Patents
Literature
2191results about "Applying solid insulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
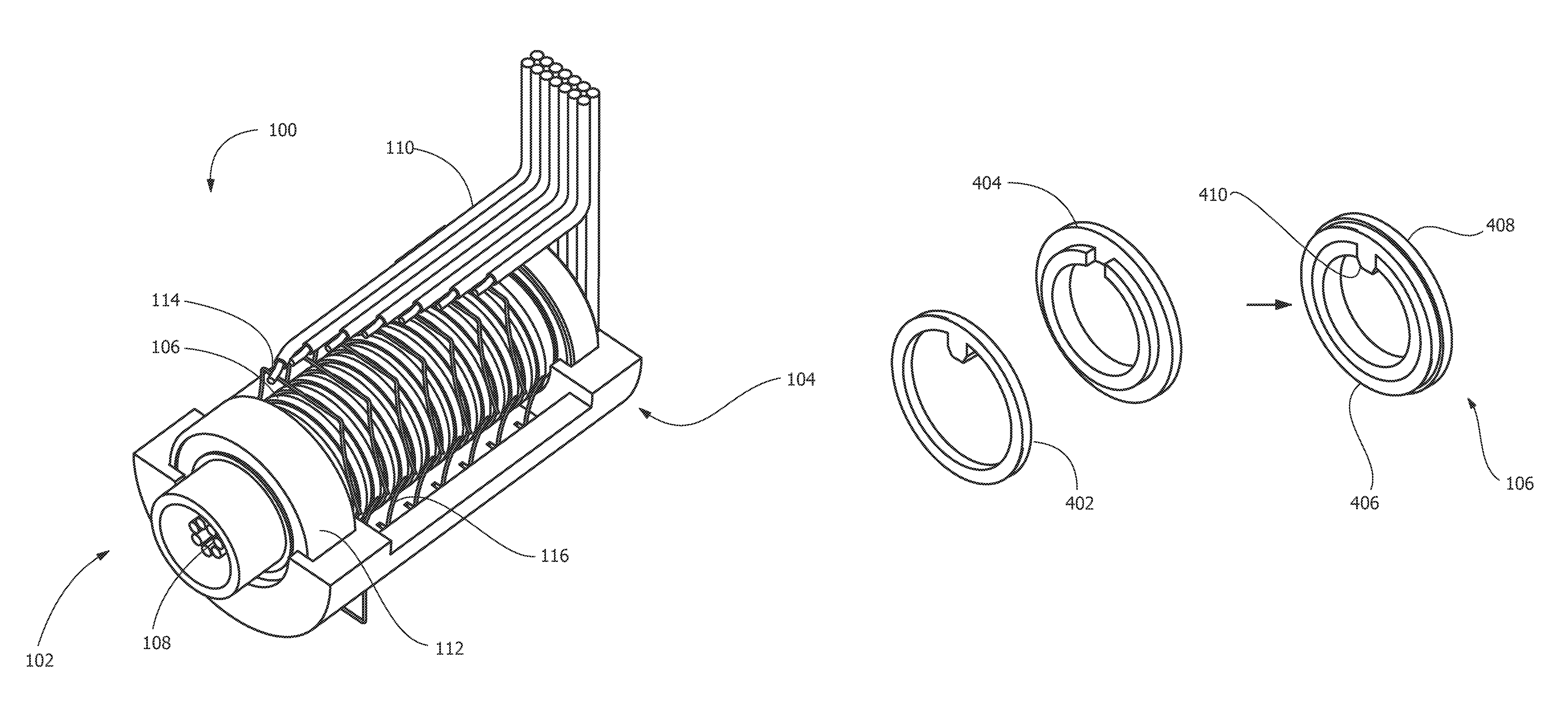
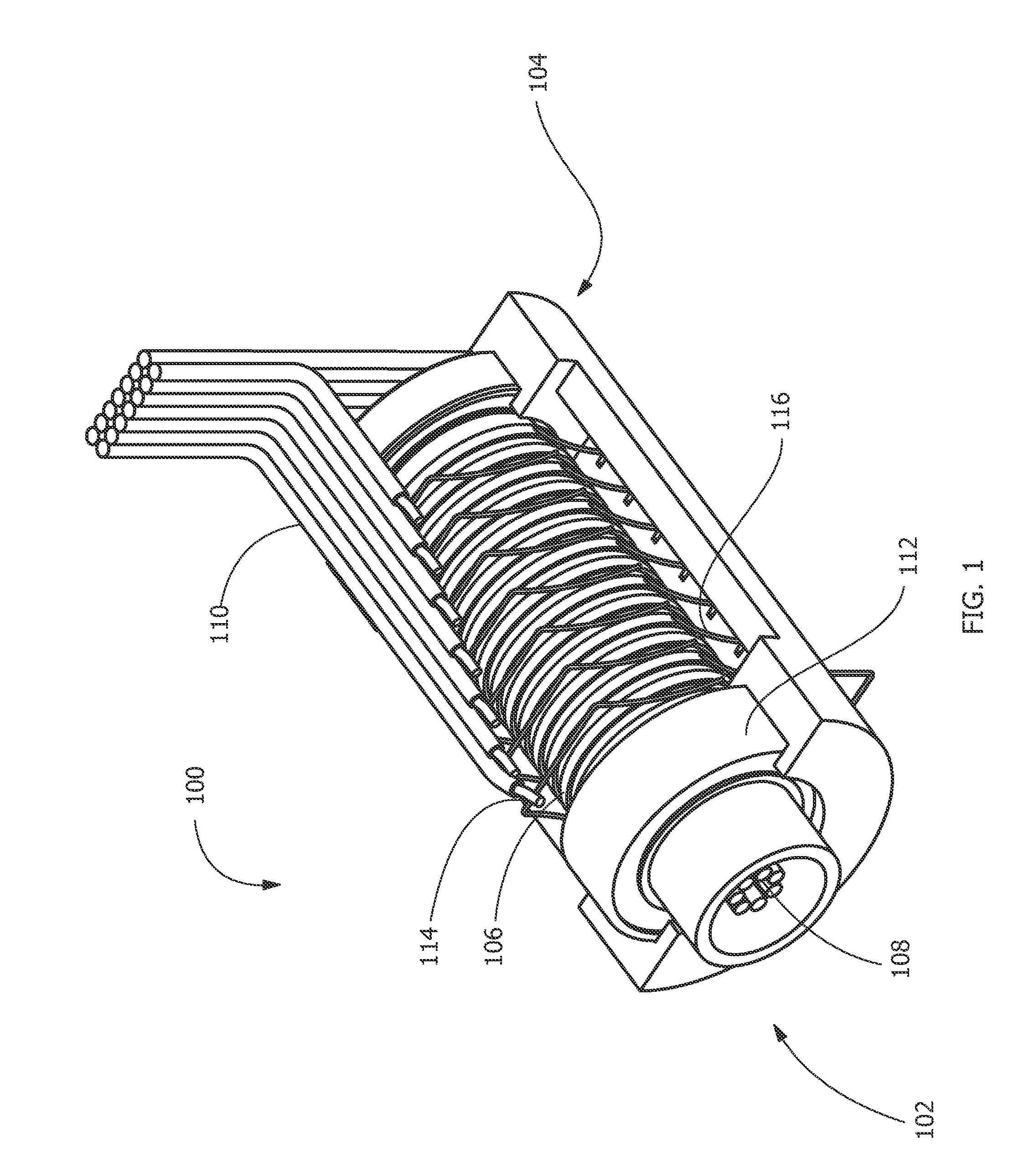
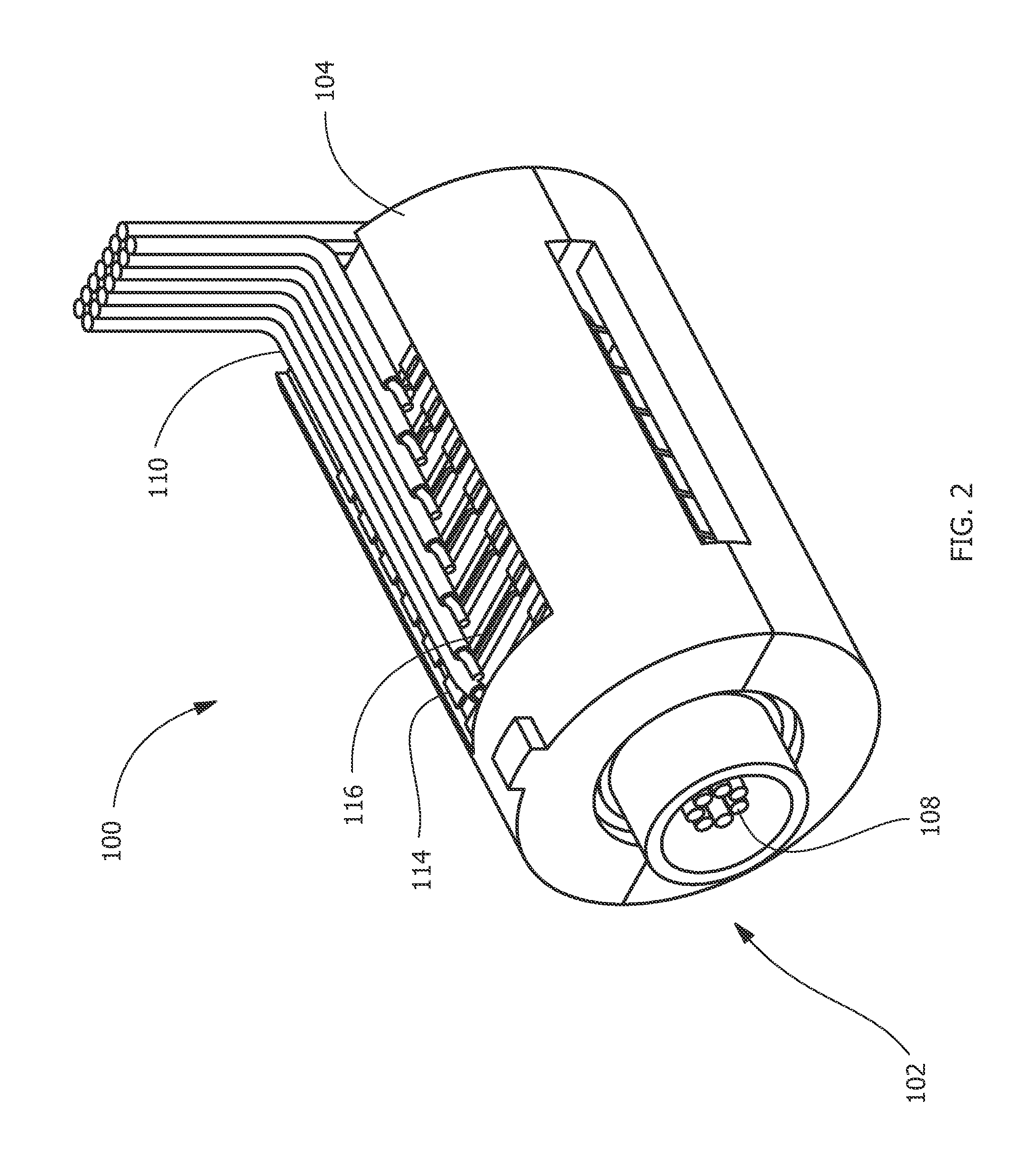
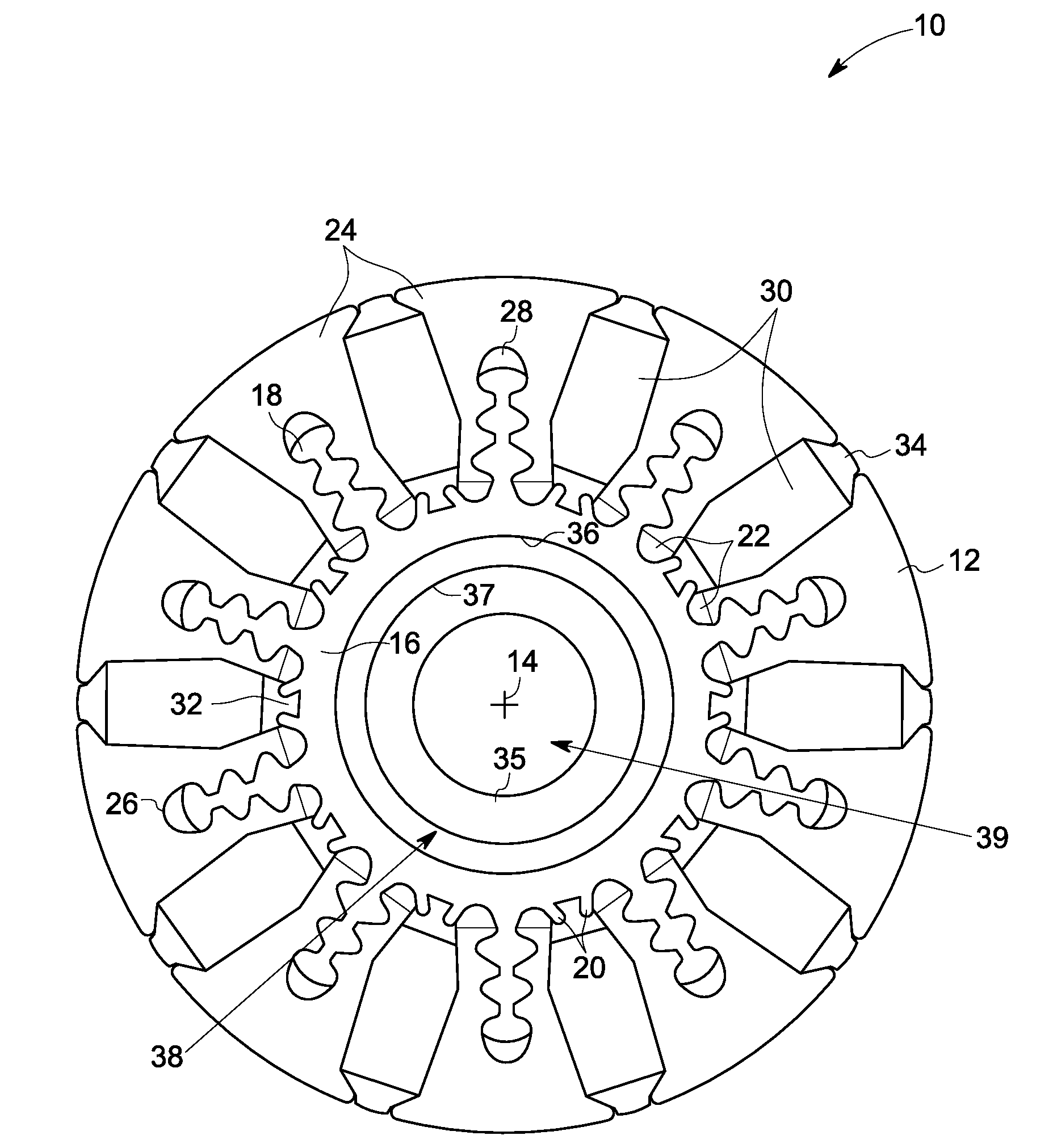
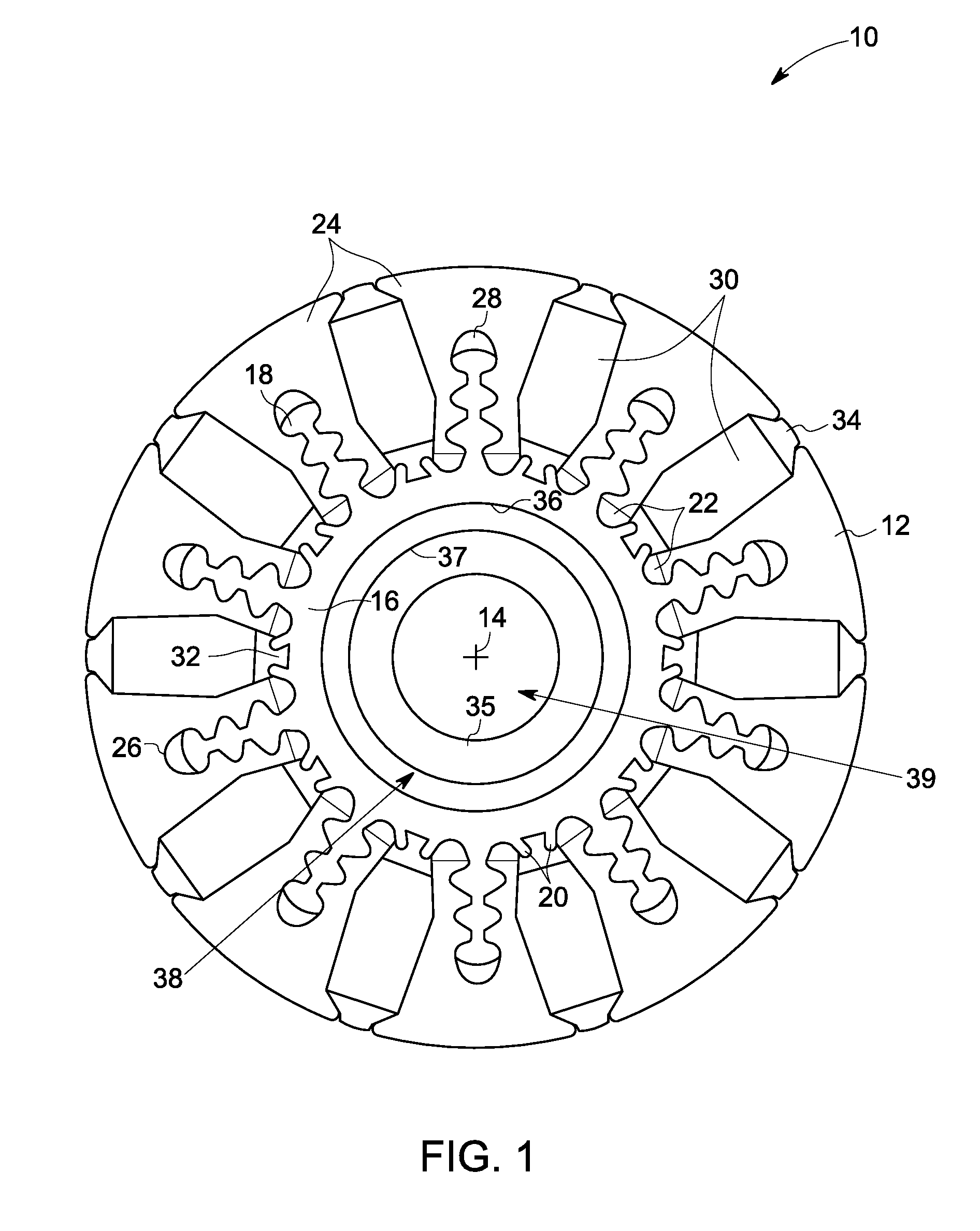
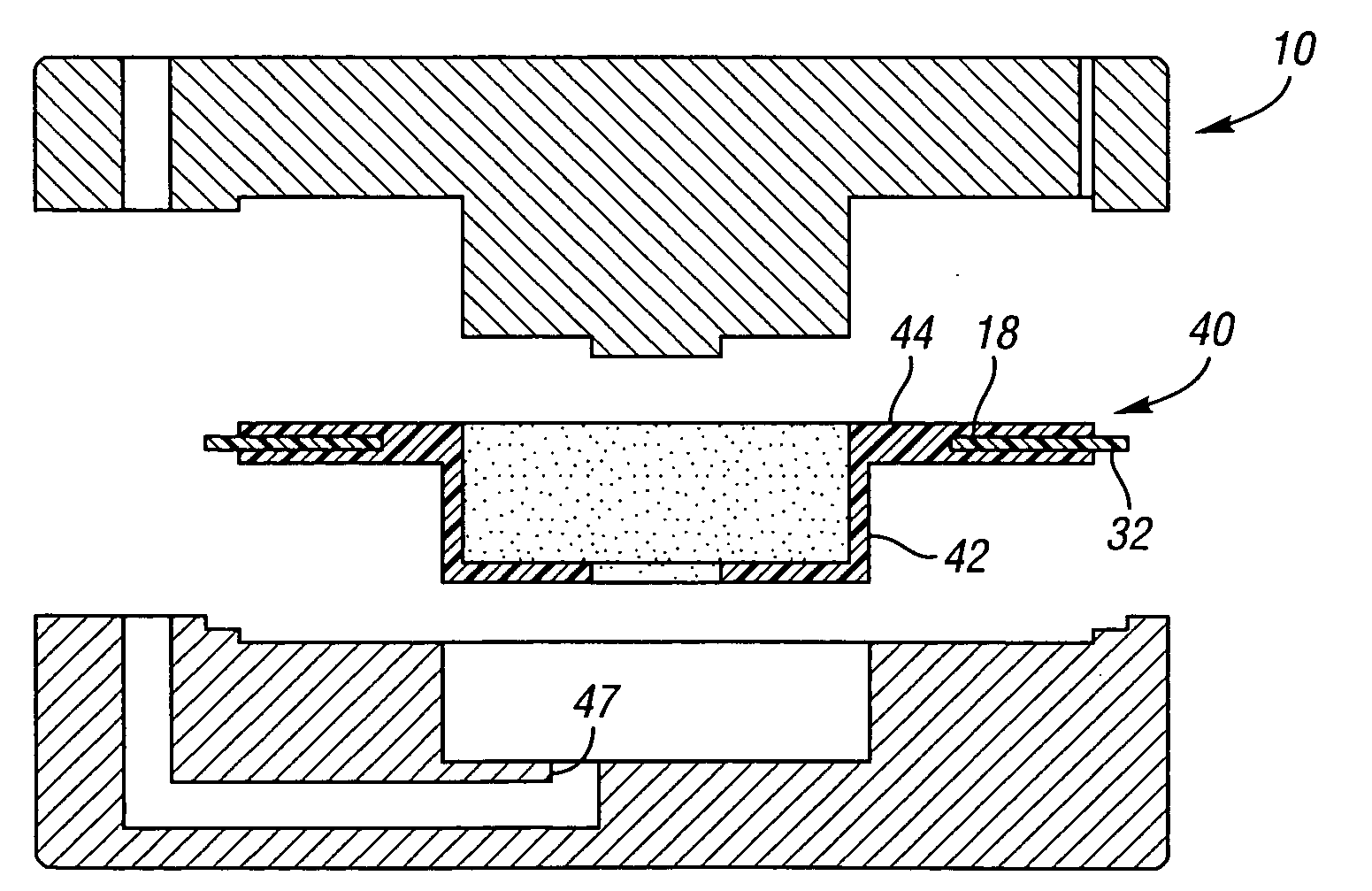
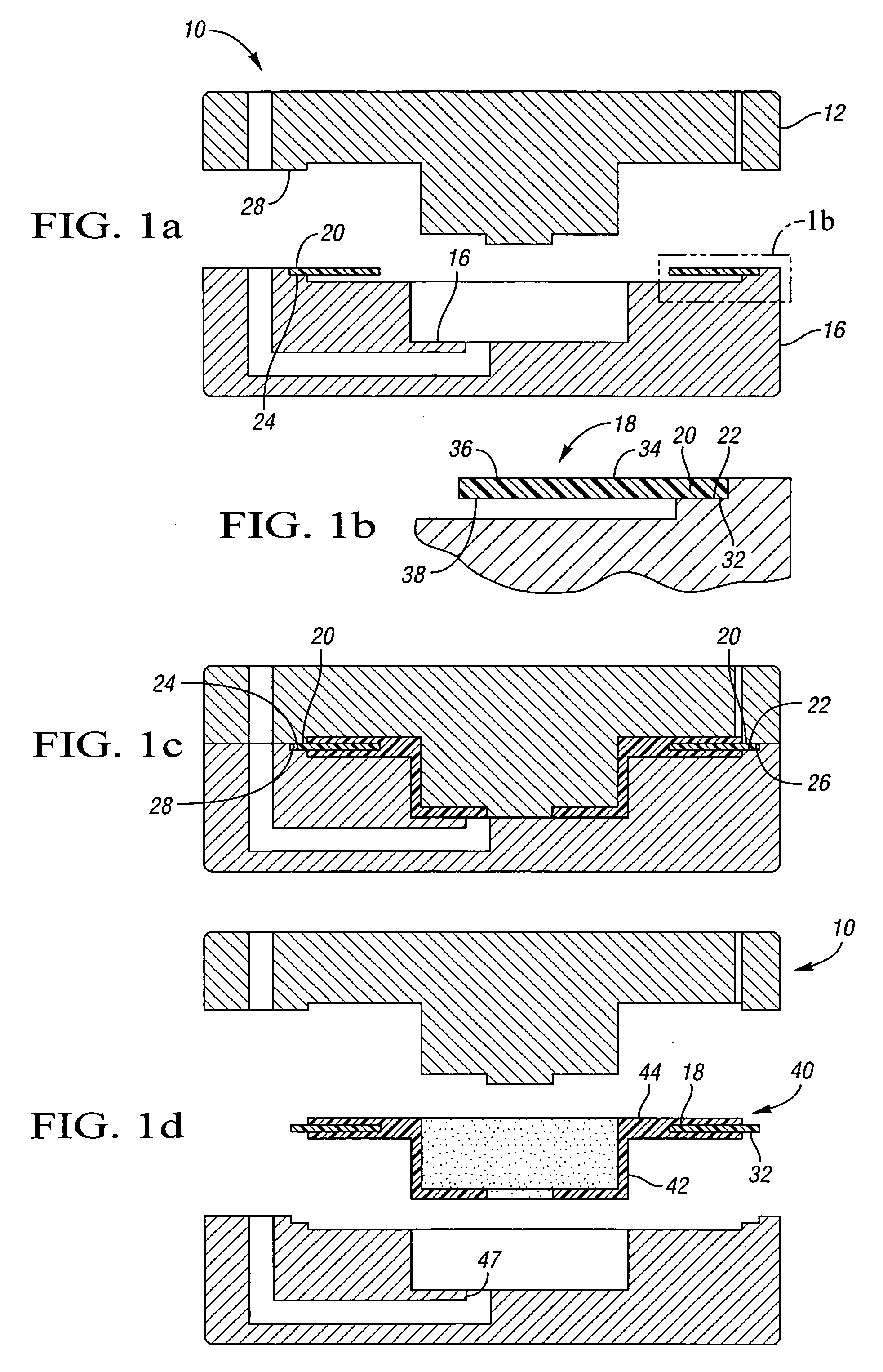
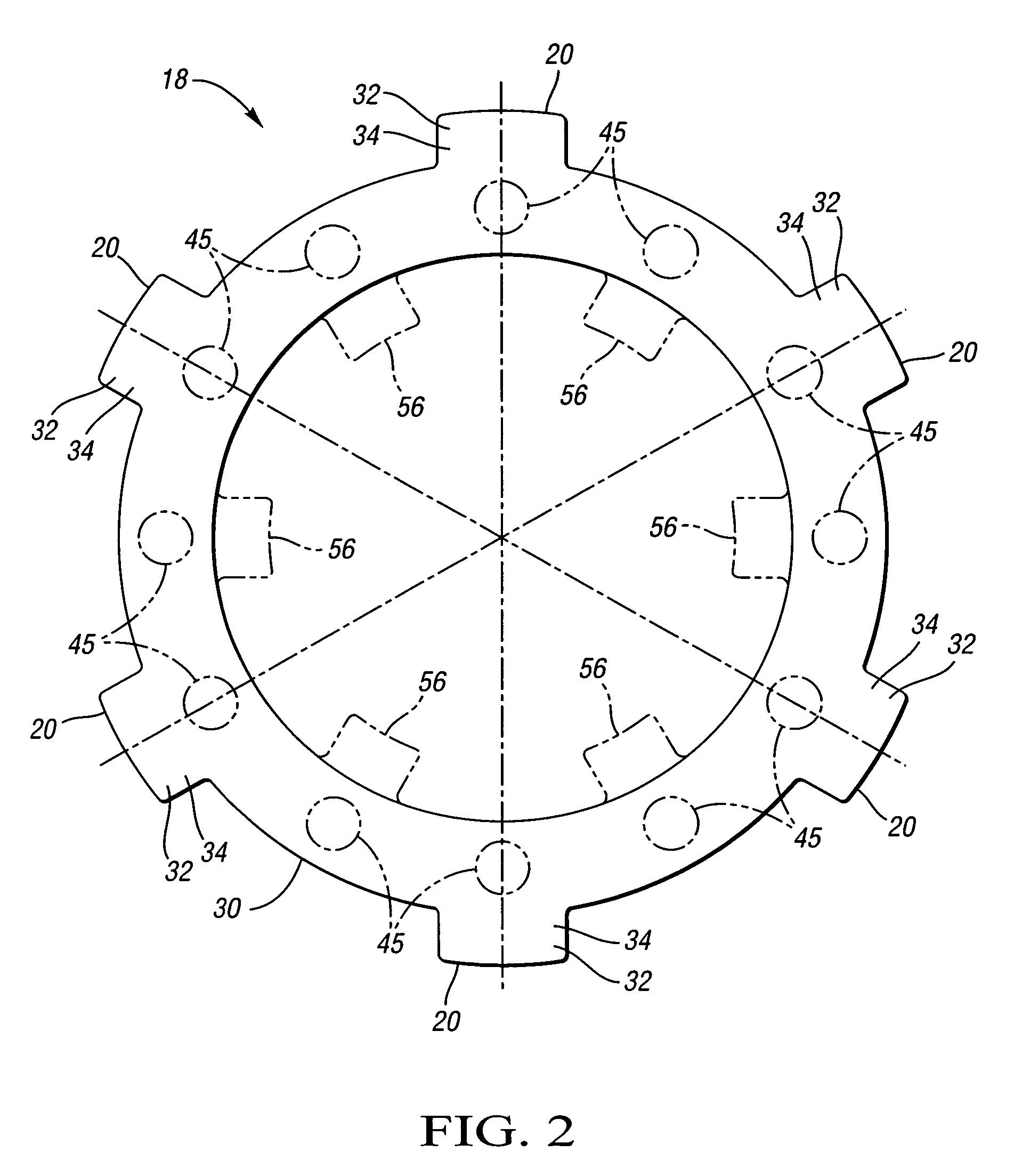
