- 1H-imidazol-4-yl)propanoic acid of formula 14; (d) brominating the imidazole ring of the compound of formula 14 to form 5-bromohercynine lactone (reactive intermediate); and (e) converting the 5-bromohercynine lactone of step (d) to (p-amino-p- carboxyethyl)ergothioneine sulfide of formula 15. The process optionally further includes one of steps (f) to (h): (f) converting the compound of formula 15 to a sulfoxide; (g) converting the compound of formula 15 to a sulfone; or (h) converting the compound of formula 15 to ergothioneine (ESH).
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CAPE TOWN
Luminescent compounds
Reporter compounds based on cyanine dyes, among others, including reactive intermediates used to synthesize the reporter compounds, and methods of synthesizing and using the reporter compounds, among others, where the reporter compounds relate generally to the following structure:
Owner:SETA BIOMEDICALS
Laminating resin with reduced styrene monomer
A laminating resin having low styrene content is provided. The resin includes a thermosetting resin and a reactive intermediate including a low molecular weight polyester oligomer endcapped with at least one (meth)acrylic acid, its ester or its anhydride thereof.
Owner:REICHHOLD INC
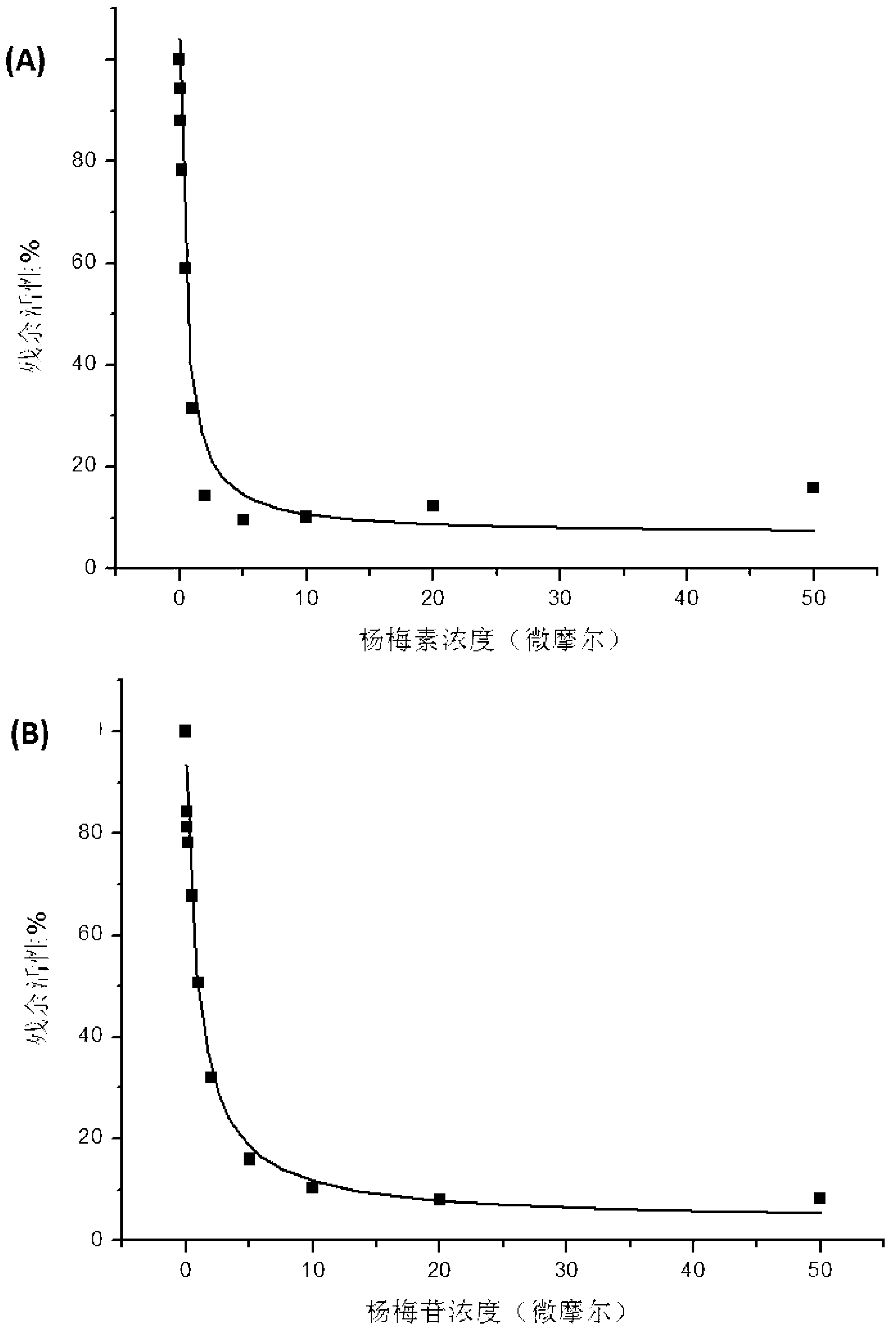
Medicine composition containing myricetrin or/and myricetin and application of medicine composition in preparation of medicine used for treating Parkinson
InactiveCN103211832AEnhance anti-inflammatoryImproves antioxidant activityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderLiver and kidneyAglycone
The invention relates to a medicine composition of myricetrin or / and myricetin aglycone thereof and levodopa or of levodopa and carbidopa and an application of myricetrin or / and myricetin aglycone thereof as a synergist in preparation of a medicine used for treating Parkinson. In vitro activity determination finds that IC50 of myricetrin and myricetin inhibiting catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) can be a micromole-nanomole scale. Rat overall pharmacokinetic study finds that blood concentration of levodopa can be increased after myricetrin and myricetin aglycone