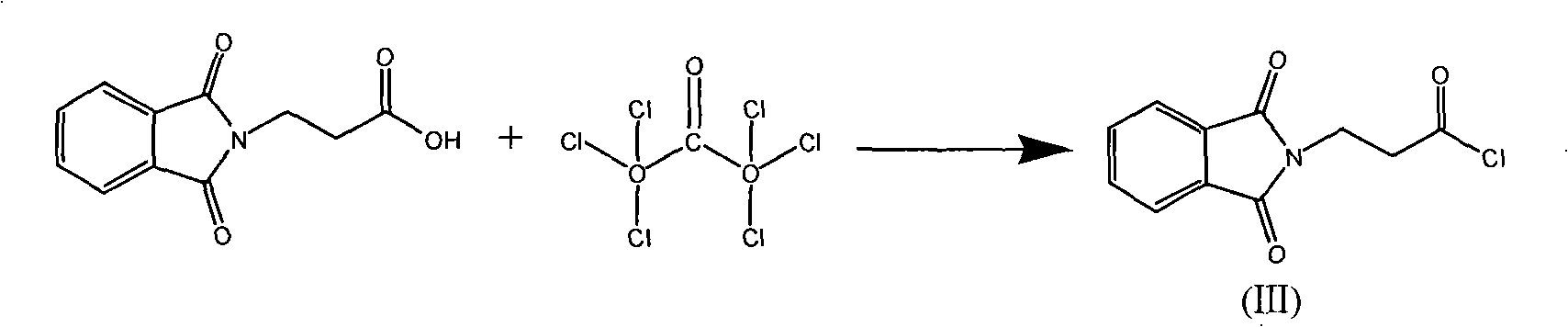
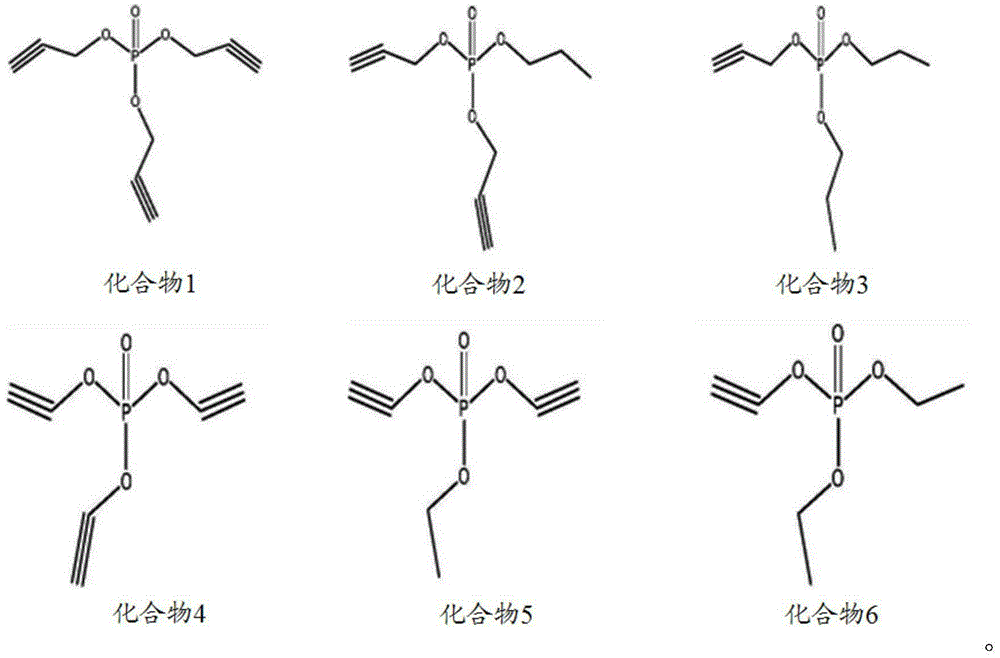
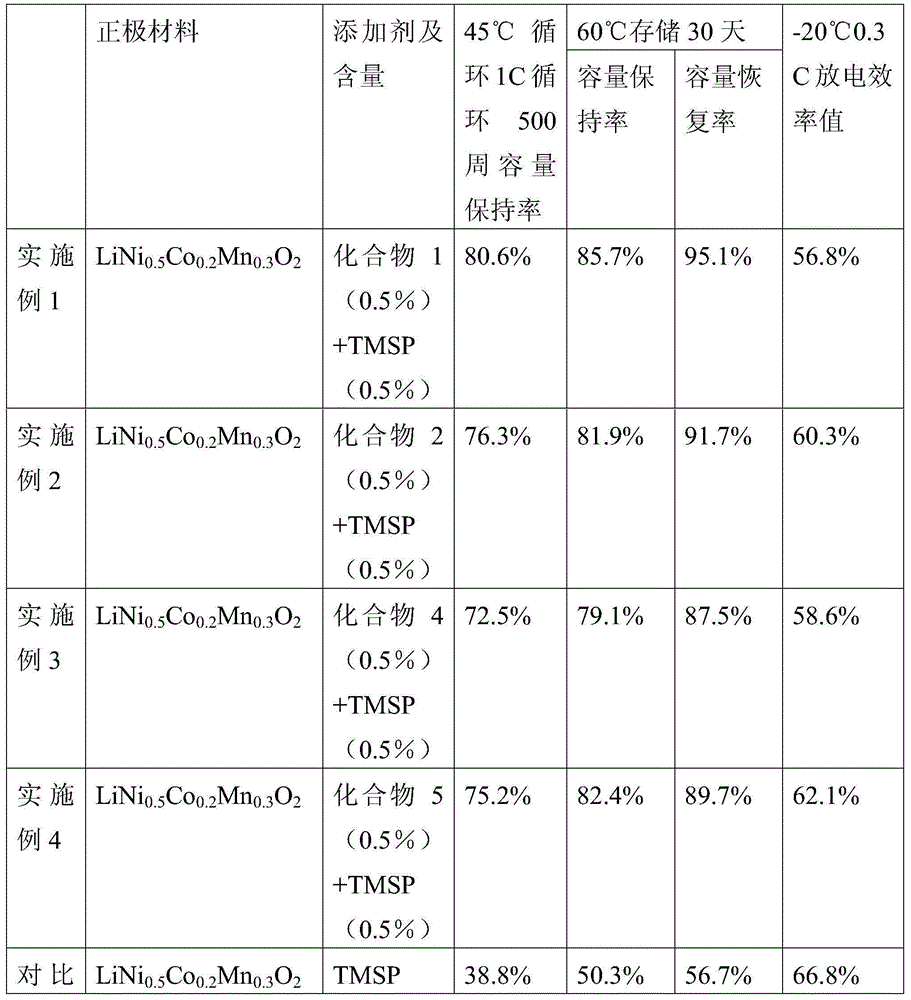
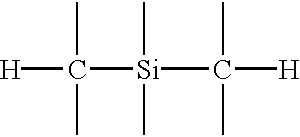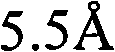Patents
Literature
649 results about "Trimethylsilane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Trimethylsilane or trimethylsilyl hydride, is a gas at ambient conditions with the formula C₃H₁₀Si. It is very flammable. Trimethylsilane is used in the semi-conductor industry as precursor to deposit dielectrics and barrier layers via plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PE-CVD).. It is also used a source gas to deposit TiSiCN hard coatings via plasma-enhanced magnetron sputtering (PEMS). It has also been used to deposit silicon carbide hard coatings via low-pressure chemical vapor deposition (LP-CVD) at relatively low temperatures <1000ᵒC. It is an expensive gas but safer to use than silane (SiH₄); and produces properties in the coatings that cannot be undertaken by multiple source gases containing silicon and carbon.
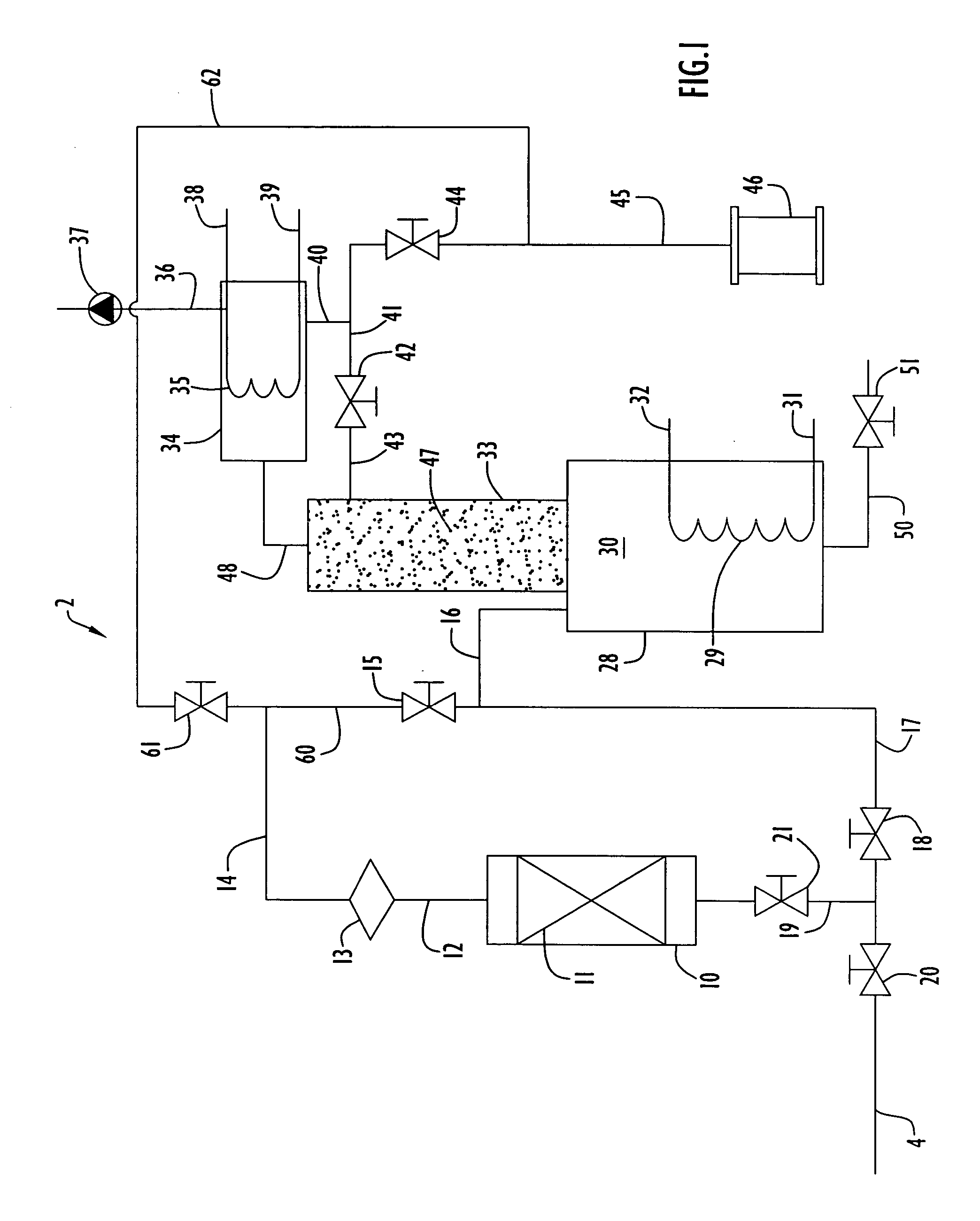
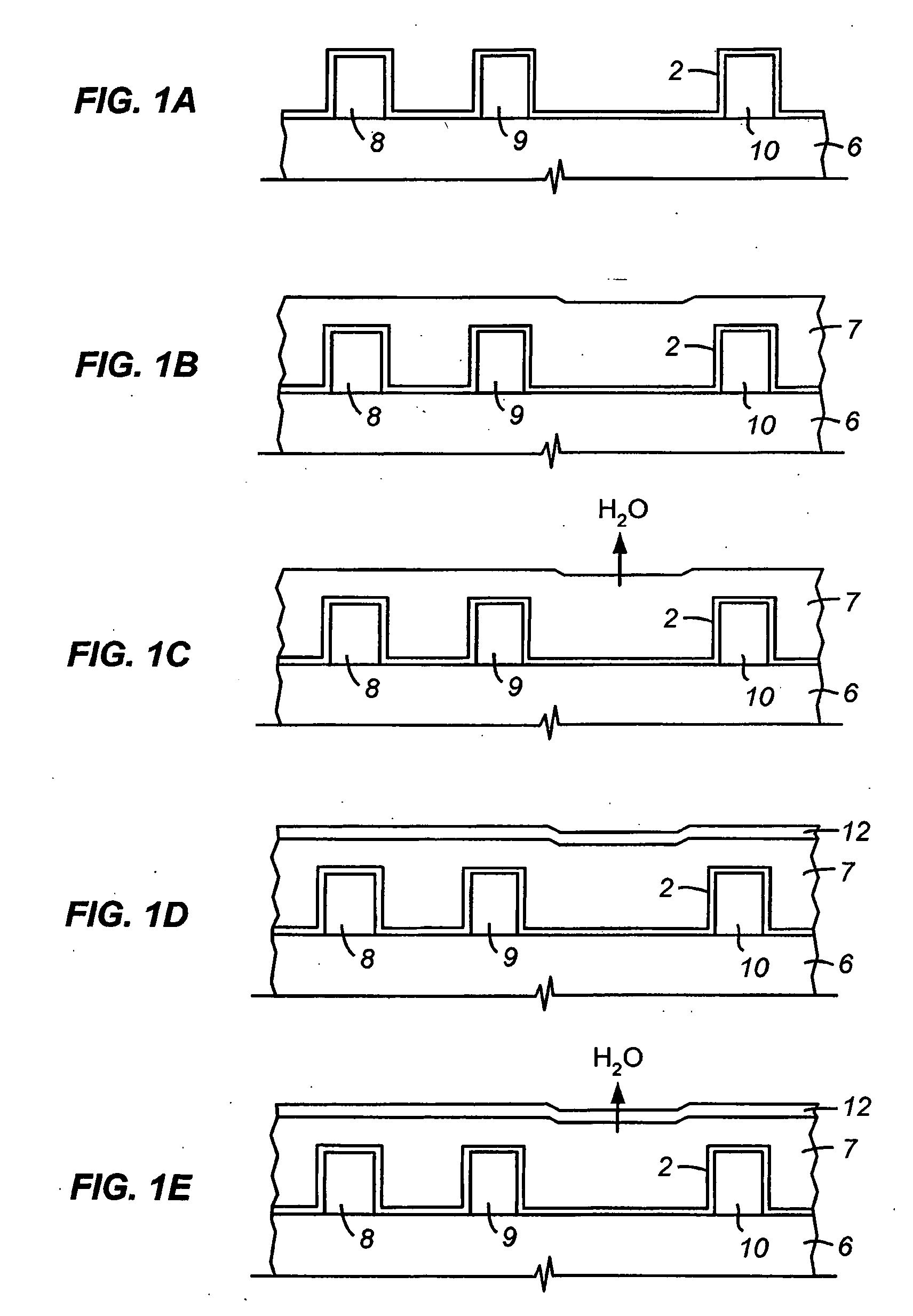
Method of depositing low k films using an oxidizing plasma
InactiveUS6593247B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTrimethylsilaneSilicon oxide
A silicon oxide layer is produced by plasma enhanced oxidation of an organosilicon compound to deposit films having a carbon content of at least 1% by atomic weight. Films having low moisture content and resistance to cracking are deposited by introducing oxygen into the processing chamber at a flow rate of less than or equal to the flow rate of the organosilicon compounds, and generating a plasma at a power density ranging between 0.9 W / cm2 and about 3.2 W / cm2. An optional carrier gas may be introduced to facilitate the deposition process at a flow rate less than or equal to the flow rate of the organosilicon compounds. The organosilicon compound preferably has 2 or 3 carbon atoms bonded to each silicon atom, such as trimethylsilane, (CH3)3SiH. An oxygen rich surface may be formed adjacent the silicon oxide layer by temporarily increasing oxidation of the organosilicon compound.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
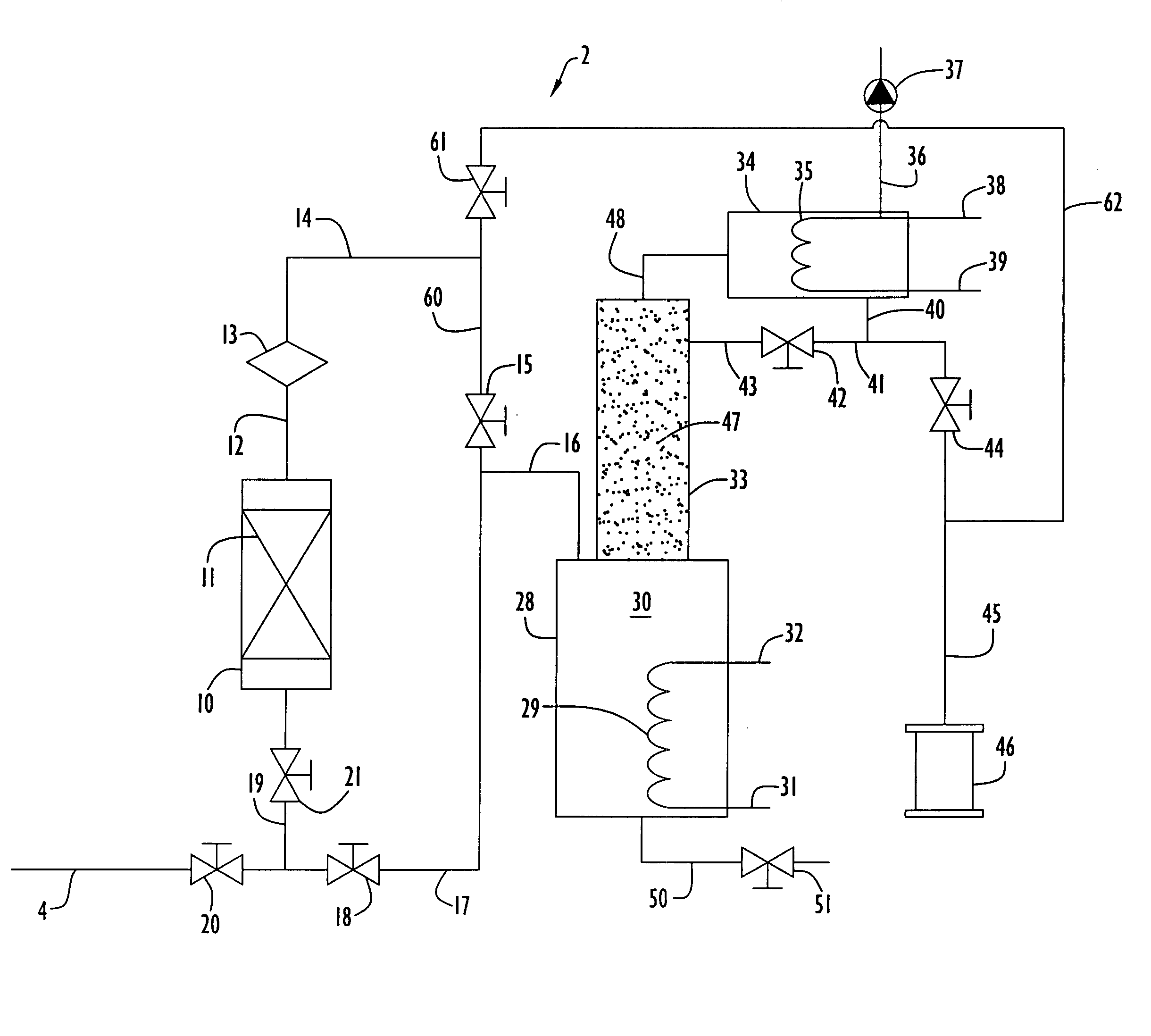
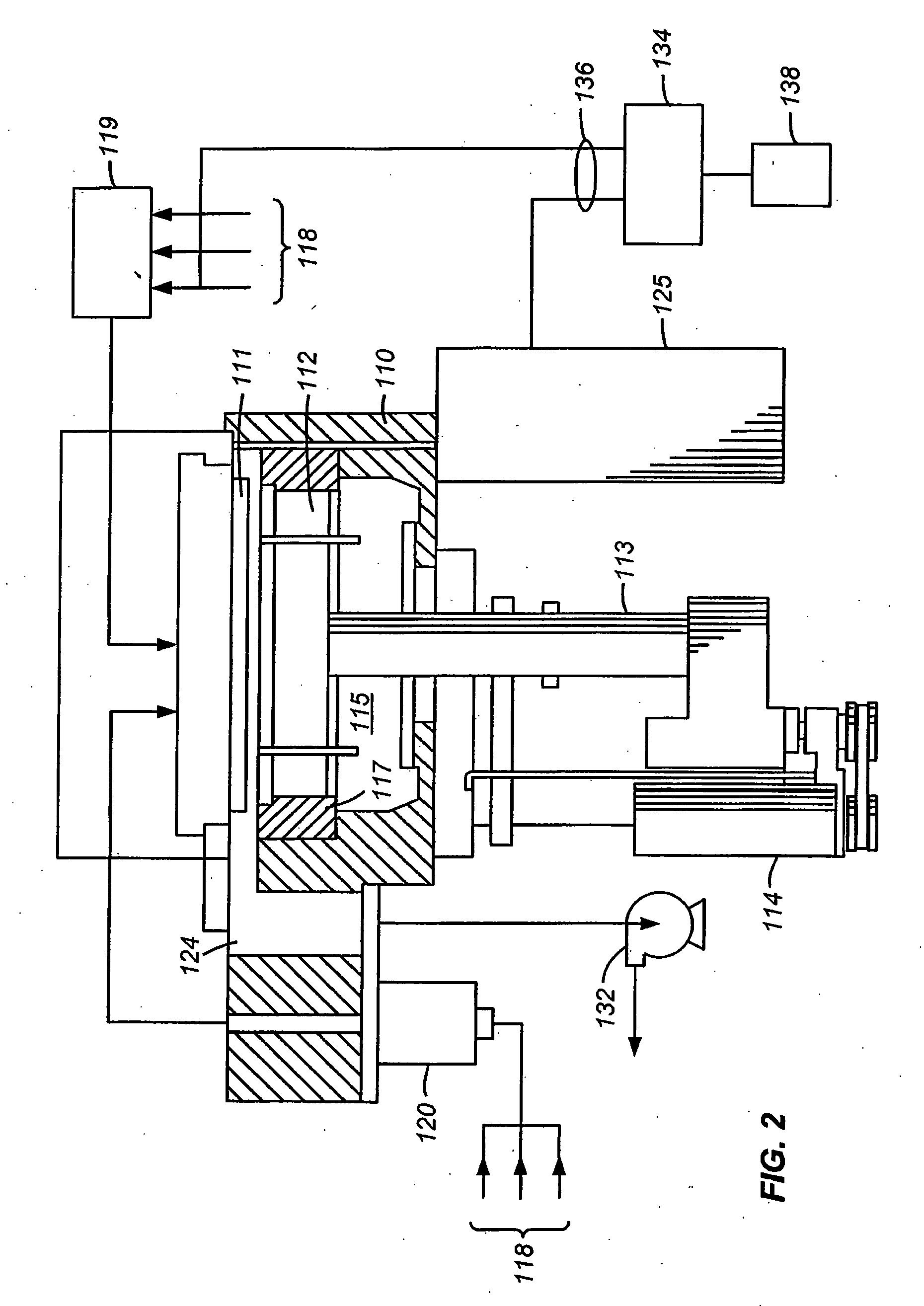
Fluid storage and delivery system utilizing low heels carbon sorbent medium
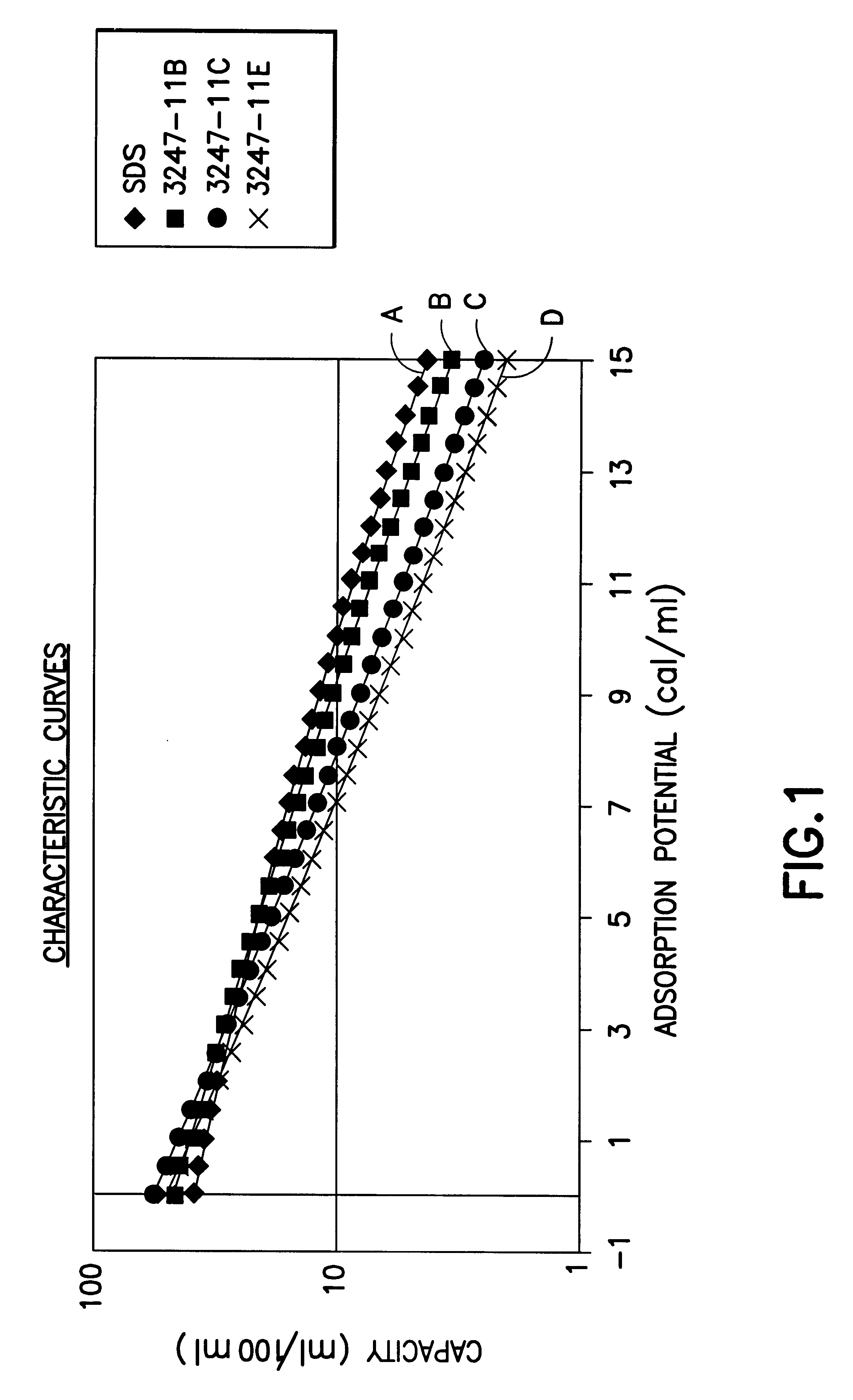
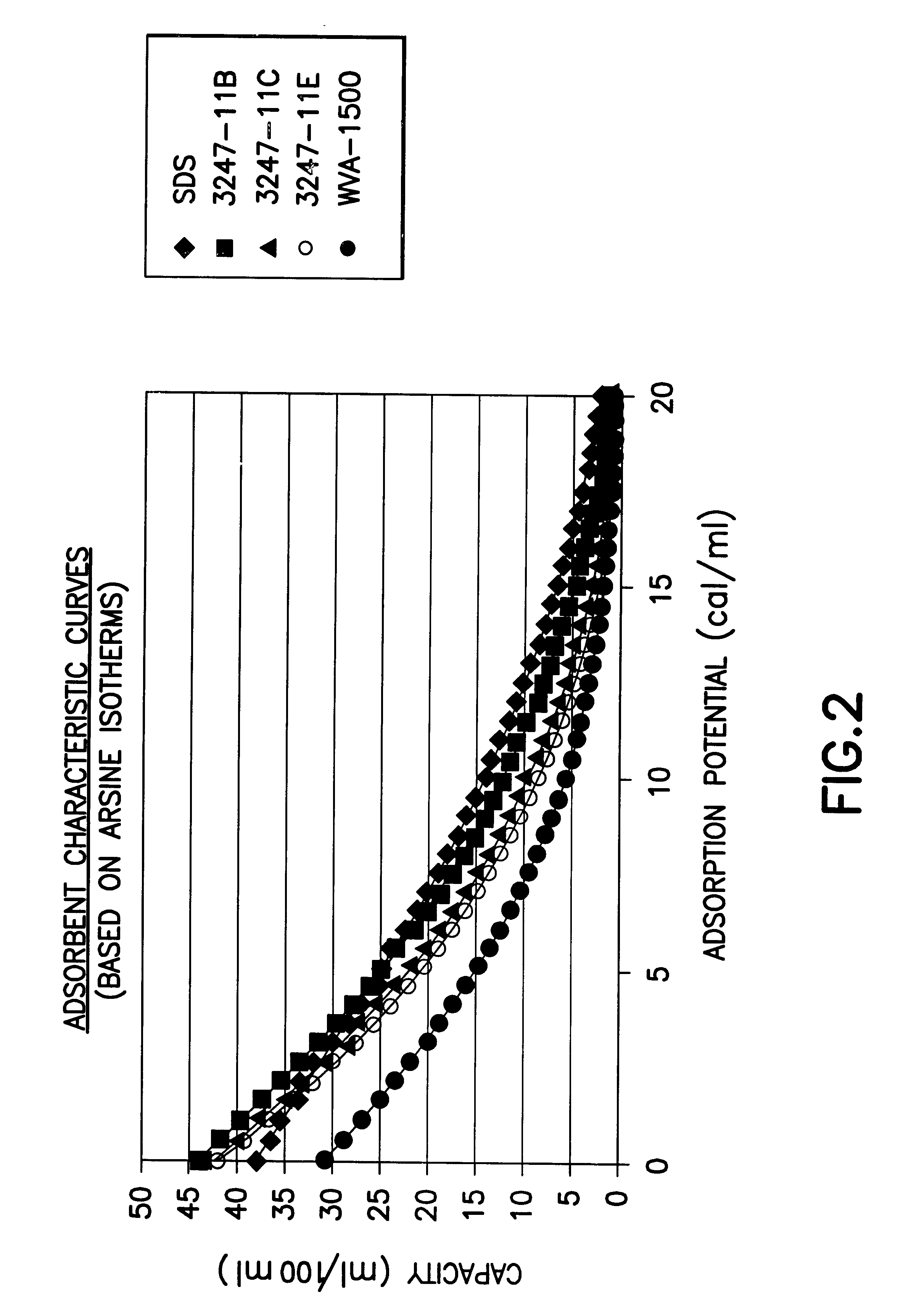
InactiveUS6592653B2Reduces sufficiencyImprove adsorption capacityGas treatmentOther chemical processesDesorptionSorbent