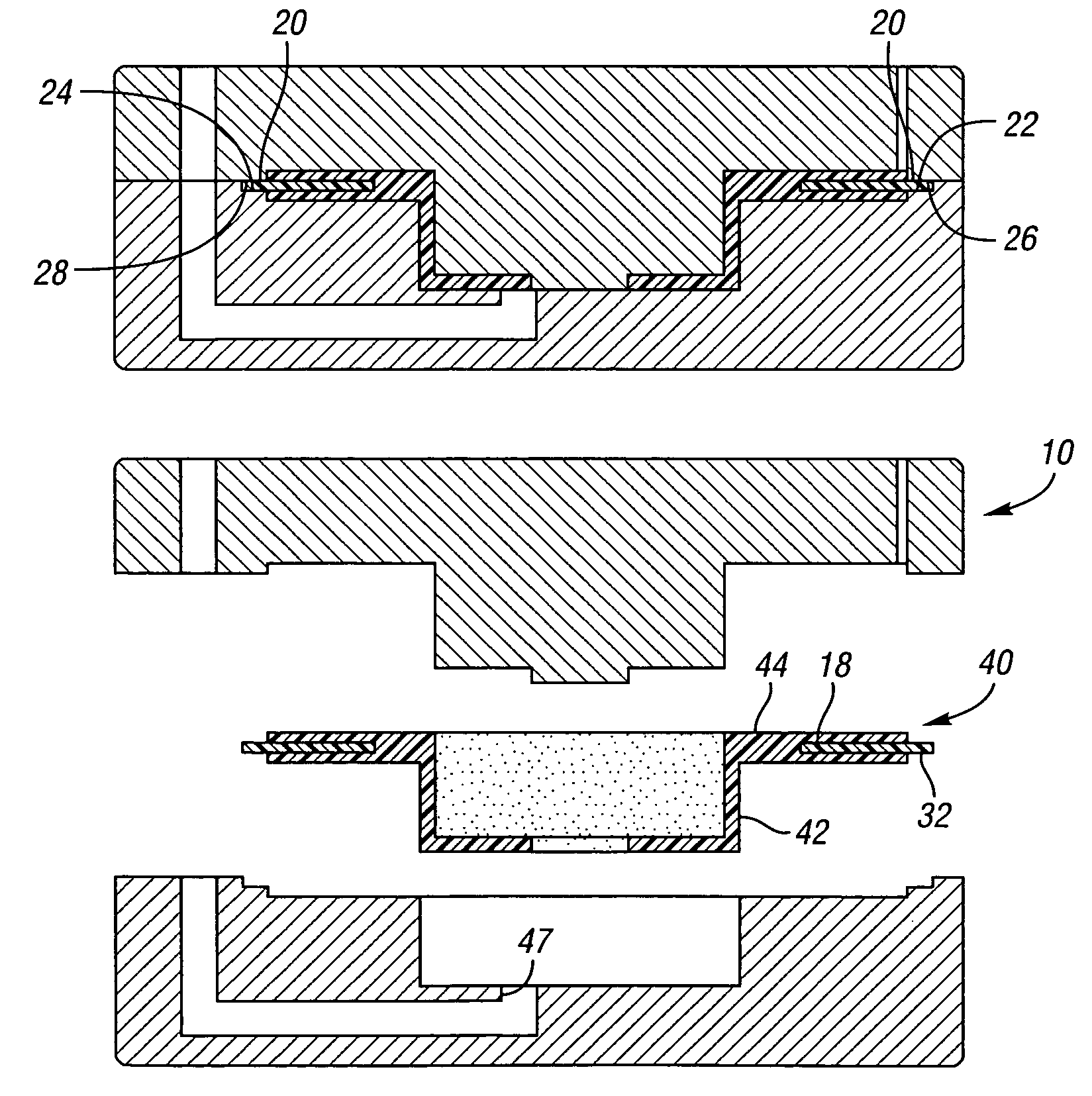
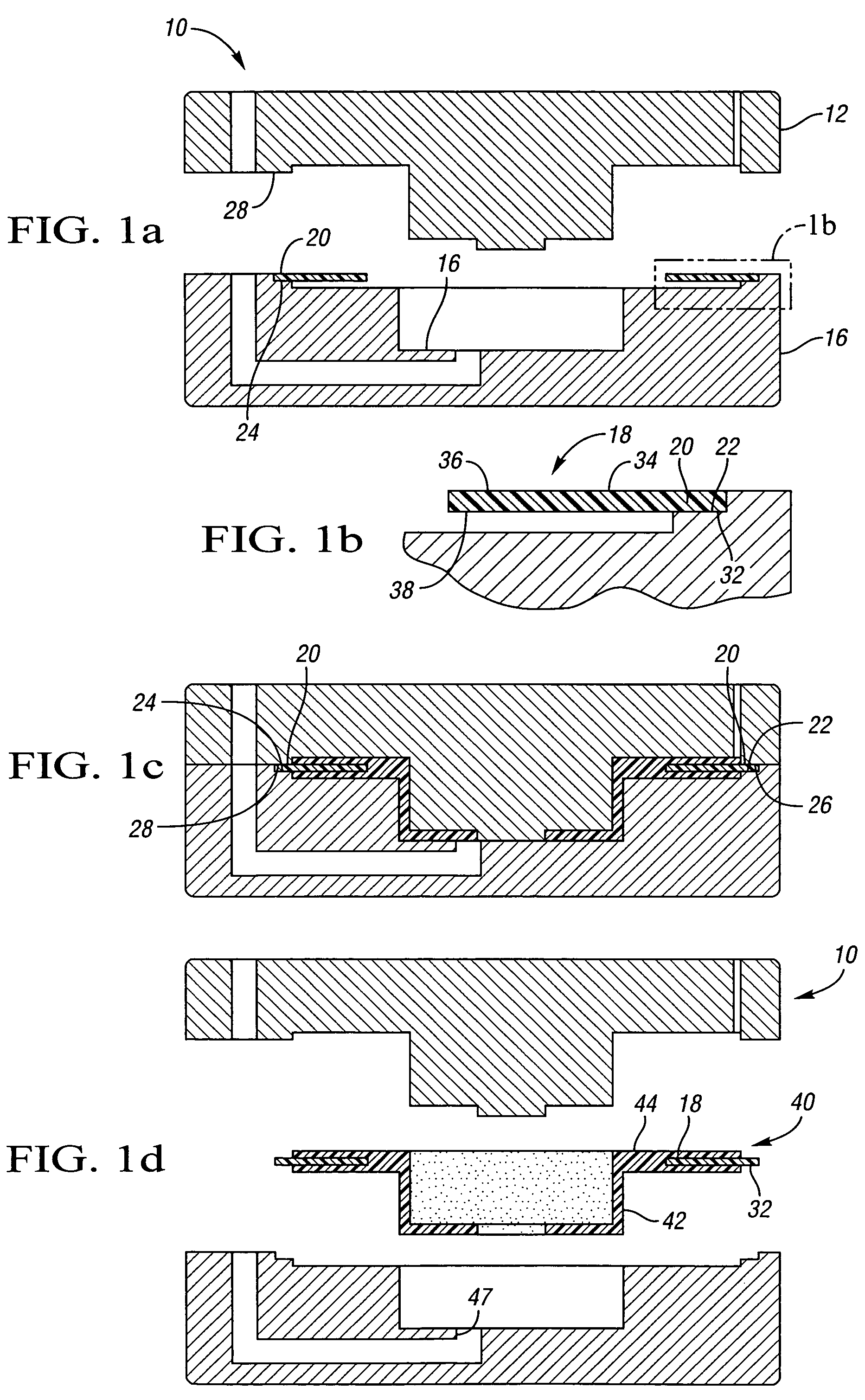
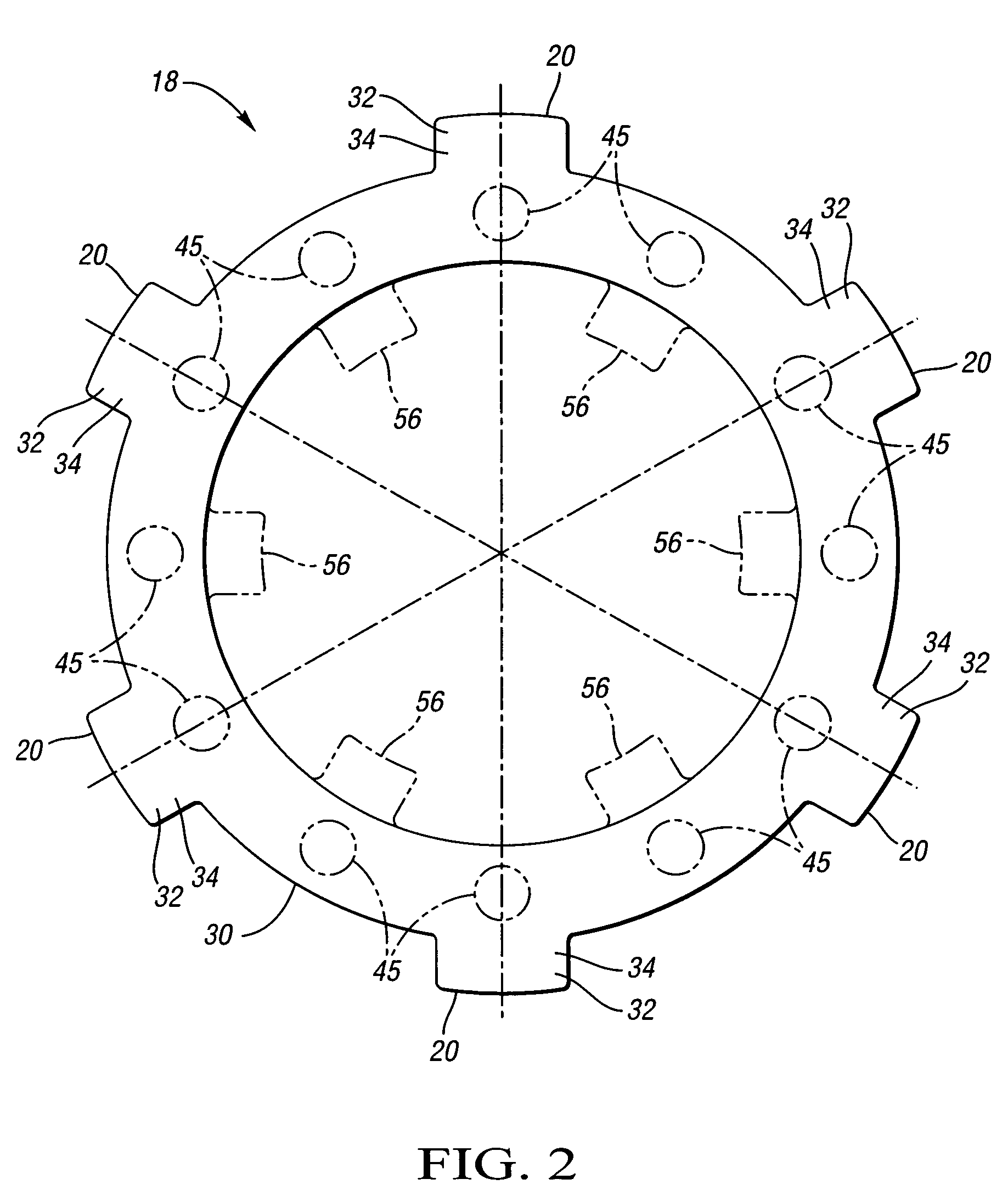
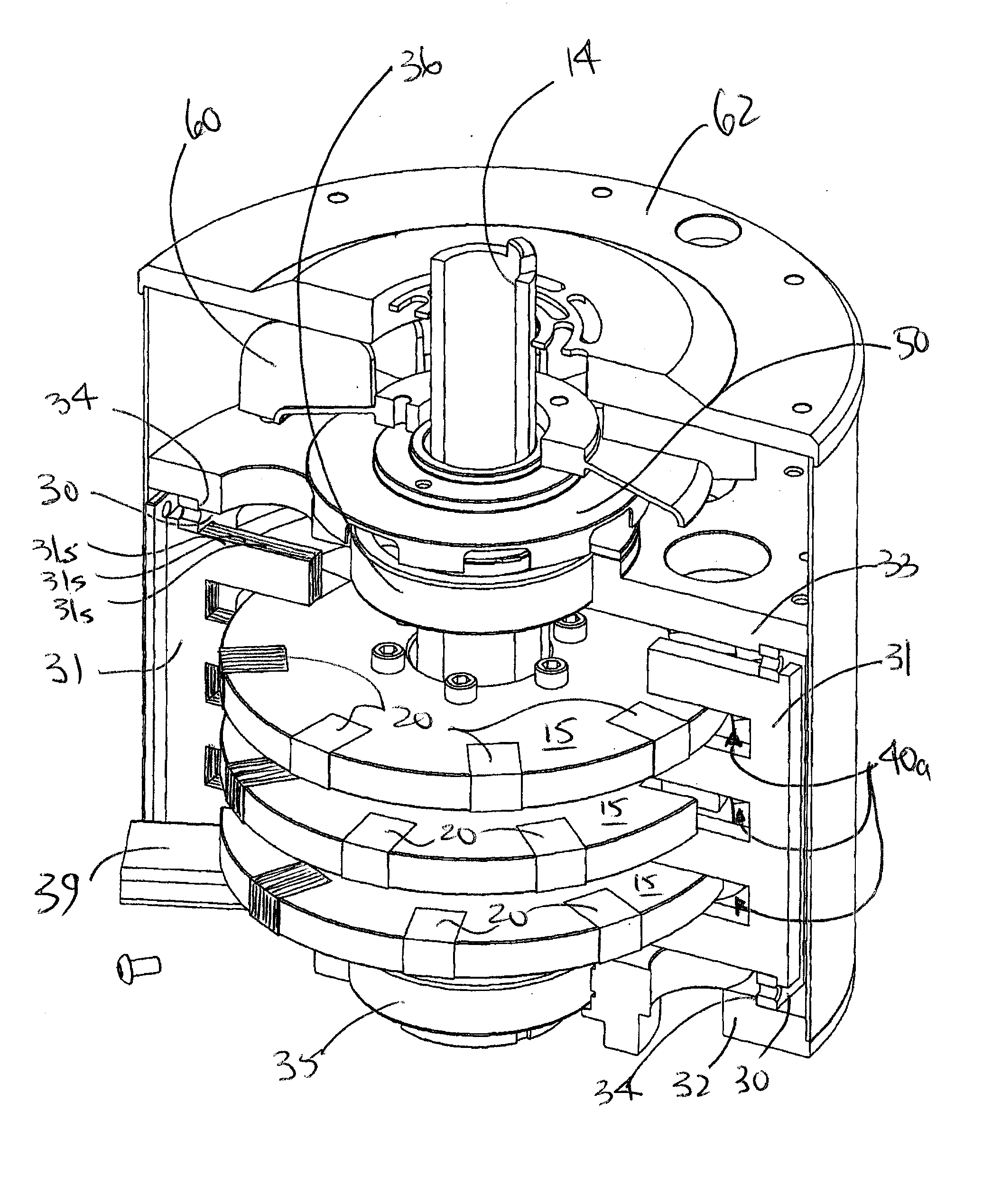
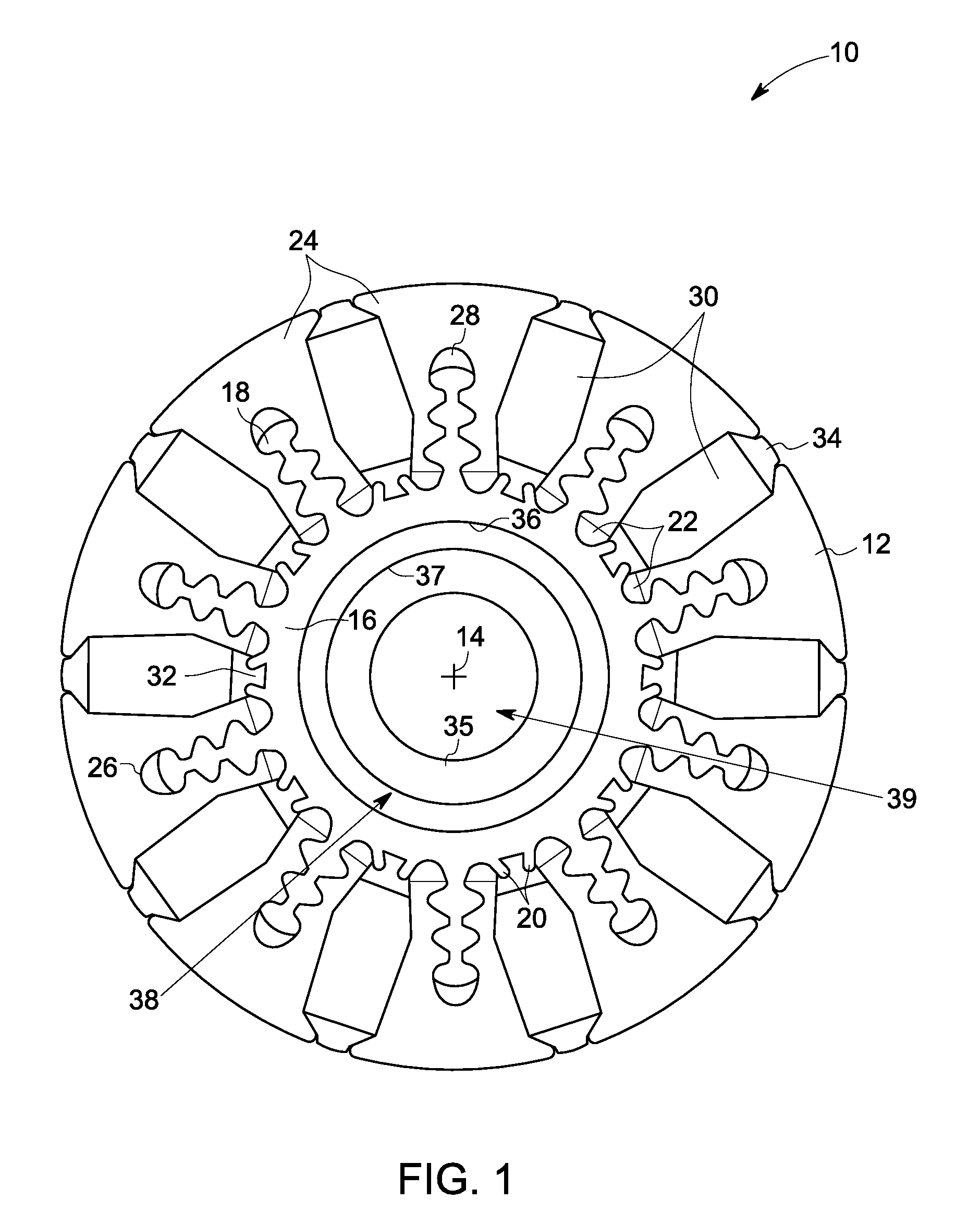
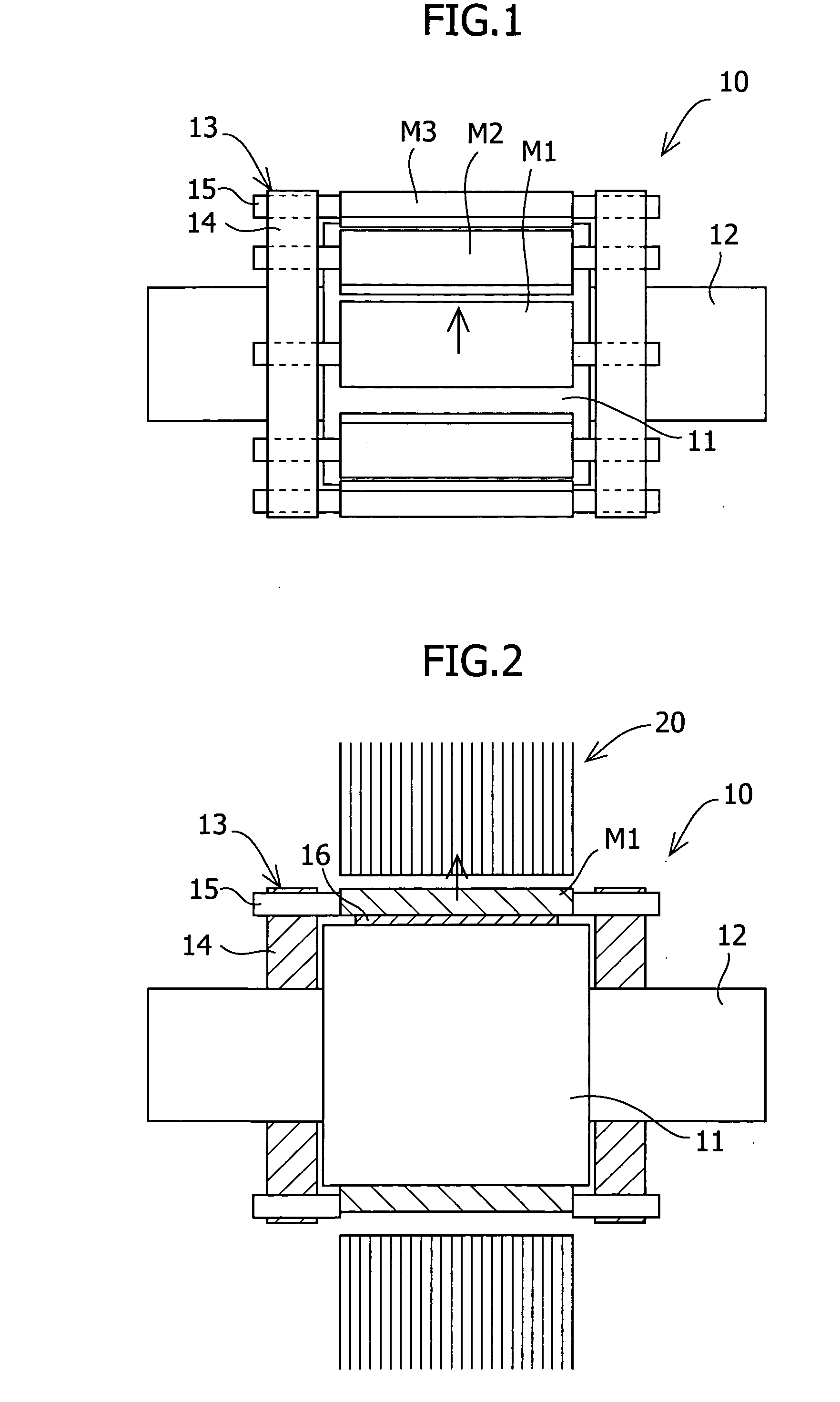
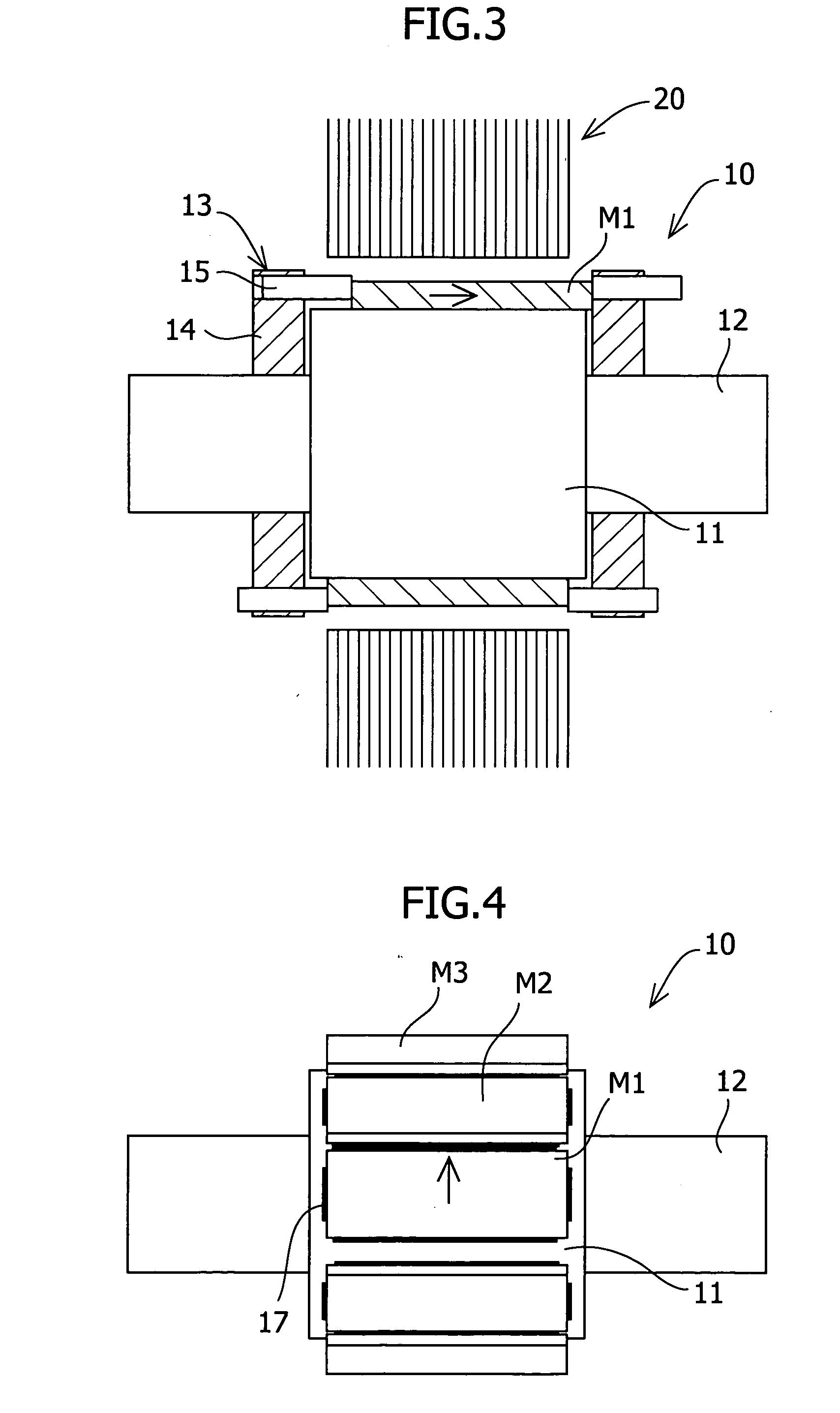
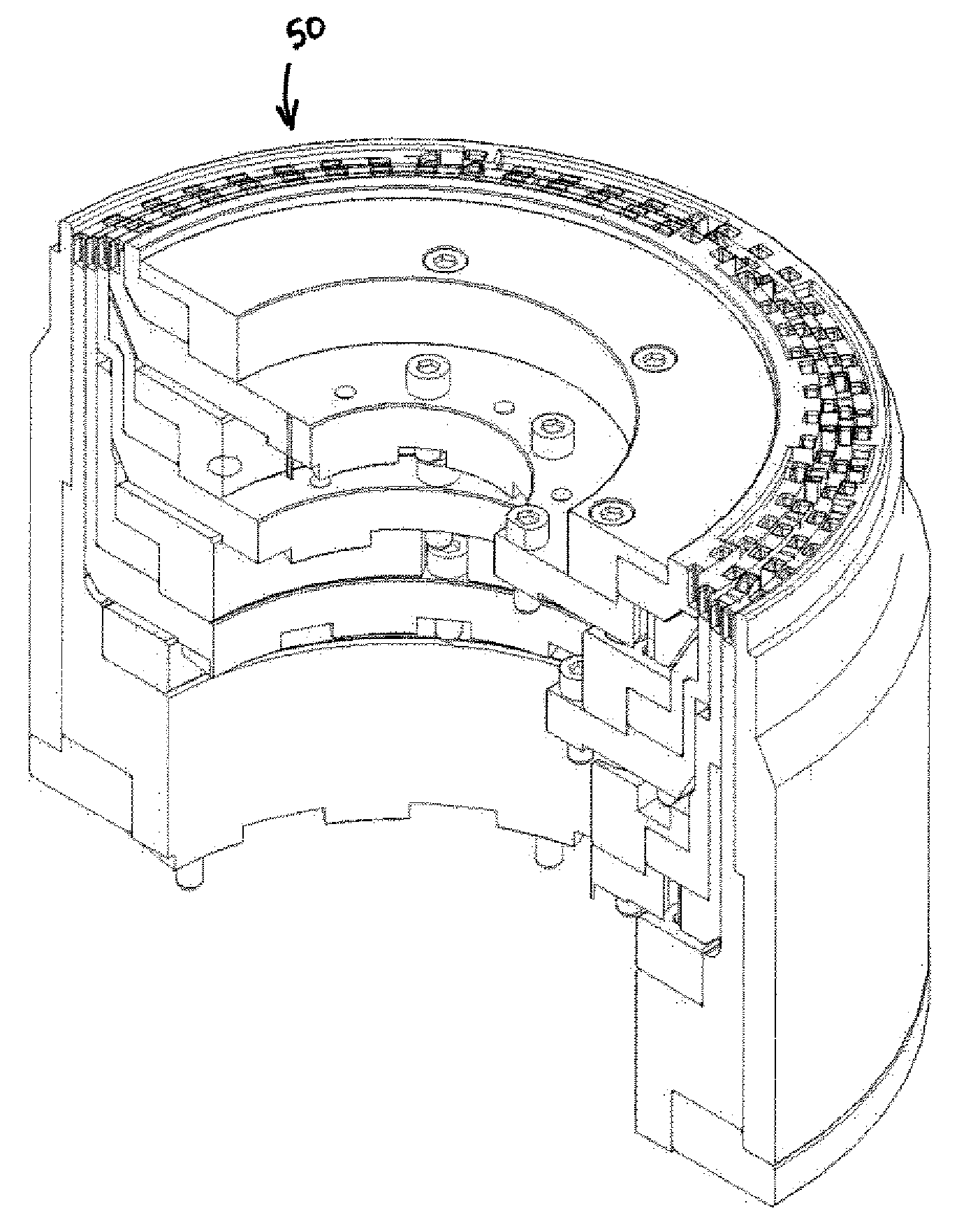
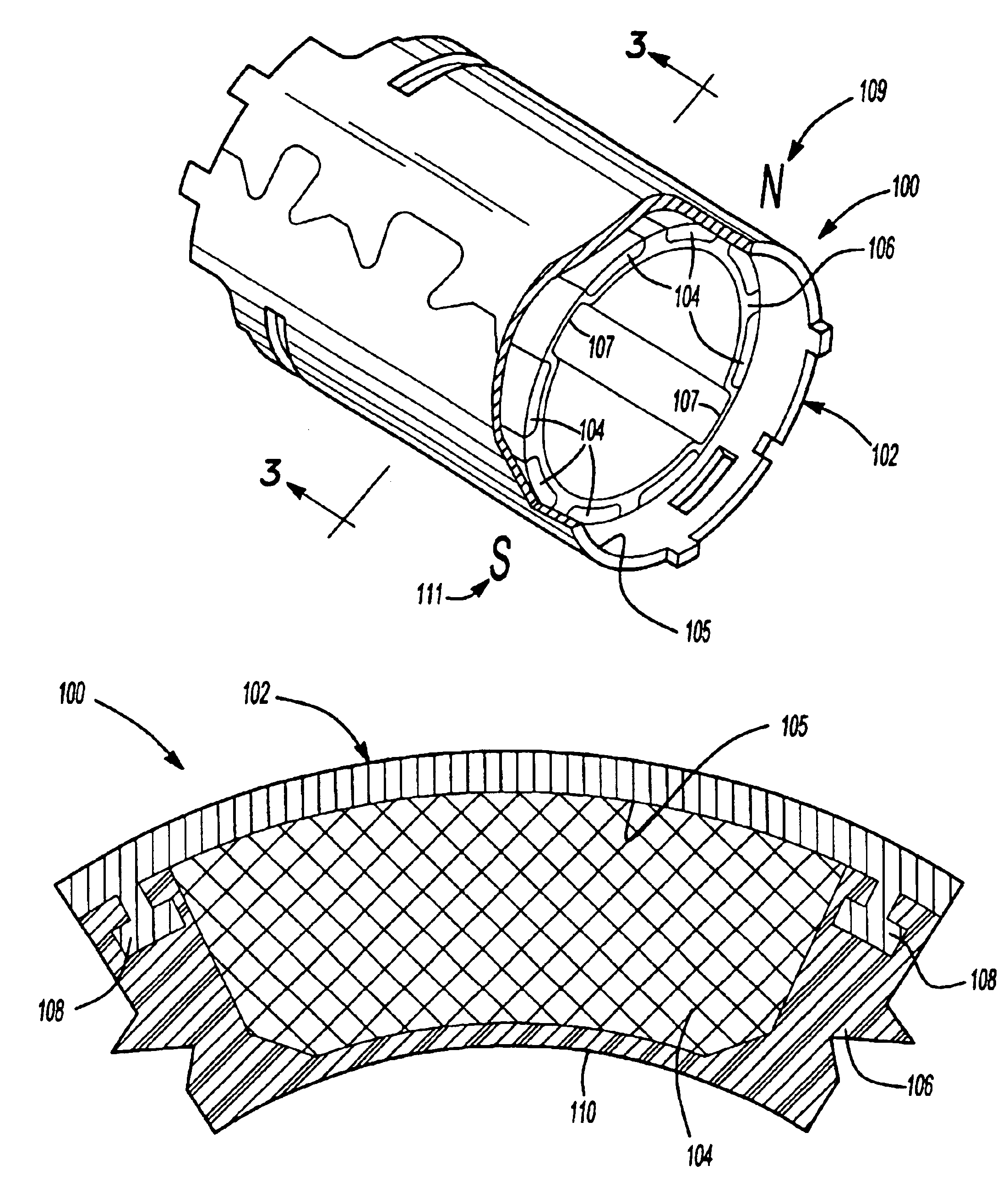
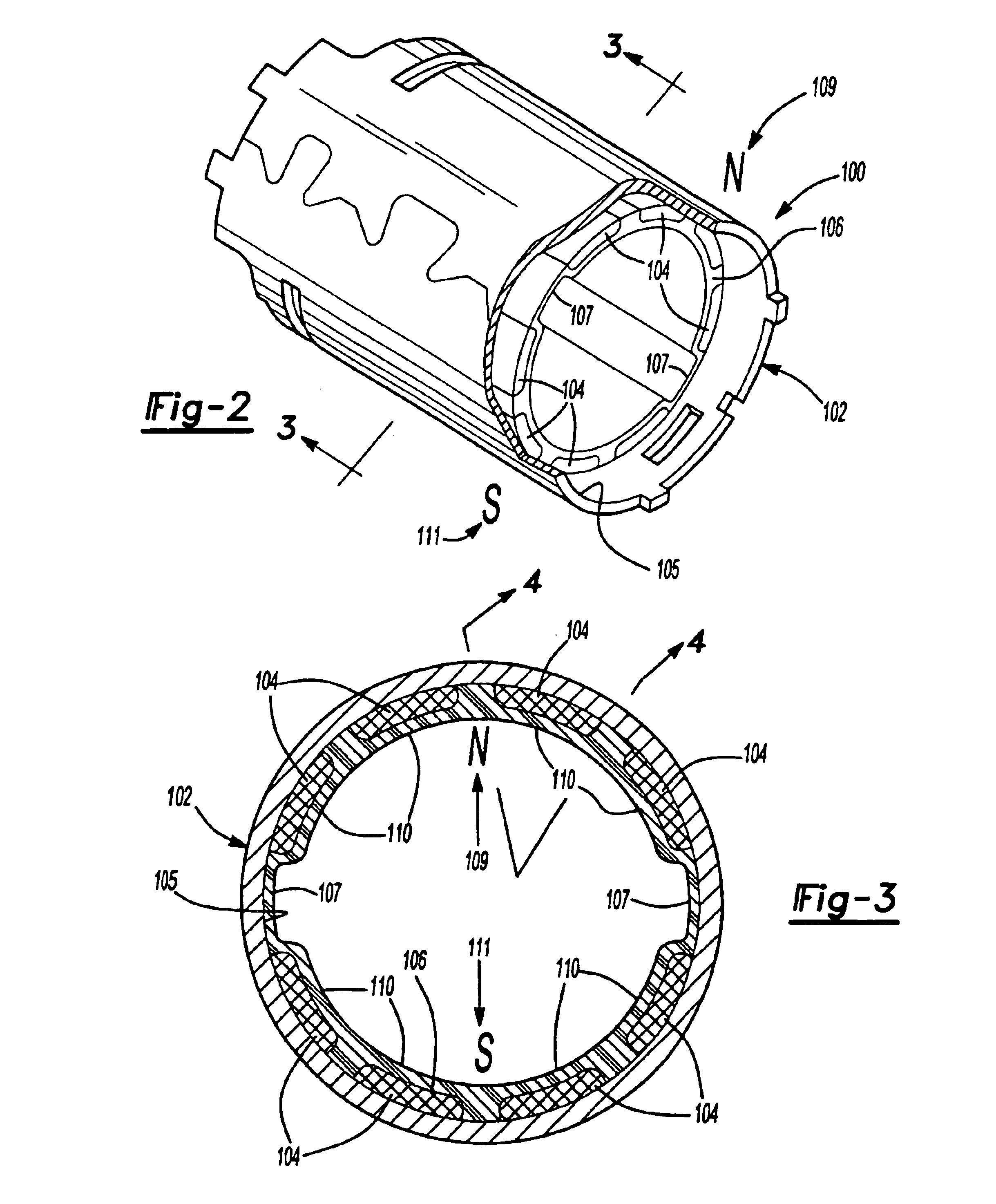
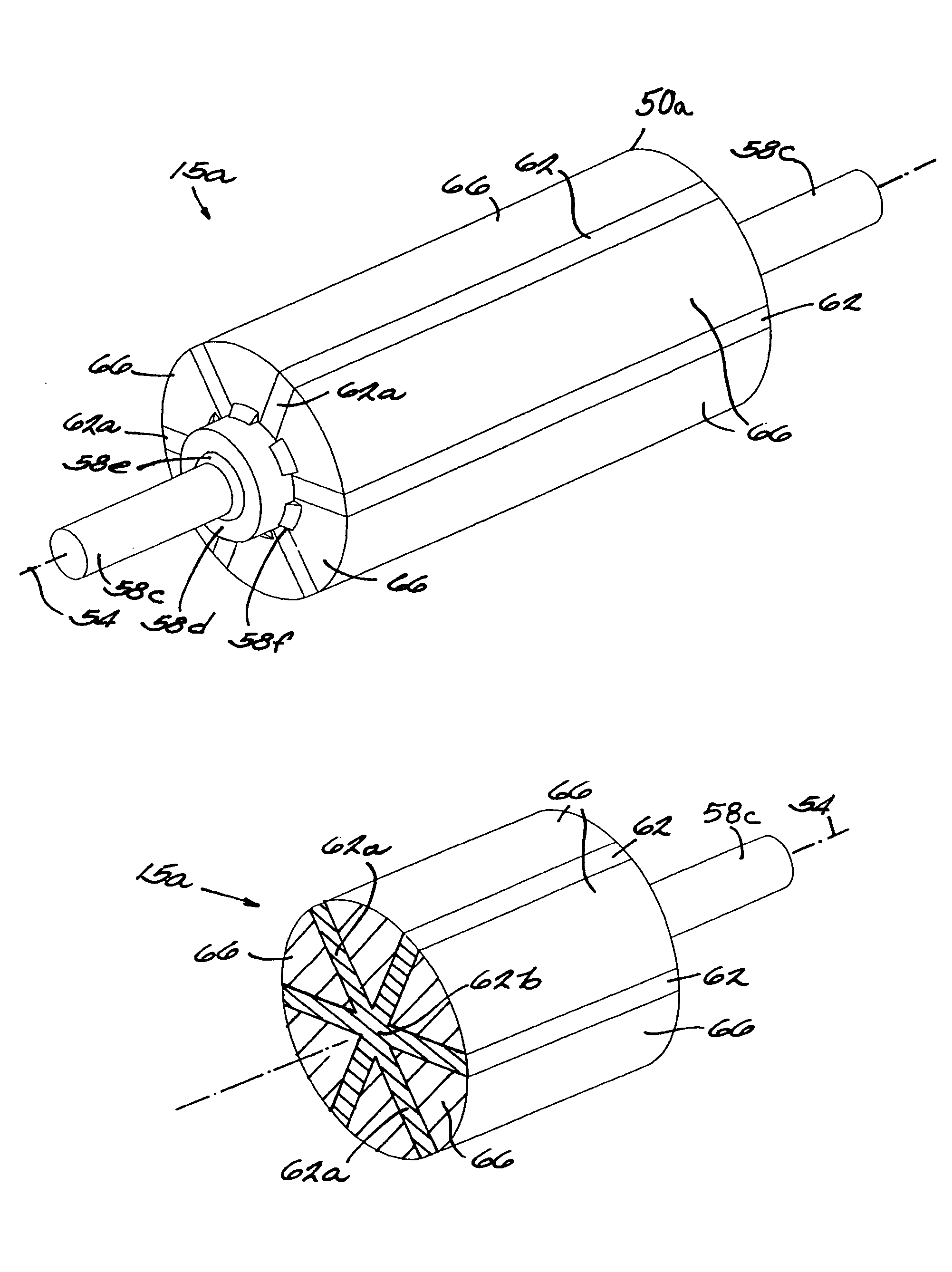