thereof and levodopa are used jointly; and myricetrin and myricetin aglycone thereof are high in safety, no obvious toxicity is produced to main visceral organ cells of a human body, and no active intermediate is produced by virtue of metabolism activation and further no damage done to organs such as liver and kidney is initiated, so that the myricetrin and myricetin aglycone thereof have a good application prospect in adjuvant therapy of Parkinson.
Owner:无锡艾德美特生物科技有限公司
Formation of [2,2]Paracyclophane and Related Compounds and Methods for the Formation of Polymers from Cyclophanes
ActiveUS20130109827A1Increase in costLimited utilityOrganic compound preparationHydrocarbons from unsaturated hydrocarbon additionReaction intermediateReactive intermediate
An improved process and method for the formation of stable intermediate cyclophanes. Embodiments describe a general method for the production of substituted and unsubstituted cyclophanes. The components include a pyrolysis reaction tube that may be electrically heated into which a flowing stream of nitrous oxide with xylene vapor in an optional inert carrier gas at atmospheric pressure. The exit gas is condensed resulting in the deposition of [2,2′]paracyclophane. Additionally a process and method whereby the reactive intermediates of the reaction described above can be directly deposited and polymerized at atmospheric pressures or thereabout is disclosed.
Owner:CARVER SCI INC
Synthetic method of spiro-oxoindole ethylene oxide derivative
The invention discloses a spiro-indolone ethylene oxide derivative obtained with an o-trimethylsilylphenyl triflate, an N-methyl isatin derivative and aryl thioether as raw materials, CsF as an alkali and an organic solvent as a solvent and through a one-pot method, wherein an active intermediate benzyne is obtained by allowing o-trimethylsilylphenyl triflate to generate 1,2- elimination under fluorinion induction. In the synthetic method, the whole reaction adopts the one-pot method, reaction substrates are friendly to the environment, operations are simple, conditions are mild, product structures are diverse, and the product is widely applied in natural products and clinical medicines.