A fluid storage and dispensing system including a vessel containing a low heel carbon sorbent having fluid adsorbed thereon, with the system arranged to effect desorption of the fluid from the sorbent for dispensing of fluid on demand. The low heel carbon sorbent preferably is characterized by at least one of the following characteristics: (i) Heel, measured for gaseous arsine (AsH3) at 20° C. at 20 Torr, of not more than 50 grams AsH3 per liter of bed of the sorbent material; (ii) Heel, measured for gaseous boron trifluoride (BF3) at 20° C. at 20 Torr, of not more than 20 grams boron trifloride per liter of bed of the sorbent material; (iii) Heel, measured for gaseous germanium tetrafluoride (GeF4) at 20° C. at 20 Torr, of not more than 250 grams AsH3 per liter of bed of the sorbent material; (iv) Heel, measured for gaseous arsenic pentafluoride (AsF5) at 20° C. at 20 Torr, of not more than 700 grams AsF5 per liter of bed of the sorbent material; (v) Heel, measured for gaseous trimethyl silane (3MS) at 20° C. at 20 Torr, of not more than 160 grams 3MS per liter of bed of the sorbent material; and (vi) Heel, measured for gaseous ethane (C2H4) at 21° C. at 25 Torr, of not more than 10 grams ethane per liter of bed of the sorbent material.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
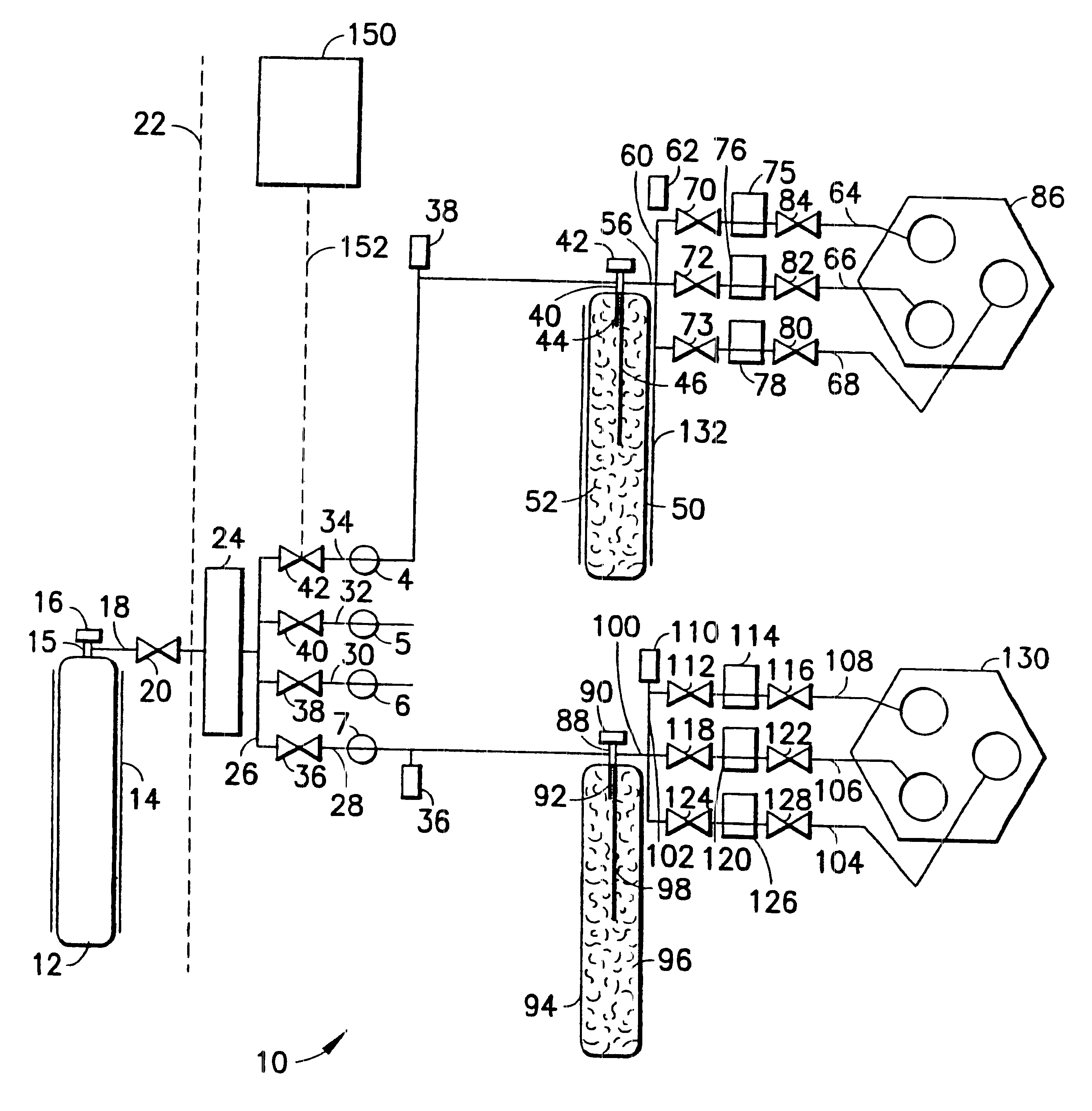
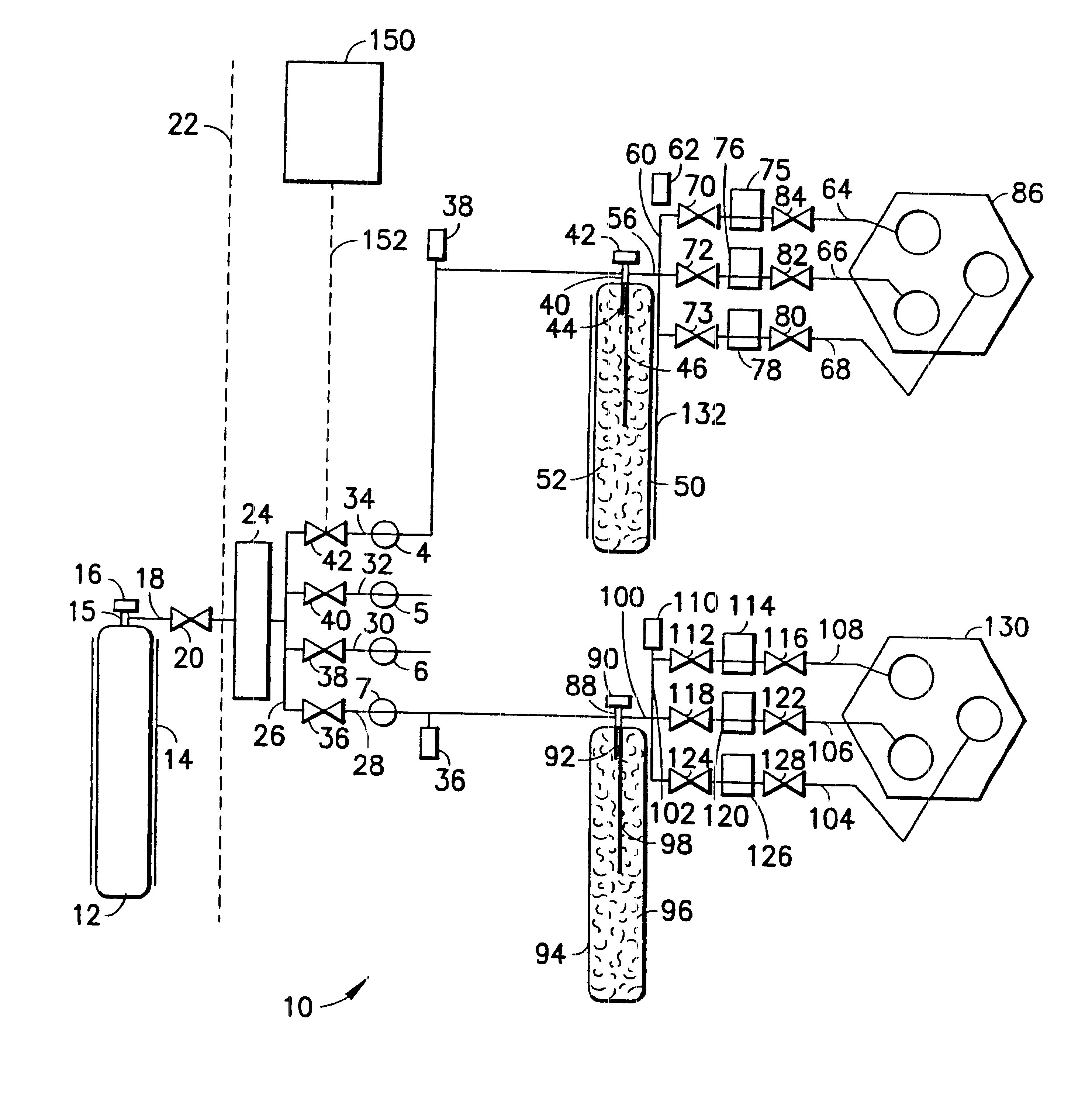
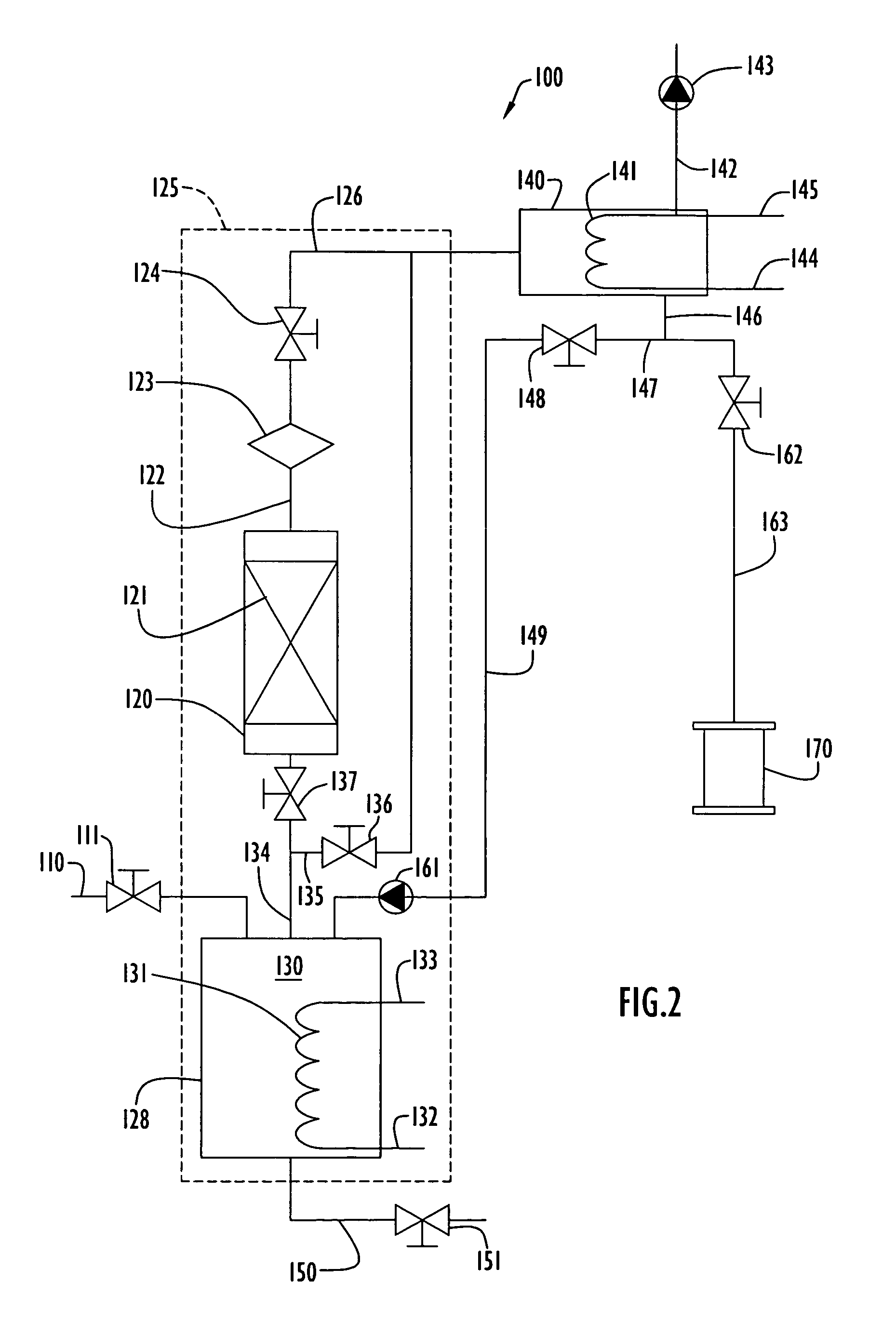
Fluid distribution system and process, and semiconductor fabrication facility utilizing same
A fluid distribution system for supplying a gas to a process facility such as a semiconductor manufacturing plant. The system includes a main fluid supply vessel coupled by flow circuitry to a local sorbent-containing supply vessel from which fluid, e.g., low pressure compressed gas, is dispensed to a fluid-consuming unit, e.g., a semiconductor manufacturing tool. A fluid pressure regulator is disposed in the flow circuitry or the main liquid supply vessel and ensures that the gas flowed to the fluid-consuming unit is at desired pressure. The system and associated method are particularly suited to the supply and utilization of liquefied compressed gases such as trimethylsilane, arsine, phosphine, and dichlorosilane.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
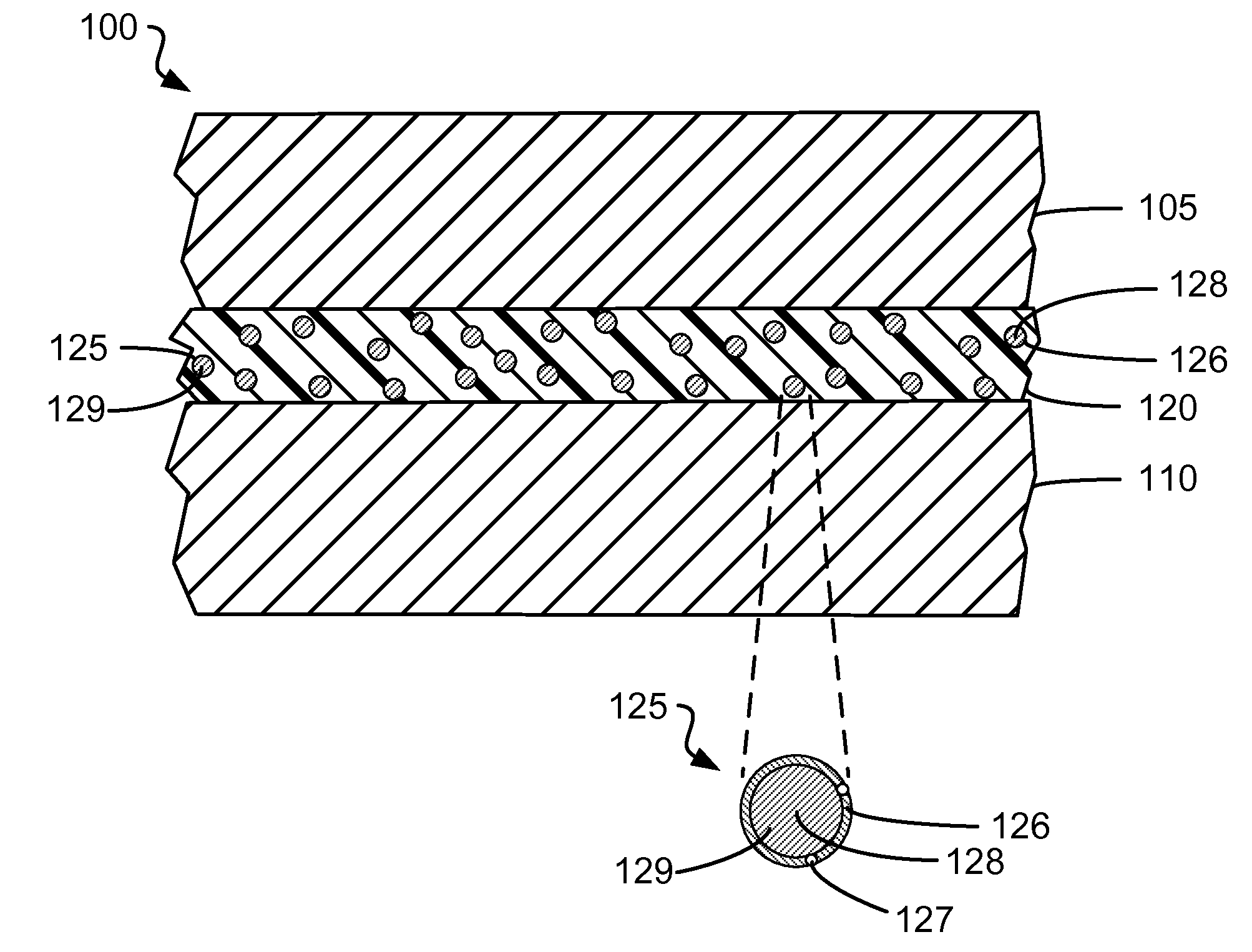
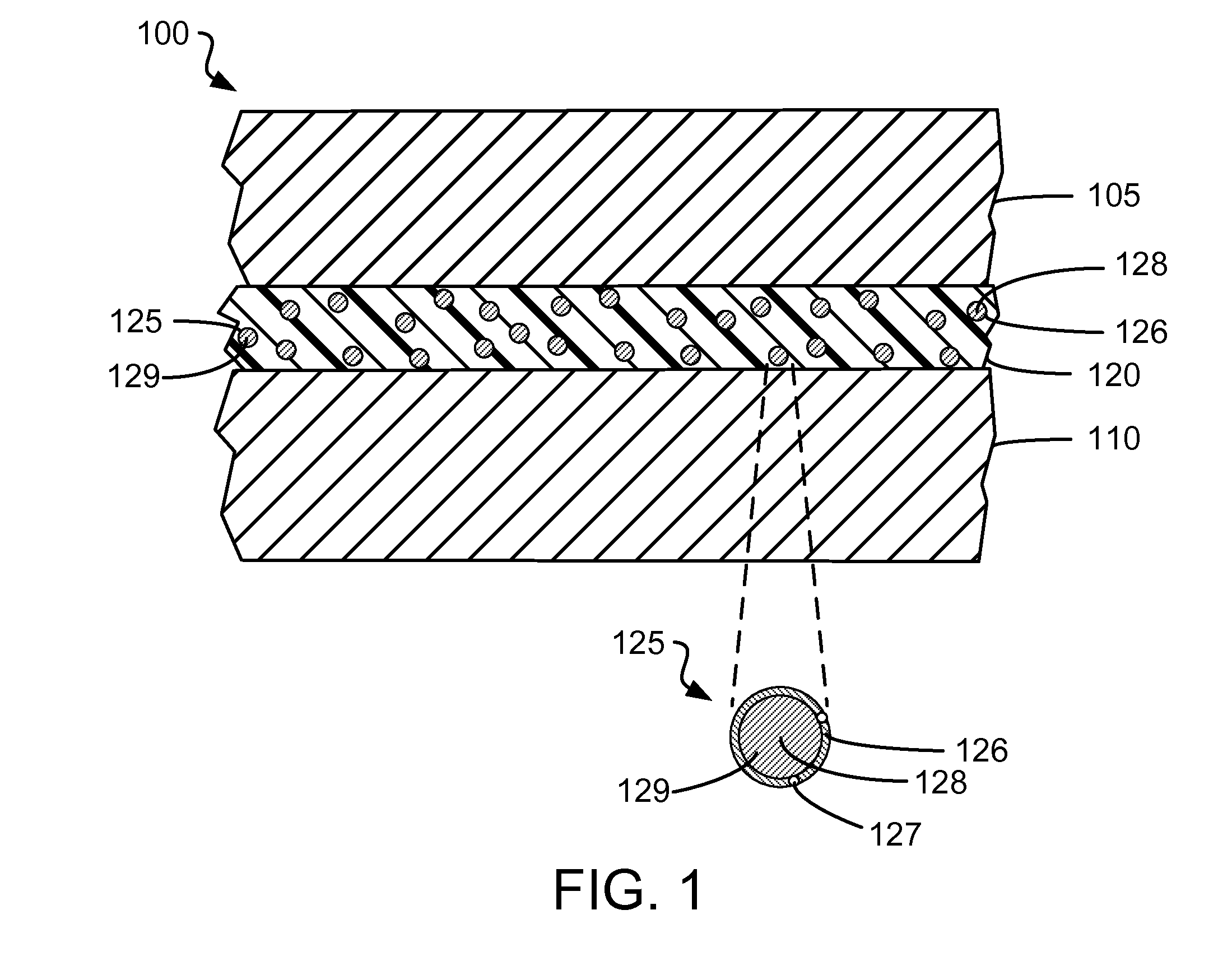
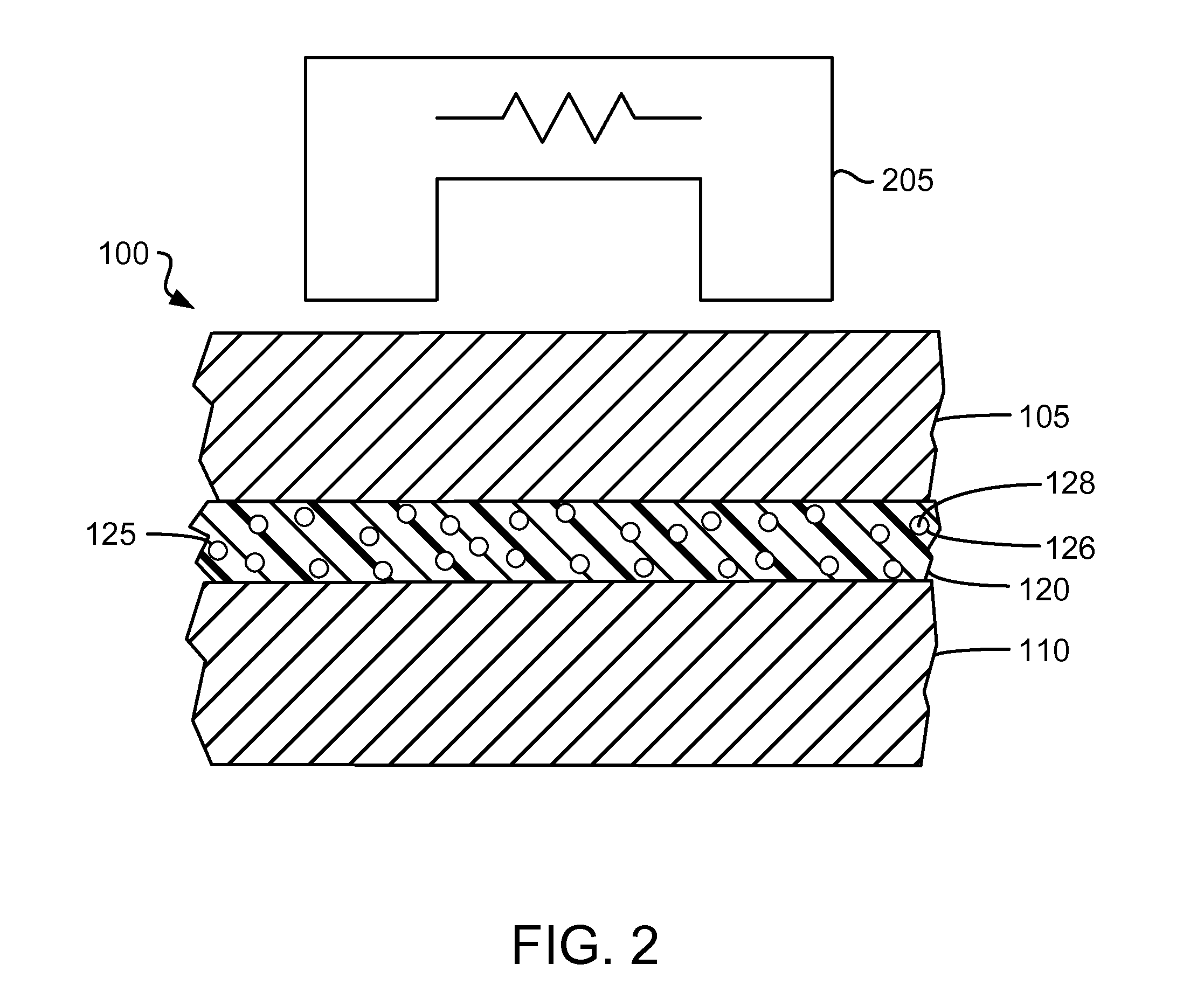
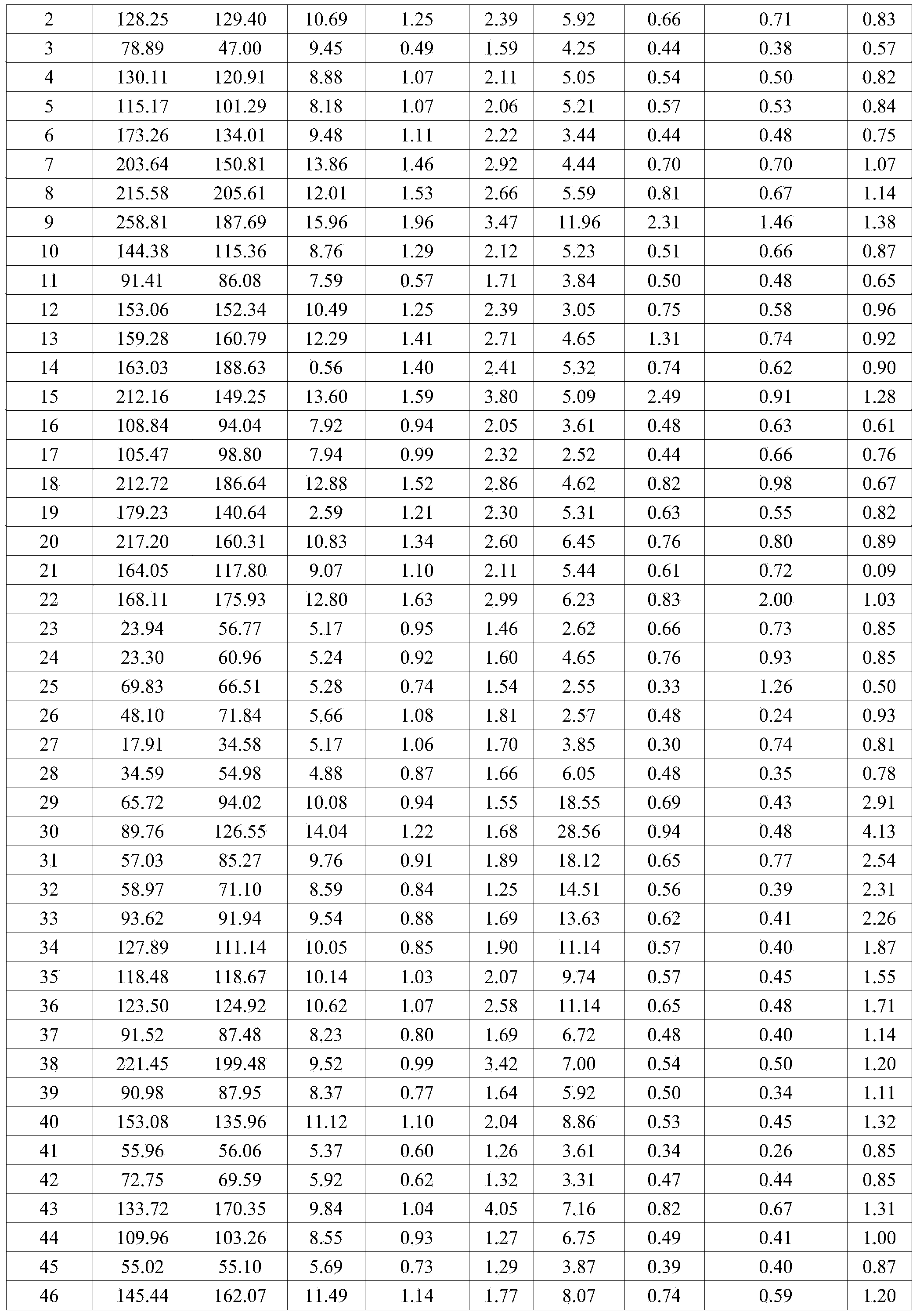
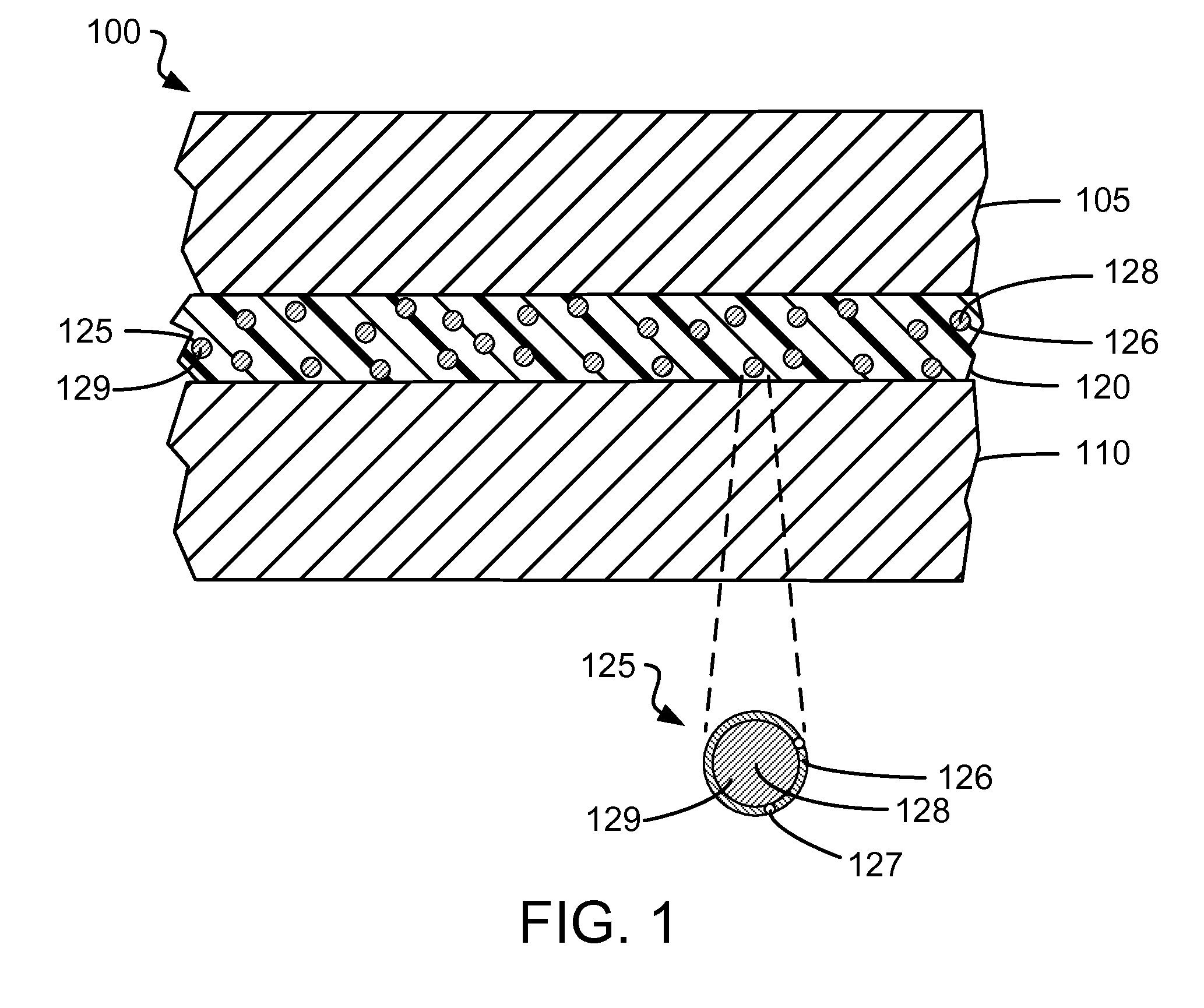
Microcapsules adapted to rupture in a magnetic field to enable easy removal of one substrate from another for enhanced reworkability
ActiveUS20130034739A1Excellent reworkabilityReduce bond strengthLamination ancillary operationsMagnetic paintsIn situ polymerizationMagnetite Nanoparticles