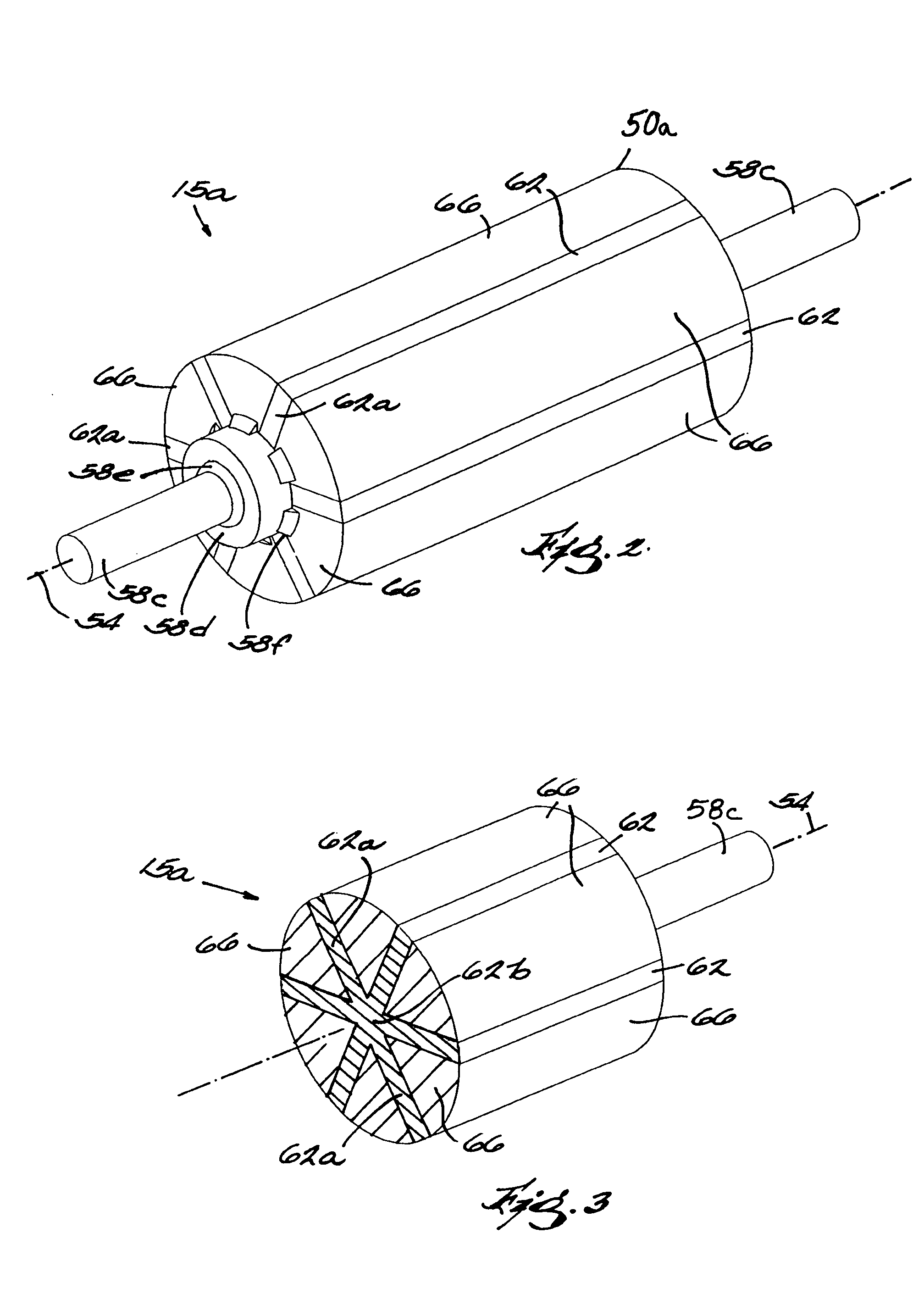
Method of fabricating a slip ring component
A process of fabricating a slip ring component, a slip ring component, and a slip ring assembly are disclosed. The process includes forming a first shot, forming a second shot, and immersion bathing the first shot and the second shot. The immersion bathing applies an electrically conductive plating to exposed surfaces of the second shot.
