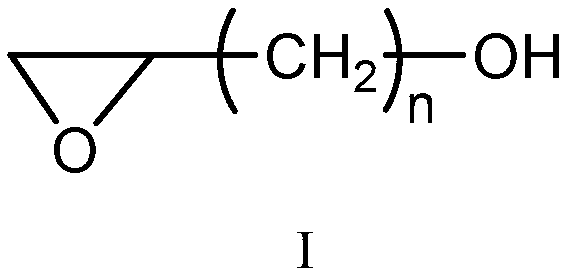Salt-free dyeing method for active dye
A salt-free dyeing and reactive dye technology, applied in the direction of dyeing, textile and papermaking, fiber processing, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the fixation and color fastness of reactive dyes, affecting the effect of salt-free dyeing, and impermeability of dyes. The effect of reducing the residual amount, shortening the reaction time, and improving the color yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] (1) Cotton fiber modification process:
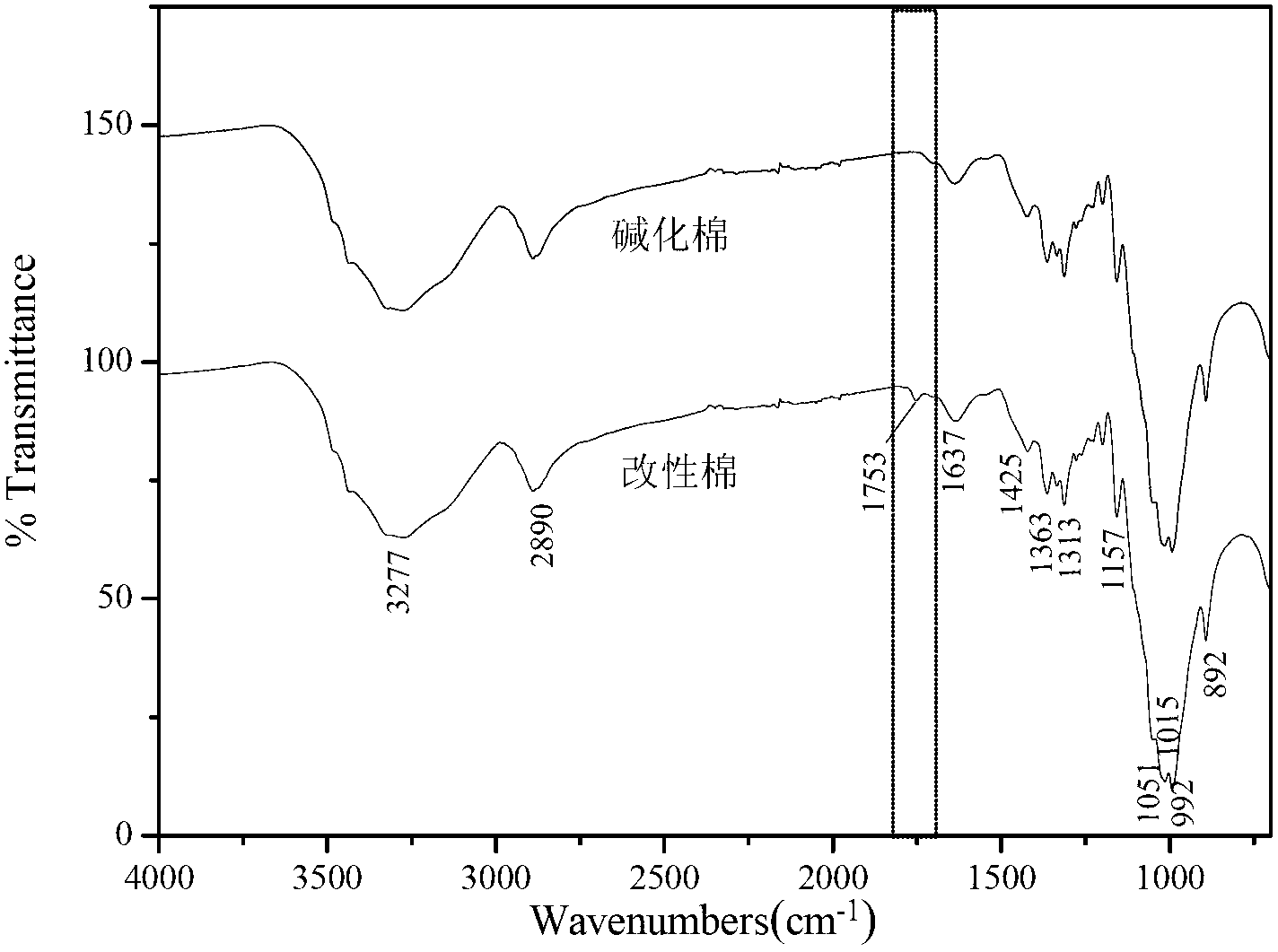
[0055] ① Put the cotton fiber in 20% caustic soda solution, bath ratio 1:30, and treat it at room temperature for 30 minutes; (see the infrared spectrum of alkalized cotton fiber figure 1 );
[0056] ②Using the soaking process, the alkalized cotton fiber is soaked in 8% hydroxyl-containing active intermediate 1 # Aqueous solution, bath ratio 1:10, stirred and reacted at 70°C for 30 minutes, then taken out, rinsed in water after taking out;
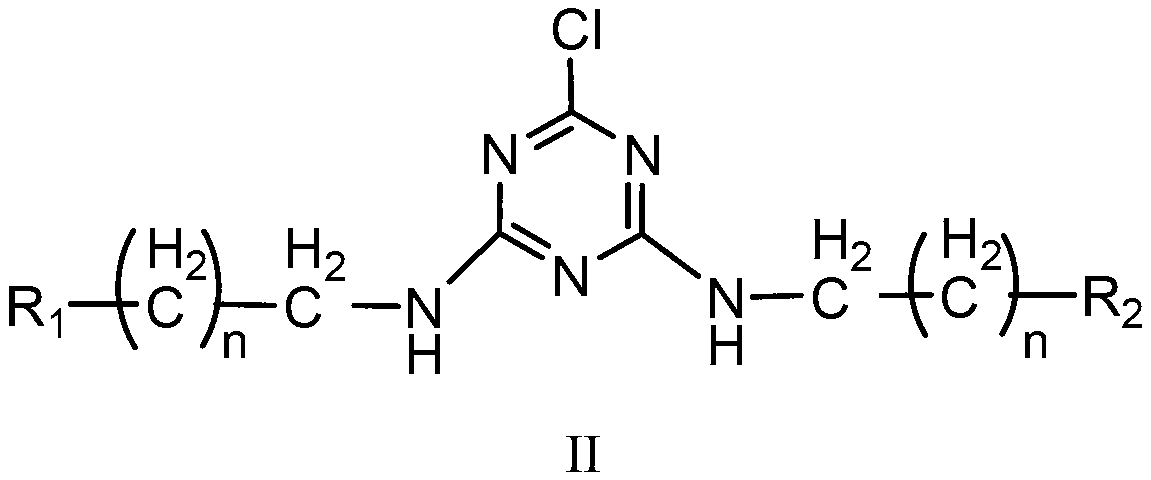
[0057] 3. Step 2. Gained modified cotton fiber adopts 6% quaternary ammonium salt 8 containing carboxylic acid groups # , 5% dicyandiamide and 2% zinc nitrate mixed aqueous solution for modification treatment, the treatment bath ratio is 1:10, first, adopt the padding process, pad the modified cotton fiber in the above mixed solution twice, roll with liquid The rate is 80%. Then the treated cotton fibers were baked and reacted at 120°C for 3 minutes, rinsed and ready to be dyed. (Infrare...
Embodiment 2
[0066] (1) Cotton fiber modification process:
[0067] Same as Example 1.
[0068] (2) Cotton fiber dyeing process:
[0069] The modified cotton fiber obtained in (1) is padded twice in 2% reactive yellow M-3RE solution, the liquid retention rate is 80%, and the dyed sample is dried; then in 2% sodium carbonate (bath ratio 1:10) Padding once, with a liquid retention rate of 80%, drying the dyed cotton at 70°C, sealing, steaming for 10 minutes, and then washing with water until neutral.
[0070] (3) Soaping process:
[0071] Same as Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0075] (1) Cotton fiber modification process:
[0076] Same as Example 1.
[0077] (2) Cotton fiber dyeing process:
[0078] The modified cotton fiber was soaked and rolled twice in 2% active yellow M-3RE solution, with a liquid retention rate of 80%, and the dyed sample was dried; then in lye solution of 2% sodium carbonate and 0.3% sodium hydroxide ( Liquor ratio 1:10) padding once, liquid retention rate 80%, seal the dyed cotton, short wet steam for 30s, take it out and wash with water until neutral.
[0079] (3) Soaping process:
[0080] Same as Example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com