An enhanced thermal interface material (TIM) gap filler for filling a gap between two substrates (e.g., between a coldplate and an electronics module) includes microcapsules adapted to rupture in a magnetic field. The microcapsules, which are distributed in a TIM gap filler, each have a shell that encapsulates a solvent. One or more organosilane-coated magnetic nanoparticles is / are covalently bound into the shell of each microcapsule. In one embodiment, (3-aminopropyl) trimethylsilane-coated magnetite nanoparticles are incorporated into the shell of a urea-formaldehyde (UF) microcapsule during in situ polymerization. To enable easy removal of one substrate affixed to another substrate by the enhanced TIM gap filler, the substrates are positioned within a magnetic field sufficient to rupture the microcapsule shells through magnetic stimulation of the organosilane-coated magnetic nanoparticles. The ruptured microcapsule shells release the solvent, which dissolves and / or swells the TIM gap filler, thereby reducing the bond strength between the substrates.
Owner:IBM CORP
Compositions and Methods for the Treatment of Inflammatory Dermatosis and Other Pathological Conditions of the Skin
InactiveUS20100080768A1Small sizeReduce appearanceOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticActive agentSjogren's disease
The present invention relates to a composition used as a vehicle for percutaneous absorption of Pharmaceutical and Cosmaceutical active agents that comprises Dimethiconol (hydroxyl-terminated polydimethydimethylsiloxane), dimethicone-350 (polydimethylsiloxane-350), cyclomethicone-5 nf (decamethylcyclopentasiloxane), alkymeth siloxane copolyol-lauryl peg / ppg 18 / 18 methicone (alkymethyl siloxane copolyol), cyclopentasiloxane and dimethicone Crosspolymer (silicone elastomer and decamethylcyclopentasiloxane), stearoxytrimethylsilane and stearyl alcohol (silicone wax), and deionized water. This composition serves several key applications: (1) it is a vehicle for percutaneous absorption of Pharmaceutical and Cosmaceutical active agents; (2) it acts as a method for utilizing other compositions in the treatment of inflammatory conditions of the skin including, but by no means limited to, atopic dermatitis (eczema), allergic contact dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitits, psoriasis, xerosis and atopia; (3) it is a treatment of inflammatory conditions of mucosae; (4) it relates to other compositions and methods for protecting and enhancing the barrier function of the skin.
Owner:MCGRAW THOMAS L +3
Purification of silicon-containing materials
InactiveUS20050054211A1Impurities increaseSilicon organic compoundsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilanesLiquid state