Owner:TYCO ELECTRONICS LOGISTICS AG (CH)
Magnetically-levitated blood pump with optimization method enabling miniaturization
ActiveUS20110237863A1Quality improvementReduce stiffnessControl devicesBlood pumpsBlood pumpMiniaturization
A magnetically-levitated blood pump with an optimization method that enables miniaturization and supercritical operation. The blood pump includes an optimized annular blood gap that increases blood flow and also provides a reduction in bearing stiffness among the permanent magnet bearings. Sensors are configured and placed optimally to provide space savings for the motor and magnet sections of the blood pump. Rotor mass is increased by providing permanent magnet placement deep within the rotor enabled by a draw rod configuration.
Owner:WORLD HEART +1
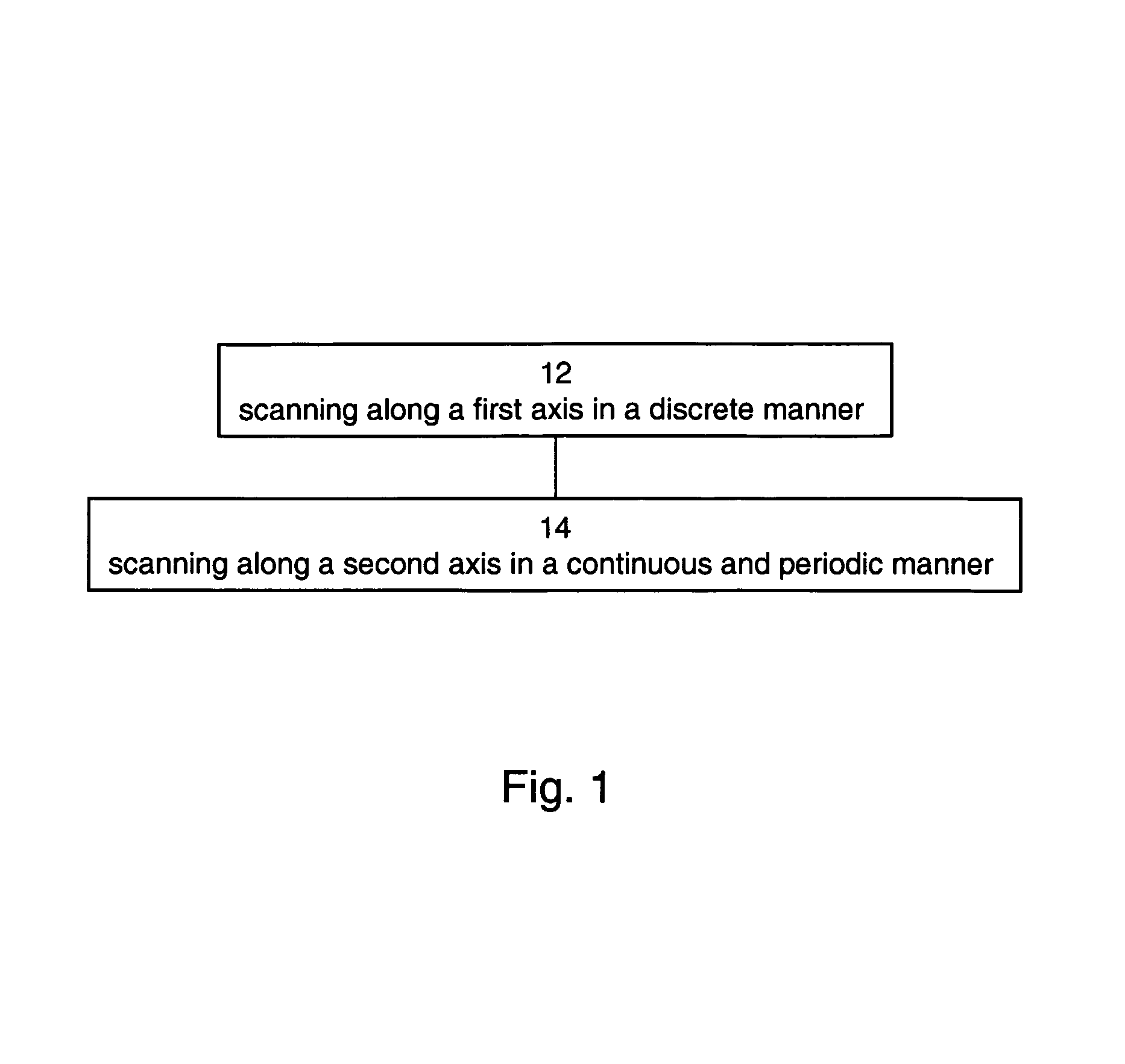
Method and device for scanning light
ActiveUS7952781B2Minimize moment-of-inertiaImprove reflectivityTelevision system scanning detailsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesLight beamPhysics
A method of scanning a light beam is disclosed. The method comprises scanning the light beam along a first axis and scanning the light beam along a second axis, such that a functional dependence of the scanning along the first axis is substantially a step-wave, and a functional dependence of the scanning along the second axis is other than a step-wave.
Owner:APPLE INC
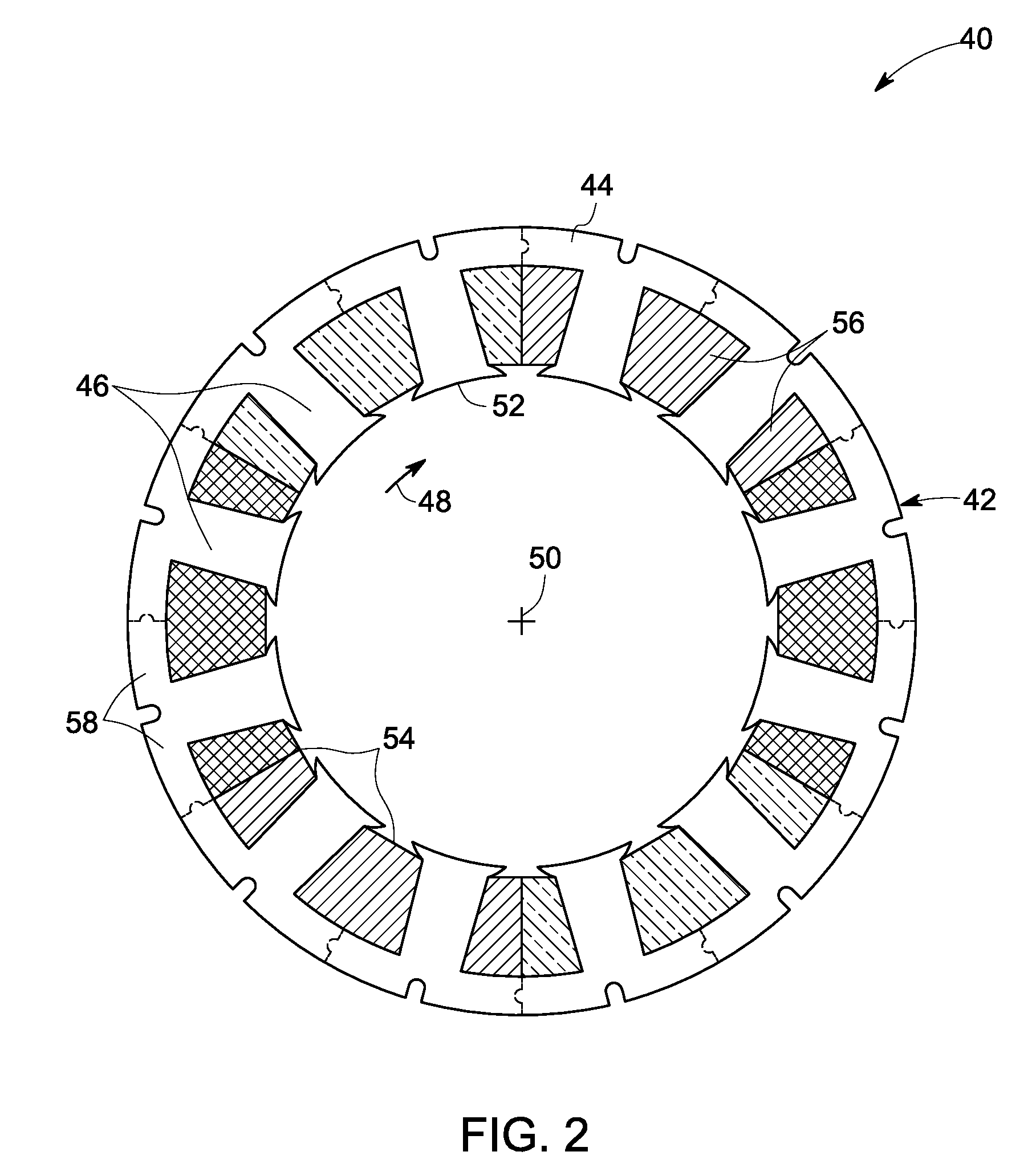
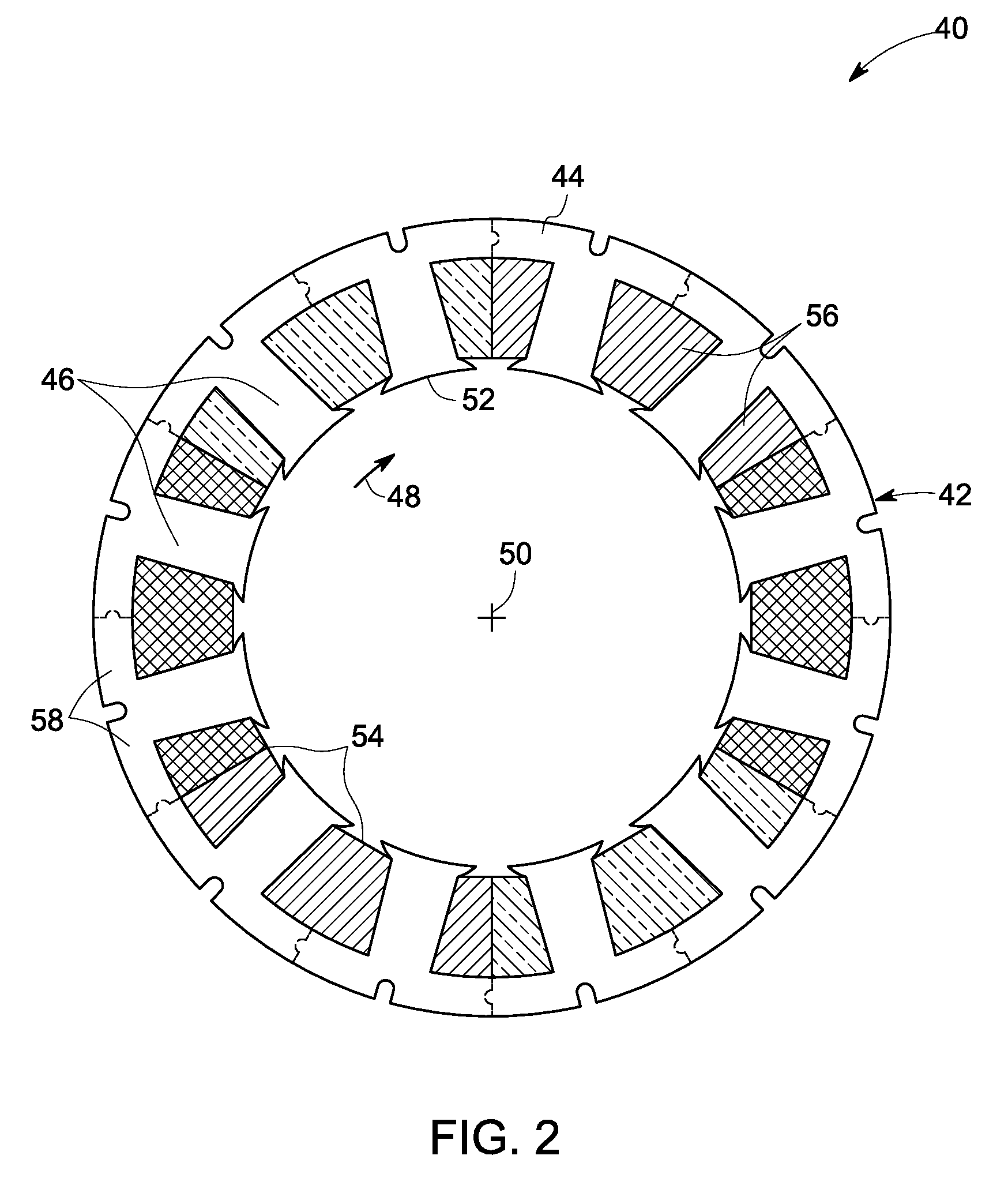
Rotor For Electric Motor
InactiveUS20090096308A1Improve efficiencyReduce manufacturing costMagnetic circuitManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesElectric machineMagnetic poles
An electric motor has an internal ferromagnetic rotor ring and an external stator. Circumferentially distributed cutouts in the rotor receive rectangular permanent magnets each having a width b and height h and the rotor ring is divided into rotor poles. The height h forms the longer side of each magnet and is radial to the motor axis. The magnets are magnetized in the width b direction with like poles oriented toward one another. A magnetic clearance is located between adjacent magnets for each inner portion of a rotor pole. The clearance does not contain magnetic material and in a center region of the rotor poles one support web connects an inner support ring with the particular rotor pole to provide mechanical support.