Owner:广东和博制药有限公司
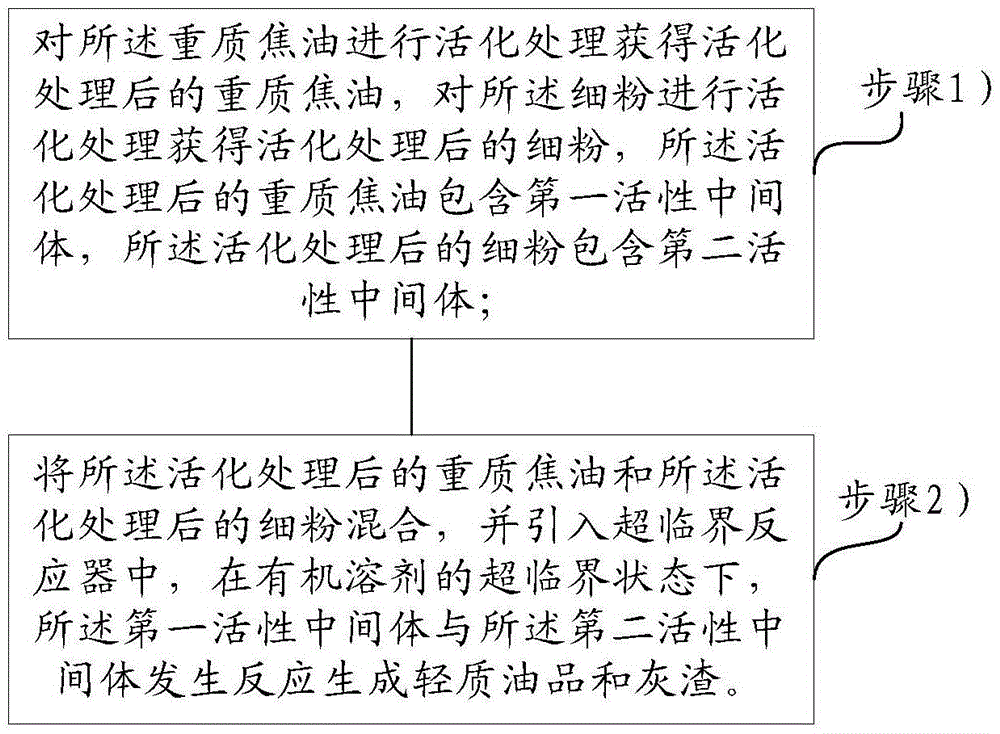
Heavy tar and fine powder treatment method
ActiveCN105647568AImprove carbon conversionIncrease profitCatalytic crackingHydrocarbon oils treatmentOrganic solventSlag
The invention relates to the technical field of coal catalytic gasification, in particular to a heavy tar and fine powder treatment method. Heavy tar and fine powder can be converted into a light-weight oil product, so that conditions are created for the clean and efficient utilization of coal. The embodiment of the invention provides the heavy tar and fine powder treatment method. The heavy tar and the fine powder respectively contain catalysts. The method comprises the following steps that activation treatment is performed on the heavy tar to obtain the heavy tar subjected to activation treatment; the activation treatment is performed on the fine powder to obtain the fine powder subjected to the activation treatment; wherein the heavy tar subjected to the activation treatment comprises a first active intermediate, and the fine powder subjected to the activation treatment comprises a second active intermediate; 2, the heavy tar subjected to the activation treatment and the fine powder subjected to the activation treatment are mixed; the mixture is introduced into a supercritical reactor; under the supercritical state of an organic solvent, the first active intermediate and the second active intermediate take a reaction to produce the light-weight oil product and ash slag.