Systems and methods of purifying a silicon-containing material include the step of directing the silicon-containing material in a liquid state through an adsorption unit including an adsorbent material to facilitate adsorption of at least one component from the silicon-containing material. Alternatively, the silicon-containing material is directed, in liquid state and / or gaseous state, through two or more purification units, including an adsorption unit, a vaporization unit, a filter unit and a condenser. The silicon-containing material can be a low-k silicon-containing material such as trimethylsilane, tetramethylsilane, dimethyldimethoxysilane, tetramethylcyclotetrasiloxane, octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane, dimethylphenyl silane, and dimethyldivinyl silane.
Owner:XU MINDI +2
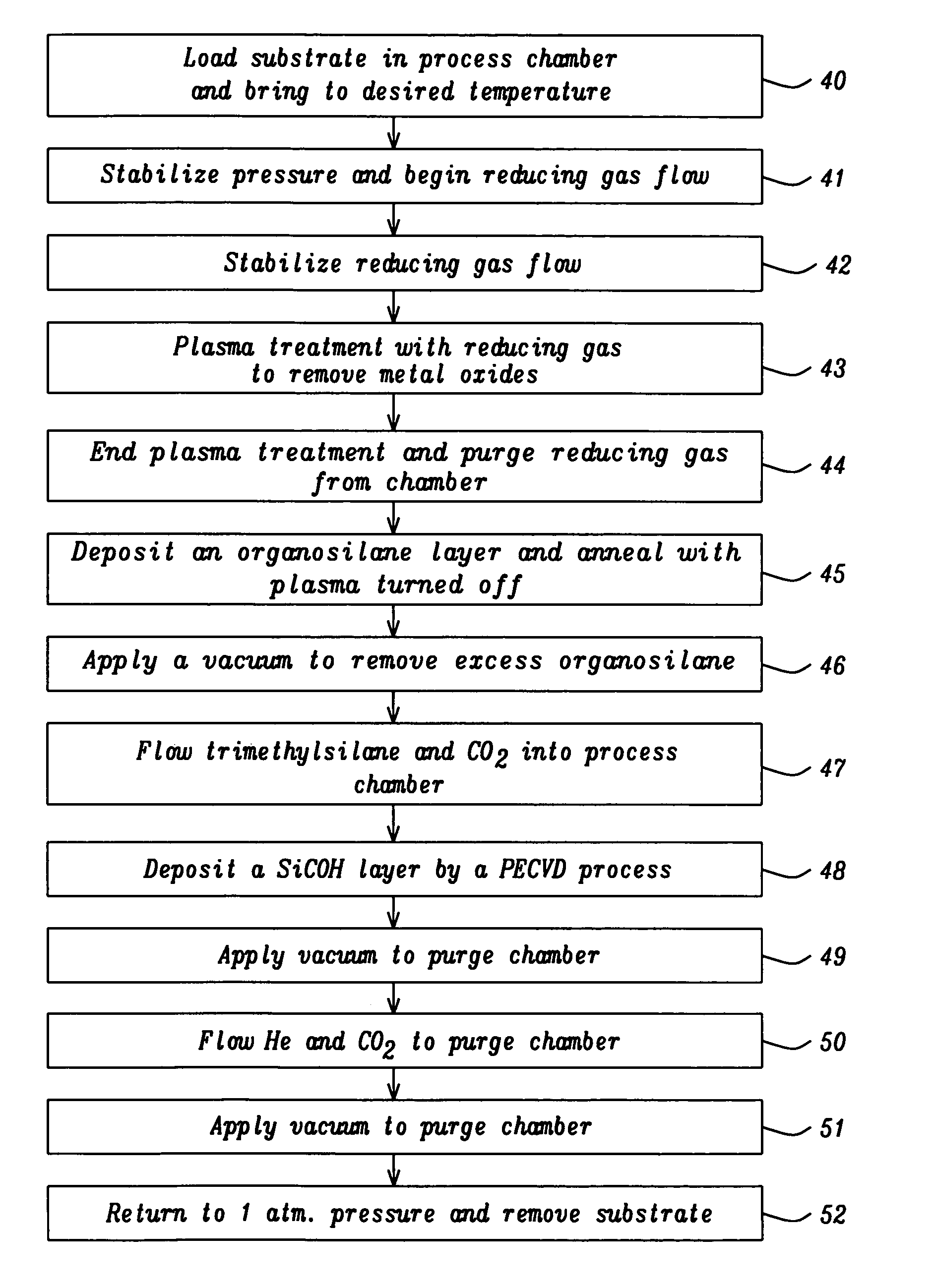
Reliability improvement of SiOC etch with trimethylsilane gas passivation in Cu damascene interconnects
InactiveUS20050245100A1Reduce leakage currentImprove throughputSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTrimethylsilaneLow leakage
A method of forming a SiCOH etch stop layer in a copper damascene process is described. A substrate with an exposed metal layer is treated with H2 or NH3 plasma to remove metal oxides. Trimethylsilane is flowed into a chamber with no RF power at about 350° C. to form at least a monolayer on the exposed metal layer. The SiCOH layer is formed by a PECVD process including trimethylsilane and CO2 source gases. Optionally, a composite SiCOH layer comprised of a low compressive stress layer on a high compressive stress layer is formed on the substrate. A conventional damascene sequence is then used to form a second metal layer on the exposed metal layer. Via Rc stability is improved and a lower leakage current is achieved with the trimethylsilane passivation layer. A composite SiCOH etch stop layer provides improved stress migration resistance compared to a single low stress SiCOH layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Semi-synthetic metal cutting fluid
InactiveCN104830513AImprove cooling effectGood anti-corrosion and anti-rustAdditivesCarboxylic saltEngineering
The invention relates to cutting fluid, in particular to semi-synthetic metal cutting fluid. The semi-synthetic metal cutting fluid is prepared by methyl levulinate, (R)-(+)-2,4-dyhydroxy-N-(3-hydroxypropyl)-3,3-dimethylbutyramide, 2-oxo-1,5-disoidum glutarate dihydrate, 4-piperidone-3-carboxylate hydrochloride and trimethylsilylketene. The semi-synthetic metal cutting fluid has good cooling, anticorrosion, antirust and lubricating performance, service life of a knife can be prolonged effectively, and excellent machining accuracy can be realized; the semi-synthetic metal cutting fluid can play a role in safely and reliably protecting and inhibiting corrosion of nonferrous metal like aluminum and steel and ferrous metal, so that time and cost for subsequent treatment can be omitted; the semi-synthetic metal cutting fluid is suitable for being widely popularized and applied in the field of the cutting fluid.