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP PRESTA AG
High speed internal permanent magnet machine
ActiveUS20100277028A1Magnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesAlternating currentMagnet
An internal permanent magnet (IPM) machine is provided. The IPM machine includes a stator assembly and a stator core. The stator core also includes multiple stator teeth. The stator assembly is further configured with stator windings to generate a magnetic field when excited with alternating currents and extends along a longitudinal axis with an inner surface defining a cavity. The IPM machine also includes a rotor assembly and a rotor core. The rotor core is disposed inside the cavity and configured to rotate about the longitudinal axis. The rotor assembly further includes a shaft. The shaft further includes multiple protrusions alternately arranged relative to multiple bottom structures provided on the shaft. The rotor assembly also includes multiple stacks of laminations disposed on the protrusions and dovetailed circumferentially around the shaft. The rotor assembly further includes multiple permanent magnets for generating a magnetic field, which interacts with the stator magnetic field to produce torque. The permanent magnets are disposed between the stacks. The rotor assembly also includes multiple bottom wedges disposed on the bottom structures of the shaft and configured to hold the multiple stacks and the multiple permanent magnets.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Axial air gap machine having stator and rotor discs formed of multiple detachable segments
InactiveUS20100007225A1Improve fault tolerancePossible to useMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsPower factorSupercapacitor
A generator or motor apparatus having a stator formed of a plurality of pairs of parallel stator segments is provided The pairs of parallel segments are connected together to form a channel in which an annular rotor moves The annular rotor also comprises a plurality of detachable segments connected together to form an annular tram operable to move through said channel Each stator segment comprises a stator winding set and each rotor segment comprises a magnet dimensioned to fit between the parallel spaced apart stator segments The apparatus may include a support structure, the rotor segments being slidably coupled to the support structure and the stator segments being attached the support structure The apparatus may be a rim generator, wind turbine generator or other electrical machine The stator winding set includes a winding, and may include other electrical or electronic components, including possibly a power factor capacitor, direct current filtering capacitor, supercapacitor, and one or more diodes The stator winding set nay be encapsulated within the stator segment
Owner:CLEAN CURRENT PARTNERSHIP
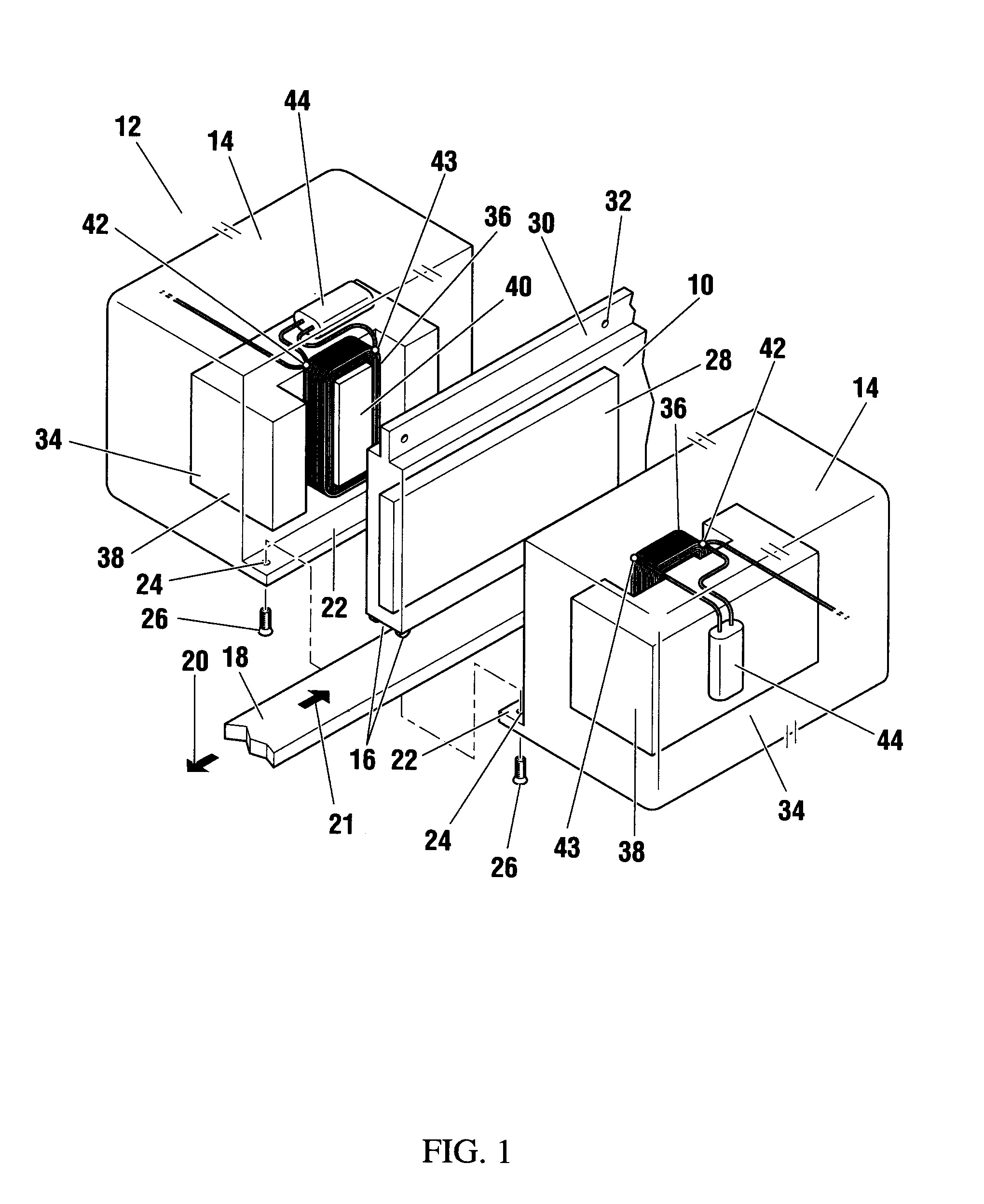
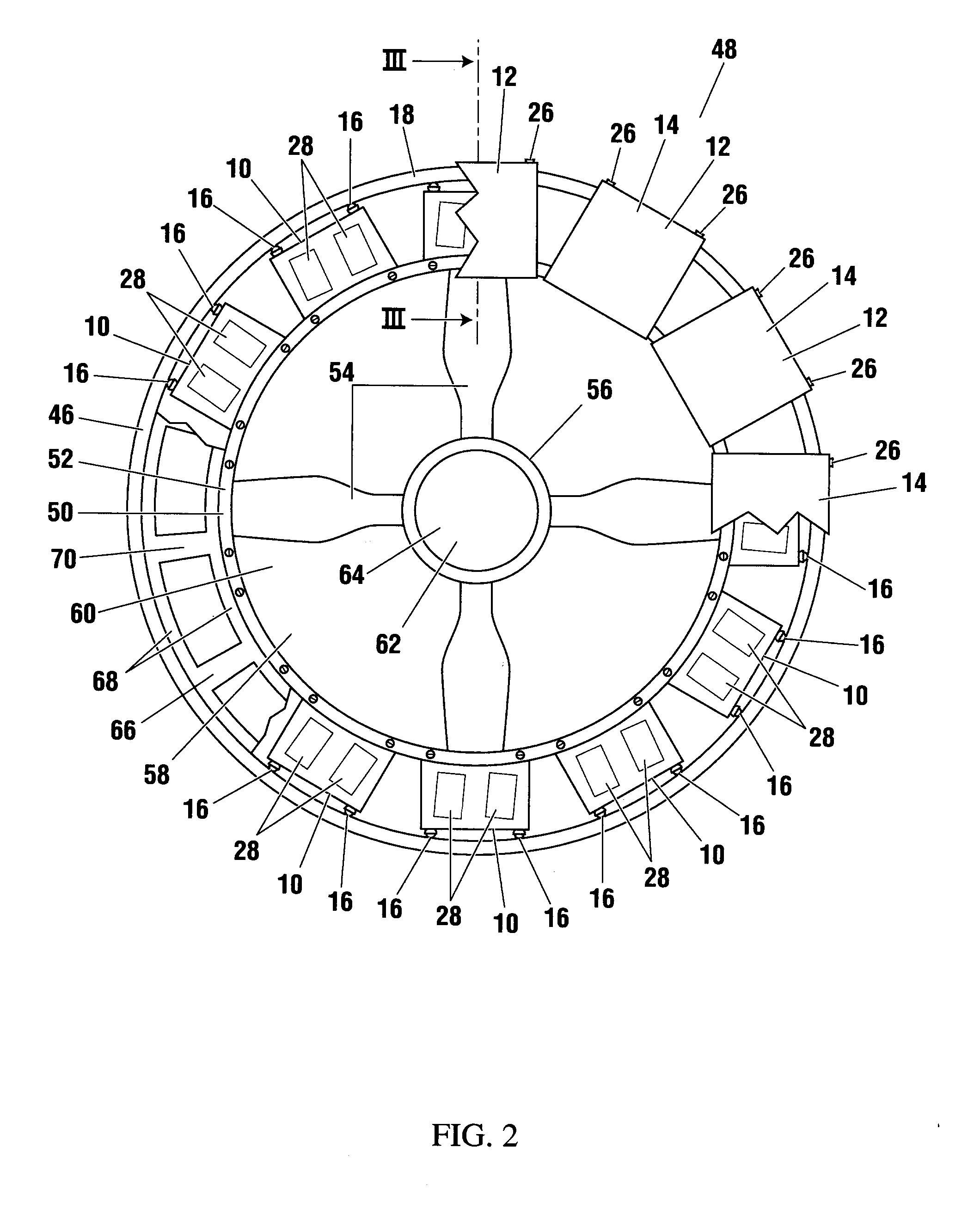
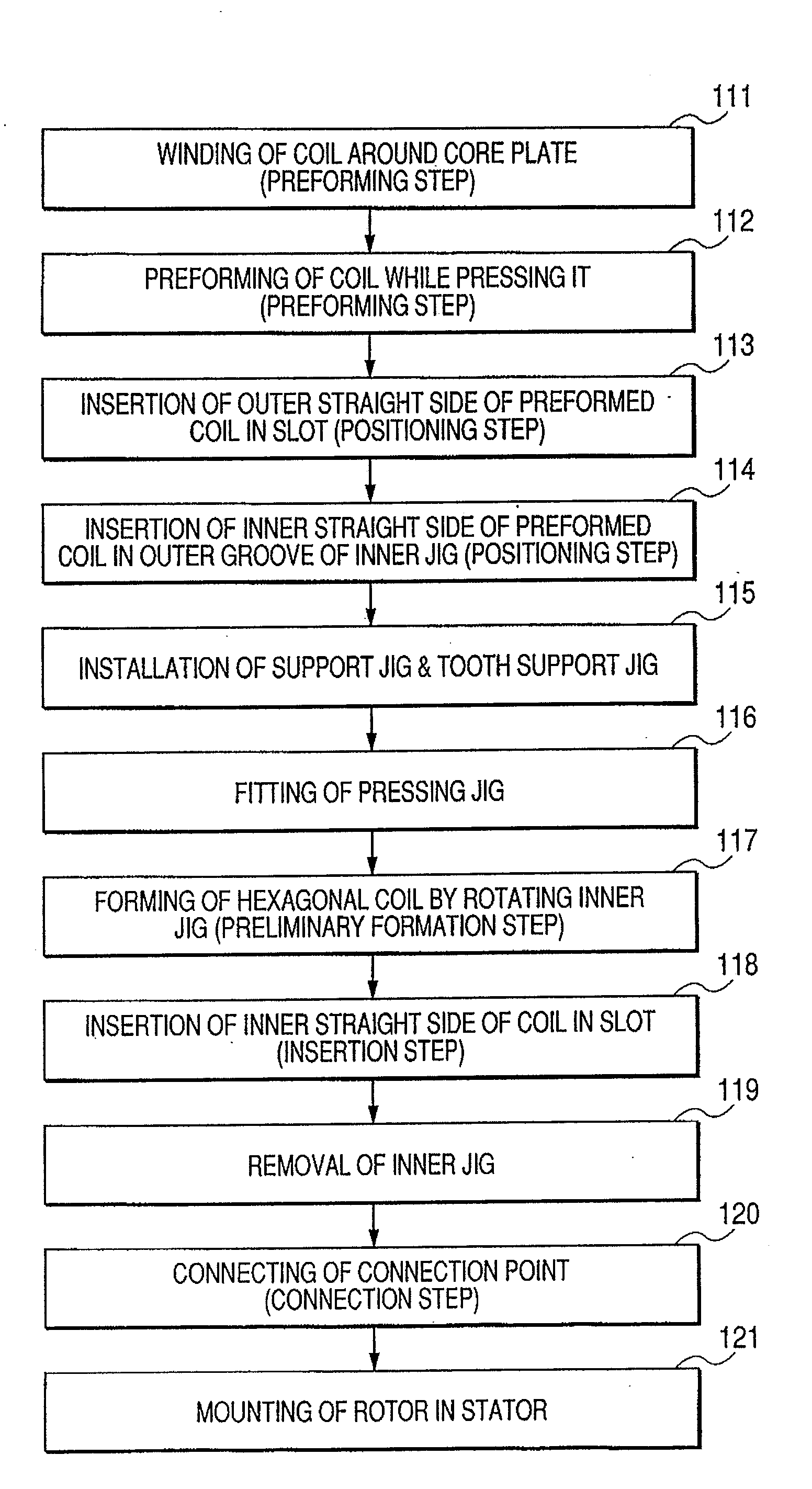
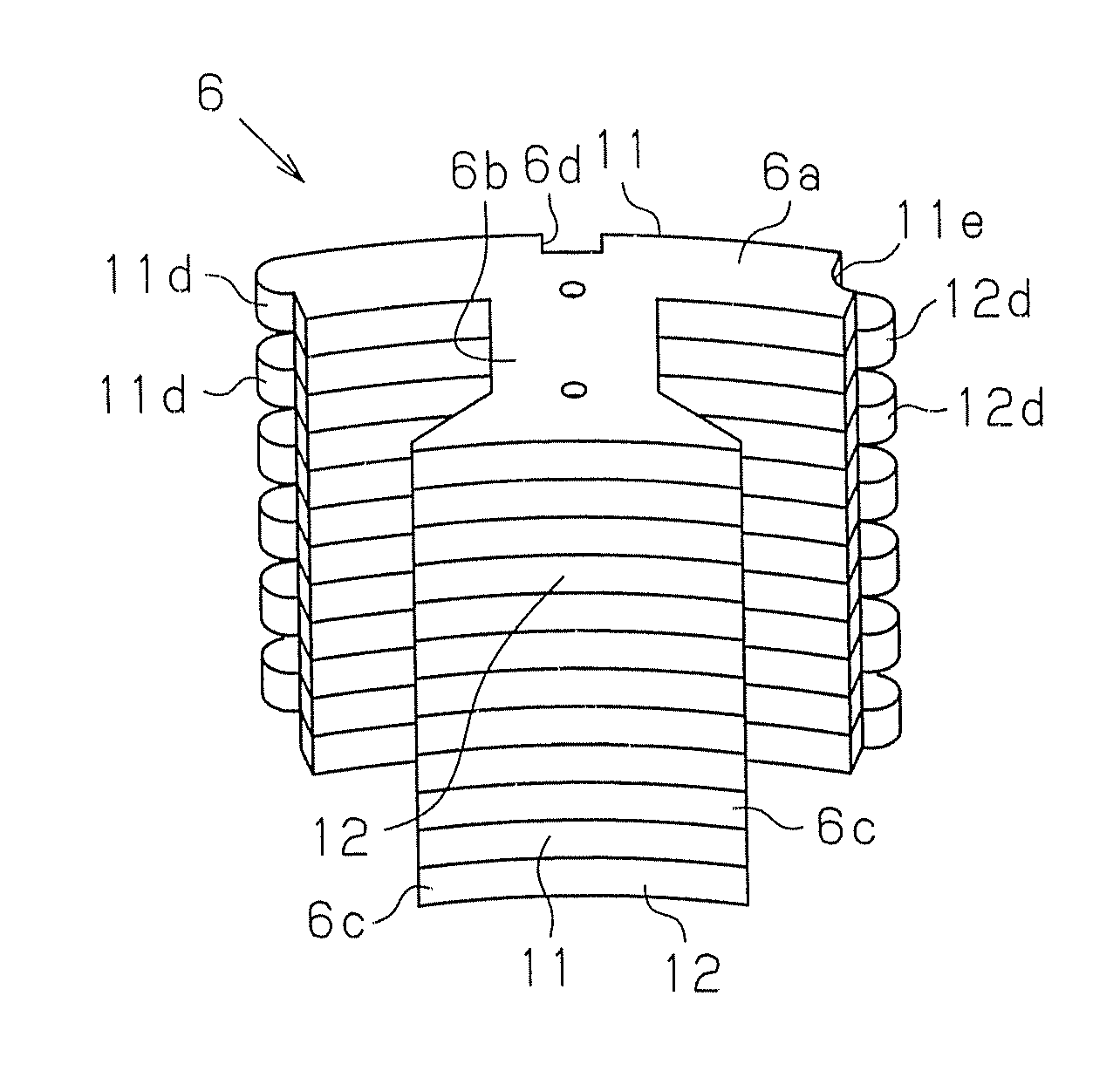
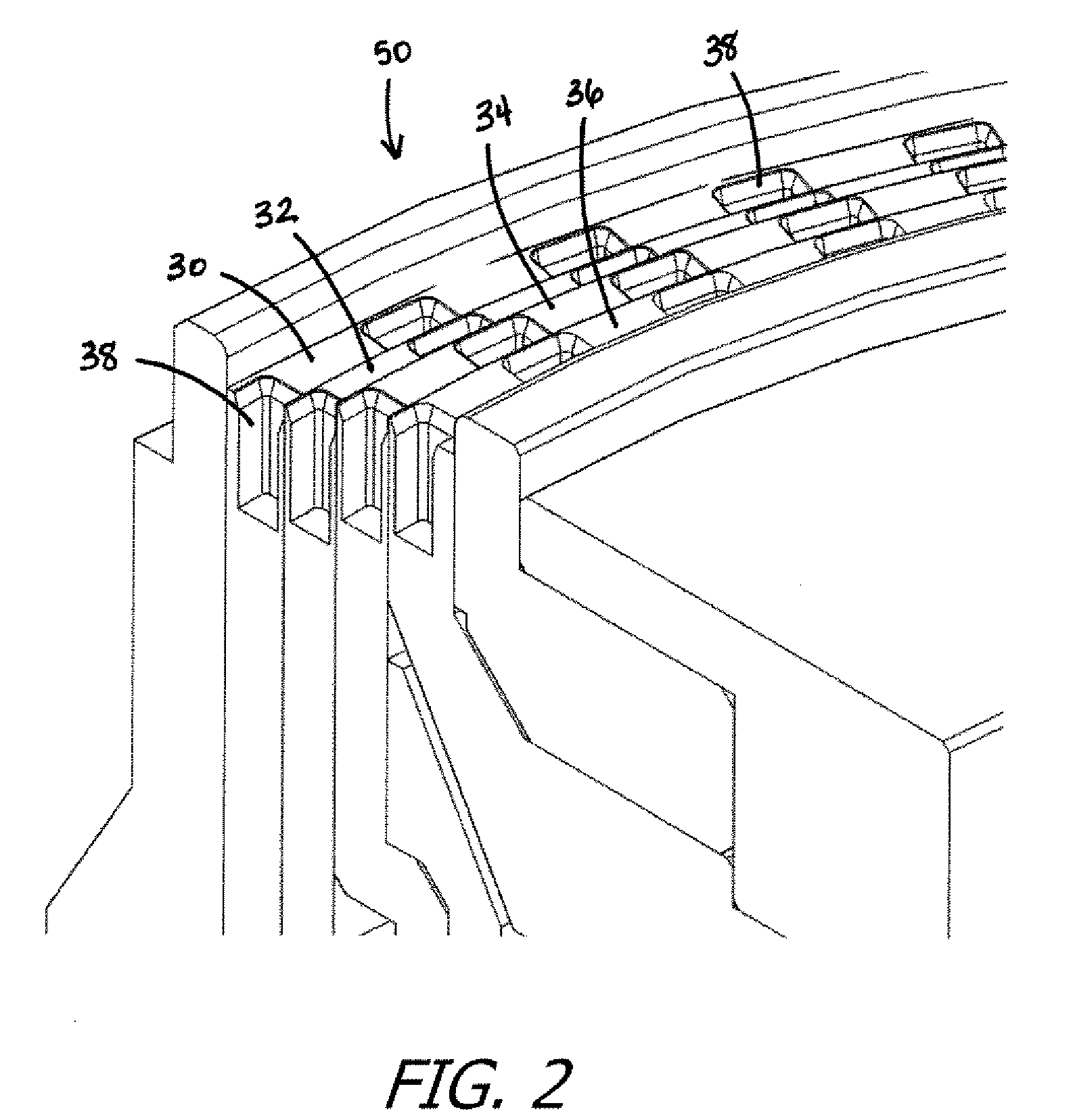
Manufacturing Method for Rotary Electric Machine and Stator
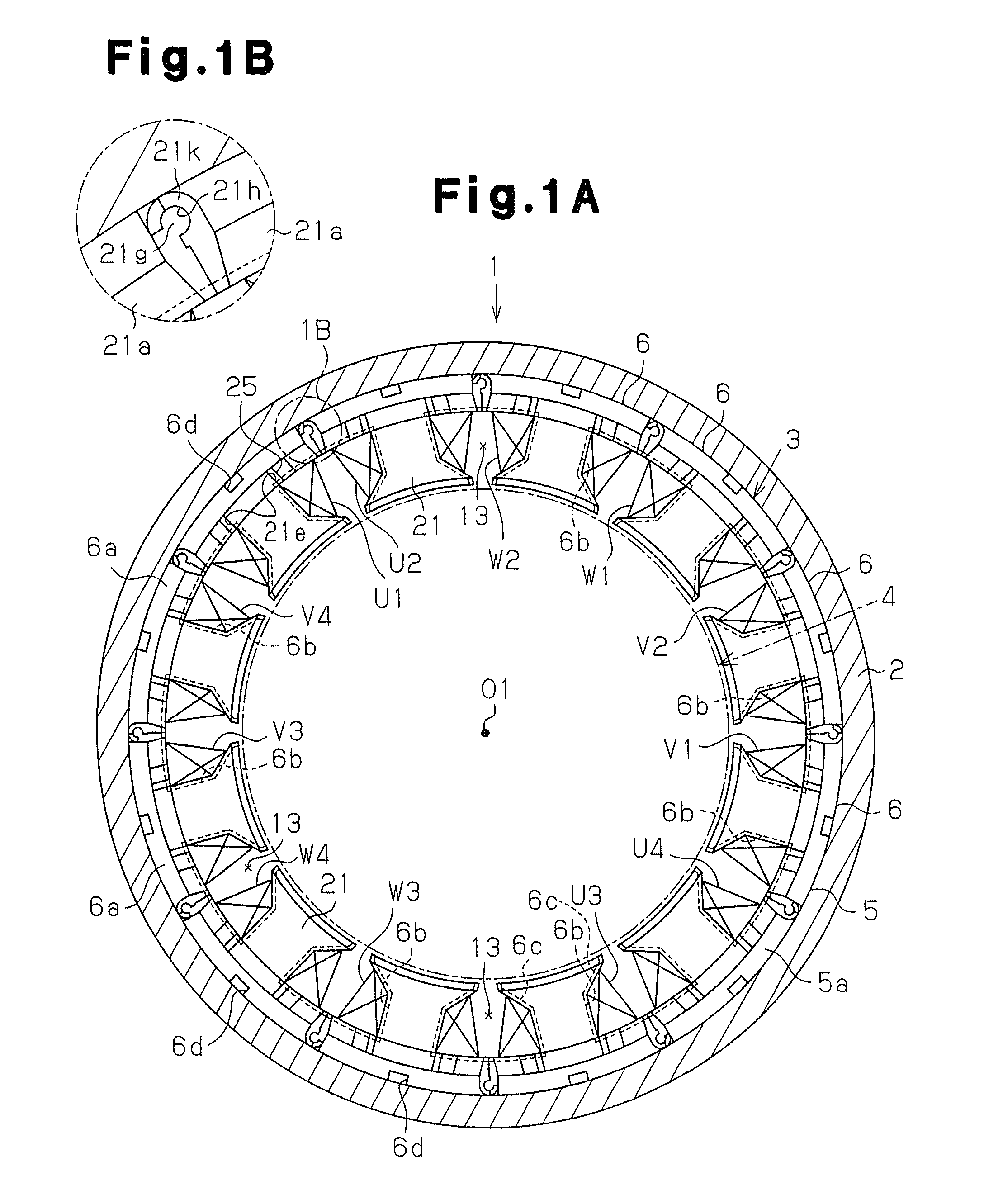
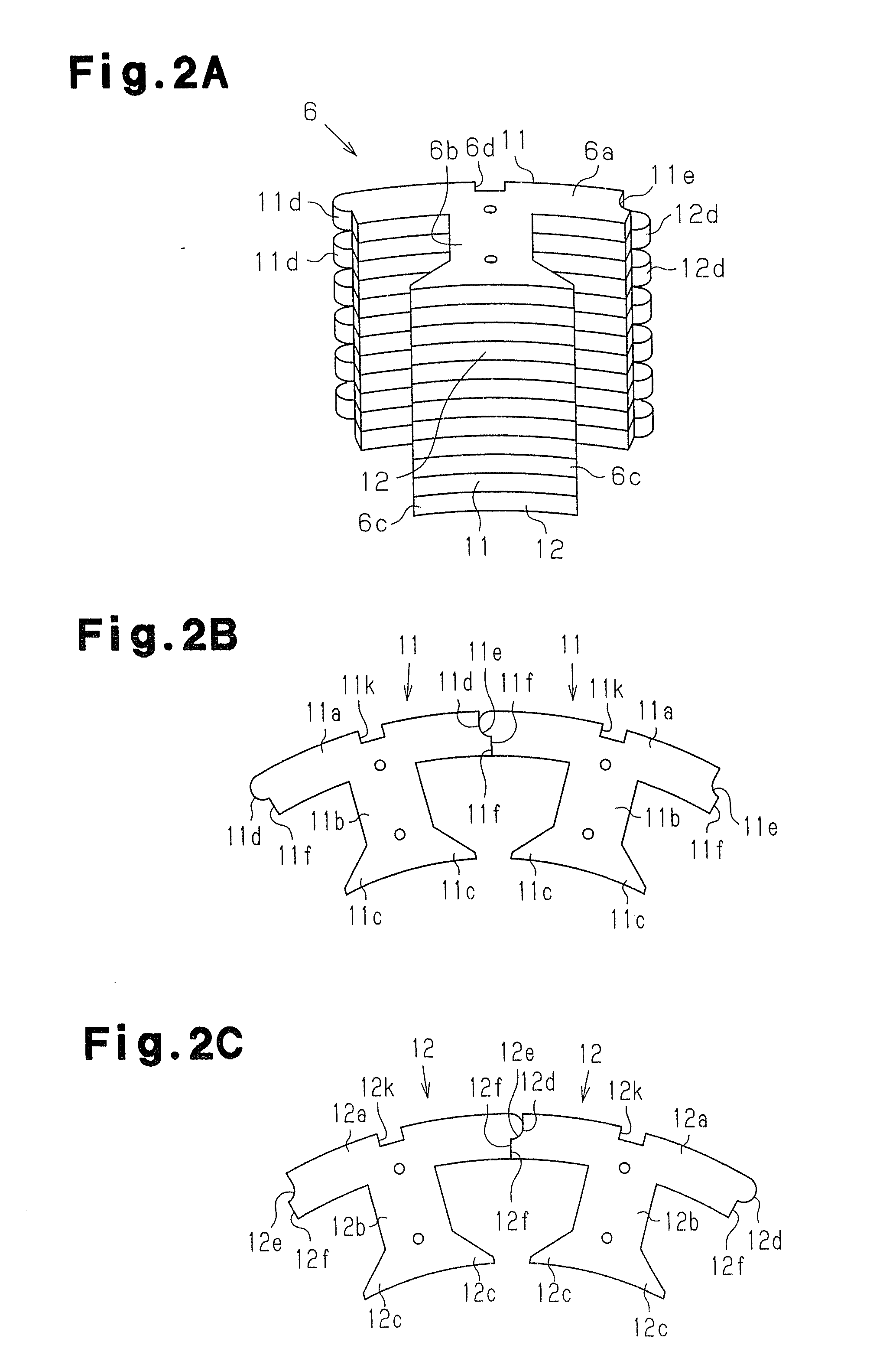
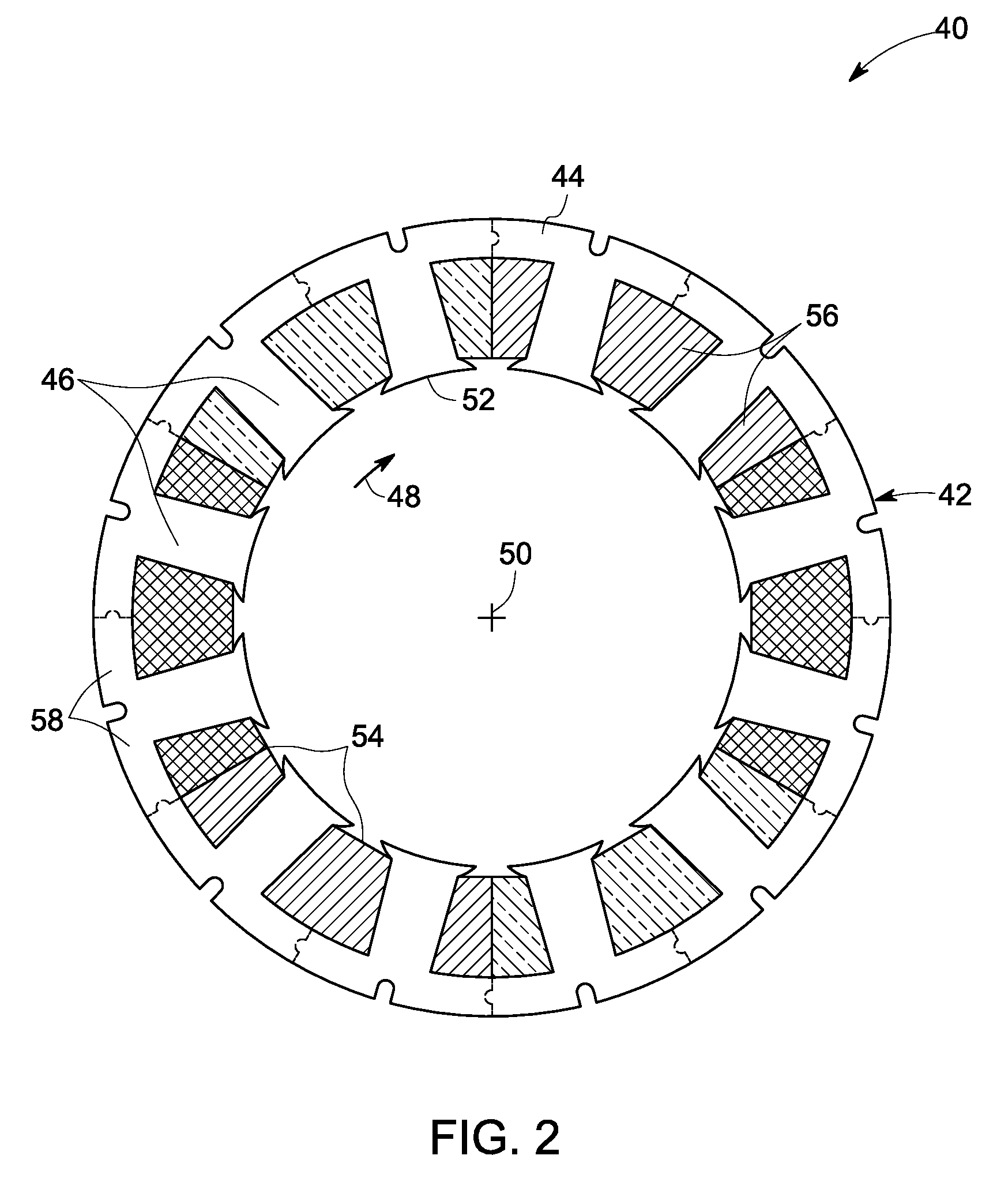
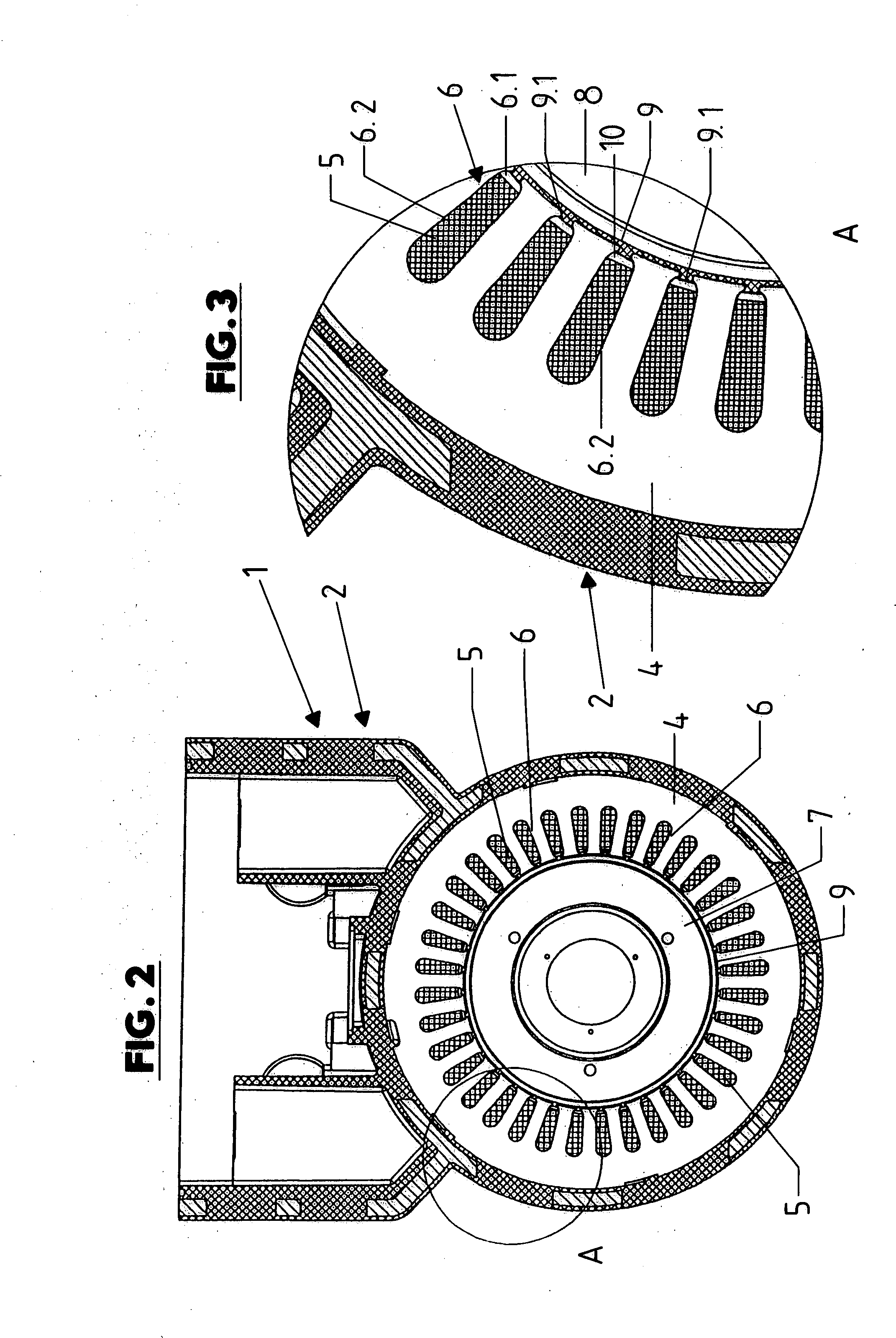
InactiveUS20080201935A1Improve productivityManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesApplying solid insulationElectrical conductorElectric machine
A manufacturing method for a rotary electric machine according to the present invention comprises steps of: (1) preforming a coil including a plurality of element coils of an insulated conductor; (2) inserting a first side of a first element coil of the element coils into a first slot of a stator core through an opening of the first slot; (3) inserting a second side of the first element coil into a second slot in which a first side of a second element coil of the element coil has been already inserted; (4) electrically connecting coil ends of a plurality of the coils to each other; and (5) rotatably mounting a rotor inside the stator core.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Armature for an electromotive device
InactiveUS6111329AMaximize conductor-packing factorMaximize conductor volume to gap ratioWindings insulation shape/form/constructionMagnetic circuit rotating partsGlass fiberEngineering
An armature for an electric motor is constructed from a pair of precision machined copper plates cut in a pattern to produce a series of axially extending surface conductive bands with each band separated from the other by an insulated cutout. The precision machined plates are rolled to form two telescoping, hollow cylinders with each cylinder having a pattern of conductive bands representing a half-electric circuit. The outer surface of the inner cylinder is wrapped with several layers of fiberglass strands for structural stability and insulation. The fiberglass wrapped inner cylinder is telescoped inside the outer cylinder. The outer surface of the telescoped structure is also wrapped with several layers of fiberglass strands for structural stability. The conductive bands from the outer cylinder being the near mirror image of the conductive bands of the inner cylinder are helically coupled to form a complete electrical circuit. The resulting tubular structure is encapsulated in a potting material for further structural stability and insulation. The result is a freestanding ironless core inductive armature coil for a DC motor with brushes. The armature also has a commutator, which is mounted at one end of the coil and is in electrical contact with the helically coupled conductive bands. An insulated flywheel and shaft assembly is mounted inside the coil with the flywheel behind the commutator for motor mounting and operation.
Owner:THINGAP
Bi-metal disc brake rotor and method of manufacturing
InactiveUS20070056815A1Avoid problemsImprove bindingMetal rolling stand detailsBraking discsMechanical engineeringMetal
The invention provides a method for manufacturing a friction damped disc brake rotor, including the steps of: (A) positioning at least one insert into a mold, wherein the insert has a body with tabs extending therefrom to hold the insert in a desired position within the mold; and (B) casting a rotor cheek of the disc brake rotor in the mold around the insert such that a portion of each tab is bonded with the rotor cheek and the body is substantially non-bonded with the rotor cheek so that the body provides a proper interfacial boundary with the cheek for damping while the bonding of the tabs with the rotor cheek prevents corrosion-causing exterior elements from reaching the interfacial boundary.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Manufacturing method of stator, and stator
ActiveUS20070182271A1Easy windingReduce connecting wiresSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit rotating partsState spaceEngineering
In a state in which a first divisional core and a second divisional core are arranged in a state spaced from each other and adjacent to each other, a first coil and a second coil are each wound around a tooth. The first coil and the second coil are in the same phase. In a state in which a plurality of divisional cores are arranged annularly so that their teeth are oriented in a radially inward direction, the first divisional core and the second divisional core are not adjacent to each other in the circumferential direction. A plurality of connection wires are shaped to converge at an end surface of a stator core. This facilitates the winding of the coils around the divisional cores. Further, the connection wires can be shortened.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Method and apparatus for forming motor winding conductors