Owner:ENN SCI & TECH DEV
Method of degrading Napolean green in waste water
InactiveCN1810676APromote degradationFast degradationWater/sewage treatment by irradiationHigh concentrationMalachite green
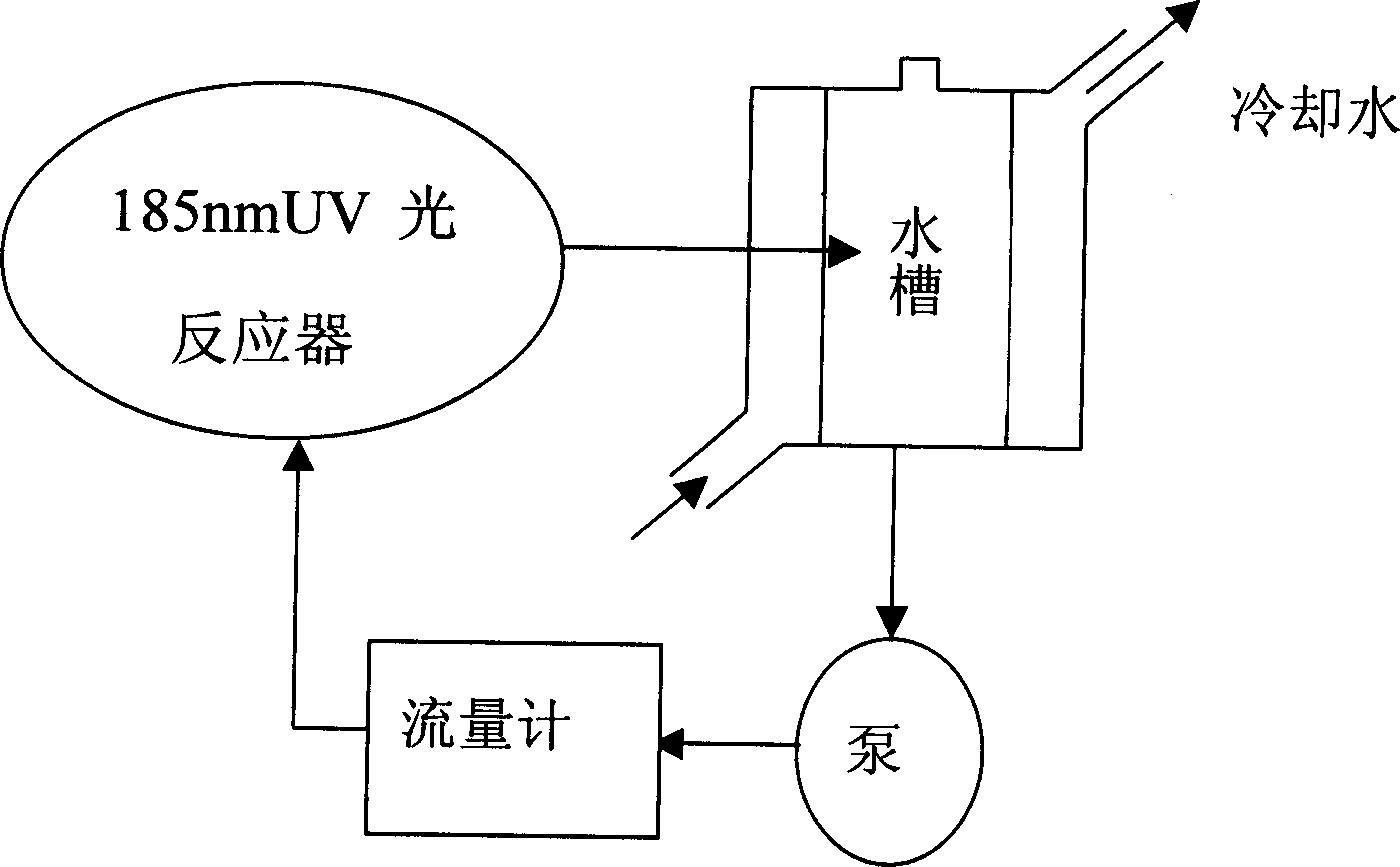
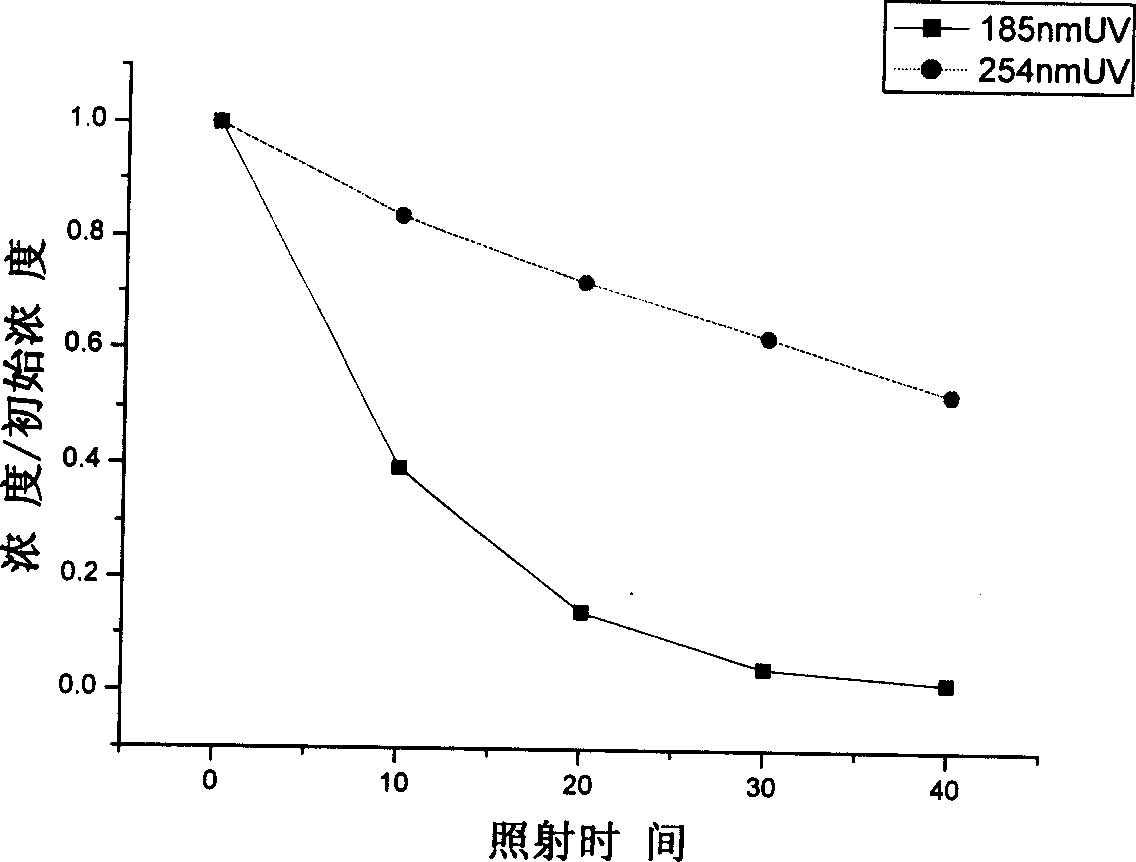
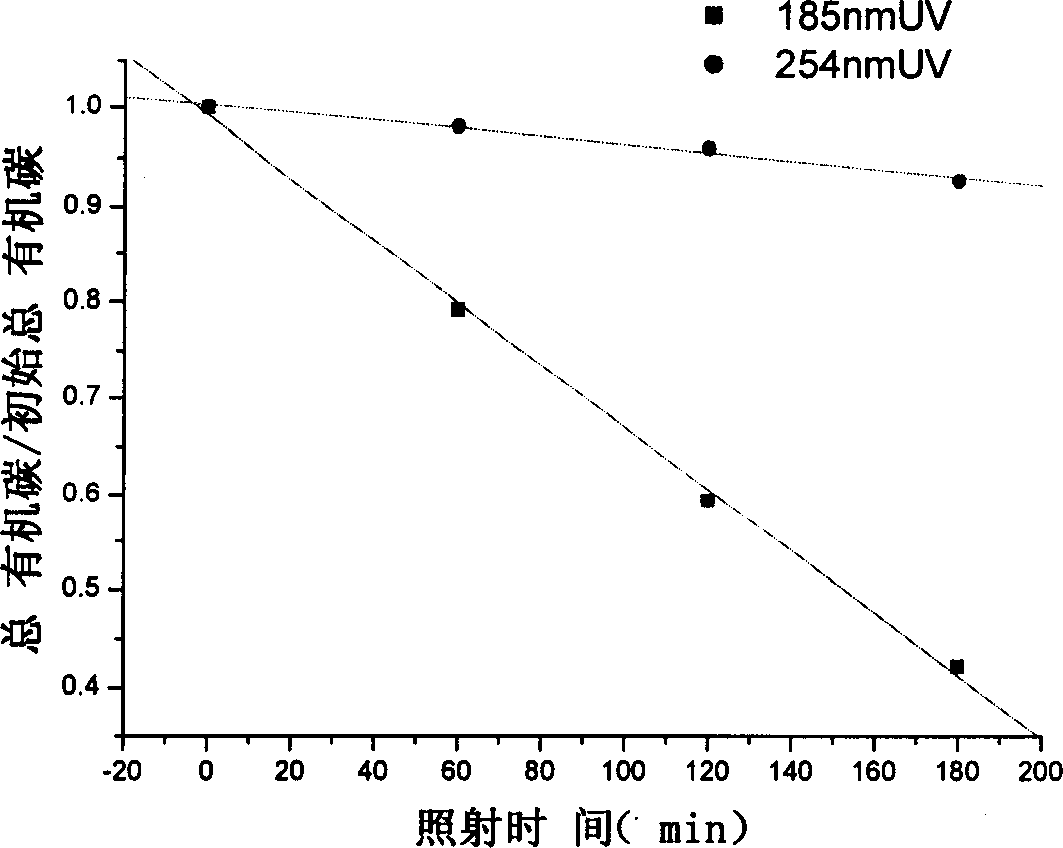
The method of degrading Napolean green in waste water is to degrade Napolean green in waste water with ultraviolet ray of 185 nm wavelength. Waste water containing Napolean green in 10 mg / L is first fed into a water tank, and then the waste water is pumped into the 185 nm ultraviolet reactor in the flow rate of 0.14-0.70 L / min while the reacted waste water is pumped into the water tank circularly in the flow rate of 40-160 L / hr. Monitoring on the Napolean green concentration of the water sample from the water tank shows that the Napolean green degrading rate in 40 min reaches over 99 % and the waste water reaches the draining stardard. The 185 nm wavelength ultraviolet ray acts on water to produce homolytic reaction of water and produce hydrated electrons in high concentration as active intermediate. The present invention has high degrading effect, high degrading speed, low running cost, no secondary pollution and other advantages.