Owner:烟台顺隆化工科技有限公司
Electrolyte suitable for silicon-carbon negative electrode lithium ion battery and silicon-carbon negative electrode lithium ion battery
ActiveCN105375066AImprove cycle performanceGood high and low temperature performanceSecondary cellsOrganic solventTrimethylsilyl
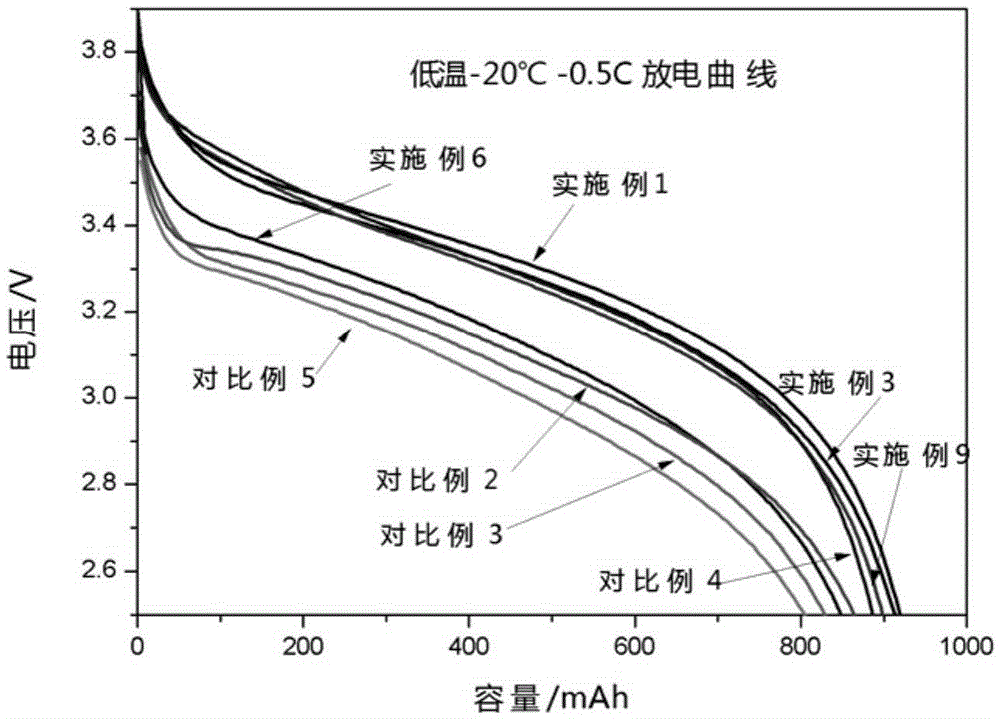
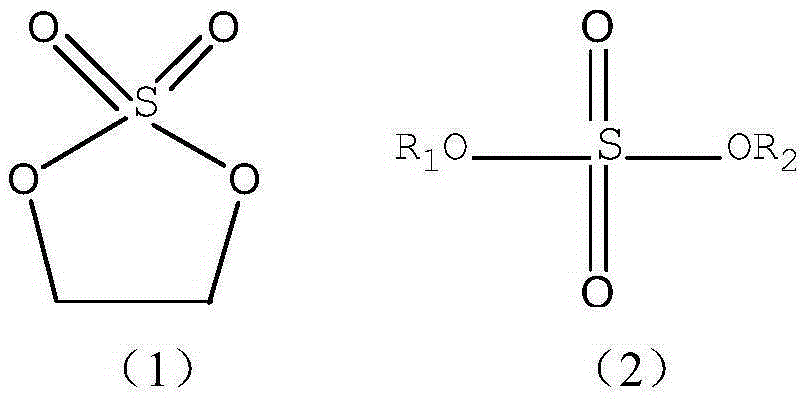
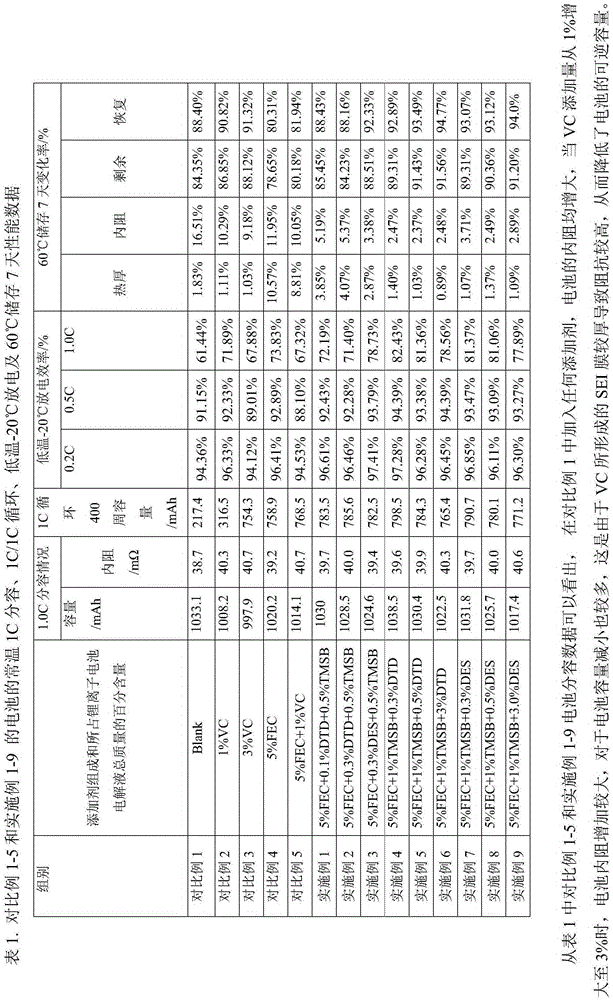
The invention relates to the technical field of lithium ion batteries, in particular to an electrolyte suitable for a silicon-carbon negative electrode lithium ion battery and the silicon-carbon negative electrode lithium ion battery. The electrolyte suitable for the lithium ion battery is prepared from a non-aqueous organic solvent, lithium salt and additives. The additives comprise fluoroethylene carbonate, tris(trimethylsilyl) borate and a sulphate compound with the formula (1) or the formula (2). Compared with the prior art, under the synergistic effect of the three additives in combined use, the capability of changing and controlling SEI composition and stability is achieved, the overall impedance of a formed SEI film is small, and the components and the structure of the SEI film are stable, so that the reversible capacity of the silicon-carbon negative electrode lithium ion battery is greatly increased, the actual discharge capability of the silicon-carbon negative electrode lithium ion battery is greatly improved, then the battery has good cycle performance and good high-and-low temperature performance, and it is guaranteed that the battery can be used within a wide ambient temperature range.
Owner:DONGGUAN SHANSHAN BATTERY MATERIALS
Covalent triazine skeleton doped hybrid membrane preparation method
ActiveCN104722212AEasy and efficient preparationGood repeatabilitySemi-permeable membranesSilanesTriflic acid
A covalent triazine skeleton doped hybrid membrane preparation method comprises the steps of (1) preparation of a covalent triazine skeleton, to be more specific, the formula is organic monomer: a trifluoromethanesulfonic acid, wherein a = 5-50, the organic monomer and the trifluoromethanesulfonic acid are rapidly mixed in a microwave reactor for synthetic of CTFs material by microwave heating, the synthesis temperature is 100 to 150 DEG C, and the synthesis time is 10 to 60 minutes; (2) preparation of a hybrid membrane solution, to be more specific, the formula is b covalent triazine skeleton powder: organic matter, b = 1wt%-60wt%, the organic matter is polydimethylsiloxane, polymethylphenyl siloxane, polyimide, polysulfone and poly trimethyl silane-1-propyne; (3) preparation of the hybrid membrane on a porous carrier by a dipping method; and (4) drying of the hybrid membrane. The hybrid membrane prepared by the method has high liquid separation performance and certain gas separation performance, and the synthesis repeatability is good.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Lithium secondary battery overcharge protection electrolyte and lithium secondary battery
InactiveCN106450461AReduce reactivityImprove cycle performanceLi-accumulatorsSecondary cells servicing/maintenanceElectrical batteryDecomposition
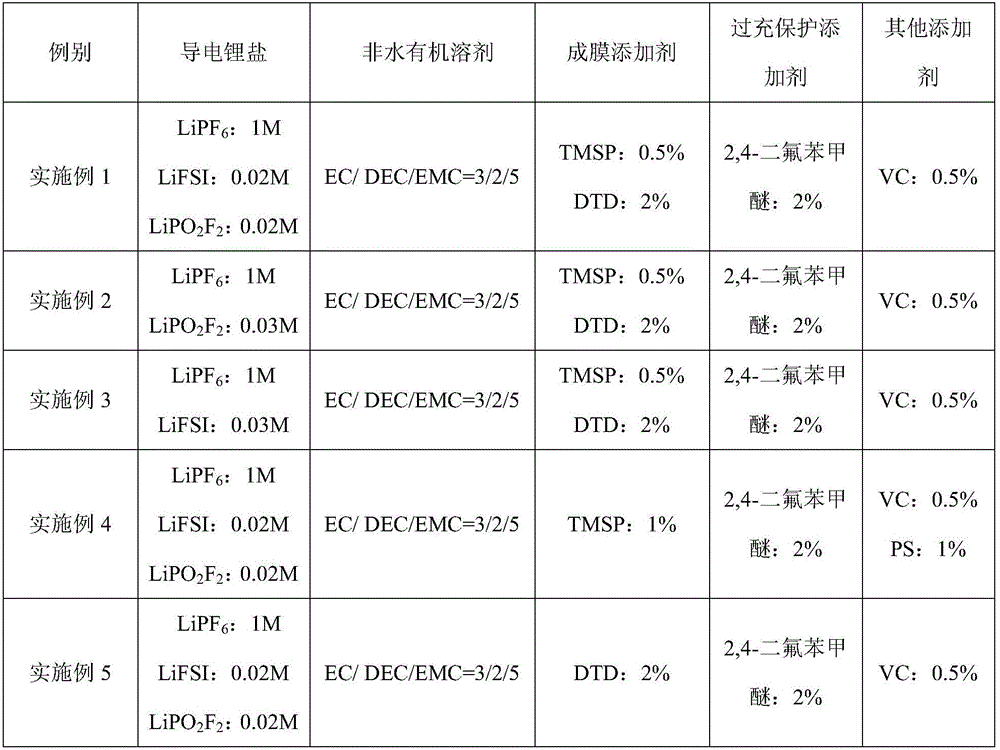
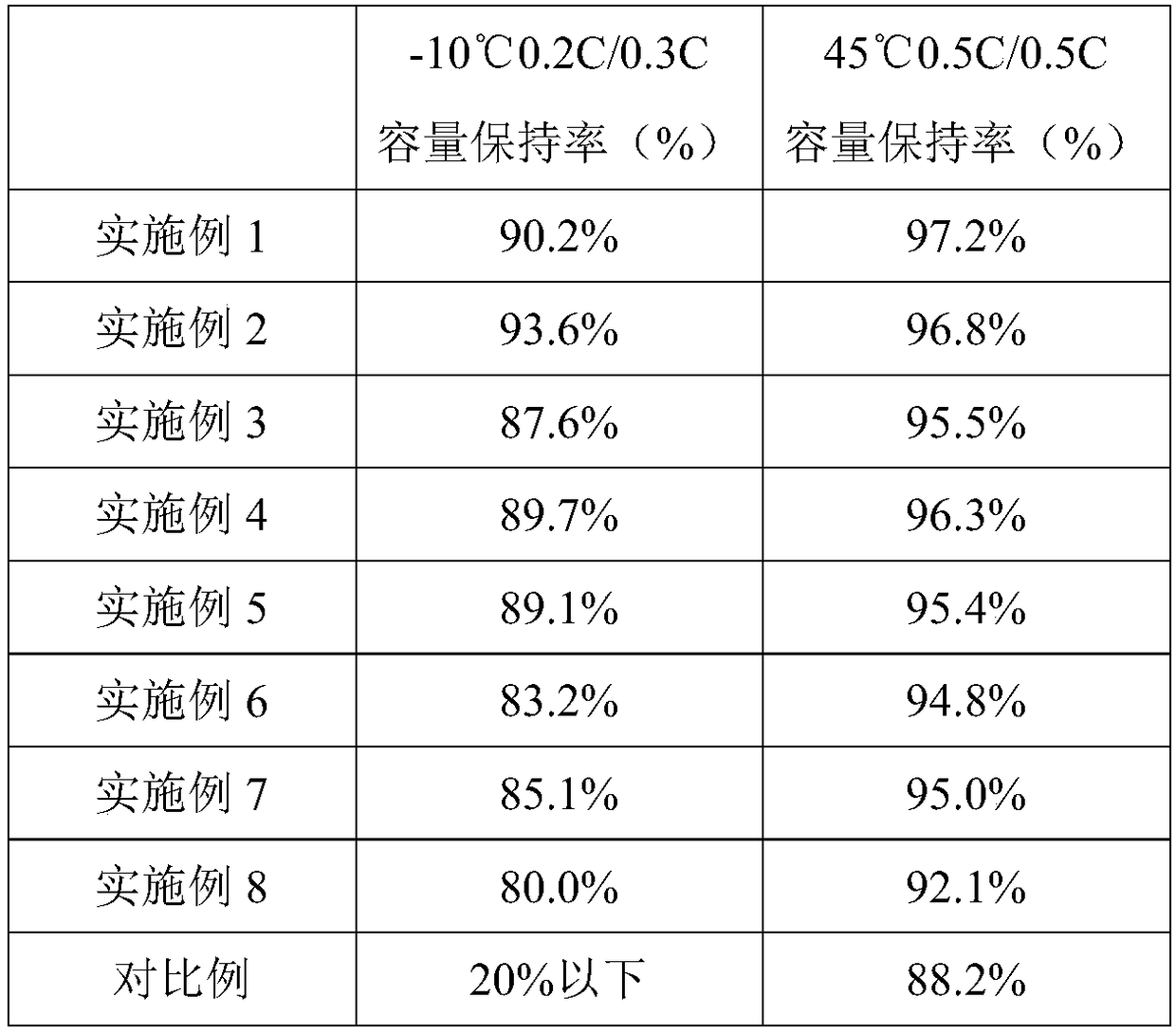
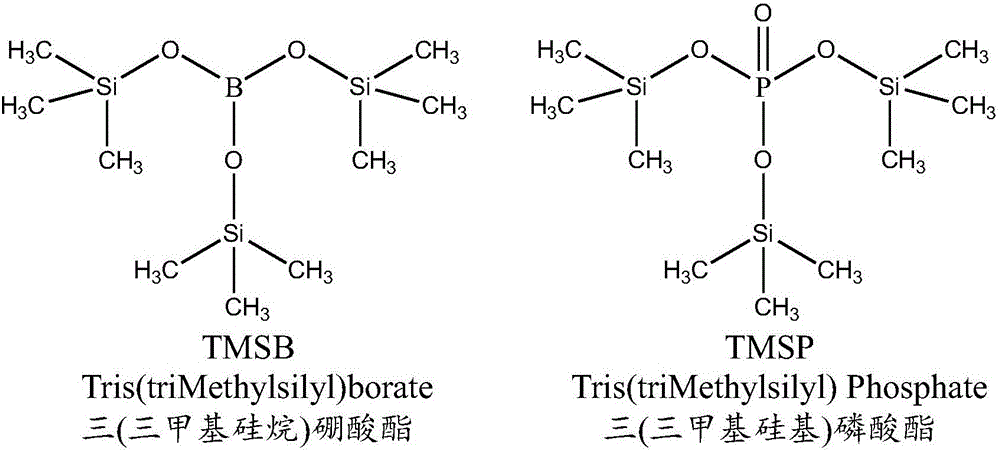
The invention discloses lithium secondary battery overcharge protection electrolyte and a lithium secondary battery. The electrolyte contains electrolyte lithium salts, non-water organic solvents, film forming additives and overcharge protection additives, wherein the film forming additives are at least one kind of materials from TMSP (tris(trimethylsilyl) phosphate) and DTD (dioxathiolane 2,2-dioxide); the overcharge protection additives comprise oxidation and reduction shuttle type overcharge protection additives. The overcharge protection additives used in the electrolyte do not take part in any reaction process at the normal work voltage of 2.75 to 4.35V; when the battery charging voltage exceeds 4.4V, the oxidation and reduction shuttle type overcharge protection additives generate oxidation and reduction shuttle current distribution and voltage limitation on the surface of an electrode; the voltage is controlled to be within a range; the intense decomposition of the electrolyte inside the battery due to too high voltage can be avoided; further, the occurrence of safety problems of combustion, explosion and the like of the battery can be prevented.
Owner:GUANGZHOU TINCI MATERIALS TECH
Lithium ion battery electrolyte and lithium ion battery
InactiveCN108767310AImprove low-temperature cycle performanceSecondary cellsCarbon compositesAluminum Ion
The invention relates to a lithium ion battery electrolyte and a lithium ion battery, and belongs to the technical field of lithium ion batteries. The lithium ion battery electrode comprises an organic solvent, an electrolyte lithium salt, a low-impedance additive and a functional additive, wherein the low-impedance additive comprises lithium difluorophosphate and lithium difluoro bis(oxalato) phosphate, the functional additive is an arbitrary one or a combination of tris(trimethylsilyl) borate and tris(trimethylsilyl) phosphate, and the functional additive accounts for 0.1-4% of the total mass of the lithium ion battery electrolyte. The lithium ion battery electrolyte can participate in negative electrode film formation, the interface impedance of the electrolyte is reduced, and the low-temperature performance of the electrolyte is improved; and a flexible and high-temperature stable electrode interface film also can be formed on a surface of a high-capacity silicon carbon composite negative electrode material, the breakage of an SEI film caused by silicon expansion during the circulation process is timely repaired, and the cycle property of the silicon carbon negative electrode lithium ion battery is improved.
Owner:CHINA AVIATION LITHIUM BATTERY LUOYANG +1
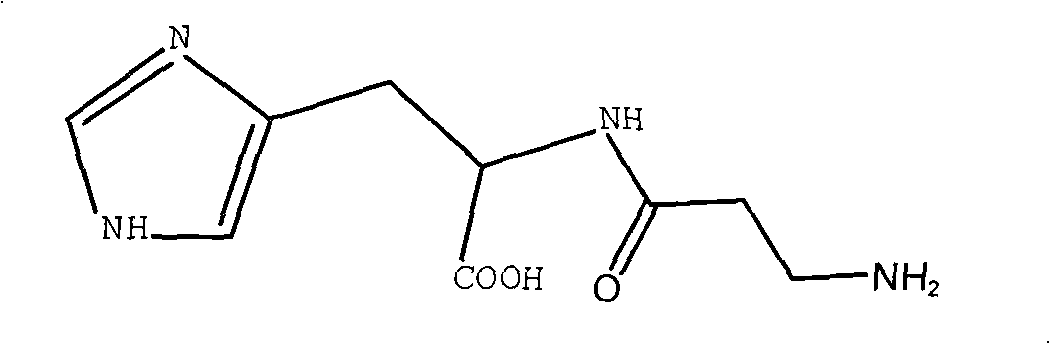
Synthetic method of L-carnosine
ActiveCN101284862AAvoid formingReduce consumptionPeptide preparation methodsBulk chemical productionHydrazine compoundOrganic synthesis
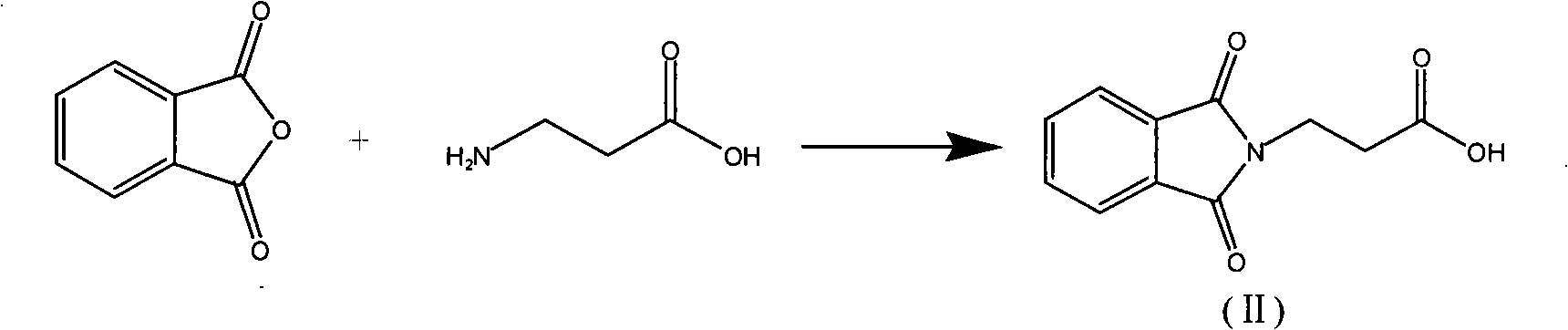
A method for synthesizing L-carnosine belongs to the organic synthesis technical field. The method is as follows: beta-alanine is dissolved in non-polar solvent to be reacted with phthalic anhydride under the catalysis of organic amine, and then phthaloyl-beta-alanine is obtained through water recrystallization; the phthaloyl-beta-alanine is dissolved in solvent to synthesize phthaloyl-beta-alanyl chloride through the chlorinated reagent of acyl chloride phthaloyl-beta-alanine; L-histidine is reacted with hexamethyl disilazane or trimethylchlorosilane to obtain L-histidine trimethylsilane protector; the protector is reacted with the phthaloyl-beta-alanyl chloride to obtain hydrochloride product with the protecting group divested by water, and then neutralization product is obtained by the hydrochloride product obtained through the neutralization condensation reaction of alkaline reagent, thereby obtaining L-carnosine crude product through the hydrazinolysis of the neutralization product by hydrazine hydrate; and the crude product is purified to obtain L-carnosine finished product. The method has low raw material consumption, short reaction procedure and high yield; moreover, the quality of synthesized L-carnosine can meet the requirements of industrial production.