ActiveUS20090178270A1Synchronous machinesAsynchronous induction motorsElectrical conductorLimited angle
Method and apparatus for forming motor winding conductors rectangular conductor wire. The method comprises populating with hairpin shaped conductors, most of a forming fixture having a plurality of pockets distributed in equal number in one or more pairs of adjacent circles, each concentric with a center of the forming fixture, at least one member defining each of the pockets in one of each pair of adjacent circles being rotatable, at least through a limited angle, with respect to a member defining the pockets in the other of the respective pair of adjacent circles, the hairpin conductors each having first and second legs integrally joined by a loop at one end thereof, with one leg of each hairpin conductor in a respective one of the pockets in a pair of adjacent circles, and rotating in a first direction, relative to each other, the members defining the pockets in each pair of circles through a predetermined angle, to permanently separate the two legs of each hairpin conductor without substantial rotation of each leg of the hairpin conductors relative to its respective pocket. Various additional features are disclosed.
Owner:TECNOMATIC
Bi-metal disc brake rotor and method of manufacturing
InactiveUS7775332B2Avoid problemsImprove bindingMetal rolling stand detailsBraking discsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention provides a method for manufacturing a friction damped disc brake rotor, including the steps of: (A) positioning at least one insert into a mold, wherein the insert has a body with tabs extending therefrom to hold the insert in a desired position within the mold; and (B) casting a rotor cheek of the disc brake rotor in the mold around the insert such that a portion of each tab is bonded with the rotor cheek and the body is substantially non-bonded with the rotor cheek so that the body provides a proper interfacial boundary with the cheek for damping while the bonding of the tabs with the rotor cheek prevents corrosion-causing exterior elements from reaching the interfacial boundary.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Axial flux switched reluctance motor and methods of manufacture
InactiveUS20100295389A1Use minimizedIron and copper lossMagnetic circuitSynchronous motorsStator coilReluctance motor
An axial flux switched reluctance motor utilizes one or more rotor discs spaced along a rotor shaft, each rotor disc having a plurality of rotor poles spaced along the periphery thereof. Stator elements are distributed circumferentially about the rotor discs and form pairs of radially extending stator poles for axially straddling the rotor discs. Stator coils as switched on to energize pairs of stator poles for forming an axial and radially inward flux path for rotating the rotor poles for minimizing the flux path before switching off the stator coil. Two or more rotor discs can be rotationally indexed for providing two or more motor phases. In manufacture, rotor discs and circumferentially extending stator coils about the periphery of each rotor disc are fit to a stator housing. Each stator element is then fit radially through the stator housing and secured thereto for straddling the rotor discs.
Owner:MSI MACHINEERING SOLUTIONS
Rotor and method of manufacturing the same and electric vehicle
A rotor includes: a rotor core fixedly attached to a rotational shaft and having a magnet-inserted hole portion; a magnet inserted into the magnet-inserted hole portion; and a resin portion injected into the magnet-inserted hole portion. The rotor core is constructed by axially stacking a plurality of electromagnetic steel sheets. The electromagnetic steel sheets include: an electromagnetic steel sheet having the magnet-inserted hole portion and a weight-reducing-purpose hole portion provided separately from the magnet-inserted hole portion; and an electromagnetic steel sheet located on at least one axial end of the rotor core and having a portion covering the hole portion formed in the electromagnetic steel sheet.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
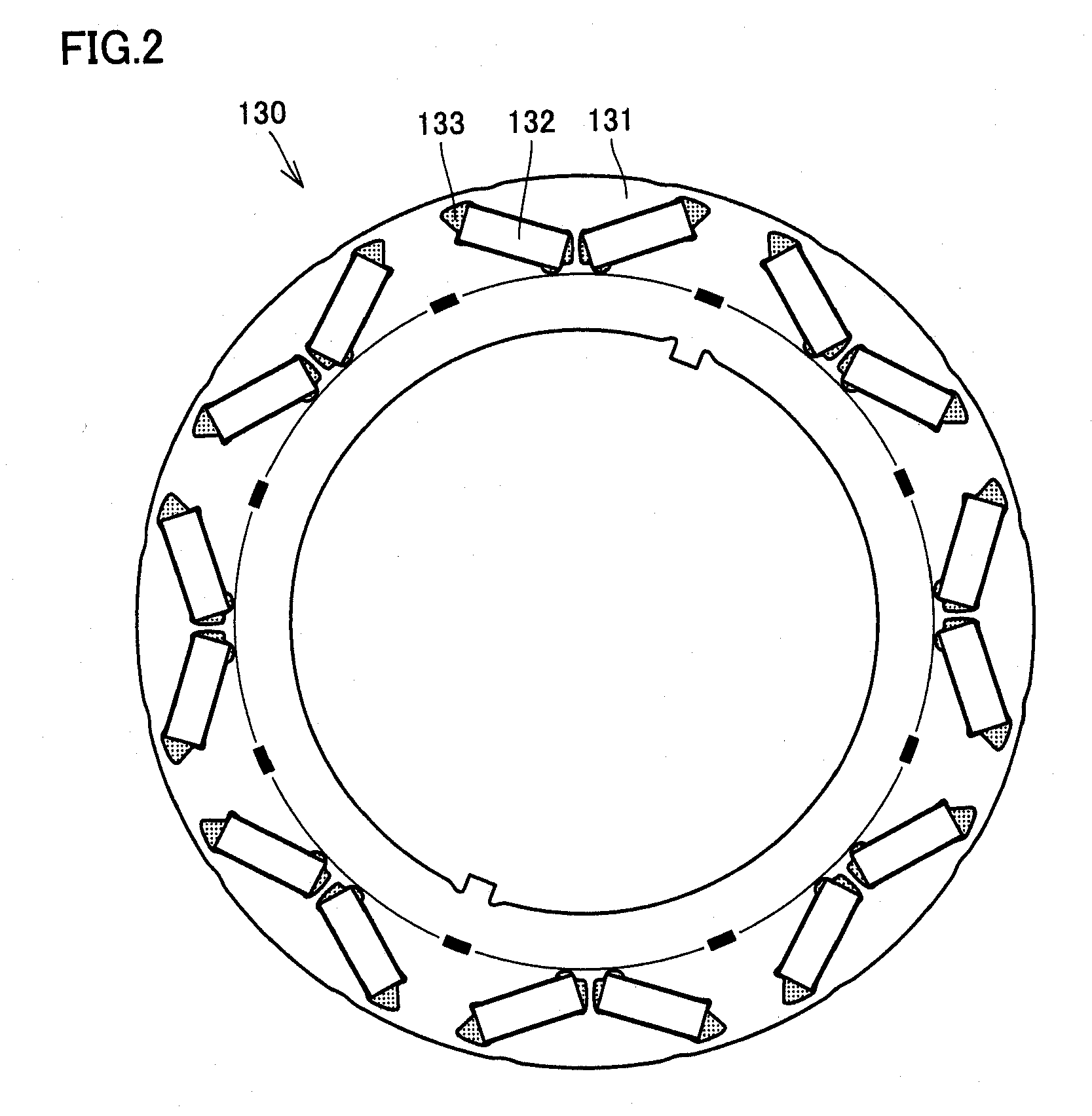
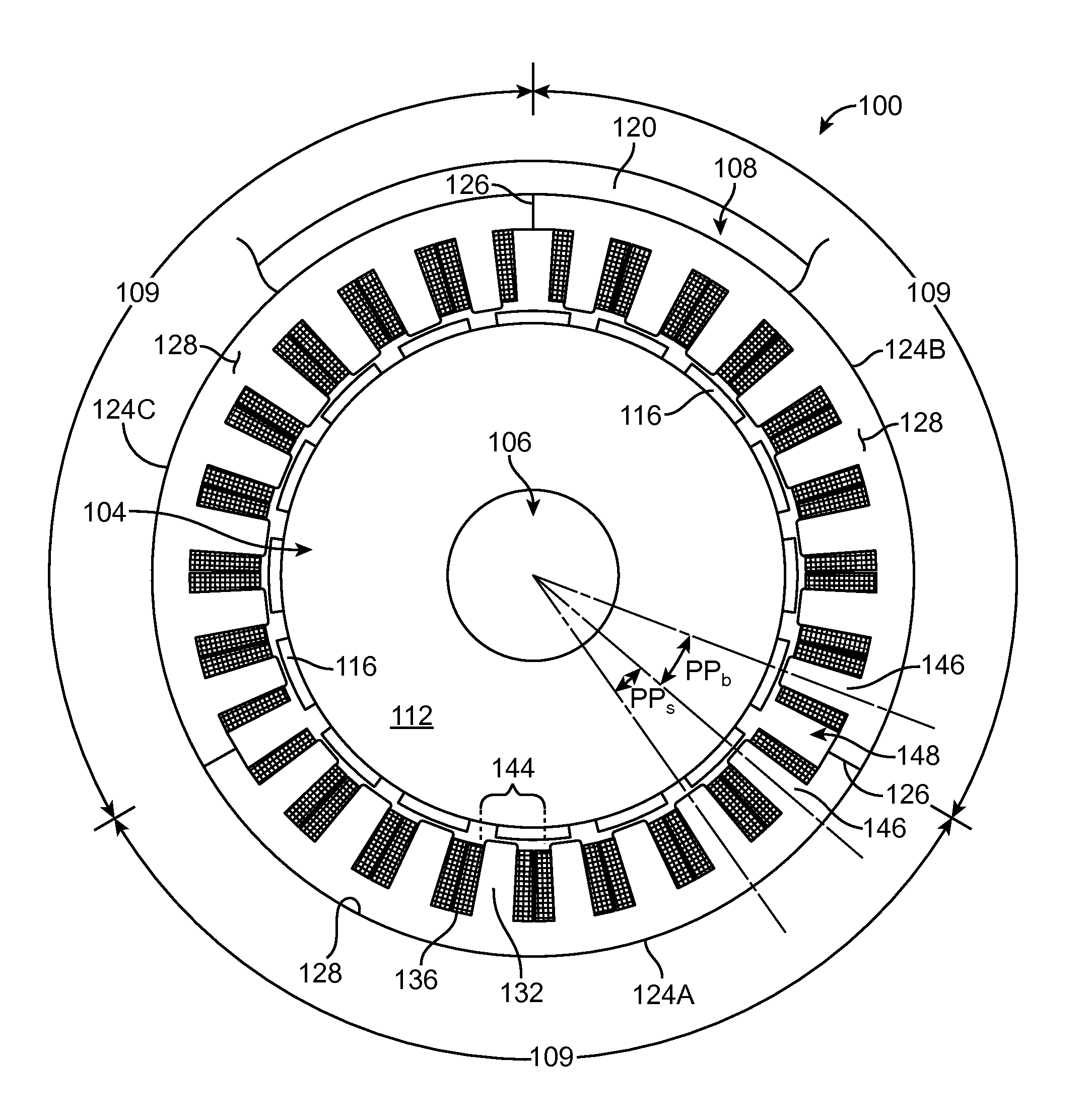
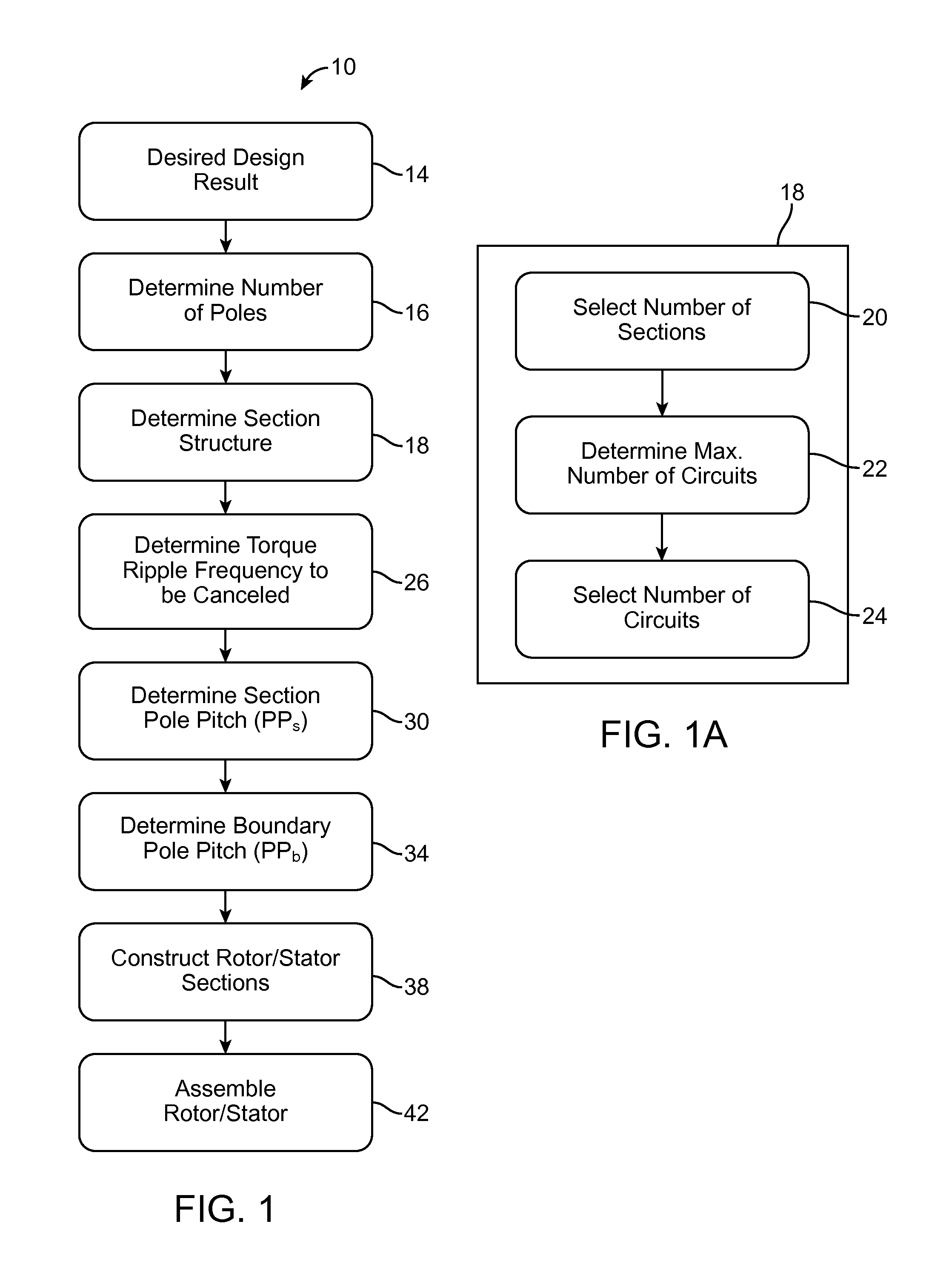
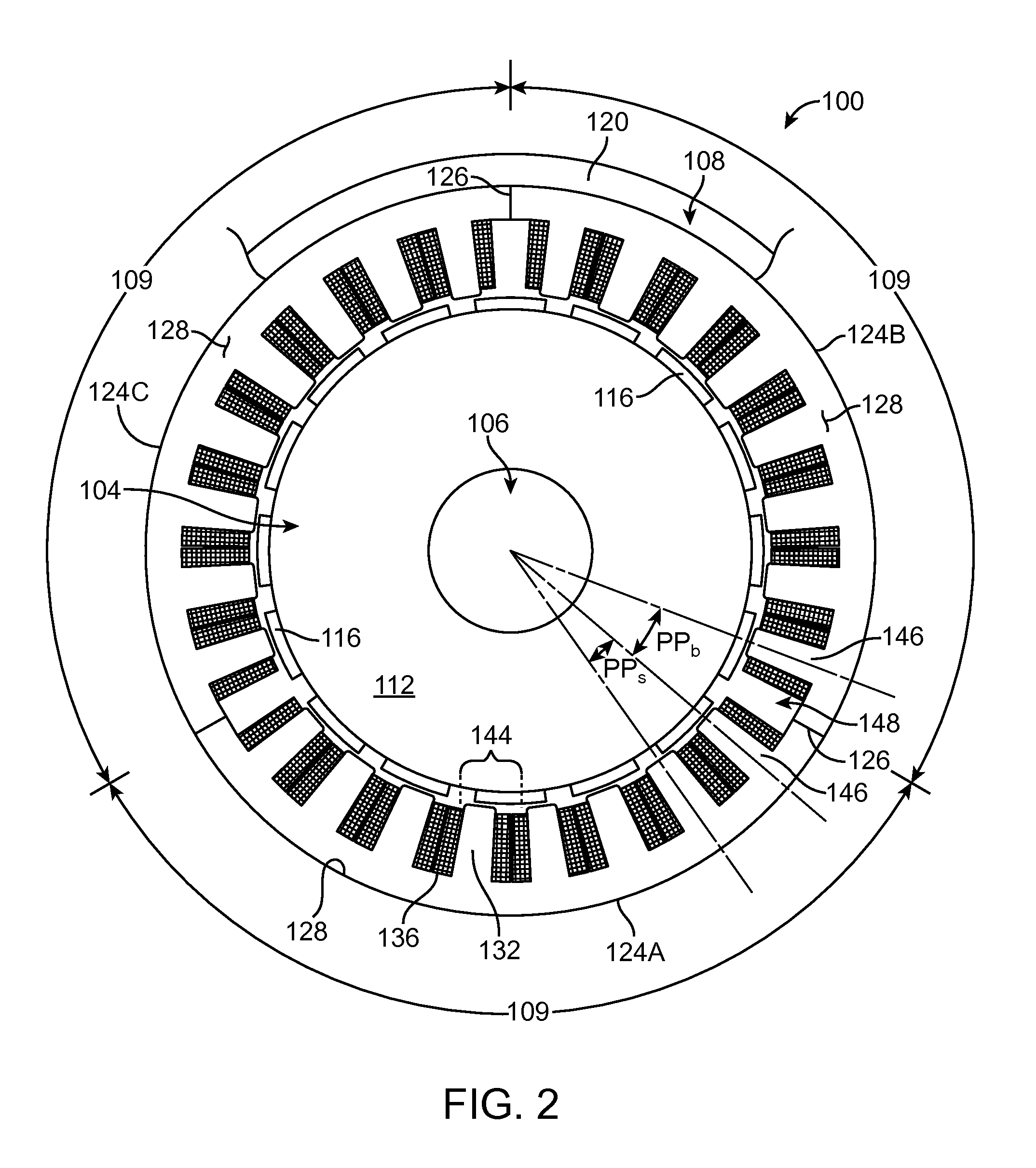
Sectionalized Electromechanical Machines Having Low Torque Ripple and Low Cogging Torque Characteristics
InactiveUS20120074797A1Reducing torque ripple torqueReducing torque cogging torqueMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsRotor magnetsControl theory
A method and apparatus for reducing or eliminating the effects of torque ripple and cogging torque and otherwise improving performance in an electromechanical machine such as a motor or generator. The rotor and / or stator is conceptually sectionalized and the sections spaced apart by amount sufficient to alleviate deleterious aspects of cogging torque and torque ripple. Positioning of the stator teeth or rotor magnets is determined based on the calculated spacing. Conceptual sections may be formed as physically individual segments. Unwound teeth may be disposed in end spaces between sections occupying less than the entire area of the end space.
Owner:WEG ELECTRIC CORP
Rotor for reluctance type rotating machine
ActiveUS7170209B2Reduce noiseReduce oscillationMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous motorsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A rotor for a reluctance type rotating machine includes a rotor core formed by stacking a number of annular core materials each of which includes magnetic concave and convex portions. The rotor core has two keys which are formed at two positions on an inner circumference of the rotor core. The positions are spaced 180 degrees apart from each other with respect to the rotor core. The rotor core is divided into a plurality of blocks and the core materials constituting at least one block have the magnetic concave and convex portions shifted by a predetermined angle relative to the core materials constituting the other or another block on the basis of a center line passing through the keys. A whole or part of the core materials of at least one block are located circumferentially 180 degrees apart form the core materials constituting the other or another block.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
Dovetail spoke internal permanent magnet machine
ActiveUS20100277017A1Improve efficiencyImprove power densityMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesAlternating currentConductor Coil
An internal permanent magnet (IPM) machine is provided. The IPM machine includes a stator assembly and a stator core. The stator core also includes multiple stator teeth. The stator assembly is further configured with stator windings to generate a stator magnetic field when excited with alternating currents and extends along a longitudinal axis with an inner surface defining a cavity. The IPM machine also includes a rotor assembly and a rotor core. The rotor core is disposed inside the includes a shaft. The shaft further includes multiple protrusions alternately arranged relative to multiple bottom structures provided on the shaft. The rotor assembly also includes multiple stacks of laminations disposed on the protrusions and dovetailed circumferentially around the shaft. The rotor assembly further includes multiple pair of permanent magnets for generating a magnetic field, which magnetic field interacts with the stator magnetic field to produce a torque. The multiple pair of permanent magnets are disposed between the stacks. The rotor assembly also includes multiple middle wedges mounted between each pair of the multiple permanent magnets.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