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Aromatic sulfenates for type 1 phototherapy
InactiveUS7427657B1Sufficient fluenceSufficient powerElectrotherapyPeptide/protein ingredientsLight treatmentUltraviolet
The present invention discloses novel sulfenate derivatives and their bioconjugates for phototherapy of tumors and other lesions. The sulfenates of the present invention are designed to absorb low-energy ultraviolet, visible, or near-infrared (NIR) region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The phototherapeutic effect is caused by direct interaction of free radicals, the reactive intermediate produced upon photofragmentation of the sulfenate moiety, with the tissue of interest.
Owner:MALLINCKRODT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![Formation of [2,2]paracyclophane and related compounds and methods for the formation of polymers from cyclophanes Formation of [2,2]paracyclophane and related compounds and methods for the formation of polymers from cyclophanes](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/4eb334cd-5ed6-4078-97fe-269a42ccd686/US08633289-20140121-D00000.png)
![Formation of [2,2]paracyclophane and related compounds and methods for the formation of polymers from cyclophanes Formation of [2,2]paracyclophane and related compounds and methods for the formation of polymers from cyclophanes](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/4eb334cd-5ed6-4078-97fe-269a42ccd686/US08633289-20140121-D00001.png)
![Formation of [2,2]paracyclophane and related compounds and methods for the formation of polymers from cyclophanes Formation of [2,2]paracyclophane and related compounds and methods for the formation of polymers from cyclophanes](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/4eb334cd-5ed6-4078-97fe-269a42ccd686/US08633289-20140121-D00002.png)



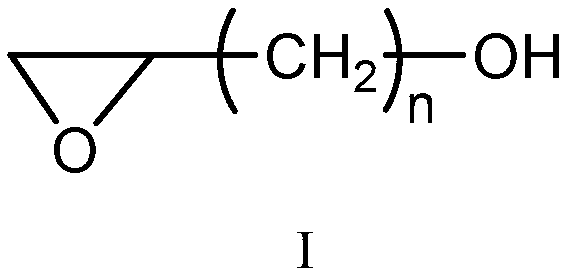


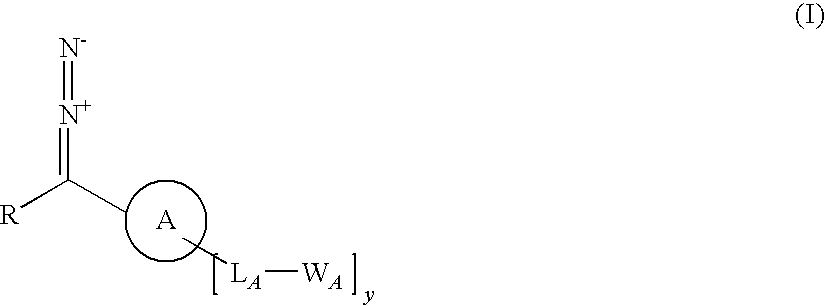
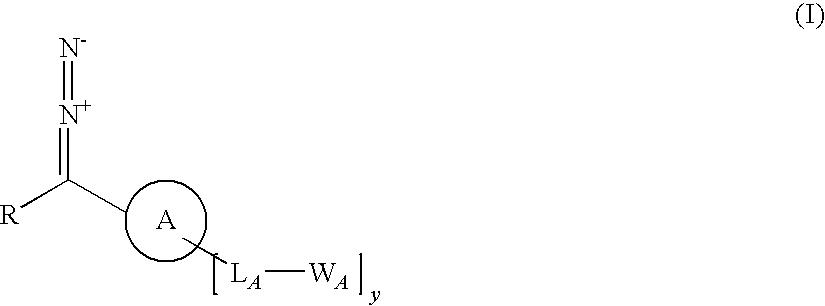
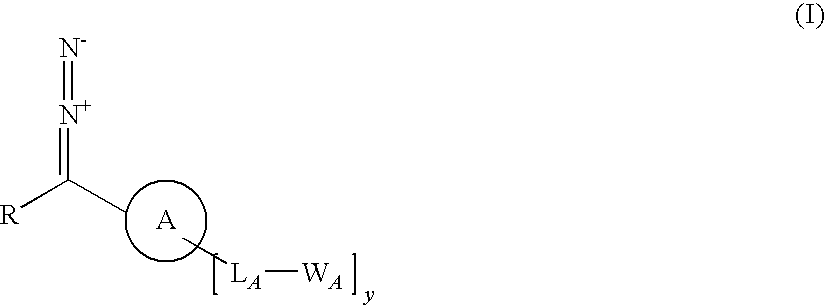
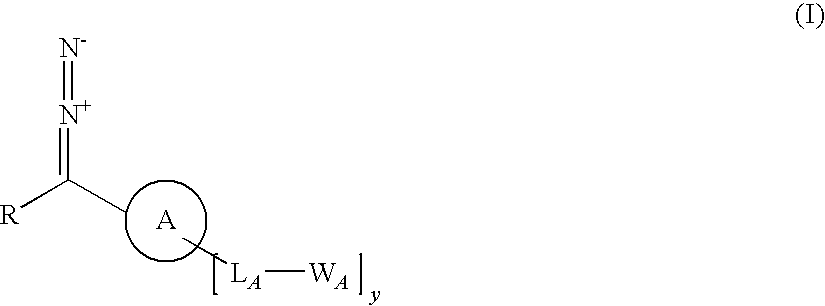