Owner:SUZHOU FUSHILAI PHARMA CO LTD
Reliability improvement of SiOC etch with trimethylsilane gas passivation in Cu damascene interconnects
InactiveUS7193325B2Reduce leakage currentImprove throughputSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTrimethylsilaneLow leakage
A method of forming a SiCOH etch stop layer in a copper damascene process is described. A substrate with an exposed metal layer is treated with H2 or NH3 plasma to remove metal oxides. Trimethylsilane is flowed into a chamber with no RF power at about 350° C. to form at least a monolayer on the exposed metal layer. The SiCOH layer is formed by a PECVD process including trimethylsilane and CO2 source gases. Optionally, a composite SiCOH layer comprised of a low compressive stress layer on a high compressive stress layer is formed on the substrate. A conventional damascene sequence is then used to form a second metal layer on the exposed metal layer. Via Rc stability is improved and a lower leakage current is achieved with the trimethylsilane passivation layer. A composite SiCOH etch stop layer provides improved stress migration resistance compared to a single low stress SiCOH layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Self-emulsified aqueous epoxy emulsion and method for preparing same
The present invention provides one kind of self-emulsifying water thinned epoxy emulsion and its production process. The self-emulsifying water thinned epoxy emulsion is produced through emulsion copolymerization with the polymer intermediate, which is obtained through polymerizing the mixed organosilicon monomer comprising alkenyl-containing trimethyl silane and octalkyl cyclotetrasiloxane and acrylic acid monomer, epoxy resin and acrylic acid monomer. The self-emulsifying water thinned epoxy emulsion has homogeneous particle size, high stability, and stable production process. The anticorrosive paint compounded with the self-emulsifying water thinned epoxy emulsion reaches the level of solvent type epoxy resin paint.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES INST OF BUILDING SCI CO LTD
Preparation method of lithium difluorophosphate
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical synthesis and in particular to a preparation method of lithium difluorophosphate. In the method, lithium difluorophosphate is obtained by reaction of lithium hexafluorophosphate with substrate. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) under the protection of protective gas, adding lithium hexafluorophosphate into an organic solvent; 2) heating the solution to a dissolving temperature to obtain solution, then dropwise adding tri(trimethylsilane)borate or tri(trimethylsilane)phosphate into the solution, and forming precipitates; and 3) heating the solution to a reaction temperature, stirring at the reaction temperature and reacting, and after the reaction is finished, sequentially filtering, washing and drying precipitates, so that pure lithium difluorophosphate is obtained. The preparation method provided by the invention can be carried out under relatively mild conditions and has relatively high yield of lithium difluorophosphate, and batch production can be carried out without requiring complex operation.
Owner:武汉海斯普林科技发展有限公司
Non-aqueous electrolyte of lithium ion battery and lithium ion battery
InactiveCN105161763AImprove high temperature performanceLower impedanceSecondary cellsPhosphateLithium-ion battery
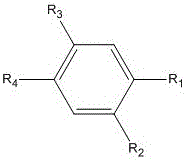
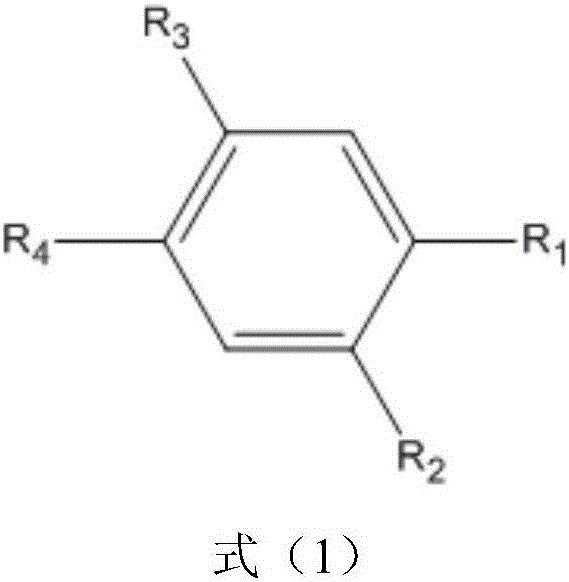
The invention discloses a non-aqueous electrolyte of a lithium ion battery and the lithium ion battery. The electrolyte comprises a non-aqueous organic solvent, a lithium salt and an additive, wherein the additive comprises substances of (A) and (B): (A) is shown in the description, wherein R1, R2 and R3 are respectively and independently selected from alkyl with carbon atoms of 1to 4, and at least one of the R1, the R2 and the R3 is unsaturated alkyl containing triple bonds; and (B) tris(trimethylsilyl) phosphate. By the non-aqueous electrolyte of the lithium ion battery, disclosed by the invention, the lithium ion battery acquires low impedance, and favorable low-temperature performance and high-temperature performance.
Owner:SHENZHEN CAPCHEM TECH CO LTD
Method for synchronously analyzing base, nucleotide, organic acid, fatty acid, amino acid and saccharide metabolic product with two-step derivation method
The invention discloses a method for synchronously analyzing a base, a nucleotide, an organic acid, a fatty acid, an amino acid and a saccharide metabolic product with a two-step derivation method. The method comprises the following steps of: performing a series of physicochemical method technical treatment such as ultrasonic treatment, centrifugation, oximation, urea removing, phosphorus removing, sulfur removing, protein removing, nitrogen blowing, vacuum drying, and trimethyl silylation derivation on biological substrate samples (such as urea, blood, cerebrospinal fluid, and tissue fluid); and detecting the biological substrate samples by adopting a gas chromatograph-mass spectrum combination technology. Due to the adoption of method, programmed treatment can be performed on the biological substrate samples simultaneously, and over 400 kinds of metabolic intermediate and final products of over five kinds of substances can be detected at one time.
Owner:王益超
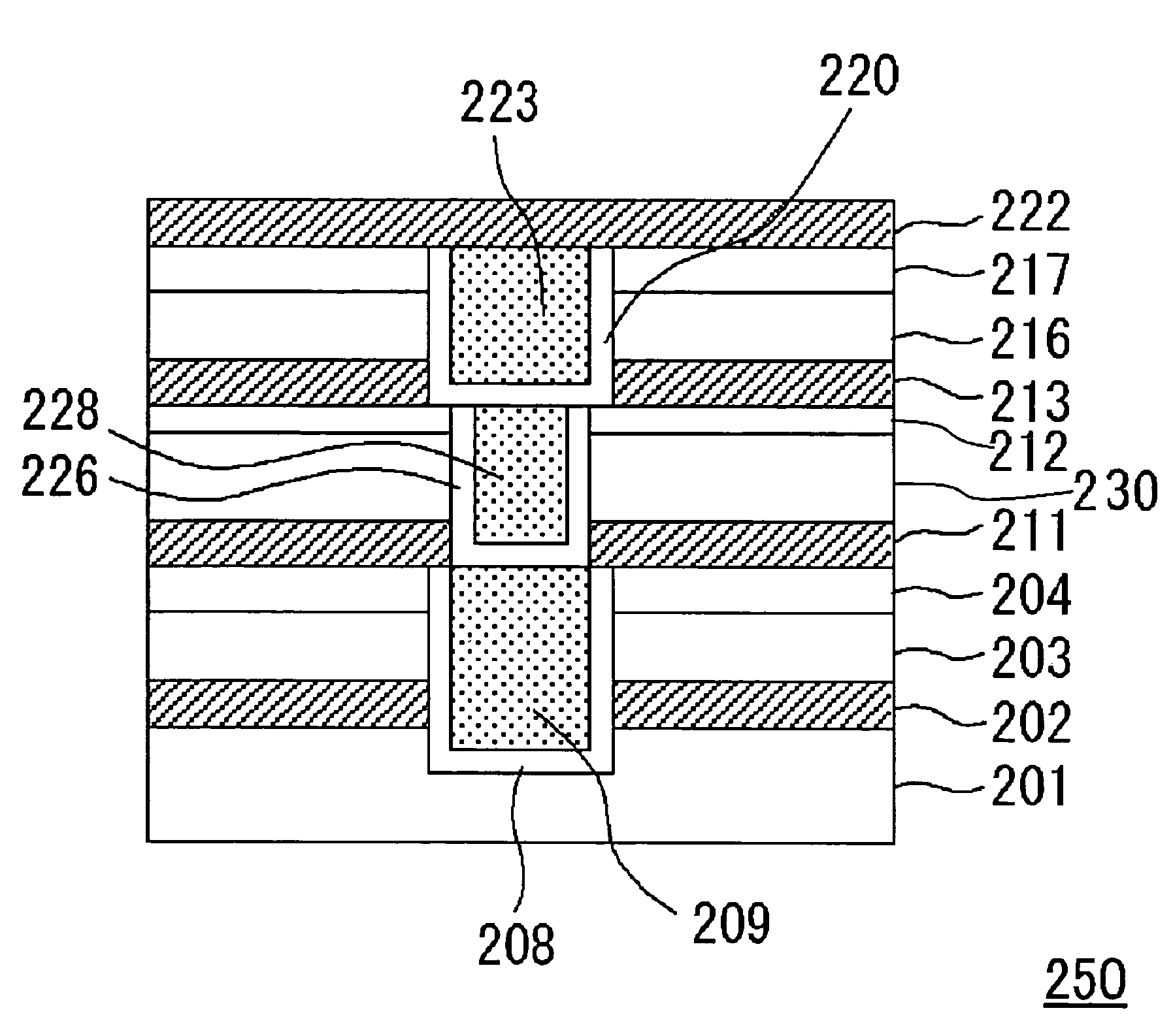
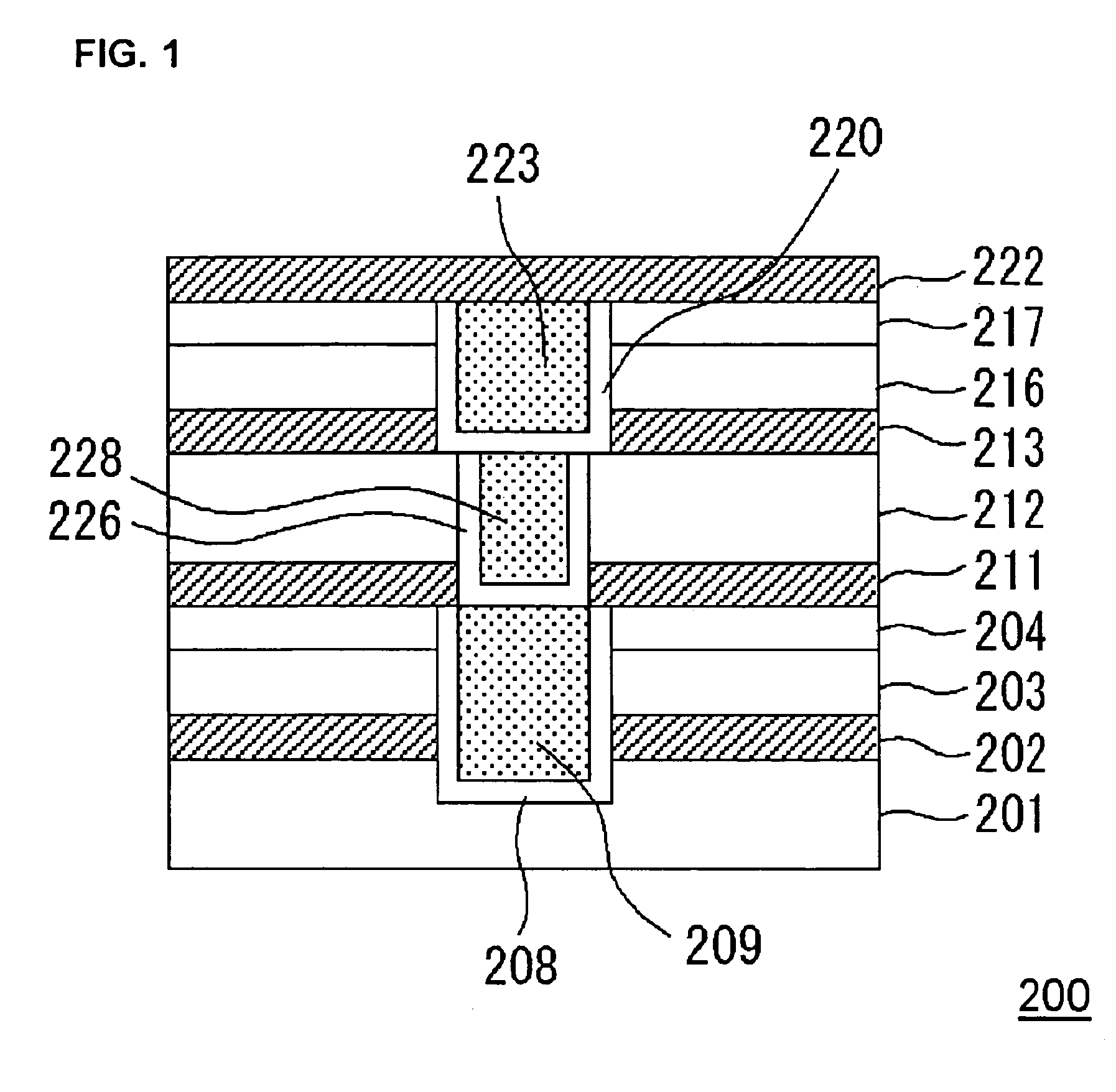
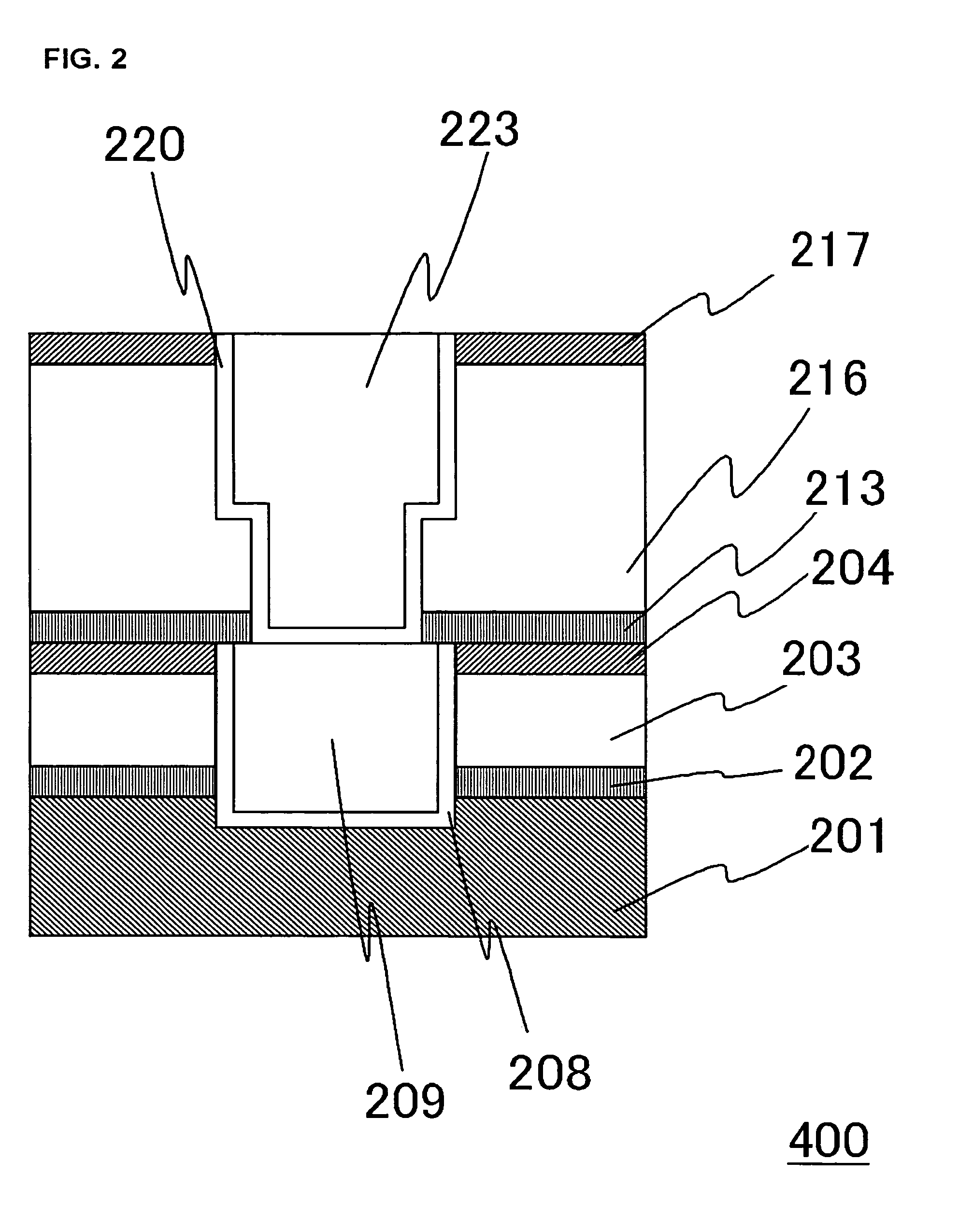
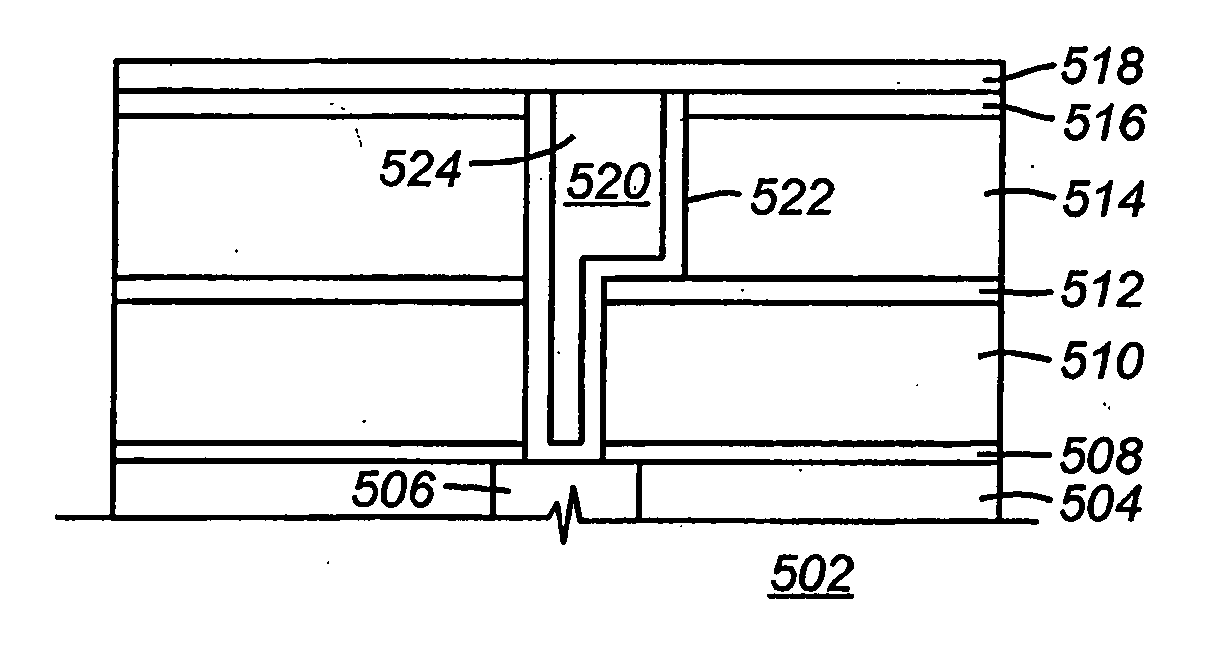
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS7531891B2Improve interlayer adhesionImprove adhesionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTrimethylsilaneSemiconductor
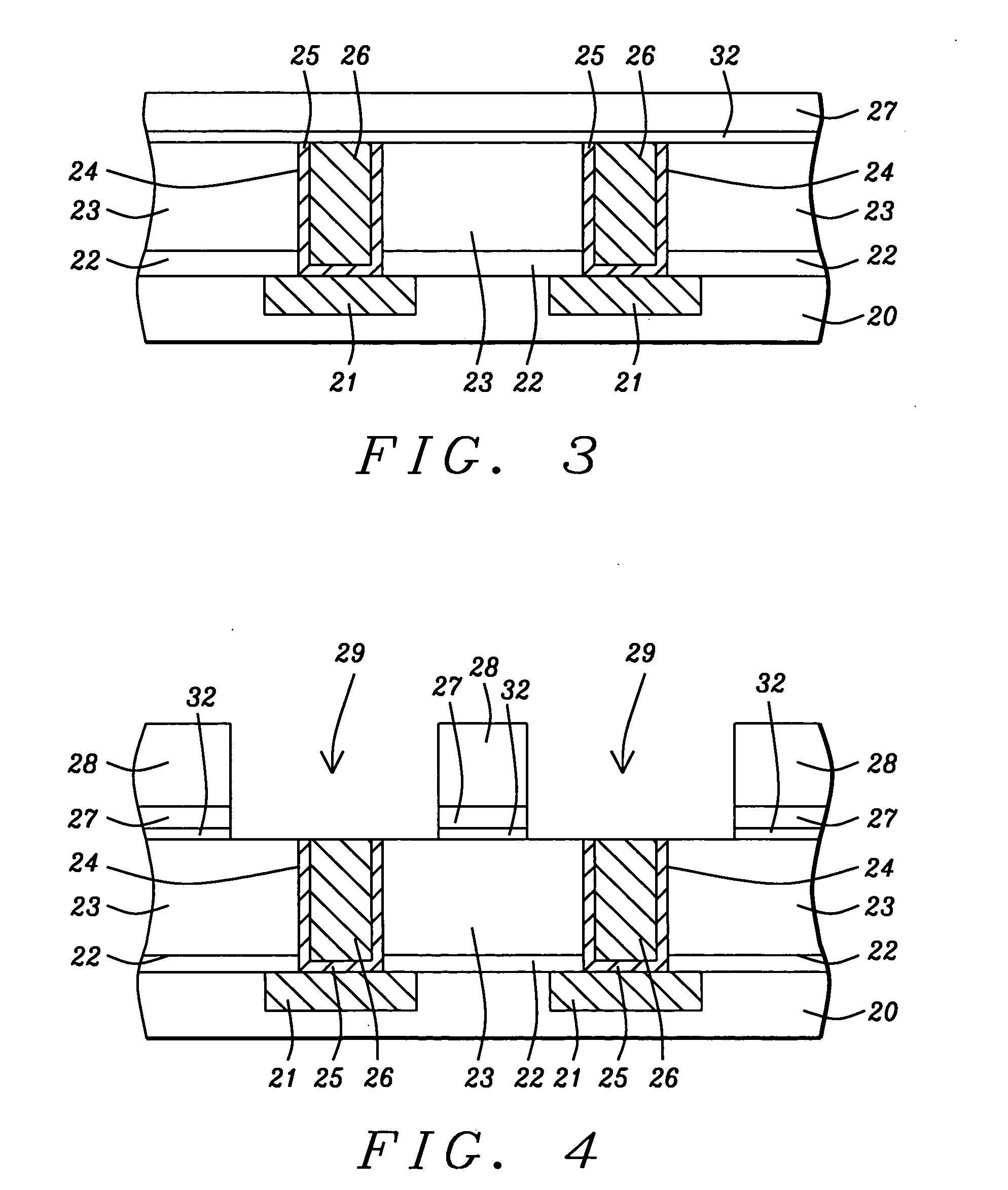