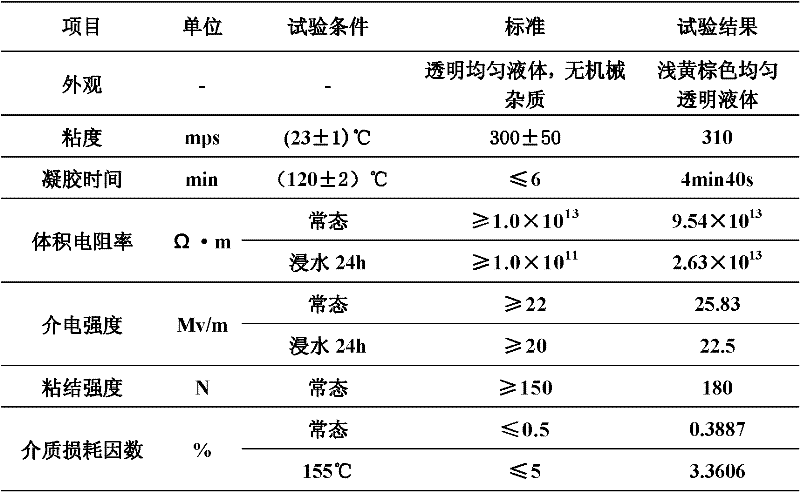
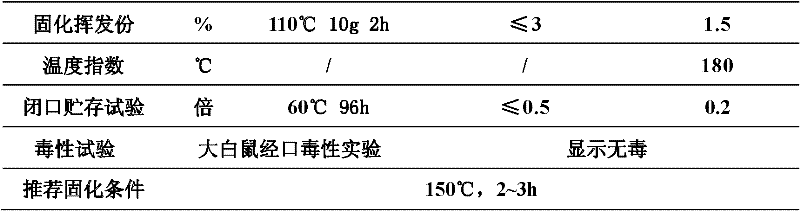
Environmentally-friendly type solvent-free impregnating resin and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102225986AConservation TrendsPromote safe productionApplying solid insulationCoils manufactureLow voltageTransformer
The invention discloses an environmentally-friendly type solvent-free impregnating resin and a preparation method thereof. The impregnating resin comprises: 100 parts by weight of one or more high heat-resistant unsaturated polyester resins, 0 to 100 parts by weight of one or more modified epoxy resins, 50 to 200 parts by weight of one or more novel reactive diluents, 0.1 to 1 parts by weight of one or more polymerization inhibitors, 1.5 to 3.8 parts by weight of one or more initiators and 0 to 2 parts by weight of one or more auxiliary agents. Under the same work conditions, a baking time of the solvent-free impregnating resin is less than about one third of a baking time of the existing conventional solvent-free type impregnating resin utilized for middle and low voltage motors and transformers, and an energy consumption of the solvent-free impregnating resin is lower than about 25% of an energy consumption of the existing conventional solvent-free type impregnating resin middle and low voltage motors and transformers.
Owner:SUZHOU JUFENG ELECTRICAL INSULATION SYST
Method and device for positioning and affixing magnets on a magnetic yoke member of a motor
InactiveUS20050246886A1Not require complex toolingGood attractionWire articlesAssembly machinesLinear motorElectric motor
A method and a device are for positioning and affixing magnets on a magnetic yoke member of an electric motor. The device includes: a nonmagnetic support for receiving the magnets, this support having a shape complementary to that of the magnetic yoke member on which the magnets are to be affixed; a magnetic element for holding the magnets in position on the nonmagnetic support, this element being arranged on the other side of the nonmagnetic support with respect to the magnets, the attraction exerted by this element on the magnets being greater than that exerted by the magnetic yoke member during the positioning of the device with respect to the yoke; a device for varying the magnetic forces present, whereby the magnetic attraction of the magnetic yoke member and / or the magnetic element on the magnets may be varied such that the magnetic force of attraction exerted by the yoke on the magnets becomes greater than that exerted by the magnetic element on them, thus provoking the transfer of the magnets to the yoke. The yoke member forms the magnetic path of a linear motor.
Owner:ETEL SA
Rotor and process for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060170301A1Efficient use ofIncrease freedomMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesCompression moldingMetallurgy
A rotor comprising bonded magnet portions mainly composed of magnet powder and a binder, which are embedded in a soft magnetic portion mainly composed of soft magnetic powder and a binder, the rotor being produced by a compression-molding method, and the magnetic pole surfaces of the bonded magnet portions being embedded in the soft magnetic portion.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Dovetail spoke internal permanent magnet machine
ActiveUS8004140B2Magnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesAlternating currentConductor Coil
An internal permanent magnet (IPM) machine is provided. The IPM machine includes a stator assembly and a stator core. The stator core also includes multiple stator teeth. The stator assembly is further configured with stator windings to generate a stator magnetic field when excited with alternating currents and extends along a longitudinal axis with an inner surface defining a cavity. The IPM machine also includes a rotor assembly and a rotor core. The rotor core is disposed inside the cavity and configured to rotate about the longitudinal axis. The rotor assembly further includes a shaft. The shaft further includes multiple protrusions alternately arranged relative to multiple bottom structures provided on the shaft. The rotor assembly also includes multiple stacks of laminations disposed on the protrusions and dovetailed circumferentially around the shaft. The rotor assembly further includes multiple pair of permanent magnets for generating a magnetic field, which magnetic field interacts with the stator magnetic field to produce a torque. The multiple pair of permanent magnets are disposed between the stacks. The rotor assembly also includes multiple middle wedges mounted between each pair of the multiple permanent magnets.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
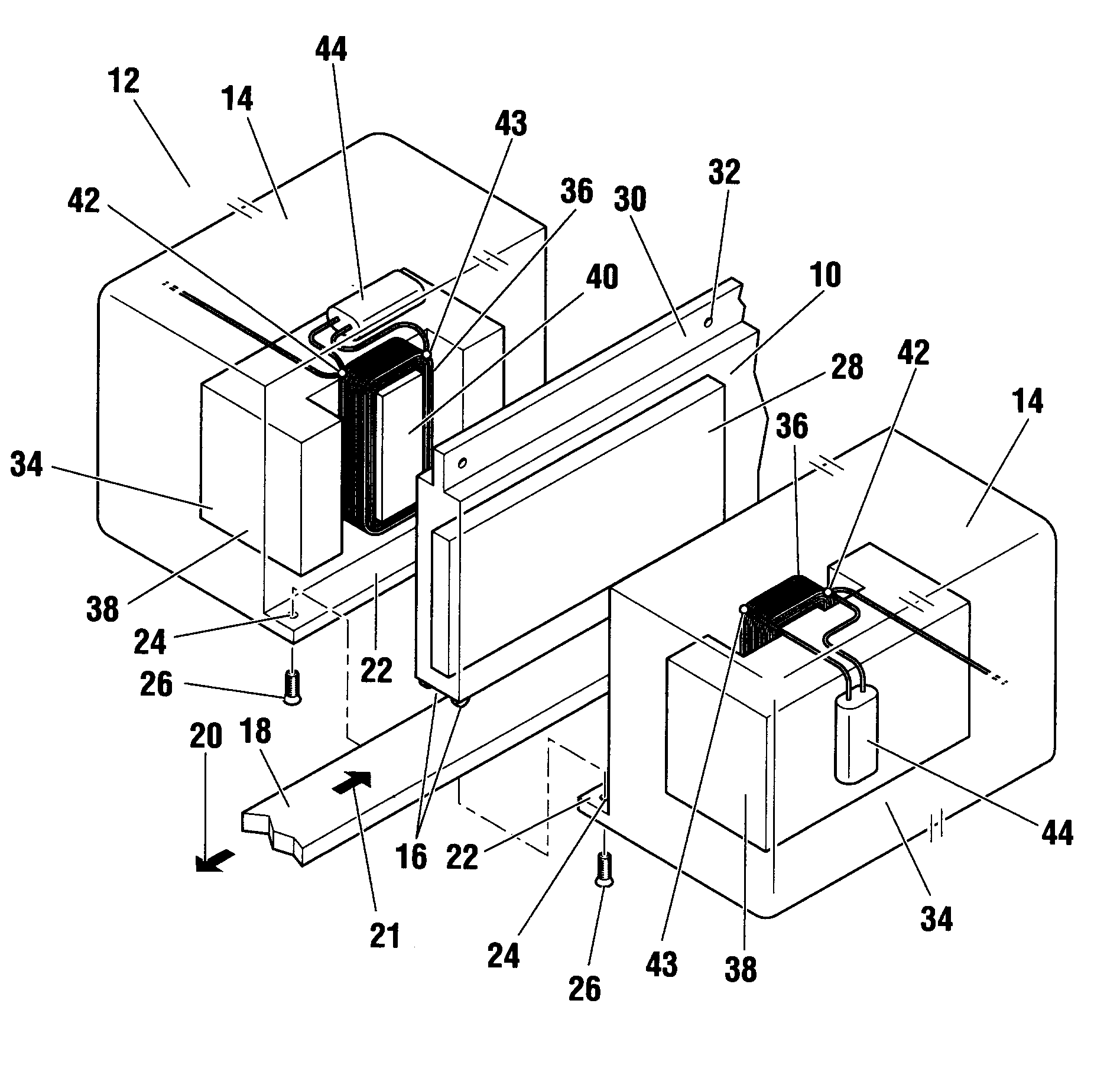
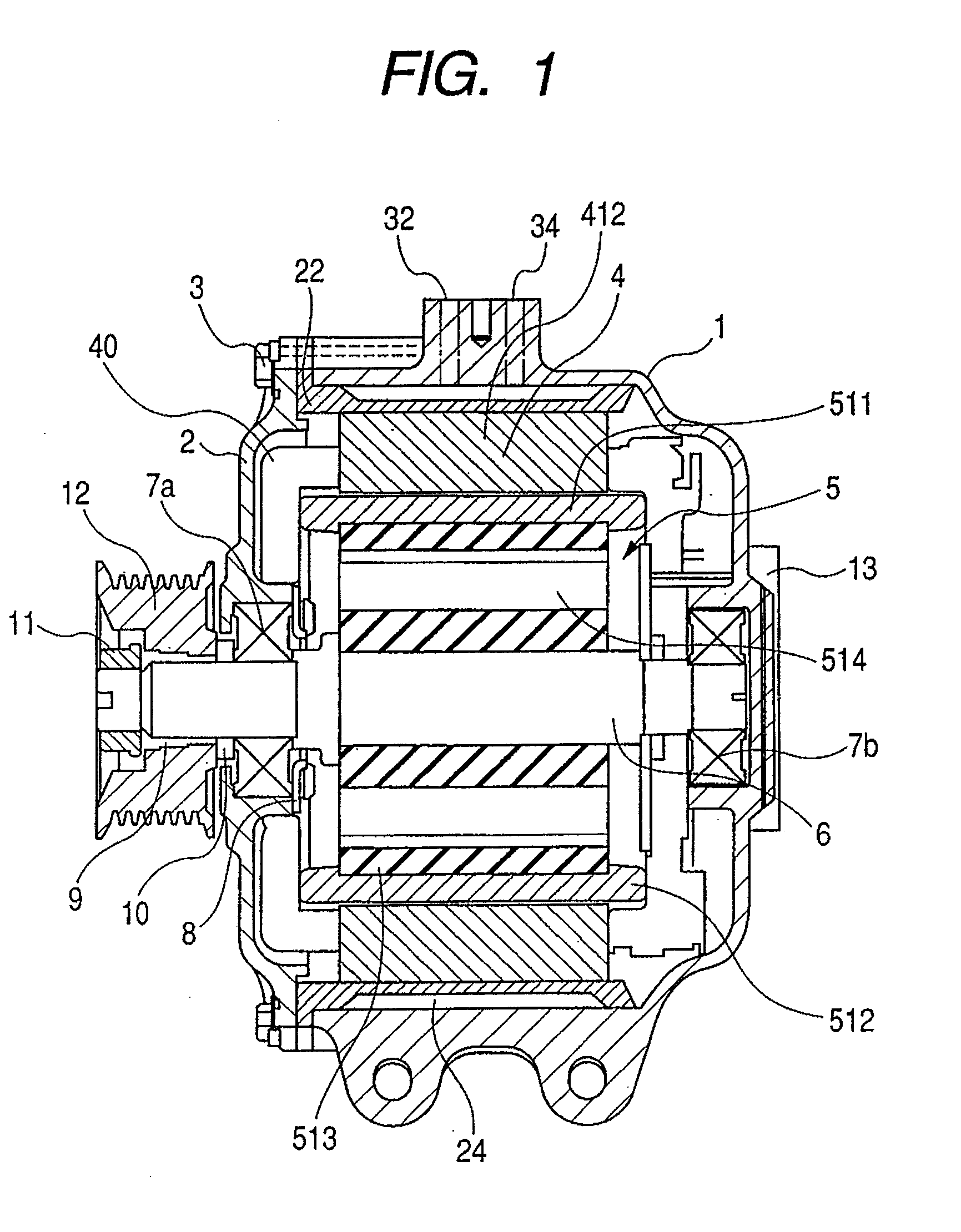
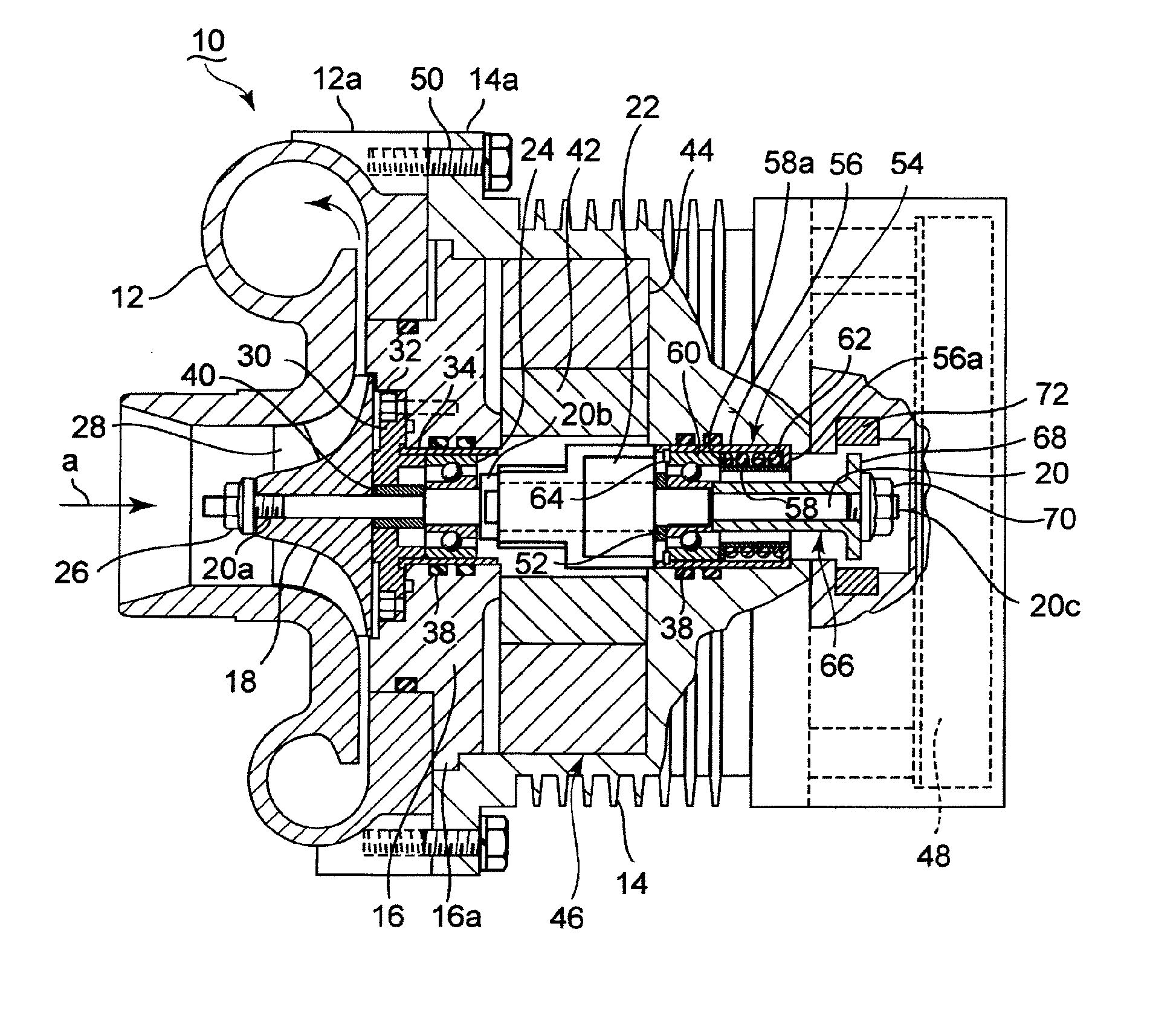
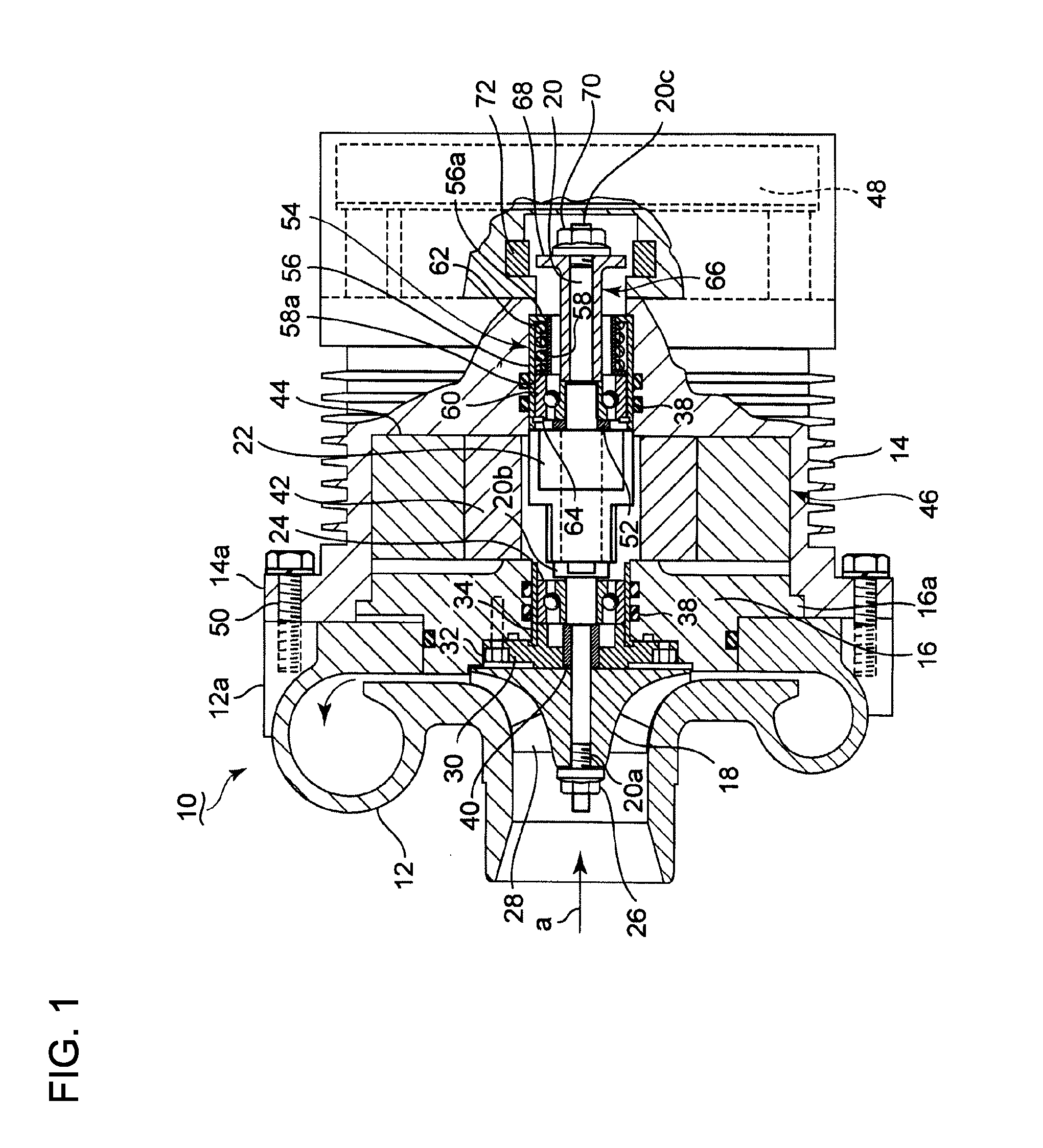
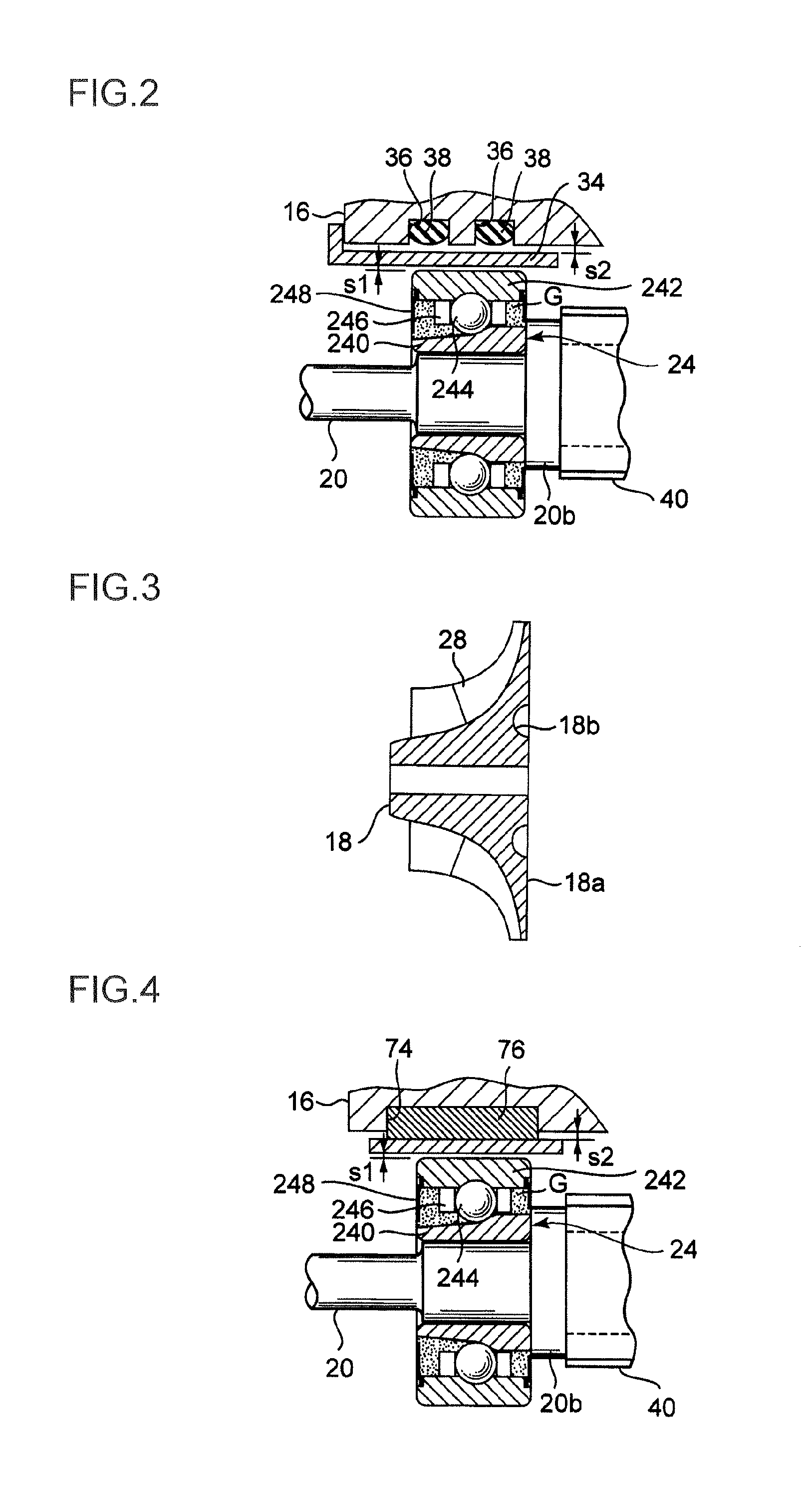
Electric supercharger, assembling method of the same, and internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20140090626A1Reduce vibrationSuppress reduction in output of rotationPump componentsBall bearingsBall bearingExternal combustion engine
It is intended to implement an electric supercharger that has a simplified architecture, is easy to assemble, produces reduced vibration and noise, and has a motor inverter, making it possible to minimize losses in motor output and rotary-shaft output. The electric supercharger is provided with the following: an integrated housing with a built-in electric motor and motor inverter; and a ball bearing and damper-sleeve structure arranged on both sides of the electric motor. The damper-sleeve structure comprises a large-diameter sleeve, a spring guide, a coil spring, and a ball bearing. A gap is formed between the ball bearings and a sleeve and the large-diameter sleeve. The inner ring or outer ring of the ball bearings are supported by various support members disposed on both sides. An elastic O-ring that elastically supports the sleeve and large-diameter sleeve is provided on the outside of the sleeves.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND ENGINE & TURBOCHARGER LTD
Insulation paper inserting machine for motor stator
InactiveCN103337935APrecise positioningEasy clampingApplying solid insulationManual insertionPulp and paper industry
The invention discloses an insulation paper inserting machine for a motor stator, which includes a working platform and a paper feeding device arranged on the working platform, wherein an indentation device and a cutting device are also mounted on the working platform; a paper guide slot is arranged between the indentation device and the cutting device; a paper pushing mechanism is matched with the cutting device; after the paper feeding device sends out a piece of insulation paper, the insulation paper passes through the indentation device, the paper guide slot and the cutting device sequentially, and then is pushed out of the cutting device by the paper pushing mechanism; the insulation paper finally enters the motor stator clamped on a stator clamping workbench on a side surface of the working platform; the stator clamping workbench is connected with the working platform via a rotating shaft, and can turn over around the rotating shaft. Through the manner, the insulation paper inserting machine for the motor stator not only has the insulation paper forming function, but also can push the clamped insulation paper into a groove of the motor stator, has efficient automatic performance, and puts an end to the low efficiency working manner of manual insertion.