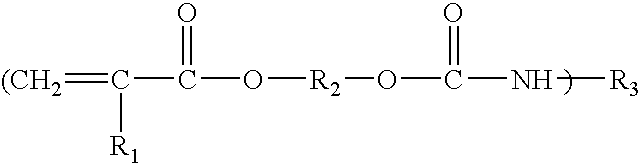
![Formation of [2,2]Paracyclophane and Related Compounds and Methods for the Formation of Polymers from Cyclophanes Formation of [2,2]Paracyclophane and Related Compounds and Methods for the Formation of Polymers from Cyclophanes](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/d1395aac-7e8f-4c9f-9836-6b6e7fde6659/US20130109827A1-20130502-D00001.png)
![Formation of [2,2]Paracyclophane and Related Compounds and Methods for the Formation of Polymers from Cyclophanes Formation of [2,2]Paracyclophane and Related Compounds and Methods for the Formation of Polymers from Cyclophanes](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/d1395aac-7e8f-4c9f-9836-6b6e7fde6659/US20130109827A1-20130502-D00002.png)
![Formation of [2,2]Paracyclophane and Related Compounds and Methods for the Formation of Polymers from Cyclophanes Formation of [2,2]Paracyclophane and Related Compounds and Methods for the Formation of Polymers from Cyclophanes](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/d1395aac-7e8f-4c9f-9836-6b6e7fde6659/US20130109827A1-20130502-C00001.png)