A semiconductor device having improved adhesiveness between films composing an interlayer insulating film is presented by providing multilayered films in the interlayer insulating films having film density distribution, in which the film density is gradually changes. A SiOC film is deposited to a thickness of 300 nm via a plasma CVD process, in which a flow rate of trimethylsilane gas is stepwise increased. In this case, the film density of the deposited SiOC film is gradually decreased by stepwise increasing the flow rate of trimethylsilane gas. Since trimethylsilane contains methyl group, trimethylsilane has more bulky molecular structure in comparison with monosilane or the like. Thus, the film density is decreased by increasing the amount of trimethylsilane in the reactant gas.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Method for forming an ultra low dielectric film by forming an organosilicon matrix and large porogens as a template for increased porosity
Ultra low K nanoporous dielectric films may be formed by chemical vapor deposition of silicon-containing components and large non-silicon containing porogens having labile groups. In accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, a low K nanoporous film may be formed by the oxidative reaction between trimethylsilane (the silicon-containing component) and alpha-terpinene (the non-silicon containing component). In accordance with certain embodiments of the present invention, the oxidant can comprise other than molecular oxygen, for example water vapor introduced in-situ or remotely, and then exposed to RF energy to generate reactive ionic species.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Novel method to deposit carbon doped SiO2 films with improved film quality
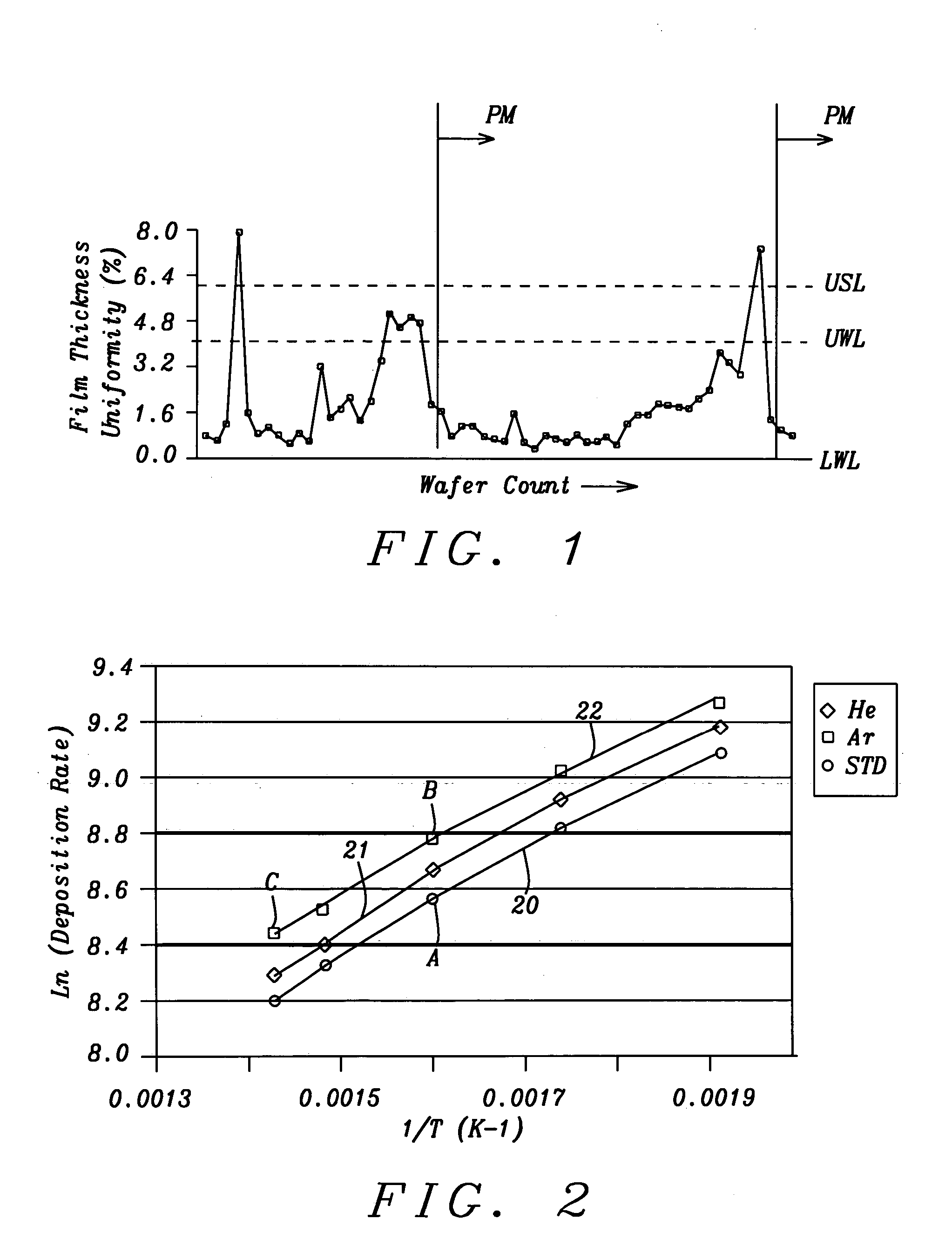
InactiveUS20050124151A1Increase deposition rateImprove film thickness uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingMetal interconnectLow leakage
A method is disclosed for depositing a Black Diamond layer in a CVD chamber. Trimethylsilane, O2, and Ar are flowed into the chamber at 300° C. to 400° C. with an O2:Ar:trimethylsilane flow rate ratio that is preferably 1:1.5:6. The resulting low k dielectric layer is formed with a higher deposition rate than when Ar is omitted and has a k value of about 3 that increases only slightly in O2 plasma. A higher density, hardness, and tensile strength are achieved in the Black Diamond layer when Ar is included in the deposition process. The addition of Ar in the deposition maintains film thickness uniformity below 2% for a longer period so that PM cleaning operations are less frequent and affords a lower fluorocarbon plasma etch rate to enable improved trench depth control in a damascene scheme. A lower leakage current and higher breakdown voltage in achieved in the resulting metal interconnect.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Process for purifying tetramethylsilane
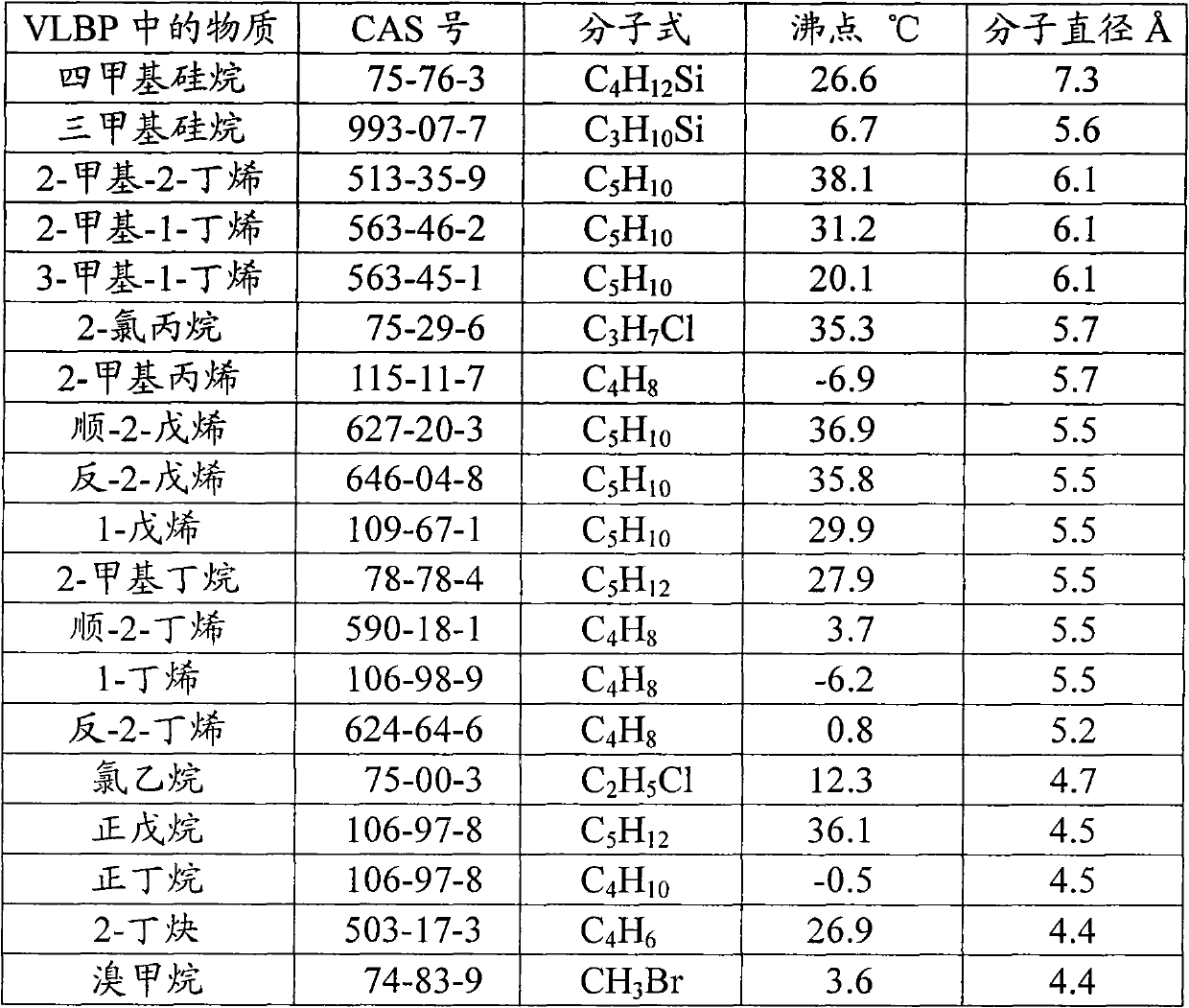
ActiveCN101955496ALow costHighly selective adsorptionSilicon organic compoundsDispersed particle separationMolecular sieveAlkane
The invention discloses a process for purifying tetramethylsilane, which comprises the following steps of: (1) pretreating fractions of a low-boiling-point substance after synthesizing methyl chlorosilane by a direct method and separating to remove a compound containing a Si-Cl bond; and (2) adsorbing impurities in separated fractions in the step (1) by using a molecular sieve and purifying to obtain the tetramethylsilane, wherein the channel diameter of the molecular sieve is 4.5 to 7.2 angstroms. The impurities in the fractions of the low-boiling-point substance are adsorbed by the molecular sieve; the molecular sieve has good selective adsorption effect on alkane, olefin, chloroalkane and trimethylsilane in the fractions of the low-boiling-point substance; the tetramethylsilane can be purified to have high purity and other impurities are not introduced; in addition, the molecular sieve can be reused after being activated and has low cost.
Owner:JIAXING UNITED CHEM +1
Composition with makeup maintaining and oil controlling effects and cosmetic
The invention discloses a composition with makeup maintaining and oil controlling effects and a cosmetic. The composition can effectively improve the migration resistance of foundation products, directionally absorb, flocculate and solidify sebum, has a good oil controlling effect, can effectively reduce the influence of sebum secreted by skin on makeup, and enables the skin to keep natural and lasting makeup. The composition with the makeup maintaining and oil controlling effects is prepared from, by weight, 0.8-2.5 parts of polydimethylsiloxane and polyol copolymer, 4-11 parts of film forming agent, 1-8 parts of functional powder and 14-33 parts of volatile silicone oil, wherein the functional powder is a mixture of synthetic fluorophlogopite, hydroxyapatite and zinc oxide; and the filmforming agent is a combination of polymethylsilsesquioxane and trimethylsiloxysilicate. The invention belongs to the technical field of cosmetics.
Owner:GUANGDONG BAWEI BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Graphite based cementing solid lubricant
ActiveCN101463288AImprove work efficiencyImprove the state of frictionAdditivesBase-materialsRare earthLubrication
The invention discloses a graphite-base bonded solid lubricant. The lubricant consists of polyamidoimide, graphite, molybdenum disulfide, rare earth fluoride, metal oxide, gamma-epoxy propoxy propyl-trimethylsilicane and a mixed organic solvent. A coating prepared by the lubricant has excellent high-temperature lubrication and wear resistance and can be used for a long time at 250 DEG C; meanwhile, the coating prepared by the lubricant has excellent abrasion resistance, thereby playing roles in protecting surface, reducing abrasion and friction coefficient, and prolonging service life of parts.