Owner:NIDE MECHANICAL EQUIP
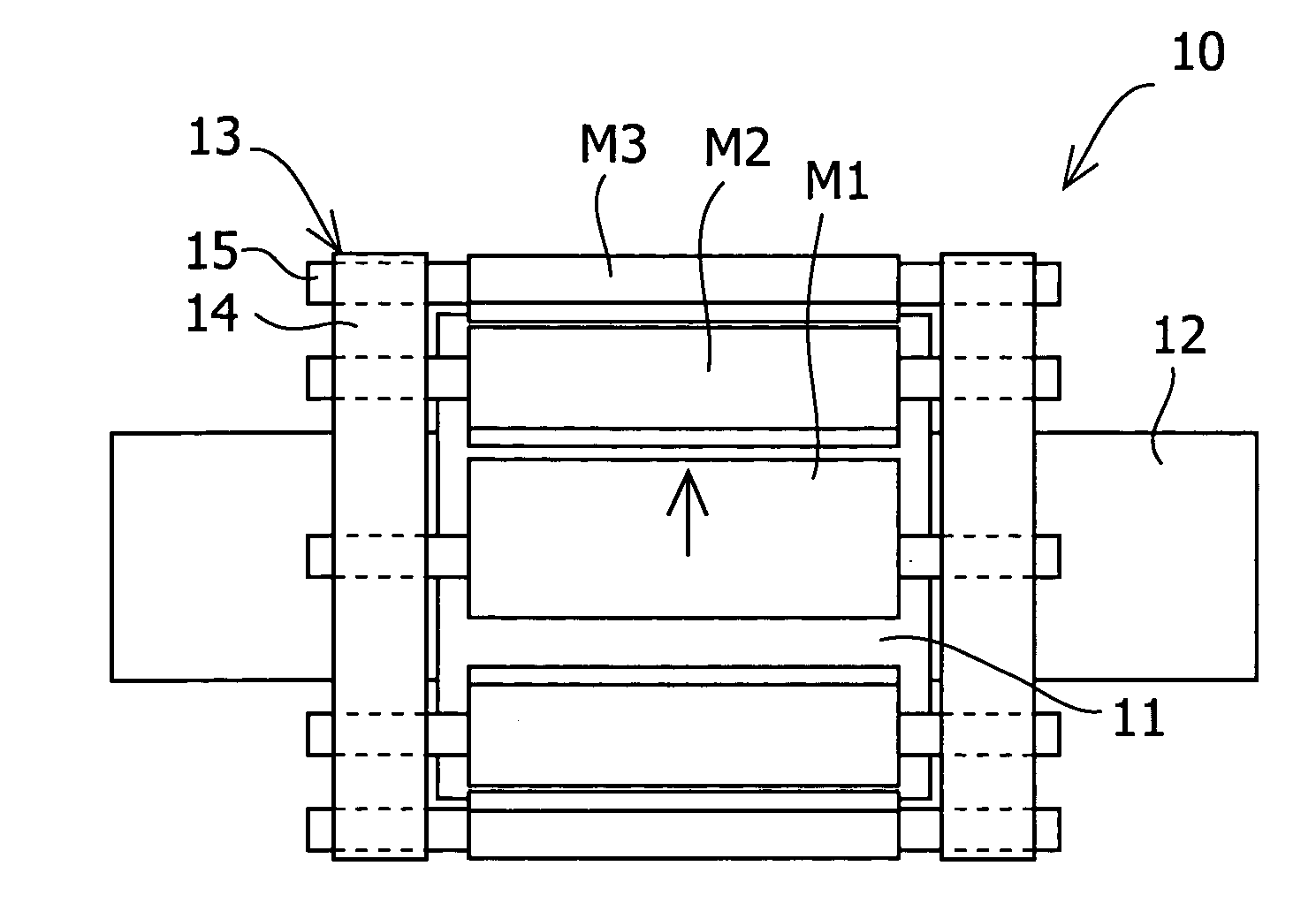
Permanent magnet motor
InactiveUS20060038457A1Reduce the cogging torque of servomotorsImprove accuracyMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesElectric power steeringElectric machine
To reduce the cogging torque of servomotors, electric power steering motors, and others, there is provided a permanent magnet motor comprising: a rotor 10 comprising a rotor yoke 11 and a plurality of permanent magnets (M1-M10); and a stator 20 comprising a stator yoke 22, salient magnetic poles 21, and armature windings 23, wherein at least one of the permanent magnets is disposed in an adjustment position that is displaced from a corresponding reference position in at least one of the circumferential, radial, and axial directions of the rotor yoke, and the plurality of permanent magnets excluding the permanent magnet disposed in the adjustment position is disposed in the reference positions, and wherein the adjustment position is set so that the permanent magnet motor in which at least one of the plurality of permanent magnets is disposed in the adjustment position has a smaller cogging torque than a permanent magnet motor in which all of the plurality of permanent magnets are disposed in the reference positions; and a method for adjusting a cogging torque of a permanent magnet motor.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Methods and apparatus for twisting rotor and stator conductor ends
ActiveUS20090302705A1Magnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machinesElectrical conductorEngineering
Methods and apparatus for twisting rectangular rotor and stator conductor ends whereby most if not all conductor ends are bent at once, radially adjacent ends being bent in opposite directions. A lost motion member may be used to bend selected conductors through lesser angles for such purposes as phase interconnection and power leads. The rectangular conductors are retained against twisting so that flat conductors will bend about an axis perpendicular to the larger dimension of the conductor cross section. Various features of the methods and apparatus are disclosed.
Owner:TECNOMATIC
Field assembly for a motor and method of making same
InactiveUS7038343B2Prevent movementGood for scrollingMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsPower toolRadial surface
A cylindrical magnet ring assembly having a cylinder magnet flux ring (102) formed with a plurality of inwardly projecting anchors (108); a plurality of permanent magnets (104), wherein the magnet can be formed with step portions (112) in the inner radial surface; a molded plastic member (106) being molded around the magnets and anchors to secure the magnets to a surface of the cylinder flux ring. There are several variations of the embodiments of the invention. Few embodiments are the following: in one aspect of the invention, magnets are inserted into magnet molded around an assembly ring (806) and the molded plastic secures the assembly ring to the flux ring; in another aspect, there are two assembly rings, a first assembly ring (is inserted into the one side of the cylinder flux ring then the second assembly ring is inserted into the other side of the cylinder flux ring and mated to the first assembly ring, after that the molded plastic secures the two assembly rings. The foregoing cylindrical magnet ring assembly is used in a stator of a motor which is used in a power tool.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
Generator rotor fretting fatigue crack repair
InactiveUS6849972B1Reduces the low and high cycle fatigue life of the rotorReduces low and high cycle fatigue lifeWindingsMagnetic circuit rotating partsFrettingClassical mechanics
A method of repairing a crack in at least one side of a dovetail portion of a generator rotor coil slot wall, the dovetail portion having received at least two axially adjacent steel wedges and including at least a radial entry surface, an inwardly tapered surface and an intermediate radial surface, the method comprising a) machining a groove at least partly along the inwardly tapered surface to remove damaged material from the coil slot wall; and b) replacing the at least two axially adjacent steel wedges.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Manufacturing method of insulation coil
ActiveUS20050097726A1Good pressure characteristicsImprove thermal conductivityWindings insulation materialWindings insulation shape/form/constructionElectrical conductorInorganic particle
On a surface of a glass cloth adhered a mica layer sheet, a mixture of inorganic particles having a thermal conductivity of at least 5 W / mK, a resin, and a solvent is applied to form a layer of the mixture of the inorganic particles, the resin, and the solvent; the layer of the mixture is reduced in thickness using a doctor blade, followed by pressurizing to form a high thermally conducting layer; the mica layer sheet on which the high thermally conducting layer is disposed is cut to obtain a mica insulating tape; and the mica insulation tape is wound around a coil conductor. As a result, an insulated coil that is excellent in the voltage endurance characteristics and has a high thermal conductivity is manufactured.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method for manufacturing an electric machine and electric machine manufactured according to said method
InactiveUS20080042498A1High mechanical strengthImprove cooling effectMagnetic circuit stationary partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesElectrical conductorElectric machine
A method for manufacturing a machine element of an electric machine, with a plurality of magnetic poles distributed around a machine axis and with at least one coil, having several conductors distributed around the machine axis and each of which is located in a groove, wherein the machine element forms a gap surface enclosing the machine axis, on which (gap surface) when the machine is mounted it adjoins a second machine element via a machine gap and is made of a plastic, and wherein at least in the recesses for the conductors, channel sections are formed through which a coolant can circulate.
Owner:SALWIT AGRARENERGIE
Spoke permanent magnet rotors for electrical machines and methods of manufacturing same
ActiveUS20050088052A1Improve performanceLow costMagnetic circuit rotating partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesPermanent magnet rotorElectric machine
A rotor assembly for an electric motor includes a spoke permanent magnet rotor and a shaft connected thereto. The spoke permanent magnet rotor has an axis of rotation, permanent magnet material, and ferro-magnetic material. The permanent magnet material extends outwardly relative to the axis of rotation to form a plurality of outwardly extending spoke portions of permanent magnet material. The ferro-magnetic material is positioned adjacent to the outwardly extending spoke portions of permanent magnet material. The shaft supports the spoke permanent magnet rotor for rotation about the axis of rotation. The permanent magnet material may circumferentially surround the axis of rotation to form a center portion of permanent magnet material. Further, the axis of rotation may pass through the permanent magnet material. The spoke permanent magnet rotor may be formed using a compaction process and / or an injection molding process.
Owner:REGAL BELOIT AMERICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com