Owner:兰州中科凯路润滑与防护技术有限公司
Makeup-free face cream containing enriched emulsion and preparation method of makeup-free face cream
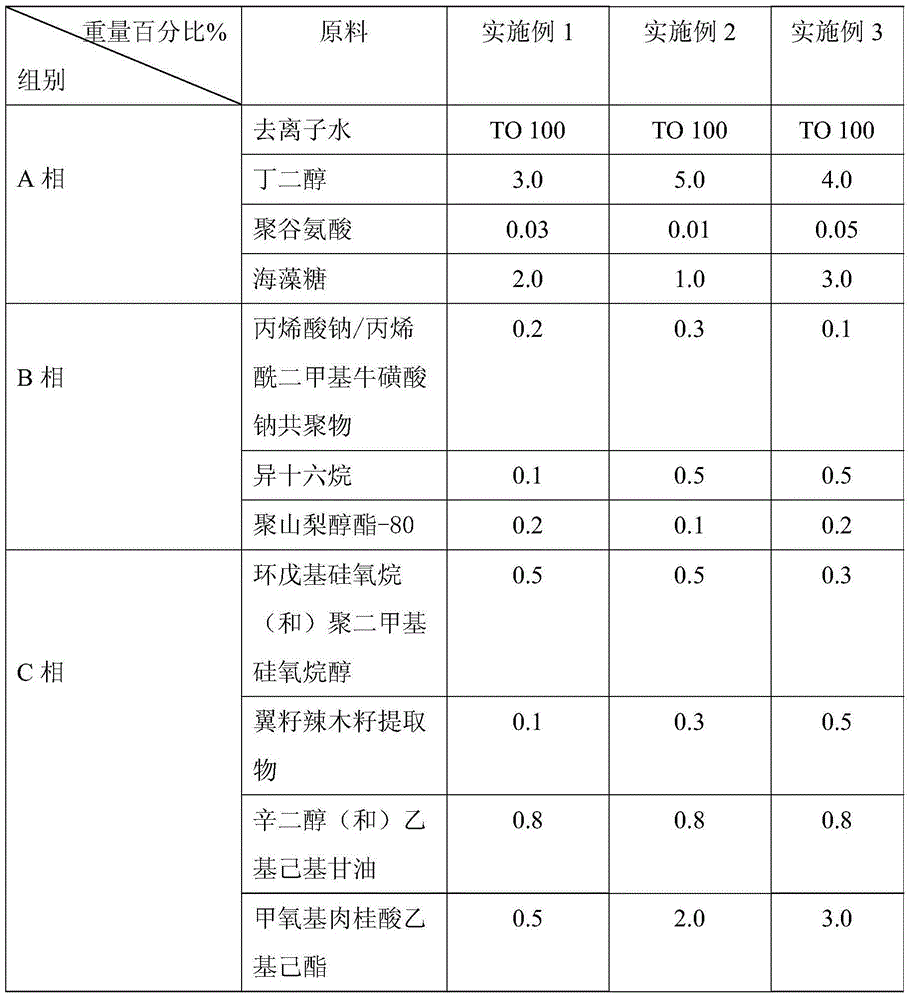
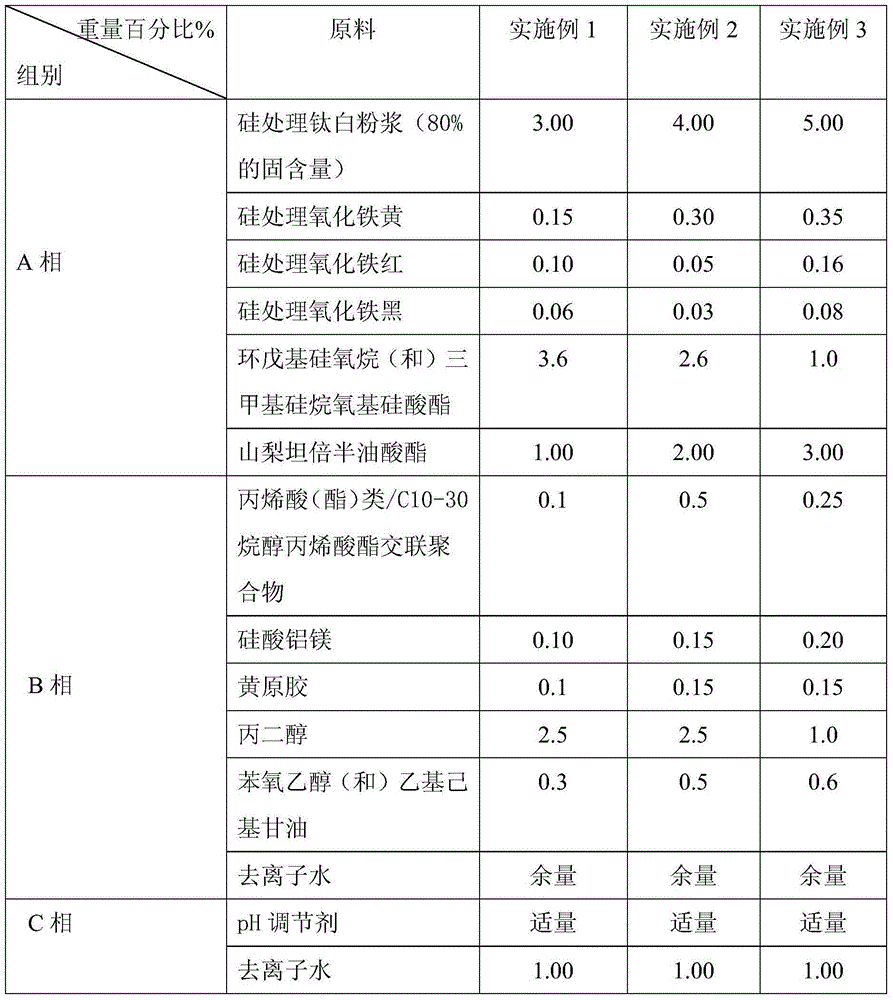
InactiveCN104825371ANatural makeupIncrease moisture contentCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAluminum silicateButanediol
The invention provides a makeup-free face cream containing enriched emulsion and a preparation method of makeup-free face cream. The makeup-free face cream comprises, by weight percentage, 10.0-30.0% of enriched emulsion and 70.0-90.0% of liquid foundation, wherein the enriched emulsion comprises butanediol, polyglutamic acid, trehalose, sodium acrylate / acrylyl dimethyl sodium taurate polymer, isohexadecane, polysorbate-80, cyclopentyl siloxane (and) dimethiconol, moringa pterygosperma extracts and the like; the liquid foundation comprises physical skin whitening agent, colorant, cyclopentyl siloxane (and) trimethyl siloxy silicate ester, sorbitan sesquioleate, acrylic acid (ester) / C10-30 alkanol acrylic ester cross-linked polymer, magnesium aluminum silicate, xanthan gum, propylene glycol and the like. The makeup-free face cream is good in water and sweat resistance, natural in makeup feeling and easy to remove and has certain skin care effect.
Owner:广州智媛生物科技有限公司
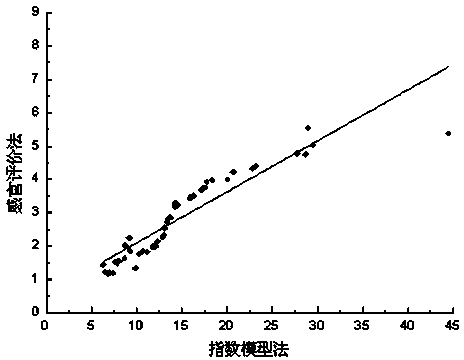
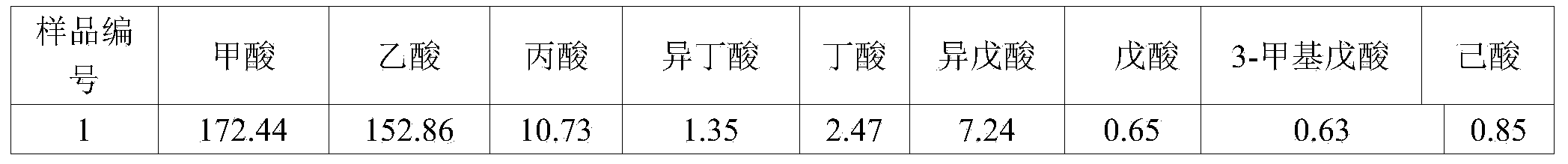
Cigarette smoke acidity index evaluation model establishment method based on gustation vitality values
ActiveCN104267153AFit closelyAddress subjectivityComponent separationVapor phase chromatographyVitality
The invention relates to a cigarette smoke acidity index evaluation model establishment method based on gustation vitality values, and belongs to the technical field of cigarette evaluation. The method comprises the steps as follows: a gas chromatograph-mass spectrometer is utilized to detect the content of organic acids in mainstream cigarette smoke with an N,O- bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide derivatization method; according to a public reported gustation threshold, the gustation vitality values of the organic acids are calculated so as to recognize key acidity substances in the mainstream cigarette smoke; a cigarette smoke acidity index evaluation model is established on the basis of the key acidity substances in the mainstream cigarette smoke; and human sense evaluation of the cigarette smoke acidity intensity is performed by a cigarette sense technician, and statistical software is adopted to perform fitting effect analysis on the cigarette smoke acidity index and a human sense evaluation value. The cigarette smoke acidity index evaluation model and a human sense evaluation method have an ideal fitting effect, the cigarette smoke acidity intensity is objectively evaluated, and the method can be used for development of the cigarette product flavor technology.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO YUNNAN IND
High-stability lithium ion battery electrolyte
ActiveCN105006594AReduce acidityReduce reactivitySecondary cellsLone electron pairCoordination complex
The invention discloses a high-stability lithium ion battery electrolyte which comprises lithium hexafluorophosphate, a nonaqueous solvent, an additive and an electrolyte stabilizing agent, wherein the electrolyte stabilizing agent is any one and more of tris(trimethylsilyl)phosphite, N, N-dimethylpropionamide and N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone. According to the invention, as P / N atoms in the electrolyte stabilizing agent have lone electron pairs, relatively low Lewis base property is achieved after a less amount of the electrolyte stabilizing agent is added into the electrolyte, the electrolyte stabilizing agent and PF5 can form a complex of six ligands, and accordingly the Lewis acidity and reaction activity of the PF5 are reduced and the colority rising caused by the reaction between the PF5 and trace impurities in the electrolyte is inhibited well; in addition, the stabilizing agent has good compatibility with a graphite cathode, and can react on the electrode surface after being added into the electrolyte to form a film, so that the cycle performance of the lithium ion battery is improved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU TINCI MATERIALS TECH
Microcapsules adapted to rupture in a magnetic field to enable easy removal of one substrate from another for enhanced reworkability
ActiveUS9186641B2Excellent reworkabilityReduce bond strengthLayered productsLaminationIn situ polymerizationTrimethylsilane
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Nano-cerium oxide-nano aluminium nitride hybridization-modified LED organic silicon encapsulation adhesive and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106221665AImprove thermal conductivityHigh refractive indexNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesMacromolecular adhesive additivesAdhesiveRefractive index
The invention discloses nano-cerium oxide-nano aluminium nitride hybridization-modified LED organic silicon encapsulation adhesive. In the preparation process of the encapsulation adhesive, the nano-cerium oxide and the nano aluminium nitride are subjected to surface treatment by a silane coupling agent and then are put into imidazolium ionic liquid to react to obtain highly-dispersed nano-powder with the surface coated by ionic liquid, octakis(trimethylsiloxy)silsesquioxane is added and is doped with an organic material, the nano-material is efficiently grafted to organic silica gel, and the organic silicon encapsulation adhesive with high heating conductivity, high refractive index and high light and heat stability is finally prepared. The organic silicon encapsulation adhesive has excellent mechanical properties and adhesive ability; the encapsulated LED lamp can maintain high luminescence property for a long time and has a longer service life.
Owner:王烽
Ionic liquid functionalized magnetic nanoparticle and preparation method and application thereof
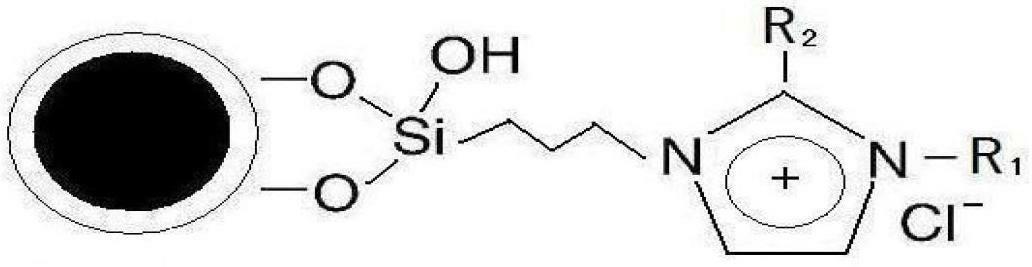
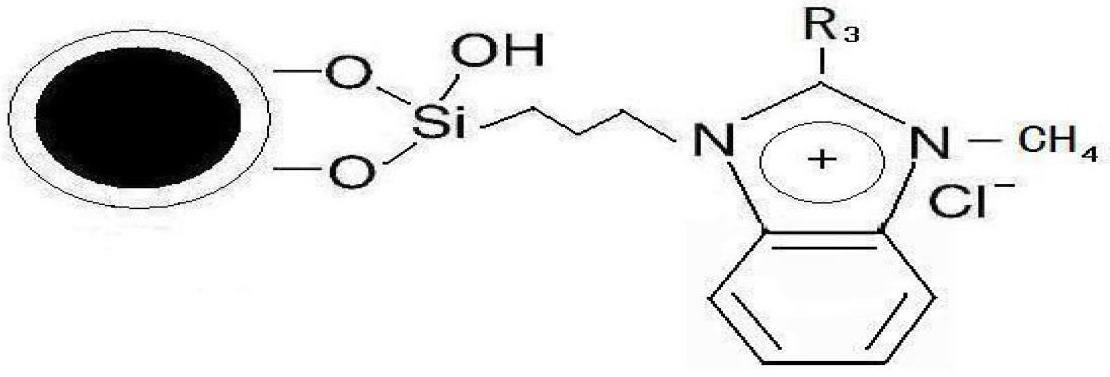
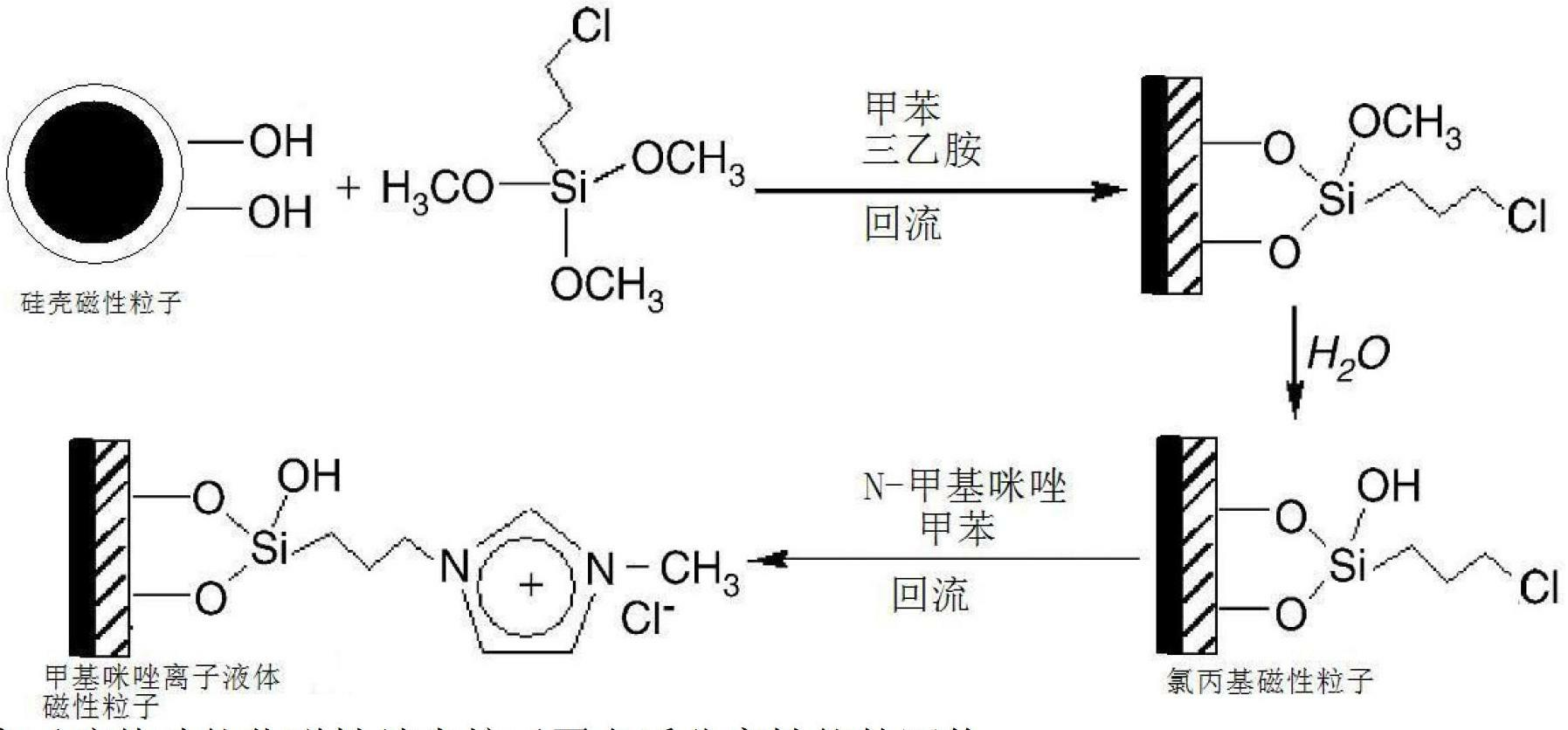
InactiveCN102641702AEasy to separateWill not pollutePeptide preparation methodsMicroballoon preparationMagnetite NanoparticlesIonic liquid
The invention relates to an ionic liquid functionalized magnetic nanoparticle and a preparation method and application thereof. FeCl3.6H2O and anhydrous sodium acetate are dissolved in glycol, and react under 200 DEG C, so that Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles are obtained; the Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles are weighed and mixed with H2O and ethanol, pH is regulated to 9 to 10, tetraethoxysilane is added for reaction, and after vacuum drying, Fe3O4 / SiO2 is obtained; the Fe3O4 / SiO2 is dispersed and suspended in toluene, and after 3-chloropropyltrimethylsilane and triethylamine are added for reaction, chloropropyl magnetic nanoparticles are obtained by way of vacuum drying; the chloropropyl magnetic nanoparticles are added into toluene, N-alkylimidazole derivative is added for reaction, and after vacuum drying, the ionic liquid functionalized magnetic nanoparticles are obtained. When being used for separating target standard protein, the ionic liquid functionalized magnetic nanoparticle has the characteristics of good selectivity and high adsorbing capacity, and cannot contaminate target separated product.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com